MAINTAINING HOMEOSTASIS - PRACTICE TEST
|
|
|
- Job Eaton
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Name: Date: 1. Which sequence of terms is in the correct order from simplest to most complex? (1) cells tissues organs organ systems (2) tissues organisms cells organ systems (3) cells tissues organ systems organs (4) organs organisms organ systems cells 2. The diagram below represents levels of organization in living things. 3. During a long-distance run on a hot day, an athlete produces large quantities of sweat. As a result, the kidneys change the rate of urine production. Why is this change important? (1) Decreased urine production increases the amino acids in the blood. (2) Increased urine production removes amino acids produced as a result of running. (3) Decreased urine production allows the body to conserve water. (4) Increased urine production allows more water to remain in the bloodstream. Which term would best represent X? (1) human (2) tissue (3) stomach (4) organelle page 1
2 4. Base your answer(s) to the following question(s) on the accompanying diagram, which represents the pathway of blood throughout the body, and on your knowledge of biology. 5. In order to enter cells and be useful to the body, starch must be (1) absorbed through the skin (2) broken down into fats and water (3) digested into simple sugars (4) converted to carbon dioxide and ATP Which structure carries oxygenated blood to the body? (1) 1 (2) 2 (3) 7 (4) 8 page 2
3 Base your answer(s) to the following question(s) on the information and graph below and on your knowledge of biology. Students were asked to design a lab that investigated the relationship between exercise and heart rate. Heart rate was determined by recording the pulse rate in beats per minute. The students hypothesized that increased exercise results in an increased heart rate. The class results for the experiment are shown in the graph below. page 3
4 6. The change in heart rate that occurs between 1 and 5 minutes of exercise is an adaptation that (1) reduces the rate at which oxygen is carried to the muscle cells 8. Base your answer(s) to the following question(s) on the diagram below and your knowledge of biology. The diagram represents an ameba, a single-celled organism, carrying out an essential life process. (2) increases the rate at which carbon dioxide is carried to the muscle cells (3) results in the production of more ATP in muscle cells (4) slows the destruction of enzymes involved in respiration of muscle cells 7. Before starch can enter a cell, it must be (1) absorbed by simple sugars (2) diffused into simple sugars (3) digested to form simple sugars (4) actively transported by simple sugars Which two body systems allow humans to carry out the same life process as the ameba in the diagram? (1) endocrine and immune (2) respiratory and reproductive (3) digestive and circulatory (4) nervous and excretory 9. The nucleus of a cell coordinates processes and activities that take place in the cell. Which two systems perform a similar function in the human body? (1) nervous and endocrine (2) digestive and reproductive (3) circulatory and respiratory (4) skeletal and muscular 10. Which molecule can diffuse from the digestive tract into the human bloodstream without first being digested? (1) protein (2) starch (3) fat (4) glucose page 4
5 11. The cytoplasm in a cell carries out a function similar to a function of which human system? (1) respiratory system (2) reproductive system (3) circulatory system (4) nervous system 12. The interaction of which two systems provides the molecules needed for the metabolic activity that takes place at ribosomes? (1) digestive and circulatory (2) reproductive and excretory (3) immune and nervous (4) respiratory and muscular 13. Which sequence represents the correct order of events for the production of necessary complex molecules after food is taken in by a multicellular animal? (1) diffusion synthesis absorption digestion circulation 14. Which system is correctly paired with its function? (1) immune system intake and distribution of oxygen to cells of the body (2) excretory system remove potentially dangerous materials from the body (3) digestive system transport energy-rich molecules to cells (4) circulatory system produce building bloc of complex compounds 15. Which body system is correctly paired with its function? (1) excretory produces antibodies to fight disease-causing organisms (2) digestive produces hormones for storage and insulation (3) circulatory transports materials for energy release in body cells (4) respiratory collects waste material for digestion 16. Which organ system in humans is most directly involved in the transport of oxygen? (2) circulation diffusion synthesis absorption digestion (3) digestion absorption circulation diffusion synthesis (4) synthesis digestion absorption diffusion circulation (1) digestive (2) nervous (3) excretory (4) circulatory page 5
6 17. The diagram below represents an interaction between parts of an organism. 19. The table below provides some information concerning organelles and organs. Function Organelle Organ gas exchange cell membrane lung nutrition food vacuole stomach Based on this information, which statement accurately compares organelles to organs? (1) Functions are carried out more efficiently by organs than by organelles. The term chemicals in this diagram represents (1) starch molecules (2) DNA molecules (2) Organs maintain homeostasis while organelles do not. (3) Organelles carry out functions similar to those of organs. (4) Organelles function in multicellular organisms while organs function in single-celled organisms. (3) hormone molecules (4) receptor molecules 18. To increase chances for a successful organ transplant, the person receiving the organ should be given special medications. The purpose of these medications is to (1) increase the immune response in the person receiving the transplant (2) decrease the immune response in the person receiving the transplant (3) decrease mutations in the person receiving the transplant (4) increase mutations in the person receiving the transplant page 6
7 20. The diagram below represents three human body systems. 22. An increase in heart rate will most likely result in (1) a decrease in metabolic rate (2) an increase in pulse rate (3) an increase in cell division (4) a decrease in body temperature Which row in the chart below correctly shows what systems A, B, and C provide for the human body? Row System A System B System C (1) blood cells glucose hormones (2) oxygen absorption gametes (3) gas exchange nutrients waste removal (4) immunity coordination carbon dioxide (1) (1) (2) (2) (3) (3) (4) (4) 23. Which two organ systems provide materials required for the human body to produce ATP? (1) reproductive and excretory (2) digestive and respiratory (3) respiratory and immune (4) digestive and reproductive 21. Which structures in diagram I and diagram II carry out a similar life function? (1) 1 and C (2) 2 and D (3) 3 and A (4) 4 and B page 7
8 24. In the diagram of a single-celled organism shown below, the arrows indicate various activities taking place. 26. Two types of human cells are shown in the diagram below. Cell A causes the cells at B to contract. This activity would be most useful for (1) lifting a book from a bookshelf Which systems perform these same activities in humans? (1) digestive, circulatory, and immune (2) excretory, respiratory, and reproductive (3) respiratory, excretory, and digestive (4) respiratory, nervous, and endocrine 25. Which two systems are most directly involved in providing molecules needed for the synthesis of fats in human cells? (1) digestive and circulatory (2) excretory and digestive (3) immune and muscular (4) reproductive and circulatory (2) coordinating the functions of organelles (3) digesting food in the small intestine (4) carrying out the process of protein synthesis 27. Which words best complete the lettered blanks in the two sentences below? Organic compounds, such as proteins and starches, are too A to diffuse into cells. Proteins are digested into B and starches are digested into C. (1) A large, B simple sugars, C amino acids (2) A small, B simple sugars, C amino acids (3) A large, B amino acids, C simple sugars (4) A small, B amino acids, C simple sugars page 8
9 28. The accompanying diagram represents events involved as energy is ultimately released from food. 30. Base your answer(s) to the following question(s) on the accompanying diagram, which represents the pathway of blood throughout the body, and on your knowledge of biology. Which row in the table below best represents the chain of Xs and letters A and B in the diagram? X-X-X-X-X-X-X A and B (1) nutrient antibodies (2) nutrient enzymes (3) hemoglobin wastes (4) hemoglobin hormones (1) (1) (2) (2) (3) (3) (4) (4) 29. The main function of the human digestive system is to (1) rid the body of cellular waste materials (2) process organic molecules so they can enter cells Which structure represents the chamber of the heart that receives oxygenated blood directly from the lungs? (1) 5 (2) 6 (3) 3 (4) The accompanying diagram represents the actions of two hormones in the human body. (3) break down glucose in order to release energy (4) change amino acids into proteins and carbohydrates This diagram best illustrates (1) recombination (2) feedback (3) insertion (4) deletion page 9
10 32. The most immediate response to a high level of blood sugar in a human is an increase in the 34. The graph below shows the levels of glucose and insulin in the blood of a human over a period of time. (1) muscle activity in the arms (2) blood flow to the digestive tract (3) activity of all cell organelles (4) release of insulin 33. The pancreas produces one hormone that lowers blood sugar level and another that increases blood sugar level. The interaction of these two hormones most directly helps humans to This graph represents (1) an allergic reaction (2) an antigen-antibody reaction (3) maintenance of homeostasis (4) autotrophic nutrition (1) maintain a balanced internal environment (2) digest needed substances for other body organs (3) dispose of wastes formed in other body organs (4) increase the rate of cellular communication page 10
11 35. The blood glucose range for a healthy adult is mg/dl. Which graph best illustrates normal blood glucose levels in a healthy adult over the course of a day? (1) 36. Base your answer(s) to the following question(s) on the diagram below and on your knowledge of biology. The diagram represents the effect of two chemical substances, A and B, in maintaining the level of glucose in the blood in humans. (2) The interaction of substances A and B is an example of (1) a genetic mutation (3) (2) homeostatic feedback (3) an immune response (4) active transport 37. Which statement is correct regarding the substances involved in these interactions? (4) (1) Substance A is insulin, which is released by cells in the pancreas. (2) Substance B is a chemical receptor molecule produced by blood cells. (3) Both substances A and B are classified as biological catalysts. (4) Substance A is a chemical that is produced by specialized blood cells. page 11
12 38. All of the cell shapes shown in the diagrams below have the same volume. Which form could absorb nutrients most efficiently and quickly? (1) (2) (3) (4) 39. The accompanying diagram can be used to illustrate a process directly involved in 41. Which statement describing the cells in a body system is correct? (1) Each cell in the system is identical to the other cells in the system, and each cell works independently of the other cells. (2) Some cells in the system may be different from the other cells in the system, but all cells are coordinated and work together. (3) Each cell in the system is different from the other cells in the system, and each cell works independently of the other cells. (4) All cells in the system are identical to each other and work together. (1) tissue repair 42. One effect of uncontrolled diabetes is that the blood might develop an acidic ph. As a result, cells may not be able to regulate their internal ph. Within these cells, this could cause a disruption of the function of biological catalysts known as (2) meiosis (3) recombination (4) sexual reproduction (1) enzymes (2) toxins (3) antibodies (4) antigens 40. Which activity is not a response of human white blood cells to pathogens? (1) engulfing and destroying bacteria (2) producing antibodies (3) identifying invaders for destruction (4) removing carbon dioxide page 12
13 43. The diagram below represents one type of white blood cell. This type of white blood cell ingests microbes. 45. Which statement accurately compares cells in the human circulatory system to cells in the human nervous system? (1) Cells in the circulatory system carry out the same life function for the organism as cells in the nervous system. A function of another type of white blood cell is to (1) prevent the loss of blood from a wound (2) produce specialized molecules that mark invaders (3) increase the number of red blood cells in the blood (4) cause gene mutations that will increase immune responses 44. Which cell structures are correctly paired with their functions? (1) The mitochondria produce enzymes, and ribosomes transport them. (2) The ribosomes make proteins, and the nucleus stores genetic information. (3) The cell membrane makes enzymes, and cytoplasm transports them. (4) The vacuole stores genetic information, and chloroplasts make proteins. (2) Cells in the circulatory system are identical in structure to cells in the nervous system. (3) Cells in the nervous system are different in structure from cells in the circulatory system, and they carry out different specialized functions. (4) Cells in the nervous system act independently, but cells in the circulatory system function together. 46. The pancreas is an organ connected to the digestive tract of humans by a duct (tube) through which digestive enzymes flow. These enzymes are important to the digestive system because they (1) form proteins needed in the stomach (2) form the acids that break down food (3) change food substances into molecules that can pass into the bloodstream and cells (4) change food materials into wastes that can be passed out of the body page 13
14 47. Studies of fat cells and thyroid cells show that fat cells have fewer mitochondria than thyroid cells. A biologist would most likely infer that fat tissue (1) does not require energy (2) has energy requirements equal to those of thyroid tissue (3) requires less energy than thyroid tissue (4) requires more energy than thyroid tissue 48. The diagram below represents a model of a biological process that occurs in humans at normal body temperature, 37 C. 49. Base your answer(s) to the following question(s) on the information below and on your knowledge of biology. Diabetes is a condition characterized by elevated blood sugar levels. One form of diabetes occurs when insulin fails to properly regulate blood sugar levels. Complications from diabetes can include nerve cell damage and poor blood flow, especially in the feet and legs. In individuals with diabetes, wounds usually take longer than normal to heal. One reason for the change in wound healing time in a diabetic is that (1) elevated hormone levels block the synthesis of glucose in immune cells Increasing body temperature to 40 C would interfere most directly with the rate of function of structure (1) A (2) B (3) C (4) D (2) nerve damage increases absorption of glucose by healthy cells (3) poor circulation reduces the supply of nutrients and oxygen to the cells (4) decreased enzyme production slows protein synthesis in pancreatic cells 50. A function of white blood cells is to (1) transport oxygen to body cells (2) produce hormones that regulate cell communication (3) carry glucose to body cells (4) protect the body against pathogens page 14
15 51. Base your answer(s) to the following question(s) on the diagram below and on your knowledge of biology. 52. Base your answer(s) to the following question(s) on the diagram below and on your knowledge of biology. Structure X most likely functions in the (1) transport of chemical messenger molecules into the cell nucleus (2) extraction of energy from nutrients (3) separation of cell contents from the outside environment Failure of structure A to function properly would most directly disrupt (1) autotrophic nutrition (2) chromosome replication (3) cellular communication (4) biological evolution (4) digestion of large molecules page 15
16 53. The diagram below represents a microscopic view of blood. Cell A protects the body by producing specific chemicals in response to pathogens. Cell A is 55. Hospital patients are often given intravenous fluids (IVs) to maintain proper levels of water and salts in the body. Great care is used in preparing these solutions. If a manufacturer accidentally prepared a batch of IV fluid that contained much more than the usual amount of salt, harm to the patient could result. The most likely effect on a patient if this incorrectly prepared IV fluid was used is that (1) a red blood cell (2) a bacteria cell (3) an insulin-producing cell (4) a white blood cell 54. In the diagram below, which letter indicates the part of the cell that carries out a function most similar to a function of the human excretory system? (1) water would move into body cells and cause them to burst (2) water would move out of body cells and cause them to dehydrate (3) salt and water would both move out of body cells and disrupt homeostasis (4) salt and water would both move into body cells and preserve homeostasis 56. The failure of the human body to effectively maintain dynamic equilibrium can result in (1) reproductive success (2) gene manipulation (3) differentiation (4) disease (1) A (2) B (3) C (4) D page 16
17 57. The diagram below represents what can happen when homeostasis in an organism is threatened. 59. A person with AIDS is likely to develop infectious diseases because the virus that causes AIDS (1) destroy cancerous cells (2) damages the immune system (3) increases the rate of antibody production Which statement provides a possible explanation for these events? (1) Antibiotics break down harmful substances by the process of digestion. (2) Some specialized cells mark and other cells engulf microbes during immune reactions. (3) Embryonic development of essential organs occurs during pregnancy. (4) Cloning removes abnormal cells produced during differentiation. 58. What usually results when an organism fails to maintain homeostasis? (1) Growth rates within organs become equal. (2) The organism becomes ill or may die. (3) A constant sugar supply for the cells is produced. (4) The water balance in the tissues of the organism stabilizes. (4) increase the rate of microbe destruction 60. When the antibiotic penicillin was first introduced, it was immediately effective in combating staphylococcus bacterial infections. After a number of years, there were outbreaks of staphylococcal infections that did not respond to treatment with penicillin. The best explanation for this situation is that (1) members of the original population of bacteria that were penicillin resistant survived and reproduced, creating a more resistant population (2) the bacteria that survived exposure to penicillin learned to avoid it (3) the bacteria that caused the new outbreaks were from populations that had never been exposed to penicillin (4) during each generation, the bacteria modified their own DNA to increase their ability to resist penicillin and passed this ability on to their descendants page 17
18 61. Typhoid fever, a disease that causes headaches, digestive upset, and a high fever, is caused by the bacterium Salmonella typhi. Typhoid can be spread from person to person by contaminated water or food or by a lack of cleanliness. Since the 19th century, the number of individuals infected with this disease has decreased. Which statement best explains why the number of people with this disease and other bacterial diseases has decreased over the last 100 years? (1) Scientists have corrected the damaged genes that cause typhoid fever and other infectious diseases. (2) Public health officials have placed better controls on the use of the toxic substances that cause these diseases. (3) Typhoid fever, like most other bacterial diseases, is often caused by a lack of proper nutrition. (4) Personal habits, such as hand washing, have greatly reduced contamination from bacteria. 63. Many viruses infect only a certain type of cell because they bind to certain (1) other viruses on the surface of the cell (2) mitochondria in the cell (3) hormones in the cell (4) receptor sites on the surface of the cell 64. Cells of the immune system are able to respond to the presence of invading organisms because they recognize the (1) antigens present on the invaders (2) antibodies present in invading pathogens (3) DNA pattern in the nuclei of viruses (4) antibiotics released from microbes 65. The human immune system fights infection by releasing 62. An infection in the body might result in a sudden (1) decrease in the activity of antigens produced by the mitochondria (2) decrease in the amount of DNA present in the nuclei of cells (3) increase in the activity of white blood cells (4) increase in the number of red blood cells (1) ATPs (2) antibiotics (3) antibodies (4) antigens page 18
19 66. An individual recovers from the common cold, which is caused by rhinovirus A. The person then becomes infected with the avian influenza virus, which causes the bird flu. Which statement best describes what will most likely happen to this person? 68. An activity that occurs in the human body is shown below. (1) He will have the symptoms of the bird flu because he is not immune to the avian influenza virus. (2) He will have the symptoms of the common cold because he is not immune to the avian influenza virus. (3) He will not have the symptoms of the bird flu because he is immune to rhinovirus A. (4) He will not have the symptoms of the common cold because the avian influenza virus causes it. 67. A 6-year-old child ate a peanut butter sandwich at snack time in school. Five minutes later, her throat became swollen and she collapsed. This allergic reaction occurred because her body (1) recognized an antigen in peanut butter and produced antibiotics against it (2) digested the white blood cells that can recognize an antigen in peanut butter (3) did not recognize an antigen in peanut butter and could not produce antibodies against it This activity helps to (1) provide protection against pathogens (2) produce antibiotics to control disease (3) eliminate harmful gene alterations (4) regulate production of ATP by the cell 69. Drugs to reduce the risk of rejection are given to organ transplant patients because the donated organ contains (1) foreign antigens (2) foreign antibodies (3) DNA molecules (4) pathogenic microbes (4) recognized an antigen in peanut butter and produced an immune response page 19
20 70. A new vaccine was developed and then tested on a large sample of individuals. This new vaccine will be considered effective if it helps prepare the body to fight future invasion by 72. Cellular communication is illustrated in the diagram below. (1) inhibiting the response of red blood cells (2) stimulating the reproduction of microbes (3) inhibiting the action of immune cells (4) stimulating the production of antibodies 71. A vaccine for the viral disease known as chicken pox would contain (1) a large amount of live virus (2) a dead or weakened form of the pathogen (3) several different antibiotics (4) a small number of white blood cells Information can be sent from (1) cell A to cell B because cell B is able to recognize signal 1 (2) cell A to cell B because cell A is able to recognize signal 2 (3) cell B to cell A because cell A is able to recognize signal 1 (4) cell B to cell A because cell B is able to recognize signal 2 page 20
21 73. The diagram below represents how HIV, the virus that causes AIDS, interacts with a certain type of white blood cell called a helper T-cell. What is one possible result of the cellular activity represented in the diagram? (1) Immune responses of an infected individual will be weakened. (2) The red blood cells of a person infected with AIDS will no longer be able to make antibodies. (3) This virus will strengthen future immune responses against blood-related diseases. 75. Base your answer(s) to the following question(s) on the information below and on your knowledge of biology. Diabetes is a condition characterized by elevated blood sugar levels. One form of diabetes occurs when insulin fails to properly regulate blood sugar levels. Complications from diabetes can include nerve cell damage and poor blood flow, especially in the feet and legs. In individuals with diabetes, wounds usually take longer than normal to heal. The failure of a cell to react in a normal manner to insulin is most likely the result of a problem with (1) vacuoles (2) receptors (3) mitochondria (4) sugars (4) Immune responses will prevent the spread of AIDS in humans. 74. Certain antibacterial soaps kill 99% of the bacteria present on hands. Constant use of these soaps could be harmful over time because (1) more pathogens may be resistant to the soap (2) microbes prevent viral diseases (3) large populations of pathogens are beneficial to the hands (4) the soap stimulates skin cell division page 21
22 76. Base your answer(s) to the following question(s) on the graph below and on your knowledge of biology. Which statement provides the best possible reason for the decrease in number of cases of bacterial pneumonia from 1940 to 1970? (1) As a result of genetic engineering, humans became immune to the bacteria. (2) Antibiotics were made available for the treatment of bacterial infections. (3) The bacteria did not respond to medical treatments. (4) As a result of sexual reproduction, the bacteria evolved into a harmless form. 77. Base your answer(s) to the following question(s) on the information below and on your knowledge of biology. The hedgehog, a small mammal native to Africa and Europe, has been introduced to the United States as an exotic pet species. Scientists have found that hedgehogs can transfer pathogens to humans and domestic animals. Foot-and-mouth viruses, Salmonella, and certain fungi are known pathogens carried by hedgehogs. As more and more of these exotic animals are brought into this country, the risk of infection increases in the human population. State one way the human immune system might respond to an invading pathogen associated with handling a hedgehog. 78. Base your answer(s) to the following question(s) on the diagram below and on your knowledge of biology. Vaccines Received by Children Patient Measles Vaccine Polio Vaccine child A child B child C Identify the system that will directly respond to these vaccines, and state the specific expected response. 79. State the specific expected result of administering these vaccines to child B. page 22
23 80. Base your answer to the following question on the information below and on your knowledge of biology. An Experimental SARS Vaccine Works in Animals Scientists reported that they had protected animals from the effects of the SARS virus by using an experimental vaccine. The SARS virus causes an acute respiratory illness in humans and other animals. This vaccine was sprayed once into the nostrils of each of four African green monkeys. Four weeks later, these monkeys were exposed to the virus that causes SARS. The monkeys showed no sign of the disease in their respiratory tracts. Blood tests confirmed the presence of proteins known as neutralizing antibodies that indicate protection against disease. The scientists also sprayed a placebo (a substance that did not contain the vaccine) into the nostrils of each of four other African green monkeys. After exposure to the virus that causes SARS, all of these monkeys developed symptoms of this condition. Briefly explain the nature of a vaccine and some steps that should be taken before a vaccine is available for public use. In your answer, be sure to include: a description of what a vaccine is 81. Base your answer(s) to the following question(s) on the information below and on your knowledge of biology. In order to enroll in most schools, students must be vaccinated against certain viral diseases, such as mumps. Even with these vaccinations, many students still suffer from other diseases. Discuss how a vaccination works and why some students still become infected with other diseases. State why a student vaccinated against mumps can still be infected by the pathogens that cause other diseases, such as chicken pox. 82. Base your answer(s) to the following question(s) on the information below and on your knowledge of biology. Proteins on the surface of a human cell and on a bird influenza virus are represented in the diagram below. Human Cell Bird In the space below, draw a change in the bird influenza virus that would allow it to infect this human cell. an explanation of why one group had a placebo sprayed into their nostrils before exposure to the virus an explanation of why scientists used monkeys to test the SARS vaccine a statement of what could be done to verify the results page 23
24 83. Explain how this change in the virus could come about. 84. Identify the relationship that exists between a virus and a human when the virus infects the human. 85. Base your answer to the following question on the information below and on your knowledge of biology. Botulinum toxin is a protein produced by the bacterium Clostridium botulinum. It causes a serious form of food poisoning in humans. In a very dilute form, it is also commonly used to eliminate some signs of aging, such as wrinkles. It does this by preventing nerves from releasing a chemical messenger called acetylcholine into the synapse (space between a nerve cell and a muscle cell). The toxin affects the process that causes the muscle cell to contract and form wrinkles. The diagram below represents a process that is involved in the formation of wrinkles. Complete the diagram by drawing an appropriate structure on the muscle cell membrane that would allow the nerve cell to communicate with the muscle cell. page 24
Unit 3 - Homeostasis in the Human Body
 Living Environment Practice Exam- Parts A and B-1 1. Base your answer to the following question on the diagram below and on your knowledge of biology. 6. Which diagram best represents a blood cell from
Living Environment Practice Exam- Parts A and B-1 1. Base your answer to the following question on the diagram below and on your knowledge of biology. 6. Which diagram best represents a blood cell from
Page 1. Name:
 Name: 5021-1 - Page 1 1) A student measures his pulse rate while he is watching television and records it. Next, he walks to a friend's house nearby and when he arrives, measures and records his pulse
Name: 5021-1 - Page 1 1) A student measures his pulse rate while he is watching television and records it. Next, he walks to a friend's house nearby and when he arrives, measures and records his pulse
6. The diagram below represents an interaction between parts of an organism.
 Endocrine Review 1. Base your answer to the following question on the diagram below and on your knowledge of biology. Each arrow in the diagram represents a different hormone released by the pituitary
Endocrine Review 1. Base your answer to the following question on the diagram below and on your knowledge of biology. Each arrow in the diagram represents a different hormone released by the pituitary
Page 1. Name: UNIT: HOMEOSTASIS TOPIC: LIFE FUNCTIONS AND MAINTENANCE OF HOMEOSTASIS
 Name: 9771-1 - Page 1 UNIT: HOMEOSTASIS TOPIC: LIFE FUNCTIONS AND MAINTENANCE OF HOMEOSTASIS 1) The arrows in the diagram below indicate the movement of materials into and out of a single-celled organism.
Name: 9771-1 - Page 1 UNIT: HOMEOSTASIS TOPIC: LIFE FUNCTIONS AND MAINTENANCE OF HOMEOSTASIS 1) The arrows in the diagram below indicate the movement of materials into and out of a single-celled organism.
Immune System Review. 1. State one way white blood cells protect the body from foreign microbes.
 Name Immune System Review Date 1. State one way white blood cells protect the body from foreign microbes. 2. Cells of the immune system are able to respond to the presence of invading organisms because
Name Immune System Review Date 1. State one way white blood cells protect the body from foreign microbes. 2. Cells of the immune system are able to respond to the presence of invading organisms because
Cell Organelles, Communication and Transport. A. A gametes; B zygote. B. A zygote; B gametes. C. A organs; B organelles. D. A organelles; B organs
 ell Organelles, ommunication and Transport Name: ate: 1. The diagram below represents a cell of a green plant. 3. Some levels of organization in a multicellular organism are shown in the sequence below.
ell Organelles, ommunication and Transport Name: ate: 1. The diagram below represents a cell of a green plant. 3. Some levels of organization in a multicellular organism are shown in the sequence below.
Unit 2 - Characteristics of Living Things
 Living Environment Answer Key to Practice Exam- Parts A and B-1 1. A fully functioning enzyme molecule is arranged in a complex three-dimensional shape. This shape determines the A) specific type of molecule
Living Environment Answer Key to Practice Exam- Parts A and B-1 1. A fully functioning enzyme molecule is arranged in a complex three-dimensional shape. This shape determines the A) specific type of molecule
bacteria review 1. Which of the following structures is not found in bacteria?
 Name: Date: 1. Which of the following structures is not found in bacteria? 5. How do human diseases caused by bacteria and diseases caused by viruses react to antibiotics? A. ribosome B. cytoplasm C. cell
Name: Date: 1. Which of the following structures is not found in bacteria? 5. How do human diseases caused by bacteria and diseases caused by viruses react to antibiotics? A. ribosome B. cytoplasm C. cell
Name # Class Date Human Body Systems Take Home Test
 Name # Class Date Human Body Systems Take Home Test 1. In the knee, the ends of the leg bones are held together primarily by A) ligaments B) smooth muscle C) tendons D) cardiac muscle 2. Which two structures
Name # Class Date Human Body Systems Take Home Test 1. In the knee, the ends of the leg bones are held together primarily by A) ligaments B) smooth muscle C) tendons D) cardiac muscle 2. Which two structures
Mid Term Review. 1. step 1, only 3. both step 1 and step 2 2. step 2, only 4. neither step 1 nor step 2
 Name Mid Term Review 1. Diagrams, tables, and graphs are used by scientists mainly to 1. design a research plan for an experiment 3. organize data 2. test a hypothesis 4. predict the independent variable
Name Mid Term Review 1. Diagrams, tables, and graphs are used by scientists mainly to 1. design a research plan for an experiment 3. organize data 2. test a hypothesis 4. predict the independent variable
Topic 1: Chemistry of Living Things
 1. Some processes that occur in a cell are listed below.1 utilize energy 2 detect changes in the environment 3 rearrange and synthesize chemical compounds 4. The diagram below represents a sequence of
1. Some processes that occur in a cell are listed below.1 utilize energy 2 detect changes in the environment 3 rearrange and synthesize chemical compounds 4. The diagram below represents a sequence of
Answer the following questions to the best of your ability.
 Answer the following questions to the best of your ability. 1. Which statement best describes cellular respiration? A) It occurs in animal cells but not in plant cells. B) It converts energy in food into
Answer the following questions to the best of your ability. 1. Which statement best describes cellular respiration? A) It occurs in animal cells but not in plant cells. B) It converts energy in food into
HOMEOSTASIS & IMMUNITY Week Two Packet
 Ms. Scott HOMEOSTASIS & IMMUNITY Week Two Packet Packet Grade: / 9 Completed notes / 30 Completed Classwork / 30 Completed Homework / 10 Packet turned in on time / 1 Name and Class are filled in / 80 Total
Ms. Scott HOMEOSTASIS & IMMUNITY Week Two Packet Packet Grade: / 9 Completed notes / 30 Completed Classwork / 30 Completed Homework / 10 Packet turned in on time / 1 Name and Class are filled in / 80 Total
Name # Class Regents Review: Characteristics of Life and Biochemistry
 Name # Class Regents Review: Characteristics of Life and Biochemistry 6. Some processes that occur in a cell are listed below. A. utilize energy B. detect changes in the environment C. rearrange and synthesize
Name # Class Regents Review: Characteristics of Life and Biochemistry 6. Some processes that occur in a cell are listed below. A. utilize energy B. detect changes in the environment C. rearrange and synthesize
Unit 4: Summary. Similarities and Differences Between Living Things
 Unit 4: Summary Similarities and Differences Between Living Things Review cell theory All living things made of cells Cells perform life functions Cells come from pre existing cells What are life functions?
Unit 4: Summary Similarities and Differences Between Living Things Review cell theory All living things made of cells Cells perform life functions Cells come from pre existing cells What are life functions?
8.L.1 Practice Questions
 Name: Date: 1. Why should antibiotics be given to a person who is ill with a bacterial disease like strep throat, but not to a person who has a viral disease like flu?. ntibiotics kill bacteria but not
Name: Date: 1. Why should antibiotics be given to a person who is ill with a bacterial disease like strep throat, but not to a person who has a viral disease like flu?. ntibiotics kill bacteria but not
***Non-living things may show one or more of these Characteristics, but NEVER ALL of them
 -Living things are highly ORGANIZED -Living things are made up of one or more CELLS -Living things use ENERGY -Living things GROW and develop -Living things RESPOND to changes in the environment -Living
-Living things are highly ORGANIZED -Living things are made up of one or more CELLS -Living things use ENERGY -Living things GROW and develop -Living things RESPOND to changes in the environment -Living
UNIT 2 - Structure and Function (ORGANS & SYSTEMS)
 UNIT 2 - Structure and Function (ORGANS & SYSTEMS) Enduring Understandings and Essential Questions 1. All living things rely on the same processes to stay alive. 2. The components of living things, from
UNIT 2 - Structure and Function (ORGANS & SYSTEMS) Enduring Understandings and Essential Questions 1. All living things rely on the same processes to stay alive. 2. The components of living things, from
Biochemical Processes are the chemical processes that occur in living things
 -The internal stability that organisms maintain is known as HOMEOSTASIS Ex: maintaining normal body temperature Biochemical Processes are the chemical processes that occur in living things -All organisms
-The internal stability that organisms maintain is known as HOMEOSTASIS Ex: maintaining normal body temperature Biochemical Processes are the chemical processes that occur in living things -All organisms
Renaissance Biology Midterm Study Guide Answers
 Renaissance Biology Midterm Study Guide Answers 2016-2017 LEARNING TARGET 1: List the characteristics of life Made of one or more cells Organization cells -> tissues -> organs -> organ systems -> organisms
Renaissance Biology Midterm Study Guide Answers 2016-2017 LEARNING TARGET 1: List the characteristics of life Made of one or more cells Organization cells -> tissues -> organs -> organ systems -> organisms
OPTIONAL GRADE 8 STUDY PACKET IMMUNE SYSTEM SC.6.L.14.5 AA
 OPTIONAL GRADE 8 STUDY PACKET IMMUNE SYSTEM SC.6.L.14.5 AA SC.6.L.14.5 AA Identify and investigate the general functions of the major systems of the human body (digestive, respiratory, circulatory, reproductive,
OPTIONAL GRADE 8 STUDY PACKET IMMUNE SYSTEM SC.6.L.14.5 AA SC.6.L.14.5 AA Identify and investigate the general functions of the major systems of the human body (digestive, respiratory, circulatory, reproductive,
Infectious Diseases through Viruses. Obj. 3.c. & 3.g.
 Infectious Diseases through Viruses Obj. 3.c. & 3.g. Diseases Caused By Cells A disease is a condition that stops the body from functioning normally. Non-infectious diseases are not spread from person
Infectious Diseases through Viruses Obj. 3.c. & 3.g. Diseases Caused By Cells A disease is a condition that stops the body from functioning normally. Non-infectious diseases are not spread from person
REVIEW SHEET HOMEOSTASIS
 1. What is Homeostasis? The maintenance of stable/constant internal environment despite changing external environment What is another term for Homeostasis? Dynamic Equilibrium Active Balancing 2.What is
1. What is Homeostasis? The maintenance of stable/constant internal environment despite changing external environment What is another term for Homeostasis? Dynamic Equilibrium Active Balancing 2.What is
10. The diagram below shows two different kinds of substances, A and B, entering a cell.
 1. In the binomial system of nomenclature, which two classification groups provide the scientific name of an organism? A) kingdom and phylum B) phylum and species C) kingdom and genus D) genus and species
1. In the binomial system of nomenclature, which two classification groups provide the scientific name of an organism? A) kingdom and phylum B) phylum and species C) kingdom and genus D) genus and species
Life Science Unit I. 4. Use the diagram to answer the question. 1. Eukaryotic cells are differentiated from prokaryotic cells because eukaryotic cells
 Name: ate: 1. Eukaryotic cells are differentiated from prokaryotic cells because eukaryotic cells. are much smaller. 4. Use the diagram to answer the question. ell iagram. have permeable membranes.. have
Name: ate: 1. Eukaryotic cells are differentiated from prokaryotic cells because eukaryotic cells. are much smaller. 4. Use the diagram to answer the question. ell iagram. have permeable membranes.. have
Name # Class Regents Review Human Body Systems
 Name # Class Regents Review Human Body Systems 1. An accident resulted in a man's hand being cut off from his arm. Paramedics arriving first on the scene placed the cut-off hand in ice. The man and his
Name # Class Regents Review Human Body Systems 1. An accident resulted in a man's hand being cut off from his arm. Paramedics arriving first on the scene placed the cut-off hand in ice. The man and his
Unit 1: Science of Life 1. Define the following terms: Hypothesis: Testable explanation for a phenomenon
 UCS BIOLOGY STUDY GUIDE FOR 1 ST SEMESTER MIDTERM EXAM 2014-2015 Unit 1: Science of Life 1. Define the following terms: Hypothesis: Testable explanation for a phenomenon Experiment: an orderly procedure
UCS BIOLOGY STUDY GUIDE FOR 1 ST SEMESTER MIDTERM EXAM 2014-2015 Unit 1: Science of Life 1. Define the following terms: Hypothesis: Testable explanation for a phenomenon Experiment: an orderly procedure
Anatomy & Physiology Student Edition. 1. Which list shows different levels or organization within a population ordered from least to most complex?
 Name: Date: 1. Which list shows different levels or organization within a population ordered from least to most complex? A. organ systems, organs, organelles, organisms B. organelles, organs, organ systems,
Name: Date: 1. Which list shows different levels or organization within a population ordered from least to most complex? A. organ systems, organs, organelles, organisms B. organelles, organs, organ systems,
Page 1. Name:
 Name: 4734-1 - Page 1 Warts result when certain viruses cause skin cells to reproduce at a high rate. This rapid reproduction of skin cells is due to the viruses stimulating cellular digestion mitotic
Name: 4734-1 - Page 1 Warts result when certain viruses cause skin cells to reproduce at a high rate. This rapid reproduction of skin cells is due to the viruses stimulating cellular digestion mitotic
Digestive and Excretory Systems
 Digestive and Excretory Systems Homeostasis Q: How are the materials that enter and leave your body related to the processes that maintain homeostasis? 30.1 How is the human body organized and regulated?
Digestive and Excretory Systems Homeostasis Q: How are the materials that enter and leave your body related to the processes that maintain homeostasis? 30.1 How is the human body organized and regulated?
Human Body Systems. Long narrow tube mixes enzymes with food Small nutrient molecules diffuse into blood
 Human Body Systems Living Environment AIS Mr. DuRoss Digestive System : Break down large food molecules into smaller parts that the body can use Mouth Esophagus Stomach Small intestine Large intestine
Human Body Systems Living Environment AIS Mr. DuRoss Digestive System : Break down large food molecules into smaller parts that the body can use Mouth Esophagus Stomach Small intestine Large intestine
Homeostasis Practice Test
 Name: ate: 1. Which statement explains the importance of maintaining a constant internal environment to ensure proper enzyme functioning? A. hanges in ph and temperature will cause the enzyme reaction
Name: ate: 1. Which statement explains the importance of maintaining a constant internal environment to ensure proper enzyme functioning? A. hanges in ph and temperature will cause the enzyme reaction
1. Arrows A, B, and C in the diagram below represent the processes necessary to make the energy stored in food available for muscle activity.
 1. Arrows A, B, and C in the diagram below represent the processes necessary to make the energy stored in food available for muscle activity. The correct sequence of processes represented by A, B, and
1. Arrows A, B, and C in the diagram below represent the processes necessary to make the energy stored in food available for muscle activity. The correct sequence of processes represented by A, B, and
Lecture 10 Immune System
 Lecture 10 Immune System Lecture 10 1. Introduction 2. Nonspecific External Defenses 3. Innate Immune Response 4. Acquired Immune Response 5. Antibiotics and Vaccines 1 The not-so-common cold A cold is
Lecture 10 Immune System Lecture 10 1. Introduction 2. Nonspecific External Defenses 3. Innate Immune Response 4. Acquired Immune Response 5. Antibiotics and Vaccines 1 The not-so-common cold A cold is
Chapter 8 Review. 4. Scientists do not consider viruses as true living organisms because they
 Chapter 8 Review Multiple Choice 1. A disruption of homeostasis can result in all of the following except A. illness C. disease B. death D. stability 2. Infectious diseases result from A. genetic defects
Chapter 8 Review Multiple Choice 1. A disruption of homeostasis can result in all of the following except A. illness C. disease B. death D. stability 2. Infectious diseases result from A. genetic defects
Topic 1: Living Things
 Topic 1: Living Things Organization of living things: Cells are the smallest units of. are the structures inside the cell. Nucleus- Contains (genetic information) that controls the production of - Read
Topic 1: Living Things Organization of living things: Cells are the smallest units of. are the structures inside the cell. Nucleus- Contains (genetic information) that controls the production of - Read
OPTIONAL BIOLOGY 1 STUDY PACKET IMMUNE SYSTEM SC.912.L AA
 OPTIONAL BIOLOGY 1 STUDY PACKET IMMUNE SYSTEM SC.912.L.14.52 AA SC.912.L.14.52 AA Explain the basic functions of the human immune system, including specific and nonspecific immune response, vaccines and
OPTIONAL BIOLOGY 1 STUDY PACKET IMMUNE SYSTEM SC.912.L.14.52 AA SC.912.L.14.52 AA Explain the basic functions of the human immune system, including specific and nonspecific immune response, vaccines and
Introduction to Body Systems
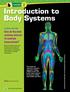 Lesson 1 Introduction to Body Systems ESSENTIAL QUESTION How do the body systems interact to maintain homeostasis? By the end of this lesson, you should be able to describe the functions of the human body
Lesson 1 Introduction to Body Systems ESSENTIAL QUESTION How do the body systems interact to maintain homeostasis? By the end of this lesson, you should be able to describe the functions of the human body
4. Base your answer to the following question on the diagram below and on your knowledge of biology.
 1. A blind student runs his fingers along a page of braille. Another student reads a page printed in a textbook. Both students are able to obtain and process the information most directly as a result of
1. A blind student runs his fingers along a page of braille. Another student reads a page printed in a textbook. Both students are able to obtain and process the information most directly as a result of
Lecture 10 Immune System
 Lecture 10 Immune System Lecture 10 1. Introduction 2. Nonspecific External Defenses 3. Innate Immune Response 4. Acquired Immune Response 5. Antibiotics and Vaccines 1 The not-so-common cold A cold is
Lecture 10 Immune System Lecture 10 1. Introduction 2. Nonspecific External Defenses 3. Innate Immune Response 4. Acquired Immune Response 5. Antibiotics and Vaccines 1 The not-so-common cold A cold is
Name # Class Regents Review Human Body Systems
 Name # Class Regents Review Human Body Systems 1. An accident resulted in a man's hand being cut off from his arm. Paramedics arriving first on the scene placed the cut-off hand in ice. The man and his
Name # Class Regents Review Human Body Systems 1. An accident resulted in a man's hand being cut off from his arm. Paramedics arriving first on the scene placed the cut-off hand in ice. The man and his
Anatomy and Physiology 2
 Anatomy and Physiology 2 The Nervous System Nerves allows organisms to detect and respond to stimuli by transmitting electrical impulses cell to cell. Can send info at high speeds! Neurons are the smallest
Anatomy and Physiology 2 The Nervous System Nerves allows organisms to detect and respond to stimuli by transmitting electrical impulses cell to cell. Can send info at high speeds! Neurons are the smallest
Disease: any change, other than an injury, that disrupts homeostasis. Pathogen: disease-causing agent such as bacteria, virus, etc.
 The Immune System Disease: any change, other than an injury, that disrupts homeostasis. Pathogen: disease-causing agent such as bacteria, virus, etc. Infectious disease- caused by pathogen Germ theory
The Immune System Disease: any change, other than an injury, that disrupts homeostasis. Pathogen: disease-causing agent such as bacteria, virus, etc. Infectious disease- caused by pathogen Germ theory
DISEASE HOW ARE DISEASES SPREAD?
 DISEASE HOW ARE DISEASES SPREAD? Starter: How is your body like a castle? Our skin is like the castle walls but microbes can enter through gaps in the defences AIM Can use simple physical models to show
DISEASE HOW ARE DISEASES SPREAD? Starter: How is your body like a castle? Our skin is like the castle walls but microbes can enter through gaps in the defences AIM Can use simple physical models to show
Unit 4: Summary. Similarities and Differences Between Living Things
 Unit 4: Summary Similarities and Differences Between Living Things Review cell theory All living things made of cells Cells perform life functions Cells come from pre existing cells What are life functions?
Unit 4: Summary Similarities and Differences Between Living Things Review cell theory All living things made of cells Cells perform life functions Cells come from pre existing cells What are life functions?
Ms. Golub & Ms. Sahar Date: Unit 2- Test #1
 Name Ms. Golub & Ms. Sahar Date: Unit 2- Test #1 1. The interaction between guard cells and a leaf opening would not be involved in A) diffusion of carbon dioxide B) maintaining homeostasis C) heterotrophic
Name Ms. Golub & Ms. Sahar Date: Unit 2- Test #1 1. The interaction between guard cells and a leaf opening would not be involved in A) diffusion of carbon dioxide B) maintaining homeostasis C) heterotrophic
Biology: Life processes are performed at the cellular level
 Biology: Life processes are performed at the cellular level What is life? What are its applications? What is the relationship between micro-organisms and macro-organisms? Student Objectives Statement Beginning
Biology: Life processes are performed at the cellular level What is life? What are its applications? What is the relationship between micro-organisms and macro-organisms? Student Objectives Statement Beginning
Test Review: Animal Systems
 Name: Date: Period: Test Review: Animal Systems This review is due on the day of your Animal Systems test. 1. Overview of Animals a. What is Homeostasis? b. Complete the levels of organization: Cells Organism
Name: Date: Period: Test Review: Animal Systems This review is due on the day of your Animal Systems test. 1. Overview of Animals a. What is Homeostasis? b. Complete the levels of organization: Cells Organism
Name: Teacher: Ms. Petrakos. Lesson #21 - Cell Transport Diffusion Review
 Name: Teacher: Ms. Petrakos Lesson #21 - Cell Transport Diffusion Review Figure 1 Base your answer to the question on the diagram below and on your knowledge of biology. The diagram represents an experimental
Name: Teacher: Ms. Petrakos Lesson #21 - Cell Transport Diffusion Review Figure 1 Base your answer to the question on the diagram below and on your knowledge of biology. The diagram represents an experimental
Laughter and the Body Systems
 Laughter and the Body Systems Laughter causes the lungs to pump out carbon dioxide, the eyes to cleanse themselves with tears, the muscles to relax, the flow of adrenaline to increase, and the cardiovascular
Laughter and the Body Systems Laughter causes the lungs to pump out carbon dioxide, the eyes to cleanse themselves with tears, the muscles to relax, the flow of adrenaline to increase, and the cardiovascular
PAP System Interaction in Animals How to systems interact to perform the function of regulation in animals? homeostasis Feedback inhibition
 PAP System Interaction in Animals How to systems interact to perform the function of regulation in animals? Animals contain a wide variety of organ systems that act together to help the individual survive.
PAP System Interaction in Animals How to systems interact to perform the function of regulation in animals? Animals contain a wide variety of organ systems that act together to help the individual survive.
C) amount of carbon dioxide absorbed by the animal B) rate of respiration of the animal
 Name: 1) A model of a section of a cell membrane is represented below. 4034-1 - Page 1 Which type of molecule is indicated by the arrow? A) carbohydrate B) protein C) lipid D) nucleotide 2) The movement
Name: 1) A model of a section of a cell membrane is represented below. 4034-1 - Page 1 Which type of molecule is indicated by the arrow? A) carbohydrate B) protein C) lipid D) nucleotide 2) The movement
UNIT 2 - Structure and Function (ORGANS & SYSTEMS)
 UNIT 2 - Structure and Function (ORGANS & SYSTEMS) Enduring Understandings and Essential Questions 1. All living things rely on the same processes to stay alive. 2. The components of living things, from
UNIT 2 - Structure and Function (ORGANS & SYSTEMS) Enduring Understandings and Essential Questions 1. All living things rely on the same processes to stay alive. 2. The components of living things, from
Regents Review Assignment #12-J07 Living Environment: Comet Part A Questions
 Part A Questions 1. A protein on the surface of HIV can attach to proteins on the surface of healthy human cells. These attachment sites on the surface of the cells are known as (1) receptor molecules
Part A Questions 1. A protein on the surface of HIV can attach to proteins on the surface of healthy human cells. These attachment sites on the surface of the cells are known as (1) receptor molecules
Chapter 6: Fighting Disease
 Chapter 6: Fighting Disease Lesson 1: Infectious Disease How Do Pathogens Cause Disease? Ancient times, people had different ideas about what caused disease. - Evil spirits - Swamp air - Imbalance of four
Chapter 6: Fighting Disease Lesson 1: Infectious Disease How Do Pathogens Cause Disease? Ancient times, people had different ideas about what caused disease. - Evil spirits - Swamp air - Imbalance of four
Cell Organization, Nutrition, Digestion, and Excretion
 Cell Organization, Nutrition, Digestion, and Excretion Cell Organization: 1. Put these terms in order from least complex to most complex: Tissue, cell, organ, organelle, organism, organ system 1. Organelle
Cell Organization, Nutrition, Digestion, and Excretion Cell Organization: 1. Put these terms in order from least complex to most complex: Tissue, cell, organ, organelle, organism, organ system 1. Organelle
Question What is the function of the immune system? Answer:
 Q1 How quickly do bacteria reproduce in ideal conditions? Every 20 minutes. Q2 If you start with 1 bacterium that reproduces every 20 minutes, how many bacteria will you have after 5 hours? 32768 Q3 Give
Q1 How quickly do bacteria reproduce in ideal conditions? Every 20 minutes. Q2 If you start with 1 bacterium that reproduces every 20 minutes, how many bacteria will you have after 5 hours? 32768 Q3 Give
Living Environment. Scientific Inquiry Exam
 Name: Class: 1. Which elements are present in all organic compounds? 1) nitrogen and carbon 3) hydrogen and oxygen 2) nitrogen and oxygen 4) hydrogen and carbon 2. Which substances are inorganic compounds?
Name: Class: 1. Which elements are present in all organic compounds? 1) nitrogen and carbon 3) hydrogen and oxygen 2) nitrogen and oxygen 4) hydrogen and carbon 2. Which substances are inorganic compounds?
8 LIFE PROCESSES NUTRITION TRANSPORT REGULATION SYNTHESIS EXCRETION GROWTH REPRODUCTION RESPIRATION
 8 LIFE PROCESSES NUTRITION REGULATION EXCRETION REPRODUCTION TRANSPORT SYNTHESIS GROWTH RESPIRATION LIFE PROCESSES Nutrition (ingestion, digestion, egestion) 1- Nutrients are used by all living things
8 LIFE PROCESSES NUTRITION REGULATION EXCRETION REPRODUCTION TRANSPORT SYNTHESIS GROWTH RESPIRATION LIFE PROCESSES Nutrition (ingestion, digestion, egestion) 1- Nutrients are used by all living things
Bacteria and Viruses
 CHAPTER 13 LESSON 3 Bacteria and Viruses What are viruses? Key Concepts What are viruses? How do viruses affect human health? What do you think? Read the two statements below and decide whether you agree
CHAPTER 13 LESSON 3 Bacteria and Viruses What are viruses? Key Concepts What are viruses? How do viruses affect human health? What do you think? Read the two statements below and decide whether you agree
Warm Up Where in a flower would you find xylem and phloem? 2. Where in a flower would you find palisade cells?
 Body Systems Warm Up 4-4-16 1. Where in a flower would you find xylem and phloem? 2. Where in a flower would you find palisade cells? 3. Where in a flower would you find root hair cells? 4. What organelle
Body Systems Warm Up 4-4-16 1. Where in a flower would you find xylem and phloem? 2. Where in a flower would you find palisade cells? 3. Where in a flower would you find root hair cells? 4. What organelle
Cell Processes Review
 1. Most green algae are able to obtain carbon dioxide from the environment and use it to synthesize organic compounds. This activity is an example of 1) hydrolysis 2) saprophytism 3) cellular respiration
1. Most green algae are able to obtain carbon dioxide from the environment and use it to synthesize organic compounds. This activity is an example of 1) hydrolysis 2) saprophytism 3) cellular respiration
Homeostasis Overview
 Homeostasis Overview Vocabulary: cell, tissue, organ, organ system, homeostasis/dynamic equilibrium/steady state, dynamic equilibrium, feedback mechanism, stimulus, response, insulin, glycogen Levels of
Homeostasis Overview Vocabulary: cell, tissue, organ, organ system, homeostasis/dynamic equilibrium/steady state, dynamic equilibrium, feedback mechanism, stimulus, response, insulin, glycogen Levels of
The Immune System: Your Defense Against Disease
 The Immune System: Your Defense Against Disease Terms: Immune System: body s primary defense against disease-causing microorganisms. Immune: condition in which a body is able to permanently fight a disease.
The Immune System: Your Defense Against Disease Terms: Immune System: body s primary defense against disease-causing microorganisms. Immune: condition in which a body is able to permanently fight a disease.
Chapter 40 The Immune System and Disease Section Review Reviewing Key Concepts. Reviewing Key Skills
 Chapter 40 The Immune System and Disease Section Review 40-1 Short Answer On the lines provided, answer the following: 1. What is a disease? 2. What are three general causes of disease? 3. Name the four
Chapter 40 The Immune System and Disease Section Review 40-1 Short Answer On the lines provided, answer the following: 1. What is a disease? 2. What are three general causes of disease? 3. Name the four
Q2: What is the circulatory system composed of? The heart and blood vessels (arteries, veins & capillaries).
 Q1: What is the word equation for aerobic respiration? Q2: What is the circulatory system composed of? Q3: How is glucose transported in plants? Glucose + Oxygen Carbon dioxide + water The heart and blood
Q1: What is the word equation for aerobic respiration? Q2: What is the circulatory system composed of? Q3: How is glucose transported in plants? Glucose + Oxygen Carbon dioxide + water The heart and blood
SEPUP ITEM BANK. Item Banks TR-253. Multiple choice. Circle the best answer.
 Item Banks Name: Teacher: School: Date: SEPUP ITEM BANK UNIT C: CELL BIOLOGY AND DISEASE Multiple choice. Circle the best answer. 1. Which of the following graphs best represents how an infectious disease
Item Banks Name: Teacher: School: Date: SEPUP ITEM BANK UNIT C: CELL BIOLOGY AND DISEASE Multiple choice. Circle the best answer. 1. Which of the following graphs best represents how an infectious disease
Organ Systems (ch21-26) Practice Questions. Name:
 1. Which one of the following types of tissue stores fat in the body? A) blood B) cartilage C) bone D) adipose tissue E) fibrous connective tissue 2. Which of the following tissues does not match its function?
1. Which one of the following types of tissue stores fat in the body? A) blood B) cartilage C) bone D) adipose tissue E) fibrous connective tissue 2. Which of the following tissues does not match its function?
Figure 1. Base your answer to the question on the information and diagram below and on your knowledge of biology.
 Name: Teacher: Lathrop Topic 3 cells CR HW #3 Figure 1 Base your answer to the question on the information and diagram below and on your knowledge of biology. Using a microscope and a wet-mount slide,
Name: Teacher: Lathrop Topic 3 cells CR HW #3 Figure 1 Base your answer to the question on the information and diagram below and on your knowledge of biology. Using a microscope and a wet-mount slide,
Exampro GCSE Biology. B2.1 Cells. Name: Class: Foundation tier. Author: Date: Time: 81. Marks: 81. Comments: Page 1 of 27
 Exampro GCSE Biology B2. Cells Foundation tier Name: Class: Author: Date: Time: 8 Marks: 8 Comments: Page of 27 Q. Diabetes is a disease in which the concentration of glucose in a person s blood may rise
Exampro GCSE Biology B2. Cells Foundation tier Name: Class: Author: Date: Time: 8 Marks: 8 Comments: Page of 27 Q. Diabetes is a disease in which the concentration of glucose in a person s blood may rise
To be able to answer a question
 1. State Problem or question 2. Gather information 3. State a hypothesis 4. Conduct Experiment 5. Observe, collect, & analyze data 6. State a conclusion7. Repeat many times Observation =Recognizing a FACT
1. State Problem or question 2. Gather information 3. State a hypothesis 4. Conduct Experiment 5. Observe, collect, & analyze data 6. State a conclusion7. Repeat many times Observation =Recognizing a FACT
Unit 2 Warm Ups. Equilibrium
 Unit 2 Warm Ups Equilibrium 1. Cell wall 2. Mitochondria 3. Chloroplast 4. Vesicle 5. Vacuole 6. Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum 7. Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum 8. Cytoskeleton 9. Lysosomes 10.Cell Membrane
Unit 2 Warm Ups Equilibrium 1. Cell wall 2. Mitochondria 3. Chloroplast 4. Vesicle 5. Vacuole 6. Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum 7. Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum 8. Cytoskeleton 9. Lysosomes 10.Cell Membrane
What is the function of the urinary system? How do the kidneys filter the blood? What are common problems with the urinary system?
 CHAPTER 24 2 The Urinary System SECTION The Digestive and Urinary Systems BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is the function of the urinary
CHAPTER 24 2 The Urinary System SECTION The Digestive and Urinary Systems BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is the function of the urinary
Biochemistry Regents Practice
 iochemistry Regents Practice Name: Date: 1. The diagram below represents a sequence of events that occurs in living things. 3. Which statement describes a similarity between all enzymes, antibodies, and
iochemistry Regents Practice Name: Date: 1. The diagram below represents a sequence of events that occurs in living things. 3. Which statement describes a similarity between all enzymes, antibodies, and
The Human Body. Mrs. Green
 The Human Body Mrs. Green Bell Work Which of the following helps the body to cool down? a) Shivering b) Sweating c) Running a fever d) Taking a deep breath Which of the following is a function of the digestive
The Human Body Mrs. Green Bell Work Which of the following helps the body to cool down? a) Shivering b) Sweating c) Running a fever d) Taking a deep breath Which of the following is a function of the digestive
The Living Environment
 Name: Class: 1. Asexual reproduction primarily involves the process of 1) pollination 3) spermatogenesis 2) mitosis 4) ovulation The Living Environment Ms. Fazio Base your answers to questions 4 and 5
Name: Class: 1. Asexual reproduction primarily involves the process of 1) pollination 3) spermatogenesis 2) mitosis 4) ovulation The Living Environment Ms. Fazio Base your answers to questions 4 and 5
Multicellular living things are able to divide up the labor required to perform life functions between the different levels of organization ( organs
 Multicellular living things are able to divide up the labor required to perform life functions between the different levels of organization ( organs and organ systems). A multicellular living thing will
Multicellular living things are able to divide up the labor required to perform life functions between the different levels of organization ( organs and organ systems). A multicellular living thing will
Interactions Among Animal Systems. Biology 10(A)
 Interactions Among Animal Systems Biology 10(A) Interactions Among Animal Systems Learning Objectives Identify major organ systems in animals Describe the interactions that occur among systems to carry
Interactions Among Animal Systems Biology 10(A) Interactions Among Animal Systems Learning Objectives Identify major organ systems in animals Describe the interactions that occur among systems to carry
Campbell's Biology: Concepts and Connections, 7e (Reece et al.) Chapter 24 The Immune System Multiple-Choice Questions
 Campbell's Biology: Concepts and Connections, 7e (Reece et al.) Chapter 24 The Immune System 24.1 Multiple-Choice Questions 1) The body's innate defenses against infection include A) several nonspecific
Campbell's Biology: Concepts and Connections, 7e (Reece et al.) Chapter 24 The Immune System 24.1 Multiple-Choice Questions 1) The body's innate defenses against infection include A) several nonspecific
Microorganisms. 3. Which of the following is one important difference between a virus and a bacterial cell?
 Name: ate: 1. How does a virus cause a person to develop a common cold? 3. Which of the following is one important difference between a virus and a bacterial cell? A. invades the host cell to reproduce.
Name: ate: 1. How does a virus cause a person to develop a common cold? 3. Which of the following is one important difference between a virus and a bacterial cell? A. invades the host cell to reproduce.
Section 40 1 Infectious Disease (pages )
 Chapter 40 The Immune System and Disease Section 40 1 Infectious Disease (pages 1031 1035) Key Concepts What causes disease? How are infectious diseases transmitted? Introduction (page 1031) 1. Any change,
Chapter 40 The Immune System and Disease Section 40 1 Infectious Disease (pages 1031 1035) Key Concepts What causes disease? How are infectious diseases transmitted? Introduction (page 1031) 1. Any change,
Section 40 1 Infectious Disease (pages )
 Chapter 40 The Immune System and Disease Section 40 1 Infectious Disease (pages 1031 1035) What causes disease? How are infectious diseases transmitted? Introduction (page 1031) 1 Any change, other than
Chapter 40 The Immune System and Disease Section 40 1 Infectious Disease (pages 1031 1035) What causes disease? How are infectious diseases transmitted? Introduction (page 1031) 1 Any change, other than
Unit 13.2: Viruses. Vocabulary capsid latency vaccine virion
 Unit 13.2: Viruses Lesson Objectives Describe the structure of viruses. Outline the discovery and origins of viruses. Explain how viruses replicate. Explain how viruses cause human disease. Describe how
Unit 13.2: Viruses Lesson Objectives Describe the structure of viruses. Outline the discovery and origins of viruses. Explain how viruses replicate. Explain how viruses cause human disease. Describe how
Science 8 Unit 1 Pack:
 Science 8 Unit 1 Pack: Name Section 1: Observing Living Things Living things have characteristics that help them survive in their environment Small organisms can observed with the help of microscopes Words
Science 8 Unit 1 Pack: Name Section 1: Observing Living Things Living things have characteristics that help them survive in their environment Small organisms can observed with the help of microscopes Words
S7L Which part of the body receives messages transmitted by nerve cells located throughout the body?
 S7L2-3 1. Which of the following is the heart's function? A. pumping blood B. breaking down food C. removing wastes from the blood D. taking in oxygen and releasing carbon dioxide 2. The body takes in
S7L2-3 1. Which of the following is the heart's function? A. pumping blood B. breaking down food C. removing wastes from the blood D. taking in oxygen and releasing carbon dioxide 2. The body takes in
*Hierarchical Organization of Multicellular Organisms
 *Hierarchical Organization of Multicellular Organisms 7.L.1.3 - Summarize the hierarchical organization of multicellular organisms from cells to tissues to organs to systems to organisms. Table of Contents
*Hierarchical Organization of Multicellular Organisms 7.L.1.3 - Summarize the hierarchical organization of multicellular organisms from cells to tissues to organs to systems to organisms. Table of Contents
NCERT SOLUTIONS OF Life Processes
 1 NCERT SOLUTIONS OF Life Processes Question 1: Why is diffusion insufficient to meet the oxygen requirements of multicellular organisms like humans? Answer: The body structure of multicellular organism
1 NCERT SOLUTIONS OF Life Processes Question 1: Why is diffusion insufficient to meet the oxygen requirements of multicellular organisms like humans? Answer: The body structure of multicellular organism
Do Now Makeups. 4. In which organelle would water and dissolved materials be stored? A. 1 B. 2 C. 3 D. 5. A. mitochondria B.
 Do Now Makeups Name: Date: 1. Which organelle is primarily concerned with the conversion of potential energy of organic compounds into suitable form for immediate use by the cell? A. mitochondria B. centrosomes
Do Now Makeups Name: Date: 1. Which organelle is primarily concerned with the conversion of potential energy of organic compounds into suitable form for immediate use by the cell? A. mitochondria B. centrosomes
S7L Which of these is an important part of the nervous system? A. spinal cord B. stomach C. veins D. muscles
 S7L-4 1. Which of these is an important part of the nervous system? A. spinal cord B. stomach C. veins D. muscles 2. To prevent disease, the human body naturally produces A. enzymes. B. antibodies. C.
S7L-4 1. Which of these is an important part of the nervous system? A. spinal cord B. stomach C. veins D. muscles 2. To prevent disease, the human body naturally produces A. enzymes. B. antibodies. C.
Infection, Detection, Prevention...
 Infection, Detection, Prevention... A disease is any change that disrupts the normal function of one or more body systems. Non infectious diseases are typically caused by exposure to chemicals or are inherited.
Infection, Detection, Prevention... A disease is any change that disrupts the normal function of one or more body systems. Non infectious diseases are typically caused by exposure to chemicals or are inherited.
Academic Year Third Term. Biology Revision sheets
 Academic Year 2015-2016 Third Term Biology Revision sheets Name: Date: Grade:9/ Part (A) Q1: Choose the letter of the choice that best answer the questions: 1. Which type of white blood cell has a specific
Academic Year 2015-2016 Third Term Biology Revision sheets Name: Date: Grade:9/ Part (A) Q1: Choose the letter of the choice that best answer the questions: 1. Which type of white blood cell has a specific
30.1 Organization of the Human Body
 30.1 Organization of the Human Body Lesson Objectives Describe how the human body is organized. Explain homeostasis. Lesson Summary Organization of the Body The levels of organization in a multicellular
30.1 Organization of the Human Body Lesson Objectives Describe how the human body is organized. Explain homeostasis. Lesson Summary Organization of the Body The levels of organization in a multicellular
Antibacterials and Antivirals
 Structure of a Bacterium: Antibacterials and Antivirals Capsule: protective layer made up of proteins, sugars and lipids Cell wall: provides the bacteria with its shape and structure Cell membrane: permeable
Structure of a Bacterium: Antibacterials and Antivirals Capsule: protective layer made up of proteins, sugars and lipids Cell wall: provides the bacteria with its shape and structure Cell membrane: permeable
Organisation. AQA Biology topic 2
 Organisation AQA Biology topic 2 2.1 Principles of Organisation Cells, tissues, organs and systems Basically, all living things are made up of cells A group of CELLS makes up a TISSUE A group of TISSUES
Organisation AQA Biology topic 2 2.1 Principles of Organisation Cells, tissues, organs and systems Basically, all living things are made up of cells A group of CELLS makes up a TISSUE A group of TISSUES
4) What causes lymph to move? Skeletal muscle contraction; smooth muscle contraction, breathing (like blood moves through veins)
 NPHS Anatomy & Physiology UNIT 10 REVIEW GUIDE Lymphatic System 1) List the three functions of the lymphatic system. transports excess fluid to the bloodstream absorbs fats helps defend the body against
NPHS Anatomy & Physiology UNIT 10 REVIEW GUIDE Lymphatic System 1) List the three functions of the lymphatic system. transports excess fluid to the bloodstream absorbs fats helps defend the body against
B. male gametes that may be carried by the wind
 1. Which characteristic of sexual reproduction has specifically favored the survival of animals that live on land? A. fusion of gametes in the outside environment B. male gametes that may be carried by
1. Which characteristic of sexual reproduction has specifically favored the survival of animals that live on land? A. fusion of gametes in the outside environment B. male gametes that may be carried by
THE IMMUNE SYSTEM BLOOD CELLS AND BLOOD VESSEL
 THE IMMUNE SYSTEM The immune system is made up of a network of cells, tissues, and organs that work together to protect the body and fight illnesses and disease. The Function of the Immune System The immune
THE IMMUNE SYSTEM The immune system is made up of a network of cells, tissues, and organs that work together to protect the body and fight illnesses and disease. The Function of the Immune System The immune
2. Complete this table to give the function of the following organelles:
 1. Label these diagrams of cells: 2. Complete this table to give the function of the following organelles: Organelle Cell Membrane Cell Wall Chloroplast Mitochondria Vacuole 3. State 2 differences between
1. Label these diagrams of cells: 2. Complete this table to give the function of the following organelles: Organelle Cell Membrane Cell Wall Chloroplast Mitochondria Vacuole 3. State 2 differences between
Classification of Diseases
 Classification of Diseases Disease Any condition that causes the systems of a plant or animal to not function properly. How diseases occur Sporadic: isolated incident in a single animal Enzootic: disease
Classification of Diseases Disease Any condition that causes the systems of a plant or animal to not function properly. How diseases occur Sporadic: isolated incident in a single animal Enzootic: disease
