Molecular Cell Biology (Bio 5068) Microtubules and their func<ons in cells. Moe Mahjoub. September 17, 2015
|
|
|
- Brenda Constance Parker
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Molecular Cell Biology (Bio 5068) Microtubules and their func<ons in cells. Moe Mahjoub September 17, 2015
2 About me From Vancouver, Canada PhD Simon Fraser University, Canada Dr. Lynne Quarmby Postdoc Stanford University Dr. Tim Stearns Washington University From September 2012 Medicine (Division of Renal Diseases) Department of Cell Biology and Physiology DBBS Programs: Molecular Cell Biology Developmental, Regenera<ve and Stem Cell Biology Biochemistry
3 Microtubules and their Func<ons Intro what is a microtubule? What do microtubules do in cells? Microtubule Organizing Center (MTOC) Mitosis Cilia
4 Microtubule Structure Cross- sec<on Hollow tube 24 nm wide ~13 protofilaments Helical structure Polar Plus ends generally distal Minus ends generally proximal (at MTOC) Composed of Tubulin α/β Heterodimer
5 Microtubule Structure & Assembly
6 Microtubule Dynamic Instability
7 The Master Nucleator γ- TuRC and microtubule nuclea<on
8 Microtubules are everywhere Q: How are heterogeneity and specificity of microtubule func<on regulated?
9 The Tubulin Superfamily
10 Microtubule Modifica<ons Poseransla<onal modifica<ons (PTM s)
11 Microtubule Motors Defini<on Microtubule- s<mulated ATPase Mo<lity along MT s Dynein Moves towards Minus End of MT s Kinesin Moves to Plus End of MT s
12 Kinesin Movement and Processivity Iden<fied in search for motors involved in axonal transport Movement required ATP
13 Kinesin Superfamily Structures
14 Kinesin Superfamily Phylogene<c Tree
15 Cytoplasmic Dynein Discovered biochemically Minus end motor for vesicle transport, MT mo<lity Requires Dynac<n complex (or other accessory proteins) for func<on
16 Model for interac<ons between dynein, dynac<n complex, microtubules, and cargo
17 Microtubule binding proteins Nucleators (e.g. γ- tubulin, Ninein): Provide the basis for microtubule nuclea<on and assembly Stabilizers (e.g. CLIP170, EB1, Tau): Promote microtubule growth through increased polymeriza<on and reduced catastrophe Destabilizers (e.g. Stathmin, KinI): Reduce average microtubule length by promo<ng catastrophe and suppressing rescue. Severers (e.g. Katanin, Spas<n): Cause breaks within the microtubule lakce, generally reducing average length of microtubules Bundlers (e.g. PRC1): Bind two (or more) microtubules and align them to form parallel or an<- parallel bundles Chaperones (e.g. Prefoldins): Promote folding and assembly of tubulin protein complexes facilita<ng polymeriza<on.
18 Microtubules are everywhere Q: How are heterogeneity and specificity of microtubule func<on regulated? Different tubulin isoforms A large number of tubulin PTMs Different motors and adaptors Diverse microtubule binding proteins
19 Organelle Trafficking - ER and Golgi Posi<oning ER & Golgi: Golgi near MTOC Minus Ends are at MTOC Golgi Posi<on Requires Dynein ER Tubular network spread about the cell Kinesin moves the tubules peripherally
20 Organelle Trafficking - ER at cell boundaries Microtubules (Red) and ER (Green)"
21 Organelle Trafficking - Melanophores Xenopus Melanophore Pigment Granule Movement Vesicles move along microtubules Vesicles carry dynein, kinesin & myosin- V Regula<on of the motors accounts for the dispersion / aggrega<on Inward Mo<on (Movie Loops)
22 Organelle Trafficking - Melanophores Xenopus Melanophore Pigment Granule Movement Vesicles move along microtubules Vesicles carry dynein, kinesin & myosin- V Regula<on of the motors accounts for the dispersion / aggrega<on Outward Mo<on (Movie Loops)
23 Microtubule- based Trafficking
24 Microtubules and their Func<ons Intro what is a microtubule? What do microtubules do in cells? Microtubule Organizing Center (MTOC) Mitosis Cilia
25 Boveri: The Centrosome as MTOC Theodore Boveri ( )" Boveri s predic<ons about centrosomes: (i) The centrosome is a cyclical structure a permanent reproducing organ of the cell. (ii) Centrosomes are part of a central apparatus or microcentrum in cells. (iii) They are dynamic centers' of cells and the true division organs of the cell. (iv) Centrioles (one or two) are contained within centrosomes (v) Centrosomes are the sole microtubule organizing centers (MTOC) in asters and spindles.
26 Boveri: The Centrosome as MTOC Theodore Boveri ( )" Boveri s predic<ons about centrosomes: (i) The centrosome is a cyclical structure a permanent reproducing organ of the cell. (ii) Centrosomes are part of a central apparatus or microcentrum in cells. (iii) They are dynamic centers' of cells and the true division organs of the cell. (iv) Centrioles (one or two) are contained within centrosomes (v) Centrosomes are the sole microtubule organizing centers (MTOC) in asters and spindles.
27 The centrosome as MTOC 1 centrosome per cell" " 2 centrioles per centrosome (in interphase)" " Centriole size is highly conserved throughout evolution:" ~250nm diameter, ~500nm length"
28 Centrosome structure higher order MT organiza<on
29 Centrosome assembly iden<fica<on of components Bornens and colleagues ( )" " Purified centrosomes on sucrose " gradients" " Very clean preps, as seen by EM and IF" Purified centrosomes are " functional:" " Incubated with purified cow " tubulin, starts nucleating MT"
30 Centrosome assembly iden<fica<on of components 2D-gel of isolated centrosomes. Authors surprised to find ~ unique proteins make up a centrosome"
31 Centrosome assembly iden<fica<on of components At least 500 unique proteins " present in centrosomes" " Appear in distinct modules or " complexes, based on subcellular " localization and function"
32 Mechanism of centrosome duplica<on Q: How can a cell make an exact copy of such an elaborate structure?
33 Centrosome duplica<on and the cell cycle G1/S" S" S" S/G2" G2/M" M/G1" Kuriyama and Borisy, 1981
34 Centrosome duplica<on and the cell cycle
35 Centriole structure establishing 9- fold symmetry Q: How is the 9- fold rota<onal symmetry of microtubules established during centriole duplica<on?
36 Centriole structure establishing 9- fold symmetry
37 Centriole structure establishing 9- fold symmetry Structure of purified, recombinant Sas6 " from zebrafish (Science 2011)" Structure of purified, recombinant Sas6 " from Chlamydomonas (Cell 2011)"
38 Centriole structure establishing 9- fold symmetry Sas6 has intrinsic symmetry when forming oligomers"
39 Centriole structure establishing 9- fold symmetry Q: But how come Sas6 doesn t just form a bunch of rings non- specifically in the cytoplasm? A: - Expression restricted to G1/S phase (temporal regula<on) - Recruited to parental centrioles (spa<al regula<on) how?!
40 Centriole structure establishing 9- fold symmetry
41 Pericentriolar material (PCM) and microtubule nuclea<on +! Amorphous cloud " +! +! -! -! -! Lots of γ-turc! -! -! + +! Lots of big, coiled-coil proteins in PCM" +!
42 Pericentriolar material (PCM) organiza<on Amorphous cloud " Amorphous no more!" Super-resolution microscopy to the rescue"
43 Pericentriolar material (PCM) organiza<on The PCM is organized into layers"
44 PCM size and ac<vity increase in mitosis Almost all of the PCM proteins increase in abundance in mitosis"
45 Microtubules and their Func<ons Intro what is a microtubule? What do microtubules do in cells? Microtubule Organizing Center (MTOC) Mitosis Cilia
46 Mitosis Stages: Spinning-Disk Confocal Images of Microtubules and DNA Prometaphase Metaphase Early Anaphase Late Anaphase Cytokinesis Onset Late Cytokinesis
47 Mito<c Spindle Assembly Centrosome duplicates and is segragated to each side of the nucleus Nuclear envelope breakdown in prophase MT s rearrange via dynamic instability
48 Spindle microtubules Chromosomes, Kinetochores and Microtubules. Super- resolu<on Microscopy (SIM).
49 Chromosome Congression to Metaphase Plate Kinetochores capture MT s Chromosomes pulled and pushed to and from poles Forces on arms Force at kinetochore
50 Metaphase to Anaphase transi<on GFP- labeled Centromeres
51 Types of microtubule- kinetochore aeachments Amphitelic Monotelic Syntelic Merotelic
52 Metaphase/Anaphase Lagging
53 Models for Chromosomes Moving to the Pole Treadmilling? Depolymeriza<on at pole (MTOC) Depolymeriza<on at Kinetochore? How to remain bound while end shrinks? Motors at Kinetochore or Pole?
54 Poleward Tubulin Flux in Anaphase Movement towards pole... Blue: Photobleach Mark, 0.7 µm/min Yellow: Edge of Chromosome, 1.2 µm/min
55 Microtubule dynamics and motors help move chromosomes in mitosis The MTOC plays a critical role in " organizing the microtubule arrays" " "
56 Abnormal regula<on of centrosome number Q: What happens if MTOC (centrosome) assembly and duplication is defective?"
57 Abnormal regula<on of centrosome number Boveri, 1914: extra centrosomes are prevalent in tumors drive genome instability?
58 Abnormal regula<on of centrosome number Ring, Hubble, Kirschner, 1982! Ganem et al. (2009) Nature"
59 Causes and consequences of centrosome amplifica<on
60 Microtubules and their Func<ons Intro what is a microtubule? What do microtubules do in cells? Microtubule Organizing Center (MTOC) Mitosis Cilia
61 The cilium in the 17 th century Drawings from van Leeuwenhoek's letter of March 18, 1678."
62 Mo<le cilia in ac<on Euplotes " Stentor"
63 Mo<le cilia in ac<on Chlamydomonas cilia Sperm Flagellum
64 Cilia on surface of epithelial cells Mo<le mul<ciliated epithelial cells are found in: Airways (lung and trachea): help clear mucus (muco- ciliary escalator) Brain (lining the ventricles): help move cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) Fallopian tube: involved in tubular fluid flow, and thus movement of sperm and ova
65 Structure of mo<le cilium: Cross- sec<on
66 Conversion of sliding to bending
67 Conversion of sliding to bending Q: If all dyneins pull together, how does the axoneme " bend back and forth?"
68 Rota<on of central pair microtubules Whole Chlamydomonas cell " with 2 cilia" Axonemes isolated from Chlamydomonas cell "
69 Mo<le cilia defects in humans Sterility" " Respiratory defects" " Hydrocephalus" " Most of the mutations are in " dyneins and assembly factors"
70 Mo<le ciliary dysfunc<on and L- R asymmetry X!
71 Mo<le ciliary dysfunc<on and L- R asymmetry Heart-looping defects and congenital heart disease"
72 Ciliary assembly - Intraflagellar Transport (IFT)
73 Ciliary assembly - Intraflagellar Transport (IFT) 20 years" later"
74 The primary cilium: non- mo<le sensory organelle Found in almost every cell type in your body:" " Epithelia" Fibroblasts" Neurons" Stem cells" we have hypothesized that these (primary) cilia may be ves9gial organelles Webber and Lee (1975)
75 The primary cilium: non- mo<le sensory organelle
76 Signaling pathways that rely on cilia Primary cilium function is required for sonic hedgehog signaling. Huangfu, et al. Nature (2003)" Shh" PKD! Shh! PDGF! Wnt! TOR! Smoothened" Smoothened"
77 Fundamental processes in cell biology X" Cell division" Extracellular" signal" X! X" Cell differentiation" X" Cell migration" X" Cell polarity and" organization"
78 Human ciliopathies due to defec<ve primary cilia we have hypothesized that these (primary) cilia may be ves9gial organelles absolutely essen<al!!! Webber and Lee (1975)
79 Microtubules and their func<ons in cells. Thank you!" " Contact:
Microtubule Forces Kevin Slep
 Microtubule Forces Kevin Slep Microtubules are a Dynamic Scaffold Microtubules in red, XMA215 family MT polymerase protein in green Some Microtubule Functions Cell Structure Polarized Motor Track (kinesins
Microtubule Forces Kevin Slep Microtubules are a Dynamic Scaffold Microtubules in red, XMA215 family MT polymerase protein in green Some Microtubule Functions Cell Structure Polarized Motor Track (kinesins
BIOLOGY - CLUTCH CH.12 - CELL DIVISION.
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: CELL DIVISION Cell division is the process by which one cell splits into two or more daughter cells. Cell division generally requires that cells produce enough materials,
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: CELL DIVISION Cell division is the process by which one cell splits into two or more daughter cells. Cell division generally requires that cells produce enough materials,
Mitosis vs. microtubule
 Mitosis vs. microtubule Anaphase-promoting complex/cyclosome (APC/C) Duplicated centrosomes align and begin separating in prophase Relation of centrosome duplication to the cell cycle. Parent centrioles
Mitosis vs. microtubule Anaphase-promoting complex/cyclosome (APC/C) Duplicated centrosomes align and begin separating in prophase Relation of centrosome duplication to the cell cycle. Parent centrioles
Centrosome & Centrioles,It s Structure,Function!!
 Centrosome & Centrioles,It s Structure,Function!! CENTROSOME In cell biology, the centrosome (Latin centrum center and Greek soma body ) is an organelle that serves as the main microtubule organizing center
Centrosome & Centrioles,It s Structure,Function!! CENTROSOME In cell biology, the centrosome (Latin centrum center and Greek soma body ) is an organelle that serves as the main microtubule organizing center
Chapter 8 The Cell Cycle
 What molecule stores your genetic information or determines everything about you? DNA a nucleic acid How are DNA molecules arranged in the nucleus? As you can see DNA is: Chapter 8 The Cell Cycle 1. Arranged
What molecule stores your genetic information or determines everything about you? DNA a nucleic acid How are DNA molecules arranged in the nucleus? As you can see DNA is: Chapter 8 The Cell Cycle 1. Arranged
Mitosis Notes AP Biology Mrs. Laux
 I. Cell Cycle-includes interphase and mitosis (IPPMAT) A. Interphase 1. accounts for 90% of the cycle 2. cell grows and copies its chromosomes in preparation for cell division 3. produces proteins and
I. Cell Cycle-includes interphase and mitosis (IPPMAT) A. Interphase 1. accounts for 90% of the cycle 2. cell grows and copies its chromosomes in preparation for cell division 3. produces proteins and
Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division. AP Biology
 Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division Chapter 12. The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth, Cell Division Where it all began You started as a cell smaller than a period at
Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division Chapter 12. The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth, Cell Division Where it all began You started as a cell smaller than a period at
APGRU4L1 Chap 12 Extra Reading Cell Cycle and Mitosis
 APGRU4L1 Chap 12 Extra Reading Cell Cycle and Mitosis Dr. Ramesh Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division 2007-2008 The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth, Cell Division 2007-2008
APGRU4L1 Chap 12 Extra Reading Cell Cycle and Mitosis Dr. Ramesh Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division 2007-2008 The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth, Cell Division 2007-2008
The Cell Cycle CHAPTER 12
 The Cell Cycle CHAPTER 12 The Key Roles of Cell Division cell division = reproduction of cells All cells come from pre-exisiting cells Omnis cellula e cellula Unicellular organisms division of 1 cell reproduces
The Cell Cycle CHAPTER 12 The Key Roles of Cell Division cell division = reproduction of cells All cells come from pre-exisiting cells Omnis cellula e cellula Unicellular organisms division of 1 cell reproduces
Chapter 3: Cells 3-1
 Chapter 3: Cells 3-1 Introduction: A. Human body consists of 75 trillion cells B. About 260 types of cells that vary in shape & size yet have much in common B. Differences in cell shape make different
Chapter 3: Cells 3-1 Introduction: A. Human body consists of 75 trillion cells B. About 260 types of cells that vary in shape & size yet have much in common B. Differences in cell shape make different
(a) Reproduction. (b) Growth and development. (c) Tissue renewal
 100 µm 200 µm 20 µm (a) Reproduction (b) Growth and development (c) Tissue renewal 1 20 µm 2 0.5 µm Chromosomes DNA molecules Chromosome arm Centromere Chromosome duplication (including DNA synthesis)
100 µm 200 µm 20 µm (a) Reproduction (b) Growth and development (c) Tissue renewal 1 20 µm 2 0.5 µm Chromosomes DNA molecules Chromosome arm Centromere Chromosome duplication (including DNA synthesis)
Cellular Reproduction, Part 1: Mitosis Lecture 10 Fall 2008
 Cell Theory 1 Cellular Reproduction, Part 1: Mitosis Lecture 10 Fall 2008 Cell theory: All organisms are made of cells All cells arise from preexisting cells How do new cells arise? Cell division the reproduction
Cell Theory 1 Cellular Reproduction, Part 1: Mitosis Lecture 10 Fall 2008 Cell theory: All organisms are made of cells All cells arise from preexisting cells How do new cells arise? Cell division the reproduction
Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division
 Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division 2007-2008 The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth, Cell Division 2007-2008 Where it all began You started as a cell smaller than a
Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division 2007-2008 The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth, Cell Division 2007-2008 Where it all began You started as a cell smaller than a
MOLECULAR CELL BIOLOGY
 Lodish Berk Kaiser Krieger scott Bretscher Ploegh Matsudaira MOLECULAR CELL BIOLOGY SEVENTH EDITION CHAPTER 18 Cell Organization and Movement II: Microtubules and Intermediate Filaments Copyright 2013
Lodish Berk Kaiser Krieger scott Bretscher Ploegh Matsudaira MOLECULAR CELL BIOLOGY SEVENTH EDITION CHAPTER 18 Cell Organization and Movement II: Microtubules and Intermediate Filaments Copyright 2013
Unduplicated. Chromosomes. Telophase
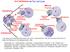 10-2 Cell Division The Cell Cycle Interphase Mitosis Prophase Cytokinesis G 1 S G 2 Chromatin in Parent Nucleus & Daughter Cells Chromatin Daughter Nuclei Telophase Mitotic Anaphase Metaphase Use what
10-2 Cell Division The Cell Cycle Interphase Mitosis Prophase Cytokinesis G 1 S G 2 Chromatin in Parent Nucleus & Daughter Cells Chromatin Daughter Nuclei Telophase Mitotic Anaphase Metaphase Use what
Mitosis. AND Cell DiVISION
 Mitosis AND Cell DiVISION Cell Division Characteristic of living things: ability to reproduce their own kind. Cell division purpose: When unicellular organisms such as amoeba divide to form offspring reproduction
Mitosis AND Cell DiVISION Cell Division Characteristic of living things: ability to reproduce their own kind. Cell division purpose: When unicellular organisms such as amoeba divide to form offspring reproduction
8.4 The cell cycle multiplies cells. 8.4 The cell cycle multiplies cells
 8.4 The cell cycle multiplies cells! Cell division is a highly orchestrated process! The cell cycle is an ordered sequence of events that extends from the time a cell is first formed from a dividing parent
8.4 The cell cycle multiplies cells! Cell division is a highly orchestrated process! The cell cycle is an ordered sequence of events that extends from the time a cell is first formed from a dividing parent
Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division
 Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth, Cell Division 2007-2008 2007-2008 Getting from there to here Going from egg to baby. the original
Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth, Cell Division 2007-2008 2007-2008 Getting from there to here Going from egg to baby. the original
Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division
 Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division 2007-2008 The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth, Cell Division 2007-2008 Getting from there to here Going from egg to baby. the original
Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division 2007-2008 The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth, Cell Division 2007-2008 Getting from there to here Going from egg to baby. the original
The Cell Cycle. Chapter 12. Biology. Edited by Shawn Lester. Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece. PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for
 Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle Edited by Shawn Lester PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions
Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle Edited by Shawn Lester PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions
Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division
 Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division 2007-2008 The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth, Cell Division Ch. 10 Where it all began You started as a cell smaller than a period
Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division 2007-2008 The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth, Cell Division Ch. 10 Where it all began You started as a cell smaller than a period
Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division
 Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division 2007-2008 The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth, Cell Division 2007-2008 Where it all began You started as a cell smaller than a
Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division 2007-2008 The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth, Cell Division 2007-2008 Where it all began You started as a cell smaller than a
The Process of Cell Division
 Lesson Overview 10.2 The Process of Cell Division THINK ABOUT IT What role does cell division play in your life? Does cell division stop when you are finished growing? Chromosomes What is the role of chromosomes
Lesson Overview 10.2 The Process of Cell Division THINK ABOUT IT What role does cell division play in your life? Does cell division stop when you are finished growing? Chromosomes What is the role of chromosomes
10-2 Cell Division. Chromosomes
 Cell Division In eukaryotes, cell division occurs in two major stages. The first stage, division of the cell nucleus, is called mitosis. The second stage, division of the cell cytoplasm, is called cytokinesis.
Cell Division In eukaryotes, cell division occurs in two major stages. The first stage, division of the cell nucleus, is called mitosis. The second stage, division of the cell cytoplasm, is called cytokinesis.
The Cell Cycle CAMPBELL BIOLOGY IN FOCUS SECOND EDITION URRY CAIN WASSERMAN MINORSKY REECE
 CAMPBELL BIOLOGY IN FOCUS URRY CAIN WASSERMAN MINORSKY REECE 9 The Cell Cycle Lecture Presentations by Kathleen Fitzpatrick and Nicole Tunbridge, Simon Fraser University SECOND EDITION Overview: The Key
CAMPBELL BIOLOGY IN FOCUS URRY CAIN WASSERMAN MINORSKY REECE 9 The Cell Cycle Lecture Presentations by Kathleen Fitzpatrick and Nicole Tunbridge, Simon Fraser University SECOND EDITION Overview: The Key
SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question.
 SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. Figure 2.1 Using Figure 2.1, match the following: 1) Rough endoplasmic reticulum 1) 2) Nucleolus 2) 3)
SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. Figure 2.1 Using Figure 2.1, match the following: 1) Rough endoplasmic reticulum 1) 2) Nucleolus 2) 3)
CMB621: Cytoskeleton. Also known as How the cell plays with LEGOs to ensure order, not chaos, is temporally and spatially achieved
 CMB621: Cytoskeleton Also known as How the cell plays with LEGOs to ensure order, not chaos, is temporally and spatially achieved Lecture(s) Overview Lecture 1: What is the cytoskeleton? Membrane interaction
CMB621: Cytoskeleton Also known as How the cell plays with LEGOs to ensure order, not chaos, is temporally and spatially achieved Lecture(s) Overview Lecture 1: What is the cytoskeleton? Membrane interaction
Cell Cycle and Mitosis
 Ch 4 BIOL 100 Cell Cycle and Mitosis The Key Roles of Cell Division Cell division Cellular reproduc2on An ability of organisms that best dis2nguishes living things from nonliving ma:er Cell Division Unicellular
Ch 4 BIOL 100 Cell Cycle and Mitosis The Key Roles of Cell Division Cell division Cellular reproduc2on An ability of organisms that best dis2nguishes living things from nonliving ma:er Cell Division Unicellular
Mitosis THE CELL CYCLE. In unicellular organisms, division of one cell reproduces the entire organism Multicellular organisms use cell division for..
 Mitosis THE CELL CYCLE In unicellular organisms, division of one cell reproduces the entire organism Multicellular organisms use cell division for.. Development from a fertilized cell Growth Repair Cell
Mitosis THE CELL CYCLE In unicellular organisms, division of one cell reproduces the entire organism Multicellular organisms use cell division for.. Development from a fertilized cell Growth Repair Cell
The Cell Cycle. Packet #9. Thursday, August 20, 2015
 1 The Cell Cycle Packet #9 2 Introduction Cell Cycle An ordered sequence of events in the life of a dividing eukaryotic cell and is a cellular asexual reproduction. The contents of the parent s cell nucleus
1 The Cell Cycle Packet #9 2 Introduction Cell Cycle An ordered sequence of events in the life of a dividing eukaryotic cell and is a cellular asexual reproduction. The contents of the parent s cell nucleus
Genetics and Cellular Function
 Genetics and Cellular Function DNA replication and the cell cycle Mitosis Mitosis Mitosis: division of cells that results in daughter cells with the same the genetic information that the original cell
Genetics and Cellular Function DNA replication and the cell cycle Mitosis Mitosis Mitosis: division of cells that results in daughter cells with the same the genetic information that the original cell
Why do cells divide? Cells divide in order to make more cells they multiply in order to create a larger surface to volume ratio!!!
 Why do cells divide? Cells divide in order to make more cells they multiply in order to create a larger surface to volume ratio!!! Chromosomes Are made of chromatin: a mass of genetic material composed
Why do cells divide? Cells divide in order to make more cells they multiply in order to create a larger surface to volume ratio!!! Chromosomes Are made of chromatin: a mass of genetic material composed
The Cell Cycle and How Cells Divide
 The Cell Cycle and How Cells Divide 1 Phases of the Cell Cycle The cell cycle consists of Interphase normal cell activity The mitotic phase cell divsion INTERPHASE Growth G 1 (DNA synthesis) Growth G 2
The Cell Cycle and How Cells Divide 1 Phases of the Cell Cycle The cell cycle consists of Interphase normal cell activity The mitotic phase cell divsion INTERPHASE Growth G 1 (DNA synthesis) Growth G 2
10-2 Cell Division mitosis. cytokinesis. Chromosomes chromosomes Slide 1 of 38
 In eukaryotes, cell division occurs in two major stages. The first stage, division of the cell nucleus, is called mitosis. The second stage, division of the cell cytoplasm, is called cytokinesis. Chromosomes
In eukaryotes, cell division occurs in two major stages. The first stage, division of the cell nucleus, is called mitosis. The second stage, division of the cell cytoplasm, is called cytokinesis. Chromosomes
Mitosis and Cellular Division. EQ: How do the cells in our body divide?
 Mitosis and Cellular Division EQ: How do the cells in our body divide? Cell division is the process by which cellular material is divided between two new daughter cells. 1 Mother Cell 2 Daughter cells.
Mitosis and Cellular Division EQ: How do the cells in our body divide? Cell division is the process by which cellular material is divided between two new daughter cells. 1 Mother Cell 2 Daughter cells.
10-2 Cell Division. Slide 1 of 38. End Show. Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
 1 of 38 Cell Division In eukaryotes, cell division occurs in two major stages. The first stage, division of the cell nucleus, is called mitosis. The second stage, division of the cell cytoplasm, is called
1 of 38 Cell Division In eukaryotes, cell division occurs in two major stages. The first stage, division of the cell nucleus, is called mitosis. The second stage, division of the cell cytoplasm, is called
The Cell Cycle. Biology
 The Cell Cycle Biology Standards you are responsible for mastering. SB1a: Explain the role of cell organelles for both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, including the cell membrane, in maintaining homeostasis
The Cell Cycle Biology Standards you are responsible for mastering. SB1a: Explain the role of cell organelles for both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, including the cell membrane, in maintaining homeostasis
Cell Cycle, Mitosis, and Microtubules. LS1A Final Exam Review Friday 1/12/07. Processes occurring during cell cycle
 Cell Cycle, Mitosis, and Microtubules LS1A Final Exam Review Friday 1/12/07 Processes occurring during cell cycle Replicate chromosomes Segregate chromosomes Cell divides Cell grows Cell Growth 1 The standard
Cell Cycle, Mitosis, and Microtubules LS1A Final Exam Review Friday 1/12/07 Processes occurring during cell cycle Replicate chromosomes Segregate chromosomes Cell divides Cell grows Cell Growth 1 The standard
Cells. Introduction: Composite Cell: Bi100 Chapter 3
 Bi100 Chapter 3 Cells Introduction: A. The human body consists of almost 100 trillion cells that vary considerably in shape and size yet have much in common. B. Differences in cell shape and composition
Bi100 Chapter 3 Cells Introduction: A. The human body consists of almost 100 trillion cells that vary considerably in shape and size yet have much in common. B. Differences in cell shape and composition
The Cell Cycle. Biology
 The Cell Cycle Biology Standards you are responsible for mastering. SB1a: Explain the role of cell organelles for both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, including the cell membrane, in maintaining homeostasis
The Cell Cycle Biology Standards you are responsible for mastering. SB1a: Explain the role of cell organelles for both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, including the cell membrane, in maintaining homeostasis
Prentice Hall Biology Slide 1 of 38
 Prentice Hall Biology 1 of 38 2 of 38 In eukaryotes, cell division occurs in two major stages. The first stage, division of the cell nucleus, is called mitosis. The second stage, division of the cell cytoplasm,
Prentice Hall Biology 1 of 38 2 of 38 In eukaryotes, cell division occurs in two major stages. The first stage, division of the cell nucleus, is called mitosis. The second stage, division of the cell cytoplasm,
-The cell s hereditary endowment of DNA -Usually packaged into chromosomes for manageability
 Binary Fission-Bacterial Cell Division -Asexual reproduction of prokaryotes -No mitosis -Circular DNA and organelles replicate, the copies migrate to opposite sides of the elongating cell, and the cell
Binary Fission-Bacterial Cell Division -Asexual reproduction of prokaryotes -No mitosis -Circular DNA and organelles replicate, the copies migrate to opposite sides of the elongating cell, and the cell
Ploidy and Human Cell Types. Cell Cycle and Mitosis. DNA and Chromosomes. Where It All Began 11/19/2014. Chapter 12 Pg
 Ploidy and Human Cell Types Cell Cycle and Mitosis Chapter 12 Pg. 228 245 Cell Types Somatic cells (body cells) have 46 chromosomes, which is the diploid chromosome number. A diploid cell is a cell with
Ploidy and Human Cell Types Cell Cycle and Mitosis Chapter 12 Pg. 228 245 Cell Types Somatic cells (body cells) have 46 chromosomes, which is the diploid chromosome number. A diploid cell is a cell with
CELL CYCLE INTRODUCTION PART I ANIMAL CELL CYCLE INTERPHASE
 CELL CYCLE INTRODUCTION The nuclei in cells of eukaryotic organisms contain chromosomes with clusters of genes, discrete units of hereditary information consisting of double-stranded DNA. Structural proteins
CELL CYCLE INTRODUCTION The nuclei in cells of eukaryotic organisms contain chromosomes with clusters of genes, discrete units of hereditary information consisting of double-stranded DNA. Structural proteins
Cell Cycle and Mitosis
 Cell Cycle and Mitosis Name Period A# THE CELL CYCLE The cell cycle, or cell-division cycle, is the series of events that take place in a eukaryotic cell between its formation and the moment it replicates
Cell Cycle and Mitosis Name Period A# THE CELL CYCLE The cell cycle, or cell-division cycle, is the series of events that take place in a eukaryotic cell between its formation and the moment it replicates
Cell division functions in 1. reproduction, 2. growth, and 3. repair
 Cell division functions in 1. reproduction, 2. growth, and 3. repair What do you think you are looking at here??? Can something like you or I do this??? Fig. 12.1 How did you start out? How did you grow?
Cell division functions in 1. reproduction, 2. growth, and 3. repair What do you think you are looking at here??? Can something like you or I do this??? Fig. 12.1 How did you start out? How did you grow?
CELL CYCLE INTRODUCTION PART I ANIMAL CELL CYCLE INTERPHASE EVOLUTION/HEREDITY UNIT. Activity #3
 AP BIOLOGY EVOLUTION/HEREDITY UNIT Unit 1 Part 3 Chapter 12 Activity #3 INTRODUCTION CELL CYCLE NAME DATE PERIOD The nuclei in cells of eukaryotic organisms contain chromosomes with clusters of genes,
AP BIOLOGY EVOLUTION/HEREDITY UNIT Unit 1 Part 3 Chapter 12 Activity #3 INTRODUCTION CELL CYCLE NAME DATE PERIOD The nuclei in cells of eukaryotic organisms contain chromosomes with clusters of genes,
The Cell Cycle. Dr. SARRAY Sameh, Ph.D
 The Cell Cycle Dr. SARRAY Sameh, Ph.D Overview When an organism requires additional cells (either for growth or replacement of lost cells), new cells are produced by cell division (mitosis) Somatic cells
The Cell Cycle Dr. SARRAY Sameh, Ph.D Overview When an organism requires additional cells (either for growth or replacement of lost cells), new cells are produced by cell division (mitosis) Somatic cells
MITOSIS AND THE CELL CYCLE PowerPoint Notes
 1 Name: Date: MITOSIS AND THE CELL CYCLE PowerPoint Notes THE FUNCTIONS OF CELL DIVISION 1. Cell division is vital for all. living organisms This is the only process that can create. new cells 2. Cell
1 Name: Date: MITOSIS AND THE CELL CYCLE PowerPoint Notes THE FUNCTIONS OF CELL DIVISION 1. Cell division is vital for all. living organisms This is the only process that can create. new cells 2. Cell
BIOLOGY 4/6/2015. Cell Cycle - Mitosis. Outline. Overview: The Key Roles of Cell Division. identical daughter cells. I. Overview II.
 2 Cell Cycle - Mitosis CAMPBELL BIOLOGY TENTH EDITION Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson Outline I. Overview II. Mitotic Phase I. Prophase II. III. Telophase IV. Cytokinesis III. Binary fission
2 Cell Cycle - Mitosis CAMPBELL BIOLOGY TENTH EDITION Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson Outline I. Overview II. Mitotic Phase I. Prophase II. III. Telophase IV. Cytokinesis III. Binary fission
The Cell Cycle. Chapter 12. PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece
 Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from Joan Sharp Overview:
Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from Joan Sharp Overview:
Outline Interphase Mitotic Stage Cell Cycle Control Apoptosis Mitosis Mitosis in Animal Cells Cytokinesis Cancer Prokaryotic Cell Division
 The Cell Cycle and Cellular Reproduction Chapter 9 Outline Interphase Mitotic Stage Cell Cycle Control Apoptosis Mitosis Mitosis in Animal Cells Cytokinesis Cancer Prokaryotic Cell Division 1 2 Interphase
The Cell Cycle and Cellular Reproduction Chapter 9 Outline Interphase Mitotic Stage Cell Cycle Control Apoptosis Mitosis Mitosis in Animal Cells Cytokinesis Cancer Prokaryotic Cell Division 1 2 Interphase
Bacterial cell. Origin of replication. Septum
 Bacterial cell Bacterial chromosome: Double-stranded DNA Origin of replication Septum 1 2 3 Chromosome Rosettes of Chromatin Loops Scaffold protein Chromatin Loop Solenoid Scaffold protein Chromatin loop
Bacterial cell Bacterial chromosome: Double-stranded DNA Origin of replication Septum 1 2 3 Chromosome Rosettes of Chromatin Loops Scaffold protein Chromatin Loop Solenoid Scaffold protein Chromatin loop
LECTURE PRESENTATIONS
 LECTURE PRESENTATIONS For CAMPBELL BIOLOGY, NINTH EDITION Jane B. Reece, Lisa A. Urry, Michael L. Cain, Steven A. Wasserman, Peter V. Minorsky, Robert B. Jackson Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle Lectures by Erin
LECTURE PRESENTATIONS For CAMPBELL BIOLOGY, NINTH EDITION Jane B. Reece, Lisa A. Urry, Michael L. Cain, Steven A. Wasserman, Peter V. Minorsky, Robert B. Jackson Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle Lectures by Erin
Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth, Cell Division
 Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth, Cell Division 2007-2008 Where it all began You started as a cell smaller than a period at the end of a sentence And now look at you How did you get from there to
Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth, Cell Division 2007-2008 Where it all began You started as a cell smaller than a period at the end of a sentence And now look at you How did you get from there to
Cell Division. During interphase, a cell s DNA is in a loose form called. It condenses into tightly coiled structures called chromosomes during.
 Cell Division The is a cell s total DNA. Prokaryotes DNA is found mostly in a single called the and also in small circles called. Eukaryotes have several DNA double helices packaged into. During interphase,
Cell Division The is a cell s total DNA. Prokaryotes DNA is found mostly in a single called the and also in small circles called. Eukaryotes have several DNA double helices packaged into. During interphase,
Cell Division Mitosis Notes
 Cell Division Mitosis Notes Cell Division process by which a cell divides into 2 new cells Why do cells need to divide? 1.Living things grow by producing more cells, NOT because each cell increases in
Cell Division Mitosis Notes Cell Division process by which a cell divides into 2 new cells Why do cells need to divide? 1.Living things grow by producing more cells, NOT because each cell increases in
Name: Date: Block: 10-2 Cell Division Worksheet
 10-2 Cell Division Worksheet W hat do you think would happen if a cell were simple to split into two, without any advance preparation? Would each daughter cell have everything it needed to survive? Because
10-2 Cell Division Worksheet W hat do you think would happen if a cell were simple to split into two, without any advance preparation? Would each daughter cell have everything it needed to survive? Because
The Cell Cycle. Chapter 12. Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece. PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for
 Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from Joan Sharp Copyright
Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from Joan Sharp Copyright
LECTURE PRESENTATIONS
 LECTURE PRESENTATIONS For CAMPBELL BIOLOGY, NINTH EDITION Jane B. Reece, Lisa A. Urry, Michael L. Cain, Steven A. Wasserman, Peter V. Minorsky, Robert B. Jackson Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle Lectures by Erin
LECTURE PRESENTATIONS For CAMPBELL BIOLOGY, NINTH EDITION Jane B. Reece, Lisa A. Urry, Michael L. Cain, Steven A. Wasserman, Peter V. Minorsky, Robert B. Jackson Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle Lectures by Erin
Chapter 10 Cell Growth and Division
 Chapter 10 Cell Growth and Division 10 1 Cell Growth 2 Limits to Cell Growth The larger a cell becomes, the more demands the cell places on its DNA. In addition, the cell has more trouble moving enough
Chapter 10 Cell Growth and Division 10 1 Cell Growth 2 Limits to Cell Growth The larger a cell becomes, the more demands the cell places on its DNA. In addition, the cell has more trouble moving enough
Chapter 2. Mitosis and Meiosis
 Chapter 2. Mitosis and Meiosis Chromosome Theory of Heredity What structures within cells correspond to genes? The development of genetics took a major step forward by accepting the notion that the genes
Chapter 2. Mitosis and Meiosis Chromosome Theory of Heredity What structures within cells correspond to genes? The development of genetics took a major step forward by accepting the notion that the genes
CH 9: The Cell Cycle Overview. Cellular Organization of the Genetic Material. Distribution of Chromosomes During Eukaryotic Cell Division
 CH 9: The Cell Cycle Overview The ability of organisms to produce more of their own kind best distinguishes living things from nonliving matter The continuity of life is based on the reproduction of cells,
CH 9: The Cell Cycle Overview The ability of organisms to produce more of their own kind best distinguishes living things from nonliving matter The continuity of life is based on the reproduction of cells,
CELL GROWTH & DIVISION
 CELL GROWTH & DIVISION 2 Reasons why cells divide 1. DNA OVERLOAD As cell grows bigger demand on DNA genetic library becomes too great Ex: Small town library has 1000 books. As town grows and more people
CELL GROWTH & DIVISION 2 Reasons why cells divide 1. DNA OVERLOAD As cell grows bigger demand on DNA genetic library becomes too great Ex: Small town library has 1000 books. As town grows and more people
Mitosis: cell division that forms identical daughter cells with the same number of chromosomes as the parent cell (duplicate and divide)
 Mitosis: cell division that forms identical daughter cells with the same number of chromosomes as the parent cell (duplicate and divide) Meiosis: cell division that forms daughter cells with half the number
Mitosis: cell division that forms identical daughter cells with the same number of chromosomes as the parent cell (duplicate and divide) Meiosis: cell division that forms daughter cells with half the number
Unit 4: Cell Division Guided Notes
 Unit 4: Cell Division Guided Notes 1 Chromosomes are structures that contain material When Eukaryotes are not dividing, DNA and Proteins are in a mass called: When the cell divides, it condenses and becomes
Unit 4: Cell Division Guided Notes 1 Chromosomes are structures that contain material When Eukaryotes are not dividing, DNA and Proteins are in a mass called: When the cell divides, it condenses and becomes
Chapter 8: Cellular Reproduction
 Chapter 8: Cellular Reproduction 1. The Cell Cycle 2. Mitosis 3. Meiosis 2 Types of Cell Division 2n 1n Mitosis: occurs in somatic cells (almost all cells of the body) generates cells identical to original
Chapter 8: Cellular Reproduction 1. The Cell Cycle 2. Mitosis 3. Meiosis 2 Types of Cell Division 2n 1n Mitosis: occurs in somatic cells (almost all cells of the body) generates cells identical to original
How Cells Divide. Chapter 10
 How Cells Divide Chapter 10 Bacterial Cell Division Bacteria divide by binary fission. -the single, circular bacterial chromosome is replicated -replication begins at the origin of replication and proceeds
How Cells Divide Chapter 10 Bacterial Cell Division Bacteria divide by binary fission. -the single, circular bacterial chromosome is replicated -replication begins at the origin of replication and proceeds
Chapter 3: Cytology. Cytology is the study of cells. Cells are the basic units of life. We are made up of trillions of cells.
 PLEASE NOTE THAT THE ITEMS IN THE TEXT THAT ARE HIGHLIGHTED IN YELLOW ARE THOSE THAT ARE TOUCHED ON IN THE READING ASSIGNMENT (PAGES 90-99) AND IN THE LECTURE. ESPECIALLY KNOW THIS MATERIAL FOR THE FIRST
PLEASE NOTE THAT THE ITEMS IN THE TEXT THAT ARE HIGHLIGHTED IN YELLOW ARE THOSE THAT ARE TOUCHED ON IN THE READING ASSIGNMENT (PAGES 90-99) AND IN THE LECTURE. ESPECIALLY KNOW THIS MATERIAL FOR THE FIRST
Cell Cycle - Introduction
 Cell Cycle - Introduction Key Concepts Cell division results in two identical cells During cell division the ability to organize DNA in time and space (location in the cell) is critical! The mitotic phase
Cell Cycle - Introduction Key Concepts Cell division results in two identical cells During cell division the ability to organize DNA in time and space (location in the cell) is critical! The mitotic phase
Mitosis and the Cell Cycle
 Mitosis and the Cell Cycle Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth & Cell Division Where it all began You started as a cell smaller than a period at the end of a sentence Getting from there to here Cell
Mitosis and the Cell Cycle Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth & Cell Division Where it all began You started as a cell smaller than a period at the end of a sentence Getting from there to here Cell
NOTES- CHAPTER 6 CHROMOSOMES AND CELL REPRODUCTION
 NOTES- CHAPTER 6 CHROMOSOMES AND CELL REPRODUCTION Section I Chromosomes Formation of New Cells by Cell Division New cells are formed when old cells divide. 1. Cell division is the same as cell reproduction.
NOTES- CHAPTER 6 CHROMOSOMES AND CELL REPRODUCTION Section I Chromosomes Formation of New Cells by Cell Division New cells are formed when old cells divide. 1. Cell division is the same as cell reproduction.
BIOLOGY. The Cell Cycle CAMPBELL. Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson. Lecture Presentation by Nicole Tunbridge and Kathleen Fitzpatrick
 CAMPBELL BIOLOGY TENTH EDITION Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson 12 The Cell Cycle Lecture Presentation by Nicole Tunbridge and Kathleen Fitzpatrick The Key Roles of Cell Division The ability
CAMPBELL BIOLOGY TENTH EDITION Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson 12 The Cell Cycle Lecture Presentation by Nicole Tunbridge and Kathleen Fitzpatrick The Key Roles of Cell Division The ability
LECTURE PRESENTATIONS
 LECTURE PRESENTATIONS For CAMPBELL BIOLOGY, NINTH EDITION Jane B. Reece, Lisa A. Urry, Michael L. Cain, Steven A. Wasserman, Peter V. Minorsky, Robert B. Jackson Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle Lectures by Erin
LECTURE PRESENTATIONS For CAMPBELL BIOLOGY, NINTH EDITION Jane B. Reece, Lisa A. Urry, Michael L. Cain, Steven A. Wasserman, Peter V. Minorsky, Robert B. Jackson Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle Lectures by Erin
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Figure 2.1 Use the diagram above to answer the following questions. 1) Which letter indicates the
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Figure 2.1 Use the diagram above to answer the following questions. 1) Which letter indicates the
Cell Division (Mitosis)
 Cell Division (Mitosis) Chromosomes The essential part of a chromosome is a single very long strand of DNA. This DNA contains all the genetic information for creating and running the organism. Each chromosome
Cell Division (Mitosis) Chromosomes The essential part of a chromosome is a single very long strand of DNA. This DNA contains all the genetic information for creating and running the organism. Each chromosome
Origin of replication. Septum
 Bacterial cell Bacterial chromosome: Double-stranded DNA Origin of replication Septum 1 2 3 Chromosome Rosettes of Chromatin Loops Chromatin Loop Solenoid Scaffold protein Scaffold protein Chromatin loop
Bacterial cell Bacterial chromosome: Double-stranded DNA Origin of replication Septum 1 2 3 Chromosome Rosettes of Chromatin Loops Chromatin Loop Solenoid Scaffold protein Scaffold protein Chromatin loop
The Cell Cycle. Chapter 12. Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece. PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for
 Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from Joan Sharp 1
Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from Joan Sharp 1
Mitosis & Meiosis. Diploid cells- (2n)- a cell that has 2 of each chromosome - 1 from mom, 1 from dad = 1 pair
 Mitosis & Meiosis Diploid cells- (2n)- a cell that has 2 of each chromosome - 1 from mom, 1 from dad = 1 pair The pair is called homologous chromosomes The homologous chromosomes contain the same gene
Mitosis & Meiosis Diploid cells- (2n)- a cell that has 2 of each chromosome - 1 from mom, 1 from dad = 1 pair The pair is called homologous chromosomes The homologous chromosomes contain the same gene
Cell Cycle and Mitosis
 Ch 12 BIOL 221 Cell Cycle and Mitosis The Key Roles of Cell Division Cell division Cellular reproduc2on An ability of organisms that best dis2nguishes living things from nonliving ma:er Cell Division Unicellular
Ch 12 BIOL 221 Cell Cycle and Mitosis The Key Roles of Cell Division Cell division Cellular reproduc2on An ability of organisms that best dis2nguishes living things from nonliving ma:er Cell Division Unicellular
Section Cell Growth. A. Limits to Cell Growth 1. DNA Overload 2. Exchanging Materials 3. Ratio of Surface Area to Volume 4.
 Getting Through Materials move through cells by diffusion. Oxygen and food move into cells, while waste products move out of cells. How does the size of a cell affect how efficiently materials get to all
Getting Through Materials move through cells by diffusion. Oxygen and food move into cells, while waste products move out of cells. How does the size of a cell affect how efficiently materials get to all
BIOLOGY. Cell Cycle - Mitosis. Outline. Overview: The Key Roles of Cell Division. identical daughter cells. I. Overview II.
 2 Cell Cycle - Mitosis CAMPBELL BIOLOGY TENTH EDITION Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson Outline I. Overview II. Mitotic Phase I. Prophase II. III. Telophase IV. Cytokinesis III. Binary fission
2 Cell Cycle - Mitosis CAMPBELL BIOLOGY TENTH EDITION Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson Outline I. Overview II. Mitotic Phase I. Prophase II. III. Telophase IV. Cytokinesis III. Binary fission
Goals. Cells. Cells: The Living Units. By the end of this lecture you should be able to describe.
 C H A P T E R 2 Cells: The Living Units Goals By the end of this lecture you should be able to describe. Similarities and differences between cells Why cells look and function differently The function
C H A P T E R 2 Cells: The Living Units Goals By the end of this lecture you should be able to describe. Similarities and differences between cells Why cells look and function differently The function
Cell Division Mitosis Notes
 Cell Division Mitosis Notes Cell Division process by which a cell divides into 2 new cells Why do cells need to divide? 1.Living things grow by producing more cells, NOT because each cell increases in
Cell Division Mitosis Notes Cell Division process by which a cell divides into 2 new cells Why do cells need to divide? 1.Living things grow by producing more cells, NOT because each cell increases in
Centrosomes and Cilia
 Centrosomes and Cilia SMC6052/BIM6028/EXMD604 William Y. Tsang Research Unit Director, Cell Division and Centrosome Biology, IRCM Chercheur Adjoint, Faculté de medécine, Université de Montréal Adjunct
Centrosomes and Cilia SMC6052/BIM6028/EXMD604 William Y. Tsang Research Unit Director, Cell Division and Centrosome Biology, IRCM Chercheur Adjoint, Faculté de medécine, Université de Montréal Adjunct
2014 Pearson Education, Inc.
 2 The Cell Cycle CAMPBELL BIOLOGY TENTH EDITION Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson The Key Roles of Cell Division The ability of organisms to produce more of their own kind best distinguishes living
2 The Cell Cycle CAMPBELL BIOLOGY TENTH EDITION Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson The Key Roles of Cell Division The ability of organisms to produce more of their own kind best distinguishes living
The questions below refer to the following terms. Each term may be used once, more than once, or not at all.
 The questions below refer to the following terms. Each term may be used once, more than once, or not at all. a) telophase b) anaphase c) prometaphase d) metaphase e) prophase 1) DNA begins to coil and
The questions below refer to the following terms. Each term may be used once, more than once, or not at all. a) telophase b) anaphase c) prometaphase d) metaphase e) prophase 1) DNA begins to coil and
Cell Division Mitosis Notes
 Cell Division Mitosis Notes Cell Division process by which a cell divides into 2 new cells Why do cells need to divide? 1.Living things grow by producing more cells, NOT because each cell increases in
Cell Division Mitosis Notes Cell Division process by which a cell divides into 2 new cells Why do cells need to divide? 1.Living things grow by producing more cells, NOT because each cell increases in
Campbell Biology in Focus (Urry) Chapter 9 The Cell Cycle. 9.1 Multiple-Choice Questions
 Campbell Biology in Focus (Urry) Chapter 9 The Cell Cycle 9.1 Multiple-Choice Questions 1) Starting with a fertilized egg (zygote), a series of five cell divisions would produce an early embryo with how
Campbell Biology in Focus (Urry) Chapter 9 The Cell Cycle 9.1 Multiple-Choice Questions 1) Starting with a fertilized egg (zygote), a series of five cell divisions would produce an early embryo with how
The Cell Cycle 4/10/12. Chapter 12. Overview: The Key Roles of Cell Division
 LECTURE PRESENTATIONS For CAMPBELL BIOLOGY, NINTH EDITION Jane B. Reece, Lisa A. Urry, Michael L. Cain, Steven A. Wasserman, Peter V. Minorsky, Robert B. Jackson Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle Lectures by Erin
LECTURE PRESENTATIONS For CAMPBELL BIOLOGY, NINTH EDITION Jane B. Reece, Lisa A. Urry, Michael L. Cain, Steven A. Wasserman, Peter V. Minorsky, Robert B. Jackson Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle Lectures by Erin
Monday, October 6 Put these items into the appropriate category:
 Monday, October 6 Put these items into the appropriate category: Active Transport Facilitated Diffusion Osmosis Simple Diffusion The smell of rotten eggs spreading through the room Requires ATP expenditure
Monday, October 6 Put these items into the appropriate category: Active Transport Facilitated Diffusion Osmosis Simple Diffusion The smell of rotten eggs spreading through the room Requires ATP expenditure
MITOSIS IN ONION ROOTLET CELLS
 Lesson 6: CELL CYCLE, MITOSIS Name: Group: MITOSIS IN ONION ROOTLET CELLS Permanent slide: onion rootlet stained with acetorcein The particular mitotic phases are visible in the onion rootlet cells. Chromosomes
Lesson 6: CELL CYCLE, MITOSIS Name: Group: MITOSIS IN ONION ROOTLET CELLS Permanent slide: onion rootlet stained with acetorcein The particular mitotic phases are visible in the onion rootlet cells. Chromosomes
You might be interested in reading an excerpt from Dimensions
 Take notes (minimum 1 page) on the following reading. Then review using the animation (link at bottom) and answer the quiz questions at the bottom of the webpage. To get credit for this assignment you
Take notes (minimum 1 page) on the following reading. Then review using the animation (link at bottom) and answer the quiz questions at the bottom of the webpage. To get credit for this assignment you
Chapter 12. The Cell Cycle
 Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle The Key Roles of Cell Division The ability of organisms to produce more of their own kind is the one characteristic that best distinguishes living things from nonliving things.
Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle The Key Roles of Cell Division The ability of organisms to produce more of their own kind is the one characteristic that best distinguishes living things from nonliving things.
Cell Division and Mitosis
 Chromatin-Uncoiled DNA during interphase Cell Division and Mitosis Chromosomes-Tightly coiled DNA Chromatid-One half of a duplicated chromosome. Each is identical and called sister chromatids Centromere-The
Chromatin-Uncoiled DNA during interphase Cell Division and Mitosis Chromosomes-Tightly coiled DNA Chromatid-One half of a duplicated chromosome. Each is identical and called sister chromatids Centromere-The
cell movement and neuronal migration
 cell movement and neuronal migration Paul Letourneau letou001@umn.edu Chapter 16; The Cytoskeleton; Molecular Biology of the Cell, Alberts et al. 1 Cell migration Cell migration in 3 steps; protrusion,
cell movement and neuronal migration Paul Letourneau letou001@umn.edu Chapter 16; The Cytoskeleton; Molecular Biology of the Cell, Alberts et al. 1 Cell migration Cell migration in 3 steps; protrusion,
General Biology. Overview: The Key Roles of Cell Division. Unicellular organisms
 General Biology Course No: BNG2003 Credits: 3.00 8. The Cell Cycle Prof. Dr. Klaus Heese Overview: The Key Roles of Cell Division The continuity of life is based upon the reproduction of cells, or cell
General Biology Course No: BNG2003 Credits: 3.00 8. The Cell Cycle Prof. Dr. Klaus Heese Overview: The Key Roles of Cell Division The continuity of life is based upon the reproduction of cells, or cell
General Biology. Overview: The Key Roles of Cell Division The continuity of life is based upon the reproduction of cells, or cell division
 General Biology Course No: BNG2003" Credits: 3.00 " " " 8. The Cell Cycle Prof. Dr. Klaus Heese Overview: The Key Roles of Cell Division The continuity of life is based upon the reproduction of cells,
General Biology Course No: BNG2003" Credits: 3.00 " " " 8. The Cell Cycle Prof. Dr. Klaus Heese Overview: The Key Roles of Cell Division The continuity of life is based upon the reproduction of cells,
Chapter 10. Cell Cycle - Mitosis
 Chapter 10 Cell Cycle - Mitosis WHAT CELL REPRODUCTION ACCOMPLISHES Cell division plays important roles in the lives of organisms. Cell division replaces damaged or lost cells permits growth allows for
Chapter 10 Cell Cycle - Mitosis WHAT CELL REPRODUCTION ACCOMPLISHES Cell division plays important roles in the lives of organisms. Cell division replaces damaged or lost cells permits growth allows for
