The Circulatory System
|
|
|
- Edwina Greene
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 The Circulatory System
2 Some Fun Facts The left side of the heart contains oxygenated blood whereas the right side has de-oxygenated blood. One drop of blood has about 5 million red blood cells and 12 thousand white blood cells. The heartbeats about million times in 365 days. 10 million blood cells die in the human body every second, the same quantity is produced at the same time. Blood circulates the entire body in 20 seconds. An average heart pumps about 450 gallons of blood everyday.
3 Some Fun Facts One of the surprising circulatory system facts is that the heartbeat is the sound of the valves opening and closing. An average adult's body has about 5 liters of blood in it and a baby's body has about 1 liter of blood in it. A human heart is a muscle which is the size of a clenched fist. Blood cells die every 4 months. The plasma in the blood is made in the liver. One of the amazing facts of circulatory system is that the heart continues to beat even when it is taken out of the body!
4 The Circulatory System The heart and circulatory system (also called the cardiovascular system) make up the network that delivers blood to the body's tissues. With each heartbeat, blood is sent throughout our bodies, carrying oxygen and nutrients to all of our cells. Every day, the approximately 5 liters of blood in your body travel many times through about 60,000 miles (96,560 kilometers) of blood vessels that branch and cross, linking the cells of our organs and body parts. From the hard-working heart, to our thickest arteries, to capillaries so thin that they can only be seen through a microscope, the cardiovascular system is our body's lifeline.
5 Components of the Circulatory System Blood Blood Vessels Arteries Veins Capillaries Heart
6 What is Blood?
7 What is Blood? Plasma Blood Cells RBC WBC Platelets Blood Types Blood Cell Disorders Blood:
8
9 Review Last Class Why is the Circulatory System so important? What are the three components of the circulatory system? What are the four components of Blood?
10 What did we learn? What is Plasma? What are Red Blood Cells? What do they do? What are White Blood Cells? What are Platelets?
11 Plasma: Primarily made up of water and over 100 dissolved solutes such as nutrients, gases, hormones, ions, and proteins. Erythrocytes: Look like miniature doughnuts (concave shape) Have a plasma membrane but lack a nucleus Carry oxygen and some carbon dioxide Mostly hemoglobin (molecule that binds to and transports gases) The formation of blood cells occurs in red bone marrow.
12 Leukocytes: White blood cells Complete cells with nuclei and organelles Crucial in defense against diseases Platelets: Essential in clotting process; stick to the damaged site and seal the break
13 Antigens An antigen is a substance that can stimulate the body to make antibodies. Antigens can be found on the surface of RBCs, or they can enter the body through an infection or transfusion. In this case, the antigen is foreign and will illicit an immune response from the body.
14 Antibodies An antibody is made by the body in response to an antigen. These are made by the WBCs and are found floating in the plasma of blood. Antibodies generally react with their antigens to agglutinate them (cause antigens to stick together; clump). In the human body, you produce the opposite antibody to your antigen. Example: Type A Blood Carry A antigens, and produce B antibodies (we will see more of this in just a little while!)
15 Blood Types Blood type is determined by the presence or absence of certain antigens on the red blood cells. There are two kinds of antigens: A and B If antigen A is present, then the individual is said to have Type A blood. Similarly, someone with whose red blood cells have antigen B on them are said to have Type B blood.
16 Question: What about Type AB? What about Type O?
17 Antigens and Antibodies The antibodies found in the blood plasma of a person with a particular blood type are always the opposite of their antigen. Example: Type A blood contains the A antigen but the B antibody Type AB blood contains both antigens but neither antibody Type O blood contains no antigens but possesses both the A and B antibody
18
19 RECAP: Antibodies and Antigens Your body does not make antibodies to the type of antigen you have because you were born with it. Problems will occur if the antigens on a donor s red blood cells become agglutinated with antibodies in the recipient s plasma. (Does not occur the other way around) Therefore, Type O is the universal donor (no antigens present) Type AB is the universal recipient (no antibodies present)
20 Types of Blood Antigens Present on RBC Antibodies Present in Blood Plasma Blood Types A A B B B A AB AB --- O -- AB
21 Why are these combinations so important? If antigens and antibodies of the same type come together, the antibodies cause the RBCs to clump together. If two samples of blood of the same type mix together, no clumping occurs. If incorrect matching of blood during a transfusion occurs, the results could be fatal. Before a transfusion occurs, the recipient s blood is always tested with the donor s blood. This is called typing.
22
23 Blood Transfusions Before a Transfusion, you must test for compatibility: Establish that the mixing of blood will not cause clumping, otherwise this can cause a blockage in an artery. Blood Typing: A sample of blood is mixed with a drop of concentrated serum containing A antibodies. Another sample of blood is mixed with a serum containing B antibodies. The presence or lack of clumping will tell you what blood type you have!
24 Let s try and figure this out: Sample Mixed with Anti-A Antibodies Sample Mixed with Anti-B Antibodies Sample Mixed with Rh Serum No clumping No clumping Clumping No clumping Clumping No Clumping Clumping No clumping Clumping Clumping Clumping No clumping Antigens Present in RBCs Blood Type
25 Let s try and figure this out: Sample Mixed with Anti-A Antibodies Sample Mixed with Anti-B Antibodies Antigens Present in RBCs Blood Type No clumping No clumping None O No clumping Clumping B B Clumping No clumping A A Clumping Clumping AB AB
26 Blood Transfusions Check this out: KBBKg
27 The Rh Factor The Rh factor is an antigen found on the red blood cells of most people. Genetically inherited Present in approximately 85% of the Canadian population
28 Rh Factor Each of the four blood types is additionally classified according to the presence of another protein on the surface of RBCs that indicates the Rh factor. If you carry this protein, you are Rh positive. If you don't carry the protein, you are Rh negative.
29
30 Rh factor and Pregnancy Other than during a blood transfusion, the other time the Rh factor can be a problem is during pregnancy. It is only an issue if the Mom is Rh negative and she becomes pregnant with an Rh positive baby.
31 Rh Incompatibility The mother s body can recognize the Rh positive factor in the baby s blood as foreign and it can stimulate an antibody response in the mother. This does not normally happen in the first pregnancy because mother and baby s blood do not normally mix until delivery. It will however be an issue for a second pregnancy.
32 Rh Incompatibility If a woman who is Rh negative and a man who is Rh positive conceive a baby, there is the potential for a baby to have a health problem. A new born whose Rh factor differs from its mother can develop Rh incompatibility or Hemolytic Disease of the New Born (HDN) This can cause clumping of the baby s RBCs, a lose in hemoglobin (cells unable to carry oxygen), massive swelling of tissues, or death. Treatment: Rh immune globulin prevents the formation of Rh antibodies
33 Are you ready to transfuse? Let s see how much you learned today about blood types and blood transfusions! edicine/landsteiner/index.html
34 The Heart and Blood Vessels The heart is a transport system pump that propels blood into the interconnecting blood vessels that move to and past the body cells Blood vessels form a closed delivery system that begins and ends at the heart (the circulatory system!) Dynamic: pulsate, constrict, and relax There are three major types of blood vessels
35
36 Moving Blood Throughout the Body: The Circulatory System Arteries Blood vessels that carry oxygen rich blood away from the heart. Capillaries A network of tiny blood vessels that connect the arteries with the veins. Veins Blood vessels that carry oxygen poor blood back to the heart.
37 Arteries Arteries are vessels that carry oxygen rich blood from the heart to other body tissues/organs. Arterioles are simply small arteries. Arterioles deliver the blood to the capillaries. Structure: The walls of arteries are thick and contain a layer of muscle. When blood is pumped out of the heart, it is forced out under high pressure. These muscular arteries are also elastic and stretch to accommodate this wave of pressure that is being pushed along. Colour of blood in arteries is bright red
38 Arteries Elastic arteries: Arteries closest to the heart (eg. Aorta) are more elastic, as they expand and recoil to accommodate changes in blood volume. Muscular arteries: arteries closer to other body organs (femoral artery) are more muscular than elastic. Note: Arteries and veins have both elastic and muscular properties.
39 Although the blood is forced into the arteries under pressure, by the time it reaches the capillaries this pressure is very low Therefore, there must be another mechanism for getting the blood back up to the heart.
40 Veins Veins carry blood the heart. Venules are smaller veins that connect to the capillaries. Within a vein are tiny valves that are regularly spaced throughout its length. These valves point in the direction in which the blood is flowing. The valves can be pushed open to allow blood to flow toward the heart, but they close to prevent any back flow. Unlike arteries, where blood flows smoothly, the blood in veins travels in small spurts Blood in veins is a dark maroon colour as a result of its low oxygen content
41
42 Check this out! dfjdoc What happens if these valves get weak?
43 Interesting Note: Varicose Veins Portions of the veins lose elasticity and become extended, preventing their valves from closing completely. This allows the blood to form bulging pools. This swelling, particularly in the legs, causes the veins to appear knotted and blue
44 Veins versus Arteries Veins also have a muscular coat in their walls, but because the pressure of blood flow is greatly reduced, this coat is much thinner than that found in the arteries. Both arteries and veins have walls that are far too thick to allow any blood plasma, nutrients, or gases to pass out into the surrounding tissue.
45
46 Still got it? Blood Composition ABO Blood Types Antigens and Antibodies Blood Vessels
47 Arteries Take blood away from the heart to the body organs/tissues No valves present Thick muscle walls Blood rich in oxygen Low in CO2 Blood is bright red in colour Veins Take blood to the heart Valves present Thin muscle walls Blood poor in oxygen High in CO2 Blood is maroon red in colour Very high pressure Very low pressure
48 So where does gas and nutrient exchange occur?
49
50 Capillaries Smallest blood vessels Very thin walls A capillary is so narrow that often only one tiny RBC can pass through at a time. It is through the walls of the capillaries, which link the arterioles to the venules that the exchange of oxygen, carbon dioxide, nutrients, wastes, and other substances takes place.
51
52 Interstitial Fluid All of the cells and tissues of the body must be continually bathed by fluids. These fluids, called interstitial fluids, enable nutrients to pass from the capillaries across the spaces between the cells to reach cell membranes. They also prevent the cells from drying out.
53 Check this out! Capillaries WxtOw
54
55 The System in Action: The Heart Located behind the rib cage, between the lungs, with its lower end slightly toward the left side. About the size of your fist approx. 300g The heart is not attached to surrounding tissue. It is suspended by the large blood vessels that are attached to it. This enables it to move loosely in place as it contracts and relaxes.
56 The Heart The heart is not one pump, but two separate pumps. Composed of special heart muscle tissue, similar to striated muscle. Incredible stamina
57 Cardiac Muscle Each cardiac muscle cell is attached to, and pulls against, other cardiac muscle cells during contractions; the muscle is not anchored to bones or other tissues. The muscle cells of the heart have an innate ability to contract and they do so spontaneously. Cells that are connected to each other have the ability co-ordinate their contractions into a common rhythm.
58 Check this out! 67KrAo
59 Heart Anatomy: The Right Side The right side of the heart is responsible for collecting blood from the body and sending it to the lungs to be oxygenated. The blood flows back, from the head and arms, to this side of the heart by way of a large vein called the superior vena cava. This vein leads into the upper right-side chamber of the heart, the RIGHT ATRIUM.
60 Heart Anatomy: The Right Side Blood from the trunk and legs enters this same chamber, the RIGHT ATRIUM, via the inferior vena cava. Both the right and left atria (plural of atrium) are thinwalled chambers which lie above the ventricles.
61 Heart Anatomy: The Right Side The RIGHT VENTRICLE has thicker, more muscular walls than the right atrium and is much larger than the right atrium. The Right Ventricle is connected to the Right Atrium via the TRICUSPID VALVE, which prevents the blood from flowing back into the atrium when the ventricle contracts. When the right ventricle contracts, it pushes blood out through the Pulmonary Valve into the PULMONARY ARTERY.
62 Check this out! Interactive Heart: it.html
63 Pulmonary Circulation The pulmonary artery is a vessel that carries the blood to the lungs where its load of carbon dioxide wastes are released and a fresh load of oxygen is absorbed. This newly oxygenated blood then flows into the left atrium via the four pulmonary veins. This portion of the circulatory system, the heart to lungs and back, is called the pulmonary circulation.
64 Heart Anatomy: The Left Side Contractions of the left atrium push the blood through the BICUSPID VALVE (or Mitral Valve) into the LEFT VENTRICLE. The left ventricle is the largest part of the heart and the most heavily muscled. As the left ventricle contracts, it must force the blood to every part of the body, from the brain to the smallest toe.
65 Systemic Circulation The blood is pushed out from the left ventricle via the aortic semilunar valve, into the largest blood vessel in the body, the aorta. This portion of the circulatory system, the systemic system, supplies blood to the remaining body system.
66
67 Valves of the Heart The tricuspid and bicuspid valves are also known as the atrio-ventricular valves, after the two chambers that they separate, the atrium and the ventricle. Pushing blood through the heart: In the right side of the heart, the tricuspid valve connects the atrium and ventricle.
68 The tricuspid valve (AV valve) is closed while the atrium is filling with blood. When this is completed, the tricuspid valve opens and a wave of contractions starts at the top of the atrium and squeezes the chamber through the valve into the right ventricle. The valve then closes. Another wave of contractions starts, this time at the bottom of the ventricle. The blood is now squeezed upward through the semilunar valve, which lies at the entrance of the pulmonary artery leading to the lungs. This process is repeated over and over with each beat of the heart. The same sequence of valve action takes place in the left side of the heart.
69 Heart Sounds The sounds produced by the heart are caused by the vibrations produced when the heart valves close and the blood bounces against the walls of the ventricles or blood vessels. The stethoscope makes it much easier to hear these sounds.
70
71 Heart Sounds The first sound: Produced when the valves between the atria and ventricles close and the semilunar valves open. This sound has a lower pitch and makes a lub sound. The second sound: Produced by the closure of the semilunar valves and the opening of the valves between the chambers. The pressure in the arteries is higher and the pitch is also somewhat higher. The sound is a short dub sound.
2.01 Remember the structures of the circulatory system
 2.01 Remember the structures of the circulatory system Essential questions What are the structures of blood? What are the structures of the circulatory system? circulatory system 2 Structures of the circulatory
2.01 Remember the structures of the circulatory system Essential questions What are the structures of blood? What are the structures of the circulatory system? circulatory system 2 Structures of the circulatory
1. Which of the following blood vessels has a thin elastic layer? A. Aorta. B. Pulmonary artery. C. Posterior vena cava. D. Mesenteric capillary.
 CIRCULATORY SYSTEM 1. Which of the following blood vessels has a thin elastic layer? A. Aorta. B. Pulmonary artery. C. Posterior vena cava. D. Mesenteric capillary. 2. Capillary beds are equipped with
CIRCULATORY SYSTEM 1. Which of the following blood vessels has a thin elastic layer? A. Aorta. B. Pulmonary artery. C. Posterior vena cava. D. Mesenteric capillary. 2. Capillary beds are equipped with
Scrub In: Red blood cells are called: Which component of blood is necessary for the initiation of the blood clotting process:
 Scrub In: Red blood cells are called: a. erythrocytes b. leukocytes c. melanocytes d. thrombocytes Which component of blood is necessary for the initiation of the blood clotting process: a. erythrocytes
Scrub In: Red blood cells are called: a. erythrocytes b. leukocytes c. melanocytes d. thrombocytes Which component of blood is necessary for the initiation of the blood clotting process: a. erythrocytes
THE HEART. Unit 3: Transportation and Respiration
 THE HEART Unit 3: Transportation and Respiration The Circulatory System Also called the Cardiovascular System Circulates blood in the body Transports nutrients, oxygen, carbon dioxide, hormones, and blood
THE HEART Unit 3: Transportation and Respiration The Circulatory System Also called the Cardiovascular System Circulates blood in the body Transports nutrients, oxygen, carbon dioxide, hormones, and blood
The Circulatory System. The Heart, Blood Vessels, Blood Types
 The Circulatory System The Heart, Blood Vessels, Blood Types The Closed Circulatory System Humans have a closed circulatory system, typical of all vertebrates, in which blood is confined to vessels and
The Circulatory System The Heart, Blood Vessels, Blood Types The Closed Circulatory System Humans have a closed circulatory system, typical of all vertebrates, in which blood is confined to vessels and
Cardiovascular System. I. Structures of the heart A. : Pericardium sack that surrounds the heart
 Cardiovascular System I. Structures of the heart A. : Pericardium sack that surrounds the heart 1. : Pericardial Cavity serous fluid filled space between the heart and the pericardium B. Heart Wall 1.
Cardiovascular System I. Structures of the heart A. : Pericardium sack that surrounds the heart 1. : Pericardial Cavity serous fluid filled space between the heart and the pericardium B. Heart Wall 1.
CIRCULATORY SYSTEM BLOOD VESSELS
 Name: Block: CIRCULATORY SYSTEM Multicellular organisms (above the level of roundworms) rely on a circulatory system to bring nutrients to, and take wastes away from, cells. In higher organisms such as
Name: Block: CIRCULATORY SYSTEM Multicellular organisms (above the level of roundworms) rely on a circulatory system to bring nutrients to, and take wastes away from, cells. In higher organisms such as
2. What makes up the most of your blood? least of your blood? 1. Look like red discs, have a pale center, no nucleus, similar in size
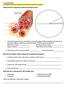 I Can Statements I can identify the major components of blood and where they are formed. Identify the four components of blood in the diagram below. 1. Label each section of the pie chart with the correct
I Can Statements I can identify the major components of blood and where they are formed. Identify the four components of blood in the diagram below. 1. Label each section of the pie chart with the correct
Bellwork Define: hemostasis anticoagulation hemophilia (Then write the underline portion of the two state standards in your notes).
 Bellwork Define: hemostasis anticoagulation hemophilia (Then write the underline portion of the two state standards in your notes). A&P Standards 31) Identify the liquid and cellular components of blood
Bellwork Define: hemostasis anticoagulation hemophilia (Then write the underline portion of the two state standards in your notes). A&P Standards 31) Identify the liquid and cellular components of blood
TOPIC 6: HUMAN HEALTH AND PHYSIOLOGY
 TOPIC 6: HUMAN HEALTH AND PHYSIOLOGY 6.2 Transport System/Circulatory Draw and label a diagram of the heart showing the four chambers, associated blood vessels, valves and the route of blood through the
TOPIC 6: HUMAN HEALTH AND PHYSIOLOGY 6.2 Transport System/Circulatory Draw and label a diagram of the heart showing the four chambers, associated blood vessels, valves and the route of blood through the
Lower Secondary Science Blood Circulatory System Notes / Advanced Notes
 Lower Secondary Science Blood Circulatory System Notes / Advanced Notes Double Circulation in Mammals In mammals, there is a double circulation (i.e. blood passes through the heart twice in one complete
Lower Secondary Science Blood Circulatory System Notes / Advanced Notes Double Circulation in Mammals In mammals, there is a double circulation (i.e. blood passes through the heart twice in one complete
Blood flows away from the heart in arteries, to the capillaries and back to the heart in the veins
 Cardiovascular System Summary Notes The cardiovascular system includes: The heart, a muscular pump The blood, a fluid connective tissue The blood vessels, arteries, veins and capillaries Blood flows away
Cardiovascular System Summary Notes The cardiovascular system includes: The heart, a muscular pump The blood, a fluid connective tissue The blood vessels, arteries, veins and capillaries Blood flows away
Introduction to Medical Careers. Cardiovascular & Circulatory Systems Chapters 11-12
 Introduction to Medical Careers Cardiovascular & Circulatory Systems Chapters 11-12 CHAPTER 11 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM I will be able to: 1. Define at least eight terms referring to the cardiovascular system.
Introduction to Medical Careers Cardiovascular & Circulatory Systems Chapters 11-12 CHAPTER 11 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM I will be able to: 1. Define at least eight terms referring to the cardiovascular system.
2. What makes up the most of your blood? least of your blood? 1. Look like red discs, have a pale center, no nucleus, similar in size
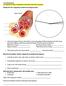 .I Can Statements I can identify the major components of blood and where they are formed. Identify the four components of blood in the diagram below. 1. Label each section of the pie chart with the correct
.I Can Statements I can identify the major components of blood and where they are formed. Identify the four components of blood in the diagram below. 1. Label each section of the pie chart with the correct
Blood Functions. Blood and the Cardiovascular System. Blood. Plasma. Erythrocytes (RBCs) Erythrocytes (RBCs) 4/7/2017
 Blood Functions Blood and the Cardiovascular System Distribution Delivery of oxygen and nutrients to all body cells; Transport of wastes to lungs and excretory organs; Transport of hormones Regulation
Blood Functions Blood and the Cardiovascular System Distribution Delivery of oxygen and nutrients to all body cells; Transport of wastes to lungs and excretory organs; Transport of hormones Regulation
Health Science 20 Circulatory System Notes
 Health Science 20 Circulatory System Notes Functions of the Circulatory System The circulatory system functions mainly as the body s transport system. It transports: o Oxygen o Nutrients o Cell waste o
Health Science 20 Circulatory System Notes Functions of the Circulatory System The circulatory system functions mainly as the body s transport system. It transports: o Oxygen o Nutrients o Cell waste o
Lesson 10 Circulatory System (Nelson p.88-93)
 Name: Date: Lesson 10 Circulatory System (Nelson p.88-93) Learning Goals: A. I can explain the primary functions of the circulatory system in animals. B. I can identify and explain all the parts of the
Name: Date: Lesson 10 Circulatory System (Nelson p.88-93) Learning Goals: A. I can explain the primary functions of the circulatory system in animals. B. I can identify and explain all the parts of the
Section 12.1 Your Cardiovascular System
 Objectives Describe the main functions of the cardiovascular system. Trace the pathway of blood through the heart. Identify three types of blood vessels and the four components of blood. Slide 1 of 31
Objectives Describe the main functions of the cardiovascular system. Trace the pathway of blood through the heart. Identify three types of blood vessels and the four components of blood. Slide 1 of 31
Circulatory Systems. All cells need to take in nutrients and expel metabolic wastes.
 Circulatory Systems All cells need to take in nutrients and expel metabolic wastes. Single celled organisms: nutrients from the environment can diffuse (or be actively transported) directly in to the cell
Circulatory Systems All cells need to take in nutrients and expel metabolic wastes. Single celled organisms: nutrients from the environment can diffuse (or be actively transported) directly in to the cell
How does the Circulatory System maintain
 How does the Circulatory System maintain -It supplies cells throughout the body with oxygen and nutrients while also ridding them of wastes. Transports materials such as: (to cells) (to attack foreign
How does the Circulatory System maintain -It supplies cells throughout the body with oxygen and nutrients while also ridding them of wastes. Transports materials such as: (to cells) (to attack foreign
12.1 The Function of Circulation
 12.1 The Function of Circulation The Circulatory System Magnetic Resonance Angiography (MRA) Heart pump beats 100 000 times a day Deliver oxygen and nutrients Function of Circulation Multicellular organisms
12.1 The Function of Circulation The Circulatory System Magnetic Resonance Angiography (MRA) Heart pump beats 100 000 times a day Deliver oxygen and nutrients Function of Circulation Multicellular organisms
Biology Unit 3 The Human Heart P
 Biology 2201 Unit 3 The Human Heart P 314-321 Structure and Function of the Human Heart Structure of the Human Heart Has four Chambers (2 Atria and 2 Ventricles) Made of Cardiac Muscle Found in Chest Cavity
Biology 2201 Unit 3 The Human Heart P 314-321 Structure and Function of the Human Heart Structure of the Human Heart Has four Chambers (2 Atria and 2 Ventricles) Made of Cardiac Muscle Found in Chest Cavity
The Function. To carry nutrients and oxygen to and remove waste from the cells of the body.
 The Function To carry nutrients and oxygen to and remove waste from the cells of the body. What makes up the circulatory system? 1. Heart 2. Blood 3. Blood vessels Blood travels from the heart to the body
The Function To carry nutrients and oxygen to and remove waste from the cells of the body. What makes up the circulatory system? 1. Heart 2. Blood 3. Blood vessels Blood travels from the heart to the body
Cardiovascular System Note-Taking Guide
 FUNctions: Name: 3-27-14 Cardiovascular System Note-Taking Guide Heart: Pumps and delivers through the body Blood: Vessels: Delivers and to the body Carries waste and Maintains homeostasis - Carries blood
FUNctions: Name: 3-27-14 Cardiovascular System Note-Taking Guide Heart: Pumps and delivers through the body Blood: Vessels: Delivers and to the body Carries waste and Maintains homeostasis - Carries blood
30.1 Respiratory and Circulatory Functions. KEY CONCEPT The respiratory and circulatory systems bring oxygen and nutrients to the cells.
 30.1 Respiratory and Circulatory Functions KEY CONCEPT The respiratory and circulatory systems bring oxygen and nutrients to the cells. 30.1 Respiratory and Circulatory Functions The respiratory and circulatory
30.1 Respiratory and Circulatory Functions KEY CONCEPT The respiratory and circulatory systems bring oxygen and nutrients to the cells. 30.1 Respiratory and Circulatory Functions The respiratory and circulatory
Blood and Heart. Student Learning Objectives:
 Blood and Heart Student Learning Objectives: Identify the major components of the blood. Identify the primary structures associated with the heart Follow the blood through the path of the circulation.
Blood and Heart Student Learning Objectives: Identify the major components of the blood. Identify the primary structures associated with the heart Follow the blood through the path of the circulation.
The circulatory system
 The circulatory system Key words Vessels heart blood plasma platelets haemoglobin To engulf arteries capillaries veins venules lymphocytes Atrium / - a ventricle tricuspid bicuspid cardiac coronary Humans
The circulatory system Key words Vessels heart blood plasma platelets haemoglobin To engulf arteries capillaries veins venules lymphocytes Atrium / - a ventricle tricuspid bicuspid cardiac coronary Humans
Learning Objectives; 1. Identify the key features of the cardiovascular system. 2. Describe the function of the cardiovascular system.
 Learning Objectives; 1. Identify the key features of the cardiovascular system. 2. Describe the function of the cardiovascular system. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=yaxna8lmoiy The Circulatory System
Learning Objectives; 1. Identify the key features of the cardiovascular system. 2. Describe the function of the cardiovascular system. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=yaxna8lmoiy The Circulatory System
Today s objectives:! - Learn BASICS of circulatory system (Heart, different veins and arteries)! - Appreciate effects and treatment for
 Today s objectives:! - Learn BASICS of circulatory system (Heart, different veins and arteries)! - Appreciate effects and treatment for hyperlipidemia! Agenda! - Review objectives for 6.2! - Video of circulatory
Today s objectives:! - Learn BASICS of circulatory system (Heart, different veins and arteries)! - Appreciate effects and treatment for hyperlipidemia! Agenda! - Review objectives for 6.2! - Video of circulatory
The Heart. Made up of 3 different tissue: cardiac muscle tissue, nerve tissue, and connective tissue.
 The Heart The Heart Made up of 3 different tissue: cardiac muscle tissue, nerve tissue, and connective tissue. Your heart pumps with a regular beat (Heart Rate) Your heart rate can change depending on
The Heart The Heart Made up of 3 different tissue: cardiac muscle tissue, nerve tissue, and connective tissue. Your heart pumps with a regular beat (Heart Rate) Your heart rate can change depending on
Unit 10 Cardiovascular System
 Unit 10 Cardiovascular System I. Functions Deliver nutrients to cells > O 2, sugars, amino acids, lipids, ions, H 2 O... Remove waste from cells > CO 2, pathogens, toxins, lactic acid... Fight off infection
Unit 10 Cardiovascular System I. Functions Deliver nutrients to cells > O 2, sugars, amino acids, lipids, ions, H 2 O... Remove waste from cells > CO 2, pathogens, toxins, lactic acid... Fight off infection
CIRCULATORY SYSTEM TASK CARDS Worksheet
 CIRCULATORY SYSTEM TASK CARDS Worksheet Name: Date: Instructions: Put the answers to each task card in the numbered boxes on the chart. 1 a) left semilunar valve / aortic valve b) blood would backflow
CIRCULATORY SYSTEM TASK CARDS Worksheet Name: Date: Instructions: Put the answers to each task card in the numbered boxes on the chart. 1 a) left semilunar valve / aortic valve b) blood would backflow
Unit 23.1: The Circulatory System
 Unit 23.1: The Circulatory System This color-enhanced image was made with an electron microscope, so the objects it depicts are extremely small. Do you know what they are? This incredible photo shows red
Unit 23.1: The Circulatory System This color-enhanced image was made with an electron microscope, so the objects it depicts are extremely small. Do you know what they are? This incredible photo shows red
Chapter 12 Cardiovascular System
 Chapter 12 Cardiovascular System Cardiovascular System Includes Heart and Blood Vessels Transports, nutrients and wastes to and from the tissues 1 The Blood Vessels Three Types of Blood Vessels Arteries:
Chapter 12 Cardiovascular System Cardiovascular System Includes Heart and Blood Vessels Transports, nutrients and wastes to and from the tissues 1 The Blood Vessels Three Types of Blood Vessels Arteries:
Chapter 27 -The Heart & Blood Vessels
 Chapter 27 -The Heart & Blood Vessels 3.2 Learning Objectives 3.2.2 Organisational Complexity of the human 1. Describe the structures and organisation of tissues in the closed circulatory system. 2. Discuss
Chapter 27 -The Heart & Blood Vessels 3.2 Learning Objectives 3.2.2 Organisational Complexity of the human 1. Describe the structures and organisation of tissues in the closed circulatory system. 2. Discuss
It s Totally Tubular, Dude!
 It s Totally Tubular, Dude! Objective: To learn the structure and function of the Cardiovascular and Lymphatic Systems Bell Work: For the following, place the items in order from most simple to most complex:
It s Totally Tubular, Dude! Objective: To learn the structure and function of the Cardiovascular and Lymphatic Systems Bell Work: For the following, place the items in order from most simple to most complex:
Ch 9 Transport of substances in humans
 Ch 9 Transport of substances in humans Think about (Ch 9, p.2) 1. Blood transports various substances and distributes heat around the body. It also plays a role in body defence. 2. Blood is a liquid tissue
Ch 9 Transport of substances in humans Think about (Ch 9, p.2) 1. Blood transports various substances and distributes heat around the body. It also plays a role in body defence. 2. Blood is a liquid tissue
THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM
 Biology 30S THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM Name: This module adapted from bblearn.merlin.mb.ca 1 Introduction to Circulation The first organ to form, and the last organ to die. The heart is the pump of life. The
Biology 30S THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM Name: This module adapted from bblearn.merlin.mb.ca 1 Introduction to Circulation The first organ to form, and the last organ to die. The heart is the pump of life. The
The Circulatory System
 The Circulatory System Science Matters Chapter 8 Introduction Living things need a transport system to carry things around the body. In humans its called The Circulatory system. The parts of the system
The Circulatory System Science Matters Chapter 8 Introduction Living things need a transport system to carry things around the body. In humans its called The Circulatory system. The parts of the system
Cardiovascular System. Heart Anatomy
 Cardiovascular System Heart Anatomy 1 The Heart Location & general description: Atria vs. ventricles Pulmonary vs. systemic circulation Coverings Walls The heart is found in the mediastinum, the medial
Cardiovascular System Heart Anatomy 1 The Heart Location & general description: Atria vs. ventricles Pulmonary vs. systemic circulation Coverings Walls The heart is found in the mediastinum, the medial
Cardiovascular System
 Cardiovascular System Cardiovascular System - Function The cardiovascular system transports, from one part of the body to another: nutrients, oxygen, ions, proteins, hormones and other signaling molecules,
Cardiovascular System Cardiovascular System - Function The cardiovascular system transports, from one part of the body to another: nutrients, oxygen, ions, proteins, hormones and other signaling molecules,
DAY ONE BLOOD. What do you know about blood? What does it do? What is it made of? Where is it made?
 BLOOD AND THE HEART DAY ONE BLOOD What do you know about blood? What does it do? What is it made of? Where is it made? BLOOD Transports gases Brings in oxygen Removes carbon dioxide MAIN FUNCTIONS OF
BLOOD AND THE HEART DAY ONE BLOOD What do you know about blood? What does it do? What is it made of? Where is it made? BLOOD Transports gases Brings in oxygen Removes carbon dioxide MAIN FUNCTIONS OF
Circulatory, Respiratory, and Excretory Systems
 34 Circulatory, Respiratory, and Excretory Systems section 1 Circulatory System Before You Read Press the tips of two fingers to the inside of your wrist, at a point just below your thumb. Can you feel
34 Circulatory, Respiratory, and Excretory Systems section 1 Circulatory System Before You Read Press the tips of two fingers to the inside of your wrist, at a point just below your thumb. Can you feel
The Circulatory System. Lesson Overview. Lesson Overview The Circulatory System
 33.1 THINK ABOUT IT More than one-third of the 1.2 million Americans who suffer a heart attack each year die. This grim evidence shows that the heart and the circulatory system it powers are vital to life.
33.1 THINK ABOUT IT More than one-third of the 1.2 million Americans who suffer a heart attack each year die. This grim evidence shows that the heart and the circulatory system it powers are vital to life.
The Circulatory System (p )
 The Circulatory System (p. 268-281) How Does Gravity Affect Blood Circulation? As with all land animals, the giraffe and the corn snake are constantly subject to the force of gravity The circulatory system
The Circulatory System (p. 268-281) How Does Gravity Affect Blood Circulation? As with all land animals, the giraffe and the corn snake are constantly subject to the force of gravity The circulatory system
The Circulatory System
 The Circulatory System Key Questions What are the functions of the circulatory system? How does the heart pump blood through the body? What are three types of blood vessels? Vocabulary myocardium atrium
The Circulatory System Key Questions What are the functions of the circulatory system? How does the heart pump blood through the body? What are three types of blood vessels? Vocabulary myocardium atrium
Circulatory System Objective sheet 3
 Circulatory System Objective sheet 3 10. Functions of blood 1) Transport oxygen and nutrients 2) Transport of carbon dioxide and waste 3) Protection against disease causing micro-organisms 4) Clotting
Circulatory System Objective sheet 3 10. Functions of blood 1) Transport oxygen and nutrients 2) Transport of carbon dioxide and waste 3) Protection against disease causing micro-organisms 4) Clotting
Chapter 16: Circulation
 Chapter 16: Circulation Section 1: The Body s Transport System Beating Heart Cardiac muscle is Striated and branched Under involuntary control by the brain stem Functions of the Cardiovascular System 1.
Chapter 16: Circulation Section 1: The Body s Transport System Beating Heart Cardiac muscle is Striated and branched Under involuntary control by the brain stem Functions of the Cardiovascular System 1.
Biology. A Guide to the Natural World. Chapter 30 Lecture Outline Transport and Exchange 1: Blood and Breath. Fifth Edition.
 Biology A Guide to the Natural World Chapter 30 Lecture Outline Transport and Exchange 1: Blood and Breath Fifth Edition David Krogh 30.1 The Cardiovascular System The Cardiovascular System The human cardiovascular
Biology A Guide to the Natural World Chapter 30 Lecture Outline Transport and Exchange 1: Blood and Breath Fifth Edition David Krogh 30.1 The Cardiovascular System The Cardiovascular System The human cardiovascular
Exam 3 Study Guide. 4) The process whereby the binding of antibodies to antigens causes RBCs to clump is called:
 Exam 3 Study Guide 1) Where does hematopoiesis produce new red blood cells: 2) Which of the following is a blood clotting disorder: 3) Treatment of hemophilia often involves: 4) The process whereby the
Exam 3 Study Guide 1) Where does hematopoiesis produce new red blood cells: 2) Which of the following is a blood clotting disorder: 3) Treatment of hemophilia often involves: 4) The process whereby the
37 1 The Circulatory System
 H T H E E A R T 37 1 The Circulatory System The circulatory system and respiratory system work together to supply cells with the nutrients and oxygen they need to stay alive. a) The respiratory system:
H T H E E A R T 37 1 The Circulatory System The circulatory system and respiratory system work together to supply cells with the nutrients and oxygen they need to stay alive. a) The respiratory system:
The Cardiovascular System home study course
 The Cardiovascular System home study course harmony house holistic therapy treatment centre and training academy www.harmony-house.org 1 Copyright 2010 by Mark and Katy Rogers All rights reserved. No part
The Cardiovascular System home study course harmony house holistic therapy treatment centre and training academy www.harmony-house.org 1 Copyright 2010 by Mark and Katy Rogers All rights reserved. No part
CIRCULATORY SYSTEM: BLOOD + BLOOD VESSELS. October 21, 2016
 CIRCULATORY SYSTEM: BLOOD + BLOOD VESSELS October 21, 2016 Review AGENDA Questions Activity Notes HEART HEART = A BIG, WET, MUSCLY PUMP Body temperature ph levels Volume of body fluid REGULATES HEART TRANSPORTS
CIRCULATORY SYSTEM: BLOOD + BLOOD VESSELS October 21, 2016 Review AGENDA Questions Activity Notes HEART HEART = A BIG, WET, MUSCLY PUMP Body temperature ph levels Volume of body fluid REGULATES HEART TRANSPORTS
Levels of Organization. Chapter 19 6/11/2012. Homeostasis & Organization of the animal body. 4 Primary Tissues
 Levels of Organization Chapter 19 Homeostasis & Organization of the animal body Chemical Cellular Tissue Organs System Level Organismic 1-2 4 Primary Tissues 1. Epithelial Tissue: covers surfaces lines
Levels of Organization Chapter 19 Homeostasis & Organization of the animal body Chemical Cellular Tissue Organs System Level Organismic 1-2 4 Primary Tissues 1. Epithelial Tissue: covers surfaces lines
Lecture 8. Heart and Circulatory System. Lecture 8
 Lecture 8 Heart and Circulatory System Lecture 8 1. Introduction 2. Blood 3. Blood Vessels & Blood Pressure 4. The Heart 5. Cardiovascular (Circulatory) System 2 1 Circulatory System Function 1. Transport
Lecture 8 Heart and Circulatory System Lecture 8 1. Introduction 2. Blood 3. Blood Vessels & Blood Pressure 4. The Heart 5. Cardiovascular (Circulatory) System 2 1 Circulatory System Function 1. Transport
The Circulatory System
 The Circulatory System Cardiovascular System Facts The average person has nearly 100,000 km of blood vessels running through them. The larger the organism, the slower the heart beats (a woman s heart will
The Circulatory System Cardiovascular System Facts The average person has nearly 100,000 km of blood vessels running through them. The larger the organism, the slower the heart beats (a woman s heart will
Questions on Transport
 Name: Questions on Transport Directions: The following questions are taken from previous IB Final Papers on Topic 6.2 (The Transport System). Answer all questions. This will serve as a study guide for
Name: Questions on Transport Directions: The following questions are taken from previous IB Final Papers on Topic 6.2 (The Transport System). Answer all questions. This will serve as a study guide for
Unit 1: Human Systems. The Circulatory System
 Unit 1: Human Systems The Circulatory System nourish all cells with oxygen, glucose, amino acids and other nutrients and carry away carbon dioxide, urea and other wastes Purposes Transport chemical messengers
Unit 1: Human Systems The Circulatory System nourish all cells with oxygen, glucose, amino acids and other nutrients and carry away carbon dioxide, urea and other wastes Purposes Transport chemical messengers
The Circulatory System. The circulatory system includes the Heart, Blood Tissue and the Blood Vessels.
 The Circulatory System The circulatory system includes the Heart, Blood Tissue and the Blood Vessels. The Circulatory System-Transport The absorption and circulation of materials throughout an organism
The Circulatory System The circulatory system includes the Heart, Blood Tissue and the Blood Vessels. The Circulatory System-Transport The absorption and circulation of materials throughout an organism
Monday 14 th May The Body Anatomy and Physiology Lesson 10 Cardio-Respiratory System
 Monday 14 th May 2018 The Body Anatomy and Physiology Lesson 10 Cardio-Respiratory System Homework 1. What is the function of the cardiovascular system? 2. List the main components of blood and describe
Monday 14 th May 2018 The Body Anatomy and Physiology Lesson 10 Cardio-Respiratory System Homework 1. What is the function of the cardiovascular system? 2. List the main components of blood and describe
The circulatory system transports blood to deliver important substances, such as oxygen, to cells and to remove wastes, such as carbon dioxide.
 Section 1: The circulatory system transports blood to deliver important substances, such as oxygen, to cells and to remove wastes, such as carbon dioxide. K What I Know W What I Want to Find Out L What
Section 1: The circulatory system transports blood to deliver important substances, such as oxygen, to cells and to remove wastes, such as carbon dioxide. K What I Know W What I Want to Find Out L What
Pearson's Comprehensive Medical Assisting Administrative and Clinical Competencies
 Pearson's Comprehensive Medical Assisting Administrative and Clinical Competencies THIRD EDITION CHAPTER 27 The Cardiovascular System Lesson 1: Overview of the Cardiovascular System Lesson Objectives Upon
Pearson's Comprehensive Medical Assisting Administrative and Clinical Competencies THIRD EDITION CHAPTER 27 The Cardiovascular System Lesson 1: Overview of the Cardiovascular System Lesson Objectives Upon
The Cardiovascular System
 CHAPTER 16 1 SECTION Circulation and Respiration The Cardiovascular System California Science Standards 7.5.a, 7.5.b, 7.6.j BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these
CHAPTER 16 1 SECTION Circulation and Respiration The Cardiovascular System California Science Standards 7.5.a, 7.5.b, 7.6.j BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these
BLOOD RUNS THROUGH YOUR BODY
 BLOOD RUNS THROUGH YOUR BODY WORKSHEET A Your heart and blood vessels make up your blood system. At the centre of your blood system is your heart. Its job is to pump the blood around your body. The rest
BLOOD RUNS THROUGH YOUR BODY WORKSHEET A Your heart and blood vessels make up your blood system. At the centre of your blood system is your heart. Its job is to pump the blood around your body. The rest
Glossary: The Cardiovascular System
 This glossary includes terms that have been introduced in Lesson 14. Student Resource 14.14 Glossary: The Cardiovascular System Anatomy Terms aorta Large artery that transports blood from the left ventricle
This glossary includes terms that have been introduced in Lesson 14. Student Resource 14.14 Glossary: The Cardiovascular System Anatomy Terms aorta Large artery that transports blood from the left ventricle
The Heart and Cardiovascular System
 The Heart and Cardiovascular System What you will learn The location of the heart 3 layers and covering of the heart Explain the function of the heart as 2 separate pumps Identify the 4 chambers of the
The Heart and Cardiovascular System What you will learn The location of the heart 3 layers and covering of the heart Explain the function of the heart as 2 separate pumps Identify the 4 chambers of the
Circulatory System. Chapter 32
 Circulatory System Chapter 32 Invertebrates w/o a Circulatory System If an organism has a sac body plan, circulatory systems are not necessary. Sac body plans mean cells are capable of gas and nutrient
Circulatory System Chapter 32 Invertebrates w/o a Circulatory System If an organism has a sac body plan, circulatory systems are not necessary. Sac body plans mean cells are capable of gas and nutrient
CHAPTER 2: BLOOD CIRCULATION AND TRANSPORT
 CHAPTER 2: BLOOD CIRCULATION AND TRANSPORT BLOOD CIRCULATION AND TRANSPORT HUMAN BEING PLANTS Function of heart Wilting Structure of heart Blood vessels: characteristics and functions Transpiration: function
CHAPTER 2: BLOOD CIRCULATION AND TRANSPORT BLOOD CIRCULATION AND TRANSPORT HUMAN BEING PLANTS Function of heart Wilting Structure of heart Blood vessels: characteristics and functions Transpiration: function
STRUCTURES OF THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM
 STRUCTURES OF THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Also called the circulatory system Consists of the heart, arteries, veins, and capillaries Main function is to pump/circulate oxygenated blood
STRUCTURES OF THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Also called the circulatory system Consists of the heart, arteries, veins, and capillaries Main function is to pump/circulate oxygenated blood
Topic 6: Human Physiology
 Topic 6: Human Physiology 6.2 The Blood System D.4 The Heart Essential Questions: 6.2 The blood system continuously transports substances to cells and simultaneously collects waste products. D.3 The chemical
Topic 6: Human Physiology 6.2 The Blood System D.4 The Heart Essential Questions: 6.2 The blood system continuously transports substances to cells and simultaneously collects waste products. D.3 The chemical
CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Worksheet
 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Worksheet NAME Section A: Blood Basics http://www.psbc.org/hematology/01_index.htm Although blood appears to be red liquid it is actually composed of yellowish liquid called plasma
CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Worksheet NAME Section A: Blood Basics http://www.psbc.org/hematology/01_index.htm Although blood appears to be red liquid it is actually composed of yellowish liquid called plasma
Chapter 27 The Heart and Blood Vessels
 Chapter 27 The Heart and Blood Vessels Most animals have a closed blood system. The blood flows continuously in vessels back to the heart. In an open system the blood is pumped into open ended tubes and
Chapter 27 The Heart and Blood Vessels Most animals have a closed blood system. The blood flows continuously in vessels back to the heart. In an open system the blood is pumped into open ended tubes and
d) Cardiovascular System Higher Human Biology
 d) Cardiovascular System Higher Human Biology What can your remember about the heart and blood vessels? What is the Cardiovascular System? The cardiovascular system, also known as the circulatory system,
d) Cardiovascular System Higher Human Biology What can your remember about the heart and blood vessels? What is the Cardiovascular System? The cardiovascular system, also known as the circulatory system,
Circulation and Respiration
 CHAPTER 20 DIRECTED READING WORKSHEET Circulation and Respiration As you read Chapter 20, which begins on page 486 of your textbook, answer the following questions. This Really Happened... (p. 486) 1.
CHAPTER 20 DIRECTED READING WORKSHEET Circulation and Respiration As you read Chapter 20, which begins on page 486 of your textbook, answer the following questions. This Really Happened... (p. 486) 1.
CIE Biology GCSE. 9: Transport in animals. Notes.
 CIE Biology GCSE 9: Transport in animals Notes The circulatory system acts as the main transport system in animals. It is made up of blood vessels such as arteries, veins and capillaries, in which blood
CIE Biology GCSE 9: Transport in animals Notes The circulatory system acts as the main transport system in animals. It is made up of blood vessels such as arteries, veins and capillaries, in which blood
And anti-b
 And anti-b Blood types cont. In addition to A and B substances, RBC can carry the Rhesus factor (Rh factor) on their membrane The Rh factor implies a positive (present) or a negative (not present) So a
And anti-b Blood types cont. In addition to A and B substances, RBC can carry the Rhesus factor (Rh factor) on their membrane The Rh factor implies a positive (present) or a negative (not present) So a
Circulation And Blood. Circulation And Blood. Circulation And Blood. Circulation And Blood. Blood 10/22/2012
 Cells in our body build their own membranes and organelles Make their own ATP Assemble their own enzymes and other proteins And may manufacture substances used elsewhere in the body To do these things,
Cells in our body build their own membranes and organelles Make their own ATP Assemble their own enzymes and other proteins And may manufacture substances used elsewhere in the body To do these things,
Circulatory System. and. Respiratory System. Ari Min, Yerim Lee and Min Ji Song THE HEART LUNGS. Monday, May 23, 2011
 Human Anatomy Circulatory System and THE HEART Respiratory System LUNGS Ari Min, Yerim Lee and Min Ji Song Purpose of the Circulatory System Function of circulatory system: exchange gases with cardiovascular
Human Anatomy Circulatory System and THE HEART Respiratory System LUNGS Ari Min, Yerim Lee and Min Ji Song Purpose of the Circulatory System Function of circulatory system: exchange gases with cardiovascular
Chapter 12. Capillaries. Circulation. The circulatory system connects with all body tissues
 Chapter 12 Circulation The circulatory system connects with all body s In many animals, microscopic blood vessels called capillaries Form an intricate network among the Red blood cell song Figure 23.1A
Chapter 12 Circulation The circulatory system connects with all body s In many animals, microscopic blood vessels called capillaries Form an intricate network among the Red blood cell song Figure 23.1A
The Circulatory System
 The Circulatory System No cell is further than that carries nutrients. Your circulatory system km of blood vessels. Your heart beats about from the beginning of life until death. During an average lifetime,
The Circulatory System No cell is further than that carries nutrients. Your circulatory system km of blood vessels. Your heart beats about from the beginning of life until death. During an average lifetime,
One system involved in exercising is the respiratory system. The respiratory system includes three main parts breathing, lungs and blood.
 By Andrea.K 2012 Grade 3 There are many different systems that help us exercise and the three main systems are the respiratory system which is about how we breathe, the circulatory system which is about
By Andrea.K 2012 Grade 3 There are many different systems that help us exercise and the three main systems are the respiratory system which is about how we breathe, the circulatory system which is about
The Cardiovascular and Lymphatic Systems Cardiovascular System Blood Vessels Blood Vessels Arteries Arteries Arteries
 CH 12 The Cardiovascular and s The Cardiovascular and s OUTLINE: Cardiovascular System Blood Vessels Blood Pressure Cardiovascular System The cardiovascular system is composed of Blood vessels This system
CH 12 The Cardiovascular and s The Cardiovascular and s OUTLINE: Cardiovascular System Blood Vessels Blood Pressure Cardiovascular System The cardiovascular system is composed of Blood vessels This system
The Cardiovascular. Parts and Functions
 The Cardiovascular Parts and Functions Parts The cardiovascular system consists of 3 major parts that work together. 1- Heart 2- Lungs 3- Blood Vessels Blood Vessels There are blood vessels that carry
The Cardiovascular Parts and Functions Parts The cardiovascular system consists of 3 major parts that work together. 1- Heart 2- Lungs 3- Blood Vessels Blood Vessels There are blood vessels that carry
learningobjectives At the end of the lesson, you should be able to: - Humans Explain the need for a transport system in multicellular
 transport in humans learningobjectives At the end of the lesson, you should be able to: - Humans Explain the need for a transport system in multicellular organisms Identify the parts of the human circulatory
transport in humans learningobjectives At the end of the lesson, you should be able to: - Humans Explain the need for a transport system in multicellular organisms Identify the parts of the human circulatory
The HEART. What is it???? Pericardium. Heart Facts. This muscle never stops working It works when you are asleep
 This muscle never stops working It works when you are asleep The HEART It works when you eat It really works when you exercise. What is it???? Located between the lungs in the mid thoracic region Apex
This muscle never stops working It works when you are asleep The HEART It works when you eat It really works when you exercise. What is it???? Located between the lungs in the mid thoracic region Apex
Circulatory System. Functions and Components of the Circulatory System. Chapter 13 Outline. Chapter 13
 Circulatory System Chapter 13 Chapter 13 Outline Functions and Components of the Circulatory System Composition of Blood Structure of the Heart Cardiac Cycle and Heart Sounds Electrical Activity of the
Circulatory System Chapter 13 Chapter 13 Outline Functions and Components of the Circulatory System Composition of Blood Structure of the Heart Cardiac Cycle and Heart Sounds Electrical Activity of the
Cardiovascular System- Heart. Miss Wheeler Unit 8
 Cardiovascular System- Heart Miss Wheeler Unit 8 Overview CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM heart vessels Made up of heart, blood vessels, and blood Functions Heart- pump blood Vessels- (veins, arteries, capillaries)
Cardiovascular System- Heart Miss Wheeler Unit 8 Overview CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM heart vessels Made up of heart, blood vessels, and blood Functions Heart- pump blood Vessels- (veins, arteries, capillaries)
Practical Histology. Cardiovascular System. Dr Narmeen S. Ahmad
 Practical Histology Cardiovascular System Dr Narmeen S. Ahmad The Cardiovascular System A closed system of the heart and blood vessels Functions of cardiovascular system: Transport nutrients, hormones
Practical Histology Cardiovascular System Dr Narmeen S. Ahmad The Cardiovascular System A closed system of the heart and blood vessels Functions of cardiovascular system: Transport nutrients, hormones
Cardiovascular System. Biology 105 Lecture 15 Chapter 12
 Cardiovascular System Biology 105 Lecture 15 Chapter 12 Outline I. Functions of cardiovascular system II. Components of the cardiovascular system: I. Blood vessels II. Heart III. Regulation of the heartbeat
Cardiovascular System Biology 105 Lecture 15 Chapter 12 Outline I. Functions of cardiovascular system II. Components of the cardiovascular system: I. Blood vessels II. Heart III. Regulation of the heartbeat
Cardiovascular System
 Cardiovascular System Purpose Transport oxygen and nutrients Take waste products away from tissues & organs Things we learned Blood pressure: the force of blood pushing against the walls of blood vessels
Cardiovascular System Purpose Transport oxygen and nutrients Take waste products away from tissues & organs Things we learned Blood pressure: the force of blood pushing against the walls of blood vessels
7.L.1.4 Circulatory System Guided Study Notes. Circulation
 1 7.L.1.4 Circulatory System Guided Study Notes Circulation Sect. 1: The Body s Transport System Sect. 2: A Closer Look at Blood Vessels Sect. 3: Blood and Lymph Sect. 4: Cardiovascular Health Sect. 1:
1 7.L.1.4 Circulatory System Guided Study Notes Circulation Sect. 1: The Body s Transport System Sect. 2: A Closer Look at Blood Vessels Sect. 3: Blood and Lymph Sect. 4: Cardiovascular Health Sect. 1:
CIRCULATION. Cardiovascular & lymphatic systems Functions. Transport Defense / immunity Homeostasis
 CIRCULATION CIRCULATION Cardiovascular & lymphatic systems Functions Transport Defense / immunity Homeostasis 2 Types of Circulatory Systems Open circulatory system Contains vascular elements Mixing of
CIRCULATION CIRCULATION Cardiovascular & lymphatic systems Functions Transport Defense / immunity Homeostasis 2 Types of Circulatory Systems Open circulatory system Contains vascular elements Mixing of
Overview: Blood Composition and Function
 Chapter 17: Blood Overview: Blood Composition and Function Overview: Blood Composition and Function Formed elements 45% of whole blood Blood cells and cell fragments Erythrocytes Red blood cells (99.9%)
Chapter 17: Blood Overview: Blood Composition and Function Overview: Blood Composition and Function Formed elements 45% of whole blood Blood cells and cell fragments Erythrocytes Red blood cells (99.9%)
Circulatory System. 3. Blood. 1. Heart. 1. Veins A blood vessel that returns blood to the heart
 Day 1. Circulatory System uman Body Transport The Circulatory System 2. ARTERIES 1. eart & VEINS 3. Blood Process: Transport Circulatory System The process where substances move (distributed) into and
Day 1. Circulatory System uman Body Transport The Circulatory System 2. ARTERIES 1. eart & VEINS 3. Blood Process: Transport Circulatory System The process where substances move (distributed) into and
The blood returns from the body and enters right atrium using the vena cava. It passes through the tricuspid valve to the right ventricle.
 The blood returns from the body and enters right atrium using the vena cava. It passes through the tricuspid valve to the right ventricle. From this camber, it passes through the pulmonary semilunar valve
The blood returns from the body and enters right atrium using the vena cava. It passes through the tricuspid valve to the right ventricle. From this camber, it passes through the pulmonary semilunar valve
The Circulatory System:
 The Circulatory System: The Body s Transport System The Circulatory System! What is the CIRCULATORY SYSTEM? A HIGHWAY NETWORK that LINKS all parts of your body. Consists of the HEART, BLOOD VESSELS, and
The Circulatory System: The Body s Transport System The Circulatory System! What is the CIRCULATORY SYSTEM? A HIGHWAY NETWORK that LINKS all parts of your body. Consists of the HEART, BLOOD VESSELS, and
Circulatory System 10.1
 1 Circulatory System 10.1 2 ARTERIES Arteries-blood vessels that carry blood away from the heart Thick walls Inner & Outer layers: connective tissue Middle layers are muscle and elastic connective tissue
1 Circulatory System 10.1 2 ARTERIES Arteries-blood vessels that carry blood away from the heart Thick walls Inner & Outer layers: connective tissue Middle layers are muscle and elastic connective tissue
TRANSPORT SYSTEM IN LIVING SMPK PENABUR JAKARTA
 TRANSPORT SYSTEM IN LIVING ORGANISM SMPK PENABUR JAKARTA Part 1 PLANT TRANSPORTATION SYSTEM A. PLANT TRANSPORT SYSTEM Transport tissue? Where? A. 1. Water Transport Water liquid matter Affected by environment
TRANSPORT SYSTEM IN LIVING ORGANISM SMPK PENABUR JAKARTA Part 1 PLANT TRANSPORTATION SYSTEM A. PLANT TRANSPORT SYSTEM Transport tissue? Where? A. 1. Water Transport Water liquid matter Affected by environment
The Cardiovascular and Lymphatic Systems
 BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues Fifth Edition Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire 12 The Cardiovascular and Lymphatic Systems Lecture Presentation Anne Gasc Hawaii Pacific University and
BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues Fifth Edition Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire 12 The Cardiovascular and Lymphatic Systems Lecture Presentation Anne Gasc Hawaii Pacific University and
