Selective reconfiguration of layer 4 visual cortical circuitry by visual deprivation
|
|
|
- Logan Henry
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Seletive reonfigurtion of lyer 4 visul ortil iruitry y visul deprivtion Arinn Mffei, Sh B Nelson & Gin G Turrigino Visul deprivtion during developmentl sensitive period mrkedly lters visul ortil response properties, ut the hnges in intrortil iruitry tht underlie these effets re poorly understood. Here we use slie preprtion of rt primry visul ortex to show tht 2 d of prior visul deprivtion erly in life inreses the exitility of lyer 4 iruitry. Slie reordings showed tht spontneous tivity of lyer 4 str pyrmidl neurons inresed 25-fold fter 2 d of visul deprivtion etween postntl dys (P) 5 nd P7. This effet ws medited y inresed net exittory nd deresed net inhiitory synpti drive. Pired reordings showed tht exittory onnetions etween str pyrmidl neurons douled in mplitude, wheres inhiitory onnetions deresed or inresed depending on the interneuron lss. These effets reversed when vision ws restored. This dynmi djustment of the exittion-inhiition lne my llow the networks within lyer 4 to mintin stle levels of tivity in the fe of vrile sensory input. Visul deprivtion hs een powerful tool for investigting the ntomil nd physiologil orreltes of experiene-dependent plstiity 3. Visul deprivtion during developmentl sensitive period indues profound hnges in visul response properties, inluding redued ortil responsiveness to visul stimultion,4 6, redued visul uity 7 nd impired orienttion tuning of ortil neurons 5,8. Mny of these physiologil hnges n e indued quite rpidly 9, nd n e reversed if deprivtion is lifted within the sensitive period,2. Despite the long history of these mnipultions, the detiled hnges tht loss of vision produes in intrortil synpti strengths, s well s the plstiity mehnisms tht underlie these hnges, re not fully understood. Here we exmine how synpti onnetivity in rodent lyer 4 is ltered y rief periods of monoulr lid suture. Lyer 4 is the min input lyer to visul ortex, nd exittory str pyrmidl neurons in lyer 4 reeive diret exittory thlmi drive, s well s reurrent exittory onnetions from other str pyrmidl neurons 3,4. This reurrent exittory iruitry is kept in hek y oth feed-forwrd nd feedk inhiition, whih re medited y distint lsses of inhiitory GABAergi interneuron 5,6. Erly in life, 2 d of monoulr deprivtion inreses the quntl mplitude of exittory synpses on str pyrmidl neurons in lyer 4 (ref. 7). In ddition, ortil inhiition my e redued y prolonged visul deprivtion 8,9, lthough how rpidly this ours nd how these hnges re expressed t the level of individul inhiitory onnetions remin unknown. Here we exmine the possiility tht visul deprivtion rewires intrortil lyer 4 iruitry through highly seletive hnges in the strengths of exittory nd inhiitory synpses. To omplish this, one eye of rt ws sutured shut etween P4 nd P7, nd ute slies of primry visul ortex were ut from the deprived nd ontrol hemispheres. We then rried out detiled nlysis of onnetivity in monoulr lyer 4 using qudruple whole-ell reordings. Beuse most of the rodent visul ortex is driven exlusively y the ontrlterl eye 2,2, monoulr deprivtion will lower visul drive to one hemisphere of the monoulr portion of visul ortex, while leving the other hemisphere unffeted 22,23. We found tht visul deprivtion drmtilly inresed the spontneous firing of str pyrmidl neurons in lyer 4, through net inrese in exittory nd net derese in inhiitory synpti drive. This ltertion in the lne etween exittion nd inhiition ws hieved through douling in the strength of exittory onnetions etween str pyrmidl neurons nd derese in the strength of feedk, ut not feed-forwrd, inhiition. This inrese in spontneous lyer 4 tivity ws ompletely reversed y reopening the eye for 2 d efore slie preprtion. These dt indite tht lyer 4 exitility my e dynmilly djusted to ompenste for ltertions in sensory drive through highly seletive hnges in intrortil synpti strength. This homeostti regultion of the exittion-inhiition lne is likely to e importnt for mintining stle ortil tivity during norml development nd my lso ontriute to the pthologil hnges in visul response properties tht re indued y sensory deprivtion. RESULTS Monoulr deprivtion inreses spontneous tivity To ssess the effets of monoulr deprivtion on lol iruit tivity, we ompred spontneous firing rtes in the monoulr region of visul ortil slies from the deprived nd nondeprived hemispheres. We initilly trgeted str pyrmidl neurons, whih re the mjor lss of exittory neuron in lyer 4 of rt primry visul or- Deprtment of Biology nd Volen Ntionl Center for Complex Systems, Brndeis University, Wlthm, Msshusetts 2454, USA. Correspondene should e ddressed to G.G.T. (turrigino@rndeis.edu). Pulished online 4 Novemer 24; doi:.38/nn35 NATURE NEUROSCIENCE VOLUME 7 NUMBER 2 DECEMBER
2 6 mv 6 mv 6 mv 5 s 5 s WC tex 3. In stndrd rtifiil ererl spinl fluid (ACSF), there ws little or no spontneous tivity. Chnging the solution to modified ACSF, whih is loser to the omposition of rt CSF in situ 24,25, initited low levels of spontneous firing of str pyrmidl neurons (Fig. ), similr to wht hs een reported in ferret prefrontl ortil slies 26. Whole-ell reordings showed tht str pyrmidl neurons in slies from the deprived hemisphere hd firing rtes tht were 25-fold higher thn those from the ontrol hemisphere (Fig.,; ontrol:.5 ±.3 Hz, n = ; deprived:.28 ±.24 Hz, n = ; P <.6). A similr inrese ws oserved using loose-pth reordings to mesure str pyrmidl neuron firing rtes extrellulrly, to void modifying firing properties through whole-ell dilysis (Fig. ; ontrol:. ±.6 Hz, n = 8; deprived: 2.9 ±.8 Hz, n = 8; P <.3). Firing tivity in modified ACSF ws ompletely olished y loking synpti trnsmission with APV, DNQX nd iuulline (Fig. ), inditing tht spontneous firing ws driven y synpti tivity. This inresed tivity in the deprived hemisphere ws highly seletive for str pyrmidl neurons. Monoulr deprivtion elevted spiking in lyer 4 regulr-spiking nonpyrmidl (RSNP) neurons y only.6-fold (Fig. ; ontrol:.57 ±.9 Hz, n = 8; deprived: 2.47 ±.38 Hz, n = 7; P <.), muh smller inrese in firing thn tht produed in str pyrmidl neurons. In ddition, the effets of monoulr deprivtion on pyrmidl neuron tivity were seletive for lyer 4: the firing rtes of lyer 2/3 pyrmidl neurons were unffeted y monoulr deprivtion t this ge (ontrol:.85 ±.45 Hz, n = ; deprived:.77 ±.25 Hz, n = 8; P =.88). When 2 d of monoulr deprivtion ws followed y removl of the suture for 2 d, str pyrmidl neuron tivity in lyer 4 ws restored to ontrol vlues (Fig. ; ontrol:.8 ±.3 Hz, n = 8; previously deprived:. ±.2 Hz, n = 8; P =.55). This reversiility suggests tht these hnges in exitility represent dynmi, ompenstory response to lowered sensory drive nd is onsistent with ehviorl dt showing tht the effets of visul deprivtion re reversile if deprivtion is lifted erly in life,2. Norm. frequeny 4 2 LP Modified ACSF Modified ACSF Modified ACSF APV, DNQX, i. RSNP REV Figure Spontneous tivity of lyer 4 str pyrmidl neurons ws inresed fter 2 d of visul deprivtion. () Representtive wholeell reordings from str pyrmidl neurons in slies from ontrol nd deprived hemispheres, illustrting the elevtion in tivity in the deprived hemisphere. () Averge spontneous firing rtes from str pyrmidl neurons () in whole-ell (WC) nd loose-pth (LP) onfigurtions, RSNP ells in the whole-ell onfigurtion nd from str pyrmidl neurons 48 h fter reopening the eye (REV). Firing rtes in the deprived hemisphere re represented reltive to the ontrol hemisphere to show the fold hnge. Asterisk indites signifint differene from ontrol. Here nd for ll susequent figures, error rs represent the s.e.m. () Exmple reording from str pyrmidl neuron from the deprived hemisphere during wsh-in (middle pnel) nd wshout (right pnel) of synpti lokers (APV, DNQX nd iuulline). Inresed firing is due to ltered synpti drive At lest three mehnisms ould ontriute to the inresed spontneous tivity of str pyrmidl neurons: inresed intrinsi exitility 27, inresed exittory synpti drive 7,28 nd deresed inhiitory synpti drive 29. To test hnges in intrinsi properties, we generted firing rte versus urrent (F I) urves in the presene of the synpti reeptor lokers APV (5 µm), DNQX (2 µm) nd iuulline (2 µm; Fig. 2,). No signifint differenes were oserved in the slopes of the liner portion of these urves (ontrol,.53 ±.7; deprived,.49 ±.4; P =.49) or in the spike threshold (Fig. 2). Monoulr deprivtion lso did not signifintly ffet resting input resistnes (ontrol: 38 ± 4 MΩ, n = ; deprived: 36 ± 56 MΩ, n = ; P =.56) nd resting memrne potentils (ontrol: 66.4 ±.6 mv, n = ; deprived: 67.3 ±.7 mv, n = ; P =.63) mesured in the presene of synpti lokers. To test whether hnges in exittory nd inhiitory synpti drive ould explin the inresed firing rtes, we reorded spontneous exittory nd inhiitory urrents onto str pyrmidl neurons y leving ongoing iruit tivity intt nd voltge lmping individul postsynpti neurons to different potentils. Exittory nd inhiitory urrents were seprted y holding the postsynpti neuron t the mesured reversl potentil (E rev ) for inhiitory postsynpti urrents (IPSCs; 4 mv; Fig. 3) or t the mesured E rev for exittory postsynpti urrents (EPSCs; + mv; Fig. 3). Integrting spontneous exittory nd inhiitory urrents over 5-min period showed tht monoulr deprivtion produed 75% inrese in exittory synpti hrge (Fig. 3,; ontrol, n = 9; deprived, n = 9; P <.) nd 46% derese in inhiitory synpti hrge (Fig. 3,; ontrol, n = 9; deprived, ms Spike rte (Hz) Figure 2 Visul deprivtion did not ffet the intrinsi exitility of str pyrmidl neurons. () Representtive reordings of lyer 4 str pyrmidl neurons in slies from ontrol nd deprived hemispheres in response to DC depolrizing urrent injetion (5 ms, 8 pa). Reordings were otined in the presene of synpti lokers. () Top pnel: verge urrent versus firing rte from str pyrmidl neurons in ontrol nd deprived hemispheres. Bottom pnel: verge spike threshold (the interpolted memrne potentil t whih dv/dt equled 2 V/s) for the ontrol nd deprived onditions. 8 pa 8 pa Spike threshold (mv) I (pa) 354 VOLUME 7 NUMBER 2 DECEMBER 24 NATURE NEUROSCIENCE
3 4 mv 4 mv 2 pa s + mv + mv pa s Figure 3 The lne etween exittory nd inhiitory synpti drive ws ltered y visul deprivtion. () Representtive reordings of spontneous EPSCs (reorded t the Cl reversl potentil) from str pyrmidl neurons in slies from ontrol nd deprived hemispheres in modified ACSF. () Representtive reordings of spontneous IPSCs (reorded t the reversl potentil for spontneous EPSCs); exmples re from the sme ontrol nd deprived neurons s in. () Averge exittory nd inhiitory hrge (otined y integrting spontneous EPSC or IPSC urrent over 5 min for eh neuron) for str pyrmidl neurons from ontrol or deprived hemispheres. dt re expressed reltive to ontrol to show the fold hnge. Asterisk indites signifint differene from ontrol. n = 9; P <.). These results show tht the lne etween exittion nd inhiition in the reurrent iruitry of lyer 4 hs shifted to fvor exittion. Monoulr deprivtion strengthens exittory onnetions Lyer 4 str pyrmidl neurons in the visul ortex reeive diret thlmi input nd reurrent exittory onnetions from other str pyrmidl neurons within lyer 4. The verge quntl mplitude of exittory synpses on str pyrmidl neurons is inresed fter 2 d of monoulr deprivtion 7. To investigte in detil how monoulr deprivtion ffets the properties of unitry exittory synpti onnetions within lyer 4, we rried out qudruple reordings from str pyrmidl neurons to find monosynptilly onneted pirs (Fig. 4). All pired reordings here nd elow were done in stndrd ACSF so there ws miniml kground synpti tivity. We found 25 onneted pirs out of 234 tested (.6%) from ontrol hemispheres nd 45 onneted pirs out of 238 tested (8.9%) from deprived hemispheres (Fig. 4; P <.25, χ 2 ). In ddition to this inrese in onnetion proility, the verge mplitude of monosynpti pyrmidl-to-pyrmidl onnetions pproximtely douled in the deprived hemisphere (Fig. 4,d; Reltive hrge _ 4 mv + mv P <.), with no signifint hnges in EPSC lteny (ontrol,.2 ±.2 ms; deprived,. ±.2 ms; P =.3) or kinetis (2 8% rise times: ontrol,.69 ±.4 ms; deprived,.64 ±.9 ms; P =.63 nd dey time onstnts: ontrol, 7.2 ±.8 ms; deprived, 8.9 ±.6 ms; P =.37). A smll ut signifint hnge ws oserved in the short-term plstiity of pyrmidl-topyrmidl onnetions in response to trins of five preisely timed presynpti spikes t 2 Hz. Connetions from the deprived hemisphere showed slightly more depression (Fig. 4,e; n = ontrol nd 7 deprived pirs; P <., one-wy ANOVA). Filure rtes nd oeffiients of vrition of EPSC mplitude were not, however, signifintly different (Fig. 4d; P =.56), suggesting tht proility of relese ws not muh ltered. Similrly, only modest hnges in short-term plstiity hve een oserved in rodent somtosensory ortex fter whisker deprivtion,3, nd tivity deprivtion in ortil nd spinl ultures inreses exittory synpti strength primrily through postsynpti hnges in reeptor umultion 28,32. A higher onnetion proility etween str pyrmidl neurons, ompnied y douling of EPSC mplitude etween onneted pirs, should ooperte to inrese the gin of exittory feedk within lyer 4. Interneurons respond differently to monoulr deprivtion Different ortil interneurons re funtionlly distint within the ortil iruit 33. A numer of studies hve suggested tht tivity deprivtion in ulture 29,34 or visul deprivtion in speies rnging from rodents to primtes 8,35 n redue ortil inhiition. Whether this redution differentilly ffets inhiition tht rises from different lsses of interneuron hs not een ssessed. Here we exmined hnges in unitry onnetions from two lsses of interneuron, fst-spiking nd RSNP ells, onto str pyrmidl neurons. Fst-spiking neurons re nondpting, high frequeny firing GABAergi inhiitory interneurons (Fig. 5), whih generte feedk inhiition onto str pyrmidl neurons 36. There were 6 onneted pa µm II/III IV 2 ms Conn. proility (%) d 2 2 I (pa) 5.5 Fil. (%) CV e Chnge (%) EPSC numer pa 5 ms Figure 4 Visul deprivtion inresed the mplitude of monosynpti onnetions etween str pyrmidl neurons. () Top: mer luid reonstrution of representtive monosynptilly onneted pir of str pyrmidl neurons in lyer 4, showing lminr position. Bottom: exmple of the typil firing pttern of str pyrmidl neurons in response to 5-ms depolrizing urrent step of pa. () Connetion proility in ontrol nd deprived hemispheres. () Representtive reording of monosynpti EPSCs (reorded t 8 mv) in response to preisely timed presynpti spikes t 2 Hz. Eh tre is the verge of repetitions. (d) EPSC mplitude (urrent; I), filure rte (Fil.) nd oeffiient of vrition (CV), verged ross onnetions from ontrol nd deprived hemispheres. (e) Averge EPSC mplitude for eh response in the 2-Hz trin (plotted s perentge of the first EPSC mplitude) for ontrol nd deprived pirs. Asterisk indites signifint differene from ontrol. NATURE NEUROSCIENCE VOLUME 7 NUMBER 2 DECEMBER
4 8 pa FS µm II/III IV 2 ms Conn. proility (%) d pirs of fst-spiking nd pyrmidl neurons out of 25 tested in ontrol hemispheres (64.%) nd of 6 in deprived hemispheres (68.8%; P =.9, χ 2 test; Fig. 5). Monoulr deprivtion indued 5% derese in the mplitude of monosynpti onnetions etween fst-spiking nd str pyrmidl neurons (Fig. 5,d; ontrol, n = 6; deprived, n = ; P <.3). No signifint hnges were oserved in synpti delys (ontrol,.8 ±.2 ms; deprived, 2. ±.3 ms; P =.43), rise times (ontrol,.4 ±.2 ms; deprived,.4 ±. ms; P =.85) nd dey time onstnts (ontrol, 2.4 ±.4 ms; deprived,.7 ±.9 ms; P =.69). This derese in mplitude ws ompnied y drmti hnge in short-term plstiity. Although ontrol onnetions showed short-term depression, onnetions from the deprived hemisphere showed pronouned short-term filittion (Fig. 5,e; n = 6 ontrol nd deprived pirs; P <., ANOVA), nd the oeffiient of vrition ws signifintly inresed in the deprived hemisphere (Fig. 5e; P <.), onsistent with redution in relese proility ontriuting to the redution in IPSC mplitude. Beuse ontrol onnetions depressed while deprived onnetions filitted, the solute mplitude of the lst IPSC in 2-Hz trin ws omprle etween onditions (ontrol, 3.4 ±.3 pa; deprived, 3.2 ±.5 pa)..5 Chnge (%) I (pa) CV IPSC numer e 4 5 pa 5 ms Figure 5 Visul deprivtion deresed the mplitude of monosynpti onnetions etween fst-spiking nd str pyrmidl neurons. () Top: mer luid reonstrution of representtive monosynptilly onneted fst-spiking nd str pyrmidl neuron pir. Bottom: typil firing pttern of fst-spiking interneuron in response to 5-ms depolrizing urrent step of 8 pa. () Connetion proility in ontrol nd deprived hemispheres. () Representtive reording of monosynpti IPSCs (reorded t 8 mv, so they pper s inwrd urrents) in response to preisely timed presynpti spikes t 2 Hz. (d) IPSC mplitude (urrent; I) nd oeffiient of vrition (CV), verged ross onnetions from ontrol nd deprived hemispheres. (e) Averge IPSC mplitude for eh IPSC in the 2-Hz trin (plotted s perentge of the first IPSC mplitude) for ontrol nd deprived pirs. Asterisk indites signifint differene from ontrol. RSNP neurons in rt visul ortil lyer 4 re regulr-spiking, modertely dpting GABAergi interneurons with ipolr morphology (Fig. 6). They reeive diret thlmi drive nd generte feed-forwrd inhiition onto str pyrmidl neurons 37. The proility of finding onneted pirs in the deprived hemisphere ws less thn hlf tht of the ontrol (Fig. 6; ontrol, 6 of 5 or 32.%; deprived, 8 of 58 or 3.8%; P <.5, χ 2 test). In ontrst to the effets of monoulr deprivtion on fst-spiking-to-pyrmidl onnetions, the mplitude of RSNP-to-pyrmidl onnetions more thn douled fter monoulr deprivtion (Fig. 6,d; P <.). Like pyrmidl-to-pyrmidl onnetions, deprivtion produed modest inrese in short-term depression with no signifint hnge in filure rte or oeffiient of vrition (Fig. 6,e; P =.62). No hnges were oserved in synpti delys (ontrol,.8 ±.3 ms; deprived,.7 ±.2; P =.9), rise times (ontrol,.2 ±.2 ms; deprived,.3 ±.2 ms; P =.73) nd dey time onstnts (ontrol,.4 ±.7; deprived,.9 ±.5 ms; P =.3). These dt indite tht str pyrmidl neurons reeive inhiition from smller frtion of RSNP neurons, ut tht eh unitry onnetion is more potent. Figure 6 Visul deprivtion inresed the mplitude of monosynpti onnetions etween RSNP nd str pyrmidl neurons ut deresed the onnetion proility. () Top, mer luid reonstrution of representtive monosynptilly onneted RSNP nd str pyrmidl neuron pir. Bottom, typil firing pttern of RSNP interneuron in response to 5-ms depolrizing urrent injetion. () Connetion proility for ontrol nd deprived hemispheres. () Representtive reording of monosynpti IPSCs (reorded t 8 mv, so they pper s inwrd urrents) in response to preisely timed presynpti spikes t 2 Hz. (d) IPSC mplitude (urrent; I), filure rte (Fil.) nd oeffiient of vrition (CV), verged ross onnetions from ontrol nd deprived hemispheres. (e) Averge IPSC mplitude for eh IPSC in the 2-Hz trin (plotted s perentge of the first EPSC mplitude) for ontrol nd deprived pirs. Asterisk indites signifint differene from ontrol. pa RSNP µm II/III IV 2 ms Conn. proility (%) d I (pa) Fil. (%) CV.5 e Chnge (%) IPSC numer 5 pa 5 ms 356 VOLUME 7 NUMBER 2 DECEMBER 24 NATURE NEUROSCIENCE
5 DISCUSSION Here we show tht pronouned effet of erly visul deprivtion in lyer 4 is highly seletive djustment of intrortil synpti strengths tht results in inresed lyer 4 exitility. Two dys of lid suture just t eye opening douled the mplitude of lol exittory onnetions nd douled the proility of finding onneted exittory pirs. In ontrst, inhiitory synpti drive ws redued through seletive hnges in inhiitory iruitry, nd these two effets ooperted to drmtilly inrese spontneous tivity within lyer 4. This indites tht reduing sensory drive erly in life inreses the exitility of lol lyer 4 iruitry. Theoretil work hs suggested tht ompenstory, or homeostti, plstiity mehnisms tht stilize neuronl or network tivity re essentil for the proess of tivity-dependent refinement 38,39, nd severl forms of homeostti plstiity hve een identified experimentlly 4. The dt presented here indite tht, in highly reurrent lyer 4 networks, this stiliztion my e hieved through oordinted set of hnges in exittory nd inhiitory iruitry. When sensory drive is redued, reurrent exittory onnetions re inresed in strength, wheres feedk inhiition is redued in strength (Supplementry Fig. online). These synpti hnges re likely to t synergistilly to produe the drmti inrese (25-fold) in spontneous str pyrmidl firing rtes tht ws oserved, lthough we nnot rule out tht other synpti hnges lso ontriute to this inresed exitility. This ompenstory inrese in lyer 4 exitility in response to lowered sensory drive my enhne the ility of lyer 4 to mplify the sensory signls it does reeive. Prolonged periods of visul deprivtion (using lid suture, drk rering or tetrodotoxin injetions) hve long een known to redue inhiition in primry visul ortex of rodents nd primtes 8,9,35,4, ut it ws not known whether different lsses of interneuron re differentilly ffeted y sensory deprivtion. Here we show tht rief visul deprivtion erly in life hs fundmentlly different effets on different lsses of inhiitory synpse. Fst-spiking interneurons generte lssi feedk inhiition on str pyrmidl neurons 36,42, nd this lss of onnetion ws redued in the deprived hemisphere. Interestingly, the short-term plstiity of this synpse underwent drmti hnge from depressing to filitting. This suggests tht fst-spiking onnetions re preferentilly redued in mplitude t low firing rtes, ut tht t high firing rtes this synpse will filitte nd more inhiition will e reruited. This my help to set n upper limit on spontneous tivity. In ontrst to fst-spiking neurons, RSNP neurons reeive diret thlmi input nd generte feed-forwrd inhiition onto str pyrmidl neurons 37. The verge mplitude of RSNP-to-pyrmidl onnetions more thn douled in the deprived hemisphere, wheres the onnetion proility ws redued to less thn hlf of ontrol vlues. This indites tht totl inhiition from RSNP neurons remins roughly onstnt ut tht str pyrmidl neurons reeive more potent inhiition from fewer RSNP neurons. These results show tht funtionlly distint lsses of inhiitory onnetion re djusted in highly seletive mnner y ltered sensory drive, nd tht the effets of erly sensory deprivtion in lyer 4 depend ritilly on the identity of the synpse nd on its role in ortil funtion. The effets of sensory deprivtion re strongly developmentlly regulted, nd different ortil lyers n hve different sensitive periods during development. For exmple, in rodents the sensitive periods for oulr dominne plstiity in inoulr visul ortex nd for whisker deprivtion plstiity in somtosensory ortex lose erly in lyer 4 (fter the first few weeks of life) ut persist signifintly lter in lyer 2/3. The effets of visul deprivtion on the quntl mplitude of exittory urrents on pyrmidl neurons lso hve lyer-speifi ritil periods 7. Lowering retinl tivity etween P4 nd P7 sled up exittory quntl urrents in lyer 4 ut not in lyer 2/3, wheres the sme deprivtion rried out etween P2 nd P23 hd no effet in lyer 4 ut insted sled up exittory quntl mplitudes in lyer 2/3 (ref. 7). These dt re onsistent with the findings reported here tht spontneous tivity in lyer 4, ut not in lyer 2/3, is inresed y lid suture etween P4 nd P7. Tken together, these studies indite tht homeostti plstiity egins in lyer 4 ut (like other forms of plstiity) shifts during development to lyer 2/3. The first few weeks of development re likely to represent the period of gretest instility in lyer 4, s thlmoortil nd intrortil synpses re rpidly forming nd there is roust thlmoortil long-term potentition, so homeostti plstiity in lyer 4 my e espeilly importnt during this developmentl window. Whether the synpti mehnisms underlying inresed lyer 4 exitility tht re desried here will generlize to other ortil lyers t lter developmentl times remins to e determined. In ddition to serving homeostti funtion, shifts in the lne etween exittion nd inhiition ould hve lrge impt on tivity-dependent iruit refinement nd funtion. Chnges in this lne lter the ese with whih synpse-speifi forms of ortil plstiity (suh s long-term potentition nd depression) n e eliited 43 nd n modify or prolong the developmentl periods during whih visul response properties re sensitive to experiene 44,45. The initition nd propgtion of tivity in ortil networks is lso influened y the exittion-inhiition lne 46, nd so the seletivity of ortil responses my e strongly ffeted when this lne is ltered. Our dt indite tht homeostti regultion of the exittion-inhiition lne my e importnt in mintining stle ortil tivity during norml development nd my lso ontriute to the pthologil hnges in visul response properties tht re indued y sensory deprivtion. METHODS Monoulr deprivtion. Eyelid suture ws done lte on P4 (just efore eye opening) during rief nesthesi with 7 mg/kg ketmine, 3.5 mg/kg xylzine hydrohloride nd.7 mg/kg epromzine mlete, intrperitonelly. The eyelid ws overed with thin lyer of xyloine gel, nd the lid ws seured with three mttress sutures. Sutures were heked every dy until nimls were killed for reording erly on P7. All methods were pproved y the Brndeis Animl Use Committee nd were rried out in ordne with the Ntionl Institutes of Helth guidelines. Eletrophysiology. Coronl slies ontining primry visul ortex were prepred from the deprived nd ontrol hemispheres, nd visulized pthlmp reordings were otined from lyer 4 of the monoulr region of V, s desried 7. Neurons were trgeted visully using infrred differentil interferene ontrst optis nd were filled with ioytin during the reording session for post ho morphologil reonstrution. Neurons were identified sed on lminr position, morphology, synpti properties nd firing properties. Neurons tht were inluded in the nlyses hd memrne potentil (V m ) elow 6 mv, n input resistne (R in ) ove 2 MΩ nd series resistne elow 5 MΩ; for the inluded neurons, these prmeters did not hnge more thn % during the reording. To mesure spontneous firing rtes, smll mount of DC urrent (generlly depolrizing) ws injeted to djust the interspike potentil to 6 mv. For loose-pth reordings, we used 2 3 MΩ pipettes filled with ACSF. A sel of 6 2 MΩ ws otined y pthing onto visully identified str pyrmidl neurons, nd extrellulr spikes were reorded. Reordings were nlyzed if spikes exeeded 5 mv nd if the sel remined stle for >5 min. For generting F-I urves, series of depolrizing urrent steps ws delivered in the presene of synpti lokers. For mesuring spontneous synpti urrents, the reversl potentil (E rev ) ws determined y voltge lmping the postsynpti neuron to different potentils (in 5 mv inrements) etween 55 nd mv for inhiitory urrents nd etween 5 nd +5 NATURE NEUROSCIENCE VOLUME 7 NUMBER 2 DECEMBER
6 mv for exittory urrents. The verge reversl potentils for EPSCs (ontrol, 8.4 ±.5 mv; deprived, 9.2 ±. mv; P =.46) nd IPSCs (ontrol, 4. ±. mv; deprived, 4. ±. mv; P =.32) were not different etween onditions, nd when orreted for juntion potentils, they were within mv of those predited with our internl nd externl solutions. Monosynpti pired reordings were otined in lyer 4 y qudruple whole-ell reordings of nery neurons s desried 47. Firing properties were ssessed in urrent lmp y delivering 5 ms depolrizing urrent steps. Reversl potentils of synpti urrents were determined y stimulting presynpti neurons while voltge lmping the postsynpti neuron to different potentils. To mesure short-term plstiity, trins of 5 presynpti tion potentils were eliited t 2 Hz (every 2 s), nd postsynpti urrents were monitored t 8 mv. Clssifition of neurons. Str pyrmidl neurons were identified s previously desried 7. Bsed on morphology, firing properties nd short-term plstiity of synpti onnetions, we identified two popultions of onnetions etween interneurons nd str pyrmidl neurons. Fst-spiking neurons were multipolr, fst spiking nd nondpting, nd their IPSCs on pyrmidl neurons showed moderte depression 3,5,42,48. RSNP neurons hd ipolr morphology nd were regulr spiking with frequeny dpttion; their IPSCs on pyrmidl neurons showed mrked depression 3,5,42,49. Note tht interneuronl properties in lyer 4 of visul ortex differ in some respets from those reported in lyer 4 of somtosensory ortex 5. Sttistil nlysis. All dt re expressed s the men ± s.e.m. for the numer of neurons (or onneted pirs) speified, nd ll sttistil tests were unpired two-tiled t-tests, exept s noted in text. Solutions. Stndrd ACSF onsists of 26 mm NCl, 3 mm KCl, 2 mm MgSO 4, 2 mm CCl 2, mm NHPO 4, 25 mm NHCO 3 nd 25 mm dextrose. For pired reordings, the Mg 2+ onentrtion ws mm. Modified ACSF (3.5 mm KCl,.5 mm MgCl 2 nd mm CCl 2 ) ws used to reord spontneous firing nd spontneous synpti urrents. The internl solution ws 2 mm KCl, mm potssium gluonte, mm HEPES,.% ioytin, 4 mm mgnesium ATP,.3 mm sodium GTP nd mm sodium phosphoretine. For mesuring spontneous synpti urrents, the internl solution ontined 2 mm KCl, mm esium methylsulfonte, mm HEPES,.% ioytin, 4 mm Mg-ATP,.3 mm N-GTP, mm sodium phosphoretine nd 3 mm QX-34. Note: Supplementry informtion is ville on the Nture Neurosiene wesite. ACKNOWLEDGMENTS We thnk R. Cudmore for help with softwre, J. Brry nd K. Essig for histology nd S. Fusi nd X.-J. Wng for helpful disussions. Supported y the Ntionl Eye Institute (EY4439) nd the Ntionl Institute on Drug Ause (DA6455). COMPETING INTERESTS STATEMENT The uthors delre tht they hve no ompeting finnil interests. Reeived Septemer; epted 3 Otoer 24 Pulished online t Huel, D.H. & Wiesel, T.N. The period of suseptiility to the physiologil effets of unilterl eye losure in kittens. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 26, (97). 2. Shtz, C.J. & Stryker, M.P. Oulr dominne in lyer IV of the t s visul ortex nd the effets of monoulr deprivtion. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 28, (978). 3. Shtz, C.J. Impulse tivity nd the ptterning of onnetions during CNS development. Neuron 5, (99). 4. Gordon, J.A. & Stryker, M.P. Experiene-dependent plstiity of inoulr responses in the primry visul ortex of the mouse. J. Neurosi. 6, (996). 5. Benevento, L.A., Bkkum, B.W., Port, J.D. & Cohen, R.S. The effets of drk-rering on the eletrophysiology of the rt visul ortex. Brin Res. 572, (992). 6. Heynen, A.J. et l. Moleulr mehnism for loss of visul ortil responsiveness following rief monoulr deprivtion. Nt. Neurosi. 6, (23). 7. Fgiolini, M., Pizzorusso, T., Berrdi, N., Domenii, L. & Mffei, L. Funtionl postntl development of the rt primry visul ortex nd the role of visul experiene: drk rering nd monoulr deprivtion. Vision Res. 34, (994). 8. White, L.E., Coppol, D.M. & Fitzptrik, D. The ontriution of sensory experiene to the mturtion of orienttion seletivity in ferret visul ortex. Nture 4, (2). 9. Th, S. & Stryker, M.P. Rpid oulr dominne plstiity requires ortil ut not geniulte protein synthesis. Neuron 34, (22).. Trhtenerg, J.T., Trepel, C. & Stryker, M.P. Rpid extrgrnulr plstiity in the sene of thlmoortil plstiity in the developing primry visul ortex. Siene 287, (2).. vn Sluyters, R.C. Reversl of the physiologil effets of rief periods of monoulr deprivtion in the kitten. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 284, 7 (978). 2. Murer, D., Lewis, T.L., Brent, H.P. & Levin, A.V. Rpid improvement in the uity of infnts fter visul input. Siene 286, 8 (999). 3. Peters, A. & Kr, D.A. The neuronl omposition of re 7 of rt visul ortex. I. The pyrmidl ells. J. Comp. Neurol. 234, (985). 4. Mrtin, K.A. Miroiruits in visul ortex. Curr. Opin. Neuroiol. 2, (22). 5. Kwguhi, Y. & Kuot, Y. GABAergi ell sutypes nd their synpti onnetions in rt frontl ortex. Cere. Cortex 7, (997). 6. Peters, A. & Kr, D.A. The neuronl omposition of re 7 of rt visul ortex. II. The nonpyrmidl ells. J. Comp. Neurol. 234, (985). 7. Desi, N.S., Cudmore, R.H., Nelson, S.B. & Turrigino, G.G. Critil periods for experiene-dependent synpti sling in visul ortex. Nt. Neurosi. 5, (22). 8. Hendry, S.H. & Jones, E.G. Redution in numer of immunostined GABAergi neurones in deprived-eye dominne olumns of monkey re 7. Nture 32, (986). 9. Benevento, L.A., Bkkum, B.W. & Cohen, R.S. γ-aminoutyri id nd somtosttin immunoretivity in the visul ortex of norml nd drk-rered rts. Brin Res. 689, (995). 2. Reid, S.N. & Jursk, J.M. The ytorhitetoni oundries of the monoulr nd inoulr res of the rt primry visul ortex. Brin Res. 563, (99). 2. Zilles, K., Wree, A., Shleiher, A. & Div, I. The monoulr nd inoulr sufields of the rt s primry visul ortex: quntittive morphologil pproh. J. Comp. Neurol. 226, (984). 22. Cleo, M., Lodovihi, C., Pizzorusso, T. & Mffei, L. Expression of the trnsription ftor Zif268 in the visul ortex of monoulrly deprived rts: effets of nerve growth ftor. Neurosiene 9, 7 26 (999). 23. Worley, P.F. et l. Constitutive expression of zif268 in neoortex is regulted y synpti tivity. Pro. Ntl Ad. Si. USA 88, 56 5 (99). 24. Chutkow, J. Metolism of mgnesium in entrl nervous system. Reltionship etween onentrtions of mgnesium in ererospinl fluid nd rin in mgnesium defiieny. Neurology 24, (974). 25. Zhng, E.T., Hnsen, A.J., Wieloh, T. & Lewitzen, M. Influene of MK-8 on rin extrellulr lium nd potssium tivities in severe hypogliemi. J. Cere. Blood Flow Met., (99). 26. Snhez-Vives, M.V. & MCormik, D. Cellulr nd network mehnisms of rhythmi reurrent tivity in neoortex. Nt. Neurosi. 3, (2). 27. Desi, N.S., Rutherford, L.C. & Turrigino, G.G. Plstiity in the intrinsi exitility of ortil pyrmidl neurons. Nt. Neurosi. 2, (999). 28. Turrigino, G.G., Leslie, K.R., Desi, N.S., Rutherford, L.C. & Nelson, S.B. Ativitydependent sling of quntl mplitude in neoortil neurons. Nture 39, (998). 29. Kilmn, V., vn Rossum, M.C. & Turrigino, G.G. Ativity deprivtion redues miniture IPSC mplitude y deresing the numer of postsynpti GABA(A) reeptors lustered t neoortil synpses. J. Neurosi. 22, (22).. Finnerty, G.T. & Connors, B.W. Sensory deprivtion without ompetition yields modest ltertions of short-term synpti dynmis. Pro. Ntl Ad. Si. USA 97, (2). 3. Finnerty, G.T., Roerts, L.S. & Connors, B.W. Sensory experiene modifies the shortterm dynmis of neoortil synpses. Nture 4, (999). 32. O Brien, R.J. et l. Ativity-dependent modultion of synpti AMPA reeptor umultion. Neuron 2, (998). 33. DeFelipe, J. Cortil interneurons: from Cjl to 2. Prog. Brin Res. 36, (22). 34. Rutherford, L.C., DeWn, A., Luer, H.M. & Turrigino, G.G. Brin-derived neurotrophi ftor medites the tivity-dependent regultion of inhiition in neoortil ultures. J. Neurosi. 7, (997). 35. Morles, B., Choi, S.Y. & Kirkwood, A. Drk rering lters the development of GABAergi trnsmission in visul ortex. J. Neurosi. 22, (22). 36. Sho, Z. & Burkhlter, A. Different lne of exittion nd inhiition in feed-forwrd nd feedk iruits of rt visul ortex. J. Neurosi. 6, (996). 37. Hjos, F., Stiger, J.F., Hlsy, K., Freund, T.F. & Zilles, K. Geniulo-ortil fferents form synpti ontts with vsotive intestinl polypeptide (VIP) immunoretive neurons of the rt visul ortex. Neurosi. Lett. 228, (997). 38. Miller, K.D. Synpti eonomis: ompetition nd oopertion in synpti plstiity. Neuron 7, (996). 39. Aott, L.F. & Nelson, S.B. Synpti plstiity: tming the est. Nt. Neurosi. 3, (2). 4. Turrigino, G.G. & Nelson, S.B. Homeostti plstiity in the developing nervous system. Nt. Rev. Neurosi. 5, 97 7 (24). 4. Hendry, S.H., Fuhs, J., debls, A.L. & Jones, E.G. Distriution nd plstiity of immunoytohemilly lolized GABAA reeptors in dult monkey visul ortex. J. Neurosi., (99). 42. Meineke, D.L. & Peters, A. GABA immunoretive neurons in rt visul ortex. J. Comp. Neurol. 26, (987). 43. Kirkwood, A. & Ber, M.F. Hein synpses in visul ortex. J. Neurosi. 4, (994). 44. Hensh, T.K. et l. Lol GABA iruit ontrol of experiene-dependent plstiity in developing visul ortex. Siene 282, (998). 358 VOLUME 7 NUMBER 2 DECEMBER 24 NATURE NEUROSCIENCE
7 45. Hung, Z.J. et l. BDNF regultes the mturtion of inhiition nd the ritil period of plstiity in mouse visul ortex. Cell 98, (999). 46. Chgn-Amiti, Y. & Connors, B.W. Horizontl spred of synhronized tivity in neoortex nd its ontrol y GABA-medited inhiition. J. Neurophysiol. 6, (989). 47. Sjostrom, P.J., Turrigino, G.G. & Nelson, S.B. Rte, timing, nd oopertivity jointly determine ortil synpti plstiity. Neuron 32, (2). 48. Deuhrs, J. & Thomson, A.M. Single xon fst inhiitory postsynpti potentils eliited y sprsely spiny interneuron in rt neoortex. Neurosiene 65, (995). 49. Peters, A. & Herrimnn, K.M. Enigmti ipolr ell of rt visul ortex. J. Comp. Neurol. 267, (988). 5. Beierlein, M., Gison, J.R. & Connors, B.W. Two dynmilly distint inhiitory networks in lyer 4 of the neoortex. J. Neurophysiol. 9, 2987 (23). NATURE NEUROSCIENCE VOLUME 7 NUMBER 2 DECEMBER
Laminar sources of synaptic input to cortical inhibitory interneurons and pyramidal neurons
 rtiles Lminr soures of synpti input to ortil inhiitory interneurons nd pyrmidl neurons J. L. Dntzker nd E. M. Cllwy Systems Neuroiology Lortories, The Slk Institute for Biologil Studies, N. Torrey Pines
rtiles Lminr soures of synpti input to ortil inhiitory interneurons nd pyrmidl neurons J. L. Dntzker nd E. M. Cllwy Systems Neuroiology Lortories, The Slk Institute for Biologil Studies, N. Torrey Pines
Input normalization by global feedforward inhibition expands cortical dynamic range
 Input normliztion y glol feedforwrd inhiition expnds ortil dynmi rnge Frédéri Pouille 1,2, Antoni Mrin-Burgin 1,2, Hillel Adesnik 1, Bssm V Atllh 1 & Mssimo Snzini 1 29 Nture Ameri, In. All rights reserved.
Input normliztion y glol feedforwrd inhiition expnds ortil dynmi rnge Frédéri Pouille 1,2, Antoni Mrin-Burgin 1,2, Hillel Adesnik 1, Bssm V Atllh 1 & Mssimo Snzini 1 29 Nture Ameri, In. All rights reserved.
LHb VTA. VTA-projecting RMTg-projecting overlay. Supplemental Figure 2. Retrograde labeling of LHb neurons. a. VTA-projecting LHb
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementl Figure 1 doi:10.1038/nture09742 Lterl 1.0 mm from midline mpfc BNST mpfc BNST Lterl 2.1 mm from midline LHA LHA Lterl 2.7 mm from midline SUPPLEMENTAL INFORMATION
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementl Figure 1 doi:10.1038/nture09742 Lterl 1.0 mm from midline mpfc BNST mpfc BNST Lterl 2.1 mm from midline LHA LHA Lterl 2.7 mm from midline SUPPLEMENTAL INFORMATION
Mechanisms underlying cross-orientation suppression in cat visual cortex
 Mehnisms underlying ross-orienttion suppression in t visul ortex 6 Nture Pulishing Group http://www.nture.om/ntureneurosiene Nihols J Priee & Dvid Ferster In simple ells of the t primry visul ortex, null-oriented
Mehnisms underlying ross-orienttion suppression in t visul ortex 6 Nture Pulishing Group http://www.nture.om/ntureneurosiene Nihols J Priee & Dvid Ferster In simple ells of the t primry visul ortex, null-oriented
Lesions of prefrontal cortex reduce attentional modulation of neuronal responses. and synchrony in V4
 Lesions of prefrontl ortex reue ttentionl moultion of neuronl responses n synhrony in V4 Georgi G. Gregoriou,, Anrew F. Rossi, 3 Leslie G Ungerleier, 4 Roert Desimone 5 Deprtment of Bsi Sienes, Fulty of
Lesions of prefrontl ortex reue ttentionl moultion of neuronl responses n synhrony in V4 Georgi G. Gregoriou,, Anrew F. Rossi, 3 Leslie G Ungerleier, 4 Roert Desimone 5 Deprtment of Bsi Sienes, Fulty of
EFFECT OF DIETARY ENZYME ON PERFORMANCE OF WEANLING PIGS
 EFFECT OF DIETARY ENZYME ON PERFORMANCE OF WEANLING PIGS Finl report sumitted to Dniso Animl Nutrition E. vn Heugten nd B. Frederik North Crolin Stte University, Deprtment of Animl Siene Summry The urrent
EFFECT OF DIETARY ENZYME ON PERFORMANCE OF WEANLING PIGS Finl report sumitted to Dniso Animl Nutrition E. vn Heugten nd B. Frederik North Crolin Stte University, Deprtment of Animl Siene Summry The urrent
P AND K IN POTATOES. Donald A Horneck Oregon State University Extension Service
 P AND K IN POTATOES Donld A Hornek Oregon Stte University Extension Servie INTRODUCTION Phosphorous nd potssium re importnt to grow high yielding nd qulity pottoes. Muh of the northwest hs hd trditionlly
P AND K IN POTATOES Donld A Hornek Oregon Stte University Extension Servie INTRODUCTION Phosphorous nd potssium re importnt to grow high yielding nd qulity pottoes. Muh of the northwest hs hd trditionlly
Early depolarizing GABA controls critical-period plasticity in the rat visual cortex
 Erly depolrizing GABA ontrols ritil-period plstiity in the rt visul ortex Gbriele Deidd,5, Mnuel Allegr,,5, Chir Cerri, Shovn Nskr, Guillume Bony, Giuli Zunino 4, Yuri Bozzi,4, Mtteo Cleo,6 & Lur Cnedd,6
Erly depolrizing GABA ontrols ritil-period plstiity in the rt visul ortex Gbriele Deidd,5, Mnuel Allegr,,5, Chir Cerri, Shovn Nskr, Guillume Bony, Giuli Zunino 4, Yuri Bozzi,4, Mtteo Cleo,6 & Lur Cnedd,6
Long-term modification of cortical synapses improves sensory perception
 Long-term modifition of ortil synpses improves sensory pereption Roert C Froemke 1 4,8, Ion Cre 1 3,8, Alison J Brker 4, Kexin Yun 4, Bryn A Seyold 4, An Rquel O Mrtins 1 3,5, Ntly Zik 1,2, Hnnh Bernstein
Long-term modifition of ortil synpses improves sensory pereption Roert C Froemke 1 4,8, Ion Cre 1 3,8, Alison J Brker 4, Kexin Yun 4, Bryn A Seyold 4, An Rquel O Mrtins 1 3,5, Ntly Zik 1,2, Hnnh Bernstein
Receptive field structure varies with layer in the primary visual cortex
 2 Nture Pulishing Group http://www.nture.om/ntureneurosiene Reeptive field struture vries with lyer in the primry visul ortex Luis M Mrtinez, Qingo Wng 2, R Cly Reid 3, Cinthi Pilli 2, José-Mñuel Alonso
2 Nture Pulishing Group http://www.nture.om/ntureneurosiene Reeptive field struture vries with lyer in the primry visul ortex Luis M Mrtinez, Qingo Wng 2, R Cly Reid 3, Cinthi Pilli 2, José-Mñuel Alonso
Learning to see: experience and attention in primary visual cortex
 2 Nture Pulishing Group http://neurosi.nture.om rtiles Lerning to see: experiene nd ttention in primry visul ortex 2 Nture Pulishing Group http://neurosi.nture.om Roy E. Crist, Wu Li nd Chrles D. Gilert
2 Nture Pulishing Group http://neurosi.nture.om rtiles Lerning to see: experiene nd ttention in primry visul ortex 2 Nture Pulishing Group http://neurosi.nture.om Roy E. Crist, Wu Li nd Chrles D. Gilert
In vivo intracellular recording and perturbation of persistent activity in a neural integrator
 rtiles 21 Nture Pulishing Group http://neurosi.nture.om 21 Nture Pulishing Group http://neurosi.nture.om In vivo intrellulr reording nd perturtion of persistent tivity in neurl integrtor E. Aksy 1,2, G.
rtiles 21 Nture Pulishing Group http://neurosi.nture.om 21 Nture Pulishing Group http://neurosi.nture.om In vivo intrellulr reording nd perturtion of persistent tivity in neurl integrtor E. Aksy 1,2, G.
I h -mediated depolarization enhances the temporal precision of neuronal integration
 Reeived 5 Apr 2 Aepted 9 Jn 2 Pulished 5 Fe 2DOI:.38/nomms22 I h -medited depolriztion enhnes the temporl preision of neuronl integrtion Ivn Pvlov, Annlis Simemi,, Leonid Svthenko, Dimitri M. Kullmnn &
Reeived 5 Apr 2 Aepted 9 Jn 2 Pulished 5 Fe 2DOI:.38/nomms22 I h -medited depolriztion enhnes the temporl preision of neuronl integrtion Ivn Pvlov, Annlis Simemi,, Leonid Svthenko, Dimitri M. Kullmnn &
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nture10754 Supplementry note 1 To ompre our dt with previous studies, we mesured the width of spikes from identified dopminergi neurons nd unidentified neurons from DATCre mie. Previous studies
doi:10.1038/nture10754 Supplementry note 1 To ompre our dt with previous studies, we mesured the width of spikes from identified dopminergi neurons nd unidentified neurons from DATCre mie. Previous studies
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:.38/nture277 d 25 25 2 Time from sound onset (ms) 25 25 2 Time from sound onset (ms) Firing rte (spikes/s) Firing rte (spikes/s).8.6..2 e f g h.8.6..2 Frtion of neurons Frtion of neurons N = 53 2 2
doi:.38/nture277 d 25 25 2 Time from sound onset (ms) 25 25 2 Time from sound onset (ms) Firing rte (spikes/s) Firing rte (spikes/s).8.6..2 e f g h.8.6..2 Frtion of neurons Frtion of neurons N = 53 2 2
ARTICLES. Lateral presynaptic inhibition mediates gain control in an olfactory circuit. Shawn R. Olsen 1 & Rachel I. Wilson 1
 doi:1.138/nture6864 ARTICLES Lterl presynpti inhiition medites gin ontrol in n olftory iruit Shwn R. Olsen 1 & Rhel I. Wilson 1 Olftory signls re trnsdued y lrge fmily of odornt reeptor proteins, eh of
doi:1.138/nture6864 ARTICLES Lterl presynpti inhiition medites gin ontrol in n olftory iruit Shwn R. Olsen 1 & Rhel I. Wilson 1 Olftory signls re trnsdued y lrge fmily of odornt reeptor proteins, eh of
The Journal of Physiology
 J Physiol 595.23 (217) pp 7185 722 7185 Heteromeri α/β glyine reeptors regulte exitility in prvlumin-expressing dorsl horn neurons through phsi nd toni glyinergi inhiition M. A. Grdwell 1,2,K.A.Boyle 3,R.J.llister
J Physiol 595.23 (217) pp 7185 722 7185 Heteromeri α/β glyine reeptors regulte exitility in prvlumin-expressing dorsl horn neurons through phsi nd toni glyinergi inhiition M. A. Grdwell 1,2,K.A.Boyle 3,R.J.llister
Methylphenidate facilitates learning-induced amygdala plasticity
 Methylphenidte filittes lerning-indued mygdl plstiity Ky M Tye 1,2, Lynne D Tye 1,3, Jkson J Cone 1, Evelien F Hekkelmn 1, Ptrii H Jnk 1,2,, & Antonello Boni 1,2,, 21 Nture Ameri, In. All rights reserved.
Methylphenidte filittes lerning-indued mygdl plstiity Ky M Tye 1,2, Lynne D Tye 1,3, Jkson J Cone 1, Evelien F Hekkelmn 1, Ptrii H Jnk 1,2,, & Antonello Boni 1,2,, 21 Nture Ameri, In. All rights reserved.
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 1.13/n7 Reltive Pprg mrna 3 1 1 Time (weeks) Interspulr Inguinl Epididyml Reltive undne..1.5. - 5 5-51 51-1 1-7 7 - - 1 1-1 Lipid droplet size ( m ) 1-3 3 - - - 1 1-1 1-1 1-175 175-3 3-31 31-5 >5
DOI: 1.13/n7 Reltive Pprg mrna 3 1 1 Time (weeks) Interspulr Inguinl Epididyml Reltive undne..1.5. - 5 5-51 51-1 1-7 7 - - 1 1-1 Lipid droplet size ( m ) 1-3 3 - - - 1 1-1 1-1 1-175 175-3 3-31 31-5 >5
SK channels and NMDA receptors form aca 2+ -mediated feedback loop in dendritic spines
 25 Nture Pulishing Group http://www.nture.om/ntureneurosiene SK hnnels nd NMDA reeptors form C 2+ -medited feedk loop in dendriti spines Thu Jennifer Ngo-Anh 1,4, Brend L Bloodgood 2,4, Mihel Lin 1, Bernrdo
25 Nture Pulishing Group http://www.nture.om/ntureneurosiene SK hnnels nd NMDA reeptors form C 2+ -medited feedk loop in dendriti spines Thu Jennifer Ngo-Anh 1,4, Brend L Bloodgood 2,4, Mihel Lin 1, Bernrdo
Supplementary Figure 1. Scheme of unilateral pyramidotomy used for detecting compensatory sprouting of intact CST axons.
 () BDA 2 weeks fter Py () AAVs Cre or GFP t P1 BDA 2 weeks fter Py CSMN CST () Py t P7 or 2 months () Py t 2 months Supplementry Figure 1. Sheme of unilterl pyrmidotomy used for deteting ompenstory sprouting
() BDA 2 weeks fter Py () AAVs Cre or GFP t P1 BDA 2 weeks fter Py CSMN CST () Py t P7 or 2 months () Py t 2 months Supplementry Figure 1. Sheme of unilterl pyrmidotomy used for deteting ompenstory sprouting
ARTICLES. Dendritic organization of sensory input to cortical neurons in vivo
 Vol 6 9 April 00 doi:0.08/nture0897 ARTICLES Dendriti orgniztion of sensory input to ortil neurons in vivo Hongbo Ji *, Nthlie L. Rohefort *, Xiowei Chen & Arthur Konnerth In sensory ortex regions, neurons
Vol 6 9 April 00 doi:0.08/nture0897 ARTICLES Dendriti orgniztion of sensory input to ortil neurons in vivo Hongbo Ji *, Nthlie L. Rohefort *, Xiowei Chen & Arthur Konnerth In sensory ortex regions, neurons
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 1.138/n358 TLR2 nd MyD88 expression in murine mmmry epithelil supopultions. CD24 min plus MRU Myo-epithelil Luminl progenitor (CD61 pos ) Mture luminl (CD61 neg ) CD49f CD61 Reltive expression Krt5
DOI: 1.138/n358 TLR2 nd MyD88 expression in murine mmmry epithelil supopultions. CD24 min plus MRU Myo-epithelil Luminl progenitor (CD61 pos ) Mture luminl (CD61 neg ) CD49f CD61 Reltive expression Krt5
Alimonti_Supplementary Figure 1. Pten +/- Pten + Pten. Pten hy. β-actin. Pten - wt hy/+ +/- wt hy/+ +/- Pten. Pten. Relative Protein level (% )
 Alimonti_Supplementry Figure 1 hy 3 4 5 3 Neo 4 5 5 Proe 5 Proe hy/ hy/ /- - 3 6 Neo β-tin d Reltive Protein level (% ) 15 1 5 hy/ /- Reltive Gene Expr. (% ) 15 1 5 hy/ /- Supplementry Figure 1 Chrteriztion
Alimonti_Supplementry Figure 1 hy 3 4 5 3 Neo 4 5 5 Proe 5 Proe hy/ hy/ /- - 3 6 Neo β-tin d Reltive Protein level (% ) 15 1 5 hy/ /- Reltive Gene Expr. (% ) 15 1 5 hy/ /- Supplementry Figure 1 Chrteriztion
Neural population coding of sound level adapts to stimulus statistics
 COMPUTATION AND SYSTEMS 25 Nture Pulishing Group http://www.nture.om/ntureneurosiene Neurl popultion oding of sound level dpts to stimulus sttistis Isel Den 1, Niol S Hrper 1,2 & Dvid MAlpine 1 Mmmls n
COMPUTATION AND SYSTEMS 25 Nture Pulishing Group http://www.nture.om/ntureneurosiene Neurl popultion oding of sound level dpts to stimulus sttistis Isel Den 1, Niol S Hrper 1,2 & Dvid MAlpine 1 Mmmls n
Imaging analysis of clock neurons reveals light buffers the wake-promoting effect of dopamine
 Imging nlysis of lok neurons revels light uffers the wke-promoting effet of dopmine Yuhu Shng 1,2, Pul Hynes 2, Niolás Pírez 2, Kyle I Hrrington 3, Fng Guo 1,2, Jordn Pollk 3, Pengyu Hong 3, Leslie C Griffith
Imging nlysis of lok neurons revels light uffers the wke-promoting effet of dopmine Yuhu Shng 1,2, Pul Hynes 2, Niolás Pírez 2, Kyle I Hrrington 3, Fng Guo 1,2, Jordn Pollk 3, Pengyu Hong 3, Leslie C Griffith
Hippocampal CA1 pyramidal cells form functionally distinct sublayers
 r t i l e s Hippompl CA pyrmidl ells form funtionlly distint sulyers Kenji Mizuseki, Kmrn Di,2, Ev Pstlkov,2 & György Buzsáki 2 Nture Ameri, In. All rights reserved. Hippompl CA pyrmidl neurons hve frequently
r t i l e s Hippompl CA pyrmidl ells form funtionlly distint sulyers Kenji Mizuseki, Kmrn Di,2, Ev Pstlkov,2 & György Buzsáki 2 Nture Ameri, In. All rights reserved. Hippompl CA pyrmidl neurons hve frequently
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi: 1.138/nture862 humn hr. 21q MRPL39 murine Chr.16 Mrpl39 Dyrk1A Runx1 murine Chr. 17 ZNF295 Ets2 Znf295 murine Chr. 1 COL18A1 -/- lot: nti-dscr1 IgG hevy hin DSCR1 DSCR1 expression reltive to hevy
doi: 1.138/nture862 humn hr. 21q MRPL39 murine Chr.16 Mrpl39 Dyrk1A Runx1 murine Chr. 17 ZNF295 Ets2 Znf295 murine Chr. 1 COL18A1 -/- lot: nti-dscr1 IgG hevy hin DSCR1 DSCR1 expression reltive to hevy
Hydrogen sulfide-induced inhibition of L-type Ca 2+ channels and insulin secretion in mouse pancreatic beta cells
 Dietologi (213) 56:533 541 DOI 1.17/s125-12-286-8 ARTICLE Hydrogen sulfide-indued inhiition of L-type C 2 hnnels nd insulin seretion in mouse pnreti et ells G. Tng & L. Zhng & G. Yng & L. Wu & R. Wng Reeived:
Dietologi (213) 56:533 541 DOI 1.17/s125-12-286-8 ARTICLE Hydrogen sulfide-indued inhiition of L-type C 2 hnnels nd insulin seretion in mouse pnreti et ells G. Tng & L. Zhng & G. Yng & L. Wu & R. Wng Reeived:
Poultry No The replacement value of betaine for DL-methionine and Choline in broiler diets
 Poultry No. 1573 The replement vlue of etine for DL-methionine nd Choline in roiler diets Key Informtion In roiler diets defiient in sulfur mino ids ut dequtely supplemented with methyl groups vi dded
Poultry No. 1573 The replement vlue of etine for DL-methionine nd Choline in roiler diets Key Informtion In roiler diets defiient in sulfur mino ids ut dequtely supplemented with methyl groups vi dded
Efficient sensory cortical coding optimizes pursuit eye movements
 ARTICE Reeived Mr 26 Aepted 29 Jul 26 Pulished 9 Sep 26 Effiient sensory ortil oding optimizes pursuit eye movements Bing iu, Mtthew V. Mellio & eslie C. Osorne,2 DOI:.38/nomms2759 OPEN In the nturl world,
ARTICE Reeived Mr 26 Aepted 29 Jul 26 Pulished 9 Sep 26 Effiient sensory ortil oding optimizes pursuit eye movements Bing iu, Mtthew V. Mellio & eslie C. Osorne,2 DOI:.38/nomms2759 OPEN In the nturl world,
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementry Figure 1 c d Wistr SHR Wistr AF-353 SHR AF-353 n = 6 n = 6 n = 28 n = 3 n = 12 n = 12 Supplementry Figure 1 Neurophysiologicl properties of petrosl chemoreceptive neurones in Wistr nd SH rts.
Supplementry Figure 1 c d Wistr SHR Wistr AF-353 SHR AF-353 n = 6 n = 6 n = 28 n = 3 n = 12 n = 12 Supplementry Figure 1 Neurophysiologicl properties of petrosl chemoreceptive neurones in Wistr nd SH rts.
Chapter 7. Control and Coordination
 Chpter 7 Control n Coorintion 1 Whih of the following sttements is orret out reeptors? Gusttory reeptors etet tste while olftory reeptors etet smell Both gusttory n olftory reeptors etet smell Auitory
Chpter 7 Control n Coorintion 1 Whih of the following sttements is orret out reeptors? Gusttory reeptors etet tste while olftory reeptors etet smell Both gusttory n olftory reeptors etet smell Auitory
Control of timing, rate and bursts of hippocampal place cells by dendritic and somatic inhibition
 Control of timing, rte nd ursts of hippompl ple ells y dendriti nd somti inhiition Séstien Royer,2, Boris V Zemelmn,5, Attil Losonzy,3, Jinhyun Kim,2, Frnes Chne, Jeffrey C Mgee & György Buzsáki,4 22 Nture
Control of timing, rte nd ursts of hippompl ple ells y dendriti nd somti inhiition Séstien Royer,2, Boris V Zemelmn,5, Attil Losonzy,3, Jinhyun Kim,2, Frnes Chne, Jeffrey C Mgee & György Buzsáki,4 22 Nture
Corollary discharge circuits for saccadic modulation of the pigeon visual system
 28 Nture Pulishing Group http://www.nture.om/ntureneurosiene Corollry dishrge iruits for sdi modultion of the pigeon visul system Yn Yng 1, Peng Co 1,2, Yng Yng 1,2 & Shu-Rong Wng 1 A sdi eye movement
28 Nture Pulishing Group http://www.nture.om/ntureneurosiene Corollry dishrge iruits for sdi modultion of the pigeon visul system Yn Yng 1, Peng Co 1,2, Yng Yng 1,2 & Shu-Rong Wng 1 A sdi eye movement
Whangarei District Council Class 4 Gambling Venue Policy
 Whngrei Distrit Counil Clss 4 Gmling Venue Poliy April 2013 Whngrei Distrit Counil Clss 4 Gmling Venue Poliy Tle of ontents Introdution... 3 1 Ojetives of the poliy in so fr s promoted y the Gmling At
Whngrei Distrit Counil Clss 4 Gmling Venue Poliy April 2013 Whngrei Distrit Counil Clss 4 Gmling Venue Poliy Tle of ontents Introdution... 3 1 Ojetives of the poliy in so fr s promoted y the Gmling At
Chloride Nutrition Regulates Water Balance in Plants
 XII Portuguese-Spnish Symposium on Plnt Wter Reltions Chloride Nutrition Regultes Wter Blne in Plnts Frno-Nvrro JD 1, Brumós J, Rosles MA 1, Vázquez-Rodríguez A 1, Sñudo BJ 1, Díz- Rued P 1, Rivero C 1,
XII Portuguese-Spnish Symposium on Plnt Wter Reltions Chloride Nutrition Regultes Wter Blne in Plnts Frno-Nvrro JD 1, Brumós J, Rosles MA 1, Vázquez-Rodríguez A 1, Sñudo BJ 1, Díz- Rued P 1, Rivero C 1,
Change detection by thalamic reticular neurons
 Chnge detetion y thlmi retiulr neurons Xiong-Jie Yu 1,2, Xin-Xiu Xu 1, Shigng He 1 & Jufng He 1,2 The thlmi retiulr nuleus (TRN) is thought to funtion in the ttentionl serhlight. We nlyzed the detetion
Chnge detetion y thlmi retiulr neurons Xiong-Jie Yu 1,2, Xin-Xiu Xu 1, Shigng He 1 & Jufng He 1,2 The thlmi retiulr nuleus (TRN) is thought to funtion in the ttentionl serhlight. We nlyzed the detetion
CONCENTATION OF MINERAL ELEMENTS IN CALLUS TISSUE CULTURE OF SOME SUNFLOWER INBRED LINES
 CONCENTATION OF MINERAL ELEMENTS IN CALLUS TISSUE CULTURE OF SOME SUNFLOWER INBRED LINES M. Sri 1, Drgn Vsi, Lj. Vsiljevi, D. Skori, Snezn Mezei nd Sloodnk Pjevi 2 ABSTRACT Conentrtion of minerl elements
CONCENTATION OF MINERAL ELEMENTS IN CALLUS TISSUE CULTURE OF SOME SUNFLOWER INBRED LINES M. Sri 1, Drgn Vsi, Lj. Vsiljevi, D. Skori, Snezn Mezei nd Sloodnk Pjevi 2 ABSTRACT Conentrtion of minerl elements
Neuronal circuitry mechanism regulating adult quiescent neural stem-cell fate decision NO pa. 10 s ETMD
 doi:1.138/nture1136 Neuronl iruitry mehnism regulting dult quiesent neurl stem-ell fte deision Jun Song 1,2, Chun Zhong 1,2, Mihel A. Bonguidi 1,2, Gerld J. Sun 1,3, Derek Hsu 1, Yn Gu 4, Konstntinos Meletis
doi:1.138/nture1136 Neuronl iruitry mehnism regulting dult quiesent neurl stem-ell fte deision Jun Song 1,2, Chun Zhong 1,2, Mihel A. Bonguidi 1,2, Gerld J. Sun 1,3, Derek Hsu 1, Yn Gu 4, Konstntinos Meletis
Olfactory behavior and physiology are disrupted in prion protein knockout mice
 Olftory ehvior nd physiology re disrupted in prion protein knokout mie Clire E Le Pihon 1, Mtthew T Vlley 1, Mgdlini Polymenidou 2,3, Alexnder T Chesler 1, Botir T Sgdullev 1,3, Adrino Aguzzi 2 & Sturt
Olftory ehvior nd physiology re disrupted in prion protein knokout mie Clire E Le Pihon 1, Mtthew T Vlley 1, Mgdlini Polymenidou 2,3, Alexnder T Chesler 1, Botir T Sgdullev 1,3, Adrino Aguzzi 2 & Sturt
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 { OI: 1.138/n31 Srifie n nlyze APs on week 1 s of iet 1 4 6 High-ft iet BrU High-ft iet BrU 4 High-ft iet BrU 6 High-ft iet BrU Lin - Lin - : C34 + : C9 + 1 1 3 1 4 1 5 C45 1 C34 1 1 1 1 3 1 4 1 5 S-1
{ OI: 1.138/n31 Srifie n nlyze APs on week 1 s of iet 1 4 6 High-ft iet BrU High-ft iet BrU 4 High-ft iet BrU 6 High-ft iet BrU Lin - Lin - : C34 + : C9 + 1 1 3 1 4 1 5 C45 1 C34 1 1 1 1 3 1 4 1 5 S-1
Tonic excitation or inhibition is set by GABA A conductance in hippocampal interneurons
 Reeive Apr Aepte 8 Jun Pulishe Jul DOI:.8/nomms77 Toni exittion or inhiition is set y GABA A onutne in hippompl interneurons Inseon Song, Leoni Svthenko & Alexey Semynov Inhiition is physiologil proess
Reeive Apr Aepte 8 Jun Pulishe Jul DOI:.8/nomms77 Toni exittion or inhiition is set y GABA A onutne in hippompl interneurons Inseon Song, Leoni Svthenko & Alexey Semynov Inhiition is physiologil proess
RESEARCH ARTICLE. Supplemental Figure 5
 11.5 2 2 11. RESEARCH ARTICLE RBC ( 1 12 /L) 1.5 1. 9.5 PLT ( 1 9 /L) 1 16 14 HGB (g/l) 19 1 17 16 9. 12 4 4 46 Cellulr & Moleulr Immunology dvne online pulition, PCV (%) 44 MCV (fl) 46 44 ; doi:1.13/mi.214.16
11.5 2 2 11. RESEARCH ARTICLE RBC ( 1 12 /L) 1.5 1. 9.5 PLT ( 1 9 /L) 1 16 14 HGB (g/l) 19 1 17 16 9. 12 4 4 46 Cellulr & Moleulr Immunology dvne online pulition, PCV (%) 44 MCV (fl) 46 44 ; doi:1.13/mi.214.16
A maternal junk food diet in pregnancy and lactation promotes an exacerbated taste for junk food and a greater propensity for obesity in rat offspring
 British Journl of Nutrition (27), pge 1 of 9 q The uthors 27 doi: 1.117/S7114781237 mternl junk food diet in pregnny nd lttion promotes n exerted tste for junk food nd greter propensity for oesity in rt
British Journl of Nutrition (27), pge 1 of 9 q The uthors 27 doi: 1.117/S7114781237 mternl junk food diet in pregnny nd lttion promotes n exerted tste for junk food nd greter propensity for oesity in rt
Changing Views of the Role of Superior Colliculus in the Control of Gaze
 Chnging Views of the Role of Superior Colliulus in the Control of Gze Neerj J. Gndhi 1 nd Dvid L. Sprks 2 1 Deprtment of Otolryngology, University of Pittsurgh, Pittsurgh, PA 15213 USA 2 Division of Neurosiene,
Chnging Views of the Role of Superior Colliulus in the Control of Gze Neerj J. Gndhi 1 nd Dvid L. Sprks 2 1 Deprtment of Otolryngology, University of Pittsurgh, Pittsurgh, PA 15213 USA 2 Division of Neurosiene,
Enrichment induces structural changes and recovery from nonspatial memory deficits in CA1 NMDAR1-knockout mice
 rtiles Enrihment indues struturl hnges nd reovery from nonsptil memory defiits in CA1 NMDAR1-knokout mie Clire Rmpon, Y-Ping Tng, Joe Goodhouse, Eiji Shimizu, Mureen Kyin nd Joe Z. Tsien Deprtment of Moleulr
rtiles Enrihment indues struturl hnges nd reovery from nonsptil memory defiits in CA1 NMDAR1-knokout mie Clire Rmpon, Y-Ping Tng, Joe Goodhouse, Eiji Shimizu, Mureen Kyin nd Joe Z. Tsien Deprtment of Moleulr
single smooth muscle cells from guinea-pig and rabbit jejunum
 BrRish Journl of Phrmology (1995) 114. 16571665 B 1995 Stokton Press All rights reserved 71188/95 $12. Effet of UK84149 on voltgetivted lium urrents of single smooth musle ells from guinepig nd rbbit jejunum
BrRish Journl of Phrmology (1995) 114. 16571665 B 1995 Stokton Press All rights reserved 71188/95 $12. Effet of UK84149 on voltgetivted lium urrents of single smooth musle ells from guinepig nd rbbit jejunum
Other Uses for Cluster Sampling
 Other Uses for Cluster Smpling Mesure hnges in the level of n ttriute Hypothesis testing versus intervl estimtion Type I n 2 errors Power of the test Mesuring ttriute t sme time in ifferent sites Exmple:
Other Uses for Cluster Smpling Mesure hnges in the level of n ttriute Hypothesis testing versus intervl estimtion Type I n 2 errors Power of the test Mesuring ttriute t sme time in ifferent sites Exmple:
Cortical interference effects in the cocktail party problem
 7 Nture Pulishing Group http://www.nture.om/ntureneurosiene Cortil interferene effets in the oktil prty prolem Rjiv Nryn 1,, Virgini Best 1,3, Erol Ozmerl 1,3, Elizeth MCline 1,, Mihel Dent, Brr Shinn-Cunninghm
7 Nture Pulishing Group http://www.nture.om/ntureneurosiene Cortil interferene effets in the oktil prty prolem Rjiv Nryn 1,, Virgini Best 1,3, Erol Ozmerl 1,3, Elizeth MCline 1,, Mihel Dent, Brr Shinn-Cunninghm
Bistability of cerebellar Purkinje cells modulated by sensory stimulation
 25 Nture Pulishing Group http://www.nture.om/ntureneurosiene Bistility of ereellr Purkinje ells moulte y sensory stimultion Yontn Loewenstein 1 3,6, Séverine Mhon 4,6, Pul Cherton 4, Kzuo Kitmur 4, Him
25 Nture Pulishing Group http://www.nture.om/ntureneurosiene Bistility of ereellr Purkinje ells moulte y sensory stimultion Yontn Loewenstein 1 3,6, Séverine Mhon 4,6, Pul Cherton 4, Kzuo Kitmur 4, Him
Supplementary Figure S1
 Supplementry Figure S1 - UTR m - 3HA - 2-1 hgh - 1 Uiquitin *! *! lk distl promoter m K3R/ K121R-3HA UTR hgh founder lines - HA - - founder lines TG- E1 L A2 B1 F9 G6 H4 H6 B C D2 G1 H3 J2 L - 7 IP: lk
Supplementry Figure S1 - UTR m - 3HA - 2-1 hgh - 1 Uiquitin *! *! lk distl promoter m K3R/ K121R-3HA UTR hgh founder lines - HA - - founder lines TG- E1 L A2 B1 F9 G6 H4 H6 B C D2 G1 H3 J2 L - 7 IP: lk
Tbp. Per Relative mrna levels Circadian Time. Liver weight/ body weight (%) n.s. Pernull
 Liver weight/ ody weight (%) Dy Body weight (g) Reltive mrna levels Reltive mrna levels Reltive mrna levels Reltive mrna levels Dy Per1 Per2 Per3 Tp 8 2 8 2. 6 2 8 12162 Cirdin Time 3 2 1 2 1 1 8 12162
Liver weight/ ody weight (%) Dy Body weight (g) Reltive mrna levels Reltive mrna levels Reltive mrna levels Reltive mrna levels Dy Per1 Per2 Per3 Tp 8 2 8 2. 6 2 8 12162 Cirdin Time 3 2 1 2 1 1 8 12162
Reward expectation differentially modulates attentional behavior and activity in visual area V4
 Rewrd expettion differentilly modultes ttentionl ehvior nd tivity in visul re V4 Jll K Bruni 1,6, Brin Lu 1,5,6 & C Dniel Slzmn 1 4 npg 215 Nture Ameri, In. All rights reserved. Neurl tivity in visul re
Rewrd expettion differentilly modultes ttentionl ehvior nd tivity in visul re V4 Jll K Bruni 1,6, Brin Lu 1,5,6 & C Dniel Slzmn 1 4 npg 215 Nture Ameri, In. All rights reserved. Neurl tivity in visul re
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:.8/nture89 4 4 Ilr -/- Ilr -/- Ilr -/- Cspse- -/- As -/- Nlrp -/- Il8 -/- Ilr -/- Supplementl figure. Inresed severity of NASH in inflmmsome-defiient mie, ut not in Ilr-defiient
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:.8/nture89 4 4 Ilr -/- Ilr -/- Ilr -/- Cspse- -/- As -/- Nlrp -/- Il8 -/- Ilr -/- Supplementl figure. Inresed severity of NASH in inflmmsome-defiient mie, ut not in Ilr-defiient
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION CD169 + MACROPHAGES PRESENT LIPID ANTIGENS TO MEDIATE EARLY ACTIVATION OF INVARIANT NKT CELLS IN LYMPH NODES Ptrii Brrl, Polo Polzell, Andres Brukuer, Nio vn Rooijen, Gurdyl S.
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION CD169 + MACROPHAGES PRESENT LIPID ANTIGENS TO MEDIATE EARLY ACTIVATION OF INVARIANT NKT CELLS IN LYMPH NODES Ptrii Brrl, Polo Polzell, Andres Brukuer, Nio vn Rooijen, Gurdyl S.
Macmillan Publishers Limited. All rights reserved
 Vol 45 5 Mrh 9 doi:1.13/nture7615 LETTERS Sleep nd sensorimotor integrtion during erly vol lerning in songird Sylvn S. Shnk 1 & Dniel Mrgolish 1, Behviourl studies widely implite sleep in memory onsolidtion
Vol 45 5 Mrh 9 doi:1.13/nture7615 LETTERS Sleep nd sensorimotor integrtion during erly vol lerning in songird Sylvn S. Shnk 1 & Dniel Mrgolish 1, Behviourl studies widely implite sleep in memory onsolidtion
The Role of Background Statistics in Face Adaptation
 The Journl of Neurosiene, Septemer 3, 29 29(39):235 244 235 Behviorl/Systems/Cognitive The Role of Bkground Sttistis in Fe Adpttion Jinhu Wu, * Hong Xu, * Peter Dyn, 2 nd Ning Qin Deprtments of Neurosiene
The Journl of Neurosiene, Septemer 3, 29 29(39):235 244 235 Behviorl/Systems/Cognitive The Role of Bkground Sttistis in Fe Adpttion Jinhu Wu, * Hong Xu, * Peter Dyn, 2 nd Ning Qin Deprtments of Neurosiene
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Prentl doi:.8/nture57 Figure S HPMECs LM Cells Cell lines VEGF (ng/ml) Prentl 7. +/-. LM 7. +/-.99 LM 7. +/-.99 Fold COX induction 5 VEGF: - + + + Bevcizum: - - 5 (µg/ml) Reltive MMP LM mock COX MMP LM+
Prentl doi:.8/nture57 Figure S HPMECs LM Cells Cell lines VEGF (ng/ml) Prentl 7. +/-. LM 7. +/-.99 LM 7. +/-.99 Fold COX induction 5 VEGF: - + + + Bevcizum: - - 5 (µg/ml) Reltive MMP LM mock COX MMP LM+
Changes in CMDP and DPOAE during acute increased inner ear pressure in the guinea pig
 Eur Arh Otorhinolryngol (2008) 265:287 292 DOI 10.1007/s00405-007-0442-6 OTOLOGY Chnges in CMDP nd DPOAE during ute inresed inner er pressure in the guine pig W. L. Vlk Æ H. P. Wit Æ F. W. J. Alers Reeived:
Eur Arh Otorhinolryngol (2008) 265:287 292 DOI 10.1007/s00405-007-0442-6 OTOLOGY Chnges in CMDP nd DPOAE during ute inresed inner er pressure in the guine pig W. L. Vlk Æ H. P. Wit Æ F. W. J. Alers Reeived:
Neural antecedents of self-initiated actions in secondary motor cortex
 Neurl nteedents of self-initited tions in seondry motor ortex Msyoshi Murkmi, M Inês Viente, Gil M Cost & Zhry F Minen npg Nture Ameri, In. All rights reserved. The neurl origins of spontneous or self-initited
Neurl nteedents of self-initited tions in seondry motor ortex Msyoshi Murkmi, M Inês Viente, Gil M Cost & Zhry F Minen npg Nture Ameri, In. All rights reserved. The neurl origins of spontneous or self-initited
The microrna mir-31 inhibits CD8 + T cell function in chronic viral infection
 A rt i l e s The mirorna mir-3 inhiits CD8 + T ell funtion in hroni virl infetion Howell F Moffett, Adm N R Crtwright, Hye-Jung Kim, Jernej Gode, Json Pyrdol, Trmo Äijö 3, Gustvo J Mrtinez,6, Anjn Ro,
A rt i l e s The mirorna mir-3 inhiits CD8 + T ell funtion in hroni virl infetion Howell F Moffett, Adm N R Crtwright, Hye-Jung Kim, Jernej Gode, Json Pyrdol, Trmo Äijö 3, Gustvo J Mrtinez,6, Anjn Ro,
Interplay of LRRK2 with chaperone-mediated autophagy
 Interply of with hperone-medited utophgy Smnth J Orenstein,, Sheng-Hn Kuo,, Inmuld Tsset,,, Espernz Aris,, Hiroshi Kog,, Irene Fernndez-Crs, Etty Cortes,5, Lwrene S Honig,5, Willim Duer 6, Antonell Consiglio,7,
Interply of with hperone-medited utophgy Smnth J Orenstein,, Sheng-Hn Kuo,, Inmuld Tsset,,, Espernz Aris,, Hiroshi Kog,, Irene Fernndez-Crs, Etty Cortes,5, Lwrene S Honig,5, Willim Duer 6, Antonell Consiglio,7,
Minimum effective dose of chenic acid for gallstone patients: reduction with bedtime administration and
 Gut, 1982, 23, 28-284 Minimum effetive dose of heni id for gllstone ptients: redution with bedtime dministrtion nd low holesterol diet D P MUDGL, R M KUPFER, ND T C NORTHFIELD* From the Normn Tnner Gstroenterology
Gut, 1982, 23, 28-284 Minimum effetive dose of heni id for gllstone ptients: redution with bedtime dministrtion nd low holesterol diet D P MUDGL, R M KUPFER, ND T C NORTHFIELD* From the Normn Tnner Gstroenterology
EFFECTS OF AN ACUTE ENTERIC DISEASE CHALLENGE ON IGF-1 AND IGFBP-3 GENE EXPRESSION IN PORCINE SKELETAL MUSCLE
 Swine Dy 22 Contents EFFECTS OF AN ACUTE ENTERIC DISEASE CHALLENGE ON IGF-1 AND IGFBP-3 GENE EXPRESSION IN PORCINE SKELETAL MUSCLE B. J. Johnson, J. P. Kyser, J. D. Dunn, A. T. Wyln, S. S. Dritz 1, J.
Swine Dy 22 Contents EFFECTS OF AN ACUTE ENTERIC DISEASE CHALLENGE ON IGF-1 AND IGFBP-3 GENE EXPRESSION IN PORCINE SKELETAL MUSCLE B. J. Johnson, J. P. Kyser, J. D. Dunn, A. T. Wyln, S. S. Dritz 1, J.
Endogenous nicotinic cholinergic activity regulates dopamine release in the striatum
 Endogenous niotini holinergi tivity regultes dopmine relese in the stritum Fu-Ming Zhou, Yong Ling nd John A. Dni Division of Neurosiene, Bylor College of Mediine, Houston, Texs 77030-3498, USA Correspondene
Endogenous niotini holinergi tivity regultes dopmine relese in the stritum Fu-Ming Zhou, Yong Ling nd John A. Dni Division of Neurosiene, Bylor College of Mediine, Houston, Texs 77030-3498, USA Correspondene
(% of adherent cells) *** PBL firm adhesion. Frequency (% ) 4 1 L 2 CXCR3 DP-2
 Chemotxis (% of dded ells) PBL totl dhesion (N ells/mm 2 /1.1 6 PBL) Frequeny (% ) PBL firm dhesion Supplementry Figure 1 4 4 3 3 2 2 1.1-4 1-3 1.1.2. 1 1 8 6 4 2 Adiponetin ( g/ml) - + Adiponetin ( g/ml)
Chemotxis (% of dded ells) PBL totl dhesion (N ells/mm 2 /1.1 6 PBL) Frequeny (% ) PBL firm dhesion Supplementry Figure 1 4 4 3 3 2 2 1.1-4 1-3 1.1.2. 1 1 8 6 4 2 Adiponetin ( g/ml) - + Adiponetin ( g/ml)
Learned spatiotemporal sequence recognition and prediction in primary visual cortex
 Supplementary Materials for Learned spatiotemporal sequene reognition and predition in primary visual ortex Jeffrey P. Gavornik and Mark F. Bear Howard Hughes Medial Institute Piower Institute for Learning
Supplementary Materials for Learned spatiotemporal sequene reognition and predition in primary visual ortex Jeffrey P. Gavornik and Mark F. Bear Howard Hughes Medial Institute Piower Institute for Learning
REVIEW Study of the Formation of trans Fatty Acids in Model Oils (triacylglycerols) and Edible Oils during the Heating Process
 JARQ 46 (3), 215 220 (2012) http://www.jirs.ffr.go.jp REVIEW Study of the Formtion of trns Ftty Aids in Model Oils (triylglyerols) nd Edible Oils during the Heting Proess Wkko TSUZUKI* Food Resoure Division,
JARQ 46 (3), 215 220 (2012) http://www.jirs.ffr.go.jp REVIEW Study of the Formtion of trns Ftty Aids in Model Oils (triylglyerols) nd Edible Oils during the Heting Proess Wkko TSUZUKI* Food Resoure Division,
BDNF release from single cells elicits local dendritic growth in nearby neurons
 BDNF relese from single ells eliits lol enriti growth in nery neurons Hley Wilson Horh 1,2 n Lwrene C. Ktz 1 1 Howr Hughes Meil Institute, Deprtment of Neuroiology, Duke University Meil Center, Box 3209,
BDNF relese from single ells eliits lol enriti growth in nery neurons Hley Wilson Horh 1,2 n Lwrene C. Ktz 1 1 Howr Hughes Meil Institute, Deprtment of Neuroiology, Duke University Meil Center, Box 3209,
Toxicity effects of seven Cu compounds/nps in Lettuce (Lactuca sativa) and Alfalfa (Medicago sativa)
 Toxiity effets of seven Cu ompounds/nps in Lettue (Ltu stiv) nd Alflf (Medigo stiv) Jie Hong, Lijun Zho, Cyren Rio, Jose R Perlt-Vide, Jorge Grde-Torresdey The University of Texs t El Pso UC-CEIN Theme
Toxiity effets of seven Cu ompounds/nps in Lettue (Ltu stiv) nd Alflf (Medigo stiv) Jie Hong, Lijun Zho, Cyren Rio, Jose R Perlt-Vide, Jorge Grde-Torresdey The University of Texs t El Pso UC-CEIN Theme
Not for Citation or Publication Without Consent of the Author
 Not for Cittion or Puliction Without Consent of the Author AN AUTOMATED SEX PHEROMONE TRAP FOR MONITORING ADULT CM AND OFM AND THE INFLUENCE OF TRAP COLOR ON MOTH AND NON-TARGET CAPTURES Brin L. Lehmn
Not for Cittion or Puliction Without Consent of the Author AN AUTOMATED SEX PHEROMONE TRAP FOR MONITORING ADULT CM AND OFM AND THE INFLUENCE OF TRAP COLOR ON MOTH AND NON-TARGET CAPTURES Brin L. Lehmn
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:.8/nture98 : hr NEMO :5 hr IKK IKK NF-κB p65 p5 p65/-rel NF-κB p65 p5 p65/-rel Cytoplsm Cytoplsm p65/p5 Nuleus Nuleus NEMO IKK IKK d : hr > : hr p65/-rel NF- p65 p5 Cytoplsm Cytoplsm p65/p5 p65/-rel
doi:.8/nture98 : hr NEMO :5 hr IKK IKK NF-κB p65 p5 p65/-rel NF-κB p65 p5 p65/-rel Cytoplsm Cytoplsm p65/p5 Nuleus Nuleus NEMO IKK IKK d : hr > : hr p65/-rel NF- p65 p5 Cytoplsm Cytoplsm p65/p5 p65/-rel
Supplementary Information
 Supplementry Informtion A new lss of plnt lipid is essentil for protetion ginst phosphorus depletion Yozo Okzki 1, Hitomi Otsuki 1, Tomoko Nrisw 1, Mkoto Koyshi 1, Storu Swi 2, Yukiko Kmide 1, Miyko Kusno
Supplementry Informtion A new lss of plnt lipid is essentil for protetion ginst phosphorus depletion Yozo Okzki 1, Hitomi Otsuki 1, Tomoko Nrisw 1, Mkoto Koyshi 1, Storu Swi 2, Yukiko Kmide 1, Miyko Kusno
Cos7 (3TP) (K): TGFβ1(h): (K)
 IP#2: IP#1: Totl Lystes luiferse tivity (K): 6-4 - (K): luiferse tivity luiferse tivity (K): 2 1 RL-: - + + + + + Sm4-3F: + - + + + + MYC-Sm3: - - - - + + TβRI-HA(T204D): - - - + - + α-ha Luiferse Ativity
IP#2: IP#1: Totl Lystes luiferse tivity (K): 6-4 - (K): luiferse tivity luiferse tivity (K): 2 1 RL-: - + + + + + Sm4-3F: + - + + + + MYC-Sm3: - - - - + + TβRI-HA(T204D): - - - + - + α-ha Luiferse Ativity
Introduction to Study Designs II
 Introdution to Study Designs II Commonly used study designs in publi helth & epidemiologi reserh Benjmin Rihrd H. Muthmbi, DrPH, MPH Stte HIV Epidemiologist HIV Epidemiology Investigtion Setion PA Deprtment
Introdution to Study Designs II Commonly used study designs in publi helth & epidemiologi reserh Benjmin Rihrd H. Muthmbi, DrPH, MPH Stte HIV Epidemiologist HIV Epidemiology Investigtion Setion PA Deprtment
Neural basis and recovery of spatial attention deficits in spatial neglect
 25 Nture Pulishing Group http://www.nture.om/ntureneurosiene Neurl sis nd reovery of sptil ttention defiits in sptil neglet Murizio Corett 1 4, Mihelle J Kinde 5, Chris Lewis 2, Arhm Z Snyder 1,3 & Ayelet
25 Nture Pulishing Group http://www.nture.om/ntureneurosiene Neurl sis nd reovery of sptil ttention defiits in sptil neglet Murizio Corett 1 4, Mihelle J Kinde 5, Chris Lewis 2, Arhm Z Snyder 1,3 & Ayelet
Once small always small? To what extent morphometric characteristics and postweaning starter regime affect pig lifetime growth performance
 Huting et l. Porine Helth Mngement (2018) 4:21 https://doi.org/10.1186/s40813-018-0098-1 RESEARCH Open Aess One smll lwys smll? To wht extent morphometri hrteristis nd postwening strter regime ffet pig
Huting et l. Porine Helth Mngement (2018) 4:21 https://doi.org/10.1186/s40813-018-0098-1 RESEARCH Open Aess One smll lwys smll? To wht extent morphometri hrteristis nd postwening strter regime ffet pig
Bioactive milk components to secure growth and gut development in preterm pigs ESTER ARÉVALO SUREDA PIGUTNET FA1401 STSM
 Bioctive milk components to secure growth nd gut development in preterm pigs ESTER ARÉVALO SUREDA PIGUTNET FA1401 STSM STSM Pigutnet FA1401 STSM 03/Septemer 30/Novemer/2017 (3 months) Host: Home: Thoms
Bioctive milk components to secure growth nd gut development in preterm pigs ESTER ARÉVALO SUREDA PIGUTNET FA1401 STSM STSM Pigutnet FA1401 STSM 03/Septemer 30/Novemer/2017 (3 months) Host: Home: Thoms
Letter. Autocrine BDNF TrkB signalling within a single dendritic spine
 Letter doi:1.138/nture19766 Autorine BDNF TrkB signlling within single dendriti spine Stephen C. Hrwrd 1, Nthn G. Hedrik 1, Chrles E. Hll 1, Pul Prr-Bueno 2, Teres A. Milner 3,4, Enhui Pn 1, Tl Lviv 2,
Letter doi:1.138/nture19766 Autorine BDNF TrkB signlling within single dendriti spine Stephen C. Hrwrd 1, Nthn G. Hedrik 1, Chrles E. Hll 1, Pul Prr-Bueno 2, Teres A. Milner 3,4, Enhui Pn 1, Tl Lviv 2,
XII. HIV/AIDS. Knowledge about HIV Transmission and Misconceptions about HIV
 XII. HIV/AIDS Knowledge bout HIV Trnsmission nd Misconceptions bout HIV One of the most importnt prerequisites for reducing the rte of HIV infection is ccurte knowledge of how HIV is trnsmitted nd strtegies
XII. HIV/AIDS Knowledge bout HIV Trnsmission nd Misconceptions bout HIV One of the most importnt prerequisites for reducing the rte of HIV infection is ccurte knowledge of how HIV is trnsmitted nd strtegies
SOME MECHANISTIC CONCEPTS IN ELECTROPHILIC ADDITION REACTIONS TO C=C BONDS
 SM MANISTI NPTS IN LTPILI AITIN ATINS T = BNS The = ond is considered to e wek se/nucleophile. The high concentrtion of electron density mkes the pi ond Lewis se, ut in order to donte electrons the pi
SM MANISTI NPTS IN LTPILI AITIN ATINS T = BNS The = ond is considered to e wek se/nucleophile. The high concentrtion of electron density mkes the pi ond Lewis se, ut in order to donte electrons the pi
Supplementary information for: Low bone mass and changes in the osteocyte network in mice lacking autophagy in the osteoblast lineage
 Supplementry informtion for: Low one mss nd chnges in the osteocyte network in mice lcking utophgy in the osteolst linege Mrilin Piemontese, Meld Onl, Jinhu Xiong, Li Hn, Jeff D. Thostenson, Mri Almeid,
Supplementry informtion for: Low one mss nd chnges in the osteocyte network in mice lcking utophgy in the osteolst linege Mrilin Piemontese, Meld Onl, Jinhu Xiong, Li Hn, Jeff D. Thostenson, Mri Almeid,
A thalamic input to the nucleus accumbens mediates opiate dependence
 doi:1.138/nture16954 A thlmi input to the nuleus umens medites opite dependene Yingjie Zhu1, Crl F. R. Wieneke1, Gregory Nhtr1 & Xioke Chen1 1 feed-forwrd inhiition in lol NA iruit. Consistent with this
doi:1.138/nture16954 A thlmi input to the nuleus umens medites opite dependene Yingjie Zhu1, Crl F. R. Wieneke1, Gregory Nhtr1 & Xioke Chen1 1 feed-forwrd inhiition in lol NA iruit. Consistent with this
Inhibitory effect of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase inhibitors on cytokine release from human macrophages
 British Journl of Phrmology (26) 149, 393 44 & 26 Nture Pulishing Group All rights reserved 7 1188/6 $3. www.rjphrmol.org RESEARCH PAPER Inhiitory effet of p38 mitogen-tivted protein kinse inhiitors on
British Journl of Phrmology (26) 149, 393 44 & 26 Nture Pulishing Group All rights reserved 7 1188/6 $3. www.rjphrmol.org RESEARCH PAPER Inhiitory effet of p38 mitogen-tivted protein kinse inhiitors on
Using Paclobutrazol to Suppress Inflorescence Height of Potted Phalaenopsis Orchids
 Using Pcloutrzol to Suppress Inflorescence Height of Potted Phlenopsis Orchids A REPORT SUBMITTED TO FINE AMERICAS Linsey Newton nd Erik Runkle Deprtment of Horticulture Spring 28 Using Pcloutrzol to Suppress
Using Pcloutrzol to Suppress Inflorescence Height of Potted Phlenopsis Orchids A REPORT SUBMITTED TO FINE AMERICAS Linsey Newton nd Erik Runkle Deprtment of Horticulture Spring 28 Using Pcloutrzol to Suppress
AJ PUTT. Hematology. Chemistry. Species: Canine Gender: Female Year of Birth: 2013 Client: PUTT
 Speies: Cnine Gender: Femle Yer of Birth: 2013 Client: PUTT Requisition #: 9034-12 Aession #: W2152816 Aount Code: 72364 Veterinrin: CARTER Pnel/Profile: Tik Pnel Add-on Senior Profile with L 4Dx Plus
Speies: Cnine Gender: Femle Yer of Birth: 2013 Client: PUTT Requisition #: 9034-12 Aession #: W2152816 Aount Code: 72364 Veterinrin: CARTER Pnel/Profile: Tik Pnel Add-on Senior Profile with L 4Dx Plus
Acute and gradual increases in BDNF concentration elicit distinct signaling and functions in neurons
 nd grdul increses in BDNF concentrtion elicit distinct signling nd functions in neurons Yunyun Ji,, Yun Lu, Feng Yng, Wnhu Shen, Tin Tze-Tsng Tng,, Linyin Feng, Shumin Dun, nd Bi Lu,.. - Grdul (normlized
nd grdul increses in BDNF concentrtion elicit distinct signling nd functions in neurons Yunyun Ji,, Yun Lu, Feng Yng, Wnhu Shen, Tin Tze-Tsng Tng,, Linyin Feng, Shumin Dun, nd Bi Lu,.. - Grdul (normlized
Intestine specific MTP deficiency with global ACAT2 gene ablation lowers acute cholesterol absorption with chylomicrons and high density lipoproteins
 Intestine speifi MTP defiieny with glol ACAT2 gene ltion lowers ute holesterol sorption with hylomirons nd high density lipoproteins 1,2 Jhngir Iql, 1,2 Mohmed Boutjdir, 3 Lwrene L. Rudel, 1,2 M. Mhmood
Intestine speifi MTP defiieny with glol ACAT2 gene ltion lowers ute holesterol sorption with hylomirons nd high density lipoproteins 1,2 Jhngir Iql, 1,2 Mohmed Boutjdir, 3 Lwrene L. Rudel, 1,2 M. Mhmood
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
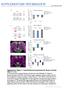 oi:1.138/nture1134 CS+ CS- MCH 3 OCT OCT 3 MCH CS- CS+ OCT MCH 3 MCH OCT 3 OCT vs MCH OCT vs MCH ppetitive memory (PI) A 1-1 Unpire onitioning DDC-GAL4/UAS-Trp UAS-Trp/+ -2 MCH OCT OCT MCH sugr OCT MCH
oi:1.138/nture1134 CS+ CS- MCH 3 OCT OCT 3 MCH CS- CS+ OCT MCH 3 MCH OCT 3 OCT vs MCH OCT vs MCH ppetitive memory (PI) A 1-1 Unpire onitioning DDC-GAL4/UAS-Trp UAS-Trp/+ -2 MCH OCT OCT MCH sugr OCT MCH
THE CARDIOVASCULAR RESPONSES OF THE RED-EARED SLIDER (TRACHEMYS SCRIPTA) ACCLIMATED TO EITHER 22 OR 5 C
 The Journl of Experimentl Biology, 765 744 () Printed in Gret Britin The Compny of Biologists Limited JEB95 765 THE CARDIOVASCULAR RESPONSES OF THE RED-EARED SLIDER (TRACHEMYS SCRIPTA) ACCLIMATED TO EITHER
The Journl of Experimentl Biology, 765 744 () Printed in Gret Britin The Compny of Biologists Limited JEB95 765 THE CARDIOVASCULAR RESPONSES OF THE RED-EARED SLIDER (TRACHEMYS SCRIPTA) ACCLIMATED TO EITHER
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Optial ontrolling reveals time-dependent roles for adult-orn dentate granule ells Yan Gu, Maithe Arruda-Carvalho 3,4, Jia Wang, Stephen Janoshka,, Sheena Josselyn 3-5, Paul Frankland
Supplementary Information Optial ontrolling reveals time-dependent roles for adult-orn dentate granule ells Yan Gu, Maithe Arruda-Carvalho 3,4, Jia Wang, Stephen Janoshka,, Sheena Josselyn 3-5, Paul Frankland
Light at night acutely impairs glucose tolerance in a time-, intensity- and wavelength-dependent manner in rats
 Dietologi (21) :1 1 DOI 1.1/s12-1-22-y ARTILE Light t night utely impirs gluose tolerne in time-, intensity- nd wvelength-dependent mnner in rts Anne-Loes Opperhuizen 1,2 & Dirk J. Stenvers 2, & Remi D.
Dietologi (21) :1 1 DOI 1.1/s12-1-22-y ARTILE Light t night utely impirs gluose tolerne in time-, intensity- nd wvelength-dependent mnner in rts Anne-Loes Opperhuizen 1,2 & Dirk J. Stenvers 2, & Remi D.
Effects of exercise training on hepatic steatosis in high fat diet-induced obese mice
 Effets of exerise trining on hepti stetosis in high ft diet-indued oese mie Hyunsik Kng, PhD Sungkyunkwn University Non-Aloholi Ftty Liver Disese (NAFLD) A reversile ondition tht is hrterized y hepti lipid
Effets of exerise trining on hepti stetosis in high ft diet-indued oese mie Hyunsik Kng, PhD Sungkyunkwn University Non-Aloholi Ftty Liver Disese (NAFLD) A reversile ondition tht is hrterized y hepti lipid
EFFECT OF SOYBEAN CYST NEMATODE ON GROWTH OF DRY BEAN. Research Report to Northarvest Bean Growers, January 19, 2009
 EFFECT OF SOYBEAN CYST NEMATODE ON GROWTH OF DRY BEAN Reserh Report to Northrvest Ben Growers, Jnury 19, 29 Berlin D. Nelson, Susilo Poromrto, n Ruell Goswmi, Dept. Plnt Pthology, NDSU Ojetive: Determine
EFFECT OF SOYBEAN CYST NEMATODE ON GROWTH OF DRY BEAN Reserh Report to Northrvest Ben Growers, Jnury 19, 29 Berlin D. Nelson, Susilo Poromrto, n Ruell Goswmi, Dept. Plnt Pthology, NDSU Ojetive: Determine
static principle: output determined by a connection with strong node dynamic principle: output (sometimes) determined by a weak (floating) node
 stti n ynmi priniple pmos network nmos network v out stti priniple: output etermine y onnetion with strong noe ynmi priniple: output (sometimes) etermine y wek (floting) noe hrging: C s is eing hrge up
stti n ynmi priniple pmos network nmos network v out stti priniple: output etermine y onnetion with strong noe ynmi priniple: output (sometimes) etermine y wek (floting) noe hrging: C s is eing hrge up
Open Access RESEARCH ARTICLE. Genetics Selection Evolution
 DOI 10.1186/s12711-016-0222-0 Genetis Seletion Evolution RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Aess Comprison of host geneti ftors influening pig response to infetion with two North Amerin isoltes of porine reprodutive
DOI 10.1186/s12711-016-0222-0 Genetis Seletion Evolution RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Aess Comprison of host geneti ftors influening pig response to infetion with two North Amerin isoltes of porine reprodutive
Supplementary Figure 1. Schematic illustrating major conclusions of this study.
 ORNs GABA A GABA B glomeruli LN PNs Supplementary Figure 1. Shemati illustrating major onlusions of this study. This study represents the most diret evidene to date of inhiitory interations etween olfatory
ORNs GABA A GABA B glomeruli LN PNs Supplementary Figure 1. Shemati illustrating major onlusions of this study. This study represents the most diret evidene to date of inhiitory interations etween olfatory
TNF-a Downregulates Filaggrin and Loricrin through c-jun N-terminal Kinase: Role for TNF-a Antagonists to Improve Skin Barrier
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE TNF- Downregultes Filggrin nd Loririn through -Jun N-terminl Kinse: Role for TNF- Antgonists to Improve Skin Brrier Byung Eui Kim, Mihel D. Howell,, Emm Guttmn,, Ptrii M. Gilleudeu, Irm
ORIGINAL ARTICLE TNF- Downregultes Filggrin nd Loririn through -Jun N-terminl Kinse: Role for TNF- Antgonists to Improve Skin Brrier Byung Eui Kim, Mihel D. Howell,, Emm Guttmn,, Ptrii M. Gilleudeu, Irm
A p75 NTR and Nogo receptor complex mediates repulsive signaling by myelin-associated glycoprotein
 A p75 NTR nd Nogo reeptor omplex medites repulsive signling y myelin-ssoited glyoprotein Sott T. Wong 1, John R. Henley 1, Kevin C. Knning 2, Kuo-hu Hung 1, Mrk Bothwell 2 nd Mu-ming Poo 1 1 Division of
A p75 NTR nd Nogo reeptor omplex medites repulsive signling y myelin-ssoited glyoprotein Sott T. Wong 1, John R. Henley 1, Kevin C. Knning 2, Kuo-hu Hung 1, Mrk Bothwell 2 nd Mu-ming Poo 1 1 Division of
