Development of the Great Vessels and Conduc6on Tissue
|
|
|
- Milton Bond
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Development of the Great Vessels and Conduc6on Tissue
2 Development of the heart fields h:p://php.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/ index.php?6tle=advanced_- _Heart_Fields! 2
3 Septa6on of the Bulbus Cordis Bulbus Cordis AV Canal Ventricle Looking at a sagital sec6on of the heart early in development the bulbus cordis is con6nuous with the ventricle which is con6nuous with the atria. As the AV canal shios to the right the bulbus move to the right as well.
4 Septa6on of the Bulbus Cordis A P A P The next three slides make the point via cross sec6ons that the aorta and pulmonary arteries rotate around each other. This means the septum between them changes posi6on from superior to inferior as well.
5 Septa6on of the Bulbus Cordis A P A P
6 Septa6on of the Bulbus Cordis A P P A
7 Migra6on of neural crest cells Neural crest cells migrate from the 3ed, 4th and 6th pharyngeal arches to form some of the popula6on of cells forming the aor6copulmonary septum.
8 Septa6on of the Bulbus Cordis Truncal (Conal) Swellings Bulbus Cordis The cardiac jelly in the region of the truncus and conus adds the neural crest cells and expands as truncal swellings.
9 Septa6on of the Bulbus Cordis Aorticopulmonary septum These swellings grow toward each other to meet and form the septum between the aorta and pulmonary artery. Aorta Pulmonary
10 Septa6on of the Bulbus Cordis 1 2 Anterior The aor6copulmonary septum then rotates as it moves inferiorly. However, the exact mechanism for that rota6on remains unclear.
11 However, the aor6copulmonary septum must form properly for the IV septum to be completed. Septa6on of the Bulbus Cordis Aorta Pulmonary Conal Ridges IV Foramen Membranous Interventricular Septum Endocarial Cushion Muscular IV Septum
12 Embryonic Circula6on Common Cardinal Vein Dorsal Aorta Anterior Cardinal Vein Brain and Spinal Cord Posterior Cardinal Vein Umbilical Aor6c Arches Yolk Sac Umbilical Vein Ventricle Atria Vitelline & Vein Blood leaves the truncus and moves to the aor6c arches. There is an aor6c arch for each pharyngeal arch.
13 Development of the Arteries Aor6c Sac Dorsal Aorta Ventral Aorta 1 st Aor6c Arch 2 nd Aor6c Arch 3 rd Aor6c Arch 4 th Aor6c Arch 5 th Aor6c Arch 6 th Aor6c Arch Internal External R. Common R. Pulmonary Pulmonary Trunk R. Subclavian L. Pulmonary Ductus Arteriosus 7 th Intersegmental Descending Aorta L. Subclavian They can be depicted this way for descrip6ve purposed explaining the fate of the arches.
14 Development of the Arteries Dorsal Aorta Ventral Aorta 1 st Aor6c Arch 2 nd Aor6c Arch 3 rd Aor6c Arch 4 th Aor6c Arch 5 th Aor6c Arch 6 th Aor6c Arch Aor6c Sac 7 th Intersegmental The first arch degenerates shortly aoer the second arch develops.
15 Development of the Arteries Dorsal Aorta Ventral Aorta 1 st Aor6c Arch 2 nd Aor6c Arch 3 rd Aor6c Arch 4 th Aor6c Arch 5 th Aor6c Arch 6 th Aor6c Arch Aor6c Sac 7 th Intersegmental The second arch degenerates shortly aoer the third arch develops
16 The distal third arch and the distal dorsal aorta form the internal caro6d artery on both sides of the body. Development of the Arteries Aor6c Sac Dorsal Aorta Ventral Aorta 1 st Aor6c Arch 2 nd Aor6c Arch 3 rd Aor6c Arch 4 th Aor6c Arch 5 th Aor6c Arch 6 th Aor6c Arch Internal External R. Common R. Pulmonary Pulmonary Trunk R. Subclavian L. Pulmonary Ductus Arteriosus 7 th Intersegmental Descending Aorta L. Subclavian
17 The proximal third arch and the ventral aorta between the 3rd and 4th arches forms the common caro6d artery on both sides of the body. Development of the Arteries Aor6c Sac Dorsal Aorta Ventral Aorta 1 st Aor6c Arch 2 nd Aor6c Arch 3 rd Aor6c Arch 4 th Aor6c Arch 5 th Aor6c Arch 6 th Aor6c Arch Internal External R. Common R. Pulmonary Pulmonary Trunk R. Subclavian L. Pulmonary Ductus Arteriosus 7 th Intersegmental Descending Aorta L. Subclavian
18 Development of the Arteries Aor6c Sac Dorsal Aorta Ventral Aorta 1 st Aor6c Arch 2 nd Aor6c Arch 3 rd Aor6c Arch 4 th Aor6c Arch 5 th Aor6c Arch 6 th Aor6c Arch Internal External R. Common R. Pulmonary Pulmonary Trunk R. Subclavian L. Pulmonary Ductus Arteriosus 7 th Intersegmental Descending Aorta L. Subclavian New vessels arise in the middle of the 3rd arch and form the external caro6d arteries.
19 Development of the Arteries Aor6c Sac Dorsal Aorta Ventral Aorta 1 st Aor6c Arch 2 nd Aor6c Arch 3 rd Aor6c Arch 4 th Aor6c Arch 5 th Aor6c Arch 6 th Aor6c Arch Internal External R. Common R. Pulmonary Pulmonary Trunk R. Subclavian L. Pulmonary Ductus Arteriosus 7 th Intersegmental Descending Aorta L. Subclavian The truncus and thefourth arch on the leo along with the dorsal aorta form the ascending aorta, the arch of the aorta and the descending aorta respec6vely.
20 Development of the Arteries Aor6c Sac Dorsal Aorta Ventral Aorta 1 st Aor6c Arch 2 nd Aor6c Arch 3 rd Aor6c Arch 4 th Aor6c Arch 5 th Aor6c Arch 6 th Aor6c Arch Internal External R. Common R. Pulmonary Pulmonary Trunk R. Subclavian L. Pulmonary Ductus Arteriosus 7 th Intersegmental Descending Aorta L. Subclavian ON the right the 4th arch and the dorsal aorta and 7th intersegmental artery form the right subclavian artery.
21 Development of the Arteries Aor6c Sac Dorsal Aorta Ventral Aorta 1 st Aor6c Arch 2 nd Aor6c Arch 3 rd Aor6c Arch 4 th Aor6c Arch 5 th Aor6c Arch 6 th Aor6c Arch Internal External R. Common R. Pulmonary Pulmonary Trunk R. Subclavian L. Pulmonary Ductus Arteriosus 7 th Intersegmental Descending Aorta L. Subclavian The 7th intersegmental artery gives rise to the leo subclavian artery.
22 Development of the Arteries Aor6c Sac Dorsal Aorta Ventral Aorta 1 st Aor6c Arch 2 nd Aor6c Arch 3 rd Aor6c Arch 4 th Aor6c Arch 5 th Aor6c Arch 6 th Aor6c Arch Internal External R. Common R. Pulmonary Pulmonary Trunk R. Subclavian L. Pulmonary Ductus Arteriosus 7 th Intersegmental Descending Aorta L. Subclavian The right ventral aorta between the 4th and 6th arches forms the brachiocephalic artery. Which then connects the aorta to the right common caro6d artery and the right subclavian artery.
23 Development of the Arteries Aor6c Sac Dorsal Aorta Ventral Aorta 1 st Aor6c Arch 2 nd Aor6c Arch 3 rd Aor6c Arch 4 th Aor6c Arch 5 th Aor6c Arch 6 th Aor6c Arch Internal External R. Common R. Pulmonary Pulmonary Trunk R. Subclavian L. Pulmonary Ductus Arteriosus 7 th Intersegmental Descending Aorta L. Subclavian The proximal sixth arch forms the right and leo pulmonary arteries along with some of the main pulmonary trunk.
24 Development of the Arteries Aor6c Sac Dorsal Aorta Ventral Aorta 1 st Aor6c Arch 2 nd Aor6c Arch 3 rd Aor6c Arch 4 th Aor6c Arch 5 th Aor6c Arch 6 th Aor6c Arch Internal External R. Common Brachiocephalic R. Pulmonary Pulmonary Trunk R. Subclavian L. Pulmonary Ductus Arteriosus 7 th Intersegmental Descending Aorta L. Subclavian On the right the distal sixth arch degenerates while on the right it remains as a shunt to take blood from the pulmonary system to the systemic system in the fetus.
25 Embryonic Circula6on Common Cardinal Vein Dorsal Aorta Anterior Cardinal Vein Brain and Spinal Cord Posterior Cardinal Vein Umbilical Aor6c Arches Yolk Sac Umbilical Vein Ventricle Atria Vitelline & Vein
26 Development of Veins anterior cardinal vein subclavian vein internal jugular vein r. & l. brachio- cephalic veins sinus venosus external jugular vein coronary sinus common cardinal vein SVC posterior cardinal vein thymicothyroid anastomosis azygos vein In terms of the veins there are the systemic veins ini6ally. They are the common cardinal veins, the anterior cardinal veins and the posterior cardinal veins.
27 Development of Veins anterior cardinal vein subclavian vein internal jugular vein r. & l. brachio- cephalic veins sinus venosus external jugular vein coronary sinus common cardinal vein SVC posterior cardinal vein thymicothyroid anastomosis azygos vein The brachiocephalic veins form from the anterior cardinal on the right and a new system of veins called the thymicothyroid anastomosis on the leo which then drains all the blood from the leo side of the head and neck to the superior vena cava.
28 Development of Veins anterior cardinal vein subclavian vein internal jugular vein r. & l. brachio- cephalic veins sinus venosus external jugular vein coronary sinus common cardinal vein SVC posterior cardinal vein thymicothyroid anastomosis azygos vein The superior vena cava develops from the right anterior cardinal vein and the right common cardinal vein.
29 Development of Veins anterior cardinal vein subclavian vein internal jugular vein r. & l. brachio- cephalic veins sinus venosus external jugular vein coronary sinus common cardinal vein SVC posterior cardinal vein thymicothyroid anastomosis azygos vein The azygos vein develops from the right posterior cardinal vein and runs posterior to the lung root before arching anteriorly to enter the SVC.
30 Development of Veins anterior cardinal vein subclavian vein internal jugular vein r. & l. brachio- cephalic veins sinus venosus external jugular vein coronary sinus common cardinal vein SVC posterior cardinal vein thymicothyroid anastomosis azygos vein The coronary sinus develops from the leo common cardinal vein.
31 Because of the development of many abdominal organs several new vessels appear. Ini6ally there is a posterior cardinal vein. Then there appears a set of subcardinal veins and supracardinal veins. These all contribute to the abdominal and pelvic vasculature. anterior cardinal v. 7 th intersegmental v. right vitelline v. sinus venosus right brachiocephalic SVC hepaac IVC internal jugular v. external jugular v. subclavian v. le? brachiocephalic right umbilical v. azygos v. hemiazygos v. right subcardinal v. subcardinal anastomosis supracardinal v. posterior cardinal anastomosis suprarenal v. renal v. postrenal IVC common iliac veins renal IVC gonadal veins
32 Development of Inferior Vena Cava The inferior vena cava develops from several sources. The renal segment develops from the right subcardinal vein (purple). anterior cardinal v. 7 th intersegmental v. right vitelline v. sinus venosus right brachiocephalic SVC hepaac IVC internal jugular v. external jugular v. subclavian v. le? brachiocephalic right umbilical v. azygos v. hemiazygos v. right subcardinal v. subcardinal anastomosis supracardinal v. posterior cardinal anastomosis suprarenal v. renal v. postrenal IVC common iliac veins renal IVC gonadal veins
33 Development of Inferior Vena Cava The inferior vena cava develops from several sources. The hepa6c segment develops from a new vessel called the hepato- subcardinal anastomosis (yellow). anterior cardinal v. 7 th intersegmental v. right vitelline v. sinus venosus right brachiocephalic SVC hepaac IVC internal jugular v. external jugular v. subclavian v. le? brachiocephalic right umbilical v. azygos v. hemiazygos v. right subcardinal v. subcardinal anastomosis supracardinal v. posterior cardinal anastomosis suprarenal v. renal v. postrenal IVC common iliac veins renal IVC gonadal veins
34 Development of Inferior Vena Cava The most proximal por6on of the inferior vena cava develops from the right vitelline vein (red). anterior cardinal v. 7 th intersegmental v. right vitelline v. sinus venosus right brachiocephalic SVC hepaac IVC internal jugular v. external jugular v. subclavian v. le? brachiocephalic right umbilical v. azygos v. hemiazygos v. right subcardinal v. subcardinal anastomosis supracardinal v. posterior cardinal anastomosis suprarenal v. renal v. postrenal IVC common iliac veins renal IVC gonadal veins
35 Development of Inferior Vena Cava The distal por6on of the inferior vena cava develops from the distal supracardinal vein and perhaps the distal posterior subcardinal vein (navy blue). anterior cardinal v. 7 th intersegmental v. right vitelline v. sinus venosus right brachiocephalic SVC hepaac IVC internal jugular v. external jugular v. subclavian v. le? brachiocephalic right umbilical v. azygos v. hemiazygos v. right subcardinal v. subcardinal anastomosis supracardinal v. posterior cardinal anastomosis suprarenal v. renal v. postrenal IVC common iliac veins renal IVC gonadal veins
36 Development of Portal Vein foregut liver umbilical veins vitelline veins The vitelline and umbilical veins arelocated on either side oof the foregut (yellow).
37 The distal vitelline veins are going to develop anastomoses between the vessels and eventually form the portal vein (and perhaps the superior mesenteric vein) (green). Development of Portal Vein foregut liver umbilical veins vitelline veins
38 Development of Veins foregut hepatic veins liver vitelline veins umbilical veins The proximal vitelline veins will form the main hepa6c veins that empty into the inferior vena cava (orange).
39 Development of Veins foregut inferior vena cava liver vitelline veins umbilical veins The proximal part of the inferior vena cava was derived from the right vitelline vein (red).
40 Development of Veins foregut ductus venosus liver umbilical veins vitelline veins As the liver and kidneys grow they obliterate the right umbilical vein. It degenerates and blood from the placenta flows through the leo umbilical vein. However, as the liver enlarges a new vessel develops so that placental blood will bypass the liver. This is the ductus venosus (blue).
41 Development of Veins foregut ductus venosus ligamentum venosum liver umbilical veins vitelline veins umbilical vein ligamentum teres A birth the umbilical vein and the ductus venosus are no longer patent and become connec6ve 6ssue cords called the ligamentum teres (purple) and the ligamentum venosum (blue) respec6vely.
42 Conversion of fetal circula6on to newborn circula6on Fetal Circula6on Umbilical vein Ductus venosus Inferior vena cava Pulmonary v. Right atrium FO LeO atrium Right ventricle LeO Ventricle Pulmonary A. DA Aorta R & L Pulmonary A Aorta Newborn circula6on Inferior vena cava Right atrium Right ventricle Pulmonary artery Lungs Pulmonary Veins LeO atrium LeO ventricle Aorta
43 At birth there is: Closure of the umbilical vein Closure of the ductus venosus Closure of the foramen ovale Closure of the ductus arteriosus. Increased O 2 par6al pressure. Bradykinins are released from the lungs. Prior to birth prostaglandins keep fetal vasculature dialated.
44 Conduc6on 6ssue!!!!! Ini6al heart myocardium From second heart field The ini6al myocardial mantle gives rise to three rings of 6ssue.
45 SA Node SA node cells develop from mesenchymal cells that are precursors of the sinus venosus 6ssue. Cells Tbx18 posi6ve. Then Tbx3 posi6ve Leads to ac6va6on of CX40 Cx43 Nppa Scn5a All SA node genes mesenchyme
46 AV Node and bundle AV Node cells Cx45 posi6ve Cx30 posi6ve Tbx3 posi6ve AV ring gives rise to AV node cells AV bundle develops from crest of muscular IV septum Rest of AV canal 6ssue becomes annulus fibrosus. Insulates atria from ventricles Otherwise accessory pathways. AV canal 6ssue
47 Mesoderm gives rise to cardiac muscle cells and endocardial cells. Neural crest cells develop into smooth muscle of ouklow tract and cardiac ganglia. Proepicardium epicardium and coronary vessels.
48 TABLE 1 Mean Heart Rates for Embryos at 6 8 Weeks GestaAon! Group Gesta6onal Age (days) Mean Heart Rate ±SD (beats/min)* 1 (n = 456) ± 14 2 (n = 522) ± 15 3 (n = 558) ± 14 4 (n = 628) ± 13 J Clin Ultrasound Jan;26(1):33-6. Embryonic heart rate in early pregnancy. Stefos TI, Lolis DE, So6riadis AJ, Ziakas GV.
49 Early Fetal Heart Rates 6 weeks 7 weeks 8 weeks 9 weeks 10 weeks FHR (bpm) 117 ± ± ± ± ± 6 Włoch A, Rozmus- Warcholinska W, Czuba B, Borowski D, Włoch S, Cnota W, Sodowski K, Szaflik K, Huhta JC. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med Jul;20(7):533-9.
50 Normal fetal heart rate is between 110 and 160 beats per minute (bpm) throughout pregnancy. Later in pregnancy the heart rate may slow as the vagal innerva6on matures.
51 h:p://php.med.unsw.edu.au/embryology/index.php? 6tle=File:Advanced_Heart_Development_Timeline.jpg 51
Development of the Heart
 Development of the Heart Thomas A. Marino, Ph.D. Temple University School of Medicine Stages of Development of the Heart 1. The horseshoe-shaped pericardial cavity. 2. The formation of the single heart
Development of the Heart Thomas A. Marino, Ph.D. Temple University School of Medicine Stages of Development of the Heart 1. The horseshoe-shaped pericardial cavity. 2. The formation of the single heart
The sinus venosus represent the venous end of the heart It receives 3 veins: 1- Common cardinal vein body wall 2- Umbilical vein from placenta 3-
 1 2 The sinus venosus represent the venous end of the heart It receives 3 veins: 1- Common cardinal vein body wall 2- Umbilical vein from placenta 3- Vitelline vein from yolk sac 3 However!!!!! The left
1 2 The sinus venosus represent the venous end of the heart It receives 3 veins: 1- Common cardinal vein body wall 2- Umbilical vein from placenta 3- Vitelline vein from yolk sac 3 However!!!!! The left
The Cardiovascular System (Part II)
 The Cardiovascular System (Part II) 黃敏銓 mchuang@ntu.edu.tw 解剖學暨細胞生物學研究所 1 Development of veins Three paired veins drain into the tubular heart of a 4-week embryo Vitelline veins: poorly oxygenated blood
The Cardiovascular System (Part II) 黃敏銓 mchuang@ntu.edu.tw 解剖學暨細胞生物學研究所 1 Development of veins Three paired veins drain into the tubular heart of a 4-week embryo Vitelline veins: poorly oxygenated blood
DEVELOPMENT OF THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM L E C T U R E 5
 DEVELOPMENT OF THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM L E C T U R E 5 REVIEW OF CARDIAC ANATOMY Heart 4 chambers Base and apex Valves Pericardial sac 3 layers: epi, myo, endo cardium Major blood vessels Aorta and its
DEVELOPMENT OF THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM L E C T U R E 5 REVIEW OF CARDIAC ANATOMY Heart 4 chambers Base and apex Valves Pericardial sac 3 layers: epi, myo, endo cardium Major blood vessels Aorta and its
Embryology of the Heart
 *Page 1A: Embryology of the Heart Human embryonic disc is divided into three layers: ectoderm, intraembryonic mesoderm, and endoderm. The embryonic disc lies between the amniotic cavity and the primary
*Page 1A: Embryology of the Heart Human embryonic disc is divided into three layers: ectoderm, intraembryonic mesoderm, and endoderm. The embryonic disc lies between the amniotic cavity and the primary
Development and teratology of cardiovascular and lymphatic systems. Repetition: Muscle tissue
 Development and teratology of cardiovascular and lymphatic systems Repetition: Muscle tissue Beginning of the cardiovascular system development the 3rd week: Hemangiogenesis (day 15 16) blood islets (insulae
Development and teratology of cardiovascular and lymphatic systems Repetition: Muscle tissue Beginning of the cardiovascular system development the 3rd week: Hemangiogenesis (day 15 16) blood islets (insulae
The Cardiovascular System (Part I) 黃敏銓 解剖學暨細胞生物學研究所
 The Cardiovascular System (Part I) 黃敏銓 解剖學暨細胞生物學研究所 1 Congenital heart defects (CHDs) 台灣兒童心臟學會 Sinus venarum Membranous septum Conus arteiosus (infundibulum) Aortic vestibule The Cardiovascular System
The Cardiovascular System (Part I) 黃敏銓 解剖學暨細胞生物學研究所 1 Congenital heart defects (CHDs) 台灣兒童心臟學會 Sinus venarum Membranous septum Conus arteiosus (infundibulum) Aortic vestibule The Cardiovascular System
Heart & vascular system I. Dawei Dong
 Heart & vascular system I Dawei Dong Lecture goal Learn the basics of heart and vascular development. Development of Heart, Blood, and Blood Vessels LEARNING GOALS: 1. explain the early development of
Heart & vascular system I Dawei Dong Lecture goal Learn the basics of heart and vascular development. Development of Heart, Blood, and Blood Vessels LEARNING GOALS: 1. explain the early development of
When you see this diagram, remember that you are looking at the embryo from above, through the amniotic cavity, where the epiblast appears as an oval
 When you see this diagram, remember that you are looking at the embryo from above, through the amniotic cavity, where the epiblast appears as an oval disc 2 Why the embryo needs the vascular system? When
When you see this diagram, remember that you are looking at the embryo from above, through the amniotic cavity, where the epiblast appears as an oval disc 2 Why the embryo needs the vascular system? When
HUMAN HEART. Learn the following structures on the heart models.
 HUMAN HEART Learn the following structures on the heart models. The human heart has four chambers that consist of the right atrium, left atrium, right ventricle, and left ventricle. The atria are smaller
HUMAN HEART Learn the following structures on the heart models. The human heart has four chambers that consist of the right atrium, left atrium, right ventricle, and left ventricle. The atria are smaller
W.S. O The University of Hong Kong
 W.S. O The University of Hong Kong Objectives: Describe early angiogenesis. Describe the heart tube formation. Describe the partitioning into a 4- chambered heart. List the formation of heart valves and
W.S. O The University of Hong Kong Objectives: Describe early angiogenesis. Describe the heart tube formation. Describe the partitioning into a 4- chambered heart. List the formation of heart valves and
Circulatory system. Lecture #2
 Circulatory system Lecture #2 The essential components of the human cardiovascular system: Heart Blood Blood vessels Arteries - blood vessels that conduct arterial blood from heart ventricle to organs
Circulatory system Lecture #2 The essential components of the human cardiovascular system: Heart Blood Blood vessels Arteries - blood vessels that conduct arterial blood from heart ventricle to organs
Development of the heart
 Development of the heart Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk abdulameerh@yahoo.com Early Development of the Circulatory System Appears in the middle of the third week, when the
Development of the heart Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk abdulameerh@yahoo.com Early Development of the Circulatory System Appears in the middle of the third week, when the
Transcription for Narration of Embryology of the Great Arteries
 Transcription for Narration of Embryology of the Great Arteries Slide 1: In this presentation I am going to describe for you the development of what are known as the great arteries. The great arteries
Transcription for Narration of Embryology of the Great Arteries Slide 1: In this presentation I am going to describe for you the development of what are known as the great arteries. The great arteries
IN THE NAME OF GOD. Development of the Heart and Vasculature
 IN THE NAME OF GOD Development of the Heart and Vasculature Overview vascular system appears (middle of 3 rd week) when the embryo is not able to satisfy its nutrition by diffusion Heart is the first functional
IN THE NAME OF GOD Development of the Heart and Vasculature Overview vascular system appears (middle of 3 rd week) when the embryo is not able to satisfy its nutrition by diffusion Heart is the first functional
W.S. O. School of Biomedical Sciences, University of Hong Kong
 W.S. O School of Biomedical Sciences, University of Hong Kong Objectives: Describe early angiogenesis. Describe the heart tube formation. Describe the partitioning into a 4- chambered heart. List the formation
W.S. O School of Biomedical Sciences, University of Hong Kong Objectives: Describe early angiogenesis. Describe the heart tube formation. Describe the partitioning into a 4- chambered heart. List the formation
Development of Blood Vessels and Fetal Circulation *
 OpenStax-CNX module: m46610 1 Development of Blood Vessels and Fetal Circulation * OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the
OpenStax-CNX module: m46610 1 Development of Blood Vessels and Fetal Circulation * OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the
Blood Vessels. Types of Blood Vessels Arteries carry blood away from the heart Capillaries smallest blood vessels. Veins carry blood toward the heart
 C H A P T E R Blood Vessels 20 Types of Blood Vessels Arteries carry blood away from the heart Capillaries smallest blood vessels The site of exchange of molecules between blood and tissue fluid Veins
C H A P T E R Blood Vessels 20 Types of Blood Vessels Arteries carry blood away from the heart Capillaries smallest blood vessels The site of exchange of molecules between blood and tissue fluid Veins
6. Development of circulatory system II. Cardiac looping. Septation of atria and ventricles. Common heart malformations.
 6. Development of circulatory system II. Cardiac looping. Septation of atria and ventricles. Common heart malformations. Formation of heart tube paired endothelial-lined heart tube is formed from blood
6. Development of circulatory system II. Cardiac looping. Septation of atria and ventricles. Common heart malformations. Formation of heart tube paired endothelial-lined heart tube is formed from blood
Figure 10.1A Transparency Master 79
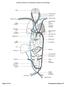 Brain Carotid arteries Jugular vein Right front leg Lungs (inflated) Cranial Right atrium To left front leg Left subclavian Bronchus capillaries Brachiocephalic vein Left atrium Dorsal aorta Right ventricle
Brain Carotid arteries Jugular vein Right front leg Lungs (inflated) Cranial Right atrium To left front leg Left subclavian Bronchus capillaries Brachiocephalic vein Left atrium Dorsal aorta Right ventricle
Chapter 14. The Cardiovascular System
 Chapter 14 The Cardiovascular System Introduction Cardiovascular system - heart, blood and blood vessels Cardiac muscle makes up bulk of heart provides force to pump blood Function - transports blood 2
Chapter 14 The Cardiovascular System Introduction Cardiovascular system - heart, blood and blood vessels Cardiac muscle makes up bulk of heart provides force to pump blood Function - transports blood 2
MODULE 2: CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM ANTOMY An Introduction to the Anatomy of the Heart and Blood vessels
 MODULE 2: CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM ANTOMY An Introduction to the Anatomy of the Heart and Blood vessels The cardiovascular system includes a pump (the heart) and the vessels that carry blood from the heart
MODULE 2: CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM ANTOMY An Introduction to the Anatomy of the Heart and Blood vessels The cardiovascular system includes a pump (the heart) and the vessels that carry blood from the heart
Large veins of the thorax Brachiocephalic veins
 Large veins of the thorax Brachiocephalic veins Right brachiocephalic vein: formed at the root of the neck by the union of the right subclavian & the right internal jugular veins. Left brachiocephalic
Large veins of the thorax Brachiocephalic veins Right brachiocephalic vein: formed at the root of the neck by the union of the right subclavian & the right internal jugular veins. Left brachiocephalic
Figure ) The specific chamber of the heart that is indicated by letter A is called the. Diff: 1 Page Ref: 364
 Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 11 The Cardiovascular System Short Answer Figure 11.1 Using Figure 11.1, identify the following: 1) The Purkinje fibers are indicated by label.
Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 11 The Cardiovascular System Short Answer Figure 11.1 Using Figure 11.1, identify the following: 1) The Purkinje fibers are indicated by label.
6. HEART AND CIRCULATORY SYSTEM I
 6. HEART AND CIRCULATORY SYSTEM I Dr. Taube P. Rothman P&S 12-520 Tpr2@columbia.edu 212-305-7930 RECOMMENDED READING: Larsen Human Embryology, 3rd Edition, pp. 195-199; 157-169 top left; 172-174; bottom
6. HEART AND CIRCULATORY SYSTEM I Dr. Taube P. Rothman P&S 12-520 Tpr2@columbia.edu 212-305-7930 RECOMMENDED READING: Larsen Human Embryology, 3rd Edition, pp. 195-199; 157-169 top left; 172-174; bottom
Circumcaval Ureter: Embryology
 european urology supplements 5 (2006) 444 448 available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.europeanurology.com Circumcaval Ureter: Embryology Arianna Lesma *, Aldo Bocciardi, Patrizio Rigatti
european urology supplements 5 (2006) 444 448 available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.europeanurology.com Circumcaval Ureter: Embryology Arianna Lesma *, Aldo Bocciardi, Patrizio Rigatti
Dr. Weyrich G07: Superior and Posterior Mediastina. Reading: 1. Gray s Anatomy for Students, chapter 3
 Dr. Weyrich G07: Superior and Posterior Mediastina Reading: 1. Gray s Anatomy for Students, chapter 3 Objectives: 1. Subdivisions of mediastinum 2. Structures in Superior mediastinum 3. Structures in Posterior
Dr. Weyrich G07: Superior and Posterior Mediastina Reading: 1. Gray s Anatomy for Students, chapter 3 Objectives: 1. Subdivisions of mediastinum 2. Structures in Superior mediastinum 3. Structures in Posterior
THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM
 Biology 30S THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM Name: This module adapted from bblearn.merlin.mb.ca 1 Introduction to Circulation The first organ to form, and the last organ to die. The heart is the pump of life. The
Biology 30S THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM Name: This module adapted from bblearn.merlin.mb.ca 1 Introduction to Circulation The first organ to form, and the last organ to die. The heart is the pump of life. The
Development of the Heart *
 OpenStax-CNX module: m46673 1 Development of the Heart * OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this section, you will
OpenStax-CNX module: m46673 1 Development of the Heart * OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this section, you will
Heart Development and Congenital Heart Disease
 Heart Development and Congenital Heart Disease Sally Dunwoodie s.dunwoodie@victorchang.edu.au Developmental and Stem Cell Biology Division Victor Chang Cardiac Research Institute for the heart of Australia...
Heart Development and Congenital Heart Disease Sally Dunwoodie s.dunwoodie@victorchang.edu.au Developmental and Stem Cell Biology Division Victor Chang Cardiac Research Institute for the heart of Australia...
Development of the Liver and Pancreas
 Development of the Liver and Pancreas Professor Alfred Cuschieri Department of Anatomy University of Malta Three glandular buds arise from the distal end of the foregut during the fourth week Day 22 -The
Development of the Liver and Pancreas Professor Alfred Cuschieri Department of Anatomy University of Malta Three glandular buds arise from the distal end of the foregut during the fourth week Day 22 -The
VESSELS: GROSS ANATOMY
 ACTIVITY 10: VESSELS AND CIRCULATION OBJECTIVES: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapter 23, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 4e. All text references are for this textbook. 2) Observe and sketch histology slide
ACTIVITY 10: VESSELS AND CIRCULATION OBJECTIVES: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapter 23, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 4e. All text references are for this textbook. 2) Observe and sketch histology slide
Chapter 4: The thoracic cavity and heart. The Heart
 Chapter 4: The thoracic cavity and heart The thoracic cavity is divided into right and left pleural cavities by a central partition, the mediastinum. The mediastinum is bounded behind by the vertebral
Chapter 4: The thoracic cavity and heart The thoracic cavity is divided into right and left pleural cavities by a central partition, the mediastinum. The mediastinum is bounded behind by the vertebral
Notes: 1)Membranous part contribute in the formation of small portion in the septal cusp.
 Embryology 9 : Slide 16 : There is a sulcus between primitive ventricular and bulbis cordis that will disappear gradually and lead to the formation of one chamber which is called bulboventricular chamber.
Embryology 9 : Slide 16 : There is a sulcus between primitive ventricular and bulbis cordis that will disappear gradually and lead to the formation of one chamber which is called bulboventricular chamber.
YOU MUST BRING GLOVES FOR THIS ACTIVITY
 ACTIVITY 10: VESSELS AND CIRCULATION OBJECTIVES: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapter 23, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 5e. All text references are for this textbook. 2) Observe and sketch histology slide
ACTIVITY 10: VESSELS AND CIRCULATION OBJECTIVES: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapter 23, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 5e. All text references are for this textbook. 2) Observe and sketch histology slide
The Blood Vessels of the Thorax
 5 The Blood Vessels of the Thorax Chapter Outline Large Arteries of the Thorax 78 The Aorta 78 Ascending Aorta and the Pericardium 78 Aneurysm of the Arch of the Aorta 78 Coarctation of the Aorta 78 Trauma
5 The Blood Vessels of the Thorax Chapter Outline Large Arteries of the Thorax 78 The Aorta 78 Ascending Aorta and the Pericardium 78 Aneurysm of the Arch of the Aorta 78 Coarctation of the Aorta 78 Trauma
The Cardiovascular System
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Cardiovascular System 11PART B The Heart: Cardiac Output Cardiac output (CO) Amount of blood pumped
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Cardiovascular System 11PART B The Heart: Cardiac Output Cardiac output (CO) Amount of blood pumped
Large Arteries of Heart
 Cardiovascular System (Part A-2) Module 5 -Chapter 8 Overview Arteries Capillaries Veins Heart Anatomy Conduction System Blood pressure Fetal circulation Susie Turner, M.D. 1/5/13 Large Arteries of Heart
Cardiovascular System (Part A-2) Module 5 -Chapter 8 Overview Arteries Capillaries Veins Heart Anatomy Conduction System Blood pressure Fetal circulation Susie Turner, M.D. 1/5/13 Large Arteries of Heart
REVIEW SHEET Anatomy of Blood Vessels
 REVIEW SHEET Anatomy of Blood Vessels Name LabTime/Date Microscopic Structure of the Blood Vessels 1. Cross-sectional views of an aftery of a vein are shown here. ldentify each; on the lines to the sides,
REVIEW SHEET Anatomy of Blood Vessels Name LabTime/Date Microscopic Structure of the Blood Vessels 1. Cross-sectional views of an aftery of a vein are shown here. ldentify each; on the lines to the sides,
The Physiology of the Fetal Cardiovascular System
 The Physiology of the Fetal Cardiovascular System Jeff Vergales, MD, MS Department of Pediatrics Division of Pediatric Cardiology jvergales@virginia.edu Disclosures I serve as the medical director for
The Physiology of the Fetal Cardiovascular System Jeff Vergales, MD, MS Department of Pediatrics Division of Pediatric Cardiology jvergales@virginia.edu Disclosures I serve as the medical director for
Lab Activity 23. Cardiac Anatomy. Portland Community College BI 232
 Lab Activity 23 Cardiac Anatomy Portland Community College BI 232 Cardiac Muscle Histology Branching cells Intercalated disc: contains many gap junctions connecting the adjacent cell cytoplasm, creates
Lab Activity 23 Cardiac Anatomy Portland Community College BI 232 Cardiac Muscle Histology Branching cells Intercalated disc: contains many gap junctions connecting the adjacent cell cytoplasm, creates
Spleen. Vertebrate hearts Pericardial cavity division in coelum. Vessel walls. Endocardium = endothelium of blood vessels. Artery elastic tissue
 Spleen White pulp macrophages, monocyte storage Red pulp - (RBC) storage, and prod n (in nonmammals) Vertebrate hearts Pericardial cavity division in coelum Endocardium = endothelium of blood vessels Fig.
Spleen White pulp macrophages, monocyte storage Red pulp - (RBC) storage, and prod n (in nonmammals) Vertebrate hearts Pericardial cavity division in coelum Endocardium = endothelium of blood vessels Fig.
3 Circulatory Pathways
 40 Chapter 3 Circulatory Pathways Systemic Arteries -Arteries carry blood away from the heart to the various organs of the body. -The aorta is the longest artery in the body; it branches to give rise to
40 Chapter 3 Circulatory Pathways Systemic Arteries -Arteries carry blood away from the heart to the various organs of the body. -The aorta is the longest artery in the body; it branches to give rise to
Vasculature and innervation of the heart. A. Bendelic Human Anatomy Department
 Vasculature and innervation of the heart A. Bendelic Human Anatomy Department Plan: 1. Arterial blood supply of the heart. Coronary arteries 2. Venous drainage of the heart. Cardiac veins 3. Innervation
Vasculature and innervation of the heart A. Bendelic Human Anatomy Department Plan: 1. Arterial blood supply of the heart. Coronary arteries 2. Venous drainage of the heart. Cardiac veins 3. Innervation
Unit 11 - The Cardiovascular System 1
 Unit 11 - The Cardiovascular System 1 I. Unit 11: The Cardiovascular System A. The Cardiovascular System 1. A closed system of the heart and blood vessels a) The heart pumps blood b) Blood vessels allow
Unit 11 - The Cardiovascular System 1 I. Unit 11: The Cardiovascular System A. The Cardiovascular System 1. A closed system of the heart and blood vessels a) The heart pumps blood b) Blood vessels allow
Lab Photo Review Sheet
 9 8 0. Posterior Median Sulcus. Central Canal. Dorsal (Posterior) Horn. Ventral (Anterior) Horn. Grey Matter. White Matter. Anterior Median Fissure 8. Ventral (Anterior) Root (ramus) 9. Dorsal (Posterior)
9 8 0. Posterior Median Sulcus. Central Canal. Dorsal (Posterior) Horn. Ventral (Anterior) Horn. Grey Matter. White Matter. Anterior Median Fissure 8. Ventral (Anterior) Root (ramus) 9. Dorsal (Posterior)
C3, 4, 5, 6, & 7 Worksheet. C3 Describe the inter-relationships of the structures of the heart
 Name: Date: C3, 4, 5, 6, & 7 Worksheet C3 Describe the inter-relationships of the structures of the heart 1. Label and give the functions of the following: a. left and right atrium: b. left and right ventricle:
Name: Date: C3, 4, 5, 6, & 7 Worksheet C3 Describe the inter-relationships of the structures of the heart 1. Label and give the functions of the following: a. left and right atrium: b. left and right ventricle:
The Cardiovascular System
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Cardiovascular System 11PART A The Cardiovascular System A closed system of the heart and blood
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Cardiovascular System 11PART A The Cardiovascular System A closed system of the heart and blood
Unit 11: The Cardiovascular System
 Unit 11: The Cardiovascular System I. The Cardiovascular System A. A closed system of the heart and blood vessels 1. The heart pumps blood 2. Blood vessels allow blood to circulate to all parts of the
Unit 11: The Cardiovascular System I. The Cardiovascular System A. A closed system of the heart and blood vessels 1. The heart pumps blood 2. Blood vessels allow blood to circulate to all parts of the
Cardiovascular Respiratory Renal/ Urinary. VOLUME 111 Nervous System. Organ ~ Systems ~
 Cardiovascular Respiratory Renal/ Urinary VOLUME 111 Nervous System Organ ~ Systems ~ Contents Section I: Cardiovascular System Chapter 1. Embryology... 3 Chapter 2. Histology... 13 Chapter 3. Anatomy...
Cardiovascular Respiratory Renal/ Urinary VOLUME 111 Nervous System Organ ~ Systems ~ Contents Section I: Cardiovascular System Chapter 1. Embryology... 3 Chapter 2. Histology... 13 Chapter 3. Anatomy...
SLIDES 6 AND 10 MM PIG SLIDES; TRANSVERSE SECTIONS AND SAGITAL; FETAL PIGS-1-8INCH; HUMAN SAGITAL DIAGRAMS:DRAWINGS OF THE PIG SECTIONS TO BE
 SLIDES 6 AND 10 MM PIG SLIDES; TRANSVERSE SECTIONS AND SAGITAL; FETAL PIGS-1-8INCH; HUMAN SAGITAL SECTION DIAGRAMS:DRAWINGS OF THE PIG SECTIONS TO BE LABELLED, AND FOUR DRAWINGS TO BE MADE. REFERENCES:PATTEN:
SLIDES 6 AND 10 MM PIG SLIDES; TRANSVERSE SECTIONS AND SAGITAL; FETAL PIGS-1-8INCH; HUMAN SAGITAL SECTION DIAGRAMS:DRAWINGS OF THE PIG SECTIONS TO BE LABELLED, AND FOUR DRAWINGS TO BE MADE. REFERENCES:PATTEN:
A. Incorrect! Think of a therapy that reduces prostaglandin synthesis. B. Incorrect! Think of a therapy that reduces prostaglandin synthesis.
 USMLE Step 1 - Problem Drill 02: Embryology Question No. 1 of 10 1. A premature infant is born with a patent ductus arteriosis. Which of the following treatments may be used as part of the treatment regimen?
USMLE Step 1 - Problem Drill 02: Embryology Question No. 1 of 10 1. A premature infant is born with a patent ductus arteriosis. Which of the following treatments may be used as part of the treatment regimen?
2. capillaries - allow exchange of materials between blood and tissue fluid
 Chapter 19 - Vascular System A. categories and general functions: 1. arteries - carry blood away from heart 2. capillaries - allow exchange of materials between blood and tissue fluid 3. veins - return
Chapter 19 - Vascular System A. categories and general functions: 1. arteries - carry blood away from heart 2. capillaries - allow exchange of materials between blood and tissue fluid 3. veins - return
CV Anatomy Quiz. Dr Ella Kim Dr Pip Green
 CV Anatomy Quiz Dr Ella Kim Dr Pip Green Q1 The location of the heart is correctly described as A) lateral to the lungs. B) medial to the sternum. C) superior to the diaphragm. D) posterior to the spinal
CV Anatomy Quiz Dr Ella Kim Dr Pip Green Q1 The location of the heart is correctly described as A) lateral to the lungs. B) medial to the sternum. C) superior to the diaphragm. D) posterior to the spinal
Lab 6: Blood. BIO104 Laboratory Handouts 147. Unit 12: Blood and Lymphatics. 1. Blood Characteristics Volume Functions Composition -
 147 Lab 6: Blood Unit 12: Blood and Lymphatics Ex. 12-1: Formed Elements (Cells) of Blood, p. 313-316 1. Blood Characteristics Volume Functions Composition - 2. Leukocytes (WBCs) a. WBC count normal b.
147 Lab 6: Blood Unit 12: Blood and Lymphatics Ex. 12-1: Formed Elements (Cells) of Blood, p. 313-316 1. Blood Characteristics Volume Functions Composition - 2. Leukocytes (WBCs) a. WBC count normal b.
Arteries. Lecture #2
 Arteries Lecture #2 The essential components of the human cardiovascular system: Heart Blood Blood vessels Arteries - blood vessels that conduct arterial blood from heart ventricle to organs and tissues
Arteries Lecture #2 The essential components of the human cardiovascular system: Heart Blood Blood vessels Arteries - blood vessels that conduct arterial blood from heart ventricle to organs and tissues
Cardiovascular System. Chapter 22
 Cardiovascular System Blood Vessels Chapter 22 Cardiac Contractions Cardiac cycle consists of alternate periods of contraction and relaxation Contraction is the systolic pressure Blood is ejected into
Cardiovascular System Blood Vessels Chapter 22 Cardiac Contractions Cardiac cycle consists of alternate periods of contraction and relaxation Contraction is the systolic pressure Blood is ejected into
Cardiovascular System
 Cardiovascular System I. Structure of the Heart A. Average adult heart is 14 cm long and 9 cm wide. B. Lies in the mediastinum. C. Enclosed in the pericardium. 1. Fibrous pericardium- Outer, tough connective
Cardiovascular System I. Structure of the Heart A. Average adult heart is 14 cm long and 9 cm wide. B. Lies in the mediastinum. C. Enclosed in the pericardium. 1. Fibrous pericardium- Outer, tough connective
THE VESSELS OF THE HEART
 1 THE VESSELS OF THE HEART The vessels of the heart include the coronary arteries, which supply the heart and the veins and lymph vessels, which drain the heart. THE CORONARY ARTERIES These are the blood
1 THE VESSELS OF THE HEART The vessels of the heart include the coronary arteries, which supply the heart and the veins and lymph vessels, which drain the heart. THE CORONARY ARTERIES These are the blood
Heart and Lungs. LUNG Coronal section demonstrates relationship of pulmonary parenchyma to heart and chest wall.
 Heart and Lungs Normal Sonographic Anatomy THORAX Axial and coronal sections demonstrate integrity of thorax, fetal breathing movements, and overall size and shape. LUNG Coronal section demonstrates relationship
Heart and Lungs Normal Sonographic Anatomy THORAX Axial and coronal sections demonstrate integrity of thorax, fetal breathing movements, and overall size and shape. LUNG Coronal section demonstrates relationship
human anatomy 2016 lecture thirteen Dr meethak ali ahmed neurosurgeon
 Heart The heart is a hollow muscular organ that is somewhat pyramid shaped and lies within the pericardium in the mediastinum. It is connected at its base to the great blood vessels but otherwise lies
Heart The heart is a hollow muscular organ that is somewhat pyramid shaped and lies within the pericardium in the mediastinum. It is connected at its base to the great blood vessels but otherwise lies
Overview of Anatomy and Physioloy II Second Year Students
 University of Baghdad College of Nursing Department of Basic Medical Sciences Overview of Anatomy and Physioloy II Second Year Students Asaad Ismail Ahmad, Ph.D. Asaad Ismail Ahmad, Ph.D. Electrolyte and
University of Baghdad College of Nursing Department of Basic Medical Sciences Overview of Anatomy and Physioloy II Second Year Students Asaad Ismail Ahmad, Ph.D. Asaad Ismail Ahmad, Ph.D. Electrolyte and
Day 5 Respiratory & Cardiovascular: Respiratory System
 Day 5 Respiratory & Cardiovascular: Respiratory System Be very careful not to damage the heart and lungs while separating the ribs! Analysis Questions-Respiratory & Cardiovascular Log into QUIA using your
Day 5 Respiratory & Cardiovascular: Respiratory System Be very careful not to damage the heart and lungs while separating the ribs! Analysis Questions-Respiratory & Cardiovascular Log into QUIA using your
This lab activity is aligned with Visible Body s A&P app. Learn more at visiblebody.com/professors
 1 This lab activity is aligned with Visible Body s A&P app. Learn more at visiblebody.com/professors 2 PRE-LAB EXERCISES: A. Watch the video 29.1 Heart Overview and make the following observations: 1.
1 This lab activity is aligned with Visible Body s A&P app. Learn more at visiblebody.com/professors 2 PRE-LAB EXERCISES: A. Watch the video 29.1 Heart Overview and make the following observations: 1.
The posterior abdominal wall. Prof. Oluwadiya KS
 The posterior abdominal wall Prof. Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.sitesled.com Posterior Abdominal Wall Lumbar vertebrae and discs. Muscles opsoas, quadratus lumborum, iliacus, transverse, abdominal wall
The posterior abdominal wall Prof. Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.sitesled.com Posterior Abdominal Wall Lumbar vertebrae and discs. Muscles opsoas, quadratus lumborum, iliacus, transverse, abdominal wall
The Cardiovascular System. Preview of Heart Action. The CV system provides oxygen & nutrients to tissues-removes wastes.
 The Cardiovascular System BIO 250 Human Anatomy & Physiology Preview of Heart Action http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=d3zdj gfddk0&nr=1 The CV system provides oxygen & nutrients to tissues-removes wastes.
The Cardiovascular System BIO 250 Human Anatomy & Physiology Preview of Heart Action http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=d3zdj gfddk0&nr=1 The CV system provides oxygen & nutrients to tissues-removes wastes.
The Heart. The Heart A muscular double pump. The Pulmonary and Systemic Circuits
 C H A P T E R 19 The Heart The Heart A muscular double pump circuit takes blood to and from the lungs Systemic circuit vessels transport blood to and from body tissues Atria receive blood from the pulmonary
C H A P T E R 19 The Heart The Heart A muscular double pump circuit takes blood to and from the lungs Systemic circuit vessels transport blood to and from body tissues Atria receive blood from the pulmonary
Large Ventricular Septal Defect with Irreversible Pulmonary Hypertension
 Week 20 Blue Is For Boys Tetralogy of Fallot Presenting Symptoms Child, 4 Cyanosis Exercise Tolerance Failure to thrive Clubbing Lower Sternal Heave Right ventricular hypertrophy Loud ejection systolic
Week 20 Blue Is For Boys Tetralogy of Fallot Presenting Symptoms Child, 4 Cyanosis Exercise Tolerance Failure to thrive Clubbing Lower Sternal Heave Right ventricular hypertrophy Loud ejection systolic
1. Which of the following blood vessels has a thin elastic layer? A. Aorta. B. Pulmonary artery. C. Posterior vena cava. D. Mesenteric capillary.
 CIRCULATORY SYSTEM 1. Which of the following blood vessels has a thin elastic layer? A. Aorta. B. Pulmonary artery. C. Posterior vena cava. D. Mesenteric capillary. 2. Capillary beds are equipped with
CIRCULATORY SYSTEM 1. Which of the following blood vessels has a thin elastic layer? A. Aorta. B. Pulmonary artery. C. Posterior vena cava. D. Mesenteric capillary. 2. Capillary beds are equipped with
Cardiovascular Anatomy Dr. Gary Mumaugh
 Cardiovascular Anatomy Dr. Gary Mumaugh Location of Heart Approximately the size of your fist Location o Superior surface of diaphragm o Left of the midline in mediastinum o Anterior to the vertebral column,
Cardiovascular Anatomy Dr. Gary Mumaugh Location of Heart Approximately the size of your fist Location o Superior surface of diaphragm o Left of the midline in mediastinum o Anterior to the vertebral column,
CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM
 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM CARDIAC SYSTEM TWO TYPES OF CIRCULATION Systemic system delivers blood to ALL body cells and carries away waste. The red blood cells use hemoglobin to carry oxygen to the cells Pulmonary
CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM CARDIAC SYSTEM TWO TYPES OF CIRCULATION Systemic system delivers blood to ALL body cells and carries away waste. The red blood cells use hemoglobin to carry oxygen to the cells Pulmonary
c) What is the name of RBC (erythrocyte) formation? Where do blood cells form?
 UNIT 6: CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM 1) List the three general functions of BLOOD. REVIEW QUESTIONS Blood 2) a) What are the three formed elements /cellular elements in blood? b) Describe the composition of the
UNIT 6: CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM 1) List the three general functions of BLOOD. REVIEW QUESTIONS Blood 2) a) What are the three formed elements /cellular elements in blood? b) Describe the composition of the
Human Anatomy, First Edition
 Human Anatomy, First Edition McKinley & O'Loughlin Chapter 22 : Heart 1 Functions of the Heart Center of the cardiovascular system, the heart. Connects to blood vessels that transport blood between the
Human Anatomy, First Edition McKinley & O'Loughlin Chapter 22 : Heart 1 Functions of the Heart Center of the cardiovascular system, the heart. Connects to blood vessels that transport blood between the
TRACE A DROP OF BLOOD FROM RIGHT EAR TO LEFT OCULOMOTOR NERVE
 TRACE A DROP OF BLOOD FROM RIGHT EAR TO LEFT OCULOMOTOR NERVE KEY: TRACE A DROP OF BLOOD FROM RIGHT EAR TO LEFT OCULOMOTOR NERVE RIGHT EAR RIGHT ATRIUM LEFT SUBCLAVIAN ARTERY RIGHT EXTERNAL JUGULAR VEIN
TRACE A DROP OF BLOOD FROM RIGHT EAR TO LEFT OCULOMOTOR NERVE KEY: TRACE A DROP OF BLOOD FROM RIGHT EAR TO LEFT OCULOMOTOR NERVE RIGHT EAR RIGHT ATRIUM LEFT SUBCLAVIAN ARTERY RIGHT EXTERNAL JUGULAR VEIN
Major Function of the Cardiovascular System. Transportation. Structures of the Cardiovascular System. Heart - muscular pump
 Structures of the Cardiovascular System Heart - muscular pump Blood vessels - network of tubes Blood - liquid transport vehicle brachiocephalic trunk superior vena cava right pulmonary arteries right pulmonary
Structures of the Cardiovascular System Heart - muscular pump Blood vessels - network of tubes Blood - liquid transport vehicle brachiocephalic trunk superior vena cava right pulmonary arteries right pulmonary
BOGOMOLETS NATIONAL MEDICAL UNIVERSITY DEPARTMENT OF HUMAN ANATOMY. Guidelines. Module 2 Topic of the lesson Aorta. Thoracic aorta.
 BOGOMOLETS NATIONAL MEDICAL UNIVERSITY DEPARTMENT OF HUMAN ANATOMY Guidelines Academic discipline HUMAN ANATOMY Module 2 Topic of the lesson Aorta. Thoracic aorta. Course 1 The number of hours 3 1. The
BOGOMOLETS NATIONAL MEDICAL UNIVERSITY DEPARTMENT OF HUMAN ANATOMY Guidelines Academic discipline HUMAN ANATOMY Module 2 Topic of the lesson Aorta. Thoracic aorta. Course 1 The number of hours 3 1. The
The Cardiovascular System
 C H A P T E R 1 4 The Cardiovascular System OBJECTIVES After studying this chapter, you should be able to: 1. Describe how the heart is positioned in the thoracic cavity. 2. List and describe the layers
C H A P T E R 1 4 The Cardiovascular System OBJECTIVES After studying this chapter, you should be able to: 1. Describe how the heart is positioned in the thoracic cavity. 2. List and describe the layers
Lab Activity 25. Blood Vessels & Circulation. Portland Community College BI 232
 Lab Activity 25 Blood Vessels & Circulation Portland Community College BI 232 Artery and Vein Histology Walls have 3 layers: Tunica intima Tunica media Tunica externa 2 Tunica Intima Is the innermost layer
Lab Activity 25 Blood Vessels & Circulation Portland Community College BI 232 Artery and Vein Histology Walls have 3 layers: Tunica intima Tunica media Tunica externa 2 Tunica Intima Is the innermost layer
Blood supply of the Heart & Conduction System. Dr. Nabil Khouri
 Blood supply of the Heart & Conduction System Dr. Nabil Khouri Arterial supply of Heart Right coronary artery Left coronary artery 3 Introduction: Coronary arteries - VASAVASORUM arising from aortic sinuses
Blood supply of the Heart & Conduction System Dr. Nabil Khouri Arterial supply of Heart Right coronary artery Left coronary artery 3 Introduction: Coronary arteries - VASAVASORUM arising from aortic sinuses
CARDIOVASCULAR DANIL HAMMOUDI.MD
 CARDIOVASCULAR DANIL HAMMOUDI.MD 18 Systemic Circulation Figure 19.19 Pulmonary Circulation Figure 19.18b 1. Thyroid gland 2. Trachea 3. Brachiocephalic 4. Common carotid 5. Internal jugular 6. Superior
CARDIOVASCULAR DANIL HAMMOUDI.MD 18 Systemic Circulation Figure 19.19 Pulmonary Circulation Figure 19.18b 1. Thyroid gland 2. Trachea 3. Brachiocephalic 4. Common carotid 5. Internal jugular 6. Superior
Organogenesis Part 2. V. Lateral Plate Mesoderm VI. Endoderm VII. Development of the Tetrapod Limb VIII. Sex Determination. V. Lateral Plate Mesoderm
 Organogenesis Part 2 V. Lateral Plate Mesoderm VI. Endoderm VII. Development of the Tetrapod Limb VIII. Sex Determination V. Lateral Plate Mesoderm chordamesoderm paraxial mesoderm intermediate mesoderm
Organogenesis Part 2 V. Lateral Plate Mesoderm VI. Endoderm VII. Development of the Tetrapod Limb VIII. Sex Determination V. Lateral Plate Mesoderm chordamesoderm paraxial mesoderm intermediate mesoderm
The Mammalian Circulatory System
 The Mammalian Heart The Mammalian Circulatory System Recall: What are the 3 cycles of the mammalian circulatory system? What are their functions? What are the three main vessel types in the mammalian circulatory
The Mammalian Heart The Mammalian Circulatory System Recall: What are the 3 cycles of the mammalian circulatory system? What are their functions? What are the three main vessel types in the mammalian circulatory
Approximately the size of your fist Location Superior surface of diaphragm Left of the midline in mediastinum Anterior to the vertebral column,
 Dr. Gary Mumaugh Approximately the size of your fist Location Superior surface of diaphragm Left of the midline in mediastinum Anterior to the vertebral column, posterior to the sternum Posteriorly the
Dr. Gary Mumaugh Approximately the size of your fist Location Superior surface of diaphragm Left of the midline in mediastinum Anterior to the vertebral column, posterior to the sternum Posteriorly the
Chapter 5: Other mediastinal structures. The Large Arteries. The Aorta. Ascending aorta
 Chapter 5: Other mediastinal structures The Large Arteries The Aorta The aorta is the main arterial trunk of the systemic circulation and in the healthy state its wall contain a large amount of yellow
Chapter 5: Other mediastinal structures The Large Arteries The Aorta The aorta is the main arterial trunk of the systemic circulation and in the healthy state its wall contain a large amount of yellow
THE VESSELS OF BLOOD CIRCULATION
 THE VESSELS OF BLOOD CIRCULATION scientistcindy.com /the-vessels-of-blood-circulation.html NOTE: You should familiarize yourself with the anatomy of the heart and have a good understanding of the flow
THE VESSELS OF BLOOD CIRCULATION scientistcindy.com /the-vessels-of-blood-circulation.html NOTE: You should familiarize yourself with the anatomy of the heart and have a good understanding of the flow
Breathing. Heart Rate
 Breathing Heart Rate Inspiration Expiration (Pressos not Stretched) Heart Rate increases with inspiration (Pressos Stretched) Heart Rate decreases with expiration Upside Down (Pressos Stretched) HR Decreases
Breathing Heart Rate Inspiration Expiration (Pressos not Stretched) Heart Rate increases with inspiration (Pressos Stretched) Heart Rate decreases with expiration Upside Down (Pressos Stretched) HR Decreases
THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM. Part 1
 THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Part 1 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Blood Heart Blood vessels What is the function of this system? What other systems does it affect? CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Functions Transport gases,
THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Part 1 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Blood Heart Blood vessels What is the function of this system? What other systems does it affect? CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Functions Transport gases,
EMBRYOLOGY NOTES. I. Summary of First Three Weeks a. Definitions b. Germ layers. Central Nervous System. III. Gastrointestinal System
 EMBRYOLOGY NOTES I. Summary of First Three Weeks a. Definitions b. Germ layers II. Central Nervous System III. Gastrointestinal System IV. Urogenital System and Homologues V. Cardiovascular System and
EMBRYOLOGY NOTES I. Summary of First Three Weeks a. Definitions b. Germ layers II. Central Nervous System III. Gastrointestinal System IV. Urogenital System and Homologues V. Cardiovascular System and
COPYRIGHTED MATERIAL. The fetal circulation CHAPTER 1. Postnatal circulation
 1 CHAPTER 1 The fetal circulation The circulation in the fetus differs from that in the adult. Knowledge of the course and distribution of the fetal circulation is important to our understanding of the
1 CHAPTER 1 The fetal circulation The circulation in the fetus differs from that in the adult. Knowledge of the course and distribution of the fetal circulation is important to our understanding of the
CARDIAC DEVELOPMENT CARDIAC DEVELOPMENT
 CARDIAC DEVELOPMENT CARDIAC DEVELOPMENT Diane E. Spicer, BS, PA(ASCP) University of Florida Dept. of Pediatric Cardiology Curator Van Mierop Cardiac Archive This lecture is given with special thanks to
CARDIAC DEVELOPMENT CARDIAC DEVELOPMENT Diane E. Spicer, BS, PA(ASCP) University of Florida Dept. of Pediatric Cardiology Curator Van Mierop Cardiac Archive This lecture is given with special thanks to
AN ATOMY OF THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM
 Student Name CHAPTER 18 AN ATOMY OF THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM T he heart is actually two pumps one moves blood to the lungs, the other pushes it out into the body. These two functions seem rather elementary
Student Name CHAPTER 18 AN ATOMY OF THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM T he heart is actually two pumps one moves blood to the lungs, the other pushes it out into the body. These two functions seem rather elementary
the Cardiovascular System I
 the Cardiovascular System I By: Dr. Nabil A Khouri MD, MsC, Ph.D MEDIASTINUM 1. Superior Mediastinum 2. inferior Mediastinum Anterior mediastinum. Middle mediastinum. Posterior mediastinum Anatomy of
the Cardiovascular System I By: Dr. Nabil A Khouri MD, MsC, Ph.D MEDIASTINUM 1. Superior Mediastinum 2. inferior Mediastinum Anterior mediastinum. Middle mediastinum. Posterior mediastinum Anatomy of
Human Anatomy Biology 351
 nnnnn 1 Human Anatomy Biology 351 Exam #2 Please place your name on the back of the last page of this exam. You must answer all questions on this exam. Because statistics demonstrate that, on average,
nnnnn 1 Human Anatomy Biology 351 Exam #2 Please place your name on the back of the last page of this exam. You must answer all questions on this exam. Because statistics demonstrate that, on average,
Circulatory System Notes
 Circulatory System Notes Functions of Circulatory System A. Transports B. Transports C. Transports D. Transports E. of fluids F. G. Regulate temperature H. Blood clotting Characteristics of various blood
Circulatory System Notes Functions of Circulatory System A. Transports B. Transports C. Transports D. Transports E. of fluids F. G. Regulate temperature H. Blood clotting Characteristics of various blood
Introduction to Anatomy. Dr. Maher Hadidi. Bayan Yanes. April/9 th /2013
 Introduction to Anatomy Dr. Maher Hadidi Bayan Yanes 27 April/9 th /2013 KEY POINTS: 1) Right side of the heart 2) Papillary muscles 3) Left side of the heart 4) Comparison between right and left sides
Introduction to Anatomy Dr. Maher Hadidi Bayan Yanes 27 April/9 th /2013 KEY POINTS: 1) Right side of the heart 2) Papillary muscles 3) Left side of the heart 4) Comparison between right and left sides
PIAF study: Placental insufficiency and aortic isthmus flow Jean-Claude Fouron, MD
 Dear colleagues, I would like to thank you very sincerely for agreeing to participate in our multicentre study on the clinical significance of recording fetal aortic isthmus flow during placental circulatory
Dear colleagues, I would like to thank you very sincerely for agreeing to participate in our multicentre study on the clinical significance of recording fetal aortic isthmus flow during placental circulatory
Part 1. Copyright 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Figure Copyright 2011 Pearson Education, Inc.
 PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Leslie Hendon University of Alabama, Birmingham C H A P T E R The Heart 19 Part 1 The Heart A muscular double pump circuit vessels transport blood to and from the
PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Leslie Hendon University of Alabama, Birmingham C H A P T E R The Heart 19 Part 1 The Heart A muscular double pump circuit vessels transport blood to and from the
Anatomy of the Heart. Figure 20 2c
 Anatomy of the Heart Figure 20 2c Pericardium & Myocardium Remember, the heart sits in it s own cavity, known as the mediastinum. The heart is surrounded by the Pericardium, a double lining of the pericardial
Anatomy of the Heart Figure 20 2c Pericardium & Myocardium Remember, the heart sits in it s own cavity, known as the mediastinum. The heart is surrounded by the Pericardium, a double lining of the pericardial
Infradiaphragmatic Total Anomalous Pulmonary Venous Return
 Infradiaphragmatic Total Anomalous Pulmonary Venous Return Report of a New and Correctable Variant J. Kent Trinkle, M.D., Gordon K. Danielson, M.D., Jacqueline A. Noonan, M.D., and Charles Stephens, M.D.
Infradiaphragmatic Total Anomalous Pulmonary Venous Return Report of a New and Correctable Variant J. Kent Trinkle, M.D., Gordon K. Danielson, M.D., Jacqueline A. Noonan, M.D., and Charles Stephens, M.D.
Mediastinum and pericardium
 Mediastinum and pericardium Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com The mediastinum: is the central compartment of the thoracic cavity surrounded by
Mediastinum and pericardium Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com The mediastinum: is the central compartment of the thoracic cavity surrounded by
