Change detection by thalamic reticular neurons
|
|
|
- Cory King
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Chnge detetion y thlmi retiulr neurons Xiong-Jie Yu 1,2, Xin-Xiu Xu 1, Shigng He 1 & Jufng He 1,2 The thlmi retiulr nuleus (TRN) is thought to funtion in the ttentionl serhlight. We nlyzed the detetion of devint ousti stimuli y TRN neurons nd the onsequenes of devine detetion on the TRN trget, the medil geniulte ody (MGB) of the rt. TRN neurons responded more strongly to pure-tone stimuli presented s devint stimuli (low pperne proility) thn those presented s stndrd stimuli (high proility) (devine-detetion index =.321). MGB neurons lso showed devine detetion in this proedure, leit to smller extent (devine-detetion index =.4). TRN neuron devine detetion either enhned (14 neurons) or suppressed (27 neurons) MGB neuronl responses to proe stimulus. Both effets were neutrlized y intivtion of the uditory TRN. Devine modultion effets were ross-modl. Devine detetion proly uses TRN neurons to trnsiently detivte surrounding TRN neurons in response to fresh stimulus, ltering uditory thlmus responses nd induing ttention shift. The dorsl thlmus relys sensory nd motor informtion to the ererl ortex nd reeives strong modultory input k from the ortex. Both thlmoortil nd ortiothlmi projetions send ollterls to the TRN of the ventrl thlmus 1,2. The TRN onsists of GABA-ontining (GABAergi) neurons, whih only projet k to the dorsl thlmus 2 4. These neurons exhiit urst firing tht, under different onditions, ours in synhrony with severl frequenies of rhythmi osilltions in the ortiothlmi networks 8. The lotion of the TRN, long with its firing ptterns nd unique onnetions, hs led to the proposl tht the TRN is importnt in the internl ttentionl serhlight 9 nd for oordinting multiple neuronl proesses y linking speifi nd nonspeifi pthwys. In the uditory setor of the TRN, neurons show vrious response ptterns to ousti stimuli, inluding the urst response, phsi ON response nd OFF response 11,12. TRN neurons re tuned to rod rnge of frequenies 12. Novel stimuli ttrt our ttention s result of devint stimulus preferene (DSP), phenomenon in whih neurons show inresed responsiveness to devint stimuli. Suh neurons hve een identified in severl rin regions, inluding the visul nd uditory ortex nd the inferior olliulus 13,14. Compred with thlmoortil neurons in the MGB, TRN neurons in the uditory setor show greter dpttion to repeted stimuli. Considering the potentil role of the TRN in the internl ttentionl serhlight or ttention shift, fst-dpting TRN neurons re likely to exhiit DSP. We used in vivo extrellulr reording nd n oddll proedure to nlyze DSP (tht is, devine detetion) in TRN neurons. We then investigted the funtionl implitions of TRN neuron DSP y exmining how the DSP ffets the responses of thlmoortil neurons ( TRN output trget) to uditory stimuli. Inter-modlity intertion ws investigted y exmining how preeding light stimulus ffets the uditory responses of the MGB neurons. RESULTS Devine detetion y TRN neurons To determine whether the fst dpttion of TRN neurons is stimulus speifi, we used n oddll proedure with omintion of two puretone stimuli (with stndrd frequeny f 1 of 14 khz nd devint frequeny f 2 of 8 khz). A lok of pure-tone stimuli onsisting of f 1,f 1,f 1,f 1,f 1,f 1 nd f 2 ws repeted 3 times. The f 1 stimuli with n interstimulus intervl (ISI) of ms eliited strong responses in oth the first nd seond trils of lok 1; however, dpttion ws pprent in susequent trils of this lok (trils 3 6; Fig. 1). Introdution of the f 2 stimulus t tril 7 evoked strong response (lok 1; Fig. 1). Reintrodution of the f 1 stimuli in loks 2 resulted in wek or sent responses. However, f 2 stimuli eliited strong responses in ll loks (Fig. 1). As shown y the rster displys of ll 3 loks (Fig. 1), the f 2 stimulus eliited muh stronger responses thn the stndrd frequeny. Next, the stndrd nd devint frequenies were swpped. The new stndrd frequeny stimulus (f 2, 8 khz) eliited strong responses in the first tril, wek responses in trils 2 4 nd no response in trils nd 6 (lok 1; Fig. 1). However, the new devint stimulus (f 1,14kHz) eliited strong response (lok 1; Fig. 1). The f 2 stimulus evoked strong response t tril 1 in lok 2, ut evoked wek or sent response in trils 2 6 (Fig. 1). Reintrodution of the oddll stimulus t lok 2 ws ssoited with only wek response. The neurons showed good responses to the first trils of the stndrd stimuli in the loks nd wek responses to the following trils of the stndrd stimuli (Fig. 1). Responses to devint f 1 stimuli (Fig. 1) were muh stronger thn those to stndrd f 1 stimuli of the sme frequeny (Fig. 1). The sme ws true of devint (Fig. 1) nd stndrd f 2 stimuli (Fig. 1). A omprison of verge responses to f 2 (Fig. 1) ndf 1 (Fig. 1d) s either stndrd or devint stimuli lerly showed tht the TRN neurons preferred devint stimuli. Anlysis of the TRN neuron exposed to pure 1 CAS-Hong Kong Joint Reserh Lortory for Visuo-Auditory Integrtion, Institute of Biophysis, Chinese Ademy of Sienes, Beijing, Chin. 2 Lortory of Applied Neurosiene, Deprtment of Rehilittion Sienes, The Hong Kong Polytehni University, Hung Hom, Kowloon, Hong Kong. Correspondene should e ddressed to J.H. (rsjufng@polyu.edu.hk) or S.H. (shignghe@moon.ip..n). Reeived Ferury; epted 19 June; pulished online 16 August 9; doi:.38/nn.2373 NATURE NEUROSCIENCE VOLUME 12 [ NUMBER 9 [ SEPTEMBER 9 116
2 Figure 1 Responses of TRN neuron to pure-tone stimuli of two frequenies presented in n oddll proedure. () Responses to 14-kHz frequeny tones (f 1 ) when presented s the stndrd tone nd to 8-kHz frequeny tones (f 2 ) when presented s the devint tone. Neuronl responses to the first of 3 loks re presented in the upper prt. Trings from the five loks re red from left to right nd top to ottom. The order of presenttion ws lok 1 (f 1,f 1, y, f 1,f 2 ), lok 2 (f 1,f 1, y, f 1,f 2 ), y lok 3 (f 1, y, f 1,f 2 ). Bloks were ontiguous in time. The lower prt of the figure shows the rster displys of 3 loks of seven sequentil tones. Only the first ms of the responses re shown in the tres nd rster disply, lthough the ISI ws ms. () Responses on reversl of the stndrd nd devint tones. (,d) Peristimulus time histogrms showing responses (tht is, firing rte) to stndrd nd devint stimuli. ** P o.1 (ANOVA). (e) Trk of reording eletrode, s shown y Nissl stin (left, the rrow indites the reording site) nd responses s funtion of stimulus frequeny t 7-dB SPL (right). Sle r represents mm. Pure tones of vrying frequenies (6 24 khz), seprted y 2-kHz intervl, were rndomly presented, with eh frequeny eing presented in trils. tones t 7-dB sound pressure level (SPL) reveled tht the responses rnged from 8 to khz (Fig. 1e). Inresing the ISI to 1 s nd ltering the pperne rtio to 9:1 of the stndrd to devint stimuli yielded similr results (see exmple of nother neuron in Fig. 2,, where f 1 ¼ 19.2 khz nd f 2 ¼ 21.2 khz, nd men dt from 19 neurons in Fig. 2). Tht is, the neuron hd stronger response to pure-tone stimuli when they were presented s the devint stimulus thn when they were presented s the stndrd stimulus. Devine detetion y MGB neurons Using the sme stimulus proedure nd prmeters, we found tht MGB neurons showed less differene in responses to pure-tone stimuli with different presenttion proilities (stndrd versus devint). In one MGB neuron (Fig. 3), we oserved omprle responses to f 1 (17.12 khz) stimuli s stndrd (9% frequeny of presenttion) nd s devint (%) s well s to f 2 (18.92 khz) stimuli s stndrd nd s devint. In ontrst, nother MGB neuron (Fig. 3) showed ovious differenes in responses to f 1 (11.42 khz) stimuli s stndrd nd s devint s well s to f 2 (12.61 khz) stimuli s stndrd nd s devint. Tril numer Tril numer 9% f 1 9% f 2 % f 1 % f 2 Firing rte (Hz) Blok numer Blok numer Firing rte (Hz) Order of the stimuli presenttion f 1 f 1 f 1 f 1 f 1 f 1 f 2 f 2 f 2 f 2 f 2 f 2 f 2 f 1 f 1 s devint f 1 s stndrd * ** Anlysis of the men responses of 41 MGB neurons using the sme proedure nd prmeters reveled trend towrd greter responses to devint stimuli thn stndrd stimuli (P ¼.8; Fig. 3). We dopted the stimulus-speifi dpttion index for eh frequeny s frequeny-speifi index SI(f i ), whih ws lulted dðf iþ sðf iþ using the eqution SIðf i Þ¼dðf ; where d(f iþ+sðf iþ i) nd s(f i ) were responses to the devint nd stndrd frequeny, respetively 16.In SI(f 2 ) versus SI(f 1 ) stter plots, the points of TRN neurons devited from the digonl more thn those of MGB neurons (Fig. 4). The greter the devition of the point from the digonl, the greter the stimulus-speifi dpttion/devine detetion tht the neuron showed. A normlized devine-detetion index SI, defined s dðf 1Þ+dðf 2Þ sðf 1Þ sðf 2Þ dðf 1Þ+sðf 1Þ+dðf 2Þ+sðf 2Þ Firing rte (Hz) e 4 3 TRN ** 8 khz s devint 8 khz s stndrd 14 khz s devint 14 khz s stndrd ; ws pproximtely 8% greter in TRN neurons (n ¼ 19) thn in MGB neurons (n ¼ 41) (.321 ±.1 versus.4 ±., men ± s.e.m., P o.1). The devine proedure lters MGB responses To investigte the funtionl implition of DSP in TRN neurons, we exmined neuronl responses in the MGB using devine proedure with n dded proe stimulus. The ojetive ws to f 2 s devint f 2 s stndrd * Tones s devint Tones s stndrd 1 n TRN = 19 Firing rte (Hz) 3 d ** 7-dB SPL Frequeny (khz) Figure 2 Differentil responses of TRN neurons to pure-tone stimuli of two frequenies presented in n oddll proedure. () Rster displys showing responses to tones of two frequenies (f 1, 19.2 khz; f 2, 21.2 khz) when presented s f 1 stndrd (9% ppering proility) nd f 2 devint (% ppering proility) or f 1 devint nd f 2 stndrd. The ISI ws 1 s. We smpled responses to the stndrd frequeny from tril numers 81 to ( trils), wheres we smpled ll of the responses to the devint frequeny ( trils,: numers 1 to ). () Peristimulus time histogrms (PSTHs) of responses shown in. () PSTHs showing the men responses of 19 TRN neurons. * P o. nd ** P o.1 (ANOVA). The ISI ws 1 s VOLUME 12 [ NUMBER 9 [ SEPTEMBER 9 NATURE NEUROSCIENCE
3 tivte the TRN neurons tht exerted inhiition/disinhiition on the reording MGB neuron nd to investigte whether the devine proedure modulted MGB neuronl responses to the proe stimulus. The devine proedure onsisted of sequene of pure-tone f 1 stimuli (stndrd), pure-tone f 2 stimuli (devint), nd proe stimulus (p), f 1, f 1, f 1, f 1, f 1, f 1, f 1, f 1, f 1, f 1, f 2 nd p (proe stimulus: noise-urst or pure tone of the est frequeny, f 3 ). In the ontrol proedure, the f 2 in the devine proedure ws repled y f 1. When n MGB neuron ws seleted, preliminry sreening ws performed to ensure tht the MGB neuron responded to the proe stimulus of either noise-urst or pure-tone of f 3 nd filed to respond to pure-tone f 1 or f 2 stimulus. Two of the MGB neurons tht we exmined (Fig. ) responded to the proe stimuli under oth ontrol nd devine proedures, ut they filed to respond to pure tones of f 1 (3.44 khz) nd f 2 (33.64 khz) (nother two exmples of MGB neurons re shown in Supplementry Fig. 1). One neuron (Fig. ) showed weker responses to the proe stimulus (p: f 3 ¼ 8-kHz tones) under the devine proedure thn under the ontrol proedure. We nmed this MGB neuron devinesuppressed neuron. Conversely, nother neuron (Fig. ) hd stronger response to the proe stimulus (p: noise) in the devine proedure nd ws referred to s devine-enhned neuron. We used n index to mesure the modultory effet of the devine proedure on MGB neuronl response (IDC), defined s RD RC R D+R C ; where R D nd R C re the responses to the proe stimulus in the devine nd ontrol proedures, respetively). A totl of 77 MGB neurons were exmined using the devine proedure. Of these, 27 were devinesuppressed neurons nd 14 were devine-enhned neurons (Fig. ). Aordingly, the verge mplitude of the suppression (IDC ¼.263 ±.47, n ¼ 27) showed trend of eing greter thn the mplitude of enhnement (IDC ¼.144 ±.37, n ¼ 14) (P ¼.98). SI (f 2 ) 1.. TRN MGB Tril numer Tril numer Firing rte (Hz) 3 MGB neuron 1 MGB neuron 2 9% f 1 9% f 2 9% f 1 9% f 2 % f 1 f 1 s devint f 1 s stndrd % f 2 % f 1 % f f 2 s devint f 2 s stndrd Figure 3 Differentil responses of MGB neurons to pure-tone stimuli presented in n oddll proedure. () Rster displys (upper two rows) nd Peristimulus time histogrms (PSTHs) (lower row) showing responses to tones of two frequenies (f 1, khz; f 2, khz) when presented s f 1 stndrd/f 2 devint or f 2 stndrd/f 1 devint. () Rster displys (upper two rows) nd PSTHs (lower row) showing responses to tones of two frequenies (f 1, khz; f 2, khz) when presented s f 1 stndrd/f 2 devint or f 2 stndrd/f 1 devint. () PSTHs showing the men responses of 41 MGB neurons. The ISI ws 1 s. ** P o.1;, not signifint (P ¼.88). f 1 s devint f 1 s stndrd ** ** f 2 s devint f 2 s stndrd Tones s devint Tones s stndrd 1 n MGB = 41 TRN intivtion suppresses devine modultion of MGB To determine whether the hnges in MBG neuron responses to the proe stimulus of the devine proedure were used y the DSP of TRN neurons, we investigted the effet of lidoineindued TRN intivtion on MGB neuronl responses to the proe stimulus (Supplementry Fig. 2). Before TRN intivtion, one MGB neuron (Fig. 6,) exhiited responses to the proe stimulus (noise urst), ut not to the pure tone of f 1 (3.44 khz) or f 2 (33.64 khz) (Fig. 6). Responses to the proe stimulus were signifintly weker (P o.1) under the devine proedure thn under the ontrol proedure (Fig. 6). After TRN intivtion, the neuron responded to the pure-tone stimulus f 2, ut not f 1. In ddition, responses to the proe stimuli were signifintly inresed under oth ontrol (182%, P o.; Fig. 6 ) nd devine proedures (3%, P o.1; Fig. 6 ), implying tht the TRN strongly inhiited the MGB. However, responses to the proe stimuli did not differ etween the ontrol nd devine proedures fter TRN intivtion (P ¼.27; Fig. 6,). This result indites tht the devine modultion of the MGB ws primrily ttriutle to the TRN. Firing rte (Hz) SI (f 1 ) Figure 4 Devine preferenes of TRN nd MGB neurons. Stter plot of SI(f 2 ) versus SI(f 1 ) in ll TRN (red) nd MGB neurons (lk). MGB Responses re modulted y preeding light stimulus The ove experiments were designed to investigte devine modultion in the sme modlity. We next investigted whether MGB neuronl responses ould e modulted in ross-modl mnner. To do this, we introdued light stimulus efore the proe sound stimulus (light-sound, light-sound proedure). One of the MGB neurons tht we exmined (Fig. 7,) hd signifintly stronger NATURE NEUROSCIENCE VOLUME 12 [ NUMBER 9 [ SEPTEMBER
4 6 MGB neuron 3 Control proedure Devine proedure 6 MGB neuron 4 Control proedure Devine proedure Tril numer 3 1, 2, 1, 2, 3 1, 2, 1, 2, 18 n MGB = 77 Tril numer f 1 f 1 p f 1 f 2 p f 1 f 1 p f f 2 p Count 12 6 Firing rte (Hz) 1, , 1,6 1,6 1, p p p p ** Control proedure * Control proedure Devine proedure Devine proedure 1,66 1,6 1, responses to the proe stimulus (noise urst) in the light-sound proedure thn in the sound proedure without the light stimulus (sound proedure) (Fig. 7,). This neuron showed no responses to light stimuli (Supplementry Fig. 3). On TRN intivtion, the neuronl response to the proe stimulus inresed signifintly in oth the sound proedure nd the light-sound proedure (P o.1; Fig. 7 ), gin implying tht the TRN strongly inhiits the dorsl thlmus. However, fter TRN intivtion, the neuronl responses to the proe stimuli in the sound nd light-sound proedures did not differ (P ¼.26; Fig. 7,). Notly, 1,6 1,6 1, 1,6 1,6 1, 1,66 1,6 1,6 1,6 1.. IDC. 1. Figure Effet of the devint-stimulus proedure on MGB neuronl responses to proe stimulus. (,) Rster displys showing responses of two MGB neurons to sequentil uditory stimulus proedures. In the ontrol stimulus proedure (left olumns), pure tones of f 1 (lue rs) were presented 11 times efore proe stimulus (lk r). In the devine proedure (right olumns), pure tones of f 1 (lue rs) were presented ten times efore devint stimulus, pure tone of f 2 (red r) nd proe stimulus (lk r). The tones nd proe stimuli hd -ms durtion with -ms rise-fll time. In, f 1 ¼ 3.44 khz, f 2 ¼ khz nd p ¼ 8kHz.In, f 1 ¼ 3.44 khz, f 2 ¼ khz nd p ¼ noise urst. Upper rster displys show neuronl responses during the whole time (2 s), wheres the lower ones show neuronl responses t the first ms fter the proe stimulus (mgnified 1: from the upper displys). Peristimulus time histogrms of MGB neuronl responses re shown t the ottom. * P o. nd ** P o.1 (ANOVA). () Distriution of the modultory effet (IDC) of TRN devine detetion on MGB neurons. Blk rs showed modultion effets ove the threshold nd gry rs showed modultion effets elow the threshold. Figure 6 Effet of TRN intivtion on modultion of MGB neuronl responses y devint proedures. (,) MGB neuronl responses to sequentil stimulus proedures in the presene of n intt () orintivtedtrn(). In the ontrol stimulus proedure, pure tones of f 1 were presented 11 times efore proe stimulus (left olumns). In the devine proedure, pure tones of f 1 were presented ten times efore devint stimulus, pure tone of f 2 nd the proe stimulus (right olumns). Neuronl responses for the whole 2 s (upper row) nd the first ms fter the proe stimulus (lower row, mgnifition 1:) re shown. f 1 ¼ 3.44 khz (lue rs), f 2 ¼ khz (red rs) nd p ¼ noise urst (lk rs). () Peristimulus time histogrms of MGB neuronl responses re shown t the ottom. ** P o.1;, not signifint, P ¼.27 (ANOVA), ontrol versus devine proedures under the sme onditions. # P o. nd ## P o.1, intt versus intive TRN. Tril numer Tril numer Firing rte (Hz) , 2 ** 1, Control proedure 1, 1,6 TRN intivtion olished the effet of the preeding light stimulus on the uditory response of the MGB neuron. We exmined the effet of light stimulus on the uditory responses of 118 MGB neurons. Of these neurons, 23 hd enhned uditory responses following the light stimulus nd hd suppressed responses. The mgnitude of the enhnement effet ws greter thn tht of the suppressive effet (.176 ±.26 versus.73 ±., P o.1). TRN intt 6 3 2, 1, 2, 6 3 1,6 1, p p p p 1,66 Devine proedure Control proedure Devine proedure 6 6 1,6 # ## 1,6 1, , 1, 2, 1,6 TRN intivted ,6 1, 1, 2, 1,6 1,6 1, 1,66 1, VOLUME 12 [ NUMBER 9 [ SEPTEMBER 9 NATURE NEUROSCIENCE
5 Tril numer 3 TRN intt 3 TRN intivted d 4 n MGB = Firing rte (Hz) 3 S L S S L S With light With light Without light Without light ## ** ## Count 1.. IDC. 1. Figure 7 Effet of preeding light stimulus on MGB neuronl responses to sound stimuli. (,) Responses to light nd sound stimulus proedures in the presene of n intt () or intive TRN (). MGB neurons were tested in ontrol proedure (left pnels) in whih only proe stimulus (S) ws presented or ross-modlity proedure (right pnels) in whih light stimulus (L, green r) ws presented efore the proe stimulus (S, lk r). The proe stimulus ws -ms noise urst with -ms rise-fll time. () Peristimulus time histogrms of responses to the proe stimulus in the presene of n intt (left) or intive TRN (right). ** P o.1 (ANOVA) for sound versus light-sound proedures under the sme onditions nd ## P o.1 (ANOVA) for intt versus intive TRN. (d) Distriution of the ross-modlity modultory effet on MGB neurons. The modultory effet (IDC) ws defined s RLS RS ;where R LS nd R RLS+RS S re the responses to the proe in light-sound nd sound proedures, respetively. Negtive vlues indite n inhiitory effet of the light stimulus nd positive vlues indite n enhned effet. Blk rs show modultion effets ove the threshold nd gry rs show modultion effets elow the threshold. DISCUSSION Using the oddll proedure, we found tht TRN neurons hve sustntilly stronger responses to pure-tone stimulus when it ppers s the devint stimulus thn when it ppers s the stndrd stimulus. Although some MGB neurons lso hd devine preferene, the devine-detetion index ws sustntilly greter in TRN neurons thn in MGB neurons. The im of the seond prt of our study ws to investigte the funtionl implition of DSP y TRN neurons. Of the 77 MGB neurons tht we exmined with the devine proedure, 41 were modulted y the devine proedure, with 27 eing devinesuppressed nd 14 eing devine-enhned neurons. The mplitude of the suppression ws greter thn tht of the enhnement. The effet of devine detetion on MGB neuronl responses to the proe stimulus vried with the frequeny used in the testing proedure (Supplementry Fig. 4). After the TRN ws intivted, the MGB neurons showed sustntil inreses in their responses to the proe stimuli under oth ontrol nd devine proedures. However, responses to the proe stimuli did not differ etween the ontrol nd devine proedures, inditing tht the modultory effet of devine detetion on the MGB neurons were mostly ttriutle to TRN neurons. Of the 118 MGB neurons tht we exmined for the ross-modl modultory effet, 23 hd enhned uditory responses following introdution of the light stimulus nd neurons hd wekened responses. The TRN neurons send strong inhiitory projetions to the dorsl thlmus 1 4. Our finding tht MGB neurons showed sustntilly inresed responses to the sme uditory stimuli fter the uditory TRN ws intivted (Fig. 6) onfirms previous findings tht TRN inhiition of the dorsl thlmus is strong nd my lst for few seonds 17. Injetion of lidoine in the TRN not only intivtes TRN neurons, ut would lso e expeted to lok the ommunition of the xons pssing through the TRN (tht is, the ortiothlmi nd thlmoortil xons). Although the xons of the thlmoortil neurons were ffeted, the effet of the lidoine ws lolized nd did not lter the genertion of tion potentils in the MGB (Figs. 6 nd 7). With the use of ontrol onditions efore nd fter the drug pplition, the modultion effet of the diret ortiothlmi projetion to the MGB ws shown to e miniml s this pthwy is primrily exittory 17,18 nd MGB neurons showed inresed responses (Figs. 6 nd 7). Using n oddll proedure 16, we hve shown for the first time, to the est of our knowledge, tht fst-dptive TRN neurons in the uditory setor hve DSP. In the uditory system, DSP hs previously een reported in inferior olliulus neurons 13,14 nd ortil neurons 16. Using the sme proedure nd prmeters, we found tht MGB neurons hd smller DSP thn TRN neurons. Although MGB neurons were lso sensitive to devint stimuli, TRN neurons were more sensitive with ISIs on the order of hundreds of milliseonds, phenomenon tht is linked to novelty detetion 14,16. Using proedure tht ould exmine the resulting effet of devine detetion y the TRN neurons, we found tht some MGB neurons showed response enhnement, wheres others showed response suppression. The suppressive effet of DSP y TRN neurons on MGB neurons is understood to e used diretly y the inhiitory input to the MGB neurons. However, the enhnement of MGB neuronl responses is proly used y disinhiition of the TRN neurons or thlmi interneurons. The DSP of one TRN neuron would inhiit other TRN neurons through their ollterls either synptilly or eletrilly 3, They my lso inhiit thlmi interneurons. In either se, this would result in the disinhiition in the dorsl thlmus (Supplementry Fig. ). Shifts in the ttentionl serhlight during novelty detetion my involve projetions from the prefrontl ortex nd from the limi system to the TRN, whih re referred to s the nonspeifi pthwys 1,,22. The distriuted limi-ortil network is n essentil omponent for memory retrievl nd novelty detetion 23 2.Deresed tivity in the nuleus umens, whih provides other limi inputs NATURE NEUROSCIENCE VOLUME 12 [ NUMBER 9 [ SEPTEMBER
6 to the TRN, ws found in lrge group of individuls with tinnitus 26. Deresed limi innervtion of the TRN neurons would e expeted to result in disinhiition of the MGB. This might ount for inresed tivity in the uditory pthwy of people suffering from tinnitus 26. The nonspeifi pthwys my supplement speifi pthwys to the TRN,22,27. Indeed, the integrtion of speifi nd nonspeifi pthwys through the TRN is involved in ttention nd ognition. Some neurons in the TRN re multi-modl nd hve projetions tht ross nulei, suggesting tht the TRN hs n intermediry role 11,12,28. The ft tht MGB neuronl responses to sound stimuli were modulted y preeding light stimulus indites tht the intermodl intertion ould our t the TRN (Supplementry Fig. ). Devine detetion y TRN neurons would enle these ells to reognize new stimulus, while inhiiting other TRN neurons through their ollterls. Our finding tht the MGB neuron ws influened y preeding pure tones of frequeny to whih it normlly did not respond (Fig. nd Supplementry Fig. 1) indites tht the modultory effet spreds eyond its response frequeny rnge. The devine detetion effet would indue shift in the serhlight to diret ttention to the stimulus 9 nd the shift of ttention through the TRN ould e ross-modl. The strong dpttion or hitution tht TRN neurons undergo in response to repetitive stimuli might redue the redundny of the environment nd shrpen ontrsts etween differing stimuli. Finlly, in the devine proedure tht we used, some MGB neurons shifted from toni mode to urst mode (Supplementry Fig. 1). The step funtion of the input-output reltionship in urst mode (tht is, the mode in whih thlmi neurons re hyperpolrized y TRN input) would enle thlmi neurons to respond more strongly thn if they were in the toni mode This is nother potentil mehnism underlying devine detetion-indued enhnement of the MGB neuronl response nd my supplement those tht we propose here (Supplementry Fig. ). METHODS Methods nd ny ssoited referenes re ville in the online version of the pper t Note: Supplementry informtion is ville on the Nture Neurosiene wesite. ACKNOWLEDGMENTS The uthors thnk A. Plmer nd M. Wlle for their ritil redings nd omments. This work ws supported y the Nturl Siene Foundtion of Chin (Overses Coopertion Fund) nd the Hong Kong Grnts Counil (PolyU 412/6M). AUTHOR CONTRIBUTIONS X.-J.Y., S.H. nd J.H. designed the experiments. X.-J.Y. nd X.-X.X. performed the experiments. X.-J.Y. nd J.H. nlyzed the results nd wrote the mnusript. Pulished online t Reprints nd permissions informtion is ville online t reprintsndpermissions/. 1. Jones, E.G. Some spets of the orgniztion of the thlmi retiulr omplex. J. Comp. Neurol. 162, (197). 2. Steride, M., Jones, E.G. & MCormik, D.A. Thlmus: Orgniztion nd Funtion (Elsevier Siene, Oxford, 1997). 3. Yen, C.T., Conley, M., Hendry, S.H. & Jones, E.G. The morphology of physiologilly identified GABAergi neurons in the somti sensory prt of the thlmi retiulr nuleus in the t. J. Neurosi., (198). 4. Houser, C.R., Vughn, J.E., Brer, R.P. & Roerts, E. GABA neurons re the mjor ell type of the nuleus retiulris thlmi. Brin Res., (198).. Deshênes, M., Mdrig-Domih, A. & Steride, M. Dendrodendriti synpses in the t retiulris thlmi nuleus: struturl sis for thlmi spindle synhroniztion. Brin Res. 334, (198). 6. Steride, M. & Deshênes, M. The thlmus s neuronl osilltor. Brin Res. 3, 1 63 (1984). 7. Bl, T. & MCormik, D.A. Mehnisms of osilltory tivity in guine-pig nuleus retiulris thlmi in vitro: mmmlin pemker. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 468, (1993). 8. MCormik, D.A. & Prine, D.A. Aetylholine indues urst firing in thlmi retiulr neurones y tivting potssium ondutne. Nture 319, 42 4 (1986). 9. Crik, F. Funtion of the thlmi retiulr omplex: the serhlight hypothesis. Pro. Ntl. Ad. Si. USA 81, (1984)..Llinás, R. & Pré, D. in Thlmus (eds. Steride M., Jones E.G. & MCormik D.A.) 1 16 (Plenum, New York, 1997). 11. Shosku, A. & Sumitomo, I. Auditory neurons in the rt thlmi retiulr nuleus. Exp. Brin Res. 49, (1983). 12. Simm, G.M., de Riupierre, F., de Riupierre, Y. & Rouiller, E.M. Dishrge properties of single units in uditory prt of retiulr nuleus of thlmus in t. J. Neurophysiol. 63, 21 (199). 13. Mlone, B.J. & Semple, M.N. Effets of uditory stimulus ontext on the representtion of frequeny in the geril inferior olliulus. J. Neurophysiol. 86, (1). 14.Pérez-González, D., Mlmier, M.S. & Covey, E. Novelty detetor neurons in the mmmlin uditory midrin. Eur. J. Neurosi. 22, ().. Yu, X.-J., Xu, X.-X., Chen, X., He, S.-G. & He, J. Slow reovery from exittion of thlmi retiulr nuleus neurons. J. Neurophysiol. 1, (9). 16. Ulnovsky, N., Ls, L. & Nelken, I. Proessing of low-proility sounds y ortil neurons. Nt. Neurosi. 6, (3). 17. Zhng, Z. et l. Cortiofugl projetion inhiits the uditory thlmus through the thlmi retiulr nuleus. J. Neurophysiol. 99, (8). 18. He, J., Yu, Y.Q., Xiong, Y., Hshikw, T. & Chn, Y.S. Modultory effet of ortil tivtion on the lemnisl uditory thlmus of the Guine pig. J. Neurophysiol. 88, 4 (2). 19. Lndismn, C.E. et l. Eletril synpses in the thlmi retiulr nuleus. J. Neurosi. 22, 2 9 (2).. Long, M.A., Lndismn, C.E. & Connors, B.W. Smll lusters of eletrilly oupled neurons generte synhronous rhythms in the thlmi retiulr nuleus. J. Neurosi. 24, (4). 21. Wrren, R.A., Agmon, A. & Jones, E.G. Osilltory synpti intertions etween ventroposterior nd retiulr neurons in mouse thlmus in vitro. J. Neurophysiol. 72, (1994). 22. Zikopoulos, B. & Brs, H. Prefrontl projetions to the thlmi retiulr nuleus form unique iruit for ttentionl mehnisms. J. Neurosi. 26, (6). 23. Knight, R. Contriution of humn hippompl region to novelty detetion. Nture 383, (1996). 24. Tiitinen, H., My, P., Reinikinen, K. & Náátánen, R. Attentive novelty detetion in humns is governed y pre-ttentive sensory memory. Nture 372, 9 92 (1994). 2. Crpenter, G.A. & Grosserg, S. Norml nd mnesi lerning, reognition nd memory y neurl model of ortio-hippompl intertions. Trends Neurosi. 16, (1993). 26. Mühlu, M. et l. Struturl rin hnges in tinnitus. Cere. Cortex 16, (6). 27. Llinás, R.R. & Pré, D. Of dreming nd wkefulness. Neurosiene 44, 21 3 (1991). 28. Crtree, J.W. & Is, J.T. New intrthlmi pthwys llowing modlity-relted nd ross-modlity swithing in the dorsl thlmus. J. Neurosi. 22, (2). 29. Jhnsen, H. & Llinás, R. Eletrophysiologil properties of guine-pig thlmi neurones: n in vitro study. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 349, 226 (1984). 3.Jhnsen, H. & Llinás, R. Ioni sis for the eletro-responsiveness nd osilltory properties of guine-pig thlmi neurones in vitro. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 349, (1984). 31. Shermn, S.M. A wke-up ll from the thlmus. Nt. Neurosi. 4, (1). 32. Guillery, R.W. & Shermn, S.M. Thlmi rely funtions nd their role in ortioortil ommunition: generliztions from the visul system. Neuron 33, (2). 117 VOLUME 12 [ NUMBER 9 [ SEPTEMBER 9 NATURE NEUROSCIENCE
7 ONLINE METHODS Animls. We used mle nd femle Wistr rts (28 36 g) with len externl ers. Anesthesi ws indued with 1. g per kg of ody weight urethne (% (wt/wt) solution, intrperitonel, Sinophrm Chemil Regent) nd mintined throughout surgery nd reording with. g per kg per h urethne. Atropine sulfte (. mg per kg, suutneous) ws dministered min efore indution of nesthesi to inhiit trhel seretion. A lol nestheti (2% (wt/vol) xyloine) ws lierlly pplied to the wound. Rts were surgilly prepred s desried previously Briefly, rts were mounted in stereotxi devie nd midline inision ws mde in the slp. A rniotomy ws performed to vertilly ess the MGB nd the uditory setor of the TRN nd the dur mter ws then removed. Throughout the experiment, the rt ws kept on heting lnket nd ody temperture ws mintined t C. All niml proedures were pproved y the Animl Sujets Ethis Suommittees of the Institute of Biophysis, Chinese Ademy of Sienes nd The Hong Kong Polytehni University. Reording. Tungsten miroeletrodes with impednes of 2 7 MO (Frederik Her) were stereotxilly implnted into the TRN nd MGB from the top of the rin, ording to rt rin tls 36. The vertil oordinte of the eletrode rry ws mesured from point slightly ove the ortil surfe. For reording, eletrodes were positioned with stepping-motor mirodrive, whih ws ontrolled from outside the soundproof room. The signl reorded y the miroeletrode, together with the ousti stimulus signl, ws mplified nd stored using OpenEX (Tuker-Dvis Tehnologies) nd Axosope softwre (Axon Instruments). The time of spike ourrene reltive to stimulus delivery ws lulted with Mtl softwre (Mthworks). Antomil onfirmtion. After the reording session, the rts were deeply nesthetized with sodium pentoritl. They were killed y trnsrdil perfusion of with.9% (wt/vol) sline followed y 4% (wt/vol) prformldehyde in.1 M phosphte uffer (ph 7.3). The rins were removed nd stored overnight in.1 M phosphte uffer ontining 3% (wt/vol) surose. Trnsverse thlmi setions of -mm thikness were stined using the Nissl method. Imges of Nissl-stined setions were overlid onto physiologil mp using the eletrode penetrtion trks nd lesions for guidne. We used eight rts to onfirm the orret positioning of the eletrodes. Aousti stimuli. Aousti stimuli were digitlly generted using omputerontrolled Auditory Worksttion (Tuker-Dvis Tehnologies) nd delivered to the er vi oupled eletrostti speker (EC1, Tuker-Dvis Tehnologies) mounted in proe. The SPL of the output of the proe ws lirted with ondenser mirophone (Center Tehnology). Oddll proedure. Stimulus frequenies eliiting optiml responses in TRN nd MGB neurons were determined. During the mjority of the experiments, we seleted two frequenies, f 1 nd f 2, tht ordered entrl frequeny (f 1 f 2 ) 1/2 equling its est frequeny nd tht hd rtio of.141 otves. Stimulus intensity ws set to 7 db. In most ses, the stndrd nd devint stimuli ourred t rtio of 9 to 1. Otherwise, this rtio ws 6 to 1, s speified. The stimuli were presented in repetitive sequene of nine stndrd tones followed y single devint tone. The ISI ws either ms or 1, ms, with sttistil omprisons eing performed on dt otined with n ISI of 1, ms. PSTHs were lulted from over 18 trils for the stndrd tone nd trils for the devint tone. Anlysis of MGB neuronl responses using the devine proedure. The devine proedure ws designed to unover possile modultory effets of the TRN devine-preferene on the responses of MGB neurons to uditory stimuli. A few prmeters of the devine proedure were modified to eliit mximl effet. The devine proedure onsisted of the following sequene of stimuli: f 1,f 1,f 1,f 1,f 1,f 1,f 1,f 1,f 1,f 1,f 2 nd p. In the ontrol proedure, f 2 ws repled with f 1 to generte the following sequene: f 1,f 1,f 1,f 1,f 1,f 1,f 1,f 1,f 1, f 1,f 1 nd p. The rtionle for this ws tht the TRN neurons would e tivted y f 2 in the devine proedure, ut not y the finl f 1 in the ontrol proedure. MGB neuronl responses to the proe stimulus were ompred under the devine nd ontrol proedures. Differenes would show the modultory effet of the TRN devine preferene. To exlude the lst dpttion effet of the responses to the preeding sequene of tones (f 1, y, f 1 or f 1,y, f 2 )onthe responses to the proe stimulus, we hose frequenies of f 1 nd f 2 tht evoked no response from the MGB neuron eing reorded. The ISI ws typilly set t ms etween onseutive f 1 stimuli nd etween f 1 nd f 2.Thef 2 stimulus ws seprted from the proe stimulus y ms, or s otherwise speified. The inter-lok stimulus ws set t 3 s. When the ISI etween f 2 nd p ws set t ms, the proe stimulus followed f 2 without ny dely, s the durtion of ll stimuli (f 1,f 2 nd p) ws set to ms. Bloks of the devine nd ontrol proedures were rndomly presented y the omputer. An index tht mesured the modultory effet on the uditory response of the MGB neurons y the preeding devine proedure, IDC, ws defined s R D R C R D+R C ; where R D nd R C re the responses to the proe stimulus in the devine nd ontrol proedures, respetively. A negtive vlue indites suppressive effet nd positive vlue indites n enhned effet. The threshold for determining modultory effet, IDC th, ws set on neurony-neuron sis. The IDC th for eh individul neuron ws lulted using the ove eqution with responses from the odd (3 trils) nd even numer (3 trils) of trils in the ontrol proedure. The definitions for IDC nd IDC th lso pply to the ross-modl proedure. When the solute vlue of IDC exeeded the solute vlue of IDC th, the neuron ws onsidered to hve undergone modultion nd ws inluded in the sttistis. Comintion of light nd sound stimuli. A light stimulus ( ms) ws presented nd ws followed y noise urst with -ms intervl (light-sound proedure). Only the sound stimulus ws presented in the ontrol proedure (sound proedure). White light ws delivered through n rry of light diodes, whih were pled inside the soundproof hmer nd ontrolled eletronilly outside the hmer. No sound ws deteted while swithing the light diodes. MGB neuronl responses to the sound stimulus were ompred under the lightsound nd sound proedures. An initil exmintion of the neuronl response to the visul stimulus lone ws performed to exlude the dpttion effet. The light-sound nd sound proedures were rndomly presented every 3 s. Neuronl response dt were sorted for eh proedure using homemde progrm. Drug pplition. Lidoine ws purhsed from Sigm. Lidoine injetions (.3 ml, mg ml 1 ) were dministered in the TRN of seven rts using miroinjetion system (Hmilton). A tungsten miroeletrode ws glued to the injetion glss pipette to monitor the tivity of the TRN. The distne etween the two tips ws pproximtely mm. Dt nlysis. Spike detetion ws rried out with OpenEX softwre (Tuker- Dvis Tehnologies). Differenes etween vrying onditions were nlyzed with ANOVA. In ll nlyses, P o. ws onsidered to e signifint. 33. He, J. On nd off pthwys segregted t the uditory thlmus of the guine pig. J. Neurosi. 21, (1). 34. Guo, Y.P. et l. Cortiothlmi synhroniztion leds to -fos expression in the uditory thlmus. Pro. Ntl. Ad. Si. USA 4, (7). 3. Xiong, Y., Yu, Y.Q., Chn, Y.S. & He, J. Effets of ortil stimultion on uditoryresponsive thlmi neurones in nesthetized guine pigs. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 6, (4). 36. Pxinos, G. & Wtson, C. The Rt Brin in Stereotxi Coordintes (Elsevier Ademi Press, Amsterdm, ). doi:.38/nn.2373 NATURE NEUROSCIENCE
LHb VTA. VTA-projecting RMTg-projecting overlay. Supplemental Figure 2. Retrograde labeling of LHb neurons. a. VTA-projecting LHb
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementl Figure 1 doi:10.1038/nture09742 Lterl 1.0 mm from midline mpfc BNST mpfc BNST Lterl 2.1 mm from midline LHA LHA Lterl 2.7 mm from midline SUPPLEMENTAL INFORMATION
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementl Figure 1 doi:10.1038/nture09742 Lterl 1.0 mm from midline mpfc BNST mpfc BNST Lterl 2.1 mm from midline LHA LHA Lterl 2.7 mm from midline SUPPLEMENTAL INFORMATION
Lesions of prefrontal cortex reduce attentional modulation of neuronal responses. and synchrony in V4
 Lesions of prefrontl ortex reue ttentionl moultion of neuronl responses n synhrony in V4 Georgi G. Gregoriou,, Anrew F. Rossi, 3 Leslie G Ungerleier, 4 Roert Desimone 5 Deprtment of Bsi Sienes, Fulty of
Lesions of prefrontl ortex reue ttentionl moultion of neuronl responses n synhrony in V4 Georgi G. Gregoriou,, Anrew F. Rossi, 3 Leslie G Ungerleier, 4 Roert Desimone 5 Deprtment of Bsi Sienes, Fulty of
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:.38/nture277 d 25 25 2 Time from sound onset (ms) 25 25 2 Time from sound onset (ms) Firing rte (spikes/s) Firing rte (spikes/s).8.6..2 e f g h.8.6..2 Frtion of neurons Frtion of neurons N = 53 2 2
doi:.38/nture277 d 25 25 2 Time from sound onset (ms) 25 25 2 Time from sound onset (ms) Firing rte (spikes/s) Firing rte (spikes/s).8.6..2 e f g h.8.6..2 Frtion of neurons Frtion of neurons N = 53 2 2
Supplementary Figure 1. Scheme of unilateral pyramidotomy used for detecting compensatory sprouting of intact CST axons.
 () BDA 2 weeks fter Py () AAVs Cre or GFP t P1 BDA 2 weeks fter Py CSMN CST () Py t P7 or 2 months () Py t 2 months Supplementry Figure 1. Sheme of unilterl pyrmidotomy used for deteting ompenstory sprouting
() BDA 2 weeks fter Py () AAVs Cre or GFP t P1 BDA 2 weeks fter Py CSMN CST () Py t P7 or 2 months () Py t 2 months Supplementry Figure 1. Sheme of unilterl pyrmidotomy used for deteting ompenstory sprouting
EFFECT OF DIETARY ENZYME ON PERFORMANCE OF WEANLING PIGS
 EFFECT OF DIETARY ENZYME ON PERFORMANCE OF WEANLING PIGS Finl report sumitted to Dniso Animl Nutrition E. vn Heugten nd B. Frederik North Crolin Stte University, Deprtment of Animl Siene Summry The urrent
EFFECT OF DIETARY ENZYME ON PERFORMANCE OF WEANLING PIGS Finl report sumitted to Dniso Animl Nutrition E. vn Heugten nd B. Frederik North Crolin Stte University, Deprtment of Animl Siene Summry The urrent
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nture10754 Supplementry note 1 To ompre our dt with previous studies, we mesured the width of spikes from identified dopminergi neurons nd unidentified neurons from DATCre mie. Previous studies
doi:10.1038/nture10754 Supplementry note 1 To ompre our dt with previous studies, we mesured the width of spikes from identified dopminergi neurons nd unidentified neurons from DATCre mie. Previous studies
Long-term modification of cortical synapses improves sensory perception
 Long-term modifition of ortil synpses improves sensory pereption Roert C Froemke 1 4,8, Ion Cre 1 3,8, Alison J Brker 4, Kexin Yun 4, Bryn A Seyold 4, An Rquel O Mrtins 1 3,5, Ntly Zik 1,2, Hnnh Bernstein
Long-term modifition of ortil synpses improves sensory pereption Roert C Froemke 1 4,8, Ion Cre 1 3,8, Alison J Brker 4, Kexin Yun 4, Bryn A Seyold 4, An Rquel O Mrtins 1 3,5, Ntly Zik 1,2, Hnnh Bernstein
Mechanisms underlying cross-orientation suppression in cat visual cortex
 Mehnisms underlying ross-orienttion suppression in t visul ortex 6 Nture Pulishing Group http://www.nture.om/ntureneurosiene Nihols J Priee & Dvid Ferster In simple ells of the t primry visul ortex, null-oriented
Mehnisms underlying ross-orienttion suppression in t visul ortex 6 Nture Pulishing Group http://www.nture.om/ntureneurosiene Nihols J Priee & Dvid Ferster In simple ells of the t primry visul ortex, null-oriented
Neural population coding of sound level adapts to stimulus statistics
 COMPUTATION AND SYSTEMS 25 Nture Pulishing Group http://www.nture.om/ntureneurosiene Neurl popultion oding of sound level dpts to stimulus sttistis Isel Den 1, Niol S Hrper 1,2 & Dvid MAlpine 1 Mmmls n
COMPUTATION AND SYSTEMS 25 Nture Pulishing Group http://www.nture.om/ntureneurosiene Neurl popultion oding of sound level dpts to stimulus sttistis Isel Den 1, Niol S Hrper 1,2 & Dvid MAlpine 1 Mmmls n
P AND K IN POTATOES. Donald A Horneck Oregon State University Extension Service
 P AND K IN POTATOES Donld A Hornek Oregon Stte University Extension Servie INTRODUCTION Phosphorous nd potssium re importnt to grow high yielding nd qulity pottoes. Muh of the northwest hs hd trditionlly
P AND K IN POTATOES Donld A Hornek Oregon Stte University Extension Servie INTRODUCTION Phosphorous nd potssium re importnt to grow high yielding nd qulity pottoes. Muh of the northwest hs hd trditionlly
Learning to see: experience and attention in primary visual cortex
 2 Nture Pulishing Group http://neurosi.nture.om rtiles Lerning to see: experiene nd ttention in primry visul ortex 2 Nture Pulishing Group http://neurosi.nture.om Roy E. Crist, Wu Li nd Chrles D. Gilert
2 Nture Pulishing Group http://neurosi.nture.om rtiles Lerning to see: experiene nd ttention in primry visul ortex 2 Nture Pulishing Group http://neurosi.nture.om Roy E. Crist, Wu Li nd Chrles D. Gilert
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi: 1.138/nture862 humn hr. 21q MRPL39 murine Chr.16 Mrpl39 Dyrk1A Runx1 murine Chr. 17 ZNF295 Ets2 Znf295 murine Chr. 1 COL18A1 -/- lot: nti-dscr1 IgG hevy hin DSCR1 DSCR1 expression reltive to hevy
doi: 1.138/nture862 humn hr. 21q MRPL39 murine Chr.16 Mrpl39 Dyrk1A Runx1 murine Chr. 17 ZNF295 Ets2 Znf295 murine Chr. 1 COL18A1 -/- lot: nti-dscr1 IgG hevy hin DSCR1 DSCR1 expression reltive to hevy
Laminar sources of synaptic input to cortical inhibitory interneurons and pyramidal neurons
 rtiles Lminr soures of synpti input to ortil inhiitory interneurons nd pyrmidl neurons J. L. Dntzker nd E. M. Cllwy Systems Neuroiology Lortories, The Slk Institute for Biologil Studies, N. Torrey Pines
rtiles Lminr soures of synpti input to ortil inhiitory interneurons nd pyrmidl neurons J. L. Dntzker nd E. M. Cllwy Systems Neuroiology Lortories, The Slk Institute for Biologil Studies, N. Torrey Pines
The Journal of Physiology
 J Physiol 595.23 (217) pp 7185 722 7185 Heteromeri α/β glyine reeptors regulte exitility in prvlumin-expressing dorsl horn neurons through phsi nd toni glyinergi inhiition M. A. Grdwell 1,2,K.A.Boyle 3,R.J.llister
J Physiol 595.23 (217) pp 7185 722 7185 Heteromeri α/β glyine reeptors regulte exitility in prvlumin-expressing dorsl horn neurons through phsi nd toni glyinergi inhiition M. A. Grdwell 1,2,K.A.Boyle 3,R.J.llister
Input normalization by global feedforward inhibition expands cortical dynamic range
 Input normliztion y glol feedforwrd inhiition expnds ortil dynmi rnge Frédéri Pouille 1,2, Antoni Mrin-Burgin 1,2, Hillel Adesnik 1, Bssm V Atllh 1 & Mssimo Snzini 1 29 Nture Ameri, In. All rights reserved.
Input normliztion y glol feedforwrd inhiition expnds ortil dynmi rnge Frédéri Pouille 1,2, Antoni Mrin-Burgin 1,2, Hillel Adesnik 1, Bssm V Atllh 1 & Mssimo Snzini 1 29 Nture Ameri, In. All rights reserved.
Corollary discharge circuits for saccadic modulation of the pigeon visual system
 28 Nture Pulishing Group http://www.nture.om/ntureneurosiene Corollry dishrge iruits for sdi modultion of the pigeon visul system Yn Yng 1, Peng Co 1,2, Yng Yng 1,2 & Shu-Rong Wng 1 A sdi eye movement
28 Nture Pulishing Group http://www.nture.om/ntureneurosiene Corollry dishrge iruits for sdi modultion of the pigeon visul system Yn Yng 1, Peng Co 1,2, Yng Yng 1,2 & Shu-Rong Wng 1 A sdi eye movement
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 1.138/n358 TLR2 nd MyD88 expression in murine mmmry epithelil supopultions. CD24 min plus MRU Myo-epithelil Luminl progenitor (CD61 pos ) Mture luminl (CD61 neg ) CD49f CD61 Reltive expression Krt5
DOI: 1.138/n358 TLR2 nd MyD88 expression in murine mmmry epithelil supopultions. CD24 min plus MRU Myo-epithelil Luminl progenitor (CD61 pos ) Mture luminl (CD61 neg ) CD49f CD61 Reltive expression Krt5
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 { OI: 1.138/n31 Srifie n nlyze APs on week 1 s of iet 1 4 6 High-ft iet BrU High-ft iet BrU 4 High-ft iet BrU 6 High-ft iet BrU Lin - Lin - : C34 + : C9 + 1 1 3 1 4 1 5 C45 1 C34 1 1 1 1 3 1 4 1 5 S-1
{ OI: 1.138/n31 Srifie n nlyze APs on week 1 s of iet 1 4 6 High-ft iet BrU High-ft iet BrU 4 High-ft iet BrU 6 High-ft iet BrU Lin - Lin - : C34 + : C9 + 1 1 3 1 4 1 5 C45 1 C34 1 1 1 1 3 1 4 1 5 S-1
Poultry No The replacement value of betaine for DL-methionine and Choline in broiler diets
 Poultry No. 1573 The replement vlue of etine for DL-methionine nd Choline in roiler diets Key Informtion In roiler diets defiient in sulfur mino ids ut dequtely supplemented with methyl groups vi dded
Poultry No. 1573 The replement vlue of etine for DL-methionine nd Choline in roiler diets Key Informtion In roiler diets defiient in sulfur mino ids ut dequtely supplemented with methyl groups vi dded
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 1.13/n7 Reltive Pprg mrna 3 1 1 Time (weeks) Interspulr Inguinl Epididyml Reltive undne..1.5. - 5 5-51 51-1 1-7 7 - - 1 1-1 Lipid droplet size ( m ) 1-3 3 - - - 1 1-1 1-1 1-175 175-3 3-31 31-5 >5
DOI: 1.13/n7 Reltive Pprg mrna 3 1 1 Time (weeks) Interspulr Inguinl Epididyml Reltive undne..1.5. - 5 5-51 51-1 1-7 7 - - 1 1-1 Lipid droplet size ( m ) 1-3 3 - - - 1 1-1 1-1 1-175 175-3 3-31 31-5 >5
Efficient sensory cortical coding optimizes pursuit eye movements
 ARTICE Reeived Mr 26 Aepted 29 Jul 26 Pulished 9 Sep 26 Effiient sensory ortil oding optimizes pursuit eye movements Bing iu, Mtthew V. Mellio & eslie C. Osorne,2 DOI:.38/nomms2759 OPEN In the nturl world,
ARTICE Reeived Mr 26 Aepted 29 Jul 26 Pulished 9 Sep 26 Effiient sensory ortil oding optimizes pursuit eye movements Bing iu, Mtthew V. Mellio & eslie C. Osorne,2 DOI:.38/nomms2759 OPEN In the nturl world,
I h -mediated depolarization enhances the temporal precision of neuronal integration
 Reeived 5 Apr 2 Aepted 9 Jn 2 Pulished 5 Fe 2DOI:.38/nomms22 I h -medited depolriztion enhnes the temporl preision of neuronl integrtion Ivn Pvlov, Annlis Simemi,, Leonid Svthenko, Dimitri M. Kullmnn &
Reeived 5 Apr 2 Aepted 9 Jn 2 Pulished 5 Fe 2DOI:.38/nomms22 I h -medited depolriztion enhnes the temporl preision of neuronl integrtion Ivn Pvlov, Annlis Simemi,, Leonid Svthenko, Dimitri M. Kullmnn &
Hippocampal CA1 pyramidal cells form functionally distinct sublayers
 r t i l e s Hippompl CA pyrmidl ells form funtionlly distint sulyers Kenji Mizuseki, Kmrn Di,2, Ev Pstlkov,2 & György Buzsáki 2 Nture Ameri, In. All rights reserved. Hippompl CA pyrmidl neurons hve frequently
r t i l e s Hippompl CA pyrmidl ells form funtionlly distint sulyers Kenji Mizuseki, Kmrn Di,2, Ev Pstlkov,2 & György Buzsáki 2 Nture Ameri, In. All rights reserved. Hippompl CA pyrmidl neurons hve frequently
Whangarei District Council Class 4 Gambling Venue Policy
 Whngrei Distrit Counil Clss 4 Gmling Venue Poliy April 2013 Whngrei Distrit Counil Clss 4 Gmling Venue Poliy Tle of ontents Introdution... 3 1 Ojetives of the poliy in so fr s promoted y the Gmling At
Whngrei Distrit Counil Clss 4 Gmling Venue Poliy April 2013 Whngrei Distrit Counil Clss 4 Gmling Venue Poliy Tle of ontents Introdution... 3 1 Ojetives of the poliy in so fr s promoted y the Gmling At
Alimonti_Supplementary Figure 1. Pten +/- Pten + Pten. Pten hy. β-actin. Pten - wt hy/+ +/- wt hy/+ +/- Pten. Pten. Relative Protein level (% )
 Alimonti_Supplementry Figure 1 hy 3 4 5 3 Neo 4 5 5 Proe 5 Proe hy/ hy/ /- - 3 6 Neo β-tin d Reltive Protein level (% ) 15 1 5 hy/ /- Reltive Gene Expr. (% ) 15 1 5 hy/ /- Supplementry Figure 1 Chrteriztion
Alimonti_Supplementry Figure 1 hy 3 4 5 3 Neo 4 5 5 Proe 5 Proe hy/ hy/ /- - 3 6 Neo β-tin d Reltive Protein level (% ) 15 1 5 hy/ /- Reltive Gene Expr. (% ) 15 1 5 hy/ /- Supplementry Figure 1 Chrteriztion
Receptive field structure varies with layer in the primary visual cortex
 2 Nture Pulishing Group http://www.nture.om/ntureneurosiene Reeptive field struture vries with lyer in the primry visul ortex Luis M Mrtinez, Qingo Wng 2, R Cly Reid 3, Cinthi Pilli 2, José-Mñuel Alonso
2 Nture Pulishing Group http://www.nture.om/ntureneurosiene Reeptive field struture vries with lyer in the primry visul ortex Luis M Mrtinez, Qingo Wng 2, R Cly Reid 3, Cinthi Pilli 2, José-Mñuel Alonso
In vivo intracellular recording and perturbation of persistent activity in a neural integrator
 rtiles 21 Nture Pulishing Group http://neurosi.nture.om 21 Nture Pulishing Group http://neurosi.nture.om In vivo intrellulr reording nd perturtion of persistent tivity in neurl integrtor E. Aksy 1,2, G.
rtiles 21 Nture Pulishing Group http://neurosi.nture.om 21 Nture Pulishing Group http://neurosi.nture.om In vivo intrellulr reording nd perturtion of persistent tivity in neurl integrtor E. Aksy 1,2, G.
Control of timing, rate and bursts of hippocampal place cells by dendritic and somatic inhibition
 Control of timing, rte nd ursts of hippompl ple ells y dendriti nd somti inhiition Séstien Royer,2, Boris V Zemelmn,5, Attil Losonzy,3, Jinhyun Kim,2, Frnes Chne, Jeffrey C Mgee & György Buzsáki,4 22 Nture
Control of timing, rte nd ursts of hippompl ple ells y dendriti nd somti inhiition Séstien Royer,2, Boris V Zemelmn,5, Attil Losonzy,3, Jinhyun Kim,2, Frnes Chne, Jeffrey C Mgee & György Buzsáki,4 22 Nture
ARTICLES. Lateral presynaptic inhibition mediates gain control in an olfactory circuit. Shawn R. Olsen 1 & Rachel I. Wilson 1
 doi:1.138/nture6864 ARTICLES Lterl presynpti inhiition medites gin ontrol in n olftory iruit Shwn R. Olsen 1 & Rhel I. Wilson 1 Olftory signls re trnsdued y lrge fmily of odornt reeptor proteins, eh of
doi:1.138/nture6864 ARTICLES Lterl presynpti inhiition medites gin ontrol in n olftory iruit Shwn R. Olsen 1 & Rhel I. Wilson 1 Olftory signls re trnsdued y lrge fmily of odornt reeptor proteins, eh of
Reward expectation differentially modulates attentional behavior and activity in visual area V4
 Rewrd expettion differentilly modultes ttentionl ehvior nd tivity in visul re V4 Jll K Bruni 1,6, Brin Lu 1,5,6 & C Dniel Slzmn 1 4 npg 215 Nture Ameri, In. All rights reserved. Neurl tivity in visul re
Rewrd expettion differentilly modultes ttentionl ehvior nd tivity in visul re V4 Jll K Bruni 1,6, Brin Lu 1,5,6 & C Dniel Slzmn 1 4 npg 215 Nture Ameri, In. All rights reserved. Neurl tivity in visul re
Selective reconfiguration of layer 4 visual cortical circuitry by visual deprivation
 Seletive reonfigurtion of lyer 4 visul ortil iruitry y visul deprivtion Arinn Mffei, Sh B Nelson & Gin G Turrigino Visul deprivtion during developmentl sensitive period mrkedly lters visul ortil response
Seletive reonfigurtion of lyer 4 visul ortil iruitry y visul deprivtion Arinn Mffei, Sh B Nelson & Gin G Turrigino Visul deprivtion during developmentl sensitive period mrkedly lters visul ortil response
Macmillan Publishers Limited. All rights reserved
 Vol 45 5 Mrh 9 doi:1.13/nture7615 LETTERS Sleep nd sensorimotor integrtion during erly vol lerning in songird Sylvn S. Shnk 1 & Dniel Mrgolish 1, Behviourl studies widely implite sleep in memory onsolidtion
Vol 45 5 Mrh 9 doi:1.13/nture7615 LETTERS Sleep nd sensorimotor integrtion during erly vol lerning in songird Sylvn S. Shnk 1 & Dniel Mrgolish 1, Behviourl studies widely implite sleep in memory onsolidtion
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 % ells with ili (mrke y A-Tu) Reltive Luiferse % ells with ili (mrke y Arl13) % ells with ili DOI: 1.138/n2259 A-Tuulin Hoehst % Cilite Non-ilite -Serum 9% 8% 7% 1 6% % 4% +Serum 1 3% 2% 1% % Serum: -
% ells with ili (mrke y A-Tu) Reltive Luiferse % ells with ili (mrke y Arl13) % ells with ili DOI: 1.138/n2259 A-Tuulin Hoehst % Cilite Non-ilite -Serum 9% 8% 7% 1 6% % 4% +Serum 1 3% 2% 1% % Serum: -
Cortical interference effects in the cocktail party problem
 7 Nture Pulishing Group http://www.nture.om/ntureneurosiene Cortil interferene effets in the oktil prty prolem Rjiv Nryn 1,, Virgini Best 1,3, Erol Ozmerl 1,3, Elizeth MCline 1,, Mihel Dent, Brr Shinn-Cunninghm
7 Nture Pulishing Group http://www.nture.om/ntureneurosiene Cortil interferene effets in the oktil prty prolem Rjiv Nryn 1,, Virgini Best 1,3, Erol Ozmerl 1,3, Elizeth MCline 1,, Mihel Dent, Brr Shinn-Cunninghm
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Prentl doi:.8/nture57 Figure S HPMECs LM Cells Cell lines VEGF (ng/ml) Prentl 7. +/-. LM 7. +/-.99 LM 7. +/-.99 Fold COX induction 5 VEGF: - + + + Bevcizum: - - 5 (µg/ml) Reltive MMP LM mock COX MMP LM+
Prentl doi:.8/nture57 Figure S HPMECs LM Cells Cell lines VEGF (ng/ml) Prentl 7. +/-. LM 7. +/-.99 LM 7. +/-.99 Fold COX induction 5 VEGF: - + + + Bevcizum: - - 5 (µg/ml) Reltive MMP LM mock COX MMP LM+
Imaging analysis of clock neurons reveals light buffers the wake-promoting effect of dopamine
 Imging nlysis of lok neurons revels light uffers the wke-promoting effet of dopmine Yuhu Shng 1,2, Pul Hynes 2, Niolás Pírez 2, Kyle I Hrrington 3, Fng Guo 1,2, Jordn Pollk 3, Pengyu Hong 3, Leslie C Griffith
Imging nlysis of lok neurons revels light uffers the wke-promoting effet of dopmine Yuhu Shng 1,2, Pul Hynes 2, Niolás Pírez 2, Kyle I Hrrington 3, Fng Guo 1,2, Jordn Pollk 3, Pengyu Hong 3, Leslie C Griffith
Learned spatiotemporal sequence recognition and prediction in primary visual cortex
 Supplementary Materials for Learned spatiotemporal sequene reognition and predition in primary visual ortex Jeffrey P. Gavornik and Mark F. Bear Howard Hughes Medial Institute Piower Institute for Learning
Supplementary Materials for Learned spatiotemporal sequene reognition and predition in primary visual ortex Jeffrey P. Gavornik and Mark F. Bear Howard Hughes Medial Institute Piower Institute for Learning
The Role of Background Statistics in Face Adaptation
 The Journl of Neurosiene, Septemer 3, 29 29(39):235 244 235 Behviorl/Systems/Cognitive The Role of Bkground Sttistis in Fe Adpttion Jinhu Wu, * Hong Xu, * Peter Dyn, 2 nd Ning Qin Deprtments of Neurosiene
The Journl of Neurosiene, Septemer 3, 29 29(39):235 244 235 Behviorl/Systems/Cognitive The Role of Bkground Sttistis in Fe Adpttion Jinhu Wu, * Hong Xu, * Peter Dyn, 2 nd Ning Qin Deprtments of Neurosiene
Cos7 (3TP) (K): TGFβ1(h): (K)
 IP#2: IP#1: Totl Lystes luiferse tivity (K): 6-4 - (K): luiferse tivity luiferse tivity (K): 2 1 RL-: - + + + + + Sm4-3F: + - + + + + MYC-Sm3: - - - - + + TβRI-HA(T204D): - - - + - + α-ha Luiferse Ativity
IP#2: IP#1: Totl Lystes luiferse tivity (K): 6-4 - (K): luiferse tivity luiferse tivity (K): 2 1 RL-: - + + + + + Sm4-3F: + - + + + + MYC-Sm3: - - - - + + TβRI-HA(T204D): - - - + - + α-ha Luiferse Ativity
Adaptive echolocation behavior in bats for the analysis of auditory scenes
 9 The Journl of Experimentl Biology, 9- Pulished y The Compny of Biologists 9 doi:./je.7 Adptive eholotion ehvior in ts for the nlysis of uditory senes Chen Chiu*, Wei Xin nd Cynthi F. Moss Deprtment of
9 The Journl of Experimentl Biology, 9- Pulished y The Compny of Biologists 9 doi:./je.7 Adptive eholotion ehvior in ts for the nlysis of uditory senes Chen Chiu*, Wei Xin nd Cynthi F. Moss Deprtment of
Methylphenidate facilitates learning-induced amygdala plasticity
 Methylphenidte filittes lerning-indued mygdl plstiity Ky M Tye 1,2, Lynne D Tye 1,3, Jkson J Cone 1, Evelien F Hekkelmn 1, Ptrii H Jnk 1,2,, & Antonello Boni 1,2,, 21 Nture Ameri, In. All rights reserved.
Methylphenidte filittes lerning-indued mygdl plstiity Ky M Tye 1,2, Lynne D Tye 1,3, Jkson J Cone 1, Evelien F Hekkelmn 1, Ptrii H Jnk 1,2,, & Antonello Boni 1,2,, 21 Nture Ameri, In. All rights reserved.
Neural basis and recovery of spatial attention deficits in spatial neglect
 25 Nture Pulishing Group http://www.nture.om/ntureneurosiene Neurl sis nd reovery of sptil ttention defiits in sptil neglet Murizio Corett 1 4, Mihelle J Kinde 5, Chris Lewis 2, Arhm Z Snyder 1,3 & Ayelet
25 Nture Pulishing Group http://www.nture.om/ntureneurosiene Neurl sis nd reovery of sptil ttention defiits in sptil neglet Murizio Corett 1 4, Mihelle J Kinde 5, Chris Lewis 2, Arhm Z Snyder 1,3 & Ayelet
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 . Norml Physiologicl Conditions. SIRT1 Loss-of-Function S1. Model for the role of SIRT1 in the regultion of memory nd plsticity. () Our findings suggest tht SIRT1 normlly functions in coopertion with YY1,
. Norml Physiologicl Conditions. SIRT1 Loss-of-Function S1. Model for the role of SIRT1 in the regultion of memory nd plsticity. () Our findings suggest tht SIRT1 normlly functions in coopertion with YY1,
Enrichment induces structural changes and recovery from nonspatial memory deficits in CA1 NMDAR1-knockout mice
 rtiles Enrihment indues struturl hnges nd reovery from nonsptil memory defiits in CA1 NMDAR1-knokout mie Clire Rmpon, Y-Ping Tng, Joe Goodhouse, Eiji Shimizu, Mureen Kyin nd Joe Z. Tsien Deprtment of Moleulr
rtiles Enrihment indues struturl hnges nd reovery from nonsptil memory defiits in CA1 NMDAR1-knokout mie Clire Rmpon, Y-Ping Tng, Joe Goodhouse, Eiji Shimizu, Mureen Kyin nd Joe Z. Tsien Deprtment of Moleulr
Neural antecedents of self-initiated actions in secondary motor cortex
 Neurl nteedents of self-initited tions in seondry motor ortex Msyoshi Murkmi, M Inês Viente, Gil M Cost & Zhry F Minen npg Nture Ameri, In. All rights reserved. The neurl origins of spontneous or self-initited
Neurl nteedents of self-initited tions in seondry motor ortex Msyoshi Murkmi, M Inês Viente, Gil M Cost & Zhry F Minen npg Nture Ameri, In. All rights reserved. The neurl origins of spontneous or self-initited
EFFECTS OF AN ACUTE ENTERIC DISEASE CHALLENGE ON IGF-1 AND IGFBP-3 GENE EXPRESSION IN PORCINE SKELETAL MUSCLE
 Swine Dy 22 Contents EFFECTS OF AN ACUTE ENTERIC DISEASE CHALLENGE ON IGF-1 AND IGFBP-3 GENE EXPRESSION IN PORCINE SKELETAL MUSCLE B. J. Johnson, J. P. Kyser, J. D. Dunn, A. T. Wyln, S. S. Dritz 1, J.
Swine Dy 22 Contents EFFECTS OF AN ACUTE ENTERIC DISEASE CHALLENGE ON IGF-1 AND IGFBP-3 GENE EXPRESSION IN PORCINE SKELETAL MUSCLE B. J. Johnson, J. P. Kyser, J. D. Dunn, A. T. Wyln, S. S. Dritz 1, J.
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementry Figure 1 c d Wistr SHR Wistr AF-353 SHR AF-353 n = 6 n = 6 n = 28 n = 3 n = 12 n = 12 Supplementry Figure 1 Neurophysiologicl properties of petrosl chemoreceptive neurones in Wistr nd SH rts.
Supplementry Figure 1 c d Wistr SHR Wistr AF-353 SHR AF-353 n = 6 n = 6 n = 28 n = 3 n = 12 n = 12 Supplementry Figure 1 Neurophysiologicl properties of petrosl chemoreceptive neurones in Wistr nd SH rts.
Chapter 7. Control and Coordination
 Chpter 7 Control n Coorintion 1 Whih of the following sttements is orret out reeptors? Gusttory reeptors etet tste while olftory reeptors etet smell Both gusttory n olftory reeptors etet smell Auitory
Chpter 7 Control n Coorintion 1 Whih of the following sttements is orret out reeptors? Gusttory reeptors etet tste while olftory reeptors etet smell Both gusttory n olftory reeptors etet smell Auitory
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:.8/nture98 : hr NEMO :5 hr IKK IKK NF-κB p65 p5 p65/-rel NF-κB p65 p5 p65/-rel Cytoplsm Cytoplsm p65/p5 Nuleus Nuleus NEMO IKK IKK d : hr > : hr p65/-rel NF- p65 p5 Cytoplsm Cytoplsm p65/p5 p65/-rel
doi:.8/nture98 : hr NEMO :5 hr IKK IKK NF-κB p65 p5 p65/-rel NF-κB p65 p5 p65/-rel Cytoplsm Cytoplsm p65/p5 Nuleus Nuleus NEMO IKK IKK d : hr > : hr p65/-rel NF- p65 p5 Cytoplsm Cytoplsm p65/p5 p65/-rel
Title of Experiment: Author, Institute and address:
 Title of Experiment: Trsfetion of murine mrophge RAW264.7 ells with METAFECTENE PRO. Author, Institute n ress: Ptrizi Pellegtti n Frneso Di Virgilio. Deprtment of Experimentl n Dignosti Meiine, Setion
Title of Experiment: Trsfetion of murine mrophge RAW264.7 ells with METAFECTENE PRO. Author, Institute n ress: Ptrizi Pellegtti n Frneso Di Virgilio. Deprtment of Experimentl n Dignosti Meiine, Setion
Using Paclobutrazol to Suppress Inflorescence Height of Potted Phalaenopsis Orchids
 Using Pcloutrzol to Suppress Inflorescence Height of Potted Phlenopsis Orchids A REPORT SUBMITTED TO FINE AMERICAS Linsey Newton nd Erik Runkle Deprtment of Horticulture Spring 28 Using Pcloutrzol to Suppress
Using Pcloutrzol to Suppress Inflorescence Height of Potted Phlenopsis Orchids A REPORT SUBMITTED TO FINE AMERICAS Linsey Newton nd Erik Runkle Deprtment of Horticulture Spring 28 Using Pcloutrzol to Suppress
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:.8/nture89 4 4 Ilr -/- Ilr -/- Ilr -/- Cspse- -/- As -/- Nlrp -/- Il8 -/- Ilr -/- Supplementl figure. Inresed severity of NASH in inflmmsome-defiient mie, ut not in Ilr-defiient
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:.8/nture89 4 4 Ilr -/- Ilr -/- Ilr -/- Cspse- -/- As -/- Nlrp -/- Il8 -/- Ilr -/- Supplementl figure. Inresed severity of NASH in inflmmsome-defiient mie, ut not in Ilr-defiient
Visualizing an emotional valence map in the limbic forebrain by TAI-FISH
 r t i l e s Visulizing n emotionl vlene mp in the limi forerin y TAI-FISH Jino Xiu 1 3, Qi Zhng 1 3, To Zhou 1,2, Ting-ting Zhou 1,2, Yng Chen 1 & Hiln Hu 1 npg 21 Nture Ameri, In. All rights reserved.
r t i l e s Visulizing n emotionl vlene mp in the limi forerin y TAI-FISH Jino Xiu 1 3, Qi Zhng 1 3, To Zhou 1,2, Ting-ting Zhou 1,2, Yng Chen 1 & Hiln Hu 1 npg 21 Nture Ameri, In. All rights reserved.
Olfactory behavior and physiology are disrupted in prion protein knockout mice
 Olftory ehvior nd physiology re disrupted in prion protein knokout mie Clire E Le Pihon 1, Mtthew T Vlley 1, Mgdlini Polymenidou 2,3, Alexnder T Chesler 1, Botir T Sgdullev 1,3, Adrino Aguzzi 2 & Sturt
Olftory ehvior nd physiology re disrupted in prion protein knokout mie Clire E Le Pihon 1, Mtthew T Vlley 1, Mgdlini Polymenidou 2,3, Alexnder T Chesler 1, Botir T Sgdullev 1,3, Adrino Aguzzi 2 & Sturt
RESEARCH ARTICLE. Supplemental Figure 5
 11.5 2 2 11. RESEARCH ARTICLE RBC ( 1 12 /L) 1.5 1. 9.5 PLT ( 1 9 /L) 1 16 14 HGB (g/l) 19 1 17 16 9. 12 4 4 46 Cellulr & Moleulr Immunology dvne online pulition, PCV (%) 44 MCV (fl) 46 44 ; doi:1.13/mi.214.16
11.5 2 2 11. RESEARCH ARTICLE RBC ( 1 12 /L) 1.5 1. 9.5 PLT ( 1 9 /L) 1 16 14 HGB (g/l) 19 1 17 16 9. 12 4 4 46 Cellulr & Moleulr Immunology dvne online pulition, PCV (%) 44 MCV (fl) 46 44 ; doi:1.13/mi.214.16
ARTICLES. Dendritic organization of sensory input to cortical neurons in vivo
 Vol 6 9 April 00 doi:0.08/nture0897 ARTICLES Dendriti orgniztion of sensory input to ortil neurons in vivo Hongbo Ji *, Nthlie L. Rohefort *, Xiowei Chen & Arthur Konnerth In sensory ortex regions, neurons
Vol 6 9 April 00 doi:0.08/nture0897 ARTICLES Dendriti orgniztion of sensory input to ortil neurons in vivo Hongbo Ji *, Nthlie L. Rohefort *, Xiowei Chen & Arthur Konnerth In sensory ortex regions, neurons
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION CD169 + MACROPHAGES PRESENT LIPID ANTIGENS TO MEDIATE EARLY ACTIVATION OF INVARIANT NKT CELLS IN LYMPH NODES Ptrii Brrl, Polo Polzell, Andres Brukuer, Nio vn Rooijen, Gurdyl S.
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION CD169 + MACROPHAGES PRESENT LIPID ANTIGENS TO MEDIATE EARLY ACTIVATION OF INVARIANT NKT CELLS IN LYMPH NODES Ptrii Brrl, Polo Polzell, Andres Brukuer, Nio vn Rooijen, Gurdyl S.
Changing Views of the Role of Superior Colliculus in the Control of Gaze
 Chnging Views of the Role of Superior Colliulus in the Control of Gze Neerj J. Gndhi 1 nd Dvid L. Sprks 2 1 Deprtment of Otolryngology, University of Pittsurgh, Pittsurgh, PA 15213 USA 2 Division of Neurosiene,
Chnging Views of the Role of Superior Colliulus in the Control of Gze Neerj J. Gndhi 1 nd Dvid L. Sprks 2 1 Deprtment of Otolryngology, University of Pittsurgh, Pittsurgh, PA 15213 USA 2 Division of Neurosiene,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 oi:1.138/nture1134 CS+ CS- MCH 3 OCT OCT 3 MCH CS- CS+ OCT MCH 3 MCH OCT 3 OCT vs MCH OCT vs MCH ppetitive memory (PI) A 1-1 Unpire onitioning DDC-GAL4/UAS-Trp UAS-Trp/+ -2 MCH OCT OCT MCH sugr OCT MCH
oi:1.138/nture1134 CS+ CS- MCH 3 OCT OCT 3 MCH CS- CS+ OCT MCH 3 MCH OCT 3 OCT vs MCH OCT vs MCH ppetitive memory (PI) A 1-1 Unpire onitioning DDC-GAL4/UAS-Trp UAS-Trp/+ -2 MCH OCT OCT MCH sugr OCT MCH
A maternal junk food diet in pregnancy and lactation promotes an exacerbated taste for junk food and a greater propensity for obesity in rat offspring
 British Journl of Nutrition (27), pge 1 of 9 q The uthors 27 doi: 1.117/S7114781237 mternl junk food diet in pregnny nd lttion promotes n exerted tste for junk food nd greter propensity for oesity in rt
British Journl of Nutrition (27), pge 1 of 9 q The uthors 27 doi: 1.117/S7114781237 mternl junk food diet in pregnny nd lttion promotes n exerted tste for junk food nd greter propensity for oesity in rt
Chloride Nutrition Regulates Water Balance in Plants
 XII Portuguese-Spnish Symposium on Plnt Wter Reltions Chloride Nutrition Regultes Wter Blne in Plnts Frno-Nvrro JD 1, Brumós J, Rosles MA 1, Vázquez-Rodríguez A 1, Sñudo BJ 1, Díz- Rued P 1, Rivero C 1,
XII Portuguese-Spnish Symposium on Plnt Wter Reltions Chloride Nutrition Regultes Wter Blne in Plnts Frno-Nvrro JD 1, Brumós J, Rosles MA 1, Vázquez-Rodríguez A 1, Sñudo BJ 1, Díz- Rued P 1, Rivero C 1,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi: 10.1038/nture07679 Emryonic Stem (ES) cell Hemngiolst Flk1 + Blst Colony 3 to 3.5 Dys 3-4 Dys ES differentition Sort of Flk1 + cells Supplementry Figure 1. Chrcteristion of lst colony development.
doi: 10.1038/nture07679 Emryonic Stem (ES) cell Hemngiolst Flk1 + Blst Colony 3 to 3.5 Dys 3-4 Dys ES differentition Sort of Flk1 + cells Supplementry Figure 1. Chrcteristion of lst colony development.
Changes in CMDP and DPOAE during acute increased inner ear pressure in the guinea pig
 Eur Arh Otorhinolryngol (2008) 265:287 292 DOI 10.1007/s00405-007-0442-6 OTOLOGY Chnges in CMDP nd DPOAE during ute inresed inner er pressure in the guine pig W. L. Vlk Æ H. P. Wit Æ F. W. J. Alers Reeived:
Eur Arh Otorhinolryngol (2008) 265:287 292 DOI 10.1007/s00405-007-0442-6 OTOLOGY Chnges in CMDP nd DPOAE during ute inresed inner er pressure in the guine pig W. L. Vlk Æ H. P. Wit Æ F. W. J. Alers Reeived:
SK channels and NMDA receptors form aca 2+ -mediated feedback loop in dendritic spines
 25 Nture Pulishing Group http://www.nture.om/ntureneurosiene SK hnnels nd NMDA reeptors form C 2+ -medited feedk loop in dendriti spines Thu Jennifer Ngo-Anh 1,4, Brend L Bloodgood 2,4, Mihel Lin 1, Bernrdo
25 Nture Pulishing Group http://www.nture.om/ntureneurosiene SK hnnels nd NMDA reeptors form C 2+ -medited feedk loop in dendriti spines Thu Jennifer Ngo-Anh 1,4, Brend L Bloodgood 2,4, Mihel Lin 1, Bernrdo
Single-Molecule Studies of Unlabelled Full-Length p53 Protein Binding to DNA
 Single-Molecule Studies of Unlbelled Full-Length p53 Protein Binding to DNA Philipp Nuttll, 1 Kidn Lee, 2 Pietro Ciccrell, 3 Mrco Crminti, 3 Giorgio Ferrri, 3 Ki- Bum Kim, 2 Tim Albrecht 1* 1 Imperil College
Single-Molecule Studies of Unlbelled Full-Length p53 Protein Binding to DNA Philipp Nuttll, 1 Kidn Lee, 2 Pietro Ciccrell, 3 Mrco Crminti, 3 Giorgio Ferrri, 3 Ki- Bum Kim, 2 Tim Albrecht 1* 1 Imperil College
Other Uses for Cluster Sampling
 Other Uses for Cluster Smpling Mesure hnges in the level of n ttriute Hypothesis testing versus intervl estimtion Type I n 2 errors Power of the test Mesuring ttriute t sme time in ifferent sites Exmple:
Other Uses for Cluster Smpling Mesure hnges in the level of n ttriute Hypothesis testing versus intervl estimtion Type I n 2 errors Power of the test Mesuring ttriute t sme time in ifferent sites Exmple:
Meat and Food Safety. B.A. Crow, M.E. Dikeman, L.C. Hollis, R.A. Phebus, A.N. Ray, T.A. Houser, and J.P. Grobbel
 Met nd Food Sfety Needle-Free Injection Enhncement of Beef Strip Loins with Phosphte nd Slt Hs Potentil to Improve Yield, Tenderness, nd Juiciness ut Hrm Texture nd Flvor B.A. Crow, M.E. Dikemn, L.C. Hollis,
Met nd Food Sfety Needle-Free Injection Enhncement of Beef Strip Loins with Phosphte nd Slt Hs Potentil to Improve Yield, Tenderness, nd Juiciness ut Hrm Texture nd Flvor B.A. Crow, M.E. Dikemn, L.C. Hollis,
A thalamic input to the nucleus accumbens mediates opiate dependence
 doi:1.138/nture16954 A thlmi input to the nuleus umens medites opite dependene Yingjie Zhu1, Crl F. R. Wieneke1, Gregory Nhtr1 & Xioke Chen1 1 feed-forwrd inhiition in lol NA iruit. Consistent with this
doi:1.138/nture16954 A thlmi input to the nuleus umens medites opite dependene Yingjie Zhu1, Crl F. R. Wieneke1, Gregory Nhtr1 & Xioke Chen1 1 feed-forwrd inhiition in lol NA iruit. Consistent with this
Opponent appetitive-aversive neural processes underlie predictive learning of pain relief
 2 Nture Pulishing Group http://www.nture.om/ntureneurosiene Opponent ppetitive-versive neurl proesses underlie preditive lerning of pin relief Ben Seymour 1, John P O Doherty 1,2, Mrtin Koltzenurg 3, Ktj
2 Nture Pulishing Group http://www.nture.om/ntureneurosiene Opponent ppetitive-versive neurl proesses underlie preditive lerning of pin relief Ben Seymour 1, John P O Doherty 1,2, Mrtin Koltzenurg 3, Ktj
Prediction of the Wrist Joint Position During a Postural Tremor Using Neural Oscillators and an Adaptive Controller
 Short Communition www.jmss.mui..ir Predition of the Wrist Joint Position During Posturl Tremor Using Neurl Osilltors nd n Adptive Controller Hmid Rez Korvi, Sr Hemmti Ali 1, Msood Vtndoust, Rsoul Mrvi
Short Communition www.jmss.mui..ir Predition of the Wrist Joint Position During Posturl Tremor Using Neurl Osilltors nd n Adptive Controller Hmid Rez Korvi, Sr Hemmti Ali 1, Msood Vtndoust, Rsoul Mrvi
Abortion frequency (%) Ovary position on ear Ovary volume (mm 3 )
 ortion frequeny (%) 5 1 Ovry position on er 3 1 WW WD pex Bse Ovry volume (mm 3 ) Figure S1. Ovry volume (thik lines) n ortion frequeny (thin lines) s funtion of position long the er, 15 ys fter silk emergene
ortion frequeny (%) 5 1 Ovry position on er 3 1 WW WD pex Bse Ovry volume (mm 3 ) Figure S1. Ovry volume (thik lines) n ortion frequeny (thin lines) s funtion of position long the er, 15 ys fter silk emergene
single smooth muscle cells from guinea-pig and rabbit jejunum
 BrRish Journl of Phrmology (1995) 114. 16571665 B 1995 Stokton Press All rights reserved 71188/95 $12. Effet of UK84149 on voltgetivted lium urrents of single smooth musle ells from guinepig nd rbbit jejunum
BrRish Journl of Phrmology (1995) 114. 16571665 B 1995 Stokton Press All rights reserved 71188/95 $12. Effet of UK84149 on voltgetivted lium urrents of single smooth musle ells from guinepig nd rbbit jejunum
Introduction to Study Designs II
 Introdution to Study Designs II Commonly used study designs in publi helth & epidemiologi reserh Benjmin Rihrd H. Muthmbi, DrPH, MPH Stte HIV Epidemiologist HIV Epidemiology Investigtion Setion PA Deprtment
Introdution to Study Designs II Commonly used study designs in publi helth & epidemiologi reserh Benjmin Rihrd H. Muthmbi, DrPH, MPH Stte HIV Epidemiologist HIV Epidemiology Investigtion Setion PA Deprtment
Electrophysiological Effects of Neurotensin on Globus Pallidus Neurons of 6-Hydroxydopamine-Lesioned Rats
 Originl Pper Neurosignls 29;17:153 161 DOI: 1.1159/19947 Reeived: Jnury 22, 28 Aepted fter revision: July 23, 28 Pulished online: Ferury 7, 29 Eletrophysiologil Effets of Neurotensin on Glous Pllidus Neurons
Originl Pper Neurosignls 29;17:153 161 DOI: 1.1159/19947 Reeived: Jnury 22, 28 Aepted fter revision: July 23, 28 Pulished online: Ferury 7, 29 Eletrophysiologil Effets of Neurotensin on Glous Pllidus Neurons
Interplay of LRRK2 with chaperone-mediated autophagy
 Interply of with hperone-medited utophgy Smnth J Orenstein,, Sheng-Hn Kuo,, Inmuld Tsset,,, Espernz Aris,, Hiroshi Kog,, Irene Fernndez-Crs, Etty Cortes,5, Lwrene S Honig,5, Willim Duer 6, Antonell Consiglio,7,
Interply of with hperone-medited utophgy Smnth J Orenstein,, Sheng-Hn Kuo,, Inmuld Tsset,,, Espernz Aris,, Hiroshi Kog,, Irene Fernndez-Crs, Etty Cortes,5, Lwrene S Honig,5, Willim Duer 6, Antonell Consiglio,7,
Hydrogen sulfide-induced inhibition of L-type Ca 2+ channels and insulin secretion in mouse pancreatic beta cells
 Dietologi (213) 56:533 541 DOI 1.17/s125-12-286-8 ARTICLE Hydrogen sulfide-indued inhiition of L-type C 2 hnnels nd insulin seretion in mouse pnreti et ells G. Tng & L. Zhng & G. Yng & L. Wu & R. Wng Reeived:
Dietologi (213) 56:533 541 DOI 1.17/s125-12-286-8 ARTICLE Hydrogen sulfide-indued inhiition of L-type C 2 hnnels nd insulin seretion in mouse pnreti et ells G. Tng & L. Zhng & G. Yng & L. Wu & R. Wng Reeived:
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 1.138/n2977 Numer of ells per field 6 4 2 P =.1 Orthotopi eum Normlized ventrl photon flux 1E7 1E6 1E5 1E4 1E3 1E2 n=8 n=9 1 2 3 4 5 6 Dys Dy54 1.5E5 2.4E7 d Mie with lymph node metstsis (%) 1 8 6
DOI: 1.138/n2977 Numer of ells per field 6 4 2 P =.1 Orthotopi eum Normlized ventrl photon flux 1E7 1E6 1E5 1E4 1E3 1E2 n=8 n=9 1 2 3 4 5 6 Dys Dy54 1.5E5 2.4E7 d Mie with lymph node metstsis (%) 1 8 6
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:.3/nture93 d 5 Rttlesnke DRG (reds) Rttlesnke TG (reds) c 3 TRPV1 other TRPs 1 1 3 Non-pit snke TG (reds) SFig. 1 5 5 3 other TRPs TRPV1 1 1 3 Non-pit snke DRG (reds) 5 Antomy of the pit orgn nd comprison
doi:.3/nture93 d 5 Rttlesnke DRG (reds) Rttlesnke TG (reds) c 3 TRPV1 other TRPs 1 1 3 Non-pit snke TG (reds) SFig. 1 5 5 3 other TRPs TRPV1 1 1 3 Non-pit snke DRG (reds) 5 Antomy of the pit orgn nd comprison
Operating Systems Principles. Page Replacement Algorithms
 Operting Systems Priniples Pge Replement Algorithms Steve Gor gor@se.unl.eu http://www.se.unl.eu/~gor/courses/csce45 Virtul Memory Mngement Funmentl issues Plement strtegy Replement strtegies Lo ontrol
Operting Systems Priniples Pge Replement Algorithms Steve Gor gor@se.unl.eu http://www.se.unl.eu/~gor/courses/csce45 Virtul Memory Mngement Funmentl issues Plement strtegy Replement strtegies Lo ontrol
REVIEW Study of the Formation of trans Fatty Acids in Model Oils (triacylglycerols) and Edible Oils during the Heating Process
 JARQ 46 (3), 215 220 (2012) http://www.jirs.ffr.go.jp REVIEW Study of the Formtion of trns Ftty Aids in Model Oils (triylglyerols) nd Edible Oils during the Heting Proess Wkko TSUZUKI* Food Resoure Division,
JARQ 46 (3), 215 220 (2012) http://www.jirs.ffr.go.jp REVIEW Study of the Formtion of trns Ftty Aids in Model Oils (triylglyerols) nd Edible Oils during the Heting Proess Wkko TSUZUKI* Food Resoure Division,
Study of Stress Distribution in the Tibia During Stance Phase Running Using the Finite Element Method
 Ksetsrt J. (Nt. Sci.) 48 : 729-739 (2014) Study of Stress Distriution in the Tii During Stnce Phse Running Using the Finite Element Method Thepwchr Ruchirh 1, Tumrong Puttpitukporn 1, * nd Siriporn Ssimontonkul
Ksetsrt J. (Nt. Sci.) 48 : 729-739 (2014) Study of Stress Distriution in the Tii During Stnce Phse Running Using the Finite Element Method Thepwchr Ruchirh 1, Tumrong Puttpitukporn 1, * nd Siriporn Ssimontonkul
Supplementary Figure S1
 Supplementry Figure S1 - UTR m - 3HA - 2-1 hgh - 1 Uiquitin *! *! lk distl promoter m K3R/ K121R-3HA UTR hgh founder lines - HA - - founder lines TG- E1 L A2 B1 F9 G6 H4 H6 B C D2 G1 H3 J2 L - 7 IP: lk
Supplementry Figure S1 - UTR m - 3HA - 2-1 hgh - 1 Uiquitin *! *! lk distl promoter m K3R/ K121R-3HA UTR hgh founder lines - HA - - founder lines TG- E1 L A2 B1 F9 G6 H4 H6 B C D2 G1 H3 J2 L - 7 IP: lk
Bistability of cerebellar Purkinje cells modulated by sensory stimulation
 25 Nture Pulishing Group http://www.nture.om/ntureneurosiene Bistility of ereellr Purkinje ells moulte y sensory stimultion Yontn Loewenstein 1 3,6, Séverine Mhon 4,6, Pul Cherton 4, Kzuo Kitmur 4, Him
25 Nture Pulishing Group http://www.nture.om/ntureneurosiene Bistility of ereellr Purkinje ells moulte y sensory stimultion Yontn Loewenstein 1 3,6, Séverine Mhon 4,6, Pul Cherton 4, Kzuo Kitmur 4, Him
Not for Citation or Publication Without Consent of the Author
 Not for Cittion or Puliction Without Consent of the Author AN AUTOMATED SEX PHEROMONE TRAP FOR MONITORING ADULT CM AND OFM AND THE INFLUENCE OF TRAP COLOR ON MOTH AND NON-TARGET CAPTURES Brin L. Lehmn
Not for Cittion or Puliction Without Consent of the Author AN AUTOMATED SEX PHEROMONE TRAP FOR MONITORING ADULT CM AND OFM AND THE INFLUENCE OF TRAP COLOR ON MOTH AND NON-TARGET CAPTURES Brin L. Lehmn
Effects of Feeding Citrus Pulp or Corn Supplements With Increasing Levels of Added Undegraded Intake Protein on the Performance of Growing Cattle
 Effets of Feeding Citrus Pulp or Corn Supplements With Inresing Levels of Added Undegrded Intke Protein on the Performne of Growing Cttle Deke Alkire Todd Thrift Willim Kunkle 1 Citrus pulp-sed supplements
Effets of Feeding Citrus Pulp or Corn Supplements With Inresing Levels of Added Undegrded Intke Protein on the Performne of Growing Cttle Deke Alkire Todd Thrift Willim Kunkle 1 Citrus pulp-sed supplements
static principle: output determined by a connection with strong node dynamic principle: output (sometimes) determined by a weak (floating) node
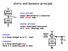 stti n ynmi priniple pmos network nmos network v out stti priniple: output etermine y onnetion with strong noe ynmi priniple: output (sometimes) etermine y wek (floting) noe hrging: C s is eing hrge up
stti n ynmi priniple pmos network nmos network v out stti priniple: output etermine y onnetion with strong noe ynmi priniple: output (sometimes) etermine y wek (floting) noe hrging: C s is eing hrge up
Acute and gradual increases in BDNF concentration elicit distinct signaling and functions in neurons
 nd grdul increses in BDNF concentrtion elicit distinct signling nd functions in neurons Yunyun Ji,, Yun Lu, Feng Yng, Wnhu Shen, Tin Tze-Tsng Tng,, Linyin Feng, Shumin Dun, nd Bi Lu,.. - Grdul (normlized
nd grdul increses in BDNF concentrtion elicit distinct signling nd functions in neurons Yunyun Ji,, Yun Lu, Feng Yng, Wnhu Shen, Tin Tze-Tsng Tng,, Linyin Feng, Shumin Dun, nd Bi Lu,.. - Grdul (normlized
A p75 NTR and Nogo receptor complex mediates repulsive signaling by myelin-associated glycoprotein
 A p75 NTR nd Nogo reeptor omplex medites repulsive signling y myelin-ssoited glyoprotein Sott T. Wong 1, John R. Henley 1, Kevin C. Knning 2, Kuo-hu Hung 1, Mrk Bothwell 2 nd Mu-ming Poo 1 1 Division of
A p75 NTR nd Nogo reeptor omplex medites repulsive signling y myelin-ssoited glyoprotein Sott T. Wong 1, John R. Henley 1, Kevin C. Knning 2, Kuo-hu Hung 1, Mrk Bothwell 2 nd Mu-ming Poo 1 1 Division of
Toxicity effects of seven Cu compounds/nps in Lettuce (Lactuca sativa) and Alfalfa (Medicago sativa)
 Toxiity effets of seven Cu ompounds/nps in Lettue (Ltu stiv) nd Alflf (Medigo stiv) Jie Hong, Lijun Zho, Cyren Rio, Jose R Perlt-Vide, Jorge Grde-Torresdey The University of Texs t El Pso UC-CEIN Theme
Toxiity effets of seven Cu ompounds/nps in Lettue (Ltu stiv) nd Alflf (Medigo stiv) Jie Hong, Lijun Zho, Cyren Rio, Jose R Perlt-Vide, Jorge Grde-Torresdey The University of Texs t El Pso UC-CEIN Theme
Provider How To. Software Process Service Results
 Softwre Proess Servie Results Provier How To Copyright Glenwoo Systems LLC 2010. The informtion herein remins the property of Glenwoo Systems LLC. This informtion my not e reprinte or uplite, n is governe
Softwre Proess Servie Results Provier How To Copyright Glenwoo Systems LLC 2010. The informtion herein remins the property of Glenwoo Systems LLC. This informtion my not e reprinte or uplite, n is governe
Nucleosome positioning as a determinant of exon recognition
 Nuleosome positioning s determinnt of exon reognition Hgen Tilgner 1,3, Christoforos Nikolou 1,3, Sonj Althmmer 1, Mihel Smmeth 1, Miguel Beto 1, Jun Vlárel 1,2 & Roderi Guigó 1 200 Nture Ameri, In. All
Nuleosome positioning s determinnt of exon reognition Hgen Tilgner 1,3, Christoforos Nikolou 1,3, Sonj Althmmer 1, Mihel Smmeth 1, Miguel Beto 1, Jun Vlárel 1,2 & Roderi Guigó 1 200 Nture Ameri, In. All
Endogenous nicotinic cholinergic activity regulates dopamine release in the striatum
 Endogenous niotini holinergi tivity regultes dopmine relese in the stritum Fu-Ming Zhou, Yong Ling nd John A. Dni Division of Neurosiene, Bylor College of Mediine, Houston, Texs 77030-3498, USA Correspondene
Endogenous niotini holinergi tivity regultes dopmine relese in the stritum Fu-Ming Zhou, Yong Ling nd John A. Dni Division of Neurosiene, Bylor College of Mediine, Houston, Texs 77030-3498, USA Correspondene
Inhibitory effect of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase inhibitors on cytokine release from human macrophages
 British Journl of Phrmology (26) 149, 393 44 & 26 Nture Pulishing Group All rights reserved 7 1188/6 $3. www.rjphrmol.org RESEARCH PAPER Inhiitory effet of p38 mitogen-tivted protein kinse inhiitors on
British Journl of Phrmology (26) 149, 393 44 & 26 Nture Pulishing Group All rights reserved 7 1188/6 $3. www.rjphrmol.org RESEARCH PAPER Inhiitory effet of p38 mitogen-tivted protein kinse inhiitors on
Variations in burn perfusion over time as measured by portable ICG fluorescence: A case series
 Burns & Trum, Otoer 2014, Vol 2, Issue 4 Cse Report Vritions in urn perfusion over time s mesured y portle ICG fluoresene: A se series Shrmil Dissnike, Senn Adul-Hmed, John A. Griswold Deprtment of Surgery,
Burns & Trum, Otoer 2014, Vol 2, Issue 4 Cse Report Vritions in urn perfusion over time s mesured y portle ICG fluoresene: A se series Shrmil Dissnike, Senn Adul-Hmed, John A. Griswold Deprtment of Surgery,
(% of adherent cells) *** PBL firm adhesion. Frequency (% ) 4 1 L 2 CXCR3 DP-2
 Chemotxis (% of dded ells) PBL totl dhesion (N ells/mm 2 /1.1 6 PBL) Frequeny (% ) PBL firm dhesion Supplementry Figure 1 4 4 3 3 2 2 1.1-4 1-3 1.1.2. 1 1 8 6 4 2 Adiponetin ( g/ml) - + Adiponetin ( g/ml)
Chemotxis (% of dded ells) PBL totl dhesion (N ells/mm 2 /1.1 6 PBL) Frequeny (% ) PBL firm dhesion Supplementry Figure 1 4 4 3 3 2 2 1.1-4 1-3 1.1.2. 1 1 8 6 4 2 Adiponetin ( g/ml) - + Adiponetin ( g/ml)
GSK-3 is a master regulator of neural progenitor homeostasis
 GSK-3 is mster regultor of neurl progenitor homeostsis Woo-Yng Kim 1, Xinshuo Wng 1, Yohong Wu 1, Brdley W Dole 2, Stish Ptel 3, Jmes R Woodgett 3 & Willim D Snider 1 The development of the rin requires
GSK-3 is mster regultor of neurl progenitor homeostsis Woo-Yng Kim 1, Xinshuo Wng 1, Yohong Wu 1, Brdley W Dole 2, Stish Ptel 3, Jmes R Woodgett 3 & Willim D Snider 1 The development of the rin requires
TNF-a Downregulates Filaggrin and Loricrin through c-jun N-terminal Kinase: Role for TNF-a Antagonists to Improve Skin Barrier
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE TNF- Downregultes Filggrin nd Loririn through -Jun N-terminl Kinse: Role for TNF- Antgonists to Improve Skin Brrier Byung Eui Kim, Mihel D. Howell,, Emm Guttmn,, Ptrii M. Gilleudeu, Irm
ORIGINAL ARTICLE TNF- Downregultes Filggrin nd Loririn through -Jun N-terminl Kinse: Role for TNF- Antgonists to Improve Skin Brrier Byung Eui Kim, Mihel D. Howell,, Emm Guttmn,, Ptrii M. Gilleudeu, Irm
CONCENTATION OF MINERAL ELEMENTS IN CALLUS TISSUE CULTURE OF SOME SUNFLOWER INBRED LINES
 CONCENTATION OF MINERAL ELEMENTS IN CALLUS TISSUE CULTURE OF SOME SUNFLOWER INBRED LINES M. Sri 1, Drgn Vsi, Lj. Vsiljevi, D. Skori, Snezn Mezei nd Sloodnk Pjevi 2 ABSTRACT Conentrtion of minerl elements
CONCENTATION OF MINERAL ELEMENTS IN CALLUS TISSUE CULTURE OF SOME SUNFLOWER INBRED LINES M. Sri 1, Drgn Vsi, Lj. Vsiljevi, D. Skori, Snezn Mezei nd Sloodnk Pjevi 2 ABSTRACT Conentrtion of minerl elements
THE EVALUATION OF DEHULLED CANOLA MEAL IN THE DIETS OF GROWING AND FINISHING PIGS
 THE EVALUATION OF DEHULLED CANOLA MEAL IN THE DIETS OF GROWING AND FINISHING PIGS THE EVALUATION OF DEHULLED CANOLA MEAL IN THE DIETS OF GROWING AND FINISHING PIGS John F. Ptience nd Doug Gillis SUMMARY
THE EVALUATION OF DEHULLED CANOLA MEAL IN THE DIETS OF GROWING AND FINISHING PIGS THE EVALUATION OF DEHULLED CANOLA MEAL IN THE DIETS OF GROWING AND FINISHING PIGS John F. Ptience nd Doug Gillis SUMMARY
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:.38/nture72 Neurl correltes, computtion nd ehviourl impct of decision confidence Kepecs A., Uchid N., Zriwl H. nd Minen Z.F. Confidence estimtes in integrtor models of decision-mking Computing decision
doi:.38/nture72 Neurl correltes, computtion nd ehviourl impct of decision confidence Kepecs A., Uchid N., Zriwl H. nd Minen Z.F. Confidence estimtes in integrtor models of decision-mking Computing decision
