Table of Contents: Part I: Introduction and Thorax
|
|
|
- Belinda Simpson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Table of Contents: Part I: Introduction and Thorax Cartoon: The Four "Birds" of the Thorax 1 Planes of the body 2 Anatomic position 3 Some common movements 4 Skeletal landmarks (upper anterior) 5 Bones of the skeleton (lower anterior) 6 Skeletal landmarks (upper posterior) 7 Skeletal landmarks (lower posterior) 8 Muscles of anterior trunk 9 Muscles of anterior thorax and abdomen 10 Section through lactating breast 11 Fibrous supporting membranes in the breast 12 Lactating breast Cartoon: Coracoid process and acromion 13 Skeletal landmarks (thorax and upper arm) 14 Skeletal landmarks (pelvis and hip) 15 Anterior thoracic muscles 16 Muscle attachments of the anterior thorax 17 Anterior thoracic wall seen from inside 18 Contents of thorax with anterior wall removed 19 Intercostal muscles 20 Intercostal muscles 21 Cross section of thoracic wall with intercostal arteries 22 Section of thoracic wall with intercostal arteries 23 Arteries of the thorax and upper arm 24 Thoracic spinal nerve 25 The pericardium 26 The interior of the posterior pericardial sac with the heart removed and the great vessels cut 27 Exterior of the heart 28 Interior of the heart 29 Trace the course of blood through the heart 30 The heart: ventricles exposed 31 Base and diaphragmatic surface of heart 32 Right atrium and right ventricle 33 Left ventricle 34 Heart valves and valve action 35 The four heart valves Cartoon: Muscle 36 Coronary arteries (most common pattern) 37 Coronary veins 38 Cardiac conducting system 39 Cardiac fibrous skeleton 40 Aortic valve and its fibrous support 41 Nerves to the heart 42 Trachea, bronchi, and mediastinal surface of the lungs 43 Bronchopulmonary segments: left lung 44 Bronchopulmonary segments: right lung 45A Bronchopulmonary segment
2 45B Bronchopulmonary segment 46 Lungs and pleura 47 The pleura and pleural recesses 48 Trachea, esophagus, and vagus nerve 49 Right mediastinum 50 Left mediastinum 51 Diaphragm 52 Azygos vein and its tributaries 53 Blood flow in the fetus 54 Fetal heart in late development 55 Circulatory changes after birth 56 Thoracic splanchnic nerves 57 Autonomic nervous system 58 Thoracic duct and related structures 59 Mediastinum after removal of heart and pericardium 60 Cross section at thorax level of bifurcation of pulmonary trunk 61 Cross section of thorax just below pulmonary valve 62 Cross section of thorax just below aortic valve 63 Cross section of thorax at level of male nipple 64 Cross section of thorax with right dome of diaphragm and right lobe of liver Part II: The Abdomen Cartoon: Duodenum 1 Segmental innervation of the skin of the anterior trunk 2 Muscles of the anterior and lateral abdominal walls I 3 Muscles of the anterior and lateral abdominal walls II 4 Muscles and layers of the anterior abdominal wall 5 External abdominal oblique aponeurosis and superficial inguinal ring 6 Inguinal canal dissection 7 Inguinal ligament and related structures 8 Lower anterior abdomen wall viewed from the inside 9 Thoracic and abdominal viscera after removal of anterior thoracic and abdominal walls 10 Thorax and abdominal viscera in relation to the skeleton, anterior view 11 Frontal (coronal) section of the trunk 12 Thoracic and abdominal viscera, left aspect 13 Thoracic and abdominal viscera, right aspect 14 Thoracic and abdominal viscera in relation to the skeleton, posterior view 15 Midsagittal section of the female peritoneal cavity 16 The stomach 17 Blood supply of the stomach 18 Stomach, duodenum, and pancreas 19 Pancreas, duodenum, and spleen Cartoon: Some Latin anatomic terms 20 Celiac trunk and its branches 21 Nerve supply of the stomach 22 The liver (hepar)
3 23 Liver, visceral surface (posterior/inferior aspect) 24A The intestines I 24B The intestines II 25 Distribution of the superior mesenteric artery and vein 26 Blood supply of the jejunum 27 Blood supply to the small intestine 28 Mucosa of jejunum and ileum 29 Blood supply of large intestine 30 Ileocecal valve, vermiform appendix, terminal ileum, and cecum 31 Arterial supply of vermiform appendix, terminal ileum, and cecum 32 The hepatic portal system 33 Posterior abdominal wall, peritoneal attachments 34 Posterior abdominal wall, kidneys, and related structures 35 The kidney I 36 The kidney II 37 Posterior abdominal wall, showing principal muscles and nerves Part III: Pelvis and Perineum Cartoon: Testicle, Latin, little witness 1 Hip (coxal) bone, lateral aspect 2 Hip bone, medial aspect 3 Hip bone lines of fusion 4 Male pelvis dissection 5 Male pelvis median section 6 Male reproductive organs 7 The penis 8 Scrotum and spermatic cord 9 The testis 10 Urethral sphincter in the male 11 Male pelvis, frontal section I 12 Male pelvis, frontal section II 13 Pelvis and perineum 14 Muscles of male perineum 15 Nerves and arteries of the male perineum 16 Male pelvis and perineal muscles 17 Arterial supply of male pelvis 18 Male urogenital tract 19 Autonomic ganglia and nerves in the male abdomen and pelvis 20 Female perineum 21 Female erectile tissue 22 Clitoris and vestibular bulb 23 Female pelvis, median section 24 Female superficial perineal muscles 25 Nerves of female perineum 26 Arteries of the female perineum 27 The uterus 28 Female pelvic diaphragm and related structures
4 29 Female pelvis from the front and above 30 Uterus and related structures 31 Female pelvic diaphragm from above 32 Arterial supply of the female pelvis 33 Muscles on medial surface of pelvis 34 Female urogenital sphincter I 35 Female striated urethral sphincter II 36 Pelvis and ligaments Part IV: The Upper Limb Cartoon: Phalanx 1 Bones of the upper extremity, anterior aspect 2 Bones of the upper extremity, posterior aspect 3 Muscles of upper extremity I 4 Muscles of upper extremity II 5 Muscles of upper extremity III 6 Right scapula (shoulder blade) 7 The humerus 8 The radius and ulna 9 Bones of the hand (manus), palmar aspect 10 Bones of the hand (manus), dorsal aspect 11 Dissection of posterior shoulder and arm 12 Nerves and arteries of the posterior shoulder 13 Quadrangular space 14 The brachial plexus: general plan 15 Brachial plexus and its nerves 16 Arteries of the posterior shoulder and arm 17 Subclavian, axillary, and brachial arteries 18 Superficial veins and nerves of the anterior arm 19 Superficial veins and nerves of the posterior arm 20 Deep dissection of the posterior arm 21 Brachial plexus III 22 Nerves of the upper right limb 23 Biceps brachii: a flexor and supinator 24 Dissection of upper arm, anterior aspect 25 Anterior forearm dissection 26 Arteries and nerves of the anterior forearm 27 Brachial plexus and major nerves of the arm 28 Pronator teres and superficial wrist flexors 29 Musculocutaneous nerve and the muscles it supplies 30 Muscular distribution of the median nerve 31 Flexor digitorum superficialis muscle 32 Flexor pollicis longus, flexor digitorum profundus, and median nerve 33 Median nerve and deep dissection of the forearm 34 Motor distribution of the ulnar nerve 35 Motor distribution of the radial nerve I 36 Motor distribution of the radial nerve II 37 Bones of the hand 38 Palmar aponeurosis and anchoring connective tissue 39 Flexor retinaculum and superficial hand muscles 40 Deep thenar, hypothenar, and interosseous muscles
5 41 Interosseous and related muscles 42 Arteries of the hand 43 Deep palmar arch and deep branch of ulnar nerve 44 Nerves and arteries of the palm 45 Superficial palmar arch: median and ulnar nerves 46 Extensor tendons on dorsum of hand 47 Radial artery and superficial branch of radial nerve 48 Dorsum of hand 49 Palmar hand: deep dissection 50 Extensor tendons on dorsum of hand 51 Synovial flexor tendon sheaths 52 Synovial extensor tendon sheaths 53 Thumb muscles I 54 Thumb muscles II 55 Palmar interosseous muscles of the hand 56 Dorsal interosseous muscles of the hand 57 Some finger movements 58 Cutaneous nerve distribution on front of arm 59 Distribution of cutaneous nerves on back of upper limb 60 Muscle attachments of the anterior arm 61 Muscle attachments of the posterior arm 62 Muscle attachments on the anterior hand 63 Frontal (coronal) section of the right wrist and hand 64 Coronal section of the right shoulder 65 Ligaments of right shoulder joint, anterior view 66 Ligaments of the right shoulder joint, posterior view 67 Ligaments of the right elbow 68 Ligaments of the right elbow, anterior aspect 69 Sagittal section of right elbow 70 Frontal section of right elbow 71 Ligaments of the right wrist, palmar aspect 72 Ligaments of the right wrist, posterior aspect 73 Hand dissected 74 Wrist cross section 75 Hand cross section I 76 Hand cross section II Part V: Back 1 Superficial back muscles 2 Typical vertebrae 3 Rib vertebra articulation 4 Vertebral column 5 Back muscles I, superficial layer 6 Back muscles II, intermediate layers 7 Back muscles III, erector spinae 8 Back muscles IV, deepest muscles 9 Back muscles V, the multifidus 10 Back muscles VI, intertransversarii and interspinales 11 Ligaments of the posterior sacrum 12 Lumbar vertebrae 13 Sacrum 14 Cross section of cervical spinal cord
6 15 Spinal cord displayed from behind 16 The cauda equina of the spinal cord 17 Arterial supply and vascular pattern to a portion of the spinal cord 18 The intervertebral disks and internal vertebral venous plexus 19 Spinal cord, meninges, and internal vertebral venous plexus 20 Typical lumbar vertebra 21 Spinal cord and spinal nerves 22 Lumbosacral spine I 23 Lumbosacral spine II Part VI: The Lower Limb 1 Bones of the lower extremity 2 Superficial muscles of the right thigh, anterior view 3 Superficial muscles of the right thigh, lateral view 4 Superficial muscles of the right thigh, posterior view 5 Superficial muscles of the leg, anterior aspect 6 Superficial muscles of the right leg, lateral aspect 7 Superficial muscles of posterior leg 8 Muscles of medial right leg 9 Right coxal bone (innominate bone, hip bone) 10 Right hip bone (coxal bone) 11 The right femur 12 Right tibia and fibula Cartoon: Fibula and tibia 13 Bones of the right foot 14 Lumbar muscles 15 Arteries of the right thigh 16 Nerves of the lumbar plexus 17 Motor distribution of the femoral nerve, I 18 Motor distribution of the femoral nerve, II 19 Deep dissection of right thigh I 20 Deep dissection of right thigh II 21 Dissection of structures deep to inguinal ligament 22 Iliopsoas muscle and femoral nerve 23 Medial thigh muscles and obturator nerve 24 Adductor magnus and obturator nerve 25 Muscles of buttock and posterior thigh 26 Gluteus maximus and iliotibial tract 27 Posterior gluteal and thigh muscles 28 Posterior muscles of right gluteal region and upper thigh 29 Deep gluteal region 30 Hamstring muscles and gluteus medius 31 Gluteus minimus, semimembranosus, and sciatic nerve 32 Deep dissection of the right thigh 33 Cross section of right thigh 34 Deep structures of the leg and popliteal fossa 35 Deep dissection of lower leg 36 Deep dissection of popliteal region 37 Muscle attachments on the anterior pelvis and femur
7 38 Muscle attachments on the posterior pelvis and femur 39 Lumbosacral plexus 40 Gastrocnemius 41 Soleus, gastrocnemius, and plantaris 42 Flexor digitorum longus and flexor hallucis longus 43 Deep muscles in the posterior leg compartment 44 Flexor hallucis longus 45 Muscles of lateral leg 46 Anterior dissection of right leg 47 Muscle attachments on the anterior leg 48 Muscle attachments 49 Bones of foot, medial aspect Cartoon: Pedigree 50 Bones of foot, inferior aspect 51 Plantar arteries 52 Plantar dissection of the right foot 53 Arteries of right knee joint 54 Arteries of the posterior leg 55 Motor distribution of the common fibular (peroneal) nerve 56 Foot: anterior-superior aspect 57 Dorsum of the foot 58 Deep dissection of plantar foot 59 Plantar muscles I 60 Plantar muscles II 61 Plantar muscles III 62 Plantar muscles IV 63 Motor distribution of the tibial nerve 64 Plantar arteries of the right foot 65 Ligaments of the hip joint 66 Frontal section of right hip joint 67 Right knee joint 68 Ligaments of the right knee 69 Right knee joint 70 Muscle attachments on the dorsum of the foot 71 Muscle attachments on plantar surface of right foot 72 Muscles of plantar foot 73 Planes of sections of right foot 74 Sections of right foot 75 Ligaments of right ankle joint and foot 76 Ligaments of the ankle joint and foot 77 Ligaments of the foot and ankle 78 Plantar ligaments of the right foot 79 Frontal section of ankle and foot 80 Incisions on plantar surface of foot 81 Incision in back of medial malleolus 82 Oblique section of the right foot 83 Cutaneous nerves of the lower extremity, anterior aspect 84 Cutaneous nerves of the lower extremity, posterior aspect Part VII: Head and Neck
8 Cartoon: Trigemini (triplets) 1 Superficial muscles of the face and neck 2 Muscles of facial expression 3 Superficial structures on the lateral head 4 Bones of the skull, anterior aspect 5 Bones of the skull, lateral aspect 6 Facial nerve 7 Landmarks on the lateral skull 8 Temporalis and masseter muscles 9 Temporalis muscle 10 Buccinator and orbicularis oris muscles 11 Median section of skull and mandible 12 Interior of the skull 13 Superficial veins of the head and neck 14 External carotid artery and its branches Cartoon: Sagitta 15 Cranial dural venous sinuses 16 Head and neck: midsagittal aspect 17 Superior sagittal sinus 18 Interior of the skull with cranial nerve exits 19 Facial nerve and its branches 20 Functional components of the facial nerve 21 Inferior surface of skull Cartoon: Temporal 22 Sphenoid bone 23 Temporal bone, external surface 24 Temporal bone, internal surface 25 Superficial muscles of the neck 26 Left side of neck I 27 Left side of neck II 28 Mandibular nerve and maxillary artery I 29 Mandibular nerve and maxillary artery II 30 The eyelid and eye in orbit 31 Extraocular muscles 32 Eye and orbit 33 Nerves of the orbit, superior aspect 34 Nerves of the orbit, lateral aspect 35 Lower half of right eye 36 Principal veins of face and orbit 37 The lacrimal apparatus 38 Dissection of ear and cast of bony labyrinth 39 Dissection of ear 40 Middle ear and ear ossicles 41 Ear ossicles and part of eardrum 42 Middle ear ossicles 43 Dissection of right ear showing middle ear and cochlea 44 Membranous labyrinth of left inner ear cut open 45 Dissection of right temporal bone showing sigmoid sinus and facial canal 46 Section through external ear, middle ear, and inner ear Cartoon: Tragus 47 Cartilages of the nose
9 48 Nasal cavity, lateral wall 49 Nasal cavity, bones and cartilages 50 Nasal cavity, lateral wall and frontal section 51 Pterygopalatine ganglion 52 Olfactory nerves and arterial supply of nasal cavity 53 Right wall of nasal cavity and ethmoidal air cells 54 Projection of paranasal sinuses on front and side of face 55 Oral and nasal cavities in sagittal section 56 Skull, coronal section 57 Sagittal section of head 58 Pharynx 59 Muscles of the tongue, pharynx, and larynx 60 Oral cavity 61 Tongue I 62 Tongue II 63 Tongue and related structures, coronal section 64 Temporomandibular joint Cartoon: Latin words used to describe parts of the nervous system 65 Mandible 66 Salivary glands 67 Oral cavity, from inside 68 Infratemporal fossa 69 Maxillary artery 70 Muscles of the pharynx 71 Arytenoid and cricoid cartilages 72 Vocal ligaments and muscles 73 Larynx, cartilages 74 Pharynx, posterior aspect 75 Arytenoid cartilages 76 Larynx, cartilages, posterior aspect 77 Larynx, nerves and muscles 78 Larynx, coronal section 79 Muscle origins and insertions on side of skull 80 Skull, inferior aspect 81 Autonomic outflow in the head I 82 Autonomic outflow in the head II Cartoon: Synapse 83 Inferior view of the brain 84 Medial view of right half of brain 85 The cranial nerves 86 Brain stem 87 Arterial supply at base of brain Cartoon: Thalamus means bedroom 88 Head frontal section: level of eyes and nasal cavity 89 Head frontal section: level of eye muscles, sinuses 90 Head frontal section: level of maxillary sinuses 91 Head frontal section: level of sphenoid sinuses 92 Head frontal section: level of optic chiasm level 93 Head frontal section: level of carotid canal 94 Head frontal section: level of pons, internal jugular vein 95 Head frontal section: level of dens of axis
General Anatomy p. 1 Organization of the Human Body p. 1 Skeleton of the Human Body p. 4 Ossification of the Bones p. 6 Bone Structure p. 8 Joints p.
 General Anatomy p. 1 Organization of the Human Body p. 1 Skeleton of the Human Body p. 4 Ossification of the Bones p. 6 Bone Structure p. 8 Joints p. 10 Principal Joints (Immovable) p. 12 Synovial Joints
General Anatomy p. 1 Organization of the Human Body p. 1 Skeleton of the Human Body p. 4 Ossification of the Bones p. 6 Bone Structure p. 8 Joints p. 10 Principal Joints (Immovable) p. 12 Synovial Joints
Acknowledgments Figure Credits List of Clinical Blue Boxes Introduction to Clinically Oriented Anatomy Approaches to Studying Anatomy p.
 Preface p. ix Acknowledgments p. xi Figure Credits p. xv List of Clinical Blue Boxes p. xix Introduction to Clinically Oriented Anatomy Approaches to Studying Anatomy p. 2 Regional Anatomy p. 2 Systemic
Preface p. ix Acknowledgments p. xi Figure Credits p. xv List of Clinical Blue Boxes p. xix Introduction to Clinically Oriented Anatomy Approaches to Studying Anatomy p. 2 Regional Anatomy p. 2 Systemic
First BHMS Anatomy Question Papers Calicut University
 First BHMS Anatomy Question Papers Calicut University 1996-2000 FIRST B.H.M.S. DEGREE EXAMINATION, DECEMBER 1996 Time: Three Hours Maximum: 100 Marks Answer any five questions. Draw diagrams wherever needed.
First BHMS Anatomy Question Papers Calicut University 1996-2000 FIRST B.H.M.S. DEGREE EXAMINATION, DECEMBER 1996 Time: Three Hours Maximum: 100 Marks Answer any five questions. Draw diagrams wherever needed.
3 Circulatory Pathways
 40 Chapter 3 Circulatory Pathways Systemic Arteries -Arteries carry blood away from the heart to the various organs of the body. -The aorta is the longest artery in the body; it branches to give rise to
40 Chapter 3 Circulatory Pathways Systemic Arteries -Arteries carry blood away from the heart to the various organs of the body. -The aorta is the longest artery in the body; it branches to give rise to
CARDIOVASCULAR DANIL HAMMOUDI.MD
 CARDIOVASCULAR DANIL HAMMOUDI.MD 18 Systemic Circulation Figure 19.19 Pulmonary Circulation Figure 19.18b 1. Thyroid gland 2. Trachea 3. Brachiocephalic 4. Common carotid 5. Internal jugular 6. Superior
CARDIOVASCULAR DANIL HAMMOUDI.MD 18 Systemic Circulation Figure 19.19 Pulmonary Circulation Figure 19.18b 1. Thyroid gland 2. Trachea 3. Brachiocephalic 4. Common carotid 5. Internal jugular 6. Superior
Definition of anatomy 1 Questions 5
 Contents Chapter 1: Introduction 1 5 Definition of anatomy 1 Questions 5 Chapter 2: Skeletal System 6 74 Skeleton 6 Skeletal system 8 Bones of superior extremity 12 Articulated skeleton of hand 17 Clinical
Contents Chapter 1: Introduction 1 5 Definition of anatomy 1 Questions 5 Chapter 2: Skeletal System 6 74 Skeleton 6 Skeletal system 8 Bones of superior extremity 12 Articulated skeleton of hand 17 Clinical
locomotice system Plastinated specimensⅠ: Silicone specimens Regional specimens and organs
 locomotice system Plastinated specimensⅠ: Silicone specimens Regional specimens and organs Art-No. Name Description The locomotor system SL001 Two hundred pieces of plastinated bones (without six The bones
locomotice system Plastinated specimensⅠ: Silicone specimens Regional specimens and organs Art-No. Name Description The locomotor system SL001 Two hundred pieces of plastinated bones (without six The bones
Regional Human Anatomy (HBA 461/561/540): Course Objectives
 Regional Human Anatomy (HBA 461/561/540): Course Objectives This is a 5-credit course that consists of 1-hour lectures followed by 3-hour labs. It is organized into three modules (see syllabus): Module
Regional Human Anatomy (HBA 461/561/540): Course Objectives This is a 5-credit course that consists of 1-hour lectures followed by 3-hour labs. It is organized into three modules (see syllabus): Module
KARPAGAM FACULTY OF MEDICAL SCIENCES & RESEARCH DEPARTMENT OF ANATOMY TEACHING SCHEDULE GENERAL ANATOMY I - MBBS
 TEACHING SCHEDULE GENERAL ANATOMY I - MBBS S.NO DATE & TIME 1. 3.10.16 Monday 2. 4.10.16 Tuesday 8 10 3. 5. 10.16 Wednesday 4. 11 1pm 5. 6.10.16 Thursday 8 10 6. 6.10.16 Thursday 12 1pm 7. 7.10.16 Friday
TEACHING SCHEDULE GENERAL ANATOMY I - MBBS S.NO DATE & TIME 1. 3.10.16 Monday 2. 4.10.16 Tuesday 8 10 3. 5. 10.16 Wednesday 4. 11 1pm 5. 6.10.16 Thursday 8 10 6. 6.10.16 Thursday 12 1pm 7. 7.10.16 Friday
Lumbar Plexus. Ventral rami L1 L4 Supplies: Major nerves.. Abdominal wall External genitalia Anteromedial thigh
 Lower Limb Nerves Lectures Objectives Describe the structure and relationships of the plexuses of the lower limb. Describe the course, relationships and structures supplied for the major nerves of the
Lower Limb Nerves Lectures Objectives Describe the structure and relationships of the plexuses of the lower limb. Describe the course, relationships and structures supplied for the major nerves of the
topographical anatomy
 Kaan Yücel M.D., Ph.D. 30. September 2014 Tuesday topographical anatomy organization of the human body as major parts or segments Head Neck Trunk thorax, abdomen, back, & pelvis/perineum Upper limbs &
Kaan Yücel M.D., Ph.D. 30. September 2014 Tuesday topographical anatomy organization of the human body as major parts or segments Head Neck Trunk thorax, abdomen, back, & pelvis/perineum Upper limbs &
Training the Clinical Anatomy Trainer Level 2 Teaching Objectives
 Training the Clinical Anatomy Trainer Level 2 Presentations o Large group teaching o Small group teaching Prosection-based teaching Osteology teaching Surface anatomy Innovative teaching Conceptual teaching
Training the Clinical Anatomy Trainer Level 2 Presentations o Large group teaching o Small group teaching Prosection-based teaching Osteology teaching Surface anatomy Innovative teaching Conceptual teaching
Due in Lab weeks because of Thanksgiving Prelab #10. Homework #8. Both sides! Both sides!
 Lab 8 MUSCLES Due in Lab 10 2 weeks because of Thanksgiving Prelab #10 Both sides! Homework #8 Both sides! Refer to Muscles 22-23 Naming of muscles Origin Site of muscle attachment that doesn t move during
Lab 8 MUSCLES Due in Lab 10 2 weeks because of Thanksgiving Prelab #10 Both sides! Homework #8 Both sides! Refer to Muscles 22-23 Naming of muscles Origin Site of muscle attachment that doesn t move during
Synapse Homework. Back page last question not counted. 4 pts total, each question worth 0.18pts. 26/34 students answered correctly!
 Synapse Homework Back page last question not counted 26/34 students answered correctly! 4 pts total, each question worth 0.18pts Business TASS hours extended! MWF 1-2pm, Willamette 204 T and Th 9:30-10:30am,
Synapse Homework Back page last question not counted 26/34 students answered correctly! 4 pts total, each question worth 0.18pts Business TASS hours extended! MWF 1-2pm, Willamette 204 T and Th 9:30-10:30am,
Fig. A.1. Frontal. plane. Transverse. plane. Sagittal plane. Copyright McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction or display.
 Fig. A.1 Frontal plane Transverse plane Sagittal plane McGraw-Hill Education/Joe DeGrandis Fig. A.2 (a) Sagittal section (b) Frontal section (c) Transverse section Table A.1 Fig. A.3 Cephalic r. (head)
Fig. A.1 Frontal plane Transverse plane Sagittal plane McGraw-Hill Education/Joe DeGrandis Fig. A.2 (a) Sagittal section (b) Frontal section (c) Transverse section Table A.1 Fig. A.3 Cephalic r. (head)
Cat Dissection. Muscular Labs
 Cat Dissection Muscular Labs Tibialis anterior External oblique Pectroalis minor Gastrocnemius Sartorius Pectoralis major Gastrocnemius Semitendinosis Sartorius External oblique Trapezius Latissimus dorsi
Cat Dissection Muscular Labs Tibialis anterior External oblique Pectroalis minor Gastrocnemius Sartorius Pectoralis major Gastrocnemius Semitendinosis Sartorius External oblique Trapezius Latissimus dorsi
YOU MUST BRING GLOVES FOR THIS ACTIVITY
 ACTIVITY 10: VESSELS AND CIRCULATION OBJECTIVES: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapter 23, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 5e. All text references are for this textbook. 2) Observe and sketch histology slide
ACTIVITY 10: VESSELS AND CIRCULATION OBJECTIVES: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapter 23, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 5e. All text references are for this textbook. 2) Observe and sketch histology slide
ANATOMY. Schedule for 2014/2015 academic school year (2x15 weeks)
 ANATOMY Schedule for 2014/2015 academic school year (2x15 weeks) SEMESTER LECTURES LAB CLASSES SEMINARS TOTAL FIRST 4 hours (2+2) 4 hours (2+2) 1 hour 135 hours SECOND 3 hours 4 hours (2+2) 2 hours 135
ANATOMY Schedule for 2014/2015 academic school year (2x15 weeks) SEMESTER LECTURES LAB CLASSES SEMINARS TOTAL FIRST 4 hours (2+2) 4 hours (2+2) 1 hour 135 hours SECOND 3 hours 4 hours (2+2) 2 hours 135
SYLLABUS BDS I PROFESSIONAL GENERAL HUMAN ANATOMY INCLUDING EMBRYOLOGY AND HISTOLOGY
 GENERAL HUMAN ANATOMY INCLUDING EMBRYOLOGY AND HISTOLOGY I. General Anatomy 1. Anatomical terms 2. Skin, superficial fascia & deep fascia 3. Cardiovascular system, portal system, collateral circulation
GENERAL HUMAN ANATOMY INCLUDING EMBRYOLOGY AND HISTOLOGY I. General Anatomy 1. Anatomical terms 2. Skin, superficial fascia & deep fascia 3. Cardiovascular system, portal system, collateral circulation
Topic list for the Anatomy end-semester exam of the First semester Academic year 2018/2019, Autumn term
 University of Szeged, Faculty of Medicine Department of Anatomy, Histology and Embryology Chairman: Prof. Antal Nógrádi MD, PhD, DSc Kossuth L. sgt. 40., H-6724 Szeged, Hungary Tel.: +36-62-545-665 P.
University of Szeged, Faculty of Medicine Department of Anatomy, Histology and Embryology Chairman: Prof. Antal Nógrádi MD, PhD, DSc Kossuth L. sgt. 40., H-6724 Szeged, Hungary Tel.: +36-62-545-665 P.
11/15/2018. Temporalis Elevates & retracts mandible. Masseter = Prime mover of jaw closure. Levator scapulae Supraspinatus Clavicle.
 Due in Lab 10 Lab 8 MUSCLES 2 weeks because of Thanksgiving Prelab #10 Both sides! Homework #8 Both sides! Refer to Muscles 22-23 Examples of Origin & Insertion Naming of muscles Origin Site of muscle
Due in Lab 10 Lab 8 MUSCLES 2 weeks because of Thanksgiving Prelab #10 Both sides! Homework #8 Both sides! Refer to Muscles 22-23 Examples of Origin & Insertion Naming of muscles Origin Site of muscle
musculoskeletal system anatomy nerves of the lower limb 2 done by: Dina sawadha & mohammad abukabeer
 musculoskeletal system anatomy nerves of the lower limb 2 done by: Dina sawadha & mohammad abukabeer #Sacral plexus : emerges from the ventral rami of the spinal segments L4 - S4 and provides motor and
musculoskeletal system anatomy nerves of the lower limb 2 done by: Dina sawadha & mohammad abukabeer #Sacral plexus : emerges from the ventral rami of the spinal segments L4 - S4 and provides motor and
Day 5 Respiratory & Cardiovascular: Respiratory System
 Day 5 Respiratory & Cardiovascular: Respiratory System Be very careful not to damage the heart and lungs while separating the ribs! Analysis Questions-Respiratory & Cardiovascular Log into QUIA using your
Day 5 Respiratory & Cardiovascular: Respiratory System Be very careful not to damage the heart and lungs while separating the ribs! Analysis Questions-Respiratory & Cardiovascular Log into QUIA using your
Honors Biology: Rat Dissection ONLINE ASSIGNMENT
 Name: Honors Biology: Rat Dissection ONLINE ASSIGNMENT You and your group members will use the Honors Biology WIKI to create an online dissection manual. The point of this assignment is to illustrate what
Name: Honors Biology: Rat Dissection ONLINE ASSIGNMENT You and your group members will use the Honors Biology WIKI to create an online dissection manual. The point of this assignment is to illustrate what
DISSECTION SCHEDULE. Session I - Hip (Front) & Thigh (Superficial)
 DISSECTION SCHEDULE Session I - Hip (Front) & Thigh (Superficial) Surface anatomy Inguinal region Gluteal region Thigh Leg Foot bones Hip bone Femur Superficial fascia Great saphenous vein Superficial
DISSECTION SCHEDULE Session I - Hip (Front) & Thigh (Superficial) Surface anatomy Inguinal region Gluteal region Thigh Leg Foot bones Hip bone Femur Superficial fascia Great saphenous vein Superficial
VESSELS: GROSS ANATOMY
 ACTIVITY 10: VESSELS AND CIRCULATION OBJECTIVES: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapter 23, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 4e. All text references are for this textbook. 2) Observe and sketch histology slide
ACTIVITY 10: VESSELS AND CIRCULATION OBJECTIVES: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapter 23, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 4e. All text references are for this textbook. 2) Observe and sketch histology slide
Biology 218 Human Anatomy. Adapted from Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 12 Surface Anatomy and Cross-Sectional Anatomy
 Adapted from Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 12 Surface Anatomy and Introduction Surface anatomy is the study of anatomical landmarks on the exterior of the human body Knowledge of surface anatomy
Adapted from Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 12 Surface Anatomy and Introduction Surface anatomy is the study of anatomical landmarks on the exterior of the human body Knowledge of surface anatomy
Year 2004 Paper one: Questions supplied by Megan
 QUESTION 47 A 58yo man is noted to have a right foot drop three days following a right total hip replacement. On examination there is weakness of right ankle dorsiflexion and toe extension (grade 4/5).
QUESTION 47 A 58yo man is noted to have a right foot drop three days following a right total hip replacement. On examination there is weakness of right ankle dorsiflexion and toe extension (grade 4/5).
A&P 1. Terminology, Orientation, Surface Landmarks & Body Cavities. Pre-Lab Exercises
 A&P 1 Terminology, Orientation, Surface Landmarks & Body Cavities Pre-Lab Exercises In this "Pre-lab Guide", we will be going over some of the content seen in the videos. However, this content is for lecture
A&P 1 Terminology, Orientation, Surface Landmarks & Body Cavities Pre-Lab Exercises In this "Pre-lab Guide", we will be going over some of the content seen in the videos. However, this content is for lecture
Nerves of the upper limb Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi. E. mail:
 Nerves of the upper limb Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com Brachial plexus Median nerve After originating from the brachial plexus in the axilla,
Nerves of the upper limb Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com Brachial plexus Median nerve After originating from the brachial plexus in the axilla,
The Human Body. Lesson Goal. Lesson Objectives 9/10/2012. Provide a brief overview of body systems, anatomy, physiology, and topographic anatomy
 The Human Body Lesson Goal Provide a brief overview of body systems, anatomy, physiology, and topographic anatomy Medial Lateral Proximal Distal Superior Inferior Anterior Lesson Objectives Explain the
The Human Body Lesson Goal Provide a brief overview of body systems, anatomy, physiology, and topographic anatomy Medial Lateral Proximal Distal Superior Inferior Anterior Lesson Objectives Explain the
Muscles of the lower extremities. Dr. Nabil khouri MD, MSc, Ph.D
 Muscles of the lower extremities Dr. Nabil khouri MD, MSc, Ph.D Posterior leg Popliteal fossa Boundaries Biceps femoris (superior-lateral) Semitendinosis and semimembranosis (superior-medial) Gastrocnemius
Muscles of the lower extremities Dr. Nabil khouri MD, MSc, Ph.D Posterior leg Popliteal fossa Boundaries Biceps femoris (superior-lateral) Semitendinosis and semimembranosis (superior-medial) Gastrocnemius
Fetal Pig Visual Dissection Guide
 Fetal Pig Visual Dissection Guide WARD470156-776 Orientation Cranial Anterior Sagittal plane Frontal plane Ventral Dorsal Transverse plane Caudal Posterior 1 Incisions 1 Gender Key Male Female Both 4 3
Fetal Pig Visual Dissection Guide WARD470156-776 Orientation Cranial Anterior Sagittal plane Frontal plane Ventral Dorsal Transverse plane Caudal Posterior 1 Incisions 1 Gender Key Male Female Both 4 3
Muscle fiber (cell) Blood vessel. Perimysium. Epimysium. Fascicle (wrapped by perimysium) Endomysium (between fibers) Tendon. Bone
 Figure 6.1 Connective tissue wrappings of skeletal muscle. Blood vessel Muscle fiber (cell) Perimysium Epimysium Fascicle (wrapped by perimysium) Tendon Endomysium (between fibers) Bone Figure 6.15 Superficial
Figure 6.1 Connective tissue wrappings of skeletal muscle. Blood vessel Muscle fiber (cell) Perimysium Epimysium Fascicle (wrapped by perimysium) Tendon Endomysium (between fibers) Bone Figure 6.15 Superficial
Section 2 - Musculo-skeletal System. A list of the first 3 digits - 72 terms
 1 Section 2 - Musculo-skeletal System A list of the first - 72 terms Index + Regional terms 2 MUSCULOSKELETAL SYSTEM 20 Musculoskeletal system: general terms 201 Skeletal system 202 Muscular system: types
1 Section 2 - Musculo-skeletal System A list of the first - 72 terms Index + Regional terms 2 MUSCULOSKELETAL SYSTEM 20 Musculoskeletal system: general terms 201 Skeletal system 202 Muscular system: types
Introduction to The Human Body
 1 Introduction to The Human Body FOCUS: The human organism is often examined at seven structural levels: chemical, organelle, cell, tissue, organ, organ system, and the organism. Anatomy examines the structure
1 Introduction to The Human Body FOCUS: The human organism is often examined at seven structural levels: chemical, organelle, cell, tissue, organ, organ system, and the organism. Anatomy examines the structure
Muscle Anatomy Review Chart
 Muscle Anatomy Review Chart BACK Superficial (5) Trapezius Transverse cervical a. Latissimus dorsi Thoracodorsal a. Rhomboideus major Dorsal scapular a. Rhomboideus minor Levator scapulae Intermediate
Muscle Anatomy Review Chart BACK Superficial (5) Trapezius Transverse cervical a. Latissimus dorsi Thoracodorsal a. Rhomboideus major Dorsal scapular a. Rhomboideus minor Levator scapulae Intermediate
Anatomy. Contents Brain (Questions)
 Anatomy 12 Contents 12.1 Brain (Questions).................................................... 683 12.2 Head and Neck (Questions)............................................. 685 12.3 Thorax (Questions)...................................................
Anatomy 12 Contents 12.1 Brain (Questions).................................................... 683 12.2 Head and Neck (Questions)............................................. 685 12.3 Thorax (Questions)...................................................
Artery 1 Head and Thoracic Arteries. Arrange the parts in the order blood flows through them.
 Artery 1 Head and Thoracic Arteries 1. Given the following parts of the aorta: 1. abdominal aorta 2. aortic arch 3. ascending aorta 4. thoracic aorta Arrange the parts in the order blood flows through
Artery 1 Head and Thoracic Arteries 1. Given the following parts of the aorta: 1. abdominal aorta 2. aortic arch 3. ascending aorta 4. thoracic aorta Arrange the parts in the order blood flows through
The posterior abdominal wall. Prof. Oluwadiya KS
 The posterior abdominal wall Prof. Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.sitesled.com Posterior Abdominal Wall Lumbar vertebrae and discs. Muscles opsoas, quadratus lumborum, iliacus, transverse, abdominal wall
The posterior abdominal wall Prof. Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.sitesled.com Posterior Abdominal Wall Lumbar vertebrae and discs. Muscles opsoas, quadratus lumborum, iliacus, transverse, abdominal wall
List of questions for the examination in Human Anatomy Faculty of Stomatology, the 1st semester. (control of theoretical knowledge)
 Pag. 1 / 5 List of questions for the examination in Human Anatomy Faculty of Stomatology, the 1st semester (control of theoretical knowledge) LOCOMOTOR APPARATUS 1. Human Anatomy and its role in medical
Pag. 1 / 5 List of questions for the examination in Human Anatomy Faculty of Stomatology, the 1st semester (control of theoretical knowledge) LOCOMOTOR APPARATUS 1. Human Anatomy and its role in medical
Table of Contents: SECTION 1 INTRODUCTION PLATES 1-7. Introduction Plates 1-7. Plate 1 Body Planes and Terms of Relationship
 Table of Contents: SECTION 1 INTRODUCTION PLATES 1-7 Introduction Plates 1-7 Plate 1 Body Planes and Terms of Relationship Plate 2 Surface Anatomy: Regions (Anterior view of female) Plate 3 Surface Anatomy:
Table of Contents: SECTION 1 INTRODUCTION PLATES 1-7 Introduction Plates 1-7 Plate 1 Body Planes and Terms of Relationship Plate 2 Surface Anatomy: Regions (Anterior view of female) Plate 3 Surface Anatomy:
Table of Contents: 1 The body. What is anatomy? 4. How can gross anatomy be studied? 4. Important anatomical terms 4. Imaging 7
 Table of Contents: 1 The body What is anatomy? 4 How can gross anatomy be studied? 4 Important anatomical terms 4 Imaging 7 Diagnostic imaging techniques 7 Nuclear medicine imaging 10 Image interpretation
Table of Contents: 1 The body What is anatomy? 4 How can gross anatomy be studied? 4 Important anatomical terms 4 Imaging 7 Diagnostic imaging techniques 7 Nuclear medicine imaging 10 Image interpretation
Key Relationships in the Upper Limb
 Key Relationships in the Upper Limb This list contains some of the key relationships that will help you identify structures in the lab. They are organized by dissection assignment as defined in the syllabus.
Key Relationships in the Upper Limb This list contains some of the key relationships that will help you identify structures in the lab. They are organized by dissection assignment as defined in the syllabus.
Anatomy 25 KEY ANATOMICAL TERMINOLOGY Guthrie
 THE FOLLOWING TERMS ARE COMMONLY USED IN ANATOMY. YOU MUST KNOW THEM IN ORDER TO FIND YOUR WAY AROUND THE BODY. CADAVER : A dead human body A NATOMICAL POSITION : The standard reference position of the
THE FOLLOWING TERMS ARE COMMONLY USED IN ANATOMY. YOU MUST KNOW THEM IN ORDER TO FIND YOUR WAY AROUND THE BODY. CADAVER : A dead human body A NATOMICAL POSITION : The standard reference position of the
Misc Anatomy. Upper Limb! 2. Lower Limb! 5. Venous Drainage! Head & neck! 8
 Misc Anatomy Upper Limb! 2 Arteries!... 2 Veins!... 2 Spaces!... 4 Lower Limb! 5 Arteries!... 5 Venous Drainage!... 6 Spaces!... 7 Head & neck! 8 Artery!... 8 Ultrasound View for IJ CVL!... 8 Arteries
Misc Anatomy Upper Limb! 2 Arteries!... 2 Veins!... 2 Spaces!... 4 Lower Limb! 5 Arteries!... 5 Venous Drainage!... 6 Spaces!... 7 Head & neck! 8 Artery!... 8 Ultrasound View for IJ CVL!... 8 Arteries
Chapter 10: Muscular System: Gross Anatomy
 Chapter 10: Muscular System: Gross Anatomy I. General Principles A. General Terminology 1. Tendons attach 2. What is an aponeurosis? 3. The points of muscle attachment are called & 4. How is the "origin"
Chapter 10: Muscular System: Gross Anatomy I. General Principles A. General Terminology 1. Tendons attach 2. What is an aponeurosis? 3. The points of muscle attachment are called & 4. How is the "origin"
Lower Limb Nerves. Clinical Anatomy
 Lower Limb Nerves Clinical Anatomy Lumbar Plexus Ventral rami L1 L4 Supplies: Abdominal wall External genitalia Anteromedial thigh Major nerves.. Lumbar Plexus Nerves relation to psoas m. : Obturator n.
Lower Limb Nerves Clinical Anatomy Lumbar Plexus Ventral rami L1 L4 Supplies: Abdominal wall External genitalia Anteromedial thigh Major nerves.. Lumbar Plexus Nerves relation to psoas m. : Obturator n.
MUSCULOSKELETAL LOWER LIMB
 MUSCULOSKELETAL LOWER LIMB Spinal Cord Lumbar and Sacral Regions Spinal cord Dorsal root ganglion Conus medullaris Cauda equina Dorsal root ganglion of the fifth lumbar nerve End of subarachnoid space
MUSCULOSKELETAL LOWER LIMB Spinal Cord Lumbar and Sacral Regions Spinal cord Dorsal root ganglion Conus medullaris Cauda equina Dorsal root ganglion of the fifth lumbar nerve End of subarachnoid space
Anatomy The study of the body's structure.
 Anatomy The study of the body's structure. * 1. Systemic- Study of each of the body's systems. 2. Regional- Study of a specific area of the body 3. Surface- Study of external features. Physiology The study
Anatomy The study of the body's structure. * 1. Systemic- Study of each of the body's systems. 2. Regional- Study of a specific area of the body 3. Surface- Study of external features. Physiology The study
FUNDEMENTALS OF ANATOMY. TBD TBD
 Course Details FUNDEMENTALS OF ANATOMY Course Title Fundamentals of Anatomy Course Number BIOL 160 Department Anatomy Credit Hours 4 Grading Type Letter Course Director Sushama Rich M.D. Director s Email
Course Details FUNDEMENTALS OF ANATOMY Course Title Fundamentals of Anatomy Course Number BIOL 160 Department Anatomy Credit Hours 4 Grading Type Letter Course Director Sushama Rich M.D. Director s Email
The body What is anatomy? p. 4 How can gross anatomy be studied? p. 4 Important anatomical terms p. 4 Imaging p. 7 Diagnostic imaging techniques p.
 The body What is anatomy? p. 4 How can gross anatomy be studied? p. 4 Important anatomical terms p. 4 Imaging p. 7 Diagnostic imaging techniques p. 7 Nuclear medicine imaging p. 10 Image interpretation
The body What is anatomy? p. 4 How can gross anatomy be studied? p. 4 Important anatomical terms p. 4 Imaging p. 7 Diagnostic imaging techniques p. 7 Nuclear medicine imaging p. 10 Image interpretation
PERIPHERAL NERVOUS SYSTEM
 CHAPTER 13 PERIPHERAL NERVOUS SYSTEM Functional division of nervous system = afferent info to the CNS ascending spinal cord = efferent info from CNS descending spinal cord somatic skin, muscles visceral
CHAPTER 13 PERIPHERAL NERVOUS SYSTEM Functional division of nervous system = afferent info to the CNS ascending spinal cord = efferent info from CNS descending spinal cord somatic skin, muscles visceral
The Human Body: An Orientation
 The Human Body: An Orientation Body standing upright Anatomical Position feet slightly apart palms facing forward thumbs point away from body Directional Terms Superior and inferior toward and away from
The Human Body: An Orientation Body standing upright Anatomical Position feet slightly apart palms facing forward thumbs point away from body Directional Terms Superior and inferior toward and away from
Anatomy of the Musculoskeletal System
 Anatomy of the Musculoskeletal System Kyle E. Rarey, Ph.D. Department of Anatomy & Cell Biology and Otolaryngology University of Florida College of Medicine Outline of Presentation Vertebral Column Upper
Anatomy of the Musculoskeletal System Kyle E. Rarey, Ph.D. Department of Anatomy & Cell Biology and Otolaryngology University of Florida College of Medicine Outline of Presentation Vertebral Column Upper
Skeleton. The left forearm is in the position of supination, the right in pronation.
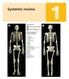 S ystemic review A Skeleton A from the front B B from behind The left forearm is in the position of supination, the right in pronation. Skull Mandible Hyoid bone Cervical vertebrae Clavicle Sternum Costal
S ystemic review A Skeleton A from the front B B from behind The left forearm is in the position of supination, the right in pronation. Skull Mandible Hyoid bone Cervical vertebrae Clavicle Sternum Costal
Applied anatomy. Types of ossification & Epiphysis Kinesiology 2
 .General Anatomy :Cell Cell division types with significance Tissues Functional correlation Syllabus for the Post of Assistant Professor / Associate Profess Terms used in Embryology Functions of bone,
.General Anatomy :Cell Cell division types with significance Tissues Functional correlation Syllabus for the Post of Assistant Professor / Associate Profess Terms used in Embryology Functions of bone,
The Language of Anatomy
 1 E x e r c i s e The Language of Anatomy If time is a problem, most of this exercise can be done as an out-of-class assignment. Time Allotment: 1/2 hour (in lab). Laboratory Materials Ordering information
1 E x e r c i s e The Language of Anatomy If time is a problem, most of this exercise can be done as an out-of-class assignment. Time Allotment: 1/2 hour (in lab). Laboratory Materials Ordering information
LANGUAGE OF ANATOMY PART 1
 1 LANGUAGE OF ANATOMY PART 1 Courtesy of Dr. Susan Maskel Western Connecticut State University 2 ANATOMICAL POSITION In the anatomical position, the human body is erect, with the feet only slightly apart,
1 LANGUAGE OF ANATOMY PART 1 Courtesy of Dr. Susan Maskel Western Connecticut State University 2 ANATOMICAL POSITION In the anatomical position, the human body is erect, with the feet only slightly apart,
MCQWeek2. All arise from the common flexor origin. The posterior aspect of the medial epicondyle is the common flexor origin.
 MCQWeek2. 1. Regarding superficial muscles of anterior compartment of the forearm: All arise from the common flexor origin. The posterior aspect of the medial epicondyle is the common flexor origin. Flexor
MCQWeek2. 1. Regarding superficial muscles of anterior compartment of the forearm: All arise from the common flexor origin. The posterior aspect of the medial epicondyle is the common flexor origin. Flexor
Chapter 7: Skeletal System: Gross Anatomy
 Chapter 7: Skeletal System: Gross Anatomy I. General Considerations A. How many bones in an average adult skeleton? B. Anatomic features of bones are based on II. Axial Skeleton A. Skull 1. Functionally
Chapter 7: Skeletal System: Gross Anatomy I. General Considerations A. How many bones in an average adult skeleton? B. Anatomic features of bones are based on II. Axial Skeleton A. Skull 1. Functionally
The Muscular System. Chapter 10 Part D. PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Karen Dunbar Kareiva Ivy Tech Community College
 Chapter 10 Part D The Muscular System Annie Leibovitz/Contact Press Images PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Karen Dunbar Kareiva Ivy Tech Community College Table 10.14: Muscles Crossing the Hip and
Chapter 10 Part D The Muscular System Annie Leibovitz/Contact Press Images PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Karen Dunbar Kareiva Ivy Tech Community College Table 10.14: Muscles Crossing the Hip and
Human Anatomy and Physiology I Laboratory Spinal and Peripheral Nerves and Reflexes
 Human Anatomy and Physiology I Laboratory Spinal and Peripheral Nerves and Reflexes 1 This lab involves the second section of the exercise Spinal Cord, Spinal Nerves, and the Autonomic Nervous System,
Human Anatomy and Physiology I Laboratory Spinal and Peripheral Nerves and Reflexes 1 This lab involves the second section of the exercise Spinal Cord, Spinal Nerves, and the Autonomic Nervous System,
Class Outline: Posterior Anatomy
 Class Outline: Posterior Anatomy 5 minutes Breath of Arrival and Attendance 5 minutes Howdy Partner 35 minutes Posterior Anatomy using Power Point Presentation 5 minutes Overview of skeletal segments 5
Class Outline: Posterior Anatomy 5 minutes Breath of Arrival and Attendance 5 minutes Howdy Partner 35 minutes Posterior Anatomy using Power Point Presentation 5 minutes Overview of skeletal segments 5
STREAM. Human Body Project Pages Website QR Code body project/
 STREAM Human Body Project Pages 1 16 Website QR Code https://sites.google.com/a/wyckoffschools.org/human body project/ Project Checklist Did you include Head a brain that can open to show the inside as
STREAM Human Body Project Pages 1 16 Website QR Code https://sites.google.com/a/wyckoffschools.org/human body project/ Project Checklist Did you include Head a brain that can open to show the inside as
Al-Balqa Applied University
 Al-Balqa Applied University Faculty Of Medicine *You can use this checklist as a guide to you for the lab. the items on this checklist represent the main features of the models that you have to know for
Al-Balqa Applied University Faculty Of Medicine *You can use this checklist as a guide to you for the lab. the items on this checklist represent the main features of the models that you have to know for
Control center! (set point)! (Change is compared! to the set point.)!
 Fig01.05 Control center! (set point)! Receptors (Change is compared! to the set point.)! Effectors! (muscles or glands)! Stimulus! (Change occurs! in internal! environment.)! Response! (Change is corrected.)
Fig01.05 Control center! (set point)! Receptors (Change is compared! to the set point.)! Effectors! (muscles or glands)! Stimulus! (Change occurs! in internal! environment.)! Response! (Change is corrected.)
Prime movers provide the major force for producing a specific movement Antagonists oppose or reverse a particular movement Synergists
 Dr. Gary Mumaugh Prime movers provide the major force for producing a specific movement Antagonists oppose or reverse a particular movement Synergists Add force to a movement Reduce undesirable or unnecessary
Dr. Gary Mumaugh Prime movers provide the major force for producing a specific movement Antagonists oppose or reverse a particular movement Synergists Add force to a movement Reduce undesirable or unnecessary
CHAPTER 7, PART II (BONES)
 Anatomy Name: CHAPTER 7, PART II (BONES) Entry #: INSTRUCTIONS: 1) READ Chapter 7, pg. 140-161. 2) Using the outline, make a note card for each underlined bone name or phrase. 3) On each note card, put
Anatomy Name: CHAPTER 7, PART II (BONES) Entry #: INSTRUCTIONS: 1) READ Chapter 7, pg. 140-161. 2) Using the outline, make a note card for each underlined bone name or phrase. 3) On each note card, put
Chapter 1: Introduction to the Human Body Test Bank
 Chapter 1: Introduction to the Human Body Test Bank MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. What is the branch of science that studies how the body functions? a. Anatomy b. Histology c. Pathology d. Physiology 2. Which word
Chapter 1: Introduction to the Human Body Test Bank MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. What is the branch of science that studies how the body functions? a. Anatomy b. Histology c. Pathology d. Physiology 2. Which word
LANGUAGE of ANATOMY PART 2. Courtesy of Dr. Susan Maskel Western Connecticut State University
 1 LANGUAGE of ANATOMY PART 2 Courtesy of Dr. Susan Maskel Western Connecticut State University 2 ACROMIAL pertaining to the point of the shoulder Note: this term was also used in Language of Anatomy Part
1 LANGUAGE of ANATOMY PART 2 Courtesy of Dr. Susan Maskel Western Connecticut State University 2 ACROMIAL pertaining to the point of the shoulder Note: this term was also used in Language of Anatomy Part
BLUE SKY SCHOOL OF PROFESSIONAL MASSAGE AND THERAPEUTIC BODYWORK. Musculoskeletal Anatomy & Kinesiology I TERMINOLOGY, STRUCTURES, & SKELETAL OVERVIEW
 BLUE SKY SCHOOL OF PROFESSIONAL MASSAGE AND THERAPEUTIC BODYWORK Musculoskeletal Anatomy & Kinesiology I TERMINOLOGY, STRUCTURES, & SKELETAL OVERVIEW MSAK101-I Session 1 Learning Objectives: 1. Define
BLUE SKY SCHOOL OF PROFESSIONAL MASSAGE AND THERAPEUTIC BODYWORK Musculoskeletal Anatomy & Kinesiology I TERMINOLOGY, STRUCTURES, & SKELETAL OVERVIEW MSAK101-I Session 1 Learning Objectives: 1. Define
The Human Muscular System Required reading before beginning this lab: Saladin, KS: Human Anatomy 5th ed (2017) Chapters 10, 11, 12 INTRODUCTION
 Biology 322: Human Anatomy The Human Muscular System Required reading before beginning this lab: Saladin, KS: Human Anatomy 5 th ed (2017) Chapters 10, 11, 12 INTRODUCTION We will use a number of lab periods
Biology 322: Human Anatomy The Human Muscular System Required reading before beginning this lab: Saladin, KS: Human Anatomy 5 th ed (2017) Chapters 10, 11, 12 INTRODUCTION We will use a number of lab periods
6e Plate# 7e Plate# Plate Title
 6e Plate# 7e Plate# Plate Title 1 8 Head and Neck: Surface Anatomy 2 9 Cutaneous Nerves of Head and Neck 3 10 Superficial Arteries and Veins of Face and Scalp 4 11 Skull: Anterior View 5 (replaced) 12
6e Plate# 7e Plate# Plate Title 1 8 Head and Neck: Surface Anatomy 2 9 Cutaneous Nerves of Head and Neck 3 10 Superficial Arteries and Veins of Face and Scalp 4 11 Skull: Anterior View 5 (replaced) 12
The arm: *For images refer back to the slides
 The arm: *For images refer back to the slides Muscles of the arm: deltoid, triceps (which is located at the back of the arm), biceps and brachialis (it lies under the biceps), brachioradialis (it lies
The arm: *For images refer back to the slides Muscles of the arm: deltoid, triceps (which is located at the back of the arm), biceps and brachialis (it lies under the biceps), brachioradialis (it lies
Group of students. - Rawan almujabili د. محمد المحتسب - 1 P a g e
 - 14 - Group of students - Rawan almujabili د. محمد المحتسب - 1 P a g e Nerves of the posterior abdominal wall The spinal cord gives off spinal nerves between the vertebrae. In the abdomen, through the
- 14 - Group of students - Rawan almujabili د. محمد المحتسب - 1 P a g e Nerves of the posterior abdominal wall The spinal cord gives off spinal nerves between the vertebrae. In the abdomen, through the
Anatomical Terminology
 Anatomical Terminology Dr. A. Ebneshahidi Anatomy Anatomy : is the study of structures or body parts and their relationships to on another. Anatomy : Gross anatomy - macroscopic. Histology - microscopic.
Anatomical Terminology Dr. A. Ebneshahidi Anatomy Anatomy : is the study of structures or body parts and their relationships to on another. Anatomy : Gross anatomy - macroscopic. Histology - microscopic.
Anatomical Considerations for Lab Practical II
 Anatomical Considerations for Lab Practical II For each of the following please be prepared to provide: Identification System Organ(s) or ducts to Function(s) location which it is attached Use your lecture
Anatomical Considerations for Lab Practical II For each of the following please be prepared to provide: Identification System Organ(s) or ducts to Function(s) location which it is attached Use your lecture
Part 1: Communication between CNS & PNS
 Ch. 6: Peripheral Nervous System Objectives: 1. Communication between CNS & PNS: afferent (sensory) pathway versus efferent (motor) pathway of information. 2. Regulation of somatic (voluntary) motor system
Ch. 6: Peripheral Nervous System Objectives: 1. Communication between CNS & PNS: afferent (sensory) pathway versus efferent (motor) pathway of information. 2. Regulation of somatic (voluntary) motor system
Lectures Muscular System 10-1
 Lectures 12-14 Muscular System 10-1 Properties of Muscle Ability of a muscle to shorten with force Capacity of muscle to respond to a stimulus Muscle can be stretched to its normal resting length and beyond
Lectures 12-14 Muscular System 10-1 Properties of Muscle Ability of a muscle to shorten with force Capacity of muscle to respond to a stimulus Muscle can be stretched to its normal resting length and beyond
Clinical Anatomy, Embryology and Imaging BMS 6115C. Summer Semester 2009 Lynn J. Romrell, Ph.D. Course Director. Course Schedule
 Anatomy, Embryology and Imaging BMS 6115C Summer Semester 2009 Lynn J. Romrell, Ph.D. Course Director Course Schedule Color codes for course activities: Anatomy Sessions Anatomic Radiology Sessions Embryology
Anatomy, Embryology and Imaging BMS 6115C Summer Semester 2009 Lynn J. Romrell, Ph.D. Course Director Course Schedule Color codes for course activities: Anatomy Sessions Anatomic Radiology Sessions Embryology
Functional anatomy and variability of the blood vessels of the upper and lower limbs. Anastasia Bendelic Human Anatomy Departament
 Functional anatomy and variability of the blood vessels of the upper and lower limbs Anastasia Bendelic Human Anatomy Departament Plan: 1. Variations of the branching pattern of the aortic arch 2. Arterial
Functional anatomy and variability of the blood vessels of the upper and lower limbs Anastasia Bendelic Human Anatomy Departament Plan: 1. Variations of the branching pattern of the aortic arch 2. Arterial
Lab no 1 Structural organization of the human body
 Physiology Lab Manual Page 1 of 6 Lab no 1 Structural organization of the human body Physiology is the science which deals with functions of the body parts, and how they work. Since function cannot be
Physiology Lab Manual Page 1 of 6 Lab no 1 Structural organization of the human body Physiology is the science which deals with functions of the body parts, and how they work. Since function cannot be
Veins of the Face and the Neck
 Veins of the Face and the Neck Facial Vein The facial vein is formed at the medial angle of the eye by the union of the supraorbital and supratrochlear veins. connected through the ophthalmic veins with
Veins of the Face and the Neck Facial Vein The facial vein is formed at the medial angle of the eye by the union of the supraorbital and supratrochlear veins. connected through the ophthalmic veins with
The Musculoskeletal System
 The Musculoskeletal System Introduction The skeletal system and muscular system are often considered together because they are close in terms of structure and function. The two systems are referred to
The Musculoskeletal System Introduction The skeletal system and muscular system are often considered together because they are close in terms of structure and function. The two systems are referred to
Human Anatomy Biology 351
 Human Anatomy Biology 351 Lower Limb Please place your name on the back of the last page of this exam. You must answer all questions on this exam. Because statistics demonstrate that, on average, between
Human Anatomy Biology 351 Lower Limb Please place your name on the back of the last page of this exam. You must answer all questions on this exam. Because statistics demonstrate that, on average, between
Anatomy&Embryology Final Exam
 Anatomy&Embryology Final Exam Done by : Maha AbuAjamieh 1. Fertilisation is more likely to occur: A) 12-24 hours after ovulation. B) 24-40 hours after ovulation. C) 40-72 hours after ovulation. 2. wrong
Anatomy&Embryology Final Exam Done by : Maha AbuAjamieh 1. Fertilisation is more likely to occur: A) 12-24 hours after ovulation. B) 24-40 hours after ovulation. C) 40-72 hours after ovulation. 2. wrong
Course Specifications
 Cairo University Faculty of Medicine Department of Anatomy Course Specifications Course title: Human Anatomy and Embryology (1 st year) (Code): ANA-101 Department offering the course: Anatomy Department
Cairo University Faculty of Medicine Department of Anatomy Course Specifications Course title: Human Anatomy and Embryology (1 st year) (Code): ANA-101 Department offering the course: Anatomy Department
Femoral Artery. Its entrance to the thigh Position Midway between ASIS and pubic symphysis
 Lower Limb Vessels Lecture Objectives Describe the major arteries of the lower limb. Describe the deep and superficial veins of the lower limb. Describe the topographical relationships of the arteries
Lower Limb Vessels Lecture Objectives Describe the major arteries of the lower limb. Describe the deep and superficial veins of the lower limb. Describe the topographical relationships of the arteries
Human Anatomy Biology 351
 nnnnn 1 Human Anatomy Biology 351 Exam #2 Please place your name on the back of the last page of this exam. You must answer all questions on this exam. Because statistics demonstrate that, on average,
nnnnn 1 Human Anatomy Biology 351 Exam #2 Please place your name on the back of the last page of this exam. You must answer all questions on this exam. Because statistics demonstrate that, on average,
Biology 2401 Muscles List for CPC models
 Biology 2401 List for CPC models Italicized muscles are dissect and similar in the cat = Dissect and note the differences in human and cat Major of the Human Head Facial Expression Epicranius frontalis
Biology 2401 List for CPC models Italicized muscles are dissect and similar in the cat = Dissect and note the differences in human and cat Major of the Human Head Facial Expression Epicranius frontalis
Rachana Sareeram. : Classes for 6 months, including examination & result. Study leave + Universrity Exam for 2 months
 Rachana Sareeram It is proposed to divide the 1-½ years of professional course into three terms as envisaged by DAME. The three terms, study leave & periodical exams can be as follows: TTerm 1 Term 2 Term
Rachana Sareeram It is proposed to divide the 1-½ years of professional course into three terms as envisaged by DAME. The three terms, study leave & periodical exams can be as follows: TTerm 1 Term 2 Term
Lecture 10 Arteries and veins of the upper limb
 Lecture 10 Arteries and veins of the upper limb 1. Identify the Subclavian, axillary, brachial (deep and superficial), radial and ulnar arteries and superficial/deep palmar arches 2. Describe the major
Lecture 10 Arteries and veins of the upper limb 1. Identify the Subclavian, axillary, brachial (deep and superficial), radial and ulnar arteries and superficial/deep palmar arches 2. Describe the major
First stage Lec.1 : Introduction. Asst.Lec.Dr.ABDULRIDHA ALASADY
 First stage 2018-2019 Lec.1 : Introduction Asst.Lec.Dr.ABDULRIDHA ALASADY Anatomy the study of the structure and shape of the body and body parts & their relationships to one another aided by dissection
First stage 2018-2019 Lec.1 : Introduction Asst.Lec.Dr.ABDULRIDHA ALASADY Anatomy the study of the structure and shape of the body and body parts & their relationships to one another aided by dissection
Introduction to Anatomical Terms. Packet #3
 Introduction to Anatomical Terms Packet #3 Directional Terms Directional terms describe the positions of structures relative to other structures or locations in the body. Introduction Superior vs. Inferior
Introduction to Anatomical Terms Packet #3 Directional Terms Directional terms describe the positions of structures relative to other structures or locations in the body. Introduction Superior vs. Inferior
Anatomical Language. Human Anatomy & Physiology Honors Ms. Chase
 Anatomical Language Human Anatomy & Physiology Honors 2014 2015 Ms. Chase Anatomical Position Body erect, feet slightly apart, palms facing forward, thumbs point away from the body DIRECTIONAL TERMS Allow
Anatomical Language Human Anatomy & Physiology Honors 2014 2015 Ms. Chase Anatomical Position Body erect, feet slightly apart, palms facing forward, thumbs point away from the body DIRECTIONAL TERMS Allow
Which Artery am I? I am one of two smaller arteries that arise from the brachial. I supply blood to the medial aspect of the forearm.
 I am one of two smaller arteries that arise from the brachial. I supply blood to the medial aspect of the forearm. A. I supply blood to the head and neck. I am large and will branch into two smaller arteries.
I am one of two smaller arteries that arise from the brachial. I supply blood to the medial aspect of the forearm. A. I supply blood to the head and neck. I am large and will branch into two smaller arteries.
Lab Exercise #5 The Muscular System Student Performance Objectives
 Student Performance Objectives The material that you are required to learn in this exercise can be found in either the lecture text or the supplemental materials provided in lab. Prior to coming to class,
Student Performance Objectives The material that you are required to learn in this exercise can be found in either the lecture text or the supplemental materials provided in lab. Prior to coming to class,
Chapter 11: The Muscular System. Copyright 2009, John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
 Chapter 11: The Muscular System Muscle Attachment Sites: Origin & Insertion n Skeletal muscles cause movements by exerting force on tendons, which pulls on bones or other structures. n Articulating bones
Chapter 11: The Muscular System Muscle Attachment Sites: Origin & Insertion n Skeletal muscles cause movements by exerting force on tendons, which pulls on bones or other structures. n Articulating bones
Nervous System. Student Learning Objectives:
 Nervous System Student Learning Objectives: Identify the primary parts of the neuron Identify the major structures of the central nervous system Identify the major structures of the peripheral nervous
Nervous System Student Learning Objectives: Identify the primary parts of the neuron Identify the major structures of the central nervous system Identify the major structures of the peripheral nervous
