Enrichment induces structural changes and recovery from nonspatial memory deficits in CA1 NMDAR1-knockout mice
|
|
|
- Gerard Fletcher
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 rtiles Enrihment indues struturl hnges nd reovery from nonsptil memory defiits in CA1 NMDAR1-knokout mie Clire Rmpon, Y-Ping Tng, Joe Goodhouse, Eiji Shimizu, Mureen Kyin nd Joe Z. Tsien Deprtment of Moleulr Biology, Prineton University, Wshington Rod, Prineton, New Jersey , USA The first two uthors ontriuted eqully to this work. Correspondene should e ddressed to J.Z.T. (jtsien@molio.prineton.edu) We produed CA1-speifi NMDA reeptor 1 suunit-knokout () mie to determine the NMDA reeptor dependene of nonsptil memory formtion nd of experiene-indued struturl plstiity in the CA1 region. mie were profoundly impired in ojet reognition, olftory disrimintion nd ontextul fer memories. Surprisingly, these defiits ould e resued y enrihing experiene. Using stereologil eletron mirosopy, we found tht enrihment indued n inrese of the synpse density in the CA1 region in knokouts s well s ontrol littermtes. Therefore, our dt indite tht CA1 NMDA reeptor tivity is ritil in hippompus-dependent nonsptil memory, ut is not essentil for experiene-indued synpti struturl hnges. Comprtive ntomil studies of hippompl ytorhiteture revel seletive expnsion of the CA1 region in the hippompus in primtes with respet to rodents nd in humns with respet to monkeys, suggesting tht this suregion is importnt in humn hippompl funtion 1. Dmge to the hippompus or the CA1 suregion in humns leds to defiits in memories of people, ojets, ples nd events ( delrtive memory ) 2 4. Similr sptil nd nonsptil memory defiits re lso oserved in vriety of lortory nimls with hippompl lesions 4,5. Reordings of neuronl tivity in the CA1 suregion of rodents during ehviorl tests show the importne of this suregion in the enoding of nonsptil informtion 6. However, the moleulr mehnisms underlying these proesses remin unknown. N-methyl-D-sprtte (NMDA) reeptors re widely distriuted in the rin 7 nd re essentil for the indution of mjor forms of long-term potentition (LTP) nd long-term depression (LTD) 8,9. Enhned NMDA reeptor funtion in the forerin improves lerning nd memory 10, inditing its ruil role in these proesses. Using the Cre/loxP-medited reomintion system, we developed region-speifi gene-knokout tehnique to generte onditionl-knokout mie in whih NMDAR1, key suunit of NMDA reeptor, ws seletively deleted in the CA1 suregion 11. These CA1-speifi NMDAR1 knokout mie lked NMDA-medited urrents nd plstiity in the CA1 region nd were profoundly impired in sptil memory tsks 12,13. In this study, our first gol ws to exmine the role of CA1 NMDA reeptor tivity in the formtion of nonsptil memory nd the effets of enrihed experiene on these memory funtions. Our seond gol ws to exmine whether enrihed experiene during dulthood ould led to struturl hnges in the CA1 region, nd whether CA1 NMDA reeptor-medited responses re required for suh struturl modifitions. Synpti struturl hnges re ssumed to e the ntomil sustrte of long-term storge of lerned experiene 14,15. For exmple, numers of dendriti spines in the hippompus inrese fter sptil lerning in dult rts 16. Bsed on findings of NMDA reeptor funtion in the developing rin 17,18, it is postulted tht NMDA reeptors might e required for ehviorl experiene-indued struturl plstiity in dult rin. However, new dendriti spines n form on mture hippompl neurons in vitro in the sene of synpti tivity 19, nd LTP hs no effet on synpse numer in the CA1 region 20. These findings imply tht the role of the NMDA reeptor in struturl hnges in dult rin might differ from tht in the developing rin. By using unised stereologil eletron mirosopy, we exmined the struturl hnges in our mie efore nd fter enrihed experiene. RESULTS NMDAR1 knokout in the CA1 region We onfirmed the omplete deletion of the NMDAR1 gene in mie using in-situ hyridiztion histohemistry. No NMDAR1 mrna ws deteted in the CA1 suregion (Fig. 1), inditing tht the geneti deletion of NMDAR1 in young dult mie ws heritle fter three yers of reeding nd ws omplete. Nonsptil lerning nd memory defiits nd ontrol mie used in ll ehviorl tests were 2 4 month-old littermtes. We used three hippompus-dependent ehviorl tsks to ssess ssoitive, nonsptil memory funtions. The hippompus is importnt in the formtion of reognition memory in oth humn ptients nd nimls 3 5. However, little is known out its ntomil sis nd its moleulr nd ellulr mehnisms 21. We evluted reognition memory with novelojet reognition-memory tsk 10. During the trining session, the totl mount of time spent exploring two ojets ws ± 3.94 seonds in ontrol mie (n = 17) nd ± 3.56 seonds in CA1- KO mie (n = 12), nd no signifint explortory preferene ws found etween ontrol nd mie (dt not shown). These oservtions indite tht these two types of mie hve the sme levels of motivtion, uriosity, nd interest in exploring novel ojets. 238 nture neurosiene volume 3 no 3 mrh 2000
2 rtiles Fig. 1. Cre/loxP-medited deletion of NR1 gene in mie (2.5 months old) is omplete. An ntisense 42-mer oligonuleotide reognizing the NR1 gene ws used for in situ hyridiztion. CTX, ortex; ST, stritum; DG, dentte gyrus. For retention tests, t 30 minutes, 2 hours nd 24 hours fter the trining (Fig. 2), one ojet ws repled y novel ojet. As expeted, ontrol mie showed signifint preferene for exploring the novel ojet during eh retention test. In ontrst, mie showed only mrginl preferene for the novel ojet (Fig. 2). A self-anova etween trining nd retention tests reveled signifint differene in ontrol mie (F 3,64 = 7.744, p < 0.001) ut not in mie. Repeted mesures of ANOVA on retention tests showed highly signifint differene etween ontrol nd mie (F 2,27 = , p < 0.001). A post-ho nlysis using Dunnett s test demonstrted signifine of this differene in retention t 30 minutes, 2 hours nd 24 hours (p < 0.05, p < 0.01 nd p < 0.01, respetively; Fig. 2). These results indite profound defiits in novel ojet reognition memory in. We then exmined olftory disrimintion memory using soil trnsmission of food preferene 22. Rodents develop preferene for foods they hve reently smelled on the reth of other individuls 23. Lesions restrited to the hippompus impir this kind of memory 24 hours fter soil intertion (trining) 24. However, the moleulr mehnisms underlying this kind of memory remin unknown 22,24. The tsk used here onsisted of three stges. First, nimls eme ustomed to eting from food up pled on the ge floor. Seond, in trining sessions, oserver mie were llowed to intert with demonstrtor mie fed with either innmon-sented (1% per weight) or oo-sented (2% per weight) food. Third, oserver mie were then tested y presenttion of oth sented foods, nd onsumption of eh food ws reorded. mie showed signifintly higher preferene for food smelled during the trining session over unsmelled food thn did mie (F 1,26 = 5.291; Fig. 3), inditing tht olftory-disrimintion memory ws impired in mie. To ensure tht this oservtion ws not due to differene in feeding ehviors, we mesured the totl mount of food tken during the retention session; this quntity did not signifintly differ Fig. 2. Impired novel-ojet reognition memory in mie. Reognition memory is expressed in terms of explortory preferene in the retention tests. The memory for ontrol (n = 17) or (n = 12) mie ws mesured t three different time intervls fter trining. The dt re expressed s men ± s.e.; p < 0.05, p < 0.01, determined y post-ho nlysis. We oserved similr results in seprte groups of nd ontrol mie. etween ontrol nd mie (1.723 ± g versus ± g, respetively). Beuse these two types of sented food were ounterlned throughout the experiments, these results indited tht the defiits oserved in mie were due neither to norml food intke nor to sent is per se. We then exmined nonsptil memory using ontextul feronditioning tsk 10. In this hippompus-dependent tsk 25, nimls lern to fer n environment y ssoiting it with n versive stimulus (foot shok). nd mie signifintly differed in ontextul freezing, ut not in freezing responses immeditely fter the shoks, in retention tests t 2 hours nd 24 hours (p < 0.05, p < 0.01, respetively; Fig. 4), inditing tht mie were impired in ontextul fer memory. However, in ued-onditioning test, whih is hippompus independent 25, freezing responses of mie to tone were similr to those of ontrol mie in retention tests t 2 hours (dt not shown) nd 24 hours (Fig. 4). In ddition, no norml noieptive responses were found in mie: urrent required to eliit flinhing/running, jumping or voliztion in the mie ws the sme s in ontrol mie (dt not shown). These dt lerly showed tht hippompus-dependent, ut not hippompusindependent, fer memory ws impired in mie. Explortory preferene (%) Explortory preferene (%) Trining session 30 min 2 h 24 h Retention intervl nture neurosiene volume 3 no 3 mrh
3 rtiles Fig. 3. Soil trnsmission of food preferene. Olftion-disrimintion memory is expressed in terms of food preferene. () The memory of either ontrol (n = 15) or (n = 13) mie ws mesured 24 h fter trining. () Food onsumption dt re expressed s men ± s.e. p < 0.05 determined y one-wy ANOVA. Enrihment-indued reovery of memory defiits These results indited profound defiit in three forms of nonsptil memory in mie. Enrihed experiene n signifintly improve performne in sptil mze tests in norml nimls 26 nd ttenute memory defiits in nimls with hippompl lesions 27. However, it is not known whether enrihed experiene n enhne performne of the nimls in the three nonsptil memory tsks we used, nor if it is le to resue the memory defiits oserved in mie. To ddress these issues, we evluted nonsptil memory using the sme tsks with dditionl groups of dult nimls fter they were trined dily in n enrihed environment for two months. In the novel-ojet reognition tsk, we oserved n inrese in preferene for exploring novel ojets in oth ontrol nd mie (n = 14; n = 12, respetively; Fig. 5). A self-anova etween trining nd retention tests reveled signifint differenes for ontrol (F 3,52 = , p < 0.001) nd mie (F 3,44 = 3.797, p < 0.05), inditing tht trining in the enrihed-environment not only enhned the performne of norml mie ut lso ttenuted the defiits in mie. An integrted sttistil nlysis of nimls with the sme genotype onfirmed the effets of trining on memory in ontrol mie (F 1,29 = 7.674, p < 0.05) nd in mie (F 1,22 = 6.674, p < 0.05). However, repeted mesures ANOVA on retention tests still reveled highly signifint group differene etween Contextul freezing (%) Cued freezing (%) Immedite freezing Pre-CS CS Totl food onsumption (grms) Food preferene (%) enrihed ontrol nd enrihed mie (F 2,24 = , p < 0.01), inditing tht enrihing experiene ould only prtilly resue the defiits oserved in the mie. In the test of soil trnsmission of food preferene, we found tht enrihed ontrol nimls (n = 15) did not inrese food preferene more thn nive nimls. This possily refleted either eiling effet or delite lne etween hoosing the preferred food nd eting ny food fter 24 hours of food deprivtion. However, food preferene of enrihed mie (n = 12) ws drmtilly inresed over tht of nive nimls (F 1,22 = 4.746, p < 0.05, Fig. 5), inditing tht the enrihed experiene ompletely resued the memory defiits in the mie. We lso oserved tht the enrihment trining signifintly enhned ontextul freezing in ontrol mie (F 1,25 = 7.366, p < 0.05) nd ompletely resued the defiits oserved in the mie (F 1,23 = , p < 0.001). No signifint differene ws found etween enrihed ontrol nd enrihed mie (Fig. 5). In ddition, ued freezing lso drmtilly inresed following enrihed experiene in oth ontrol (F 1,25 = 6.213, p < 0.05) nd mie (F 1,23 = 4.372, p < 0.001; Fig. 5d). These results lerly indite tht the enrihed experiene ould enhne these two kinds of fer memory in ontrol nimls nd ould resue the defiits in mie. Fig. 4. Fer-onditioning tsks. () Contextul fer onditioning. Memory is expressed s perent of freezing responses. Immedite lerning indites the freezing response during the 30 s immeditely fter shok in the trining session. Contextul fer memory in ontrols (n = 14) nd (n = 12) ws mesured 24 h fter trining. () Cued fer onditioning. Memory is expressed s perentge of freezing responses. There ws no signifint differene in proportion of freezing responses either t pre-cs or retention test etween ontrol mie (n = 14) nd the mie (n = 12). All dt re expressed s men ± s.e.; p < 0.01, determined y one-wy ANOVA. Similr results were otined from nother set of experiments. 240 nture neurosiene volume 3 no 3 mrh 2000
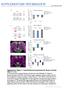
4 rtiles Explortory preferene (%) Food preferene (%) Nive Enrihed Nive Enrihed Enrihment-indued ntomil hnges Wht re the moleulr nd struturl mehnisms underlying the enrihment-indued effets? Enrihed experiene promotes vrious iohemil nd morphologil hnges in severl rin regions 26, Synpti struturl hnges re elieved to e the ntomil sustrte of long-term storge of lerned experiene, nd it is ssumed tht NMDA reeptors re required for experiene-dependent ntomil hnges in the dult rin. As the first step towrd the geneti dissetion of the moleulr mehnisms of experiene-indued struturl plstiity in the dult hippompl CA1 region, we used light nd eletron mirosopy to exmine the effets of enrihment on ntomil hnges in the CA1 region nd the role of the NMDA reeptor in this effet. Nissl-stined tissue of mie shows no gross ntomil normlity 12. We used the Golgi-impregntion tehnique 32 to initilly ssess dendriti strutures. Golgi-impregnted CA1 pyrmidl neurons of ontrol nd nive nimls presented similr dendriti morphology (Fig. 6 nd ). Quntittive nlysis of dendriti-spine density on CA1 pyrmidl ells reveled no signifint differene etween nive ontrol (8.1 ± 0.8 spines per 10 µm of pil dendrite, men ± s.e.) nd nive mie (8.6 ± 0.6 spines; Fig. 6). This suggests tht onditionl knokout of the NMDAR1 gene in the CA1 region, whih ours in the postntl third nd fourth weeks, did not result in norml spine density. To hrterize the effets of enrihment on dendriti spine density, we then ounted the numer of spines on dendrites of Fig. 6. Enrihment-indued inrese in CA1 spine density in oth norml ontrol nd mie. Photomirogrphs of Golgi-impregnted pil dendriti segments of CA1 pyrmidl neurons of nive ontrol () nd nive () mie. () Brs represent stter plot of individul verge numers of dendriti spines per 10 µm length of CA1 pyrmidl dendriti segments. Dimonds represent group mens ± s.e. (n = 3 for eh group). The sexes (M or F) nd ges in months of nimls in eh olumn (from top to ottom) re nive norml ontrol (M, 3.5; M, 4; M, 3.5), enrihed norml ontrol (M, 3.5; M, 5; M, 4.5), nive CA1- KO (M, 4.5; M, 5; M, 4) nd enrihed (M, 5; M, 5; M, 4.5). p < 0.05, Mnn-Whitney U-test. d Cued freezing (%) Contextul freezing (%) Nive Enrihed Nive Enrihed Fig. 5. Effets of enrihed experiene on nonsptil memory in oth ontrol nd mie. () Enrihed experiene inresed explortory preferene in oth ontrol (n = 14) nd (n = 12) mie in the novelojet reognition tsk. () Enrihed experiene resued memory defiits of (n = 12) mie in the soil trnsmission of food preferene. For ontrol mie, n = 15. () Enrihed experiene enhned ontextul freezing response in oth ontrol (n = 13) nd (n = 11) mie in the fer-onditioning tsk. There ws no signifint differene in immedite freezing etween the two groups (dt not shown). (d) Enrihed experiene inresed ued freezing in the fer-onditioning tsk. There ws no signifint differene in pre-cs freezing or ued freezing etween ontrol mie (n = 13) nd (n = 11) mie. All dt re expressed s men ± s.e. p < 0.05, p < 0.01, p < in one-wy ANOVA. CA1 pyrmidl ells of enrihed nimls. We oserved signifintly higher density of dendriti spines in enrihed ontol mie ompred with nive nimls (10.8 ± 1.1 versus 8.1 ± 0.8; p < 0.05; Fig. 6). This is onsistent with previous report of inresed spine density on CA1 neurons in rts fter enrihment 16. Surprisingly, enrihment similrly inresed spine density in mie (10.0 ± 0.3 versus 8.6 ± 0.6; p < 0.05). Sttistil nlysis reveled no signifint differene etween enrihed ontol nd enrihed nimls (Fig. 6). Dendriti spines per 10 µm Nive Enrihed Nive Enrihed nture neurosiene volume 3 no 3 mrh
5 rtiles Fig. 7. Enrihment-indued inrese in CA1 synpse density in oth ontrol nd mie. Representtive eletron photomirogrphs illustrting synpses (indited y rrows) in the strtum rditum of the CA1 region of nive ontrols (), nive mie (), enrihed ontrols () nd enrihed mie (d). Sle rs, 1 µm. (e) Dimonds represent group mens ± s.e. of estimted synpti densities in the strtum rditum of the CA1 region efore nd fter enrihment, lulted with the stereologil disetor. Brs represent stter plot of the CA1 synpti density in individul nimls in eh group. The sexes (M or F) nd ges in months of nimls in eh olumn re (from top to ottom) nive ontrol (M, 4.5; M, 5; M, 4; M, 4; M, 3; M, 3.5; M, 4), enrihed ontrol (M, 4.5; M, 5; M, 5.5; M, 4; M, 5), nive (M, 4; M, 4.5; F, 3.5; M, 4) nd enrihed (M, 3.5; F, 4; M, 4.5; M, 5). p < 0.05, determined y Mnn-Whitney U-test. d These dt indite tht enrihed experiene resulted in hnges in dendriti-spine density nd suggest tht this inrese in spine density n our in the sene of NMDA reeptor tivity. These results re onsistent with the finding tht mture CA1 pyrmidl neurons in vitro n grow spines in sene of NMDA-reeptor tivtion 19. However, Golgi stining should e interpreted utiously. First, this method does not revel spines hidden eneth or sitting ove the dendriti segment, thus, spine density mesured this wy proly underestimtes the tul numer of spines. Seond, some rnhed spine heds reeive no innervtion 33 ; therefore, spine density should not e simply extrpolted to synpse density. To ddress these onerns, we used eletron mirosopy to quntittively nlyze synpse density in the strtum rditum of the CA1 hippompl region (Fig. 7 d). We ensured unised smpling y using the stereologil disetor tehnique 34,35. No signifint differene in synpti density ws oserved etween nive ontrol mie (76.9 ± 1.9 synpses per 100 µm 3, men ± s.e.) nd nive mie (70.0 ± 4.4 synpses, Fig. 7e). However, fter the enrihment trining, ontrol nimls showed signifint inrese of CA1 synpti density (93.8 ± 5.3) over the nive ontrol group (p < 0.05). Synpti density ws lso strikingly higher in trined mie (91.2 ± 2.9) ompred to the nive group (p < 0.01, Fig. 7e). Furthermore, no signifint differene in synpti density ws found etween enrihed ontrol nd enrihed mie. These dt indite tht enrihed experiene promotes synpti struturl hnges in the CA1 hippompl region. Furthermore, these results suggest tht the NMDA reeptor is not required for the inrese of CA1 synpti density. e Synpses per 100 µm 3 Nive Enrihed Nive Enrihed (n = 7) (n = 5) (n = 4) (n = 4) mie To investigte the possile differentil effet of enrihment nd NMDA reeptor tivity on hnges in the density of synpti sutypes, we exmined the distriution of CA1 synpses in three mjor sulsses (non-perforted, perforted nd shft synpses) tegorized ording to the profile of the postsynpti density (PSD) in pirs of seril setions. The PSD ws lssified s non-perforted if the thikening ws ontinuous or s perforted if the PSD ws interrupted y eletron-luent regions (Fig. 8). Synpses with symmetri PSDs on dendriti shfts were identified using Gry s riteri 36 Fig. 8. Mjor sulsses of CA1 synpses in the CA1 region. (, ) Eletron mirogrphs illustrting the ultrstruture of different types of synpses in the strtum rditum of CA1. Sle rs, 0.5 µm. () Non-perforted xospinous synpse (np) nd perforted xospinous synpse (p). () Axodendriti synpses involving dendriti shfts (s). (, d) Estimted distriution of CA1 synpses in the tegories desried ove for ontrol () nd (d) nimls, either nive or rered in n enrihed environment. Synpti densities were lulted per surfe re nd then expressed s the numer of synpses per 100 µm 3 y using the stereologil oeffiient otined with the disetor method. The dt re expressed s men ± s.e.; p < 0.05, Mnn-Whitney U-test. Synpses per 100 µm 3 Synpses per 100 µm 3 Perforted Non-perforted Shft d Nive ontrol Enrihed ontrol Nive Enrihed 242 nture neurosiene volume 3 no 3 mrh 2000
6 rtiles nd were ounted seprtely from those on dendriti spines (Fig. 8). We found signifintly higher density of non-perforted synpses in ontrol mie fter enrihment (77.1 ± 5.2, men ± s.e.) thn in nive ontrol nimls (62.6 ± 2.3, p < 0.05; Fig. 8). Remrkly, enrihment lso signifintly inresed the density of non-perforted synpses in mie (78.3 ± 5.4 versus 60.7 ± 5.1; p < 0.05; Fig. 8d), wheres the densities of perforted nd shft synpses remined unhnged fter enrihment in oth ontrol nd mie. For etter oservtion of the synpti struturl hnges, sophistited pproh using three-dimensionl reonstrution of synpses viewed through seril eletron mirogrphs would e vlule 33. Possile tissue shrinkge during the emedding proess n e ruled out s explntion for these findings. First, the effet is synpse speifi. If there were generlized shrinkge in the enrihed nimls with no other hnge, then ll types of synpses should e ffeted uniformly. Seond, the mitohondril rosssetionl dimeters were uniform ross the nive nd enrihed onditions, showing tht no generlized shrinkge of individul proess ourred (dt not shown). DISCUSSION Here we exmined three kinds of nonsptil memory in mie lking NMDAR1 in the CA1 region. Our nlysis provides evidene supporting the importnt role of NMDA reeptor tivity in the CA1 region for the formtion of hippompus-dependent nonsptil memory. Tking into ount the defiit in sptil lerning in the mie 12, we onlude tht NMDA reeptor tivity in CA1 is essentil for the formtion of oth sptil nd nonsptil memory. More interestingly, we found tht the memory defiits ssoited with the disruption of the hippompl NMDA reeptor ould e resued y dily trining in n enrihed environment. We show tht ehviorl experiene n enhne lerning nd memory in the mutnt nimls. Thus, the memory defiits oserved in genti mutnt nimls re not neessrily irreversile, nd enrihed experiene ould promote reovery of some of the defiits. To investigte further the possile ellulr mehnisms underlying these enrihment effets, we systemtilly evluted the ntomil hnges using light nd eletron mirosopy. We showed tht enrihed experiene promotes signifint inrese in synpse density in the CA1 hippompl field. Beuse there is no neurogenesis in the CA1 region 26, the inresed synpse density is likely to reflet higher numer of synpses per neuron rther thn n inresed numer of pyrmidl ells in CA1. At the ultrstruturl level, we showed tht mie lking the NMDA reeptor in the CA1 region lso inrese synpti density following exposure to n enrihed environment. This suggests tht NMDA-reeptor tivity is not required for struturl plstiity in the CA1 region of dult nimls indued y ehviorl experiene, nd thus the moleulr mehnism underlying dult tivitydependent struturl plstiity is very different from mehnisms tive in the developing rin 17,18. As synpti plstiity n lso e indued in the CA1 region y n NMDA reeptor-independent proess 37,38 suh s LTP dependent on voltge-gted lium hnnels, other mehnisms might serve s puttive ndidtes for experiene-indued struturl plstiity in dult rin. It remins to e determined whether the enrihment-indued inrese in CA1 synpti density hs ny funtionl role in the onomitnt ehviorl effets. It is likely tht other rin regions my undergo similr iohemil nd struturl hnges fter enrihment, nd lso might prtiipte in the enrihment-indued ehviorl improvement. Enhned synpti oinidene detetion in the forerin of trnsgeni mie vi upregultion of suunit 2B of the NMDA reeptor lso leds to overll enhnement of lerning nd memory 10. Thus, hnges in the omposition (for instne, rtio of NR2A to NR2B suunits) of the NMDA reeptor omplex my e possile mehnism for the enrihmentindued effets. Tken together, these findings indite tht lerning nd memory might e enhned in mmmls y geneti ftors s well s ehviorl experiene. METHODS Animls. The nd ontrol mie were produed s desried 11. Throughout the ehviorl nd histologil experiments, oservers were lind to the genotype of n individul niml. In situ hyridiztion. Desried proedures 10 were used. Briefly, n ntisense 42-mer oligonuleotide proe (5 -ACCACTCTTTCTATC CTG CAG GTT CTT CCT CCA CAC GTT-3 ), whih reognizes NR1 exon 20, ws end leled with [ 35 S]-dATP. After hyridizing with the oligonuleotide proe ( pm per slide) t 47 C for 24 h, rin setions (20 µm) were wshed in 2 SSC t room temperture (RT) followed y two wshes in 0.2 SSC t 60 C nd one wsh in 0.1 SSC t RT. Interestingly, preliminry oservtions indited tht the deletion of the NR1 gene in six-month-old knokouts seemed to spred to other forerin regions suh s the ortex, proly refleting the reomintion threshold effet s the CMKII promoter-driven Cre umulted. Enrihed environment trining. Adult littermtes (1.5 2 months old) were rndomly distriuted into two experimentl groups. One group ws kept in stndrd ges (nive group) nd the other group trined in n enrihed environment for three hours dily for two months (enrihed group). The enrihment trining ws rried out in speilly designed oxes (1.5 m 0.8 m 0.8 m), in whih vrious toys, running wheels nd smll houses were hnged every other dy to enourge explortion. Food nd wter were lso ville in the oxes. Beuse eletrophysiologil, ehviorl nd ntomil experiments showed similr results for wild-type nd Cre trnsgeni mie, these two genotypes of mie were pooled together s ontrols. Novel-ojet reognition tsk nd fer-onditioning tsks. The experimentl protool ws the sme s desried previously 10, exept tht the durtion of the trining period in the ojet-reognition tsk ws 15 min. Soil trnsmission of food preferene tsk. In this experiment, oserver mie were tested for memory nd demonstrtor wild-type mie were used to intert with oservers ording to desried proedure 22. After intertion, the oservers were deprived of food for 24 h nd then tested for memory. During testing, oservers were offered oth innmon- nd oo-sented food for 2 h, nd onsumption of eh food ws susequently mesured. The preferred food hd the sme sent s food eten y the demonstrtor with whom the oserver interted. Preferene ws lulted s perentge rtio of the mount of preferred food onsumed over 50% of the totl mount of food onsumed. Histology. For eletron mirosopy, ontol groups were omposed of mles, months old. The nive mie were 3 mles (4.5, 4 nd 4 months) nd 1 femle (3.5 months), nd the enrihed mie were 3 mles (5, 4.5 nd 3.5 months) nd 1 femle (4 months). Beuse CA1 dendriti spine density in rts flututes over the estrous yle 39, femles were killed during proestrus, the stge t whih the spine numers of femle rts pproh those of mle rts (lthough it is not known whether the sme phenomenon exists in mie). Animls were nesthetized nd perfused with 2% prformldehyde, 2% glutrldehyde nd 1.5% sturted piri id in 0.1 M phosphte uffer (ph 7.4) nd postfixed overnight in the sme solution. Following modified version of the single-setion Golgi impregntion tehnique 32, 100 µm-thik oronl setions were ut with virtome into th of 3% potssium dihromte in distilled wter nd inuted overnight in this solution. The slide ssemlies were inuted in the drk in solution of 1.5% silver nitrte for 2 dys. For eletron mirosopy, we used virtome to ut 250 µm-thik oronl setions into th of 0.1 M sodium odylte uffer. Hippompl nture neurosiene volume 3 no 3 mrh
7 rtiles setions orresponding to figures of the mouse rin tls 40 were disseted, rinsed in distilled wter nd postfixed in 1% osmium tetroxide followed with 1% ferroynide-redued osmium tetroxide. Tissues were rinsed, stined en lo overnight in 1% queous urnyl ette, rinsed nd dehydrted nd susequently infiltrted nd flt emedded with Emed 812 resin. Setions (0.5 µm) were ut nd stined with 1% toluidine lue. Setions were exmined to determine how the lok should e trimmed for ultrthin setioning to inlude the pex of the CA1 pyrmidl ell lyer, from the strtum rditum to the strtum lunosum moleulre. Ultrthin setions were ut with dimond knife, pled on ron Formvroted slot grids nd stined with 1% urnyl ette nd led itrte. Setion thikness ws mesured y snning eletron mirosope mesurements to rnge from to µm, depending on the series. Dt nlysis: spine density. Golgi-impregnted dendriti segments seleted for nlysis were loted µm from the pyrmidl ell odies in the strtum rditum, elonged to thoroughly impregnted pyrmidl neuron, remined pproximtely in the plne of fous nd were >10 µm in length nd µm in width. Clultions of spine density were otined y mesuring dendriti segments mthing the ove riteri (ontrol enrihed n = 37, nive n = 38, enrihed n = 41 nd ontrol nive n = 43) from ge- nd sex-lned sets of 3 nimls of eh group. These segments represented totl dendriti length of µm per group of mie. Dt nlysis: synpse density. Synpse density ws estimted y the disetor method 34,35. From eh rin, 15 eletron mirogrphs of seprte regions within the strtum rditum, µm from the pyrmidl ell lyer, were tken from different setions t 10,000 on JEOL 100C eletron mirosope to rete 15 referene plnes. The mirogrphs overed n re of pproximtely 2100 µm 2 per niml. Mirogrphs of extly the sme regions were tken on n djent setion to rete look-up plnes. The numer of synpses ontined in referene plne ut sent in the orresponding look-up plne (Q i ) ws ounted to determine the numer of synpses present within the volume defined y the referene plne, the look-up plne nd the distne etween them (h i ). Two sides of the retngulr piture were ssigned rndomly s inlusion or exlusion edges to rete ounting frme tht minimized potentil edge effets ross smples 41. To inrese the smpling reliility, synpses were ounted over totl re of 8,400 14,700 µm 2 from 600 eletron mirogrphs for eh experimentl group of mie. Setion thikness (h i ) ws determined y snning eletron mirosope mesurements (see Histology). Estimted synpse density (est N v ) ws lulted s est N v = ΣQ i / Σ (A i h i ) Note: Additionl methods detils n e found on the Nture Neurosiene we site ( ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS We thnk E. Gould for help with stereology nd sttistis nd reding the mnusript, nd P. Tnpt for tehnil dvie onerning the Golgi method. This work ws supported in prt y postdotorl fellowship from Fondtion pour l Reherhe Medile to C.R. nd y grnts from Prineton University, Bekmn Foundtion nd NIH to J.Z.T. RECEIVED 12 OCTOBER; ACCEPTED 28 DECEMBER Rosene, D. L. & Vn Hoesen, G. W. in Cererl Cortex Vol. 6: Further Aspets of Cortil Funtion, Inluding Hippompus (eds. Jones, E. G. & Petes, A.) (Plenum, New York, 1987). 2. Soville, W. B. & Milner, B. Loss of reent memory fter ilterl hippompl lesion. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psyhitry 20, (1957). 3. Zol-Morgn, S., Squire, L. R. & Amrl, D. G. Humn mnesi nd the medil temporl region: enduring memory impirment following ilterl lesion limited to field CA1 of the hippompus. J. Neurosi. 6, (1986). 4. Squire L. R. Memory nd the hippompus: synthesis from findings with rts, monkeys, nd humns. Psyhol. Rev. 99, (1992). 5. Mumy, D. G. et l. Ishemi-indued ojet-reognition defiits in rts re ttenuted y hippompl ltion efore or soon fter ishemi. Behv. Neurosi. 110, (1996). 6. Wood, E. R., Dudhenko, P. A. & Eihenum, H. The glol reord of memory in hippompl neuronl tivity. Nture 397, (1999). 7. Moriyoshi, K. et l. Moleulr loning nd hrteriztion of the rt NMDA reeptor. Nture 354, (1991). 8. Nioll, R. A. & Mlenk, R. C. Expression mehnisms underlying NMDA reeptor-dependent long-term potentition. Ann. NY Ad. Si. 868, (1999). 9. Ber, M. F. & Mlenk, R. C. Synpti plstiity: LTP nd LTD. Curr. Opin. Neuroiol. 4, (1994). 10. Tng, Y.-P. et l. Geneti enhnement of lerning nd memory in mie. Nture 401, (1999). 11. Tsien, J. Z. et l. Suregion- nd ell type-restrited gene knokout in mouse rin. Cell 87, (1996). 12. Tsien, J. Z., Huert, P. T. & Tonegw, S. The essentil role of hippompl CA1 NMDA reeptor-dependent synpti plstiity in sptil memory. Cell 87, (1996). 13. MHugh, T. J., Blum, K. I., Tsien, J. Z., Tonegw, S. & Wilson, M. A. Impired hippompl representtion of spe in CA1-speifi NMDAR1 knokout mie. Cell 87, (1996). 14. Woolf, N. J. A struturl sis for memory storge in mmmls. Prog. Neuroiol. 55, (1998). 15. Biley, C. H. & Kndel, E. R. Struturl hnges ompnying memory storge. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 55, (1993). 16. Moser, M. B., Trommld, M. & Andersen, P. An inrese in dendriti spine density on hippompl CA1 pyrmidl ells following sptil lerning in dult rts suggests the formtion of new synpses. Pro. Ntl. Ad. Si. USA 91, (1994). 17. Goodmn, C. S. & Shtz, C. J. Developmentl mehnisms tht generte preise ptterns of neuronl onnetivity. Cell 72, Suppl (1993). 18. Li, Y., Erzurumlu, R. S., Chen, C., Jhveri, S. & Tonegw, S. Whisker-relted neuronl ptterns fil to develop in the trigeminl rinstem nulei of NMDAR1 knokout mie. Cell 76, (1994). 19. Kirov, S. A. & Hrris, K. M. Dendrites re more spiny on mture hippompl neurons when synpses re intivted. Nt. Neurosi. 10, (1999). 20. Sorr, K. E. & Hrris, K. M. Stility in synpse numer nd size t 2 hr fter long-term potentition in hippompl re CA1. J. Neurosi. 18, (1998). 21. Mnsuy, I. M., Myford, M., Jo, B., Kndel, E. R. & Bh, M. E. Restrited nd regulted overexpression revels lineurin s key omponent in the trnsition from short-term to long-term memory. Cell 92, (1998). 22. Kogn, J. H. et l. Sped trining indues norml long-term memory in CREB mutnt mie. Curr. Biol. 7, 1 11 (1996). 23. Strupp, B. J. & Levitsky, D. A. Soil trnsmission of food preferenes in dult hooded rts (Rttus norvegius). J. Comp. Psyhol. 98, (1984). 24. Bunsey, M. & Eihenum, H. Seletive dmge to the hippompl region loks long-term retention of nturl nd nonsptil stimulus-stimulus ssoition. Hippompus 5, (1995). 25. Phillips, R. G. & LeDoux, J. E. Differentil ontriution of mygdl nd hippompus to ued nd ontextul fer onditioning. Behv. Neurosi. 106, (1992). 26. Kempermnn, G., Kuhn, G. H. & Gge, F. H. More hippompl neurons in dult mie living in n enrihed environment. Nture 386, (1997). 27. Dlrymple-Alford, J. C. & Benton, D. Preopertive differentil housing nd dorsl hippompl lesions in rts. Behv. Neurosi. 98, (1984). 28. Rosenzweig, M. R. Environmentl omplexity, ererl hnge, nd ehvior. Am. Psyhol. 21, (1966). 29. Dimond, M. C. Enrihing Heredity: The Impt of the Environment on the Antomy of the Brin (Free Press, New York, 1988). 30. Fil, B. A., Joye, J. N. & Greenough, W. T. Environmentl omplexity modultes growth of grnule ell dendrites in developing ut not dult hippompus of rts. Exp. Neurol. 59, (1978). 31. Greenough, W. T., Withers, G. S. & Wlle, C. S. in The Biology of Memory (eds. Squire, L. R. & Lindenum, E.) (Shttuer, Stuttgrt, 1990). 32. Gott, P. L & Somogyi, J. The single Golgi impregntion proedure: methodologil desription. J. Neurosi. Methods 11, (1984). 33. Sorr, K. E., Fil, J. C. & Hrris, K. M. Critil ssessment of the involvement of perfortions, spinules, nd spine rnhing in hippompl synpse formtion. J. Comp. Neurol. 398, (1998). 34. Sterio, D. C. The unised estimtion of numer nd sizes of prtiles using the disetor. J. Miros. 134, (1984). 35. DeGroot, D. M. G. & Biermn, E. P. B. A ritil evlution of methods for estimting the numeril density of synpses. J. Neurosi. Methods 18, (1986). 36. Gry, E. G. Axosomti nd xodendriti synpses of the ererl ortex: An eletron mirosopi study. J. Ant. 83, (1959). 37. Nioll, R. A. & Mlenk, R. C. Contrsting properties of two forms of longterm potentition in the hippompus. Nture 377, (1995). 38. Stevens, C. F. & Sullivn, J. Synpti plstiity. Curr. Biol. 8, R (1998). 39. Woolley, C. S., Gould, E., Frnkfurt, M. & MEwen, B. S. Nturlly ourring flutution in dendriti spine density on dult hippompl pyrmidl neurons. J. Neurosi. 10, (1990). 40. Frnklin, K. B. J. & Pxinos, G. The mouse rin in stereotxi oordintes. (Ademi, Sn Diego, 1997). 41. Gundersen, H. J. G. Notes on the estimtion of the numeril density of ritrry profiles: the edge effet. J. Miros. 111, (1977). 244 nture neurosiene volume 3 no 3 mrh 2000
LHb VTA. VTA-projecting RMTg-projecting overlay. Supplemental Figure 2. Retrograde labeling of LHb neurons. a. VTA-projecting LHb
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementl Figure 1 doi:10.1038/nture09742 Lterl 1.0 mm from midline mpfc BNST mpfc BNST Lterl 2.1 mm from midline LHA LHA Lterl 2.7 mm from midline SUPPLEMENTAL INFORMATION
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementl Figure 1 doi:10.1038/nture09742 Lterl 1.0 mm from midline mpfc BNST mpfc BNST Lterl 2.1 mm from midline LHA LHA Lterl 2.7 mm from midline SUPPLEMENTAL INFORMATION
EFFECT OF DIETARY ENZYME ON PERFORMANCE OF WEANLING PIGS
 EFFECT OF DIETARY ENZYME ON PERFORMANCE OF WEANLING PIGS Finl report sumitted to Dniso Animl Nutrition E. vn Heugten nd B. Frederik North Crolin Stte University, Deprtment of Animl Siene Summry The urrent
EFFECT OF DIETARY ENZYME ON PERFORMANCE OF WEANLING PIGS Finl report sumitted to Dniso Animl Nutrition E. vn Heugten nd B. Frederik North Crolin Stte University, Deprtment of Animl Siene Summry The urrent
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi: 1.138/nture862 humn hr. 21q MRPL39 murine Chr.16 Mrpl39 Dyrk1A Runx1 murine Chr. 17 ZNF295 Ets2 Znf295 murine Chr. 1 COL18A1 -/- lot: nti-dscr1 IgG hevy hin DSCR1 DSCR1 expression reltive to hevy
doi: 1.138/nture862 humn hr. 21q MRPL39 murine Chr.16 Mrpl39 Dyrk1A Runx1 murine Chr. 17 ZNF295 Ets2 Znf295 murine Chr. 1 COL18A1 -/- lot: nti-dscr1 IgG hevy hin DSCR1 DSCR1 expression reltive to hevy
Supplementary Figure 1. Scheme of unilateral pyramidotomy used for detecting compensatory sprouting of intact CST axons.
 () BDA 2 weeks fter Py () AAVs Cre or GFP t P1 BDA 2 weeks fter Py CSMN CST () Py t P7 or 2 months () Py t 2 months Supplementry Figure 1. Sheme of unilterl pyrmidotomy used for deteting ompenstory sprouting
() BDA 2 weeks fter Py () AAVs Cre or GFP t P1 BDA 2 weeks fter Py CSMN CST () Py t P7 or 2 months () Py t 2 months Supplementry Figure 1. Sheme of unilterl pyrmidotomy used for deteting ompenstory sprouting
Alimonti_Supplementary Figure 1. Pten +/- Pten + Pten. Pten hy. β-actin. Pten - wt hy/+ +/- wt hy/+ +/- Pten. Pten. Relative Protein level (% )
 Alimonti_Supplementry Figure 1 hy 3 4 5 3 Neo 4 5 5 Proe 5 Proe hy/ hy/ /- - 3 6 Neo β-tin d Reltive Protein level (% ) 15 1 5 hy/ /- Reltive Gene Expr. (% ) 15 1 5 hy/ /- Supplementry Figure 1 Chrteriztion
Alimonti_Supplementry Figure 1 hy 3 4 5 3 Neo 4 5 5 Proe 5 Proe hy/ hy/ /- - 3 6 Neo β-tin d Reltive Protein level (% ) 15 1 5 hy/ /- Reltive Gene Expr. (% ) 15 1 5 hy/ /- Supplementry Figure 1 Chrteriztion
Learning to see: experience and attention in primary visual cortex
 2 Nture Pulishing Group http://neurosi.nture.om rtiles Lerning to see: experiene nd ttention in primry visul ortex 2 Nture Pulishing Group http://neurosi.nture.om Roy E. Crist, Wu Li nd Chrles D. Gilert
2 Nture Pulishing Group http://neurosi.nture.om rtiles Lerning to see: experiene nd ttention in primry visul ortex 2 Nture Pulishing Group http://neurosi.nture.om Roy E. Crist, Wu Li nd Chrles D. Gilert
Poultry No The replacement value of betaine for DL-methionine and Choline in broiler diets
 Poultry No. 1573 The replement vlue of etine for DL-methionine nd Choline in roiler diets Key Informtion In roiler diets defiient in sulfur mino ids ut dequtely supplemented with methyl groups vi dded
Poultry No. 1573 The replement vlue of etine for DL-methionine nd Choline in roiler diets Key Informtion In roiler diets defiient in sulfur mino ids ut dequtely supplemented with methyl groups vi dded
Olfactory behavior and physiology are disrupted in prion protein knockout mice
 Olftory ehvior nd physiology re disrupted in prion protein knokout mie Clire E Le Pihon 1, Mtthew T Vlley 1, Mgdlini Polymenidou 2,3, Alexnder T Chesler 1, Botir T Sgdullev 1,3, Adrino Aguzzi 2 & Sturt
Olftory ehvior nd physiology re disrupted in prion protein knokout mie Clire E Le Pihon 1, Mtthew T Vlley 1, Mgdlini Polymenidou 2,3, Alexnder T Chesler 1, Botir T Sgdullev 1,3, Adrino Aguzzi 2 & Sturt
Lesions of prefrontal cortex reduce attentional modulation of neuronal responses. and synchrony in V4
 Lesions of prefrontl ortex reue ttentionl moultion of neuronl responses n synhrony in V4 Georgi G. Gregoriou,, Anrew F. Rossi, 3 Leslie G Ungerleier, 4 Roert Desimone 5 Deprtment of Bsi Sienes, Fulty of
Lesions of prefrontl ortex reue ttentionl moultion of neuronl responses n synhrony in V4 Georgi G. Gregoriou,, Anrew F. Rossi, 3 Leslie G Ungerleier, 4 Roert Desimone 5 Deprtment of Bsi Sienes, Fulty of
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 { OI: 1.138/n31 Srifie n nlyze APs on week 1 s of iet 1 4 6 High-ft iet BrU High-ft iet BrU 4 High-ft iet BrU 6 High-ft iet BrU Lin - Lin - : C34 + : C9 + 1 1 3 1 4 1 5 C45 1 C34 1 1 1 1 3 1 4 1 5 S-1
{ OI: 1.138/n31 Srifie n nlyze APs on week 1 s of iet 1 4 6 High-ft iet BrU High-ft iet BrU 4 High-ft iet BrU 6 High-ft iet BrU Lin - Lin - : C34 + : C9 + 1 1 3 1 4 1 5 C45 1 C34 1 1 1 1 3 1 4 1 5 S-1
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 1.13/n7 Reltive Pprg mrna 3 1 1 Time (weeks) Interspulr Inguinl Epididyml Reltive undne..1.5. - 5 5-51 51-1 1-7 7 - - 1 1-1 Lipid droplet size ( m ) 1-3 3 - - - 1 1-1 1-1 1-175 175-3 3-31 31-5 >5
DOI: 1.13/n7 Reltive Pprg mrna 3 1 1 Time (weeks) Interspulr Inguinl Epididyml Reltive undne..1.5. - 5 5-51 51-1 1-7 7 - - 1 1-1 Lipid droplet size ( m ) 1-3 3 - - - 1 1-1 1-1 1-175 175-3 3-31 31-5 >5
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:.8/nture89 4 4 Ilr -/- Ilr -/- Ilr -/- Cspse- -/- As -/- Nlrp -/- Il8 -/- Ilr -/- Supplementl figure. Inresed severity of NASH in inflmmsome-defiient mie, ut not in Ilr-defiient
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:.8/nture89 4 4 Ilr -/- Ilr -/- Ilr -/- Cspse- -/- As -/- Nlrp -/- Il8 -/- Ilr -/- Supplementl figure. Inresed severity of NASH in inflmmsome-defiient mie, ut not in Ilr-defiient
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 . Norml Physiologicl Conditions. SIRT1 Loss-of-Function S1. Model for the role of SIRT1 in the regultion of memory nd plsticity. () Our findings suggest tht SIRT1 normlly functions in coopertion with YY1,
. Norml Physiologicl Conditions. SIRT1 Loss-of-Function S1. Model for the role of SIRT1 in the regultion of memory nd plsticity. () Our findings suggest tht SIRT1 normlly functions in coopertion with YY1,
Whangarei District Council Class 4 Gambling Venue Policy
 Whngrei Distrit Counil Clss 4 Gmling Venue Poliy April 2013 Whngrei Distrit Counil Clss 4 Gmling Venue Poliy Tle of ontents Introdution... 3 1 Ojetives of the poliy in so fr s promoted y the Gmling At
Whngrei Distrit Counil Clss 4 Gmling Venue Poliy April 2013 Whngrei Distrit Counil Clss 4 Gmling Venue Poliy Tle of ontents Introdution... 3 1 Ojetives of the poliy in so fr s promoted y the Gmling At
SK channels and NMDA receptors form aca 2+ -mediated feedback loop in dendritic spines
 25 Nture Pulishing Group http://www.nture.om/ntureneurosiene SK hnnels nd NMDA reeptors form C 2+ -medited feedk loop in dendriti spines Thu Jennifer Ngo-Anh 1,4, Brend L Bloodgood 2,4, Mihel Lin 1, Bernrdo
25 Nture Pulishing Group http://www.nture.om/ntureneurosiene SK hnnels nd NMDA reeptors form C 2+ -medited feedk loop in dendriti spines Thu Jennifer Ngo-Anh 1,4, Brend L Bloodgood 2,4, Mihel Lin 1, Bernrdo
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:.38/nture277 d 25 25 2 Time from sound onset (ms) 25 25 2 Time from sound onset (ms) Firing rte (spikes/s) Firing rte (spikes/s).8.6..2 e f g h.8.6..2 Frtion of neurons Frtion of neurons N = 53 2 2
doi:.38/nture277 d 25 25 2 Time from sound onset (ms) 25 25 2 Time from sound onset (ms) Firing rte (spikes/s) Firing rte (spikes/s).8.6..2 e f g h.8.6..2 Frtion of neurons Frtion of neurons N = 53 2 2
P AND K IN POTATOES. Donald A Horneck Oregon State University Extension Service
 P AND K IN POTATOES Donld A Hornek Oregon Stte University Extension Servie INTRODUCTION Phosphorous nd potssium re importnt to grow high yielding nd qulity pottoes. Muh of the northwest hs hd trditionlly
P AND K IN POTATOES Donld A Hornek Oregon Stte University Extension Servie INTRODUCTION Phosphorous nd potssium re importnt to grow high yielding nd qulity pottoes. Muh of the northwest hs hd trditionlly
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 1.138/n358 TLR2 nd MyD88 expression in murine mmmry epithelil supopultions. CD24 min plus MRU Myo-epithelil Luminl progenitor (CD61 pos ) Mture luminl (CD61 neg ) CD49f CD61 Reltive expression Krt5
DOI: 1.138/n358 TLR2 nd MyD88 expression in murine mmmry epithelil supopultions. CD24 min plus MRU Myo-epithelil Luminl progenitor (CD61 pos ) Mture luminl (CD61 neg ) CD49f CD61 Reltive expression Krt5
Supplementary Figure S1
 Supplementry Figure S1 - UTR m - 3HA - 2-1 hgh - 1 Uiquitin *! *! lk distl promoter m K3R/ K121R-3HA UTR hgh founder lines - HA - - founder lines TG- E1 L A2 B1 F9 G6 H4 H6 B C D2 G1 H3 J2 L - 7 IP: lk
Supplementry Figure S1 - UTR m - 3HA - 2-1 hgh - 1 Uiquitin *! *! lk distl promoter m K3R/ K121R-3HA UTR hgh founder lines - HA - - founder lines TG- E1 L A2 B1 F9 G6 H4 H6 B C D2 G1 H3 J2 L - 7 IP: lk
Laminar sources of synaptic input to cortical inhibitory interneurons and pyramidal neurons
 rtiles Lminr soures of synpti input to ortil inhiitory interneurons nd pyrmidl neurons J. L. Dntzker nd E. M. Cllwy Systems Neuroiology Lortories, The Slk Institute for Biologil Studies, N. Torrey Pines
rtiles Lminr soures of synpti input to ortil inhiitory interneurons nd pyrmidl neurons J. L. Dntzker nd E. M. Cllwy Systems Neuroiology Lortories, The Slk Institute for Biologil Studies, N. Torrey Pines
Long-term modification of cortical synapses improves sensory perception
 Long-term modifition of ortil synpses improves sensory pereption Roert C Froemke 1 4,8, Ion Cre 1 3,8, Alison J Brker 4, Kexin Yun 4, Bryn A Seyold 4, An Rquel O Mrtins 1 3,5, Ntly Zik 1,2, Hnnh Bernstein
Long-term modifition of ortil synpses improves sensory pereption Roert C Froemke 1 4,8, Ion Cre 1 3,8, Alison J Brker 4, Kexin Yun 4, Bryn A Seyold 4, An Rquel O Mrtins 1 3,5, Ntly Zik 1,2, Hnnh Bernstein
Hippocampal CA1 pyramidal cells form functionally distinct sublayers
 r t i l e s Hippompl CA pyrmidl ells form funtionlly distint sulyers Kenji Mizuseki, Kmrn Di,2, Ev Pstlkov,2 & György Buzsáki 2 Nture Ameri, In. All rights reserved. Hippompl CA pyrmidl neurons hve frequently
r t i l e s Hippompl CA pyrmidl ells form funtionlly distint sulyers Kenji Mizuseki, Kmrn Di,2, Ev Pstlkov,2 & György Buzsáki 2 Nture Ameri, In. All rights reserved. Hippompl CA pyrmidl neurons hve frequently
Methylphenidate facilitates learning-induced amygdala plasticity
 Methylphenidte filittes lerning-indued mygdl plstiity Ky M Tye 1,2, Lynne D Tye 1,3, Jkson J Cone 1, Evelien F Hekkelmn 1, Ptrii H Jnk 1,2,, & Antonello Boni 1,2,, 21 Nture Ameri, In. All rights reserved.
Methylphenidte filittes lerning-indued mygdl plstiity Ky M Tye 1,2, Lynne D Tye 1,3, Jkson J Cone 1, Evelien F Hekkelmn 1, Ptrii H Jnk 1,2,, & Antonello Boni 1,2,, 21 Nture Ameri, In. All rights reserved.
Supplementary information to accompany the manuscript entitled:
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 Supplementry informtion to ompny the mnusript entitled: A mternl junk food diet in pregnny nd lttion promotes n exerted tste for junk food nd greter propensity
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 Supplementry informtion to ompny the mnusript entitled: A mternl junk food diet in pregnny nd lttion promotes n exerted tste for junk food nd greter propensity
Selective reconfiguration of layer 4 visual cortical circuitry by visual deprivation
 Seletive reonfigurtion of lyer 4 visul ortil iruitry y visul deprivtion Arinn Mffei, Sh B Nelson & Gin G Turrigino Visul deprivtion during developmentl sensitive period mrkedly lters visul ortil response
Seletive reonfigurtion of lyer 4 visul ortil iruitry y visul deprivtion Arinn Mffei, Sh B Nelson & Gin G Turrigino Visul deprivtion during developmentl sensitive period mrkedly lters visul ortil response
Minimum effective dose of chenic acid for gallstone patients: reduction with bedtime administration and
 Gut, 1982, 23, 28-284 Minimum effetive dose of heni id for gllstone ptients: redution with bedtime dministrtion nd low holesterol diet D P MUDGL, R M KUPFER, ND T C NORTHFIELD* From the Normn Tnner Gstroenterology
Gut, 1982, 23, 28-284 Minimum effetive dose of heni id for gllstone ptients: redution with bedtime dministrtion nd low holesterol diet D P MUDGL, R M KUPFER, ND T C NORTHFIELD* From the Normn Tnner Gstroenterology
A maternal junk food diet in pregnancy and lactation promotes an exacerbated taste for junk food and a greater propensity for obesity in rat offspring
 British Journl of Nutrition (27), pge 1 of 9 q The uthors 27 doi: 1.117/S7114781237 mternl junk food diet in pregnny nd lttion promotes n exerted tste for junk food nd greter propensity for oesity in rt
British Journl of Nutrition (27), pge 1 of 9 q The uthors 27 doi: 1.117/S7114781237 mternl junk food diet in pregnny nd lttion promotes n exerted tste for junk food nd greter propensity for oesity in rt
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION CD169 + MACROPHAGES PRESENT LIPID ANTIGENS TO MEDIATE EARLY ACTIVATION OF INVARIANT NKT CELLS IN LYMPH NODES Ptrii Brrl, Polo Polzell, Andres Brukuer, Nio vn Rooijen, Gurdyl S.
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION CD169 + MACROPHAGES PRESENT LIPID ANTIGENS TO MEDIATE EARLY ACTIVATION OF INVARIANT NKT CELLS IN LYMPH NODES Ptrii Brrl, Polo Polzell, Andres Brukuer, Nio vn Rooijen, Gurdyl S.
Mechanisms underlying cross-orientation suppression in cat visual cortex
 Mehnisms underlying ross-orienttion suppression in t visul ortex 6 Nture Pulishing Group http://www.nture.om/ntureneurosiene Nihols J Priee & Dvid Ferster In simple ells of the t primry visul ortex, null-oriented
Mehnisms underlying ross-orienttion suppression in t visul ortex 6 Nture Pulishing Group http://www.nture.om/ntureneurosiene Nihols J Priee & Dvid Ferster In simple ells of the t primry visul ortex, null-oriented
Chloride Nutrition Regulates Water Balance in Plants
 XII Portuguese-Spnish Symposium on Plnt Wter Reltions Chloride Nutrition Regultes Wter Blne in Plnts Frno-Nvrro JD 1, Brumós J, Rosles MA 1, Vázquez-Rodríguez A 1, Sñudo BJ 1, Díz- Rued P 1, Rivero C 1,
XII Portuguese-Spnish Symposium on Plnt Wter Reltions Chloride Nutrition Regultes Wter Blne in Plnts Frno-Nvrro JD 1, Brumós J, Rosles MA 1, Vázquez-Rodríguez A 1, Sñudo BJ 1, Díz- Rued P 1, Rivero C 1,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 oi:1.138/nture1134 CS+ CS- MCH 3 OCT OCT 3 MCH CS- CS+ OCT MCH 3 MCH OCT 3 OCT vs MCH OCT vs MCH ppetitive memory (PI) A 1-1 Unpire onitioning DDC-GAL4/UAS-Trp UAS-Trp/+ -2 MCH OCT OCT MCH sugr OCT MCH
oi:1.138/nture1134 CS+ CS- MCH 3 OCT OCT 3 MCH CS- CS+ OCT MCH 3 MCH OCT 3 OCT vs MCH OCT vs MCH ppetitive memory (PI) A 1-1 Unpire onitioning DDC-GAL4/UAS-Trp UAS-Trp/+ -2 MCH OCT OCT MCH sugr OCT MCH
RESEARCH ARTICLE. Supplemental Figure 5
 11.5 2 2 11. RESEARCH ARTICLE RBC ( 1 12 /L) 1.5 1. 9.5 PLT ( 1 9 /L) 1 16 14 HGB (g/l) 19 1 17 16 9. 12 4 4 46 Cellulr & Moleulr Immunology dvne online pulition, PCV (%) 44 MCV (fl) 46 44 ; doi:1.13/mi.214.16
11.5 2 2 11. RESEARCH ARTICLE RBC ( 1 12 /L) 1.5 1. 9.5 PLT ( 1 9 /L) 1 16 14 HGB (g/l) 19 1 17 16 9. 12 4 4 46 Cellulr & Moleulr Immunology dvne online pulition, PCV (%) 44 MCV (fl) 46 44 ; doi:1.13/mi.214.16
Input normalization by global feedforward inhibition expands cortical dynamic range
 Input normliztion y glol feedforwrd inhiition expnds ortil dynmi rnge Frédéri Pouille 1,2, Antoni Mrin-Burgin 1,2, Hillel Adesnik 1, Bssm V Atllh 1 & Mssimo Snzini 1 29 Nture Ameri, In. All rights reserved.
Input normliztion y glol feedforwrd inhiition expnds ortil dynmi rnge Frédéri Pouille 1,2, Antoni Mrin-Burgin 1,2, Hillel Adesnik 1, Bssm V Atllh 1 & Mssimo Snzini 1 29 Nture Ameri, In. All rights reserved.
Control of timing, rate and bursts of hippocampal place cells by dendritic and somatic inhibition
 Control of timing, rte nd ursts of hippompl ple ells y dendriti nd somti inhiition Séstien Royer,2, Boris V Zemelmn,5, Attil Losonzy,3, Jinhyun Kim,2, Frnes Chne, Jeffrey C Mgee & György Buzsáki,4 22 Nture
Control of timing, rte nd ursts of hippompl ple ells y dendriti nd somti inhiition Séstien Royer,2, Boris V Zemelmn,5, Attil Losonzy,3, Jinhyun Kim,2, Frnes Chne, Jeffrey C Mgee & György Buzsáki,4 22 Nture
I h -mediated depolarization enhances the temporal precision of neuronal integration
 Reeived 5 Apr 2 Aepted 9 Jn 2 Pulished 5 Fe 2DOI:.38/nomms22 I h -medited depolriztion enhnes the temporl preision of neuronl integrtion Ivn Pvlov, Annlis Simemi,, Leonid Svthenko, Dimitri M. Kullmnn &
Reeived 5 Apr 2 Aepted 9 Jn 2 Pulished 5 Fe 2DOI:.38/nomms22 I h -medited depolriztion enhnes the temporl preision of neuronl integrtion Ivn Pvlov, Annlis Simemi,, Leonid Svthenko, Dimitri M. Kullmnn &
Change detection by thalamic reticular neurons
 Chnge detetion y thlmi retiulr neurons Xiong-Jie Yu 1,2, Xin-Xiu Xu 1, Shigng He 1 & Jufng He 1,2 The thlmi retiulr nuleus (TRN) is thought to funtion in the ttentionl serhlight. We nlyzed the detetion
Chnge detetion y thlmi retiulr neurons Xiong-Jie Yu 1,2, Xin-Xiu Xu 1, Shigng He 1 & Jufng He 1,2 The thlmi retiulr nuleus (TRN) is thought to funtion in the ttentionl serhlight. We nlyzed the detetion
Other Uses for Cluster Sampling
 Other Uses for Cluster Smpling Mesure hnges in the level of n ttriute Hypothesis testing versus intervl estimtion Type I n 2 errors Power of the test Mesuring ttriute t sme time in ifferent sites Exmple:
Other Uses for Cluster Smpling Mesure hnges in the level of n ttriute Hypothesis testing versus intervl estimtion Type I n 2 errors Power of the test Mesuring ttriute t sme time in ifferent sites Exmple:
Imaging analysis of clock neurons reveals light buffers the wake-promoting effect of dopamine
 Imging nlysis of lok neurons revels light uffers the wke-promoting effet of dopmine Yuhu Shng 1,2, Pul Hynes 2, Niolás Pírez 2, Kyle I Hrrington 3, Fng Guo 1,2, Jordn Pollk 3, Pengyu Hong 3, Leslie C Griffith
Imging nlysis of lok neurons revels light uffers the wke-promoting effet of dopmine Yuhu Shng 1,2, Pul Hynes 2, Niolás Pírez 2, Kyle I Hrrington 3, Fng Guo 1,2, Jordn Pollk 3, Pengyu Hong 3, Leslie C Griffith
Chapter 7. Control and Coordination
 Chpter 7 Control n Coorintion 1 Whih of the following sttements is orret out reeptors? Gusttory reeptors etet tste while olftory reeptors etet smell Both gusttory n olftory reeptors etet smell Auitory
Chpter 7 Control n Coorintion 1 Whih of the following sttements is orret out reeptors? Gusttory reeptors etet tste while olftory reeptors etet smell Both gusttory n olftory reeptors etet smell Auitory
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 1.138/n2977 Numer of ells per field 6 4 2 P =.1 Orthotopi eum Normlized ventrl photon flux 1E7 1E6 1E5 1E4 1E3 1E2 n=8 n=9 1 2 3 4 5 6 Dys Dy54 1.5E5 2.4E7 d Mie with lymph node metstsis (%) 1 8 6
DOI: 1.138/n2977 Numer of ells per field 6 4 2 P =.1 Orthotopi eum Normlized ventrl photon flux 1E7 1E6 1E5 1E4 1E3 1E2 n=8 n=9 1 2 3 4 5 6 Dys Dy54 1.5E5 2.4E7 d Mie with lymph node metstsis (%) 1 8 6
Receptive field structure varies with layer in the primary visual cortex
 2 Nture Pulishing Group http://www.nture.om/ntureneurosiene Reeptive field struture vries with lyer in the primry visul ortex Luis M Mrtinez, Qingo Wng 2, R Cly Reid 3, Cinthi Pilli 2, José-Mñuel Alonso
2 Nture Pulishing Group http://www.nture.om/ntureneurosiene Reeptive field struture vries with lyer in the primry visul ortex Luis M Mrtinez, Qingo Wng 2, R Cly Reid 3, Cinthi Pilli 2, José-Mñuel Alonso
Once small always small? To what extent morphometric characteristics and postweaning starter regime affect pig lifetime growth performance
 Huting et l. Porine Helth Mngement (2018) 4:21 https://doi.org/10.1186/s40813-018-0098-1 RESEARCH Open Aess One smll lwys smll? To wht extent morphometri hrteristis nd postwening strter regime ffet pig
Huting et l. Porine Helth Mngement (2018) 4:21 https://doi.org/10.1186/s40813-018-0098-1 RESEARCH Open Aess One smll lwys smll? To wht extent morphometri hrteristis nd postwening strter regime ffet pig
Reward expectation differentially modulates attentional behavior and activity in visual area V4
 Rewrd expettion differentilly modultes ttentionl ehvior nd tivity in visul re V4 Jll K Bruni 1,6, Brin Lu 1,5,6 & C Dniel Slzmn 1 4 npg 215 Nture Ameri, In. All rights reserved. Neurl tivity in visul re
Rewrd expettion differentilly modultes ttentionl ehvior nd tivity in visul re V4 Jll K Bruni 1,6, Brin Lu 1,5,6 & C Dniel Slzmn 1 4 npg 215 Nture Ameri, In. All rights reserved. Neurl tivity in visul re
Cos7 (3TP) (K): TGFβ1(h): (K)
 IP#2: IP#1: Totl Lystes luiferse tivity (K): 6-4 - (K): luiferse tivity luiferse tivity (K): 2 1 RL-: - + + + + + Sm4-3F: + - + + + + MYC-Sm3: - - - - + + TβRI-HA(T204D): - - - + - + α-ha Luiferse Ativity
IP#2: IP#1: Totl Lystes luiferse tivity (K): 6-4 - (K): luiferse tivity luiferse tivity (K): 2 1 RL-: - + + + + + Sm4-3F: + - + + + + MYC-Sm3: - - - - + + TβRI-HA(T204D): - - - + - + α-ha Luiferse Ativity
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nture10754 Supplementry note 1 To ompre our dt with previous studies, we mesured the width of spikes from identified dopminergi neurons nd unidentified neurons from DATCre mie. Previous studies
doi:10.1038/nture10754 Supplementry note 1 To ompre our dt with previous studies, we mesured the width of spikes from identified dopminergi neurons nd unidentified neurons from DATCre mie. Previous studies
Macmillan Publishers Limited. All rights reserved
 Vol 45 5 Mrh 9 doi:1.13/nture7615 LETTERS Sleep nd sensorimotor integrtion during erly vol lerning in songird Sylvn S. Shnk 1 & Dniel Mrgolish 1, Behviourl studies widely implite sleep in memory onsolidtion
Vol 45 5 Mrh 9 doi:1.13/nture7615 LETTERS Sleep nd sensorimotor integrtion during erly vol lerning in songird Sylvn S. Shnk 1 & Dniel Mrgolish 1, Behviourl studies widely implite sleep in memory onsolidtion
Early depolarizing GABA controls critical-period plasticity in the rat visual cortex
 Erly depolrizing GABA ontrols ritil-period plstiity in the rt visul ortex Gbriele Deidd,5, Mnuel Allegr,,5, Chir Cerri, Shovn Nskr, Guillume Bony, Giuli Zunino 4, Yuri Bozzi,4, Mtteo Cleo,6 & Lur Cnedd,6
Erly depolrizing GABA ontrols ritil-period plstiity in the rt visul ortex Gbriele Deidd,5, Mnuel Allegr,,5, Chir Cerri, Shovn Nskr, Guillume Bony, Giuli Zunino 4, Yuri Bozzi,4, Mtteo Cleo,6 & Lur Cnedd,6
Interplay of LRRK2 with chaperone-mediated autophagy
 Interply of with hperone-medited utophgy Smnth J Orenstein,, Sheng-Hn Kuo,, Inmuld Tsset,,, Espernz Aris,, Hiroshi Kog,, Irene Fernndez-Crs, Etty Cortes,5, Lwrene S Honig,5, Willim Duer 6, Antonell Consiglio,7,
Interply of with hperone-medited utophgy Smnth J Orenstein,, Sheng-Hn Kuo,, Inmuld Tsset,,, Espernz Aris,, Hiroshi Kog,, Irene Fernndez-Crs, Etty Cortes,5, Lwrene S Honig,5, Willim Duer 6, Antonell Consiglio,7,
Effects of physical exercise on working memory and prefrontal cortex function in post-stroke patients
 Effects of physicl exercise on working memory nd prefrontl cortex function in post-stroke ptients M Moriy, C Aoki, K Sktni Grdute School of Helth Sciences Reserch, Mjor of Physicl Therpy, TeikyoHeisei
Effects of physicl exercise on working memory nd prefrontl cortex function in post-stroke ptients M Moriy, C Aoki, K Sktni Grdute School of Helth Sciences Reserch, Mjor of Physicl Therpy, TeikyoHeisei
Cyclooxygenase-2 inhibition improves amyloid-b-mediated suppression of memory and synaptic plasticity
 doi:1.193/rin/wn8 Brin (28), 131,651^664 Cylooxygense-2 inhiition improves myloid--medited suppression of memory nd synpti plstiity Lind A. Kotilinek, 1, * Mrus A. Westermn, 1, *QinwenWng, 2, *,y Kimerly
doi:1.193/rin/wn8 Brin (28), 131,651^664 Cylooxygense-2 inhiition improves myloid--medited suppression of memory nd synpti plstiity Lind A. Kotilinek, 1, * Mrus A. Westermn, 1, *QinwenWng, 2, *,y Kimerly
EFFECT OF SOYBEAN CYST NEMATODE ON GROWTH OF DRY BEAN. Research Report to Northarvest Bean Growers, January 19, 2009
 EFFECT OF SOYBEAN CYST NEMATODE ON GROWTH OF DRY BEAN Reserh Report to Northrvest Ben Growers, Jnury 19, 29 Berlin D. Nelson, Susilo Poromrto, n Ruell Goswmi, Dept. Plnt Pthology, NDSU Ojetive: Determine
EFFECT OF SOYBEAN CYST NEMATODE ON GROWTH OF DRY BEAN Reserh Report to Northrvest Ben Growers, Jnury 19, 29 Berlin D. Nelson, Susilo Poromrto, n Ruell Goswmi, Dept. Plnt Pthology, NDSU Ojetive: Determine
Time-lapse imaging of disease progression in deep brain areas using fluorescence microendoscopy
 Time-lpse imging of disese progression in deep rin res using fluoresene miroendosopy Roert P J Brretto 1,6, Tony H Ko 1,6, Juergen C Jung 1,6, Tmmy J Wng 1, George Cpps 1, Allison C Wters 1, Yniv Ziv 1,
Time-lpse imging of disese progression in deep rin res using fluoresene miroendosopy Roert P J Brretto 1,6, Tony H Ko 1,6, Juergen C Jung 1,6, Tmmy J Wng 1, George Cpps 1, Allison C Wters 1, Yniv Ziv 1,
Neural population coding of sound level adapts to stimulus statistics
 COMPUTATION AND SYSTEMS 25 Nture Pulishing Group http://www.nture.om/ntureneurosiene Neurl popultion oding of sound level dpts to stimulus sttistis Isel Den 1, Niol S Hrper 1,2 & Dvid MAlpine 1 Mmmls n
COMPUTATION AND SYSTEMS 25 Nture Pulishing Group http://www.nture.om/ntureneurosiene Neurl popultion oding of sound level dpts to stimulus sttistis Isel Den 1, Niol S Hrper 1,2 & Dvid MAlpine 1 Mmmls n
Cortical interference effects in the cocktail party problem
 7 Nture Pulishing Group http://www.nture.om/ntureneurosiene Cortil interferene effets in the oktil prty prolem Rjiv Nryn 1,, Virgini Best 1,3, Erol Ozmerl 1,3, Elizeth MCline 1,, Mihel Dent, Brr Shinn-Cunninghm
7 Nture Pulishing Group http://www.nture.om/ntureneurosiene Cortil interferene effets in the oktil prty prolem Rjiv Nryn 1,, Virgini Best 1,3, Erol Ozmerl 1,3, Elizeth MCline 1,, Mihel Dent, Brr Shinn-Cunninghm
Visualizing an emotional valence map in the limbic forebrain by TAI-FISH
 r t i l e s Visulizing n emotionl vlene mp in the limi forerin y TAI-FISH Jino Xiu 1 3, Qi Zhng 1 3, To Zhou 1,2, Ting-ting Zhou 1,2, Yng Chen 1 & Hiln Hu 1 npg 21 Nture Ameri, In. All rights reserved.
r t i l e s Visulizing n emotionl vlene mp in the limi forerin y TAI-FISH Jino Xiu 1 3, Qi Zhng 1 3, To Zhou 1,2, Ting-ting Zhou 1,2, Yng Chen 1 & Hiln Hu 1 npg 21 Nture Ameri, In. All rights reserved.
LKB1 and AMPK regulate synaptic remodeling in old age
 LKB1 nd AMPK regulte synpti remodeling in old ge Melnie A Smuel 1,8, P Emnuel Voinesu 1,8, Brendn N Lilley 1, Rf de Co 2, Mr Foretz 3 5, Benoit Viollet 3 5, Bsil Pwlyk, Mihel A Snderg, Demetrios G Vvvs
LKB1 nd AMPK regulte synpti remodeling in old ge Melnie A Smuel 1,8, P Emnuel Voinesu 1,8, Brendn N Lilley 1, Rf de Co 2, Mr Foretz 3 5, Benoit Viollet 3 5, Bsil Pwlyk, Mihel A Snderg, Demetrios G Vvvs
Optimisation of diets for Atlantic cod (Gadus morhua) broodstock: effect of arachidonic acid on egg & larval quality
 Optimistion of diets for Atlntic cod (Gdus morhu) roodstock: effect of rchidonic cid on egg & lrvl qulity Dr Gordon Bell, Ms. An Blnco, Dr Bill Roy, Dr Derek Roertson, Dr Jim Henderson nd Mr Richrd Prickett,
Optimistion of diets for Atlntic cod (Gdus morhu) roodstock: effect of rchidonic cid on egg & lrvl qulity Dr Gordon Bell, Ms. An Blnco, Dr Bill Roy, Dr Derek Roertson, Dr Jim Henderson nd Mr Richrd Prickett,
Effects of Feeding Citrus Pulp or Corn Supplements With Increasing Levels of Added Undegraded Intake Protein on the Performance of Growing Cattle
 Effets of Feeding Citrus Pulp or Corn Supplements With Inresing Levels of Added Undegrded Intke Protein on the Performne of Growing Cttle Deke Alkire Todd Thrift Willim Kunkle 1 Citrus pulp-sed supplements
Effets of Feeding Citrus Pulp or Corn Supplements With Inresing Levels of Added Undegrded Intke Protein on the Performne of Growing Cttle Deke Alkire Todd Thrift Willim Kunkle 1 Citrus pulp-sed supplements
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 2 weeks high holesterol diet 2 weeks high holesterol diet 2 weeks high holesterol diet 2 μm Mrophges Crystls Hoehst μm Mrophges Crystls Hoehst Hoehst Crystls Mrophges 2 μm 2 μm Supplementry Fig. 1: Erly
2 weeks high holesterol diet 2 weeks high holesterol diet 2 weeks high holesterol diet 2 μm Mrophges Crystls Hoehst μm Mrophges Crystls Hoehst Hoehst Crystls Mrophges 2 μm 2 μm Supplementry Fig. 1: Erly
The Role of Background Statistics in Face Adaptation
 The Journl of Neurosiene, Septemer 3, 29 29(39):235 244 235 Behviorl/Systems/Cognitive The Role of Bkground Sttistis in Fe Adpttion Jinhu Wu, * Hong Xu, * Peter Dyn, 2 nd Ning Qin Deprtments of Neurosiene
The Journl of Neurosiene, Septemer 3, 29 29(39):235 244 235 Behviorl/Systems/Cognitive The Role of Bkground Sttistis in Fe Adpttion Jinhu Wu, * Hong Xu, * Peter Dyn, 2 nd Ning Qin Deprtments of Neurosiene
EFFECTS OF AN ACUTE ENTERIC DISEASE CHALLENGE ON IGF-1 AND IGFBP-3 GENE EXPRESSION IN PORCINE SKELETAL MUSCLE
 Swine Dy 22 Contents EFFECTS OF AN ACUTE ENTERIC DISEASE CHALLENGE ON IGF-1 AND IGFBP-3 GENE EXPRESSION IN PORCINE SKELETAL MUSCLE B. J. Johnson, J. P. Kyser, J. D. Dunn, A. T. Wyln, S. S. Dritz 1, J.
Swine Dy 22 Contents EFFECTS OF AN ACUTE ENTERIC DISEASE CHALLENGE ON IGF-1 AND IGFBP-3 GENE EXPRESSION IN PORCINE SKELETAL MUSCLE B. J. Johnson, J. P. Kyser, J. D. Dunn, A. T. Wyln, S. S. Dritz 1, J.
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 % ells with ili (mrke y A-Tu) Reltive Luiferse % ells with ili (mrke y Arl13) % ells with ili DOI: 1.138/n2259 A-Tuulin Hoehst % Cilite Non-ilite -Serum 9% 8% 7% 1 6% % 4% +Serum 1 3% 2% 1% % Serum: -
% ells with ili (mrke y A-Tu) Reltive Luiferse % ells with ili (mrke y Arl13) % ells with ili DOI: 1.138/n2259 A-Tuulin Hoehst % Cilite Non-ilite -Serum 9% 8% 7% 1 6% % 4% +Serum 1 3% 2% 1% % Serum: -
Title of Experiment: Author, Institute and address:
 Title of Experiment: Trsfetion of murine mrophge RAW264.7 ells with METAFECTENE PRO. Author, Institute n ress: Ptrizi Pellegtti n Frneso Di Virgilio. Deprtment of Experimentl n Dignosti Meiine, Setion
Title of Experiment: Trsfetion of murine mrophge RAW264.7 ells with METAFECTENE PRO. Author, Institute n ress: Ptrizi Pellegtti n Frneso Di Virgilio. Deprtment of Experimentl n Dignosti Meiine, Setion
Stable reprogrammed heterokaryons form spontaneously in Purkinje neurons after bone marrow transplant
 Stle reprogrmmed heterokryons form spontneously in Purkinje neurons fter one mrrow trnsplnt Jmes M. Weimnn 1,2,Cls B. Johnsson 1,Angeli Trejo 1 nd Helen M. Blu 1,2 Heterokryons re the produt of ell fusion
Stle reprogrmmed heterokryons form spontneously in Purkinje neurons fter one mrrow trnsplnt Jmes M. Weimnn 1,2,Cls B. Johnsson 1,Angeli Trejo 1 nd Helen M. Blu 1,2 Heterokryons re the produt of ell fusion
(% of adherent cells) *** PBL firm adhesion. Frequency (% ) 4 1 L 2 CXCR3 DP-2
 Chemotxis (% of dded ells) PBL totl dhesion (N ells/mm 2 /1.1 6 PBL) Frequeny (% ) PBL firm dhesion Supplementry Figure 1 4 4 3 3 2 2 1.1-4 1-3 1.1.2. 1 1 8 6 4 2 Adiponetin ( g/ml) - + Adiponetin ( g/ml)
Chemotxis (% of dded ells) PBL totl dhesion (N ells/mm 2 /1.1 6 PBL) Frequeny (% ) PBL firm dhesion Supplementry Figure 1 4 4 3 3 2 2 1.1-4 1-3 1.1.2. 1 1 8 6 4 2 Adiponetin ( g/ml) - + Adiponetin ( g/ml)
Effect of topiramate on hippocampus-dependent spatial memory in rats
 Phrmologil Reports 0, 65, 5 6 ISSN 7-0 Copyright 0 y Institute of Phrmology Polish Ademy of Sienes Effet of topirmte on hippompus-dependent sptil memory in rts Bogus³w Pietrzk, Agnieszk Konopk, Jku Wojieszk
Phrmologil Reports 0, 65, 5 6 ISSN 7-0 Copyright 0 y Institute of Phrmology Polish Ademy of Sienes Effet of topirmte on hippompus-dependent sptil memory in rts Bogus³w Pietrzk, Agnieszk Konopk, Jku Wojieszk
Effects of exercise training on hepatic steatosis in high fat diet-induced obese mice
 Effets of exerise trining on hepti stetosis in high ft diet-indued oese mie Hyunsik Kng, PhD Sungkyunkwn University Non-Aloholi Ftty Liver Disese (NAFLD) A reversile ondition tht is hrterized y hepti lipid
Effets of exerise trining on hepti stetosis in high ft diet-indued oese mie Hyunsik Kng, PhD Sungkyunkwn University Non-Aloholi Ftty Liver Disese (NAFLD) A reversile ondition tht is hrterized y hepti lipid
In vivo intracellular recording and perturbation of persistent activity in a neural integrator
 rtiles 21 Nture Pulishing Group http://neurosi.nture.om 21 Nture Pulishing Group http://neurosi.nture.om In vivo intrellulr reording nd perturtion of persistent tivity in neurl integrtor E. Aksy 1,2, G.
rtiles 21 Nture Pulishing Group http://neurosi.nture.om 21 Nture Pulishing Group http://neurosi.nture.om In vivo intrellulr reording nd perturtion of persistent tivity in neurl integrtor E. Aksy 1,2, G.
Efficient sensory cortical coding optimizes pursuit eye movements
 ARTICE Reeived Mr 26 Aepted 29 Jul 26 Pulished 9 Sep 26 Effiient sensory ortil oding optimizes pursuit eye movements Bing iu, Mtthew V. Mellio & eslie C. Osorne,2 DOI:.38/nomms2759 OPEN In the nturl world,
ARTICE Reeived Mr 26 Aepted 29 Jul 26 Pulished 9 Sep 26 Effiient sensory ortil oding optimizes pursuit eye movements Bing iu, Mtthew V. Mellio & eslie C. Osorne,2 DOI:.38/nomms2759 OPEN In the nturl world,
ARTICLES. Lateral presynaptic inhibition mediates gain control in an olfactory circuit. Shawn R. Olsen 1 & Rachel I. Wilson 1
 doi:1.138/nture6864 ARTICLES Lterl presynpti inhiition medites gin ontrol in n olftory iruit Shwn R. Olsen 1 & Rhel I. Wilson 1 Olftory signls re trnsdued y lrge fmily of odornt reeptor proteins, eh of
doi:1.138/nture6864 ARTICLES Lterl presynpti inhiition medites gin ontrol in n olftory iruit Shwn R. Olsen 1 & Rhel I. Wilson 1 Olftory signls re trnsdued y lrge fmily of odornt reeptor proteins, eh of
Lipid Composition of Egg Yolk and Serum in Laying Hens Fed Diets Containing Black Cumin (Nigella sativa)
 Interntionl Journl of Poultry Siene 5 (6): 574-578, 2006 ISSN 682-8356 Asin Network for Sientifi Informtion, 2006 Lipid Composition of Egg Yolk nd Serum in Lying Hens Fed Diets Contining Blk Cumin (Nigell
Interntionl Journl of Poultry Siene 5 (6): 574-578, 2006 ISSN 682-8356 Asin Network for Sientifi Informtion, 2006 Lipid Composition of Egg Yolk nd Serum in Lying Hens Fed Diets Contining Blk Cumin (Nigell
The Journal of Physiology
 J Physiol 595.23 (217) pp 7185 722 7185 Heteromeri α/β glyine reeptors regulte exitility in prvlumin-expressing dorsl horn neurons through phsi nd toni glyinergi inhiition M. A. Grdwell 1,2,K.A.Boyle 3,R.J.llister
J Physiol 595.23 (217) pp 7185 722 7185 Heteromeri α/β glyine reeptors regulte exitility in prvlumin-expressing dorsl horn neurons through phsi nd toni glyinergi inhiition M. A. Grdwell 1,2,K.A.Boyle 3,R.J.llister
Neuronal circuitry mechanism regulating adult quiescent neural stem-cell fate decision NO pa. 10 s ETMD
 doi:1.138/nture1136 Neuronl iruitry mehnism regulting dult quiesent neurl stem-ell fte deision Jun Song 1,2, Chun Zhong 1,2, Mihel A. Bonguidi 1,2, Gerld J. Sun 1,3, Derek Hsu 1, Yn Gu 4, Konstntinos Meletis
doi:1.138/nture1136 Neuronl iruitry mehnism regulting dult quiesent neurl stem-ell fte deision Jun Song 1,2, Chun Zhong 1,2, Mihel A. Bonguidi 1,2, Gerld J. Sun 1,3, Derek Hsu 1, Yn Gu 4, Konstntinos Meletis
Neural basis and recovery of spatial attention deficits in spatial neglect
 25 Nture Pulishing Group http://www.nture.om/ntureneurosiene Neurl sis nd reovery of sptil ttention defiits in sptil neglet Murizio Corett 1 4, Mihelle J Kinde 5, Chris Lewis 2, Arhm Z Snyder 1,3 & Ayelet
25 Nture Pulishing Group http://www.nture.om/ntureneurosiene Neurl sis nd reovery of sptil ttention defiits in sptil neglet Murizio Corett 1 4, Mihelle J Kinde 5, Chris Lewis 2, Arhm Z Snyder 1,3 & Ayelet
ARTICLES. Dendritic organization of sensory input to cortical neurons in vivo
 Vol 6 9 April 00 doi:0.08/nture0897 ARTICLES Dendriti orgniztion of sensory input to ortil neurons in vivo Hongbo Ji *, Nthlie L. Rohefort *, Xiowei Chen & Arthur Konnerth In sensory ortex regions, neurons
Vol 6 9 April 00 doi:0.08/nture0897 ARTICLES Dendriti orgniztion of sensory input to ortil neurons in vivo Hongbo Ji *, Nthlie L. Rohefort *, Xiowei Chen & Arthur Konnerth In sensory ortex regions, neurons
Nucleosome positioning as a determinant of exon recognition
 Nuleosome positioning s determinnt of exon reognition Hgen Tilgner 1,3, Christoforos Nikolou 1,3, Sonj Althmmer 1, Mihel Smmeth 1, Miguel Beto 1, Jun Vlárel 1,2 & Roderi Guigó 1 200 Nture Ameri, In. All
Nuleosome positioning s determinnt of exon reognition Hgen Tilgner 1,3, Christoforos Nikolou 1,3, Sonj Althmmer 1, Mihel Smmeth 1, Miguel Beto 1, Jun Vlárel 1,2 & Roderi Guigó 1 200 Nture Ameri, In. All
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementry Figure 1 c d Wistr SHR Wistr AF-353 SHR AF-353 n = 6 n = 6 n = 28 n = 3 n = 12 n = 12 Supplementry Figure 1 Neurophysiologicl properties of petrosl chemoreceptive neurones in Wistr nd SH rts.
Supplementry Figure 1 c d Wistr SHR Wistr AF-353 SHR AF-353 n = 6 n = 6 n = 28 n = 3 n = 12 n = 12 Supplementry Figure 1 Neurophysiologicl properties of petrosl chemoreceptive neurones in Wistr nd SH rts.
Variations in burn perfusion over time as measured by portable ICG fluorescence: A case series
 Burns & Trum, Otoer 2014, Vol 2, Issue 4 Cse Report Vritions in urn perfusion over time s mesured y portle ICG fluoresene: A se series Shrmil Dissnike, Senn Adul-Hmed, John A. Griswold Deprtment of Surgery,
Burns & Trum, Otoer 2014, Vol 2, Issue 4 Cse Report Vritions in urn perfusion over time s mesured y portle ICG fluoresene: A se series Shrmil Dissnike, Senn Adul-Hmed, John A. Griswold Deprtment of Surgery,
Endogenous nicotinic cholinergic activity regulates dopamine release in the striatum
 Endogenous niotini holinergi tivity regultes dopmine relese in the stritum Fu-Ming Zhou, Yong Ling nd John A. Dni Division of Neurosiene, Bylor College of Mediine, Houston, Texs 77030-3498, USA Correspondene
Endogenous niotini holinergi tivity regultes dopmine relese in the stritum Fu-Ming Zhou, Yong Ling nd John A. Dni Division of Neurosiene, Bylor College of Mediine, Houston, Texs 77030-3498, USA Correspondene
CAUSES OF DIARRHEA, PNEUMONIA, AND ABORTION IN 1991 CATTLE SUBMISSIONS TO THE KSU VETERINARY DIAGNOSTIC LABORATORY
 CAUSES OF DIARRHEA, PNEUMONIA, AND ABORTION IN 1991 CATTLE SUBMISSIONS TO THE KSU VETERINARY DIAGNOSTIC LABORATORY 1 1 2 R. K. Frnk, M. W. Vorhies, nd M. M. Chengpp Summry Cuses of dirrhe, pneumoni, nd
CAUSES OF DIARRHEA, PNEUMONIA, AND ABORTION IN 1991 CATTLE SUBMISSIONS TO THE KSU VETERINARY DIAGNOSTIC LABORATORY 1 1 2 R. K. Frnk, M. W. Vorhies, nd M. M. Chengpp Summry Cuses of dirrhe, pneumoni, nd
A thalamic input to the nucleus accumbens mediates opiate dependence
 doi:1.138/nture16954 A thlmi input to the nuleus umens medites opite dependene Yingjie Zhu1, Crl F. R. Wieneke1, Gregory Nhtr1 & Xioke Chen1 1 feed-forwrd inhiition in lol NA iruit. Consistent with this
doi:1.138/nture16954 A thlmi input to the nuleus umens medites opite dependene Yingjie Zhu1, Crl F. R. Wieneke1, Gregory Nhtr1 & Xioke Chen1 1 feed-forwrd inhiition in lol NA iruit. Consistent with this
Supplementary information for: Low bone mass and changes in the osteocyte network in mice lacking autophagy in the osteoblast lineage
 Supplementry informtion for: Low one mss nd chnges in the osteocyte network in mice lcking utophgy in the osteolst linege Mrilin Piemontese, Meld Onl, Jinhu Xiong, Li Hn, Jeff D. Thostenson, Mri Almeid,
Supplementry informtion for: Low one mss nd chnges in the osteocyte network in mice lcking utophgy in the osteolst linege Mrilin Piemontese, Meld Onl, Jinhu Xiong, Li Hn, Jeff D. Thostenson, Mri Almeid,
Letter. Autocrine BDNF TrkB signalling within a single dendritic spine
 Letter doi:1.138/nture19766 Autorine BDNF TrkB signlling within single dendriti spine Stephen C. Hrwrd 1, Nthn G. Hedrik 1, Chrles E. Hll 1, Pul Prr-Bueno 2, Teres A. Milner 3,4, Enhui Pn 1, Tl Lviv 2,
Letter doi:1.138/nture19766 Autorine BDNF TrkB signlling within single dendriti spine Stephen C. Hrwrd 1, Nthn G. Hedrik 1, Chrles E. Hll 1, Pul Prr-Bueno 2, Teres A. Milner 3,4, Enhui Pn 1, Tl Lviv 2,
Bioactive milk components to secure growth and gut development in preterm pigs ESTER ARÉVALO SUREDA PIGUTNET FA1401 STSM
 Bioctive milk components to secure growth nd gut development in preterm pigs ESTER ARÉVALO SUREDA PIGUTNET FA1401 STSM STSM Pigutnet FA1401 STSM 03/Septemer 30/Novemer/2017 (3 months) Host: Home: Thoms
Bioctive milk components to secure growth nd gut development in preterm pigs ESTER ARÉVALO SUREDA PIGUTNET FA1401 STSM STSM Pigutnet FA1401 STSM 03/Septemer 30/Novemer/2017 (3 months) Host: Home: Thoms
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi: 1.138/nnno.211.41 Sili nd titnium dioxide nnoprtiles use pregnny omplitions in mie Kohei Ymshit, Ysuo Yoshiok, Kzum Higshisk, Kzuy Mimur, Yuki Morishit, Mstoshi Nozki, Tokuyuki
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi: 1.138/nnno.211.41 Sili nd titnium dioxide nnoprtiles use pregnny omplitions in mie Kohei Ymshit, Ysuo Yoshiok, Kzum Higshisk, Kzuy Mimur, Yuki Morishit, Mstoshi Nozki, Tokuyuki
LETTER. Aberrant light directly impairs mood and learning through melanopsin-expressing neurons
 oi:1.138/nture11673 Aerrnt light iretly impirs moo n lerning through melnopsin-expressing neurons Tr A. LeGtes 1 *, Cr M. Altimus 1 *,HuiWng 2, Hey-Kyoung Lee 2, Sunggu Yng 2, Hiqing Zho 1, Alfreo Kirkwoo
oi:1.138/nture11673 Aerrnt light iretly impirs moo n lerning through melnopsin-expressing neurons Tr A. LeGtes 1 *, Cr M. Altimus 1 *,HuiWng 2, Hey-Kyoung Lee 2, Sunggu Yng 2, Hiqing Zho 1, Alfreo Kirkwoo
University of Groningen
 University of Groningen The prevlene of sesonl ffetive disorder in the Netherlnds Mersh, PPA; Middendorp, HM; Bouhuys, Antoinette; Beersm, DGM; vn den Hoofdkker, RH; Middendorp, Hermine M. Pulished in:
University of Groningen The prevlene of sesonl ffetive disorder in the Netherlnds Mersh, PPA; Middendorp, HM; Bouhuys, Antoinette; Beersm, DGM; vn den Hoofdkker, RH; Middendorp, Hermine M. Pulished in:
REVIEW Study of the Formation of trans Fatty Acids in Model Oils (triacylglycerols) and Edible Oils during the Heating Process
 JARQ 46 (3), 215 220 (2012) http://www.jirs.ffr.go.jp REVIEW Study of the Formtion of trns Ftty Aids in Model Oils (triylglyerols) nd Edible Oils during the Heting Proess Wkko TSUZUKI* Food Resoure Division,
JARQ 46 (3), 215 220 (2012) http://www.jirs.ffr.go.jp REVIEW Study of the Formtion of trns Ftty Aids in Model Oils (triylglyerols) nd Edible Oils during the Heting Proess Wkko TSUZUKI* Food Resoure Division,
Genome-wide nucleosome positioning during embryonic stem cell development
 Genome-wide nuleosome positioning during emryoni stem ell development Vldimir B Teif 1,2, Yevhen Vinshtein 2,3, Mïwen Cudron-Herger 1,2, Jn-Philipp Mllm 1,2, Croline Mrth 1,2, Thoms Höfer 2,3 & Krsten
Genome-wide nuleosome positioning during emryoni stem ell development Vldimir B Teif 1,2, Yevhen Vinshtein 2,3, Mïwen Cudron-Herger 1,2, Jn-Philipp Mllm 1,2, Croline Mrth 1,2, Thoms Höfer 2,3 & Krsten
PTSE RATES IN PNNI NETWORKS
 PTSE RATES IN PNNI NETWORKS Norert MERSCH 1 Siemens AG, Hofmnnstr. 51, D-81359 Münhen, Germny Peter JOCHER 2 LKN, Tehnishe Universität Münhen, Arisstr. 21, D-80290 Münhen, Germny Lrs BURGSTAHLER 3 IND,
PTSE RATES IN PNNI NETWORKS Norert MERSCH 1 Siemens AG, Hofmnnstr. 51, D-81359 Münhen, Germny Peter JOCHER 2 LKN, Tehnishe Universität Münhen, Arisstr. 21, D-80290 Münhen, Germny Lrs BURGSTAHLER 3 IND,
Treadmill exercise improves behavioral outcomes and spatial learning memory through up-regulation of reelin signaling pathway in autistic rats
 Originl Artile http://dx.doi.org/1.12965/jer.133 Journl of Exerise Rehilittion 213;9(2):22-229 Tredmill exerise improves ehviorl outomes nd sptil lerning memory through up-regultion of reelin signling
Originl Artile http://dx.doi.org/1.12965/jer.133 Journl of Exerise Rehilittion 213;9(2):22-229 Tredmill exerise improves ehviorl outomes nd sptil lerning memory through up-regultion of reelin signling
PROVEN ANTICOCCIDIAL IN NEW FORMULATION
 PROVEN ANTICOCCIDIAL IN NEW FORMULATION Coxidin 100 microgrnulte A coccidiosttic dditive for roilers, chickens rered for lying nd turkeys Contins 100 g of monensin sodium per kg Aville s homogenous grnules
PROVEN ANTICOCCIDIAL IN NEW FORMULATION Coxidin 100 microgrnulte A coccidiosttic dditive for roilers, chickens rered for lying nd turkeys Contins 100 g of monensin sodium per kg Aville s homogenous grnules
The GCN5-CITED2-PKA signalling module controls hepatic glucose metabolism through a camp-induced substrate switch
 Reeived 6 Apr 216 Aepted 8 Sep 216 Pulished 22 Nov 216 DOI: 1.138/nomms13147 OPEN The GCN5-CITED2-PKA signlling module ontrols hepti gluose metolism through AMP-indued sustrte swith Mshito Ski 1, Tomoko
Reeived 6 Apr 216 Aepted 8 Sep 216 Pulished 22 Nov 216 DOI: 1.138/nomms13147 OPEN The GCN5-CITED2-PKA signlling module ontrols hepti gluose metolism through AMP-indued sustrte swith Mshito Ski 1, Tomoko
VTA CRF neurons mediate the aversive effects of nicotine withdrawal and promote intake escalation
 CRF neurons medite the versive effets of niotine withdrwl nd promote intke esltion Tryn E Grieder 1, Meliss A Hermn 2, Cndie Contet 2, Lur A Tn 3, Hetor Vrgs-Perez 1, Ami Cohen 2, Mihl Chwlek 1, Geith
CRF neurons medite the versive effets of niotine withdrwl nd promote intke esltion Tryn E Grieder 1, Meliss A Hermn 2, Cndie Contet 2, Lur A Tn 3, Hetor Vrgs-Perez 1, Ami Cohen 2, Mihl Chwlek 1, Geith
Tbp. Per Relative mrna levels Circadian Time. Liver weight/ body weight (%) n.s. Pernull
 Liver weight/ ody weight (%) Dy Body weight (g) Reltive mrna levels Reltive mrna levels Reltive mrna levels Reltive mrna levels Dy Per1 Per2 Per3 Tp 8 2 8 2. 6 2 8 12162 Cirdin Time 3 2 1 2 1 1 8 12162
Liver weight/ ody weight (%) Dy Body weight (g) Reltive mrna levels Reltive mrna levels Reltive mrna levels Reltive mrna levels Dy Per1 Per2 Per3 Tp 8 2 8 2. 6 2 8 12162 Cirdin Time 3 2 1 2 1 1 8 12162
Abortion frequency (%) Ovary position on ear Ovary volume (mm 3 )
 ortion frequeny (%) 5 1 Ovry position on er 3 1 WW WD pex Bse Ovry volume (mm 3 ) Figure S1. Ovry volume (thik lines) n ortion frequeny (thin lines) s funtion of position long the er, 15 ys fter silk emergene
ortion frequeny (%) 5 1 Ovry position on er 3 1 WW WD pex Bse Ovry volume (mm 3 ) Figure S1. Ovry volume (thik lines) n ortion frequeny (thin lines) s funtion of position long the er, 15 ys fter silk emergene
Neural antecedents of self-initiated actions in secondary motor cortex
 Neurl nteedents of self-initited tions in seondry motor ortex Msyoshi Murkmi, M Inês Viente, Gil M Cost & Zhry F Minen npg Nture Ameri, In. All rights reserved. The neurl origins of spontneous or self-initited
Neurl nteedents of self-initited tions in seondry motor ortex Msyoshi Murkmi, M Inês Viente, Gil M Cost & Zhry F Minen npg Nture Ameri, In. All rights reserved. The neurl origins of spontneous or self-initited
AJ PUTT. Hematology. Chemistry. Species: Canine Gender: Female Year of Birth: 2013 Client: PUTT
 Speies: Cnine Gender: Femle Yer of Birth: 2013 Client: PUTT Requisition #: 9034-12 Aession #: W2152816 Aount Code: 72364 Veterinrin: CARTER Pnel/Profile: Tik Pnel Add-on Senior Profile with L 4Dx Plus
Speies: Cnine Gender: Femle Yer of Birth: 2013 Client: PUTT Requisition #: 9034-12 Aession #: W2152816 Aount Code: 72364 Veterinrin: CARTER Pnel/Profile: Tik Pnel Add-on Senior Profile with L 4Dx Plus
Desiccation enhances rapid cold hardening in the flesh fly Sarcophaga bullata: evidence for cross tolerance between rapid physiological responses
 J Comp Physiol B (217) 187:79 86 DOI 1.17/s36-16-13- ORIGINAL PAPER Desition enhnes rpid old hrdening in the flesh fly Srophg ullt: evidene for ross tolerne etween rpid physiologil responses Shu Xi Yi
J Comp Physiol B (217) 187:79 86 DOI 1.17/s36-16-13- ORIGINAL PAPER Desition enhnes rpid old hrdening in the flesh fly Srophg ullt: evidene for ross tolerne etween rpid physiologil responses Shu Xi Yi
Mediating Multi-Party Negotiation Through Marker-Based Tracking of Mobile Phones
 Mediting Multi-Prty Negotition Through Mrker-sed Trking of Moile Phones Mihel Rohs Deutshe Telekom Lortories TU erlin, Germny mihel.rohs@telekom.de hristin Kry Informtis Reserh Institute Newstle University,
Mediting Multi-Prty Negotition Through Mrker-sed Trking of Moile Phones Mihel Rohs Deutshe Telekom Lortories TU erlin, Germny mihel.rohs@telekom.de hristin Kry Informtis Reserh Institute Newstle University,
