The mirna-184 drives renal fibrosis by targeting HIF1AN in vitro and in vivo
|
|
|
- Lucy Wilcox
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 NEPHROLOGY - ORIGINAL PAPER The mirna-184 drives renal fibrosis by targeting HIF1AN in vitro and in vivo Bin Chen 1 Received: 18 December 2017 / Accepted: 3 November 2018 The Author(s) 2018 Abstract Progressive renal fibrosis is the last phase of chronic kidney disease and results in renal failure. Micro-RNA has been demonstrated as important agent to drive organ fibrosis. However, the precise mechanisms are not fully understood. Here, we found mirna-184 as a critical mediator to promote the renal fibrosis by targeting HIF1AN. In Vivo, mirna-184 expression levels remarkably increased both in patients serum and in unilateral ureteral obstruction kidneys, as well as induced the expression of COL1A1 and COL3A1. Furthermore, transfection of NRK49F cells with mirna-184 mimics down-regulated HIF1AN, transfection of NRK49F cells with mirna-184 inhibitor up-regulated HIF1AN, while the cells transfected with mirna-184 inhibitor exerted the opposite effect. When the cells were co-transfected with mirna-184 mimics and HIF1AN, the expression of α-sma, GTGF, COL1A1, and COL3A1 at mrna level was apparently decreased when compared with mirna-184 mimic-transfected cells, which was strengthened when transfected with mirna-184 inhibitor. Thus, mirna-184 is an important agent to promote the fibrosis though binding to HIF1AN, and may be a promising novel target in treatment of renal fibrosis. Keywords MiRNA-184 HIF1AN Renal fibrosis Introduction Renal fibrosis is the final stage that manifesting the chronic kidney disease and leading to impairment of kidney function [1, 2]. A typical hallmark of tubule interstitial fibrosis is composed of myofibroblast accumulation, excessive deposition of extracellular matrix (ECM) as well as the renal tubules destruction [3, 4]. Other critical characteristics include accumulation of inflammatory leucocytes, which causes loss of renal function further [5, 6]. Fibrosis is key element of the high morbidity and mortality rates, especially related to some diseases, such as diabetic nephropathy. However, concrete therapeutic options for this target are not yet available in clinical application. Recent studies show that mirna can be involved in regulating numerous molecular and cellular processes, as well as its role in diseases and therapeutic potential [7 10]. * Bin Chen chenbincbin@126.com Micro-RNAs are a class of short noncoding RNAs of approximate 22 nucleotides in length, and they can regulate gene expression via post-translation and induction of mrna degradation [11]. A certain number of mirna have been considered to be associated with fibrotic processes in some relevant diseases, including mir-29, mir-192, and mir-21 [12 15]. It s reported that these mirnas are induced by TGF-ß1 in renal cells [16], but another study demonstrates that TGF-ß1 deduces mir-192 expression in human tubular epithelial cells [17]. The normalization of their expression could alleviate fibrosis in vitro and in vivo model, which suggests that focusing on these mirnas could be a method to improve renal fibrosis disease [16]. Therefore, our study aimed to investigate mirna profiling in the kidneys, and also to identify the potential mechanism in renal fibrosis. Moreover, we carried out intervention studies to determine the role of mirna-184 in promoting the renal fibrosis. Finally, we determined whether suppressing the H1F1 might be a target by which mirna-184 regulates renal impairment. 1 Kidney Department, Zhenhai People s Hospital of Ningbo City (Ningbo No.7 Hospital), 718 Nanerxi Road, Luotuo Subdistrict, Zhenhai, Ningbo, People s Republic of China Vol.:( )
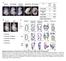
2 Materials and methods Experimental animals A UUO kidney disease model was induced in C57 mice by left ureteral ligation in accordance with a previously described method [18]. After raising for 1 week, they were randomly divided into four group, one was sham surgery group with 10% DMSO intraperitoneal injection as control, and others were UUO models with CORM at doses of 2.5 mg/kg, 10 mg/kg, and 15 mg/kg, respectively, each group of 6 mice. Mice were killed after administration for 14 days, and the supernatant from eyeball blood was collected though centrifugation and stored at 80º. Kidney tissues were collected and processed for evaluation of mir-184 as well as for immunohistochemistry, western blot, and real time PCR. Cell culture and transfection NRK49F cells were cultured in Dulbecco s modified Eagle s medium, 10% fetal calf serum (FCS), 1% glutamine, 1% nonessential amino acids, and antibiotics at 37 C, 5% CO 2 under humidified conditions. For the first time, we used Angiotensin II (R&D Systems) to stimulate the cells to determine mirna-184 expression levels. Moreover, NRK49F cells were respectively transfected with 30 nm mirna-184 mimics (Ambion, Austin, TX), mirna-184 inhibitor (Ambion, Austin, TX), negative control mirna mimics (Ambion), or mirna-184 inhibitor in six well plates using siport Neo-FX (Ambion) according to the manufacturer s instructions. After transient transfection, the cells were synchronized by culturing them in low-glucose medium without serum for 24 h. NRK49F cells were then stimulated with AngII in accordance with our protocols. Quantitative RT PCR The assay was carried out as previously described [19]. Quantitative RT (qrt)-pcr analyses of mir-184, HIF1AN mrna, α-sma mrna, GTGF mrna, COL1A1 mrna, and COL3A1 mrna were carried out in RNA isolated from patients serum or mice kidney tissue using specific TaqMan assays (Life Technologies). GAPDH was used as an internal control. Luciferase reporter assays NRK49F cells were co-transfected with a construct containing the human HIF1AN 3 untranslated region (UTR) downstream of the Firefly luciferase gene, the co-reporter vector pmir-report encoding the Renilla luciferase and mir-184 mimics. After culturing for 36 h, the activity of biluciferase was analyzed after cells were lysed with the passive lysis buffer by the Dual-Luciferase Reporter Assay System (Promega, Madison, WI, USA). Western blot Transfected NRK49F cells were also collected according to our protocols. Western blot analysis was carried out as previously described [20, 21], with primary antibodies against α-sma (Sigma, US) and HIF1AN (Sigma, US). GAPDH was used as an internal control. Histology Changes in renal morphology were examined in H&E and MASSON staining. The kidney tissues were fixed, fully automatic dehydrated, paraffin-embedded, and sliced into tissue sections (4 mm). All the slices were stained with hematoxylin for nuclei, and Masson s trichrome stain (Solarbio, China) was performed according to the manufacturer s specific instructions. Results The mirna 184 expression levels in vivo To determine whether mirna-184 plays a role in the progression of kidney fibrosis, we detected the mirna-184 expression levels in serum from both health group and observation group with kidney fibrosis, and to analyze the differences between the two groups. The results showed that mirna-184 expression levels were significantly increased compared with the health group as shown in Fig. 1a. Meanwhile, we used the qrt-pcr to detect the levels of mirna- 184 in mice kidney of sham operation group and of unilateral ureteral obstruction (UUO) group. Of note, the mirna-184 expression levels in UUO group were significantly increased than those in the sham operation group as shown in Fig. 1b. These data indicated that mirna-184 may play a key role in the development of fibrotic responses in the kidney. MiRNA 184 induces α SMA expression in vitro We used NRK49F, a rat renal fibroblasts line, for mechanistic study to causal model of mirna-184 on renal fibrosis. Angiotensin II, albuminuria and TGF-β could contribute to tubule interstitial impairment and fibrosis in renal diseases [22, 23]. In order to investigate whether the stimuli could trigger mir-184 expression in renal fibroblasts line, we exposed NRK49F cells to AngII for 36 h. Quantity RT- PCR results showed that mirna expression levels were
3 Fig. 2 MiRNA-184 induces α-sma expression in vitro. a mirna- 184 expression levels stimulated with AngII were determined by qrt-pcr assays. b α-sma expression levels stimulated with AngII and AngII + mirna-184 were determined by Western blotting analysis. **Statistically highly significant, P < 0.01 Fig. 1 MiRNA-184 expression levels in vivo. a mirna-184 expression levels in both observation group and health group were determined by qrt-pcr assays. b mirna-184 expression levels in mice kidney of sham operation group and of UUO group were determined by qrt-pcr assays. **Statistically highly significant, P < 0.01 apparently increased after NRK49F was stimulated with AngII, as shown in Fig. 2a. Transfection of NRK49F cells with mirna-184 mimics and under stimulation with AngII resulted in a significant increase in α-sma compared with negative control mimic-transfected cells. Western blotting analysis indicated that mirna-184 could cause a sustained up-regulation of the α-sma expression (Fig. 2b). HIF1AN is a target of mirna 184 To demonstrate the target gene of mirna-184, mirna target prediction algorithms miranda and EIMMo were employed together with the micro-rna body map web tool. We focused on the HIF1AN (Fig. 3a) because we investigated the micro-rna target gene database and made such a prediction. In order to prove that HIF1AN is a true mirna- 184 target, we carried out luciferase reporter assay employing a plasmid pmir-report with full-length 3 -UTR of HIF1AN downstream of the luciferase gene. When the plasmid named pmir-hif1an-wt was built, we performed overlapping PCR assay to construct plasmid pmir-hif1an-mut Fig. 3 HIF1AN is a target of mirna-184. a 3 -UTR of HIF1AN binding to mirna-184 as indicated. b The plasmid pmir-hif1anmut was constructed by overlapping PCR assay. c Luciferase activity in NRK49F cells co-transfected with the reporter plasmid containing the HIF1AN 3 -UTR downstream of the Firefly luciferase gene, the co-reporter vector pmir-report encoding the Renilla luciferase and with mir-184 mimic. **Statistically highly significant, P < 0.01 (Fig. 3b). To detect whether mirna-184 could regulate the HIF1AN expression, NRF49F cells were co-transfected with mirna-184 mimics and reporter plasmid. As shown
4 in Fig. 3c, compared with pmir-report cells, it was showed that luciferase activity of pmir-hif1an-mut was significant decreased, but that of pmir-hif1an-mut had no statistical changes. Taken together, these results suggested that mirna-184 could suppress HIF1AN expression by binding 3 -UTR of HIF1AN. MiRNA 184 regulates HIF1AN expression in mrna and protein levels To estimate whether mirna-184 could regulate HIF1AN in mrna levels, we performed qrt-pcr assay to determine the mrna levels of HIF1AN. As shown in Fig. 4a, transfection of NRF49F cells with mirna-184 mimics showed a significant reduction in HIF1AN expression at mrna levels compared with negative control mirna mimic-transfected cells. As shown in Fig. 5a, transfection of NRF49F cells with mirna-184 inhibitor showed a significant increase in HIF1AN mrna compared with negative control mirna mimic-transfected cells. Meanwhile, we carried out Western blot assay to detect the expression levels of HIF1AN. As shown in Fig. 4b, consistent with HIF1AN mrna down-regulation, HIF1AN protein expression of NRF49F cells transfected with mirna-184 mimics resulted in a significant reduction compared with negative control mirna mimic-transfected cells. As shown in Fig. 5b, HIF1AN protein expression of NRF49F cells transfected with mirna- 184 inhibitor resulted in a significant increase compared with negative control mirna mimic-transfected cells. Based on the above results, we found that mirna-184 could downregulate HIF1AN expression in mrna and protein levels. MiRNA 184 promotes the progression of renal fibrosis inhibited by HIF1AN In order to validate that mirna-184 promoted the progression of renal fibrosis by inhibiting HIF1AN expression, qrt-pcr assay was performed to determine the expression of α-sma, GTGF, COL1A1, and COL3A1. We identified that above indictors in cells transfected with mirna-184 mimics were significantly increased compared with negative control mirna mimic-transfected cells. However, α-sma, GTGF, COL1A1, and COL3A1 mrna expression in cells co-transfected with mirna-184 mimics and HIF1AN were apparently decreased when compared with mirna-184 mimics-transfected cells (Fig. 6a d). In addition, the expression of above parameters were significant down-regulated when transfected with mirna-184 inhibitor (Fig. 7a d). Notably, mirna-184 promoted the progression of renal fibrosis, which could be inhibited by HIF1AN. In a word, HIF1AN involves in the progression of renal fibrosis mediated by mirna-184. Renal fibrosis morphology in UUO mice associated with mirna 184 modulation Fig. 4 MiRNA-184 regulates HIF1AN expression in mrna and protein levels. Co-transfection of NRF49F cells with mirna-184 mimics and negative control mirna mimic. a HIF1AN mrna expression was suppressed by mirna-184. b HIF1AN protein expression was suppressed by mirna-184. **Statistically highly significant, P < 0.01 Based on the in vitro data indicating the effect of mirna- 184 in the progression of renal fibrosis, we moved towards in vivo study to demonstrate the mirna-184 regulated the consequent fibrosis. HE staining results showed that the structure of renal tubules and glomerulus were clear, the epithelial cells arranged neatly, the basement membrane of small organs was intact, and no obvious cell infiltration was observed in the interstitium in the sham-operated mice. However, in the UUO mice, there was renal glomerular dilatation, epithelial cell degeneration, and necrosis, indicating UUO kidney was successfully modeled. The injection of mirna-184 into the tail vein resulted in more pronounced renal tubular dilatation and increased degeneration and necrosis of epithelial cells. Moreover, we analyzed the changes of renal fibrosis in mice performing Masson s trichrome staining. The results showed that the area of renal fibrosis and extracellular matrix deposition were significantly increased in UUO mice with mirna-184 injection compared with sham-operated mice and UUO mice (Fig. 8a). Consistent with in vitro results of COL1A1 and COL3A1 mrna expression, we found that the expression levels of COL1A1 and COL3A1 mrna in sham-operated
5 mice and UUO mice were significantly decreased than those in UUO mice injected with mirna-184 (Fig. 8b, c). The above results showed that mirna-184 could significantly promote progression of renal fibrosis. Statistical analysis Descriptive statistics were calculated and shown in figures. One-way ANOVA analysis was performed for multiple group comparisons. The Student s t-test was used for comparison between two groups. P values less than 0.05 was considered statistically significant difference. The statistical analysis was performed using SPSS software (SPSS for windows 17.0, SPSS Inc.). Discussion Fig. 5 MiRNA-184 inhibitor regulates HIF1AN expression in mrna and protein levels. Co-transfection of NRF49F cells with mirna- 184 inhibitor or negative control mirna mimic. a HIF1AN mrna expression was up-regulated by mirna-184 inhibitor. b HIF1AN protein expression was up-regulated by mirna-184 inhibitor. **Statistically highly significant, P < 0.01 Renal fibrosis is the final common stage of any form of progressive kidney disease, resulting in renal impairment. For a long-term study, we have been exploring the relevant molecular mechanisms involving in the development of renal fibrosis and identified that the mir-324-3p/prep complex and mir-433 exerted effect during the fibrotic process [24, 25]. Here, we focused on mirna-184 and demonstrated that is a key agent during the renal fibrosis. Little information is available pertaining to mirna-184 expression in the kidney. Some reporters showed that renal mirna profiling of rodents displayed upregulated mir-184 Fig. 6 MiRNA-184 promotes the progression of renal fibrosis inhibited by HIF1AN. Cotransfection of NRF49F cells with mirna-184 mimics, negative control mirna mimic and mirna-184 mimics + HIF1AN. a α-sma mrna expression. b GTGF mrna expression. c COL1A1 mrna expression. d COL3A1 mrna expression. **Statistically highly significant, P < 0.01
6 Fig. 7 The effect mirna-184 inhibitor at mirna expression levels of α-sma, GTGF, COL1A1 and COL3A1. Co-transfection of NRF49F cells with mirna-184 inhibitor. a α-sma mrna expression. b GTGF mrna expression. c COL1A1 mrna expression. d COL3A1 mrna expression. **Statistically highly significant, P < 0.01 in aged kidneys, indicating that epigenetic regulation of renal aging likely occurred via inhibiting mirna-184 targeted genes [26, 27]. Zan chi et al. [28] established a link between abnormal tubular mir-184 and tubule interstitial fibrosis in the diabetic kidneys through suppression of the target LPP3, which plays a critical role in modulating biosynthesis of lipid phosphates involved in multi-organ fibrosis and in cell signal transduction [29, 30]. In this study, we added new finding that mirna-184 is a positive agent binding HIF1AN as a potential target during the fibrosis. HIF1AN, an asparaginyl (Asn) hydroxylase, is able to modulate the activities of important biological regulators (such as HIF1a [31], IĸB [32], Notch [33]) through hydroxylation. It has been reported that HIF-1α exerted an effect in hypoxia- and chronic kidney disease-induced fibrosis, while genetic knock-down of HIF-1α in renal epithelial cells led to a significant reduction in collagen deposition, including COL1A1 and COL3A1 [34]. Mahon et al. revealed that HIF1AN considered as an important inhibitor can interact with Hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF)-1α to negatively regulate the HIF-1α transcriptional activity [35]. Therefore, HIF1AN can be regarded as a critical agent implicated in the process of renal fibrosis. It s reported that Micro-RNAs suppress their target gene though binding their 3 UTR to induce protein translational inhibition or mrna degradation [31]. In order to identify whether mirna-184 could target HIF1AN gene, we detected the expression levels of HIF1AN in rat kidney fibroblasts overexpressing mirna-184 in the mirna and protein levels. Notably, both mrna and protein levels of HIF1AN were apparently inhibited by mirna-184 when compared with the control (Fig. 4a, b). While both mrna and protein levels of HIF1AN were apparently promoted by mirna-184 inhibitor when compared with the control (Fig. 5a, b). To further determine whether mirna-184 modulates HIF1AN by binding its 3 UTR, we generated luciferase reporter linked to full-length 3 -UTR of HIF1AN and NRF49F cells were co-transfected with mirna-184 mimics and reporter plasmid. Compared with pmir-report cells, it was showed that luciferase activity of pmir-hif1an-wt
7 we confirmed that the expression levels of COL1A1 and COL3A1 mrna in mice injected with mirna-184 were significantly elevated (Fig. 8b), indicating mirna-184 may play a critically pathological role in fibrosis. In addition, we had a new finding that HIF1AN, a target of mirna-184 during renal fibrosis, exerts its ability to regulate mirna- 184-induced the expression of fibrotic markers to facilitate fibrosis. In conclusion, the present study provides the novel finding that mirna-184 plays a role in renal fibrosis by targeting HIF1AN. Combination of in vitro and in vivo data showed the opportunity that targeting mirna-184 in association with angiotensin II lowing medicine to have potential effect in renal injury disease. However, whether mirna-184 is a rooted factor or it has an additional role in the development of renal fibrosis needs to be further studied. Fig. 8 Renal fibrosis morphology in UUO mice associated with mirna-184 modulation. UUO mice model was established and make an injection of mirna-184 into the tail vein. a HE and MAS- SON staining of mice kidney in various groups. b COL1A1 mrna expression. c COL3A1 mrna expression. *Statistically significant, P < 0.05 was significantly decreased, which indicated that mirna- 184 suppressed its target gene HIF1AN expression by specifically binding its 3 -UTR. Above findings of target gene of mirna-184 were consistent with the theory that the target sites of micro-rna could be enriched in multiple components of the same signaling pathway [36, 37]. Angotens in II is a critical mediator of proteinuria and fibrosis, which failed to induce mirna-184 expression in rat kidney cells. It s able to express angiotensin II type 1 receptors [38], suggesting that angiotensin II is lack of a direct effect on mirna-184. In contrast, one interesting finding of our study is that Angiotensin II is an effective trigger for mirna-184 expression in rat kidney fibroblasts (Fig. 2a). In addition, Western blotting analysis revealed that mirna- 184 could cause a sustained up-regulation of the α-sma, CTGF, COL1A1, and COL3A1 expression (Figs. 2b, 6a, b). And mirna-184 inhibitor could cause a sustained downregulation of the α-sma, CTGF, COL1A1 and COL3A1 expression (Fig. 7a, b). The fibrotic markers, such as collagens [39 41], could be induced involved in the signaling conduction pathway to promote the fibrosis and could be control involved in the signaling conduction pathway to suppress the fibrosis. Previous studies [42 44] described that TGFβ1 enhanced α-sma, COL1A1, COL3A1, and CTGF levels to drive renal fibrosis mediated by the mir-433. In cardiac fibrosis, elevated COL3A1 has been described in early myocardial remodeling, while COL1A1 accumulation is observed at a later stage [45]. Importantly, in UUO model, Compliance with ethical standards Conflict of interest The authors declare no competing financial interests. Ethical approval All applicable international, national, and/or institutional guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed. And all procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/ or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License ( iveco mmons.org/licen ses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. References 1. Remuzzi G, Bertani T (1998) Pathophysiology of progressive nephropathies. N Engl J Med 339(20): Iwano M, Neilson EG (2004) Mechanisms of tubulointerstitial fibrosis. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens 13(3): Müller GA, Zeisberg M, Strutz F (2000) The importance of tubulointerstitial damage in progressive renal disease. Nephrol Dial Transpl 15(Suppl 6):76 4. Deng C, Zheng J, Wan W et al (2013) Suppression of cell proliferation and collagen production in cultured, human hypertrophic scar fibroblasts by Sp1 decoy oligodeoxynucleotide. Mol Med Rep 7(3): Navarro-González JF, Mora-Fernández C, Muros de Fuentes M, García-Pérez J (2011) Inflammatory molecules and pathways in the pathogenesis of diabetic nephropathy. Nat Rev Nephrol 7(6): Loeffler I, Wolf G (2015) Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in diabetic nephropathy: fact or fiction? Cells 4(4): Chung AC, Dong Y, Yang W,et al (2013) Smad7 suppresses renal fibrosis via altering expression of TGF-β/Smad3-regulated micro- RNAs. Mol Ther J Am Soc Gene Ther 21(2):388
8 8. Lorenzen JM, Haller H, Thum T (2011) MicroRNAs as mediators and therapeutic targets in chronic kidney disease. Nat Rev Nephrol 7(5): Kato M, Natarajan R (2015) MicroRNAs in diabetic nephropathy: functions, biomarkers, and therapeutic targets. Ann NY Acad Sci 1353: Zhong X, Chung ACK, Chen HY et al (2013) mir-21 is a key therapeutic target for renal injury in a mouse model of type 2 diabetes. Diabetologia 56(3): Zavadil J, Narasimhan M, Blumenberg M et al (2007) Transforming growth factor-beta and microrna:mrna regulatory networks in epithelial plasticity. Cells Tissues Organs 185(1 3): Wang G, Kwan BC, Lai FM et al (2012) Urinary mir-21, mir- 29, and mir-93: novel biomarkers of fibrosis. Am J Nephrol 36(5): Kato M, Natarajan R (2014) Diabetic nephropathy emerging epigenetic mechanisms. Nat Rev Nephrol 10(9): Kato M, Zhang J, Wang M et al (2007) MicroRNA-192 in diabetic kidney glomeruli and its function in TGF-β-induced collagen expression via inhibition of E-Box repressors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104(9): Qin W, Chung AC, Huang XR et al (2011) TGF-β/Smad3 signaling promotes renal fibrosis by inhibiting mir-29. J Am Soc Nephrol 22(8): Zoja C, Cattaneo S, Fiordaliso F et al (2011) Distinct cardiac and renal effects of ETA receptor antagonist and ACE inhibitor in experimental type 2 diabetes. Am J Physiol Ren Physiol 301(5):F Krupa A, Jenkins R, Luo DD et al (2010) Loss of MicroRNA-192 promotes fibrogenesis in diabetic nephropathy. J Am Soc Nephrol 21(3): Lan HY, Mu W, Tomita N et al (2003) Inhibition of renal fibrosis by gene transfer of inducible Smad7 using ultrasound-microbubble system in rat UUO model. J Am Soc Nephrol 14(6): Liu G, Friggeri A, Yang Y et al (2009) mir-147, a microrna that is induced upon Toll-like receptor stimulation, regulates murine macrophage inflammatory responses. Proc Natl Acad Sci 106(37): Yang F, Huang XR, Chung AC et al (2010) Essential role for Smad3 in angiotensin II-induced tubular epithelial-mesenchymal transition. J Pathol 221(4): Koka V, Xiao RH, Chung ACK et al (2008) Angiotensin II upregulates angiotensin I-converting enzyme (ACE), but down-regulates ACE2 via the AT1-ERK/p38 MAP kinase pathway. Am J Pathol 172(5): Arora MK, Singh UK (2013) Molecular mechanisms in the pathogenesis of diabetic nephropathy: an update. Vascul Pharmacol 58(4): Macconi D, Remuzzi G, Benigni A (2014) Key fibrogenic mediators: old players. Renin-angiotensin system. Kidney Int Suppl 4(1): Macconi D, Tomasoni S, Romagnani P et al (2012) MicroRNA p promotes renal fibrosis and is a target of ACE inhibition. J Am Soc Nephrol 23(9): Li R, Chung AC, Dong K et al (2013) The microrna mir-433 promotes renal fibrosis by amplifying the TGF-β/Smad3-Azin1 pathway. Kidney Int 84(6): Bai XY, Ma Y, Ding R et al (2011) mir-335 and mir-34a Promote renal senescence by suppressing mitochondrial antioxidativeenzymes. J Am Soc Nephrol 22(7): Liu X, Fu B, Chen D et al (2015) mir-184 and mir-150 promote renal glomerular mesangial cell aging by targeting Rab1a and Rab31. Exp Cell Res 336(2): Zanchi C, Macconi D, Trionfini P et al (2017) MicroRNA-184 is a downstream effector of albuminuria driving renal fibrosis in rats with diabetic nephropathy. Diabetologia 60(6): Sciorra VA, Morris AJ (1999) Sequential actions of phospholipase D and phosphatidic acid phosphohydrolase 2b generate diglyceride in mammalian cells. Mol Biol Cell 10(11): Brindley DN, English D, Pilquil C et al (2002) Lipid phosphate phosphatases regulate signal transduction through glycerolipids and sphingolipids. Biochim Biophys Acta 1582(1 3): Lando D, Peet DJ, Gorman JJ et al Lando D, Peet DJ, Gorman JJ, Whelan DA, Whitelaw ML, Bruick RK (2002) FIH-1 is an asparaginyl hydroxylase enzyme that regulates the transcriptional activity of hypoxia-inducible factor. Genes Dev 16: Devries IL, Hampton-Smith RJ, Mulvihill MM et al (2010) Consequences of IkappaB alpha hydroxylation by the factor inhibiting HIF (FIH). Febs Lett 584(23): Chan MC, Atasoylu O, Hodson E et al (2015) Potent and selective triazole-based inhibitors of the hypoxia-inducible factor prolyl-hydroxylases with activity in the murine brain. PLoS ONE 10(7):e Nayak BK, Shanmugasundaram K, Friedrichs WE et al (2016) HIF-1 mediates renal fibrosis in OVE26 type 1 diabetic mice. Diabetes 65(5): Mahon PC, Hirota K, Semenza GL (2001) FIH-1: a novel protein that interacts with HIF-1α and VHL to mediate repression of HIF-1 transcriptional activity. Genes Dev 15(20): Tsang JS, Ebert MS, Oudenaarden AV (2010) Genome-wide dissection of MicroRNA functions and cotargeting networks using gene set signatures. Mol Cell 38(1): Zhou L, Xue H, Yuan P et al (2010) Angiotensin AT1 receptor activation mediates high glucose-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition in renal proximal tubular cells. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol 37(9):e152 e Chung AC, Lan HY (2011) Chemokines in renal injury. J Am Soc Nephrol 22: Li ZI, Chung AC, Zhou L et al (2011) C-reactive protein promotes acute renal inflammation and fibrosis in unilateral ureteral obstructive nephropathy in mice. Lab Investig 91(6): Liu F, Chen HY, Huang XR et al (2011) C-reactive protein promotes diabetic kidney disease in a mouse model of type 1 diabetes. Diabetologia 54(10): Landau G, Bercovich Z, Park MH et al (2010) The role of polyamines in supporting growth of mammalian cells is mediated through their requirement for translation initiation and elongation. J Biol Chem 285(17): Cucoranu I, Clempus R, Dikalova A et al (2005) NAD(P)H oxidase 4 mediates transforming growth factor-beta1-induced differentiation of cardiac fibroblasts into myofibroblasts. Circ Res 97: Roberts AB (1998) Molecular and cell biology of TGF-beta. Miner Electrol Metab 24(2 3): Zhang R, Zhang YY, Huang XR et al (2010) C-reactive protein promotes cardiac fibrosis and inflammation in angiotensin II induced hypertensive cardiac disease. Hypertension 55(4): Graham HK, Horn M, Trafford AW (2008) Extracellular matrix profiles in the progression to heart failure. Acta Physiol 194(1):3 21
Supplementary Figure 1:
 Supplementary Figure 1: (A) Whole aortic cross-sections stained with Hematoxylin and Eosin (H&E), 7 days after porcine-pancreatic-elastase (PPE)-induced AAA compared to untreated, healthy control aortas
Supplementary Figure 1: (A) Whole aortic cross-sections stained with Hematoxylin and Eosin (H&E), 7 days after porcine-pancreatic-elastase (PPE)-induced AAA compared to untreated, healthy control aortas
Figure S1. Reduction in glomerular mir-146a levels correlate with progression to higher albuminuria in diabetic patients.
 Supplementary Materials Supplementary Figures Figure S1. Reduction in glomerular mir-146a levels correlate with progression to higher albuminuria in diabetic patients. Figure S2. Expression level of podocyte
Supplementary Materials Supplementary Figures Figure S1. Reduction in glomerular mir-146a levels correlate with progression to higher albuminuria in diabetic patients. Figure S2. Expression level of podocyte
renoprotection therapy goals 208, 209
 Subject Index Aldosterone, plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 induction 163, 164, 168 Aminopeptidases angiotensin II processing 64 66, 214 diabetic expression 214, 215 Angiotensin I intrarenal compartmentalization
Subject Index Aldosterone, plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 induction 163, 164, 168 Aminopeptidases angiotensin II processing 64 66, 214 diabetic expression 214, 215 Angiotensin I intrarenal compartmentalization
Transforming growth factor-b1 stimulates hedgehog signaling to promote epithelial mesenchymal transition after kidney injury
 Transforming growth factor-b1 stimulates hedgehog signaling to promote epithelial mesenchymal transition after kidney injury Hong Lu 1, Bicheng Chen 2, Weilong Hong 2, Yong Liang 2 and Yongheng Bai 2 1
Transforming growth factor-b1 stimulates hedgehog signaling to promote epithelial mesenchymal transition after kidney injury Hong Lu 1, Bicheng Chen 2, Weilong Hong 2, Yong Liang 2 and Yongheng Bai 2 1
Niki Prakoura. Calreticulin upregulation in renal fibrosis
 Calreticulin upregulation in renal fibrosis Niki Prakoura Section of Histology, Center of Basic Research, Biomedical Research Foundation of the Academy of Athens, Athens, Greece EuroKUP meeting, Madrid,
Calreticulin upregulation in renal fibrosis Niki Prakoura Section of Histology, Center of Basic Research, Biomedical Research Foundation of the Academy of Athens, Athens, Greece EuroKUP meeting, Madrid,
Introduction. Acute sodium overload produces renal tubulointerstitial inflammation in normal rats
 Acute sodium overload produces renal tubulointerstitial inflammation in normal rats MI Roson, et al. Kidney International (2006) Introduction Present by Kanya Bunnan and Wiraporn paebua Tubular sodium
Acute sodium overload produces renal tubulointerstitial inflammation in normal rats MI Roson, et al. Kidney International (2006) Introduction Present by Kanya Bunnan and Wiraporn paebua Tubular sodium
Molecular signaling cascade of mirnas in causing Diabetes Nephropathy
 www.bioinformation.net Hypothesis Volume 9(8) Molecular signaling cascade of mirnas in causing Diabetes Nephropathy Dyave Gowda Padmashree & Narayanaswamy Ramachra Swamy* Department of Biochemistry, Central
www.bioinformation.net Hypothesis Volume 9(8) Molecular signaling cascade of mirnas in causing Diabetes Nephropathy Dyave Gowda Padmashree & Narayanaswamy Ramachra Swamy* Department of Biochemistry, Central
Title: Intermedin attenuates renal fibrosis by induction of heme oxygenase-1 in rats with unilateral ureteral obstruction
 Author's response to reviews Title: Intermedin attenuates renal fibrosis by induction of heme oxygenase-1 in rats with unilateral ureteral obstruction Authors: Xi Qiao (qiaoxi7347@126.com) Lihua Wang (lihuawang236@126.com)
Author's response to reviews Title: Intermedin attenuates renal fibrosis by induction of heme oxygenase-1 in rats with unilateral ureteral obstruction Authors: Xi Qiao (qiaoxi7347@126.com) Lihua Wang (lihuawang236@126.com)
Down-regulation of mir-23a inhibits high glucose-induced EMT and renal fibrogenesis by up-regulation of SnoN
 Human Cell (2018) 31:22 32 https://doi.org/10.1007/s13577-017-0180-z RESEARCH ARTICLE Down-regulation of mir-23a inhibits high glucose-induced EMT and renal fibrogenesis by up-regulation of SnoN Haiping
Human Cell (2018) 31:22 32 https://doi.org/10.1007/s13577-017-0180-z RESEARCH ARTICLE Down-regulation of mir-23a inhibits high glucose-induced EMT and renal fibrogenesis by up-regulation of SnoN Haiping
Histone modifications in kidney disease
 Histone modifications in kidney disease Masaomi Nangaku Division of Nephrology and Endocrinology The University of Tokyo Graduate School of Medicine Japan Mimura, Tanaka, & Nangaku. Semin Nephrol 2013
Histone modifications in kidney disease Masaomi Nangaku Division of Nephrology and Endocrinology The University of Tokyo Graduate School of Medicine Japan Mimura, Tanaka, & Nangaku. Semin Nephrol 2013
CHAPTER I INTRODUCTION. Nowadays chronic kidney disease (CKD) becomes one. of the most common diseases found in the population.
 CHAPTER I INTRODUCTION I.1 Background Nowadays chronic kidney disease (CKD) becomes one of the most common diseases found in the population. Based on community survey that is held by PERNEFRI (Perhimpunan
CHAPTER I INTRODUCTION I.1 Background Nowadays chronic kidney disease (CKD) becomes one of the most common diseases found in the population. Based on community survey that is held by PERNEFRI (Perhimpunan
Loss of Klotho Contributes to Kidney Injury by Derepression of Wnt/b-Catenin Signaling
 Loss of Klotho Contributes to Kidney Injury by Derepression of Wnt/b-Catenin Signaling Lili Zhou,* Yingjian Li, Dong Zhou, Roderick J. Tan, and Youhua Liu* *Division of Nephrology, Nanfang Hospital, Southern
Loss of Klotho Contributes to Kidney Injury by Derepression of Wnt/b-Catenin Signaling Lili Zhou,* Yingjian Li, Dong Zhou, Roderick J. Tan, and Youhua Liu* *Division of Nephrology, Nanfang Hospital, Southern
Hypoxia-induced microrna-155 promotes fibrosis in proximal tubule cells
 MOLECULAR MEDICINE REPORTS 11: 4555-4560, 2015 Hypoxia-induced microrna-155 promotes fibrosis in proximal tubule cells SHENPING XIE, HUAIZHOU CHEN, FEI LI, SHU WANG and JUNJUN GUO Renal Transplantation
MOLECULAR MEDICINE REPORTS 11: 4555-4560, 2015 Hypoxia-induced microrna-155 promotes fibrosis in proximal tubule cells SHENPING XIE, HUAIZHOU CHEN, FEI LI, SHU WANG and JUNJUN GUO Renal Transplantation
Analysis of regulatory T cell subsets in the peripheral blood of immunoglobulin A nephropathy (IgAN) patients
 Analysis of regulatory T cell subsets in the peripheral blood of immunoglobulin A nephropathy (IgAN) patients S. Yang, B. Chen, J. Shi, F. Chen, J. Zhang and Z. Sun Department of Nephrology, Huaihe Hospital
Analysis of regulatory T cell subsets in the peripheral blood of immunoglobulin A nephropathy (IgAN) patients S. Yang, B. Chen, J. Shi, F. Chen, J. Zhang and Z. Sun Department of Nephrology, Huaihe Hospital
Reviewers' comments: Reviewer #1 (Remarks to the Author):
 Reviewers' comments: Reviewer #1 (Remarks to the Author): The manuscript by Wu et al describes critical role of RNA binding protein CUGBP1 in the development of TGF-beta-mediated liver fibrosis. The activation
Reviewers' comments: Reviewer #1 (Remarks to the Author): The manuscript by Wu et al describes critical role of RNA binding protein CUGBP1 in the development of TGF-beta-mediated liver fibrosis. The activation
mir 375 inhibits the proliferation of gastric cancer cells by repressing ERBB2 expression
 EXPERIMENTAL AND THERAPEUTIC MEDICINE 7: 1757-1761, 2014 mir 375 inhibits the proliferation of gastric cancer cells by repressing ERBB2 expression ZHI YONG SHEN *, ZI ZHEN ZHANG *, HUA LIU, EN HAO ZHAO
EXPERIMENTAL AND THERAPEUTIC MEDICINE 7: 1757-1761, 2014 mir 375 inhibits the proliferation of gastric cancer cells by repressing ERBB2 expression ZHI YONG SHEN *, ZI ZHEN ZHANG *, HUA LIU, EN HAO ZHAO
Ανάπτυξη Βιοτράπεζας για την Ανίχνευση Πρώιμων Βιοδεικτών σε Ασθενείς με Χρόνια Νεφρική Νόσο
 Ανάπτυξη Βιοτράπεζας για την Ανίχνευση Πρώιμων Βιοδεικτών σε Ασθενείς με Χρόνια Νεφρική Νόσο ΔΗΜΗΤΡΙΟΣ Σ. ΓΟΥΜΕΝΟΣ Νεφρολογικό και Μεταμοσχευτικό Κέντρο Πανεπιστημιακό Νοσοκομείο Πατρών Causes of chronic
Ανάπτυξη Βιοτράπεζας για την Ανίχνευση Πρώιμων Βιοδεικτών σε Ασθενείς με Χρόνια Νεφρική Νόσο ΔΗΜΗΤΡΙΟΣ Σ. ΓΟΥΜΕΝΟΣ Νεφρολογικό και Μεταμοσχευτικό Κέντρο Πανεπιστημιακό Νοσοκομείο Πατρών Causes of chronic
MOLECULAR MEDICINE REPORTS 10: 39-44, 2014
 MOLECULAR MEDICINE REPORTS 10: 39-44, 2014 Epithelial mesenchymal transition and apoptosis of renal tubular epithelial cells are associated with disease progression in patients with IgA nephropathy JUNXIA
MOLECULAR MEDICINE REPORTS 10: 39-44, 2014 Epithelial mesenchymal transition and apoptosis of renal tubular epithelial cells are associated with disease progression in patients with IgA nephropathy JUNXIA
Salt Sensitivity: Mechanisms, Diagnosis, and Clinical Relevance
 Salt Sensitivity: Mechanisms, Diagnosis, and Clinical Relevance Matthew R. Weir, MD Professor and Director Division of Nephrology University of Maryland School of Medicine Overview Introduction Mechanisms
Salt Sensitivity: Mechanisms, Diagnosis, and Clinical Relevance Matthew R. Weir, MD Professor and Director Division of Nephrology University of Maryland School of Medicine Overview Introduction Mechanisms
High AU content: a signature of upregulated mirna in cardiac diseases
 https://helda.helsinki.fi High AU content: a signature of upregulated mirna in cardiac diseases Gupta, Richa 2010-09-20 Gupta, R, Soni, N, Patnaik, P, Sood, I, Singh, R, Rawal, K & Rani, V 2010, ' High
https://helda.helsinki.fi High AU content: a signature of upregulated mirna in cardiac diseases Gupta, Richa 2010-09-20 Gupta, R, Soni, N, Patnaik, P, Sood, I, Singh, R, Rawal, K & Rani, V 2010, ' High
Uncovering the mechanisms of wound healing and fibrosis
 Any Questions??? Ask now or contact support support@sabiosciences.com 1-888-503-3187 International customers: SABio@Qiagen.com Uncovering the mechanisms of wound healing and fibrosis Webinar related questions:
Any Questions??? Ask now or contact support support@sabiosciences.com 1-888-503-3187 International customers: SABio@Qiagen.com Uncovering the mechanisms of wound healing and fibrosis Webinar related questions:
Original Article mir-216a-5p promotes mesangial cell proliferation by targeting FoxO1 in diabetic nephropathy
 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2019;12(1):344-355 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0085617 Original Article mir-216a-5p promotes mesangial cell proliferation by targeting FoxO1 in diabetic nephropathy Cong Huang
Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2019;12(1):344-355 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0085617 Original Article mir-216a-5p promotes mesangial cell proliferation by targeting FoxO1 in diabetic nephropathy Cong Huang
HIF-inducible mir-191 promotes migration in breast cancer through complex regulation of TGFβ-signaling in hypoxic microenvironment.
 HIF-inducible mir-9 promotes migration in breast cancer through complex regulation of TGFβ-signaling in hypoxic microenvironment. Neha Nagpal, Hafiz M Ahmad, Shibu Chameettachal3, Durai Sundar, Sourabh
HIF-inducible mir-9 promotes migration in breast cancer through complex regulation of TGFβ-signaling in hypoxic microenvironment. Neha Nagpal, Hafiz M Ahmad, Shibu Chameettachal3, Durai Sundar, Sourabh
BioScience Trends. 2017; 11(1):
 Original Article BioScience Trends. 2017; 11(1):77-84. 77 DOI: 10.5582/bst.2016.01224 Knocking down TCF8 inhibits high glucose- and angiotensin IIinduced epithelial to mesenchymal transition in podocytes
Original Article BioScience Trends. 2017; 11(1):77-84. 77 DOI: 10.5582/bst.2016.01224 Knocking down TCF8 inhibits high glucose- and angiotensin IIinduced epithelial to mesenchymal transition in podocytes
Soft Agar Assay. For each cell pool, 100,000 cells were resuspended in 0.35% (w/v)
 SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL AND METHODS Soft Agar Assay. For each cell pool, 100,000 cells were resuspended in 0.35% (w/v) top agar (LONZA, SeaKem LE Agarose cat.5004) and plated onto 0.5% (w/v) basal agar.
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL AND METHODS Soft Agar Assay. For each cell pool, 100,000 cells were resuspended in 0.35% (w/v) top agar (LONZA, SeaKem LE Agarose cat.5004) and plated onto 0.5% (w/v) basal agar.
Aberrant Promoter CpG Methylation is a Mechanism for Lack of Hypoxic Induction of
 Aberrant Promoter CpG Methylation is a Mechanism for Lack of Hypoxic Induction of PHD3 in a Diverse Set of Malignant Cells Abstract The prolyl-hydroxylase domain family of enzymes (PHD1-3) plays an important
Aberrant Promoter CpG Methylation is a Mechanism for Lack of Hypoxic Induction of PHD3 in a Diverse Set of Malignant Cells Abstract The prolyl-hydroxylase domain family of enzymes (PHD1-3) plays an important
RNA interference induced hepatotoxicity results from loss of the first synthesized isoform of microrna-122 in mice
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION RNA interference induced hepatotoxicity results from loss of the first synthesized isoform of microrna-122 in mice Paul N Valdmanis, Shuo Gu, Kirk Chu, Lan Jin, Feijie Zhang,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION RNA interference induced hepatotoxicity results from loss of the first synthesized isoform of microrna-122 in mice Paul N Valdmanis, Shuo Gu, Kirk Chu, Lan Jin, Feijie Zhang,
Enhancer of Zeste Homolog 2 Inhibition Attenuates Renal Fibrosis by Maintaining Smad7 and Phosphatase and Tensin Homolog Expression
 Enhancer of Zeste Homolog 2 Inhibition Attenuates Renal Fibrosis by Maintaining Smad7 and Phosphatase and Tensin Homolog Expression Xiaoxu Zhou,* Xiujuan Zang,* Murugavel Ponnusamy,* Monica V. Masucci,*
Enhancer of Zeste Homolog 2 Inhibition Attenuates Renal Fibrosis by Maintaining Smad7 and Phosphatase and Tensin Homolog Expression Xiaoxu Zhou,* Xiujuan Zang,* Murugavel Ponnusamy,* Monica V. Masucci,*
As outlined under External contributions (see appendix 7.1), the group of Prof. Gröne at the
 3 RESULTS As outlined under External contributions (see appendix 7.1), the group of Prof. Gröne at the DKFZ in Heidelberg (Dept. of Cellular and Molecular pathology) contributed to this work by performing
3 RESULTS As outlined under External contributions (see appendix 7.1), the group of Prof. Gröne at the DKFZ in Heidelberg (Dept. of Cellular and Molecular pathology) contributed to this work by performing
Over-Activation of Hypoxia-Inducible Transcription Factor 1 alpha (HIF)-1α by Chronic Hypoxia Mediates Chronic Ischemic Renal Injury
 Over-Activation of Hypoxia-Inducible Transcription Factor 1 alpha (HIF)-1α by Chronic Hypoxia Mediates Chronic Ischemic Renal Injury Romesh Dhaduk Department of Pharmocology and Toxicology Virginia Commonwealth
Over-Activation of Hypoxia-Inducible Transcription Factor 1 alpha (HIF)-1α by Chronic Hypoxia Mediates Chronic Ischemic Renal Injury Romesh Dhaduk Department of Pharmocology and Toxicology Virginia Commonwealth
Analysis on the mechanism of reduced nephron number and the pathological progression of chronic renal failure in Astrin deficient rats
 Analysis on the mechanism of reduced nephron number and the pathological progression of chronic renal failure in Astrin deficient rats Summary of Doctoral Thesis Hidenori Yasuda Graduate School of Veterinary
Analysis on the mechanism of reduced nephron number and the pathological progression of chronic renal failure in Astrin deficient rats Summary of Doctoral Thesis Hidenori Yasuda Graduate School of Veterinary
MicroRNA sponges: competitive inhibitors of small RNAs in mammalian cells
 MicroRNA sponges: competitive inhibitors of small RNAs in mammalian cells Margaret S Ebert, Joel R Neilson & Phillip A Sharp Supplementary figures and text: Supplementary Figure 1. Effect of sponges on
MicroRNA sponges: competitive inhibitors of small RNAs in mammalian cells Margaret S Ebert, Joel R Neilson & Phillip A Sharp Supplementary figures and text: Supplementary Figure 1. Effect of sponges on
Chapter 2. Investigation into mir-346 Regulation of the nachr α5 Subunit
 15 Chapter 2 Investigation into mir-346 Regulation of the nachr α5 Subunit MicroRNA s (mirnas) are small (< 25 base pairs), single stranded, non-coding RNAs that regulate gene expression at the post transcriptional
15 Chapter 2 Investigation into mir-346 Regulation of the nachr α5 Subunit MicroRNA s (mirnas) are small (< 25 base pairs), single stranded, non-coding RNAs that regulate gene expression at the post transcriptional
An Epstein-Barr virus-encoded microrna targets PUMA to promote host cell survival
 An Epstein-Barr virus-encoded microrna targets to promote host cell survival The Journal of Experimental Medicine 205(11): 2551-2560, 2008. 1 Elizabeth Yee-Wai Choy, Kam-Leung Siu, Kin-Hang Kok, Raymond
An Epstein-Barr virus-encoded microrna targets to promote host cell survival The Journal of Experimental Medicine 205(11): 2551-2560, 2008. 1 Elizabeth Yee-Wai Choy, Kam-Leung Siu, Kin-Hang Kok, Raymond
Supplementary Figure 1. Expression of CUGBP1 in non-parenchymal liver cells treated with TGF-β
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Expression of CUGBP1 in non-parenchymal liver cells treated with TGF-β and LPS. Non-parenchymal liver cells were isolated and treated with or without TGF-β
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Expression of CUGBP1 in non-parenchymal liver cells treated with TGF-β and LPS. Non-parenchymal liver cells were isolated and treated with or without TGF-β
Long non-coding RNA-H19 antagonism protects against renal
 /, Vol. 7, No. 32 Long non-coding RNA-H19 antagonism protects against renal fibrosis Hong Xie 1, Jing-Dong Xue 1, Feng Chao 1, Yan-Feng Jin 1, Qiang Fu 1 1 Department of Urology, Shanghai Jiao Tong University
/, Vol. 7, No. 32 Long non-coding RNA-H19 antagonism protects against renal fibrosis Hong Xie 1, Jing-Dong Xue 1, Feng Chao 1, Yan-Feng Jin 1, Qiang Fu 1 1 Department of Urology, Shanghai Jiao Tong University
Clinical significance of CD44 expression in children with hepatoblastoma
 Clinical significance of CD44 expression in children with hepatoblastoma H.-Y. Cai 1 *, B. Yu 1 *, Z.-C. Feng 2, X. Qi 1 and X.-J. Wei 1 1 Department of General Surgery, General Hospital of Beijing Military
Clinical significance of CD44 expression in children with hepatoblastoma H.-Y. Cai 1 *, B. Yu 1 *, Z.-C. Feng 2, X. Qi 1 and X.-J. Wei 1 1 Department of General Surgery, General Hospital of Beijing Military
MEK/ERK INHIBITORS: A PROOF-OF-CONCEPT STUDY IN LUNG FIBROSIS
 MEK/ERK INHIBITORS: A PROOF-OF-CONCEPT STUDY IN LUNG FIBROSIS Andrew Leask Departments of Dentistry and Physiology and Pharmacology University of Western Ontario Dental Sciences Building London ON Canada
MEK/ERK INHIBITORS: A PROOF-OF-CONCEPT STUDY IN LUNG FIBROSIS Andrew Leask Departments of Dentistry and Physiology and Pharmacology University of Western Ontario Dental Sciences Building London ON Canada
Expression of P311, a transforming growth factor beta latency-associated protein-binding protein, in human kidneys with IgA nephropathy
 Int Urol Nephrol (2010) 42:811 819 DOI 10.1007/s11255-009-9681-3 NEPHROLOGY - ORIGINAL PAPER Expression of P311, a transforming growth factor beta latency-associated protein-binding protein, in human kidneys
Int Urol Nephrol (2010) 42:811 819 DOI 10.1007/s11255-009-9681-3 NEPHROLOGY - ORIGINAL PAPER Expression of P311, a transforming growth factor beta latency-associated protein-binding protein, in human kidneys
Downregulation of serum mir-17 and mir-106b levels in gastric cancer and benign gastric diseases
 Brief Communication Downregulation of serum mir-17 and mir-106b levels in gastric cancer and benign gastric diseases Qinghai Zeng 1 *, Cuihong Jin 2 *, Wenhang Chen 2, Fang Xia 3, Qi Wang 3, Fan Fan 4,
Brief Communication Downregulation of serum mir-17 and mir-106b levels in gastric cancer and benign gastric diseases Qinghai Zeng 1 *, Cuihong Jin 2 *, Wenhang Chen 2, Fang Xia 3, Qi Wang 3, Fan Fan 4,
mirna Dr. S Hosseini-Asl
 mirna Dr. S Hosseini-Asl 1 2 MicroRNAs (mirnas) are small noncoding RNAs which enhance the cleavage or translational repression of specific mrna with recognition site(s) in the 3 - untranslated region
mirna Dr. S Hosseini-Asl 1 2 MicroRNAs (mirnas) are small noncoding RNAs which enhance the cleavage or translational repression of specific mrna with recognition site(s) in the 3 - untranslated region
Novel therapeutic approach for kidney fibrosis
 University of Sydney Novel therapeutic approach for kidney fibrosis DAVID HARRIS 30/09/17 Westmead Hospital Cadnapaphornchai CJASN 2014;9:889 Liraglutide: Renal Outcomes Mann JFE et al. N Engl J Med 2017;377:839-848
University of Sydney Novel therapeutic approach for kidney fibrosis DAVID HARRIS 30/09/17 Westmead Hospital Cadnapaphornchai CJASN 2014;9:889 Liraglutide: Renal Outcomes Mann JFE et al. N Engl J Med 2017;377:839-848
Renal angiotensin II up-regulation and myofibroblast activation in human membranous nephropathy
 Kidney International, Vol. 64, Supplement 86 (2003), pp. Renal angiotensin II up-regulation and myofibroblast activation in human membranous nephropathy SERGIO A. MEZZANO, CLAUDIO A. AROS, ALEJANDRA DROGUETT,
Kidney International, Vol. 64, Supplement 86 (2003), pp. Renal angiotensin II up-regulation and myofibroblast activation in human membranous nephropathy SERGIO A. MEZZANO, CLAUDIO A. AROS, ALEJANDRA DROGUETT,
Sestrin2 and BNIP3 (Bcl-2/adenovirus E1B 19kDa-interacting. protein3) regulate autophagy and mitophagy in renal tubular cells in. acute kidney injury
 Sestrin2 and BNIP3 (Bcl-2/adenovirus E1B 19kDa-interacting protein3) regulate autophagy and mitophagy in renal tubular cells in acute kidney injury by Masayuki Ishihara 1, Madoka Urushido 2, Kazu Hamada
Sestrin2 and BNIP3 (Bcl-2/adenovirus E1B 19kDa-interacting protein3) regulate autophagy and mitophagy in renal tubular cells in acute kidney injury by Masayuki Ishihara 1, Madoka Urushido 2, Kazu Hamada
PREPARED FOR: U.S. Army Medical Research and Materiel Command Fort Detrick, MD
 AD Award Number: W81XWH-11-1-0126 TITLE: Chemical strategy to translate genetic/epigenetic mechanisms to breast cancer therapeutics PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Xiang-Dong Fu, PhD CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION:
AD Award Number: W81XWH-11-1-0126 TITLE: Chemical strategy to translate genetic/epigenetic mechanisms to breast cancer therapeutics PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Xiang-Dong Fu, PhD CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION:
MiR-196a Regulates High Glucose-Induced Mesangial Cell Hypertrophy by Targeting p27 kip1
 569055JLAXXX10.1177/2211068215569055Journal of Laboratory AutomationWang et al. research-article2015 Original Report MiR-196a Regulates High Glucose-Induced Mesangial Cell Hypertrophy by Targeting p27
569055JLAXXX10.1177/2211068215569055Journal of Laboratory AutomationWang et al. research-article2015 Original Report MiR-196a Regulates High Glucose-Induced Mesangial Cell Hypertrophy by Targeting p27
HEK293FT cells were transiently transfected with reporters, N3-ICD construct and
 Supplementary Information Luciferase reporter assay HEK293FT cells were transiently transfected with reporters, N3-ICD construct and increased amounts of wild type or kinase inactive EGFR. Transfections
Supplementary Information Luciferase reporter assay HEK293FT cells were transiently transfected with reporters, N3-ICD construct and increased amounts of wild type or kinase inactive EGFR. Transfections
Transforming growth factor-b1-mediated renal fibrosis is dependent on the regulation of transforming growth factor receptor 1 expression by let-7b
 basic research http://www.kidney-international.org & International Society of Nephrology Transforming growth factor-b-mediated renal fibrosis is dependent on the regulation of transforming growth factor
basic research http://www.kidney-international.org & International Society of Nephrology Transforming growth factor-b-mediated renal fibrosis is dependent on the regulation of transforming growth factor
mir-132 inhibits lung cancer cell migration and invasion by targeting SOX4
 Original Article inhibits lung cancer cell migration and invasion by targeting SOX4 Yang Li, Lingling Zu, Yuli Wang, Min Wang, Peirui Chen, Qinghua Zhou Tianjin Key Laboratory of Lung Cancer Metastasis
Original Article inhibits lung cancer cell migration and invasion by targeting SOX4 Yang Li, Lingling Zu, Yuli Wang, Min Wang, Peirui Chen, Qinghua Zhou Tianjin Key Laboratory of Lung Cancer Metastasis
Berberine Sensitizes Human Ovarian Cancer Cells to Cisplatin Through mir-93/ PTEN/Akt Signaling Pathway
 Chen Accepted: et al.: February Berberine 24, Sensitizes 2015 Ovarian Cancer Cells to Cisplatin www.karger.com/cpb 956 1421-9778/15/0363-0956$39.50/0 Original Paper This is an Open Access article licensed
Chen Accepted: et al.: February Berberine 24, Sensitizes 2015 Ovarian Cancer Cells to Cisplatin www.karger.com/cpb 956 1421-9778/15/0363-0956$39.50/0 Original Paper This is an Open Access article licensed
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI:.38/ncb3399 a b c d FSP DAPI 5mm mm 5mm 5mm e Correspond to melanoma in-situ Figure a DCT FSP- f MITF mm mm MlanaA melanoma in-situ DCT 5mm FSP- mm mm mm mm mm g melanoma in-situ MITF MlanaA mm mm
DOI:.38/ncb3399 a b c d FSP DAPI 5mm mm 5mm 5mm e Correspond to melanoma in-situ Figure a DCT FSP- f MITF mm mm MlanaA melanoma in-situ DCT 5mm FSP- mm mm mm mm mm g melanoma in-situ MITF MlanaA mm mm
Understanding Root Cause: Pathogenesis of Hepatic Fibrosis
 10/1/12 Understanding Root Cause: Pathogenesis of Hepatic Fibrosis Hepatitis C Virus Mild inflammation Inflammation Fibrosis Cirrhosis 1 10/1/12 Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Steatosis Steatohepatitis
10/1/12 Understanding Root Cause: Pathogenesis of Hepatic Fibrosis Hepatitis C Virus Mild inflammation Inflammation Fibrosis Cirrhosis 1 10/1/12 Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Steatosis Steatohepatitis
Epithelial to Mesenchymal Transition in Renal Fibrogenesis: Pathologic Significance, Molecular Mechanism, and Therapeutic Intervention
 REVIEW J Am Soc Nephrol 15: 1 12, 2004 Epithelial to Mesenchymal Transition in Renal Fibrogenesis: Pathologic Significance, Molecular Mechanism, and Therapeutic Intervention YOUHUA LIU Division of Cellular
REVIEW J Am Soc Nephrol 15: 1 12, 2004 Epithelial to Mesenchymal Transition in Renal Fibrogenesis: Pathologic Significance, Molecular Mechanism, and Therapeutic Intervention YOUHUA LIU Division of Cellular
hemodynamic stress. A. Echocardiographic quantification of cardiac dimensions and function in
 SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE LEGENDS Supplemental Figure 1. Fbn1 C1039G/+ hearts display normal cardiac function in the absence of hemodynamic stress. A. Echocardiographic quantification of cardiac dimensions and
SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE LEGENDS Supplemental Figure 1. Fbn1 C1039G/+ hearts display normal cardiac function in the absence of hemodynamic stress. A. Echocardiographic quantification of cardiac dimensions and
microrna Therapeutics Harnessing the power of micrornas to target multiple pathways of disease
 microrna Therapeutics Harnessing the power of micrornas to target multiple pathways of disease January 2018 Safe Harbor Statement Statements contained in this presentation regarding matters that are not
microrna Therapeutics Harnessing the power of micrornas to target multiple pathways of disease January 2018 Safe Harbor Statement Statements contained in this presentation regarding matters that are not
The BMP-7 Smad1/5/8 Pathway Promotes Kidney Repair After Obstruction Induced Renal Injury
 The BMP-7 Smad1/5/8 Pathway Promotes Kidney Repair After Obstruction Induced Renal Injury Scott R. Manson, Robert A. Niederhoff, Keith A. Hruska and Paul F. Austin* From the Division of Pediatric Urology,
The BMP-7 Smad1/5/8 Pathway Promotes Kidney Repair After Obstruction Induced Renal Injury Scott R. Manson, Robert A. Niederhoff, Keith A. Hruska and Paul F. Austin* From the Division of Pediatric Urology,
cells ISSN
 Cells 2015, 4, 631-652; doi:10.3390/cells4040631 Review OPEN ACCESS cells ISSN 2073-4409 www.mdpi.com/journal/cells Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition in Diabetic Nephropathy: Fact or Fiction? Ivonne
Cells 2015, 4, 631-652; doi:10.3390/cells4040631 Review OPEN ACCESS cells ISSN 2073-4409 www.mdpi.com/journal/cells Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition in Diabetic Nephropathy: Fact or Fiction? Ivonne
Journal Club. 03/04/2012 Lama Nazzal
 Journal Club 03/04/2012 Lama Nazzal NOTCH and the kidneys Is an evolutionarily conserved cell cell communication mechanism. Is a regulator of cell specification, differentiation, and tissue patterning.
Journal Club 03/04/2012 Lama Nazzal NOTCH and the kidneys Is an evolutionarily conserved cell cell communication mechanism. Is a regulator of cell specification, differentiation, and tissue patterning.
Original Article Chana 1 exhibits a promising role in the inhibition of renal kidney fibrosis in rat model
 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2016;9(7):6959-6964 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0022474 Original Article Chana 1 exhibits a promising role in the inhibition of renal kidney fibrosis in rat model Li-Hua Ma
Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2016;9(7):6959-6964 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0022474 Original Article Chana 1 exhibits a promising role in the inhibition of renal kidney fibrosis in rat model Li-Hua Ma
Hasan Fattah 4/30/2013
 Hasan Fattah 4/30/2013 49 yo hispanic male, ho HIV(CD4 229), currently on HAART, course c/b AIDS, Presents with two days ho fever, SOB, blood tinged sputum, and visible hematuria. ROS: no skin rash, joint
Hasan Fattah 4/30/2013 49 yo hispanic male, ho HIV(CD4 229), currently on HAART, course c/b AIDS, Presents with two days ho fever, SOB, blood tinged sputum, and visible hematuria. ROS: no skin rash, joint
micro-rnas as biomarkers in children who underwent surgery for CHD
 micro-rnas as biomarkers in children who underwent surgery for CHD mentors: Dr. Yael Nevo-Caspi & Prof. Gidi Paret Or Bercovich Liat Mor What will we talk about Congenital heart defects (CHD) Scientific
micro-rnas as biomarkers in children who underwent surgery for CHD mentors: Dr. Yael Nevo-Caspi & Prof. Gidi Paret Or Bercovich Liat Mor What will we talk about Congenital heart defects (CHD) Scientific
Cardiovascular Protection and the RAS
 Cardiovascular Protection and the RAS Katalin Kauser, MD, PhD, DSc Senior Associate Director, Boehringer Ingelheim Pharmaceutical Inc. Micardis Product Pipeline Scientific Support Ridgefield, CT, USA Cardiovascular
Cardiovascular Protection and the RAS Katalin Kauser, MD, PhD, DSc Senior Associate Director, Boehringer Ingelheim Pharmaceutical Inc. Micardis Product Pipeline Scientific Support Ridgefield, CT, USA Cardiovascular
Acetyl 11 keto β boswellic acid ameliorates renal interstitial fibrosis via Klotho/TGF β/smad signalling pathway
 Received: 27 February 2018 Accepted: 5 June 2018 DOI: 10.1111/jcmm.13766 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Acetyl 11 keto β boswellic acid ameliorates renal interstitial fibrosis via Klotho/TGF β/smad signalling pathway
Received: 27 February 2018 Accepted: 5 June 2018 DOI: 10.1111/jcmm.13766 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Acetyl 11 keto β boswellic acid ameliorates renal interstitial fibrosis via Klotho/TGF β/smad signalling pathway
Fibroblasts in Kidney Fibrosis Emerge via Endothelialto-Mesenchymal
 BRIEF COMMUNICATION www.jasn.org Fibroblasts in Kidney Fibrosis Emerge via Endothelialto-Mesenchymal Transition Elisabeth M. Zeisberg,* Scott E. Potenta,* Hikaru Sugimoto,* Michael Zeisberg,* and Raghu
BRIEF COMMUNICATION www.jasn.org Fibroblasts in Kidney Fibrosis Emerge via Endothelialto-Mesenchymal Transition Elisabeth M. Zeisberg,* Scott E. Potenta,* Hikaru Sugimoto,* Michael Zeisberg,* and Raghu
Original Article Differential microrna expression in the serum of patients with nephrotic syndrome and clinical correlation analysis
 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2015;8(6):7282-7286 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0008575 Original Article Differential microrna expression in the serum of patients with nephrotic syndrome and clinical correlation
Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2015;8(6):7282-7286 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0008575 Original Article Differential microrna expression in the serum of patients with nephrotic syndrome and clinical correlation
Regenerative Medicine for Sclerotic Disorders
 Regenerative Medicine Regenerative Medicine for Sclerotic Disorders JMAJ 7(7): 3 37, Toshikazu NAKAMURA rofessor, Division of Molecular Regenerative Medicine, Course of Advanced Medicine, Osaka University
Regenerative Medicine Regenerative Medicine for Sclerotic Disorders JMAJ 7(7): 3 37, Toshikazu NAKAMURA rofessor, Division of Molecular Regenerative Medicine, Course of Advanced Medicine, Osaka University
Postn MCM Smad2 fl/fl Postn MCM Smad3 fl/fl Postn MCM Smad2/3 fl/fl. Postn MCM. Tgfbr1/2 fl/fl TAC
 A Smad2 fl/fl Smad3 fl/fl Smad2/3 fl/fl Tgfbr1/2 fl/fl 1. mm B Tcf21 MCM Tcf21 MCM Smad3 fl/fl Tcf21 MCM Smad2/3 fl/fl Tcf21 MCM Tgfbr1/2 fl/fl αmhc MCM C 1. mm 1. mm D Smad2 fl/fl Smad3 fl/fl Smad2/3
A Smad2 fl/fl Smad3 fl/fl Smad2/3 fl/fl Tgfbr1/2 fl/fl 1. mm B Tcf21 MCM Tcf21 MCM Smad3 fl/fl Tcf21 MCM Smad2/3 fl/fl Tcf21 MCM Tgfbr1/2 fl/fl αmhc MCM C 1. mm 1. mm D Smad2 fl/fl Smad3 fl/fl Smad2/3
2015 ICDM, 15-17, Jejudob Island, Korea Recent Advances in Diabetic Microvascular Complications. DPP-4 Inhibition and Diabetic Nephropathy
 2015 ICDM, 15-17, Jejudob Island, Korea Recent Advances in Diabetic Microvascular Complications DPP-4 Inhibition and Diabetic Nephropathy Daisuke Koya Department of Diabetology & Endocrinology Kanazawa
2015 ICDM, 15-17, Jejudob Island, Korea Recent Advances in Diabetic Microvascular Complications DPP-4 Inhibition and Diabetic Nephropathy Daisuke Koya Department of Diabetology & Endocrinology Kanazawa
Original Article Regulation of diabetes-induced inflammation in macrophages by microrna-26a-5p
 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2016;9(10):10074-10079 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0034290 Original Article Regulation of diabetes-induced inflammation in macrophages by microrna-26a-5p Xin-Ge Yue, Su-Jun
Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2016;9(10):10074-10079 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0034290 Original Article Regulation of diabetes-induced inflammation in macrophages by microrna-26a-5p Xin-Ge Yue, Su-Jun
MicroRNA and Male Infertility: A Potential for Diagnosis
 Review Article MicroRNA and Male Infertility: A Potential for Diagnosis * Abstract MicroRNAs (mirnas) are small non-coding single stranded RNA molecules that are physiologically produced in eukaryotic
Review Article MicroRNA and Male Infertility: A Potential for Diagnosis * Abstract MicroRNAs (mirnas) are small non-coding single stranded RNA molecules that are physiologically produced in eukaryotic
Summary 255 Research Summary
 Chapter 10 Summary Nephrolithiasis remains a public health problem around the world, affecting 12% of the adult population. The prevalence and incidence of kidney stones are increasing with global warming,
Chapter 10 Summary Nephrolithiasis remains a public health problem around the world, affecting 12% of the adult population. The prevalence and incidence of kidney stones are increasing with global warming,
Expression of mir-146a-5p in patients with intracranial aneurysms and its association with prognosis
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2018; 22: 726-730 Expression of mir-146a-5p in patients with intracranial aneurysms and its association with prognosis H.-L. ZHANG 1, L. LI 2, C.-J.
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2018; 22: 726-730 Expression of mir-146a-5p in patients with intracranial aneurysms and its association with prognosis H.-L. ZHANG 1, L. LI 2, C.-J.
CYLD Negatively Regulates Transforming Growth Factor-β Signaling via Deubiquitinating Akt
 Supplementary Information CYLD Negatively Regulates Transforming Growth Factor-β Signaling via Deubiquitinating Akt Jae Hyang Lim, Hirofumi Jono, Kensei Komatsu, Chang-Hoon Woo, Jiyun Lee, Masanori Miyata,
Supplementary Information CYLD Negatively Regulates Transforming Growth Factor-β Signaling via Deubiquitinating Akt Jae Hyang Lim, Hirofumi Jono, Kensei Komatsu, Chang-Hoon Woo, Jiyun Lee, Masanori Miyata,
Amniotic fluid stem cells provide considerable advantages in epidermal. regeneration: B7H4 creates a moderate inflammation
 Amniotic fluid stem cells provide considerable advantages in epidermal regeneration: B7H4 creates a moderate inflammation microenvironment to promote wound repair Qing Sun 1, +, Fang Li 1, +, Hong Li 2,
Amniotic fluid stem cells provide considerable advantages in epidermal regeneration: B7H4 creates a moderate inflammation microenvironment to promote wound repair Qing Sun 1, +, Fang Li 1, +, Hong Li 2,
Role of Inflammatory and Progenitor Cells in Pulmonary Vascular Remodeling: Potential Role for Targeted Therapies. Traditional Hypothesis Stress
 3/1/212 Role of Inflammatory and Progenitor Cells in Pulmonary Vascular Remodeling: Potential Role for Targeted Therapies K.R. Stenmark University of Colorado Denver, CO 845 Prominent Fibroproliferative
3/1/212 Role of Inflammatory and Progenitor Cells in Pulmonary Vascular Remodeling: Potential Role for Targeted Therapies K.R. Stenmark University of Colorado Denver, CO 845 Prominent Fibroproliferative
A Normal Exencephaly Craniora- Spina bifida Microcephaly chischisis. Midbrain Forebrain/ Forebrain/ Hindbrain Spinal cord Hindbrain Hindbrain
 A Normal Exencephaly Craniora- Spina bifida Microcephaly chischisis NTD Number of embryos % among NTD Embryos Exencephaly 52 74.3% Craniorachischisis 6 8.6% Spina bifida 5 7.1% Microcephaly 7 1% B Normal
A Normal Exencephaly Craniora- Spina bifida Microcephaly chischisis NTD Number of embryos % among NTD Embryos Exencephaly 52 74.3% Craniorachischisis 6 8.6% Spina bifida 5 7.1% Microcephaly 7 1% B Normal
An epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition-inducing potential of. granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor in colon. cancer
 An epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition-inducing potential of granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor in colon cancer Yaqiong Chen, Zhi Zhao, Yu Chen, Zhonglin Lv, Xin Ding, Renxi Wang, He Xiao,
An epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition-inducing potential of granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor in colon cancer Yaqiong Chen, Zhi Zhao, Yu Chen, Zhonglin Lv, Xin Ding, Renxi Wang, He Xiao,
Vitamin D Receptor Attenuates Renal Fibrosis by Suppressing the Renin-Angiotensin System
 BASIC RESEARCH www.jasn.org Vitamin D Receptor Attenuates Renal Fibrosis by Suppressing the Renin-Angiotensin System Yan Zhang,* Juan Kong,* Dilip K. Deb,* Anthony Chang, and Yan Chun Li* Departments of
BASIC RESEARCH www.jasn.org Vitamin D Receptor Attenuates Renal Fibrosis by Suppressing the Renin-Angiotensin System Yan Zhang,* Juan Kong,* Dilip K. Deb,* Anthony Chang, and Yan Chun Li* Departments of
Adenosine Signaling Increases Proinflammatory and Profibrotic Mediators through Activation of a Functional Adenosine 2B Receptor in Renal Fibroblasts
 Available online at www.annclinlabsci.org Annals of Clinical & Laboratory Science, vol. 46, no. 4, 2016 339 Adenosine Signaling Increases Proinflammatory and Profibrotic Mediators through Activation of
Available online at www.annclinlabsci.org Annals of Clinical & Laboratory Science, vol. 46, no. 4, 2016 339 Adenosine Signaling Increases Proinflammatory and Profibrotic Mediators through Activation of
Blockade of Wnt/ -Catenin Signaling by Paricalcitol Ameliorates Proteinuria and Kidney Injury
 BASIC RESEARCH www.jasn.org Blockade of Wnt/ -Catenin Signaling by Paricalcitol Ameliorates Proteinuria and Kidney Injury Weichun He, Young Sun Kang, Chunsun Dai, and Youhua Liu Department of Pathology,
BASIC RESEARCH www.jasn.org Blockade of Wnt/ -Catenin Signaling by Paricalcitol Ameliorates Proteinuria and Kidney Injury Weichun He, Young Sun Kang, Chunsun Dai, and Youhua Liu Department of Pathology,
Supplementary Figure 1 (Related with Figure 4). Molecular consequences of Eed deletion. (a) ChIP analysis identifies 3925 genes that are associated
 Supplementary Figure 1 (Related with Figure 4). Molecular consequences of Eed deletion. (a) ChIP analysis identifies 3925 genes that are associated with the H3K27me3 mark in chondrocytes (see Table S1,
Supplementary Figure 1 (Related with Figure 4). Molecular consequences of Eed deletion. (a) ChIP analysis identifies 3925 genes that are associated with the H3K27me3 mark in chondrocytes (see Table S1,
Sphingosine-1-phosphate signaling and cardiac fibrosis. Department of Physiology, Kanazawa University School of Medicine, Kanazawa, Japan
 96 Special Issue: Cellular and Molecular Bases for Fibrotic Diseases Review Article Sphingosine-1-phosphate signaling and cardiac fibrosis Noriko Takuwa 1, 2, ), Yasuo Okamoto 1), Kazuaki Yoshioka 1) and
96 Special Issue: Cellular and Molecular Bases for Fibrotic Diseases Review Article Sphingosine-1-phosphate signaling and cardiac fibrosis Noriko Takuwa 1, 2, ), Yasuo Okamoto 1), Kazuaki Yoshioka 1) and
C57BL/6 Mice are More Appropriate. than BALB/C Mice in Inducing Dilated Cardiomyopathy with Short-Term Doxorubicin Treatment
 Original Article C57BL/6 Mice are More Appropriate Acta Cardiol Sin 2012;28:236 240 Heart Failure & Cardiomyopathy C57BL/6 Mice are More Appropriate than BALB/C Mice in Inducing Dilated Cardiomyopathy
Original Article C57BL/6 Mice are More Appropriate Acta Cardiol Sin 2012;28:236 240 Heart Failure & Cardiomyopathy C57BL/6 Mice are More Appropriate than BALB/C Mice in Inducing Dilated Cardiomyopathy
Utility of Circulating micrornas in Cardiovascular Disease
 Utility of Circulating micrornas in Cardiovascular Disease Pil-Ki Min, MD, PhD Cardiology Division, Gangnam Severance Hospital, Yonsei University College of Medicine Introduction Biology of micrornas Circulating
Utility of Circulating micrornas in Cardiovascular Disease Pil-Ki Min, MD, PhD Cardiology Division, Gangnam Severance Hospital, Yonsei University College of Medicine Introduction Biology of micrornas Circulating
Section Title. Subject Index
 Section Title Subject Index Acute kidney injury definitions 287 289 hypoxia 287, 290 overview 286, 287 sublethal tubular injury adaptive responses 292, 293 combination of sublethal injuries 291, 292 detection
Section Title Subject Index Acute kidney injury definitions 287 289 hypoxia 287, 290 overview 286, 287 sublethal tubular injury adaptive responses 292, 293 combination of sublethal injuries 291, 292 detection
Effect of erythropoietin on the expression of dynamin-related protein-1 in rat renal interstitial fibrosis
 EXPERIMENTAL AND THERAPEUTIC MEDICINE 9: 2065-2071, 2015 Effect of erythropoietin on the expression of dynamin-related protein-1 in rat renal interstitial fibrosis XIAN FENG ZHAO 1, YAN HONG LIU 2, ZI
EXPERIMENTAL AND THERAPEUTIC MEDICINE 9: 2065-2071, 2015 Effect of erythropoietin on the expression of dynamin-related protein-1 in rat renal interstitial fibrosis XIAN FENG ZHAO 1, YAN HONG LIU 2, ZI
Identifying Metabolic Phenotype Switches in Cancer Cells Using the Agilent Seahorse XF Analyzer in an Hypoxic Environment
 Identifying Metabolic Phenotype Switches in Cancer Cells Using the Agilent Seahorse XF Analyzer in an Hypoxic Environment Application Note Introduction Decreased oxygen levels, or hypoxia, and hypoxic-mediated
Identifying Metabolic Phenotype Switches in Cancer Cells Using the Agilent Seahorse XF Analyzer in an Hypoxic Environment Application Note Introduction Decreased oxygen levels, or hypoxia, and hypoxic-mediated
HDAC Dependent Transcriptional Repression of Bmp-7 Potentiates TGF-b Mediated Renal Fibrosis in Obstructive Uropathy
 HDAC Dependent Transcriptional Repression of Bmp-7 Potentiates TGF-b Mediated Renal Fibrosis in Obstructive Uropathy Scott R. Manson, Joseph B. Song, Keith A. Hruska and Paul F. Austin* From the Division
HDAC Dependent Transcriptional Repression of Bmp-7 Potentiates TGF-b Mediated Renal Fibrosis in Obstructive Uropathy Scott R. Manson, Joseph B. Song, Keith A. Hruska and Paul F. Austin* From the Division
Supplementary Figure 1 IL-27 IL
 Tim-3 Supplementary Figure 1 Tc0 49.5 0.6 Tc1 63.5 0.84 Un 49.8 0.16 35.5 0.16 10 4 61.2 5.53 10 3 64.5 5.66 10 2 10 1 10 0 31 2.22 10 0 10 1 10 2 10 3 10 4 IL-10 28.2 1.69 IL-27 Supplementary Figure 1.
Tim-3 Supplementary Figure 1 Tc0 49.5 0.6 Tc1 63.5 0.84 Un 49.8 0.16 35.5 0.16 10 4 61.2 5.53 10 3 64.5 5.66 10 2 10 1 10 0 31 2.22 10 0 10 1 10 2 10 3 10 4 IL-10 28.2 1.69 IL-27 Supplementary Figure 1.
Morphogens: What are they and why should we care?
 Morphogens: What are they and why should we care? Historic, Theoretical Mechanism of Action Nucleoprotein: the specific trophic cellular material extracted from the cell nucleus. DNA and RNA which regulates
Morphogens: What are they and why should we care? Historic, Theoretical Mechanism of Action Nucleoprotein: the specific trophic cellular material extracted from the cell nucleus. DNA and RNA which regulates
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/2/1/ra81/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Delivery of MicroRNA-126 by Apoptotic Bodies Induces CXCL12- Dependent Vascular Protection Alma Zernecke,* Kiril Bidzhekov,
www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/2/1/ra81/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Delivery of MicroRNA-126 by Apoptotic Bodies Induces CXCL12- Dependent Vascular Protection Alma Zernecke,* Kiril Bidzhekov,
REVIEW ARTICLE NEWER BIOMARKERS IN EARLY DIABETIC NEPHROPATHY
 JCD REVIEW ARTICLE NEWER BIOMARKERS IN EARLY DIABETIC NEPHROPATHY SAPTARSHI MUKHOPADHYAY* *FACULTY (DEPARTMENT OF MEDICINE), B R SINGH HOSPITAL (EASTERN RAILWAY), KOLKATA. INTRODUCTION renal disease. It
JCD REVIEW ARTICLE NEWER BIOMARKERS IN EARLY DIABETIC NEPHROPATHY SAPTARSHI MUKHOPADHYAY* *FACULTY (DEPARTMENT OF MEDICINE), B R SINGH HOSPITAL (EASTERN RAILWAY), KOLKATA. INTRODUCTION renal disease. It
SLOWING PROGRESSION OF KIDNEY DISEASE. Mark Rosenberg MD University of Minnesota
 SLOWING PROGRESSION OF KIDNEY DISEASE Mark Rosenberg MD University of Minnesota OUTLINE 1. Epidemiology of progression 2. Therapy to slow progression a. Blood Pressure control b. Renin-angiotensin-aldosterone
SLOWING PROGRESSION OF KIDNEY DISEASE Mark Rosenberg MD University of Minnesota OUTLINE 1. Epidemiology of progression 2. Therapy to slow progression a. Blood Pressure control b. Renin-angiotensin-aldosterone
mir-7a regulation of Pax6 in neural stem cells controls the spatial origin of forebrain dopaminergic neurons
 Supplemental Material mir-7a regulation of Pax6 in neural stem cells controls the spatial origin of forebrain dopaminergic neurons Antoine de Chevigny, Nathalie Coré, Philipp Follert, Marion Gaudin, Pascal
Supplemental Material mir-7a regulation of Pax6 in neural stem cells controls the spatial origin of forebrain dopaminergic neurons Antoine de Chevigny, Nathalie Coré, Philipp Follert, Marion Gaudin, Pascal
Potential Role of Sphingosine 1-Phosphate in the. Pathogenesis of Rheumatoid Arthritis
 Potential Role of Sphingosine 1-Phosphate in the Pathogenesis of Rheumatoid Arthritis COMMENTARY for Zhao, C., Fernandes, M.J., Turgeon, M., Tancrede, S., Di Battista, J., Poubelle, P.E. and Bourgoin,
Potential Role of Sphingosine 1-Phosphate in the Pathogenesis of Rheumatoid Arthritis COMMENTARY for Zhao, C., Fernandes, M.J., Turgeon, M., Tancrede, S., Di Battista, J., Poubelle, P.E. and Bourgoin,
About OMICS International Conferences
 About OMICS Group OMICS Group is an amalgamation of Open Access publications and worldwide international science conferences and events. Established in the year 2007 with the sole aim of making the information
About OMICS Group OMICS Group is an amalgamation of Open Access publications and worldwide international science conferences and events. Established in the year 2007 with the sole aim of making the information
Prof. Andrzej Wiecek Department of Nephrology, Endocrinology and Metabolic Diseases Medical University of Silesia Katowice, Poland.
 What could be the role of renal denervation in chronic kidney disease? Andrzej Wiecek, Katowice, Poland Chairs: Peter J. Blankestijn, Utrecht, The Netherlands Jonathan Moss, Glasgow, UK Prof. Andrzej Wiecek
What could be the role of renal denervation in chronic kidney disease? Andrzej Wiecek, Katowice, Poland Chairs: Peter J. Blankestijn, Utrecht, The Netherlands Jonathan Moss, Glasgow, UK Prof. Andrzej Wiecek
A clinical syndrome, composed mainly of:
 Nephritic syndrome We will discuss: 1)Nephritic syndrome: -Acute postinfectious (poststreptococcal) GN -IgA nephropathy -Hereditary nephritis 2)Rapidly progressive GN (RPGN) A clinical syndrome, composed
Nephritic syndrome We will discuss: 1)Nephritic syndrome: -Acute postinfectious (poststreptococcal) GN -IgA nephropathy -Hereditary nephritis 2)Rapidly progressive GN (RPGN) A clinical syndrome, composed
Inflammation in heart failure: biomarker, bystander or mediator
 Inflammation in heart failure: biomarker, bystander or mediator Novel matricellular proteins to target Javier Díez, MD, PhD. Centre of Applied Medical Research and University Clinic School of Medicine,
Inflammation in heart failure: biomarker, bystander or mediator Novel matricellular proteins to target Javier Díez, MD, PhD. Centre of Applied Medical Research and University Clinic School of Medicine,
Mesenchymal progenitor cells in intramuscular connective tissue development
 Mesenchymal progenitor cells in intramuscular connective tissue development Min Du, Ph.D. Professor and Endowed Chair Department of Animal Sciences Washington State University Pullman, WA Beef Quality:
Mesenchymal progenitor cells in intramuscular connective tissue development Min Du, Ph.D. Professor and Endowed Chair Department of Animal Sciences Washington State University Pullman, WA Beef Quality:
