Points To Remember. Biology Class - 11
|
|
|
- Gregory Sharp
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Points To Remember Blood : A special connective tissue that circulates in principal vascular system of man and other vertebrates consisting of fluid matrix, plasma and formed elements. Plasma : The liquid part of blood or lymph which is straw coloured, viscous fluid and conta (only lymbphocytes) ins about 90-92% of water and 6-8% proteins. Lymph : A clear yellowish, slightly alkaline, coagulable fluid, containing white blood cells in a liquid resembling blood plasma. Serum : Blood plasma from which fibrinogen and other clotting factors have been removed. Heart Beat : The rhythmic contraction and relaxation of the heart, which includes one systole (contraction phase) and one diastole (relaxation phase) of the heart. Heart beat count of healthy person is 72 times per minute. Cardiac output : The amount of blood pumped by heart per minute is called cardiac or heart output. The value of cardiac output of a normal person is about = 5040 ml or about 5L per minutes. Electrocardiograph : (ECG) the machine used to record electrocardiogram. Electrocardiogram ECG : The graphic record of the electric current produced by the excitation of the cardiac muscles. It is composed of a P wave, QRS wave. (complex) and T wave (Refer fig. 18.3, page 286 (for a standard ECG) (NCERT class XI Biology) 160 Biology Class - 11
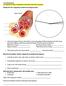
2 Name and Number/ Structure Life Span and Function Percentage Formation (A) Erythrocytes RBCs Red colour Formed from birth Transport of oxygen to 5.5 million Circular, biconcave onward by red bone and some amount per cubic millimetre of denucleated, elastic marrow Life-120 days of carbon dioxide blood lack of cell organelles excess RBCs are through haemoglobin like ER, ribosomes, mitochondria etc. stored in spleen (B) Leucocytes Colourless rounded Formed in red bone Acts as soldiers (WBCs) or irregular, marrow, Lymph scavenger and some per cubic mm of nucleated 12 to nodes, spleen and help in healing blood 20mm wide, life 1-4 thymus days (i) Agranulocytes (a) Large rounded Lymph nodes, Non Phagocytic Lymphocytes 20-45% nucleus, 6-10 mm spleen, thymus red secrete antibodies of leucocytes bone marrow, life few days to months or even years (b) Monocytes 6-8% Largest of all (12-15 Red Bone marrow, phagocytic, very leucocytes, mm) bean shaped life hours motiles engulf (ii) Granulocytes nucleus germs (a) Eosinophils 2-3% bilobed nucleus, Red Bone marrow, play role in immunity of leucocytes granules in cytoplasm life 4 to 8 hrs. in non phagocytic blood (b) Basophils 0-5% of Three lobed nucleus Red Bone marrow, release heparin and leucocytes (s-shaped) life 4 to 8 hours in histamine blood (c) Neutrophils 60- Many lobed nucleus Red Bone marrow, phogocytic, engulf 65% of leucocytes fine granules life 4 to 8 hours in germ and dead cells blood (C) Platelets Colourless, rounded Red Bone marrow help in blood clotting thrombocytes or oval, or irregular worm out ones 1,50,000-3,50,000 non-nucleated phagocytized in blood mm 3 of blood fragments Body Fluids and Circulation 161
3 Blood Pressure The resistance offered by the lumen of the artery to the flow of Blood. Cardiac Cycle : The rhythmic contraction and dilation of different parts of heart in one beat. Hypertension : The condition when blood pressure is higher than normal (120/80 mmhg) Systole : Contraction of heart muscles. Diastole : Relaxation of heart muscles. Lymph The colourless mobile fluid connective tissue drains into the lymphatic capillaries from the intercellular spaces. It is formed by squeezing of blood through capillaries, within tissues. Its flow is unidirectional i.e., from tissues to heart. Composition : It is composed of fluid matrix, plasma, white blood corpuscles or leucocytes. Functions : (i) It drains excess tissue from extra cellular spaces back into the blood, (ii) It contain lymphocytes and antibodies. (iii) It transport digested fats. 162 Biology Class - 11
4 It is the mesodermally derived organ situated in thoracic cavity in between the two lungs. Protected by a double membrane covering called Pericardium. Four chambers two (left and right) atria, and two ventricels (left and right) Inner-artrial septum separates the two atria and inter ventricular septum separates the two ventricles, while the atria and ventricles are separated by atrioventricular septum. The valves between right atrium and right ventricle is tricuspid while between left atrium and ventricle is bicuspid or mitral value. The opening of the right and the left ventricles into the pulmonary artery and the aorta are guarded by semilunar values. The value allow the flow of blood only in one direction, i.e., from atria to ventricles and from ventricles to pulmonary artery or aorta. Functions of Blood Transport, of food, respiratory gases (O 2 and CO 2 ), hormones, metabolic intermediates, waste products, supply of raw materials, regulation of water balance, regulation of ph and body temperature, and provides immunity. Blood Clotting Injured Tissue Blood Platelets Releases Disintegrate and release Thromboplastins Platelet thromboplastin Ca++ Proteins Ca+ Proteins Thrombokinase Inactivates heparin and catalyses Ca++ Prothrombin Thrombin Catalyses Fibrinogen Fibrin (Fibrin + Blood cells Clot or Coagulum) Body Fluids and Circulation 163
5 Bipod Groups Blood Antigen (on Anti body : (in Possible recipients Possible donors Remarks Group the Surface plasma) having blood group having blood of R.B.Cs) group A A Anti B A.AB O,A B B Anti A B, AB O,B, AB A and B None AB O,A,B,AB Universal recipient Universal 0 None Anti A and anti O/A,B,AB O Donor Rh (Rhesus) Group : B Discovered by Landsteiner and Wiener in The antigen found on the surface of RBCs. The presence of this antigen is termed as Rh-positive (Rh+) and its absence as (Rh ). It plays a crucial role in childs birth born out of a marriage between Rh woman and Rh+ man, causing to produce anti Rh antibodies. SAN (Sino-artrial node) : A patch of tissues present in the right upper corner of the right atrium, acts are pacemaker due to having a unique property of self exitation. AVN (Atrio Ventricular Node) : A mass of tissues seen in the lower left corner of the right atrium close to the atrio-ventricular septum. Fresh wave of contraction generated here, passes over both the ventricles simultaneously along the bundle of his. Heart Valves Tricuspid Valve : The valves formed of three muscular flaps or cups, which guard the opening between the right atrium and the right ventricle. Bicuspid Valve (Mitral Valve) : The valves which guard the opening between the left atrium and the left ventricle, made up of two flaps. Semilunar Valves : The valves present at the opening of the right and the left ventricles and allow the entry of blood into pulmonary artery and the aorta respectively. Reading of ECG : P Wave represents the electrical excitation (or depolarisation) of the atria and leads to the contraction of both the atria. 164 Biology Class - 11
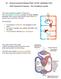
6 QRS complex : represents the depolarisation of the ventricles, which initiates the ventricular contraction. T Wave : represents the return of the ventricles from excited to normal state (repolarisation). The end of T-wave marks the end of sytole. Double circulation : The passage of same blood twice through heart in order to complete one cycle. eg. (i) The blood pumped by the right ventricle (deoxygenated blood) is transported through pulmonary artery to lungs where CO 2 is exchanged with O 2 through diffusion and returns back to the heart through pulmonary vein. It is called pulmonary circulation. (ii) The oxygenated blood from left ventricle is transported through aorta to different body parts (cells and tissues) where O 2 is exchanged with CO 2 through diffusion and then returned back to the heart through vena-cava. It is called systemic circulation. Disorders of circulatory System Hypertension (High blood Pressure) : It results from narrowing of arterial lumen and reduced elasticity of arterial walls in old age. It can cause rupturing of capillaries. It is a silent killer. Coronary Artery Disease : (CAD) Atherosclerosis. The supply of the blood to heart muscles is affected. It is caused by deposits of Calcium, fat, cholesterol and fibrous tissues to make the lumen of arteries narrower. Angina Pectoris : Caused due to arteriosclerosis, when no enough oxygen is reaching the heart muscle due to which the person experiences acute chest pain. Heart attack : Caused when the heart muscle is suddenly damaged by an inadequate blood supply. Cardiac arrest : The state in which the heart stops beating. Arteriosclerosis : The state of herding of arteries and arterioles due to thickening of the fibrous tissue and consequent loss of elasticity. It causes hypertension. Questions Very Short Answer Questions (1 mark each) 1. Name the instrument used for measuring blood pressure. 2. What is lymph node? 3. A cardiologist observed an enlarged QRS wave in the ECG of a patient. What does it indicate? Body Fluids and Circulation 165
7 4. Name the enzyme that catalyses the formation of carbonic acid in erythrocytes. 5. What is systemic circulation? 6. Give two examples of extra-cellular fluids. 7. What name is given to the blood vessels which generally bring blood to an organ? 8. Which adrenal hormone accelerates the heart beat under normal conditions? 9. Name the blood vessel that carries blood from the intestine to liver. 10. Define cardiac cycle. 11. Name the protein found in RBCs. 12. What happens to a person suffering from hemophilia? Short Answer Questions-I (2 marks each) 13. Explain when and how the two sounds of heart are produced. 14. Define joint diastole. What are constituents of the conducting system of human heart? 15. Give the names of various types of formed elements present in the blood. Short Answer Questions-II (3 marks each) 16. Draw a diagram showing schematic plan of blood circulation in human. 17. Why is the SA node called pacemaker of the heart? Write its full from. 18. In the following diagram of section of a human heart, label a, b, c, d, e and f. 19. What is lymph? Describe its circulation in brief. 20. What is stroke volume? What is its relation with cardiac output? 166 Biology Class - 11
8 21. A person suffering from fever is advised to take blood test. What may happen to his WBC count and why? Long Answer Questions (5 marks each) 22. Neena is having blood group A-ve while her husband s blood group is O +ve. Their first child is having blood gp. A +ve. Her second child was born with severe anemia and jaundice. What could be the reason? How this situation could have been avoided? 23. Draw a diagram to show the internal structure of human heart. Lable any two heart chambers, any two heart valves and chordae tendinae in it. 24. Describe the structure of human heart. 25. What is cardiac cycle? Describe the event that occur during it. 26. Explain Rh grouping and its incompatibility in humans. Answers Very Short Answer (1 mark each) 1. Sphygmomanometer. 2. A lymph node is speicalised structure in lymphatic vessel concerned with the alteration of foreign bodies by the lymphocytes. 3. QRS waves denotes ventricular contraction of heart which may be normal or abnormal. 4. Carbonic anhydrase. 5. The kind of blood circulation that is concerned with the supply of oxygenated blood from the left ventrice to all body parts and return of oxygenated blood to the right atrium of heart. 6. Interstitial fluid and blood plasma. 7. Afferent blood vessel. 8. Noradrenalin. 9. Hepatic portal vein. 10. A regular sequence of three events (i) auricular systole (ii) ventricular systole and (iii) Joint diastole during the completion of one heart beat. Body Fluids and Circulation 167
9 11. Haemoglobin. 12. The person suffering from haemophilia lacks clotting factors in blood, which result the defective clotting mechanism. In case of injury the person is at a risk of blood loss. Short Answer-I (2 mark each) 13. (i) Lubb the first second which is low pitched, is caused by the closure of bicuspid and tricuspid valves. (ii) Dup the second sound which is high pitched, is caused by the closure or semilunar valves. 14. In a cardiac cycle when both atria and ventricles are in a diastole and are relaxed simultaneously is called a joint diastole. Conducting system constitutes : SA node AV node Bundle of His Purkinje fibres. 15. Erythrocytes, lymphocytes, monocytes, neutrophils * eosinophils, basophils and platelets. 16. SA node being self excitatory initiate a wave of contraction in the heart. SA node Sino Atrial Node. Short Answer-II (3 marks each) 17. Refer fig. 18.4, page 287 (NCERT Text Book Class XI-Biology) 18. Refer fig. 18.2, page 283 (NCERT Text Book Class XI-Biology) 19. Refer contend fig. 18.2, page 282 (NCERT Text Book Class XI-Biology) 20. During one cardiac cycle or one heart beat the volume of blood pumped by the heart is called stroke volume. This is normally 70 ml. In one minute the heart beats about 72 times and the amount of blood pumped per minute is called cardiac output. This is usually 4900 ml. or 5 litres. 21. The WBC count of this person may show an increase from the normal range. As pathogens may be present in his body, so the body is producing more WBCs to fight against those pathogens. WBC count is a good tool to asses the presence of infection in a sick person. 168 Biology Class - 11
10 Long Answer (5 marks each) 22. During her first pregnancy with her first Rh +ve child, her body prepared antibodies against Rh antigen in her blood. In second pregnancy these Rh antibodies from mother leaked into the blood of foetus (Rh +ve) and destroyed foetus RBCs. It was the cause of severe anemia. This situation could have been avoided if she had got herself administered anti; Rh antibodies immediately after first deliver to kill Rh antibodies. 23. Refer fig. 18.2, page 283 (NCERT Text Book Class XI-Biology) 24. Refer content , page 283 (NCERT Text Book Class XI-Biology) 25. Refer content , page 284 (NCERT Text Book Class XI-Biology) 26. Refer content , page 281 (NCERT Text Book Class XI-Biology) Body Fluids and Circulation 169
Visit For All NCERT solutions, CBSE sample papers, Question papers, Notes for Class 6 to 12. Chapter -18
 Chapter -18 BODY FLUIDS AND CIRCULATION POINTS TO REMEMBER Blood : A special connective tissue that circulates in principal vascular system of man and other vertebrates consisting of fluid matrix, plasma
Chapter -18 BODY FLUIDS AND CIRCULATION POINTS TO REMEMBER Blood : A special connective tissue that circulates in principal vascular system of man and other vertebrates consisting of fluid matrix, plasma
CBSE Quick Revision Notes (Class-11 Biology) CHAPTER-18 BODY FLUIDS AND CIRCULATION
 CBSE Quick Revision Notes (Class-11 Biology) CHAPTER-18 BODY FLUIDS AND CIRCULATION Body fluids are the medium of transport of nutrients, oxygen and other important substance in the body. Body Fluids Intracellular
CBSE Quick Revision Notes (Class-11 Biology) CHAPTER-18 BODY FLUIDS AND CIRCULATION Body fluids are the medium of transport of nutrients, oxygen and other important substance in the body. Body Fluids Intracellular
Class XI Chapter 18 Body Fluids and Circulation Biology
 Question 1: Name the components of the formed elements in the blood and mention one major function of each of them. The component elements in the blood are: (1) Erythrocytes: They are the most abundant
Question 1: Name the components of the formed elements in the blood and mention one major function of each of them. The component elements in the blood are: (1) Erythrocytes: They are the most abundant
CHAPTER 18 BODY FLUIDS AND CIRCULATION MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS
 101 CHAPTER 18 BODY FLUIDS AND CIRCULATION MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. Which of the following cells does not exhibit phagocytotic activity a. Monocyte b. Neutrophil c. Basophil d. Macrophage 2. One of
101 CHAPTER 18 BODY FLUIDS AND CIRCULATION MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. Which of the following cells does not exhibit phagocytotic activity a. Monocyte b. Neutrophil c. Basophil d. Macrophage 2. One of
1. Name the components of the formed elements in the blood and mention one major function of each of them.
 CLASS XI BIOLOGY Body Fluids And Circulation 1. Name the components of the formed elements in the blood and mention one major function of each of them. Formed Elements in Blood And Their Functions: Erythrocytes
CLASS XI BIOLOGY Body Fluids And Circulation 1. Name the components of the formed elements in the blood and mention one major function of each of them. Formed Elements in Blood And Their Functions: Erythrocytes
CHAPTER 18 BODY FLUIDS AND CIRCULATION
 278 BIOLOGY CHAPTER 18 BODY FLUIDS AND CIRCULATION 18.1 Blood 18.2 Lymph (Tissue Fluid) 18.3 Circulatory Pathways 18.4 Double Circulation 18.5 Regulation of Cardiac Activity 18.6 Disorders of Circulatory
278 BIOLOGY CHAPTER 18 BODY FLUIDS AND CIRCULATION 18.1 Blood 18.2 Lymph (Tissue Fluid) 18.3 Circulatory Pathways 18.4 Double Circulation 18.5 Regulation of Cardiac Activity 18.6 Disorders of Circulatory
SAPTARSHI CLASSES PVT. LTD.
 SAPTARSHI CLASSES PVT. LTD. NEET TEST No 220317 Time : 1 Hr BIOLOGY CIRCULATION 1) c 2) a 3) d 4) c 5) c 6) c 7) c 8) a 9) d 10) d 11) d 12) c 13) d 14) b 15) b 16) c 17) a 18) b 19) c 20) a 21) b 22)
SAPTARSHI CLASSES PVT. LTD. NEET TEST No 220317 Time : 1 Hr BIOLOGY CIRCULATION 1) c 2) a 3) d 4) c 5) c 6) c 7) c 8) a 9) d 10) d 11) d 12) c 13) d 14) b 15) b 16) c 17) a 18) b 19) c 20) a 21) b 22)
Class X Chapter 7 The Circulatory System Biology REVIEW QUESTIONS: A. MULTIPLE CHOICE TYPE: (Select the most appropriate option in each case)
 REVIEW QUESTIONS: A. MULTIPLE CHOICE TYPE: (Select the most appropriate option in each case) Question 1: Agranulocytes are: (a) lymphocytes and monocytes (b) lymphocytes and basophils (c) eosinophils and
REVIEW QUESTIONS: A. MULTIPLE CHOICE TYPE: (Select the most appropriate option in each case) Question 1: Agranulocytes are: (a) lymphocytes and monocytes (b) lymphocytes and basophils (c) eosinophils and
1. Which of the following blood vessels has a thin elastic layer? A. Aorta. B. Pulmonary artery. C. Posterior vena cava. D. Mesenteric capillary.
 CIRCULATORY SYSTEM 1. Which of the following blood vessels has a thin elastic layer? A. Aorta. B. Pulmonary artery. C. Posterior vena cava. D. Mesenteric capillary. 2. Capillary beds are equipped with
CIRCULATORY SYSTEM 1. Which of the following blood vessels has a thin elastic layer? A. Aorta. B. Pulmonary artery. C. Posterior vena cava. D. Mesenteric capillary. 2. Capillary beds are equipped with
Chapter 9 Homeostasis and Circulation
 1 Chapter 9 Homeostasis and Circulation Section 9.1 Homeostasis: Life in the Balance Outcomes: I can explain homeostasis I can describe the importance of homeostasis to living things I can explain the
1 Chapter 9 Homeostasis and Circulation Section 9.1 Homeostasis: Life in the Balance Outcomes: I can explain homeostasis I can describe the importance of homeostasis to living things I can explain the
Scrub In: Red blood cells are called: Which component of blood is necessary for the initiation of the blood clotting process:
 Scrub In: Red blood cells are called: a. erythrocytes b. leukocytes c. melanocytes d. thrombocytes Which component of blood is necessary for the initiation of the blood clotting process: a. erythrocytes
Scrub In: Red blood cells are called: a. erythrocytes b. leukocytes c. melanocytes d. thrombocytes Which component of blood is necessary for the initiation of the blood clotting process: a. erythrocytes
Topic 6: Human Physiology
 Topic 6: Human Physiology 6.2 The Blood System D.4 The Heart Essential Questions: 6.2 The blood system continuously transports substances to cells and simultaneously collects waste products. D.3 The chemical
Topic 6: Human Physiology 6.2 The Blood System D.4 The Heart Essential Questions: 6.2 The blood system continuously transports substances to cells and simultaneously collects waste products. D.3 The chemical
Cardiovascular System. Biology 105 Lecture 15 Chapter 12
 Cardiovascular System Biology 105 Lecture 15 Chapter 12 Outline I. Functions of cardiovascular system II. Components of the cardiovascular system: I. Blood vessels II. Heart III. Regulation of the heartbeat
Cardiovascular System Biology 105 Lecture 15 Chapter 12 Outline I. Functions of cardiovascular system II. Components of the cardiovascular system: I. Blood vessels II. Heart III. Regulation of the heartbeat
Chapter 16: Circulation
 Chapter 16: Circulation Section 1: The Body s Transport System Beating Heart Cardiac muscle is Striated and branched Under involuntary control by the brain stem Functions of the Cardiovascular System 1.
Chapter 16: Circulation Section 1: The Body s Transport System Beating Heart Cardiac muscle is Striated and branched Under involuntary control by the brain stem Functions of the Cardiovascular System 1.
aliasyraf.wordpress.com
 aliasyraf.wordpress.com 1.1 Understanding the importance of having a transport system in some multicellular organisms 1.1 Understanding the importance of having a transport system in some multicellular
aliasyraf.wordpress.com 1.1 Understanding the importance of having a transport system in some multicellular organisms 1.1 Understanding the importance of having a transport system in some multicellular
The Circulatory System. The Heart, Blood Vessels, Blood Types
 The Circulatory System The Heart, Blood Vessels, Blood Types The Closed Circulatory System Humans have a closed circulatory system, typical of all vertebrates, in which blood is confined to vessels and
The Circulatory System The Heart, Blood Vessels, Blood Types The Closed Circulatory System Humans have a closed circulatory system, typical of all vertebrates, in which blood is confined to vessels and
Biology 1442 Supplemental Instruction Worksheet Cardiovascular System Jacaruso - 1 -
 Biology 1442 Supplemental Instruction Worksheet Cardiovascular System Jacaruso - 1-2. Organs of a closed circulatory system: A. Have valves a. Arteriole B. Regulate blood flow b. Artery C. Lead to heart
Biology 1442 Supplemental Instruction Worksheet Cardiovascular System Jacaruso - 1-2. Organs of a closed circulatory system: A. Have valves a. Arteriole B. Regulate blood flow b. Artery C. Lead to heart
The Cardiovascular System home study course
 The Cardiovascular System home study course harmony house holistic therapy treatment centre and training academy www.harmony-house.org 1 Copyright 2010 by Mark and Katy Rogers All rights reserved. No part
The Cardiovascular System home study course harmony house holistic therapy treatment centre and training academy www.harmony-house.org 1 Copyright 2010 by Mark and Katy Rogers All rights reserved. No part
Circulatory System Objective sheet 3
 Circulatory System Objective sheet 3 10. Functions of blood 1) Transport oxygen and nutrients 2) Transport of carbon dioxide and waste 3) Protection against disease causing micro-organisms 4) Clotting
Circulatory System Objective sheet 3 10. Functions of blood 1) Transport oxygen and nutrients 2) Transport of carbon dioxide and waste 3) Protection against disease causing micro-organisms 4) Clotting
2.01 Remember the structures of the circulatory system
 2.01 Remember the structures of the circulatory system Essential questions What are the structures of blood? What are the structures of the circulatory system? circulatory system 2 Structures of the circulatory
2.01 Remember the structures of the circulatory system Essential questions What are the structures of blood? What are the structures of the circulatory system? circulatory system 2 Structures of the circulatory
Cardiovascular. Function of the cardiovascular system is to transport blood containing: Nutrients Waste Hormones Immune cells Oxygen
 Cardiovascular The Cardiovascular System - Arteries Arteries Cardiovascular System Function of the cardiovascular system is to transport blood containing: Carry blood away from heart Carotid arteries Deliver
Cardiovascular The Cardiovascular System - Arteries Arteries Cardiovascular System Function of the cardiovascular system is to transport blood containing: Carry blood away from heart Carotid arteries Deliver
Types of circulatory systems
 Types of circulatory systems Open system Mostly invertebrates Low pressure Haemocoel Suitable for small organisms Closed system Vertebrates High pressure Blood remains in blood vessels Separate tissue
Types of circulatory systems Open system Mostly invertebrates Low pressure Haemocoel Suitable for small organisms Closed system Vertebrates High pressure Blood remains in blood vessels Separate tissue
Unit 10 Cardiovascular System
 Unit 10 Cardiovascular System I. Functions Deliver nutrients to cells > O 2, sugars, amino acids, lipids, ions, H 2 O... Remove waste from cells > CO 2, pathogens, toxins, lactic acid... Fight off infection
Unit 10 Cardiovascular System I. Functions Deliver nutrients to cells > O 2, sugars, amino acids, lipids, ions, H 2 O... Remove waste from cells > CO 2, pathogens, toxins, lactic acid... Fight off infection
Lower Secondary Science Blood Circulatory System Notes / Advanced Notes
 Lower Secondary Science Blood Circulatory System Notes / Advanced Notes Double Circulation in Mammals In mammals, there is a double circulation (i.e. blood passes through the heart twice in one complete
Lower Secondary Science Blood Circulatory System Notes / Advanced Notes Double Circulation in Mammals In mammals, there is a double circulation (i.e. blood passes through the heart twice in one complete
The Cardiovascular and Lymphatic Systems Cardiovascular System Blood Vessels Blood Vessels Arteries Arteries Arteries
 CH 12 The Cardiovascular and s The Cardiovascular and s OUTLINE: Cardiovascular System Blood Vessels Blood Pressure Cardiovascular System The cardiovascular system is composed of Blood vessels This system
CH 12 The Cardiovascular and s The Cardiovascular and s OUTLINE: Cardiovascular System Blood Vessels Blood Pressure Cardiovascular System The cardiovascular system is composed of Blood vessels This system
CIRCULATORY SYSTEM TASK CARDS Worksheet
 CIRCULATORY SYSTEM TASK CARDS Worksheet Name: Date: Instructions: Put the answers to each task card in the numbered boxes on the chart. 1 a) left semilunar valve / aortic valve b) blood would backflow
CIRCULATORY SYSTEM TASK CARDS Worksheet Name: Date: Instructions: Put the answers to each task card in the numbered boxes on the chart. 1 a) left semilunar valve / aortic valve b) blood would backflow
Circulatory System Review
 Circulatory System Review 1. Know the diagrams of the heart, internal and external. a) What is the pericardium? What is myocardium? What is the septum? b) Explain the 4 valves of the heart. What is their
Circulatory System Review 1. Know the diagrams of the heart, internal and external. a) What is the pericardium? What is myocardium? What is the septum? b) Explain the 4 valves of the heart. What is their
The Cardiovascular and Lymphatic Systems
 BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues Fifth Edition Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire 12 The Cardiovascular and Lymphatic Systems Lecture Presentation Anne Gasc Hawaii Pacific University and
BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues Fifth Edition Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire 12 The Cardiovascular and Lymphatic Systems Lecture Presentation Anne Gasc Hawaii Pacific University and
The Circulatory System. The circulatory system includes the Heart, Blood Tissue and the Blood Vessels.
 The Circulatory System The circulatory system includes the Heart, Blood Tissue and the Blood Vessels. The Circulatory System-Transport The absorption and circulation of materials throughout an organism
The Circulatory System The circulatory system includes the Heart, Blood Tissue and the Blood Vessels. The Circulatory System-Transport The absorption and circulation of materials throughout an organism
Mammalian Transport and The Heart
 Cardiovascular System AS-G, Chapters 8-9 Blood flows through the body in a closed system (circuit) driven by the pumping power of the heart Closed vs open: does the system have vessels contained the entire
Cardiovascular System AS-G, Chapters 8-9 Blood flows through the body in a closed system (circuit) driven by the pumping power of the heart Closed vs open: does the system have vessels contained the entire
Blood and Heart. Student Learning Objectives:
 Blood and Heart Student Learning Objectives: Identify the major components of the blood. Identify the primary structures associated with the heart Follow the blood through the path of the circulation.
Blood and Heart Student Learning Objectives: Identify the major components of the blood. Identify the primary structures associated with the heart Follow the blood through the path of the circulation.
Chapter 10 The Circulatory & Lymphatic Systems
 Biology 12 Name: Human Biology Per: Date: Chapter 10 The Circulatory & Lymphatic Systems Complete using BC Biology 12, pages 298 325 10.1 The Blood Vessels pages 298-299 1. Label the blood vessels in this
Biology 12 Name: Human Biology Per: Date: Chapter 10 The Circulatory & Lymphatic Systems Complete using BC Biology 12, pages 298 325 10.1 The Blood Vessels pages 298-299 1. Label the blood vessels in this
Cardiovascular System. I. Structures of the heart A. : Pericardium sack that surrounds the heart
 Cardiovascular System I. Structures of the heart A. : Pericardium sack that surrounds the heart 1. : Pericardial Cavity serous fluid filled space between the heart and the pericardium B. Heart Wall 1.
Cardiovascular System I. Structures of the heart A. : Pericardium sack that surrounds the heart 1. : Pericardial Cavity serous fluid filled space between the heart and the pericardium B. Heart Wall 1.
Chapter 12. Capillaries. Circulation. The circulatory system connects with all body tissues
 Chapter 12 Circulation The circulatory system connects with all body s In many animals, microscopic blood vessels called capillaries Form an intricate network among the Red blood cell song Figure 23.1A
Chapter 12 Circulation The circulatory system connects with all body s In many animals, microscopic blood vessels called capillaries Form an intricate network among the Red blood cell song Figure 23.1A
The Mammalian Circulatory System
 The Mammalian Heart The Mammalian Circulatory System Recall: What are the 3 cycles of the mammalian circulatory system? What are their functions? What are the three main vessel types in the mammalian circulatory
The Mammalian Heart The Mammalian Circulatory System Recall: What are the 3 cycles of the mammalian circulatory system? What are their functions? What are the three main vessel types in the mammalian circulatory
Bellwork Define: hemostasis anticoagulation hemophilia (Then write the underline portion of the two state standards in your notes).
 Bellwork Define: hemostasis anticoagulation hemophilia (Then write the underline portion of the two state standards in your notes). A&P Standards 31) Identify the liquid and cellular components of blood
Bellwork Define: hemostasis anticoagulation hemophilia (Then write the underline portion of the two state standards in your notes). A&P Standards 31) Identify the liquid and cellular components of blood
2.02 Understand the functions and disorders of the circulatory system
 2.02 Understand the functions and disorders of the circulatory system 2.02 Understand the functions and disorders of the circulatory system Essential questions: What are the functions of blood? What are
2.02 Understand the functions and disorders of the circulatory system 2.02 Understand the functions and disorders of the circulatory system Essential questions: What are the functions of blood? What are
Transport in Animals (IGCSE Biology Syllabus )
 Transport in Animals (IGCSE Biology Syllabus 2016-2018) Blood o Red blood cells: heamoglobin and oxygen transport o White blood cells: phagocyte phagocytosis (engulf pathogen, vesicles fuse with vacuole,
Transport in Animals (IGCSE Biology Syllabus 2016-2018) Blood o Red blood cells: heamoglobin and oxygen transport o White blood cells: phagocyte phagocytosis (engulf pathogen, vesicles fuse with vacuole,
Glossary: The Cardiovascular System
 This glossary includes terms that have been introduced in Lesson 14. Student Resource 14.14 Glossary: The Cardiovascular System Anatomy Terms aorta Large artery that transports blood from the left ventricle
This glossary includes terms that have been introduced in Lesson 14. Student Resource 14.14 Glossary: The Cardiovascular System Anatomy Terms aorta Large artery that transports blood from the left ventricle
CIRCULATION & GAS EXCHANGE
 AP BIOLOGY ACTIVITY2.13 Text:Campbell,v.8,chapter42 NAME DATE HOUR CIRCULATION & GAS EXCHANGE 1. In general, what is the function of transport systems? 2. What method/structure do most invertebrates use
AP BIOLOGY ACTIVITY2.13 Text:Campbell,v.8,chapter42 NAME DATE HOUR CIRCULATION & GAS EXCHANGE 1. In general, what is the function of transport systems? 2. What method/structure do most invertebrates use
TRANSPORT SYSTEM IN LIVING SMPK PENABUR JAKARTA
 TRANSPORT SYSTEM IN LIVING ORGANISM SMPK PENABUR JAKARTA Part 1 PLANT TRANSPORTATION SYSTEM A. PLANT TRANSPORT SYSTEM Transport tissue? Where? A. 1. Water Transport Water liquid matter Affected by environment
TRANSPORT SYSTEM IN LIVING ORGANISM SMPK PENABUR JAKARTA Part 1 PLANT TRANSPORTATION SYSTEM A. PLANT TRANSPORT SYSTEM Transport tissue? Where? A. 1. Water Transport Water liquid matter Affected by environment
Circulatory System. 3. Blood. 1. Heart. 1. Veins A blood vessel that returns blood to the heart
 Day 1. Circulatory System uman Body Transport The Circulatory System 2. ARTERIES 1. eart & VEINS 3. Blood Process: Transport Circulatory System The process where substances move (distributed) into and
Day 1. Circulatory System uman Body Transport The Circulatory System 2. ARTERIES 1. eart & VEINS 3. Blood Process: Transport Circulatory System The process where substances move (distributed) into and
Transport in Animals. Gastrovascular cavities. Nutrients and gases can move by processes such as diffusion and active transport.
 Transport in Animals Gastrovascular cavities flatworms and cnidarians Nutrients and gases can move by processes such as diffusion and active transport. Figure 42.1 Internal transport in the cnidarian
Transport in Animals Gastrovascular cavities flatworms and cnidarians Nutrients and gases can move by processes such as diffusion and active transport. Figure 42.1 Internal transport in the cnidarian
Chapter 23. Circulation
 Chapter 23 Circulation Standards CORE: I can describe the components and function of blood. I can describe structure and function of blood vessels. I can compare and contrast systemic and pulmonary systems.
Chapter 23 Circulation Standards CORE: I can describe the components and function of blood. I can describe structure and function of blood vessels. I can compare and contrast systemic and pulmonary systems.
The Circulatory System (p )
 The Circulatory System (p. 268-281) How Does Gravity Affect Blood Circulation? As with all land animals, the giraffe and the corn snake are constantly subject to the force of gravity The circulatory system
The Circulatory System (p. 268-281) How Does Gravity Affect Blood Circulation? As with all land animals, the giraffe and the corn snake are constantly subject to the force of gravity The circulatory system
Section 5.1 The heart and heart disease
 Section 5.1 The heart and heart disease Mammals are too large to rely on diffusion. They need a circulatory system to move substances around the body. Blood moves down pressure gradients, from high to
Section 5.1 The heart and heart disease Mammals are too large to rely on diffusion. They need a circulatory system to move substances around the body. Blood moves down pressure gradients, from high to
Chapter 9 Homeostasis and Circulation. Biology 2201
 Chapter 9 Homeostasis and Circulation Biology 2201 Homeostasis The steady state of conditions inside a living organism that allows it to function properly Homeostasis is the dynamic equilibrium of the
Chapter 9 Homeostasis and Circulation Biology 2201 Homeostasis The steady state of conditions inside a living organism that allows it to function properly Homeostasis is the dynamic equilibrium of the
Chapter 27 The Heart and Blood Vessels
 Chapter 27 The Heart and Blood Vessels Most animals have a closed blood system. The blood flows continuously in vessels back to the heart. In an open system the blood is pumped into open ended tubes and
Chapter 27 The Heart and Blood Vessels Most animals have a closed blood system. The blood flows continuously in vessels back to the heart. In an open system the blood is pumped into open ended tubes and
CIRCULATION. Cardiovascular & lymphatic systems Functions. Transport Defense / immunity Homeostasis
 CIRCULATION CIRCULATION Cardiovascular & lymphatic systems Functions Transport Defense / immunity Homeostasis 2 Types of Circulatory Systems Open circulatory system Contains vascular elements Mixing of
CIRCULATION CIRCULATION Cardiovascular & lymphatic systems Functions Transport Defense / immunity Homeostasis 2 Types of Circulatory Systems Open circulatory system Contains vascular elements Mixing of
This is a TRANSPORT system that allows every cell: i) uptake of nutrients ( ex. oxygen, glucose) ii) excretes wastes (ex C02, ammonia)
 Biology 20 Unit D This is a TRANSPORT system that allows every cell: i) uptake of nutrients ( ex. oxygen, glucose) ii) excretes wastes (ex C02, ammonia) requires action of: heart: muscular force to move
Biology 20 Unit D This is a TRANSPORT system that allows every cell: i) uptake of nutrients ( ex. oxygen, glucose) ii) excretes wastes (ex C02, ammonia) requires action of: heart: muscular force to move
Blood Functions. Blood and the Cardiovascular System. Blood. Plasma. Erythrocytes (RBCs) Erythrocytes (RBCs) 4/7/2017
 Blood Functions Blood and the Cardiovascular System Distribution Delivery of oxygen and nutrients to all body cells; Transport of wastes to lungs and excretory organs; Transport of hormones Regulation
Blood Functions Blood and the Cardiovascular System Distribution Delivery of oxygen and nutrients to all body cells; Transport of wastes to lungs and excretory organs; Transport of hormones Regulation
CIE Biology GCSE. 9: Transport in animals. Notes.
 CIE Biology GCSE 9: Transport in animals Notes The circulatory system acts as the main transport system in animals. It is made up of blood vessels such as arteries, veins and capillaries, in which blood
CIE Biology GCSE 9: Transport in animals Notes The circulatory system acts as the main transport system in animals. It is made up of blood vessels such as arteries, veins and capillaries, in which blood
07 Human transport Biology Notes IGCSE Cambridge #69 Transport in humans - the circulatory system
 07 Human transport Biology Notes IGCSE Cambridge 2014 #69 Transport in humans - the circulatory system The main transport system of human is the circulatory system, a system of tubes (blood vessels) with
07 Human transport Biology Notes IGCSE Cambridge 2014 #69 Transport in humans - the circulatory system The main transport system of human is the circulatory system, a system of tubes (blood vessels) with
d) Cardiovascular System Higher Human Biology
 d) Cardiovascular System Higher Human Biology What can your remember about the heart and blood vessels? What is the Cardiovascular System? The cardiovascular system, also known as the circulatory system,
d) Cardiovascular System Higher Human Biology What can your remember about the heart and blood vessels? What is the Cardiovascular System? The cardiovascular system, also known as the circulatory system,
Cardiovascular System. Chapters 11, 12
 Cardiovascular System Chapters 11, 12 Oxygen enters the cardiovascular system by diffusing from alveoli into blood cells in the capillaries, then binding to hemoglobin in red blood cells. Blood Hematology-
Cardiovascular System Chapters 11, 12 Oxygen enters the cardiovascular system by diffusing from alveoli into blood cells in the capillaries, then binding to hemoglobin in red blood cells. Blood Hematology-
THE HEART. Unit 3: Transportation and Respiration
 THE HEART Unit 3: Transportation and Respiration The Circulatory System Also called the Cardiovascular System Circulates blood in the body Transports nutrients, oxygen, carbon dioxide, hormones, and blood
THE HEART Unit 3: Transportation and Respiration The Circulatory System Also called the Cardiovascular System Circulates blood in the body Transports nutrients, oxygen, carbon dioxide, hormones, and blood
Chapter 12 Cardiovascular System
 Chapter 12 Cardiovascular System Cardiovascular System Includes Heart and Blood Vessels Transports, nutrients and wastes to and from the tissues 1 The Blood Vessels Three Types of Blood Vessels Arteries:
Chapter 12 Cardiovascular System Cardiovascular System Includes Heart and Blood Vessels Transports, nutrients and wastes to and from the tissues 1 The Blood Vessels Three Types of Blood Vessels Arteries:
12.1 The Function of Circulation
 12.1 The Function of Circulation The Circulatory System Magnetic Resonance Angiography (MRA) Heart pump beats 100 000 times a day Deliver oxygen and nutrients Function of Circulation Multicellular organisms
12.1 The Function of Circulation The Circulatory System Magnetic Resonance Angiography (MRA) Heart pump beats 100 000 times a day Deliver oxygen and nutrients Function of Circulation Multicellular organisms
37 1 The Circulatory System
 H T H E E A R T 37 1 The Circulatory System The circulatory system and respiratory system work together to supply cells with the nutrients and oxygen they need to stay alive. a) The respiratory system:
H T H E E A R T 37 1 The Circulatory System The circulatory system and respiratory system work together to supply cells with the nutrients and oxygen they need to stay alive. a) The respiratory system:
Circulatory System. Chapter 32
 Circulatory System Chapter 32 Invertebrates w/o a Circulatory System If an organism has a sac body plan, circulatory systems are not necessary. Sac body plans mean cells are capable of gas and nutrient
Circulatory System Chapter 32 Invertebrates w/o a Circulatory System If an organism has a sac body plan, circulatory systems are not necessary. Sac body plans mean cells are capable of gas and nutrient
CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Worksheet
 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Worksheet NAME Section A: Blood Basics http://www.psbc.org/hematology/01_index.htm Although blood appears to be red liquid it is actually composed of yellowish liquid called plasma
CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Worksheet NAME Section A: Blood Basics http://www.psbc.org/hematology/01_index.htm Although blood appears to be red liquid it is actually composed of yellowish liquid called plasma
Lesson 10 Circulatory System (Nelson p.88-93)
 Name: Date: Lesson 10 Circulatory System (Nelson p.88-93) Learning Goals: A. I can explain the primary functions of the circulatory system in animals. B. I can identify and explain all the parts of the
Name: Date: Lesson 10 Circulatory System (Nelson p.88-93) Learning Goals: A. I can explain the primary functions of the circulatory system in animals. B. I can identify and explain all the parts of the
Circulation And Blood. Circulation And Blood. Circulation And Blood. Circulation And Blood. Blood 10/22/2012
 Cells in our body build their own membranes and organelles Make their own ATP Assemble their own enzymes and other proteins And may manufacture substances used elsewhere in the body To do these things,
Cells in our body build their own membranes and organelles Make their own ATP Assemble their own enzymes and other proteins And may manufacture substances used elsewhere in the body To do these things,
Chapter 14. The Cardiovascular System
 Chapter 14 The Cardiovascular System Introduction Cardiovascular system - heart, blood and blood vessels Cardiac muscle makes up bulk of heart provides force to pump blood Function - transports blood 2
Chapter 14 The Cardiovascular System Introduction Cardiovascular system - heart, blood and blood vessels Cardiac muscle makes up bulk of heart provides force to pump blood Function - transports blood 2
C I R C U L A T I O N I N A N I M A L
 C I R C U L A T I O N I N A N I M A L Open type of circulatory system. ---If the blood flows through large spaces called sinuses then it is called as open circulatory system. The blood does not flow through
C I R C U L A T I O N I N A N I M A L Open type of circulatory system. ---If the blood flows through large spaces called sinuses then it is called as open circulatory system. The blood does not flow through
Name: Date: Class: Unit 5 Outline: Blood and the Cardiovascular System
 Name: Date: Class: Unit 5 Outline: Blood and the Cardiovascular System Blood and RBCs Blood The only Classified as a Non-living matrix = Blood Composition tissue in the human body tissue cells = formed
Name: Date: Class: Unit 5 Outline: Blood and the Cardiovascular System Blood and RBCs Blood The only Classified as a Non-living matrix = Blood Composition tissue in the human body tissue cells = formed
ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY HOMEWORK CHAPTER 11 AND 12
 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY HOMEWORK CHAPTER 11 AND 12 Name Identify the following: 1) The Purkinje fibers are indicated by label. 2) The sinoatrial (SA) node is indicated by letter. 3) The specific chamber
ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY HOMEWORK CHAPTER 11 AND 12 Name Identify the following: 1) The Purkinje fibers are indicated by label. 2) The sinoatrial (SA) node is indicated by letter. 3) The specific chamber
Ch 9 Transport of substances in humans
 Ch 9 Transport of substances in humans Think about (Ch 9, p.2) 1. Blood transports various substances and distributes heat around the body. It also plays a role in body defence. 2. Blood is a liquid tissue
Ch 9 Transport of substances in humans Think about (Ch 9, p.2) 1. Blood transports various substances and distributes heat around the body. It also plays a role in body defence. 2. Blood is a liquid tissue
Introduction to Medical Careers. Cardiovascular & Circulatory Systems Chapters 11-12
 Introduction to Medical Careers Cardiovascular & Circulatory Systems Chapters 11-12 CHAPTER 11 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM I will be able to: 1. Define at least eight terms referring to the cardiovascular system.
Introduction to Medical Careers Cardiovascular & Circulatory Systems Chapters 11-12 CHAPTER 11 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM I will be able to: 1. Define at least eight terms referring to the cardiovascular system.
Circulation. Circulation = is a process used for the transport of oxygen, carbon! dioxide, nutrients and wastes through-out the body
 Circulation Circulation = is a process used for the transport of oxygen, carbon! dioxide, nutrients and wastes through-out the body Heart = muscular organ about the size of your fist which pumps blood.
Circulation Circulation = is a process used for the transport of oxygen, carbon! dioxide, nutrients and wastes through-out the body Heart = muscular organ about the size of your fist which pumps blood.
Cardiovascular System Notes: Heart Disease & Disorders
 Cardiovascular System Notes: Heart Disease & Disorders Interesting Heart Facts The Electrocardiograph (ECG) was invented in 1902 by Willem Einthoven Dutch Physiologist. This test is still used to evaluate
Cardiovascular System Notes: Heart Disease & Disorders Interesting Heart Facts The Electrocardiograph (ECG) was invented in 1902 by Willem Einthoven Dutch Physiologist. This test is still used to evaluate
Circulatory System. - Consists of a pumping heart and blood vessels. Two types of circulatory fluids: Blood OR Hemolymph
 Introduction - The major transportation fluid in the body. - 8% of the total body fluids. Roles of the Cardiovascular system: 1- Transport of substances (O 2, CO 2, nutrients, and hormones) 2- Regulation
Introduction - The major transportation fluid in the body. - 8% of the total body fluids. Roles of the Cardiovascular system: 1- Transport of substances (O 2, CO 2, nutrients, and hormones) 2- Regulation
Chapter 27 -The Heart & Blood Vessels
 Chapter 27 -The Heart & Blood Vessels 3.2 Learning Objectives 3.2.2 Organisational Complexity of the human 1. Describe the structures and organisation of tissues in the closed circulatory system. 2. Discuss
Chapter 27 -The Heart & Blood Vessels 3.2 Learning Objectives 3.2.2 Organisational Complexity of the human 1. Describe the structures and organisation of tissues in the closed circulatory system. 2. Discuss
CIRCULATORY SYSTEM BLOOD VESSELS
 Name: Block: CIRCULATORY SYSTEM Multicellular organisms (above the level of roundworms) rely on a circulatory system to bring nutrients to, and take wastes away from, cells. In higher organisms such as
Name: Block: CIRCULATORY SYSTEM Multicellular organisms (above the level of roundworms) rely on a circulatory system to bring nutrients to, and take wastes away from, cells. In higher organisms such as
Circulatory System. Circulatory System
 Circulatory System Transportation system of the body There are two types of circulatory systems: 1. Open Circulatory System pumps blood to open ended vessels into the body cavities containing organs, then
Circulatory System Transportation system of the body There are two types of circulatory systems: 1. Open Circulatory System pumps blood to open ended vessels into the body cavities containing organs, then
Unit 1: Human Systems. The Circulatory System
 Unit 1: Human Systems The Circulatory System nourish all cells with oxygen, glucose, amino acids and other nutrients and carry away carbon dioxide, urea and other wastes Purposes Transport chemical messengers
Unit 1: Human Systems The Circulatory System nourish all cells with oxygen, glucose, amino acids and other nutrients and carry away carbon dioxide, urea and other wastes Purposes Transport chemical messengers
10. Thick deposits of lipids on the walls of blood vessels, called, can lead to serious circulatory issues. A. aneurysm B. atherosclerosis C.
 Heart Student: 1. carry blood away from the heart. A. Arteries B. Veins C. Capillaries 2. What is the leading cause of heart attack and stroke in North America? A. alcohol B. smoking C. arteriosclerosis
Heart Student: 1. carry blood away from the heart. A. Arteries B. Veins C. Capillaries 2. What is the leading cause of heart attack and stroke in North America? A. alcohol B. smoking C. arteriosclerosis
Blood flows away from the heart in arteries, to the capillaries and back to the heart in the veins
 Cardiovascular System Summary Notes The cardiovascular system includes: The heart, a muscular pump The blood, a fluid connective tissue The blood vessels, arteries, veins and capillaries Blood flows away
Cardiovascular System Summary Notes The cardiovascular system includes: The heart, a muscular pump The blood, a fluid connective tissue The blood vessels, arteries, veins and capillaries Blood flows away
The circulatory system
 The circulatory system Key words Vessels heart blood plasma platelets haemoglobin To engulf arteries capillaries veins venules lymphocytes Atrium / - a ventricle tricuspid bicuspid cardiac coronary Humans
The circulatory system Key words Vessels heart blood plasma platelets haemoglobin To engulf arteries capillaries veins venules lymphocytes Atrium / - a ventricle tricuspid bicuspid cardiac coronary Humans
Circulatory System Review ANSWERS
 Circulatory System Review ANSWERS 1. Know the diagrams of the heart, internal and external. a) What is the pericardium? Double membranous sac that surrounds the heart What is myocardium? The muscle tissue
Circulatory System Review ANSWERS 1. Know the diagrams of the heart, internal and external. a) What is the pericardium? Double membranous sac that surrounds the heart What is myocardium? The muscle tissue
Major Function of the Cardiovascular System. Transportation. Structures of the Cardiovascular System. Heart - muscular pump
 Structures of the Cardiovascular System Heart - muscular pump Blood vessels - network of tubes Blood - liquid transport vehicle brachiocephalic trunk superior vena cava right pulmonary arteries right pulmonary
Structures of the Cardiovascular System Heart - muscular pump Blood vessels - network of tubes Blood - liquid transport vehicle brachiocephalic trunk superior vena cava right pulmonary arteries right pulmonary
2/28/18. Cardiovascular System. Introduction. Anatomy. Chapter 26. Body is 60% to 80% fluid (by volume) Systems responsible for fluid movement are:
 Cardiovascular System Chapter 26 1 Introduction Body is 60% to 80% fluid (by volume) Systems responsible for fluid movement are: - Cardiovascular helps move fluid - Lymphatic Both called pick-up and delivery
Cardiovascular System Chapter 26 1 Introduction Body is 60% to 80% fluid (by volume) Systems responsible for fluid movement are: - Cardiovascular helps move fluid - Lymphatic Both called pick-up and delivery
Human Circulatory System
 Human Circulatory System The human circulatory system functions to transport blood and oxygen from the lungs to the various tissues of the body. The heart pumps the blood throughout the body, which carries
Human Circulatory System The human circulatory system functions to transport blood and oxygen from the lungs to the various tissues of the body. The heart pumps the blood throughout the body, which carries
C3, 4, 5, 6, & 7 Worksheet. C3 Describe the inter-relationships of the structures of the heart
 Name: Date: C3, 4, 5, 6, & 7 Worksheet C3 Describe the inter-relationships of the structures of the heart 1. Label and give the functions of the following: a. left and right atrium: b. left and right ventricle:
Name: Date: C3, 4, 5, 6, & 7 Worksheet C3 Describe the inter-relationships of the structures of the heart 1. Label and give the functions of the following: a. left and right atrium: b. left and right ventricle:
The Circulatory System. Blood and Blood Pressure
 The Circulatory System Blood and Blood Pressure Blood Total volume = 8-9% of body mass Average person = 5 L of blood DYK? Blood is actually a tissue! Plasma: - water, proteins, salts, gases, nutrients,
The Circulatory System Blood and Blood Pressure Blood Total volume = 8-9% of body mass Average person = 5 L of blood DYK? Blood is actually a tissue! Plasma: - water, proteins, salts, gases, nutrients,
Cardiovascular System. Supplementary Information
 Cardiovascular System Supplementary Information THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM - 1 - THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM FUNCTION Transport system carrying nutrient, gases, hormones and waste products to and from the
Cardiovascular System Supplementary Information THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM - 1 - THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM FUNCTION Transport system carrying nutrient, gases, hormones and waste products to and from the
Cardiovascular System Note-Taking Guide
 FUNctions: Name: 3-27-14 Cardiovascular System Note-Taking Guide Heart: Pumps and delivers through the body Blood: Vessels: Delivers and to the body Carries waste and Maintains homeostasis - Carries blood
FUNctions: Name: 3-27-14 Cardiovascular System Note-Taking Guide Heart: Pumps and delivers through the body Blood: Vessels: Delivers and to the body Carries waste and Maintains homeostasis - Carries blood
Levels of Organization. Chapter 19 6/11/2012. Homeostasis & Organization of the animal body. 4 Primary Tissues
 Levels of Organization Chapter 19 Homeostasis & Organization of the animal body Chemical Cellular Tissue Organs System Level Organismic 1-2 4 Primary Tissues 1. Epithelial Tissue: covers surfaces lines
Levels of Organization Chapter 19 Homeostasis & Organization of the animal body Chemical Cellular Tissue Organs System Level Organismic 1-2 4 Primary Tissues 1. Epithelial Tissue: covers surfaces lines
Test Review Circulatory System Chapters
 Test Review Circulatory System Chapters 13-2010 1. The tissue that forms the tight fitting sac around the heart is the a. parietal pericardium c. myocardium b. visceral pericardium d. endocardium 2. Which
Test Review Circulatory System Chapters 13-2010 1. The tissue that forms the tight fitting sac around the heart is the a. parietal pericardium c. myocardium b. visceral pericardium d. endocardium 2. Which
4. The two inferior chambers of the heart are known as the atria. the superior and inferior vena cava, which empty into the left atrium.
 Answer each statement true or false. If the statement is false, change the underlined word to make it true. 1. The heart is located approximately between the second and fifth ribs and posterior to the
Answer each statement true or false. If the statement is false, change the underlined word to make it true. 1. The heart is located approximately between the second and fifth ribs and posterior to the
The Heart. Happy Friday! #takeoutyournotes #testnotgradedyet
 The Heart Happy Friday! #takeoutyournotes #testnotgradedyet Introduction Cardiovascular system distributes blood Pump (heart) Distribution areas (capillaries) Heart has 4 compartments 2 receive blood (atria)
The Heart Happy Friday! #takeoutyournotes #testnotgradedyet Introduction Cardiovascular system distributes blood Pump (heart) Distribution areas (capillaries) Heart has 4 compartments 2 receive blood (atria)
7.L.1.4 Circulatory System Guided Study Notes. Circulation
 1 7.L.1.4 Circulatory System Guided Study Notes Circulation Sect. 1: The Body s Transport System Sect. 2: A Closer Look at Blood Vessels Sect. 3: Blood and Lymph Sect. 4: Cardiovascular Health Sect. 1:
1 7.L.1.4 Circulatory System Guided Study Notes Circulation Sect. 1: The Body s Transport System Sect. 2: A Closer Look at Blood Vessels Sect. 3: Blood and Lymph Sect. 4: Cardiovascular Health Sect. 1:
IB TOPIC 6.2 THE BLOOD SYSTEM
 IB TOPIC 6.2 THE BLOOD SYSTEM THE BLOOD SYSTEM TERMS TO KNOW circulation ventricle artery vein 6.2.U1 - Arteries convey blood at high pressure from the ventricles to the tissues of the body Circulation
IB TOPIC 6.2 THE BLOOD SYSTEM THE BLOOD SYSTEM TERMS TO KNOW circulation ventricle artery vein 6.2.U1 - Arteries convey blood at high pressure from the ventricles to the tissues of the body Circulation
Cardiac Cycle. Each heartbeat is called a cardiac cycle. First the two atria contract at the same time.
 The Heartbeat Cardiac Cycle Each heartbeat is called a cardiac cycle. First the two atria contract at the same time. Next the two ventricles contract at the same time. Then all the chambers relax. http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=frd3k6lkhws
The Heartbeat Cardiac Cycle Each heartbeat is called a cardiac cycle. First the two atria contract at the same time. Next the two ventricles contract at the same time. Then all the chambers relax. http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=frd3k6lkhws
CIRCULATION OF BODY FLUIDS
 Circulation of Body Fluids MODULE - 2 15 CIRCULATION OF BODY FLUIDS The body of almost all the animals, has some form of fluid circulating in the body. Such fluids constitute the distributing system (to
Circulation of Body Fluids MODULE - 2 15 CIRCULATION OF BODY FLUIDS The body of almost all the animals, has some form of fluid circulating in the body. Such fluids constitute the distributing system (to
BLOOD I. Composition and Function of Blood
 BLOOD I. Composition and Function of Blood A. Components 1. Blood is the only fluid tissue 2. Has living blood cells and nonliving fluid matrix 3. Breakdown of blood sample a. Formed elements b. Plasma
BLOOD I. Composition and Function of Blood A. Components 1. Blood is the only fluid tissue 2. Has living blood cells and nonliving fluid matrix 3. Breakdown of blood sample a. Formed elements b. Plasma
2. What makes up the most of your blood? least of your blood? 1. Look like red discs, have a pale center, no nucleus, similar in size
 .I Can Statements I can identify the major components of blood and where they are formed. Identify the four components of blood in the diagram below. 1. Label each section of the pie chart with the correct
.I Can Statements I can identify the major components of blood and where they are formed. Identify the four components of blood in the diagram below. 1. Label each section of the pie chart with the correct
Health Science 20 Circulatory System Notes
 Health Science 20 Circulatory System Notes Functions of the Circulatory System The circulatory system functions mainly as the body s transport system. It transports: o Oxygen o Nutrients o Cell waste o
Health Science 20 Circulatory System Notes Functions of the Circulatory System The circulatory system functions mainly as the body s transport system. It transports: o Oxygen o Nutrients o Cell waste o
1. Label the Diagram using the following terms: artery, arterioles, vein, venules, capillaries, valve, inner wall, middle wall, outer wall
 Bio 20 Ms. Nyboer Arteries, Veins, Capillaries, and the Heart Structure and Function Workbook Use your textbook (Ch. 10) and notes to fill in this workbook Part A: Arteries, Veins, Capillaries 1. Label
Bio 20 Ms. Nyboer Arteries, Veins, Capillaries, and the Heart Structure and Function Workbook Use your textbook (Ch. 10) and notes to fill in this workbook Part A: Arteries, Veins, Capillaries 1. Label
