Lymphatic system (cont d)
|
|
|
- Tracy Miller
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Circulatory System Objectives Understand the roles of the cardiovascular and lymphatic systems and their relationship to each other Know the tissue layers that characterize blood vessels Know the anatomical and functional differences between arteries, veins and capillaries Distinguish systemic and pulmonary circulation and portal circulation Describe differences in adult and fetal circulation with respect to the hepatic portal and pulmonary systems Know the cellular components of blood Know where hematopoeisis occurs and where blood cells are removed from circulation Know the relationship of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) to blood Relate the function of the following organs to the circulatory system: spleen, thymus, lymph nodes, tonsils, carotid bodies, hypothalamus, brown fat, lungs, kidneys, liver, bone marrow, endocrine glands, choroid plexus
2 Major divisions of the circulatory system Cardiovascular system functions distributes nutrients, wastes, O 2, CO 2, hormones thermoregulation, osmoregulation, physiological homeostasis components heart, arteries, veins, capillaries blood Lymphatic system (cont d)
3 Major divisions of the circulatory system Lymphatic system functions immune response, lipid absorption, returns fluids from tissues to venous cardiovascular system components Lymph Capillaries, Vessels, Ducts Lymph Organs Lymph Nodes Thymus Spleen Tonsils Peyer s Patches Vermiform Appendix Lymph
4 Layers of the cardiovascular system listed from luminal to superficial: Vessels Heart Endothelium Tunica Intima Endocardium Muscle and CT Tunica Media Myocardium Covering Tunica Adventitia Pericardium General terms Collateral Circulation Anastomosis
5 Arteries by definition: conduct blood away from heart typically conduct O 2 -rich blood exceptions are pulmonary arteries and umbilical arteries narrow diameter (than veins) thicker wall (than veins) Tunica Intima maybe Stratified Squamous Epithelium Tunica Media alternating bands of Smooth Muscle and Elastic CT high pressure located deep (not merely subcutaneous) except to pass joints typically co-occur with veins and nerves of same name
6 Veins by definition: conduct blood towards the heart typically conduct O 2 -depleted blood exceptions are pulmonary veins and umbilical vein large diameter thin wall low pressure passive valves two tier system of both superficial (subcutaneous) and deep vessels Capillaries leaky vessels consist only of Tunica Intima only
7 Blood Plasma extracellular matrix water, dissolved salts, proteins, nutrients, urea, hormones, CO 2 Albumin osmolarity Fibrinogen clotting Globulins immune response Formed elements of blood cellular Hematopoiesis from pleuripotent stem or progenitor cells Red Bone Marrow in adults Yolk Sac, Spleen, Liver, Kidneys in embryo and fetus
8 Erythrocytes or Red Blood Cells (RBC s) carry hemoglobin, four-ringed protein that binds iron (hence O 2 ) most numerous blood cell type biconcave anucleate 7.5 µm in diameter Rollo formation ~120 day lifespan unlike leucocytes, RBC s do not escape capillaries
9 Leucocytes or White Blood Cells (WBC s) Granulocytes or Polymorphonuclear Cells extracellular digestion by release of lytic enzymes innate immune response types distinguished by hemotoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining Neutrophils neutral ph, red and blue most numerous granulocyte, major constituent of pus Eosinophils acid, red Basophils and Mast Cells basic, blue produce edema, release heparin and histamine Agranulocytes Monocytes or Macrophages (mature) amoeboid cells, internal digestion by phagocytosis Lymphocytes many types: t-lymphocytes, b-lymphocytes, natural killer-lymphocytes recognize, target, and kill antigens adaptive immune response Thrombocytes or blood platelets small pieces of cells involved in clotting
10 Heart Pericardial cavity middle mediastinum Parietal Pericardium Serous Pericardium Fibrous Pericardium Heart suspended by great vessels superiorly (anterior and posterior) tissue layers of heart Visceral pericardium (or simply pericardium ) serosa Myocardium cardiac striated muscle Endocardium simple squamous epithelium margins of the heart superior sternal angle to 4 th thoracic intervertebral disc right ½ inch parasternal apex left midclavicular line or ½ inch medial to areola in males inferior xiphisternal joint to 8 th thoracic intervertebral disc
11 Pulmonary circulation to and from lungs Systemic circulation to and from body Intrinsic circulation of the heart Hepatic Portal circulation separated as right and left chambers of the heart 2 Atria (s. atrium) 2 Ventricles Interatrial Septum Interventricular Septum Atrioventricular Septum
12 Systemic circulation Superior vena cava from upper ½ body Inferior vena cava from lower ½ body Coronary sinus intrinsic circulation of heart Right atrium Right ventricle Pulmonary circuit Pulmonary trunk to pulmonary arteries Lungs Pulmonary veins Left atrium Left ventricle Systemic circulation Ascending Aorta to everything
13 General features of Atria smaller and thinner walled than ventricles Musculi Pectinati Auricles Atria separated from one another by Interatrial Septum Atria separated from ventricles by Atrioventricular Septum contains Atrioventricular (AV) Node beginning of Moderator Band
14 Right Atrium Sinus Venosus posterior right, smooth surface receives Superior and Inferior Venae Cavae and Coronary Sinus Crista Terminalis Sinoatrial (SA) Node the pacemaker Fossa Ovalis vestige of Foramen Ovale (fetal interatrial bypass) Left Atrium receives Upper and Lower Right and Upper and Lower Left Pulmonary Veins
15 General Features of Ventricles larger and thicker walled than atria Trabeculae Carnae Atrioventricular (AV) Valves active, muscular Cusps Chordae Tendineae Papillary muscles Semilunar Valves passive Ventricles separated from one another by interventricular septum contains Moderator Band or Purkinje Fibers
16 Right Ventricle Right AV or Tricuspid Valve three cusps opening of Pulmonary Trunk anterior superior left Pulmonary Semilunar Valve Left Ventricle Left AV or Bicuspid or Mitral Valve two cusps opening of Ascending Aorta anterior superior right Aortic Semilunar Valve
17 Electrical conduction of the heart Sinoatrial Node pacemaker Atrioventricular Node Moderator Band or Bundle of HIS or Purkinje Fibers
18 Locations to listen to heart valves Aortic Semilunar Right 2 nd intercostal space parasternal Pulmonary Semilunar Left 2 nd intercostal space parasternal Tricuspid Right 5 th intercostal space parasternal Bicuspid or Mitral Left 5 th intercostal space midclavicular
19 Fetal circulation fetal structure R&L Umbilical Arteries Umbilical Vein Ductus Venosus (also Portal Sinus Foramen Ovale Ductus Arteriosus fate Vesical Arteries and Median Umbilical Ligament Ligamentum Teres in Falciform Ligament Ligamentum Venosus Hepatic Portal Vein) Fossa Ovalis Ligamentum Arteriosum
20 Fetal Definitive
21 Branches of the Thoracic Aorta listed in order of branching 1) Ascending Aorta branches: Right and Left Coronary Arteries 2) Aortic Arch branches: a) Brachiocephalic Artery branches: i) Right Common Carotid ii) Right Subclavian Artery b) Left Common Carotid Artery c) Left Subclavian Artery 3) Descending Aorta branches: segmental Esophageal and Intercostal arteries
22 Superior Vena Cava venous counterpart to the Thoracic Aorta drains entire upper half of body located to right side of Aortic Arch, on mediastinal surface of right lung begins with the union of Right and Left Brachiocephalic Veins terminates in Sinus Venosus of Right Atrium Tributaries 1) Left Brachiocephalic or Left Innominate Vein long, horizontal, anterior to branches of aortic arch begins with union of L Subclavian and L Internal Jugular Veins 2) Right Brachiocephalic or Right Innominate Vein short, vertical begins with union of R Subclavian and R Internal Jugular Veins 3) Azygos Vein drains right Intercostal Veins drains left Intercostal Veins via Hemiazygos Veins
23 Branches of the Abdominal Aorta listed in order of branching 1) Coeliac Trunk to superior abdominal organs 2) Superior Mesenteric Artery to Jejunum, Ileum, Large Intestine up to and including Transverse Colon 3) Right and Left Renal Arteries 4) Right and Left Gonadal (Testicular or Ovarian) Arteries 5) Inferior Mesenteric Artery to Descending and Sigmoid Colons and superior Rectum 6) Right and Left Common Iliac Arteries to pelvic region and lower limbs
24 Inferior Vena Cava venous counterpart to the Abdominal Aorta drains entire lower half of body its main tributaries are those corresponding only to paired arterial branches of the Abdominal Aorta, except the Hepatic vein located to right side of Abdominal Aorta, anterior to lumbar vertebrae begins with the union of the Right and Left Common Iliac veins terminates in Sinus Venosus of Right Atrium
25 Tributaries of the Inferior Vena Cava listed in order of union 1) Right and Left Common Iliac Veins 2) Right Gonadal (Testicular or Ovarian) Vein 3) Right and Left Renal Veins Left Renal Vein - long, crosses anterior to Abdominal Aorta tributary of Left Renal Vein: Left Gonadal (Testicular or Ovarian) Vein 4) Hepatic Vein
26 Arterial Branches
27 Intrinsic circulation of the heart Coronary Arteries vs Cardiac Veins Branches of Right Coronary Artery Marginal (coronary) Artery on right margin of heart Circumflex (Coronary) Artery (right side) at Atrioventricular Septum
28 Branches of Left Coronary Artery Anterior Interventricular or Descending Artery at anterior interventricular septum anastomoses with Posterior Interventricular Artery Circumflex (Coronary) Artery (left side) branch: Posterior Interventricular or Descending Artery at posterior interventricular septum anastomoses with Anterior Interventricular Artery
29 Cardiac veins Small Cardiac Vein corresponds to Marginal Artery on right margin of heart Great Cardiac Vein corresponds to Anterior Interventricular Artery at anterior interventricular septum Middle Cardiac Vein corresponds to Posterior Interventricular Artery at Posterior Interventricular Septum Coronary Sinus alongside Circumflex Artery at Atrioventricular Septum receives Cardiac Veins and drains into Sinus Venosus of Right Atrium
30 All subsequent descriptions are for paired right and left vessels even though this is not specified in each case
31 Branches of the Common Carotid Arteries and their branches ends in two terminal branches at level of laryngeal eminence in carotid triangle 1) Internal Carotid Artery major branches of the Internal Carotid Artery: a) Middle Cerebral Artery to majority of Cerebrum via Carotid Canal passes through the Cavernous Sinus (a venous dural sinus surrounding the sella turcica) b) Ophthalmic Artery to orbit via optic canal select branches of Ophthalmic Artery: i) Central Artery enters eye within optic nerve branches of the Central Artery: Superior and Inferior Temporal Arteries to retina Superior and Inferior Nasal Arteries to retina ii) Supraorbital Artery 2) External Carotid Artery (continued)
32 Branches of the External Carotid Artery and its branches 1) Lingual Artery to tongue 2) Facial Artery crosses face from mandibular ramus to medial orbit 3) Superficial Temporal Artery to temporal fossa, scalp 4) Occipital Artery 5) Maxillary Artery to muscles of mastication, palate, teeth, and infraorbital region select branches of maxillary artery: a) Sphenopalatine Artery to nasal cavity and palate b) Middle Meningeal Artery to cranial cavity via foramen spinosum c) Alveolar Arteries (3) to teeth d) Infraorbital Artery to middle face
33
34 Branches of the Subclavian Arteries and their branches 1) Vertebral Artery to cranial cavity via foramen magnum 2) Thyrocervical Trunk to scapular and cervical regions 3) Internal Thoracic Artery 4) Costocervical Trunk 5) Dorsal Scapular Artery 6) Axillary Artery (terminal branch, simply a change of name) Subclavian Artery Axillary Artery at first rib to anterior and lateral thoracic regions branches: a) Thoracoacromial Artery (travels with Lateral Pectoral nerve) b) Subscapular Artery c) Lateral Thoracic artery (travels with Long Thoracic nerve) d) Circumflex Humeral Artery e) Brachial Artery (terminal branch) Axillary Artery Brachial Artery at Teres Major muscle (continued)
35 Location of the Brachial Artery Proximally: on medial side of brachium between anterior and posterior compartments but within anterior compartment Distally: medial to tendon of biceps brachii in antecubital region Major Branches of the Brachial Artery 1) Profunda Brachii Artery serves posterior compartment 2) Superior and Inferior Ulnar Collateral Arteries 3) Radial Artery (one terminal branch of brachial artery) terminates in manus as: Deep Palmar Arch anastomoses with Ulnar Artery 4) Ulnar Artery (another terminal branch of brachial artery) branches: Common Interosseous Artery and its branches: Anterior Interosseous Artery Posterior Interosseous Artery terminates in manus as: Superficial Palmar Arch anastomoses with Radial Artery
36
37 Circulation of the cranial cavity 1) Internal Carotid Artery Middle Cerebral Artery (at carotid canal) serves frontal, parietal, and temporal lobes of the cerebrum passes through Cavernous Sinus (a venous plexus of the dural sinuses) four levels from deep to superficial emerges through Central Sulcus or Fissure between frontal and parietal lobes of cerebrum emerges through Sylvian or Lateral Sulcus or Fissure between frontal and temporal lobes of cerebrum branches: Anterior Cerebral Artery - to anterior inferior frontal lobe Right and Left Anterior Cerebral Arteries anastomose via: Anterior Communicating Artery Posterior Communicating Artery an anastomosis with posterior cerebral artery (continued)
38 Circulation of the cranial cavity 2) Right and Left Vertebral arteries anastomose to form: Basilar artery (unpaired) branches: Cerebellar arteries Posterior cerebral artery terminal paired branches anastomoses with middle cerebral artery via posterior communicating artery 3) Middle meningeal Artery to meninges and calvarium
39
40 Branches of the coeliac trunk and their unpaired major branches 1) Left Gastric Artery branches to lesser curvature of stomach and esophagus 2) Common Hepatic Artery branches: a) Hepatic Artery b) Gastroduodenal Artery branches to (right side of) greater curvature of stomach, duodenum, and head and neck of pancreas 3) Splenic Artery branches to fundus and (left side of) greater curvature of stomach, and body and tail of pancreas
41 Branches of Common Iliac arteries and their major branches 1) Internal iliac Artery branches: a) Iliolumbar Artery (serves iliopsoas muscle) b) Lateral Sacral Artery c) Superior and Inferior Gluteal Arteries d) Umbilical Artery of fetus or Superior Vesical Artery of adult e) Uterine and Vaginal Arteries of female or Inferior Vesical Artery of male f) Middle Rectal ( Middle Hemorrhoidal ) Artery g) Obturator artery to obturator muscles h) Internal Pudendal Artery - to perineum Branch (one among many): Inferior Rectal ( Inferior Hemorrhoidal ) Artery 2) External Iliac artery (continued)
42 Branches of Internal Iliac artery
43 Branches of Internal Iliac artery
44 Branches of External Iliac Artery and its branches 1) Inferior Epigastric artery 2) Circumflex Iliac artery 3) Femoral Artery (terminal branch a simple change of name) External Iliac Artery femoral artery at inguinal ligament Branches of Femoral Artery: a) External Pudendal arteries to external genitalia, i.e., scrotum in males or labia majora in females b) Profunda Femoris Artery to muscles of medial and posterior compartments its branches: Medial and Lateral Circumflex Femoral Arteries and their branches descend medial and lateral thigh c) Popliteal Artery (terminal branch, a simple change of name) Femoral Artery Popliteal Artery at adductor hiatus (continued)
45
46 Branches of Popliteal Artery and their major branches 1) Genicular arteries (superior medial and lateral, inferior medial and lateral) 2) Sural Arteries 3) Anterior Tibial Artery (terminal branch of Popliteal Artery) branch (terminal): Dorsalis Pedis Artery 4) Posterior Tibial Artery (terminal branch of Popliteal Artery) branches: a) Peroneal Artery b) Medial and Lateral Plantar Arteries (terminal branches of Posterior Tibial Artery)
47
48 Pulse Superficial Temporal Artery temporal fossa Carotid Artery (Common or External) anterior to sternocleidomastoid at level of laryngeal eminence Brachial Artery antecubital fossa medial to tendon of biceps brachii Radial Artery anterior distal radius Femoral Artery femoral triangle Popliteal Artery popliteal fossa Posterior Tibial Artery posterior to medial malleolus Dorsalis Pedis Artery between tendons of extensor hallucis longus and extensor digitorum longus
49 Venous drainage of the Head and Neck for most arteries there are corresponding veins of the same name except: Internal, External, and Common Carotid arteries veins with no corresponding arteries: 1) Internal Jugular Vein drains cranial cavity, anterior face, tongue and pharynx Sigmoid Dural Sinus Internal Jugular Vein at jugular foramen major tributaries: a) Facial Vein b) Lingual Vein 2) External Jugular Vein drains lateral and posterior scalp, posterior face, infratemporal fossa major tributaries: a) Maxillary Vein b) Superficial Temporal Vein 3) Anterior Jugular Vein drains superficial thyroid region
50 Brain Ventricles, Cerebrospinal Fluid, Meninges, Dural Sinuses Choroid Plexus a capillary-like structure within some ventricles Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF) blood filtrate produced by choroid plexus that bathes the central nervous system from within and without Structures filled with CSF: 1) Subarachnoid Space 2) Brain Ventricles - derivatives of the embryological neural tube (CNS) a) Lateral Ventricles in paired cerebral hemispheres of forebrain b) Third Ventricle between right and left thalami and within hypothalamus of forebrain c) Cerebral Aqueduct narrow tube in midbrain uniting third and fourth ventricles d) Fourth Ventricle between cerebellum and pons of hindbrain e) Central Canal of the spinal cord
51 Meninges 1) Pia Mater 2) Arachnoid Mater Subarchnoid Space location of CSF between pia and arachnoid maters Arachnoid Villi drain CSF from subarachnoid space to dural sinuses 3) Dura Mater continuous with periosteum of calvarium and vertebral canal extensions of dura extending into fissures of brain: a) Falx Cerebri midsagittal septum between cerebral hemispheres b) Falx Cerebelli midsagittal septum between cerebellar hemispheres c) Tentorium Cerebelli horizontal septum between occipital lobes of cerebrum and cerebellum
52 Dural Sinuses 1) Superior Sagittal Sinus superior margin of falx cerebri inferior to sagittal suture 2) Inferior Sagittal Sinus along inferior margin of falx cerebri 3) Straight Sinus along union of falx cerebri and tentorium cerebelli 4) Transverse Sinuses along lateral margin of tentorium cerebelli Superior Sagittal Sinus Right Transverse Sinus at internal occipital protuberance Straight Sinus Left Transverse Sinus at internal occipital protuberance 5) Sigmoid Sinuses continuation of Transverse Sinuses sigmoid sinus Internal Jugular Vein at jugular foramen (continued)
53 Dural Sinuses (continued) 6) Cavernous Sinus venous plexus surrounding Sella Turcica passed through by Internal Carotid Artery, niii, niv, nv 1, nv 2, nvi receives Ophthalmic Vein* drains indirectly to Transverse and Sigmoid sinuses * Facial Vein anastomoses with Ophthalmic Vein, unlike arteries of same names this is a superficial venous pathway into the cranial cavity and potential source of infection
54
55 Hepatic Portal Vein terminates in liver tributaries: 1) Splenic Vein 2) Superior Mesenteric Vein 3) Inferior Mesenteric Vein
56 Venous drainage of the upper extremity and girdle for every artery there are corresponding veins of the same name Superficial veins with no corresponding arteries: 1) Cephalic Vein drains dorsum of hand, lateral antebrachium and brachium ends in Axillary Vein at Deltopectoral Triangle 2) Basilic Vein Anterior medial antebrachium and medial brachium ends in Brachial Vein 3) Median Cubital Vein Antecubital anastomosis of Cephalic and Basilic Veins
57 Venous drainage of the lower extremity and pelvic region for every artery there are corresponding veins of the same name Superficial veins with no corresponding arteries: Great or Long Saphenous Vein drains medial crus and thigh ends in Femoral Vein in femoral triangle Short Saphenous Vein drains sural region ends in Popliteal Vein in popliteal region
58 Lymphatic system Functions Immune response lipid absorption removes dead blood cells from circulation, produces bilirubin returns fluids and mobile leucocytes from extracellular tissues to venous cardiovascular system
59 Terminal lymph vessels 1) Right Lymphatic duct drains upper right ¼ of body terminates in right subclavian vein 2) Thoracic duct drains all but upper right ¼ of body terminates in left subclavian vein Cysterna Chyli bulb-like expansion of inferior end of thoracic duct
60 Lymph Nodes scattered and concentrated in locations throughout body, especially major joints, the cervical region, and digestive organs Leucocytes within nodes attack antigens and impede them from circulating Afferent and Efferent lymph vessels - lead to and from nodes parts of the node: Capsule Trabeculae Nodules Germinal Centers site of maturation and acquisition of new antibodies by b-lymphocytes and their clonal proliferation Reticular fibers Macrophages and Lymphocytes
61 Distribution of Select Major Groups of Lymph Nodes of head: Parotid Submaxillary or Submandibular Occipital of neck: Cervical superior and inferior deep surround internal jugular veins Superficial superior anterior triangle (continued)
62 Distribution of Select Major Groups of Lymph Nodes of upper limb and girdle: Axillary Pectoral, Subclavicular, Subscapular, Brachial of lower limb and girdle (including genitals and perineum): Inguinal femoral triangle of thoracic cavity: Tracheobronchial, Intercostal Mediastinal mostly concentrated around arteries of abdominal Cavity: Lumbar efferents to cisterna chyli many groups, mostly concentrated around and named after all arteries and their branches, as well as viscera of pelvic cavity (e.g., rectum)
63 Thymus site of maturation of t-lymphocytes primarily in youth located posterior to manubrium in superior mediastinum size at age 2 (maximal): from laryngeal eminence to mid-sternal body size at adolescence (replaced by adipose): jugular notch to sternal angle
64 Spleen blood filter removes dead erythrocytes from circulation populated by monocytes and macrophages degrades hemoglobin to bilirubin (subsequently excreted by liver) located in left hypochondriac region, to left of stomach Capsule Cords of Billroth reticular fibers
HUMAN HEART. Learn the following structures on the heart models.
 HUMAN HEART Learn the following structures on the heart models. The human heart has four chambers that consist of the right atrium, left atrium, right ventricle, and left ventricle. The atria are smaller
HUMAN HEART Learn the following structures on the heart models. The human heart has four chambers that consist of the right atrium, left atrium, right ventricle, and left ventricle. The atria are smaller
CARDIOVASCULAR DANIL HAMMOUDI.MD
 CARDIOVASCULAR DANIL HAMMOUDI.MD 18 Systemic Circulation Figure 19.19 Pulmonary Circulation Figure 19.18b 1. Thyroid gland 2. Trachea 3. Brachiocephalic 4. Common carotid 5. Internal jugular 6. Superior
CARDIOVASCULAR DANIL HAMMOUDI.MD 18 Systemic Circulation Figure 19.19 Pulmonary Circulation Figure 19.18b 1. Thyroid gland 2. Trachea 3. Brachiocephalic 4. Common carotid 5. Internal jugular 6. Superior
Lab Photo Review Sheet
 9 8 0. Posterior Median Sulcus. Central Canal. Dorsal (Posterior) Horn. Ventral (Anterior) Horn. Grey Matter. White Matter. Anterior Median Fissure 8. Ventral (Anterior) Root (ramus) 9. Dorsal (Posterior)
9 8 0. Posterior Median Sulcus. Central Canal. Dorsal (Posterior) Horn. Ventral (Anterior) Horn. Grey Matter. White Matter. Anterior Median Fissure 8. Ventral (Anterior) Root (ramus) 9. Dorsal (Posterior)
3 Circulatory Pathways
 40 Chapter 3 Circulatory Pathways Systemic Arteries -Arteries carry blood away from the heart to the various organs of the body. -The aorta is the longest artery in the body; it branches to give rise to
40 Chapter 3 Circulatory Pathways Systemic Arteries -Arteries carry blood away from the heart to the various organs of the body. -The aorta is the longest artery in the body; it branches to give rise to
Cardiovascular System. Chapter 22
 Cardiovascular System Blood Vessels Chapter 22 Cardiac Contractions Cardiac cycle consists of alternate periods of contraction and relaxation Contraction is the systolic pressure Blood is ejected into
Cardiovascular System Blood Vessels Chapter 22 Cardiac Contractions Cardiac cycle consists of alternate periods of contraction and relaxation Contraction is the systolic pressure Blood is ejected into
KEY - Sample Exam Biology 2050 Circulatory and Lymphatic Systems - KEY
 KEY - Sample Exam Biology 2050 Circulatory and Lymphatic Systems - KEY Note: Not all of the lymphatic system will be on the actual exam next Monday so disregard any questions that deal with something that
KEY - Sample Exam Biology 2050 Circulatory and Lymphatic Systems - KEY Note: Not all of the lymphatic system will be on the actual exam next Monday so disregard any questions that deal with something that
YOU MUST BRING GLOVES FOR THIS ACTIVITY
 ACTIVITY 10: VESSELS AND CIRCULATION OBJECTIVES: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapter 23, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 5e. All text references are for this textbook. 2) Observe and sketch histology slide
ACTIVITY 10: VESSELS AND CIRCULATION OBJECTIVES: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapter 23, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 5e. All text references are for this textbook. 2) Observe and sketch histology slide
MODULE 2: CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM ANTOMY An Introduction to the Anatomy of the Heart and Blood vessels
 MODULE 2: CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM ANTOMY An Introduction to the Anatomy of the Heart and Blood vessels The cardiovascular system includes a pump (the heart) and the vessels that carry blood from the heart
MODULE 2: CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM ANTOMY An Introduction to the Anatomy of the Heart and Blood vessels The cardiovascular system includes a pump (the heart) and the vessels that carry blood from the heart
Figure ) The specific chamber of the heart that is indicated by letter A is called the. Diff: 1 Page Ref: 364
 Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 11 The Cardiovascular System Short Answer Figure 11.1 Using Figure 11.1, identify the following: 1) The Purkinje fibers are indicated by label.
Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 11 The Cardiovascular System Short Answer Figure 11.1 Using Figure 11.1, identify the following: 1) The Purkinje fibers are indicated by label.
Sample Exam Biology 2050 Circulatory and Lymphatic Systems
 Sample Exam Biology 2050 Circulatory and Lymphatic Systems Note: Not all of the lymphatic system will be on the actual exam next Monday so disregard any questions that deal with something that wasn t covered
Sample Exam Biology 2050 Circulatory and Lymphatic Systems Note: Not all of the lymphatic system will be on the actual exam next Monday so disregard any questions that deal with something that wasn t covered
VESSELS: GROSS ANATOMY
 ACTIVITY 10: VESSELS AND CIRCULATION OBJECTIVES: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapter 23, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 4e. All text references are for this textbook. 2) Observe and sketch histology slide
ACTIVITY 10: VESSELS AND CIRCULATION OBJECTIVES: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapter 23, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 4e. All text references are for this textbook. 2) Observe and sketch histology slide
Cardiovascular System
 Cardiovascular System I. Structure of the Heart A. Average adult heart is 14 cm long and 9 cm wide. B. Lies in the mediastinum. C. Enclosed in the pericardium. 1. Fibrous pericardium- Outer, tough connective
Cardiovascular System I. Structure of the Heart A. Average adult heart is 14 cm long and 9 cm wide. B. Lies in the mediastinum. C. Enclosed in the pericardium. 1. Fibrous pericardium- Outer, tough connective
Lab Activity 25. Blood Vessels & Circulation. Portland Community College BI 232
 Lab Activity 25 Blood Vessels & Circulation Portland Community College BI 232 Artery and Vein Histology Walls have 3 layers: Tunica intima Tunica media Tunica externa 2 Tunica Intima Is the innermost layer
Lab Activity 25 Blood Vessels & Circulation Portland Community College BI 232 Artery and Vein Histology Walls have 3 layers: Tunica intima Tunica media Tunica externa 2 Tunica Intima Is the innermost layer
Chapter 14. The Cardiovascular System
 Chapter 14 The Cardiovascular System Introduction Cardiovascular system - heart, blood and blood vessels Cardiac muscle makes up bulk of heart provides force to pump blood Function - transports blood 2
Chapter 14 The Cardiovascular System Introduction Cardiovascular system - heart, blood and blood vessels Cardiac muscle makes up bulk of heart provides force to pump blood Function - transports blood 2
BIOL 353 Pre-Professional Human Anatomy Exam IV FA 2018 page 1 of 8
 BIOL 353 Pre-Professional Human Anatomy Exam IV FA 2018 page 1 of 8 IMPORTANT INSTRUCTIONS: ANSWER ONLY 50 QUESTIONS. Do not answer more than 50 questions. If you answer more than 50 questions, then you
BIOL 353 Pre-Professional Human Anatomy Exam IV FA 2018 page 1 of 8 IMPORTANT INSTRUCTIONS: ANSWER ONLY 50 QUESTIONS. Do not answer more than 50 questions. If you answer more than 50 questions, then you
Anatomy and Physiology, Spring 2015 Exam II: Form A April 9, Name Student Number
 Anatomy and Physiology, Spring 2015 Exam II: Form A April 9, 2015 Name Student Number For Questions 1 2 refer to the following table. 1 Ventricular pressure is greater than aortic 6 AV valve is open 2
Anatomy and Physiology, Spring 2015 Exam II: Form A April 9, 2015 Name Student Number For Questions 1 2 refer to the following table. 1 Ventricular pressure is greater than aortic 6 AV valve is open 2
Day 5 Respiratory & Cardiovascular: Respiratory System
 Day 5 Respiratory & Cardiovascular: Respiratory System Be very careful not to damage the heart and lungs while separating the ribs! Analysis Questions-Respiratory & Cardiovascular Log into QUIA using your
Day 5 Respiratory & Cardiovascular: Respiratory System Be very careful not to damage the heart and lungs while separating the ribs! Analysis Questions-Respiratory & Cardiovascular Log into QUIA using your
Biology 323 Human Anatomy for Biology Majors Lecture 11 Dr. Stuart S. Sumida. Peripheral Circulation
 Biology 323 Human Anatomy for Biology Majors Lecture 11 Dr. Stuart S. Sumida Peripheral Circulation Structures of the Splanchnopleure: receive unpaired vessels of the abdominal aorta. Structures of the
Biology 323 Human Anatomy for Biology Majors Lecture 11 Dr. Stuart S. Sumida Peripheral Circulation Structures of the Splanchnopleure: receive unpaired vessels of the abdominal aorta. Structures of the
THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM. Part 1
 THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Part 1 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Blood Heart Blood vessels What is the function of this system? What other systems does it affect? CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Functions Transport gases,
THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Part 1 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Blood Heart Blood vessels What is the function of this system? What other systems does it affect? CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Functions Transport gases,
Unit 11 - The Cardiovascular System 1
 Unit 11 - The Cardiovascular System 1 I. Unit 11: The Cardiovascular System A. The Cardiovascular System 1. A closed system of the heart and blood vessels a) The heart pumps blood b) Blood vessels allow
Unit 11 - The Cardiovascular System 1 I. Unit 11: The Cardiovascular System A. The Cardiovascular System 1. A closed system of the heart and blood vessels a) The heart pumps blood b) Blood vessels allow
Identify the lines used in anatomical surface descriptions of the thorax. median line mid-axillary line mid-clavicular line
 L 14 A B O R A T O R Y Thorax THORACIC WALL Identify the lines used in anatomical surface descriptions of the thorax. median line mid-axillary line mid-clavicular line Identify the surface landmarks of
L 14 A B O R A T O R Y Thorax THORACIC WALL Identify the lines used in anatomical surface descriptions of the thorax. median line mid-axillary line mid-clavicular line Identify the surface landmarks of
Lab 6: Blood. BIO104 Laboratory Handouts 147. Unit 12: Blood and Lymphatics. 1. Blood Characteristics Volume Functions Composition -
 147 Lab 6: Blood Unit 12: Blood and Lymphatics Ex. 12-1: Formed Elements (Cells) of Blood, p. 313-316 1. Blood Characteristics Volume Functions Composition - 2. Leukocytes (WBCs) a. WBC count normal b.
147 Lab 6: Blood Unit 12: Blood and Lymphatics Ex. 12-1: Formed Elements (Cells) of Blood, p. 313-316 1. Blood Characteristics Volume Functions Composition - 2. Leukocytes (WBCs) a. WBC count normal b.
The Cardiovascular System
 C H A P T E R 1 4 The Cardiovascular System OBJECTIVES After studying this chapter, you should be able to: 1. Describe how the heart is positioned in the thoracic cavity. 2. List and describe the layers
C H A P T E R 1 4 The Cardiovascular System OBJECTIVES After studying this chapter, you should be able to: 1. Describe how the heart is positioned in the thoracic cavity. 2. List and describe the layers
THE AORTA AND IT S MAJOR BRANCHES
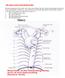 1 THE AORTA AND IT S MAJOR BRANCHES The aorta commences at the aortic valve, above the vestible of the left ventricle and terminates at the level of the fourth lumbar vertebra (L4), where it bifurcates
1 THE AORTA AND IT S MAJOR BRANCHES The aorta commences at the aortic valve, above the vestible of the left ventricle and terminates at the level of the fourth lumbar vertebra (L4), where it bifurcates
2. right heart = pulmonary pump takes blood to lungs to pick up oxygen and get rid of carbon dioxide
 A. location in thorax, in inferior mediastinum posterior to sternum medial to lungs superior to diaphragm anterior to vertebrae orientation - oblique apex points down and to the left 2/3 of mass on left
A. location in thorax, in inferior mediastinum posterior to sternum medial to lungs superior to diaphragm anterior to vertebrae orientation - oblique apex points down and to the left 2/3 of mass on left
The Cardiovascular System
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Cardiovascular System 11PART B The Heart: Cardiac Output Cardiac output (CO) Amount of blood pumped
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Cardiovascular System 11PART B The Heart: Cardiac Output Cardiac output (CO) Amount of blood pumped
Unit 11: The Cardiovascular System
 Unit 11: The Cardiovascular System I. The Cardiovascular System A. A closed system of the heart and blood vessels 1. The heart pumps blood 2. Blood vessels allow blood to circulate to all parts of the
Unit 11: The Cardiovascular System I. The Cardiovascular System A. A closed system of the heart and blood vessels 1. The heart pumps blood 2. Blood vessels allow blood to circulate to all parts of the
CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM
 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM CARDIAC SYSTEM TWO TYPES OF CIRCULATION Systemic system delivers blood to ALL body cells and carries away waste. The red blood cells use hemoglobin to carry oxygen to the cells Pulmonary
CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM CARDIAC SYSTEM TWO TYPES OF CIRCULATION Systemic system delivers blood to ALL body cells and carries away waste. The red blood cells use hemoglobin to carry oxygen to the cells Pulmonary
CV Anatomy Quiz. Dr Ella Kim Dr Pip Green
 CV Anatomy Quiz Dr Ella Kim Dr Pip Green Q1 The location of the heart is correctly described as A) lateral to the lungs. B) medial to the sternum. C) superior to the diaphragm. D) posterior to the spinal
CV Anatomy Quiz Dr Ella Kim Dr Pip Green Q1 The location of the heart is correctly described as A) lateral to the lungs. B) medial to the sternum. C) superior to the diaphragm. D) posterior to the spinal
the Cardiovascular System I
 the Cardiovascular System I By: Dr. Nabil A Khouri MD, MsC, Ph.D MEDIASTINUM 1. Superior Mediastinum 2. inferior Mediastinum Anterior mediastinum. Middle mediastinum. Posterior mediastinum Anatomy of
the Cardiovascular System I By: Dr. Nabil A Khouri MD, MsC, Ph.D MEDIASTINUM 1. Superior Mediastinum 2. inferior Mediastinum Anterior mediastinum. Middle mediastinum. Posterior mediastinum Anatomy of
Figure 10.1A Transparency Master 79
 Brain Carotid arteries Jugular vein Right front leg Lungs (inflated) Cranial Right atrium To left front leg Left subclavian Bronchus capillaries Brachiocephalic vein Left atrium Dorsal aorta Right ventricle
Brain Carotid arteries Jugular vein Right front leg Lungs (inflated) Cranial Right atrium To left front leg Left subclavian Bronchus capillaries Brachiocephalic vein Left atrium Dorsal aorta Right ventricle
General Anatomy p. 1 Organization of the Human Body p. 1 Skeleton of the Human Body p. 4 Ossification of the Bones p. 6 Bone Structure p. 8 Joints p.
 General Anatomy p. 1 Organization of the Human Body p. 1 Skeleton of the Human Body p. 4 Ossification of the Bones p. 6 Bone Structure p. 8 Joints p. 10 Principal Joints (Immovable) p. 12 Synovial Joints
General Anatomy p. 1 Organization of the Human Body p. 1 Skeleton of the Human Body p. 4 Ossification of the Bones p. 6 Bone Structure p. 8 Joints p. 10 Principal Joints (Immovable) p. 12 Synovial Joints
REVIEW SHEET Anatomy of Blood Vessels
 REVIEW SHEET Anatomy of Blood Vessels Name LabTime/Date Microscopic Structure of the Blood Vessels 1. Cross-sectional views of an aftery of a vein are shown here. ldentify each; on the lines to the sides,
REVIEW SHEET Anatomy of Blood Vessels Name LabTime/Date Microscopic Structure of the Blood Vessels 1. Cross-sectional views of an aftery of a vein are shown here. ldentify each; on the lines to the sides,
Chapter 20 (1) The Heart
 Chapter 20 (1) The Heart Learning Objectives Describe the location and structure of the heart Describe the path of a drop of blood from the superior vena cava or inferior vena cava through the heart out
Chapter 20 (1) The Heart Learning Objectives Describe the location and structure of the heart Describe the path of a drop of blood from the superior vena cava or inferior vena cava through the heart out
The Cardiovascular System
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Cardiovascular System 11PART A The Cardiovascular System A closed system of the heart and blood
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Cardiovascular System 11PART A The Cardiovascular System A closed system of the heart and blood
Circulatory system. Lecture #2
 Circulatory system Lecture #2 The essential components of the human cardiovascular system: Heart Blood Blood vessels Arteries - blood vessels that conduct arterial blood from heart ventricle to organs
Circulatory system Lecture #2 The essential components of the human cardiovascular system: Heart Blood Blood vessels Arteries - blood vessels that conduct arterial blood from heart ventricle to organs
Large veins of the thorax Brachiocephalic veins
 Large veins of the thorax Brachiocephalic veins Right brachiocephalic vein: formed at the root of the neck by the union of the right subclavian & the right internal jugular veins. Left brachiocephalic
Large veins of the thorax Brachiocephalic veins Right brachiocephalic vein: formed at the root of the neck by the union of the right subclavian & the right internal jugular veins. Left brachiocephalic
Blood Vessels. Types of Blood Vessels Arteries carry blood away from the heart Capillaries smallest blood vessels. Veins carry blood toward the heart
 C H A P T E R Blood Vessels 20 Types of Blood Vessels Arteries carry blood away from the heart Capillaries smallest blood vessels The site of exchange of molecules between blood and tissue fluid Veins
C H A P T E R Blood Vessels 20 Types of Blood Vessels Arteries carry blood away from the heart Capillaries smallest blood vessels The site of exchange of molecules between blood and tissue fluid Veins
2) Gas exchange occurs in all the below EXCEPT: A) alveolar sac B) respiratory bronchioles C) alveolar ducts D) terminal bronchioles
 Exam 2 Version A Anatomy 125 Spring 2011 Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) The median cubital vein connects the and veins. A)
Exam 2 Version A Anatomy 125 Spring 2011 Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) The median cubital vein connects the and veins. A)
The Cardiovascular System
 11 The Cardiovascular System Yong Jeong, MD, PhD Department of Bio and Brain Engineering The Cardiovascular System A closed system of the heart and blood vessels The heart pumps blood Blood vessels allow
11 The Cardiovascular System Yong Jeong, MD, PhD Department of Bio and Brain Engineering The Cardiovascular System A closed system of the heart and blood vessels The heart pumps blood Blood vessels allow
The Lymphoid System Pearson Education, Inc.
 23 The Lymphoid System Introduction The lymphoid system consists of: Lymph Lymphatic vessels Lymphoid organs An Overview of the Lymphoid System Lymph consists of: Interstitial fluid Lymphocytes Macrophages
23 The Lymphoid System Introduction The lymphoid system consists of: Lymph Lymphatic vessels Lymphoid organs An Overview of the Lymphoid System Lymph consists of: Interstitial fluid Lymphocytes Macrophages
Femoral Artery. Its entrance to the thigh Position Midway between ASIS and pubic symphysis
 Lower Limb Vessels Lecture Objectives Describe the major arteries of the lower limb. Describe the deep and superficial veins of the lower limb. Describe the topographical relationships of the arteries
Lower Limb Vessels Lecture Objectives Describe the major arteries of the lower limb. Describe the deep and superficial veins of the lower limb. Describe the topographical relationships of the arteries
Dr. Weyrich G07: Superior and Posterior Mediastina. Reading: 1. Gray s Anatomy for Students, chapter 3
 Dr. Weyrich G07: Superior and Posterior Mediastina Reading: 1. Gray s Anatomy for Students, chapter 3 Objectives: 1. Subdivisions of mediastinum 2. Structures in Superior mediastinum 3. Structures in Posterior
Dr. Weyrich G07: Superior and Posterior Mediastina Reading: 1. Gray s Anatomy for Students, chapter 3 Objectives: 1. Subdivisions of mediastinum 2. Structures in Superior mediastinum 3. Structures in Posterior
Welcome to the Structure & Development Dissector. Section I
 Welcome to the Structure & Development Dissector The vast majority of questions will be drawn from structures present in the checklist; however, we reserve the right to use a structure or two that is not
Welcome to the Structure & Development Dissector The vast majority of questions will be drawn from structures present in the checklist; however, we reserve the right to use a structure or two that is not
Chapter 13. Cardiovascular System
 Chapter 13 Cardiovascular System 1 Introduction A. The cardiovascular system consists of the heart and vessels (arteries, capillaries and veins.) B. A functional cardiovascular system is vital for supplying
Chapter 13 Cardiovascular System 1 Introduction A. The cardiovascular system consists of the heart and vessels (arteries, capillaries and veins.) B. A functional cardiovascular system is vital for supplying
The Heart. The Heart A muscular double pump. The Pulmonary and Systemic Circuits
 C H A P T E R 19 The Heart The Heart A muscular double pump circuit takes blood to and from the lungs Systemic circuit vessels transport blood to and from body tissues Atria receive blood from the pulmonary
C H A P T E R 19 The Heart The Heart A muscular double pump circuit takes blood to and from the lungs Systemic circuit vessels transport blood to and from body tissues Atria receive blood from the pulmonary
Mediastinum and pericardium
 Mediastinum and pericardium Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com The mediastinum: is the central compartment of the thoracic cavity surrounded by
Mediastinum and pericardium Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com The mediastinum: is the central compartment of the thoracic cavity surrounded by
Misc Anatomy. Upper Limb! 2. Lower Limb! 5. Venous Drainage! Head & neck! 8
 Misc Anatomy Upper Limb! 2 Arteries!... 2 Veins!... 2 Spaces!... 4 Lower Limb! 5 Arteries!... 5 Venous Drainage!... 6 Spaces!... 7 Head & neck! 8 Artery!... 8 Ultrasound View for IJ CVL!... 8 Arteries
Misc Anatomy Upper Limb! 2 Arteries!... 2 Veins!... 2 Spaces!... 4 Lower Limb! 5 Arteries!... 5 Venous Drainage!... 6 Spaces!... 7 Head & neck! 8 Artery!... 8 Ultrasound View for IJ CVL!... 8 Arteries
Brain ميهاربا لض اف دمح ا د The Meninges 1- Dura Mater of the Brain endosteal layer does not extend meningeal layer falx cerebri tentorium cerebelli
 .احمد د فاضل ابراهيم Lecture 15 Brain The Meninges Three protective membranes or meninges surround the brain in the skull: the dura mater, the arachnoid mater, and the pia mater 1- Dura Mater of the Brain
.احمد د فاضل ابراهيم Lecture 15 Brain The Meninges Three protective membranes or meninges surround the brain in the skull: the dura mater, the arachnoid mater, and the pia mater 1- Dura Mater of the Brain
Cardiovascular system:
 Cardiovascular system: Mediastinum: The mediastinum: lies between the right and left pleura and lungs. It extends from the sternum in front to the vertebral column behind, and from the root of the neck
Cardiovascular system: Mediastinum: The mediastinum: lies between the right and left pleura and lungs. It extends from the sternum in front to the vertebral column behind, and from the root of the neck
Circulatory System: Introduction. Dr. Carmen E. Rexach Anatomy 35 Mt. San Antonio College
 Circulatory System: Introduction Dr. Carmen E. Rexach Anatomy 35 Mt. San Antonio College Components Cardiovascular system Lymphatic system Cardiovascular system Heart, blood vessels, blood Functions: transport
Circulatory System: Introduction Dr. Carmen E. Rexach Anatomy 35 Mt. San Antonio College Components Cardiovascular system Lymphatic system Cardiovascular system Heart, blood vessels, blood Functions: transport
Copy Right- Hongqi ZHANG-Department of Anatomy-Fudan University. Systematic Anatomy. Angiology Part 4. Veins. Dr.Hongqi Zhang ( 张红旗 )
 Systematic Anatomy Angiology Part 4 Veins Dr.Hongqi Zhang ( 张红旗 ) Email: zhanghq58@126.com 1 General introduction of the veins Vessel which return the blood back to atrium No pulsation,veneous blood, metabolic
Systematic Anatomy Angiology Part 4 Veins Dr.Hongqi Zhang ( 张红旗 ) Email: zhanghq58@126.com 1 General introduction of the veins Vessel which return the blood back to atrium No pulsation,veneous blood, metabolic
Artery 1 Head and Thoracic Arteries. Arrange the parts in the order blood flows through them.
 Artery 1 Head and Thoracic Arteries 1. Given the following parts of the aorta: 1. abdominal aorta 2. aortic arch 3. ascending aorta 4. thoracic aorta Arrange the parts in the order blood flows through
Artery 1 Head and Thoracic Arteries 1. Given the following parts of the aorta: 1. abdominal aorta 2. aortic arch 3. ascending aorta 4. thoracic aorta Arrange the parts in the order blood flows through
Lab 1 Blood Composition and formed elements
 Lab 1 Blood Composition and formed elements Plasma 55% of whole blood 90% water 8% proteins from liver 2% misc. Nutrients: AA, glucose, lipids vitamins, minerals Wastes: urea, uric acid, creatine, ammonium
Lab 1 Blood Composition and formed elements Plasma 55% of whole blood 90% water 8% proteins from liver 2% misc. Nutrients: AA, glucose, lipids vitamins, minerals Wastes: urea, uric acid, creatine, ammonium
This is not a required assignment but it is recommended.
 SU 12 Name: This is not a required assignment but it is recommended. BIO 116 - Anatomy & Physiology II Practice Assignment 2 - The Respiratory and Cardiovascular Systems 1. The exchange of oxygen and carbon
SU 12 Name: This is not a required assignment but it is recommended. BIO 116 - Anatomy & Physiology II Practice Assignment 2 - The Respiratory and Cardiovascular Systems 1. The exchange of oxygen and carbon
ACTIVITY 9: BLOOD AND HEART BLOOD
 ACTIVITY 9: BLOOD AND HEART OBJECTIVES: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapters 21 & 22, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 4e. All text references are for this textbook. Read dissection instructions BEFORE YOU
ACTIVITY 9: BLOOD AND HEART OBJECTIVES: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapters 21 & 22, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 4e. All text references are for this textbook. Read dissection instructions BEFORE YOU
Read Chapters 21 & 22, McKinley et al
 ACTIVITY 9: BLOOD AND HEART OBJECTIVES: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapters 21 & 22, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 5e. All text references are for this textbook. Read dissection instructions BEFORE YOU
ACTIVITY 9: BLOOD AND HEART OBJECTIVES: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapters 21 & 22, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 5e. All text references are for this textbook. Read dissection instructions BEFORE YOU
Breathing. Heart Rate
 Breathing Heart Rate Inspiration Expiration (Pressos not Stretched) Heart Rate increases with inspiration (Pressos Stretched) Heart Rate decreases with expiration Upside Down (Pressos Stretched) HR Decreases
Breathing Heart Rate Inspiration Expiration (Pressos not Stretched) Heart Rate increases with inspiration (Pressos Stretched) Heart Rate decreases with expiration Upside Down (Pressos Stretched) HR Decreases
SYLLABUS BDS I PROFESSIONAL GENERAL HUMAN ANATOMY INCLUDING EMBRYOLOGY AND HISTOLOGY
 GENERAL HUMAN ANATOMY INCLUDING EMBRYOLOGY AND HISTOLOGY I. General Anatomy 1. Anatomical terms 2. Skin, superficial fascia & deep fascia 3. Cardiovascular system, portal system, collateral circulation
GENERAL HUMAN ANATOMY INCLUDING EMBRYOLOGY AND HISTOLOGY I. General Anatomy 1. Anatomical terms 2. Skin, superficial fascia & deep fascia 3. Cardiovascular system, portal system, collateral circulation
First BHMS Anatomy Question Papers Calicut University
 First BHMS Anatomy Question Papers Calicut University 1996-2000 FIRST B.H.M.S. DEGREE EXAMINATION, DECEMBER 1996 Time: Three Hours Maximum: 100 Marks Answer any five questions. Draw diagrams wherever needed.
First BHMS Anatomy Question Papers Calicut University 1996-2000 FIRST B.H.M.S. DEGREE EXAMINATION, DECEMBER 1996 Time: Three Hours Maximum: 100 Marks Answer any five questions. Draw diagrams wherever needed.
The posterior abdominal wall. Prof. Oluwadiya KS
 The posterior abdominal wall Prof. Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.sitesled.com Posterior Abdominal Wall Lumbar vertebrae and discs. Muscles opsoas, quadratus lumborum, iliacus, transverse, abdominal wall
The posterior abdominal wall Prof. Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.sitesled.com Posterior Abdominal Wall Lumbar vertebrae and discs. Muscles opsoas, quadratus lumborum, iliacus, transverse, abdominal wall
Cardiovascular System
 Hole s Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology David Shier Jackie Butler Ricki Lewis Created by Dr. Melissa Eisenhauer Head Athletic Trainer/Assistant Professor Trevecca Nazarene University Chapter 13
Hole s Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology David Shier Jackie Butler Ricki Lewis Created by Dr. Melissa Eisenhauer Head Athletic Trainer/Assistant Professor Trevecca Nazarene University Chapter 13
Bio& 242, Unit 3/ Lab 4 Blood Vessels, Lymphatic System and Blood Pressure G. Blevins/ G. Brady Summer 2009
 Bio& 242, Unit 3/ Lab 4 Blood Vessels, Lymphatic System and Blood Pressure G. Blevins/ G. Brady Summer 2009 Major Arteries and for arteries and veins with common names your answer must include either artery
Bio& 242, Unit 3/ Lab 4 Blood Vessels, Lymphatic System and Blood Pressure G. Blevins/ G. Brady Summer 2009 Major Arteries and for arteries and veins with common names your answer must include either artery
c) What is the name of RBC (erythrocyte) formation? Where do blood cells form?
 UNIT 6: CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM 1) List the three general functions of BLOOD. REVIEW QUESTIONS Blood 2) a) What are the three formed elements /cellular elements in blood? b) Describe the composition of the
UNIT 6: CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM 1) List the three general functions of BLOOD. REVIEW QUESTIONS Blood 2) a) What are the three formed elements /cellular elements in blood? b) Describe the composition of the
DESCRIPTION: This is the part of the trunk, which is located between the root of the neck and the superior border of the abdominal region.
 1 THE THORACIC REGION DESCRIPTION: This is the part of the trunk, which is located between the root of the neck and the superior border of the abdominal region. SHAPE : T It has the shape of a truncated
1 THE THORACIC REGION DESCRIPTION: This is the part of the trunk, which is located between the root of the neck and the superior border of the abdominal region. SHAPE : T It has the shape of a truncated
THE VESSELS OF BLOOD CIRCULATION
 THE VESSELS OF BLOOD CIRCULATION scientistcindy.com /the-vessels-of-blood-circulation.html NOTE: You should familiarize yourself with the anatomy of the heart and have a good understanding of the flow
THE VESSELS OF BLOOD CIRCULATION scientistcindy.com /the-vessels-of-blood-circulation.html NOTE: You should familiarize yourself with the anatomy of the heart and have a good understanding of the flow
Human Anatomy, First Edition
 Human Anatomy, First Edition McKinley & O'Loughlin Chapter 22 : Heart 1 Functions of the Heart Center of the cardiovascular system, the heart. Connects to blood vessels that transport blood between the
Human Anatomy, First Edition McKinley & O'Loughlin Chapter 22 : Heart 1 Functions of the Heart Center of the cardiovascular system, the heart. Connects to blood vessels that transport blood between the
Veins of the Face and the Neck
 Veins of the Face and the Neck Facial Vein The facial vein is formed at the medial angle of the eye by the union of the supraorbital and supratrochlear veins. connected through the ophthalmic veins with
Veins of the Face and the Neck Facial Vein The facial vein is formed at the medial angle of the eye by the union of the supraorbital and supratrochlear veins. connected through the ophthalmic veins with
human anatomy 2016 lecture thirteen Dr meethak ali ahmed neurosurgeon
 Heart The heart is a hollow muscular organ that is somewhat pyramid shaped and lies within the pericardium in the mediastinum. It is connected at its base to the great blood vessels but otherwise lies
Heart The heart is a hollow muscular organ that is somewhat pyramid shaped and lies within the pericardium in the mediastinum. It is connected at its base to the great blood vessels but otherwise lies
Fig. A.1. Frontal. plane. Transverse. plane. Sagittal plane. Copyright McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction or display.
 Fig. A.1 Frontal plane Transverse plane Sagittal plane McGraw-Hill Education/Joe DeGrandis Fig. A.2 (a) Sagittal section (b) Frontal section (c) Transverse section Table A.1 Fig. A.3 Cephalic r. (head)
Fig. A.1 Frontal plane Transverse plane Sagittal plane McGraw-Hill Education/Joe DeGrandis Fig. A.2 (a) Sagittal section (b) Frontal section (c) Transverse section Table A.1 Fig. A.3 Cephalic r. (head)
2. capillaries - allow exchange of materials between blood and tissue fluid
 Chapter 19 - Vascular System A. categories and general functions: 1. arteries - carry blood away from heart 2. capillaries - allow exchange of materials between blood and tissue fluid 3. veins - return
Chapter 19 - Vascular System A. categories and general functions: 1. arteries - carry blood away from heart 2. capillaries - allow exchange of materials between blood and tissue fluid 3. veins - return
Cat Dissection. Muscular Labs
 Cat Dissection Muscular Labs Tibialis anterior External oblique Pectroalis minor Gastrocnemius Sartorius Pectoralis major Gastrocnemius Semitendinosis Sartorius External oblique Trapezius Latissimus dorsi
Cat Dissection Muscular Labs Tibialis anterior External oblique Pectroalis minor Gastrocnemius Sartorius Pectoralis major Gastrocnemius Semitendinosis Sartorius External oblique Trapezius Latissimus dorsi
Anatomy of the Blood Vessels
 Biology 212: Anatomy and Physiology II Anatomy of the Blood Vessels References: Saladin, KS: Anatomy and Physiology, The Unity of Form and Function 8 th (2018). Required reading before beginning this lab:
Biology 212: Anatomy and Physiology II Anatomy of the Blood Vessels References: Saladin, KS: Anatomy and Physiology, The Unity of Form and Function 8 th (2018). Required reading before beginning this lab:
ANATOMY 2 LEARNING TARGETS
 ANATOMY 2 LEARNING TARGETS NERVOUS SYSTEM 1. Distinguish between the parts of the central nervous system and the peripheral nervous system. 2. Identify the neuron as the basic structural and functional
ANATOMY 2 LEARNING TARGETS NERVOUS SYSTEM 1. Distinguish between the parts of the central nervous system and the peripheral nervous system. 2. Identify the neuron as the basic structural and functional
Cardiovascular Anatomy Dr. Gary Mumaugh
 Cardiovascular Anatomy Dr. Gary Mumaugh Location of Heart Approximately the size of your fist Location o Superior surface of diaphragm o Left of the midline in mediastinum o Anterior to the vertebral column,
Cardiovascular Anatomy Dr. Gary Mumaugh Location of Heart Approximately the size of your fist Location o Superior surface of diaphragm o Left of the midline in mediastinum o Anterior to the vertebral column,
This lab activity is aligned with Visible Body s A&P app. Learn more at visiblebody.com/professors
 1 This lab activity is aligned with Visible Body s A&P app. Learn more at visiblebody.com/professors 2 PRE-LAB EXERCISES: A. Watch the video 29.1 Heart Overview and make the following observations: 1.
1 This lab activity is aligned with Visible Body s A&P app. Learn more at visiblebody.com/professors 2 PRE-LAB EXERCISES: A. Watch the video 29.1 Heart Overview and make the following observations: 1.
Anatomy of the Heart. Figure 20 2c
 Anatomy of the Heart Figure 20 2c Pericardium & Myocardium Remember, the heart sits in it s own cavity, known as the mediastinum. The heart is surrounded by the Pericardium, a double lining of the pericardial
Anatomy of the Heart Figure 20 2c Pericardium & Myocardium Remember, the heart sits in it s own cavity, known as the mediastinum. The heart is surrounded by the Pericardium, a double lining of the pericardial
1. Which of the following blood vessels has a thin elastic layer? A. Aorta. B. Pulmonary artery. C. Posterior vena cava. D. Mesenteric capillary.
 CIRCULATORY SYSTEM 1. Which of the following blood vessels has a thin elastic layer? A. Aorta. B. Pulmonary artery. C. Posterior vena cava. D. Mesenteric capillary. 2. Capillary beds are equipped with
CIRCULATORY SYSTEM 1. Which of the following blood vessels has a thin elastic layer? A. Aorta. B. Pulmonary artery. C. Posterior vena cava. D. Mesenteric capillary. 2. Capillary beds are equipped with
LECTURE 5. Anatomy of the heart
 LECTURE 5. Anatomy of the heart Main components of the CVS: Heart Blood circulatory system arterial compartment haemomicrocirculatory (=microvascular) compartment venous compartment Lymphatic circulatory
LECTURE 5. Anatomy of the heart Main components of the CVS: Heart Blood circulatory system arterial compartment haemomicrocirculatory (=microvascular) compartment venous compartment Lymphatic circulatory
Approximately the size of your fist Location Superior surface of diaphragm Left of the midline in mediastinum Anterior to the vertebral column,
 Dr. Gary Mumaugh Approximately the size of your fist Location Superior surface of diaphragm Left of the midline in mediastinum Anterior to the vertebral column, posterior to the sternum Posteriorly the
Dr. Gary Mumaugh Approximately the size of your fist Location Superior surface of diaphragm Left of the midline in mediastinum Anterior to the vertebral column, posterior to the sternum Posteriorly the
END-SEMESTER EXAM 2018 ANATOMY, HISTOLOGY AND EMBRYOLOGY FACULTY OF MEDICINE, 2 ND SEMESTER
 University of Szeged, Faculty of Medicine Department of Anatomy, Histology and Embryology Chairman: Prof. Antal Nógrádi MD, PhD, DSc Kossuth L. sgt. 40., H-6724 Szeged, Hungary Tel.: +36-62-545-665 P.
University of Szeged, Faculty of Medicine Department of Anatomy, Histology and Embryology Chairman: Prof. Antal Nógrádi MD, PhD, DSc Kossuth L. sgt. 40., H-6724 Szeged, Hungary Tel.: +36-62-545-665 P.
AP2 Lab 1 - Blood & Heart
 AP2 Lab 1 - Blood & Heart Project 1 - Formed Elements Identification & Recognition See fig. 17.10 and Table 17.2. Instructor may also provide other images. Note: See Fig. 17.11 All formed elements are
AP2 Lab 1 - Blood & Heart Project 1 - Formed Elements Identification & Recognition See fig. 17.10 and Table 17.2. Instructor may also provide other images. Note: See Fig. 17.11 All formed elements are
Heart Anatomy. 7/5/02 Stephen G Davenport 1
 Heart Anatomy Copyright 1999, Stephen G. Davenport, No part of this publication may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system, or transmitted, in any form without prior written permission. 7/5/02 Stephen
Heart Anatomy Copyright 1999, Stephen G. Davenport, No part of this publication may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system, or transmitted, in any form without prior written permission. 7/5/02 Stephen
Cardiovascular System. Biology 105 Lecture 15 Chapter 12
 Cardiovascular System Biology 105 Lecture 15 Chapter 12 Outline I. Functions of cardiovascular system II. Components of the cardiovascular system: I. Blood vessels II. Heart III. Regulation of the heartbeat
Cardiovascular System Biology 105 Lecture 15 Chapter 12 Outline I. Functions of cardiovascular system II. Components of the cardiovascular system: I. Blood vessels II. Heart III. Regulation of the heartbeat
The Cardiovascular and Lymphatic Systems Cardiovascular System Blood Vessels Blood Vessels Arteries Arteries Arteries
 CH 12 The Cardiovascular and s The Cardiovascular and s OUTLINE: Cardiovascular System Blood Vessels Blood Pressure Cardiovascular System The cardiovascular system is composed of Blood vessels This system
CH 12 The Cardiovascular and s The Cardiovascular and s OUTLINE: Cardiovascular System Blood Vessels Blood Pressure Cardiovascular System The cardiovascular system is composed of Blood vessels This system
A closed system of the heart/blood. Function: The heart pumps blood. Blood vessels allow blood to circulate throughout the body
 A closed system of the heart/blood The heart pumps blood It is no more than a transportation pump Blood vessels allow blood to circulate throughout the body MILES of blood vessels intricate network At
A closed system of the heart/blood The heart pumps blood It is no more than a transportation pump Blood vessels allow blood to circulate throughout the body MILES of blood vessels intricate network At
Biology 105 Human Biology QZM CVS. Cardiovascular System. Name these Vessels, Valves and Chambers
 Cardiovascular System Name these Vessels, Valves and Chambers 1. The heart and pericardium are located within the and medial to the A) pleural cavities B) peritoneal cavity C) cardiac skeleton D) mediastinum
Cardiovascular System Name these Vessels, Valves and Chambers 1. The heart and pericardium are located within the and medial to the A) pleural cavities B) peritoneal cavity C) cardiac skeleton D) mediastinum
Scrub In: Red blood cells are called: Which component of blood is necessary for the initiation of the blood clotting process:
 Scrub In: Red blood cells are called: a. erythrocytes b. leukocytes c. melanocytes d. thrombocytes Which component of blood is necessary for the initiation of the blood clotting process: a. erythrocytes
Scrub In: Red blood cells are called: a. erythrocytes b. leukocytes c. melanocytes d. thrombocytes Which component of blood is necessary for the initiation of the blood clotting process: a. erythrocytes
Cardiovascular. Function of the cardiovascular system is to transport blood containing: Nutrients Waste Hormones Immune cells Oxygen
 Cardiovascular The Cardiovascular System - Arteries Arteries Cardiovascular System Function of the cardiovascular system is to transport blood containing: Carry blood away from heart Carotid arteries Deliver
Cardiovascular The Cardiovascular System - Arteries Arteries Cardiovascular System Function of the cardiovascular system is to transport blood containing: Carry blood away from heart Carotid arteries Deliver
Chapter 14. Circulatory System Images. VT-122 Anatomy & Physiology II
 Chapter 14 Circulatory System Images VT-122 Anatomy & Physiology II The mediastinum Dog heart Dog heart Cat heart Dog heart ultrasound Can see pericardium as distinct bright line Pericardial effusion Fluid
Chapter 14 Circulatory System Images VT-122 Anatomy & Physiology II The mediastinum Dog heart Dog heart Cat heart Dog heart ultrasound Can see pericardium as distinct bright line Pericardial effusion Fluid
IP UNIVERSITATEA DE STAT DE MEDICINĂ ŞI FARMACIE NICOLAE TESTEMIŢANU FACULTATEA MEDICINĂ nr. 1 CATEDRA DE ANATOMIE A OMULUI
 IP UNIVERSITATEA DE STAT DE MEDICINĂ ŞI FARMACIE NICOLAE TESTEMIŢANU FACULTATEA MEDICINĂ nr. 1 CATEDRA DE ANATOMIE A OMULUI MD 2004, Chişinău, Republica Moldova, bd. Ştefan cel Mare, 192, tel.: +373.22.205349
IP UNIVERSITATEA DE STAT DE MEDICINĂ ŞI FARMACIE NICOLAE TESTEMIŢANU FACULTATEA MEDICINĂ nr. 1 CATEDRA DE ANATOMIE A OMULUI MD 2004, Chişinău, Republica Moldova, bd. Ştefan cel Mare, 192, tel.: +373.22.205349
Chapter 5: Other mediastinal structures. The Large Arteries. The Aorta. Ascending aorta
 Chapter 5: Other mediastinal structures The Large Arteries The Aorta The aorta is the main arterial trunk of the systemic circulation and in the healthy state its wall contain a large amount of yellow
Chapter 5: Other mediastinal structures The Large Arteries The Aorta The aorta is the main arterial trunk of the systemic circulation and in the healthy state its wall contain a large amount of yellow
AN ATOMY OF THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM
 Student Name CHAPTER 18 AN ATOMY OF THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM T he heart is actually two pumps one moves blood to the lungs, the other pushes it out into the body. These two functions seem rather elementary
Student Name CHAPTER 18 AN ATOMY OF THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM T he heart is actually two pumps one moves blood to the lungs, the other pushes it out into the body. These two functions seem rather elementary
LYMPHATIC ANATOMY LAB. BIO 139 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY II MARY CATHERINE FLATH, Ph.D.
 LYMPHATIC ANATOMY LAB BIO 139 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY II MARY CATHERINE FLATH, Ph.D. THE LYMPHATIC SYSTEM ORGANS PRIMARY BONE MARROW THYMUS SECONDARY LYMPH NODES SPLEEN FUNCTIONS CONTROL DISEASE TRANSPORT
LYMPHATIC ANATOMY LAB BIO 139 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY II MARY CATHERINE FLATH, Ph.D. THE LYMPHATIC SYSTEM ORGANS PRIMARY BONE MARROW THYMUS SECONDARY LYMPH NODES SPLEEN FUNCTIONS CONTROL DISEASE TRANSPORT
THE HEART. A. The Pericardium - a double sac of serous membrane surrounding the heart
 THE HEART I. Size and Location: A. Fist-size weighing less than a pound (250 to 350 grams). B. Located in the mediastinum between the 2 nd rib and the 5 th intercostal space. 1. Tipped to the left, resting
THE HEART I. Size and Location: A. Fist-size weighing less than a pound (250 to 350 grams). B. Located in the mediastinum between the 2 nd rib and the 5 th intercostal space. 1. Tipped to the left, resting
The cardiovascular system
 The cardiovascular system Components of the Cardiovascular system Heart Vessels: Arteries Capillaries Veins Functions of CVS: Transportation system where blood is the transporting vehicle Carries oxygen,
The cardiovascular system Components of the Cardiovascular system Heart Vessels: Arteries Capillaries Veins Functions of CVS: Transportation system where blood is the transporting vehicle Carries oxygen,
Histology of Blood Vessels and Bone Marrow. A. Human Heart Model B. Preserved Sheep Heart. Vessels Cranial to the Diaphragm
 Name Date Introduction to Dissection Lab Exercise #1: Lab Exercise #2: Lab Exercise #3: Lab Exercise #4: Lab Exercise #5: Lab Exercise #6: Blood Formed Elements Histology of Blood Vessels and Bone Marrow
Name Date Introduction to Dissection Lab Exercise #1: Lab Exercise #2: Lab Exercise #3: Lab Exercise #4: Lab Exercise #5: Lab Exercise #6: Blood Formed Elements Histology of Blood Vessels and Bone Marrow
Chapter 20: Cardiovascular System: The Heart
 Chapter 20: Cardiovascular System: The Heart I. Functions of the Heart A. List and describe the four functions of the heart: 1. 2. 3. 4. II. Size, Shape, and Location of the Heart A. Size and Shape 1.
Chapter 20: Cardiovascular System: The Heart I. Functions of the Heart A. List and describe the four functions of the heart: 1. 2. 3. 4. II. Size, Shape, and Location of the Heart A. Size and Shape 1.
The Cardiovascular System (Part II)
 The Cardiovascular System (Part II) 黃敏銓 mchuang@ntu.edu.tw 解剖學暨細胞生物學研究所 1 Development of veins Three paired veins drain into the tubular heart of a 4-week embryo Vitelline veins: poorly oxygenated blood
The Cardiovascular System (Part II) 黃敏銓 mchuang@ntu.edu.tw 解剖學暨細胞生物學研究所 1 Development of veins Three paired veins drain into the tubular heart of a 4-week embryo Vitelline veins: poorly oxygenated blood
Mediastinum It is a thick movable partition between the two pleural sacs & lungs. It contains all the structures which lie
 Dr Jamila EL medany OBJECTIVES At the end of the lecture, students should be able to: Define the Mediastinum. Differentiate between the divisions of the mediastinum. List the boundaries and contents of
Dr Jamila EL medany OBJECTIVES At the end of the lecture, students should be able to: Define the Mediastinum. Differentiate between the divisions of the mediastinum. List the boundaries and contents of
