The world's most advanced cell metabolism analyzer
|
|
|
- David Newton
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 O 2 O 2 O 2 O 2 + H H + + H H + + H H + O 2 O 2 O 2 O 2 O 2 The world's most advanced cell metabolism analyzer
2 The Era of Cellular Bioenergetics
3
4 Cellular Bioenergetics for the 21 st Century XF e 96 Analyzer XF e 24 Analyzer XFp Analyzer
5 O 2 O 2 O 2 O 2 O 2 O 2 O 2 O 2 O 2 + H H + + H H + H + H +
6 XF e Analyzers Measure the Two Major Energy Pathways Extracellular Acidification Rate (ECAR) = Glycolysis Oxygen Consumption Rate (OCR) = Mitochondrial Respiration
7 Measuring Mitochondrial Respiration and Glycolysis in a Microplate Disposable probes Fiber-optic waveguide XF Culture Plate Oxygen Fluorescent sensor Cells Well 1 Well 2
8 mm Hg (OCR) ph (ECAR) Measuring Mitochondrial Respiration and Glycolysis in a Microplate C2 C2 C2 C2 C2 C2 C2 C2 C2 C2 C2 C2 C2 C2 C2 C2 C2 C2 C2 C2 C2 C2 C2 C2 C2 C2 C2 C2 C2 C2 C2 C2 C2 C2 C2 C2 C2 C2 OCR C2 C2 C2 C2 C2 C2 C2 C2 C2 C2 ECAR C2 C2 C2 C2 C2 C2 C2 C Time (min) The biocartridge is raised, A bringing temporary the system microchamber back to baseline is formed The rate is calculated from the slope Well 1 Well 2
9 Aerobic Respiration (OCR, pmoles/min) Automated Drug Injection Ports Enable Kinetic, Functional Data 4 Injection Ports/Well Samples injected automatically 600 More Aerobic More Energy 500 FCCP Less Energy 2-DG 2-DG + Rot Basal Rot Glycolysis (ECAR, mph/min) More Glycolytic
10 XF Metabolic Phenotype Assay - PhenoGram Neurons Pluripotent Stem Cells Measures the metabolic state of cells: Less Metabolic Aerobic Glycolytic More Metabolic Memory T Cells H460 Lung Cancer Cells Warburg Effect Reverse Warburg Effect
11 XF e Bioenergetics of Cells and Tissues Eye Brain Rat retinal Retinal punch Cortical neurons Synaptosomes Skin Heart MCF7 breast cancer Epithelial cells Cardiomyocytes Heart mitochondria Liver Pancreas HepG2 liver cells Hepatocytes INS1 beta cells Whole Islets Kidney Fibroblasts Podocytes Renal Proximal Tubules Fibroblasts Cybrids Blood Fat Lymphocytes PBMC SC adipocytes Adipose tissue myotubes L6 myoblasts Muscle
12 Islet Capture Microplate for tissue analysis (XFe24 only)
13 ATP Demand All cells carry an energy reserve that determines how they will handle an overload or chronic stress ATP Demand Functional, Healthy Disease, Aging Max Capacity Max Capacity Reserve Reserve Demand Demand time time Cells have an energy reserve to handle acute stress demands
14 Electron Transfer Chain FCCP H + e- H +
15 XF CELL MITO STRESS TEST The Gold Standard That Makes You a Bioenergetics Expert Rotenone Antimycin FCCP X X Oligomycin Basal Respiration ATP Production Maximal Respiration H + X Proton Leak Non-mitochondrial Respiration XF e Mito Stress Test
16 NEURODEGENERATION Spare Capacity Reveals More Than Basal Metabolism 0 24 BASELINE OLIGO FCCP ROT / MYX Sod2 +/+ Cell type: Mouse CD-1 Synaptosomes Free Radic Biol Med Apr 1; 50(7): Impaired spare respiratory capacity in cortical synaptosomes from Sod2 null mice Flynn J M, Choi S W, Day N U, Gerencser A A, Hubbard A and Melov S
17 Patient-Derived Sample
18 TRANSLATIONAL MEDICINE Human samples and related diseases Airway smooth muscle cells Epidermal melanocytes Fibroblast ipscs ips-derived cardiomyocytes Keratinocytes Leukemia cells Leukocytes Lymphoblastoid cell lines Myotube and myoblast PBMCs Platelets T cells Trophoblast AML Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia Autism Barth syndrome Behr s Syndrome Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease CLL Cockayne syndrome Diabetes Encephalopathy HIV Leigh syndrome Leukemia Melanoma Methylmalonic aciduria MELAS MERRF MLASA Pakinson s disease Paroxysmal nonkinesigenic dyskinesia Preeclampsia Pemphigus vulgaris Sickle cell disease SLE Spastic Paraplegia Valosin containing protein (VCP) disease Xeroderma pigmentosum group A
19 TRANSLATIONAL MEDICINE Stress Test Identifies Mitochondrial Dysfunction in Diseases Cell type: Lymphocytes Patient Cell type: Fibroblasts Patient HIV * Lower spare capacity in patients Data courtesy of Sher Hendrickson NCI/NIH Frederick Patient Cell type: Fibroblasts Parkinson s Disease Lower spare capacity in patient Data courtesy of James Bennet Lab University of Virginia Patient Cell type: Fibroblasts Autism * Higher spare capacity in patient Multiple acyl-coa dehydrogenase deficiency (MADD) ** Higher spare capacity in patient Data courtesy of Dr. Pinar Coskun, Department of Neurobiology and Behavior at UC Irvine PLoS One Dec 17; 4(12):e8329. Song Y et al
20 NEWS
21 % of baseline rate % of control ATP level % of baseline rate % of control ATP level High Glycolytic Capacity and Impaired Oxidative Phosphorylation in Tumor cells Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 2007; 292:C % 140% A % 140% 250% A549 Otto Warburg % 120% 120% 200% 200% 100% 80% 100% 80% 150% 150% 60% 60% 100% 100% 40% 20% 0% OCR ECAR ATP Oligomycin (mm) Oligomycin (mm) 40% 20% 0% 50% 0% OCR ECAR ATP 2-Deoxyglucose (mm) deoxyglucose (mm) 50% 0%
22 Hereditary Leiomyomatosis and Renal Cell Cancer Model: Glycolytic Flux in FH/LDH-A deficient cells Mol Cancer Ther 2009; 8(3): Glucose Lots of ATP ATP Glycolysis NAD + NADH Electron Transport Chain NADH NAD + Pyruvate NAD + NADH O 2 Lactate & H + Kreb Cycle ATP FH shrna CO 2
23 Hereditary Leiomyomatosis and Renal Cell Cancer Model: Glycolytic Flux in FH/LDH-A deficient cells Mol Cancer Ther 2009; 8(3): Glucose Lots of ATP ATP Glycolysis NAD + NADH Electron Transport Chain NADH NAD + Pyruvate NAD + NADH O 2 Lactate & H + Kreb Cycle ATP FH shrna CO 2
24 Hereditary Leiomyomatosis and Renal Cell Cancer Model: Glycolytic Flux in FH/LDH-A deficient cells
25 OCR (pmol min -1 ) XF Assays Measure Metabolic Switching Gene Induced Substrate Induced Signaling Pathway Induced 400 Aerobic More Metabolic 300 Fh1 fl/fl -Glc 200 Fh1 -/-CL1 +Glc 100 Less Fh1 -/-CL19 Metabolic Glycolytic ECAR (mph per min) Kidney epithelial cells +/- fumarate hydratase Mantle cell lymphoma cells +/- glucose Adipocytes +/- Hedgehog ligand Haem oxygenase is synthetically lethal with the tumour suppressor fumarate hydratase. Frezza et al. Nature Aug 17;477(7363): Switching from aerobic glycolysis to oxidative phosphorylation modulates the sensitivity of mantle cell lymphoma cells to TRAIL. Robinson et al. Oncogene Nov 29;31(48): Hedgehog partial agonism drives Warburg-like metabolism in muscle and brown fat. Teperino R, et al., Cell Oct 12;151(2):
26 Prostate Cancer Cells Display Glycolytic Phenotype PC-3M PCS Cell type: Prostate Tumor Cells Primary Prostate Epithelial Cells Glycolytic phenotype would be susceptible to free base lysine buffer therapy. J Cancer Sci Ther 2011, S1 Free Base Lysine Increases Survival and Reduces Metastasis in Prostate Cancer Model Mibrahim-Hashim, et al
27 XF Assays Reveals Hedgehog-Induced Switch to a Glycolytic Phenotype Aerobic More Metabolic Smoothened agonist Less Metabolic Glycolytic Hedgehog signaling via SAG [smoothened agonist] shifts adipocytes to a glycolytic phenotype Smoothened knock-outs [Smo-sh] ] lose the ability to utilize glucose
28 PTEN Elevation Shifts Cellular Energy Metabolism toward Mitochondrial Respiration Cell type: mouse embryonic fibroblasts Anti-Warburg state Systemic Elevation of PTEN Induces a Tumor-Suppressive Metabolic State Cell; 2012 Mar (1):49-62.
29 Spheroid Microplate for 3D analysis (XFe96 only)
30 Now you can measure cell metabolism and characterize metabolic phenotypes under hypoxic conditions Cell type:mcf-7 cells
31 Single & Dual Chamber System with XF analyzer University of Oxford University of California, San Diego
32 OCR (% baseline) CARDIOVASCULAR Stress Test Sensitivity Reveals Sub-Lethal Stress Response and Mechanism XF Cell Mito Stress Test 0 µ M HNE 5 µ M HNE 10 µ M HNE 20 µ M HNE Oligo FCCP Antimycin A 150 HNE Time (min) Cell type: Neonatal Rat Ventricular Myocytes Biochem J Nov 15;425(1): Importance of the bioenergetic reserve capacity in response to cardiomyocyte stress induced by 4-hydroxynonenal Bradford G. Hill, Brian P. Dranka, Luyun Zou, John C. Chatham and Victor M. Darley-Usmar
33 IMMUNOLOGY Spare Capacity Affects Memory T Cell Development and Survival Naïve T cells Effector T cells Memory T cells Cell type: Mouse Lymphocytes Spleen & Lymph Nodes Mitochondrial respiratory capacity is a critical regulator of CD8+ T cell memory development van der Windt, JW, and Pearce, EL, Washington School of Medicine. Immunity 2011 December 28
34 IMMUNOLOGY Spare Capacity in CD8+ T Cells is Dependent on Mitochondrial Fatty Acid Oxidation Cell type: Mouse Lymphocytes Spleen & Lymph Nodes Fatty acid source is FBS Mitochondrial respiratory capacity is a critical regulator of CD8+ T cell memory development van der Windt, JW, and Pearce, EL, Washington School of Medicine. Immunity 2011 December 28
35 OCR % from baseline AUC OCR Induction Metformin Enhances FAO and Lowers Glucose Oxidation in C2C12 Myotubes Wu Poster; GRC Molecular and Cellular Bioenergetics, A. Kinetics B. AUC untreated + BSA (veh cont.) untreated + Glucose untreated + PA-BSA Metformin + Glucose Metformin + PA-BSA Metformin + BSA Time (Min) -500 Metformin (1mM) Glucose (25mM) Palmitate (150μM)
36 XF Assays can detect catabolism of exogenous and/or endogenous substrates C2C12 myoblasts = Etomoxir Johan Auwerx Nature 2009; 458:
37 XF e Palmitate-BSA FAO Reagent Provides the first fully validated and standardized Palmitate-BSA FAO reagent: No substrate preparation Activity tested Quality controlled
38 Drug hits that shift energy metabolism Gohil et al. Nat Biotech Mar; 28(3):249-55
39 Effects of meclizine on cellular energy metabolism Gohil et al. Nat Biotech Mar; 28(3):249-55
40 Meclizine is neuroprotective in models of Huntington s disease Meclizine (0, 5, 10, 12.5, 25, 37.5 and 50 um) Human Molecular Genetics, 2011
41 ES cell quality check and differentiation study Highly glycolytic Specific metabolic profile
42 Stem cell replacement therapy for Huntington s disease Genetic Correction of Huntington's Disease Phenotypes in Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells Cell Stem Cell; 2012 Aug 3. 11(2):
43 Programmed hpsc-derived brown adipocytes demonstrate mature functional properties MPC:mesenchymal progenitor cells Programming human pluripotent stem cells into white and brown adipocytes Nat Cell Biol; 2012 Jan (2):
44 Programmed hpsc-derived brown adipocytes demonstrate mature functional properties. CEBPB : CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein beta PRDM16 : PR domain containing 16 hmsc : Adipogenic differentiation was carried out for 21 days Programming human pluripotent stem cells into white and brown adipocytes Nat Cell Biol; 2012 Jan (2):
45 The bioenergetic changes associated with inducing pluripotency influence reprogramming efficiency The metabolome of induced pluripotent stem cells reveals metabolic changes occurring in somatic cell reprogramming Cell Res; 2012 Jan (1):
46 Summary Whole Physiologic Real-Time Higher-throughput
47 The Paper Best Machine choice to analyze whole metabolism 28 Nature, 28 Cell & 2 Science
48 Seahorse Bioscience
49 Facebook 海馬新樂園
50 Cell-bio biotechnology Office: Jack Chou 周家豪 Sales specialist
CELL METABOLISM REVEALED
 O 2 O 2 O 2 O 2 + H H + + H H + + H H + O 2 O 2 O 2 O 2 O 2 CELL METABOLISM REVEALED The Era of Cellular Bioenergetics Cellular Bioenergetics for the 21 st Century XF e 96 Analyzer XF e 24 Analyzer XF
O 2 O 2 O 2 O 2 + H H + + H H + + H H + O 2 O 2 O 2 O 2 O 2 CELL METABOLISM REVEALED The Era of Cellular Bioenergetics Cellular Bioenergetics for the 21 st Century XF e 96 Analyzer XF e 24 Analyzer XF
Agilent Technologies: Seahorse XF Introduction
 Agilent Technologies: Seahorse XF Introduction Tools for investigating cell metabolism diagnostic procedures. 1 The Engines Cells Generate Energy via Two Metabolic Pathways Glycolysis [ H + ] Respiration
Agilent Technologies: Seahorse XF Introduction Tools for investigating cell metabolism diagnostic procedures. 1 The Engines Cells Generate Energy via Two Metabolic Pathways Glycolysis [ H + ] Respiration
Cell Metabolism Assays. for. Immunology. Research
 the immunity-metabolism link Cell Metabolism Assays for Immunology Research GOLD STANDARD ASSAYS FOR MEASURING METABOLIC RePROGRAMMING Metabolic Signatures Cell activation, amplification, and effector
the immunity-metabolism link Cell Metabolism Assays for Immunology Research GOLD STANDARD ASSAYS FOR MEASURING METABOLIC RePROGRAMMING Metabolic Signatures Cell activation, amplification, and effector
CELLULAR BIOENERGETICS FOR THE 21st CENTURY
 CELLULAR BIOENERGETICS FOR THE 21st CENTURY Seahorse XF Extracellular Flux Analyzers XF Extracellular Flux Analyzer PROVIDING A NEW WINDOW INTO CELLULAR BIOENERGETICS Before Seahorse developed With an
CELLULAR BIOENERGETICS FOR THE 21st CENTURY Seahorse XF Extracellular Flux Analyzers XF Extracellular Flux Analyzer PROVIDING A NEW WINDOW INTO CELLULAR BIOENERGETICS Before Seahorse developed With an
Application Note. Introduction
 Simultaneously Measuring Oxidation of Exogenous and Endogenous Fatty Acids Using the XF Palmitate-BSA FAO Substrate with the Agilent Seahorse XF Cell Mito Stress Test Application Note Introduction The
Simultaneously Measuring Oxidation of Exogenous and Endogenous Fatty Acids Using the XF Palmitate-BSA FAO Substrate with the Agilent Seahorse XF Cell Mito Stress Test Application Note Introduction The
Identifying Metabolic Phenotype Switches in Cancer Cells Using the Agilent Seahorse XF Analyzer in an Hypoxic Environment
 Identifying Metabolic Phenotype Switches in Cancer Cells Using the Agilent Seahorse XF Analyzer in an Hypoxic Environment Application Note Introduction Decreased oxygen levels, or hypoxia, and hypoxic-mediated
Identifying Metabolic Phenotype Switches in Cancer Cells Using the Agilent Seahorse XF Analyzer in an Hypoxic Environment Application Note Introduction Decreased oxygen levels, or hypoxia, and hypoxic-mediated
Quantifying Cellular ATP Production Rate Using Agilent Seahorse XF Technology
 White Paper Quantifying Cellular ATP Production Rate Using Agilent Seahorse XF Technology Authors Natalia Romero George Rogers Andy Neilson Brian P. Dranka Agilent Technologies, Inc., Lexington, MA, USA
White Paper Quantifying Cellular ATP Production Rate Using Agilent Seahorse XF Technology Authors Natalia Romero George Rogers Andy Neilson Brian P. Dranka Agilent Technologies, Inc., Lexington, MA, USA
Performing Bioenergetic Analysis: Seahorse XFe96 Analyzer
 icell Cardiomyocytes 2 Application Protocol Performing Bioenergetic Analysis: Seahorse XFe96 Analyzer Introduction The myocardium is the most metabolically active tissue in the body and is highly sensitive
icell Cardiomyocytes 2 Application Protocol Performing Bioenergetic Analysis: Seahorse XFe96 Analyzer Introduction The myocardium is the most metabolically active tissue in the body and is highly sensitive
Human induced pluripotent stem cell derived cardiomyocytes are a more relevant model for assessing drug-induced effects on mitochondrial function
 Human induced pluripotent stem cell derived cardiomyocytes are a more relevant model for assessing drug-induced effects on mitochondrial function than H9C2 cells 16 January 2013 SLAS2013 Presentation Outline
Human induced pluripotent stem cell derived cardiomyocytes are a more relevant model for assessing drug-induced effects on mitochondrial function than H9C2 cells 16 January 2013 SLAS2013 Presentation Outline
Cell Metabolism Assays. for OMICS. Research
 Gene-Protein-metabolism links Cell Metabolism Assays for OMICS Research STANDARD Parameters of Functional METABOLIsm Genomics Cells use gene expression to synthesize proteins and other products that are
Gene-Protein-metabolism links Cell Metabolism Assays for OMICS Research STANDARD Parameters of Functional METABOLIsm Genomics Cells use gene expression to synthesize proteins and other products that are
Rapid Analysis of Glycolytic and Oxidative Substrate Flux of Cancer Cells in a Microplate
 Rapid Analysis of Glycolytic and Oxidative Substrate Flux of Cancer Cells in a Microplate Lisa S. Pike Winer, Min Wu* Seahorse Bioscience Inc., North Billerica, Massachusetts, United States of America
Rapid Analysis of Glycolytic and Oxidative Substrate Flux of Cancer Cells in a Microplate Lisa S. Pike Winer, Min Wu* Seahorse Bioscience Inc., North Billerica, Massachusetts, United States of America
Ryan McGarrigle, Ph.D.
 Cardiomyocyte function characterised through combined analysis of metabolic flux, beat rate and cellular oxygenation and its application in in vitro ischemia reperfusion modelling Ryan McGarrigle, Ph.D.
Cardiomyocyte function characterised through combined analysis of metabolic flux, beat rate and cellular oxygenation and its application in in vitro ischemia reperfusion modelling Ryan McGarrigle, Ph.D.
Cellular metabolism made easy: Microplate assays for mitochondrial function & glycolytic flux
 Cellular metabolism made easy: Microplate assays for mitochondrial function & glycolytic flux Convenient Microplate Based Analysis of Cell Metabolism Resuspend Add Reagent Measure A simple push-button
Cellular metabolism made easy: Microplate assays for mitochondrial function & glycolytic flux Convenient Microplate Based Analysis of Cell Metabolism Resuspend Add Reagent Measure A simple push-button
Metabolism and the extracellular flux bioanalyzer. Bioenergetics and Metabolism
 7/3/8 Metabolism and the extracellular flux bioanalyzer Jianhua Zhang Department of Pathology University of Alabama at Birmingham 8 Bioenergetics and Metabolism Neurodegeneration: Parkinson s, Huntington
7/3/8 Metabolism and the extracellular flux bioanalyzer Jianhua Zhang Department of Pathology University of Alabama at Birmingham 8 Bioenergetics and Metabolism Neurodegeneration: Parkinson s, Huntington
XF Data Normalization by the Agilent Seahorse XF Imaging and Normalization System
 Application Note Normalization XF Data Normalization by the Agilent Seahorse XF Imaging and Normalization System Authors Yoonseok Kam Kellie Chadwick Ned Jastromb Brian P. Dranka Agilent Technologies,
Application Note Normalization XF Data Normalization by the Agilent Seahorse XF Imaging and Normalization System Authors Yoonseok Kam Kellie Chadwick Ned Jastromb Brian P. Dranka Agilent Technologies,
Islet Oxygen Consumption Assay using the XF24 Islet Capture Microplate Shirihai Lab and Seahorse Bioscience Aug
 1 Islet Oxygen Consumption Assay using the XF24 Islet Capture Microplate Shirihai Lab and Seahorse Bioscience Aug 6 2009 XF Analyzers are most commonly used with an adherent monolayer of cells attached
1 Islet Oxygen Consumption Assay using the XF24 Islet Capture Microplate Shirihai Lab and Seahorse Bioscience Aug 6 2009 XF Analyzers are most commonly used with an adherent monolayer of cells attached
MitoXpress FAO Assay. For the measurement of Fatty Acid Oxidation
 MitoXpress FAO Assay For the measurement of Fatty Acid Oxidation Companion Kit to be used in combination with Luxcel s MitoXpress Xtra - Oxygen Consumption Assay ILLUMINATING DISCOVERY TABLE OF CONTENTS
MitoXpress FAO Assay For the measurement of Fatty Acid Oxidation Companion Kit to be used in combination with Luxcel s MitoXpress Xtra - Oxygen Consumption Assay ILLUMINATING DISCOVERY TABLE OF CONTENTS
AWARD NUMBER: W81XWH TITLE: BIOENERGETICS OF STROMAL CELLS AS A PREDICTOR OF AGGRESSIVE PROSTATE CANCER
 AWARD NUMBER: W81XWH-14-1-0255 TITLE: BIOENERGETICS OF STROMAL CELLS AS A PREDICTOR OF AGGRESSIVE PROSTATE CANCER PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Praveen K. Vayalil RECIPIENT: University of Alabama at Birmingham
AWARD NUMBER: W81XWH-14-1-0255 TITLE: BIOENERGETICS OF STROMAL CELLS AS A PREDICTOR OF AGGRESSIVE PROSTATE CANCER PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Praveen K. Vayalil RECIPIENT: University of Alabama at Birmingham
Islet Assay Using the Agilent Seahorse XF24 Islet Capture Microplate
 Islet Assay Using the Agilent Seahorse XF24 Islet Capture Microplate Technical Overview Introduction Agilent Seahorse XF Analyzers are most commonly used with an adherent monolayer of cells attached to
Islet Assay Using the Agilent Seahorse XF24 Islet Capture Microplate Technical Overview Introduction Agilent Seahorse XF Analyzers are most commonly used with an adherent monolayer of cells attached to
Supplementary Figure 1
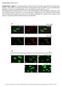 Supplementary Figure 1. (A) Representative confocal analysis of cardiac mesenchymal cells from nondiabetic (ND-CMSC) and diabetic (D-CMSC) immunostained with anti-h3k9ac and anti-h3k27me3 antibodies. Analysis
Supplementary Figure 1. (A) Representative confocal analysis of cardiac mesenchymal cells from nondiabetic (ND-CMSC) and diabetic (D-CMSC) immunostained with anti-h3k9ac and anti-h3k27me3 antibodies. Analysis
Cellular Pathways That Harvest Chemical Energy. Cellular Pathways That Harvest Chemical Energy. Cellular Pathways In General
 Cellular Pathways That Harvest Chemical Energy A. Obtaining Energy and Electrons from Glucose Lecture Series 12 Cellular Pathways That Harvest Chemical Energy B. An Overview: Releasing Energy from Glucose
Cellular Pathways That Harvest Chemical Energy A. Obtaining Energy and Electrons from Glucose Lecture Series 12 Cellular Pathways That Harvest Chemical Energy B. An Overview: Releasing Energy from Glucose
Christian Frezza MRC Cancer Unit
 Christian Frezza MRC Cancer Unit What is cancer? What is cancer? Douglas Hanahan, Robert A. Weinberg; The Hallmarks of Cancer Cell, Volume 100, Issue 1, 7 January 2000, Pages 57 70 Cancer cells need energy
Christian Frezza MRC Cancer Unit What is cancer? What is cancer? Douglas Hanahan, Robert A. Weinberg; The Hallmarks of Cancer Cell, Volume 100, Issue 1, 7 January 2000, Pages 57 70 Cancer cells need energy
ab Fatty Acid Oxidation Assay
 Version 3 Last updated 22 June 2017 ab217602 Fatty Acid Oxidation Assay For the convenient measurement of Fatty Acid Oxidation (FAO) in live cells when used in combination with Extracellular Oxygen Consumption
Version 3 Last updated 22 June 2017 ab217602 Fatty Acid Oxidation Assay For the convenient measurement of Fatty Acid Oxidation (FAO) in live cells when used in combination with Extracellular Oxygen Consumption
Fatty Acid Oxidation Assay on the XF24 Analyzer
 Fatty Acid Oxidation Assay on the XF24 Analyzer Mitochondria oxidize a variety of fuels to generate ATP through oxidative phosphorylation. Cells can utilize fatty acid, glucose and amino acids as their
Fatty Acid Oxidation Assay on the XF24 Analyzer Mitochondria oxidize a variety of fuels to generate ATP through oxidative phosphorylation. Cells can utilize fatty acid, glucose and amino acids as their
ANALYSIS OF THE LEVEL OF OXIDATIVE PHOSPHORYLATION IN BREAST CANCER CELL TYPES. Bratislav M. Janjic
 ANALYSIS OF THE LEVEL OF OXIDATIVE PHOSPHORYLATION IN BREAST CANCER CELL TYPES by Bratislav M. Janjic Diplom in Biology, Univerziteta u Beogradu, Yugoslavia, 1996 Submitted to the Graduate Faculty of the
ANALYSIS OF THE LEVEL OF OXIDATIVE PHOSPHORYLATION IN BREAST CANCER CELL TYPES by Bratislav M. Janjic Diplom in Biology, Univerziteta u Beogradu, Yugoslavia, 1996 Submitted to the Graduate Faculty of the
Name Class Date. 1. Cellular respiration is the process by which the of "food"
 Name Class Date Cell Respiration Introduction Cellular respiration is the process by which the chemical energy of "food" molecules is released and partially captured in the form of ATP. Carbohydrates,
Name Class Date Cell Respiration Introduction Cellular respiration is the process by which the chemical energy of "food" molecules is released and partially captured in the form of ATP. Carbohydrates,
Respiration. Respiration. How Cells Harvest Energy. Chapter 7
 How Cells Harvest Energy Chapter 7 Respiration Organisms can be classified based on how they obtain energy: autotrophs: are able to produce their own organic molecules through photosynthesis heterotrophs:
How Cells Harvest Energy Chapter 7 Respiration Organisms can be classified based on how they obtain energy: autotrophs: are able to produce their own organic molecules through photosynthesis heterotrophs:
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information van der Windt et al. 10.1073/pnas.1221740110 SI Materials and Methods Mice and Reagents. C57BL/6 and major histocompatibility complex class I-restricted OVA-specific T-cell receptor
Supporting Information van der Windt et al. 10.1073/pnas.1221740110 SI Materials and Methods Mice and Reagents. C57BL/6 and major histocompatibility complex class I-restricted OVA-specific T-cell receptor
Energy Transformation: Cellular Respiration Outline 1. Sources of cellular ATP 2. Turning chemical energy of covalent bonds between C-C into energy
 Energy Transformation: Cellular Respiration Outline 1. Sources of cellular ATP 2. Turning chemical energy of covalent bonds between C-C into energy for cellular work (ATP) 3. Importance of electrons and
Energy Transformation: Cellular Respiration Outline 1. Sources of cellular ATP 2. Turning chemical energy of covalent bonds between C-C into energy for cellular work (ATP) 3. Importance of electrons and
A cell has enough ATP to last for about three seconds.
 Energy Transformation: Cellular Respiration Outline 1. Energy and carbon sources in living cells 2. Sources of cellular ATP 3. Turning chemical energy of covalent bonds between C-C into energy for cellular
Energy Transformation: Cellular Respiration Outline 1. Energy and carbon sources in living cells 2. Sources of cellular ATP 3. Turning chemical energy of covalent bonds between C-C into energy for cellular
Cellular Respiration Checkup Quiz. 1. Of the following products, which is produced by both anaerobic respiration and aerobic respiration in humans?
 1. Of the following products, which is produced by both anaerobic respiration and aerobic respiration in humans? I. Pyruvate II. III. ATP Lactate A. I only B. I and II only C. I, II and III D. II and III
1. Of the following products, which is produced by both anaerobic respiration and aerobic respiration in humans? I. Pyruvate II. III. ATP Lactate A. I only B. I and II only C. I, II and III D. II and III
How Cells Release Chemical Energy. Chapter 7
 How Cells Release Chemical Energy Chapter 7 7.1 Overview of Carbohydrate Breakdown Pathways All organisms (including photoautotrophs) convert chemical energy of organic compounds to chemical energy of
How Cells Release Chemical Energy Chapter 7 7.1 Overview of Carbohydrate Breakdown Pathways All organisms (including photoautotrophs) convert chemical energy of organic compounds to chemical energy of
3.2 Aerobic Respiration
 3.2 Aerobic Respiration Aerobic Cellular Respiration Catabolic pathways Breaks down energy-rich compounds to make ATP Requires oxygen Occurs in different parts of the cell C 6 H 12 O 6 (s) + 6O 2 (g) 6CO
3.2 Aerobic Respiration Aerobic Cellular Respiration Catabolic pathways Breaks down energy-rich compounds to make ATP Requires oxygen Occurs in different parts of the cell C 6 H 12 O 6 (s) + 6O 2 (g) 6CO
Metabolism of Herpes Simplex Virus 1 infected RAW macrophages
 Metabolism of Herpes Simplex Virus 1 infected RAW 264.7 macrophages A thesis submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Master of Science By Mary Kathryn Jenkins B.S., Bowling
Metabolism of Herpes Simplex Virus 1 infected RAW 264.7 macrophages A thesis submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Master of Science By Mary Kathryn Jenkins B.S., Bowling
Harvesting energy: photosynthesis & cellular respiration part 1I
 Harvesting energy: photosynthesis & cellular respiration part 1I Agenda I. Overview (Big Pictures) of Photosynthesis & Cellular Respiration II. Making Glucose - Photosynthesis III. Making ATP - Cellular
Harvesting energy: photosynthesis & cellular respiration part 1I Agenda I. Overview (Big Pictures) of Photosynthesis & Cellular Respiration II. Making Glucose - Photosynthesis III. Making ATP - Cellular
Supplementary Table 1 Gene clone ID for ShRNA-mediated gene silencing TNFα downstream signals in in vitro Symbol Gene ID RefSeqID Clone ID
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 Supplementary Table 1 Gene clone ID for ShRNA-mediated gene silencing TNFα downstream
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 Supplementary Table 1 Gene clone ID for ShRNA-mediated gene silencing TNFα downstream
How Cells Harvest Energy. Chapter 7. Respiration
 How Cells Harvest Energy Chapter 7 Respiration Organisms classified on how they obtain energy: autotrophs: produce their own organic molecules through photosynthesis heterotrophs: live on organic compounds
How Cells Harvest Energy Chapter 7 Respiration Organisms classified on how they obtain energy: autotrophs: produce their own organic molecules through photosynthesis heterotrophs: live on organic compounds
Harvesting energy: photosynthesis & cellular respiration
 Harvesting energy: photosynthesis & cellular respiration Learning Objectives Know the relationship between photosynthesis & cellular respiration Know the formulae of the chemical reactions for photosynthesis
Harvesting energy: photosynthesis & cellular respiration Learning Objectives Know the relationship between photosynthesis & cellular respiration Know the formulae of the chemical reactions for photosynthesis
RESPIRATION Worksheet
 A.P. Bio L.C. RESPIRATION Worksheet 1. In the conversion of glucose and oxygen to carbon dioxide and water a) which molecule becomes reduced? b) which molecule becomes oxidized? c) what happens to the
A.P. Bio L.C. RESPIRATION Worksheet 1. In the conversion of glucose and oxygen to carbon dioxide and water a) which molecule becomes reduced? b) which molecule becomes oxidized? c) what happens to the
3.7 CELLULAR RESPIRATION. How are these two images related?
 3.7 CELLULAR RESPIRATION How are these two images related? CELLULAR RESPIRATION Cellular respiration is the process whereby the body converts the energy that we get from food (glucose) into an energy form
3.7 CELLULAR RESPIRATION How are these two images related? CELLULAR RESPIRATION Cellular respiration is the process whereby the body converts the energy that we get from food (glucose) into an energy form
The Journal of Physiology
 J Physiol 594.24 (216) pp 7197 7213 7197 TECHNIQUES FOR PHYSIOLOGY Development of a high-throughput method for real-time assessment of cellular metabolism in intact long skeletal muscle fibre bundles Rui
J Physiol 594.24 (216) pp 7197 7213 7197 TECHNIQUES FOR PHYSIOLOGY Development of a high-throughput method for real-time assessment of cellular metabolism in intact long skeletal muscle fibre bundles Rui
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Respiration Practice Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Which of the following statements describes NAD+? A) NAD+ can donate
Respiration Practice Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Which of the following statements describes NAD+? A) NAD+ can donate
Reading Assignments. A. Energy and Energy Conversions. Lecture Series 9 Cellular Pathways That Harvest Chemical Energy. gasoline) or elevated mass.
 Lecture Series 9 Cellular Pathways That Harvest Chemical Energy Reading Assignments Review Chapter 3 Energy, Catalysis, & Biosynthesis Read Chapter 13 How Cells obtain Energy from Food Read Chapter 14
Lecture Series 9 Cellular Pathways That Harvest Chemical Energy Reading Assignments Review Chapter 3 Energy, Catalysis, & Biosynthesis Read Chapter 13 How Cells obtain Energy from Food Read Chapter 14
Bioenergetic characterization of mouse podocytes
 Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 299: C464 C476, 2010. First published May 5, 2010; doi:10.1152/ajpcell.00563.2009. Bioenergetic characterization of mouse podocytes Yoshifusa Abe, 1,2 Toru Sakairi, 1 Hiroshi
Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 299: C464 C476, 2010. First published May 5, 2010; doi:10.1152/ajpcell.00563.2009. Bioenergetic characterization of mouse podocytes Yoshifusa Abe, 1,2 Toru Sakairi, 1 Hiroshi
Collin County Community College BIOL Muscle Physiology. Muscle Length-Tension Relationship
 Collin County Community College BIOL 2401 Muscle Physiology 1 Muscle Length-Tension Relationship The Length-Tension Relationship Another way that muscle cells can alter their force capability, is determined
Collin County Community College BIOL 2401 Muscle Physiology 1 Muscle Length-Tension Relationship The Length-Tension Relationship Another way that muscle cells can alter their force capability, is determined
BIO 311C Spring Lecture 27 Monday 5 Apr. 1
 BIO 311C Spring 2010 Lecture 27 Monday 5 Apr. 1 Review Metabolic Pathways and Processes that Participate in Respiration - Glycolysis Occurs in the cytoplasmic matrix - Pyruvate dehydrogenase - Krebs Cycle
BIO 311C Spring 2010 Lecture 27 Monday 5 Apr. 1 Review Metabolic Pathways and Processes that Participate in Respiration - Glycolysis Occurs in the cytoplasmic matrix - Pyruvate dehydrogenase - Krebs Cycle
Bioenergetics: Energy for Exercise. Chapter 3 pp 28-47
 Bioenergetics: Energy for Exercise Chapter 3 pp 28-47 ATP ATP Adenosine Ribose 3 Phosphates ATP ATP ATP ATP ATP ATP ATP ATP ATP Energy Out ADP + P ATP ATP Energy Out ADP + P ATP ATP Energy Out Energy In
Bioenergetics: Energy for Exercise Chapter 3 pp 28-47 ATP ATP Adenosine Ribose 3 Phosphates ATP ATP ATP ATP ATP ATP ATP ATP ATP Energy Out ADP + P ATP ATP Energy Out ADP + P ATP ATP Energy Out Energy In
New tools bring greater understanding to cellular metabolism research
 New tools bring greater understanding to cellular metabolism research Mourad Ferhat, Ph.D, 7 Juin 2017 FDSS Users Meeting, Hamamatsu mourad.ferhat@promega.com Today s talk : focus on new cell-based assays
New tools bring greater understanding to cellular metabolism research Mourad Ferhat, Ph.D, 7 Juin 2017 FDSS Users Meeting, Hamamatsu mourad.ferhat@promega.com Today s talk : focus on new cell-based assays
BIOCHEMISTRY. Glycolysis. by Dr Jaya Vejayan Faculty of Industrial Sciences & Technology
 BIOCHEMISTRY Glycolysis by Dr Jaya Vejayan Faculty of Industrial Sciences & Technology email: jayavejayan@ump.edu.my Chapter Description Overview This chapter is related to carbohydrate catabolism. It
BIOCHEMISTRY Glycolysis by Dr Jaya Vejayan Faculty of Industrial Sciences & Technology email: jayavejayan@ump.edu.my Chapter Description Overview This chapter is related to carbohydrate catabolism. It
Unit 2: Metabolic Processes
 How is energy obtained biologically? Recall: Red Ox Reactions Unit 2: Metabolic Processes Oxidation Is the chief mechanism by which chemical potential energy is released This energy comes from reduced
How is energy obtained biologically? Recall: Red Ox Reactions Unit 2: Metabolic Processes Oxidation Is the chief mechanism by which chemical potential energy is released This energy comes from reduced
Time after injection (hours) ns ns
 Platelet life span (% iotinylated platelets) 1 8 6 4 2 4 24 48 72 96 Time after injection (hours) 6 4 2 IgG GPIα GPIβ GPII GPVI Receptor expression (GeoMean, fluorescence inteity) Supplementary figure
Platelet life span (% iotinylated platelets) 1 8 6 4 2 4 24 48 72 96 Time after injection (hours) 6 4 2 IgG GPIα GPIβ GPII GPVI Receptor expression (GeoMean, fluorescence inteity) Supplementary figure
3.7.1 Define cell respiration [Cell respiration is the controlled release of energy from organic compounds in cells to form ATP]
![3.7.1 Define cell respiration [Cell respiration is the controlled release of energy from organic compounds in cells to form ATP] 3.7.1 Define cell respiration [Cell respiration is the controlled release of energy from organic compounds in cells to form ATP]](/thumbs/72/66350985.jpg) 3.7 Cell respiration ( Chapter 9 in Campbell's book) 3.7.1 Define cell respiration [Cell respiration is the controlled release of energy from organic compounds in cells to form ATP] Organic compounds store
3.7 Cell respiration ( Chapter 9 in Campbell's book) 3.7.1 Define cell respiration [Cell respiration is the controlled release of energy from organic compounds in cells to form ATP] Organic compounds store
How Did Energy-Releasing Pathways Evolve? (cont d.)
 How Did Energy-Releasing Pathways Evolve? (cont d.) 7.1 How Do Cells Access the Chemical Energy in Sugars? In order to use the energy stored in sugars, cells must first transfer it to ATP The energy transfer
How Did Energy-Releasing Pathways Evolve? (cont d.) 7.1 How Do Cells Access the Chemical Energy in Sugars? In order to use the energy stored in sugars, cells must first transfer it to ATP The energy transfer
METABOLIC VULNERABILITIES OF CANCER. Eyal Gottlieb
 METABOLIC VULNERABILITIES OF CANCER Eyal Gottlieb METABOLIC VULNERABILITIES OF CANCER Eyal Gottlieb Cancer and metabolism: the anabolic angle glucose glucose-6-phosphate Ribose-5-phosphate ADP + Pi Serine
METABOLIC VULNERABILITIES OF CANCER Eyal Gottlieb METABOLIC VULNERABILITIES OF CANCER Eyal Gottlieb Cancer and metabolism: the anabolic angle glucose glucose-6-phosphate Ribose-5-phosphate ADP + Pi Serine
Metabolism Energy Pathways Biosynthesis. Catabolism Anabolism Enzymes
 Topics Microbial Metabolism Metabolism Energy Pathways Biosynthesis 2 Metabolism Catabolism Catabolism Anabolism Enzymes Breakdown of complex organic molecules in order to extract energy and dform simpler
Topics Microbial Metabolism Metabolism Energy Pathways Biosynthesis 2 Metabolism Catabolism Catabolism Anabolism Enzymes Breakdown of complex organic molecules in order to extract energy and dform simpler
Respiration. Respiration. Respiration. How Cells Harvest Energy. Chapter 7
 How Cells Harvest Energy Chapter 7 Organisms can be classified based on how they obtain energy: autotrophs: are able to produce their own organic molecules through photosynthesis heterotrophs: live on
How Cells Harvest Energy Chapter 7 Organisms can be classified based on how they obtain energy: autotrophs: are able to produce their own organic molecules through photosynthesis heterotrophs: live on
AP BIOLOGY Chapter 7 Cellular Respiration =
 1 AP BIOLOGY Chapter 7 Cellular Respiration = Day 1 p. I. Overview A. Cellular Respiration 1. Respiration breathing, exchange of O 2 for CO 2 2. Cellular respiration aerobic harvesting of energy from food
1 AP BIOLOGY Chapter 7 Cellular Respiration = Day 1 p. I. Overview A. Cellular Respiration 1. Respiration breathing, exchange of O 2 for CO 2 2. Cellular respiration aerobic harvesting of energy from food
BIO16 Mapua Institute of Technology
 BIO16 Mapua Institute of Technology The Marathon If somebody challenged you to a run a race, how should you prepare to win? 1. Practice 2. Eat the right foods 3. Drink the right liquids Energy All living
BIO16 Mapua Institute of Technology The Marathon If somebody challenged you to a run a race, how should you prepare to win? 1. Practice 2. Eat the right foods 3. Drink the right liquids Energy All living
Metabolism. Chapter 8 Microbial Metabolism. Metabolic balancing act. Catabolism Anabolism Enzymes. Topics. Metabolism Energy Pathways Biosynthesis
 Chapter 8 Microbial Metabolism Topics Metabolism Energy Pathways Biosynthesis Catabolism Anabolism Enzymes Metabolism 1 2 Metabolic balancing act Catabolism and anabolism simple model Catabolism Enzymes
Chapter 8 Microbial Metabolism Topics Metabolism Energy Pathways Biosynthesis Catabolism Anabolism Enzymes Metabolism 1 2 Metabolic balancing act Catabolism and anabolism simple model Catabolism Enzymes
Bio 111 Study Guide Chapter 7 Cellular Respiration & Fermentation
 Bio 111 Study Guide Chapter 7 Cellular Respiration & Fermentation BEFORE CLASS: Reading: Read the whole chapter from pp. 141-158. In Concept 7.1, pay special attention to oxidation & reduction and the
Bio 111 Study Guide Chapter 7 Cellular Respiration & Fermentation BEFORE CLASS: Reading: Read the whole chapter from pp. 141-158. In Concept 7.1, pay special attention to oxidation & reduction and the
ab Glycolysis Stress Test Companion Assay
 Version 1 Last updated 12 July 2017 ab222945 Glycolysis Stress Test Companion Assay For the characterization of glycolytic stress in live cells when used in combination with Glycolysis Assay [Extracellular
Version 1 Last updated 12 July 2017 ab222945 Glycolysis Stress Test Companion Assay For the characterization of glycolytic stress in live cells when used in combination with Glycolysis Assay [Extracellular
Role of cellular bioenergetics in smooth muscle cell proliferation induced by platelet-derived growth factor
 Biochem. J. (2010) 428, 255 267 (Printed in Great Britain) doi:10.1042/bj20100090 255 Role of cellular bioenergetics in smooth muscle cell proliferation induced by platelet-derived growth factor Jessica
Biochem. J. (2010) 428, 255 267 (Printed in Great Britain) doi:10.1042/bj20100090 255 Role of cellular bioenergetics in smooth muscle cell proliferation induced by platelet-derived growth factor Jessica
Chapter 7 Cellular Respiration and Fermentation*
 Chapter 7 Cellular Respiration and Fermentation* *Lecture notes are to be used as a study guide only and do not represent the comprehensive information you will need to know for the exams. Life Is Work
Chapter 7 Cellular Respiration and Fermentation* *Lecture notes are to be used as a study guide only and do not represent the comprehensive information you will need to know for the exams. Life Is Work
LKB1 Deficient Non-small Cell Lung Cancer Cells are Vulnerable to Energy Stress Induced by ATP Depletion
 Texas Medical Center Library DigitalCommons@TMC UT GSBS Dissertations and Theses (Open Access) Graduate School of Biomedical Sciences 12-2014 LKB1 Deficient Non-small Cell Lung Cancer Cells are Vulnerable
Texas Medical Center Library DigitalCommons@TMC UT GSBS Dissertations and Theses (Open Access) Graduate School of Biomedical Sciences 12-2014 LKB1 Deficient Non-small Cell Lung Cancer Cells are Vulnerable
Cellular Respiration
 Cellular I can describe cellular respiration Cellular respiration is a series of metabolic pathways releasing energy from a foodstuff e.g. glucose. This yields energy in the form of ATP adenosine P i P
Cellular I can describe cellular respiration Cellular respiration is a series of metabolic pathways releasing energy from a foodstuff e.g. glucose. This yields energy in the form of ATP adenosine P i P
Class XI Chapter 14 Respiration in Plants Biology. 1. It is a biochemical process. 1. It is a physiochemical process.
 Question 1: Differentiate between (a) Respiration and Combustion (b) Glycolysis and Krebs cycle (c) Aerobic respiration and Fermentation (a) Respiration and combustion Respiration Combustion 1. It is a
Question 1: Differentiate between (a) Respiration and Combustion (b) Glycolysis and Krebs cycle (c) Aerobic respiration and Fermentation (a) Respiration and combustion Respiration Combustion 1. It is a
Chapter 9. Cellular Respiration and Fermentation
 Chapter 9 Cellular Respiration and Fermentation Energy flows into an ecosystem as sunlight and leaves as heat Photosynthesis generates O 2 and organic molecules, which are used in cellular respiration
Chapter 9 Cellular Respiration and Fermentation Energy flows into an ecosystem as sunlight and leaves as heat Photosynthesis generates O 2 and organic molecules, which are used in cellular respiration
4. Which step shows a split of one molecule into two smaller molecules? a. 2. d. 5
 1. Which of the following statements about NAD + is false? a. NAD + is reduced to NADH during both glycolysis and the citric acid cycle. b. NAD + has more chemical energy than NADH. c. NAD + is reduced
1. Which of the following statements about NAD + is false? a. NAD + is reduced to NADH during both glycolysis and the citric acid cycle. b. NAD + has more chemical energy than NADH. c. NAD + is reduced
Investigating the Effect of Energy Substrates and LPS-activation on the In Vitro Energy Metabolism of BV-2, RAW264.
 Investigating the Effect of Energy Substrates and LPS-activation on the In Vitro Energy Metabolism of BV-2, RAW264.7 and VM-M3 Cells Author: Ashley Kaye Brown Persistent link: http://hdl.handle.net/2345/bc-ir:106811
Investigating the Effect of Energy Substrates and LPS-activation on the In Vitro Energy Metabolism of BV-2, RAW264.7 and VM-M3 Cells Author: Ashley Kaye Brown Persistent link: http://hdl.handle.net/2345/bc-ir:106811
III. 6. Test. Respiració cel lular
 III. 6. Test. Respiració cel lular Chapter Questions 1) What is the term for metabolic pathways that release stored energy by breaking down complex molecules? A) anabolic pathways B) catabolic pathways
III. 6. Test. Respiració cel lular Chapter Questions 1) What is the term for metabolic pathways that release stored energy by breaking down complex molecules? A) anabolic pathways B) catabolic pathways
In glycolysis, glucose is converted to pyruvate. If the pyruvate is reduced to lactate, the pathway does not require O 2 and is called anaerobic
 Glycolysis 1 In glycolysis, glucose is converted to pyruvate. If the pyruvate is reduced to lactate, the pathway does not require O 2 and is called anaerobic glycolysis. If this pyruvate is converted instead
Glycolysis 1 In glycolysis, glucose is converted to pyruvate. If the pyruvate is reduced to lactate, the pathway does not require O 2 and is called anaerobic glycolysis. If this pyruvate is converted instead
The citric acid cycle Sitruunahappokierto Citronsyracykeln
 The citric acid cycle Sitruunahappokierto Citronsyracykeln Ove Eriksson BLL/Biokemia ove.eriksson@helsinki.fi Metabolome: The complete set of small-molecule metabolites to be found in a cell or an organism.
The citric acid cycle Sitruunahappokierto Citronsyracykeln Ove Eriksson BLL/Biokemia ove.eriksson@helsinki.fi Metabolome: The complete set of small-molecule metabolites to be found in a cell or an organism.
NOTES: Ch 9 Cellular Respiration: Harvesting Chemical Energy Part 1: The Overview
 NOTES: Ch 9 Cellular Respiration: Harvesting Chemical Energy Part 1: The Overview Overview: Life Is Work Living cells require energy from outside sources Some animals, such as the giant panda, obtain energy
NOTES: Ch 9 Cellular Respiration: Harvesting Chemical Energy Part 1: The Overview Overview: Life Is Work Living cells require energy from outside sources Some animals, such as the giant panda, obtain energy
Biol 219 Lec 7 Fall 2016
 Cellular Respiration: Harvesting Energy to form ATP Cellular Respiration and Metabolism Glucose ATP Pyruvate Lactate Acetyl CoA NAD + Introducing The Players primary substrate for cellular respiration
Cellular Respiration: Harvesting Energy to form ATP Cellular Respiration and Metabolism Glucose ATP Pyruvate Lactate Acetyl CoA NAD + Introducing The Players primary substrate for cellular respiration
 Question 1: Differentiate between (a) Respiration and Combustion (b) Glycolysis and Krebs cycle (c) Aerobic respiration and Fermentation (a) Respiration and combustion Respiration Combustion 1. It is a
Question 1: Differentiate between (a) Respiration and Combustion (b) Glycolysis and Krebs cycle (c) Aerobic respiration and Fermentation (a) Respiration and combustion Respiration Combustion 1. It is a
How Cells Harvest Chemical Energy
 How Cells Harvest Chemical Energy Chapter 6 Introduction: How Is a Marathoner Different from a Sprinter? Individuals inherit various percentages of the two main types of muscle fibers, slow and fast The
How Cells Harvest Chemical Energy Chapter 6 Introduction: How Is a Marathoner Different from a Sprinter? Individuals inherit various percentages of the two main types of muscle fibers, slow and fast The
BCH Graduate Survey of Biochemistry
 BCH 5045 Graduate Survey of Biochemistry Instructor: Charles Guy Producer: Ron Thomas Director: Marsha Durosier Lecture 44 Slide sets available at: http://hort.ifas.ufl.edu/teach/guyweb/bch5045/index.html
BCH 5045 Graduate Survey of Biochemistry Instructor: Charles Guy Producer: Ron Thomas Director: Marsha Durosier Lecture 44 Slide sets available at: http://hort.ifas.ufl.edu/teach/guyweb/bch5045/index.html
Energy metabolism - the overview
 Energy metabolism - the overview Josef Fontana EC - 40 Overview of the lecture Important terms of the energy metabolism The overview of the energy metabolism The main pathways of the energy metabolism
Energy metabolism - the overview Josef Fontana EC - 40 Overview of the lecture Important terms of the energy metabolism The overview of the energy metabolism The main pathways of the energy metabolism
OAT Biology - Problem Drill 03: Cell Processes - Metabolism and Cellular Respiration
 OAT Biology - Problem Drill 03: Cell Processes - Metabolism and Cellular Respiration Question No. 1 of 10 1. What is the final electron acceptor in aerobic respiration? Question #01 (A) NADH (B) Mitochondria
OAT Biology - Problem Drill 03: Cell Processes - Metabolism and Cellular Respiration Question No. 1 of 10 1. What is the final electron acceptor in aerobic respiration? Question #01 (A) NADH (B) Mitochondria
Respiration 30/04/2013. Dr.M.R.Vaezi K., Hakim Sabzevari University
 Respiration Metabolism - the sum of all the chemical reactions that occur in the body. It is comprised of: anabolism synthesis of molecules, requires input of energy catabolism break down of molecules,
Respiration Metabolism - the sum of all the chemical reactions that occur in the body. It is comprised of: anabolism synthesis of molecules, requires input of energy catabolism break down of molecules,
Metabolism of cardiac muscle. Dr. Mamoun Ahram Cardiovascular system, 2013
 Metabolism of cardiac muscle Dr. Mamoun Ahram Cardiovascular system, 2013 References This lecture Mark s Basic Medical Biochemistry, 4 th ed., p. 890-891 Hand-out Why is this topic important? Heart failure
Metabolism of cardiac muscle Dr. Mamoun Ahram Cardiovascular system, 2013 References This lecture Mark s Basic Medical Biochemistry, 4 th ed., p. 890-891 Hand-out Why is this topic important? Heart failure
Cellular Respiration. Cellular Respiration. C 6 H 12 O 6 + 6O > 6CO 2 + 6H energy. Heat + ATP. You need to know this!
 Cellular Respiration LISA Biology Cellular Respiration C 6 H 12 O 6 + 6O 2 - - - - - > 6CO 2 + 6H 2 0 + energy You need to know this! Heat + ATP 1 Did that equation look familiar? * The equation for cellular
Cellular Respiration LISA Biology Cellular Respiration C 6 H 12 O 6 + 6O 2 - - - - - > 6CO 2 + 6H 2 0 + energy You need to know this! Heat + ATP 1 Did that equation look familiar? * The equation for cellular
3. Distinguish between aerobic and anaerobic in terms of cell respiration. Outline the general process of both.
 3.7 Cell Respiration 1. Define cell respiration. Cell respiration is the controlled release of energy from organic molecules in cells to form ATP. 2. State the equation for the process of cell respiration.
3.7 Cell Respiration 1. Define cell respiration. Cell respiration is the controlled release of energy from organic molecules in cells to form ATP. 2. State the equation for the process of cell respiration.
Enzymes what are they?
 Topic 11 (ch8) Microbial Metabolism Topics Metabolism Energy Pathways Biosynthesis 1 Catabolism Anabolism Enzymes Metabolism 2 Metabolic balancing act Catabolism Enzymes involved in breakdown of complex
Topic 11 (ch8) Microbial Metabolism Topics Metabolism Energy Pathways Biosynthesis 1 Catabolism Anabolism Enzymes Metabolism 2 Metabolic balancing act Catabolism Enzymes involved in breakdown of complex
Energy Production In A Cell (Chapter 25 Metabolism)
 Energy Production In A Cell (Chapter 25 Metabolism) Large food molecules contain a lot of potential energy in the form of chemical bonds but it requires a lot of work to liberate the energy. Cells need
Energy Production In A Cell (Chapter 25 Metabolism) Large food molecules contain a lot of potential energy in the form of chemical bonds but it requires a lot of work to liberate the energy. Cells need
CHY2026: General Biochemistry UNIT 7& 8: CARBOHYDRATE METABOLISM
 CHY2026: General Biochemistry UNIT 7& 8: CARBOHYDRATE METABOLISM Metabolism Bioenergetics is the transfer and utilization of energy in biological systems The direction and extent to which a chemical reaction
CHY2026: General Biochemistry UNIT 7& 8: CARBOHYDRATE METABOLISM Metabolism Bioenergetics is the transfer and utilization of energy in biological systems The direction and extent to which a chemical reaction
Active Learning Exercise 5. Cellular Respiration
 Name Biol 211 - Group Number Active Learning Exercise 5. Cellular Respiration Reference: Chapter 9 (Biology by Campbell/Reece, 8 th ed.) 1. Give the overall balanced chemical equation for aerobic cellular
Name Biol 211 - Group Number Active Learning Exercise 5. Cellular Respiration Reference: Chapter 9 (Biology by Campbell/Reece, 8 th ed.) 1. Give the overall balanced chemical equation for aerobic cellular
Ch. 9 Cell Respiration. Title: Oct 15 3:24 PM (1 of 53)
 Ch. 9 Cell Respiration Title: Oct 15 3:24 PM (1 of 53) Essential question: How do cells use stored chemical energy in organic molecules and to generate ATP? Title: Oct 15 3:28 PM (2 of 53) Title: Oct 19
Ch. 9 Cell Respiration Title: Oct 15 3:24 PM (1 of 53) Essential question: How do cells use stored chemical energy in organic molecules and to generate ATP? Title: Oct 15 3:28 PM (2 of 53) Title: Oct 19
1 Respiration is a vital process in living organisms. All organisms carry out glycolysis. The Krebs cycle also occurs in some organisms.
 1 Respiration is a vital process in living organisms. All organisms carry out glycolysis. The Krebs cycle also occurs in some organisms. (a) The diagram below shows some of the stages in glycolysis, using
1 Respiration is a vital process in living organisms. All organisms carry out glycolysis. The Krebs cycle also occurs in some organisms. (a) The diagram below shows some of the stages in glycolysis, using
Metabolism. Metabolic pathways. BIO 5099: Molecular Biology for Computer Scientists (et al) Lecture 11: Metabolic Pathways
 BIO 5099: Molecular Biology for Computer Scientists (et al) Lecture 11: Metabolic Pathways http://compbio.uchsc.edu/hunter/bio5099 Larry.Hunter@uchsc.edu Metabolism Metabolism is the chemical change of
BIO 5099: Molecular Biology for Computer Scientists (et al) Lecture 11: Metabolic Pathways http://compbio.uchsc.edu/hunter/bio5099 Larry.Hunter@uchsc.edu Metabolism Metabolism is the chemical change of
BIOLOGY - CLUTCH CH.9 - RESPIRATION.
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: REDOX REACTIONS Redox reaction a chemical reaction that involves the transfer of electrons from one atom to another Oxidation loss of electrons Reduction gain of electrons
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: REDOX REACTIONS Redox reaction a chemical reaction that involves the transfer of electrons from one atom to another Oxidation loss of electrons Reduction gain of electrons
Cellular Respiration
 Cellular Respiration C 6 H 12 O 6 + 6O 2 -----> 6CO 2 + 6H 2 0 + energy (heat and ATP) 1. Energy Capacity to move or change matter Forms of energy are important to life include Chemical, radiant (heat
Cellular Respiration C 6 H 12 O 6 + 6O 2 -----> 6CO 2 + 6H 2 0 + energy (heat and ATP) 1. Energy Capacity to move or change matter Forms of energy are important to life include Chemical, radiant (heat
2
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 What is the fate of Pyruvate? Stages of Cellular Respiration GLYCOLYSIS PYRUVATE OX. KREBS CYCLE ETC 2 The Krebs Cycle does your head suddenly hurt? 3 The Krebs Cycle An Overview
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 What is the fate of Pyruvate? Stages of Cellular Respiration GLYCOLYSIS PYRUVATE OX. KREBS CYCLE ETC 2 The Krebs Cycle does your head suddenly hurt? 3 The Krebs Cycle An Overview
Biology 30 Structure & Function of Cells (Part 2) Bioenergetics: Energy: Potential energy: Examples: Kinetic energy. Examples:
 Biology 30 Structure & Function of Cells (Part 2) Bioenergetics: Energy: Potential energy: Examples: Kinetic energy Examples: Energy can be transformed: Thermodynamics: First law of Thermodynamics: Second
Biology 30 Structure & Function of Cells (Part 2) Bioenergetics: Energy: Potential energy: Examples: Kinetic energy Examples: Energy can be transformed: Thermodynamics: First law of Thermodynamics: Second
Biological Science 101 General Biology
 Lecture Seven: Cellular Respiration Ch. 9, Pgs. 163-181 Figs. 9.2-9.20 Biological Science 101 General Biology Cellular Respiration: - A series of processes that is involved in converting food to energy
Lecture Seven: Cellular Respiration Ch. 9, Pgs. 163-181 Figs. 9.2-9.20 Biological Science 101 General Biology Cellular Respiration: - A series of processes that is involved in converting food to energy
Muscle Metabolism. Dr. Nabil Bashir
 Muscle Metabolism Dr. Nabil Bashir Learning objectives Understand how skeletal muscles derive energy at rest, moderate exercise, and strong exercise. Recognize the difference between aerobic and anaerobic
Muscle Metabolism Dr. Nabil Bashir Learning objectives Understand how skeletal muscles derive energy at rest, moderate exercise, and strong exercise. Recognize the difference between aerobic and anaerobic
Grade of steatosis. group Case No. Supplementary Figure 1:
 a Supplementary Figure 1: b group Case No Grade of steatosis 15m AL 2746 NN 1 15m AL 2746 BN 1 15m AL 2638 2LN 3 15m AL 2638 2RN 3 12m AL 2640 RN 0 12m AL 2640 BN 1 12m AL 2640 LN 2 12m AL 2635 NN 2 12m
a Supplementary Figure 1: b group Case No Grade of steatosis 15m AL 2746 NN 1 15m AL 2746 BN 1 15m AL 2638 2LN 3 15m AL 2638 2RN 3 12m AL 2640 RN 0 12m AL 2640 BN 1 12m AL 2640 LN 2 12m AL 2635 NN 2 12m
Pyruvate + NADH + H + ==== Lactate + NAD +
 1 UNIVERSITY OF PAPUA NEW GUINEA SCHOOL OF MEDICINE AND HEALTH SCIENCES DIVISION OF BASIC MEDICAL SCIENCES DISCIPLINE OF BIOCHEMISTRY AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY PBL SEMINAR ANAEROBIC METABOLISM - An Overview
1 UNIVERSITY OF PAPUA NEW GUINEA SCHOOL OF MEDICINE AND HEALTH SCIENCES DIVISION OF BASIC MEDICAL SCIENCES DISCIPLINE OF BIOCHEMISTRY AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY PBL SEMINAR ANAEROBIC METABOLISM - An Overview
Medical Biochemistry and Molecular Biology department
 Medical Biochemistry and Molecular Biology department Cardiac Fuels [Sources of energy for the Cardiac muscle] Intended learning outcomes of the lecture: By the end of this lecture you would be able to:-
Medical Biochemistry and Molecular Biology department Cardiac Fuels [Sources of energy for the Cardiac muscle] Intended learning outcomes of the lecture: By the end of this lecture you would be able to:-
Higher Biology. Unit 2: Metabolism and Survival Topic 2: Respiration. Page 1 of 25
 Higher Biology Unit 2: Metabolism and Survival Topic 2: Respiration Page 1 of 25 Sub Topic: Respiration I can state that: All living cells carry out respiration. ATP is the energy currency of the cell
Higher Biology Unit 2: Metabolism and Survival Topic 2: Respiration Page 1 of 25 Sub Topic: Respiration I can state that: All living cells carry out respiration. ATP is the energy currency of the cell
