The Axial Skeleton. C h a p t e r. PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College - North Harris
|
|
|
- Amelia Cole
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 C h a p t e r 7 The Axial Skeleton PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College - North Harris Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings
2 An Introduction to the Axial Skeleton Structures of Bones Articulations Contacts with other bones Landmarks (Bone Markings; Marks) Areas of muscle and ligament attachment Foramina Openings for nerves and blood vessels
3 The Axial Skeleton The axial skeleton Forms the longitudinal axis of the body Has 80 bones The skull: 8 cranial bones 14 facial bones Bones associated with the skull: 6 auditory ossicles the hyoid bone
4 The Axial Skeleton The axial skeleton The vertebral column 24 vertebrae (singular = vertebra) The sacrum The coccyx The thoracic cage 24 ribs The sternum Peel-Away of Whole Axial Skeleton
5 The Axial Skeleton Figure 7 1 The Axial Skeleton.
6 The Axial Skeleton Figure 7 1 The Axial Skeleton.
7 The Axial Skeleton Functions of the Axial Skeleton Supports and protects organs in body cavities Attaches to muscles of Head, neck, and trunk Respiration Appendicular skeleton
8 The Skull The skull protects The brain Entrances to respiratory system Entrance to digestive system The skull contains 22 bones 8 cranial bones: Form the braincase or cranium 14 facial bones: Protect and support entrances to digestive and respiratory tracts The Adult Skull
9 The Skull Figure 7 2 Cranial and Facial Subdivisions of the Skull.
10 The Skull Cranial Bones Enclose the cranial cavity Which contains the brain And its fluids, blood vessels, nerves, and membranes Facial Bones Superficial facial bones For muscle attachment Deep facial bones Separate the oral and nasal cavities Form the nasal septum
11 The Skull Figure 7 3a The Adult Skull.
12 The Skull Figure 7 3b The Adult Skull.
13 The Skull Figure 7 3c The Adult Skull.
14 The Skull Figure 7 3d The Adult Skull.
15 The Skull Figure 7 3e The Adult Skull.
16 The Skull Figure 7 4a The Sectional Anatomy of the Skull.
17 The Skull Figure 7 4b The Sectional Anatomy of the Skull.
18 The Skull Superficial Facial Bones Maxillae = maxillary bones Lacrimal Nasal Zygomatic Mandible Deep Facial Bones Palatine bones Inferior nasal conchae Vomer
19 The Skull Sinuses Cavities that decrease the weight of the skull Sutures Lined with mucous membranes Protect the entrances of the respiratory system The immovable joints of the skull The four major sutures Lambdoid suture Coronal suture Sagittal suture Squamous suture
20 The Skull Lambdoid Suture Separates occipital from parietal bones May contain sutural (Wormian) bones Coronal Suture Attaches frontal bone to parietal bones The calvaria (skullcap) Consists of occipital, parietal, and frontal bones Sagittal Suture Between the parietal bones From lambdoid suture to coronal suture Squamous Sutures Form boundaries between temporal bones and parietal bones
21 The Cranial Bones of the Skull The Cranial Bones Occipital bone Parietal bones Frontal bone Temporal bones Sphenoid Ethmoid
22 The Cranial Bones of the Skull The Occipital Bone Functions of the occipital bone Forms the posterior and inferior surfaces of the cranium Articulations of the occipital bone Parietal bones Temporal bones Sphenoid First cervical vertebra (atlas) Marks of the occipital bone External occipital protuberance External occipital crest: to attach ligaments
23 The Cranial Bones of the Skull The Occipital Bone Marks of the occipital bone Occipital condyles: articulate with neck Inferior and superior nuchal lines: attachment site of muscles and ligaments Foramina of the occipital bone Foramen magnum: connects cranial and spinal cavities Jugular foramen: for jugular vein Hypoglossal canals: for hypoglossal nerves
24 The Cranial Bones of the Skull Figure 7 5a The Occipital and Parietal Bones.
25 The Cranial Bones of the Skull The Parietal Bones Functions of the parietal bones Forms part of the superior and lateral surfaces of the cranium Articulations of the parietal bones Other parietal bone Occipital bone Temporal bone Frontal bone Sphenoid
26 The Cranial Bones of the Skull The Parietal Bones Marks of the parietal bones Superior and inferior temporal lines: to attach temporalis muscle Grooves for cranial blood vessels
27 The Cranial Bones of the Skull Figure 7 5b The Occipital and Parietal Bones.
28 The Cranial Bones of the Skull The Frontal bone Functions of the frontal bone Forms the anterior cranium and upper eye sockets Contains frontal sinuses Articulations of the frontal Bone Parietal bone Maxilla Metopic suture Ethmoid Lacrimal bone Zygomatic bone Sphenoid Nasal bone
29 The Cranial Bones of the Skull The Frontal Bone Marks of the frontal bone Frontal squama (forehead) Supra-orbital margin (protects eye) Lacrimal fossa (for tear ducts) Frontal sinuses Foramina of the frontal bone Supra-orbital foramen: for blood vessels of eyebrows, eyelids, and frontal sinuses Supra-orbital notch: an incomplete supra-orbital foramen
30 The Cranial Bones of the Skull Figure 7 6a The Frontal Bone.
31 The Cranial Bones of the Skull Figure 7 6b The Frontal Bone.
32 The Cranial Bones of the Skull The Temporal Bones Functions of the temporal bones Part of lateral walls of cranium and zygomatic arches Articulate with mandible Surround and protect inner ear Attach muscles of jaws and head Articulations of the temporal bones Zygomatic bone Sphenoid Parietal bone Occipital bone Mandible
33 The Cranial Bones of the Skull Marks of the Temporal Bones Squamous part: borders the squamous suture Mandibular fossa: articulates with the mandible Zygomatic process Inferior to the squamous portion Articulates with temporal process of zygomatic bone Forms zygomatic arch (cheekbone) Mastoid process For muscle attachment Contains mastoid air cells connected to middle ear
34 The Cranial Bones of the Skull Marks of the Temporal Bones Styloid process To attach tendons and ligaments of the hyoid, tongue, and pharynx Petrous part Encloses structures of the inner ear Auditory ossicles Three tiny bones in tympanic cavity (middle ear) Transfer sound from tympanic membrane (eardrum) to inner ear
35 The Cranial Bones of the Skull Foramina of the Temporal Bones Carotid canal: for internal carotid artery Foramen lacerum For carotid and small arteries Hyaline cartilage Auditory tube External acoustic meatus (canal): ends at tympanic membrane Stylomastoid foramen: for facial nerve Internal acoustic meatus (canal) For blood vessels and nerves of the inner ear Facial nerve
36 The Cranial Bones of the Skull Figure 7 7a The Temporal Bones.
37 The Cranial Bones of the Skull Figure 7 7b The Temporal Bones.
38 The Cranial Bones of the Skull Figure 7 7c The Temporal Bones.
39 The Cranial Bones of the Skull The Sphenoid Functions of the Sphenoid Part of the floor of the cranium Unites cranial and facial bones Strengthens sides of the skull Contains sphenoidal sinuses
40 The Cranial Bones of the Skull Articulations of the Sphenoid Ethmoid Frontal bone Occipital bone Parietal bone Temporal bone Palatine bones Zygomatic bones Maxillae Vomer
41 The Cranial Bones of the Skull Marks of the Sphenoid Sphenoid body At the central axis of the sphenoid Sella turcica Saddle-shaped enclosure On the superior surface of the body Hypophyseal fossa A depression within the sella turcica Holds the pituitary gland
42 The Cranial Bones of the Skull Marks of the Sphenoid Sphenoidal sinuses On either side of the body Inferior to the sella turcica Lesser wings Anterior to the sella turcica Greater wings Form part of the cranial floor Sphenoidal spine Posterior wall of the orbit Pterygoid processes Form pterygoid plates To attach muscles of the lower jaw and soft palate
43 The Cranial Bones of the Skull Foramina of the Sphenoid Optic canals: for optic nerves Superior orbital fissure: for blood vessels and nerves of the orbit Foramen rotundum: for blood vessels and nerves of the face Foramen ovale: for blood vessels and nerves of the face Foramen spinosum: for blood vessels and nerves of the jaws
44 The Cranial Bones of the Skull Figure 7 8a The Sphenoid.
45 The Cranial Bones of the Skull Figure 7 8b The Sphenoid.
46 The Cranial Bones of the Skull The Ethmoid Functions of the ethmoid Forms anteromedial floor of the cranium Roof of the nasal cavity Part of the nasal septum and medial orbital wall Contains ethmoidal air cells (network of sinuses)
47 The Cranial Bones of the Skull Articulations of the Ethmoid Frontal bone Sphenoid Nasal bone Lacrimal bone Palatine bone Maxillary bones Inferior nasal conchae Vomer
48 The Cranial Bones of the Skull Three Parts of the Ethmoid The cribriform plate Floor of the cranium Roof of the nasal cavity Contains the crista galli The two lateral masses Ethmoidal labyrinth (ethmoidal air cells) Superior nasal conchae Middle nasal conchae The perpendicular plate Part of the nasal septum
49 The Cranial Bones of the Skull Foramina of the Ethmoid Olfactory foramina In the cribriform plate For olfactory nerves
50 The Cranial Bones of the Skull Figure 7 9 The Ethmoid.
51 The Cranial Bones of the Skull Figure 7 9 The Ethmoid.
52 The Facial Bones of the Skull The Facial Bones Maxillae (maxillary bones) Palatine bones Nasal bones Vomer Inferior nasal conchae Zygomatic bones Lacrimal bones Mandible
53 The Facial Bones of the Skull The Maxillae Functions of the maxillae Support upper teeth Form inferior orbital rim Form lateral margins of external nares Form upper jaw and hard palate Contain maxillary sinuses (largest sinuses)
54 The Facial Bones of the Skull Articulations of the Maxillae Frontal bones Ethmoid With one another All other facial bones except the mandible
55 The Facial Bones of the Skull Marks of the Maxillae Orbital rim:protects eye and orbit Anterior nasal spine: attaches cartilaginous anterior nasal septum Alveolar processes: borders the mouth and supports upper teeth Palatine processes: form the hard palate (roof of mouth) Maxillary sinuses: to lighten bone Nasolacrimal canal: protects lacrimal sac and nasolacrimal duct
56 The Facial Bones of the Skull Foramina of the Maxillae Infra-orbital foramen For sensory nerve to brain (via foramen rotundum of sphenoid) Inferior orbital fissure For cranial nerves and blood vessels
57 The Facial Bones of the Skull Figure 7 10a The Maxillae and Palatine Bones.
58 The Facial Bones of the Skull The Palatine Bones Functions of the palatine bones Form the posterior portion of the hard palate Contribute to the floors of the orbits Articulations of the palatine bones With other palatine bone Maxillae Sphenoid Ethmoid Inferior nasal conchae Vomer
59 The Facial Bones of the Skull Divisions of the Palatine Bones Horizontal plate: posterior part of hard palate Perpendicular plate: from horizontal plate to orbital process of orbit floor Foramina of the Palatine Bones Many in the lateral portion of the horizontal plate For small blood vessels and nerves of the roof of the mouth
60 The Facial Bones of the Skull Figure 7 10 b and c The Maxillae and Palatine Bones.
61 The Facial Bones of the Skull The Nasal Bones Functions of the nasal bones Support the bridge of the nose Connect to cartilages of the distal part of the nose (external nares) Articulations of the nasal bones With other nasal bones Ethmoid Frontal bones Maxillae
62 The Facial Bones of the Skull The Vomer Functions of the vomer Forms the inferior portion of the bony nasal septum Articulations of the vomer Sphenoid Ethmoid Palatine bones Maxillae Cartilaginous part of the nasal septum
63 The Facial Bones of the Skull The Inferior Nasal Conchae Functions of the inferior nasal conchae To create air turbulence in the nasal cavity To increase the epithelial surface area To warm and humidify inhaled air Articulations of the inferior nasal conchae Ethmoid Maxillae Palatine bones Lacrimal bones
64 The Facial Bones of the Skull The Zygomatic Bones Functions of the zygomatic bones Contribute to the rim and lateral wall of the orbit Form part of the zygomatic arch Articulations of the zygomatic bones Sphenoid Frontal bone Temporal bones Maxillae
65 The Facial Bones of the Skull Marks of the zygomatic bones Temporal process Meets the zygomatic process of the temporal bone Foramina of the zygomatic bones Zygomaticofacial foramen For sensory nerves of cheeks
66 The Facial Bones of the Skull The Lacrimal Bones Functions of the lacrimal bones The smallest facial bones Form part of the medial wall of the orbit Articulations of the lacrimal bones Frontal bone Maxillae Ethmoid
67 The Facial Bones of the Skull The Lacrimal Bones Marks of the lacrimal bones Lacrimal sulcus: location of the lacrimal sac leads to the nasolacrimal canal (between orbit and nasal cavity)
68 The Facial Bones of the Skull Figure 7 11 The Smaller Bones of the Face.
69 The Facial Bones of the Skull The Mandible Functions of the mandible Forms the lower jaw Articulations of the mandible Mandibular fossae of the temporal bones
70 The Facial Bones of the Skull Marks of the Mandible Body of the mandible: horizontal portion Alveolar processes: support the lower teeth Mental protuberance: attaches facial muscles A depression on the medial surface: for submandibular salivary gland Mylohyoid line: for insertion of the mylohyoid muscle (floor of mouth)
71 The Facial Bones of the Skull Marks of the Mandible Ramus: ascending from the mandibular angle on either side Condylar process: articulates with temporal bone at temporomandibular joint Coronoid process: insertion point for temporalis muscle (closes the jaws) Mandibular notch: separates condylar and coronoid processes
72 The Facial Bones of the Skull The Mandible Foramina of the mandible Mental foramina: for sensory nerves of lips and chin Mandibular foramen: entrance to the mandibular canal for blood vessels and nerves of lower teeth
73 The Facial Bones of the Skull The Hyoid Bone Functions of the hyoid bone Supports the larynx Attaches muscles of the larynx, pharynx, and tongue Articulations of the hyoid bone Connects lesser horns to styloid processes of temporal bones
74 The Facial Bones of the Skull Marks of the Hyoid Bone Body of the hyoid Attaches muscles of larynx, tongue, and pharynx Greater horns (greater cornua) Support larynx Attach muscles of the tongue Lesser horns (lesser cornua) Attach stylohyoid ligaments Support hyoid and larynx
75 The Facial Bones of the Skull Figure 7 12a The Mandible and Hyoid Bone.
76 The Facial Bones of the Skull Figure 7 12b The Mandible and Hyoid Bone.
77 The Facial Bones of the Skull Figure 7 12c The Mandible and Hyoid Bone.
78 Foramina and Fissures of the Skull
79 Foramina and Fissures of the Skull
80 Foramina and Fissures of the Skull
81 The Orbital Complex Forms the eye sockets (orbits) Frontal bone (roof) Maxilla (floor) Maxillary, lacrimal, and ethmoid bones (orbital rim and medial wall) Sphenoid and palatine bones
82 The Orbital Complex Figure 7 13 The Orbital Complex.
83 The Orbital Complex Figure 7 13 The Orbital Complex.
84 The Orbital Complex Bones of the nasal cavities and paranasal sinuses Frontal bone, sphenoid, and ethmoid Superior wall of nasal cavities Maxillae, lacrimal bones, ethmoid, and inferior nasal conchae Lateral walls of nasal cavities Maxillae and nasal bones Bridge of nose
85 The Orbital Complex Figure 7 14a The Nasal Complex.
86 The Orbital Complex Figure 7 14b The Nasal Complex.
87 The Orbital Complex Paranasal Sinuses Air-filled chambers connected to the nasal cavities Lighten skull bones Provide mucous epithelium (flushes nasal cavities)
88 Fontanelles The Infant Skull Grows rapidly Is large compared to the body Has many ossification centers Fusion is not complete at birth Two frontal bones Four occipital bones Several sphenoidal and temporal elements
89 Fontanelles Fontanelles (sometimes spelled fontanels) Are areas of fibrous connective tissue (soft spots) Cover unfused sutures in the infant skull Allow the skull to flex during birth Anterior fontanelle: frontal, sagittal, and coronal sutures Occipital fontanelle: lambdoid and sagittal sutures Sphenoidal fontanelles: squamous and coronal sutures Mastoid fontanelles: squamous and lambdoid sutures
90 Fontanelles Figure 7 15a The Skull of an Infant.
91 Fontanelles Figure 7 15b The Skull of an Infant.
92 The Vertebral Column The spine or vertebral column Protects the spinal cord Supports the head and body 26 bones 24 vertebrae, the sacrum, and the coccyx The Vertebral Column
93 The Vertebral Column Figure 7 16 The Vertebral Column.
94 The Vertebral Column Vertebrae The neck Seven cervical vertebrae The upper back 12 thoracic vertebrae Each articulates with one or more pair of ribs The lower back Five lumbar vertebrae
95 The Vertebral Column The Sacrum and Coccyx The fifth lumbar vertebra articulates with the sacrum The sacrum articulates with the coccyx
96 The Vertebral Column Four Curvatures of the Vertebral Column Cervical curve Thoracic curve Lumbar curve Sacral curve
97 The Vertebral Column Thoracic and sacral curves Are called primary curves (present during fetal development) Or accommodation curves (accommodate internal organs) Lumbar and cervical curves Are called secondary curves (appear after birth) Or compensation curves (shift body weight for upright posture)
98 The Vertebral Column Figure 7 17 Abnormal Curvatures of the Spine.
99 The Vertebral Column Structure of a Vertebra The vertebral body (centrum) Transfers weight along the spine The vertebral arch Posterior margin of vertebral foramen The articular processes Lateral projections between laminae and pedicles
100 The Vertebral Column Figure 7 18a Vertebral Anatomy.
101 The Vertebral Column Figure 7 18c Vertebral Anatomy.
102 The Vertebral Column Structure of a Vertebra The vertebral arch Pedicles: walls of the vertebral arch Laminae: roof of the vertebral arch Spinous process: projection where vertebral laminae fuse Transverse process: projection where laminae join pedicles
103 The Vertebral Column Structure of a Vertebra The articular processes Superior articular process Inferior articular process: have articular facets on articular faces
104 The Vertebral Column Figure 7 18 Vertebral Anatomy.
105 The Vertebral Column Vertebral Foramina Intervertebral foramina Gaps between pedicles of adjacent vertebrae For nerve connections to spinal cord Vertebral canal Formed by vertebral foramina Encloses the spinal cord Intervertebral Discs Are pads of fibrous cartilage Separate the vertebral bodies Absorb shocks
106 The Vertebral Column Figure 7 18 Vertebral Anatomy.
107 Vertebral Regions Vertebral Regions Vertebrae are numbered By region, from top (superior) to bottom(inferior) C 1 articulates with skull, L 5 with sacrum Vertebrae of each region Have characteristics determined by functions
108 Vertebral Regions Regions of the Vertebral Column Cervical (C) Thoracic (T) Lumbar (L) Sacral (S) Coccygeal (Co)
109 Vertebral Regions The Cervical Vertebrae Small body (support only head) Large vertebral foramen (largest part of spinal cord) Concave superior surface Slopes posterior to anterior C 1 (atlas) has no spinous process All others have short spinous processes tip of each spinous process is notched (bifid)
110 Vertebral Regions Figure 7 19 The Cervical Vertebrae.
111 Vertebral Regions The Cervical Vertebrae Transverse processes Are fused to costal processes Which encircle transverse foramina (protect arteries and veins) Atlas (C 1 ) Articulates with occipital condyles of skull Has no body or spinous process Has a large, round foramen within anterior and posterior arches
112 Vertebral Regions Figure 7 19 The Cervical Vertebrae.
113 Vertebral Regions The Cervical Vertebrae Axis (C 2 ) Supports the atlas Has heavy spinous process To attach muscles of head and neck Axis and atlas bodies fuse during development to form the dens Vertebra prominens (C 7 ) Transitions to thoracic vertebrae Has a long spinous process with a broad tubercle Has large transverse processes Ligamentum nuchae (elastic ligament) extends from C 7 to skull Rotation of Cervical Vertebrae
114 Vertebral Regions Figure 7 19 The Cervical Vertebrae.
115 Vertebral Regions Figure 7 19 The Cervical Vertebrae.
116 Vertebral Regions Thoracic vertebrae (T 1 T 12 ) Have heart-shaped bodies Larger bodies than in C 1 C 7 Smaller vertebral foramen than in C 1 C 7 Long, slender spinous processes Dorsolateral surfaces of body have costal facets: Which articulate with heads of ribs
117 Vertebral Regions Thoracic vertebrae (T 1 T 12 ) T 1 T 10 Have transverse costal facets On thick transverse processes for rib articulation Ribs at T 1 T 10 Contact costal and transverse costal facets T 1 T 8 articulate with two pairs of ribs At superior and inferior costal facets T 9 T 11 articulate with one pair of ribs T 10 T 12 transition to lumbar vertebrae 3D Rotation of Thoracic Vertebrae
118 Vertebral Regions Figure 7 20a The Thoracic Vertebrae.
119 Vertebral Regions Figure 7 20b The Thoracic Vertebrae.
120 Vertebral Regions Figure 7 20c The Thoracic Vertebrae.
121 Vertebral Regions Lumbar vertebrae (L 1 L 5 ) Largest vertebrae Oval-shaped bodies Thicker bodies than T 1 T 12 No costal or transverse costal facets Triangular vertebral foramen Superior articular processes Face up and in Inferior articular processes Face down and out
122 Vertebral Regions Lumbar vertebrae (L 1 L 5 ) Transverse processes Slender Project dorsolaterally Spinous process: Short, heavy For attachment of lower back muscles 3D Rotation of Lumbar Vertebrae
123 Vertebral Regions Figure 7 21a The Lumbar Vertebrae.
124 Vertebral Regions Figure 7 21b The Lumbar Vertebrae.
125 Vertebral Regions Figure 7 21c The Lumbar Vertebrae.
126 Vertebral Regions
127 Vertebral Regions
128 Vertebral Regions
129 Vertebral Regions The sacrum Is curved, more in males than in females Protects reproductive, urinary, and digestive organs Attaches The axial skeleton to pelvic girdle of appendicular skeleton Broad muscles that move the thigh The adult sacrum Consists of five fused sacral vertebrae Fuses between puberty and ages Leaving transverse lines
130 Vertebral Regions The sacrum Sacral canal Replaces the vertebral canal Sacral cornua Horn shaped Formed by laminae of the fifth sacral vertebra Which do not meet at midline Sacral hiatus Opening at the inferior end of the sacral canal Formed by ridges of sacral cornua Covered by connective tissues
131 Vertebral Regions The sacrum Median sacral crest Fused spinous processes Four pairs of sacral foramina open to either side Lateral sacral crest Fused transverse processes Attach to muscles of lower back and hip
132 Vertebral Regions The sacrum Auricular surface Thick, flattened area Articulates with pelvic girdle (forming sacroiliac joint) Sacral tuberosity Rough area Attaches ligaments of the sacroiliac joint
133 Vertebral Regions The sacrum Four regions of the sacrum Base: the broad superior surface Ala: wings at either side of the base to attach muscles Sacral promontory: at the center of the base Apex: the narrow inferior portion articulates with the coccyx
134 Vertebral Regions The coccyx Attaches ligaments and a constricting muscle of the anus Mature coccyx Consists of three to five fused coccygeal vertebrae First two coccygeal vertebrae: Have transverse processes Have unfused vertebral arches Coccygeal cornua Formed by laminae of first coccygeal vertebra 3D Rotation of Sacrum and Coccyx
135 Vertebral Regions Figure 7 22 The Sacrum and Coccyx.
136 The Thoracic Cage The skeleton of the chest Supports the thoracic cavity Consists of: thoracic vertebrae ribs sternum (breastbone) The Rib Cage Formed of ribs and sternum
137 The Thoracic Cage Figure 7 23a The Thoracic Cage.
138 The Thoracic Cage Figure 7 23b The Thoracic Cage.
139 The Thoracic Cage Functions of the Thoracic Cage Protects organs of the thoracic cavity Heart, lungs, and thymus Attaches muscles For respiration Of the vertebral column Of the pectoral girdle Of the upper limbs
140 The Thoracic Cage Ribs Are mobile Can absorb shock Functions of ribs Rib movements (breathing): affect width and depth of thoracic cage changing its volume
141 The Thoracic Cage Figure 7 24c The Ribs.
142 The Thoracic Cage Ribs (costae) Are 12 pairs of long, curved, flat bones Extending from the thoracic vertebrae Ribs are divided into two types True ribs False ribs
143 The Thoracic Cage Ribs 1 7 (true ribs) Vertebrosternal ribs Connected to the sternum by costal cartilages Ribs 8 12 (false ribs) Do not attach directly to the sternum Vertebrochondral ribs (ribs 8 10) Fuse together Merge with cartilage before reaching the sternum Floating or vertebral ribs (ribs 11 12) Connect only to the vertebrae and back muscles Have no connection with the sternum
144 The Thoracic Cage Figure 7 23 The Thoracic Cage.
145 The Thoracic Cage Structures of the Ribs The head (capitulum) At the vertebral end of the rib Has superior and inferior articular facets The neck The short area between the head and the tubercle
146 The Thoracic Cage Structures of the Ribs The tubercle (tuberculum) A small dorsal elevation Has an auricular facet that contacts the facet of its thoracic vertebra (at T 1 T 10 only) The tubercular body (shaft) Attaches muscles of the pectoral girdle and trunk Attaches to the intercostal muscles that move the ribs
147 The Thoracic Cage Figure 7 24a The Ribs.
148 The Thoracic Cage Figure 7 24b The Ribs.
149 The Thoracic Cage The sternum A flat bone In the midline of the thoracic wall Three parts of the sternum The manubrium The sternal body The xiphoid process
150 The Thoracic Cage Manubrium The superior portion of sternum Broad, triangular shape Articulates with clavicles (collarbones) Articulates with cartilages of first rib pair Has a jugular notch, a shallow indentation between clavicular articulations
151 The Thoracic Cage The sternal body Is tongue-shaped Attaches to the manubrium Attaches to costal cartilages of ribs 2 7 The xiphoid process Is the smallest part of the sternum Attaches to the sternal body Attaches to diaphragm and rectus abdominis muscles
152 The Thoracic Cage Figure 7 23 The Thoracic Cage.
153 The Thoracic Cage Development of the Sternum The developing sternal body Consists of four unfused bones Completes fusion about age 25 Leaving transverse lines The xiphoid process Is the last part of sternum to fuse Can easily be broken away
Biology 218 Human Anatomy. Adapted from Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 6 The Skeletal System: Axial Division
 Adapted from Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 6 The Skeletal System: Axial Division Introduction The axial skeleton: Composed of bones along the central axis of the body Divided into three regions:
Adapted from Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 6 The Skeletal System: Axial Division Introduction The axial skeleton: Composed of bones along the central axis of the body Divided into three regions:
APPENDICULAR SKELETON 126 AXIAL SKELETON SKELETAL SYSTEM. Cranium. Skull. Face. Skull and associated bones. Auditory ossicles. Associated bones.
 SKELETAL SYSTEM 206 AXIAL SKELETON 80 APPENDICULAR SKELETON 26 Skull Skull and associated s 29 Cranium Face Auditory ossicles 8 4 6 Associated s Hyoid Thoracic cage 25 Sternum Ribs 24 Vertebrae 24 column
SKELETAL SYSTEM 206 AXIAL SKELETON 80 APPENDICULAR SKELETON 26 Skull Skull and associated s 29 Cranium Face Auditory ossicles 8 4 6 Associated s Hyoid Thoracic cage 25 Sternum Ribs 24 Vertebrae 24 column
Chapter 7. Skeletal System
 Chapter 7 Skeletal System 1 Skull A. The skull is made up of 22 bones: 8 cranial bones, 13 facial bones, and the mandible. B. The Cranium encloses and protects the brain, provides attachments for muscles,
Chapter 7 Skeletal System 1 Skull A. The skull is made up of 22 bones: 8 cranial bones, 13 facial bones, and the mandible. B. The Cranium encloses and protects the brain, provides attachments for muscles,
Cranium Facial bones. Sternum Rib
 Figure 7.1 The human skeleton. Skull Thoracic cage (ribs and sternum) Cranium Facial bones Sternum Rib Bones of pectoral girdle Vertebral column Sacrum Vertebra Bones of pelvic girdle (a) Anterior view
Figure 7.1 The human skeleton. Skull Thoracic cage (ribs and sternum) Cranium Facial bones Sternum Rib Bones of pectoral girdle Vertebral column Sacrum Vertebra Bones of pelvic girdle (a) Anterior view
Chapter 7 Part A The Skeleton
 Chapter 7 Part A The Skeleton Why This Matters Understanding the anatomy of the skeleton enables you to anticipate problems such as pelvic dimensions that may affect labor and delivery The Skeleton The
Chapter 7 Part A The Skeleton Why This Matters Understanding the anatomy of the skeleton enables you to anticipate problems such as pelvic dimensions that may affect labor and delivery The Skeleton The
THE SKELETAL SYSTEM. Focus on the Skull
 THE SKELETAL SYSTEM Focus on the Skull Review Anatomical Terms Anterior/Posterior Dorsal/Ventral Medial/Lateral Superior/Inferior Bone Markings - Review Projections for attachment of muscles, ligaments
THE SKELETAL SYSTEM Focus on the Skull Review Anatomical Terms Anterior/Posterior Dorsal/Ventral Medial/Lateral Superior/Inferior Bone Markings - Review Projections for attachment of muscles, ligaments
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I Laboratory Version B Name Section. REVIEW SHEET Exercise 10 Axial Skeleton
 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I Laboratory Version B Name Section REVIEW SHEET Exercise 10 Axial Skeleton 1 POINT EACH. THE SKULL MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. The major components of the axial skeleton include the 7. The
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I Laboratory Version B Name Section REVIEW SHEET Exercise 10 Axial Skeleton 1 POINT EACH. THE SKULL MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. The major components of the axial skeleton include the 7. The
Skeletal System -Axial System. Chapter 7 Part A
 Skeletal System -Axial System Chapter 7 Part A Skeleton Learn: Names of the s. Identify specific landmarks that allow: Bones to fit into each other, Organs to fit into the cavities, Muscles to attach,
Skeletal System -Axial System Chapter 7 Part A Skeleton Learn: Names of the s. Identify specific landmarks that allow: Bones to fit into each other, Organs to fit into the cavities, Muscles to attach,
YOU MUST BRING YOUR OWN GLOVES FOR THIS ACTIVITY.
 ACTIVITY 3: AXIAL SKELETON AND LONG BONE DISSECTION Objectives: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapter 7, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 5e. All text references are for this textbook. Learning the meanings
ACTIVITY 3: AXIAL SKELETON AND LONG BONE DISSECTION Objectives: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapter 7, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 5e. All text references are for this textbook. Learning the meanings
Bones of the skull & face
 Bones of the skull & face Cranium= brain case or helmet Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. The cranium is composed of eight bones : frontal Occipital
Bones of the skull & face Cranium= brain case or helmet Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. The cranium is composed of eight bones : frontal Occipital
Skeletal system. Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi. E. mail:
 Skeletal system Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com Functions of Bone and The Skeletal System Support: The skeleton serves as the structural framework
Skeletal system Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com Functions of Bone and The Skeletal System Support: The skeleton serves as the structural framework
Anatomy and Physiology. Bones, Sutures, Teeth, Processes and Foramina of the Human Skull
 Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 6 DRO Bones, Sutures, Teeth, Processes and Foramina of the Human Skull Name: Period: Bones of the Human Skull Bones of the Cranium: Frontal bone: forms the forehead and the
Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 6 DRO Bones, Sutures, Teeth, Processes and Foramina of the Human Skull Name: Period: Bones of the Human Skull Bones of the Cranium: Frontal bone: forms the forehead and the
AXIAL SKELETON SKULL
 AXIAL SKELETON SKULL CRANIAL BONES (8 total flat bones w/ 2 paired) 1. Frontal forms forehead & upper portion of eyesocket (orbital) 2. Parietal paired bones; form superior & lateral walls of cranium 3.
AXIAL SKELETON SKULL CRANIAL BONES (8 total flat bones w/ 2 paired) 1. Frontal forms forehead & upper portion of eyesocket (orbital) 2. Parietal paired bones; form superior & lateral walls of cranium 3.
ACTIVITY 3: AXIAL SKELETON AND LONG BONE DISSECTION COW BONE DISSECTION
 ACTIVITY 3: AXIAL SKELETON AND LONG BONE DISSECTION Objectives: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapter 7, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 4e. All text references are for this textbook. Learning the meanings
ACTIVITY 3: AXIAL SKELETON AND LONG BONE DISSECTION Objectives: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapter 7, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 4e. All text references are for this textbook. Learning the meanings
Anatomy and Physiology 1 Chapter 7 self quiz Pro, Dima Darwish,MD.
 Anatomy and Physiology 1 Chapter 7 self quiz Pro, Dima Darwish,MD. 1) How many bones make up the axial skeleton? A) 50 B) 60 C) 70 D) 80 E) 90 2) Which of the following is a function of the axial skeleton?
Anatomy and Physiology 1 Chapter 7 self quiz Pro, Dima Darwish,MD. 1) How many bones make up the axial skeleton? A) 50 B) 60 C) 70 D) 80 E) 90 2) Which of the following is a function of the axial skeleton?
Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 07: The Skeletal System Axial Skeleton
 Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 07: The Skeletal System Axial Skeleton Question No. 1 of 10 Which of the following statements about the axial skeleton is correct? Question #01 A. The axial
Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 07: The Skeletal System Axial Skeleton Question No. 1 of 10 Which of the following statements about the axial skeleton is correct? Question #01 A. The axial
Structure Location Function
 Frontal Bone Cranium forms the forehead and roof of the orbits Occipital Bone Cranium forms posterior and inferior portions of the cranium Temporal Bone Cranium inferior to the parietal bone forms the
Frontal Bone Cranium forms the forehead and roof of the orbits Occipital Bone Cranium forms posterior and inferior portions of the cranium Temporal Bone Cranium inferior to the parietal bone forms the
Axial skeleton bones and markings
 Axial skeleton bones and markings Skull Cranial bones Frontal x 1 Supraorbital foramen Occipital x 1 Foramen magnum Occipital condyles Superior nuchal line Inferior nuchal line Anterior cranial fossa External
Axial skeleton bones and markings Skull Cranial bones Frontal x 1 Supraorbital foramen Occipital x 1 Foramen magnum Occipital condyles Superior nuchal line Inferior nuchal line Anterior cranial fossa External
Chapter 8A. The Skeletal System: The Axial Skeleton. The Skeletal System: The Axial Skeleton. Types of Bones. Types of Bones
 Chapter 8A The Skeletal System: The Axial Skeleton The Skeletal System: The Axial Skeleton 206 named bones Axial Skeleton 80 bones lie along longitudinal axis skull, hyoid, vertebrae, ribs, sternum, ear
Chapter 8A The Skeletal System: The Axial Skeleton The Skeletal System: The Axial Skeleton 206 named bones Axial Skeleton 80 bones lie along longitudinal axis skull, hyoid, vertebrae, ribs, sternum, ear
Chapter 7: Skeletal System: Gross Anatomy
 Chapter 7: Skeletal System: Gross Anatomy I. General Considerations A. How many bones in an average adult skeleton? B. Anatomic features of bones are based on II. Axial Skeleton A. Skull 1. Functionally
Chapter 7: Skeletal System: Gross Anatomy I. General Considerations A. How many bones in an average adult skeleton? B. Anatomic features of bones are based on II. Axial Skeleton A. Skull 1. Functionally
Chapter 7 The Skeletal System:The Axial Skeleton
 Chapter 7 The Skeletal System:The Axial Skeleton Axial Skeleton 80 bones lie along longitudinal axis skull, hyoid, vertebrae, ribs, sternum, ear ossicles Appendicular Skeleton 126 bones upper & lower limbs
Chapter 7 The Skeletal System:The Axial Skeleton Axial Skeleton 80 bones lie along longitudinal axis skull, hyoid, vertebrae, ribs, sternum, ear ossicles Appendicular Skeleton 126 bones upper & lower limbs
Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
 E. VERTEBRAL COLUMN 1. The vertebral column extends from the skull to the pelvis and forms the vertical axis of the skeleton. 2. The vertebral column is composed of vertebrae that are separated by intervertebral
E. VERTEBRAL COLUMN 1. The vertebral column extends from the skull to the pelvis and forms the vertical axis of the skeleton. 2. The vertebral column is composed of vertebrae that are separated by intervertebral
Crafton Hills College Human Anatomy & Physiology Axial Skeleton
 A. Major Divisions Crafton Hills College Human Anatomy & Physiology Axial keleton 1. Axial: Part of skeleton lies along long axis of body 2. Appendicular: Bones & features of the appendages B. AXIAL KELETON
A. Major Divisions Crafton Hills College Human Anatomy & Physiology Axial keleton 1. Axial: Part of skeleton lies along long axis of body 2. Appendicular: Bones & features of the appendages B. AXIAL KELETON
Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Figure Sectioned spinous process. Interspinous.
 PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Janice Meeking, Mount Royal College C H A P T E R 7 The Skeleton: Part B Vertebral Column Transmits weight of trunk to lower limbs Surrounds and protects spinal cord
PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Janice Meeking, Mount Royal College C H A P T E R 7 The Skeleton: Part B Vertebral Column Transmits weight of trunk to lower limbs Surrounds and protects spinal cord
o Diaphysis o Area where red marrow is found o Area where yellow marrow is found o Epiphyseal plate AXIAL SKELETON Skull
 64 Anatomy & Physiology Coloring Workbook 7. Figure 5-2A is a midlevel, cross-sectional view of the diaphysis of the femur. Label the membrane that lines the cavity and the membrane that covers the outside
64 Anatomy & Physiology Coloring Workbook 7. Figure 5-2A is a midlevel, cross-sectional view of the diaphysis of the femur. Label the membrane that lines the cavity and the membrane that covers the outside
The Skeletal System: Axial Skeleton
 The Skeletal System: Axial Skeleton The Big Idea The Axial Skeleton & Homeostasis The bones of the axial skeleton contribute to homeostasis by protecting many of the body s organs such as the brain, spinal
The Skeletal System: Axial Skeleton The Big Idea The Axial Skeleton & Homeostasis The bones of the axial skeleton contribute to homeostasis by protecting many of the body s organs such as the brain, spinal
CHAPTER 7, PART II (BONES)
 Anatomy Name: CHAPTER 7, PART II (BONES) Entry #: INSTRUCTIONS: 1) READ Chapter 7, pg. 140-161. 2) Using the outline, make a note card for each underlined bone name or phrase. 3) On each note card, put
Anatomy Name: CHAPTER 7, PART II (BONES) Entry #: INSTRUCTIONS: 1) READ Chapter 7, pg. 140-161. 2) Using the outline, make a note card for each underlined bone name or phrase. 3) On each note card, put
Biology 2401 The Skeletal System
 Biology 2401 The Skeletal System Purpose: The lab will describe the microscopic and gross anatomy of bone, identify bones of the body, and identify important bone markings. I. Overview of the Skeleton
Biology 2401 The Skeletal System Purpose: The lab will describe the microscopic and gross anatomy of bone, identify bones of the body, and identify important bone markings. I. Overview of the Skeleton
TEST YOURSELF- Chapter 7
 TEST YOURSELF- Chapter 7 Cranial Bones 1. Give the name of the bone for each of the following markings. Some of the markings are found on more than one bone. List all that apply. Cranium a. Frontal squama:
TEST YOURSELF- Chapter 7 Cranial Bones 1. Give the name of the bone for each of the following markings. Some of the markings are found on more than one bone. List all that apply. Cranium a. Frontal squama:
Exercise 10. The Axial Skeleton
 Exercise 10 The Axial Skeleton The Axial Skeleton Consists of the skeletal structures found along the midline of the body. Includes the skull, hyoid, vertebrae, ribs, sternum, and sacrum. The cartilages
Exercise 10 The Axial Skeleton The Axial Skeleton Consists of the skeletal structures found along the midline of the body. Includes the skull, hyoid, vertebrae, ribs, sternum, and sacrum. The cartilages
External Acoustic Meatus. Mastoid Process. Zygomatic Process. Temporal Bone
 Bone lab review 1. Frontal Bone 2. Supra-Orbital Foramen 3. Orbit (Orbital Cavity) 4. Superior Orbital Fissure 5. Inferior Orbital Fissure 6. Zygomatic Bone 7. Infra-Orbital Foramen 8. Maxilla 9. Mandible
Bone lab review 1. Frontal Bone 2. Supra-Orbital Foramen 3. Orbit (Orbital Cavity) 4. Superior Orbital Fissure 5. Inferior Orbital Fissure 6. Zygomatic Bone 7. Infra-Orbital Foramen 8. Maxilla 9. Mandible
Skull-2. Norma Basalis Interna Norma Basalis Externa. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology
 Skull-2 Norma Basalis Interna Norma Basalis Externa Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Norma basalis interna Base of the skull- superior view The interior of the base of the
Skull-2 Norma Basalis Interna Norma Basalis Externa Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Norma basalis interna Base of the skull- superior view The interior of the base of the
An Introduction to the Axial Skeleton. Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings
 An Introduction to the Axial Skeleton Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings Terms: Structures of Bones Articulations: Contacts with other bones Landmarks (Bone
An Introduction to the Axial Skeleton Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings Terms: Structures of Bones Articulations: Contacts with other bones Landmarks (Bone
Spring Written By: J. E. Sutton. Contents: I. Overview of the Skeleton: II. Appendicular Skeleton III. Axial Skeleton IV.
 Spring 2012 Written By: J. E. Sutton Contents: I. Overview of the Skeleton: II. Appendicular Skeleton III. Axial Skeleton IV. Articulations Overview of the Skeleton: I. Orientation to Human Skeleton: a.
Spring 2012 Written By: J. E. Sutton Contents: I. Overview of the Skeleton: II. Appendicular Skeleton III. Axial Skeleton IV. Articulations Overview of the Skeleton: I. Orientation to Human Skeleton: a.
Bone Flashcards for 10a
 Bone Flashcards for 0a CLAVICLE (collar bone). Sternal extremity (end) flat end. Acromial extremity (end) rounded end. SCAPULA (shoulder blade). Right or left scapula?. Superior border (superior margin).
Bone Flashcards for 0a CLAVICLE (collar bone). Sternal extremity (end) flat end. Acromial extremity (end) rounded end. SCAPULA (shoulder blade). Right or left scapula?. Superior border (superior margin).
Human Anatomy & Physiology I Dr. Sullivan Unit VIIIa The Axial Skeleton Chapter 8 (Sections )
 Human Anatomy & Physiology I Dr. Sullivan Unit VIIIa The Axial Skeleton Chapter 8 (Sections 8.1-8.3) I. Divisions of the skeletal system a) An adult human skeleton has 206 named bones b) Most are paired
Human Anatomy & Physiology I Dr. Sullivan Unit VIIIa The Axial Skeleton Chapter 8 (Sections 8.1-8.3) I. Divisions of the skeletal system a) An adult human skeleton has 206 named bones b) Most are paired
Labs 9 and 10. Classification of Bones. Bone Shapes 1/05/13. Skeletal system overview. Bone are identified by:
 Labs 9 and 10 Skeletal system overview Classification of Bones Bone are identified by: shape internal tissues bone markings 1. Flat bones 2. Long bones 3. Short bones 4. Irregular bones 5. Sutural bones
Labs 9 and 10 Skeletal system overview Classification of Bones Bone are identified by: shape internal tissues bone markings 1. Flat bones 2. Long bones 3. Short bones 4. Irregular bones 5. Sutural bones
Axial Skeleton: Vertebrae and Thorax
 Axial Skeleton: Vertebrae and Thorax Function of the vertebral column (spine or backbone): 1) 2) 3) Composition of Vertebral column The vertebral column is formed by 33 individual vertebrae (some of which
Axial Skeleton: Vertebrae and Thorax Function of the vertebral column (spine or backbone): 1) 2) 3) Composition of Vertebral column The vertebral column is formed by 33 individual vertebrae (some of which
Skeletal system overview. Classification of Bones
 Skeletal system overview BIOL241 Lab #9 Classification of Bones Bone are identified by: shape internal tissues bone markings 1 1. Flat bones 2. Long bones 3. Short bones 4. Irregular bones 5. Sutural bones
Skeletal system overview BIOL241 Lab #9 Classification of Bones Bone are identified by: shape internal tissues bone markings 1 1. Flat bones 2. Long bones 3. Short bones 4. Irregular bones 5. Sutural bones
BIO 137 AXIAL SKELETON BONE STUDY THE HUMAN SKELETON
 BIO 137 THE AXIAL SKELETON MARY CATHERINE FLATH, Ph.D. THE HUMAN SKELETON AXIAL SKULL HYOID THORACIC CAGE VERTEBRAL COLUMN APPENDICULAR PECTORAL GIRDLE UPPER LIMBS PELVIC GIRDLE LOWER LIMBS AXIAL SKELETON
BIO 137 THE AXIAL SKELETON MARY CATHERINE FLATH, Ph.D. THE HUMAN SKELETON AXIAL SKULL HYOID THORACIC CAGE VERTEBRAL COLUMN APPENDICULAR PECTORAL GIRDLE UPPER LIMBS PELVIC GIRDLE LOWER LIMBS AXIAL SKELETON
11/25/2012. Chapter 7 Part 2: Bones! Skeletal Organization. The Skull. Skull Bones to Know Cranium
 Chapter 7 Part 2: Bones! 5) Distinguish between the axial and appendicular skeletons and name the major parts of each 6) Locate and identify the bones and the major features of the bones that compose the
Chapter 7 Part 2: Bones! 5) Distinguish between the axial and appendicular skeletons and name the major parts of each 6) Locate and identify the bones and the major features of the bones that compose the
BONE CHALLENGE DANIL HAMMOUDI.MD
 BONE CHALLENGE DANIL HAMMOUDI.MD Bone Basic functions? A. support B. protection C. movement assistance in D. RBC formation-hemopoiesis E. mineral homeostasis +importance of calcium F. energy supply -yellow
BONE CHALLENGE DANIL HAMMOUDI.MD Bone Basic functions? A. support B. protection C. movement assistance in D. RBC formation-hemopoiesis E. mineral homeostasis +importance of calcium F. energy supply -yellow
SKULL AS A WHOLE + ANTERIOR CRANIAL FOSSA
 SKULL AS A WHOLE + ANTERIOR CRANIAL FOSSA LEARNING OBJECTIVES At the end of this lecture, the student should be able to know: Parts of skeleton (axial and appendicular) Parts of skull Sutures of skull
SKULL AS A WHOLE + ANTERIOR CRANIAL FOSSA LEARNING OBJECTIVES At the end of this lecture, the student should be able to know: Parts of skeleton (axial and appendicular) Parts of skull Sutures of skull
Overview of the Skeleton: Bone Markings
 Name Overview of the Skeleton: Bone Markings Match the terms in column B with the appropriate description in column A. Column A 1. sharp, slender process* 2. small rounded projection* 3. narrow ridge of
Name Overview of the Skeleton: Bone Markings Match the terms in column B with the appropriate description in column A. Column A 1. sharp, slender process* 2. small rounded projection* 3. narrow ridge of
the Skeletal System provided by Academic Web Services Grand Canyon University
 Anatomy Resource Center Study Guides the Skeletal System HEAD & NECK REGIONAL VIEW SKULL BONES CRANIUM FACE SKULL LANDMARKS ANTERIOR SIDE SUPERIOR/INFERIOR VERTEBRAL COLUMN VERTEBRAL REGIONS CERVICAL C1
Anatomy Resource Center Study Guides the Skeletal System HEAD & NECK REGIONAL VIEW SKULL BONES CRANIUM FACE SKULL LANDMARKS ANTERIOR SIDE SUPERIOR/INFERIOR VERTEBRAL COLUMN VERTEBRAL REGIONS CERVICAL C1
Vertebral Column. Backbone consists of 26 vertebrae. Five vertebral regions. Cervical
 Vertebral Column Backbone consists of 26 vertebrae. Five vertebral regions Cervical vertebrae (7) in the neck. Thoracic vertebrae (12) in the thorax. Lumbar vertebrae (5) in the lower back. Sacrum (5,
Vertebral Column Backbone consists of 26 vertebrae. Five vertebral regions Cervical vertebrae (7) in the neck. Thoracic vertebrae (12) in the thorax. Lumbar vertebrae (5) in the lower back. Sacrum (5,
Skeletal System: Skull.
 Skeletal System: Skull www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz Bones of the Skull SPLANCHNOCRANIUM Nasal (2) Maxilla (2) Lacrimal (2) Zygomatic (2) Palatine (2) Inferior concha (2) Vomer Mandible NEUROCRANIUM Frontal
Skeletal System: Skull www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz Bones of the Skull SPLANCHNOCRANIUM Nasal (2) Maxilla (2) Lacrimal (2) Zygomatic (2) Palatine (2) Inferior concha (2) Vomer Mandible NEUROCRANIUM Frontal
Bio 5/6 5 The Skeletal System Study Guide
 Name: THE SKELETAL SYSTEM: 5 The Skeletal System Study Guide Period: The skeleton is constructed of two of the most supportive tissues found in the human body - cartilage and bone. Besides supporting and
Name: THE SKELETAL SYSTEM: 5 The Skeletal System Study Guide Period: The skeleton is constructed of two of the most supportive tissues found in the human body - cartilage and bone. Besides supporting and
Chapter 7 Part B The Skeleton
 Chapter 7 Part B The Skeleton 7.2 The Vertebral Column General Characteristics Extends from skull to pelvis Also called spine or spinal column Functions to transmit weight of trunk to lower limbs, surround
Chapter 7 Part B The Skeleton 7.2 The Vertebral Column General Characteristics Extends from skull to pelvis Also called spine or spinal column Functions to transmit weight of trunk to lower limbs, surround
University of Palestine. Midterm Exam 2013/2014 Total Grade:
 Course No: DNTS2208 Course Title: Head and Neck Anatomy Date: 09/11/2013 No. of Questions: (50) Time: 1hour Using Calculator (No) University of Palestine Midterm Exam 2013/2014 Total Grade: Instructor
Course No: DNTS2208 Course Title: Head and Neck Anatomy Date: 09/11/2013 No. of Questions: (50) Time: 1hour Using Calculator (No) University of Palestine Midterm Exam 2013/2014 Total Grade: Instructor
The Skeletal System. Parts of the skeletal system. Bones (Skeleton) Joints Cartilages Ligaments
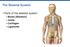 The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system Bones (Skeleton) Joints Cartilages Ligaments Functions of the Bones Support Internal framework of the body Protection Skull and vertebrae protect brain
The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system Bones (Skeleton) Joints Cartilages Ligaments Functions of the Bones Support Internal framework of the body Protection Skull and vertebrae protect brain
Dr.Noor Hashem Mohammad Lecture (5)
 Dr.Noor Hashem Mohammad Lecture (5) 2016-2017 If the mandible is discarded, the anterior part of this aspect of the skull is seen to be formed by the hard palate. The palatal processes of the maxillae
Dr.Noor Hashem Mohammad Lecture (5) 2016-2017 If the mandible is discarded, the anterior part of this aspect of the skull is seen to be formed by the hard palate. The palatal processes of the maxillae
Perpendicular Plate Zygomatic Bone. Mental Foramen Mandible
 Glabella Frontal Middle Nasal Concha Nasal Lacrimal Perpendicular Plate Zygomatic Inferior Nasal Concha Maxilla Mental Mandible Skull (anterior view) Squamosal Suture Coronal Suture Frontal Parietal Nasal
Glabella Frontal Middle Nasal Concha Nasal Lacrimal Perpendicular Plate Zygomatic Inferior Nasal Concha Maxilla Mental Mandible Skull (anterior view) Squamosal Suture Coronal Suture Frontal Parietal Nasal
Skull basic structures. Neurocranium
 Assoc. Prof. Květuše Lovásová, M.V.D., PhD. Skull basic structures Skull consists of two groups of bones: neurocranium (bones forming the brain box) splanchnocranium (bones forming the facial skeleton)
Assoc. Prof. Květuše Lovásová, M.V.D., PhD. Skull basic structures Skull consists of two groups of bones: neurocranium (bones forming the brain box) splanchnocranium (bones forming the facial skeleton)
Lab Exercise #04 The Skeletal System Student Performance Objectives
 Lab Exercise #04 The Skeletal System Student Performance Objectives The material that you are required to learn in this exercise can be found in either the lecture text or the supplemental materials provided
Lab Exercise #04 The Skeletal System Student Performance Objectives The material that you are required to learn in this exercise can be found in either the lecture text or the supplemental materials provided
SKELETON FUNCTIONS OF BONE:
 SKELETON FUNCTIONS OF BONE: SKELETON: 1. Performs a mechanical function in forming the skeletal support of the body and in forming a leverage system whereby work and movement are possible. 2. Serves as
SKELETON FUNCTIONS OF BONE: SKELETON: 1. Performs a mechanical function in forming the skeletal support of the body and in forming a leverage system whereby work and movement are possible. 2. Serves as
Riverside Community College Anatomy & Physiology 2B SPRING 2012 EXAM #1-ABC (Nervous System)
 Riverside Community College Anatomy & Physiology 2B SPRING 2012 EXAM #1-ABC (Nervous System) Name: 1) This vertebra is an example of a(n). 1) A) thoracic B) axis C) atlas D) lumbar E) sacral 1 2) W hich
Riverside Community College Anatomy & Physiology 2B SPRING 2012 EXAM #1-ABC (Nervous System) Name: 1) This vertebra is an example of a(n). 1) A) thoracic B) axis C) atlas D) lumbar E) sacral 1 2) W hich
Anatomy images for MSS practical exam- 2019
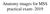 Anatomy images for MSS practical exam- 2019 Ilium Ischium Pubis Acetabulaum Iliac crest Iliac tubercle ASIS (muscle and ligament attached) AIIS (muscle attached) PSIS PIIS Ischial spine Ischial tuberosity
Anatomy images for MSS practical exam- 2019 Ilium Ischium Pubis Acetabulaum Iliac crest Iliac tubercle ASIS (muscle and ligament attached) AIIS (muscle attached) PSIS PIIS Ischial spine Ischial tuberosity
Skeletal System - Prelab 1
 Skeletal System - Prelab 1 1. Which bones contain the paranasal sinuses? What function do the sinuses serve? 2. What two areas are separated from each other by the hard palate? Name the two bones that
Skeletal System - Prelab 1 1. Which bones contain the paranasal sinuses? What function do the sinuses serve? 2. What two areas are separated from each other by the hard palate? Name the two bones that
Human Anatomy - Problem Drill 06: The Skeletal System Axial Skeleton & Articualtions
 Human Anatomy - Problem Drill 06: The Skeletal System Axial Skeleton & Articualtions Question No. 1 of 10 Instructions: (1) Read the problem and answer choices carefully, (2) Work the problems on paper
Human Anatomy - Problem Drill 06: The Skeletal System Axial Skeleton & Articualtions Question No. 1 of 10 Instructions: (1) Read the problem and answer choices carefully, (2) Work the problems on paper
locomotice system Plastinated specimensⅠ: Silicone specimens Regional specimens and organs
 locomotice system Plastinated specimensⅠ: Silicone specimens Regional specimens and organs Art-No. Name Description The locomotor system SL001 Two hundred pieces of plastinated bones (without six The bones
locomotice system Plastinated specimensⅠ: Silicone specimens Regional specimens and organs Art-No. Name Description The locomotor system SL001 Two hundred pieces of plastinated bones (without six The bones
University of Palestine. Midterm Exam 2013/2014 Total Grade:
 [ Course No: DNTS2208 Course Title: Head and Neck Anatomy Date: 17/11/1024 No. of Questions: (52) Time: 2hours Using Calculator (No) University of Palestine Midterm Exam 2013/2014 Total Grade: Instructor
[ Course No: DNTS2208 Course Title: Head and Neck Anatomy Date: 17/11/1024 No. of Questions: (52) Time: 2hours Using Calculator (No) University of Palestine Midterm Exam 2013/2014 Total Grade: Instructor
Bones Ethmoid bone Inferior nasal concha Lacrimal bone Maxilla Nasal bone Palatine bone Vomer Zygomatic bone Mandible
 splanchnocranium - Consists of part of skull that is derived from branchial arches - The facial bones are the bones of the anterior and lower human skull Bones Ethmoid bone Inferior nasal concha Lacrimal
splanchnocranium - Consists of part of skull that is derived from branchial arches - The facial bones are the bones of the anterior and lower human skull Bones Ethmoid bone Inferior nasal concha Lacrimal
Musculoskeletal System (Part A-1) Module 7 -Chapter 10 Overview. Functions
 Musculoskeletal System (Part A-1) Module 7 -Chapter 10 Overview Susie Turner, M.D. 1/8/13 Muscles Attachments Bones Bone types Surface features of bones Divisions of the skeletal system Joints or Articulations
Musculoskeletal System (Part A-1) Module 7 -Chapter 10 Overview Susie Turner, M.D. 1/8/13 Muscles Attachments Bones Bone types Surface features of bones Divisions of the skeletal system Joints or Articulations
Biology 210 Chapter 8: Skeletal Tissues Supplement 1
 Biology 210 Chapter 8: Skeletal Tissues Supplement 1 By John McGill Material contributed by Beth Wyatt & Jack Bagwell DIVISIONS OF THE SKELETAL SYSTEM AXIAL SKELETON (80 BONES) Bones of the Head, Neck,
Biology 210 Chapter 8: Skeletal Tissues Supplement 1 By John McGill Material contributed by Beth Wyatt & Jack Bagwell DIVISIONS OF THE SKELETAL SYSTEM AXIAL SKELETON (80 BONES) Bones of the Head, Neck,
The Skull DANIL HAMMOUDI.MD
 The Skull DANIL HAMMOUDI.MD summary of bones/structures in Chapter 15 of the manual need tp be print as soon as possible http://www.mnsu.edu/emuseum/biology/humananatomy/skeletal/skul l/frontal/frontal.html
The Skull DANIL HAMMOUDI.MD summary of bones/structures in Chapter 15 of the manual need tp be print as soon as possible http://www.mnsu.edu/emuseum/biology/humananatomy/skeletal/skul l/frontal/frontal.html
Nervous & Skeletal Systems. Virtual Science University
 Nervous & Skeletal Systems Virtual Science University 1 Nervous & Skeletal Systems Texas TEK B.10(A) The student will interpret the function of systems in organisms (humans) including the nervous and skeletal
Nervous & Skeletal Systems Virtual Science University 1 Nervous & Skeletal Systems Texas TEK B.10(A) The student will interpret the function of systems in organisms (humans) including the nervous and skeletal
SKULL / CRANIUM BONES OF THE NEUROCRANIUM (7) Occipital bone (1) Sphenoid bone (1) Temporal bone (2) Frontal bone (1) Parietal bone (2)
 Important! 1. Memorizing these pages only does not guarantee the succesfull passing of the midterm test or the semifinal exam. 2. The handout has not been supervised, and I can not guarantee, that these
Important! 1. Memorizing these pages only does not guarantee the succesfull passing of the midterm test or the semifinal exam. 2. The handout has not been supervised, and I can not guarantee, that these
Dr. Sami Zaqout, IUG Medical School
 The skull The skull is composed of several separate bones united at immobile joints called sutures. Exceptions? Frontal bone Occipital bone Vault Cranium Sphenoid bone Zygomatic bones Base Ethmoid bone
The skull The skull is composed of several separate bones united at immobile joints called sutures. Exceptions? Frontal bone Occipital bone Vault Cranium Sphenoid bone Zygomatic bones Base Ethmoid bone
A. Incorrect! The axial skeleton includes bones of the skull, inner ear, chest and spinal column.
 Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 07: The Skeletal System II No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following statements about the axial skeleton is correct? A. The axial skeleton includes bones of the skull,
Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 07: The Skeletal System II No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following statements about the axial skeleton is correct? A. The axial skeleton includes bones of the skull,
The Axial Skeleton Hyoid Bone. Lecture Overview. Marieb s Human Anatomy and Physiology. Chapter 7 The Axial and Appendicular Skeleton Lecture 14
 Marieb s Human Anatomy and Physiology Marieb Hoehn Chapter 7 The Axial and Appendicular Skeleton Lecture 14 1 Axial Skeleton Hyoid bone Bones of the orbit Paranasal sinuses Infantile skull Vertebral column
Marieb s Human Anatomy and Physiology Marieb Hoehn Chapter 7 The Axial and Appendicular Skeleton Lecture 14 1 Axial Skeleton Hyoid bone Bones of the orbit Paranasal sinuses Infantile skull Vertebral column
View of a Skull, 1489 by Leonardo Da Vinci. Kaan Yücel M.D., Ph.D Tuesday
 View of a Skull, 1489 by Leonardo Da Vinci Kaan Yücel M.D., Ph.D. 26.11.2013 Tuesday 1.SKULL skeleton of the head cranium 22 bones excluding ossicles of the ear 1.SKULL Mandible Lower jaw bone Neurocranium
View of a Skull, 1489 by Leonardo Da Vinci Kaan Yücel M.D., Ph.D. 26.11.2013 Tuesday 1.SKULL skeleton of the head cranium 22 bones excluding ossicles of the ear 1.SKULL Mandible Lower jaw bone Neurocranium
THE THORACIC WALL. Boundaries Posteriorly by the thoracic part of the vertebral column. Anteriorly by the sternum and costal cartilages
 THE THORACIC WALL Boundaries Posteriorly by the thoracic part of the vertebral column Anteriorly by the sternum and costal cartilages Laterally by the ribs and intercostal spaces Superiorly by the suprapleural
THE THORACIC WALL Boundaries Posteriorly by the thoracic part of the vertebral column Anteriorly by the sternum and costal cartilages Laterally by the ribs and intercostal spaces Superiorly by the suprapleural
Skeletal System. It s all about the bones!!!
 Skeletal System It s all about the bones!!! The Skeletal System in Action!! The Skeletal System in Action! https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=icwllrqkv cg&list=plzile25upgebvru0jneppcabh0fhktgt Q 1. FYI 5
Skeletal System It s all about the bones!!! The Skeletal System in Action!! The Skeletal System in Action! https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=icwllrqkv cg&list=plzile25upgebvru0jneppcabh0fhktgt Q 1. FYI 5
Important Parts of Bones
 Important Parts of Bones For 2015 Know: Humerus (posterior) Clavical Femur (Anterior) Foot Hand Mandible Os Coxa Scapula Skull (Anterior, Inferior, Lateral) Sternum Humerus (posterior) A. olecranon fossa
Important Parts of Bones For 2015 Know: Humerus (posterior) Clavical Femur (Anterior) Foot Hand Mandible Os Coxa Scapula Skull (Anterior, Inferior, Lateral) Sternum Humerus (posterior) A. olecranon fossa
Anatomy and Physiology II. Review Spine and Neck
 Anatomy and Physiology II Review Spine and Neck Spine regions How many cervical vertibrae are there? 7 The curvature is the cervical region posterior? Concave posterior How many thoracic? And curvature?
Anatomy and Physiology II Review Spine and Neck Spine regions How many cervical vertibrae are there? 7 The curvature is the cervical region posterior? Concave posterior How many thoracic? And curvature?
in compact bone, large vertical canals carrying blood vessels and nerves. in compact bone, large horizontal canals carrying blood vessels and nerves.
 Carl Christensen, PhD Skeletal System (Bones`) Bio. 2304 Human Anatomy 1. Identify a term for each of the following: shaft of a long bone ends of a long bone ossified remnant of the "growth plate" connective
Carl Christensen, PhD Skeletal System (Bones`) Bio. 2304 Human Anatomy 1. Identify a term for each of the following: shaft of a long bone ends of a long bone ossified remnant of the "growth plate" connective
Anatomy Skull and Spinal Cord
 1 Anatomy Skull and Spinal Cord 1. Skull The skull is anterior to the spinal column and is the bony structure that encases the brain. Its purpose is to protect the brain and allow attachments for the facial
1 Anatomy Skull and Spinal Cord 1. Skull The skull is anterior to the spinal column and is the bony structure that encases the brain. Its purpose is to protect the brain and allow attachments for the facial
The SKELETAL System. The framework of bones and cartilage which protect organs, and provides a lever system that allows locomotion.
 The SKELETAL System The framework of bones and cartilage which protect organs, and provides a lever system that allows locomotion. Functions of the Skeletal System Support Protection Movement Facilitation
The SKELETAL System The framework of bones and cartilage which protect organs, and provides a lever system that allows locomotion. Functions of the Skeletal System Support Protection Movement Facilitation
Introduction to Local Anesthesia and Review of Anatomy
 5-Sep Introduction and Anatomy Review 12-Sep Neurophysiology and Pain 19-Sep Physiology and Pharmacology part 1 26-Sep Physiology and Pharmacology part 2 Introduction to Local Anesthesia and Review of
5-Sep Introduction and Anatomy Review 12-Sep Neurophysiology and Pain 19-Sep Physiology and Pharmacology part 1 26-Sep Physiology and Pharmacology part 2 Introduction to Local Anesthesia and Review of
Infratemporal fossa: Tikrit University college of Dentistry Dr.Ban I.S. head & neck Anatomy 2 nd y.
 Infratemporal fossa: This is a space lying beneath the base of the skull between the lateral wall of the pharynx and the ramus of the mandible. It is also referred to as the parapharyngeal or lateral pharyngeal
Infratemporal fossa: This is a space lying beneath the base of the skull between the lateral wall of the pharynx and the ramus of the mandible. It is also referred to as the parapharyngeal or lateral pharyngeal
Lab 6, 7, 8: Skeletal System
 107 Lab 6, 7, 8: Skeletal System Adult Skull Bony orbit (FLEZMS) Frontal bone supraorbital foramen frontal sinus Lacrimal bone Ethmoid bone perpendicular plate of ethmoid middle nasal conchae cribriform
107 Lab 6, 7, 8: Skeletal System Adult Skull Bony orbit (FLEZMS) Frontal bone supraorbital foramen frontal sinus Lacrimal bone Ethmoid bone perpendicular plate of ethmoid middle nasal conchae cribriform
Skull-2. Norma Basalis Interna. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Assistant Professor of Anatomy and Histology
 Skull-2 Norma Basalis Interna Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Assistant Professor of Anatomy and Histology Norma basalis interna Base of the skull- superior view The interior of the base of the skull is divided into
Skull-2 Norma Basalis Interna Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Assistant Professor of Anatomy and Histology Norma basalis interna Base of the skull- superior view The interior of the base of the skull is divided into
Objectives continued- Answer each of the objectives on a separate sheet of paper to demonstrate content mastery. Attach answers to back of packet.
 Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 5: The Skeletal System Name: Objectives- By the end of this chapter I will be able to: 1. Identify the subdivisions of the skeleton as axial or appendicular. 2. List at least
Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 5: The Skeletal System Name: Objectives- By the end of this chapter I will be able to: 1. Identify the subdivisions of the skeleton as axial or appendicular. 2. List at least
SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question.
 Exam Name SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. Figure 7.1 Using Figure 7.1, match the following: 1) Articulates with hip bones of the pelvis.
Exam Name SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. Figure 7.1 Using Figure 7.1, match the following: 1) Articulates with hip bones of the pelvis.
A&P 1 Skeletal Lab Week 1 Pre-lab Guide Skeletal Background Information
 A&P 1 Skeletal Lab Week 1 Pre-lab Guide Skeletal Background Information Note: These notes are very similar to those found in your lecture notes. This info is for BOTH LECTURE AND LAB! Read through them
A&P 1 Skeletal Lab Week 1 Pre-lab Guide Skeletal Background Information Note: These notes are very similar to those found in your lecture notes. This info is for BOTH LECTURE AND LAB! Read through them
BIOLOGY 113 LABORATORY Skeletal System
 BIOLOGY 113 LABORATORY Skeletal System Objectives Distinguish between the axial and appendicular skeleton. Distinguish between the cranium and facial skeleton. Locate and name the bones of the skull and
BIOLOGY 113 LABORATORY Skeletal System Objectives Distinguish between the axial and appendicular skeleton. Distinguish between the cranium and facial skeleton. Locate and name the bones of the skull and
The Thoracic Cage ANATOMY 2: THORACIC CAGE AND VERTEBRAL COLUMN
 ANATOMY 2: THORACIC CAGE AND VERTEBRAL COLUMN PSK 4U Mr. S. Kelly North Grenville DHS The Thoracic Cage 7 true ribs 3 false ribs 2 floating ribs Clavicle = collarbone Manubrium Sternum Xiphoid Process
ANATOMY 2: THORACIC CAGE AND VERTEBRAL COLUMN PSK 4U Mr. S. Kelly North Grenville DHS The Thoracic Cage 7 true ribs 3 false ribs 2 floating ribs Clavicle = collarbone Manubrium Sternum Xiphoid Process
Lab Unit One Flashcards
 CLAVICLE (collar bone). Sternal extremity (end) flat end. Acromial extremity (end) rounded end.. Conoid tubercle near round end SCAPULA (shoulder blade). Right or left scapula?. Superior border (superior
CLAVICLE (collar bone). Sternal extremity (end) flat end. Acromial extremity (end) rounded end.. Conoid tubercle near round end SCAPULA (shoulder blade). Right or left scapula?. Superior border (superior
Frontal Anterior cranium Supraorbital margins. Glabella Frontal sinus Coronal suture Parietal Superior/lateral cranium Sagittal suture
 The Skeleton Outline PART 1: THE AXIAL SKELETON I. The skull consists of 8 cranial bones and 14 facial bones (pp. 200 218; Figs. 7.1 7.18; Table 7.1). A. The cranial and facial bones form the framework
The Skeleton Outline PART 1: THE AXIAL SKELETON I. The skull consists of 8 cranial bones and 14 facial bones (pp. 200 218; Figs. 7.1 7.18; Table 7.1). A. The cranial and facial bones form the framework
Chapter 7: Head & Neck
 Chapter 7: Head & Neck Osteology I. Overview A. Skull The cranium is composed of irregularly shaped bones that are fused together at unique joints called sutures The skull provides durable protection from
Chapter 7: Head & Neck Osteology I. Overview A. Skull The cranium is composed of irregularly shaped bones that are fused together at unique joints called sutures The skull provides durable protection from
Bone List Anatomy
 1 Frontal Bone Skull 2 Parietal Bone Skull 3 Occipital Bone Skull 4 Temporal Bone Skull 5 Coronal Suture Skull 6 Sagittal Suture Skull 7 Squamous suture Skull 8 Lambdoid Suture Skull 9 Surpaorbital Ridge
1 Frontal Bone Skull 2 Parietal Bone Skull 3 Occipital Bone Skull 4 Temporal Bone Skull 5 Coronal Suture Skull 6 Sagittal Suture Skull 7 Squamous suture Skull 8 Lambdoid Suture Skull 9 Surpaorbital Ridge
Chapter 7: Skeletal System
 Chapter 7: Skeletal System The Skeletal System Introduction P. 182 Bone is an organ made up of tissues: It is made up of the following components. Cartilage Blood Nerves Bone Connective Bone Classification
Chapter 7: Skeletal System The Skeletal System Introduction P. 182 Bone is an organ made up of tissues: It is made up of the following components. Cartilage Blood Nerves Bone Connective Bone Classification
Anatomy Made Easy MSS
 Anatomy Made Easy MSS part #1 هذا الملف يشمل تفريغ المحاضرة الثانية لعون بدءا من الصفحة 11 وحتى األخير Done By :MohamedA. Diabat Edited by Awn Academic team The Axial Skeleton The axial skeleton consist
Anatomy Made Easy MSS part #1 هذا الملف يشمل تفريغ المحاضرة الثانية لعون بدءا من الصفحة 11 وحتى األخير Done By :MohamedA. Diabat Edited by Awn Academic team The Axial Skeleton The axial skeleton consist
The Thoracic Cage. Role of the Thoracic Cage 2/13/2019. Anatomy 2: Thoracic Cage and Vertebral Column
 PSK 4U Mr. S. Kelly North Grenville DHS Anatomy 2: Thoracic Cage and Column The Thoracic Cage 7 true ribs 3 false ribs 2 floating ribs Clavicle = collarbone Manubrium Sternum Xiphoid Process 12 thoracic
PSK 4U Mr. S. Kelly North Grenville DHS Anatomy 2: Thoracic Cage and Column The Thoracic Cage 7 true ribs 3 false ribs 2 floating ribs Clavicle = collarbone Manubrium Sternum Xiphoid Process 12 thoracic
Anatomy and Physiology II. Spine
 Anatomy and Physiology II Spine Bones and Other Structures Vertibrae Contains Cervical, Thoracic, Lumbar, Sacral and Coccygeal regions We use Capital letters to refer to these (C, T, L, S, and Co) and
Anatomy and Physiology II Spine Bones and Other Structures Vertibrae Contains Cervical, Thoracic, Lumbar, Sacral and Coccygeal regions We use Capital letters to refer to these (C, T, L, S, and Co) and
Axial Skeleton BONE TERMINOLOGY FEATURES
 Axial Skeleton BONE TERMINOLOGY FEATURES Tuberosity Rounded area on bone often roughened for muscle attachment. Tubercle Rounded projection on bone. This is called a tuberosity on the femur. Crest Ridgeline
Axial Skeleton BONE TERMINOLOGY FEATURES Tuberosity Rounded area on bone often roughened for muscle attachment. Tubercle Rounded projection on bone. This is called a tuberosity on the femur. Crest Ridgeline
THEME 2. VERTEBRAE (GENERAL DATA). CERVICAL, THORACIC AND LUMBAR VERTEBRAE. SACRUM. COCCYX. THE VERTEBRAL COLUMN AS A WHOLE
 THEME 2. VERTEBRAE (GENERAL DATA). CERVICAL, THORACIC AND LUMBAR VERTEBRAE. SACRUM. COCCYX. THE VERTEBRAL COLUMN AS A WHOLE Osteology of the Vertebral Column Bone Description vertebra Notes a vertebra
THEME 2. VERTEBRAE (GENERAL DATA). CERVICAL, THORACIC AND LUMBAR VERTEBRAE. SACRUM. COCCYX. THE VERTEBRAL COLUMN AS A WHOLE Osteology of the Vertebral Column Bone Description vertebra Notes a vertebra
1TRUNK: BODY WALL AND SPINE
 TRUNK: BODY WALL AND SPINE SURFACE ANATOMY SKELETON JOINTS & LIGAMENTS MUSCLES VASCULATURE NERVES SPINAL CORD & VERTEBRAL CANAL ANTERIOR BODY WALL & MAMMARY GLAND LATERAL BODY WALL INGUINAL REGION SUPERFICIAL
TRUNK: BODY WALL AND SPINE SURFACE ANATOMY SKELETON JOINTS & LIGAMENTS MUSCLES VASCULATURE NERVES SPINAL CORD & VERTEBRAL CANAL ANTERIOR BODY WALL & MAMMARY GLAND LATERAL BODY WALL INGUINAL REGION SUPERFICIAL
Labs 6, 7, 8: Skeletal System
 153 Labs 6, 7, 8: Skeletal System Unit 6: Skeletal System: Bone tissue, Bones and Joints (p. 105-152) Ex. 6-1: Histology of Osseous Tissue, p. 113 Model: Osteon Tiss Lamella Osteocyte Lacunae Canaliculi
153 Labs 6, 7, 8: Skeletal System Unit 6: Skeletal System: Bone tissue, Bones and Joints (p. 105-152) Ex. 6-1: Histology of Osseous Tissue, p. 113 Model: Osteon Tiss Lamella Osteocyte Lacunae Canaliculi
