Exercise Physiology. High-Density Lipoprotein Maintains Skeletal Muscle Function by Modulating Cellular Respiration in Mice
|
|
|
- Scott Todd
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Exercise Physiology High-Density Lipoprotein Mintins Skeletl Muscle Function by Modulting Cellulr Respirtion in Mice Mrit Lehti, PhD; Elizbeth Doneln, MS; Willim Abplnlp, MS; Omr Al-Mssdi, PhD; Kirk M. Hbegger, PhD; Jon Weber, BS; Chndler Ress, BS; Johnnes Mnsfeld, MS; Sonl Somvnshi, MS; Chitrng Trivedi, PhD; Michel Keuper, PhD; Tej Ogrjsek, BS; Cynthi Striese; Sebstin Cucuruz; Pul T. Pfluger, PhD; Rdhkrishn Krishn, PhD; Scott M. Gordon, PhD; R.A. Gngni D. Silv, PhD; Serge Luquet, PhD; Julien Cstel, BS; Srh Mrtinez, MS; Dvid D Alessio, MD; W. Sen Dvidson, PhD; Susnn M. Hofmnn, MD Downloded from by on July 26, 2018 Bckground Abnorml glucose metbolism is centrl feture of disorders with incresed rtes of crdiovsculr disese. Low levels of high-density lipoprotein (HDL) re key predictor for crdiovsculr disese. We used genetic mouse models with incresed HDL levels (polipoprotein A-I trnsgenic [poa-i tg]) nd reduced HDL levels (poa-i deficient [poa-i ko]) to investigte whether HDL modultes mitochondril bioenergetics in skeletl muscle. Methods nd Results ApoA-I ko mice exhibited fsting hyperglycemi nd impired glucose tolernce test compred with wild-type mice. Mitochondri isolted from gstrocnemius muscle of poa-i ko mice displyed mrkedly blunted ATP synthesis. Endurnce cpcity during exercise exhustion test ws impired in poa-i ko mice. HDL directly enhnced glucose oxidtion by incresing glycolysis nd mitochondril respirtion rte in C2C12 muscle cells. ApoA-I tg mice exhibited lower fsting glucose levels, improved glucose tolernce test, incresed lctte levels, reduced ft mss, ssocited with protection ginst ge-induced decline of endurnce cpcity compred with wild-type mice. Circulting levels of fibroblst growth fctor 21, novel biomrker for mitochondril respirtory chin deficiencies nd inhibitor of white dipose lipolysis, were significntly reduced in poa-i tg mice. Consistent with n increse in glucose utiliztion of skeletl muscle, geneticlly incresed HDL nd poa-i levels in mice prevented high-ft diet induced impirment of glucose homeostsis. Conclusions In view of impired mitochondril function nd decresed HDL levels in type 2 dibetes mellitus, our findings indicte tht HDL-rising therpies my preserve muscle mitochondril function nd ddress key spects of type 2 dibetes mellitus beyond crdiovsculr disese. (Circultion. 2013;128: ) Key Words: cellulr respirtion cholesterol, HDL exercise obesity Recent yers hve seen n lrming rise in the incidence of crdiovsculr disese linked to obesity-relted metbolic fctors. 1 Epidemiologicl studies hve confirmed strong ssocition between ft intke, plsm cholesterol levels, nd crdiovsculr disese mortlity rtes. 2 5 Of prticulr concern is the incidence of dibetes mellitus in obese ptients, becuse dibetes mellitus itself crries substntilly elevted crdiovsculr disese risk. 6 One of the strongest independent predictors of crdiovsculr disese is low level of high-density lipoprotein (HDL) prticles nd their mjor protein constituent polipoprotein A-I (poa-i). 7,8 Besides its criticl role in reverse cholesterol trnsport nd cellulr cholesterol efflux, poa-i lso hs nti-inflmmtory, ntithrombotic, nd ntioxidnt functions tht contribute to its well-known ntitherogenic function Low circulting HDL nd poa-i levels re lso hllmrk of insulin-resistnce, pthologicl precondition leding to type 2 dibetes mellitus (T2D). 11,13 It remins uncler, however, whether circulting HDL levels exert n effect on insulin resistnce nd the development of dibetes mellitus. Editoril see p 2349 Clinicl Perspective on p 2371 Received Jnury 23, 2013; ccepted September 16, From the Dibetes Reserch Deprtment (IDO nd IDR), Helmholtz Zentrum München, Germn Reserch Center for Environmentl Helth, München/ Neuherberg, Germny (M.L., M.K., T.O., C.S., S.C., P.T.P., S.M.H.); Metbolic Diseses Institute, Division of Endocrinology, Deprtment of Internl Medicine, University of Cincinnti, Cincinnti, OH (M.L., E.D., W.A., O.A.-M., K.M.H., J.W., C.R., J.M., S.S., C.T., R.K., S.M.G., R.A.G.D.S., D.D., W.S.D., S.M.H.); LIKES Reserch Center for Sport nd Helth Sciences, Jyväskylä, Finlnd (M.L.); Energy Metbolism Lbortory ETH Zurich (Swiss Federl Institute of Technology), Zurich, Switzerlnd (J.M.); Deprtment of Phrmcology nd Toxicology, Zydus Reserch Centre, Cdil Helthcre Limited, Ahmedbd, Indi (C.T.); Univ Pris Diderot, Sorbonne Pris Cité, Unité de Biologie Fonctionnelle et Adpttive, Pris, Frnce (S.L., J.C., S.M.); Centre Ntionl de l Recherche Scientifique, Pris, Frnce (S.L., J.C., S.M.); nd Medizinische Klinik, Ludwig Mximilins University, Munich, Germny (S.M.H.). The online-only Dt Supplement is vilble with this rticle t /-/DC1. Correspondence to Susnn M. Hofmnn, MD, Dibetes Reserch Deprtment, Institute for Dibetes nd Regenertion, Helmholtz Center Munich, Germn Reserch Center for Environmentl Helth, GmbH, Ingolstädter Lndstrsse 1, Neuherberg, Germny. E-mil susnn.hofmnn@helmholtz-muenchen.de 2013 Americn Hert Assocition, Inc. Circultion is vilble t DOI: /CIRCULATIONAHA
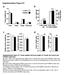
2 Lehti et l ApoA-I Enhnces Glucose Oxidtion in Skeletl Muscle 2365 Downloded from by on July 26, 2018 Severl lines of evidence suggest tht HDL nd poa-i modulte glucose homeostsis: Infusions of reconstituted HDL prticles hve been shown to reduce circulting glucose levels nd increse insulin levels in ptients with T2D through insulin-dependent nd -independent mechnisms. 14 Cell-bsed ssys hve confirmed tht both HDL components poa-i nd poa-ii increse β-cell insulin secretion. 15 HDL nd poa-i hve been lso demonstrted to directly enhnce glucose uptke in cultured mouse nd humn skeletl muscle cells, thus confirming n insulinindependent effect of HDL. 14,16 Thus, these results show tht HDL nd poa-i re enhncing musculr glucose uptke. In ddition to glucose uptke, intrcellulr glucose metbolism is known to ply pivotl role in the pthogenesis for insulin resistnce nd dibetes mellitus. After entry into the muscle cell, glucose is oxidized through mitochondril phosphoryltion to ATP s n energy source for cellulr metbolism. Glucose is lso used to generte glycogen nd converted into ft (lipogenesis) for storge nd lter use s energy. 17 All 3 metbolic routes hve been shown to contribute to the development of dibetes mellitus. First, oxidtive phosphoryltion nd ATP synthesis re impired in skeletl muscle from reltives of ptients with T2D, strongly suggesting tht defects in mitochondril oxidtive metbolism re primry cuse of insulin resistnce. 18 Second, dysfunctionl muscle glycogen synthesis hs been reported to ply dominnt role in insulin resistnce of dibetic ptients. 19 Consistently, defects in insulin-medited glucose oxidtion, glycogen synthesis, nd storge hve been lredy reveled in skeletl muscle from individuls with norml glucose tolernce but with peripherl insulin resistnce, 20 underscoring the importnce of intrmyocellulr glucose metbolism s crucil plyer in the development of insulin resistnce. Finlly, n excessive conversion of glucose into lipid resulting from defects in mitochondril function leds to ccumultion of intrmyocellulr triglycerides, which lso hs been implicted in insulin resistnce in severl popultion studies. 21 Although it hs been shown tht HDL nd poa-i do increse glucose uptke in muscle cells nd thus decrese circulting glucose levels, it hs not been determined whether HDL nd poa-i lso ffect intrcellulr glucose oxidtion, glycogen synthesis, nd lipogenesis. In this study, we investigted the requirement for circulting HDL nd poa-i in norml glucose oxidtion of skeletl muscle using genetic loss- nd gin-of-function mouse model. We show tht, in the bsence of poa-i, mitochondril oxidtive phosphoryltion is reduced in skeletl muscle, resulting in incresed circulting glucose levels nd impired musculr function. We provide in vitro nd in vivo evidence tht HDL nd poa-i enhnce glycolysis nd mitochondril oxidtive phosphoryltion rtes of glucose. Overexpression of poa-i in mice resulted in protection ginst ge-induced decline of endurnce cpcity, ginst ge-induced ft mss gin, nd ginst diet-induced hyperglycemi. Improved mitochondril function in poa-i trnsgenic (poa-i tg) mice ws further confirmed indirectly by the mrked reduction of circulting fibroblst growth fctor 21 (FGF-21), novel biomrker for mitochondril dysfunction. Our findings point to key role for circulting HDL nd poa-i in regulting skeletl muscle metbolism nd highlight possible trget for the tretment of metbolic diseses such s insulin resistnce nd T2D. Methods An expnded online-only Methods nd Results section is vilble in the online-only Dt Supplement. Mice Age-mtched mle poa-i deficient (poa-i ko), humn poa-i tg, nd control (wild-type [wt]) C57/Bl6J mice (The Jckson Lbortories, Br Hrbor, ME) were housed in specific pthogen free fcilities with 12-hour light/12-hour drk cycle nd were fed bsl rodent chow 5058 PicoLb Mouse Diet 20 (LbDiet, Richmond, IN). Mice tht underwent the diet-induced obesity study were fed lowft diet contining 4.8% ft by weight (D12328; Reserch Diets, New Brunswick, NJ) or high-ft diet contining 35.8% ft by weight (D12330; Reserch Diets) for 12 weeks. All experimentl procedures conformed to institutionl guidelines for niml experiments nd were pproved by the Institutionl Animl Cre nd Use Committee (IACUC) t the University of Cincinnti. Respirtion Studies in Isolted Skeletl Muscle Mitochondri nd Cultured Muscle Cells After euthniztion, gstrocnemius muscles were hrvested nd mitochondri were isolted immeditely s described. 22 Muscle mitochondri respirtion mesurements were mde in triplicte by the Sehorse 24XF nlyzer (Sehorse Biosciences Inc., North Billeric, MA). For the determintion of extrcellulr cidifiction rte (ECAR) nd mitochondril oxygen consumption rte in the murine skeletl muscle C2C12 cell line (ATCC, Mnsss, Virgini), cells were incubted for 4 hours with incresing mounts of humn HDL nd 4,5 mg/ml glucose using the Sehorse XF24 nlyzer s published. 23 Results Circulting HDL Is Required for Norml Glucose Homeostsis To understnd the role of circulting HDL levels in glucose homeostsis, we used genetic loss- nd gin-of-function mouse model for poa-i, the min protein component of HDL. Fst protein liquid chromtogrphy (FPLC) nlysis of polipoprotein profiles reveled severely reduced HDL prticle concentrtion in poa-i ko nd mrkedly incresed HDL prticle concentrtion in humn poa-i tg mice compred with wt controls (Figure 1A nd 1B). ApoA-I ko mice exhibited incresed heptic triglyceride content compred with wt nd poa-i tg mice (Figure 1C). We detected mrkedly higher fsting glucose nd HbA1c levels in chow-fed poa-i ko mice compred with wt littermtes (Figure 1E nd F). In contrst, poa-i tg mice hd significntly lower fsting glucose levels compred with wt littermtes (Figure 1E). Response to intrperitonel glucose tolernce test ws impired in poa-i ko nd improved in poa-i tg mice compred with wt littermtes (Figure 1D). These results indicte tht circulting HDL levels re importnt for the efficient clernce of glucose from the circultion. To find out which tissue is responsible for HDL-medited improvement of glucose tolernce nd whether HDL modultes bsl or insulin-medited uptke of glucose, we determined deoxyglucose uptke under euglycemic-hyperinsulinemic clmp conditions (Figure 1G nd Figure I in the online-only Dt Supplement). This nlysis reveled
3 2366 Circultion November 26, 2013 Figure 1. High-density lipoprotein (HDL) modultes whole body glucose homeostsis through direct effect on glycolytic muscle fibers: Fsting cholesterol (A) levels, lipoprotein profiles (B, HDL=frction 40 53), heptic triglyceride levels (C), glucose tolernce tests (D), fsting glucose levels (E), nd HbA1c levels (F; n=6 15 per group); deoxyglucose uptke (G) in tibilis lterlis nterior (TLA) muscle, extensor digitorum longus (EDL) muscle, soleus (SOL) muscle, gstrocnemius (GAST) muscle, subcutneous dipose tissue (ScAT), nd liver under hyperinsulinemiceuglycemic clmp conditions (n=6 8 per group); bsl nd insulin-induced AKT phosphoryltion in qudriceps muscle (H, n=2 3 per group), glycogen content in qudriceps (I) nd liver (J) of chow fed nd ge-mtched wt (open brs, filled circles), polipoprotein A-I trnsgenic (poa-i tg; filled brs, open squres), nd polipoprotein A-I deficient mice (poa-i ko; htched brs, open tringles; n=6 14 per group). AUC indictes re under the curve; exe, exercised; nd sed, sedentry. Dt re expressed s mens±sem. P<0.05; P<0.005; P< vs wt mice; P<0.05 vs sedentry wt mice, b P<0.05 vs sedentry poa-i tg mice, c P<0.001 vs exercised poa-i ko mice. Downloded from by on July 26, 2018 significnt decrese of glucose trnsport in muscles with high content of glycolytic (white) fibers IIB like the tibilis lterlis nterior nd the extensor digitorum longus muscle of poa-i ko mice compred with wt nd poa-i tg mice. However, no difference ws observed in muscles with high content of oxidtive (red) fibers I nd IIA, like the soleus, or in muscles with mixed content of IIA nd IIB fibers, like the gstrocnemius muscle. Becuse white fibers re fr less responsive to insulin thn red fibers s result of mrkedly lower protein levels of glucose trnsporter 4 (GLUT4), the rte-limiting trnsporter for insulin-medited glucose uptke, we conclude tht poa-i is modulting glucose trnsport in muscle directly nd independently of insulin. Similr glucose trnsport rtes in ft nd liver of wt, poa-i tg nd poa-i ko mice rule out these tissues s potentil meditors for the HDL-medited effect on glucose metbolism nd point to muscle-specific effect of HDL (Figure 1G). Assessment of AKT ctivtion fter cute insulin injection s downstrem trget for insulin signling reveled tht insulin incresed AKT phosphoryltion in qudriceps muscle of wt nd poa-i ko mice to the sme extent (Figure 1H). In contrst, poa-i tg mice showed mrkedly enhnced bsl AKT phosphoryltion (2.7±1-fold over wt nd 2.4±0.2-fold over poa-i ko mice) with no further increse fter insulin injection (Figure 1H). These results lso point to n insulin-independent effect of HDL on skeletl muscle. Glycogen levels re n importnt determinnt of exercise cpcity, 27 nd defects in glycogen synthesis hve been shown to ply dominnt role in the development of insulin resistnce. 19 To understnd whether circulting HDL levels re lso modulting intrcellulr glycogen storge, we ssessed glycogen levels in skeletl muscle of sedentry nd exercised wt, poa-i tg, nd poa-i ko mice. Although muscle glycogen levels were similr between sedentry groups, exercised poa-i ko mice filed to increse glycogen levels to the sme extent s wt nd poa-i tg mice (Figure 1I). These results suggest tht in bsence of poa-i, metbolic dpttions to exercise re hmpered in skeletl muscle. Becuse liver glycogen is quntittively more importnt thn muscle glycogen for endurnce cpcity in rodents, we lso determined heptic glycogen content in our mouse groups: Sedentry poa-i ko mice exhibited mrkedly incresed glycogen levels compred with wt mice. However, upon trining glycogen ws severely reduced in poa-i ko mice wheres it incresed in exercised wt nd poa-i tg mice (Figure 1J). Our results indicte tht glycogen metbolism is dysfunctionl in the bsence of poa-i.
4 Lehti et l ApoA-I Enhnces Glucose Oxidtion in Skeletl Muscle 2367 Downloded from by on July 26, 2018 HDL Modultes Muscle Function Through n Effect on Mitochondril Bioenergetics We chrcterized body composition nd muscle function in our gin- nd loss-of-function models. Len mss ws significntly decresed in poa-i ko mice (Figure 2A nd 2B) compred with wt littermtes nd, conversely, slightly incresed in poa-i tg mice. Becuse loss of len mss typiclly reflects ltered muscle biology, we next tested for differences in musculr function by determining oxidtive cpcity of skeletl muscle in endurnce tests using mouse tredmills. We found tht reduced circulting HDL in poa-i ko mice correlted with considerbly decresed endurnce cpcity (Figure 2D). Our results suggest tht circulting HDL nd poa-i ply n importnt role in norml skeletl muscle metbolism nd function. To understnd whether HDL nd poa-i cn lter mitochondril function in skeletl muscle in vivo, we nlyzed mitochondril bioenergetics using Sehorse nlyzer. In the bsence of poa-i, oxygen consumption rte ws mrkedly reduced nd ATP synthesis ws clerly blunted in mitochondri isolted from gstrocnemius muscle (Figure 2E). Elevted HDL ws ssocited with moderte increse in ATP synthesis (Figure 2E). This smll enhncement of mitochondril ATP synthesis ws ssocited with increses in expression of the ATP synthse α nd β subunits in muscle homogente of poa-i tg mice compred with wt mice (Figure 2F nd 2G). In contrst, no differences in oxygen consumption rte were detected in mitochondri isolted from liver between the different genotypes (Figure II in the online-only Dt Figure 2. Norml high-density lipoprotein (HDL) levels re required for proper function of skeletl muscle mitochondri. Body composition (A C), distnce covered during tredmill exercise to exhustion test (n=15 per group; D), oxygen consumption rte (OCR) in mitochondri isolted from gstrocnemius muscle in bsl stte (Stte II), fter ddition of ADP (Stte III), nd fter ddition of the ATP synthse inhibitor oligomycin (Stte IVo; E), nd protein expression of ATP synthse subunit A nd B (F nd G) in gstrocnemius muscle homogentes of chow-fed wild-type (wt; open brs), polipoprotein A-I trnsgenic (poa-i tg; filled brs), nd polipoprotein A-I deficient mice (poa-i ko; htched brs) mice (n=4 per group). Dt re expressed s mens±sem. P<0.05, P<0.005, P< vs wt mice. Supplement). These results provide evidence tht circulting HDL is required for norml mitochondril function in skeletl muscle. HDL nd ApoA-I Directly Enhnce Cellulr Respirtion of Glucose in Skeletl Muscle nd Prevent Age-Induced Decline of Endurnce Cpcity To ddress whether the observed effect of HDL on mitochondril bioenergetics occurs cell utonomously in skeletl muscle, we pplied cell-bsed in vitro ssys. Using Sehorse XF24 nlyzer we detected tht HDL isolted from humn subjects increses glycolysis nd oxygen consumption rte in murine C2C12 myoblsts in dose dependent mnner (Figure 3A nd 3B). Subsequently we determined tht HDL nd poa-i, but not LDL or phospholipid vesicles, enhnced glycolysis considerbly (Figure 3C). Our results indicte tht HDL nd poa-i directly ffect the brekdown of glucose by incresing both components of cellulr respirtion, glycolysis nd mitochondril oxidtive phosphoryltion. Thus, the observed effects on cellulr respirtion re direct nd cell utonomous, nd re specific to HDL nd poa-i. Our observtions tht norml circulting HDL levels re required for proper skeletl muscle function rised the question whether incresing HDL levels bove norml circulting HDL concentrtions further improve skeletl muscle glucose utiliztion nd muscle function in vivo. We therefore nlyzed fsting glucose nd lctte levels in mice with norml (wt) nd geneticlly rised HDL levels (poa-i tg). Consistent with n increse in glucose utiliztion, we found tht physiologiclly relevnt increses in HDL levels correlted strongly with reduced fsting glucose levels compred with wt mice (Figure 3D). HDL-induced increses in glycolysis were reflected by higher circulting lctte levels (Figure 3E). To ddress the question whether rising HDL levels my further improve musculr function we investigted whether ge-induced decline in muscle performnce is prevented in poa-i tg mice. Endurnce cpcity ws better mintined in ging poa-i tg mice thn wt mice (Figure 3F). Thus, HDL nd poa-i pper to ply role in the preservtion of muscle function during ging by directly enhncing glucose utiliztion in skeletl muscle. Rising HDL Levels Decreses Ft Mss in Assocition With Reduced Circulting FGF21 Levels nd Enhnced Free Ftty Acid Relese From White Adipose Tissue To ddress whether HDL-enhnced musculr metbolism lso results in lener phenotype, we monitored body composition of poa-i tg nd wt mice for 10 months: Age-induced increses in ft mss did not occur in poa-i tg mice. Sedentry poa-i tg mice retined remrkbly stble ft mss throughout their life spn (Figure 4A). To understnd whether the observed difference in ft mss is similr to tht induced by chronic physicl ctivity, we compred ft mss of sedentry poa-i tg mice to tht of poa-i tg nd wt mice subjected to dily erobic exercise trining throughout the study. As shown in Figure 4A, sedentry poa-i tg mice exhibit ft mss vlues close to the levels of running mice. These results suggest tht rising HDL levels under sedentry conditions my led to
5 2368 Circultion November 26, 2013 A ECAR (fold increse) ECAR (fold difference) HDL (ug/ml) Ctrl Glucose ug/ml HDL(PL) 0 Control HDL LDL PLV Glucose C D E F ApoA-I - + B Glucose (mg/dl) OCR (fold increse) HDL (ug/ml) Ctrl Glucose ug/ml HDL (PL) Lctte (mmol/l) Figure 3. High-density lipoprotein (HDL) nd polipoprotein A-I (poa-i) enhnce cellulr respirtion of glucose in skeletl muscle nd prevent ge-induced decline of endurnce cpcity. A nd B, Extrcellulr cidifiction rte (ECAR) nd oxygen consumption rte (OCR) in C2C12 myoblsts incubted with glucose (5 mmol/l, open brs) nd incresing mounts of HDL (closed brs). C, ECAR in C2C12 myoblsts incubted with glucose (5 mmol/l, open br), glucose nd HDL (100 ug/ml, closed brs), low-density lipoprotein (LDL; 100 ug/ml, htched brs), phospholipid vesicles (100 ug/ml, htched brs), nd poa-i (sme protein concentrtion s HDL; n=7 12 per group). Dt in A, B, nd C re expressed s mens±sem. P<0.05, vs cells incubted with glucose only. Fsting glucose (D), fsting lctte (E), nd chnge of distnce covered during tredmill exercise exhustion tests (F) performed 8 weeks prt in ging wild-type (wt; open brs) nd polipoprotein A-I trnsgenic (poa-i tg; closed brs) mice (n=15 per group). Dt in D, E, nd F re expressed s mens±sem. P<0.05, P<0.005 vs wt mice. Downloded from by on July 26, 2018 lener phenotype tht seems metboliclly more similr to physicl ctive condition. FGF21, novel biomrker for mitochondril deficiencies, 31 is incresed in ptients with the metbolic syndrome nd correltes inversely with circulting HDL levels in humns nd monkeys. 32,33 We mesured FGF21 levels in sedentry poa-i tg nd wt mice s n dditionl indictor of improved mitochondril function. Both heptic expression nd circulting levels of FGF21 were significntly lower in poa-i tg mice compred with wt mice (Figure 4B nd 4C). We propose tht enhnced musculr mitochondril function in poa-i tg mice is reflected B heptic FGF211.6 A Ft mss (g) C FGF21 (pg/ml) time (months) Figure 4. Rising high-density lipoprotein (HDL) levels decreses body ft mss in ssocition with reduced circulting fibroblst growth fctor 21 (FGF21) levels nd enhnced free ftty cid (FFA) relese from white dipose tissue. A, Ft mss of sedentry (dotted lines) nd tredmill exercised (continuous lines) wildtype (wt; circles) nd polipoprotein A-I trnsgenic (poa-i tg; squres) on chow. Fsting heptic FGF21 expression levels (B), fsting circulting FGF21 levels (C), nd fsting FFA levels (D) of sedentry wt (open brs) nd poa-i tg mice (closed brs; n=6 7 per group). Dt re expressed s mens±sem. P<0.05, P< vs wt mice. D FFA (mmol/l) by lower circulting FGF21 levels. FGF21 is lso known to inhibit lipolysis in white dipose tissue. 34,35 To understnd whether the reduction of ft mss my be prtly ttributble to n increse in ftty cid relese from white dipose tissue we nlyzed fsting free ftty cid levels. As shown in Figure 4D, we found tht free ftty cid levels were incresed in poa-i tg mice compred with wt mice, indicting tht lipolysis in white dipose tissue is enhnced. Consequently, FGF21-medited inhibition of lipolysis my be reduced in poa-i tg mice. Rising HDL Protects Aginst Diet-Induced Hyperglycemi Through Incresed Glucose Utiliztion To investigte the therpeutic potentil of HDL in metbolic disese, we fed ge-mtched mle poa-i tg nd wt mice HFD for 12 weeks nd nlyzed body composition nd whole body glucose homeostsis. Although rising circulting HDL levels did not protect ginst diet-induced obesity (Figure 5A nd 5B), fsting glucose levels were significntly lower in poa-i tg mice compred with wt mice throughout the HFD feeding study (Figure 5C). This difference ws even incresed compred with the difference observed when mice were fed chow diet (dt not shown). HbA1c levels were slightly reduced in poa-i tg mice compred with wt mice (3.8±0.2 vs 4.2±0.08 %, n=8). Mice of either group developed fsting hyperinsulinemi to the sme extent (Figure 5D). However, glucose tolernce test reveled tht rising HDL levels improves the development of diet-induced impirment of glucose homeostsis (Figure 5E) independently of body-weight gin nd diet-induced hyperinsulinemi. Discussion The present studies estblish tht circulting HDL is required for norml glucose homeostsis in skeletl muscle. We show tht poa-i directly increses glucose utiliztion by enhncing cellulr respirtion in skeletl muscle cells. Furthermore, incresed poa-i, nd presumbly incresed HDL levels, led to reduced body ft mss nd enhnced free ftty cid relese by white dipose tissue vi mechnism tht involves
6 Lehti et l ApoA-I Enhnces Glucose Oxidtion in Skeletl Muscle 2369 Downloded from by on July 26, 2018 A Body weight (g) C Glucose (mg/dl) B % ft mss D Insulin (ng/ml) E Glucose (mg/dl) min Figure 5. Rising high-density lipoprotein (HDL) protects ginst diet-induced hyperglycemi through incresed glucose utiliztion. Body composition (A nd B), fsting glucose (C), nd fsting insulin (D) levels of diet-induced obese wild-type (wt; open brs) nd polipoprotein A-I trnsgenic (poa-i tg; closed brs) mice. E, Glucose tolernce test in diet-induced obese wt (closed circles, open brs) nd poa-i tg mice (open qudrnts, closed brs; n=7 8 per group). AUC indictes re under the curve. Dt re expressed s mens±sem. P<0.05, P<0.005, P< vs wt mice. reduction of circulting FGF21 levels. Tken together, these findings estblish key role for circulting poa-i in mintining muscle metbolism nd function nd suggest novel role for HDL or some of its subspecies in the prevention nd tretment of metbolic diseses. Our finding tht HDL nd poa-i directly enhnce glucose oxidtion in the skeletl muscle cell provides dditionl support for the hypothesis tht HDL nd poa-i exert intrcellulr functions independent of their lipid trnsport function. Previously, Drew et l 14 reported tht the ctions of HDL nd poa-i on glucose uptke occur through receptor-medited event involving ABCA1, n ABC clss of trnsporter. The uthors suggested tht, in ddition to mediting reverse cholesterol trnsport, HDL lso initites clcium-sensitive signling cscde through ABCA1. Consistent with those findings, Hn et l 16 showed tht selectively extrcting cholesterol from the plsm membrne using methyl bet-cyclodextrin hd no effect on AMPK phosphoryltion in C2C12 myotubes, indicting tht cholesterol efflux itself does not ffect AMPK phosphoryltion in skeletl muscle. However, HDL nd poa-i my lso medite their effect on glucose uptke through lterntive pthwys to ABCA1 signling. Accordingly, Hn et l 16 provided in vitro evidence tht endocytosis of poa-i through the clthrin-dependent pthwy is required for poa-i-medited AMPK nd ACC ctivtion. HDL hs been lso shown to trnsport nd deliver endogenous micrornas to recipient cells with functionl gene regultory consequences. 36 ApoA-I my lso coloclize with lipid droplets nd mitochondri within the skeletl muscle cell, 37 further strengthening the hypothesis tht poa-i cts intrcellulrly besides through its known surfce receptors. Thus, lthough there is some evidence tht HDL my medite its effects on glucose uptke through one of its known receptors, it seems obvious tht lterntive nd not yet determined underlying mechnisms re involved. AUC Our present study provides in vivo nd in vitro evidence tht HDL nd poa-i increse glucose oxidtion, thus giving insight into how the cell hndles HDL-enhnced glucose entry downstrem of AMPK ctivtion. Our finding tht skeletl muscle ATP synthesis is severely blunted in the bsence of poa-i ex vivo in ssocition with n impirment of endurnce cpcity highlights for the first time the importnce of circulting HDL in norml muscle cell metbolism. Drew nd collegues previously showed tht plmitte oxidtion is incresed in humn skeletl muscle cells incubted with HDL or poa-i. 14 Their results complement ours by determining the effect of HDLmedited AMPK ctivtion on ftty cid utiliztion nd, tken together, give more detiled view of HDL-induced intrcellulr metbolic pthwys. There is recent evidence tht HDL prticles lso increse glycogen synthesis in the rt skeletl muscle cell line L6 38 fter n overnight strvtion period. In contrst, we did not detect differences in glycogen content in muscle of poa-i ko or poa-i tg mice compred with wt mice. We think tht this discrepncy my rise s result of different experimentl conditions. Our niml experiments did not include fsting period nd my therefore better portry the stte of norml intrcellulr glycogen content. Our in vitro results determining tht glycolysis rtes in skeletl muscle re mrkedly incresed by HDL nd poa-i were confirmed by our in vivo findings tht fsting lctte levels were significntly higher in mice with geneticlly rised HDL nd poa-i levels. One explntion for this observtion is tht t the point when glycogen stores in skeletl muscle hve been replenished, the glucose tken up is converted into lctte to mintin enhnced glucose utiliztion. The lctte relesed by skeletl muscle is tken up by the liver nd converted into glycogen by the so-clled indirect pthwy of glycogen synthesis to preserve this energy for the future. 20 Our findings tht lctte levels re incresed in poa-i tg mice suggest tht this my enhnce the Cori cycle nd llow lctte relesed by skeletl muscle to be used for oxidtion but lso for nbolic purposes by ll tissues. According to this hypothesis, the lctte tken up would then be converted to pyruvte, precursor for cetyl-coa, which hs mny importnt nbolic functions. 20 In light of our observtion tht poa-i tg mice exhibit lower ge-induced decline in muscle performnce compred with ge-mtched wt mice, we conclude tht the endurnce cpcity my be better preserved prtilly through n incresed flux through the Cori cycle in ddition to the enhncement in glucose oxidtion. Simultneously, HDL prticles lso increse glucose uptke in cultured dipocytes vi mechnism involving GLUT 4 trnsloction nd AMPK ctivtion. 38 Becuse dipose tissue releses significnt mounts of lctte, 39 our observtions tht fsting lctte levels were incresed nd ft mss ws reduced in poa-i tg mice my be in prt ttributble to dipocytes not completely using the glucose tken up, but insted relesing it s lctte which then serves s substrte in the Cori cycle for nbolic processes in other tissues. This conclusion is supported by lener body composition of poa- I tg mice. In contrst to dt provided by Run et l, 40 we show tht poa-i tg mice re not protected ginst diet-induced obesity. Although the initil difference in ft mss disppered fter 12 weeks on HFD, poa-i tg mice exhibited mrkedly lower glucose levels nd better glucose tolernce thn wt mice,
7 2370 Circultion November 26, 2013 Downloded from by on July 26, 2018 indicting tht rising HDL levels my offer potentil therpeutic option for obese nd insulin-resistnt ptients who do not respond to weight-reducing mesures. Our studies furthermore my provide some intriguing insights into the inverse reltionship of circulting HDL nd FGF21 levels. A recent multi-center study showed tht mesuring circulting FGF21 concentrtions relibly identified primry respirtory chin deficiencies in skeletl muscle of humns. The uthors report tht circulting FGF21 levels re bout 10-fold incresed in ptients with mitochondril disorders compred with helthy individuls, nd their dt suggest tht FGF21 induction is triggered by primry respirtory chin deficiencies. 31 Bsed on our findings presented herein we propose tht FGF21 expression hs been downregulted by the improved mitochondril function in poa-i tg mice. FGF21 is lso known to function s n inhibitor of lipolysis in mice, monkeys, nd humn subjects ,41 FGF21 is minly expressed in the liver nd thymus, nd once secreted into circultion, it exerts its effects on dipose tissue like n endocrine hormone by binding its receptor β-klotho. 34 Thus, our finding tht FGF21 levels re reduced in poa-i tg mice my point to n dditionl novel mechnism by which geneticlly rised HDL modultes lipolysis. A number of intervention studies hve shown tht cute nd long-term physicl exercise hve cler beneficil effect on circulting HDL levels nd on glucose tolernce in helthy subjects nd in elderly, overweight, nd dyslipidemic ptients Putting our findings into perspective, we propose tht, besides its direct effects on glucose tolernce, physicl ctivity my lso enhnce glucose oxidtion indirectly by incresing HDL levels. Our rtionle is supported by the finding tht physicl ctivity induced increses in HDL levels correlte strongly with the upregultion of gene expression sets for glycolysis nd oxidtive phosphoryltion in physiclly ctive versus inctive co-twins in recently published Gene Set Enrichment Anlysis. 45 Although the underlying mechnisms for the ssocition between upregulted skeletl muscle metbolic pthwys nd high circulting HDL levels in physicl ctive subjects re lrgely unknown, it seems plusible tht current therpeutic pproches to rise HDL levels my prtly mimic exercise-medited effects on glucose homeostsis. In conclusion, our studies show strong evidence tht HDL nd poa-i re required for norml glucose homeostsis nd muscle mitochondril function. We provide evidence tht the key HDL component poa-i directly increses glucose utiliztion by enhncing cellulr respirtion in skeletl muscle cells. Furthermore, we demonstrte tht geneticlly rising HDL levels leds to reduction in ft mss in ssocition with decrese in circulting FGF21 levels. Becuse low nd dysfunctionl HDL might contribute to the excerbtion of insulin resistnce, therpeutic pproches to rise HDL levels nd improve HDL function my not only benefit ptients with crdiovsculr disese but lso improve metbolic diseses such s insulin resistnce nd T2D. Acknowledgments We thnk the Cincinnti Mouse Metbolic Phenotyping Center Ntionl Institutes of Helth (NIH) U24DK59630 for providing the tredmill equipment in our endurnce exercise experiments. We re grteful for the sttisticl dvice provided by Gbriele Kstenmüller t the Helmholtz Zentrum München. Sources of Funding This work ws supported by the bsic science grnt 1-10-BS-72 from the Americn Dibetes Assocition, the Ntionl Institutes of Helth grnt 2K12HD grnted to Susnn M. Hofmnn, nd in prt by the Helmholtz Allince ICEMED - Imging nd Curing Environmentl Metbolic Diseses, through the Inititive nd Networking Fund of the Helmholtz Assocition. Mrit Lehti hs been supported by the Acdemy of Finlnd. None. Disclosures References 1. Smper-Ternent R, Snih Al S. Obesity in Older Adults: Epidemiology nd Implictions for Disbility nd Disese. Rev Clin Gerontol. 2012; 22: Rees K, Dykov M, Wrd K, Thorogood M, Brunner E. Dietry dvice for reducing crdiovsculr risk. Cochrne Dtbse Syst Rev. 2013;3:CD Frohlich J, Al-Srrf A. Crdiovsculr risk nd therosclerosis prevention. Crdiovsc Pthol. 2013;22: Hooper L, Summerbell CD, Thompson R, Sills D, Roberts FG, Moore HJ, Dvey Smith G. Reduced or modified dietry ft for preventing crdiovsculr disese. Cochrne Dtbse Syst Rev. 2012;5:CD Ooi EM, Ng TW, Wtts GF, Brrett PH. Dietry ftty cids nd lipoprotein metbolism: new insights nd updtes. Curr Opin Lipidol. 2013;24: Howrd BV, Tskinen MR. CVD in women. Nutr Metb Crdiovsc Dis. 2010;20: Boden WE. High-density lipoprotein cholesterol s n independent risk fctor in crdiovsculr disese: ssessing the dt from Frminghm to the Veterns Affirs High Density Lipoprotein Intervention Tril. Am J Crdiol. 2000;86(12A):19L 22L. 8. McNeill AM, Ktz R, Girmn CJ, Rosmond WD, Wgenknecht LE, Brzily JI, Trcy RP, Svge PJ, Jckson SA. Metbolic syndrome nd crdiovsculr disese in older people: The crdiovsculr helth study. J Am Geritr Soc. 2006;54: Gordon SM, Hofmnn S, Askew DS, Dvidson WS. High density lipoprotein: it s not just bout lipid trnsport nymore. Trends Endocrinol Metb. 2011;22: Rder DJ, Tll AR. The not-so-simple HDL story: Is it time to revise the HDL cholesterol hypothesis? Nt Med. 2012;18: Lewis GF, Rder DJ. New insights into the regultion of HDL metbolism nd reverse cholesterol trnsport. Circ Res. 2005;96: Lrch DB, degom EM, Rder DJ. Trgeting high density lipoproteins in the prevention of crdiovsculr disese? Curr Crdiol Rep. 2012;14: ACCORD (Action to Control Crdiovsculr Risk in Dibetes) Study Group, Ginsberg HN, Elm MB, Lovto LC, Crouse JR 3rd, Leiter LA, Linz P, Friedewld WT, Buse JB, Gerstein HC, Probstfield J, Grimm RH, Ismil-Beigi F, Bigger JT, Goff DC Jr, Cushmn WC, Simons-Morton DG, Byington RP. Effects of combintion lipid therpy in type 2 dibetes mellitus.n Engl J Med. 2010;362: Drew BG, Duffy SJ, Formos MF, Ntoli AK, Henstridge DC, Penfold SA, Thoms WG, Mukhmedov N, de Courten B, Forbes JM, Yp FY, Kye DM, vn Hll G, Febbrio MA, Kemp BE, Sviridov D, Steinberg GR, Kingwell BA. High-density lipoprotein modultes glucose metbolism in ptients with type 2 dibetes mellitus. Circultion. 2009;119: Fryirs MA, Brter PJ, Appvoo M, Tuch BE, Tbet F, Hether AK, Rye KA. Effects of high-density lipoproteins on pncretic bet-cell insulin secretion. Arterioscler Thromb Vsc Biol. 2010;30: Hn R, Li R, Ding Q, Wng Z, Luo X, Zhng Y, Cui G, He J, Liu W, Chen Y. Apolipoprotein A-I stimultes AMP-ctivted protein kinse nd improves glucose metbolism. Dibetologi. 2007;50: McArdle WD, Ktch FI, Ktch VL. Exercise physiology: Nutrition, energy, nd humn performnce. Wolters Kluwer Helth, Sivitz WI, Yorek MA. Mitochondril dysfunction in dibetes: from moleculr mechnisms to functionl significnce nd therpeutic opportunities. Antioxid Redox Signl. 2010;12:
8 Lehti et l ApoA-I Enhnces Glucose Oxidtion in Skeletl Muscle 2371 Downloded from by on July 26, Shulmn GI, Rothmn DL, Jue T, Stein P, DeFronzo RA, Shulmn RG. Quntittion of muscle glycogen synthesis in norml subjects nd subjects with non-insulin-dependent dibetes by 13C nucler mgnetic resonnce spectroscopy. N Engl J Med. 1990;322: LeRoith D, Olefsky JM, Tylor SI. Dibetes Mellitus: A Fundmentl nd Clinicl Text - 3rd Ed. Bltimore, MD: Lippincott, Willims & Wilkins; Coen PM, Goodpster BH. Role of intrmyocellur lipids in humn helth. Trends Endocrinol Metb. 2012;23: Messer JI, Jckmn MR, Willis WT. Pyruvte nd citric cid cycle crbon requirements in isolted skeletl muscle mitochondri. Am J Physiol, Cell Physiol. 2004;286:C565 C Costnzo-Grvey DL, Pfluger PT, Dougherty MK, Stock JL, Boehm M, Chik O, Fernndez MR, Fisher K, Kortum RL, Hong EG, Jun JY, Ko HJ, Schreiner A, Volle DJ, Treece T, Swift AL, Winer M, Chen D, Wu M, Leon LR, Shw AS, McNeish J, Kim JK, Morrison DK, Tschöp MH, Lewis RE. KSR2 is n essentil regultor of AMP kinse, energy expenditure, nd insulin sensitivity. Cell Metb. 2009;10: Kern M, Wells JA, Stephens JM, Elton CW, Friedmn JE, Tpscott EB, Pekl PH, Dohm GL. Insulin responsiveness in skeletl muscle is determined by glucose trnsporter (Glut4) protein level. Biochem J. 1990;270: Jmes DE, Jenkins AB, Kregen EW. Heterogeneity of insulin ction in individul muscles in vivo: euglycemic clmp studies in rts. Am J Physiol. 1985;248(5 Pt 1):E567 E Shortreed KE, Kruse MP, Hung JH, Dhnni D, Mordi J, Ceddi RB, Hwke TJ. Muscle-specific dpttions, impired oxidtive cpcity nd mintennce of contrctile function chrcterize diet-induced obese mouse skeletl muscle. PLoS ONE. 2009;4:e Pederson BA, Cope CR, Schroeder JM, Smith MW, Irimi JM, Thurberg BL, DePoli-Roch AA, Roch PJ. Exercise cpcity of mice geneticlly lcking muscle glycogen synthse: in mice, muscle glycogen is not essentil for exercise. J Biol Chem. 2005;280: Terjung RL, Bldwin KM, Molé PA, Klinkerfuss GH, Holloszy JO. Effect of running to exhustion on skeletl muscle mitochondri: biochemicl study. Am J Physiol. 1972;223: Bldwin KM, Reitmn JS, Terjung RL, Winder WW, Holloszy JO. Substrte depletion in different types of muscle nd in liver during prolonged running. Am J Physiol. 1973;225: Reitmn J, Bldwin KM, Holloszy JO. Intrmusculr triglyceride utiliztion by red, white, nd intermedite skeletl muscle nd hert during exhusting exercise. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1973;142: Suomlinen A, Elo JM, Pietiläinen KH, Hkonen AH, Sevstinov K, Korpel M, Isohnni P, Mrjvr SK, Tyni T, Kiuru-Enri S, Pihko H, Drin N, Õunp K, Kluijtmns LA, Petu A, Buzkov J, Bindoff LA, Annunen-Rsil J, Uusim J, Rissnen A, Yki-Järvinen H, Hirno M, Tulinius M, Smeitink J, Tyynism H. FGF-21 s biomrker for musclemnifesting mitochondril respirtory chin deficiencies: dignostic study. Lncet Neurol. 2011;10: Hojmn P, Pedersen M, Nielsen AR, Krogh-Mdsen R, Yfnti C, Akerstrom T, Nielsen S, Pedersen BK. Fibroblst growth fctor-21 is induced in humn skeletl muscles by hyperinsulinemi. Dibetes. 2009;58: Khritonenkov A, Wroblewski VJ, Koester A, Chen YF, Clutinger CK, Tigno XT, Hnsen BC, Shnfelt AB, Etgen GJ. The metbolic stte of dibetic monkeys is regulted by fibroblst growth fctor-21. Endocrinology. 2007;148: Arner P, Pettersson A, Mitchell PJ, Dunbr JD, Khritonenkov A, Rydén M. FGF21 ttenutes lipolysis in humn dipocytes - possible link to improved insulin sensitivity. FEBS Lett. 2008;582: Hott Y, Nkmur H, Konishi M, Murt Y, Tkgi H, Mtsumur S, Inoue K, Fushiki T, Itoh N. Fibroblst growth fctor 21 regultes lipolysis in white dipose tissue but is not required for ketogenesis nd triglyceride clernce in liver. Endocrinology. 2009;150: Vickers KC, Plmisno BT, Shoucri BM, Shmburek RD, Remley AT. MicroRNAs re trnsported in plsm nd delivered to recipient cells by high-density lipoproteins. Nt Cell Biol. 2011;13: Zhng H, Wng Y, Li J, Yu J, Pu J, Li L, Zhng H, Zhng S, Peng G, Yng F, Liu P. Proteome of skeletl muscle lipid droplet revels ssocition with mitochondri nd polipoprotein -I. J Proteome Res. 2011;10: Zhng Q, Zhng Y, Feng H, Guo R, Jin L, Wn R, Wng L, Chen C, Li S. High density lipoprotein (HDL) promotes glucose uptke in dipocytes nd glycogen synthesis in muscle cells. PLoS ONE. 2011;6:e Thcker SV, Nickel M, DiGirolmo M. Effects of food restriction on lctte production from glucose by rt dipocytes. Am J Physiol. 1987;253(4 Pt 1):E336 E Run X, Li Z, Zhng Y, Yng L, Pn Y, Wng Z, Feng GS, Chen Y. Apolipoprotein A-I possesses n nti-obesity effect ssocited with increse of energy expenditure nd up-regultion of UCP1 in brown ft. J Cell Mol Med. 2011;15: Li X, Ge H, Weiszmnn J, Hecht R, Li YS, Vénint MM, Xu J, Wu X, Lindberg R, Li Y. Inhibition of lipolysis my contribute to the cute regultion of plsm FFA nd glucose by FGF21 in ob/ob mice. FEBS Lett. 2009;583: Nestel PJ, Podkolinski M, Fidge NH. Mrked increse in high density lipoproteins in mountineers. Atherosclerosis. 1979;34: Olchw B, Kingwell BA, Hong A, Schneider L, Miyzki O, Nestel P, Sviridov D. Physicl fitness nd reverse cholesterol trnsport. Arterioscler Thromb Vsc Biol. 2004;24: Sviridov D, Kingwell B, Hong A, Drt A, Nestel P. Single session exercise stimultes formtion of pre bet 1-HDL in leg muscle. J Lipid Res. 2003;44: Kujl UM, Mäkinen VP, Heinonen I, Soininen P, Kngs AJ, Leskinen TH, Rhkil P, Würtz P, Kovnen V, Cheng S, Sipilä S, Hirvenslo M, Telm R, Tmmelin T, Svolinen MJ, Pout A, O Reilly PF, Mäntyselkä P, Viikri J, Kähönen M, Lehtimäki T, Elliott P, Vnhl MJ, Ritkri OT, Järvelin MR, Kprio J, Kinulinen H, Al-Korpel M. Long-term leisure-time physicl ctivity nd serum metbolome. Circultion. 2013;127: Clinicl Perspective Abnorml glucose metbolism, rnging from insulin resistnce to type 2 dibetes mellitus, is centrl feture of disorders ssocited with incresed rtes of crdiovsculr disese. Successfully preventing nd treting these disorders resides mong the gret public helth chllenges of our times. One of the strongest predictors of crdiovsculr disese in the metbolic syndrome is low level of high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol nd its mjor protein constituent polipoprotein A-I (poa-i). Infusions of reconstituted HDL rising circulting poa-i levels reduce plsm glucose nd promote glucose uptke in skeletl muscle of type 2 dibetes mellitus ptients. Our series of discoveries showing tht rising HDL levels by overexpressing humn poa-i in mice increses skeletl muscle glycolysis, ATP synthesis nd endurnce cpcity leding to improved glucose metbolism nd reduced ft mss is therefore highly relevnt. As mtter of fct, our results for the first time link low HDL levels with the mitochondril dysfunction observed in type 2 dibetes mellitus. ApoA-I nlogues re now cliniclly tested for prevention of therosclerosis. Bsed on our findings described herein, these nlogs my offer underpprecited potentil nd offer dditionl therpeutic opportunities for dibetes mellitus. Efficcious nd sfe compounds trgeting multiple spects of the metbolic syndrome do not currently exist, but re urgently needed. Moreover, with optimized poa-i nlogues lredy vilble, swift trnsltion of our reserch towrd clinicl use ppers quite doble.
* * * * * liver kidney ileum. Supplementary Fig.S1
 Supplementry Fig.S1 liver kidney ileum Fig.S1. Orlly delivered Fexrmine is intestinlly-restricted Mice received vehicle or Fexrmine (100mg/kg) vi per os (PO) or intrperitonel (IP) injection for 5 dys (n=3/group).
Supplementry Fig.S1 liver kidney ileum Fig.S1. Orlly delivered Fexrmine is intestinlly-restricted Mice received vehicle or Fexrmine (100mg/kg) vi per os (PO) or intrperitonel (IP) injection for 5 dys (n=3/group).
SESSIONE I: RELATORI. Ghrelin: from oroxigenic signal to metabolic master regulator?
 SESSIONE I: RELATORI Ghrelin: from oroxigenic signl to metbolic mster regultor? Prof. Rocco Brzzoni Professore ssocito di Medicin Intern Università degli Studi di Trieste Ghrelin: d segnle oressizznte
SESSIONE I: RELATORI Ghrelin: from oroxigenic signl to metbolic mster regultor? Prof. Rocco Brzzoni Professore ssocito di Medicin Intern Università degli Studi di Trieste Ghrelin: d segnle oressizznte
2018 American Diabetes Association. Published online at
 Supplementry Figure S1. Ft-1 mice exhibit reduced diposity when fed n HFHS diet. WT nd ft-1 mice were fed either control or n HFHS diet for 18 weeks. A: Representtive photogrphs for side-by-side comprison
Supplementry Figure S1. Ft-1 mice exhibit reduced diposity when fed n HFHS diet. WT nd ft-1 mice were fed either control or n HFHS diet for 18 weeks. A: Representtive photogrphs for side-by-side comprison
Feeding state and age dependent changes in melaninconcentrating hormone expression in the hypothalamus of broiler chickens
 Supplementry Mterils Epub: No 2017_23 Vol. 65, 2018 https://doi.org/10.183/bp.2017_23 Regulr pper Feeding stte nd ge dependent chnges in melninconcentrting hormone expression in the hypothlmus of broiler
Supplementry Mterils Epub: No 2017_23 Vol. 65, 2018 https://doi.org/10.183/bp.2017_23 Regulr pper Feeding stte nd ge dependent chnges in melninconcentrting hormone expression in the hypothlmus of broiler
A. Kinoshita 1, L. Locher 2, R. Tienken 3, U. Meyer 3, S. Dänicke 3, J. Rehage 4, K. Huber 5
 Effects of dietry nicin supplementtion on heptic expression of FoxO nd genes involved in glucose production in diry cows during the trnsition period A. Kinoshit, L. Locher, R. Tienken 3, U. Meyer 3, S.
Effects of dietry nicin supplementtion on heptic expression of FoxO nd genes involved in glucose production in diry cows during the trnsition period A. Kinoshit, L. Locher, R. Tienken 3, U. Meyer 3, S.
Effects of physical exercise on working memory and prefrontal cortex function in post-stroke patients
 Effects of physicl exercise on working memory nd prefrontl cortex function in post-stroke ptients M Moriy, C Aoki, K Sktni Grdute School of Helth Sciences Reserch, Mjor of Physicl Therpy, TeikyoHeisei
Effects of physicl exercise on working memory nd prefrontl cortex function in post-stroke ptients M Moriy, C Aoki, K Sktni Grdute School of Helth Sciences Reserch, Mjor of Physicl Therpy, TeikyoHeisei
Myricetin Ameliorates Defective Post-Receptor Insulin Signaling via
 Evidence-Bsed Complementry nd Alterntive Medicine Volume 211, Article ID 15752, 9 pges doi:1.193/ecm/neq17 Originl Article Ameliortes Defective Post-Receptor Insulin Signling vi β-endorphin Signling in
Evidence-Bsed Complementry nd Alterntive Medicine Volume 211, Article ID 15752, 9 pges doi:1.193/ecm/neq17 Originl Article Ameliortes Defective Post-Receptor Insulin Signling vi β-endorphin Signling in
EFFECTS OF INGREDIENT AND WHOLE DIET IRRADIATION ON NURSERY PIG PERFORMANCE
 Swine Dy 21 EFFECTS OF INGREDIENT AND WHOLE DIET IRRADIATION ON NURSERY PIG PERFORMANCE J. M. DeRouchey, M. D. Tokch, J. L. Nelssen, R. D. Goodbnd, S. S. Dritz 1, J. C. Woodworth, M. J. Webster, B. W.
Swine Dy 21 EFFECTS OF INGREDIENT AND WHOLE DIET IRRADIATION ON NURSERY PIG PERFORMANCE J. M. DeRouchey, M. D. Tokch, J. L. Nelssen, R. D. Goodbnd, S. S. Dritz 1, J. C. Woodworth, M. J. Webster, B. W.
TE INTERRELATIONSHIP. Studies of the development of diabetic ketosis in the rat. * Research Career Development Awardee 5-K3-AM 9968,
 Studies of the development of dibetic ketosis in the rt Jurgen M. Meier, J. Denis McGrry, Gerld R. Floon, Roger H. Unger, nd Dniel W. Foster* Deprtments of Internl Medicine nd Biochemistry, The University
Studies of the development of dibetic ketosis in the rt Jurgen M. Meier, J. Denis McGrry, Gerld R. Floon, Roger H. Unger, nd Dniel W. Foster* Deprtments of Internl Medicine nd Biochemistry, The University
Serum nesfatin-1 levels are decreased in pregnant women newly diagnosed with gestational diabetes
 originl rticle Serum nesftin-1 levels re decresed in pregnnt women newly dignosed with gesttionl dibetes Esr Nur Ademoglu 1, Suheyl Gorr 2, Muge Keskin 3, Ayse Crlioglu 4, Rifki Ucler 5, Husmettin Erdmr
originl rticle Serum nesftin-1 levels re decresed in pregnnt women newly dignosed with gesttionl dibetes Esr Nur Ademoglu 1, Suheyl Gorr 2, Muge Keskin 3, Ayse Crlioglu 4, Rifki Ucler 5, Husmettin Erdmr
PNEUMOVAX 23 is recommended by the CDC for all your appropriate adult patients at increased risk for pneumococcal disease 1,2 :
 PNEUMOVAX 23 is recommended y the CDC for ll your pproprite dult ptients t incresed risk for pneumococcl disese 1,2 : Adults ged
PNEUMOVAX 23 is recommended y the CDC for ll your pproprite dult ptients t incresed risk for pneumococcl disese 1,2 : Adults ged
Effect of environmental stress on biochemical and physiological features in cultured fish
 Effect of environmentl stress on biochemicl nd physiologicl fetures in cultured fish Toshiki Nkno, Toshiysu Ymguchi, nd Yoshihiro Ochii Grd. Sch. Agric. Sci., Tohoku Univ., Sendi, Jpn Fmous Smuri Mr. Msmune
Effect of environmentl stress on biochemicl nd physiologicl fetures in cultured fish Toshiki Nkno, Toshiysu Ymguchi, nd Yoshihiro Ochii Grd. Sch. Agric. Sci., Tohoku Univ., Sendi, Jpn Fmous Smuri Mr. Msmune
Analysis of Regulatory of Interrelated Activity of Hepatocyte and Hepatitis B Viruses
 Interntionl Journl of Biomedicl Mterils Reserch 8 6(): -7 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ijbmr doi:.648/j.ijbmr.86. ISSN: 33-756 (Print) ISSN: 33-7579 (Online) Anlysis of Regultory of Interrelted
Interntionl Journl of Biomedicl Mterils Reserch 8 6(): -7 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ijbmr doi:.648/j.ijbmr.86. ISSN: 33-756 (Print) ISSN: 33-7579 (Online) Anlysis of Regultory of Interrelted
Abstract ABSTRACT #69. Abstract. Introduction & Methods. Methods & Results. Results. Results & Conclusions
 Effects of dietry β-glucn on Growth Performnce, Dirrhe, nd Gut Permeility of Wening Pigs Experimentlly Infected with Pthogenic E. coli Kwngwook Kim, Amy Ehrlich, Vivin Perng, Jennifer Chse, Helen Ryould,
Effects of dietry β-glucn on Growth Performnce, Dirrhe, nd Gut Permeility of Wening Pigs Experimentlly Infected with Pthogenic E. coli Kwngwook Kim, Amy Ehrlich, Vivin Perng, Jennifer Chse, Helen Ryould,
Myricetin Ameliorates Defective Post-Receptor Insulin Signaling via b-endorphin Signaling in the Skeletal Muscles of Fructose-Fed Rats
 ecam Advnce Access published Mrch 3, 2010 ecam 2010;Pge 1 of 9 doi:10.1093/ecm/neq017 Originl Article Ameliortes Defective Post-Receptor Insulin Signling vi b-endorphin Signling in the Skeletl Muscles
ecam Advnce Access published Mrch 3, 2010 ecam 2010;Pge 1 of 9 doi:10.1093/ecm/neq017 Originl Article Ameliortes Defective Post-Receptor Insulin Signling vi b-endorphin Signling in the Skeletl Muscles
Ulk λ PPase. 32 P-Ulk1 32 P-GST-TSC2. Ulk1 GST (TSC2) : Ha-Ulk1 : AMPK. WB: Ha (Ulk1) : Glu. h CON - Glu - A.A WB: LC3 AMPK-WT AMPK-DKO
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb2152 C.C + - + - : Glu b Ulk1 - - + λ PPse c AMPK + - + + : ATP P-GST-TSC2 WB: Flg (Ulk1) WB Ulk1 WB: H (Ulk1) GST (TSC2) C.C d e WT K46R - + - + : H-Ulk1 : AMPK - + - + + + AMPK H-Ulk1
DOI: 10.1038/ncb2152 C.C + - + - : Glu b Ulk1 - - + λ PPse c AMPK + - + + : ATP P-GST-TSC2 WB: Flg (Ulk1) WB Ulk1 WB: H (Ulk1) GST (TSC2) C.C d e WT K46R - + - + : H-Ulk1 : AMPK - + - + + + AMPK H-Ulk1
A Comparison of Serum Magnesium Level in Pregnant Women with and without Gestational Diabetes Mellitus (GDM)
 Brief Report J Bbol Univ Med Sci Vol 18, Issu 12; Dec 2016. P:71-75 A Comprison of Serum Mgnesium Level in Pregnnt Women with nd without Gesttionl Dibetes Mellitus (GDM) Z. Bouzri (MD) 1, F. Elmi(MD) 2,
Brief Report J Bbol Univ Med Sci Vol 18, Issu 12; Dec 2016. P:71-75 A Comprison of Serum Mgnesium Level in Pregnnt Women with nd without Gesttionl Dibetes Mellitus (GDM) Z. Bouzri (MD) 1, F. Elmi(MD) 2,
Supplementary Online Content
 Supplementry Online Content Zulmn DM, Pl Chee C, Ezeji-Okoye SC, et l. Effect of n intensive outptient progrm to ugment primry cre for high-need Veterns Affirs ptients: rndomized clinicl tril. JAMA Intern
Supplementry Online Content Zulmn DM, Pl Chee C, Ezeji-Okoye SC, et l. Effect of n intensive outptient progrm to ugment primry cre for high-need Veterns Affirs ptients: rndomized clinicl tril. JAMA Intern
Effect of kazunoko lipid on the concentrations of plasma glucose and lipids and liver lipids in mice
 Effect of kzunoko lipid on the concentrtions of plsm glucose nd lipids nd liver lipids in mice Ntionl Food Reserch Institute Tomoyuki Higuchi, Nouy Shiri nd Hirmitsu Suzuki INTRODUCTION Kzunoko, which
Effect of kzunoko lipid on the concentrtions of plsm glucose nd lipids nd liver lipids in mice Ntionl Food Reserch Institute Tomoyuki Higuchi, Nouy Shiri nd Hirmitsu Suzuki INTRODUCTION Kzunoko, which
The effect of dietary α-linolenic acid levels on regulation of omega-3 lipid synthesis in rat
 The effect of dietry α-linolenic cid levels on regultion of omeg-3 lipid synthesis in rt Wei-Chun Tu School of Agriculture Food nd Wine The University of Adelide Conversion of PUFA to LCPUFA PUFA LCPUFA
The effect of dietry α-linolenic cid levels on regultion of omeg-3 lipid synthesis in rt Wei-Chun Tu School of Agriculture Food nd Wine The University of Adelide Conversion of PUFA to LCPUFA PUFA LCPUFA
Low Fasting Triglycerides: Hallmark of the Healthy Large Hip?
 nture publishing group rticles Low Fsting Triglycerides: Hllmrk of the Helthy Lrge Hip? Johnnes B. Ruige 1 nd Luc F. Vn Gl 2 Body ft distribution modultes risk for type 2 dibetes mellitus. We evluted potentilly
nture publishing group rticles Low Fsting Triglycerides: Hllmrk of the Helthy Lrge Hip? Johnnes B. Ruige 1 nd Luc F. Vn Gl 2 Body ft distribution modultes risk for type 2 dibetes mellitus. We evluted potentilly
Hypertension, hyperinsulinaemia and obesity in middle-aged Finns with impaired glucose tolerance
 Journl of Humn Hypertension (1998) 12, 265 269 1998 Stockton Press. All rights reserved 0950-9240/98 $12.00 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Hypertension, hyperinsulinemi nd obesity in middle-ged Finns with impired glucose
Journl of Humn Hypertension (1998) 12, 265 269 1998 Stockton Press. All rights reserved 0950-9240/98 $12.00 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Hypertension, hyperinsulinemi nd obesity in middle-ged Finns with impired glucose
EFFECTS OF AN ACUTE ENTERIC DISEASE CHALLENGE ON IGF-1 AND IGFBP-3 GENE EXPRESSION IN PORCINE SKELETAL MUSCLE
 Swine Dy 22 Contents EFFECTS OF AN ACUTE ENTERIC DISEASE CHALLENGE ON IGF-1 AND IGFBP-3 GENE EXPRESSION IN PORCINE SKELETAL MUSCLE B. J. Johnson, J. P. Kyser, J. D. Dunn, A. T. Wyln, S. S. Dritz 1, J.
Swine Dy 22 Contents EFFECTS OF AN ACUTE ENTERIC DISEASE CHALLENGE ON IGF-1 AND IGFBP-3 GENE EXPRESSION IN PORCINE SKELETAL MUSCLE B. J. Johnson, J. P. Kyser, J. D. Dunn, A. T. Wyln, S. S. Dritz 1, J.
Beetroot juice and exercise: pharmacodynamic and dose-response relationships
 J Appl Physiol 115: 325 336, 2013. First published My 2, 2013; doi:10.1152/jpplphysiol.00372.2013. Beetroot juice nd exercise: phrmcodynmic nd dose-response reltionships Lee J. Wylie, 1 Jmes Kelly, 1 Stephen
J Appl Physiol 115: 325 336, 2013. First published My 2, 2013; doi:10.1152/jpplphysiol.00372.2013. Beetroot juice nd exercise: phrmcodynmic nd dose-response reltionships Lee J. Wylie, 1 Jmes Kelly, 1 Stephen
Cyanidin-3-O-glucoside ameliorates lipid and glucose accumulation in C57BL/6J mice via activation of PPAR-α and AMPK
 3 rd Interntionl Conference nd Exhiition on Nutrition & Food Sciences Septemer 23-25, 214 Vlenci, Spin Cynidin-3-O-glucoside meliortes lipid nd glucose ccumultion in C57BL/6J mice vi ctivtion of PPAR-α
3 rd Interntionl Conference nd Exhiition on Nutrition & Food Sciences Septemer 23-25, 214 Vlenci, Spin Cynidin-3-O-glucoside meliortes lipid nd glucose ccumultion in C57BL/6J mice vi ctivtion of PPAR-α
Invasive Pneumococcal Disease Quarterly Report. July September 2017
 Invsive Pneumococcl Disese Qurterly Report July September 2017 Prepred s prt of Ministry of Helth contrct for scientific services by Rebekh Roos Helen Heffernn October 2017 Acknowledgements This report
Invsive Pneumococcl Disese Qurterly Report July September 2017 Prepred s prt of Ministry of Helth contrct for scientific services by Rebekh Roos Helen Heffernn October 2017 Acknowledgements This report
Activation of Skeletal Muscle Casein Kinase 11 by Insulin is not Diminished in Subjects with Insulin Resistance
 Activtion of Skeletl Muscle Csein Kinse 11 by Insulin is not Diminished in Subjects with Insulin Resistnce Ryo Med, Itmr Rz, Frncesco Zurlo, nd Jmes Sommercorn Clinicl Dibetes nd Nutrition Section, Ntionl
Activtion of Skeletl Muscle Csein Kinse 11 by Insulin is not Diminished in Subjects with Insulin Resistnce Ryo Med, Itmr Rz, Frncesco Zurlo, nd Jmes Sommercorn Clinicl Dibetes nd Nutrition Section, Ntionl
Efficacy of Pembrolizumab in Patients With Advanced Melanoma With Stable Brain Metastases at Baseline: A Pooled Retrospective Analysis
 Efficcy of Pembrolizumb in Ptients With Advnced Melnom With Stble Brin Metstses t Bseline: A Pooled Retrospective Anlysis Abstrct 1248PD Hmid O, Ribs A, Dud A, Butler MO, Crlino MS, Hwu WJ, Long GV, Ancell
Efficcy of Pembrolizumb in Ptients With Advnced Melnom With Stble Brin Metstses t Bseline: A Pooled Retrospective Anlysis Abstrct 1248PD Hmid O, Ribs A, Dud A, Butler MO, Crlino MS, Hwu WJ, Long GV, Ancell
Preservative Resistance in Yeast Species
 APPLIED AND ENVIRONMENTAL MICROBIOLOGY, Nov. 1989, p. 2995-2999 Vol. 55, No. 11 99-224/89/112995-5$2./ Copyright 1989, Americn Society for Microbiology Reltionships mong Cell Size, Membrne Permebility,
APPLIED AND ENVIRONMENTAL MICROBIOLOGY, Nov. 1989, p. 2995-2999 Vol. 55, No. 11 99-224/89/112995-5$2./ Copyright 1989, Americn Society for Microbiology Reltionships mong Cell Size, Membrne Permebility,
Reducing the Risk. Logic Model
 Reducing the Risk Logic Model ETR (Eduction, Trining nd Reserch) is nonprofit orgniztion committed to providing science-bsed innovtive solutions in helth nd eduction designed to chieve trnsformtive chnge
Reducing the Risk Logic Model ETR (Eduction, Trining nd Reserch) is nonprofit orgniztion committed to providing science-bsed innovtive solutions in helth nd eduction designed to chieve trnsformtive chnge
In the treatment of cardiovascular disease (CVD), national
 n report n Beyond LDL Cholesterol: The Role of Elevted Triglycerides nd Low HDL Cholesterol in Residul CVD Risk Remining After Sttin Therpy Peter Algon Jr, MD, FACC In the tretment of crdiovsculr disese
n report n Beyond LDL Cholesterol: The Role of Elevted Triglycerides nd Low HDL Cholesterol in Residul CVD Risk Remining After Sttin Therpy Peter Algon Jr, MD, FACC In the tretment of crdiovsculr disese
Supplementary Figure S1
 Supplementry Figure S Tissue weights (g).... Liver Hert Brin Pncres Len mss (g) 8 6 -% +% 8 6 Len mss Len mss (g) (% ody weight) Len mss (% ody weight) c Tiilis nterior weight (g).6...... Qudriceps weight
Supplementry Figure S Tissue weights (g).... Liver Hert Brin Pncres Len mss (g) 8 6 -% +% 8 6 Len mss Len mss (g) (% ody weight) Len mss (% ody weight) c Tiilis nterior weight (g).6...... Qudriceps weight
On the suppression of plasma nonesterified fatty acids by insulin during enhanced intravascular lipolysis in humans
 Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metb 289: E849 E856, 2005. First published June 21, 2005; doi:10.1152/jpendo.00073.2005. On the suppression of plsm nonesterified ftty cids by insulin during enhnced intrvsculr
Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metb 289: E849 E856, 2005. First published June 21, 2005; doi:10.1152/jpendo.00073.2005. On the suppression of plsm nonesterified ftty cids by insulin during enhnced intrvsculr
Background Pears (Pyrus L.) are one of the leading cultivated fruit trees in China following apples and oranges in planting area and fruit yield.
 Nnjing Agriculturl University Potssium enhnces the sugr ssimiltion in leves nd fruit y regulting the expression of key genes involved in sugr metolism of Asin pers Cixi Dong, Chngwei Shen, Yngchun Xu College
Nnjing Agriculturl University Potssium enhnces the sugr ssimiltion in leves nd fruit y regulting the expression of key genes involved in sugr metolism of Asin pers Cixi Dong, Chngwei Shen, Yngchun Xu College
PROVEN ANTICOCCIDIAL IN NEW FORMULATION
 PROVEN ANTICOCCIDIAL IN NEW FORMULATION Coxidin 100 microgrnulte A coccidiosttic dditive for roilers, chickens rered for lying nd turkeys Contins 100 g of monensin sodium per kg Aville s homogenous grnules
PROVEN ANTICOCCIDIAL IN NEW FORMULATION Coxidin 100 microgrnulte A coccidiosttic dditive for roilers, chickens rered for lying nd turkeys Contins 100 g of monensin sodium per kg Aville s homogenous grnules
The RUTHERFORD-2 trial in heterozygous FH: Results and implications
 The RUTHERFORD-2 tril in heterozygous FH: Results nd implictions Slide deck kindly supplied s n eductionl resource by Professor Derick Rl MD PhD Crbohydrte & Lipid Metbolism Reserch Unit University of
The RUTHERFORD-2 tril in heterozygous FH: Results nd implictions Slide deck kindly supplied s n eductionl resource by Professor Derick Rl MD PhD Crbohydrte & Lipid Metbolism Reserch Unit University of
Shamsuddin M. Mamun, U. Focken, G. Francis and K. Becker University of Hohenheim, Stuttgart, Germany. September 2004
 A GROWTH PERFORMANCE AND METABOLIC RATES OF GENETICALLY IMPROVED AND CONVENTIONAL STRAINS OF NILE TILAPIA, OREOCHROMIS NILOTICUS (L.) Shmsuddin M. Mmun, U. Focken, G. Frncis nd K. Becker University of
A GROWTH PERFORMANCE AND METABOLIC RATES OF GENETICALLY IMPROVED AND CONVENTIONAL STRAINS OF NILE TILAPIA, OREOCHROMIS NILOTICUS (L.) Shmsuddin M. Mmun, U. Focken, G. Frncis nd K. Becker University of
Glucose delivery is a major determinant of glucose utilisation in the ischemic myocardium with a residual coronary flow
 Crdiovsculr Reserch 9 (1998) 81 92 Glucose delivery is mjor determinnt of glucose utilistion in the ischemic myocrdium with residul coronry flow * Lind M. King, Lionel H. Opie MRC/UCT Ischemic Hert Disese
Crdiovsculr Reserch 9 (1998) 81 92 Glucose delivery is mjor determinnt of glucose utilistion in the ischemic myocrdium with residul coronry flow * Lind M. King, Lionel H. Opie MRC/UCT Ischemic Hert Disese
Journal of Hainan Medical University 2017; 23(2): Journal of Hainan Medical University.
 Journl of Hinn Medicl University 2017; 23(2): 151-155 151 Journl of Hinn Medicl University http://www.hnykdxxb.com Reltionship between DEXA bone minerl density mesurement results nd serum cytokines s well
Journl of Hinn Medicl University 2017; 23(2): 151-155 151 Journl of Hinn Medicl University http://www.hnykdxxb.com Reltionship between DEXA bone minerl density mesurement results nd serum cytokines s well
How adaptations of substrate utilization regulate body composition
 (27) 1 6 & 27 Nture Pulishing Group All rights reserved 37-565/7 $3. www.nture.com/ijo ORIGINAL ARTICLE How dpttions of sustrte utiliztion regulte ody composition KD Hll, HL Bin nd CC Chow Lortory of Biologicl
(27) 1 6 & 27 Nture Pulishing Group All rights reserved 37-565/7 $3. www.nture.com/ijo ORIGINAL ARTICLE How dpttions of sustrte utiliztion regulte ody composition KD Hll, HL Bin nd CC Chow Lortory of Biologicl
Comparison of three simple methods for the
 J. clin. Pth. (1967), 2, 5 Comprison of three simple methods for the ssessment of 'free' thyroid hormone T. M. D. GIMLETTE1 From the Rdio-Isotope Lbortory, St. Thoms's Hospitl, London SYNOPSIS A dilysis
J. clin. Pth. (1967), 2, 5 Comprison of three simple methods for the ssessment of 'free' thyroid hormone T. M. D. GIMLETTE1 From the Rdio-Isotope Lbortory, St. Thoms's Hospitl, London SYNOPSIS A dilysis
obesità nel bambino: epidemiologia e prevenzione
 Obesità, Nutrizione e Stili di vit. Trento 31 Mrzo 27 obesità nel bmbino: epidemiologi e prevenzione Cludio Mffeis Diprtimento Mterno Infntile e Biologi-Genetic Sezione di Peditri - Università di Veron
Obesità, Nutrizione e Stili di vit. Trento 31 Mrzo 27 obesità nel bmbino: epidemiologi e prevenzione Cludio Mffeis Diprtimento Mterno Infntile e Biologi-Genetic Sezione di Peditri - Università di Veron
Relationship between serum irisin, glycemic indices, and renal function in type 2 diabetic patients
 J Renl Inj Prev. 2017; 6(2): 88-92. http://journlrip.com Journl of Renl Injury Prevention DOI: 10.15171/jrip.2017.17 Reltionship between serum irisin, glycemic indices, nd renl function in type 2 dibetic
J Renl Inj Prev. 2017; 6(2): 88-92. http://journlrip.com Journl of Renl Injury Prevention DOI: 10.15171/jrip.2017.17 Reltionship between serum irisin, glycemic indices, nd renl function in type 2 dibetic
Northern blot analysis
 Northern blot nlysis RNA SCD RNA SCD FAS C c-9 t-1 C c-9 t-1 PRE PI PDMI PRE PI PDMI PRE PDMI PIM An W c-9, t-11 t-1, c-12 C 5 2 4 1 um C 5 2 4 1 um Angus dipocytes expressed SCD higher thn Wgyu dipocyte
Northern blot nlysis RNA SCD RNA SCD FAS C c-9 t-1 C c-9 t-1 PRE PI PDMI PRE PI PDMI PRE PDMI PIM An W c-9, t-11 t-1, c-12 C 5 2 4 1 um C 5 2 4 1 um Angus dipocytes expressed SCD higher thn Wgyu dipocyte
Optimisation of diets for Atlantic cod (Gadus morhua) broodstock: effect of arachidonic acid on egg & larval quality
 Optimistion of diets for Atlntic cod (Gdus morhu) roodstock: effect of rchidonic cid on egg & lrvl qulity Dr Gordon Bell, Ms. An Blnco, Dr Bill Roy, Dr Derek Roertson, Dr Jim Henderson nd Mr Richrd Prickett,
Optimistion of diets for Atlntic cod (Gdus morhu) roodstock: effect of rchidonic cid on egg & lrvl qulity Dr Gordon Bell, Ms. An Blnco, Dr Bill Roy, Dr Derek Roertson, Dr Jim Henderson nd Mr Richrd Prickett,
Effect of Sitagliptin and Glimepiride on Glucose Homeostasis and camp Levels in Peripheral Tissues of HFD/STZ Diabetic Rats
 Americn Journl of Biomedicl Reserch, 2014, Vol. 2, No. 3, 52-60 Avilble online t http://pubs.sciepub.com/jbr/2/3/3 Science nd Eduction Publishing DOI:10.12691/jbr-2-3-3 Effect of Sitgliptin nd Glimepiride
Americn Journl of Biomedicl Reserch, 2014, Vol. 2, No. 3, 52-60 Avilble online t http://pubs.sciepub.com/jbr/2/3/3 Science nd Eduction Publishing DOI:10.12691/jbr-2-3-3 Effect of Sitgliptin nd Glimepiride
Effect of supplemental fat from dried distillers grains with solubles or corn oil on cow performance, IGF-1, GH, and NEFA concentrations 1
 Effect of supplementl ft from dried distillers grins with solules or corn oil on cow performnce, IGF-1, GH, nd NEFA concentrtions 1 Aigil Brtosh 2, Cody Wright 3, Aimee Wertz-Lutz 4, nd George Perry 5
Effect of supplementl ft from dried distillers grins with solules or corn oil on cow performnce, IGF-1, GH, nd NEFA concentrtions 1 Aigil Brtosh 2, Cody Wright 3, Aimee Wertz-Lutz 4, nd George Perry 5
Clinical Study Report Synopsis Drug Substance Naloxegol Study Code D3820C00018 Edition Number 1 Date 01 February 2013 EudraCT Number
 EudrCT Number 2012-001531-31 A Phse I, Rndomised, Open-lbel, 3-wy Cross-over Study in Helthy Volunteers to Demonstrte the Bioequivlence of the Nloxegol 25 mg Commercil nd Phse III Formultions nd to Assess
EudrCT Number 2012-001531-31 A Phse I, Rndomised, Open-lbel, 3-wy Cross-over Study in Helthy Volunteers to Demonstrte the Bioequivlence of the Nloxegol 25 mg Commercil nd Phse III Formultions nd to Assess
The potential future of targeted radionuclide therapy: implications for occupational exposure? P. Covens
 The potentil future of trgeted rdionuclide therpy: implictions for occuptionl exposure? Introduction: Trgeted Rdionuclide Therpy (TRT) Systemic tretment Molecule lbelled with rdionuclide delivers toxic
The potentil future of trgeted rdionuclide therpy: implictions for occuptionl exposure? Introduction: Trgeted Rdionuclide Therpy (TRT) Systemic tretment Molecule lbelled with rdionuclide delivers toxic
CheckMate 153: Randomized Results of Continuous vs 1-Year Fixed-Duration Nivolumab in Patients With Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
 CheckMte 53: Rndomized Results of Continuous vs -Yer Fixed-Durtion Nivolumb in Ptients With Advnced Non-Smll Cell Lung Cncer Abstrct 297O Spigel DR, McCleod M, Hussein MA, Wterhouse DM, Einhorn L, Horn
CheckMte 53: Rndomized Results of Continuous vs -Yer Fixed-Durtion Nivolumb in Ptients With Advnced Non-Smll Cell Lung Cncer Abstrct 297O Spigel DR, McCleod M, Hussein MA, Wterhouse DM, Einhorn L, Horn
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 . Norml Physiologicl Conditions. SIRT1 Loss-of-Function S1. Model for the role of SIRT1 in the regultion of memory nd plsticity. () Our findings suggest tht SIRT1 normlly functions in coopertion with YY1,
. Norml Physiologicl Conditions. SIRT1 Loss-of-Function S1. Model for the role of SIRT1 in the regultion of memory nd plsticity. () Our findings suggest tht SIRT1 normlly functions in coopertion with YY1,
GDF11 Protects against Endothelial Injury and Reduces Atherosclerotic Lesion Formation in Apolipoprotein E-Null Mice
 originl rticle The Americn Society of Gene & Cell Therpy Protects ginst Endothelil Injury nd Reduces Atherosclerotic Lesion Formtion in Apolipoprotein E-Null Mice Wen Mei, Gungd Xing, Yixing Li 2, Hun
originl rticle The Americn Society of Gene & Cell Therpy Protects ginst Endothelil Injury nd Reduces Atherosclerotic Lesion Formtion in Apolipoprotein E-Null Mice Wen Mei, Gungd Xing, Yixing Li 2, Hun
ENERGY CONTENT OF BARLEY
 ENERGY CONTENT OF BARLEY VARIATION IN THE DIETARY ENERGY CONTENT OF BARLEY Shwn Firbirn, John Ptience, Hnk Clssen nd Ruurd Zijlstr SUMMARY Formultion of commercil pig diets requires n incresing degree
ENERGY CONTENT OF BARLEY VARIATION IN THE DIETARY ENERGY CONTENT OF BARLEY Shwn Firbirn, John Ptience, Hnk Clssen nd Ruurd Zijlstr SUMMARY Formultion of commercil pig diets requires n incresing degree
Review article. Key words non specific low back pain, exercise therapy, stretching, motor control. Grade D
 Spinl Surgery 31 2 140 144 2017 総説 Review rticle Astrct Exercise therpy is useful for low ck pin. Exercise therpy ims to improve posturl lignment, muscle strength, nd endurnce, nd lso contriutes to pin
Spinl Surgery 31 2 140 144 2017 総説 Review rticle Astrct Exercise therpy is useful for low ck pin. Exercise therpy ims to improve posturl lignment, muscle strength, nd endurnce, nd lso contriutes to pin
ABSTRACT. Marek s disease virus (MDV) infection causes atherosclerosis, and prior
 ABSTRACT Title of Document: Directed By: COMPARATIVE STUDY OF LIPOPROTEIN METABOLISM IN MAREK S DISEASE SUSCEPTIBLE AND RESISTANT LINES Ping Yun, Mster of Science, 2010 Assistnt professor Dr. Jiuzhou Song,
ABSTRACT Title of Document: Directed By: COMPARATIVE STUDY OF LIPOPROTEIN METABOLISM IN MAREK S DISEASE SUSCEPTIBLE AND RESISTANT LINES Ping Yun, Mster of Science, 2010 Assistnt professor Dr. Jiuzhou Song,
Abrogation of adenosine A 1 receptor signalling improves metabolic regulation in mice by modulating oxidative stress and inflammatory responses
 Dibetologi (21) :11 12 DOI 1.17/s12-1-7- ARTICLE Abrogtion of denosine receptor signlling improves metbolic regultion in mice by modulting oxidtive stress nd inflmmtory responses Ting Yng 1 & Xing Go 2
Dibetologi (21) :11 12 DOI 1.17/s12-1-7- ARTICLE Abrogtion of denosine receptor signlling improves metbolic regultion in mice by modulting oxidtive stress nd inflmmtory responses Ting Yng 1 & Xing Go 2
Effects of Weight Reduction on Serum Vaspin Concentrations in Obese Subjects: Modification by Insulin Resistance
 nture publishing group rticles Effects of Weight Reduction on Serum Vspin Concentrtions in Obese Subjects: Modifiction by Insulin Resistnce Hye M. Chng 1, He J. Lee 1, Hye S. Prk 1, Je H. Kng 2, Kyung
nture publishing group rticles Effects of Weight Reduction on Serum Vspin Concentrtions in Obese Subjects: Modifiction by Insulin Resistnce Hye M. Chng 1, He J. Lee 1, Hye S. Prk 1, Je H. Kng 2, Kyung
Hormonal networks involved in phosphate deficiencyinduced cluster root formation of Lupinus albus L.
 Institute of Crop Science (34h) Hormonl networks involved in phosphte deficiencyinduced cluster root formtion of Lupinus lus L. For PSP5 in Montpellier, 214 Zhengrui Wng, A.B.M. Moshiur Rhmn, Guoying Wng,
Institute of Crop Science (34h) Hormonl networks involved in phosphte deficiencyinduced cluster root formtion of Lupinus lus L. For PSP5 in Montpellier, 214 Zhengrui Wng, A.B.M. Moshiur Rhmn, Guoying Wng,
Relationship between food availability, glycerol and glycogen levels in lowtemperature challenged rainbow smelt Osmerus mordax
 866 The Journl of Experimentl Biology, 866-87 Published by The Compny of Biologists 7 doi:.4/jeb.749 Reltionship between food vilbility, glycerol nd glycogen levels in lowtemperture chllenged rinbow smelt
866 The Journl of Experimentl Biology, 866-87 Published by The Compny of Biologists 7 doi:.4/jeb.749 Reltionship between food vilbility, glycerol nd glycogen levels in lowtemperture chllenged rinbow smelt
Sex Differences in High-fat Diet-induced Obesity, Metabolic Alterations and Learning, and Synaptic Plasticity Deficits in Mice
 nture publishing group Sex Differences in High-ft Diet-induced Obesity, Metbolic Altertions nd Lerning, nd Synptic Plsticity Deficits in Mice Ling-Ling Hwng 1,2, Chien-Hu Wng 3, Tzu-Ling Li 2, Shih-Dr
nture publishing group Sex Differences in High-ft Diet-induced Obesity, Metbolic Altertions nd Lerning, nd Synptic Plsticity Deficits in Mice Ling-Ling Hwng 1,2, Chien-Hu Wng 3, Tzu-Ling Li 2, Shih-Dr
Effects of 6-Month Sitagliptin Treatment on Insulin and Glucagon Responses in Korean Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
 Originl Article Others Dibetes Metb J 215;39:335-341 http://dx.doi.org/1.493/dmj.215.39.4.335 pissn 2233-679 eissn 2233-687 DIABETES & METABOLISM JOURNAL Effects of 6-Month Sitgliptin Tretment on Insulin
Originl Article Others Dibetes Metb J 215;39:335-341 http://dx.doi.org/1.493/dmj.215.39.4.335 pissn 2233-679 eissn 2233-687 DIABETES & METABOLISM JOURNAL Effects of 6-Month Sitgliptin Tretment on Insulin
Effects of Rosiglitazone on Inflammation in Otsuka Long-Evans Tokushima Fatty Rats
 Originl Article Koren Dibetes J 21;34:191-199 doi: 1.493/kdj.21.34.3.191 pissn 1976-918 eissn 293-265 Effects of Rosiglitzone on Inflmmtion in Otsuk Long-Evns Tokushim Ftty Rts Jin Woo Lee 1, Il Seong
Originl Article Koren Dibetes J 21;34:191-199 doi: 1.493/kdj.21.34.3.191 pissn 1976-918 eissn 293-265 Effects of Rosiglitzone on Inflmmtion in Otsuk Long-Evns Tokushim Ftty Rts Jin Woo Lee 1, Il Seong
ARTICLE. E. Pavlova 1, N. Atanassova 1, C. McKinnell 2, R.M. Sharpe 2 1 Institute of Experimental Morphology, Pathology and Anthropology with Museum,
 DOI:.554/5YRTIMB..3 OPPOSITE MODELS OF EXPRESSION OF ANDROGEN RECEPTOR (AR) AND RETINOIC ACID RECEPTOR-α (RAR-α) IN THE ONSET OF MALE GERM CELL DEVELOPMENT IN HORMONALLY MANIPULATED RATS E. Pvlov, N. Atnssov,
DOI:.554/5YRTIMB..3 OPPOSITE MODELS OF EXPRESSION OF ANDROGEN RECEPTOR (AR) AND RETINOIC ACID RECEPTOR-α (RAR-α) IN THE ONSET OF MALE GERM CELL DEVELOPMENT IN HORMONALLY MANIPULATED RATS E. Pvlov, N. Atnssov,
Scientific research on the biological value of olive oil
 Scientific reserch on the biologicl vlue olive oil Cov F.G. Ally M. (ed.). L' économie de l' olivier Pr : CIHEAM Options Méditerrnéennes : Série Etudes; n. 1988-V 1988 pges 149-152 Article vilble on le
Scientific reserch on the biologicl vlue olive oil Cov F.G. Ally M. (ed.). L' économie de l' olivier Pr : CIHEAM Options Méditerrnéennes : Série Etudes; n. 1988-V 1988 pges 149-152 Article vilble on le
Fetal programming of coronary heart disease
 364 Review Fetl progrmming of coronry hert disese Dvid J.P. Brker People who develop coronry hert disese grow differently from other people both in utero nd during childhood. Slow growth during fetl life
364 Review Fetl progrmming of coronry hert disese Dvid J.P. Brker People who develop coronry hert disese grow differently from other people both in utero nd during childhood. Slow growth during fetl life
BMI and Mortality: Results From a National Longitudinal Study of Canadian Adults
 nture publishing group BMI nd Mortlity: Results From Ntionl Longitudinl Study of Cndin Adults Hether M. Orpn 1, Jen-Mrie Berthelot 2,3, Mrk S. Kpln 4, Dvid H. Feeny 5,6, Bentson McFrlnd 7 nd Nncy A. Ross
nture publishing group BMI nd Mortlity: Results From Ntionl Longitudinl Study of Cndin Adults Hether M. Orpn 1, Jen-Mrie Berthelot 2,3, Mrk S. Kpln 4, Dvid H. Feeny 5,6, Bentson McFrlnd 7 nd Nncy A. Ross
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:1.138/nture1794 BR EPFs BRI1? ERECTA TMM BSKs YDA PP2A BSU1 BIN2 pbzr1/2 BZR1/2 MKK4/5/7/9 MPK3/6 SPCH Cell growth Stomtl production Supplementry Figure 1. The model of BR nd stomtl signling pthwys.
doi:1.138/nture1794 BR EPFs BRI1? ERECTA TMM BSKs YDA PP2A BSU1 BIN2 pbzr1/2 BZR1/2 MKK4/5/7/9 MPK3/6 SPCH Cell growth Stomtl production Supplementry Figure 1. The model of BR nd stomtl signling pthwys.
Effect on Glycemic, Blood Pressure, and Lipid Control according to Education Types
 Originl Article http://dx.doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2011.35.6.580 pissn 2233-6079 eissn 2233-6087 D I A B E T E S & M E T A B O L I S M J O U R N A L Effect on Glycemic, Blood Pressure, nd Lipid Control ccording
Originl Article http://dx.doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2011.35.6.580 pissn 2233-6079 eissn 2233-6087 D I A B E T E S & M E T A B O L I S M J O U R N A L Effect on Glycemic, Blood Pressure, nd Lipid Control ccording
Meat and Food Safety. B.A. Crow, M.E. Dikeman, L.C. Hollis, R.A. Phebus, A.N. Ray, T.A. Houser, and J.P. Grobbel
 Met nd Food Sfety Needle-Free Injection Enhncement of Beef Strip Loins with Phosphte nd Slt Hs Potentil to Improve Yield, Tenderness, nd Juiciness ut Hrm Texture nd Flvor B.A. Crow, M.E. Dikemn, L.C. Hollis,
Met nd Food Sfety Needle-Free Injection Enhncement of Beef Strip Loins with Phosphte nd Slt Hs Potentil to Improve Yield, Tenderness, nd Juiciness ut Hrm Texture nd Flvor B.A. Crow, M.E. Dikemn, L.C. Hollis,
Clinical statistics analysis on the characteristics of pneumoconiosis of Chinese miner population
 Originl Article Clinicl sttistics nlysis on the chrcteristics of pneumoconiosis of Chinese miner popultion Mei-Fng Wng 1 *, Run-Ze Li 2 *, Ying Li 2, Xue-Qin Cheng 1, Jun Yng 1, Wen Chen 3, Xing-Xing Fn
Originl Article Clinicl sttistics nlysis on the chrcteristics of pneumoconiosis of Chinese miner popultion Mei-Fng Wng 1 *, Run-Ze Li 2 *, Ying Li 2, Xue-Qin Cheng 1, Jun Yng 1, Wen Chen 3, Xing-Xing Fn
Supplementary figure 1
 Supplementry figure 1 Dy 8 post LCMV infection Vsculr Assoc. Prenchym Dy 3 post LCMV infection 1 5 6.7.29 1 4 1 3 1 2 88.9 4.16 1 2 1 3 1 4 1 5 1 5 1.59 5.97 1 4 1 3 1 2 21.4 71 1 2 1 3 1 4 1 5 1 5.59.22
Supplementry figure 1 Dy 8 post LCMV infection Vsculr Assoc. Prenchym Dy 3 post LCMV infection 1 5 6.7.29 1 4 1 3 1 2 88.9 4.16 1 2 1 3 1 4 1 5 1 5 1.59 5.97 1 4 1 3 1 2 21.4 71 1 2 1 3 1 4 1 5 1 5.59.22
THE EVALUATION OF DEHULLED CANOLA MEAL IN THE DIETS OF GROWING AND FINISHING PIGS
 THE EVALUATION OF DEHULLED CANOLA MEAL IN THE DIETS OF GROWING AND FINISHING PIGS THE EVALUATION OF DEHULLED CANOLA MEAL IN THE DIETS OF GROWING AND FINISHING PIGS John F. Ptience nd Doug Gillis SUMMARY
THE EVALUATION OF DEHULLED CANOLA MEAL IN THE DIETS OF GROWING AND FINISHING PIGS THE EVALUATION OF DEHULLED CANOLA MEAL IN THE DIETS OF GROWING AND FINISHING PIGS John F. Ptience nd Doug Gillis SUMMARY
Research Article Protective Effect of Short-Term Genistein Supplementation on the Early Stage in Diabetes-Induced Renal Damage
 Meditors of Inflmmtion Volume 2013, rticle ID 510212, 14 pges http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/510212 Reserch rticle Protective Effect of Short-Term Genistein Supplementtion on the Erly Stge in Dibetes-Induced
Meditors of Inflmmtion Volume 2013, rticle ID 510212, 14 pges http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/510212 Reserch rticle Protective Effect of Short-Term Genistein Supplementtion on the Erly Stge in Dibetes-Induced
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 X p -lu c ct ivi ty doi:.8/nture8 S CsA - THA + DAPI Merge FSK THA TUN Supplementry Figure : A. Ad-Xp luc ctivity in primry heptocytes exposed to FSK, THA, or TUN s indicted. Luciferse ctivity normlized
X p -lu c ct ivi ty doi:.8/nture8 S CsA - THA + DAPI Merge FSK THA TUN Supplementry Figure : A. Ad-Xp luc ctivity in primry heptocytes exposed to FSK, THA, or TUN s indicted. Luciferse ctivity normlized
Safety and Tolerability of Subcutaneous Sarilumab and Intravenous Tocilizumab in Patients With RA
 Sfety nd Tolerbility of Subcutneous Srilumb nd Intrvenous Tocilizumb in Ptients With RA Pul Emery, 1 Jun Rondon, 2 Anju Grg, 3 Hubert vn Hoogstrten, 3 Neil M.H. Grhm, 4 Ming Liu, 4 Nncy Liu, 3 Jnie Prrino,
Sfety nd Tolerbility of Subcutneous Srilumb nd Intrvenous Tocilizumb in Ptients With RA Pul Emery, 1 Jun Rondon, 2 Anju Grg, 3 Hubert vn Hoogstrten, 3 Neil M.H. Grhm, 4 Ming Liu, 4 Nncy Liu, 3 Jnie Prrino,
Regulation by nutritional status of lipids and apolipoproteins A-I, A4, and A-IV in inbred mice
 Regultion by nutritionl sttus of lipids nd polipoproteins A-I, A4, nd A-IV in inbred mice R. C. LeBoeuf,' M. Cldwell, nd E. Kirk Deprtment of Medicine, University of Wshington, Settle, WA 98195 Abrtrct
Regultion by nutritionl sttus of lipids nd polipoproteins A-I, A4, nd A-IV in inbred mice R. C. LeBoeuf,' M. Cldwell, nd E. Kirk Deprtment of Medicine, University of Wshington, Settle, WA 98195 Abrtrct
Inhibition of adipocyte differentiation in 3T3-L1 cell line by quercetin or isorhamnetin
 Louisin Stte University LSU Digitl Commons LSU Mster's Theses Grdute School 2012 Inhibition of dipocyte differentition in 3T3-L1 cell line by quercetin or isorhmnetin Din Gbriel Crvjl-Aldz Louisin Stte
Louisin Stte University LSU Digitl Commons LSU Mster's Theses Grdute School 2012 Inhibition of dipocyte differentition in 3T3-L1 cell line by quercetin or isorhmnetin Din Gbriel Crvjl-Aldz Louisin Stte
Acute and gradual increases in BDNF concentration elicit distinct signaling and functions in neurons
 nd grdul increses in BDNF concentrtion elicit distinct signling nd functions in neurons Yunyun Ji,, Yun Lu, Feng Yng, Wnhu Shen, Tin Tze-Tsng Tng,, Linyin Feng, Shumin Dun, nd Bi Lu,.. - Grdul (normlized
nd grdul increses in BDNF concentrtion elicit distinct signling nd functions in neurons Yunyun Ji,, Yun Lu, Feng Yng, Wnhu Shen, Tin Tze-Tsng Tng,, Linyin Feng, Shumin Dun, nd Bi Lu,.. - Grdul (normlized
EVALUATION OF DIFFERENT COPPER SOURCES AS A GROWTH PROMOTER IN SWINE FINISHING DIETS 1
 Swine Dy 2001 Contents EVALUATION OF DIFFERENT COPPER SOURCES AS A GROWTH PROMOTER IN SWINE FINISHING DIETS 1 C. W. Hstd, S. S. Dritz 2, J. L. Nelssen, M. D. Tokch, nd R. D. Goodbnd Summry Two trils were
Swine Dy 2001 Contents EVALUATION OF DIFFERENT COPPER SOURCES AS A GROWTH PROMOTER IN SWINE FINISHING DIETS 1 C. W. Hstd, S. S. Dritz 2, J. L. Nelssen, M. D. Tokch, nd R. D. Goodbnd Summry Two trils were
Evaluation of Apelin and Insulin Resistance in Patients with PCOS and Therapeutic Effect of Drospirenone-Ethinylestradiol Plus Metformin
 e-issn 1643-3750 DOI: 10.12659/MSM.894926 Received: 2015.06.08 Accepted: 2015.07.29 Published: 2015.08.28 Evlution of Apelin nd Insulin Resistnce in Ptients with PCOS nd Therpeutic Effect of Drospirenone-Ethinylestrdiol
e-issn 1643-3750 DOI: 10.12659/MSM.894926 Received: 2015.06.08 Accepted: 2015.07.29 Published: 2015.08.28 Evlution of Apelin nd Insulin Resistnce in Ptients with PCOS nd Therpeutic Effect of Drospirenone-Ethinylestrdiol
% Inhibition of MERS pseudovirus infection. 0 h 0.5 h 1 h 2 h 4 h 6 h Time after virus addition
 % Inhiition of MERS pseudovirus infection 1 8 h.5 h 1 h 2 h 4 h 6 h Time fter virus ddition Supplementry Figure S1. Inhiition of on MERS pseudovirus infection t the different intervls postinfection. A
% Inhiition of MERS pseudovirus infection 1 8 h.5 h 1 h 2 h 4 h 6 h Time fter virus ddition Supplementry Figure S1. Inhiition of on MERS pseudovirus infection t the different intervls postinfection. A
Effect of Oral Administration of Propylene Glycol on Serum Glucose Concentrations in Periparturient Dairy Cows
 Ksetsrt J. (Nt. Sci.) 37 : 145-149 (2003) Effect of Orl Administrtion of Propylene Glycol on Serum Glucose Concentrtions in Periprturient Diry Cows Theer Rukkwmsuk, Nrongpol Petploi, Ing-orn Preechnvinit,
Ksetsrt J. (Nt. Sci.) 37 : 145-149 (2003) Effect of Orl Administrtion of Propylene Glycol on Serum Glucose Concentrtions in Periprturient Diry Cows Theer Rukkwmsuk, Nrongpol Petploi, Ing-orn Preechnvinit,
The glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor is essential for postprandial lipoprotein synthesis and secretion in hamsters and mice
 DOI.7/s-9-- ARTICLE The glucgon-like peptide receptor is essentil for postprndil lipoprotein synthesis nd secretion in hmsters nd mice J. Hsieh & C. Longuet & C. L. Bker & B. Qin & L. M. Federico & D.
DOI.7/s-9-- ARTICLE The glucgon-like peptide receptor is essentil for postprndil lipoprotein synthesis nd secretion in hmsters nd mice J. Hsieh & C. Longuet & C. L. Bker & B. Qin & L. M. Federico & D.
British Journal of Nutrition
 (11), 16, 1449 1456 q The Authors 11 doi:1.117/s71145111917 Fish oil comined with SCFA synergisticlly prevent tissue ccumultion of NEFA during weight loss in oese mice Miken H. Pedersen 1,, Lotte Luritzen
(11), 16, 1449 1456 q The Authors 11 doi:1.117/s71145111917 Fish oil comined with SCFA synergisticlly prevent tissue ccumultion of NEFA during weight loss in oese mice Miken H. Pedersen 1,, Lotte Luritzen
Effect of Various Doses of Cinnamon on Lipid Profile in Diabetic Individuals
 Pkistn Journl of Nutrition 2 (5): 312-319, 2003 Asin Network for Scientific Informtion 2003 Effect of Vrious Doses of Cinnmon on Lipid Profile in Dibetic Individuls Alm Khn, Mhpr Sfdr nd Mohmmd Muzffr
Pkistn Journl of Nutrition 2 (5): 312-319, 2003 Asin Network for Scientific Informtion 2003 Effect of Vrious Doses of Cinnmon on Lipid Profile in Dibetic Individuls Alm Khn, Mhpr Sfdr nd Mohmmd Muzffr
Extraction and Some Functional Properties of Protein Extract from Rice Bran
 Ksetsrt J. (Nt. Sci.) 40 : 209-214 (2006) Extrction nd Some Functionl Properties of Protein Extrct from Rice Brn Chockchi Theerkulkit*, Siree Chiseri nd Siriwt Mongkolknchnsiri ABSTRACT Rice brn protein
Ksetsrt J. (Nt. Sci.) 40 : 209-214 (2006) Extrction nd Some Functionl Properties of Protein Extrct from Rice Brn Chockchi Theerkulkit*, Siree Chiseri nd Siriwt Mongkolknchnsiri ABSTRACT Rice brn protein
Research Article Dietary Consumption of Virgin Coconut Oil Ameliorates Lipid Profiles in Diabetic Rats
 Physiology Journl, Article ID 256236, 5 pges http://dx.doi.org/1.1155/214/256236 Reserch Article Dietry Consumption of Virgin Coconut Oil Ameliortes Lipid Profiles in Dibetic Rts A. M. Akinnug, 1 S. O.
Physiology Journl, Article ID 256236, 5 pges http://dx.doi.org/1.1155/214/256236 Reserch Article Dietry Consumption of Virgin Coconut Oil Ameliortes Lipid Profiles in Dibetic Rts A. M. Akinnug, 1 S. O.
The Effects of Small Sized Rice Bowl on Carbohydrate Intake and Dietary Patterns in Women with Type 2 Diabetes
 Originl Article doi: 10.4093/kdj.2010.34.3.166 pissn 1976-9180 eissn 2093-2650 The Effects of Smll Sized Rice Bowl on Crbohydrte Intke nd Dietry Ptterns in Women with Type 2 Dibetes Hee-Jung Ahn 1, *,
Originl Article doi: 10.4093/kdj.2010.34.3.166 pissn 1976-9180 eissn 2093-2650 The Effects of Smll Sized Rice Bowl on Crbohydrte Intke nd Dietry Ptterns in Women with Type 2 Dibetes Hee-Jung Ahn 1, *,
Mecadox. Improves pig performance in a wide range of health and growing conditions. (Carbadox) Talk With a Phibro Expert:
 SWINE (Crbdox) Improves pig performnce in wide rnge of helth nd growing conditions The Advntge Over the yers, medicted feed dditive hs proven to be cost-effective mngement tool for improving pig performnce
SWINE (Crbdox) Improves pig performnce in wide rnge of helth nd growing conditions The Advntge Over the yers, medicted feed dditive hs proven to be cost-effective mngement tool for improving pig performnce
CHAPTER- 3 ANALYSIS OF PATHOPHYSIOLOGICAL MARKER ENZYMES, LIPID AND PROTEIN PROFILES IN CONTROL AND EXPERIMENTAL ANIMALS
 CHAPTER- 3 CHAPTER- 3 ANALYSIS OF PATHOPHYSIOLOGICAL MARKER ENZYMES, LIPID AND PROTEIN PROFILES IN CONTROL AND EXPERIMENTAL ANIMALS 3.1. INTRODUCTION The liver, hs vriety of trnsminse to synthesize nd
CHAPTER- 3 CHAPTER- 3 ANALYSIS OF PATHOPHYSIOLOGICAL MARKER ENZYMES, LIPID AND PROTEIN PROFILES IN CONTROL AND EXPERIMENTAL ANIMALS 3.1. INTRODUCTION The liver, hs vriety of trnsminse to synthesize nd
Compound K attenuates glucose intolerance and hepatic steatosis through AMPK-dependent pathways in type 2 diabetic OLETF rats
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Koren J Intern Med 218;33:347-355 Compound K ttenutes glucose intolernce nd heptic stetosis through AMPK-dependent pthwys in type 2 dibetic OLETF rts Yoo-Cheol Hwng 1, D-Hee Oh 1, Moon
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Koren J Intern Med 218;33:347-355 Compound K ttenutes glucose intolernce nd heptic stetosis through AMPK-dependent pthwys in type 2 dibetic OLETF rts Yoo-Cheol Hwng 1, D-Hee Oh 1, Moon
Expression of Three Cell Cycle Inhibitors during Development of Adipose Tissue
 Expression of Three Cell Cycle Inhiitors during Development of Adipose Tissue Jiin Zhng Deprtment of Animl Sciences Advisor: Michel E. Dvis Co-dvisor: Kichoon Lee Development of niml dipose tissue Hypertrophy
Expression of Three Cell Cycle Inhiitors during Development of Adipose Tissue Jiin Zhng Deprtment of Animl Sciences Advisor: Michel E. Dvis Co-dvisor: Kichoon Lee Development of niml dipose tissue Hypertrophy
Metabolic Syndrome and Health-related Quality of Life in Obese Individuals Seeking Weight Reduction
 Metbolic Syndrome nd Helth-relted Qulity of Life in Obese Individuls Seeking Weight Reduction Adm Gilden Tsi 1, Thoms A. Wdden 1, Dvid B. Srwer 1, Robert I. Berkowitz 1, Leslie G. Womble 1, Louise A. Hesson
Metbolic Syndrome nd Helth-relted Qulity of Life in Obese Individuls Seeking Weight Reduction Adm Gilden Tsi 1, Thoms A. Wdden 1, Dvid B. Srwer 1, Robert I. Berkowitz 1, Leslie G. Womble 1, Louise A. Hesson
Acid-Poly-L-Lysine Complex on Encephalomyocarditis Virus
 ANTimICROsIAL AozWu AND CHEMoTHERAPY, Oct. 1976, p. 668-676 Copyright C 1976 Americn Society for Microbiology Vol. 10, No. 4 Printed in U.S.A. Effect of Tretment with Exogenous Interferon, Polyinosinic
ANTimICROsIAL AozWu AND CHEMoTHERAPY, Oct. 1976, p. 668-676 Copyright C 1976 Americn Society for Microbiology Vol. 10, No. 4 Printed in U.S.A. Effect of Tretment with Exogenous Interferon, Polyinosinic
Identification and selective expansion of functionally superior T cells expressing chimeric antigen receptors
 Identifiction nd selective expnsion of functionlly superior T cells expressing chimeric ntigen receptors The Hrvrd community hs mde this rticle openly vilble. Plese shre how this ccess benefits you. Your
Identifiction nd selective expnsion of functionlly superior T cells expressing chimeric ntigen receptors The Hrvrd community hs mde this rticle openly vilble. Plese shre how this ccess benefits you. Your
Effect of Endotoxin on Pyruvate Kinase Activity in Mouse Liver
 INFECTION AND IMMUNITY, Aug. 1971, p. 138-142 Copyright 1971 Americn Society for Microbiology Vol. 4, No. 2 Prinzted in U.S.A. Effect of Endotoxin on Pyruvte Kinse Activity in Mouse Liver IRVIN S. SNYDER,
INFECTION AND IMMUNITY, Aug. 1971, p. 138-142 Copyright 1971 Americn Society for Microbiology Vol. 4, No. 2 Prinzted in U.S.A. Effect of Endotoxin on Pyruvte Kinse Activity in Mouse Liver IRVIN S. SNYDER,
XII. HIV/AIDS. Knowledge about HIV Transmission and Misconceptions about HIV
 XII. HIV/AIDS Knowledge bout HIV Trnsmission nd Misconceptions bout HIV One of the most importnt prerequisites for reducing the rte of HIV infection is ccurte knowledge of how HIV is trnsmitted nd strtegies
XII. HIV/AIDS Knowledge bout HIV Trnsmission nd Misconceptions bout HIV One of the most importnt prerequisites for reducing the rte of HIV infection is ccurte knowledge of how HIV is trnsmitted nd strtegies
PHYSIOLOGICAL AND PROTEOMIC RESPONSES OF TOBACCO SEEDLINGS EXPOSED TO SILVER NANOPARTICLES
 PHYSIOLOGICAL AND PROTEOMIC RESPONSES OF TOBACCO SEEDLINGS EXPOSED TO SILVER NANOPARTICLES Rent Bi Deprtment of Biology, Fculty of Science, University of Zgre INTRODUCTION Nnoprticles (NPs) Silver nnoprticles
PHYSIOLOGICAL AND PROTEOMIC RESPONSES OF TOBACCO SEEDLINGS EXPOSED TO SILVER NANOPARTICLES Rent Bi Deprtment of Biology, Fculty of Science, University of Zgre INTRODUCTION Nnoprticles (NPs) Silver nnoprticles
Effects of Endurance Exercise and High-Fat Diet on Insulin Resistance and Ceramide Contents of Skeletal Muscle in Sprague-Dawley Rats
 Originl Article Koren Dibetes J 21;34:244-252 doi: 1.493/kdj.21.34.4.244 pissn 1976-918 eissn 293-265 Effects of Endurnce Exercise nd High-Ft Diet on Insulin Resistnce nd Cermide Contents of Skeletl Muscle
Originl Article Koren Dibetes J 21;34:244-252 doi: 1.493/kdj.21.34.4.244 pissn 1976-918 eissn 293-265 Effects of Endurnce Exercise nd High-Ft Diet on Insulin Resistnce nd Cermide Contents of Skeletl Muscle
Leptin and C-peptide Level in North Indians in Relation to Subjects Underlying Type Two Diabetes Mellitus
 Reserch Article Jyoti Jin 1 *, Rti Mthur 1, Mnsi Jh 1, Schdev Ydv 2 1 Deprtment of Biochemistry, SMS Medicl College nd Hospitl, Jipur, Rjsthn, Indi. 2 Assistnt Professor, Deprtment of Phrmcy, Bnsthli University,
Reserch Article Jyoti Jin 1 *, Rti Mthur 1, Mnsi Jh 1, Schdev Ydv 2 1 Deprtment of Biochemistry, SMS Medicl College nd Hospitl, Jipur, Rjsthn, Indi. 2 Assistnt Professor, Deprtment of Phrmcy, Bnsthli University,
