SK channels and NMDA receptors form aca 2+ -mediated feedback loop in dendritic spines
|
|
|
- Ethelbert Bryan
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
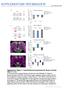
1 25 Nture Pulishing Group SK hnnels nd NMDA reeptors form C 2+ -medited feedk loop in dendriti spines Thu Jennifer Ngo-Anh 1,4, Brend L Bloodgood 2,4, Mihel Lin 1, Bernrdo L Stini 2, Jmes Mylie 3 & John P Adelmn 1 Smll-ondutne C 21 -tivted K 1 hnnels (SK hnnels) influene the indution of synpti plstiity t hippompl CA3 CA1 synpses. We find tht in mie, SK hnnels re lolized to dendriti spines, nd their tivity redues the mplitude of evoked synpti potentils in n NMDA reeptor (NMDAR)-dependent mnner. Using omined two-photon lser snning mirosopy nd two-photon lser unging of glutmte, we show tht SK hnnels regulte NMDAR-dependent C 21 influx within individul spines. SK hnnels re tightly oupled to synptilly tivted C 21 soures, nd their tivity redues the mplitude of NMDAR-dependent C 21 trnsients. These effets re medited y feedk loop within the spine hed; during n exittory postsynpti potentil (EPSP), C 21 influx opens SK hnnels tht provide lol shunting urrent to redue the EPSP nd promote rpid Mg 21 lok of the NMDAR. Thus, loking SK hnnels filittes the indution of long-term potentition y enhning NMDAR-dependent C 21 signls within dendriti spines. In CA1 hippompl neurons, pmin-sensitive SK hnnels modulte firing frequeny y ontriuting to the fter-hyperpolriztion (AHP) tht follows n tion potentil 1 3. Additionlly, loking SK hnnels with pmin filittes the indution of long-term potentition (LTP) t Shffer ollterl CA1 synpses. shifts the point of infletion etween long-term depression (LTD) nd long-term potentition (LTP) suh tht lower stimulus frequenies 4 n generte LTP. Results from ehviorl experiments prllel the effets indued y pmin in rin slies. rosses the lood-rin rrier 5, nd intrperitonel injetion filittes the quisition of hippompl-dependent lerning tsks suh s loting the hidden pltform in the Morris wter mze, nd novel ojet reognition 4. Severl forms of long-term plstiity t the CA3 CA1 synpses re triggered y C 2+ influx through NMDARs, nd the kinetis nd mplitudeofevokedc 2+ trnsients in the postsynpti ell determine the diretion nd extent of synpti plstiity. A reltively smller nd prolonged C 2+ uildup results in LTD, wheres lrger, more trnsient inrese fvors LTP Exmintion of C 2+ signls within CA1 dendriti spines demonstrtes tht synpti stimultion results in NMDAR-medited inreses in C 2+ tht re limited to the spine hed housing the tivted synpse 13. At resting potentils, NMDARs re lrgely loked y extrellulr Mg 2+ ions 14. The pprent ffinity of Mg 2+ for the reeptor is strongly voltge-dependent, nd C 2+ influx is gretly entuted y depolriztion. Thus, memrne potentil exerts strong influene on spine C 2+ trnsients, whih influenes downstrem C 2+ -dependent proesses suh s the indution of synpti plstiity. Here we show tht SK hnnels re lolized to dendriti spines nd ply role in shping synpti responses. -sensitive SK hnnels re tivted y synptilly evoked C 2+ trnsients nd t to redue the mgnitude of exittory postsynpti potentils (EPSPs) mesured t the som. This negtive regultion ours within individul spines, where SK hnnels respond to rpid inreses in C 2+ nd redue the mplitude of NMDAR-medited C 2+ trnsients. The effets of different C 2+ uffers show tht SK hnnels re positioned within synptilly tivted C 2+ signling mirodomin nd t rpidly to influene the EPSP. RESULTS SK hnnel distriution in ultured hippompl neurons We expressed mouse SK2 hnnels hroring n extrellulr triplemy epitope tg (msk2-my) 15 nd green fluoresent protein (GFP) in dissoited, ultured neurons from re CA1 of the hippompus. Live-ell immunostining with monolonl ntiody to my (ntimy) performed 1 week fter trnsfetion showed tht virtully every spine ws lerly deorted with SK2 hnnels (Fig. 1). Immunoretivity ws lso present in lusters within the dendriti shfts nd in the som. Thus, exogenously expressed SK2 hnnels lolize to dendriti spines where they re positioned long with NMDARs in the onfined C 2+ signling domin of glutmtergi synpses. inreses synptilly evoked EPSPs We reorded the effets of pmin on suthreshold EPSPs in whole-ell urrent-lmped CA1 neurons in ute slies from mouse 1 Vollum Institute, Oregon Helth & Siene University, 3181 SW Sm Jkson Prk Rod, Portlnd, Oregon 97239, USA. 2 Deprtment of Neuroiology, Hrvrd Medil Shool, 2 Longwood Ave., Goldenson 316, Boston, Msshusetts 2115, USA. 3 Deprtment of Ostetris nd Gyneology, Oregon Helth & Siene University, 3181 SW Sm Jkson Prk Rod, Portlnd, Oregon 97239, USA. 4 These uthors ontriuted eqully to this work. Correspondene should e ddressed to J.P.A. (delmn@ohsu.edu). Pulished online 24 April 25; doi:1.138/nn VOLUME 8 [ NUMBER 5 [ MAY 25 NATURE NEUROSCIENCE
2 Reurrent xon Figure 1 Live-ell immunostining of ultured hippompl neuron expressing msk2-my (red) nd ytosoli GFP (green). SK2 hnnel immunoretivity n e seen in virtully every spine. Clusters of SK2 immunoretivity were deteted in the dendriti shfts nd reurrent xon. Although osured y the intensity of the GFP fluoresene, more homogeneous SK2 stining pttern ws deteted in the som. 25 Nture Pulishing Group s Reurrent xon Initil xon hippompus. After whole-ell formtion, we pplied 1-ms urrent pulse to the strtum rditum, nd we djusted the stimulus strength to pproximtely one-third of the threshold needed to evoke n tion potentil, yielding EPSPs with mplitudes of 2 8 mv. Bloking NMDA reeptors with (D(-)-2-mino-5-phosphono-vleri id; 1 mm) redued suthreshold EPSP mplitudes to n verge of % of the ontrol, nd pplition of with 6-yno-7-nitroquinoxline- 2,3-dione (CNQX; 2 mm) to lok -mino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4- isoxzole propioni id reeptors (AMPARs) essentilly eliminted the EPSPs, reduing the verge mplitude to % of the ontrol (n ¼ 3; dt not shown). These dt show tht lthough the EPSP results primrily from tivtion of AMPARs, smll ut mesurle ontriution is mde y urrent flow through NMDARs. To determine whether pmin-sensitive SK hnnels shpe the synpti potentil, EPSPs were reorded every 2 s efore (ontrol solution) nd fter wsh-in of pmin (1 nm; Fig. 2). In representtive ell (Fig. 2,), the pek EPSP, mesured from the Figure 2 SK hnnels modulte synptilly evoked EPSPs. () Plot of EPSP mplitude (top), input resistne (middle) nd memrne potentil (ottom) from representtive ell during wsh-in of pmin (1 nm) nd pmin plus (1 mm). () Averge of 2 EPSPs quired in ontrol onditions, in the presene of pmin or in the presene of pmin plus. () Summry plot of the EPSP mplitude reltive to the seline period during wsh-in of pmin nd in the presene of pmin plus (n ¼ 5 ells). (d) Averge of 15 summted EPSPs under ontrol onditions nd in the presene of pmin from representtive ell. Arrowheds indite stimulus times (five pulses t 1 Hz). (e) Summry plot of the effets of pmin on the summted EPSP (n ¼ 5 ells). The times of drug pplition re indited y the horizontl rs. Sle r: 1 mv in, 2mVind, 25ms for nd d. Error rs re men 7 s.e.m. verge of 2 EPSPs, inresed from 3.3 mv in the ontrol solution to 5.6 mv fter pmin pplition. Susequent pplition of (1 mm) reversed the pmin-indued inrese of the EPSP mplitude; in the presene of pmin nd, the pek of the verged EPSP ws 2.5 mv. On verge, pmin inresed the mplitude of the EPSP to % of the ontrol (P o.5, n ¼ 5) nd susequent opplition of redued the EPSP mplitude to % of the ontrol (Fig. 2 nd Tle 1). The pmin effet ws oserved in every ell tested. SK hnnels re the only known trgets for pmin, ut pmin does not relily wsh out of the slie. Therefore, the effets of D-tuourrine (dtc; 1 mm) 16, more reversile though less seletive SK hnnel loker, were lso exmined. In six ells tested, dtc inresed the mplitude of the EPSP to % (P o.5) of the ontrol. The inrese indued y dtc ws lrgely, though not ompletely, reversed upon wshout ( % of the ontrol; P ¼.5; Tle 1). The indution of long-term potentition usully requires repetitive synpti tivtion, nd pmin shifts the threshold for the indution of synpti plstiity to lower stimulus frequenies 4,17. Therefore, we exmined the effet of pmin on the summted EPSP during synptilly evoked trin of five pulses t 1 Hz. In representtive ell (Fig. 2d) pmin inresed the verge summted EPSP y 4 mv to 153% of the ontrol. Aross five ells tested, pmin V rest R inp EPSP (mv) (MΩ) (mv) d EPSP (% of ontrol) e EPSP (% of ontrol) NATURE NEUROSCIENCE VOLUME 8 [ NUMBER 5 [ MAY
3 Tle 1 Effets of pmin on synptilly evoked EPSPs Condition (n) EPSP (mv) Slope (V/s) HW (ms) Rise time (ms) ( %) ( %) (5) ( %) (84 7 8%) Nture Pulishing Group dtc ( %) ( %) Wshout (6) ( %) ( %) (78 7 5%) (8 7 4%) (7) (96 7 3%) (93 7 5%) (.2 mm Mg 2+ ) (6) ( %), ( %) (CNQX) (9) ( %) ( %) (5) ( %) nd Nd nd (5 mm BAPTA) (6) (89 7 3%) ( %) (5 mm EGTA) (8) ( %) ( %) (1 mm BAPTA) (5) ( %) ( %) Properties of synptilly evoked responses. Slope is defined s the mximum rte of rise of the EPSP. Rise time is defined s the time required for the EPSP torisefrom2to8% of the mximum mplitude. Hlf-width (HW) is the width of the synpti potentil mesured t 5% of the mximum mplitude. Numers in prentheses re perentge of the ontrol for eh ondition. P o.5 ompred with ontrol. P o.5 ompred with inrese in norml th solution. pplition inresed the summted EPSP to % of the ontrol (P o.5; Fig. 2e). NMDAR tivity is required for pmin sensitivity of EPSPs Dendriti spines re utonomous C 2+ signling omprtments highly speilized for the rpid lrge-mplitude C 2+ flututions tht underlie synpti plstiity 13. The results presented ove suggest tht the effets of pmin on the mplitude of the EPSP re due to regultion of NMDARs in response to synptilly evoked inreses in C 2+.Therefore, pplying NMDAR lokers suh s efore pmin should olude pmin s effets. Indeed, loking NMDARs with redued Figure 3 -indued EPSP inreses require NMDAR tivity. () Averge of 25 EPSPs in ontrol onditions, in the presene of, or in the presene of plus pmin from representtive ell. () Summry plot of the effets of or plus pmin pplition on EPSP peks (n ¼ 7 ells). () Averge EPSPs in solutions ontining.2 mm externl Mg 2+ or.2 mm Mg 2+ plus pmin. (d) Summry plot of the effets of pmin pplition on EPSP peks in the presene of low externl [Mg 2+ ] (n ¼ 6). (e) Averge evoked EPSPs reorded in the presene of CNQX nd no Mg 2+ (ontrol) nd with the dditionl pplition of pmin or plus pmin. Exmples re shown in whih the NMDAR-dependent EPSP ws lerly visile (top) or not detetle (ottom) efore pmin pplition. (f) Summry plot of the effets of pmin nd pmin plus on the pek of the isolted NMDAR-medited EPSP (n ¼ 5). The times of drug pplition re indited y the horizontl rs. Sle r: 1mVfor,,.5 mv for e, nd 25 ms for,,e. Error rs re men 7 s.e.m. the EPSP to % of the ontrol (P o.5), nd susequent pplition of with pmin hd no effet on the EPSP mplitude (96 7 3% of the vlue reorded with, n ¼ 7; Fig. 3, nd Tle 1). e Low Mg 2+ + EPSP (% of ontrol) EPSP (% of ontrol) EPSP (% of ontrol) NMDAR only + + d f VOLUME 8 [ NUMBER 5 [ MAY 25 NATURE NEUROSCIENCE
4 yield detetle EPSP. inresed the NMDAR-medited EPSP to % of tht in the presene of CNQX (P o.5, n ¼ 9), nd susequent pplition of to five of the ells essentilly eliminted the EPSP ( of the ontrol; Fig. 3e,f nd Tle 1). 25 Nture Pulishing Group PPF (% of ontrol) Figure 4 hs no effet on pired pulse filittion. () Synptilly evoked EPSP pirs (1-ms inter-pulse intervl) under ontrol onditions nd in the presene of pmin from representtive ell. Sle r: 1 mv, 25 ms. () Summry plot of PPF reltive to ontrol vlues during pplition of pmin s indited y the horizontl r (n ¼ 6 ells). Error rs re men 7 s.e.m. SK hnnels re tivted y hnges in intrellulr C 2+, suggesting tht ugmenting synptilly evoked C 2+ influx should inrese SK hnnel tivtion nd mplify the effet of pmin on the EPSP. As B8% of the C 2+ trnsient in dendriti spines is due to C 2+ influx through NMDARs (see elow), reduing Mg 2+ lok of NMDARs y lowering the externl Mg 2+ onentrtion ([Mg 2+ ]) to.2 mm should result in lrger synptilly evoked C 2+ influx. Under these onditions, pmin pplition inresed the EPSP to % of the ontrol (P o.5, n ¼ 6), whih ws lrger thn the pmin-indued inrese when externl [Mg 2+ ]ws1mm(p o.5; Fig. 3,d nd Tle 1). Preinution with oluded the pmin-indued hnge in the EPSP in the presene of.2 mm Mg 2+ (dt not shown). We exmined the effets of pmin on the isolted NMDAR omponent of the response y reording EPSPs while loking AMPARs (Fig. 3e,f). In initil experiments, setting the stimulus strength in ontrol onditions to one-third of threshold ompromised the ility of the stimulus to relily eliit n EPSP fter ddition of AMPAR lokers, lthough susequent pplition of pmin showed n EPSP tht ws eliminted y (Fig. 3e). To enhne the NMDAR omponent, the stimulus strength ws inresed in AMPAR lokers to 2 inreses EPSPs y postsynpti mehnism The model presented ove suggests tht pmin ts postsynptilly, ut th pplition of pmin my hve oth pre- nd postsynpti effets. Pired-pulse filittion (PPF), defined s the rtio of the mplitude of the seond EPSP to tht of the first fter losely delivered pir of stimuli, is sensitive ssy of presynpti hnges in glutmte relese proility 18. When we pplied pired-pulse stimultions seprted y 1 ms, pmin pplition inresed the peks of the EPSPs without ltering PPF ( in the ontrol, in the presene of pmin, n ¼ 6; Fig. 4,). This result is onsistent with postsynpti site of tion of pmin. inreses synptilly evoked spine C 2+ influx Tken together, our results suggest tht SK hnnels reside in the dendriti spine hed, lose to synptilly evoked C 2+ soures. If opening SK hnnels imposes repolriztion tht fvors Mg 2+ lok of NMDARs, then loking SK hnnels with pmin should inrese the mplitude nd prolong the durtion of NMDAR-medited C 2+ influx. To test this hypothesis, spine C 2+ trnsients were exmined with two-photon lser snning mirosopy while the synpse on the visulized spine ws stimulted with two-photon lser unging of 4-methoxy-7-nitroindolinyl (MNI)-glutmte (Fig. 5; ref.19).twophoton lser unging llows the seletive stimultion of the synpse on ny visulized spine, nd euse of the rief nd fol relese of glutmte, it n e used to urtely mimi the time ourse of innte synpti events in hippompl pyrmidl neurons 2. Furthermore, two-photon lser unging is dvntgeous over eletril stimultion of xonl fiers euse it llows the true stimultion of single synpse on the ell, voiding stimultion of multiple synpses tht my led to seondry tivtion of tive ondutnes, ltering the EPSP mplitude nd time ourse. Lstly, y ypssing the presynpti terminl, filures of synpti trnsmission re voided nd tril-to-tril vriility is redued, llowing popultion omprison of synpti responses in ontrol onditions nd in the presene of pmin. Figure 5 Single synpse responses nd NMDAR-dependent spine C 2+ signls evoked with two-photon unging of glutmte. () Imge of n pil spiny dendrite of CA1 hippompl pyrmidl neuron olleted with twophoton lser snning mirosopy (left). Fluoresene from the red Alex Fluor 594 hnnel is shown. Simultneously reorded green (Fluo-5F) nd red (Alex Fluor 594) fluoresene (right) were olleted in line sns tht interset the spine hed nd neighoring dendrite indited y the dshed line (left). The urrent ws evoked y.5-ms, 72-nm glutmte unging pulse direted t the spine indited y the rrowhed. Inreses in green fluoresene, inditive of elevtions in intrellulr C 2+, were limited to the stimulted spine hed. Sle r: 1 mm (left), 25 ms (right). () For the spine depited in, unging prmeters were set to evoked B15-pA uepsc (top). After swithing to urrent-lmp mode nd leving the unging pulse unhnged, the uepsp (middle) nd fluoresene trnsient (DG/R syn,ottom) were reorded. () Representtive uepsc (top), uepsp (middle) nd ompnying C 2+ trnsient (ottom) reorded in the presene of NMDAR lokers (2 mm CPP nd 4 mm MK81). Eh tre is the verge of ten trils. Sle r: 6 pa (top),.45 mv (middle), 3% G/R (ottom), nd 25 ms. uepsc uepsp G/R syn CPP+MK81 NATURE NEUROSCIENCE VOLUME 8 [ NUMBER 5 [ MAY
5 Tle 2 Properties of single-spine unging evoked responses. uepsc uepsp Condition (n) Amplitude (pa) Rise time (ms) HW (ms) Amplitude (mv) Rise time (ms) HW (ms) (24) (1 7 3%) (1 7 9%) (1 7 7%) (1 7 1%) (1 7 11%) (1 7 1%) 25 Nture Pulishing Group (25) CA1 pyrmidl neurons were filled with the C 2+ -sensitive fluorophore Fluo-5F (3 mm) to reord C 2+ trnsients nd with the C 2+ - independent fluorophore Alex Fluor 594 (1 mm) to visulize spines nd dendrites. Both fluorophores re effiiently two-photon exited y 81-nm lser light, with Fluo-5F emitting in the green (5 56 nm) nd Alex Fluor 594 emitting in the red ( nm). Under these onditions, hnges in green fluoresene reltive to resting red fluoresene (DG/R) re linerly proportionl to inreses in intrellulr [C 2+ ] fter suthreshold synpti stimultion 13. We seleted spines within the proximl (o15 mm) pil dendrite for nlysis. Cells were initilly held in voltge lmp, nd we set the unging lser pulse durtion nd mplitude to evoke B15-pA synpti urrent (uepsc; Fig. 5,top,ndTle 2). The mplifier ws susequently swithed to urrent-lmp mode, nd the ungingevoked EPSP (uepsp) nd synptilly evoked C 2+ trnsient were monitored with the sme unging prmeters (Fig. 5, middle, ottom). The fluoresene trnsient ompnying the uepsp ws reorded in line sn mode (5 Hz) from the stimulted spine hed (DG/R syn ) nd the neighoring prent dendrite. In sl onditions, the uepsp hd n mplitude of mv, 2 8% rise time (the time required for the EPSP to rise from 2 to 8% of its mximum mplitude) of ms nd hlf-width (the width of the synpti potentil mesured t 5% of the mximum mplitude) of 3 7 3ms (properties of the uepsc nd uepsp re summrized in Tle 2). The uepsp ws ompnied y n inrese in spine C 2+ levels (DG/R syn ¼ %) tht rose quikly (2 8% rise time ¼ ms) nd ws limited to the stimulted spine. After stimultion, C 2+ remins elevted in the spine hed euse of the slow lerne of C 2+ from the spine in the presene of C 2+ inditor 13. (97 7 3%) ( %) ( %) (19 7 8%) ( %) ( %) CPP + MK81 (21) (97 7 5%) ( %) ( %) ( %) ( %) ( %) + CPP + MK81 (22) (99 7 5%) ( %) ( %) ( %) (89 7 7%) (1 7 1%) Rise time is defined s the time required for the EPSP or EPSC to rise from 2 to 8% of the mximum mplitude.hw is the width of the synpti urrent or potentil mesured t 5% of the mximum mplitude. In prentheses for eh ondition re men 7 s.e.m. expressed s perentge of the men vlue in the ontrol ondition. P o.5 y ANOVA, ompring mesurements in ontrol onditions with mesurements in the presene of pmin; or ompring mesurements in the presene of CPP plus MK81 with mesurements in the presene of pmin plus CPP plus MK81. To onfirm tht the evoked C 2+ influx ws due to tivtion of NMDARs, the sme experiments were repeted in the presene of the NMDAR ntgonists 2-roxypiperzin-4-yl-propyl-1-1 phosphoni id (CPP, 2 mm) nd MK81 (4 mm; Fig. 5). In these onditions, the uepsc nd uepsp were unhnged from ontrol onditions (Tle 2) wheres the mplitude of synptilly evoked C 2+ trnsients ws redued to % DG/R syn (17% of the ontrol levels). Thus, C 2+ influx through NMDARs ontriutes the mjority of the C 2+ evoked y uepsps. The effet of tivtion of SK hnnels on the mplitude of the C 2+ trnsients within individul spine heds tht ontin tive synpses ws exmined in popultion of ells exposed to pmin (1 nm). The properties of the uepsc were unffeted, nd the uepsp ws slightly inresed (Fig. 6 nd Tle 2). The smller effet on synpti potentils seen here is likely due to the redued SK hnnel tivtion in uepsc uepsp G/R syn CPP+MK81 Figure 6 Bloking SK hnnels with pmin inreses NMDAR-medited spine C 2+ trnsients. () Averge uepsc, uepsp nd DG/R syn under ontrol onditions nd in the presene of pmin (n ¼ 24 nd 25 spines, respetively). () Averge uepsc (top), uepsp (middle) nd DG/R syn (ottom) in the presene of NMDAR lokers (lk) nd NMDAR lokers + pmin (red; n ¼ 21 nd 22 spines, respetively). Sle r: 6 pa (top),.45 mv (middle) nd 6% G/R (ottom), nd 25 ms for,. The shded region shows the men 7 s.e.m. for eh verge tre. () Comprison of the C 2+ trnsient mplitude nd rise time eh ondition. *, P o.5 ompred with ontrol. G/R syn (%) 1 5 * * * CPP+MK Ap+CPP+MK Rise time (ms) 3 15 * CPP+MK Ap+CPP+MK 646 VOLUME 8 [ NUMBER 5 [ MAY 25 NATURE NEUROSCIENCE
6 25 Nture Pulishing Group Figure 7 Effets of BAPTA nd EGTA on the pmin-indued inrese of the EPSP. (,) Synptilly evoked EPSPs were reorded in ontrol onditions or in the presene of pmin with either 5 mm BAPTA or 5 mm EGTA in the pth pipette s indited. (,d) Summry plots of the effets of pmin on EPSP peks for intrellulr solutions ontining 5 mm BAPTA (; n ¼ 1 ells) or 5 mm EGTA (d; n ¼ 8 ells). The time period of pmin pplition is indited y the rs. Sle r: 1 mv nd 25 ms. Error rs re men 7 s.e.m. the presene of the BAPTA-sed inditor Fluo-5F nd the lrge vriility of single-synpse evoked potentils (oeffiient of vrition of B5%). The mplitude nd the rising phse of uepsp-evoked C 2+ influx in the presene of pmin were inresed to % DG/R syn nd ms, or 172% nd 169% of the ontrol, respetively. The effets of SK hnnel lokge require tive NMDARs, euse in the presene of CPP plus MK81, the uepsc, uepsp, nd DG/R syn were identil in ontrol onditions nd in the presene of pmin (Fig. 6). Thus, fter tivtion of single synpse, SK hnnels t within the tive spine to redue the mplitude of NMDAR-medited C 2+ trnsients. SK hnnels nd C 2+ soures form mirodomin Our results indited tht SK hnnels re loted on the spine nd regulte C 2+ influx into the tive spine hed in response to synptilly tivted C 2+ soures. To estimte the distne etween SK hnnels nd the C 2+ soure tht tivtes them, synptilly evoked EPSPs were reorded in the presene of BAPTA, rpid C 2+ heltor, or EGTA, slower C 2+ heltor, in the internl solution. When the neuron ws dilyzed with 5 mm BAPTA, the effets of pmin on the EPSP mplitude were oluded (89 7 3% of the ontrol, n ¼ 6; Fig. 7, nd Tle 1). In ontrst, when 5 mm EGTA ws inluded in the pipette solution, pplition of pmin inresed the EPSP to % of the ontrol (P o.5, n ¼ 8; Fig. 7,d nd Tle 1), whih ws not different from the inrese indued y pmin in the ontrol internl solution. Additionlly, with 1 mm BAPTA in the pipette solution, the pmin-medited inreses of the EPSP were % of the ontrol (P o.5, n ¼ 5; Tle 1). These results further support postsynpti tion y pmin nd, notly, re onsistent with lose sptil oupling etween SK hnnels nd synptilly tivted C 2+ soures within individul spine heds. DISCUSSION The entrl finding of this work is tht in dendriti spines of CA1 neurons, C 2+ entry fter synpti tivtion opens SK hnnels tht t to limit the mplitude of synpti potentils nd redue C 2+ influx through NMDARs. As desried elow, this feedk loop is engged y the tivity of single synpse nd regultes NMDAR-evoked C 2+ influx within the tive spine hed. As NMDAR-medited C 2+ is quntittively ritil to the proesses underlying the indution of synpti plstiity 6 12, this feedk loop likely ounts for the effets of pmin on the threshold for LTP indution. Furthermore, our results suggest tht SK hnnel modultion offers powerful mehnism to fine-tune the indution of synpti plstiity. Effetsofpminofsynptiresponses Bloking SK hnnels with pmin inreses the synptilly evoked EPSP mplitude. This effet is prevented y pretretment with NMDAR lokers nd is still present when the NMDAR omponent of the EPSP is isolted. Thus, NMDARs re neessry nd suffiient for the effets of pmin on the EPSP, nd pmin inreses synpti potentils y enhning the normlly smll ontriution of the 5 mm BAPTA 5 mm EGTA d EPSP (% of ontrol) EPSP (% of ontrol) NMDAR to the EPSP. The lrge effet tht pmin hs on NMDAR tivtion is prtiulrly evident when the isolted NMDAR omponent of the EPSP is exmined. Despite the smll, or in severl ells, undetetle, NMDAR-medited response to synpti stimultion, pmin pplition demonstrted prominent -sensitive EPSP. As NMDARs re responsile for the mjority of the C 2+ influx into the spine hed evoked y unging, their inresed tivtion in the presene of pmin oosts spine hed C 2+ trnsients y 72%. The effets of pmin on spine C 2+ trnsients were, y neessity, monitored in ells loded with C 2+ inditors tht redue the mplitude of evoked C 2+ trnsients nd susequent tivtion of SK hnnels. Therefore, pmin pplition is likely to inrese synptilly evoked spine C 2+ trnsients even more roustly in neurons free of BAPTAsed C 2+ uffers. lso inreses the initil slope of the EPSP to similr extent tht it inreses the mplitude (Tle 1). The initil slope ws mesured s the mximum rte of rise of the EPSP, whih usully ours etween 1 nd 2% of the rise time (B2 msintotheepsp). The initil slope ws inresed for oth the rpidly rising, mixed AMPAR- nd NMDAR-medited EPSP, nd for the slower, isolted NMDAR-medited EPSP, whih hd 2 8% rise times of ms nd ms, respetively. Is the effet of pmin on the rte of rise of the EPSP omptile with the slow opening of NMDARs? The mrosopi kinetis of the synptilly evoked NMDAR-medited omponent of the EPSP, whih rehes pek in out 2 ms (refs. 21,22), hs een ttriuted to the intrinsi gting kinetis of the hnnel 23,24. Complementry single-hnnel reords show tht gting is omplited, ut heterologously expressed NMDARs re tivted with 1 9% rise times of B7 11 ms (refs. 25,26). The predominnt omponent of Mg 2+ unloking of NMDARs is very fst, ourring in B1 ms (ref. 27) nd is not rte-limiting. Tken together, these dt suggest tht t lest smll numer of NMDARs open erly in the response nd ontriute to the rising phse nd pek of the EPSP. These erly-opening hnnels my lso provide the soure of C 2+ tht rpidly tivtes pmin-sensitive SK hnnels. Regultion of synpti responses y SK hnnels Our dt indite tht SK hnnels re loted ner glutmtergi synpses in dendriti spines. We demonstrte tht exogenously expressed SK2 hnnels re trgeted to spine heds nd tht tivtion of single synpse engges SK hnnels to regulte NMDAR-dependent C 2+ influx within the tive spine hed. Wht synptilly evoked C 2+ soures open SK hnnels? Our results demonstrte tht B8% of the spine hed C 2+ influx is ontriuted y NMDARs, nd the remining 2% is likely to reflet tivtion of voltge-sensitive C 2+ hnnels, whih in spines of hippompl pyrmidl neurons re NATURE NEUROSCIENCE VOLUME 8 [ NUMBER 5 [ MAY
7 25 Nture Pulishing Group R-type 28,29. Thus, rpid C 2+ influx through NMDARs tht open in the erly portion of the EPSP (see ove), long with possile ontriution from voltge-sensitive C 2+ hnnels, is likely to provide the signl tht tivtes SK hnnels. The lose ssoition etween synptilly tivted C 2+ soures nd SK hnnels is supported y results showing tht 5 mm BAPTA, rpid C 2+ heltor, is ple of interepting the C 2+ ions efore they enounter SK hnnels, wheres the slower C 2+ heltor EGTA, t the sme onentrtion, does not lok the effet. The hrteristi distne for the diffusion of C 2+ inpthree ffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffi dimensions efore pture y uffer n e pproximted y 6D C =k on ½ufferŠ,whereD C is the diffusion oeffiient of C 2+, k on is the pprent forwrd rte onstnt of C 2+ inding to the uffer nd [uffer] is the free uffer onentrtion. Using k on of M 1 s 1 for BAPTA nd D C of 22 mm 2 s 1 (ref. 3), C 2+ will diffuse hrteristi distne of 26 nm efore pture y 5 mm BAPTA nd 58 nm efore pture y 1 mm BAPTA. Therefore, the distne etween the two popultions of hnnels my e estimted t B25 5 nm, nd C 2+ ions will enounter n SK hnnel within B2 ms ofenteringthespine. As suthreshold synpti stimultion inreses verge C 2+ levels within the spine hed to pproximtely 7 nm (ref. 13), tivted C 2+ soures re likely to lolly provide sturting onentrtion (43 mm) of C 2+ to the SK hnnels, so tht the intrinsi gting kinetis of the SK hnnels will influene the EPSP. Rpid pplition of sturting onentrtions of C 2+ to heterologously expressed SK hnnels shows tht tivtion time onstnts n e o5 ms (ref. 31; unpulished results, J.M., J.P.A.), onsistent with their influene on the initil slope of the EPSP. The oupling etween single L-type C 2+ hnnels nd SK hnnels on the som of CA1 neurons hs een exmined erlier 32,33 ; ltenies s short s.9 ms were demonstrted etween the opening of L-type hnnels nd SK hnnels, onsistent with seprtion of B1 nm 34. Our results re onsistent with previous demonstrtions of oupling etween NMDARs nd C 2+ -tivted K + hnnels on ultured hippompl neurons. It hs een shown previously tht pplition of NMDA to ultured postntl rt hippompl neurons evoked C 2+ - tivted K + urrent tht ws prtilly inhiited y dtc ut ws not loked y pmin 35. In more reent study, NMDA ws pplied to the som of ultured hippompl neurons, nd tivtion of n SK urrent ws oserved in pproximtely hlf of the ells. 36 Tht study lso showed tht the musrine-sensitive, slowly tivting C 2+ - tivted K + urrent ws sometimes tivted y NMDA pplition, ut oupling to lrge-ondutne C 2+ -tivted hnnels (BK hnnels) ws not oserved 36, s hs een reported for olftory neurons 37. In dopmine neurons, NMDA reeptor tivtion my derese n ssoited SK urrent 38. SK2 hnnels re of the sutype whih is likely responsile for the pmin-indued effets on EPSPs, C 2+ trnsients nd synpti plstiity. A reent study using SK knokout mie showed tht SK2 hnnels ount for the pmin-sensitive urrents in CA1 neurons 39. Consistent with this, we demonstrte tht immunohistohemistry of SK2-trnsfeted CA1 neuronl ultures detets SK2 hnnels in virtully every spine. In ddition, SK2 hnnels re seen in within the dendriti shfts, where SK hnnel tivtion ffets plteu potentils nd the spred of dendriti C 2+ spikes y influening voltge-gted C 2+ hnnels 4. SK2 immunoretivity is lso oserved throughout the som, nd this popultion my medite the pmin-indued inrese of CA1 exitility 4,34,41. Therefore, seprte popultions of SK2 hnnels in CA1 neurons oupy disrete suellulr loles where they ouple with different C 2+ soures to serve distint physiologil roles. METHODS Cell ulture nd trnsfetion. Primry ultures were prepred from the CA1 re of hippompi of P1 2 mie s desried previously 42. Briefly, CA1 re from neworn mie were dissoited y ppin tretment nd triturtion nd plted on ed of stroytes t density of B7,1 ells m 2.Neuronswere ultured in MEM nd supplemented with 5% horse serum. After 7 14 d in ulture, ells were trnsfeted with Lipofetmine2 (Invitrogen). Immunoytohemistry ws performed 5 7 d fter trnsfetion. At tht time, the neurons hd rnhing dendriti rors nd well developed spines. Immunoytohemistry. To detet triple-my leled msk2 protein on the ell surfe, live ells were inuted with nti-my mouse monolonl ntiody (Invitrogen) for 1 h (37 1C, 5% CO 2 ), wshed, fixed, nd permeilized in 4% prformldehyde/4% surose in PBS for 3 min t room temperture ( C) nd wshed gin. Neurons were pre-inuted in loking solution (5% norml got serum/1% BSA) for 3 min t room temperture, nd then inuted for 1 h in Cy3-onjugted seondry ntiody (Jkson ImmunoReserh). Smples were mounted with Antifde mounting medium efore visuliztion. Imging ws performed using Lei DM-RXA mirosope equipped with Zeiss Pln Neofluor 4/NA1.4 nd 63/NA1.25 oil immersion ojetive lenses nd Prineton Instruments Miromx CCD mer. Imges were quired with MetMorph quisition nd nlysis softwre. Slie preprtion. All proedures were done in ordne with the guidelines of the Animl Cre Committees of the Oregon Helth & Siene University nd Hrvrd University. Hippompl slies were prepred from C57BL/6J mie from postntl dy for imging-unging experiments nd from postntl week 4 6 for eletrophysiology experiments. Animls were nesthetized y intrperitonel injetion with either ketmine-xyloine oktil or isofluorne, nd depitted. The ererl hemispheres were quikly removed nd pled into old rtifiil ererospinl fluid (ACSF) nd equilirted with 95%O 2 /5%CO 2. Hippompi were removed, pled onto n gr lok, nd trnsferred into sliing hmer ontining surose-acsf or holine-acsf. Trnsverse hippompl slies (3 375 mm) were ut with Lei VT1s nd trnsferred into holding hmer ontining regulr ACSF (in mm: 125 NCl, 2.5 KCl, 21.4 NHCO 3,1.25NH 2 PO 4, 2. CCl 2, 1. MgCl 2,11.1gluose)nd equilirted with 95%O 2 /5%CO 2. Slies were inuted t 35 1C for 3 45 min nd then for synptilly evoked responses were llowed to reover t room temperture ( C) for Z1.5 hrs efore reordings were performed. Eletrophysiology. For synptilly evoked reordings, CA1 pyrmidl ells were visulized with infrred differentil interferene ontrst optis (Zeiss Axioskop 2FS) nd CCD mer (Sony). Whole-ell pth-lmp reordings were otined from CA1 pyrmidl ells using n Axopth 2A mplifier (Axon Instruments), digitized using n ITC-16 nlog-to-digitl onverter (InstruTeh) nd trnsferred to omputer using Pulse softwre (Hek Elektronik). Pth pipettes (open pipette resistne, MO), if not otherwise noted, were filled with solution ontining (in mm) 14 KMeSO 4, 8 NCl, 1 MgCl 2, 1 HEPES, 5 MgATP,.5 EGTA(pH 7.3). EPSPs were reorded in whole-ell urrent-lmp mode. A ipolr tungsten eletrode (FHC) ws used to stimulte presynpti xons in strtum rditum. Pirotoxin (.1 mm) ws dded in most experiments to redue GABAergi ontriutions. The input resistne ws determined from B7-pA hyperpolrizing urrent injetion pulse given 8 ms fter eh synptilly evoked EPSP. Suthreshold EPSPs were eliited y 1-ms urrent injetions tht were pproximtely one-third of the stimulus required for evoking n tion potentil. In some experiments, the mgnitude of the pmin-indued inrese of the EPSP eliited tion potentils. Under these onditions, the stimulus strength ws redued to pproximtely one-qurter of threshold. Reordings were mde using n Axon 2A mplifier (Axon Instruments) interfed to Mintosh G4 with n ITC-16 omputer interfe (Instruteh Corp). Dt were filtered t 5 khz nd olleted t smple frequeny of 2 khz using Pulse (Hek Elektronik). All reordings used ells with resting memrne potentil less thn 6mV tht did not hnge y more thn 2 mv during n experiment nd with stle input resistne tht did not hnge y more thn 5%. Dt nlysis. Dt were nlyzed using IGOR (WveMetris). The slope of the rising phse of the EPSP ws determined from its first derivtive nd tken s 648 VOLUME 8 [ NUMBER 5 [ MAY 25 NATURE NEUROSCIENCE
8 25 Nture Pulishing Group the mximum vlue during the first hlf of the rising phse. Dt re expressed s men 7 s.e.m. Pired t-tests or ANOVA ws used to determine signifine; P o.5 ws onsidered signifint. Phrmology. (Cliohem), DL- (Toris Cookson), CPP (Toris Cookson), nd MK81 (Toris Cookson) were dissolved in distilled wter, nd CNQX, NBQX, nd Pirotoxin (Toris Cookson) in ethnol to produe stok solutions (1, onentrted) nd dded to the externl medium. Two-photon unging nd imging. Comined two-photon unging of MNI-glutmte nd two-photon intrellulr C 2+ imging ws performed using modified, ustom two-photon lser snning mirosope 43 tht is desried fully elsewhere 19. Briefly, the outputs of two Ti: Spphire lsers (Mir/Verdi, Coherent) were independently modulted with Pokels ells (35 8 nd 35 5, Conoptis) nd omined using polrizing optis. Glutmte ws unged using.2.6 ms pulses of 72 nm light, nd Alex Fluor 594 nd Fluo-5F were exited with 81 nm light. Fluoresene ws olleted in line sn mode (5 Hz) with rief interruption (2 ms) during whih the snning mirrors were redireted to the seleted spine nd the unging pulse ws triggered. Fluoresene trnsients were quntified s inreses in green (Fluo-5F) fluoresene from seline divided y resting red (Alex Fluor 594) fluoresene. This method provides quntifition tht is insensitive to smll hnges in resting C 2+ nd independent of spine volume 13. In our reording onditions, DG/R is linerly proportionl to D[C 2+ ]towithin B2% (ref. 13). Off-line dt nlysis ws performed using ustom softwre written in Igor Pro (Wvemetris) nd MATLAB. MNI-glutmte ws inluded in the th t 5 mm. Cells were filled with 3 mm Fluo-5F to report intrellulr C 2+ trnsients nd 1 mm Alex Fluor- 594 to imge neuronl morphology. Neurons were llowed to fill for 1 2 min efore eginning C 2+ imging. Spines on seondry nd tertiry dendrites within 15 mm of the som were seleted for nlysis. uepscs nd uepsps were monitored with n Axopth 2B nd were filtered t 2 khz nd smpled t 1 khz. ACKNOWLEDGMENTS We thnk T. Tzounopoulos nd C. Jhr for helpful disussions. We lso thnk G. Bnker nd S. Keh-Petrie for ssistne with hippompl ultures. This work ws supported y Ntionl Institutes of Helth grnts to J.M. nd J.P.A., nd y grnts to B.L.S. from the Whitker Foundtion nd the Serle Sholr s progrm. COMPETING INTERESTS STATEMENT The uthors delre tht they hve no ompeting finnil interests. Reeived 11 Mrh; epted 29 Mrh 25 Pulished online t 1. Zhng, L. & MBin, C.J. Potssium ondutnes underlying repolriztion nd fterhyperpolriztion in rt CA1 hippompl interneurons. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 488, (1995). 2. Sh, P. & Mlhln, E.M. C 2+ -tivted K + urrents underlying the fterhyperpolriztion in guine pig vgl neurons: role for C 2+ -tivted C 2+ relese. Neuron 7, (1991). 3. Lorenzon, N.M. & Foehring, R.C. Reltionship etween repetitive firing nd fterhyperpolriztions in humn neoortil neurons. J. Neurophysiol. 67, (1992). 4. Stkmn, R.W. et l. Smll ondutne C 2+ -tivted K + hnnels modulte synpti plstiity nd memory enoding. J. Neurosi. 22, (22). 5. Hermnn, E.. Phrmol. Ther. 25, (1984). 6. Lismn, J. A mehnism for the He nd the nti-he proesses underlying lerning nd memory. Pro. Ntl. Ad. Si. USA 86, (1989). 7. Mulkey, R.M. & Mlenk, R.C. Mehnisms underlying indution of homosynpti longterm depression in re CA1 of the hippompus. Neuron 9, (1992). 8. Dudek, S.M. & Ber, M.F. Homosynpti long-term depression in re CA1 of hippompus nd effets of N-methyl-d-sprtte reeptor lokde. Pro. Ntl. Ad. Si. USA 89, (1992). 9. Artol, A. & Singer, W. Long-term depression of exittory synpti trnsmission nd its reltionship to long-term potentition. Trends Neurosi. 16, (1993). 1. Bliss, T.V. & Collingridge, G.L. A synpti model of memory long-term potentition in the hippompus. Nture 361, (1993). 11. Cummings, J.A., Mulkey, R.M., Nioll, R.A. & Mlenk, R.C. C 2+ signling requirements for long term depression in the hippompus. Neuron 16, (1996). 12. Yng, S.N., Tng, Y.G. & Zuker, R.S. Seletive indution of LTP nd LTD y postsynpti [C 2+ ] i elevtion. J. Neurophysiol. 81, (1999). 13. Stini, B.L., Oertner, T.G. & Svood, K. The life yle of C 2+ ions in dendriti spines. Neuron 33, (22). 14. Myer, M.L., Westrook, G.L. & Guthrie, P.B. Voltge-dependent lok y Mg 2+ of NMDA responses in spinl ord neurones. Nture 39, (1984). 15. Lee, W.S., Ngo-Anh, T.J., Bruening-Wright, A., Mylie, J. & Adelmn, J.P. Smll ondutne C 2+ -tivted K + hnnels nd lmodulin: ell surfe expression nd gting. J. Biol. Chem. 278, (23). 16. Ishii, T.M., Mylie, J. & Adelmn, J.P. Determinnts of pmin nd D-tuourrine lok in SK potssium hnnels. J. Biol. Chem. 272, (1997). 17. Behnish, T. & Reymnn, K.G. Inhiition of pmin-sensitive lium dependent potssium hnnels filitte the indution of long-term potentition in the CA1 region of rt hippompus in vitro. Neurosi. Lett. 253, (1998). 18. Ktz, B. & Miledi, R. The role of lium in neuromusulr filittion. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 195, (1968). 19. Crter, A.G. & Stini, B.L. Stte-dependent lium signling in dendriti spines of stritl medium spiny neurons. Neuron 44, (24). 2. Mtsuzki, M. et l. Dendriti spine geometry is ritil for AMPA reeptor expression in hippompl CA1 pyrmidl neurons. Nt. Neurosi. 4, (21). 21. Bekkers, J.M. & Stevens, C.F. NMDA nd non-nmda reeptors re o-lolized t individul exittory synpses in ultured rt hippompus. Nture 341, (1989). 22. Hestrin, S., Nioll, R.A., Perkel, D.J. & Sh, P. Anlysis of exittory synpti tion in pyrmidl ells using whole-ell reording from rt hippompl slies. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 422, (199). 23. Hestrin, S., Sh, P. & Nioll, R.A. Mehnisms generting the time ourse of dul omponent exittory synpti urrents reorded in hippompl slies. Neuron 5, (199). 24. Lester, R.A.J., Clements, J.D., Westrook, G.L. & Jhr, C.E. Chnnel kinetis determine the time ourse of NMDA reeptor-medited synpti urrents. Nture 346, (199). 25. Popesu, G., Roert, A., Howe, J.R. & Auerh, A. Retion mehnism determines NMDA reeptor response to repetitive stimultion. Nture 43, (24). 26. Erreger, K., Drvid, S.M., Bnke, T.G., Wyllie, D.J. & Trynelis, S.F. Suunit-speifi gting ontrols rt NR1/NR2A nd NR1/NR2B NMDA hnnel kinetis nd synpti signling profiles. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 563, (25). 27. Kmp, B.M., Clements, J., Jons, P. & Sturt, G.J. Kinetis of Mg 2+ unlok of NMDA reeptors: implitions for spike-timing dependent synpti plstiity. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 556, (24). 28. Stini, B.L. & Svood, K. Anlysis of lium hnnels in single spines using optil flutution nlysis. Nture 48, (2). 29. Ysud, R., Stini, B.L. & Svood, K. Plstiity of lium hnnels in dendriti spines. Nt. Neurosi. 6, (23). 3. Nrghi, M. & Neher, E. Linerized uffered C 2+ diffusion in mirodomins nd its implitions for lultion of [C 2+ ] t the mouth of lium hnnel. J. Neurosi. 17, (1997). 31. Xi, X-M. et l. Mehnism of lium gting in smll-ondutne lium-tivted potssium hnnels. Nture 395, (1998). 32. Hirsherg, B., Mylie, J., Adelmn, J.P. & Mrrion, N.V. Gting of reominnt smll ondutne C-tivted K + hnnels y lium. J. Gen. Physiol. 111, (1998). 33. Hirsherg, B., Mylie, J., Adelmn, J.P. & Mrrion, N.V. Gting properties of single SK hnnels inhippomplca1 pyrmidlneurons.biophys. J. 77, (1999). 34. Mrrion, N.V. & Tvlin, S.J. Seletive tivtion of C 2+ -tivted K + hnnels y o-lolized C 2+ hnnels in hippompl neurons. Nture 395, 9 95 (1998). 35. Zorumski, C.F., Thio, L.L., Clrk, G.D. & Clifford, D.B. Clium influx through N-methyl- D-sprtte hnnels tivtes potssium urrent in postntl rt hippompl neurons. Neurosi. Lett. 99, (1989). 36. Shh, M.M. & Hylett, D.G.K. + urrents generted y NMDA reeptor tivtion in rt hippompl pyrmidl neurons. J. Neurophysiol. 87, (22). 37. Isson, J.S. & Murphy, G.J. Glutmte-medited extrsynpti inhiition: diret oupling of NMDA reeptors to C 2+ -tivted K + hnnels. Neuron 31, (21). 38. Pul, K., Keith, D.J. & Johnson, S.W. Modultion of lium-tivted potssium smll ondutne (SK) urrent in rt dopmine neurons of the ventrl tegmentl re. Neurosi. Lett. 348, (23). 39. Bond, C.T. et l. Smll ondutne C 2+ -tivted K + hnnel knok-out mie revel the identity of lium-dependent fterhyperpolriztion urrents. J. Neurosi. 24, (24). 4. Ci, X. et l. Unique roles of SK nd Kv4.2 potssium hnnels in dendriti integrtion. Neuron 44, (24). 41. Stoker, M., Kruse, M. & Pedrzni, P. An pmin-sensitive C 2+ -tivted K + urrent in hippompl pyrmidl neurons. Pro. Ntl. Ad. Si. USA 96, (1999). 42. Goslin, K., Asmussen, H. & Bnker, G. in Culturing Nerve Cells. 2 nd edn. (eds. Goslin, K. & Bnker, G.) (MIT Press, Cmridge, Msshusetts, USA, 1998). 43. Pologruto, T.A., Stini, B.L. & Svood, K. SnImge: flexile softwre for operting lser snning mirosopes. Biomed. Eng. Online 2, 13(23). NATURE NEUROSCIENCE VOLUME 8 [ NUMBER 5 [ MAY
LHb VTA. VTA-projecting RMTg-projecting overlay. Supplemental Figure 2. Retrograde labeling of LHb neurons. a. VTA-projecting LHb
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementl Figure 1 doi:10.1038/nture09742 Lterl 1.0 mm from midline mpfc BNST mpfc BNST Lterl 2.1 mm from midline LHA LHA Lterl 2.7 mm from midline SUPPLEMENTAL INFORMATION
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementl Figure 1 doi:10.1038/nture09742 Lterl 1.0 mm from midline mpfc BNST mpfc BNST Lterl 2.1 mm from midline LHA LHA Lterl 2.7 mm from midline SUPPLEMENTAL INFORMATION
EFFECT OF DIETARY ENZYME ON PERFORMANCE OF WEANLING PIGS
 EFFECT OF DIETARY ENZYME ON PERFORMANCE OF WEANLING PIGS Finl report sumitted to Dniso Animl Nutrition E. vn Heugten nd B. Frederik North Crolin Stte University, Deprtment of Animl Siene Summry The urrent
EFFECT OF DIETARY ENZYME ON PERFORMANCE OF WEANLING PIGS Finl report sumitted to Dniso Animl Nutrition E. vn Heugten nd B. Frederik North Crolin Stte University, Deprtment of Animl Siene Summry The urrent
I h -mediated depolarization enhances the temporal precision of neuronal integration
 Reeived 5 Apr 2 Aepted 9 Jn 2 Pulished 5 Fe 2DOI:.38/nomms22 I h -medited depolriztion enhnes the temporl preision of neuronl integrtion Ivn Pvlov, Annlis Simemi,, Leonid Svthenko, Dimitri M. Kullmnn &
Reeived 5 Apr 2 Aepted 9 Jn 2 Pulished 5 Fe 2DOI:.38/nomms22 I h -medited depolriztion enhnes the temporl preision of neuronl integrtion Ivn Pvlov, Annlis Simemi,, Leonid Svthenko, Dimitri M. Kullmnn &
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 1.13/n7 Reltive Pprg mrna 3 1 1 Time (weeks) Interspulr Inguinl Epididyml Reltive undne..1.5. - 5 5-51 51-1 1-7 7 - - 1 1-1 Lipid droplet size ( m ) 1-3 3 - - - 1 1-1 1-1 1-175 175-3 3-31 31-5 >5
DOI: 1.13/n7 Reltive Pprg mrna 3 1 1 Time (weeks) Interspulr Inguinl Epididyml Reltive undne..1.5. - 5 5-51 51-1 1-7 7 - - 1 1-1 Lipid droplet size ( m ) 1-3 3 - - - 1 1-1 1-1 1-175 175-3 3-31 31-5 >5
Selective reconfiguration of layer 4 visual cortical circuitry by visual deprivation
 Seletive reonfigurtion of lyer 4 visul ortil iruitry y visul deprivtion Arinn Mffei, Sh B Nelson & Gin G Turrigino Visul deprivtion during developmentl sensitive period mrkedly lters visul ortil response
Seletive reonfigurtion of lyer 4 visul ortil iruitry y visul deprivtion Arinn Mffei, Sh B Nelson & Gin G Turrigino Visul deprivtion during developmentl sensitive period mrkedly lters visul ortil response
The Journal of Physiology
 J Physiol 595.23 (217) pp 7185 722 7185 Heteromeri α/β glyine reeptors regulte exitility in prvlumin-expressing dorsl horn neurons through phsi nd toni glyinergi inhiition M. A. Grdwell 1,2,K.A.Boyle 3,R.J.llister
J Physiol 595.23 (217) pp 7185 722 7185 Heteromeri α/β glyine reeptors regulte exitility in prvlumin-expressing dorsl horn neurons through phsi nd toni glyinergi inhiition M. A. Grdwell 1,2,K.A.Boyle 3,R.J.llister
Supplementary Figure 1. Scheme of unilateral pyramidotomy used for detecting compensatory sprouting of intact CST axons.
 () BDA 2 weeks fter Py () AAVs Cre or GFP t P1 BDA 2 weeks fter Py CSMN CST () Py t P7 or 2 months () Py t 2 months Supplementry Figure 1. Sheme of unilterl pyrmidotomy used for deteting ompenstory sprouting
() BDA 2 weeks fter Py () AAVs Cre or GFP t P1 BDA 2 weeks fter Py CSMN CST () Py t P7 or 2 months () Py t 2 months Supplementry Figure 1. Sheme of unilterl pyrmidotomy used for deteting ompenstory sprouting
Input normalization by global feedforward inhibition expands cortical dynamic range
 Input normliztion y glol feedforwrd inhiition expnds ortil dynmi rnge Frédéri Pouille 1,2, Antoni Mrin-Burgin 1,2, Hillel Adesnik 1, Bssm V Atllh 1 & Mssimo Snzini 1 29 Nture Ameri, In. All rights reserved.
Input normliztion y glol feedforwrd inhiition expnds ortil dynmi rnge Frédéri Pouille 1,2, Antoni Mrin-Burgin 1,2, Hillel Adesnik 1, Bssm V Atllh 1 & Mssimo Snzini 1 29 Nture Ameri, In. All rights reserved.
Laminar sources of synaptic input to cortical inhibitory interneurons and pyramidal neurons
 rtiles Lminr soures of synpti input to ortil inhiitory interneurons nd pyrmidl neurons J. L. Dntzker nd E. M. Cllwy Systems Neuroiology Lortories, The Slk Institute for Biologil Studies, N. Torrey Pines
rtiles Lminr soures of synpti input to ortil inhiitory interneurons nd pyrmidl neurons J. L. Dntzker nd E. M. Cllwy Systems Neuroiology Lortories, The Slk Institute for Biologil Studies, N. Torrey Pines
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi: 1.138/nture862 humn hr. 21q MRPL39 murine Chr.16 Mrpl39 Dyrk1A Runx1 murine Chr. 17 ZNF295 Ets2 Znf295 murine Chr. 1 COL18A1 -/- lot: nti-dscr1 IgG hevy hin DSCR1 DSCR1 expression reltive to hevy
doi: 1.138/nture862 humn hr. 21q MRPL39 murine Chr.16 Mrpl39 Dyrk1A Runx1 murine Chr. 17 ZNF295 Ets2 Znf295 murine Chr. 1 COL18A1 -/- lot: nti-dscr1 IgG hevy hin DSCR1 DSCR1 expression reltive to hevy
Mechanisms underlying cross-orientation suppression in cat visual cortex
 Mehnisms underlying ross-orienttion suppression in t visul ortex 6 Nture Pulishing Group http://www.nture.om/ntureneurosiene Nihols J Priee & Dvid Ferster In simple ells of the t primry visul ortex, null-oriented
Mehnisms underlying ross-orienttion suppression in t visul ortex 6 Nture Pulishing Group http://www.nture.om/ntureneurosiene Nihols J Priee & Dvid Ferster In simple ells of the t primry visul ortex, null-oriented
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 1.138/n358 TLR2 nd MyD88 expression in murine mmmry epithelil supopultions. CD24 min plus MRU Myo-epithelil Luminl progenitor (CD61 pos ) Mture luminl (CD61 neg ) CD49f CD61 Reltive expression Krt5
DOI: 1.138/n358 TLR2 nd MyD88 expression in murine mmmry epithelil supopultions. CD24 min plus MRU Myo-epithelil Luminl progenitor (CD61 pos ) Mture luminl (CD61 neg ) CD49f CD61 Reltive expression Krt5
In vivo intracellular recording and perturbation of persistent activity in a neural integrator
 rtiles 21 Nture Pulishing Group http://neurosi.nture.om 21 Nture Pulishing Group http://neurosi.nture.om In vivo intrellulr reording nd perturtion of persistent tivity in neurl integrtor E. Aksy 1,2, G.
rtiles 21 Nture Pulishing Group http://neurosi.nture.om 21 Nture Pulishing Group http://neurosi.nture.om In vivo intrellulr reording nd perturtion of persistent tivity in neurl integrtor E. Aksy 1,2, G.
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nture10754 Supplementry note 1 To ompre our dt with previous studies, we mesured the width of spikes from identified dopminergi neurons nd unidentified neurons from DATCre mie. Previous studies
doi:10.1038/nture10754 Supplementry note 1 To ompre our dt with previous studies, we mesured the width of spikes from identified dopminergi neurons nd unidentified neurons from DATCre mie. Previous studies
P AND K IN POTATOES. Donald A Horneck Oregon State University Extension Service
 P AND K IN POTATOES Donld A Hornek Oregon Stte University Extension Servie INTRODUCTION Phosphorous nd potssium re importnt to grow high yielding nd qulity pottoes. Muh of the northwest hs hd trditionlly
P AND K IN POTATOES Donld A Hornek Oregon Stte University Extension Servie INTRODUCTION Phosphorous nd potssium re importnt to grow high yielding nd qulity pottoes. Muh of the northwest hs hd trditionlly
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:.38/nture277 d 25 25 2 Time from sound onset (ms) 25 25 2 Time from sound onset (ms) Firing rte (spikes/s) Firing rte (spikes/s).8.6..2 e f g h.8.6..2 Frtion of neurons Frtion of neurons N = 53 2 2
doi:.38/nture277 d 25 25 2 Time from sound onset (ms) 25 25 2 Time from sound onset (ms) Firing rte (spikes/s) Firing rte (spikes/s).8.6..2 e f g h.8.6..2 Frtion of neurons Frtion of neurons N = 53 2 2
Lesions of prefrontal cortex reduce attentional modulation of neuronal responses. and synchrony in V4
 Lesions of prefrontl ortex reue ttentionl moultion of neuronl responses n synhrony in V4 Georgi G. Gregoriou,, Anrew F. Rossi, 3 Leslie G Ungerleier, 4 Roert Desimone 5 Deprtment of Bsi Sienes, Fulty of
Lesions of prefrontl ortex reue ttentionl moultion of neuronl responses n synhrony in V4 Georgi G. Gregoriou,, Anrew F. Rossi, 3 Leslie G Ungerleier, 4 Roert Desimone 5 Deprtment of Bsi Sienes, Fulty of
Letter. Autocrine BDNF TrkB signalling within a single dendritic spine
 Letter doi:1.138/nture19766 Autorine BDNF TrkB signlling within single dendriti spine Stephen C. Hrwrd 1, Nthn G. Hedrik 1, Chrles E. Hll 1, Pul Prr-Bueno 2, Teres A. Milner 3,4, Enhui Pn 1, Tl Lviv 2,
Letter doi:1.138/nture19766 Autorine BDNF TrkB signlling within single dendriti spine Stephen C. Hrwrd 1, Nthn G. Hedrik 1, Chrles E. Hll 1, Pul Prr-Bueno 2, Teres A. Milner 3,4, Enhui Pn 1, Tl Lviv 2,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:.8/nture89 4 4 Ilr -/- Ilr -/- Ilr -/- Cspse- -/- As -/- Nlrp -/- Il8 -/- Ilr -/- Supplementl figure. Inresed severity of NASH in inflmmsome-defiient mie, ut not in Ilr-defiient
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:.8/nture89 4 4 Ilr -/- Ilr -/- Ilr -/- Cspse- -/- As -/- Nlrp -/- Il8 -/- Ilr -/- Supplementl figure. Inresed severity of NASH in inflmmsome-defiient mie, ut not in Ilr-defiient
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 . Norml Physiologicl Conditions. SIRT1 Loss-of-Function S1. Model for the role of SIRT1 in the regultion of memory nd plsticity. () Our findings suggest tht SIRT1 normlly functions in coopertion with YY1,
. Norml Physiologicl Conditions. SIRT1 Loss-of-Function S1. Model for the role of SIRT1 in the regultion of memory nd plsticity. () Our findings suggest tht SIRT1 normlly functions in coopertion with YY1,
Title of Experiment: Author, Institute and address:
 Title of Experiment: Trsfetion of murine mrophge RAW264.7 ells with METAFECTENE PRO. Author, Institute n ress: Ptrizi Pellegtti n Frneso Di Virgilio. Deprtment of Experimentl n Dignosti Meiine, Setion
Title of Experiment: Trsfetion of murine mrophge RAW264.7 ells with METAFECTENE PRO. Author, Institute n ress: Ptrizi Pellegtti n Frneso Di Virgilio. Deprtment of Experimentl n Dignosti Meiine, Setion
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 { OI: 1.138/n31 Srifie n nlyze APs on week 1 s of iet 1 4 6 High-ft iet BrU High-ft iet BrU 4 High-ft iet BrU 6 High-ft iet BrU Lin - Lin - : C34 + : C9 + 1 1 3 1 4 1 5 C45 1 C34 1 1 1 1 3 1 4 1 5 S-1
{ OI: 1.138/n31 Srifie n nlyze APs on week 1 s of iet 1 4 6 High-ft iet BrU High-ft iet BrU 4 High-ft iet BrU 6 High-ft iet BrU Lin - Lin - : C34 + : C9 + 1 1 3 1 4 1 5 C45 1 C34 1 1 1 1 3 1 4 1 5 S-1
Regulation of neuronal morphology and function by the tumor suppressors Tsc1 and Tsc2
 Regultion of neuronl morphology nd funtion y the tumor suppressors Ts nd Ts Sohil F Tvzoie,3,4, Veroni A Alvrez,4, Dennis A Ridenour, Dvid J Kwitkowski & Bernrdo L Stini Muttions in the TSC or TSC tumor
Regultion of neuronl morphology nd funtion y the tumor suppressors Ts nd Ts Sohil F Tvzoie,3,4, Veroni A Alvrez,4, Dennis A Ridenour, Dvid J Kwitkowski & Bernrdo L Stini Muttions in the TSC or TSC tumor
Hydrogen sulfide-induced inhibition of L-type Ca 2+ channels and insulin secretion in mouse pancreatic beta cells
 Dietologi (213) 56:533 541 DOI 1.17/s125-12-286-8 ARTICLE Hydrogen sulfide-indued inhiition of L-type C 2 hnnels nd insulin seretion in mouse pnreti et ells G. Tng & L. Zhng & G. Yng & L. Wu & R. Wng Reeived:
Dietologi (213) 56:533 541 DOI 1.17/s125-12-286-8 ARTICLE Hydrogen sulfide-indued inhiition of L-type C 2 hnnels nd insulin seretion in mouse pnreti et ells G. Tng & L. Zhng & G. Yng & L. Wu & R. Wng Reeived:
ARTICLES. Lateral presynaptic inhibition mediates gain control in an olfactory circuit. Shawn R. Olsen 1 & Rachel I. Wilson 1
 doi:1.138/nture6864 ARTICLES Lterl presynpti inhiition medites gin ontrol in n olftory iruit Shwn R. Olsen 1 & Rhel I. Wilson 1 Olftory signls re trnsdued y lrge fmily of odornt reeptor proteins, eh of
doi:1.138/nture6864 ARTICLES Lterl presynpti inhiition medites gin ontrol in n olftory iruit Shwn R. Olsen 1 & Rhel I. Wilson 1 Olftory signls re trnsdued y lrge fmily of odornt reeptor proteins, eh of
Enrichment induces structural changes and recovery from nonspatial memory deficits in CA1 NMDAR1-knockout mice
 rtiles Enrihment indues struturl hnges nd reovery from nonsptil memory defiits in CA1 NMDAR1-knokout mie Clire Rmpon, Y-Ping Tng, Joe Goodhouse, Eiji Shimizu, Mureen Kyin nd Joe Z. Tsien Deprtment of Moleulr
rtiles Enrihment indues struturl hnges nd reovery from nonsptil memory defiits in CA1 NMDAR1-knokout mie Clire Rmpon, Y-Ping Tng, Joe Goodhouse, Eiji Shimizu, Mureen Kyin nd Joe Z. Tsien Deprtment of Moleulr
Long-term modification of cortical synapses improves sensory perception
 Long-term modifition of ortil synpses improves sensory pereption Roert C Froemke 1 4,8, Ion Cre 1 3,8, Alison J Brker 4, Kexin Yun 4, Bryn A Seyold 4, An Rquel O Mrtins 1 3,5, Ntly Zik 1,2, Hnnh Bernstein
Long-term modifition of ortil synpses improves sensory pereption Roert C Froemke 1 4,8, Ion Cre 1 3,8, Alison J Brker 4, Kexin Yun 4, Bryn A Seyold 4, An Rquel O Mrtins 1 3,5, Ntly Zik 1,2, Hnnh Bernstein
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 1.138/n2977 Numer of ells per field 6 4 2 P =.1 Orthotopi eum Normlized ventrl photon flux 1E7 1E6 1E5 1E4 1E3 1E2 n=8 n=9 1 2 3 4 5 6 Dys Dy54 1.5E5 2.4E7 d Mie with lymph node metstsis (%) 1 8 6
DOI: 1.138/n2977 Numer of ells per field 6 4 2 P =.1 Orthotopi eum Normlized ventrl photon flux 1E7 1E6 1E5 1E4 1E3 1E2 n=8 n=9 1 2 3 4 5 6 Dys Dy54 1.5E5 2.4E7 d Mie with lymph node metstsis (%) 1 8 6
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 2 weeks high holesterol diet 2 weeks high holesterol diet 2 weeks high holesterol diet 2 μm Mrophges Crystls Hoehst μm Mrophges Crystls Hoehst Hoehst Crystls Mrophges 2 μm 2 μm Supplementry Fig. 1: Erly
2 weeks high holesterol diet 2 weeks high holesterol diet 2 weeks high holesterol diet 2 μm Mrophges Crystls Hoehst μm Mrophges Crystls Hoehst Hoehst Crystls Mrophges 2 μm 2 μm Supplementry Fig. 1: Erly
(% of adherent cells) *** PBL firm adhesion. Frequency (% ) 4 1 L 2 CXCR3 DP-2
 Chemotxis (% of dded ells) PBL totl dhesion (N ells/mm 2 /1.1 6 PBL) Frequeny (% ) PBL firm dhesion Supplementry Figure 1 4 4 3 3 2 2 1.1-4 1-3 1.1.2. 1 1 8 6 4 2 Adiponetin ( g/ml) - + Adiponetin ( g/ml)
Chemotxis (% of dded ells) PBL totl dhesion (N ells/mm 2 /1.1 6 PBL) Frequeny (% ) PBL firm dhesion Supplementry Figure 1 4 4 3 3 2 2 1.1-4 1-3 1.1.2. 1 1 8 6 4 2 Adiponetin ( g/ml) - + Adiponetin ( g/ml)
ARTICLES. Dendritic organization of sensory input to cortical neurons in vivo
 Vol 6 9 April 00 doi:0.08/nture0897 ARTICLES Dendriti orgniztion of sensory input to ortil neurons in vivo Hongbo Ji *, Nthlie L. Rohefort *, Xiowei Chen & Arthur Konnerth In sensory ortex regions, neurons
Vol 6 9 April 00 doi:0.08/nture0897 ARTICLES Dendriti orgniztion of sensory input to ortil neurons in vivo Hongbo Ji *, Nthlie L. Rohefort *, Xiowei Chen & Arthur Konnerth In sensory ortex regions, neurons
Whangarei District Council Class 4 Gambling Venue Policy
 Whngrei Distrit Counil Clss 4 Gmling Venue Poliy April 2013 Whngrei Distrit Counil Clss 4 Gmling Venue Poliy Tle of ontents Introdution... 3 1 Ojetives of the poliy in so fr s promoted y the Gmling At
Whngrei Distrit Counil Clss 4 Gmling Venue Poliy April 2013 Whngrei Distrit Counil Clss 4 Gmling Venue Poliy Tle of ontents Introdution... 3 1 Ojetives of the poliy in so fr s promoted y the Gmling At
Interplay of LRRK2 with chaperone-mediated autophagy
 Interply of with hperone-medited utophgy Smnth J Orenstein,, Sheng-Hn Kuo,, Inmuld Tsset,,, Espernz Aris,, Hiroshi Kog,, Irene Fernndez-Crs, Etty Cortes,5, Lwrene S Honig,5, Willim Duer 6, Antonell Consiglio,7,
Interply of with hperone-medited utophgy Smnth J Orenstein,, Sheng-Hn Kuo,, Inmuld Tsset,,, Espernz Aris,, Hiroshi Kog,, Irene Fernndez-Crs, Etty Cortes,5, Lwrene S Honig,5, Willim Duer 6, Antonell Consiglio,7,
Alimonti_Supplementary Figure 1. Pten +/- Pten + Pten. Pten hy. β-actin. Pten - wt hy/+ +/- wt hy/+ +/- Pten. Pten. Relative Protein level (% )
 Alimonti_Supplementry Figure 1 hy 3 4 5 3 Neo 4 5 5 Proe 5 Proe hy/ hy/ /- - 3 6 Neo β-tin d Reltive Protein level (% ) 15 1 5 hy/ /- Reltive Gene Expr. (% ) 15 1 5 hy/ /- Supplementry Figure 1 Chrteriztion
Alimonti_Supplementry Figure 1 hy 3 4 5 3 Neo 4 5 5 Proe 5 Proe hy/ hy/ /- - 3 6 Neo β-tin d Reltive Protein level (% ) 15 1 5 hy/ /- Reltive Gene Expr. (% ) 15 1 5 hy/ /- Supplementry Figure 1 Chrteriztion
Imaging analysis of clock neurons reveals light buffers the wake-promoting effect of dopamine
 Imging nlysis of lok neurons revels light uffers the wke-promoting effet of dopmine Yuhu Shng 1,2, Pul Hynes 2, Niolás Pírez 2, Kyle I Hrrington 3, Fng Guo 1,2, Jordn Pollk 3, Pengyu Hong 3, Leslie C Griffith
Imging nlysis of lok neurons revels light uffers the wke-promoting effet of dopmine Yuhu Shng 1,2, Pul Hynes 2, Niolás Pírez 2, Kyle I Hrrington 3, Fng Guo 1,2, Jordn Pollk 3, Pengyu Hong 3, Leslie C Griffith
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 % ells with ili (mrke y A-Tu) Reltive Luiferse % ells with ili (mrke y Arl13) % ells with ili DOI: 1.138/n2259 A-Tuulin Hoehst % Cilite Non-ilite -Serum 9% 8% 7% 1 6% % 4% +Serum 1 3% 2% 1% % Serum: -
% ells with ili (mrke y A-Tu) Reltive Luiferse % ells with ili (mrke y Arl13) % ells with ili DOI: 1.138/n2259 A-Tuulin Hoehst % Cilite Non-ilite -Serum 9% 8% 7% 1 6% % 4% +Serum 1 3% 2% 1% % Serum: -
Endogenous nicotinic cholinergic activity regulates dopamine release in the striatum
 Endogenous niotini holinergi tivity regultes dopmine relese in the stritum Fu-Ming Zhou, Yong Ling nd John A. Dni Division of Neurosiene, Bylor College of Mediine, Houston, Texs 77030-3498, USA Correspondene
Endogenous niotini holinergi tivity regultes dopmine relese in the stritum Fu-Ming Zhou, Yong Ling nd John A. Dni Division of Neurosiene, Bylor College of Mediine, Houston, Texs 77030-3498, USA Correspondene
Supplementary Figure 1. Schematic illustrating major conclusions of this study.
 ORNs GABA A GABA B glomeruli LN PNs Supplementary Figure 1. Shemati illustrating major onlusions of this study. This study represents the most diret evidene to date of inhiitory interations etween olfatory
ORNs GABA A GABA B glomeruli LN PNs Supplementary Figure 1. Shemati illustrating major onlusions of this study. This study represents the most diret evidene to date of inhiitory interations etween olfatory
Methylphenidate facilitates learning-induced amygdala plasticity
 Methylphenidte filittes lerning-indued mygdl plstiity Ky M Tye 1,2, Lynne D Tye 1,3, Jkson J Cone 1, Evelien F Hekkelmn 1, Ptrii H Jnk 1,2,, & Antonello Boni 1,2,, 21 Nture Ameri, In. All rights reserved.
Methylphenidte filittes lerning-indued mygdl plstiity Ky M Tye 1,2, Lynne D Tye 1,3, Jkson J Cone 1, Evelien F Hekkelmn 1, Ptrii H Jnk 1,2,, & Antonello Boni 1,2,, 21 Nture Ameri, In. All rights reserved.
Control of timing, rate and bursts of hippocampal place cells by dendritic and somatic inhibition
 Control of timing, rte nd ursts of hippompl ple ells y dendriti nd somti inhiition Séstien Royer,2, Boris V Zemelmn,5, Attil Losonzy,3, Jinhyun Kim,2, Frnes Chne, Jeffrey C Mgee & György Buzsáki,4 22 Nture
Control of timing, rte nd ursts of hippompl ple ells y dendriti nd somti inhiition Séstien Royer,2, Boris V Zemelmn,5, Attil Losonzy,3, Jinhyun Kim,2, Frnes Chne, Jeffrey C Mgee & György Buzsáki,4 22 Nture
A p75 NTR and Nogo receptor complex mediates repulsive signaling by myelin-associated glycoprotein
 A p75 NTR nd Nogo reeptor omplex medites repulsive signling y myelin-ssoited glyoprotein Sott T. Wong 1, John R. Henley 1, Kevin C. Knning 2, Kuo-hu Hung 1, Mrk Bothwell 2 nd Mu-ming Poo 1 1 Division of
A p75 NTR nd Nogo reeptor omplex medites repulsive signling y myelin-ssoited glyoprotein Sott T. Wong 1, John R. Henley 1, Kevin C. Knning 2, Kuo-hu Hung 1, Mrk Bothwell 2 nd Mu-ming Poo 1 1 Division of
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 oi:1.138/nture1134 CS+ CS- MCH 3 OCT OCT 3 MCH CS- CS+ OCT MCH 3 MCH OCT 3 OCT vs MCH OCT vs MCH ppetitive memory (PI) A 1-1 Unpire onitioning DDC-GAL4/UAS-Trp UAS-Trp/+ -2 MCH OCT OCT MCH sugr OCT MCH
oi:1.138/nture1134 CS+ CS- MCH 3 OCT OCT 3 MCH CS- CS+ OCT MCH 3 MCH OCT 3 OCT vs MCH OCT vs MCH ppetitive memory (PI) A 1-1 Unpire onitioning DDC-GAL4/UAS-Trp UAS-Trp/+ -2 MCH OCT OCT MCH sugr OCT MCH
Neural population coding of sound level adapts to stimulus statistics
 COMPUTATION AND SYSTEMS 25 Nture Pulishing Group http://www.nture.om/ntureneurosiene Neurl popultion oding of sound level dpts to stimulus sttistis Isel Den 1, Niol S Hrper 1,2 & Dvid MAlpine 1 Mmmls n
COMPUTATION AND SYSTEMS 25 Nture Pulishing Group http://www.nture.om/ntureneurosiene Neurl popultion oding of sound level dpts to stimulus sttistis Isel Den 1, Niol S Hrper 1,2 & Dvid MAlpine 1 Mmmls n
Learning to see: experience and attention in primary visual cortex
 2 Nture Pulishing Group http://neurosi.nture.om rtiles Lerning to see: experiene nd ttention in primry visul ortex 2 Nture Pulishing Group http://neurosi.nture.om Roy E. Crist, Wu Li nd Chrles D. Gilert
2 Nture Pulishing Group http://neurosi.nture.om rtiles Lerning to see: experiene nd ttention in primry visul ortex 2 Nture Pulishing Group http://neurosi.nture.om Roy E. Crist, Wu Li nd Chrles D. Gilert
Cos7 (3TP) (K): TGFβ1(h): (K)
 IP#2: IP#1: Totl Lystes luiferse tivity (K): 6-4 - (K): luiferse tivity luiferse tivity (K): 2 1 RL-: - + + + + + Sm4-3F: + - + + + + MYC-Sm3: - - - - + + TβRI-HA(T204D): - - - + - + α-ha Luiferse Ativity
IP#2: IP#1: Totl Lystes luiferse tivity (K): 6-4 - (K): luiferse tivity luiferse tivity (K): 2 1 RL-: - + + + + + Sm4-3F: + - + + + + MYC-Sm3: - - - - + + TβRI-HA(T204D): - - - + - + α-ha Luiferse Ativity
TNF-a Downregulates Filaggrin and Loricrin through c-jun N-terminal Kinase: Role for TNF-a Antagonists to Improve Skin Barrier
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE TNF- Downregultes Filggrin nd Loririn through -Jun N-terminl Kinse: Role for TNF- Antgonists to Improve Skin Brrier Byung Eui Kim, Mihel D. Howell,, Emm Guttmn,, Ptrii M. Gilleudeu, Irm
ORIGINAL ARTICLE TNF- Downregultes Filggrin nd Loririn through -Jun N-terminl Kinse: Role for TNF- Antgonists to Improve Skin Brrier Byung Eui Kim, Mihel D. Howell,, Emm Guttmn,, Ptrii M. Gilleudeu, Irm
Neuronal circuitry mechanism regulating adult quiescent neural stem-cell fate decision NO pa. 10 s ETMD
 doi:1.138/nture1136 Neuronl iruitry mehnism regulting dult quiesent neurl stem-ell fte deision Jun Song 1,2, Chun Zhong 1,2, Mihel A. Bonguidi 1,2, Gerld J. Sun 1,3, Derek Hsu 1, Yn Gu 4, Konstntinos Meletis
doi:1.138/nture1136 Neuronl iruitry mehnism regulting dult quiesent neurl stem-ell fte deision Jun Song 1,2, Chun Zhong 1,2, Mihel A. Bonguidi 1,2, Gerld J. Sun 1,3, Derek Hsu 1, Yn Gu 4, Konstntinos Meletis
A thalamic input to the nucleus accumbens mediates opiate dependence
 doi:1.138/nture16954 A thlmi input to the nuleus umens medites opite dependene Yingjie Zhu1, Crl F. R. Wieneke1, Gregory Nhtr1 & Xioke Chen1 1 feed-forwrd inhiition in lol NA iruit. Consistent with this
doi:1.138/nture16954 A thlmi input to the nuleus umens medites opite dependene Yingjie Zhu1, Crl F. R. Wieneke1, Gregory Nhtr1 & Xioke Chen1 1 feed-forwrd inhiition in lol NA iruit. Consistent with this
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION CD169 + MACROPHAGES PRESENT LIPID ANTIGENS TO MEDIATE EARLY ACTIVATION OF INVARIANT NKT CELLS IN LYMPH NODES Ptrii Brrl, Polo Polzell, Andres Brukuer, Nio vn Rooijen, Gurdyl S.
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION CD169 + MACROPHAGES PRESENT LIPID ANTIGENS TO MEDIATE EARLY ACTIVATION OF INVARIANT NKT CELLS IN LYMPH NODES Ptrii Brrl, Polo Polzell, Andres Brukuer, Nio vn Rooijen, Gurdyl S.
Other Uses for Cluster Sampling
 Other Uses for Cluster Smpling Mesure hnges in the level of n ttriute Hypothesis testing versus intervl estimtion Type I n 2 errors Power of the test Mesuring ttriute t sme time in ifferent sites Exmple:
Other Uses for Cluster Smpling Mesure hnges in the level of n ttriute Hypothesis testing versus intervl estimtion Type I n 2 errors Power of the test Mesuring ttriute t sme time in ifferent sites Exmple:
Acute and gradual increases in BDNF concentration elicit distinct signaling and functions in neurons
 nd grdul increses in BDNF concentrtion elicit distinct signling nd functions in neurons Yunyun Ji,, Yun Lu, Feng Yng, Wnhu Shen, Tin Tze-Tsng Tng,, Linyin Feng, Shumin Dun, nd Bi Lu,.. - Grdul (normlized
nd grdul increses in BDNF concentrtion elicit distinct signling nd functions in neurons Yunyun Ji,, Yun Lu, Feng Yng, Wnhu Shen, Tin Tze-Tsng Tng,, Linyin Feng, Shumin Dun, nd Bi Lu,.. - Grdul (normlized
Supplementary Figure S1
 Supplementry Figure S1 - UTR m - 3HA - 2-1 hgh - 1 Uiquitin *! *! lk distl promoter m K3R/ K121R-3HA UTR hgh founder lines - HA - - founder lines TG- E1 L A2 B1 F9 G6 H4 H6 B C D2 G1 H3 J2 L - 7 IP: lk
Supplementry Figure S1 - UTR m - 3HA - 2-1 hgh - 1 Uiquitin *! *! lk distl promoter m K3R/ K121R-3HA UTR hgh founder lines - HA - - founder lines TG- E1 L A2 B1 F9 G6 H4 H6 B C D2 G1 H3 J2 L - 7 IP: lk
Hippocampal CA1 pyramidal cells form functionally distinct sublayers
 r t i l e s Hippompl CA pyrmidl ells form funtionlly distint sulyers Kenji Mizuseki, Kmrn Di,2, Ev Pstlkov,2 & György Buzsáki 2 Nture Ameri, In. All rights reserved. Hippompl CA pyrmidl neurons hve frequently
r t i l e s Hippompl CA pyrmidl ells form funtionlly distint sulyers Kenji Mizuseki, Kmrn Di,2, Ev Pstlkov,2 & György Buzsáki 2 Nture Ameri, In. All rights reserved. Hippompl CA pyrmidl neurons hve frequently
Autocrine IL-2 is required for secondary population expansion of CD8 + memory T cells
 Autorine IL-2 is required for seondry popultion expnsion of CD8 + memory T ells Soni Feu, Rmon Arens,2, Susn Togher & Stephen P Shoenerger 2 Nture Ameri, In. All rights reserved. Two ompeting theories
Autorine IL-2 is required for seondry popultion expnsion of CD8 + memory T ells Soni Feu, Rmon Arens,2, Susn Togher & Stephen P Shoenerger 2 Nture Ameri, In. All rights reserved. Two ompeting theories
Chapter 7. Control and Coordination
 Chpter 7 Control n Coorintion 1 Whih of the following sttements is orret out reeptors? Gusttory reeptors etet tste while olftory reeptors etet smell Both gusttory n olftory reeptors etet smell Auitory
Chpter 7 Control n Coorintion 1 Whih of the following sttements is orret out reeptors? Gusttory reeptors etet tste while olftory reeptors etet smell Both gusttory n olftory reeptors etet smell Auitory
Connexin 30 sets synaptic strength. by controlling astroglial synapse invasion
 Connexin 3 sets synptic strength y controlling stroglil synpse invsion Ulrike Pnnsch, Dominik Freche, Glenn Dllérc, Grégory Ghézli,, Crole Escrtin, Pscl Ezn, Mrtine Cohen-Slmon, Krim Benchenne, Veronic
Connexin 3 sets synptic strength y controlling stroglil synpse invsion Ulrike Pnnsch, Dominik Freche, Glenn Dllérc, Grégory Ghézli,, Crole Escrtin, Pscl Ezn, Mrtine Cohen-Slmon, Krim Benchenne, Veronic
BDNF release from single cells elicits local dendritic growth in nearby neurons
 BDNF relese from single ells eliits lol enriti growth in nery neurons Hley Wilson Horh 1,2 n Lwrene C. Ktz 1 1 Howr Hughes Meil Institute, Deprtment of Neuroiology, Duke University Meil Center, Box 3209,
BDNF relese from single ells eliits lol enriti growth in nery neurons Hley Wilson Horh 1,2 n Lwrene C. Ktz 1 1 Howr Hughes Meil Institute, Deprtment of Neuroiology, Duke University Meil Center, Box 3209,
Tonic excitation or inhibition is set by GABA A conductance in hippocampal interneurons
 Reeive Apr Aepte 8 Jun Pulishe Jul DOI:.8/nomms77 Toni exittion or inhiition is set y GABA A onutne in hippompl interneurons Inseon Song, Leoni Svthenko & Alexey Semynov Inhiition is physiologil proess
Reeive Apr Aepte 8 Jun Pulishe Jul DOI:.8/nomms77 Toni exittion or inhiition is set y GABA A onutne in hippompl interneurons Inseon Song, Leoni Svthenko & Alexey Semynov Inhiition is physiologil proess
WesternBright Quantum
 WesternBright Quntum Quntify hemiluminesent Western lots over wie ynmi rnge WesternBright Quntum is new hemiluminesent regent speilly formulte for CCD imging. This novel Horserish peroxise (HRP) sustrte
WesternBright Quntum Quntify hemiluminesent Western lots over wie ynmi rnge WesternBright Quntum is new hemiluminesent regent speilly formulte for CCD imging. This novel Horserish peroxise (HRP) sustrte
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi: 1.138/nnno.211.41 Sili nd titnium dioxide nnoprtiles use pregnny omplitions in mie Kohei Ymshit, Ysuo Yoshiok, Kzum Higshisk, Kzuy Mimur, Yuki Morishit, Mstoshi Nozki, Tokuyuki
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi: 1.138/nnno.211.41 Sili nd titnium dioxide nnoprtiles use pregnny omplitions in mie Kohei Ymshit, Ysuo Yoshiok, Kzum Higshisk, Kzuy Mimur, Yuki Morishit, Mstoshi Nozki, Tokuyuki
Efficient sensory cortical coding optimizes pursuit eye movements
 ARTICE Reeived Mr 26 Aepted 29 Jul 26 Pulished 9 Sep 26 Effiient sensory ortil oding optimizes pursuit eye movements Bing iu, Mtthew V. Mellio & eslie C. Osorne,2 DOI:.38/nomms2759 OPEN In the nturl world,
ARTICE Reeived Mr 26 Aepted 29 Jul 26 Pulished 9 Sep 26 Effiient sensory ortil oding optimizes pursuit eye movements Bing iu, Mtthew V. Mellio & eslie C. Osorne,2 DOI:.38/nomms2759 OPEN In the nturl world,
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Optial ontrolling reveals time-dependent roles for adult-orn dentate granule ells Yan Gu, Maithe Arruda-Carvalho 3,4, Jia Wang, Stephen Janoshka,, Sheena Josselyn 3-5, Paul Frankland
Supplementary Information Optial ontrolling reveals time-dependent roles for adult-orn dentate granule ells Yan Gu, Maithe Arruda-Carvalho 3,4, Jia Wang, Stephen Janoshka,, Sheena Josselyn 3-5, Paul Frankland
Neuroligin-1 dependent competition regulates cortical synaptogenesis and synapse number
 Neuroligin- epenent ompetition regultes ortil synptogenesis n synpse numer Hyung-Be Kwon,3, Yevgeni Kozorovitskiy, Won-Jong Oh 2, Rui T Peixoto, Nzi Akhtr, Jessi L Sulnier, Chenghu Gu 2 & Bernro L Stini
Neuroligin- epenent ompetition regultes ortil synptogenesis n synpse numer Hyung-Be Kwon,3, Yevgeni Kozorovitskiy, Won-Jong Oh 2, Rui T Peixoto, Nzi Akhtr, Jessi L Sulnier, Chenghu Gu 2 & Bernro L Stini
single smooth muscle cells from guinea-pig and rabbit jejunum
 BrRish Journl of Phrmology (1995) 114. 16571665 B 1995 Stokton Press All rights reserved 71188/95 $12. Effet of UK84149 on voltgetivted lium urrents of single smooth musle ells from guinepig nd rbbit jejunum
BrRish Journl of Phrmology (1995) 114. 16571665 B 1995 Stokton Press All rights reserved 71188/95 $12. Effet of UK84149 on voltgetivted lium urrents of single smooth musle ells from guinepig nd rbbit jejunum
Changing Views of the Role of Superior Colliculus in the Control of Gaze
 Chnging Views of the Role of Superior Colliulus in the Control of Gze Neerj J. Gndhi 1 nd Dvid L. Sprks 2 1 Deprtment of Otolryngology, University of Pittsurgh, Pittsurgh, PA 15213 USA 2 Division of Neurosiene,
Chnging Views of the Role of Superior Colliulus in the Control of Gze Neerj J. Gndhi 1 nd Dvid L. Sprks 2 1 Deprtment of Otolryngology, University of Pittsurgh, Pittsurgh, PA 15213 USA 2 Division of Neurosiene,
Receptive field structure varies with layer in the primary visual cortex
 2 Nture Pulishing Group http://www.nture.om/ntureneurosiene Reeptive field struture vries with lyer in the primry visul ortex Luis M Mrtinez, Qingo Wng 2, R Cly Reid 3, Cinthi Pilli 2, José-Mñuel Alonso
2 Nture Pulishing Group http://www.nture.om/ntureneurosiene Reeptive field struture vries with lyer in the primry visul ortex Luis M Mrtinez, Qingo Wng 2, R Cly Reid 3, Cinthi Pilli 2, José-Mñuel Alonso
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 oi:1.138/nture1138 Supplementl Figure 1 Inflmmtory Monoytes Host ells CCR2 CCL2 Disseminting Tumor Cells Metstsis Assoite Mrophges VEGF Extrvstion & Metstti Seeing Supplementl Figure 1 The t from this
oi:1.138/nture1138 Supplementl Figure 1 Inflmmtory Monoytes Host ells CCR2 CCL2 Disseminting Tumor Cells Metstsis Assoite Mrophges VEGF Extrvstion & Metstti Seeing Supplementl Figure 1 The t from this
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Prentl doi:.8/nture57 Figure S HPMECs LM Cells Cell lines VEGF (ng/ml) Prentl 7. +/-. LM 7. +/-.99 LM 7. +/-.99 Fold COX induction 5 VEGF: - + + + Bevcizum: - - 5 (µg/ml) Reltive MMP LM mock COX MMP LM+
Prentl doi:.8/nture57 Figure S HPMECs LM Cells Cell lines VEGF (ng/ml) Prentl 7. +/-. LM 7. +/-.99 LM 7. +/-.99 Fold COX induction 5 VEGF: - + + + Bevcizum: - - 5 (µg/ml) Reltive MMP LM mock COX MMP LM+
Using Paclobutrazol to Suppress Inflorescence Height of Potted Phalaenopsis Orchids
 Using Pcloutrzol to Suppress Inflorescence Height of Potted Phlenopsis Orchids A REPORT SUBMITTED TO FINE AMERICAS Linsey Newton nd Erik Runkle Deprtment of Horticulture Spring 28 Using Pcloutrzol to Suppress
Using Pcloutrzol to Suppress Inflorescence Height of Potted Phlenopsis Orchids A REPORT SUBMITTED TO FINE AMERICAS Linsey Newton nd Erik Runkle Deprtment of Horticulture Spring 28 Using Pcloutrzol to Suppress
RESEARCH ARTICLE. Supplemental Figure 5
 11.5 2 2 11. RESEARCH ARTICLE RBC ( 1 12 /L) 1.5 1. 9.5 PLT ( 1 9 /L) 1 16 14 HGB (g/l) 19 1 17 16 9. 12 4 4 46 Cellulr & Moleulr Immunology dvne online pulition, PCV (%) 44 MCV (fl) 46 44 ; doi:1.13/mi.214.16
11.5 2 2 11. RESEARCH ARTICLE RBC ( 1 12 /L) 1.5 1. 9.5 PLT ( 1 9 /L) 1 16 14 HGB (g/l) 19 1 17 16 9. 12 4 4 46 Cellulr & Moleulr Immunology dvne online pulition, PCV (%) 44 MCV (fl) 46 44 ; doi:1.13/mi.214.16
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementry Figure 1 c d Wistr SHR Wistr AF-353 SHR AF-353 n = 6 n = 6 n = 28 n = 3 n = 12 n = 12 Supplementry Figure 1 Neurophysiologicl properties of petrosl chemoreceptive neurones in Wistr nd SH rts.
Supplementry Figure 1 c d Wistr SHR Wistr AF-353 SHR AF-353 n = 6 n = 6 n = 28 n = 3 n = 12 n = 12 Supplementry Figure 1 Neurophysiologicl properties of petrosl chemoreceptive neurones in Wistr nd SH rts.
EFFECTS OF AN ACUTE ENTERIC DISEASE CHALLENGE ON IGF-1 AND IGFBP-3 GENE EXPRESSION IN PORCINE SKELETAL MUSCLE
 Swine Dy 22 Contents EFFECTS OF AN ACUTE ENTERIC DISEASE CHALLENGE ON IGF-1 AND IGFBP-3 GENE EXPRESSION IN PORCINE SKELETAL MUSCLE B. J. Johnson, J. P. Kyser, J. D. Dunn, A. T. Wyln, S. S. Dritz 1, J.
Swine Dy 22 Contents EFFECTS OF AN ACUTE ENTERIC DISEASE CHALLENGE ON IGF-1 AND IGFBP-3 GENE EXPRESSION IN PORCINE SKELETAL MUSCLE B. J. Johnson, J. P. Kyser, J. D. Dunn, A. T. Wyln, S. S. Dritz 1, J.
The microrna mir-31 inhibits CD8 + T cell function in chronic viral infection
 A rt i l e s The mirorna mir-3 inhiits CD8 + T ell funtion in hroni virl infetion Howell F Moffett, Adm N R Crtwright, Hye-Jung Kim, Jernej Gode, Json Pyrdol, Trmo Äijö 3, Gustvo J Mrtinez,6, Anjn Ro,
A rt i l e s The mirorna mir-3 inhiits CD8 + T ell funtion in hroni virl infetion Howell F Moffett, Adm N R Crtwright, Hye-Jung Kim, Jernej Gode, Json Pyrdol, Trmo Äijö 3, Gustvo J Mrtinez,6, Anjn Ro,
Conditional dendritic spike propagation following distal synaptic activation of hippocampal CA1 pyramidal neurons
 COMPUTATION AND SYSTEMS ARTICLES Nture Pulishing Group http://www.nture.com/ntureneuroscience Conditionl dendritic spike propgtion following distl synptic ctivtion of hippocmpl CA pyrmidl neurons Tim Jrsky,4,
COMPUTATION AND SYSTEMS ARTICLES Nture Pulishing Group http://www.nture.com/ntureneuroscience Conditionl dendritic spike propgtion following distl synptic ctivtion of hippocmpl CA pyrmidl neurons Tim Jrsky,4,
Inhibitory effect of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase inhibitors on cytokine release from human macrophages
 British Journl of Phrmology (26) 149, 393 44 & 26 Nture Pulishing Group All rights reserved 7 1188/6 $3. www.rjphrmol.org RESEARCH PAPER Inhiitory effet of p38 mitogen-tivted protein kinse inhiitors on
British Journl of Phrmology (26) 149, 393 44 & 26 Nture Pulishing Group All rights reserved 7 1188/6 $3. www.rjphrmol.org RESEARCH PAPER Inhiitory effet of p38 mitogen-tivted protein kinse inhiitors on
Change detection by thalamic reticular neurons
 Chnge detetion y thlmi retiulr neurons Xiong-Jie Yu 1,2, Xin-Xiu Xu 1, Shigng He 1 & Jufng He 1,2 The thlmi retiulr nuleus (TRN) is thought to funtion in the ttentionl serhlight. We nlyzed the detetion
Chnge detetion y thlmi retiulr neurons Xiong-Jie Yu 1,2, Xin-Xiu Xu 1, Shigng He 1 & Jufng He 1,2 The thlmi retiulr nuleus (TRN) is thought to funtion in the ttentionl serhlight. We nlyzed the detetion
Supplementary figure 1
 Supplementry figure 1 Dy 8 post LCMV infection Vsculr Assoc. Prenchym Dy 3 post LCMV infection 1 5 6.7.29 1 4 1 3 1 2 88.9 4.16 1 2 1 3 1 4 1 5 1 5 1.59 5.97 1 4 1 3 1 2 21.4 71 1 2 1 3 1 4 1 5 1 5.59.22
Supplementry figure 1 Dy 8 post LCMV infection Vsculr Assoc. Prenchym Dy 3 post LCMV infection 1 5 6.7.29 1 4 1 3 1 2 88.9 4.16 1 2 1 3 1 4 1 5 1 5 1.59 5.97 1 4 1 3 1 2 21.4 71 1 2 1 3 1 4 1 5 1 5.59.22
The GCN5-CITED2-PKA signalling module controls hepatic glucose metabolism through a camp-induced substrate switch
 Reeived 6 Apr 216 Aepted 8 Sep 216 Pulished 22 Nov 216 DOI: 1.138/nomms13147 OPEN The GCN5-CITED2-PKA signlling module ontrols hepti gluose metolism through AMP-indued sustrte swith Mshito Ski 1, Tomoko
Reeived 6 Apr 216 Aepted 8 Sep 216 Pulished 22 Nov 216 DOI: 1.138/nomms13147 OPEN The GCN5-CITED2-PKA signlling module ontrols hepti gluose metolism through AMP-indued sustrte swith Mshito Ski 1, Tomoko
Introduction to Study Designs II
 Introdution to Study Designs II Commonly used study designs in publi helth & epidemiologi reserh Benjmin Rihrd H. Muthmbi, DrPH, MPH Stte HIV Epidemiologist HIV Epidemiology Investigtion Setion PA Deprtment
Introdution to Study Designs II Commonly used study designs in publi helth & epidemiologi reserh Benjmin Rihrd H. Muthmbi, DrPH, MPH Stte HIV Epidemiologist HIV Epidemiology Investigtion Setion PA Deprtment
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:.8/nture98 : hr NEMO :5 hr IKK IKK NF-κB p65 p5 p65/-rel NF-κB p65 p5 p65/-rel Cytoplsm Cytoplsm p65/p5 Nuleus Nuleus NEMO IKK IKK d : hr > : hr p65/-rel NF- p65 p5 Cytoplsm Cytoplsm p65/p5 p65/-rel
doi:.8/nture98 : hr NEMO :5 hr IKK IKK NF-κB p65 p5 p65/-rel NF-κB p65 p5 p65/-rel Cytoplsm Cytoplsm p65/p5 Nuleus Nuleus NEMO IKK IKK d : hr > : hr p65/-rel NF- p65 p5 Cytoplsm Cytoplsm p65/p5 p65/-rel
ARTICLES. Host-reactive CD8 + memory stem cells in graft-versushost. Yi Zhang, Gerard Joe, Elizabeth Hexner, Jiang Zhu & Stephen G Emerson
 Host-retive CD8 + memory stem ells in grft-versushost disese Yi Zhng, Gerrd Joe, Elizeth Hexner, Jing Zhu & Stephen G Emerson Grft-versus-host disese (GVHD) is used y lloretive donor T ells tht trigger
Host-retive CD8 + memory stem ells in grft-versushost disese Yi Zhng, Gerrd Joe, Elizeth Hexner, Jing Zhu & Stephen G Emerson Grft-versus-host disese (GVHD) is used y lloretive donor T ells tht trigger
Poultry No The replacement value of betaine for DL-methionine and Choline in broiler diets
 Poultry No. 1573 The replement vlue of etine for DL-methionine nd Choline in roiler diets Key Informtion In roiler diets defiient in sulfur mino ids ut dequtely supplemented with methyl groups vi dded
Poultry No. 1573 The replement vlue of etine for DL-methionine nd Choline in roiler diets Key Informtion In roiler diets defiient in sulfur mino ids ut dequtely supplemented with methyl groups vi dded
Reward expectation differentially modulates attentional behavior and activity in visual area V4
 Rewrd expettion differentilly modultes ttentionl ehvior nd tivity in visul re V4 Jll K Bruni 1,6, Brin Lu 1,5,6 & C Dniel Slzmn 1 4 npg 215 Nture Ameri, In. All rights reserved. Neurl tivity in visul re
Rewrd expettion differentilly modultes ttentionl ehvior nd tivity in visul re V4 Jll K Bruni 1,6, Brin Lu 1,5,6 & C Dniel Slzmn 1 4 npg 215 Nture Ameri, In. All rights reserved. Neurl tivity in visul re
Cyclooxygenase-2 inhibition improves amyloid-b-mediated suppression of memory and synaptic plasticity
 doi:1.193/rin/wn8 Brin (28), 131,651^664 Cylooxygense-2 inhiition improves myloid--medited suppression of memory nd synpti plstiity Lind A. Kotilinek, 1, * Mrus A. Westermn, 1, *QinwenWng, 2, *,y Kimerly
doi:1.193/rin/wn8 Brin (28), 131,651^664 Cylooxygense-2 inhiition improves myloid--medited suppression of memory nd synpti plstiity Lind A. Kotilinek, 1, * Mrus A. Westermn, 1, *QinwenWng, 2, *,y Kimerly
Activation of Akt as a Mechanism for Tumor Immune Evasion
 The Amerin Soiety of Gene Therpy originl rtile Ativtion of Akt s Mehnism for Tumor Immune Evsion Kyung Hee Noh 1, Te Heung Kng 1, Jin Hee Kim 1, Sr I Pi 2, Ken Y Lin 3, Chien-Fu Hung 4, T-C Wu 4 7 nd Te
The Amerin Soiety of Gene Therpy originl rtile Ativtion of Akt s Mehnism for Tumor Immune Evsion Kyung Hee Noh 1, Te Heung Kng 1, Jin Hee Kim 1, Sr I Pi 2, Ken Y Lin 3, Chien-Fu Hung 4, T-C Wu 4 7 nd Te
VTA CRF neurons mediate the aversive effects of nicotine withdrawal and promote intake escalation
 CRF neurons medite the versive effets of niotine withdrwl nd promote intke esltion Tryn E Grieder 1, Meliss A Hermn 2, Cndie Contet 2, Lur A Tn 3, Hetor Vrgs-Perez 1, Ami Cohen 2, Mihl Chwlek 1, Geith
CRF neurons medite the versive effets of niotine withdrwl nd promote intke esltion Tryn E Grieder 1, Meliss A Hermn 2, Cndie Contet 2, Lur A Tn 3, Hetor Vrgs-Perez 1, Ami Cohen 2, Mihl Chwlek 1, Geith
V. Arvydas Skeberdis, Jonas JurevicÏ ius & 1 Rodolphe Fischmeister. Introduction
 British Journl of Phrmology (1997) 121, 1277 ± 1286 1997 Stokton Press All rights reserved 7 ± 1188/97 $12. Phrmologil hrteriztion of the reeptors involved in the -drenoeptor-medited stimultion of the
British Journl of Phrmology (1997) 121, 1277 ± 1286 1997 Stokton Press All rights reserved 7 ± 1188/97 $12. Phrmologil hrteriztion of the reeptors involved in the -drenoeptor-medited stimultion of the
YAP transcriptionally regulates COX-2 expression and GCCSysm-4 (G-4), a dual YAP/COX-2 inhibitor, overcomes drug resistance in colorectal cancer
 Li et l. Journl of Experimentl & Clinil Cner Reserh (7) 36:44 DOI.86/s346-7-6-3 RESEARCH Open Aess trnsriptionlly regultes expression nd GCCSysm-4 (G-4), dul / inhiitor, overomes drug resistne in oloretl
Li et l. Journl of Experimentl & Clinil Cner Reserh (7) 36:44 DOI.86/s346-7-6-3 RESEARCH Open Aess trnsriptionlly regultes expression nd GCCSysm-4 (G-4), dul / inhiitor, overomes drug resistne in oloretl
PTSE RATES IN PNNI NETWORKS
 PTSE RATES IN PNNI NETWORKS Norert MERSCH 1 Siemens AG, Hofmnnstr. 51, D-81359 Münhen, Germny Peter JOCHER 2 LKN, Tehnishe Universität Münhen, Arisstr. 21, D-80290 Münhen, Germny Lrs BURGSTAHLER 3 IND,
PTSE RATES IN PNNI NETWORKS Norert MERSCH 1 Siemens AG, Hofmnnstr. 51, D-81359 Münhen, Germny Peter JOCHER 2 LKN, Tehnishe Universität Münhen, Arisstr. 21, D-80290 Münhen, Germny Lrs BURGSTAHLER 3 IND,
Stable reprogrammed heterokaryons form spontaneously in Purkinje neurons after bone marrow transplant
 Stle reprogrmmed heterokryons form spontneously in Purkinje neurons fter one mrrow trnsplnt Jmes M. Weimnn 1,2,Cls B. Johnsson 1,Angeli Trejo 1 nd Helen M. Blu 1,2 Heterokryons re the produt of ell fusion
Stle reprogrmmed heterokryons form spontneously in Purkinje neurons fter one mrrow trnsplnt Jmes M. Weimnn 1,2,Cls B. Johnsson 1,Angeli Trejo 1 nd Helen M. Blu 1,2 Heterokryons re the produt of ell fusion
Research Article The Protection of Hepatocyte Cells from the Effects of Oxidative Stress by Treatment with Vitamin E in Conjunction with DTT
 Hindwi Pulishing Corportion Journl of Biomediine nd Biotehnology Volume 21, Artile ID 486267, 7 pges doi:1.1155/21/486267 Reserh Artile The Protetion of Heptoyte Cells from the Effets of Oxidtive Stress
Hindwi Pulishing Corportion Journl of Biomediine nd Biotehnology Volume 21, Artile ID 486267, 7 pges doi:1.1155/21/486267 Reserh Artile The Protetion of Heptoyte Cells from the Effets of Oxidtive Stress
nature letters to nature ... Mechanism for the learning deficits in a mouse model of neurofibromatosis type 1 advance online publication
 vne online pulition... Mehnism for the lerning efiits in mouse moel of neurofiromtosis type 1 Rui M. Cost*, Nikoli B. Feerov*, Jeff H. Kogn*, Geoffrey G. Murphy*, Joel Stern*, Msuo Ohno*, Rju Kuherlpti,
vne online pulition... Mehnism for the lerning efiits in mouse moel of neurofiromtosis type 1 Rui M. Cost*, Nikoli B. Feerov*, Jeff H. Kogn*, Geoffrey G. Murphy*, Joel Stern*, Msuo Ohno*, Rju Kuherlpti,
Chloride Nutrition Regulates Water Balance in Plants
 XII Portuguese-Spnish Symposium on Plnt Wter Reltions Chloride Nutrition Regultes Wter Blne in Plnts Frno-Nvrro JD 1, Brumós J, Rosles MA 1, Vázquez-Rodríguez A 1, Sñudo BJ 1, Díz- Rued P 1, Rivero C 1,
XII Portuguese-Spnish Symposium on Plnt Wter Reltions Chloride Nutrition Regultes Wter Blne in Plnts Frno-Nvrro JD 1, Brumós J, Rosles MA 1, Vázquez-Rodríguez A 1, Sñudo BJ 1, Díz- Rued P 1, Rivero C 1,
Visualizing an emotional valence map in the limbic forebrain by TAI-FISH
 r t i l e s Visulizing n emotionl vlene mp in the limi forerin y TAI-FISH Jino Xiu 1 3, Qi Zhng 1 3, To Zhou 1,2, Ting-ting Zhou 1,2, Yng Chen 1 & Hiln Hu 1 npg 21 Nture Ameri, In. All rights reserved.
r t i l e s Visulizing n emotionl vlene mp in the limi forerin y TAI-FISH Jino Xiu 1 3, Qi Zhng 1 3, To Zhou 1,2, Ting-ting Zhou 1,2, Yng Chen 1 & Hiln Hu 1 npg 21 Nture Ameri, In. All rights reserved.
Bistability of cerebellar Purkinje cells modulated by sensory stimulation
 25 Nture Pulishing Group http://www.nture.om/ntureneurosiene Bistility of ereellr Purkinje ells moulte y sensory stimultion Yontn Loewenstein 1 3,6, Séverine Mhon 4,6, Pul Cherton 4, Kzuo Kitmur 4, Him
25 Nture Pulishing Group http://www.nture.om/ntureneurosiene Bistility of ereellr Purkinje ells moulte y sensory stimultion Yontn Loewenstein 1 3,6, Séverine Mhon 4,6, Pul Cherton 4, Kzuo Kitmur 4, Him
Olfactory behavior and physiology are disrupted in prion protein knockout mice
 Olftory ehvior nd physiology re disrupted in prion protein knokout mie Clire E Le Pihon 1, Mtthew T Vlley 1, Mgdlini Polymenidou 2,3, Alexnder T Chesler 1, Botir T Sgdullev 1,3, Adrino Aguzzi 2 & Sturt
Olftory ehvior nd physiology re disrupted in prion protein knokout mie Clire E Le Pihon 1, Mtthew T Vlley 1, Mgdlini Polymenidou 2,3, Alexnder T Chesler 1, Botir T Sgdullev 1,3, Adrino Aguzzi 2 & Sturt
r 1996 Stockton Press All rights reserved /96 $12.00 inhibitors of NO in cirrhotic rats although other workers have
 British Journl of Phrmology (1996) 118, 435-441 r 1996 Stokton Press All rights reserved 7-1188/96 $12. Vsoonstritor responsiveness of the rt mesenteri rteril ed in irrhosis 'Ver Rlevi, Roert T. Mthie,
British Journl of Phrmology (1996) 118, 435-441 r 1996 Stokton Press All rights reserved 7-1188/96 $12. Vsoonstritor responsiveness of the rt mesenteri rteril ed in irrhosis 'Ver Rlevi, Roert T. Mthie,
Early depolarizing GABA controls critical-period plasticity in the rat visual cortex
 Erly depolrizing GABA ontrols ritil-period plstiity in the rt visul ortex Gbriele Deidd,5, Mnuel Allegr,,5, Chir Cerri, Shovn Nskr, Guillume Bony, Giuli Zunino 4, Yuri Bozzi,4, Mtteo Cleo,6 & Lur Cnedd,6
Erly depolrizing GABA ontrols ritil-period plstiity in the rt visul ortex Gbriele Deidd,5, Mnuel Allegr,,5, Chir Cerri, Shovn Nskr, Guillume Bony, Giuli Zunino 4, Yuri Bozzi,4, Mtteo Cleo,6 & Lur Cnedd,6
The Hippo/YAP pathway interacts with EGFR signaling and HPV oncoproteins to regulate cervical cancer progression
 Reserh Artile The Hippo/ pthwy interts with EGFR signling nd HPV onoproteins to regulte ervil ner progression Chuno He 1,, Dgn Mo 1,3, Guohu Hu 1,, Xingmin Lv 1, Xingheng Chen, Peter C Angeletti 5, Jixin
Reserh Artile The Hippo/ pthwy interts with EGFR signling nd HPV onoproteins to regulte ervil ner progression Chuno He 1,, Dgn Mo 1,3, Guohu Hu 1,, Xingmin Lv 1, Xingheng Chen, Peter C Angeletti 5, Jixin
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:.3/nture93 d 5 Rttlesnke DRG (reds) Rttlesnke TG (reds) c 3 TRPV1 other TRPs 1 1 3 Non-pit snke TG (reds) SFig. 1 5 5 3 other TRPs TRPV1 1 1 3 Non-pit snke DRG (reds) 5 Antomy of the pit orgn nd comprison
doi:.3/nture93 d 5 Rttlesnke DRG (reds) Rttlesnke TG (reds) c 3 TRPV1 other TRPs 1 1 3 Non-pit snke TG (reds) SFig. 1 5 5 3 other TRPs TRPV1 1 1 3 Non-pit snke DRG (reds) 5 Antomy of the pit orgn nd comprison
