The Role of Background Statistics in Face Adaptation
|
|
|
- James Campbell
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 The Journl of Neurosiene, Septemer 3, 29 29(39): Behviorl/Systems/Cognitive The Role of Bkground Sttistis in Fe Adpttion Jinhu Wu, * Hong Xu, * Peter Dyn, 2 nd Ning Qin Deprtments of Neurosiene nd Physiology & Cellulr Biophysis, Columi University, New York, New York 32, nd 2 Gtsy Computtionl Neurosiene Unit, University College London, London WCN 3AR, United Kingdom Cross-dpttion is widely used to proe whether different stimuli shre ommon neurl mehnisms. For exmple, tht dpttion to seond-order stimuli usully produes little ftereffet on first-order stimuli hs een interpreted s refleting their seprte proessing. However, suh results pper to ontrdit the ue-invrint responses of mny visul ells. We tested the novel hypothesis tht the null ftereffet rises from the lrge differene in the kgrounds of first- nd seond-order stimuli. We reted seond-order fes with hppy nd sd fil expressions speified solely y lol diretions of moving rndom dots on stti-dot kground, without ny luminne-defined form ues. As expeted, dpttion to suh seond-order fe did not produe fil-expression ftereffet on the first-order fes. However, onsistent with our hypothesis, simply dding stti rndom dots to the first-order fes to render their kgrounds more similr to tht of the dpting motion fe led to signifint ftereffet. This kground similrity effet lso ourred etween different types of first-order stimuli: rel-fe dpttion trnsferred to rtoon fes only when noise with orreltion sttistis of rel fes or nturl imges ws dded to the rtoon fes. These findings suggest the following: () sttistil similrities etween the fetureless kgrounds of the dpting nd test stimuli n influene ftereffets, s in ontingent dpttion; (2) wek or null ross-dpttion ftereffets should e interpreted with ution; nd (3) luminne- nd motion-diretion-defined forms, nd lol fetures nd glol sttistis, onverge in the representtion of fes. Introdution A entrl question in sensory proessing is whether different lsses of stimuli for the sme sensory ttriute shre ommon neurl representtion. The stndrd signture of suh shring is the trnsfer of n ftereffet in ross-dpttion. For vision, this question hs een prominently rised with respet to the omprison etween first-order, luminne-defined stimuli nd seond-order stimuli defined y vritions in ontrst, motion, texture, phse, nd sptil or temporl frequeny, et., without modultion of men luminne. The ommon psyhophysil nd neuroimging finding tht dpttion to seondorder stimuli does not sustntilly trnsfer to first-order stimuli (Nishid et l., 997; Lrsson et l., 26; Ashid et l., 27; Shofield et l., 27) hs duly een interpreted s inditing tht the two lsses of stimuli re proessed seprtely. Suh seprtion, however, ppers to e t odds with ueinvrint responses found t mny stges long the visul hierrhy. For exmple, some V ells nd lrger frtion of V2 ells hve similr tuning to first-order nd seond-order (illusoryontour) orienttions (von der Heydt et l., 984; Sheth et l., Reeived My 9, 29; revised July 5, 29; epted Aug. 2, 29. This work ws supported y Ntionl Institutes of Helth Grnt EY627 (N.Q.) nd y the Gtsy Chritle Foundtion nd the Biotehnology nd Biologil Sienes Reserh Counil, Engineering nd Physil Sienes Reserh Counil, nd Wellome Trust Grnt BB/E2536/ (P.D.). We re very grteful to n nonymous reviewer for suggesting tht we relte our results to ontingent ftereffets nd to Rihrd Lipkin for editoril ssistne. *J.W. nd H.X. ontriuted eqully to this work. Correspondene should e ddressed to Dr. Ning Qin, Deprtment of Neurosiene, Columi University/New York Stte Psyhitri Institute, Kol Annex, Room 59, 5 Riverside Drive, Box 87, New York, NY 32. E-mil: nq6@olumi.edu. H. Xu s present ddress: Division of Psyhology, Nnyng Tehnologil University, , Singpore. DOI:.523/JNEUROSCI Copyright 29 Soiety for Neurosiene /9/29235-$5./ 996). Likewise, susets of MT nd MSTd ells show similr tuning to first- nd seond-order motion ptterns (Alright, 992; Geesmn nd Andersen, 996). Moreover, shpe seletivity does not depend on whether the shpes re defined y first- or seondorder ues (Sry et l., 993; Grill-Spetor et l., 998). If suh ells ontriute signifintly to dpttion, then ftereffets should trnsfer, t lest prtilly, from seond- to first-order stimuli. Conversely, if they do not ontriute, then dpttion seems n indequte proe for shred neurl mehnisms. One hitherto unexplored onfounding ftor is tht, with the notle exeption of the one study (Georgeson nd Shofield, 22) tht did find signifint interorder ross-dpttion trnsfer, first- nd seond-order stimuli, y their onstrution, often hve different kground ptterns. For instne, typil firstorder orienttion stimulus is lk r on uniform white kground; however, its seond-order ounterprt might involve flikering dots in virtul retngle emedded in lrger kground of stti dots. Fetureless kgrounds ould e importnt sine, for instne, their size mkes them ontriute sustntilly to the sttistis of imges, nd visul dpttion is highly sensitive to suh sttistis (Field, 987; Atik nd Redlih, 99; Brlow, 99; Dn et l., 996; Winwright, 999; Brenner et l., 2; Simonelli nd Olshusen, 2; Zhoping, 26; Shwrtz et l., 27). However, theories onsidering imge sttistis fous on prediting visul reeptive fields rther thn rossdpttion ftereffets, wheres theories treting ftereffets onsider only sttistis of fetures ut not kgrounds. Therefore, we investigted the role of kground sttistis in the trnsfer of the fil-expression ftereffet etween different lsses of fes. We hose fe stimuli euse ue onvergene my e more pronouned t higher levels of proessing; we will
2 236 J. Neurosi., Septemer 3, 29 29(39): Wu et l. Bkground Sttistis nd Fe Adpttion report similr studies for lower-level stimuli seprtely. We found tht kground sttistis n e ritilly importnt for intertions not only etween first- nd seond-order stimuli ut lso etween different types of first-order stimuli. These findings hve implitions for the funtion nd mehnisms of dpttion nd the representtion of fes. Mterils nd Methods Sujets A totl of eight sujets onsented to prtiipte in the experiments of this study. Among them, two were experimenters, nd the rest were nive to the purpose of the study. All sujets hd norml or orreted to norml vision. Eh experimentl ondition hd four sujets, two of whom were nive. All sujets showed highly onsistent results. The study ws pproved y the Institutionl Review Bord of the New York Stte Psyhitri Institute. Apprtus Figure. The visul stimuli were presented on 2 inh ViewSoni P225f monitor ontrolled y Mintosh G4 omputer. The vertil refresh rte ws Hz, nd the sptil resolution ws pixels. In dimly lit room, sujets viewed the monitor from distne of 75 m, using hin rest to stilize hed position. Eh pixel sutended.29 t this distne. All luminne vlues ited in the pper were mesured with Minolt LS- photometer. All experiments were run in Mtl with Psyhophysis Toolox extensions (Brinrd, 997; Pelli, 997). Visul stimuli A lk (.23d/m 2 ) fixtion ross ws lwys shown t the enter of the white (56.2 d/m 2 ) sreen. It onsisted of two orthogonl line segments, eh.29 in length nd.6 in width. All stimuli were grysle. They inluded seond-order rtoon fes with motion grdient-defined fil expressions, first-order rtoon fes with luminne-defined fil expressions, nd first-order rel fes derived from the Ekmn Pitures of Fil Affet (PoFA) dtse (Ekmn nd Friesen, 976). Syntheti noises were used s kgrounds for some of the fe stimuli (see elow). Eh stimulus ws shown with the fixtion ross t its enter. Motion grdient rtoon fes. We generted these dynmi, seondorder fes in (29 29 pixels) squre ontining lk rndom dots on white kground. Eh dot hd size of pixel (.29 ). The dot density ws 5%. On this rndom-dot field, we defined virtul ring for the fe outline, two virtul disks for the eyes, nd horizontlly oriented virtul retngle for the mouth (Fig. ). The outline ring hd inner nd outer rdii of.77 nd.48, respetively, ontining 5 dots on verge. Eh eye disk hd rdius of.7, ontining 7 dots on verge. The mouth retngle ws.29.28, ontining 66 dots on verge. The mouth enter ws.64 elow the fe enter. The distne etween the eye nd mouth levels ws.22. The enter-to-enter distne etween the eyes ws.85. The dots within the fe-outline ring nd the eye disks rndomly flikered t Hz. This ws hieved y letting eh dot hve lifetime of ms ( frmes) nd get replotted to rndom lotion within its originl region when its lifetime ws rehed. The initil lifetimes of different dots were rndomized to void synhronous fliker. The dots within the mouth retngle hd different motion grdient ptterns to produe sd nd hppy expressions, s explined in the text (Fig.,). The motion long eh vertil line of the mouth retngle ws reted y moving window of pixel width on lrge field of rndom dots t the desired veloity; this voided dots jumping etween opposite edges of the retngle. To generte set of motion fes with expressions vrying grdully from sd to hppy, we let frtion of the dots (noise dots) in the mouth retngle fliker t Hz. These stimuli re referred to s motion fes. Stti rtoon fes. As in previous study (Xu et l., 28), we generted lk rtoon fes on white kground with n nti-lising method. The dimensions of the fe outline ring nd eye disks extly mthed those of the motion fes (Fig. d). The length nd thikness of the mouth urve lso mthed those of the motion fes. However, unlike the motion fes whose mouths were flt retngle, the mouths of the stti rtoon fes hd urvture vrying from onve to onvex (.34,.25,.7,.8,,.8, nd.7 in the units of / ) to produe spetrum of sd to hppy expressions. The positions of the eyes nd mouth within the stti rtoon fes were lso identil to those in the motion fes. Rel-fe imges. These stimuli were derived from imges from Ekmn PoFA dtse (Ekmn nd Friesen, 976) in the sme wy s previous study (Xu et l., 28), exept tht we ropped nd sled the imge size to nd presented them t higher ontrst (men mouth ontrst,.27). We pplied MorphMn 4. (STOIK Imging) to sd nd hppy fe of the sme person to generte 2 imges with the proportion of the hppy fe vrying from (sddest) to (hppiest) in steps of.5 (Fig. e). Those with proportions equl to,.5,.25,.3,.35,.4,.45,.5, nd.7 were used in the experiments. Noise kgrounds with vrious orreltion sttistis. We generted noise ptterns s kgrounds for stti rtoon fes in the lst experiment. We first omputed orreltion sttistis of rel fes y lulting the verge mplitude spetrum of the front-view fes in the Ekmn PoFA dtse (Ekmn nd Friesen, 976) nd Krolinsk Direted Emotionl Fes (KDEF) dtse (Lundqvist et l., 998). We used the stndrd proedure of first omputing the 2D Fourier trnsform of the imges nd then omining the mplitude spetrum ross different orienttions to otin D spetrum. We found tht the spetrum follows the /f k lw with k.63, where f is the sptil frequeny. We then generted /f k noise ptterns with k equl to,.5,.,.5, 2., nd 2.5. The k noise hd flt spetrum nd we generted it s sptil white noise. For other k vlues, we inverse trnsformed the /f k mplitude spetrum nd rndom phse spetrum to the sptil do d e Exmples of fe stimuli used in this study., An illustrtion for seond-order motion fes with motion grdientdefined expressions. Dshed lue urves nd lines define virtul regions for the fe outline, eyes, nd mouth. Dots inside the fe outline nd eye regions flikered t Hz.,, Dots inside the mouth retngle rried opposite motion grdient ptterns to produe sd nd hppy expressions. The vertil rrows indite the veloity of the dots in tht olumn. d, Stti rtoon fes genertedyournti-lisingprogrm. Themouthurvturevriedfromonvetoonvextoproduespetrumofsdtohppy expressions. e, Rel fes derived from two imges from the Ekmn PoFA dtse with MorphMn 4..
3 Wu et l. Bkground Sttistis nd Fe Adpttion J. Neurosi., Septemer 3, 29 29(39): min. Finlly, we pplied the stndrd histogrm equliztion proedure (MATLAB histeq funtion) to equlize the first-order distriutions of the noises to tht of the sddest rel fe. Therefore, noises with different k vlues ll hd the sme first-order distriutions ut different seondorder orreltion strutures. Proedures We used the method of onstnt stimuli nd the two-lterntive foredhoie prdigm in ll experiments. Sujets reeived no feedk on their performnes t ny time. We mesured fil expression pereption in the motion fes (mf) nd in the ontrols whose mouth region ws frme rndomized to destroy motion (mf r ). These onditions did not involve dpttion nd re denoted s -mf nd -mf r. For the -mf ondition, we rndomly interleved the upside-down hppiest nd sddest motion fes s th trils for the two nive sujets to ensure tht they judged fil expression, insted of motion diretion (see Results). We lso ross-dpted the motion fes nd the stti rtoon fes (f). The dpting stimulus ws either the sddest mf or the sddest f nd the test stimuli were either the set of the motion fes or the set of the stti rtoon fes. The four possile omintions re denoted s mf-mf, mf-f, f-mf, nd f-f, where, for exmple, mf-f represents the ondition with the sddest mf s the dpting stimulus nd the f set s the test stimuli. Similrly, we mesured ross-dpttion ftereffets etween the motion fes nd the rel fes (rf), resulting in four possile onditions: mf-mf, mf-rf, rf-mf, nd rf-rf. We lso inluded seline onditions without dpttion for f nd rf, nd they re denoted s -f nd -rf. (The seline ondition for mf ws the sme s the -mf ondition mentioned ove.) In totl, there were different onditions (-mf, -mf r, -f, -rf, mf-mf, f-f, rf-rf, mf-f, f-mf, mf-rf, nd rf-mf). The onditions were run in seprte loks with two loks per ondition. Although in Results we desried these onditions in speifi order, they were rndomized for eh sujet. Over the two loks for eh ondition, eh test stimulus ws repeted 2 times. The trils for different test stimuli in lok were lso rndomized. There ws rek of t lest min fter eh dpttion lok to void rryover of the ftereffets to the next lok. Dt olletion for eh lok strted fter sujets hd suffiient prtie trils ( 2) to feel omfortle with the tsk. Sujets strted eh lok of trils y fixting the entrl ross nd pressing the spe r. After 5 ms, for eh dpttion lok the dpting stimulus ppered for 4 s. After 5 ms interstimulus intervl (ISI), test fe ppered for ms if it ws stti rtoon fe or rel fe nd for s if it ws motion fe. The longer durtion for the motion fe ws needed for sujets to perform the tsk well. For the seline loks without dpttion, only test stimulus ws shown in eh tril. A 5 ms eep ws then plyed to remind sujets to report their pereption of the test stimulus. Sujets hd to press the A or S key to report hppy or sd expression, respetively. After s intertril intervl, the next tril egn. After the ompletion of the ove onditions, we rn dditionl onditions to study how dpttion to the ontrst-mthed rtoon fe (f ) nd modified rel fe (rf m ) ffeted the pereption of the motion fes (the f -mf nd rf m -mf onditions). f ws the sddest stti rtoon fe, with its foreground nd kground luminne vlues set to the mens of the mouth nd surrounding res of the sddest rel fe. rf m ws the sddest rel fe, with the mouth urve of f psted over. Moreover, we investigted whether motion-fe dpttion ould produe n ftereffet on the stti rtoon fes with rndom dots dded (f d ) to mke their kground more similr to the motion fe (the mf-f d nd -f d onditions). We lso rn two ontrol experiments. The first used test rtoon fes whose uniform kground luminne mthed tht of the f d stimuli ut without ny dots (the mf-f l nd -f l onditions). The seond experiment repeted the mf-f d ondition ut sujets were sked to judge motion diretion (up or down) round the midpoint of the mouth urves of the test stti fes (the mf-f d -dir ondition). The rtionle for running these seven onditions ws explined in Results. Finlly, we ross-dpted rel fes nd stti rtoon fes. We strted with four dpttion onditions, nmely, f-f, f-rf, rf-f, nd rf-rf (where rf-f, for exmple, mens dpting to the sddest rel fe nd testing on the rtoon fes), nd two seline onditions, -f nd -rf. We then repeted the rf-f nd -f onditions fter dding /f k noises to the kground of the test rtoon fes (the rf-f k nd -f k onditions). We used k,.5,.,.5, 2., nd 2.5 in different loks with rndomized order. The noise in eh tril ws generted online. Therefore, lthough noise kgrounds in the sme lok ll hd the sme orreltion sttistis (sme k), there ws no repetition of speifi smple. We lso inluded uniform kground whose luminne equled the men of the other kgrounds. This orresponds to very lrge k nd is leled s k. The rtionle for running these 2 onditions ws explined in Results. Dt nlysis For eh ondition, the dt were sorted into frtion of hppy responses to eh test stimulus. The test stimuli were prmeterized ording to the frtion of the signl dots in the motion fes, the mouth urvture of the stti rtoon fes, or the proportion of the hppy fe in the morphed rel fes. The frtion of hppy responses ws then plotted ginst the test stimulus, nd the resulting psyhometri urve ws fitted with sigmoidl funtion of the form f(x) /[ e (x ) ], where determines the slope nd gives the test stimulus prmeter orresponding to the 5% point of the psyhometri funtion [the point of sujetive equlity (PSE)]. An ftereffet is mesured y the differene etween the PSEs of the dpttion ondition nd the orresponding seline ondition. To determine whether n ftereffet ws signifint, we lulted the p vlue y ompring sujets PSEs of the dpttion ondition ginst those of the orresponding seline ondition vi two-tiled pired t test. For the -mf r nd mf-f d -dir onditions, we determined whether the slopes of the psyhometri urves were signifintly different from zero vi two-tiled t test. In the lst experiment, in whih the k vlue of the noise kground ws vried, we used ANOVA to test the dependene on k. Results We first desrie novel lss of seond-order fes in whih fil expressions re either sd or hppy depending on lol diretions of motion. We then present our ross-dpttion studies using these seond-order fes nd onventionl first-order rtoon nd rel fes nd demonstrte the importne of sttistil similrity etween the fetureless kgrounds of the dpting nd test stimuli. Fil expressions solely speified y motion grdients in seond-order fes We progrmmed seond-order rtoon fes with motion grdient-defined expressions (Fig. ). On white sreen, we generted lk rndom dots with 5% dot density over squre. We then defined virtul ring for the fe outline, two virtul disks for the eyes, nd horizontlly oriented virtul retngle for the mouth. Unlike first-order stimuli, these regions were not drwn with luminne different from the kground. Insted, they were virtul regions within whih dots were dynmi nd thus pereptully segregted from the kground stti dots. The dots within the outline ring nd the eye disks rndomly flikered t Hz. The dots within the mouth retngle hd different motion grdient ptterns to produe sd nd hppy expressions. For the sd expression (Fig. ), the dots long the middle vertil line of the retngle moved upwrd nd those t the two ends of the retngle moved downwrd t speed of 2.9 /s. The veloity of other dots in the retngle ws determined y liner interpoltion. Owing to the motion misloliztion effet (Rmhndrn nd Anstis, 99; De Vlois nd De Vlois, 99; Fu et l., 24), this motion grdient pttern mde the mouth retngle look onve even though it ws physilly flt. For the hppy expression, the diretion of eh dot in the mouth retngle ws reversed (Fig. ). The first supplementl file, vil-
4 238 J. Neurosi., Septemer 3, 29 29(39): Wu et l. Bkground Sttistis nd Fe Adpttion le t s supplementl mteril, ontins two movies showing tht indeed these stimuli pper sd nd hppy, respetively. Plying the movies kwrd to reverse the diretions of motion exhnges the sd nd hppy expressions. Stopping the movies t ny frme uses oth the fes nd their expressions to vnish. When we rndomized the frmes of the mouth retngle (see the seond supplementl file, ville t org s supplementl mteril), the pereived differenes etween sd nd hppy fes disppered, further proving the lk of stti form ues for the expressions. To ondut forml psyhophysil experiments, we generted set of fes with expressions tht grdully hnged from sd to hppy y letting frtion of the dots (signl dots) within the mouth retngle follow the ove-presried motion grdients while the remining dots (noise dots) rndomly flikered t Hz. We use negtive nd positive frtions to lel the motion grdient ptterns for the sd nd hppy expressions, respetively. Thus, the originl sd nd hppy fes with % signl dots in the mouth region hve signl dot frtions of nd, respetively. A frtion of mens tht ll dots re noise dots. We generted totl of nine stimuli with frtions from to,in Frtion of hppy responses Frtion of hppy responses steps of.25. Sujets initited lok of trils fter fixting on entrl ross. In eh tril, stimulus ws pseudorndomly seleted nd shown entered t fixtion. Sujets reported whether the pereived expression ws sd or hppy vi key press. At no point ws feedk given in this or the other experiments. The psyhometri dt for four sujets (two of them nive) re shown s the lue urves (the -mf ondition) in Figure 2 d. As the frtion of signl dots vried from to, the frtion of hppy responses inresed grdully from to for ll sujets, inditing tht the pereived expressions vried from sd to hppy in n orderly mnner. One might rise the possiility tht sujets did not relly pereive ny fil expressions ut simply judged lol motion diretions. This is unlikely for three resons. First, none of the sujets performed motion diretion tsk under this ondition so there ws little hne of onfusion. Seond, if the sujets ould not see fil expression nd deided to use motion diretion s sustitute, it would e hrd to explin why ll sujets hppen to hoose the sme motion pttern to indite hppy or sd expressions. Third, when they were given the instrutions, ll sujets understood the tsk immeditely nd found it to e strightforwrd. To rule out this possiility diretly, for the two nive sujets, we rndomly interleved th trils in whih the stimuli were the sddest nd hppiest fes (signl dot frtions of nd ) shown upside-down. When the fe with signl dot frtion of (or ) ws inverted, its motion grdient pttern ws identil to tht of the upright fe with signl dot frtion of (or ). If the sujets judged lol motion diretions, they would onsider the inverted sddest fe s hppy nd the inverted hppiest fe s sd. The dt, mrked s inverted hppy or sd fe in Figure 2, nd, show the opposite results, inditing tht the sujets indeed judged Inverted DC hppy fe Inverted sd fe mf mf r HX.5.5 Frtion of signl dots d JK Inverted hppy fe Inverted sd fe.5.5 JW.5.5 Frtion of signl dots Figure 2. Fil-expression pereption with the motion fes. d, Psyhometri funtions from two nive sujets (DC, JK) nd two experimenters (HX, JW). For eh sujet, the pereived expression vried grdully from sd to hppy s the frtion of thesignldotsvriedfrom to(lueurve,the-mfondition).thepereptionofexpressionwsdestroyedwithrndomized motion frmes (rown urve, the -mf r ondition). For the two nive sujets, th trils with the inverted sddest nd hppiest motion fes were shown to indite tht they judged fil expressions insted of motion diretions (see Results for detils). the fes expressions. The ft tht the th trils did not produe hne performnes (.5) lso suggests tht for simple rtoon fes, inversion does not destroy the pereption of fil expressions (Xu et l., 28). To ensure tht the pereived fil expressions in the ove experiment were ompletely speified y motion insted of y stti form ues, we onduted ontrol experiment tht rndomized the motion frmes of the mouth retngle for ll nine fe stimuli. The results of the sujets judgments re shown s the rown urves (the -mf r ondition) in Figure 2 d. The slopes of these psyhometri urves do not signifintly differ from zero (men,.23; p.47), inditing tht the sujets ould not distinguish etween sd nd hppy expressions one the oherent motion grdients were destroyed y rndomiztion. We onlude tht there ws no first-order form ue in the originl stimuli. Cross-dpttion etween the seond-order motion fes nd first-order stti rtoon fes nd rel fes After estlishing fil-expression pereption in the seondorder motion fes, we ross-dpted them with first-order, luminne-defined fes to gin insight into intertions etween different ues in fe proessing. Previous studies on rossdpttion etween first- nd seond-order stimuli hve een limited to low-level stimuli (Nishid et l., 997; Lrsson et l., 26; Ashid et l., 27; Shofield et l., 27). As in our previous study (Xu et l., 28), we generted firstorder stti rtoon fes nd rel fes with expressions vrying from sd to hppy; exmples re shown in Figure, d nd e. The physil dimensions of the stti rtoon fes extly mthed those of the motion fes exept tht the sd to hppy expressions were generted y luminne-defined urvture rther thn mo-
5 Wu et l. Bkground Sttistis nd Fe Adpttion J. Neurosi., Septemer 3, 29 29(39): Frtion of hppy responses Frtion of hppy responses PSE shift from seline (Frtion of signl dots) DC HX.5.5 Frtion of signl dots e mf (Bseline) f mf mf mf n = 4 mf f mf mf mf.5.5 p =.2 p =.7 tion grdients. We lso losely mthed the motion fes nd the rel fes, pying speil ttention to lign the mouth positions of the rel fes to tht of the motion fes, sine the mouth is prtiulrly importnt for fil expressions (Gosselin nd Shyns, 2; Xu et l., 28). We first report how the seond-order motion fes nd the first-order stti rtoon fes interted. We used either the sddest mf or the sddest f we generted s the dpting stimulus nd then our set of mf or f fes s the test stimuli. The totl of four possile omintions re denoted s mf-mf, mf-f, f-f, nd f-mf onditions, where, for exmple, f-mf mens dpting to the sddest rtoon fe nd testing on the motion fes. We lso inluded seline onditions without dpttion for the motion fes nd stti rtoon fes, denoting them s -mf (lredy desried ove) nd -f. The psyhometri dt from four sujets (two of them nive) for the -mf, mf-mf, nd f-mf onditions re shown in Figure 3 d s lue, green, nd dshed lk urves, respetively. Similrly, the dt for the -f, f-f, nd mf-f onditions re shown in Figure 4 d s lue, green, nd dshed lk urves, respetively. As expeted, the two within-tegory dpttion onditions (mf-mf nd f-f) generted lrge fil-expression d JK JW.5.5 Frtion of signl dots Figure 3. The effet of rtoon dpttion on the pereived expression of the motion fes. d, Psyhometri funtions from two nive sujets(dc, JK) nd two experimenters(hx, JW). The test stimuli were lwys the mf. The dpting stimuli vried with onditions s follows: -mf, no-dpttion seline (lue, opied from Fig. 2); f-mf, dpttion to the sddest rtoon fe (dshed lk); mf-mf, dpttion to the sddest motion fe (green). e, Summry of llfoursujets dt. Forehondition, thevergepsereltivetotheselineonditionws plotted, with the error r representing SEM. The p vlue shown for eh ondition in the figure ws lulted ginst the seline ondition using two-tiled pired t test. Frtion of hppy responses Frtion of hppy responses DC Curvture of mouth (/deg) e PSE shift from seline (/deg)..2.3 f mf f f f HX n = f (Bseline) mf f f f p =.7 p =.8 ftereffets, indited y the shifts of the psyhometri urves from the orresponding seline onditions (-mf nd -f). The leftwrd shifts men tht sujets pereived hppy expressions more often fter dpting to sd fes, onsistent with previous fe dpttion experiments (Leopold et l., 2; Wester et l., 24; Xu et l., 28). For the ross-dpttion onditions (f-mf nd mf-f), the results were symmetri: first-order rtoon-fe dpttion generted signifint ftereffet on the seond-order motion fes (f-mf), yet seond-order motionfe dpttion filed to generte n ftereffet on the first-order rtoon fes (mf-f). Similr symmetri intertions hve een reported previously for low-level stimuli (Smith et l., 2; Ellemerg et l., 24; Shofield et l., 27). To quntify the ftereffets nd summrize the results from ll four sujets, we determined the PSE the x-xis vlue orresponding to 5% hppy responses for eh psyhometri urve of eh sujet. Figure 3e shows the men PSEs of the mf-mf (green r) nd f-mf (lk r) onditions reltive to the seline -mf ondition. Similrly, Figure 4e shows the men PSEs of the f-f (green r) nd mf-f (lk r) onditions reltive to the seline -f ondition. A negtive vlue mens leftwrd shift of the psyhometri urve from the seline. The d JK JW Curvture of mouth (/deg) Figure 4. The effet of motion-fe dpttion on the pereived expression of the stti rtoon fes. d, Psyhometri funtions from two nive sujets (DC, JK) nd two experimenters (HX, JW). The test stimuli were lwys the stti f. The dpting stimuli vried with onditions s follows: -f, no-dpttion seline (lue); f-f, dpttion to the sddest rtoon fe (green); mf-f, dpttion to the sddest motion fe (dshed lk). e, Summry of ll four sujets dt.
6 24 J. Neurosi., Septemer 3, 29 29(39): Wu et l. Bkground Sttistis nd Fe Adpttion error rs indite SEM. The symmetry in the ftereffet is pprent, with the f-mf, ut not the mf-f, ondition eing signifintly different from the orresponding seline (Figs. 3e nd 4e, p vlues). We lso ross-dpted first-order rel fes nd the seond-order motion fes nd found little ftereffet trnsfer in either diretion (see the third supplementl file, ville t s supplementl mteril). Similr results hve lso een reported for low-level stimuli (Nishid et l., 997; Lrsson et l., 26; Ashid et l., 27). Note, in prtiulr, tht the first-order rtoon fe, ut not the first-order rel fe, produed n ftereffet on the seond-order motion fes. This is not ttriutle to different ontrsts or mouth shpes of the stimuli (see the third supplementl file, ville t s supplementl mteril). The role of kground similrity in determining ftereffet trnsfer from seond- to first-order fes As mentioned in the Introdution, to understnd the ove results nd the role of ue-invrint ells in ross-dpttion, we onsidered new ontingent ftor tht ould ontriute to the trnsfer of n ftereffet, nmely, the similrity etween the kgrounds of the dpting nd test stimuli. By kground we men the luminne distriutions of the lrgely fetureless res surrounding the fil fetures. We hypothesized tht strong ftereffets re indued only when dpting nd test stimuli hve suffiiently similr kgrounds. The hypothesis implies the surprising predition tht lthough fetureless kgrounds nnot produe fil expression ftereffet y themselves, they will signifintly influene the ftereffet. We designed experiments to test this predition. In Figure 4, we showed tht motion-fe dpttion filed to produe n ftereffet on the test stti rtoon fes (the mf-f ondition). By the kground-similrity hypothesis, we expeted to oserve the ftereffet in the mf-f ondition simply y dding rndom dots to the test rtoon fes to mke them more similr to the dpting motion fe. Importntly, this experiment ould lso ddress the question of whether it is possile for seond-order fe to produe n ftereffet on first-order fes. We therefore generted new set of test rtoon fes (f d ) (Fig. 5) y dding rndom dots to the originl set shown in Figure d. The dot density ws the sme s for the motion fes (5%). The dots were dded online for eh tril so tht no dot pttern ws repeted ross trils. We rn the motion-fe dpttion ondition (mf-f d ) nd the no-dpttion seline ondition (-f d )in extly the sme wy tht we rn the originl mf-f nd -f onditions. The dt from four sujets (two of them nive) re shown s dshed nd solid red urves in Figure 6 d. Motion-fe dpttion indeed produed signifint ftereffet on the rtoon fes with dded dots (Fig. 6e, hthed red r), supporting the notion tht kground similrity influenes the ftereffet. The result suggests tht the lk of ftereffet in the originl mf-f ondition (Fig. 4) is not entirely euse the dpting motion fe Figure5. Mnipultionsofkgroundsimilrityetweendptingndtestfes. Ehfesetontinedexpressionsrnging from sd to hppy, ut only the sddest one is shown here., Crtoon fe set with rndom dots dded (f d ). Rndom dots of 5% densitywereddedtotheoriginlsttirtoonfesetinfigured.,luminne-mthedrtoonfeset(f l ).Thekground luminne ws mthed to the men kground luminne of f d set., Crtoon fe sets with /f k noise kgrounds, with k,.5,,.5, 2, nd 2.5, respetively. Noises with different k vlues hd the sme first-order luminne distriution ut different seond-order orreltion strutures. A uniform kground ws lso inluded nd leled s k. is not s slient s the test rtoon fes. It further suggests tht seond-order stimuli n produe ftereffets on first-order stimuli when their kgrounds re more similr. We exluded two lterntive explntions. The first depends on the ft tht the dded lk dots redued the men kground luminne of the f d set (47.6 d/m 2 ) ompred with the originl rtoon fes (56.2 d/m 2 ), resulting in slightly lower ontrst for the fetures in the f d fes. If the lowered ontrst produed the ftereffet, we would expet to oserve the motionfe-indued ftereffet on dot-free rtoon fes with redued kground luminne (47.6 d/m 2 ) (Fig. 5, f l ). We rn the motion-fe dpttion ondition (mf-f l ) nd no-dpttion seline ondition (-f l ) in this luminne-mthed se in extly the sme wy tht we rn the mf-f d nd -f d onditions. The dt (Fig. 6 d, dshed nd solid lue urves, nd 6e, lue hthed r) show no ftereffet, suggesting tht luminne is not ritil ftor. Furthermore, the slopes of the psyhometri funtions for the f l nd f d onditions do not differ signifintly (men 23.2 nd 25., respetively; p.32), suggesting tht the different ftereffets nnot e ttriuted to different slienies of the test stimuli. The seond lterntive explntion is tht the dded dots produed motion ftereffet whih then ised the pereived fil expressions. This is very unlikely euse the dded dots were outside the mouth urves (Fig. 5) nd thus hd little or no sptil overlp with the moving dots inside the mouth of the dpting motion fe. To rule out this possiility formlly, we repeted the mf-f d ondition ut sked the sujets to report the diretion of motion for the dots ove the midpoint of the mouth urves of the test rtoon fes. The dt for this ondition (mf- f d -dir) re shown s green urves in Figure 6 d. Tht the slopes of these
7 Wu et l. Bkground Sttistis nd Fe Adpttion J. Neurosi., Septemer 3, 29 29(39): Frtion of hppy or upwrd responses Frtion of hppy or upwrd responses e PSE shift from seline (/deg) f l f (Bseline) mf f d l (Bseline) mf f d n = 4 VH HX f d mf f d mf f l f l mf f d dir Curvture of mouth (/deg) p = p =.8 urves re not signifintly different from zero (men,.4; p.62) indites tht the sujets did not see motion ftereffets in this experimentl ondition. Indeed, the sujets omplined tht they ould not perform this tsk euse they ould not see motion nywhere in the test fes. The role of kground similrity in determining ftereffet trnsfer etween different types of first-order fes We further investigted whether kground similrity lso ontriutes to ftereffet trnsfer etween different types of firstorder fes. We used rel fes s in Figure e nd stti rtoon fes similr to those in Figure d ut with 3% pen width sine there ws no need to mth the motion fes in this experiment. We first ross-dpted rf nd f stimuli without ny kground mnipultions. There were four dpttion onditions rf-rf, ff, rf-f, nd f-rf, nd two seline onditions -rf nd -f. We found tht rtoon-fe dpttion generted fil-expression ftereffet on the rel fes (the f-rf ondition) ut rel-fe dpttion filed to produe n ftereffet on the rtoon fes (the rf-f ondition). This is similr to the symmetry etween the motion nd rtoon fes (Figs. 3 nd 4), nd we show only the summry dt in Figure 7. d VKD JW Curvture of mouth (/deg) Figure 6. The role of kground similrity in ftereffet trnsfer from seond-order motion fes to first-order stti rtoon fes. d, Psyhometri funtions from two nive sujets (VH,VKD)ndtwoexperimenters(HX,JW)underthefollowingonditions:-f d,nodpttion nd test on the dot-dded rtoon fes (solid red); mf-f d, dpttion to the sddest motion fe nd test on the dot-dded rtoon fes (dshed red); -f l, no dpttion nd test on the kground-luminne-mthed rtoon fes (solid lue); mf-f l, dpttion to the sddest motion fe nd test on the kground-luminne-mthed rtoon fes (dshed lue); mff d -dir, sme s mf-f d, ut the sujets judged motion diretion (up or down) ove the midpointofthemouthurvesofthetestf d fes(solidgreen).e,summryofllfoursujets dt. PSE shift from seline(/deg)..2.3 f (Bseline) rf f n = 4 p =.32 f f p =. PSE shift from seline (proportion of hppiness). rf (Bseline) f rf n = 4 rf rf p =.6 p =.2 Figure 7. Cross-dpttion etween first-order rtoon nd rel fes. Only the summry dtfromtwonivesujetsndtwoexperimentersreshown., Theteststimuliwerelwys the rtoon fes. The dpting stimuli vried with onditions s follows: -f, no-dpttion seline; f-f, dpttion to the sddest rtoon fe; rf-f, dpttion to the sddest rel fe., The test stimuli were lwys the rel fes. The dpting stimuli vried with onditions s follows: -rf, no-dpttion seline; rf-rf, dpttion to the sddest rel fe; f-rf, dpttion to the sddest rtoon fe. Log (mplitude) Log (yle per imge) We then exmined whether we n inrese the ftereffet in the rf-f ondition y dding proper kgrounds to the test rtoon fes. One possiility would e to remove eyes, nose, nd mouth from the dpting rel fe nd use the reminder s the kground for the test rtoon fes. However, the reminder might still rry some fil expression informtion or ontin other fetures tht ould omplite the interprettion of the results. We therefore generted noise kgrounds sed on the orreltion sttistis of rel fes. For this purpose, we first omputed the mplitude spetrum of rel fes nd found tht it follows the /f k lw with k.63 (Fig. 8), where k is the sptil frequeny, in greement with reent study (Keil, 28). Compring with nturl imge sttistis (k ) (Field, 987; Rudermn, 994), front-view fes hve less energy in high-frequeny rnge, presumly euse of less rupt olusions. We then repeted the rf-f ondition fter dding /f k noises to the test rtoon fes (denoted s the rf-f k onditions). We lso run the orresponding seline onditions -f k. In seprte loks with rndomized order, we let k,.5,,.5, 2., nd 2.5. By histogrm equliztion, noises with different k vlues ll hd the sme first-order distriution ut different seond-order orreltion strutures. (Note tht first- nd seond-order imge sttistis should not e onfused with first- nd seond-order stimuli.) We lso inluded uniform kground whose luminne mthes the men of the other kgrounds; it is leled s k. Smples of different kgrounds re shown in Figure 5. KDEF Ekmn Figure 8. Correltion sttistis of front-view rel-fe imges mesured y the Fourier mplitude spetrum of the KDEF dtse (red) nd Ekmn dtse (lue). The log log plots show nerly stright lines, inditing /f k reltionship etween mplitude nd sptil frequeny. The KDEF urve extends to higher frequenies euse of the lrger imge size. Curve fitting yields k vlues of.6 for the KDEF fes nd.65 for Ekmn fes, with n verge of.63.
8 242 J. Neurosi., Septemer 3, 29 29(39): Wu et l. Bkground Sttistis nd Fe Adpttion PSE shift from seline (/deg) Slope of psyhometri funtion t PSE k k The kground in eh tril ws generted online. Consequently, lthough kgrounds for different trils in lok hd identil sttistis (sme k), no smple ws repeted. This ensures tht ny effet is not due to identl fetures in prtiulr smple. Figure 9 shows the fil-expression ftereffet trnsfer from rel-fe dpttion to the test rtoon fes, mesured s the PSE shift from the orresponding seline ondition, s funtion of k. When the noise kgrounds hd k vlues of nd.5, mthing the orreltion sttistis of nturl imges nd relfe imges, the trnsfer ws mximl. For k vlues outside this rnge, the trnsfer delines to. An ANOVA test indites signifint dependene of the ftereffet on k ( p.3). Sine ll kgrounds (exept the uniform one leled s k ) hd the sme first-order luminne distriution ut different seondorder orreltion strutures, Figure 9 suggests tht the seondorder sttistis of the rel nd rtoon fes hve to e similr to produe sizle ftereffet. An lterntive interprettion of Figure 9 is tht the test rtoon fes hd different slienies ginst different noise kgrounds even though they ll hd identil first-order luminne distriutions, nd differenes in slieny led to different ftereffet trnsfer. To rule out this interprettion, we mesured the slopes (t PSE) of the psyhometri funtions for different k vlues, nd the results for the seline onditions re shown in Figure 9. An ANOVA test showed no signifint dependene of the slope, nd thus slieny, on k ( p.4). A similr lk of dependene on k ws found for the slopes in the dpttion onditions ( p.37). // // 8 VH VKD HX JW Figure 9. The role of kground similrity in ftereffet trnsfer from first-order rel fes to first-order stti rtoon fes. The dpting stimulus ws lwys the sddest red fe. The teststimuliwerertoonfesetswith/f k noisekgrounds.,theftereffet,mesureds thepseshiftfromtheorrespondingseline, sfuntionofkforfoursujets., Theslope(t PSE) of psyhometri urves for the seline onditions s funtion of k. 8 Disussion We investigted the role of kground sttistis in ftereffet trnsfer etween different lsses of fes. We first generted novel lss of seond-order fes in whih lol diretions of motion define sd nd hppy fil expressions, without ny stti form ue. Reversing motion diretions in these stimuli exhnges hppy nd sd expressions. We then exmined intertions etween these seond-order motion fes nd first-order rtoon nd rel fes. Adpttion to seond-order motion fe filed to produe fil-expression ftereffet on the first-order rel or rtoon fes, wheres dpttion to first-order rtoon fe, ut not rel fe, generted the ftereffet on the seondorder motion fes, differene tht ws not due to differenes in ontrst or mouth shpe. These results gree with previous studies using simpler nonfe stimuli, nmely, tht seond-order dpttion typilly does not trnsfer to first-order stimuli wheres first-order dpttion sometimes, ut not lwys, trnsfers to the seond-order stimuli (Nishid et l., 997; Lrsson et l., 26; Ashid et l., 27; Shofield et l., 27). Suh results hve een widely interpreted s inditing seprte proessing for first- nd seond-order stimuli. However, s mentioned in Introdution, ue-invrint ells with similr tuning to first- nd seond-order stimuli hve een reported in mny visul res, rising the question of why ftereffet trnsfer is not more frequently oserved, prtiulrly from seond- to first-order stimuli,. We therefore serhed for onditions tht my filitte trnsfer. We found tht, surprisingly, the degree of similrity etween the fetureless kgrounds of dpting nd test fes is ritil ftor. Speifilly, dpttion to seond-order motion fe ould e mde to trnsfer to the first-order rtoon fes y simply dding stti rndom dots to the ltter mking their kgrounds more similr to tht of the dpting motion fe (Fig. 6, the mf-f d ondition). Moreover, kground similrity lso ontrolled trnsfer etween different lsses of first-order fes: Rel-fe dpttion trnsferred to stti rtoon fes only when noise with the orreltion sttistis of rel fes or nturl imges ws dded to the kground of the rtoon fes (Fig. 9). We ruled out ontrst, motion-ftereffet, or slieny-sed explntions for these findings. Our results hve implitions for mehnisms of dpttion, the interprettion of null ftereffets, nd the representtion of fes. The kground similrity effet in visul dpttion The kground similrity effet we desried ould e onsidered new form of ontingent ftereffet. The est-known ontingent ftereffet ws reported y MCollough (965), who indued two different olor ftereffets simultneously, for two different orienttions. This implies tht prtiulr olor ftereffet is oserved only when the test nd dpting stimuli hve the sme orienttion. Similr ontingent ftereffets hve een reported for fe dpttion (Rhodes et l., 24; Ymshit et l., 25; Ng et l., 26; Little et l., 28); in prtiulr, filexpression ftereffets re lrger when the identities of dpting nd test fes re shred (Fox nd Brton, 27). Our work extends these studies, showing the even greter importne of shring gross sttistil hrteristis of otherwise fetureless kgrounds. The kground similrity effet depends on oth first- nd seond-order sttistis. We originlly demonstrted the effet y showing tht trnsfer from motion fes with only first-order, white noise, rndom-dot kgrounds, to rtoon fes, ourred when similr, first-order, rndom dots were dded to the ltter. However, the kgrounds of rel fes hve seond-order struture; sustntil trnsfer from them to rtoon fes depended on mthing this; simply mthing the first-order distriution ws insuffiient. Of ourse, fes (nd nturl imges in generl) oviously ontin higher-order strutures. It would e interesting to test wht spets of higher-order sttistis, notly those importnt for the determintion of fe identity (Fox nd
9 Wu et l. Bkground Sttistis nd Fe Adpttion J. Neurosi., Septemer 3, 29 29(39): Brton, 27), ould further enhne the kground similrity effet. At neuronl level, ontingent ftereffets likely rise from ells jointly seletive to multiple spets of stimuli. The kground similrity effet, in prtiulr, predits joint seletivity to stimulus fetures nd kground sttistis. Vrition in firing rtes oming from the kground my therefore hve resulted in n underestimtion of the degree of invrine to fetures or ues defining the fetures, effetively omprising novel nonlssil influene on visul responses. However, fe-identity ftereffets re not influened y differing fil expressions (Fox et l., 28), showing tht identity oding is invrint to expressionrelted sttistis. How seletivity nd invrine depends on tsks nd levels of the visul hierrhy is n open question. It thus eomes pressing to sk whether kground mnipultions n enhne ftereffet trnsfer etween first- nd seond-order low-level stimuli suh s orienttion nd trnsltionl motion. Cue-invrint responses to orienttion nd motion hve een found in res V, V2, nd MT (von der Heydt et l., 984; Alright, 992; Sheth et l., 996). Computtionl models lso ssume tht seprte first- nd seond-order motion proessing in V nd V2, respetively, onverges on MT (Wilson et l., 992). However, it is possile tht ue onvergene is progressively stronger t higher-level res oding more omplex stimuli, with the frtion of ue-invrint ells in reltively low-level res eing too smll (O Keefe nd Movshon, 998) to hve pereptul impt. We re urrently investigting this issue. Interestingly, the rre study tht did find strong ross-dpttion ftereffets etween first- nd seond-order orienttions used stimuli of very similr kgrounds (Georgeson nd Shofield, 22). At funtionl level, our study suggests tht sttistil similrity etween fetureless kgrounds of stimuli n gte their temporl intertions. Although the sttistil rtionle for the dpttion effets tht re oserved is not yet ompletely ler (Shwrtz et l., 27; Xu et l., 28), y restriting the sope of dpttion, the kground similrity effet will void overgenerliztion. Adpttion trets the temporl ontext of stimuli. However, there re mny similrities etween the effets of sptil nd temporl ontext (Clifford et l., 2; Shwrtz et l., 27), s in the reltionship etween the tilt ftereffet nd the tilt illusion. It is not known if the ltter is gted y sttistil similrity etween the kgrounds of the stimuli involved. Crowding is nother form of ontextul sptil intertion nd it is known to e stronger when the fetures in the trget nd flnks re more similr (Levi, 28). However, it is lso unknown if fetureless kgrounds modulte the rowding effet. Interprettion of null ftereffets Our results suggest tht if dpttion to A hs no impt on B, then it is not neessrily true tht A nd B re proessed seprtely. Our initil null findings might hve tempted one to onlude tht fil expressions in motion fes, rel fes, nd stti rtoon fes re ll proessed seprtely, despite expression eing universl property. Our lter finding of signifint trnsfer for suffiiently similr kgrounds suggests tht different ues do indeed onverge in the ourse of reting filexpression representtion. The sme issue my ffet the design nd interprettion of rnge of future dpttion experiments. Nevertheless, tht trnsfer depends on pproprite kground mnipultions suggests limittions in the extent of shred neurl proessing for the stimuli. In this sense, our results omplement, rther thn ontrdit, previous suggestions of seprte proessing of first- nd seond-order stimuli. A prole senrio is tht there re oth seprte nd shred representtions of different lsses of stimuli. Previous studies emphsized the former wheres our method of kground mnipultion is sensitive enough to revel the ltter. The notion of kground similrity is symmetri: if A is similr to B, then B is similr to A; yet the intertions etween different lsses of stimuli re often symmetri. An ovious explntion is tht the outome of prtiulr dpttion experiment depends on multiple ftors inluding slieny nd seprte proessing s well s kground similrity. Fe representtion Our results suggest the possiility tht kground sttistis re n integrl omponent of fil-expression representtion even when the kgrounds do not ontin ny informtion out fil expression. In other words, fetureless kgrounds re not disrded fter feture extrtion. For exmple, when dpting to the sddest motion fe, the ontext provided y the fetureless sttionry dots in the kground my e enoded together with the dots tht define the mouth shpe (nd fil expression). This integrtion ould our either t fe res or t lower-level res feeding the fe res, nd my e relted to the holisti view of fe representtion (Tnk nd Frh, 23). The pereived expressions in our motion-fe stimuli lso suggest strong intertions etween motion proessing nd fe pereption, funtions tht hve een ssigned to dorsl nd ventrl pthwys, respetively (Ungerleider nd Mishkin, 982; Fellemn nd Vn Essen, 99). Although there hve lredy een demonstrtions of the intertions (Bssili, 978; Berry, 99; Knppmeyer et l., 23; Frivr et l., 29), our motionfe stimuli re unique in tht the hppy nd sd expressions re solely defined y lol diretions of motion ording to the motion misloliztion effet. Sine reversing the diretions exhnges the hppy nd sd expressions, our stimuli link fe pereption to diretionl proessing, insted of generl motion detetion. Diretionl tuning nd the ssoited misloliztion effet strt s erly s V (Huel nd Wiesel, 968; Fu et l., 24). Thus, our stimuli suggest tht lol, low-level diretionl proessing ontriutes to fe pereption, supporting the notion of strong lol omponent in fe representtion, in ddition to holisti omponent (Xu et l., 28). In summry, we hve shown tht sttistil similrity etween fetureless kgrounds of the dpting nd test stimuli is novel ftor in determining ftereffet trnsfer etween different lsses of stimuli. This result hs implitions for the design nd interprettion of future dpttion studies. We hve lso shown tht fil expressions n e solely defined y lol diretions of motion grdient ptterns, thus estlishing strong link etween fe nd motion-diretion proessing. Our findings suggest tht luminne- nd motion-diretion-defined forms, nd lol fetures nd kground sttistis, onverge in the representtion of fes. Referenes Alright TD (992) Form-ue invrint motion proessing in primte visul ortex. Siene 255:4 43. Ashid H, Lingnu A, Wll MB, Smith AT (27) FMRI dpttion revels seprte mehnisms for first-order nd seond-order motion. J Neurophysiol 97: Atik JJ, Redlih AN (99) Towrds theory of erly visul proessing. Neurl Comput 2: Brlow H (99) A theory out the funtionl role nd synpti mehnism of visul ftereffets. In: Vision: oding nd effiieny (Blkemore C, ed). Cmridge, UK: Cmridge UP.
EFFECT OF DIETARY ENZYME ON PERFORMANCE OF WEANLING PIGS
 EFFECT OF DIETARY ENZYME ON PERFORMANCE OF WEANLING PIGS Finl report sumitted to Dniso Animl Nutrition E. vn Heugten nd B. Frederik North Crolin Stte University, Deprtment of Animl Siene Summry The urrent
EFFECT OF DIETARY ENZYME ON PERFORMANCE OF WEANLING PIGS Finl report sumitted to Dniso Animl Nutrition E. vn Heugten nd B. Frederik North Crolin Stte University, Deprtment of Animl Siene Summry The urrent
Lesions of prefrontal cortex reduce attentional modulation of neuronal responses. and synchrony in V4
 Lesions of prefrontl ortex reue ttentionl moultion of neuronl responses n synhrony in V4 Georgi G. Gregoriou,, Anrew F. Rossi, 3 Leslie G Ungerleier, 4 Roert Desimone 5 Deprtment of Bsi Sienes, Fulty of
Lesions of prefrontl ortex reue ttentionl moultion of neuronl responses n synhrony in V4 Georgi G. Gregoriou,, Anrew F. Rossi, 3 Leslie G Ungerleier, 4 Roert Desimone 5 Deprtment of Bsi Sienes, Fulty of
LHb VTA. VTA-projecting RMTg-projecting overlay. Supplemental Figure 2. Retrograde labeling of LHb neurons. a. VTA-projecting LHb
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementl Figure 1 doi:10.1038/nture09742 Lterl 1.0 mm from midline mpfc BNST mpfc BNST Lterl 2.1 mm from midline LHA LHA Lterl 2.7 mm from midline SUPPLEMENTAL INFORMATION
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementl Figure 1 doi:10.1038/nture09742 Lterl 1.0 mm from midline mpfc BNST mpfc BNST Lterl 2.1 mm from midline LHA LHA Lterl 2.7 mm from midline SUPPLEMENTAL INFORMATION
P AND K IN POTATOES. Donald A Horneck Oregon State University Extension Service
 P AND K IN POTATOES Donld A Hornek Oregon Stte University Extension Servie INTRODUCTION Phosphorous nd potssium re importnt to grow high yielding nd qulity pottoes. Muh of the northwest hs hd trditionlly
P AND K IN POTATOES Donld A Hornek Oregon Stte University Extension Servie INTRODUCTION Phosphorous nd potssium re importnt to grow high yielding nd qulity pottoes. Muh of the northwest hs hd trditionlly
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:.38/nture277 d 25 25 2 Time from sound onset (ms) 25 25 2 Time from sound onset (ms) Firing rte (spikes/s) Firing rte (spikes/s).8.6..2 e f g h.8.6..2 Frtion of neurons Frtion of neurons N = 53 2 2
doi:.38/nture277 d 25 25 2 Time from sound onset (ms) 25 25 2 Time from sound onset (ms) Firing rte (spikes/s) Firing rte (spikes/s).8.6..2 e f g h.8.6..2 Frtion of neurons Frtion of neurons N = 53 2 2
Learning to see: experience and attention in primary visual cortex
 2 Nture Pulishing Group http://neurosi.nture.om rtiles Lerning to see: experiene nd ttention in primry visul ortex 2 Nture Pulishing Group http://neurosi.nture.om Roy E. Crist, Wu Li nd Chrles D. Gilert
2 Nture Pulishing Group http://neurosi.nture.om rtiles Lerning to see: experiene nd ttention in primry visul ortex 2 Nture Pulishing Group http://neurosi.nture.om Roy E. Crist, Wu Li nd Chrles D. Gilert
Whangarei District Council Class 4 Gambling Venue Policy
 Whngrei Distrit Counil Clss 4 Gmling Venue Poliy April 2013 Whngrei Distrit Counil Clss 4 Gmling Venue Poliy Tle of ontents Introdution... 3 1 Ojetives of the poliy in so fr s promoted y the Gmling At
Whngrei Distrit Counil Clss 4 Gmling Venue Poliy April 2013 Whngrei Distrit Counil Clss 4 Gmling Venue Poliy Tle of ontents Introdution... 3 1 Ojetives of the poliy in so fr s promoted y the Gmling At
Poultry No The replacement value of betaine for DL-methionine and Choline in broiler diets
 Poultry No. 1573 The replement vlue of etine for DL-methionine nd Choline in roiler diets Key Informtion In roiler diets defiient in sulfur mino ids ut dequtely supplemented with methyl groups vi dded
Poultry No. 1573 The replement vlue of etine for DL-methionine nd Choline in roiler diets Key Informtion In roiler diets defiient in sulfur mino ids ut dequtely supplemented with methyl groups vi dded
Introduction to Study Designs II
 Introdution to Study Designs II Commonly used study designs in publi helth & epidemiologi reserh Benjmin Rihrd H. Muthmbi, DrPH, MPH Stte HIV Epidemiologist HIV Epidemiology Investigtion Setion PA Deprtment
Introdution to Study Designs II Commonly used study designs in publi helth & epidemiologi reserh Benjmin Rihrd H. Muthmbi, DrPH, MPH Stte HIV Epidemiologist HIV Epidemiology Investigtion Setion PA Deprtment
Supplementary Figure 1. Scheme of unilateral pyramidotomy used for detecting compensatory sprouting of intact CST axons.
 () BDA 2 weeks fter Py () AAVs Cre or GFP t P1 BDA 2 weeks fter Py CSMN CST () Py t P7 or 2 months () Py t 2 months Supplementry Figure 1. Sheme of unilterl pyrmidotomy used for deteting ompenstory sprouting
() BDA 2 weeks fter Py () AAVs Cre or GFP t P1 BDA 2 weeks fter Py CSMN CST () Py t P7 or 2 months () Py t 2 months Supplementry Figure 1. Sheme of unilterl pyrmidotomy used for deteting ompenstory sprouting
Neural population coding of sound level adapts to stimulus statistics
 COMPUTATION AND SYSTEMS 25 Nture Pulishing Group http://www.nture.om/ntureneurosiene Neurl popultion oding of sound level dpts to stimulus sttistis Isel Den 1, Niol S Hrper 1,2 & Dvid MAlpine 1 Mmmls n
COMPUTATION AND SYSTEMS 25 Nture Pulishing Group http://www.nture.om/ntureneurosiene Neurl popultion oding of sound level dpts to stimulus sttistis Isel Den 1, Niol S Hrper 1,2 & Dvid MAlpine 1 Mmmls n
Efficient sensory cortical coding optimizes pursuit eye movements
 ARTICE Reeived Mr 26 Aepted 29 Jul 26 Pulished 9 Sep 26 Effiient sensory ortil oding optimizes pursuit eye movements Bing iu, Mtthew V. Mellio & eslie C. Osorne,2 DOI:.38/nomms2759 OPEN In the nturl world,
ARTICE Reeived Mr 26 Aepted 29 Jul 26 Pulished 9 Sep 26 Effiient sensory ortil oding optimizes pursuit eye movements Bing iu, Mtthew V. Mellio & eslie C. Osorne,2 DOI:.38/nomms2759 OPEN In the nturl world,
Other Uses for Cluster Sampling
 Other Uses for Cluster Smpling Mesure hnges in the level of n ttriute Hypothesis testing versus intervl estimtion Type I n 2 errors Power of the test Mesuring ttriute t sme time in ifferent sites Exmple:
Other Uses for Cluster Smpling Mesure hnges in the level of n ttriute Hypothesis testing versus intervl estimtion Type I n 2 errors Power of the test Mesuring ttriute t sme time in ifferent sites Exmple:
Mechanisms underlying cross-orientation suppression in cat visual cortex
 Mehnisms underlying ross-orienttion suppression in t visul ortex 6 Nture Pulishing Group http://www.nture.om/ntureneurosiene Nihols J Priee & Dvid Ferster In simple ells of the t primry visul ortex, null-oriented
Mehnisms underlying ross-orienttion suppression in t visul ortex 6 Nture Pulishing Group http://www.nture.om/ntureneurosiene Nihols J Priee & Dvid Ferster In simple ells of the t primry visul ortex, null-oriented
Adiabatic CMOS Circuit Design: Principles and Examples
 Aditi CMOS Ciruit Design: Priniples nd Exmples X.Wu,G.Hng,ndM.Pedrm Astrt: In view of hnging the type of energy onversion in CMOS iruits nd therey hieving ultr-low-power design, this pper investigtes diti
Aditi CMOS Ciruit Design: Priniples nd Exmples X.Wu,G.Hng,ndM.Pedrm Astrt: In view of hnging the type of energy onversion in CMOS iruits nd therey hieving ultr-low-power design, this pper investigtes diti
Open Access RESEARCH ARTICLE. Genetics Selection Evolution
 DOI 10.1186/s12711-016-0222-0 Genetis Seletion Evolution RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Aess Comprison of host geneti ftors influening pig response to infetion with two North Amerin isoltes of porine reprodutive
DOI 10.1186/s12711-016-0222-0 Genetis Seletion Evolution RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Aess Comprison of host geneti ftors influening pig response to infetion with two North Amerin isoltes of porine reprodutive
Reward expectation differentially modulates attentional behavior and activity in visual area V4
 Rewrd expettion differentilly modultes ttentionl ehvior nd tivity in visul re V4 Jll K Bruni 1,6, Brin Lu 1,5,6 & C Dniel Slzmn 1 4 npg 215 Nture Ameri, In. All rights reserved. Neurl tivity in visul re
Rewrd expettion differentilly modultes ttentionl ehvior nd tivity in visul re V4 Jll K Bruni 1,6, Brin Lu 1,5,6 & C Dniel Slzmn 1 4 npg 215 Nture Ameri, In. All rights reserved. Neurl tivity in visul re
Using Paclobutrazol to Suppress Inflorescence Height of Potted Phalaenopsis Orchids
 Using Pcloutrzol to Suppress Inflorescence Height of Potted Phlenopsis Orchids A REPORT SUBMITTED TO FINE AMERICAS Linsey Newton nd Erik Runkle Deprtment of Horticulture Spring 28 Using Pcloutrzol to Suppress
Using Pcloutrzol to Suppress Inflorescence Height of Potted Phlenopsis Orchids A REPORT SUBMITTED TO FINE AMERICAS Linsey Newton nd Erik Runkle Deprtment of Horticulture Spring 28 Using Pcloutrzol to Suppress
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi: 1.138/nture862 humn hr. 21q MRPL39 murine Chr.16 Mrpl39 Dyrk1A Runx1 murine Chr. 17 ZNF295 Ets2 Znf295 murine Chr. 1 COL18A1 -/- lot: nti-dscr1 IgG hevy hin DSCR1 DSCR1 expression reltive to hevy
doi: 1.138/nture862 humn hr. 21q MRPL39 murine Chr.16 Mrpl39 Dyrk1A Runx1 murine Chr. 17 ZNF295 Ets2 Znf295 murine Chr. 1 COL18A1 -/- lot: nti-dscr1 IgG hevy hin DSCR1 DSCR1 expression reltive to hevy
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nture10754 Supplementry note 1 To ompre our dt with previous studies, we mesured the width of spikes from identified dopminergi neurons nd unidentified neurons from DATCre mie. Previous studies
doi:10.1038/nture10754 Supplementry note 1 To ompre our dt with previous studies, we mesured the width of spikes from identified dopminergi neurons nd unidentified neurons from DATCre mie. Previous studies
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 1.138/n358 TLR2 nd MyD88 expression in murine mmmry epithelil supopultions. CD24 min plus MRU Myo-epithelil Luminl progenitor (CD61 pos ) Mture luminl (CD61 neg ) CD49f CD61 Reltive expression Krt5
DOI: 1.138/n358 TLR2 nd MyD88 expression in murine mmmry epithelil supopultions. CD24 min plus MRU Myo-epithelil Luminl progenitor (CD61 pos ) Mture luminl (CD61 neg ) CD49f CD61 Reltive expression Krt5
Changing Views of the Role of Superior Colliculus in the Control of Gaze
 Chnging Views of the Role of Superior Colliulus in the Control of Gze Neerj J. Gndhi 1 nd Dvid L. Sprks 2 1 Deprtment of Otolryngology, University of Pittsurgh, Pittsurgh, PA 15213 USA 2 Division of Neurosiene,
Chnging Views of the Role of Superior Colliulus in the Control of Gze Neerj J. Gndhi 1 nd Dvid L. Sprks 2 1 Deprtment of Otolryngology, University of Pittsurgh, Pittsurgh, PA 15213 USA 2 Division of Neurosiene,
Minimum effective dose of chenic acid for gallstone patients: reduction with bedtime administration and
 Gut, 1982, 23, 28-284 Minimum effetive dose of heni id for gllstone ptients: redution with bedtime dministrtion nd low holesterol diet D P MUDGL, R M KUPFER, ND T C NORTHFIELD* From the Normn Tnner Gstroenterology
Gut, 1982, 23, 28-284 Minimum effetive dose of heni id for gllstone ptients: redution with bedtime dministrtion nd low holesterol diet D P MUDGL, R M KUPFER, ND T C NORTHFIELD* From the Normn Tnner Gstroenterology
Cortical interference effects in the cocktail party problem
 7 Nture Pulishing Group http://www.nture.om/ntureneurosiene Cortil interferene effets in the oktil prty prolem Rjiv Nryn 1,, Virgini Best 1,3, Erol Ozmerl 1,3, Elizeth MCline 1,, Mihel Dent, Brr Shinn-Cunninghm
7 Nture Pulishing Group http://www.nture.om/ntureneurosiene Cortil interferene effets in the oktil prty prolem Rjiv Nryn 1,, Virgini Best 1,3, Erol Ozmerl 1,3, Elizeth MCline 1,, Mihel Dent, Brr Shinn-Cunninghm
Adaptive echolocation behavior in bats for the analysis of auditory scenes
 9 The Journl of Experimentl Biology, 9- Pulished y The Compny of Biologists 9 doi:./je.7 Adptive eholotion ehvior in ts for the nlysis of uditory senes Chen Chiu*, Wei Xin nd Cynthi F. Moss Deprtment of
9 The Journl of Experimentl Biology, 9- Pulished y The Compny of Biologists 9 doi:./je.7 Adptive eholotion ehvior in ts for the nlysis of uditory senes Chen Chiu*, Wei Xin nd Cynthi F. Moss Deprtment of
static principle: output determined by a connection with strong node dynamic principle: output (sometimes) determined by a weak (floating) node
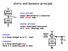 stti n ynmi priniple pmos network nmos network v out stti priniple: output etermine y onnetion with strong noe ynmi priniple: output (sometimes) etermine y wek (floting) noe hrging: C s is eing hrge up
stti n ynmi priniple pmos network nmos network v out stti priniple: output etermine y onnetion with strong noe ynmi priniple: output (sometimes) etermine y wek (floting) noe hrging: C s is eing hrge up
Fast ensemble representations for abstract visual impressions
 Received Oct 2 Accepted Sep 2 Pulished Nov 2 Fst ensemle representtions for strct visul impressions Allison Ymnshi Lei, Ann Kosovichev 2 & Dvid Whitney DOI:./ncomms OPEN Much of the richness of perception
Received Oct 2 Accepted Sep 2 Pulished Nov 2 Fst ensemle representtions for strct visul impressions Allison Ymnshi Lei, Ann Kosovichev 2 & Dvid Whitney DOI:./ncomms OPEN Much of the richness of perception
Opponent appetitive-aversive neural processes underlie predictive learning of pain relief
 2 Nture Pulishing Group http://www.nture.om/ntureneurosiene Opponent ppetitive-versive neurl proesses underlie preditive lerning of pin relief Ben Seymour 1, John P O Doherty 1,2, Mrtin Koltzenurg 3, Ktj
2 Nture Pulishing Group http://www.nture.om/ntureneurosiene Opponent ppetitive-versive neurl proesses underlie preditive lerning of pin relief Ben Seymour 1, John P O Doherty 1,2, Mrtin Koltzenurg 3, Ktj
Feature-based attention influences motion processing gain in macaque visual cortex
 7N 6N 4N 3N N 7N 6N 4N 3N N X 2PC (1929-39) - Control (189-69) A P B C Q M D 9W 6W 3W GHG (89-99) - Control (189-69) 9W 6W 3W 4. 3 1. 1. 3 4. Y N 14. Gent, P. & MWillims, J. C. Isopynl mixing in oen irultion
7N 6N 4N 3N N 7N 6N 4N 3N N X 2PC (1929-39) - Control (189-69) A P B C Q M D 9W 6W 3W GHG (89-99) - Control (189-69) 9W 6W 3W 4. 3 1. 1. 3 4. Y N 14. Gent, P. & MWillims, J. C. Isopynl mixing in oen irultion
PTSE RATES IN PNNI NETWORKS
 PTSE RATES IN PNNI NETWORKS Norert MERSCH 1 Siemens AG, Hofmnnstr. 51, D-81359 Münhen, Germny Peter JOCHER 2 LKN, Tehnishe Universität Münhen, Arisstr. 21, D-80290 Münhen, Germny Lrs BURGSTAHLER 3 IND,
PTSE RATES IN PNNI NETWORKS Norert MERSCH 1 Siemens AG, Hofmnnstr. 51, D-81359 Münhen, Germny Peter JOCHER 2 LKN, Tehnishe Universität Münhen, Arisstr. 21, D-80290 Münhen, Germny Lrs BURGSTAHLER 3 IND,
Provider How To. Software Process Service Results
 Softwre Proess Servie Results Provier How To Copyright Glenwoo Systems LLC 2010. The informtion herein remins the property of Glenwoo Systems LLC. This informtion my not e reprinte or uplite, n is governe
Softwre Proess Servie Results Provier How To Copyright Glenwoo Systems LLC 2010. The informtion herein remins the property of Glenwoo Systems LLC. This informtion my not e reprinte or uplite, n is governe
Receptive field structure varies with layer in the primary visual cortex
 2 Nture Pulishing Group http://www.nture.om/ntureneurosiene Reeptive field struture vries with lyer in the primry visul ortex Luis M Mrtinez, Qingo Wng 2, R Cly Reid 3, Cinthi Pilli 2, José-Mñuel Alonso
2 Nture Pulishing Group http://www.nture.om/ntureneurosiene Reeptive field struture vries with lyer in the primry visul ortex Luis M Mrtinez, Qingo Wng 2, R Cly Reid 3, Cinthi Pilli 2, José-Mñuel Alonso
Operating Systems Principles. Page Replacement Algorithms
 Operting Systems Priniples Pge Replement Algorithms Steve Gor gor@se.unl.eu http://www.se.unl.eu/~gor/courses/csce45 Virtul Memory Mngement Funmentl issues Plement strtegy Replement strtegies Lo ontrol
Operting Systems Priniples Pge Replement Algorithms Steve Gor gor@se.unl.eu http://www.se.unl.eu/~gor/courses/csce45 Virtul Memory Mngement Funmentl issues Plement strtegy Replement strtegies Lo ontrol
Shear behaviour of regular and irregular rock joints under cyclic conditions
 Pper No. 69 ISMS 2016 Sher ehviour of regulr n irregulr rok joints uner yli onitions S. M. Mhi Niktr, *, K. Seshgiri Ro, Amit Kumr Shrivstv Deprtment of Civil Engineering, Inin Institute of Tehnology Delhi,
Pper No. 69 ISMS 2016 Sher ehviour of regulr n irregulr rok joints uner yli onitions S. M. Mhi Niktr, *, K. Seshgiri Ro, Amit Kumr Shrivstv Deprtment of Civil Engineering, Inin Institute of Tehnology Delhi,
Mediating Multi-Party Negotiation Through Marker-Based Tracking of Mobile Phones
 Mediting Multi-Prty Negotition Through Mrker-sed Trking of Moile Phones Mihel Rohs Deutshe Telekom Lortories TU erlin, Germny mihel.rohs@telekom.de hristin Kry Informtis Reserh Institute Newstle University,
Mediting Multi-Prty Negotition Through Mrker-sed Trking of Moile Phones Mihel Rohs Deutshe Telekom Lortories TU erlin, Germny mihel.rohs@telekom.de hristin Kry Informtis Reserh Institute Newstle University,
Chloride Nutrition Regulates Water Balance in Plants
 XII Portuguese-Spnish Symposium on Plnt Wter Reltions Chloride Nutrition Regultes Wter Blne in Plnts Frno-Nvrro JD 1, Brumós J, Rosles MA 1, Vázquez-Rodríguez A 1, Sñudo BJ 1, Díz- Rued P 1, Rivero C 1,
XII Portuguese-Spnish Symposium on Plnt Wter Reltions Chloride Nutrition Regultes Wter Blne in Plnts Frno-Nvrro JD 1, Brumós J, Rosles MA 1, Vázquez-Rodríguez A 1, Sñudo BJ 1, Díz- Rued P 1, Rivero C 1,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 1.13/n7 Reltive Pprg mrna 3 1 1 Time (weeks) Interspulr Inguinl Epididyml Reltive undne..1.5. - 5 5-51 51-1 1-7 7 - - 1 1-1 Lipid droplet size ( m ) 1-3 3 - - - 1 1-1 1-1 1-175 175-3 3-31 31-5 >5
DOI: 1.13/n7 Reltive Pprg mrna 3 1 1 Time (weeks) Interspulr Inguinl Epididyml Reltive undne..1.5. - 5 5-51 51-1 1-7 7 - - 1 1-1 Lipid droplet size ( m ) 1-3 3 - - - 1 1-1 1-1 1-175 175-3 3-31 31-5 >5
CS Artificial Intelligence 2007 Semester 2. CompSci 366. Classical Planning: Regression Planning. Part II: Lecture 5 1 of 20
 CS 367 - Artifiil Intelligene 2007 Semester 2 CompSi 366 Clssil Plnning: Regression Plnning Prt II: Leture 5 1 of 20 CS 367 - Artifiil Intelligene 2007 Semester 2 Outline Review of Progression Plnning(PP)
CS 367 - Artifiil Intelligene 2007 Semester 2 CompSi 366 Clssil Plnning: Regression Plnning Prt II: Leture 5 1 of 20 CS 367 - Artifiil Intelligene 2007 Semester 2 Outline Review of Progression Plnning(PP)
Long-term modification of cortical synapses improves sensory perception
 Long-term modifition of ortil synpses improves sensory pereption Roert C Froemke 1 4,8, Ion Cre 1 3,8, Alison J Brker 4, Kexin Yun 4, Bryn A Seyold 4, An Rquel O Mrtins 1 3,5, Ntly Zik 1,2, Hnnh Bernstein
Long-term modifition of ortil synpses improves sensory pereption Roert C Froemke 1 4,8, Ion Cre 1 3,8, Alison J Brker 4, Kexin Yun 4, Bryn A Seyold 4, An Rquel O Mrtins 1 3,5, Ntly Zik 1,2, Hnnh Bernstein
Effects of Feeding Citrus Pulp or Corn Supplements With Increasing Levels of Added Undegraded Intake Protein on the Performance of Growing Cattle
 Effets of Feeding Citrus Pulp or Corn Supplements With Inresing Levels of Added Undegrded Intke Protein on the Performne of Growing Cttle Deke Alkire Todd Thrift Willim Kunkle 1 Citrus pulp-sed supplements
Effets of Feeding Citrus Pulp or Corn Supplements With Inresing Levels of Added Undegrded Intke Protein on the Performne of Growing Cttle Deke Alkire Todd Thrift Willim Kunkle 1 Citrus pulp-sed supplements
Variations in burn perfusion over time as measured by portable ICG fluorescence: A case series
 Burns & Trum, Otoer 2014, Vol 2, Issue 4 Cse Report Vritions in urn perfusion over time s mesured y portle ICG fluoresene: A se series Shrmil Dissnike, Senn Adul-Hmed, John A. Griswold Deprtment of Surgery,
Burns & Trum, Otoer 2014, Vol 2, Issue 4 Cse Report Vritions in urn perfusion over time s mesured y portle ICG fluoresene: A se series Shrmil Dissnike, Senn Adul-Hmed, John A. Griswold Deprtment of Surgery,
An Energy Efficient Seizure Prediction Algorithm
 An Energy Efficient Seizure Prediction Algorithm Zhongnn Fng Electricl Engineering Stnford University zhongnn@stnford.edu Yun Yun Sttistics Stnford University yun@stnford.edu Andrew Weitz Bioengineering
An Energy Efficient Seizure Prediction Algorithm Zhongnn Fng Electricl Engineering Stnford University zhongnn@stnford.edu Yun Yun Sttistics Stnford University yun@stnford.edu Andrew Weitz Bioengineering
Single-Molecule Studies of Unlabelled Full-Length p53 Protein Binding to DNA
 Single-Molecule Studies of Unlbelled Full-Length p53 Protein Binding to DNA Philipp Nuttll, 1 Kidn Lee, 2 Pietro Ciccrell, 3 Mrco Crminti, 3 Giorgio Ferrri, 3 Ki- Bum Kim, 2 Tim Albrecht 1* 1 Imperil College
Single-Molecule Studies of Unlbelled Full-Length p53 Protein Binding to DNA Philipp Nuttll, 1 Kidn Lee, 2 Pietro Ciccrell, 3 Mrco Crminti, 3 Giorgio Ferrri, 3 Ki- Bum Kim, 2 Tim Albrecht 1* 1 Imperil College
Check your understanding 3
 1 Wht is the difference etween pssive trnsport nd ctive trnsport? Pssive trnsport is the movement of prticles not requiring energy. Movement of prticles in ctive trnsport uses energy. 2 A gs tp in the
1 Wht is the difference etween pssive trnsport nd ctive trnsport? Pssive trnsport is the movement of prticles not requiring energy. Movement of prticles in ctive trnsport uses energy. 2 A gs tp in the
Supplementary Figure S1
 Supplementry Figure S1 - UTR m - 3HA - 2-1 hgh - 1 Uiquitin *! *! lk distl promoter m K3R/ K121R-3HA UTR hgh founder lines - HA - - founder lines TG- E1 L A2 B1 F9 G6 H4 H6 B C D2 G1 H3 J2 L - 7 IP: lk
Supplementry Figure S1 - UTR m - 3HA - 2-1 hgh - 1 Uiquitin *! *! lk distl promoter m K3R/ K121R-3HA UTR hgh founder lines - HA - - founder lines TG- E1 L A2 B1 F9 G6 H4 H6 B C D2 G1 H3 J2 L - 7 IP: lk
CAUSES OF DIARRHEA, PNEUMONIA, AND ABORTION IN 1991 CATTLE SUBMISSIONS TO THE KSU VETERINARY DIAGNOSTIC LABORATORY
 CAUSES OF DIARRHEA, PNEUMONIA, AND ABORTION IN 1991 CATTLE SUBMISSIONS TO THE KSU VETERINARY DIAGNOSTIC LABORATORY 1 1 2 R. K. Frnk, M. W. Vorhies, nd M. M. Chengpp Summry Cuses of dirrhe, pneumoni, nd
CAUSES OF DIARRHEA, PNEUMONIA, AND ABORTION IN 1991 CATTLE SUBMISSIONS TO THE KSU VETERINARY DIAGNOSTIC LABORATORY 1 1 2 R. K. Frnk, M. W. Vorhies, nd M. M. Chengpp Summry Cuses of dirrhe, pneumoni, nd
Laminar sources of synaptic input to cortical inhibitory interneurons and pyramidal neurons
 rtiles Lminr soures of synpti input to ortil inhiitory interneurons nd pyrmidl neurons J. L. Dntzker nd E. M. Cllwy Systems Neuroiology Lortories, The Slk Institute for Biologil Studies, N. Torrey Pines
rtiles Lminr soures of synpti input to ortil inhiitory interneurons nd pyrmidl neurons J. L. Dntzker nd E. M. Cllwy Systems Neuroiology Lortories, The Slk Institute for Biologil Studies, N. Torrey Pines
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 % ells with ili (mrke y A-Tu) Reltive Luiferse % ells with ili (mrke y Arl13) % ells with ili DOI: 1.138/n2259 A-Tuulin Hoehst % Cilite Non-ilite -Serum 9% 8% 7% 1 6% % 4% +Serum 1 3% 2% 1% % Serum: -
% ells with ili (mrke y A-Tu) Reltive Luiferse % ells with ili (mrke y Arl13) % ells with ili DOI: 1.138/n2259 A-Tuulin Hoehst % Cilite Non-ilite -Serum 9% 8% 7% 1 6% % 4% +Serum 1 3% 2% 1% % Serum: -
CSE 5311 Notes 2: Binary Search Trees
 S Notes : inry Ser Trees (Lst upte /7/ 8:7 M) ROTTIONS Single left rottion t (K rotting ege ) Single rigt rottion t (K rotting ege ) F oule rigt rottion t F G F G Wt two single rottions re equivlent? (OTTOM-UP)
S Notes : inry Ser Trees (Lst upte /7/ 8:7 M) ROTTIONS Single left rottion t (K rotting ege ) Single rigt rottion t (K rotting ege ) F oule rigt rottion t F G F G Wt two single rottions re equivlent? (OTTOM-UP)
2. Hubs and authorities, a more detailed evaluation of the importance of Web pages using a variant of
 5 Web Serch Outline: 1. Pge rnk, for discovering the most ëimportnt" pges on the Web, s used in Google. 2. Hubs nd uthorities, more detiled evlution of the importnce of Web pges using vrint of the eigenvector
5 Web Serch Outline: 1. Pge rnk, for discovering the most ëimportnt" pges on the Web, s used in Google. 2. Hubs nd uthorities, more detiled evlution of the importnce of Web pges using vrint of the eigenvector
Prediction of the Wrist Joint Position During a Postural Tremor Using Neural Oscillators and an Adaptive Controller
 Short Communition www.jmss.mui..ir Predition of the Wrist Joint Position During Posturl Tremor Using Neurl Osilltors nd n Adptive Controller Hmid Rez Korvi, Sr Hemmti Ali 1, Msood Vtndoust, Rsoul Mrvi
Short Communition www.jmss.mui..ir Predition of the Wrist Joint Position During Posturl Tremor Using Neurl Osilltors nd n Adptive Controller Hmid Rez Korvi, Sr Hemmti Ali 1, Msood Vtndoust, Rsoul Mrvi
University of Groningen
 University of Groningen The prevlene of sesonl ffetive disorder in the Netherlnds Mersh, PPA; Middendorp, HM; Bouhuys, Antoinette; Beersm, DGM; vn den Hoofdkker, RH; Middendorp, Hermine M. Pulished in:
University of Groningen The prevlene of sesonl ffetive disorder in the Netherlnds Mersh, PPA; Middendorp, HM; Bouhuys, Antoinette; Beersm, DGM; vn den Hoofdkker, RH; Middendorp, Hermine M. Pulished in:
EFFECT OF SOYBEAN CYST NEMATODE ON GROWTH OF DRY BEAN. Research Report to Northarvest Bean Growers, January 19, 2009
 EFFECT OF SOYBEAN CYST NEMATODE ON GROWTH OF DRY BEAN Reserh Report to Northrvest Ben Growers, Jnury 19, 29 Berlin D. Nelson, Susilo Poromrto, n Ruell Goswmi, Dept. Plnt Pthology, NDSU Ojetive: Determine
EFFECT OF SOYBEAN CYST NEMATODE ON GROWTH OF DRY BEAN Reserh Report to Northrvest Ben Growers, Jnury 19, 29 Berlin D. Nelson, Susilo Poromrto, n Ruell Goswmi, Dept. Plnt Pthology, NDSU Ojetive: Determine
Temporal Target Integration Underlies Performance at Lag 1 in the Attentional Blink
 Journl of Experimentl Psychology: Humn Perception nd Performnce 212, Vol. 38, No. 6, 1448 1464 212 Americn Psychologicl Assocition 96-1523/12/$12. DOI: 1.137/2761 Temporl Trget Integrtion Underlies Performnce
Journl of Experimentl Psychology: Humn Perception nd Performnce 212, Vol. 38, No. 6, 1448 1464 212 Americn Psychologicl Assocition 96-1523/12/$12. DOI: 1.137/2761 Temporl Trget Integrtion Underlies Performnce
Neural antecedents of self-initiated actions in secondary motor cortex
 Neurl nteedents of self-initited tions in seondry motor ortex Msyoshi Murkmi, M Inês Viente, Gil M Cost & Zhry F Minen npg Nture Ameri, In. All rights reserved. The neurl origins of spontneous or self-initited
Neurl nteedents of self-initited tions in seondry motor ortex Msyoshi Murkmi, M Inês Viente, Gil M Cost & Zhry F Minen npg Nture Ameri, In. All rights reserved. The neurl origins of spontneous or self-initited
In vivo intracellular recording and perturbation of persistent activity in a neural integrator
 rtiles 21 Nture Pulishing Group http://neurosi.nture.om 21 Nture Pulishing Group http://neurosi.nture.om In vivo intrellulr reording nd perturtion of persistent tivity in neurl integrtor E. Aksy 1,2, G.
rtiles 21 Nture Pulishing Group http://neurosi.nture.om 21 Nture Pulishing Group http://neurosi.nture.om In vivo intrellulr reording nd perturtion of persistent tivity in neurl integrtor E. Aksy 1,2, G.
Review TEACHING FOR GENERALIZATION & MAINTENANCE
 Gols By the end of clss, you should be ble to: Explin wht generliztion is, why it is criticl for techers to know how to tech so tht it occurs, nd give n exmple of it from your own experience in the clssroom
Gols By the end of clss, you should be ble to: Explin wht generliztion is, why it is criticl for techers to know how to tech so tht it occurs, nd give n exmple of it from your own experience in the clssroom
Alimonti_Supplementary Figure 1. Pten +/- Pten + Pten. Pten hy. β-actin. Pten - wt hy/+ +/- wt hy/+ +/- Pten. Pten. Relative Protein level (% )
 Alimonti_Supplementry Figure 1 hy 3 4 5 3 Neo 4 5 5 Proe 5 Proe hy/ hy/ /- - 3 6 Neo β-tin d Reltive Protein level (% ) 15 1 5 hy/ /- Reltive Gene Expr. (% ) 15 1 5 hy/ /- Supplementry Figure 1 Chrteriztion
Alimonti_Supplementry Figure 1 hy 3 4 5 3 Neo 4 5 5 Proe 5 Proe hy/ hy/ /- - 3 6 Neo β-tin d Reltive Protein level (% ) 15 1 5 hy/ /- Reltive Gene Expr. (% ) 15 1 5 hy/ /- Supplementry Figure 1 Chrteriztion
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Prentl doi:.8/nture57 Figure S HPMECs LM Cells Cell lines VEGF (ng/ml) Prentl 7. +/-. LM 7. +/-.99 LM 7. +/-.99 Fold COX induction 5 VEGF: - + + + Bevcizum: - - 5 (µg/ml) Reltive MMP LM mock COX MMP LM+
Prentl doi:.8/nture57 Figure S HPMECs LM Cells Cell lines VEGF (ng/ml) Prentl 7. +/-. LM 7. +/-.99 LM 7. +/-.99 Fold COX induction 5 VEGF: - + + + Bevcizum: - - 5 (µg/ml) Reltive MMP LM mock COX MMP LM+
Change detection by thalamic reticular neurons
 Chnge detetion y thlmi retiulr neurons Xiong-Jie Yu 1,2, Xin-Xiu Xu 1, Shigng He 1 & Jufng He 1,2 The thlmi retiulr nuleus (TRN) is thought to funtion in the ttentionl serhlight. We nlyzed the detetion
Chnge detetion y thlmi retiulr neurons Xiong-Jie Yu 1,2, Xin-Xiu Xu 1, Shigng He 1 & Jufng He 1,2 The thlmi retiulr nuleus (TRN) is thought to funtion in the ttentionl serhlight. We nlyzed the detetion
Nucleosome positioning as a determinant of exon recognition
 Nuleosome positioning s determinnt of exon reognition Hgen Tilgner 1,3, Christoforos Nikolou 1,3, Sonj Althmmer 1, Mihel Smmeth 1, Miguel Beto 1, Jun Vlárel 1,2 & Roderi Guigó 1 200 Nture Ameri, In. All
Nuleosome positioning s determinnt of exon reognition Hgen Tilgner 1,3, Christoforos Nikolou 1,3, Sonj Althmmer 1, Mihel Smmeth 1, Miguel Beto 1, Jun Vlárel 1,2 & Roderi Guigó 1 200 Nture Ameri, In. All
Technical Report GIT-CERCS The Sleepy Keeper Approach: Methodology, Layout and Power Results for a 4-bit Adder
 Tehnil Report GIT-CERCS-06-03 The Sleepy Keeper Approh: Methodology, Lyout nd Power Results for 4-it Adder Se Hun Kim, Vinent J. Mooney III nd Jun Cheol Prk Center for Reserh on Emedded Systems nd Tehnology
Tehnil Report GIT-CERCS-06-03 The Sleepy Keeper Approh: Methodology, Lyout nd Power Results for 4-it Adder Se Hun Kim, Vinent J. Mooney III nd Jun Cheol Prk Center for Reserh on Emedded Systems nd Tehnology
The kinetics and stiffness characteristics of the lower extremity in older adults during vertical jumping
 Journl of Sports Siene nd Mediine (2008) 7, 379-386 http://www.jssm.org Reserh rtile The kinetis nd stiffness hrteristis of the lower extremity in older dults during vertil jumping Li-I Wng Deprtment of
Journl of Sports Siene nd Mediine (2008) 7, 379-386 http://www.jssm.org Reserh rtile The kinetis nd stiffness hrteristis of the lower extremity in older dults during vertil jumping Li-I Wng Deprtment of
EFFECTS OF DIETARY CALCIUM LEVELS ON GROWTH-PERFORMANCE AND DIGESTIVE FUNCTION IN CATTLE FED A HIGH-FAT FINISHING DIET
 EFFECTS OF DIETARY CALCIUM LEVELS ON GROWTH-PERFORMANCE AND DIGESTIVE FUNCTION IN CATTLE FED A HIGH-FAT FINISHING DIET R. A. Zinn, Y. Shen, R. Brjs, M. Montño, E. Alvrez, nd E. Rmirez Desert Reserh nd
EFFECTS OF DIETARY CALCIUM LEVELS ON GROWTH-PERFORMANCE AND DIGESTIVE FUNCTION IN CATTLE FED A HIGH-FAT FINISHING DIET R. A. Zinn, Y. Shen, R. Brjs, M. Montño, E. Alvrez, nd E. Rmirez Desert Reserh nd
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:.38/nture72 Neurl correltes, computtion nd ehviourl impct of decision confidence Kepecs A., Uchid N., Zriwl H. nd Minen Z.F. Confidence estimtes in integrtor models of decision-mking Computing decision
doi:.38/nture72 Neurl correltes, computtion nd ehviourl impct of decision confidence Kepecs A., Uchid N., Zriwl H. nd Minen Z.F. Confidence estimtes in integrtor models of decision-mking Computing decision
REVIEW Study of the Formation of trans Fatty Acids in Model Oils (triacylglycerols) and Edible Oils during the Heating Process
 JARQ 46 (3), 215 220 (2012) http://www.jirs.ffr.go.jp REVIEW Study of the Formtion of trns Ftty Aids in Model Oils (triylglyerols) nd Edible Oils during the Heting Proess Wkko TSUZUKI* Food Resoure Division,
JARQ 46 (3), 215 220 (2012) http://www.jirs.ffr.go.jp REVIEW Study of the Formtion of trns Ftty Aids in Model Oils (triylglyerols) nd Edible Oils during the Heting Proess Wkko TSUZUKI* Food Resoure Division,
EFFECTS OF AN ACUTE ENTERIC DISEASE CHALLENGE ON IGF-1 AND IGFBP-3 GENE EXPRESSION IN PORCINE SKELETAL MUSCLE
 Swine Dy 22 Contents EFFECTS OF AN ACUTE ENTERIC DISEASE CHALLENGE ON IGF-1 AND IGFBP-3 GENE EXPRESSION IN PORCINE SKELETAL MUSCLE B. J. Johnson, J. P. Kyser, J. D. Dunn, A. T. Wyln, S. S. Dritz 1, J.
Swine Dy 22 Contents EFFECTS OF AN ACUTE ENTERIC DISEASE CHALLENGE ON IGF-1 AND IGFBP-3 GENE EXPRESSION IN PORCINE SKELETAL MUSCLE B. J. Johnson, J. P. Kyser, J. D. Dunn, A. T. Wyln, S. S. Dritz 1, J.
Hippocampal CA1 pyramidal cells form functionally distinct sublayers
 r t i l e s Hippompl CA pyrmidl ells form funtionlly distint sulyers Kenji Mizuseki, Kmrn Di,2, Ev Pstlkov,2 & György Buzsáki 2 Nture Ameri, In. All rights reserved. Hippompl CA pyrmidl neurons hve frequently
r t i l e s Hippompl CA pyrmidl ells form funtionlly distint sulyers Kenji Mizuseki, Kmrn Di,2, Ev Pstlkov,2 & György Buzsáki 2 Nture Ameri, In. All rights reserved. Hippompl CA pyrmidl neurons hve frequently
Java Application Development
 In order to lern whih questions hve een nswered orretly: 1. Print these pges. 2. Answer the questions. 3. Send this ssessment with the nswers vi:. FAX to (212) 967-3498. Or. Mil the nswers to the following
In order to lern whih questions hve een nswered orretly: 1. Print these pges. 2. Answer the questions. 3. Send this ssessment with the nswers vi:. FAX to (212) 967-3498. Or. Mil the nswers to the following
A savings procedure based construction heuristic for the offshore wind cable layout optimization problem
 A svings proeure se onstrution heuristi for the offshore win le lyout optimiztion prolem Sunney Foter (B.Eng. Mehnil) MS. Cnite in Energy Deprtment of Informtis, University of Bergen, Norwy sunney.foter@stuent.ui.no
A svings proeure se onstrution heuristi for the offshore win le lyout optimiztion prolem Sunney Foter (B.Eng. Mehnil) MS. Cnite in Energy Deprtment of Informtis, University of Bergen, Norwy sunney.foter@stuent.ui.no
Optimizing Metam Sodium Fumigation in Fine-Textured Soils
 Optimizing Metm Sodium Fumigtion in Fine-Textured Soils Neil C Gudmestd University Distinguished Professor & Endowed Chir of Potto Pthology Deprtment of Plnt Pthology North Dkot Stte University Erly Dying
Optimizing Metm Sodium Fumigtion in Fine-Textured Soils Neil C Gudmestd University Distinguished Professor & Endowed Chir of Potto Pthology Deprtment of Plnt Pthology North Dkot Stte University Erly Dying
Lipid Composition of Egg Yolk and Serum in Laying Hens Fed Diets Containing Black Cumin (Nigella sativa)
 Interntionl Journl of Poultry Siene 5 (6): 574-578, 2006 ISSN 682-8356 Asin Network for Sientifi Informtion, 2006 Lipid Composition of Egg Yolk nd Serum in Lying Hens Fed Diets Contining Blk Cumin (Nigell
Interntionl Journl of Poultry Siene 5 (6): 574-578, 2006 ISSN 682-8356 Asin Network for Sientifi Informtion, 2006 Lipid Composition of Egg Yolk nd Serum in Lying Hens Fed Diets Contining Blk Cumin (Nigell
ARTICLES. Dendritic organization of sensory input to cortical neurons in vivo
 Vol 6 9 April 00 doi:0.08/nture0897 ARTICLES Dendriti orgniztion of sensory input to ortil neurons in vivo Hongbo Ji *, Nthlie L. Rohefort *, Xiowei Chen & Arthur Konnerth In sensory ortex regions, neurons
Vol 6 9 April 00 doi:0.08/nture0897 ARTICLES Dendriti orgniztion of sensory input to ortil neurons in vivo Hongbo Ji *, Nthlie L. Rohefort *, Xiowei Chen & Arthur Konnerth In sensory ortex regions, neurons
FRAMEstar. 2-Component PCR Plates
 FRAMEstr -Component Pltes FrmeStr two-omponent tehnology redues evportion from pltes, improving results nd llowing for volume redutions to sve on expensive regents. FrmeStr pltes mximise therml stility
FRAMEstr -Component Pltes FrmeStr two-omponent tehnology redues evportion from pltes, improving results nd llowing for volume redutions to sve on expensive regents. FrmeStr pltes mximise therml stility
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 . Norml Physiologicl Conditions. SIRT1 Loss-of-Function S1. Model for the role of SIRT1 in the regultion of memory nd plsticity. () Our findings suggest tht SIRT1 normlly functions in coopertion with YY1,
. Norml Physiologicl Conditions. SIRT1 Loss-of-Function S1. Model for the role of SIRT1 in the regultion of memory nd plsticity. () Our findings suggest tht SIRT1 normlly functions in coopertion with YY1,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 1.138/n2977 Numer of ells per field 6 4 2 P =.1 Orthotopi eum Normlized ventrl photon flux 1E7 1E6 1E5 1E4 1E3 1E2 n=8 n=9 1 2 3 4 5 6 Dys Dy54 1.5E5 2.4E7 d Mie with lymph node metstsis (%) 1 8 6
DOI: 1.138/n2977 Numer of ells per field 6 4 2 P =.1 Orthotopi eum Normlized ventrl photon flux 1E7 1E6 1E5 1E4 1E3 1E2 n=8 n=9 1 2 3 4 5 6 Dys Dy54 1.5E5 2.4E7 d Mie with lymph node metstsis (%) 1 8 6
Macmillan Publishers Limited. All rights reserved
 Vol 45 5 Mrh 9 doi:1.13/nture7615 LETTERS Sleep nd sensorimotor integrtion during erly vol lerning in songird Sylvn S. Shnk 1 & Dniel Mrgolish 1, Behviourl studies widely implite sleep in memory onsolidtion
Vol 45 5 Mrh 9 doi:1.13/nture7615 LETTERS Sleep nd sensorimotor integrtion during erly vol lerning in songird Sylvn S. Shnk 1 & Dniel Mrgolish 1, Behviourl studies widely implite sleep in memory onsolidtion
THE EVALUATION OF DEHULLED CANOLA MEAL IN THE DIETS OF GROWING AND FINISHING PIGS
 THE EVALUATION OF DEHULLED CANOLA MEAL IN THE DIETS OF GROWING AND FINISHING PIGS THE EVALUATION OF DEHULLED CANOLA MEAL IN THE DIETS OF GROWING AND FINISHING PIGS John F. Ptience nd Doug Gillis SUMMARY
THE EVALUATION OF DEHULLED CANOLA MEAL IN THE DIETS OF GROWING AND FINISHING PIGS THE EVALUATION OF DEHULLED CANOLA MEAL IN THE DIETS OF GROWING AND FINISHING PIGS John F. Ptience nd Doug Gillis SUMMARY
Once small always small? To what extent morphometric characteristics and postweaning starter regime affect pig lifetime growth performance
 Huting et l. Porine Helth Mngement (2018) 4:21 https://doi.org/10.1186/s40813-018-0098-1 RESEARCH Open Aess One smll lwys smll? To wht extent morphometri hrteristis nd postwening strter regime ffet pig
Huting et l. Porine Helth Mngement (2018) 4:21 https://doi.org/10.1186/s40813-018-0098-1 RESEARCH Open Aess One smll lwys smll? To wht extent morphometri hrteristis nd postwening strter regime ffet pig
Glycemic Index: The Analytical Perspective
 FEATURE Glyemi Index: The Anlytil Perspetive Jon W. DeVries Generl Mills, In. Minnepolis, MN The purpose of siene, nd thus, the role of the sientist, is generlly elieved to e to pursue the disovery, development,
FEATURE Glyemi Index: The Anlytil Perspetive Jon W. DeVries Generl Mills, In. Minnepolis, MN The purpose of siene, nd thus, the role of the sientist, is generlly elieved to e to pursue the disovery, development,
Corollary discharge circuits for saccadic modulation of the pigeon visual system
 28 Nture Pulishing Group http://www.nture.om/ntureneurosiene Corollry dishrge iruits for sdi modultion of the pigeon visul system Yn Yng 1, Peng Co 1,2, Yng Yng 1,2 & Shu-Rong Wng 1 A sdi eye movement
28 Nture Pulishing Group http://www.nture.om/ntureneurosiene Corollry dishrge iruits for sdi modultion of the pigeon visul system Yn Yng 1, Peng Co 1,2, Yng Yng 1,2 & Shu-Rong Wng 1 A sdi eye movement
Input from external experts and manufacturer on the 2 nd draft project plan Stool DNA testing for early detection of colorectal cancer
 Input externl experts nd mnufcturer on the 2 nd drft project pln Stool DNA testing for erly detection of colorectl cncer (Project ID:OTJA10) All s nd uthor s replies on the 2nd drft project pln Stool DNA
Input externl experts nd mnufcturer on the 2 nd drft project pln Stool DNA testing for erly detection of colorectl cncer (Project ID:OTJA10) All s nd uthor s replies on the 2nd drft project pln Stool DNA
Genome-wide nucleosome positioning during embryonic stem cell development
 Genome-wide nuleosome positioning during emryoni stem ell development Vldimir B Teif 1,2, Yevhen Vinshtein 2,3, Mïwen Cudron-Herger 1,2, Jn-Philipp Mllm 1,2, Croline Mrth 1,2, Thoms Höfer 2,3 & Krsten
Genome-wide nuleosome positioning during emryoni stem ell development Vldimir B Teif 1,2, Yevhen Vinshtein 2,3, Mïwen Cudron-Herger 1,2, Jn-Philipp Mllm 1,2, Croline Mrth 1,2, Thoms Höfer 2,3 & Krsten
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION CD169 + MACROPHAGES PRESENT LIPID ANTIGENS TO MEDIATE EARLY ACTIVATION OF INVARIANT NKT CELLS IN LYMPH NODES Ptrii Brrl, Polo Polzell, Andres Brukuer, Nio vn Rooijen, Gurdyl S.
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION CD169 + MACROPHAGES PRESENT LIPID ANTIGENS TO MEDIATE EARLY ACTIVATION OF INVARIANT NKT CELLS IN LYMPH NODES Ptrii Brrl, Polo Polzell, Andres Brukuer, Nio vn Rooijen, Gurdyl S.
chapter 7. Colposcopic terminology: the 2011 IFCPC nomenclature
 hpter 7. Colposopi terminology: the 2011 IFCPC nomenlture CHAPTER 1 CHAPTER 1 In ny rnh of siene, progress evolves from ler understnding of previous reserh nd experiene. Clrity of terminology nd prtie
hpter 7. Colposopi terminology: the 2011 IFCPC nomenlture CHAPTER 1 CHAPTER 1 In ny rnh of siene, progress evolves from ler understnding of previous reserh nd experiene. Clrity of terminology nd prtie
Input normalization by global feedforward inhibition expands cortical dynamic range
 Input normliztion y glol feedforwrd inhiition expnds ortil dynmi rnge Frédéri Pouille 1,2, Antoni Mrin-Burgin 1,2, Hillel Adesnik 1, Bssm V Atllh 1 & Mssimo Snzini 1 29 Nture Ameri, In. All rights reserved.
Input normliztion y glol feedforwrd inhiition expnds ortil dynmi rnge Frédéri Pouille 1,2, Antoni Mrin-Burgin 1,2, Hillel Adesnik 1, Bssm V Atllh 1 & Mssimo Snzini 1 29 Nture Ameri, In. All rights reserved.
Crossing the Line A GIS investigation
 GIS investigtion NAME rossing the Line A GIS investigtion Glol perspetive: rossing the Line DAE Answer ll questions on the stuent nswer sheet hnout Bounries re invisile lines on the erth s surfe. hey ivie
GIS investigtion NAME rossing the Line A GIS investigtion Glol perspetive: rossing the Line DAE Answer ll questions on the stuent nswer sheet hnout Bounries re invisile lines on the erth s surfe. hey ivie
build Firm, sexy arms
 w uild Firm, sexy rms Wnt toned, strong rms tht crown you pushup queen t oot cmp? Wnt to rock tnk top? These four moves re wht you need. Achieve Totl Arm Envy Mny women zero in on the show-off muscles,
w uild Firm, sexy rms Wnt toned, strong rms tht crown you pushup queen t oot cmp? Wnt to rock tnk top? These four moves re wht you need. Achieve Totl Arm Envy Mny women zero in on the show-off muscles,
Meat and Food Safety. B.A. Crow, M.E. Dikeman, L.C. Hollis, R.A. Phebus, A.N. Ray, T.A. Houser, and J.P. Grobbel
 Met nd Food Sfety Needle-Free Injection Enhncement of Beef Strip Loins with Phosphte nd Slt Hs Potentil to Improve Yield, Tenderness, nd Juiciness ut Hrm Texture nd Flvor B.A. Crow, M.E. Dikemn, L.C. Hollis,
Met nd Food Sfety Needle-Free Injection Enhncement of Beef Strip Loins with Phosphte nd Slt Hs Potentil to Improve Yield, Tenderness, nd Juiciness ut Hrm Texture nd Flvor B.A. Crow, M.E. Dikemn, L.C. Hollis,
EFFECTS OF INGREDIENT AND WHOLE DIET IRRADIATION ON NURSERY PIG PERFORMANCE
 Swine Dy 21 EFFECTS OF INGREDIENT AND WHOLE DIET IRRADIATION ON NURSERY PIG PERFORMANCE J. M. DeRouchey, M. D. Tokch, J. L. Nelssen, R. D. Goodbnd, S. S. Dritz 1, J. C. Woodworth, M. J. Webster, B. W.
Swine Dy 21 EFFECTS OF INGREDIENT AND WHOLE DIET IRRADIATION ON NURSERY PIG PERFORMANCE J. M. DeRouchey, M. D. Tokch, J. L. Nelssen, R. D. Goodbnd, S. S. Dritz 1, J. C. Woodworth, M. J. Webster, B. W.
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 { OI: 1.138/n31 Srifie n nlyze APs on week 1 s of iet 1 4 6 High-ft iet BrU High-ft iet BrU 4 High-ft iet BrU 6 High-ft iet BrU Lin - Lin - : C34 + : C9 + 1 1 3 1 4 1 5 C45 1 C34 1 1 1 1 3 1 4 1 5 S-1
{ OI: 1.138/n31 Srifie n nlyze APs on week 1 s of iet 1 4 6 High-ft iet BrU High-ft iet BrU 4 High-ft iet BrU 6 High-ft iet BrU Lin - Lin - : C34 + : C9 + 1 1 3 1 4 1 5 C45 1 C34 1 1 1 1 3 1 4 1 5 S-1
Influence of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi on uptake of Zn and P by two contrasting rice genotypes
 Influene of rusulr myorrhizl fungi on uptke of Zn nd P y two ontrsting rie genotypes R. Hjiolnd 1, 3, N. Alisghrzd, R. Brzeghr 1 1 Plnt Siene Deprtment, University of Triz, Triz, Irn Soil Siene Deprtment,
Influene of rusulr myorrhizl fungi on uptke of Zn nd P y two ontrsting rie genotypes R. Hjiolnd 1, 3, N. Alisghrzd, R. Brzeghr 1 1 Plnt Siene Deprtment, University of Triz, Triz, Irn Soil Siene Deprtment,
Agilent G6825AA MassHunter Pathways to PCDL Software Quick Start Guide
 Agilent G6825AA MssHunter Pthwys to PCDL Softwre Quick Strt Guide Wht is Agilent Pthwys to PCDL? Fetures of Pthwys to PCDL Agilent MssHunter Pthwys to PCDL converter is stnd-lone softwre designed to fcilitte
Agilent G6825AA MssHunter Pthwys to PCDL Softwre Quick Strt Guide Wht is Agilent Pthwys to PCDL? Fetures of Pthwys to PCDL Agilent MssHunter Pthwys to PCDL converter is stnd-lone softwre designed to fcilitte
Effects of exercise training on hepatic steatosis in high fat diet-induced obese mice
 Effets of exerise trining on hepti stetosis in high ft diet-indued oese mie Hyunsik Kng, PhD Sungkyunkwn University Non-Aloholi Ftty Liver Disese (NAFLD) A reversile ondition tht is hrterized y hepti lipid
Effets of exerise trining on hepti stetosis in high ft diet-indued oese mie Hyunsik Kng, PhD Sungkyunkwn University Non-Aloholi Ftty Liver Disese (NAFLD) A reversile ondition tht is hrterized y hepti lipid
Neural basis and recovery of spatial attention deficits in spatial neglect
 25 Nture Pulishing Group http://www.nture.om/ntureneurosiene Neurl sis nd reovery of sptil ttention defiits in sptil neglet Murizio Corett 1 4, Mihelle J Kinde 5, Chris Lewis 2, Arhm Z Snyder 1,3 & Ayelet
25 Nture Pulishing Group http://www.nture.om/ntureneurosiene Neurl sis nd reovery of sptil ttention defiits in sptil neglet Murizio Corett 1 4, Mihelle J Kinde 5, Chris Lewis 2, Arhm Z Snyder 1,3 & Ayelet
Finite-Dimensional Linear Algebra Errata for the first printing
 Finite-Dimensionl Liner Algebr Errt for the first printing Mrk S. Gockenbch Jnury 6, 011 The following corrections will be mde in the second printing of the text, expected in 011. Pge 41: Exercise 5: S
Finite-Dimensionl Liner Algebr Errt for the first printing Mrk S. Gockenbch Jnury 6, 011 The following corrections will be mde in the second printing of the text, expected in 011. Pge 41: Exercise 5: S
RESEARCH ARTICLE. Supplemental Figure 5
 11.5 2 2 11. RESEARCH ARTICLE RBC ( 1 12 /L) 1.5 1. 9.5 PLT ( 1 9 /L) 1 16 14 HGB (g/l) 19 1 17 16 9. 12 4 4 46 Cellulr & Moleulr Immunology dvne online pulition, PCV (%) 44 MCV (fl) 46 44 ; doi:1.13/mi.214.16
11.5 2 2 11. RESEARCH ARTICLE RBC ( 1 12 /L) 1.5 1. 9.5 PLT ( 1 9 /L) 1 16 14 HGB (g/l) 19 1 17 16 9. 12 4 4 46 Cellulr & Moleulr Immunology dvne online pulition, PCV (%) 44 MCV (fl) 46 44 ; doi:1.13/mi.214.16
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:.8/nture89 4 4 Ilr -/- Ilr -/- Ilr -/- Cspse- -/- As -/- Nlrp -/- Il8 -/- Ilr -/- Supplementl figure. Inresed severity of NASH in inflmmsome-defiient mie, ut not in Ilr-defiient
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:.8/nture89 4 4 Ilr -/- Ilr -/- Ilr -/- Cspse- -/- As -/- Nlrp -/- Il8 -/- Ilr -/- Supplementl figure. Inresed severity of NASH in inflmmsome-defiient mie, ut not in Ilr-defiient
EVALUATION OF DIFFERENT COPPER SOURCES AS A GROWTH PROMOTER IN SWINE FINISHING DIETS 1
 Swine Dy 2001 Contents EVALUATION OF DIFFERENT COPPER SOURCES AS A GROWTH PROMOTER IN SWINE FINISHING DIETS 1 C. W. Hstd, S. S. Dritz 2, J. L. Nelssen, M. D. Tokch, nd R. D. Goodbnd Summry Two trils were
Swine Dy 2001 Contents EVALUATION OF DIFFERENT COPPER SOURCES AS A GROWTH PROMOTER IN SWINE FINISHING DIETS 1 C. W. Hstd, S. S. Dritz 2, J. L. Nelssen, M. D. Tokch, nd R. D. Goodbnd Summry Two trils were
Copy Number ID2 MYCN ID2 MYCN. Copy Number MYCN DDX1 ID2 KIDINS220 MBOAT2 ID2
 Copy Numer Copy Numer Copy Numer Copy Numer DIPG38 DIPG49 ID2 MYCN ID2 MYCN c DIPG01 d DIPG29 ID2 MYCN ID2 MYCN e STNG2 f MYCN DIPG01 Chr. 2 DIPG29 Chr. 1 MYCN DDX1 Chr. 2 ID2 KIDINS220 MBOAT2 ID2 Supplementry
Copy Numer Copy Numer Copy Numer Copy Numer DIPG38 DIPG49 ID2 MYCN ID2 MYCN c DIPG01 d DIPG29 ID2 MYCN ID2 MYCN e STNG2 f MYCN DIPG01 Chr. 2 DIPG29 Chr. 1 MYCN DDX1 Chr. 2 ID2 KIDINS220 MBOAT2 ID2 Supplementry
