2 The Skeletal System
|
|
|
- Linda Barbara Skinner
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 4 Answer Key for PAL TM 3.0 Lab Guide 2 The Skeletal System Axial Skeleton Skull Self Review Exercise 2.1 A. Temporal B. Zygomatic C. Sphenoid D. Ethmoid E. Maxilla F. Mandible G. Vomer H. Inferior nasal concha I. Lacrimal J. Nasal Exercise 2.2 A. External acoustic meatus B. Lambdoid suture C. External occipital protuberance D. Mastoid process E. Styloid process F. Zygomatic process Exercise 2.3 A. Parietal B. Sutural C. Superior nuchal line D. External occipital protuberance Exercise 2.4 A. Lesser wing of sphenoid B. Greater wing of sphenoid C. Occipital D. Temporal E. Sella turcica F. Cribriform plate G. Crista galli H. Frontal Exercise 2.5 A. Olfactory foramina B. Optic canal C. Foramen spinosum D. Foramen lacerum Exercise 2.6 A. Palatine B. Sphenoid C. Temporal D. Mastoid process E. Occipital F. Occipital condyle G. Vomer H. Zygomatic Exercise 2.7 A. Frontal B. Ethmoid C. Lacrimal D. Palatine K. Frontal L. Glabella M. Inferior orbital fissure N. Infraorbital foramen O. Nasal spine P. Mental foramen Q. Alveolar margin R. Perpendicular plate S. Superior orbital fissure T. Supraorbital foramen/supraorbital notch G. Pterygoid process H. Nasal spine I. Temporal process J. Lacrimal fossa K. Squamous suture L. Coronal suture E. Occipital F. Temporal G. Lambdoid suture H. Sagittal suture I. Superior orbital fissure J. Internal acoustic meatus K. Hypoglossal canal L. Foramen magnum M. Jugular foramen N. Foramen rotundum O. Optic canal E. Foramen magnum F. Jugular foramen G. Carotid canal H. Foramen ovale I. Maxilla J. Mandibular fossa K. Foramen spinosum L. Foramen lacerum M. Foramen magnum N. Jugular foramen O. Carotid canal P. Foramen ovale E. Maxilla F. Zygomatic G. Sphenoid
2 Answer Key for PAL TM 3.0 Lab Guide 5 Exercise 2.8 A. Greater horn B. Lesser horn C. Body Vertebral Column Self Review Exercise 2.9 A. Spinous processes B. Intervertebral foramina C. Intervertebral discs D. Sacrum and (sacral) curvature Exercise 2.10 A. Transverse process B. Superior articular facet Exercise 2.11 A. Vertebral foramen B. Pedicle C. Transverse process D. Dens (odontoid process) E. Superior articular facet Exercise 2.12 A. Vertebral foramen B. Lamina C. Superior articular facet D. Pedicle Exercise 2.13 A. Transverse process B. Transverse costal facet C. Spinous process D. Inferior articular process Exercise 2.14 A. Sacral canal B. Median sacral crest C. Sacral hiatus D. Coccyx E. Cervical vertebrae and curvature F. Thoracic vertebrae and curvature G. Lumbar vertebrae and curvature C. Anterior arch D. Lateral mass F. Lamina G. Body H. Inferior articular facet I. Spinous process J. Transverse foramen E. Body F. Transverse process G. Transverse foramen H. Spinous process E. Costal demifacet F. Body G. Costal facet H. Superior articular process and facet E. Sacral foramina F. Ala G. Superior articular facet H. Body Thoracic Cage Self Review Exercise 2.15 A. Clavicular notch B. Manubrium C. Sternal angle Exercise 2.16 A. Costal groove B. Articular tubercle and facet C. Neck D. Body E. Xiphoid process F. Jugular notch D. Head E. Costal angle F. Body Bone Rotation Questions Axial Skeleton A. Anterior view B. Inferior view C. Posterosuperior view Axial Skeleton Quiz 1. Temporal 2. Parietal bones 3. Tympanic 4. Mandibular fossa; temporal bone
3 6 Answer Key for PAL TM 3.0 Lab Guide 5. frontal, sphenoid, ethmoid, maxilla, zygomatic, lacrimal, palatine 6. temporal, zygomatic 7. Posterior to the ear 8. Ethmoid (perpendicular plate) and vomer 9. a. external acoustic meatus yes b. jugular foramen yes c. internal acoustic meatus yes d. carotid canal yes e. foramen spinosum no f. foramen ovale no g. foramen rotundum no h. optic canal no 10. cervical: 7; thoracic: 12; lumbar: 5; sacrum: 5; coccyx: Transverse foramina 12. Transverse costal facets 13. Anterior manubrium, body, xiphoid process True ribs have direct connections to the sternum via individual costal cartilages. The first three pairs of false ribs attach indirectly to the sternum via fused costal cartilages. The final two pairs of false ribs, the floating ribs, have no attachment to the sternum. 17. Hyoid; axial skeleton 18. Cribriform plate: olfactory nerves; Optic canals: optic nerves 19. Bones: maxillae, frontal, sphenoid, ethmoid Functions: warm and humidify air, lighten skull; sound resonance 20. Vertebral arteries: transverse foramina of cervical vertebrae; foramen magnum Internal carotid arteries: carotid canals Internal jugular veins: jugular foramina 1. Normal: An intervertebral disc has an inner pocket of gelatinous material called the nucleus pulposus. Surrounding the nucleus pulposus is the anulus fibrosus, a tough connective tissue layer consisting of fibrocartilage and collagen fibers. Herniated: If the anulus fibrosis is ruptured by age-related degeneration or physical trauma, protrusion of the nucleus pulposus into the vertebral foramen occurs. The herniation presses on spinal nerves and/or the spinal cord and causes numbness and/or severe pain. 2. Primary curvature: Develops when an infant is able to hold up its head Secondary curvature: develops when a child is able to sit and stand Appendicular Skeleton Pectoral Girdle Self Review Exercise 2.17 A. Acromial end B. Conoid tubercle C. Sternal end Exercise 2.18 A. Acromion B. Lateral angle and neck C. Subscapular fossa D. Lateral (axillary) border E. Inferior angle F. Medial (vertebral) border G. Superior angle H. Superior border I. Coracoid process J. Supraspinous fossa K. Spine L. Infraspinous fossa M. Infraglenoid tubercle N. Glenoid fossa (cavity) O. Acromion Upper Limb Self Review Exercise 2.19 A. Greater tubercle B. Intertubercular sulcus (groove) C. Deltoid tuberosity D. Radial fossa E. Capitulum F. Trochlea G. Coronoid fossa H. Lesser tubercle I. Head J. Anatomical neck K. Surgical neck L. Radial groove M. Medial supracondylar ridge N. Medial epicondyle O. Olecranon fossa P. Lateral epicondyle Q. Lateral supracondylar ridge R. Shaft
4 Answer Key for PAL TM 3.0 Lab Guide 7 Exercise 2.20 A. Olecranon process B. Styloid process C. Head D. Interosseous border Exercise 2.21 A. Head B. Neck C. Shaft Exercise 2.22 A. Metacarpal 1 B. Phalanges of digit 1 C. Distal phalanx of digit 3 D. Middle phalanx of digit 3 E. Proximal phalanx of digit 3 F. Phalanges of digit 5 G. Metacarpal 5 H. Pisiform E. Shaft F. Radial notch G. Coronoid process H. Trochlear notch D. Styloid process E. Interosseous border (crest) F. Radial tuberosity I. Hamate J. Capitate K. Triquetral L. Lunate M. Scaphoid N. Trapezium O. Trapezoid Pelvic Girdle Self Review Exercise 2.23 A. Iliac fossa B. Iliac crest C. Obturator foramen Exercise 2.24 A. Posterior superior iliac spine B. Sacrum C. Coccyx D. Ischial tuberosity Exercise 2.25 A. Coccyx B. Body (of sacrum) C. Iliac crest D. Iliac fossa D. Ischial tuberosity E. Pubic symphysis F. Acetabulum G. Pubic tubercle E. Ischial spine F. Posterior inferior iliac spine G. Greater sciatic notch H. Iliac crest E. Superior articular process F. Pubic crest G. Ischial spine Lower Limb Self Review Exercise 2.26 A. Greater trochanter B. Shaft C. Lateral epicondyle D. Patellar surface E. Medial epicondyle F. Lesser trochanter G. Neck H. Head I. Medial supracondylar line Exercise 2.27 A. Lateral condyle B. Tibial tuberosity C. Anterior crest D. Medial malleolus J. Adductor tubercle K. Medial condyle L. Intercondylar fossa M. Lateral condyle N. Lateral supracondylar line O. Linea aspera P. Gluteal tuberosity Q. Intertrochanteric crest E. Medial condyle F. Interosseous crest (border) G. Fibular notch H. Articular facet for head of fibula Exercise 2.28 A. Head B. Interosseus border (crest) C. Lateral malleolus
5 8 Answer Key for PAL TM 3.0 Lab Guide Exercise 2.29 A. Calcaneus B. Cuboid C. Lateral cuneiform D. Metatarsals E. Middle phalanges F. Distal phalanges G. Proximal phalanges H. Medial cuneiform I. Intermediate cuneiform J. Navicular K. Talus Bone Rotation Questions Appendicular Skeleton Question 1 A. Anterior view B. Posterior view Question 2 A. Lateral view B. Medial view C. Posterior view Question 3 A. Posterior view B. Medial view C. Lateral view Appendicular Skeleton Quiz 1. Acromion 2. Humerus, head 3. Ulna, scaphoid, lunate, and triquetrum/triquetral 4. trapezium, triquetral/triquetrum, trapezoid, pisiform, scaphoid, capitate, lunate, hamate 5. Olecranon process 6. Radius 7. a. 5th middle phalanx 8. a. humerus b. clavicle c. humerus d. scapula e. humerus f. ulna g. radius and ulna h. scapula 9. pubis, ischium, ilium 10. Femur, head 11. Tibia 12. Calcaneus 13. Ischial tuberosity 14. The patella articulates with the patellar surface of the femur. 15. c. lateral cuneiform 16. a. femur b. tibia c. fibula d. tibia e. patella f. femur g. tibia 17. Pubic angle is larger in the female (80 90 ); ilium is flared; ischial tuberosities are farther apart than in male; tilted more forward than male; true pelvis is broad and shallow
6 Answer Key for PAL TM 3.0 Lab Guide 9 1. The anterior border of the carpal tunnel consists of the transverse ligament which connects the hamate and pisiform to the trapezium. The posterior border consists of the carpal bones which come together to form a concavity anteriorly. Thus, a tunnel is formed through which the median nerve and the tendons of flexor muscles pass. Overuse of the flexor muscles can cause the tendons to inflame and compress the median nerve. 2. Bone growth is stimulated by weight-bearing activities. The deltoid muscle of the body builder applies more force to the humerus at its attachment site, which results in a large deltoid tuberosity. Joints Human Cadaver Self Review Exercise 2.30 A. Acetabular labrum B. Head of femur C. Greater trochanter Exercise 2.31 A. Medial condyle of femur B. Medial condyle of tibia C. Patellar ligament D. Head of fibula E. Lateral condyle of tibia F. Lateral condyle of femur G. Patella H. Quadriceps tendon/tendon of quadriceps femoris muscle D. Lesser trochanter E. Neck of femur F. Acetabulum I. Posterior cruciate ligament J. Medial meniscus K. Anterior cruciate ligament L. Medial collateral ligament/tibial collateral ligament M. Lateral meniscus N. Lateral collateral ligament/fibular collateral ligament Human Cadaver Quiz 1. Femur, tibia, patella 2. a. knee b. knee c. hip d. hip e. knee 3. Cartilaginous 4. a. synovial b. cartilaginous c. synovial d. cartilaginous e. synovial f. fibrous g. synovial h. synovial i. cartilaginous j. fibrous 1. The distal femur and proximal tibia are removed. They are replaced by metal and/or plastic implants shaped like the femoral and tibial condyles. 2. A sesamoid bone is a short bone that develops within a tendon. The patella is located within the tendon of the quadriceps femoris, a group of four muscles that extends the knee. Distal to the patella the tendon becomes the patellar ligament, which inserts onto the tibial tuberosity. Thus, the entire extensor mechanism of the knee includes the quadriceps, the quadriceps tendon, the patella, the patellar ligament, and the tibial tuberosity. The patella acts as a fulcrum to increase the force exerted by the quadriceps during knee extension. Anatomical Models Self Review Exercise 2.32 A. Acromioclavicular ligament B. Coracoacromial ligament C. Coracohumeral ligament D. Biceps brachii tendon E. Humerus F. Teres major muscle G. Capsular ligaments H. Clavicle I. Acromioclavicular ligament J. Supraspinatus muscle & tendon K. Scapula L. Infraspinatus muscle & tendon M. Teres major muscle N. Teres minor muscle & tendon O. Biceps brachii tendon P. Coracohumeral ligament
7 10 Answer Key for PAL TM 3.0 Lab Guide Exercise 2.33 A. Ulna B. Radius C. Anular ligament D. Radial collateral ligament Exercise 2.34 A. Iliofemoral ligament B. Femur C. Pubofemoral ligament Exercise 2.35 A. Articular surface of lateral condyle of femur B. Anterior cruciate ligament C. Articular surface of lateral condyle of tibia D. Tibial tuberosity E. Patellar ligament F. Tendon of quadriceps femoris muscle/ quadriceps tendon G. Patella E. Humerus F. Anular ligament G. Ulnar collateral ligament D. Coxal/hip bone E. Iliofemoral ligament F. Ischiofemoral ligament H. Articular surface of medial condyle of tibia I. Articular surface of medial condyle of femur J. Medial meniscus K. Tibial collateral ligament/medial collateral ligament L. Posterior cruciate ligament M. Lateral meniscus N. Fibular collateral ligament/lateral collateral ligament Exercise 2.36 A. Sacroiliac joints B. Pubic symphysis C. Intervertebral disc Anatomical Models Quiz 1. three 2. a. pelvic b. elbow c. knee d. hip e. knee f. elbow g. knee h. knee i. elbow j. hip k. knee 3. Ball-and-socket 4. Tibial (medial) collateral ligament, medial meniscus, anterior cruciate ligament 5. a. ball-and-socket b. plane c. hinge d. condyloid e. ball-and-socket f. condyloid g. pivot h. plane i. hinge j. pivot k. saddle 1. The joint capsule 2. Synovial membrane or synovium 3. The presence of crystals initiates a localized immune-mediated inflammation of the joint. An increase in fluid within the joint causes it to swell and can result in damage to the soft tissues of the joint. Tissues of the Skeletal System Histology Self Review Exercise 2.37 A. Chondrocytes in lacunae B. Matrix C. Hyaline cartilage D. Perichondrium Exercise 2.38 A. Matrix B. Chondrocytes in lacunae
8 Answer Key for PAL TM 3.0 Lab Guide 11 Exercise 2.39 A. Elastic cartilage B. Perichondrium Exercise 2.40 A. Lamellae B. Perforating canal C. Osteons (Haversian systems)/central canals Exercise 2.41 A. Bone marrow B. Trabeculae of spongy bone C. Osteoclast D. Trabeculae of woven bone Exercise 2.42 A. Cartilaginous epiphysis B. Diaphysis C. Periosteal bone collar D. Periosteum E. Skin C. Matrix D. Chondrocytes in lacunae D. Central canal E. Canaliculi F. Lacunae G. Lamella E. Endosteum F. Osteogenic cells G. Osteoblasts H. Periosteum F. Resting zone G. Proliferation zone H. Hypertrophic zone I. Calcification zone J. Ossification zone Histology Quiz 1. Lacuna/lacunae 2. Elastic cartilage 3. b. resting zone 4. c. hypertrophic zone 5. Trabeculae 6. a. both b. compact bone only c. both d. both e. compact bone only f. compact bone only g. both 7. Hyaline cartilage 8. Fibrocartilage 9. Osteoblasts: make and secrete bone matrix; Osteoclasts: resorb bone matrix 1. Estrogen inhibits osteoclast activity in premenopausal women. With menopause, however, estrogen levels sharply decline. As a result, bone resorption outpaces bone deposition in older women, leading to fragile bones. Note that certain bone fractures cause excessive bleeding that can be fatal. This is particularly a problem for those who are infirm, elderly, and living alone. 2. The nutrient-rich blood supply to cartilage is limited to the surrounding perichondrium and does not extend into the cartilage itself. Consequently, it takes longer for chondroblasts to create new, healthy cartilage. Skeletal System Lab Practical 1. Maxilla 2. Mandible 3. Vomer 4. External acoustic meatus 5. Mastoid process 6. Zygomatic process 7. Temporal process/temporal process of zygomatic bone 8. Greater wing of sphenoid 9. Crista galli 10. Sella turcica 11. Occipital bone 12. Atlas/C1 13. Transverse foramen 14. Thoracic 15. Spinous process 16. Greater tubercle 17. Head 18. Lesser tubercle 19. Patellar surface 20. Medial condyle 21. Adductor tubercle 22. Fibula 23. Lateral malleolus 24. Medial malleolus 25. Cuboid 26. Calcaneus 27. Talus 28. Acromion 29. Spine 30. Medial/vertebral border 31. Medial meniscus 32. Quadriceps tendon/tendon of quadriceps femoris group 33. Fibular (lateral) collateral ligament 34. Acromioclavicular ligament 35. Coracoacromial ligament 36. Scapula 37. Central canal 38. Lacunae 39. Perichondrium 40. Chondrocytes (in lacunae)
Biology 2401 The Skeletal System
 Biology 2401 The Skeletal System Purpose: The lab will describe the microscopic and gross anatomy of bone, identify bones of the body, and identify important bone markings. I. Overview of the Skeleton
Biology 2401 The Skeletal System Purpose: The lab will describe the microscopic and gross anatomy of bone, identify bones of the body, and identify important bone markings. I. Overview of the Skeleton
Bone Flashcards for 10a
 Bone Flashcards for 0a CLAVICLE (collar bone). Sternal extremity (end) flat end. Acromial extremity (end) rounded end. SCAPULA (shoulder blade). Right or left scapula?. Superior border (superior margin).
Bone Flashcards for 0a CLAVICLE (collar bone). Sternal extremity (end) flat end. Acromial extremity (end) rounded end. SCAPULA (shoulder blade). Right or left scapula?. Superior border (superior margin).
Axial skeleton bones and markings
 Axial skeleton bones and markings Skull Cranial bones Frontal x 1 Supraorbital foramen Occipital x 1 Foramen magnum Occipital condyles Superior nuchal line Inferior nuchal line Anterior cranial fossa External
Axial skeleton bones and markings Skull Cranial bones Frontal x 1 Supraorbital foramen Occipital x 1 Foramen magnum Occipital condyles Superior nuchal line Inferior nuchal line Anterior cranial fossa External
bio4165 lab quiz 1 Posterior View Anterior View Lateral View Anterior View bio fall.quarter lab.quiz.1...page.1 of 6
 B A Posterior View D C E Lateral View bio.4165...fall.quarter.2005...lab.quiz.1...page.1 of 6 F I G 35 Posterior View H bio.4165...fall.quarter.2005...lab.quiz.1...page.2 of 6 J Posterior View L K Inferior
B A Posterior View D C E Lateral View bio.4165...fall.quarter.2005...lab.quiz.1...page.1 of 6 F I G 35 Posterior View H bio.4165...fall.quarter.2005...lab.quiz.1...page.2 of 6 J Posterior View L K Inferior
Riverside Community College Anatomy & Physiology 2B SPRING 2012 EXAM #1-ABC (Nervous System)
 Riverside Community College Anatomy & Physiology 2B SPRING 2012 EXAM #1-ABC (Nervous System) Name: 1) This vertebra is an example of a(n). 1) A) thoracic B) axis C) atlas D) lumbar E) sacral 1 2) W hich
Riverside Community College Anatomy & Physiology 2B SPRING 2012 EXAM #1-ABC (Nervous System) Name: 1) This vertebra is an example of a(n). 1) A) thoracic B) axis C) atlas D) lumbar E) sacral 1 2) W hich
Perpendicular Plate Zygomatic Bone. Mental Foramen Mandible
 Glabella Frontal Middle Nasal Concha Nasal Lacrimal Perpendicular Plate Zygomatic Inferior Nasal Concha Maxilla Mental Mandible Skull (anterior view) Squamosal Suture Coronal Suture Frontal Parietal Nasal
Glabella Frontal Middle Nasal Concha Nasal Lacrimal Perpendicular Plate Zygomatic Inferior Nasal Concha Maxilla Mental Mandible Skull (anterior view) Squamosal Suture Coronal Suture Frontal Parietal Nasal
Spring Written By: J. E. Sutton. Contents: I. Overview of the Skeleton: II. Appendicular Skeleton III. Axial Skeleton IV.
 Spring 2012 Written By: J. E. Sutton Contents: I. Overview of the Skeleton: II. Appendicular Skeleton III. Axial Skeleton IV. Articulations Overview of the Skeleton: I. Orientation to Human Skeleton: a.
Spring 2012 Written By: J. E. Sutton Contents: I. Overview of the Skeleton: II. Appendicular Skeleton III. Axial Skeleton IV. Articulations Overview of the Skeleton: I. Orientation to Human Skeleton: a.
Bone List Anatomy
 1 Frontal Bone Skull 2 Parietal Bone Skull 3 Occipital Bone Skull 4 Temporal Bone Skull 5 Coronal Suture Skull 6 Sagittal Suture Skull 7 Squamous suture Skull 8 Lambdoid Suture Skull 9 Surpaorbital Ridge
1 Frontal Bone Skull 2 Parietal Bone Skull 3 Occipital Bone Skull 4 Temporal Bone Skull 5 Coronal Suture Skull 6 Sagittal Suture Skull 7 Squamous suture Skull 8 Lambdoid Suture Skull 9 Surpaorbital Ridge
External Acoustic Meatus. Mastoid Process. Zygomatic Process. Temporal Bone
 Bone lab review 1. Frontal Bone 2. Supra-Orbital Foramen 3. Orbit (Orbital Cavity) 4. Superior Orbital Fissure 5. Inferior Orbital Fissure 6. Zygomatic Bone 7. Infra-Orbital Foramen 8. Maxilla 9. Mandible
Bone lab review 1. Frontal Bone 2. Supra-Orbital Foramen 3. Orbit (Orbital Cavity) 4. Superior Orbital Fissure 5. Inferior Orbital Fissure 6. Zygomatic Bone 7. Infra-Orbital Foramen 8. Maxilla 9. Mandible
the Skeletal System provided by Academic Web Services Grand Canyon University
 Anatomy Resource Center Study Guides the Skeletal System HEAD & NECK REGIONAL VIEW SKULL BONES CRANIUM FACE SKULL LANDMARKS ANTERIOR SIDE SUPERIOR/INFERIOR VERTEBRAL COLUMN VERTEBRAL REGIONS CERVICAL C1
Anatomy Resource Center Study Guides the Skeletal System HEAD & NECK REGIONAL VIEW SKULL BONES CRANIUM FACE SKULL LANDMARKS ANTERIOR SIDE SUPERIOR/INFERIOR VERTEBRAL COLUMN VERTEBRAL REGIONS CERVICAL C1
Lab Unit One Flashcards
 CLAVICLE (collar bone). Sternal extremity (end) flat end. Acromial extremity (end) rounded end.. Conoid tubercle near round end SCAPULA (shoulder blade). Right or left scapula?. Superior border (superior
CLAVICLE (collar bone). Sternal extremity (end) flat end. Acromial extremity (end) rounded end.. Conoid tubercle near round end SCAPULA (shoulder blade). Right or left scapula?. Superior border (superior
Chapter 7: Skeletal System: Gross Anatomy
 Chapter 7: Skeletal System: Gross Anatomy I. General Considerations A. How many bones in an average adult skeleton? B. Anatomic features of bones are based on II. Axial Skeleton A. Skull 1. Functionally
Chapter 7: Skeletal System: Gross Anatomy I. General Considerations A. How many bones in an average adult skeleton? B. Anatomic features of bones are based on II. Axial Skeleton A. Skull 1. Functionally
Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D. 1 SCCC BIO130 Lab 7 Appendicular Skeleton & Articulations
 The Skeletal System II: Appendicular Skeleton and Articulations Exercises 11, 13 (begins: page 145 in 9 th and 10 th editions) Exercises 10, 11 (begins: page 147 in 11 th edition, page 149 in 12 th edition)
The Skeletal System II: Appendicular Skeleton and Articulations Exercises 11, 13 (begins: page 145 in 9 th and 10 th editions) Exercises 10, 11 (begins: page 147 in 11 th edition, page 149 in 12 th edition)
TEST YOURSELF- Chapter 7
 TEST YOURSELF- Chapter 7 Cranial Bones 1. Give the name of the bone for each of the following markings. Some of the markings are found on more than one bone. List all that apply. Cranium a. Frontal squama:
TEST YOURSELF- Chapter 7 Cranial Bones 1. Give the name of the bone for each of the following markings. Some of the markings are found on more than one bone. List all that apply. Cranium a. Frontal squama:
Exercise Science Section 2: The Skeletal System
 Exercise Science Section 2: The Skeletal System An Introduction to Health and Physical Education Ted Temertzoglou Paul Challen ISBN 1-55077-132-9 Role of the Skeleton Protection Framework Attachments for
Exercise Science Section 2: The Skeletal System An Introduction to Health and Physical Education Ted Temertzoglou Paul Challen ISBN 1-55077-132-9 Role of the Skeleton Protection Framework Attachments for
Skeletal System - Prelab 1
 Skeletal System - Prelab 1 1. Which bones contain the paranasal sinuses? What function do the sinuses serve? 2. What two areas are separated from each other by the hard palate? Name the two bones that
Skeletal System - Prelab 1 1. Which bones contain the paranasal sinuses? What function do the sinuses serve? 2. What two areas are separated from each other by the hard palate? Name the two bones that
The Appendicular Skeleton
 8 The Appendicular Skeleton PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris 8-1 The Pectoral Girdle The Pectoral Girdle Also called shoulder girdle Connects the
8 The Appendicular Skeleton PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris 8-1 The Pectoral Girdle The Pectoral Girdle Also called shoulder girdle Connects the
BIOLOGY 113 LABORATORY Skeletal System
 BIOLOGY 113 LABORATORY Skeletal System Objectives Distinguish between the axial and appendicular skeleton. Distinguish between the cranium and facial skeleton. Locate and name the bones of the skull and
BIOLOGY 113 LABORATORY Skeletal System Objectives Distinguish between the axial and appendicular skeleton. Distinguish between the cranium and facial skeleton. Locate and name the bones of the skull and
Biology 218 Human Anatomy. Adapted from Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 7 The Skeletal System Appendicular Division
 Adapted from Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 7 The Skeletal System Appendicular Division Introduction The appendicular skeleton includes: Pectoral girdle Shoulder bones Upper limbs Pelvic girdle
Adapted from Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 7 The Skeletal System Appendicular Division Introduction The appendicular skeleton includes: Pectoral girdle Shoulder bones Upper limbs Pelvic girdle
BONE CHALLENGE DANIL HAMMOUDI.MD
 BONE CHALLENGE DANIL HAMMOUDI.MD Bone Basic functions? A. support B. protection C. movement assistance in D. RBC formation-hemopoiesis E. mineral homeostasis +importance of calcium F. energy supply -yellow
BONE CHALLENGE DANIL HAMMOUDI.MD Bone Basic functions? A. support B. protection C. movement assistance in D. RBC formation-hemopoiesis E. mineral homeostasis +importance of calcium F. energy supply -yellow
SKELETAL SYSTEM 206. AXIAL SKELETON 80 APPENDICULAR SKELETON 126 (see Figure 6.1) Clavicle. Clavicle. Pectoral girdles. Scapula. Scapula.
 SKELETAL SYSTEM 206 AXIAL SKELETON 80 APPENDICULAR SKELETON 126 (see Figure 6.1) Pectoral girdles 4 Clavicle Scapula 2 2 Clavicle Scapula Humerus 2 Humerus Upper limbs 60 Radius 2 Ulna Carpal bones Metacarpal
SKELETAL SYSTEM 206 AXIAL SKELETON 80 APPENDICULAR SKELETON 126 (see Figure 6.1) Pectoral girdles 4 Clavicle Scapula 2 2 Clavicle Scapula Humerus 2 Humerus Upper limbs 60 Radius 2 Ulna Carpal bones Metacarpal
Chapter 8. The Appendicular Skeleton. Lecture Presentation by Lee Ann Frederick University of Texas at Arlington Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 8 The Appendicular Skeleton Lecture Presentation by Lee Ann Frederick University of Texas at Arlington An Introduction to the Appendicular Skeleton The Appendicular Skeleton 126 bones Allows us
Chapter 8 The Appendicular Skeleton Lecture Presentation by Lee Ann Frederick University of Texas at Arlington An Introduction to the Appendicular Skeleton The Appendicular Skeleton 126 bones Allows us
Lab Exercise #04 The Skeletal System Student Performance Objectives
 Lab Exercise #04 The Skeletal System Student Performance Objectives The material that you are required to learn in this exercise can be found in either the lecture text or the supplemental materials provided
Lab Exercise #04 The Skeletal System Student Performance Objectives The material that you are required to learn in this exercise can be found in either the lecture text or the supplemental materials provided
Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology
 Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology 1 Chapter 7 Skeletal System Bone Classification Long Bones Short Bones Flat Bones Irregular Bones Sesamoid (Round) Bones 2 Parts of a Long Bone epiphysis distal proximal
Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology 1 Chapter 7 Skeletal System Bone Classification Long Bones Short Bones Flat Bones Irregular Bones Sesamoid (Round) Bones 2 Parts of a Long Bone epiphysis distal proximal
Lab 6, 7, 8: Skeletal System
 107 Lab 6, 7, 8: Skeletal System Adult Skull Bony orbit (FLEZMS) Frontal bone supraorbital foramen frontal sinus Lacrimal bone Ethmoid bone perpendicular plate of ethmoid middle nasal conchae cribriform
107 Lab 6, 7, 8: Skeletal System Adult Skull Bony orbit (FLEZMS) Frontal bone supraorbital foramen frontal sinus Lacrimal bone Ethmoid bone perpendicular plate of ethmoid middle nasal conchae cribriform
Lab Activity 9. Appendicular Skeleton Martini Chapter 8. Portland Community College BI 231
 Lab Activity 9 Appendicular Skeleton Martini Chapter 8 Portland Community College BI 231 Appendicular Skeleton Upper & Lower extremities Shoulder Girdle Pelvic Girdle 2 Humerus 3 Humerus: Proximal End
Lab Activity 9 Appendicular Skeleton Martini Chapter 8 Portland Community College BI 231 Appendicular Skeleton Upper & Lower extremities Shoulder Girdle Pelvic Girdle 2 Humerus 3 Humerus: Proximal End
Labs 6, 7, 8: Skeletal System
 153 Labs 6, 7, 8: Skeletal System Unit 6: Skeletal System: Bone tissue, Bones and Joints (p. 105-152) Ex. 6-1: Histology of Osseous Tissue, p. 113 Model: Osteon Tiss Lamella Osteocyte Lacunae Canaliculi
153 Labs 6, 7, 8: Skeletal System Unit 6: Skeletal System: Bone tissue, Bones and Joints (p. 105-152) Ex. 6-1: Histology of Osseous Tissue, p. 113 Model: Osteon Tiss Lamella Osteocyte Lacunae Canaliculi
Axial Skeleton BONE TERMINOLOGY FEATURES
 Axial Skeleton BONE TERMINOLOGY FEATURES Tuberosity Rounded area on bone often roughened for muscle attachment. Tubercle Rounded projection on bone. This is called a tuberosity on the femur. Crest Ridgeline
Axial Skeleton BONE TERMINOLOGY FEATURES Tuberosity Rounded area on bone often roughened for muscle attachment. Tubercle Rounded projection on bone. This is called a tuberosity on the femur. Crest Ridgeline
10/11/2009. What is wrong with this picture? BONE PICTURE EXAM MARS / IN WHAT PART OF THE BONE DO YOU FIND THIS TISSUE SLIDE?
 What is wrong with this picture? BONE PICTURE EXAM MARS 2008 1/ IN WHAT PART OF THE BONE DO YOU FIND THIS TISSUE SLIDE? 1 2/ IDENTIFY THIS TISSUE? 3/what is wrong in this picture? 2 4/ Identify these cells
What is wrong with this picture? BONE PICTURE EXAM MARS 2008 1/ IN WHAT PART OF THE BONE DO YOU FIND THIS TISSUE SLIDE? 1 2/ IDENTIFY THIS TISSUE? 3/what is wrong in this picture? 2 4/ Identify these cells
Biology 218 Human Anatomy
 Chapter 8 Adapted from Tortora 10 th ed. LECTURE OUTLINE A. Introduction (p. 203) 1. The appendicular skeleton contains 126 bones that form: i. two pectoral (shoulder) girdles two upper limbs i one pelvic
Chapter 8 Adapted from Tortora 10 th ed. LECTURE OUTLINE A. Introduction (p. 203) 1. The appendicular skeleton contains 126 bones that form: i. two pectoral (shoulder) girdles two upper limbs i one pelvic
PRE-LAB EXERCISES. Before we get started, look up the definitions of these common bone marking terms: Canal: Condyle: Facet: Fissure:
 1 PRE-LAB EXERCISES When studying the skeletal system, the bones are often sorted into two broad categories: the axial skeleton and the appendicular skeleton. This lab focuses on the appendicular skeleton,
1 PRE-LAB EXERCISES When studying the skeletal system, the bones are often sorted into two broad categories: the axial skeleton and the appendicular skeleton. This lab focuses on the appendicular skeleton,
APPENDICULAR SKELETON 126 AXIAL SKELETON SKELETAL SYSTEM. Cranium. Skull. Face. Skull and associated bones. Auditory ossicles. Associated bones.
 SKELETAL SYSTEM 206 AXIAL SKELETON 80 APPENDICULAR SKELETON 26 Skull Skull and associated s 29 Cranium Face Auditory ossicles 8 4 6 Associated s Hyoid Thoracic cage 25 Sternum Ribs 24 Vertebrae 24 column
SKELETAL SYSTEM 206 AXIAL SKELETON 80 APPENDICULAR SKELETON 26 Skull Skull and associated s 29 Cranium Face Auditory ossicles 8 4 6 Associated s Hyoid Thoracic cage 25 Sternum Ribs 24 Vertebrae 24 column
Anatomy Lab: The skeletal system. Part I: Vertebrae and Thoracic cage
 ANA Lab: Bone 1 Anatomy Lab: The skeletal system Part I: Vertebrae and Thoracic cage Spine (Vertebrae) Body Vertebral arch Vertebral canal Pedicle Lamina Spinous process Transverse process Sup. articular
ANA Lab: Bone 1 Anatomy Lab: The skeletal system Part I: Vertebrae and Thoracic cage Spine (Vertebrae) Body Vertebral arch Vertebral canal Pedicle Lamina Spinous process Transverse process Sup. articular
Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology Tenth Edition. Chapter 7
 PowerPoint Lecture Outlines to accompany Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology Tenth Edition Shier Butler Lewis Chapter 7 Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or
PowerPoint Lecture Outlines to accompany Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology Tenth Edition Shier Butler Lewis Chapter 7 Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or
Pectoral (Shoulder) Girdle
 Chapter 8 Skeletal System: Appendicular Skeleton Pectoral girdle Pelvic girdle Upper limbs Lower limbs 8-1 Pectoral (Shoulder) Girdle Consists of scapula and clavicle Clavicle articulates with sternum
Chapter 8 Skeletal System: Appendicular Skeleton Pectoral girdle Pelvic girdle Upper limbs Lower limbs 8-1 Pectoral (Shoulder) Girdle Consists of scapula and clavicle Clavicle articulates with sternum
The Appendicular Skeleton
 8 The Appendicular Skeleton PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris An Introduction to the Appendicular Skeleton Learning Outcomes 8-1 Identify the bones
8 The Appendicular Skeleton PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris An Introduction to the Appendicular Skeleton Learning Outcomes 8-1 Identify the bones
Cranium Facial bones. Sternum Rib
 Figure 7.1 The human skeleton. Skull Thoracic cage (ribs and sternum) Cranium Facial bones Sternum Rib Bones of pectoral girdle Vertebral column Sacrum Vertebra Bones of pelvic girdle (a) Anterior view
Figure 7.1 The human skeleton. Skull Thoracic cage (ribs and sternum) Cranium Facial bones Sternum Rib Bones of pectoral girdle Vertebral column Sacrum Vertebra Bones of pelvic girdle (a) Anterior view
Bio 5/6 5 The Skeletal System Study Guide
 Name: THE SKELETAL SYSTEM: 5 The Skeletal System Study Guide Period: The skeleton is constructed of two of the most supportive tissues found in the human body - cartilage and bone. Besides supporting and
Name: THE SKELETAL SYSTEM: 5 The Skeletal System Study Guide Period: The skeleton is constructed of two of the most supportive tissues found in the human body - cartilage and bone. Besides supporting and
Anatomy & Physiology Skeletal System Worksheet
 1. Name the five functions of the skeleton. c) d) e) Anatomy & Physiology Skeletal System Worksheet 2. The term for the shaft of a bone is:. 3. The bony struts found in spongy bone are called. 4. In ossification,
1. Name the five functions of the skeleton. c) d) e) Anatomy & Physiology Skeletal System Worksheet 2. The term for the shaft of a bone is:. 3. The bony struts found in spongy bone are called. 4. In ossification,
Important Parts of Bones
 Important Parts of Bones For 2015 Know: Humerus (posterior) Clavical Femur (Anterior) Foot Hand Mandible Os Coxa Scapula Skull (Anterior, Inferior, Lateral) Sternum Humerus (posterior) A. olecranon fossa
Important Parts of Bones For 2015 Know: Humerus (posterior) Clavical Femur (Anterior) Foot Hand Mandible Os Coxa Scapula Skull (Anterior, Inferior, Lateral) Sternum Humerus (posterior) A. olecranon fossa
Chapter 8B. The Skeletal System: Appendicular Skeleton. The Appendicular Skeleton. Clavicle. Pectoral (Shoulder) Girdle
 The Appendicular Skeleton Chapter 8B The Skeletal System: Appendicular Skeleton 126 bones Pectoral (shoulder) girdle Pelvic (hip) girdle Upper limbs Lower limbs Functions primarily to facilitate movement
The Appendicular Skeleton Chapter 8B The Skeletal System: Appendicular Skeleton 126 bones Pectoral (shoulder) girdle Pelvic (hip) girdle Upper limbs Lower limbs Functions primarily to facilitate movement
Ch. 5 - Skeletal System
 Ch. 5 - Skeletal System Bones are living, ever-changing structures. This allows them grow and adapt to new situations that the body encounters. The functions of the skeletal system: 1) support bones are
Ch. 5 - Skeletal System Bones are living, ever-changing structures. This allows them grow and adapt to new situations that the body encounters. The functions of the skeletal system: 1) support bones are
Anatomy images for MSS practical exam- 2019
 Anatomy images for MSS practical exam- 2019 Ilium Ischium Pubis Acetabulaum Iliac crest Iliac tubercle ASIS (muscle and ligament attached) AIIS (muscle attached) PSIS PIIS Ischial spine Ischial tuberosity
Anatomy images for MSS practical exam- 2019 Ilium Ischium Pubis Acetabulaum Iliac crest Iliac tubercle ASIS (muscle and ligament attached) AIIS (muscle attached) PSIS PIIS Ischial spine Ischial tuberosity
Biology 152 Appendicular Skeleton Anatomy Objectives
 Biology 152 Appendicular Skeleton Anatomy Objectives We will learn proper bone names, left/right/medial, and the parts of bones in this exercise. Start by learning the names of the bones. As you gain comfort
Biology 152 Appendicular Skeleton Anatomy Objectives We will learn proper bone names, left/right/medial, and the parts of bones in this exercise. Start by learning the names of the bones. As you gain comfort
Bio 103 Skeletal System 45
 45 Lecture Outline: SKELETAL SYSTEM [Chapters 7, 8] Introduction A. Components B. Functions 1. 2. 3. 4. Classification and Parts A. Bone Shapes 1. Long: 2. Short: 3. Flat: 4. Irregular: 5. Sesamoid: B.
45 Lecture Outline: SKELETAL SYSTEM [Chapters 7, 8] Introduction A. Components B. Functions 1. 2. 3. 4. Classification and Parts A. Bone Shapes 1. Long: 2. Short: 3. Flat: 4. Irregular: 5. Sesamoid: B.
SKELETON FUNCTIONS OF BONE:
 SKELETON FUNCTIONS OF BONE: SKELETON: 1. Performs a mechanical function in forming the skeletal support of the body and in forming a leverage system whereby work and movement are possible. 2. Serves as
SKELETON FUNCTIONS OF BONE: SKELETON: 1. Performs a mechanical function in forming the skeletal support of the body and in forming a leverage system whereby work and movement are possible. 2. Serves as
10/12/2010. Upper Extremity. Pectoral (Shoulder) Girdle. Clavicle (collarbone) Skeletal System: Appendicular Skeleton
 Skeletal System: Appendicular Skeleton Pectoral girdle Pelvic girdle Upper limbs Lower limbs 8-1 Pectoral (Shoulder) Girdle Consists of scapula and clavicle Clavicle articulates with sternum (Sternoclavicular
Skeletal System: Appendicular Skeleton Pectoral girdle Pelvic girdle Upper limbs Lower limbs 8-1 Pectoral (Shoulder) Girdle Consists of scapula and clavicle Clavicle articulates with sternum (Sternoclavicular
BIO 137 AXIAL SKELETON BONE STUDY THE HUMAN SKELETON
 BIO 137 THE AXIAL SKELETON MARY CATHERINE FLATH, Ph.D. THE HUMAN SKELETON AXIAL SKULL HYOID THORACIC CAGE VERTEBRAL COLUMN APPENDICULAR PECTORAL GIRDLE UPPER LIMBS PELVIC GIRDLE LOWER LIMBS AXIAL SKELETON
BIO 137 THE AXIAL SKELETON MARY CATHERINE FLATH, Ph.D. THE HUMAN SKELETON AXIAL SKULL HYOID THORACIC CAGE VERTEBRAL COLUMN APPENDICULAR PECTORAL GIRDLE UPPER LIMBS PELVIC GIRDLE LOWER LIMBS AXIAL SKELETON
Nervous & Skeletal Systems. Virtual Science University
 Nervous & Skeletal Systems Virtual Science University 1 Nervous & Skeletal Systems Texas TEK B.10(A) The student will interpret the function of systems in organisms (humans) including the nervous and skeletal
Nervous & Skeletal Systems Virtual Science University 1 Nervous & Skeletal Systems Texas TEK B.10(A) The student will interpret the function of systems in organisms (humans) including the nervous and skeletal
Introduction. Skeletal Nomenclature. Lesson One: Bones of the Upper Extremity. Shoulder Girdle: Clavicle. Scapula: Bony Markings
 Chapter 14 Skeletal Nomenclature Susan G. Salvo Bones help locate muscles Can also be areas to avoid Chapter divided into 5 lessons covering bones, bony markings, and joints Introduction 1 2 Lesson One:
Chapter 14 Skeletal Nomenclature Susan G. Salvo Bones help locate muscles Can also be areas to avoid Chapter divided into 5 lessons covering bones, bony markings, and joints Introduction 1 2 Lesson One:
Chapter 8 The Skeletal System: The Appendicular Skeleton. Copyright 2009 John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
 Chapter 8 The Skeletal System: The Appendicular Skeleton Appendicular Skeleton The primary function is movement It includes bones of the upper and lower limbs Girdles attach the limbs to the axial skeleton
Chapter 8 The Skeletal System: The Appendicular Skeleton Appendicular Skeleton The primary function is movement It includes bones of the upper and lower limbs Girdles attach the limbs to the axial skeleton
Chapter 7. Skeletal System
 Chapter 7 Skeletal System 1 Skull A. The skull is made up of 22 bones: 8 cranial bones, 13 facial bones, and the mandible. B. The Cranium encloses and protects the brain, provides attachments for muscles,
Chapter 7 Skeletal System 1 Skull A. The skull is made up of 22 bones: 8 cranial bones, 13 facial bones, and the mandible. B. The Cranium encloses and protects the brain, provides attachments for muscles,
11/25/2012. Chapter 7 Part 2: Bones! Skeletal Organization. The Skull. Skull Bones to Know Cranium
 Chapter 7 Part 2: Bones! 5) Distinguish between the axial and appendicular skeletons and name the major parts of each 6) Locate and identify the bones and the major features of the bones that compose the
Chapter 7 Part 2: Bones! 5) Distinguish between the axial and appendicular skeletons and name the major parts of each 6) Locate and identify the bones and the major features of the bones that compose the
The Skeletal System. overview of the skeleton. the skull. the vertebral column and. thoracic cage. the pectoral girdle and upper limb
 The Skeletal System Parietal bone Frontal bone overview of the skeleton Skull the vertebral column and Mandible Mandible Pectoral girdle the skull Maxilla Clavicle Scapula Sternum Thoracic cage Humerus
The Skeletal System Parietal bone Frontal bone overview of the skeleton Skull the vertebral column and Mandible Mandible Pectoral girdle the skull Maxilla Clavicle Scapula Sternum Thoracic cage Humerus
YOU MUST BRING YOUR OWN GLOVES FOR THIS ACTIVITY.
 ACTIVITY 3: AXIAL SKELETON AND LONG BONE DISSECTION Objectives: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapter 7, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 5e. All text references are for this textbook. Learning the meanings
ACTIVITY 3: AXIAL SKELETON AND LONG BONE DISSECTION Objectives: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapter 7, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 5e. All text references are for this textbook. Learning the meanings
Labs 9 and 10. Classification of Bones. Bone Shapes 1/05/13. Skeletal system overview. Bone are identified by:
 Labs 9 and 10 Skeletal system overview Classification of Bones Bone are identified by: shape internal tissues bone markings 1. Flat bones 2. Long bones 3. Short bones 4. Irregular bones 5. Sutural bones
Labs 9 and 10 Skeletal system overview Classification of Bones Bone are identified by: shape internal tissues bone markings 1. Flat bones 2. Long bones 3. Short bones 4. Irregular bones 5. Sutural bones
Biology 218 Human Anatomy. Adapted from Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 6 The Skeletal System: Axial Division
 Adapted from Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 6 The Skeletal System: Axial Division Introduction The axial skeleton: Composed of bones along the central axis of the body Divided into three regions:
Adapted from Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 6 The Skeletal System: Axial Division Introduction The axial skeleton: Composed of bones along the central axis of the body Divided into three regions:
Chapter 7: Skeletal System
 Chapter 7: Skeletal System The Skeletal System Introduction P. 182 Bone is an organ made up of tissues: It is made up of the following components. Cartilage Blood Nerves Bone Connective Bone Classification
Chapter 7: Skeletal System The Skeletal System Introduction P. 182 Bone is an organ made up of tissues: It is made up of the following components. Cartilage Blood Nerves Bone Connective Bone Classification
Skeletal system overview. Classification of Bones
 Skeletal system overview BIOL241 Lab #9 Classification of Bones Bone are identified by: shape internal tissues bone markings 1 1. Flat bones 2. Long bones 3. Short bones 4. Irregular bones 5. Sutural bones
Skeletal system overview BIOL241 Lab #9 Classification of Bones Bone are identified by: shape internal tissues bone markings 1 1. Flat bones 2. Long bones 3. Short bones 4. Irregular bones 5. Sutural bones
ACTIVITY 3: AXIAL SKELETON AND LONG BONE DISSECTION COW BONE DISSECTION
 ACTIVITY 3: AXIAL SKELETON AND LONG BONE DISSECTION Objectives: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapter 7, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 4e. All text references are for this textbook. Learning the meanings
ACTIVITY 3: AXIAL SKELETON AND LONG BONE DISSECTION Objectives: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapter 7, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 4e. All text references are for this textbook. Learning the meanings
Nervous/Vascular/Skeletal Systems
 L 2 A B O R A T O R Y Nervous/Vascular/Skeletal Systems NERVOUS SYSTEM Identify the structures associated with the central nervous system and the peripheral nervous system. Identify the location of gray
L 2 A B O R A T O R Y Nervous/Vascular/Skeletal Systems NERVOUS SYSTEM Identify the structures associated with the central nervous system and the peripheral nervous system. Identify the location of gray
Chapter 8A. The Skeletal System: The Axial Skeleton. The Skeletal System: The Axial Skeleton. Types of Bones. Types of Bones
 Chapter 8A The Skeletal System: The Axial Skeleton The Skeletal System: The Axial Skeleton 206 named bones Axial Skeleton 80 bones lie along longitudinal axis skull, hyoid, vertebrae, ribs, sternum, ear
Chapter 8A The Skeletal System: The Axial Skeleton The Skeletal System: The Axial Skeleton 206 named bones Axial Skeleton 80 bones lie along longitudinal axis skull, hyoid, vertebrae, ribs, sternum, ear
Figure ) The area that causes the lengthwise growth of a long bone is indicated by letter. Diff: 2 Page Ref:
 Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 5 The Skeletal System Short Answer Figure 5.1 Using Figure 5.1, identify the following: 1) Spongy bone is indicated by letter. Diff: 1 Page Ref:
Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 5 The Skeletal System Short Answer Figure 5.1 Using Figure 5.1, identify the following: 1) Spongy bone is indicated by letter. Diff: 1 Page Ref:
Frontal Anterior cranium Supraorbital margins. Glabella Frontal sinus Coronal suture Parietal Superior/lateral cranium Sagittal suture
 The Skeleton Outline PART 1: THE AXIAL SKELETON I. The skull consists of 8 cranial bones and 14 facial bones (pp. 200 218; Figs. 7.1 7.18; Table 7.1). A. The cranial and facial bones form the framework
The Skeleton Outline PART 1: THE AXIAL SKELETON I. The skull consists of 8 cranial bones and 14 facial bones (pp. 200 218; Figs. 7.1 7.18; Table 7.1). A. The cranial and facial bones form the framework
Cornell Notes Name: Date: Topic: CH 5. Subject: The Skeletal System
 Cornell Notes Name: Date: Topic: CH 5 Questions/Main Ideas: Record Notes: We are revisiting Ch 3B on Connective Tissue prior to our study of Ch 5 Skeletal start on p.91-95 I. Types of Connective A. Bone
Cornell Notes Name: Date: Topic: CH 5 Questions/Main Ideas: Record Notes: We are revisiting Ch 3B on Connective Tissue prior to our study of Ch 5 Skeletal start on p.91-95 I. Types of Connective A. Bone
Overview of the Skeleton: Bone Markings
 Name Overview of the Skeleton: Bone Markings Match the terms in column B with the appropriate description in column A. Column A 1. sharp, slender process* 2. small rounded projection* 3. narrow ridge of
Name Overview of the Skeleton: Bone Markings Match the terms in column B with the appropriate description in column A. Column A 1. sharp, slender process* 2. small rounded projection* 3. narrow ridge of
Chapter 8. The Pectoral Girdle & Upper Limb
 Chapter 8 The Pectoral Girdle & Upper Limb Pectoral Girdle pectoral girdle (shoulder girdle) supports the arm consists of two on each side of the body // clavicle (collarbone) and scapula (shoulder blade)
Chapter 8 The Pectoral Girdle & Upper Limb Pectoral Girdle pectoral girdle (shoulder girdle) supports the arm consists of two on each side of the body // clavicle (collarbone) and scapula (shoulder blade)
Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology Eleventh Edition. Mrs. Hummer. Chapter 7 Skeletal System
 Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology Eleventh Edition Mrs. Hummer Chapter 7 Skeletal System 1 Chapter 7 Skeletal System Bone Classification Long Bones Short Bones Flat Bones Irregular Bones Sesamoid (Round)
Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology Eleventh Edition Mrs. Hummer Chapter 7 Skeletal System 1 Chapter 7 Skeletal System Bone Classification Long Bones Short Bones Flat Bones Irregular Bones Sesamoid (Round)
Skeletal System. Supplementary Information
 Skeletal System Supplementary Information COMMON ANATOMICAL TERMS Planes run through the body side to side and front to back eg. median plane Surfaces of the body are also named eg. anterior surface This
Skeletal System Supplementary Information COMMON ANATOMICAL TERMS Planes run through the body side to side and front to back eg. median plane Surfaces of the body are also named eg. anterior surface This
Chapter 08 Lecture Outline
 Chapter 08 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction or
Chapter 08 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction or
CHAPTER 7, PART II (BONES)
 Anatomy Name: CHAPTER 7, PART II (BONES) Entry #: INSTRUCTIONS: 1) READ Chapter 7, pg. 140-161. 2) Using the outline, make a note card for each underlined bone name or phrase. 3) On each note card, put
Anatomy Name: CHAPTER 7, PART II (BONES) Entry #: INSTRUCTIONS: 1) READ Chapter 7, pg. 140-161. 2) Using the outline, make a note card for each underlined bone name or phrase. 3) On each note card, put
Copyright 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings. Dr. Nabil khouri
 Dr. Nabil khouri Appendicular Skeleton The appendicular skeleton is made up of the bones of the upper and lower limbs and their girdles Two girdles: Pectoral girdles attach the upper limbs to the body
Dr. Nabil khouri Appendicular Skeleton The appendicular skeleton is made up of the bones of the upper and lower limbs and their girdles Two girdles: Pectoral girdles attach the upper limbs to the body
Objectives continued- Answer each of the objectives on a separate sheet of paper to demonstrate content mastery. Attach answers to back of packet.
 Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 5: The Skeletal System Name: Objectives- By the end of this chapter I will be able to: 1. Identify the subdivisions of the skeleton as axial or appendicular. 2. List at least
Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 5: The Skeletal System Name: Objectives- By the end of this chapter I will be able to: 1. Identify the subdivisions of the skeleton as axial or appendicular. 2. List at least
8.2: Fibrous Joints. There are three (3) types of fibrous joints (synarthroses): Syndesmosis Suture Gomphosis. Interosseus membrane of leg.
 8.1: Introduction Are known as articulations Functional junctions between bones Bind parts of skeletal system together Make bone growth possible Permit parts of the skeleton to change shape during childbirth
8.1: Introduction Are known as articulations Functional junctions between bones Bind parts of skeletal system together Make bone growth possible Permit parts of the skeleton to change shape during childbirth
Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
 E. VERTEBRAL COLUMN 1. The vertebral column extends from the skull to the pelvis and forms the vertical axis of the skeleton. 2. The vertebral column is composed of vertebrae that are separated by intervertebral
E. VERTEBRAL COLUMN 1. The vertebral column extends from the skull to the pelvis and forms the vertical axis of the skeleton. 2. The vertebral column is composed of vertebrae that are separated by intervertebral
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology
 Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14 th Edition CHAPTER 8 The Skeletal System: The Appendicular Skeleton The Appendicular Skeleton The 126 bones of the appendicular skeleton are primarily concerned
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14 th Edition CHAPTER 8 The Skeletal System: The Appendicular Skeleton The Appendicular Skeleton The 126 bones of the appendicular skeleton are primarily concerned
Chapter 7 Part C The Skeleton
 Chapter 7 Part C The Skeleton Part 2 The Appendicular Skeleton Consists of bones of the limbs and their girdles Pectoral girdle Attaches upper limbs to body trunk Pelvic girdle Attaches lower limbs to
Chapter 7 Part C The Skeleton Part 2 The Appendicular Skeleton Consists of bones of the limbs and their girdles Pectoral girdle Attaches upper limbs to body trunk Pelvic girdle Attaches lower limbs to
TEST BANK FOR THE HUMAN BODY IN HEALTH AND ILLNESS 5TH EDITION BY BARBARA HERLIHY Chapter 8: Skeletal System
 Link download Full : http://testbankair.com/download/test-bank-for-thehuman-body-in-health-and-illness-5th-edition-by-barbara-herlihy/ TEST BANK FOR THE HUMAN BODY IN HEALTH AND ILLNESS 5TH EDITION BY
Link download Full : http://testbankair.com/download/test-bank-for-thehuman-body-in-health-and-illness-5th-edition-by-barbara-herlihy/ TEST BANK FOR THE HUMAN BODY IN HEALTH AND ILLNESS 5TH EDITION BY
Chapter 8 The Skeletal System: The Appendicular Skeleton. Copyright 2009 John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
 Chapter 8 The Skeletal System: The Appendicular Skeleton Appendicular Skeleton It includes bones of the upper and lower limbs Girdles attach the limbs to the axial skeleton The pectoral girdle consists
Chapter 8 The Skeletal System: The Appendicular Skeleton Appendicular Skeleton It includes bones of the upper and lower limbs Girdles attach the limbs to the axial skeleton The pectoral girdle consists
BIOL 2010 Human Anatomy & Physiology I -- Exam 3 -Form A- Name:
 BIOL 2010 Human Anatomy & Physiology I -- Exam 3 -Form A- Name: 1. Another name for the bones of the hand is A. phalanges. B. metacarpals. C. tarsals. D. carpals. 2. If you stand on tiptoes to reach something
BIOL 2010 Human Anatomy & Physiology I -- Exam 3 -Form A- Name: 1. Another name for the bones of the hand is A. phalanges. B. metacarpals. C. tarsals. D. carpals. 2. If you stand on tiptoes to reach something
I. Organization of the Skeletal System A. Types of Bone Tissue - Architectural Arrangement 1. Compact (Dense) Bone 2. Spongy (Cancellous) Bone B.
 I. Organization of the Skeletal System A. Types of Bone Tissue - Architectural Arrangement 1. Compact (Dense) Bone 2. Spongy (Cancellous) Bone B. Bone Structure 1. Periosteum a. Osteoblasts b. Osteocytes
I. Organization of the Skeletal System A. Types of Bone Tissue - Architectural Arrangement 1. Compact (Dense) Bone 2. Spongy (Cancellous) Bone B. Bone Structure 1. Periosteum a. Osteoblasts b. Osteocytes
THE SKELETAL SYSTEM. Focus on the Skull
 THE SKELETAL SYSTEM Focus on the Skull Review Anatomical Terms Anterior/Posterior Dorsal/Ventral Medial/Lateral Superior/Inferior Bone Markings - Review Projections for attachment of muscles, ligaments
THE SKELETAL SYSTEM Focus on the Skull Review Anatomical Terms Anterior/Posterior Dorsal/Ventral Medial/Lateral Superior/Inferior Bone Markings - Review Projections for attachment of muscles, ligaments
Chapter 07. Lecture Outline. See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables pre-inserted into PowerPoint without notes and animations.
 Chapter 07 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables pre-inserted into PowerPoint without notes and animations. 1-1 Chapter 7 Skeletal System Gross Anatomy 7.1 Skeletal
Chapter 07 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables pre-inserted into PowerPoint without notes and animations. 1-1 Chapter 7 Skeletal System Gross Anatomy 7.1 Skeletal
Human Skeletal Anatomy
 C H P T E R Human Skeletal natomy Detail of Compact one CHPTER Figure - Skull: Face ONE. Frontal. Inferior concha. Lacrimal. Nasal. Parietal. Sphenoid. Temporal. Vomer. Zygomatic (malar). Maxilla FORMIN
C H P T E R Human Skeletal natomy Detail of Compact one CHPTER Figure - Skull: Face ONE. Frontal. Inferior concha. Lacrimal. Nasal. Parietal. Sphenoid. Temporal. Vomer. Zygomatic (malar). Maxilla FORMIN
The Skeletal System: Axial Skeleton
 The Skeletal System: Axial Skeleton The Big Idea The Axial Skeleton & Homeostasis The bones of the axial skeleton contribute to homeostasis by protecting many of the body s organs such as the brain, spinal
The Skeletal System: Axial Skeleton The Big Idea The Axial Skeleton & Homeostasis The bones of the axial skeleton contribute to homeostasis by protecting many of the body s organs such as the brain, spinal
Chapter 8 *Lecture PowerPoint The Skeletal System
 Chapter 8 *Lecture PowerPoint The Skeletal System *See separate FlexArt PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Introduction Many organs are named for their
Chapter 8 *Lecture PowerPoint The Skeletal System *See separate FlexArt PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Introduction Many organs are named for their
Lab 1: body, skeletal and axial systems
 Lab 1: body, skeletal and axial systems Types of tissue Epithelia tissue - Sheets of tissue covering other tissues or linin cavities - Protective tissue e.g. skin - Cell types: squamous, cuboid, columnar
Lab 1: body, skeletal and axial systems Types of tissue Epithelia tissue - Sheets of tissue covering other tissues or linin cavities - Protective tissue e.g. skin - Cell types: squamous, cuboid, columnar
The Skeletal System. Yong Jeong, MD, PhD Department of Bio and Brain Engineering
 5 The Skeletal System Yong Jeong, MD, PhD Department of Bio and Brain Engineering The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system Bones (skeleton) Joints Cartilages Ligaments Two subdivisions of the skeleton
5 The Skeletal System Yong Jeong, MD, PhD Department of Bio and Brain Engineering The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system Bones (skeleton) Joints Cartilages Ligaments Two subdivisions of the skeleton
Chapter 7 - Skeletal System
 Chapter 7 - Skeletal System 7.1 Introduction A. Bones contain a variety of very active tissues. B. Each bone is made up of several types of tissues and thus is an organ. C. Bone functions include: muscle
Chapter 7 - Skeletal System 7.1 Introduction A. Bones contain a variety of very active tissues. B. Each bone is made up of several types of tissues and thus is an organ. C. Bone functions include: muscle
Overview of the Skeleton
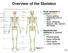 Overview of the Skeleton Skull Pectoral girdle Thoracic cage Pelvis Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Frontal bone Maxilla Mandible Clavicle Scapula
Overview of the Skeleton Skull Pectoral girdle Thoracic cage Pelvis Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Frontal bone Maxilla Mandible Clavicle Scapula
Chapter 8 Outline. Pectoral Girdle Upper Limb Pelvic Girdle Lower Limb Aging of the Appendicular Skeleton Development of the Appendicular Skeleton
 Chapter 8 Outline Pectoral Girdle Upper Limb Pelvic Girdle Lower Limb Aging of the Appendicular Skeleton Development of the Appendicular Skeleton Figure 8.1 Appendicular Skeleton Pectoral Girdle Clavicle
Chapter 8 Outline Pectoral Girdle Upper Limb Pelvic Girdle Lower Limb Aging of the Appendicular Skeleton Development of the Appendicular Skeleton Figure 8.1 Appendicular Skeleton Pectoral Girdle Clavicle
B. Each bone is made up of several types of tissues and so is an organ.
 Ch 7 Skeletal System Introduction: A. Bones are very active tissues B. Each bone is made up of several types of tissues and so is an organ. C. Bone functions include: muscle attachment, protection and
Ch 7 Skeletal System Introduction: A. Bones are very active tissues B. Each bone is made up of several types of tissues and so is an organ. C. Bone functions include: muscle attachment, protection and
Appendicular Skeleton. Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi
 Appendicular Skeleton Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi a.alnuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk abdulameerh@yahoo.com Hi Prof, It is great to hear from you, I really enjoyed your teaching last year. You taught me the hardest
Appendicular Skeleton Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi a.alnuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk abdulameerh@yahoo.com Hi Prof, It is great to hear from you, I really enjoyed your teaching last year. You taught me the hardest
Bones of the skull & face
 Bones of the skull & face Cranium= brain case or helmet Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. The cranium is composed of eight bones : frontal Occipital
Bones of the skull & face Cranium= brain case or helmet Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. The cranium is composed of eight bones : frontal Occipital
UNIT 4 - SKELETAL SYSTEM LECTURE NOTES
 UNIT 4 - SKELETAL SYSTEM LECTURE NOTES 4.01 FUNCTIONS OF THE SKELETAL SYSTEM A. Support 1. Provides a framework for the body 2. Supports soft tissue 3. Serves as a point of attachment for ligaments, tendons,
UNIT 4 - SKELETAL SYSTEM LECTURE NOTES 4.01 FUNCTIONS OF THE SKELETAL SYSTEM A. Support 1. Provides a framework for the body 2. Supports soft tissue 3. Serves as a point of attachment for ligaments, tendons,
THE SKELETAL SYSTEM. Focus on the Pectoral Girdle
 THE SKELETAL SYSTEM Focus on the Pectoral Girdle Appendicular Skeleton 126 bones Includes bones of the limbs (arms and legs) Pectoral girdle (shoulder) Pelvic girdle (hip) Pectoral Girdle (the shoulder)
THE SKELETAL SYSTEM Focus on the Pectoral Girdle Appendicular Skeleton 126 bones Includes bones of the limbs (arms and legs) Pectoral girdle (shoulder) Pelvic girdle (hip) Pectoral Girdle (the shoulder)
Crafton Hills College Human Anatomy & Physiology Axial Skeleton
 A. Major Divisions Crafton Hills College Human Anatomy & Physiology Axial keleton 1. Axial: Part of skeleton lies along long axis of body 2. Appendicular: Bones & features of the appendages B. AXIAL KELETON
A. Major Divisions Crafton Hills College Human Anatomy & Physiology Axial keleton 1. Axial: Part of skeleton lies along long axis of body 2. Appendicular: Bones & features of the appendages B. AXIAL KELETON
The Skeletal System. Mosby items and derived items 2010, 2006, 2002, 1997, 1992 by Mosby, Inc., an affiliate of Elsevier Inc.
 The Skeletal System Functions of Skeletal System Provides internal framework that supports the body Protects internal organs Helps fight disease by producing white blood cells 2 Functions of Skeletal System
The Skeletal System Functions of Skeletal System Provides internal framework that supports the body Protects internal organs Helps fight disease by producing white blood cells 2 Functions of Skeletal System
Ch. 5 Skeletal Tissues
 Ch. 5 Skeletal Tissues Human Anatomy B. Classification of bones 1. Bone types by structure a. Compact dense, smooth appearance b. Spongy a.k.a. cancellous, needlelike cells & much open space 2. Types by
Ch. 5 Skeletal Tissues Human Anatomy B. Classification of bones 1. Bone types by structure a. Compact dense, smooth appearance b. Spongy a.k.a. cancellous, needlelike cells & much open space 2. Types by
