I h -mediated depolarization enhances the temporal precision of neuronal integration
|
|
|
- Willa Jones
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Reeived 5 Apr 2 Aepted 9 Jn 2 Pulished 5 Fe 2DOI:.38/nomms22 I h -medited depolriztion enhnes the temporl preision of neuronl integrtion Ivn Pvlov, Annlis Simemi,, Leonid Svthenko, Dimitri M. Kullmnn & Mtthew C. Wlker Feed-forwrd inhiition medited y ionotropi GABA A reeptors ontriutes to the temporl preision of neuronl signl integrtion. These reeptors exert their inhiitory effet y shunting exittory urrents nd y hyperpolrizing neurons. The reltive roles of these mehnisms in neuronl omputtions re, however, inompletely understood. In this study, we show tht y depolrizing the resting memrne potentil reltive to the reversl potentil for GABA A reeptors, the hyperpolriztion-tivted mixed tion urrent (I h ) mintins voltge grdient for fst synpti inhiition in hippompl pyrmidl ells. Phrmologil or geneti ltion of I h rodens the depolrizing phse of fferent synpti wveforms y hyperpolrizing the resting memrne potentil. This inreses the integrtion time window for tion potentil genertion. These results indite tht the hyperpolrizing omponent of GABA A reeptormedited inhiition hs n importnt role in mintining the temporl fidelity of oinidene detetion nd suggest previously unreognized mehnism y whih I h modultes informtion proessing in the hippompus. Deprtment of Clinil nd Experimentl Epilepsy, UCL Institute of Neurology, London WCN 3GB, UK. Present ddress: Synpti Physiology Setion, Ntionl Institute of Neurologil Disorders nd Stroke, Ntionl Institutes of Helth, Bethesd, Mrylnd , USA. Correspondene nd requests for mterils should e ddressed to M.C.W. (emil: mwlker@ion.ul..uk ). NATURE COMMUNICATIONS 2:99 DOI:.38/nomms Mmilln Pulishers Limited. All rights reserved.
2 M iroeletrode nd eletroenephlogrphy studies show tht groups of neurons n fire synhronously with milliseond preision. To mintin temporl fidelity of informtion enoding, neurons t predominntly s oinidene detetors rther thn neuronl integrtors 2. The preision of oinidene detetion in pyrmidl ells depends ritilly on feed-forwrd inhiition 3,4. Suh inhiition, medited y GABA A reeptors, ts oth y shunting exittory urrents (shunting inhiition) nd y hyperpolrizing neurons (voltge inhiition) 5. Shunting inhiition redues the mplitude nd durtion of exittory postsynpti potentils (EPSPs) y inresing the memrne ondutne. The hyperpolrizing tion of inhiitory postsynpti potentils (IPSPs), on the other hnd, offsets the depolriztion medited y EPSPs nd is long lsting, resulting in iphsi EPSP IPSP sequene in mny neurons 5. It hs een suggested tht the temporl preision of neuronl integrtion lso depends on I h, ut this effet hs een ttriuted to HCN-medited shunting of exittory inputs 6. Ih is mixed tioni urrent with reversl potentil of ~ 3 mv present in neurons throughout the rin (for reviews see refs 7, 8). As I h is present t resting memrne potentil, it depolrizes neurons 9. I h hs mrked effet on dendriti proessing y diretly shunting exittory inputs 2,3 nd through intertions with other memrne ondutnes 4,5. Consequently, loking I h filittes the temporl summtion of EPSPs nd tion potentil firing during repetitive stimultion 2,3,6. As Ih n lso ffet IPSP kinetis 7,8, we sked wht effet I h lokde hs on oinidene detetion, when inhiition is left intt. Here, we report tht loking I h results in signifint rodening of the window for neuronl integrtion. This, however, is not due to the influene of I h on PSP kinetis, ut rther is seondry to the hyperpolrizing effet of I h lokde. Indeed, I h is required to mintin the hyperpolrizing tion of synptilly relesed GABA, nd so, loking I h rodens the exittory phse of the EPSP IPSP sequene evoked y fferent stimultion. These results show n essentil role for I h in determining the reltive vlues of the resting memrne potentil ( V R ) nd the reversl potentil for GABA A reeptor-medited urrents ( E GABA(A) ), nd lso show tht hyperpolrizing inhiition is neessry for temporlly preise neuronl integrtion of synpti inputs. Results Bloking I h inreses the integrtion time window. We ss ess e d oinidene detetion y reording from CA pyrmidl ells Figure Blok of I h widens the oinidene-detetion time window. ( ) Two Shffer ollterl pthwys ( nd ) were stimulted on either side of the reorded neuron ~ 3 μ m wy from the som to evoke EPSP IPSP sequenes. ( ) Both pthwys were then tivted t different interstimulus intervls. Tres show smple responses. Stimultion intensities were djusted so tht the proility of evoking tion potentil ws 5 % when the two stimuli were delivered simultneously. ( ) Summry grph of proility of evoking n tion potentil ginst the intervl etween stimultions ( n = 9). ( d ) Smple experiment demonstrting hnge in the oinidene-detetion time window following I h lokde with ZD Top: Smple tres reorded in response to stimultion of two pthwys in ontrol nd fter pplition of ZD-7288; middle: rster plots of spike genertion; ottom: frequeny histogrms showing spike proility t different intervls etween stimuli. ( e ) Summry grph of reltive proility of firing t different interstimulus intervls in ontrol onditions (open olumns) nd in the presene of ZD-7288 (shded olumns; n = 6 ; P =. for differene). ( f ) The proility of evoking n tion potentil y simultneous tivtion of oth pthwys under seline onditions nd fter the redjustment of stimulus intensity following I h lok (open irles: individul reordings; losed irles: verged dt; n = 6 ). Error rs represent s.e.m. NATURE COMMUNICATIONS DOI:.38/nomms22 using grmiidin perforted-pth in urrent-lmp mode 9. We stimulted two seprte popultions of Shffer ollterls ( Fig. ) representing wek nd strong synpti inputs (see Methods). The stimulus intensities were djusted so tht simultneous tivtion of the two pthwys resulted pproximtely in 5 % hne of the neuron spiking. We then mesured the spike proility while systemtilly vrying the interstimulus intervl. As previously reported, the spike proility deresed s the intervl inresed ( Fig., ). We used μ M ZD-7288 to lok I h. Agin onsistent with previous studies 9,, this resulted in hyperpolriztion, n inrese in input resistne nd omplete dispperne of the hrteristi depolrizing sg of the memrne potentil following hyperpolrizing step urrent injetion ( Supplementry Fig. S ). We then redjusted the stimultion intensities to mth the spiking proility for simultneous stimultion oserved under ontrol onditions. Bloking I h resulted in signifint rodening of the 2 ms 9 ms 6 ms 3 ms ms +3 ms +6 ms +9 ms +2 ms d e Normlized spike proility Cyle Normlized spike proility mv 2 ms 2 mv 2 ms ±3 ±6 ±9 ±2 2 ms Normlized spike proility f ZD Mximum spike proility ZD NATURE COMMUNICATIONS 2:99 DOI:.38/nomms Mmilln Pulishers Limited. All rights reserved.
3 NATURE COMMUNICATIONS DOI:.38/nomms22 ARTICLE time window for integrtion of the two input stimuli ( Fig. d f ; n = 6; repeted mesures nlysis of vrine (ANOVA): F (,5) = 5.5, P =.). We further onfirmed this effet using ell-tthed reordings t ner physiologil temperture nd with the sme stimultion prdigm ( Supplementry Fig. S2 ; n = 4; repeted mesures ANOVA: F(,3) = 37.3, P =.9 for the effet of ZD-7288). V R (mv) ZD-7288 ZD PTX Bloking I h prolongs exittion through hyperpolriztion. Input summtion in the ove experiments depends on the time ourse of the EPSP IPSP sequene 4,9,2. The long memrne time onstnt of hippompl prinipl ells permits EPSP summtion over lrge time window, ut disynpti feed-forwrd inhiition limits the temporl summtion of the exittory inputs y urtiling the EPSPs 4,9. I h ould influene the EPSP IPSP sequene profile y ltering memrne ondutne 2,22, interneuron reruitment 23 nd / or V R 9. To ddress the reltive roles of these effets of I h, we evoked n EPSP IPSP sequene in CA pyrmidl ells y stimulting Shffer ollterls, nd then loked I h with nd without orreting the memrne voltge ( Fig. 2 ). Bloking I h with ZD-7288 ompletely olished the hyperpolrizing omponent of the EPSP IPSP sequene nd resulted in onsiderle rodening of the hlf-width of the depolrizing phse of the response to 25 ± 27 % of ontrol ( n = 4; P =.3; Fig. 2, ). We first exmined whether the effet of I h lok on the EPSP IPSP sequene ould e entirely ounted for y hyperpolriztion of V R. Following the pplition of ZD-7288, V R ws returned to the seline level y injeting onstnt urrent into the reorded neuron nd the EPSP IPSP sequene ws gin reorded ( Fig. 2 ). Almost full reovery of the hyperpolrizing phse of the response ws oserved (8 ± 8 % of the seline mplitude efore ZD-7288 pplition; n = 4 ; P =.). In these experiments, there ws only reltively smll inrese in pek mplitude (36 ± % ; P =.4) nd hlf-width (39 ± 9 % ; P =.2) of the depolriztion, onsistent with some diret effet of I h on the EPSPs; these effets were signifintly smller thn those oserved with the ddition of ZD-7288 without urrent injetion (tht is, without orreting the neuronl hyperpolriztion; P =.2 nd P =.4 for mplitude nd hlf-width of depolrizing phse of the EPSP IPSP sequene, respetively ( Fig. 2 )). The hnges in the EPSP mplitude nd hlf-width following ZD-7288 pplition nd diret urrent injetion ( Fig. 2 ) were similr to those oserved when testing the effet of ZD-7288 on EPSPs when GABA A reeptors were lso loked with μm pirotoxin ( Fig. 2, V R ws fixed t the ontrol level with diret urrent injetions). These results rgue ginst signifint ontriution of non-speifi effets of ZD-7288 on presynpti funtion 24. In ddition, euse of the limited spe lmp in our experimentl onditions (see Methods), reovery of the hyperpolrizing omponent of the postsynpti response y urrent injetion indites tht the mjority of the inhiitory synpses reruited y Shffer ollterl stimultion impinge either lose to the som or on proximl dendrites of pyrmidl ells. This is in line with previous findings tht feed-forwrd inhiition in hippompl CA pyrmidl neurons underlying temporlly preise synpti integrtion is predominntly perisomti 4. We further tested the effet of I h lok on GABA A reeptor-medited trnsmission, s I h hs een reported to e present in some interneurons 23,25,26. We stimulted Shffer ollterls nd reorded in whole-ell voltge-lmp onfigurtion with the memrne potentil lmped to mv (the reversl potentil for glutmtergi urrents) to isolte inhiitory postsynpti urrent (IPSCs). Consistent with the results otined in urrent lmp, ZD-7288 only redued the IPSC mplitude y 7.5 ± 3 % (n = 3). The effet of I h on the EPSP IPSP sequene n therefore e lrgely ttriuted to the I h -dependent depolriztion of V R nd to the loss of the hyperpolrizing tion of the IPSPs. Does shunting inhiition lso modify the EPSP IPSP sequene? To test this, we pplied the GABA A reeptor ntgonist V m (mv) ZD-7288 ZD-7288+DC 2 ms % Chnge ZD-7288+DC 25 ms pirotoxin with I h loked. This resulted in further prolongtion of the EPSPs, inditing n dditionl role of shunting inhiition in regulting the shpe of the EPSP IPSP sequene ( Fig. 2 ). One predition from these results is tht geneti ltion of I h should similrly hyperpolrize neurons, hnge the driving fore for hloride nd prolong the depolrizing phse of the EPSP IPSP sequene. We exmined HCN knokout mie nd ompred them with wild-type littermte ontrols. Consistent with previous studies 27,28, HCN knokouts lked the I h -medited memrne potentil sg following hyperpolrizing step urrent injetion ( Fig. 3 ). The resting memrne potentil of pyrmidl ells ws more hyperpolrized in the knokout mie ( 72.6 ± 2.) ompred with 3 2 Depolriztion mplitude % Chnge Amplitude Depolriztion hlf-width 4 ms Hlf-width Figure 2 Ih lok olishes the hyperpolrizing phse of the EPSP IPSP sequene. ( ) EPSP IPSP sequenes were evoked in CA pyrmidl ells y Shffer ollterl stimultion s in Figure. Conseutive tres from representtive experiment showing shift in V R following ZD pplition, ssoited olition of the GABA A reeptor-medited hyperpolrizing omponent of the EPSP IPSP sequene (GABA B reeptors re loked with 5 μ M CGP52432) nd the overll ontriution of inhiition reveled y susequent pplition of pirotoxin (PTX). ( ) Summry of ZD-7288 effet on EPSP IPSP hrteristis with (diret urrent (DC)) nd without onstnt urrent injetion to ompenste for ZD-7288-indued shift in V R (n = 4 ells; shded olumns: ZD-7288, open olumns: ZD DC). Overlpped verged tres re shown on the left (prepulse seline is normlized). ( ) Effet of pplition of ZD-7288 on the mplitude nd durtion of phrmologilly isolted EPSPs, while mintining V R with urrent injetion ( n = 7; reordings were mde in the presene of 5 μ M CGP52432 nd μ M pirotoxin); this effet is similr to the effet of ZD-7288 on the EPSP IPSP sequene + DC ( ). Br hrts represent perentge hnge of ontrol vlues; error rs represent s.e.m.; P <.5, P <., P <.. NATURE COMMUNICATIONS 2:99 DOI:.38/nomms Mmilln Pulishers Limited. All rights reserved. 3
4 V m (mv) WT KO d WT KO e V R (mv) WT 5 ms E GABAA (mv) KO wild-type littermte ontrol nimls ( 6.9 ±.6 mv; P =.37; Fig. 3 ); however, E GABA(A) ws similr in oth genotypes ( Fig. 3,d ). As predited, the hyperpolrizing phse of the EPSP IPSP sequene ws either sent or redued in the knokout nimls, nd the width of the EPSPs ws rodened to 93.4 ± 8.4 % of the wildtype vlue ( P =.9; Fig. 3e ). I h mintins V R more depolrized thn E GABA(A). The results thus fr indite tht I h -dependent neuronl depolriztion is neessry to mintin hyperpolrizing effet of GABA A reeptor urrents. We diretly tested this hypothesis using grmiidin perfortedpth urrent-lmp reordings, whih minimize perturtion of the internl Cl onentrtion. E GABA(A) ws determined from the reversl potentil of evoked IPSPs, nd ws uniformly negtive to V R (men E GABA(A) V R : 5.2 ±. mv; n = 2; P =.3; Fig. 4 ). In ll ells, pplition of ZD-7288 resulted in signifint negtive shift in V R ( 8.6 ±.9 mv; P = ; n = 2; Fig. 4, ). In ontrst, inhiition of I h led to only smll depolrizing shift in E GABA(A) (2. ±.8 mv; P =.3; Fig. 4d ). The net effet of loking I h ws to mke V R more negtive thn E GABA(A) in out of 2 ells (men E GABA(A) V R : 5.5 ±.3 mv; n = 2; P =.3; Fig. 4e ). This demonstrtes mjor role of I h in mintining hyperpolrizing driving fore for fst GABAergi trnsmission. Correting V R fter I h lok restores oinidene detetion. Although the rodening of input integrtion is onsistent with the hypothesis tht GABA A reeptor-medited hyperpolriztion is required to mintin the nrrow time window for oinidene detetion, n lterntive potentil explntion is tht I h hs profound effet upon dendriti exitility nd temporl summtion of exittory inputs 2,3. To distinguish etween these hypotheses, we repeted the oinidene-detetion experiments, ut depolrized the neuron following ddition of ZD-7288 to return the resting IPSP mplitude (mv) V m (mv) WT KO 2 V R KO V R WT 8 WT mv 6 t V R +DC t V R 4 KO 4 ms +DC Figure 3 HCN deletion results in the loss of the hyperpolrizing effets of GABA A reeptor-medited inhiition. ( ) Exmple tres showing voltge responses to urrent steps injetions in wild-type (WT) mie nd HCN knokout (KO) mie. ( ) An exmple plot showing tht, unlike WT mie, HCN KO mie lked hyperpolrizing GABA A reeptor-medited driving fore. Dt points were fitted with seond-order polynomil funtion. ( ) Comprison of V R in HCN KO mie nd WT mie (WT: n = 5; KO: n = 8). (d ) Summry plot of E GABA(A) in oth genotypes (WT: n = 5; KO: n = 4). (e ) Smple tres showing tht the KO mie displyed no hyperpolrizing phse t V R, wheres WT nimls hd iphsi EPSP IPSP sequene. The hyperpolrizing IPSPs eme pprent in the KO mie when ells were depolrized y DC injetion. Conversely, the IPSP ws less evident when pyrmidl ells from WT mie were hyperpolrized. Error rs represent s.e.m.; P <.. % V R hnge V R (mv) e NATURE COMMUNICATIONS DOI:.38/nomms E GABA A (mv) V m (mv) ms 2 Time (min) ZD-7288 V R mv ZD-7288 ( μm) memrne potentil to the seline level. Using this protool, we oserved no hnge in the time window for integrtion ( Fig. 5 ; n = 5; repeted mesures ANOVA: F (,4) =.374, P =.57). This implies tht it is primrily the depolrizing effet of I h nd loss of the hyperpolrizing effet of GABA A reeptor urrents tht mintins the nrrow oinidene detetion for input integrtion. A further 5 5 IPSP mplitude (mv) V R (mv) d E GABA A (mv) E GABAA > V R 5 3 E GABAA < V R ZD-7288 Figure 4 Bloking I h hnges the V R E GABA(A) reltionship in CA pyrmidl ells. ( ) In ontrol onditions, ll ells hd negtive E GABA(A) ompred with V R (n = 2). Smple IPSPs t different memrne potentils from typil experiment re shown in the inset. Dt points were fitted with seond-order polynomil funtion. ( ) Time ourse of the hnges in V R following the pplition of ZD-7288 ( n = 2). ( ) Effet of ZD-7288 on V R (filled irles re men vlues, open irles re dt from individul experiments; n = 2). (d ) Effet of I h lok on E GABA(A) (filled irles re men vlues, open irles re dt from individul experiments; n = 2). ( e ) Summry grph showing the effet of ZD-7288 on E GABA(A) nd V R. E GABA(A) eme more depolrized thn V R in out of 2 ells (open irles: ontrol, filled irles: in ZD-7288). Error rs represent s.e.m.; P <.5, P <.. 4 NATURE COMMUNICATIONS 2:99 DOI:.38/nomms Mmilln Pulishers Limited. All rights reserved.
5 NATURE COMMUNICATIONS DOI:.38/nomms22 ARTICLE Cyle Normlized spike proility Normlized spike proility ms ±3 ±6 ±9 predition from this is tht simple hyperpolriztion with I h intt would widen the oinidene-detetion time window, whih is indeed the se ( n = 5, repeted mesures ANOVA: F(,4) = 8.2, P =.46; Supplementry Fig. S3 ). Hyperpolrizing inhiition underlies temporl preision. A possile onfounder in the ove experiments is tht in order to mintin 5 % spiking proility, we hd to djust the stimultion intensity to ompenste for the memrne hyperpolriztion, potentilly ffeting interneuron reruitment. This would tend to inrese the interneuron reruitment nd therefore would e expeted to nrrow the integrtion time window (in ontrst to the rodening tht we oserved). Nevertheless, to ontrol for this nd to ddress the question of whether loss of the hyperpolriztion effet of GABA A ±2 Mximum spike proility ZD DC ms ZD+DC Figure 5 Repolriztion restores temporl preision when I h is loked. ( ) Spike proility t different intervls etween stimuli in ontrol onditions nd in the presene of ZD-7288 when neurons were repolrized to their initil V R y DC injetion, therefore restoring the iphsi shpe of the EPSP IPSP sequene. Top: smple tres; middle: rster plots of spikes initited y stimultion of the two pthwys t different dely intervls; ottom: spike proility distriution grphs. ( ) Averged dt from five experiments (open olumns: ontrol, shded olumns: ZD DC; P =.57). ( ) Proility of tion potentil genertion for synhronous stimultion of oth pthwys efore nd fter pplition of ZD-7288 ( n = 5). Error rs represent s.e.m. reeptor urrents is suffiient to explin our results, we onstruted simple integrte-nd-fire model of neuron tht reeives two inputs. Eh input onsisted of n exittory followed y n inhiitory ondutne, nd the prmeters were djusted to simulte the kinetis of the experimentlly otined EPSP IPSP sequene wveform (see Methods; Fig. 6 ). In greement with the experimentl findings, systemti vrition of the dely etween the two inputs reveled nrrow integrtion time window for spike genertion ( Fig. 6 ). Hyperpolriztion of V R rodens the integrtion time window. R emov ing I h from the modelled ell, hyperpolrized the memrne from 7 to 8 mv nd led to n inrese in the width of the integrtion time window ( Fig. 6 ; the re under the spike proility urve ws inresed y 26.3 ± 2.3 % ; P <.). This effet ws roust nd reltively insensitive to vrying EPSP nd IPSP kineti prmeters, dely times etween exittory nd inhiitory synpse tivtion, s well s synpse lotions on the dendrites ( Supplementry Fig. S4 ). We lso systemtilly hnged the mximl proility of tion potentil genertion to test whether this ould ffet our experimentl results. The effet of memrne potentil hyperpolriztion ws onstnt ross wide rnge of tested proility vlues ( Supplementry Fig. S5 ). To determine whether the effet on the integrtion window in the simultions ws due to the ondutne or voltge effet of I h removl, we repolrized the neuronl som k to 7 mv y introduing depolrizing urrent. In greement with experimentl oservtions, this restored the width of the time window for integrtion, inditing ruil role for the depolrizing tion of I h (Fig. 6d ). We next sked whether the effet tht we oserved ws due to the voltge hnge itself rther thn the hnge in the polrity of GABA A reeptor-medited trnsmission. We therefore ssessed the effets of memrne potentil on the integrtion time window in the sene of GABAergi trnsmission. As expeted 4, removing feed-forwrd inhiition rodened the integrtion time window y 6.8 ± 6.7 %. However, the width of the window ws minimlly ffeted y hnges in V R in the rnge oserved in our experiments nd simultions ( Fig. 7 ; n inrese of 3. ±.4 % with mv hyperpolriztion). In the ove simultions, the mgnitude of the inhiitory synpti ondutne ws fixed to mth the simulted EPSP IPSP wveform with tht oserved experimentlly. We therefore tested the effet of different inhiitory synpti ondutnes. In ll instnes, hyperpolrizing V R, so tht the IPSPs eme depolrizing, widened the integrtion time window. This effet initilly inresed with inreses in the IPSP mplitude ( Fig. 7 ) up to mximum nd then deresed proly euse of the inresing shunting versus voltge effet of inhiitory synpses. Finlly, we onsidered the possile onfounding effet of vriility in the size of the inhiitory ondutne. At high stimultion intensity, the inhiitory ondutne is reltively invrint 29. However, t lower stimultion intensities, inhiitory ondutnes vry with stimultion intensity (nd mgnitude of exittory ondutne). We therefore ovried the ondutnes of exittory nd inhiitory synpses (see Methods) to model this sitution. Under these onditions, the window of integrtion ws still inresed following hyperpolriztion of the neuron y 38. ±.4 % ompred with 2.2 ± 2.6 %, with onstnt inhiitory synpti ondutnes ( Fig. 7 ; P <.5). Disussion We hve shown tht I h is neessry to mintin hyperpolrizing driving fore for GABA A reeptor-medited trnsmission y depolrizing the resting memrne potentil of pyrmidl ells. Hyperpolrizing the resting memrne potentil through phrmologil inhiition of I h or deletion of HCN results in depolrizing GABA A reeptor-medited potentils nd rodening of the exittory phse NATURE COMMUNICATIONS 2:99 DOI:.38/nomms Mmilln Pulishers Limited. All rights reserved. 5
6 NATURE COMMUNICATIONS DOI:.38/nomms22 Normlized spike proility d Normlized spike proility Normlized spike proility Experimentl EPSP EPSP IPSP sequene 2 3. ±.5 ±.. ±.5 Simulted 2 ±. ±.5 2 ms 3 ±.5 ±2. ±2.5 ±3. ±2. ±2.5 ±3. Figure 6 I h -medited hyperpolriztion rodens the integrtion time window in n integrte-nd-fire neuronl model. ( ) Suessive tivtion of exittory nd inhiitory ondutnes in simple integrtend-fire neuron ws used to produe n EPSP IPSP sequene similr to tht oserved experimentlly. ( ) Simultion of two pthwys tivted with different delys (see Methods) resulted in nrrow integrtion time window. Synpti strength ws djusted so tht the pek proility of tion potentil genertion remined t 5 %. ( ) Removl of I h from the dendrites hyperpolrized the modelled neuron y mv. The grph shows spike proility t different intervls etween stimuli with (open rs) nd without I h (red rs) in the modelled neuron. ( d ) The effet of I h removl ws olished when the neuronl som ws repolrized y DC injetion (open rs: ontrol with I h, lue rs: no I h repolrized). Dt re presented s mens of 3 rounds of simultions, error rs represent s.e.m. Normlized spike proility AUC (% hnge) AUC (% of ontrol) ± ±2 of the EPSP IPSP sequene, leding to prolonged time window for synpti integrtion. These results lso demonstrte n importnt nd unexpeted role of voltge inhiition. I h hnnels re densely expressed in the dendriti rour of CA pyrmidl ells 2. A signifint proportion of these hnnels is tive ± IPSP mgnitude (g i ) Constnt G IPSP Adjusted G IPSP Figure 7 The effets of hnging the mgnitude of inhiitory ondutnes on the width of the integrtion time window. ( ) In the sene of feed-forwrd inhiition (no IPSPs), the integrtion time window eme roder. Under suh onditions, memrne hyperpolriztion did not hnge the width of oinidene detetion, inditing tht hnges in the polrizing effet of GABA A reeptor-medited urrents, rther thn the V R vlue itself, determine neuronl integrtion (open rs: V m = 7 mv no IPSP; hthed rs: V m = 8 mv no IPSP; red rs: V m = 7 mv with IPSP). ( ) The effet of vrying the strength of inhiitory onnetions on the width of the integrtion time window ssessed s the hnge in the re under the spike proility urve (AUC). ( ) The effet of hyperpolriztion on the oinidene-detetion time window when inhiitory synpti ondutnes were sled with exittory ondutnes, mimiking the sitution when inhiitory inputs onto neuron re not sturted. Dt re presented s mens of 3 rounds of simultions, error rs represent s.e.m.; P <.5, P <., P <.. ± NATURE COMMUNICATIONS 2:99 DOI:.38/nomms Mmilln Pulishers Limited. All rights reserved.
7 NATURE COMMUNICATIONS DOI:.38/nomms22 ARTICLE t rest, reduing the memrne resistne nd neuronl time onstnt. These effets of I h hve een shown to determine the time ourse of EPSPs onto CA pyrmidl ells 2. The previous studies hve onentrted on the impt of I h on the integrtion properties of exittory inputs, with GABA A reeptor-medited inhiition loked. However, GABAergi inhiition hs profound effet on the width of the integrtion time window of exittory inputs 4. The reltive roles of shunting nd hyperpolrizing inhiition in mintining preise oinidene detetion hve not een ddressed. Although one study hs onsidered the effet of I h on the integrtion time window without GABA A reeptor lokde 6, tht work ws performed in whole-ell mode, with the memrne potentil of the neurons fixed nd the reversl potentil of GABA A responses set to e depolrizing. In hippompl neurons, E GABA(A) is negtive to V R y the end of the seond postntl week 3, so tht GABA A reeptor-medited potentils predominntly hyperpolrize the postsynpti memrne in dult tissue, for exmple, see ref. ( 3 ). In dult neurons, E GABA(A) is minly determined y the Cl otrnsporter KCC2, whih uses the trnsmemrne K + grdient to mintin low intrellulr Cl onentrtion, therey lmping the reversl potentil for Cl (E Cl ) loser to tht of K + (E K ) 3. E GABA(A) is, however, more depolrized thn E Cl due to the permeility of the GABA A reeptors to HCO 3 ions 32. Therefore, to mintin hyperpolrizing IPSPs, V R lso hs to e depolrized reltive to E GABA(A). A numer of ondutnes my ontriute to this depolriztion (suh s persistent sodium urrents nd lek ondutnes); in CA pyrmidl ells, I h provides signifint depolrizing drive t resting memrne potentil. In our study, this effet of I h ws more evident with phrmologil lok thn with geneti ltion, perhps euse of ompenstory hnges in other ondutnes in the HCN knokout mie. We hve shown tht I h sets the polrity of GABAergi events y mking V R more depolrized thn E GABA(A), nd most of the effets of I h on the EPSP IPSP sequene n e resued y repolrizing V R to its seline vlue, rguing for mjor role of GABAergi voltge inhiition in regulting the integrtion properties of synpti inputs of CA pyrmidl ells. As oserved in our study nd in other studies, for exmple, see ref. ( 33 ), GABA A reeptor tivtion n still shunt EPSPs even when E GABA(A) is more depolrized thn V R. However, the reltive importne of shunting nd hyperpolrizing effets of inhiition for neuronl omputtions nd preise timing of tion potentil genertion hs reeived muh less ttention. Some experimentl nd theoretil studies hve suggested tht the hyperpolrizing effets of GABAergi neurotrnsmission re ritil for network synhroniztion, for exmple, see ref. ( 34 ), wheres others emphsize the role of shunting inhiition in osilltory ehviour of interonneted neurons 35. The ility of I h to swith the inhiitory mode of GABAergi signls from hyperpolrizing to shunting or depolrizing dds further omplexity in defining the omputtionl properties of hippompl neurons 36. Further, it might e expeted tht the lrge, erly shunting effet of GABAergi inhiition hs the predominnt prt in urtiling the EPSPs. Our results, however, undersore the ontriution of GABA A reeptor-medited hyperpolriztion in determining the temporl preision of oinidene detetion y hippompl pyrmidl neurons. How does hnging the GABA A reeptor-medited response from hyperpolrizing trnslte to n inresed integrtion time? Although shunting is mintined regrdless of the polriztion of GABA A reeptor-medited responses (see Fig. 2 ) ttenuting the EPSPs generted in response to the seond stimultion, this ttenution would e muh stronger when the IPSP produes hyperpolriztion. More importntly, euse the voltge effet of n IPSP outlsts its shunting effet 33, it would hve n impt on the exittory potentils over n extended period. In the sitution when the hyperpolrizing phse of the GABAergi response is olished (nd even more so if the polrity of the GABA A response is hnged), this would filitte EPSP summtion. Therefore, the hyperpolriztion tht results from inhiition of I h results in onsiderle inrese in the hlf-width of the time window for oinidene detetion. Inhiition of other memrne ondutnes through hyperpolriztion nnot ount for this, s voltge hnges of similr mgnitudes, when I h is loked, result in miniml hnge in the memrne resistne or time onstnt. The ritil role of hyperpolriztion for oinidene detetion hs extensive implitions, s nything tht lters the polrity of GABA A reeptor-medited trnsmission will ffet the time window for input integrtion. This would inlude either shift in E GABA(A) (for exmple, due to loss or inhiition of KCC2) or hnges in resting memrne potentil medited through, for exmple, hnges in memrne potssium ondutnes. We hve therefore shown the ritil role of GABA A reeptor-medited hyperpolriztion in informtion proessing nd n unexpeted mehnism y whih I h n modulte oinidene detetion. As I h is regulted y developmentl 37, physiologil 38 nd pthologil proesses 6,39 42, suh proesses my onsequently ffet the properties of GABA A reeptor-medited signlling nd the temporl fidelity of oinidene detetion. This my ontriute to ognitive nd psyhitri onsequenes of epilepsy y inresing the proility of errnt ssoitions. Moreover, the mgnitude of somti I h is dependent upon exittory synpti tivity, nd this hs een proposed to e homeostti mehnism regulting neuronl exitility 38. We further hypothesize tht suh mehnism my hve n dditionl homeostti role y nrrowing the time window for oinidene detetion with inreses in neuronl tivity nd onversely rodening the time window for integrtion when synpti tivity dereses. The role of I h in restriting temporl input integrtion my lso ontriute to explining the enhned lerning ehviour oserved in HCN knokout mie 27, whih my our t the expense of loss of temporl disrimintion of inputs. Methods Eletrophysiology. We used trnsverse hippompl slies (35 μm) from 3 6- week-old mle Sprgue Dwley rts, or HCN knokout mie nd their wild-type littermte ontrols. The HCN knokout nimls were re-derived from tht desried previously, nd mintined on 29SVEV kground 27,28. Animls were killed ording to shedule of the UK Animls (Sientifi Proedures) At 986. The rins were rpidly removed, disseted nd ut with Lei VTS virtome in ie-old solution ontining (in mm) surose (7), NCl (8), KCl (2.5), MgCl 2 (7), CCl 2 (.5), NHCO 3 (25), NH 2 PO 4 (.25) nd gluose (22), nd were equilirted with 95 % O 2 /5 % CO 2 (ph 7.4). The slies were llowed to reover in n interfe hmer ( > h) t room temperture efore eing trnsferred to the reording hmer. Storge nd perfusion solutions ontined (in mm) NCl (9), KCl (2.5), MgSO 4 (.3), CCl 2 (2.5), NHCO 3 (26.2), NH 2 PO 4 () nd gluose (22), nd were gssed with 95 % O 2 /5 % CO 2. All reordings, exept for those in Figures, 5 nd Supplementry Figure S3, were rried out t 32 C. Current-lmp whole-ell reordings ( Supplementry Fig. S ) were performed using pipettes (3 5 M Ω ) filled with n intrellulr solution ontining (in mm) K-gluonte (45), NCl (8), KOH HEPES (), EGTA (.2), Mg-ATP (2) nd N 3 -GTP (.3); ph 7.2; 29 mosm. Grmiidin (5 μg ml ) ws dded for perforted-pth reordings 43, nd pth pipettes (8 2 MΩ ) were front-filled with grmiidin-free solution; either QX-34 Br (5 mm) ws dded or [Cl ] ws inresed to 26 mm (E Cl = 4 mv) to monitor pth integrity. Series resistne ws monitored throughout. Dt quisition egn when the series resistne ws < 5 MΩ (5 2 min fter otining ell-tthed onfigurtion). To isolte GABA A reeptor-medited IPSPs, NMDA, AMPA nd GABA B reeptors were loked with AP5 (5 μ M), NBQX (2 μ M) nd CGP52432 (5 μ M), respetively. Constnt urrent stimuli were delivered to Shffer ollterls through ipolr stinless steel eletrodes pled in strtum rditum. Monosynpti IPSPs were evoked y positioning the stimulting eletrode lose to the reording site. EPSP IPSP sequenes were evoked y positioning the eletrodes in strtum rditum t lest 3 μ m wy from the reording site; CGP52432 (5 μ M) ws dded to the perfuste. Although pplition of CGP52432 redued the durtion of the hyperpolrizing phse y 6 ± 3 % (Supplementry Fig. S6 ), it did not ffet the depolrizing omponent. Two Shffer ollterl pthwys were stimulted for the oinidene-detetion protool ( Figs nd 5, Supplementry Fig. S3 ). Experiments were performed in the presene of 5 μ M AP5 (to void spike timing-dependent plstiity) nd 5 μm CGP AP5 hd miniml impt on the exittory phse of the EPSP IPSP sequene, deresing the hlf-width y 4 ± 4 % (more thn n order of mgnitude smller thn the impt of hnging the polrity of GABA A responses; Supplementry NATURE COMMUNICATIONS 2:99 DOI:.38/nomms Mmilln Pulishers Limited. All rights reserved. 7
8 NATURE COMMUNICATIONS DOI:.38/nomms22 Fig. S6d f ). To ensure reording stility, these experiments were performed t room temperture (23 25 C); this inresed the time ourse of the synpti responses ( Supplementry Fig. S7 ), ut the shpe of the EPSP IPSP wveform ws mintined. Although modelling indited tht this does not qulittively hnge the experimentl findings ( Supplementry Fig. S4 ), we onfirmed this with ell-tthed reordings t 32 C (Supplementry Fig. S2 ). These experiments were performed using pth pipettes (8 2 MΩ ) filled with ACSF in voltge-lmp with the voltge set so tht no urrent ws injeted under seline onditions. As fferent input strength to the hippompus n vry onsiderly, we stimulted wek nd strong input; the mplitude of the response in one pthwy ws djusted to e pproximtely twie thn tht in the other pthwy. In the ell-tthed experiments, the wek pthwy ws stimulted t pproximtely hlf-threshold intensity, wheres the strong pthwy stimultion ws set lose to the firing threshold. Stimultion intensities were djusted to otin ~ 5 % spike proility when the two pthwys were tivted simultneously. The two pthwys were stimulted with n interstimulus dely vrying from 2 to + 2 ms in 3 ms steps (thus the order of inputs ws reversed over the rnge investigted). To void ny onfounding effets of symmetri distriution of spike proilities, the dt re presented s the verged vlues from orresponding points on either side of the mximum. In some experiments, onstnt urrent injetion ws used to repolrize the somti memrne potentil. Under our experimentl onditions, there is spe lmp error in distl dendrites. However, s we oserved experimentlly tht somti urrent injetion restored the hyperpolriztion phse of the EPSP IPSP wveform, we onlude tht feed-forwrd inhiition in our study ws predominntly perisomti ( Supplementry Fig. S8 ). For experiments on the effet of I h lok on the mgnitude of IPSCs, the intrellulr solution ontined (in mm) Cs-methnesulfonte (2), NCl (8), HEPES (), EGTA (.2), MgCl 2 (.2), Mg-ATP (2), N 3 -GTP (.3) nd QX-34 Br (5 mm); 29 mosm. Shffer ollterls were stimulted in the presene of AP5 nd CGP Neurons were voltge-lmped t mv (lose to the reversl potentil for AMPA reeptor-medited response), nd outwrd GABA A reeptormedited urrents were ompred in the sene nd presene of ZD All reordings were otined using MultiClmp 7B mplifier ( Moleulr Devies ), filtered t 2 khz nd digitized t 5 khz. LView ( Ntionl Instruments ) softwre ws used for dt quisition nd off-line nlysis. Chemils were purhsed from Toris Cookson or Sigm-Aldrih. Modelling. All simultions were onduted with NEURON 7. (ref. 44) on multimode luster 45. The Hodgkin Huxley neuron model onsisted of ylindril som (dimeter = length = 2 μ m) nd two identil dendrites (3 μ m dimeter nd 2 μ m long). The xil resistne ( R ) ws 35.4 Ohm m ; memrne pitne ( C m ) ws μf m 2. The somti memrne hd N + nd K + ondutnes with the following pek vlues: g N =.2 S m 2, g K =.36 S m 2 (E K = 77 mv nd E N = + ). The dendriti memrne hd pssive lek urrent ( g ps = ms m 2 nd E ps = 8 mv) nd I h (g Ih = ms m 2, kinetis s in ref. 2). V R ws 7 mv. Removl of I h hyperpolrized the neuron y mv. In suh onditions,.4 na injeted into the som ws neessry to repolrize the memrne potentil to 7 mv. All simultions were performed with either V R = 7 mv (seline onditions) or 8 mv (hyperpolrized onditions). Deterministi tion potentil genertion ws prevented y introduing Poisson-distriuted ondutnes of uniformly distriuted vrile mgnitude (.9. ns; τ rise =. ms; τ dey = ms; reversl potentil = V R to void signifint memrne potentil flututions) into the ell t men frequeny of, Hz. Eh dendrite hd glutmtergi nd GABAergi synpses, loted t 8 nd 4 μ m from the som, respetively. The dul-exponentil formlism in the Exp2Syn funtion of neuron simultor ws used to determine the time ourse of synpti ondutnes: gs( t) = Gm(exp( t/ t) exp( t/ t2)), () where g s (t ) is the synpti ondutne t time t fter tivtion; τ is the rise time onstnt (7 ms for glutmtergi synpses nd 5 ms for GABAergi synpses); τ 2 is the dey time onstnt (35 ms for glutmtergi synpses nd 5 ms for GABAergi synpses) nd G m is the vlue of the mximum synpti ondutne. To simulte the EPSP IPSP sequene, there ws 7 ms dely from EPSPs to IPSPs. The reversl potentils were set t 75 nd mv for GABAergi nd glutmtergi synpses, respetively. Th e left exittory nd inhiitory synpti ondutnes ( G ESL nd G ISL ) were twie the right synpti ondutnes ( G ESR nd G ISR ). The onset time of the left EPSP IPSP sequene ws fixed wheres tht of the right vried from to + ms. To lulte the time distriution of the spike proility, interstimulus intervls were divided into.5 ms ins. The proility of tion potentil genertion ws determined using 3 rounds of ten synpti stimultions with 5 ms intervl etween trils, initited with different seed. The intervl etween stimuli ws suffiient to llow the model neuron to reh initil stedystte onditions. The men numer of tion potentils per in ( M i ) nd s.e. ( ε i ) were lulted. Are under the spike proility urve ws used to quntify hnges in the oinidene-detetion time window. The s.e. of the surfe under the distriution ws defined s: e = N 2 in ei i=, pmx where N is the numer of ins, in is the in size nd p mx is the mximum proility of the distriution. The s.e. of the rtio of surfes S / S2 ws defined s: 2 e e ess = + 2 S S S 2 S. 2 2 The mximl proility of tion potentil genertion (.5) ws set y sling synpti ondutnes with the prmeter Stim: Stim G ESL nd Stim G ESR. The strengths of inhiitory synpses were set to G ISL = 45 ns nd G ISR = 225 ns for left nd right synpse, respetively, for the mjority of simultions. For Figure 7, the strength of inhiitory onnetions vried s indited. For simultions presented in Figure 7 in ddition to exittory ondutnes, we lso sled inhiitory ondutnes: Stim G ISL nd Stim G ISR. Simultions with mximl proilities from.2 to.85 were performed ( Supplementry Fig. S5 ). In these experiments, the tul mximl spike proility ws determined post ho. Sttistis. Two-tiled Student s t -test (pired or independent) nd repeted mesures ANOVA were used for sttistil nlysis. P <.5 for signifint differenes. Dt re presented s men ± s.e.m. Referenes (2) (3). Konig, P., Engel, A. K. & Singer, W. Integrtor or oinidene detetor? The role of the ortil neuron revisited. Trends Neurosi. 9, 3 37 (996 ). 2. Aeles, M. Role of the ortil neuron: integrtor or oinidene detetor? Isrel J. Med. Si. 8, (982 ). 3. Buzski, G. Feed-forwrd inhiition in the hippompl formtion. Prog. Neuroiol. 22, 3 53 (984 ). 4. Pou i l l e, F. & S n zi n i, M. E n for e me nt of temp or l fi delity in pyrmidl ells y somti feed-forwrd inhiition. Siene 293, (2 ). 5. E l es, J. The Ferrier leture: the nture of entrl inhiition. Pro. R. So. Lond. B 53, (96 ). 6. Berger, T. & Lusher, H. R. Timing nd preision of spike initition in lyer V pyrmidl ells of the rt somtosensory ortex. Cere. Cortex 3, (23 ). 7. Ppe, H. C. Queer urrent nd pemker: the hyperpolriztion-tivted tion urrent in neurons. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 58, (996 ). 8. Roinson, R. B. & Siegelum, S. A. Hyperpolriztion-tivted tion urrents: from moleules to physiologil funtion. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 65, (23 ). 9. Gsprini, S. & DiFrneso, D. Ation of the hyperpolriztion-tivted urrent (Ih) loker ZD 7288 in hippompl CA neurons. Pflug. Arh. 435, 99 6 (997 ).. Mferri, G., Mngoni, M., Lzzri, A. & DiFrneso, D. Properties of the hyperpolriztion-tivted urrent in rt hippompl CA pyrmidl ells. J. Neurophysiol. 69, (993 ).. Spr uston, N. & Joh nston, D. Pe r for te d p th- l mp n lysis of t he p ss ive memrne properties of three lsses of hippompl neurons. J. Neurophysiol. 67, (992 ). 2. Mge e, J. C. D end r it i l h normlizes temporl summtion in hippompl CA neurons. Nt. Neurosi. 2, (999 ). 3. Poolos, N. P., Migliore, M. & Johnston, D. Phrmologil upregultion of h-hnnels redues the exitility of pyrmidl neuron dendrites. Nt. Neurosi. 5, (22 ). 4. George, M. S., Aott, L. F. & Siegelum, S. A. HCN hyperpolriztiontivted tion hnnels inhiit EPSPs y intertions with M-type K(+) hnnels. Nt. Neurosi. 2, (29 ). 5. Tsy, D., Dudmn, J. T. & Siegelum, S. A. HCN hnnels onstrin synptilly evoked C 2+ spikes in distl dendrites of CA pyrmidl neurons. Neuron 56, (27 ). 6. Shh, M. M., Anderson, A. E., Leung, V., Lin, X. & Johnston, D. Seizureindued plstiity of h hnnels in entorhinl ortil lyer III pyrmidl neurons. Neuron 44, (24 ). 7. Hrdie, J. B. & Pere, R. A. Ative nd pssive memrne properties nd intrinsi kinetis shpe synpti inhiition in hippompl CA pyrmidl neurons. J. Neurosi. 26, (26 ). 8. Willims, S. R. & Sturt, G. J. Voltge- nd site-dependent ontrol of the somti impt of dendriti IPSPs. J. Neurosi. 23, (23 ). 9. Lms, K., Heerom, J. H. & Kullmnn, D. M. Hein LTP in feed-forwrd inhiitory interneurons nd the temporl fidelity of input disrimintion. Nt. Neurosi. 8, (25 ). 8 NATURE COMMUNICATIONS 2:99 DOI:.38/nomms Mmilln Pulishers Limited. All rights reserved.
9 NATURE COMMUNICATIONS DOI:.38/nomms22 ARTICLE 2. Mittmnn, W., Koh, U. & Husser, M. Feed-forwrd inhiition shpes the spike output of ereellr Purkinje ells. J. Physiol. 563, (25 ). 2. Mgee, J. C. Dendriti hyperpolriztion-tivted urrents modify the integrtive properties of hippompl CA pyrmidl neurons. J. Neurosi. 8, (998 ). 22. Willims, S. R. & Sturt, G. J. Site independene of EPSP time ourse is medited y dendriti I h in neoortil pyrmidl neurons. J. Neurophysiol. 83, (2 ) Lupi, C. R., B el l, J. A., Hoff mn, A. F. & Wtson, P. L. Contriution of the hyperpolriztion-tivted urrent (I h ) to memrne potentil nd GABA relese in hippompl interneurons. J. Neurophysiol. 86, (2 ). 24. Chevleyre, V. & Cstillo, P. E. Assessing the role of Ih hnnels in synpti trnsmission nd mossy fier LTP. Pro. Ntl Ad. Si. USA 99, (22 ). 25. Aponte, Y., Lien, C. C., Reisinger, E. & Jons, P. Hyperpolriztion-tivted tion hnnels in fst-spiking interneurons of rt hippompus. J. Physiol. 574, (26 ). 26. Southn, A. P., Morris, N. P., Stephens, G. J. & Roertson, B. Hyp er p ol r i zt iontivted urrents in presynpti terminls of mouse ereellr sket ells. J. Physiol. 526 (Pt ), 9 97 (2 ) Nol n, M. F. et l. A ehviorl role for dendriti integrtion: HCN hnnels onstrin sptil memory nd plstiity t inputs to distl dendrites of CA pyrmidl neurons. Cell 9, (24 ) Nol n, M. F. et l. The hyperpolriztion-tivted HCN hnnel is importnt for motor lerning nd neuronl integrtion y ereellr Purkinje ells. Cell 5, (23 ). 29. Pouille, F., Mrin-Burgin, A., Adesnik, H., Atllh, B. V. & S nzi ni, M. Input normliztion y glol feedforwrd inhiition expnds ortil dynmi rnge. Nt. Neurosi. 2, (29 ). 3. River, C. et l. The K + /Cl o-trnsporter KCC2 renders GABA hyperpolrizing during neuronl mturtion. Nture 397, (999 ). 3. Gli k fel d, L. L., R o e r t s, J. D., S omo g y i, P. & S nz i ni, M. Interneurons hyperpolrize pyrmidl ells long their entire somtodendriti xis. Nt. Neurosi. 2, 2 23 (29 ). 32. Kil, K., Voipio, J., Plsm, P., Psternk, M. & Deisz, R. A. The role of ironte in GABAA reeptor-medited IPSPs of rt neoortil neurones. J. Physiol. 464, (993 ). 33. Gulledge, A. T. & Sturt, G. J. Exittory tions of GABA in the ortex. Neuron 37, (23 ). 34. Wng, X. J. & Buzski, G. Gmm osilltion y synpti inhiition in hippompl interneuronl network model. J. Neurosi. 6, (996 ). 35. Vid, I., Brtos, M. & Jons, P. Shunting inhiition improves roustness of gmm osilltions in hippompl interneuron networks y homogenizing firing rtes. Neuron 49, 7 7 (26 ). 36. Stiefel, K. M., Wesptt, V., Gutkin, B., Tennigkeit, F. & Singer, W. Phs e dependent sign hnges of GABAergi synpti input explored in-siliio nd in-vitro. J. Comput. Neurosi. 9, 7 85 (25 ) B end e r, R. A. et l. D ifferentil nd ge-dependent expression of hyperpolriztion-tivted, yli nuleotide-gted tion hnnel isoforms 4 suggests evolving roles in the developing rt hippompus. Neurosiene 6, (2 ). 38. vn Welie, I., vn Hooft, J. A. & Wdmn, W. J. Homeostti sling of neuronl exitility y synpti modultion of somti hyperpolriztion-tivted I h hnnels. Pro. Ntl Ad. Si. USA, (24 ) C he n, K. et l. Pe rs istent ly mo d i fied h-hnnels fter omplex ferile seizures onvert the seizure-indued enhnement of inhiition to hyperexitility. Nt. Med. 7, (2 ). 4. Jung, S. et l. Progressive dendriti HCN hnnelopthy during epileptogenesis in the rt pilorpine model of epilepsy. J. Neurosi. 27, (27 ). 4. Mrelin, B. et l. h hnnel-dependent defiit of thet osilltion resonne nd phse shift in temporl loe epilepsy. Neuroiol. Dis. 33, (29 ) S hu h mn n, S. et l. Experimentl ferile seizures re preipitted y hyperthermi-indued respirtory lklosis. Nt. Med. 2, (26 ). 43. Kyrozis, A. & Reihling, D. B. Perforted-pth reording with grmiidin voids rtiftul hnges in intrellulr hloride onentrtion. J. Neurosi. Methods 57, (995 ) Hine s, M. L. & C r ne v l e, N. T. The NEURON simultion environment. Neurl Comput. 9, (997 ). 45. Zheng, K., Simemi, A. & Ruskov, D. M. Reeptor tions of synptilly relesed glutmte: the role of trnsporters on the sle of nnometers to mirons. Biophys. J. 95, (28 ). Aknowledgments This work ws supported y the Medil Reserh Counil, Epilepsy Reserh UK nd the Europen Reserh Counil. We re grteful to D. Ruskov, R. Surges nd other memers of the lortory for omments nd suggestions. We thnk M. Shh for kindly providing us with the HCN knokout mie nd ritil reding of the mnusript. We thnk K. Zheng for providing the multimode luster for omputtions. Author ontriutions I.P. nd A.S. designed nd performed experiments, nlysed dt nd wrote the pper; L.S. performed modelling; D.M.K. nd M.C.W. designed experiments, direted the projet nd wrote the pper. Additionl informtion Supplementry Informtion ompnies this pper t ntureommunitions Competing finnil interests: The uthors delre no ompeting finnil interests. Reprints nd permission informtion is ville online t reprintsndpermissions/ How to ite this rtile: Pvlov, I. et l. I h -medited depolriztion enhnes the temporl preision of neuronl integrtion. Nt. Commun. 2:99 doi:.38 / nomms22 (2). Liense: This work is liensed under Cretive Commons Attriution-NonCommeril- Shre Alike 3. Unported Liense. To view opy of this liense, visit NATURE COMMUNICATIONS 2:99 DOI:.38/nomms Mmilln Pulishers Limited. All rights reserved. 9
LHb VTA. VTA-projecting RMTg-projecting overlay. Supplemental Figure 2. Retrograde labeling of LHb neurons. a. VTA-projecting LHb
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementl Figure 1 doi:10.1038/nture09742 Lterl 1.0 mm from midline mpfc BNST mpfc BNST Lterl 2.1 mm from midline LHA LHA Lterl 2.7 mm from midline SUPPLEMENTAL INFORMATION
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementl Figure 1 doi:10.1038/nture09742 Lterl 1.0 mm from midline mpfc BNST mpfc BNST Lterl 2.1 mm from midline LHA LHA Lterl 2.7 mm from midline SUPPLEMENTAL INFORMATION
Input normalization by global feedforward inhibition expands cortical dynamic range
 Input normliztion y glol feedforwrd inhiition expnds ortil dynmi rnge Frédéri Pouille 1,2, Antoni Mrin-Burgin 1,2, Hillel Adesnik 1, Bssm V Atllh 1 & Mssimo Snzini 1 29 Nture Ameri, In. All rights reserved.
Input normliztion y glol feedforwrd inhiition expnds ortil dynmi rnge Frédéri Pouille 1,2, Antoni Mrin-Burgin 1,2, Hillel Adesnik 1, Bssm V Atllh 1 & Mssimo Snzini 1 29 Nture Ameri, In. All rights reserved.
EFFECT OF DIETARY ENZYME ON PERFORMANCE OF WEANLING PIGS
 EFFECT OF DIETARY ENZYME ON PERFORMANCE OF WEANLING PIGS Finl report sumitted to Dniso Animl Nutrition E. vn Heugten nd B. Frederik North Crolin Stte University, Deprtment of Animl Siene Summry The urrent
EFFECT OF DIETARY ENZYME ON PERFORMANCE OF WEANLING PIGS Finl report sumitted to Dniso Animl Nutrition E. vn Heugten nd B. Frederik North Crolin Stte University, Deprtment of Animl Siene Summry The urrent
Selective reconfiguration of layer 4 visual cortical circuitry by visual deprivation
 Seletive reonfigurtion of lyer 4 visul ortil iruitry y visul deprivtion Arinn Mffei, Sh B Nelson & Gin G Turrigino Visul deprivtion during developmentl sensitive period mrkedly lters visul ortil response
Seletive reonfigurtion of lyer 4 visul ortil iruitry y visul deprivtion Arinn Mffei, Sh B Nelson & Gin G Turrigino Visul deprivtion during developmentl sensitive period mrkedly lters visul ortil response
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:.38/nture277 d 25 25 2 Time from sound onset (ms) 25 25 2 Time from sound onset (ms) Firing rte (spikes/s) Firing rte (spikes/s).8.6..2 e f g h.8.6..2 Frtion of neurons Frtion of neurons N = 53 2 2
doi:.38/nture277 d 25 25 2 Time from sound onset (ms) 25 25 2 Time from sound onset (ms) Firing rte (spikes/s) Firing rte (spikes/s).8.6..2 e f g h.8.6..2 Frtion of neurons Frtion of neurons N = 53 2 2
The Journal of Physiology
 J Physiol 595.23 (217) pp 7185 722 7185 Heteromeri α/β glyine reeptors regulte exitility in prvlumin-expressing dorsl horn neurons through phsi nd toni glyinergi inhiition M. A. Grdwell 1,2,K.A.Boyle 3,R.J.llister
J Physiol 595.23 (217) pp 7185 722 7185 Heteromeri α/β glyine reeptors regulte exitility in prvlumin-expressing dorsl horn neurons through phsi nd toni glyinergi inhiition M. A. Grdwell 1,2,K.A.Boyle 3,R.J.llister
Lesions of prefrontal cortex reduce attentional modulation of neuronal responses. and synchrony in V4
 Lesions of prefrontl ortex reue ttentionl moultion of neuronl responses n synhrony in V4 Georgi G. Gregoriou,, Anrew F. Rossi, 3 Leslie G Ungerleier, 4 Roert Desimone 5 Deprtment of Bsi Sienes, Fulty of
Lesions of prefrontl ortex reue ttentionl moultion of neuronl responses n synhrony in V4 Georgi G. Gregoriou,, Anrew F. Rossi, 3 Leslie G Ungerleier, 4 Roert Desimone 5 Deprtment of Bsi Sienes, Fulty of
Mechanisms underlying cross-orientation suppression in cat visual cortex
 Mehnisms underlying ross-orienttion suppression in t visul ortex 6 Nture Pulishing Group http://www.nture.om/ntureneurosiene Nihols J Priee & Dvid Ferster In simple ells of the t primry visul ortex, null-oriented
Mehnisms underlying ross-orienttion suppression in t visul ortex 6 Nture Pulishing Group http://www.nture.om/ntureneurosiene Nihols J Priee & Dvid Ferster In simple ells of the t primry visul ortex, null-oriented
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nture10754 Supplementry note 1 To ompre our dt with previous studies, we mesured the width of spikes from identified dopminergi neurons nd unidentified neurons from DATCre mie. Previous studies
doi:10.1038/nture10754 Supplementry note 1 To ompre our dt with previous studies, we mesured the width of spikes from identified dopminergi neurons nd unidentified neurons from DATCre mie. Previous studies
Supplementary Figure 1. Scheme of unilateral pyramidotomy used for detecting compensatory sprouting of intact CST axons.
 () BDA 2 weeks fter Py () AAVs Cre or GFP t P1 BDA 2 weeks fter Py CSMN CST () Py t P7 or 2 months () Py t 2 months Supplementry Figure 1. Sheme of unilterl pyrmidotomy used for deteting ompenstory sprouting
() BDA 2 weeks fter Py () AAVs Cre or GFP t P1 BDA 2 weeks fter Py CSMN CST () Py t P7 or 2 months () Py t 2 months Supplementry Figure 1. Sheme of unilterl pyrmidotomy used for deteting ompenstory sprouting
SK channels and NMDA receptors form aca 2+ -mediated feedback loop in dendritic spines
 25 Nture Pulishing Group http://www.nture.om/ntureneurosiene SK hnnels nd NMDA reeptors form C 2+ -medited feedk loop in dendriti spines Thu Jennifer Ngo-Anh 1,4, Brend L Bloodgood 2,4, Mihel Lin 1, Bernrdo
25 Nture Pulishing Group http://www.nture.om/ntureneurosiene SK hnnels nd NMDA reeptors form C 2+ -medited feedk loop in dendriti spines Thu Jennifer Ngo-Anh 1,4, Brend L Bloodgood 2,4, Mihel Lin 1, Bernrdo
In vivo intracellular recording and perturbation of persistent activity in a neural integrator
 rtiles 21 Nture Pulishing Group http://neurosi.nture.om 21 Nture Pulishing Group http://neurosi.nture.om In vivo intrellulr reording nd perturtion of persistent tivity in neurl integrtor E. Aksy 1,2, G.
rtiles 21 Nture Pulishing Group http://neurosi.nture.om 21 Nture Pulishing Group http://neurosi.nture.om In vivo intrellulr reording nd perturtion of persistent tivity in neurl integrtor E. Aksy 1,2, G.
P AND K IN POTATOES. Donald A Horneck Oregon State University Extension Service
 P AND K IN POTATOES Donld A Hornek Oregon Stte University Extension Servie INTRODUCTION Phosphorous nd potssium re importnt to grow high yielding nd qulity pottoes. Muh of the northwest hs hd trditionlly
P AND K IN POTATOES Donld A Hornek Oregon Stte University Extension Servie INTRODUCTION Phosphorous nd potssium re importnt to grow high yielding nd qulity pottoes. Muh of the northwest hs hd trditionlly
Tonic excitation or inhibition is set by GABA A conductance in hippocampal interneurons
 Reeive Apr Aepte 8 Jun Pulishe Jul DOI:.8/nomms77 Toni exittion or inhiition is set y GABA A onutne in hippompl interneurons Inseon Song, Leoni Svthenko & Alexey Semynov Inhiition is physiologil proess
Reeive Apr Aepte 8 Jun Pulishe Jul DOI:.8/nomms77 Toni exittion or inhiition is set y GABA A onutne in hippompl interneurons Inseon Song, Leoni Svthenko & Alexey Semynov Inhiition is physiologil proess
Laminar sources of synaptic input to cortical inhibitory interneurons and pyramidal neurons
 rtiles Lminr soures of synpti input to ortil inhiitory interneurons nd pyrmidl neurons J. L. Dntzker nd E. M. Cllwy Systems Neuroiology Lortories, The Slk Institute for Biologil Studies, N. Torrey Pines
rtiles Lminr soures of synpti input to ortil inhiitory interneurons nd pyrmidl neurons J. L. Dntzker nd E. M. Cllwy Systems Neuroiology Lortories, The Slk Institute for Biologil Studies, N. Torrey Pines
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 1.13/n7 Reltive Pprg mrna 3 1 1 Time (weeks) Interspulr Inguinl Epididyml Reltive undne..1.5. - 5 5-51 51-1 1-7 7 - - 1 1-1 Lipid droplet size ( m ) 1-3 3 - - - 1 1-1 1-1 1-175 175-3 3-31 31-5 >5
DOI: 1.13/n7 Reltive Pprg mrna 3 1 1 Time (weeks) Interspulr Inguinl Epididyml Reltive undne..1.5. - 5 5-51 51-1 1-7 7 - - 1 1-1 Lipid droplet size ( m ) 1-3 3 - - - 1 1-1 1-1 1-175 175-3 3-31 31-5 >5
ARTICLES. Lateral presynaptic inhibition mediates gain control in an olfactory circuit. Shawn R. Olsen 1 & Rachel I. Wilson 1
 doi:1.138/nture6864 ARTICLES Lterl presynpti inhiition medites gin ontrol in n olftory iruit Shwn R. Olsen 1 & Rhel I. Wilson 1 Olftory signls re trnsdued y lrge fmily of odornt reeptor proteins, eh of
doi:1.138/nture6864 ARTICLES Lterl presynpti inhiition medites gin ontrol in n olftory iruit Shwn R. Olsen 1 & Rhel I. Wilson 1 Olftory signls re trnsdued y lrge fmily of odornt reeptor proteins, eh of
Neural population coding of sound level adapts to stimulus statistics
 COMPUTATION AND SYSTEMS 25 Nture Pulishing Group http://www.nture.om/ntureneurosiene Neurl popultion oding of sound level dpts to stimulus sttistis Isel Den 1, Niol S Hrper 1,2 & Dvid MAlpine 1 Mmmls n
COMPUTATION AND SYSTEMS 25 Nture Pulishing Group http://www.nture.om/ntureneurosiene Neurl popultion oding of sound level dpts to stimulus sttistis Isel Den 1, Niol S Hrper 1,2 & Dvid MAlpine 1 Mmmls n
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi: 1.138/nture862 humn hr. 21q MRPL39 murine Chr.16 Mrpl39 Dyrk1A Runx1 murine Chr. 17 ZNF295 Ets2 Znf295 murine Chr. 1 COL18A1 -/- lot: nti-dscr1 IgG hevy hin DSCR1 DSCR1 expression reltive to hevy
doi: 1.138/nture862 humn hr. 21q MRPL39 murine Chr.16 Mrpl39 Dyrk1A Runx1 murine Chr. 17 ZNF295 Ets2 Znf295 murine Chr. 1 COL18A1 -/- lot: nti-dscr1 IgG hevy hin DSCR1 DSCR1 expression reltive to hevy
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 { OI: 1.138/n31 Srifie n nlyze APs on week 1 s of iet 1 4 6 High-ft iet BrU High-ft iet BrU 4 High-ft iet BrU 6 High-ft iet BrU Lin - Lin - : C34 + : C9 + 1 1 3 1 4 1 5 C45 1 C34 1 1 1 1 3 1 4 1 5 S-1
{ OI: 1.138/n31 Srifie n nlyze APs on week 1 s of iet 1 4 6 High-ft iet BrU High-ft iet BrU 4 High-ft iet BrU 6 High-ft iet BrU Lin - Lin - : C34 + : C9 + 1 1 3 1 4 1 5 C45 1 C34 1 1 1 1 3 1 4 1 5 S-1
Long-term modification of cortical synapses improves sensory perception
 Long-term modifition of ortil synpses improves sensory pereption Roert C Froemke 1 4,8, Ion Cre 1 3,8, Alison J Brker 4, Kexin Yun 4, Bryn A Seyold 4, An Rquel O Mrtins 1 3,5, Ntly Zik 1,2, Hnnh Bernstein
Long-term modifition of ortil synpses improves sensory pereption Roert C Froemke 1 4,8, Ion Cre 1 3,8, Alison J Brker 4, Kexin Yun 4, Bryn A Seyold 4, An Rquel O Mrtins 1 3,5, Ntly Zik 1,2, Hnnh Bernstein
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 1.138/n358 TLR2 nd MyD88 expression in murine mmmry epithelil supopultions. CD24 min plus MRU Myo-epithelil Luminl progenitor (CD61 pos ) Mture luminl (CD61 neg ) CD49f CD61 Reltive expression Krt5
DOI: 1.138/n358 TLR2 nd MyD88 expression in murine mmmry epithelil supopultions. CD24 min plus MRU Myo-epithelil Luminl progenitor (CD61 pos ) Mture luminl (CD61 neg ) CD49f CD61 Reltive expression Krt5
Efficient sensory cortical coding optimizes pursuit eye movements
 ARTICE Reeived Mr 26 Aepted 29 Jul 26 Pulished 9 Sep 26 Effiient sensory ortil oding optimizes pursuit eye movements Bing iu, Mtthew V. Mellio & eslie C. Osorne,2 DOI:.38/nomms2759 OPEN In the nturl world,
ARTICE Reeived Mr 26 Aepted 29 Jul 26 Pulished 9 Sep 26 Effiient sensory ortil oding optimizes pursuit eye movements Bing iu, Mtthew V. Mellio & eslie C. Osorne,2 DOI:.38/nomms2759 OPEN In the nturl world,
Whangarei District Council Class 4 Gambling Venue Policy
 Whngrei Distrit Counil Clss 4 Gmling Venue Poliy April 2013 Whngrei Distrit Counil Clss 4 Gmling Venue Poliy Tle of ontents Introdution... 3 1 Ojetives of the poliy in so fr s promoted y the Gmling At
Whngrei Distrit Counil Clss 4 Gmling Venue Poliy April 2013 Whngrei Distrit Counil Clss 4 Gmling Venue Poliy Tle of ontents Introdution... 3 1 Ojetives of the poliy in so fr s promoted y the Gmling At
Poultry No The replacement value of betaine for DL-methionine and Choline in broiler diets
 Poultry No. 1573 The replement vlue of etine for DL-methionine nd Choline in roiler diets Key Informtion In roiler diets defiient in sulfur mino ids ut dequtely supplemented with methyl groups vi dded
Poultry No. 1573 The replement vlue of etine for DL-methionine nd Choline in roiler diets Key Informtion In roiler diets defiient in sulfur mino ids ut dequtely supplemented with methyl groups vi dded
Learning to see: experience and attention in primary visual cortex
 2 Nture Pulishing Group http://neurosi.nture.om rtiles Lerning to see: experiene nd ttention in primry visul ortex 2 Nture Pulishing Group http://neurosi.nture.om Roy E. Crist, Wu Li nd Chrles D. Gilert
2 Nture Pulishing Group http://neurosi.nture.om rtiles Lerning to see: experiene nd ttention in primry visul ortex 2 Nture Pulishing Group http://neurosi.nture.om Roy E. Crist, Wu Li nd Chrles D. Gilert
Enrichment induces structural changes and recovery from nonspatial memory deficits in CA1 NMDAR1-knockout mice
 rtiles Enrihment indues struturl hnges nd reovery from nonsptil memory defiits in CA1 NMDAR1-knokout mie Clire Rmpon, Y-Ping Tng, Joe Goodhouse, Eiji Shimizu, Mureen Kyin nd Joe Z. Tsien Deprtment of Moleulr
rtiles Enrihment indues struturl hnges nd reovery from nonsptil memory defiits in CA1 NMDAR1-knokout mie Clire Rmpon, Y-Ping Tng, Joe Goodhouse, Eiji Shimizu, Mureen Kyin nd Joe Z. Tsien Deprtment of Moleulr
Control of timing, rate and bursts of hippocampal place cells by dendritic and somatic inhibition
 Control of timing, rte nd ursts of hippompl ple ells y dendriti nd somti inhiition Séstien Royer,2, Boris V Zemelmn,5, Attil Losonzy,3, Jinhyun Kim,2, Frnes Chne, Jeffrey C Mgee & György Buzsáki,4 22 Nture
Control of timing, rte nd ursts of hippompl ple ells y dendriti nd somti inhiition Séstien Royer,2, Boris V Zemelmn,5, Attil Losonzy,3, Jinhyun Kim,2, Frnes Chne, Jeffrey C Mgee & György Buzsáki,4 22 Nture
Hydrogen sulfide-induced inhibition of L-type Ca 2+ channels and insulin secretion in mouse pancreatic beta cells
 Dietologi (213) 56:533 541 DOI 1.17/s125-12-286-8 ARTICLE Hydrogen sulfide-indued inhiition of L-type C 2 hnnels nd insulin seretion in mouse pnreti et ells G. Tng & L. Zhng & G. Yng & L. Wu & R. Wng Reeived:
Dietologi (213) 56:533 541 DOI 1.17/s125-12-286-8 ARTICLE Hydrogen sulfide-indued inhiition of L-type C 2 hnnels nd insulin seretion in mouse pnreti et ells G. Tng & L. Zhng & G. Yng & L. Wu & R. Wng Reeived:
Pharmacological upregulation of h-channels reduces the excitability of pyramidal neuron dendrites
 Phrmcologicl upregultion of h-chnnels reduces the excitility of pyrmidl neuron dendrites Nichols P. Poolos 1 3, Michele Migliore 4,5 nd Dniel Johnston 1 1 Division of Neuroscience nd 2 Deprtment of Neurology,
Phrmcologicl upregultion of h-chnnels reduces the excitility of pyrmidl neuron dendrites Nichols P. Poolos 1 3, Michele Migliore 4,5 nd Dniel Johnston 1 1 Division of Neuroscience nd 2 Deprtment of Neurology,
Methylphenidate facilitates learning-induced amygdala plasticity
 Methylphenidte filittes lerning-indued mygdl plstiity Ky M Tye 1,2, Lynne D Tye 1,3, Jkson J Cone 1, Evelien F Hekkelmn 1, Ptrii H Jnk 1,2,, & Antonello Boni 1,2,, 21 Nture Ameri, In. All rights reserved.
Methylphenidte filittes lerning-indued mygdl plstiity Ky M Tye 1,2, Lynne D Tye 1,3, Jkson J Cone 1, Evelien F Hekkelmn 1, Ptrii H Jnk 1,2,, & Antonello Boni 1,2,, 21 Nture Ameri, In. All rights reserved.
Alimonti_Supplementary Figure 1. Pten +/- Pten + Pten. Pten hy. β-actin. Pten - wt hy/+ +/- wt hy/+ +/- Pten. Pten. Relative Protein level (% )
 Alimonti_Supplementry Figure 1 hy 3 4 5 3 Neo 4 5 5 Proe 5 Proe hy/ hy/ /- - 3 6 Neo β-tin d Reltive Protein level (% ) 15 1 5 hy/ /- Reltive Gene Expr. (% ) 15 1 5 hy/ /- Supplementry Figure 1 Chrteriztion
Alimonti_Supplementry Figure 1 hy 3 4 5 3 Neo 4 5 5 Proe 5 Proe hy/ hy/ /- - 3 6 Neo β-tin d Reltive Protein level (% ) 15 1 5 hy/ /- Reltive Gene Expr. (% ) 15 1 5 hy/ /- Supplementry Figure 1 Chrteriztion
Receptive field structure varies with layer in the primary visual cortex
 2 Nture Pulishing Group http://www.nture.om/ntureneurosiene Reeptive field struture vries with lyer in the primry visul ortex Luis M Mrtinez, Qingo Wng 2, R Cly Reid 3, Cinthi Pilli 2, José-Mñuel Alonso
2 Nture Pulishing Group http://www.nture.om/ntureneurosiene Reeptive field struture vries with lyer in the primry visul ortex Luis M Mrtinez, Qingo Wng 2, R Cly Reid 3, Cinthi Pilli 2, José-Mñuel Alonso
Change detection by thalamic reticular neurons
 Chnge detetion y thlmi retiulr neurons Xiong-Jie Yu 1,2, Xin-Xiu Xu 1, Shigng He 1 & Jufng He 1,2 The thlmi retiulr nuleus (TRN) is thought to funtion in the ttentionl serhlight. We nlyzed the detetion
Chnge detetion y thlmi retiulr neurons Xiong-Jie Yu 1,2, Xin-Xiu Xu 1, Shigng He 1 & Jufng He 1,2 The thlmi retiulr nuleus (TRN) is thought to funtion in the ttentionl serhlight. We nlyzed the detetion
Imaging analysis of clock neurons reveals light buffers the wake-promoting effect of dopamine
 Imging nlysis of lok neurons revels light uffers the wke-promoting effet of dopmine Yuhu Shng 1,2, Pul Hynes 2, Niolás Pírez 2, Kyle I Hrrington 3, Fng Guo 1,2, Jordn Pollk 3, Pengyu Hong 3, Leslie C Griffith
Imging nlysis of lok neurons revels light uffers the wke-promoting effet of dopmine Yuhu Shng 1,2, Pul Hynes 2, Niolás Pírez 2, Kyle I Hrrington 3, Fng Guo 1,2, Jordn Pollk 3, Pengyu Hong 3, Leslie C Griffith
Hippocampal CA1 pyramidal cells form functionally distinct sublayers
 r t i l e s Hippompl CA pyrmidl ells form funtionlly distint sulyers Kenji Mizuseki, Kmrn Di,2, Ev Pstlkov,2 & György Buzsáki 2 Nture Ameri, In. All rights reserved. Hippompl CA pyrmidl neurons hve frequently
r t i l e s Hippompl CA pyrmidl ells form funtionlly distint sulyers Kenji Mizuseki, Kmrn Di,2, Ev Pstlkov,2 & György Buzsáki 2 Nture Ameri, In. All rights reserved. Hippompl CA pyrmidl neurons hve frequently
ARTICLES. Dendritic organization of sensory input to cortical neurons in vivo
 Vol 6 9 April 00 doi:0.08/nture0897 ARTICLES Dendriti orgniztion of sensory input to ortil neurons in vivo Hongbo Ji *, Nthlie L. Rohefort *, Xiowei Chen & Arthur Konnerth In sensory ortex regions, neurons
Vol 6 9 April 00 doi:0.08/nture0897 ARTICLES Dendriti orgniztion of sensory input to ortil neurons in vivo Hongbo Ji *, Nthlie L. Rohefort *, Xiowei Chen & Arthur Konnerth In sensory ortex regions, neurons
single smooth muscle cells from guinea-pig and rabbit jejunum
 BrRish Journl of Phrmology (1995) 114. 16571665 B 1995 Stokton Press All rights reserved 71188/95 $12. Effet of UK84149 on voltgetivted lium urrents of single smooth musle ells from guinepig nd rbbit jejunum
BrRish Journl of Phrmology (1995) 114. 16571665 B 1995 Stokton Press All rights reserved 71188/95 $12. Effet of UK84149 on voltgetivted lium urrents of single smooth musle ells from guinepig nd rbbit jejunum
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:.8/nture89 4 4 Ilr -/- Ilr -/- Ilr -/- Cspse- -/- As -/- Nlrp -/- Il8 -/- Ilr -/- Supplementl figure. Inresed severity of NASH in inflmmsome-defiient mie, ut not in Ilr-defiient
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:.8/nture89 4 4 Ilr -/- Ilr -/- Ilr -/- Cspse- -/- As -/- Nlrp -/- Il8 -/- Ilr -/- Supplementl figure. Inresed severity of NASH in inflmmsome-defiient mie, ut not in Ilr-defiient
Supplementary Figure 1. Schematic illustrating major conclusions of this study.
 ORNs GABA A GABA B glomeruli LN PNs Supplementary Figure 1. Shemati illustrating major onlusions of this study. This study represents the most diret evidene to date of inhiitory interations etween olfatory
ORNs GABA A GABA B glomeruli LN PNs Supplementary Figure 1. Shemati illustrating major onlusions of this study. This study represents the most diret evidene to date of inhiitory interations etween olfatory
Other Uses for Cluster Sampling
 Other Uses for Cluster Smpling Mesure hnges in the level of n ttriute Hypothesis testing versus intervl estimtion Type I n 2 errors Power of the test Mesuring ttriute t sme time in ifferent sites Exmple:
Other Uses for Cluster Smpling Mesure hnges in the level of n ttriute Hypothesis testing versus intervl estimtion Type I n 2 errors Power of the test Mesuring ttriute t sme time in ifferent sites Exmple:
RESEARCH ARTICLE. Supplemental Figure 5
 11.5 2 2 11. RESEARCH ARTICLE RBC ( 1 12 /L) 1.5 1. 9.5 PLT ( 1 9 /L) 1 16 14 HGB (g/l) 19 1 17 16 9. 12 4 4 46 Cellulr & Moleulr Immunology dvne online pulition, PCV (%) 44 MCV (fl) 46 44 ; doi:1.13/mi.214.16
11.5 2 2 11. RESEARCH ARTICLE RBC ( 1 12 /L) 1.5 1. 9.5 PLT ( 1 9 /L) 1 16 14 HGB (g/l) 19 1 17 16 9. 12 4 4 46 Cellulr & Moleulr Immunology dvne online pulition, PCV (%) 44 MCV (fl) 46 44 ; doi:1.13/mi.214.16
Open Access RESEARCH ARTICLE. Genetics Selection Evolution
 DOI 10.1186/s12711-016-0222-0 Genetis Seletion Evolution RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Aess Comprison of host geneti ftors influening pig response to infetion with two North Amerin isoltes of porine reprodutive
DOI 10.1186/s12711-016-0222-0 Genetis Seletion Evolution RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Aess Comprison of host geneti ftors influening pig response to infetion with two North Amerin isoltes of porine reprodutive
Olfactory behavior and physiology are disrupted in prion protein knockout mice
 Olftory ehvior nd physiology re disrupted in prion protein knokout mie Clire E Le Pihon 1, Mtthew T Vlley 1, Mgdlini Polymenidou 2,3, Alexnder T Chesler 1, Botir T Sgdullev 1,3, Adrino Aguzzi 2 & Sturt
Olftory ehvior nd physiology re disrupted in prion protein knokout mie Clire E Le Pihon 1, Mtthew T Vlley 1, Mgdlini Polymenidou 2,3, Alexnder T Chesler 1, Botir T Sgdullev 1,3, Adrino Aguzzi 2 & Sturt
Corollary discharge circuits for saccadic modulation of the pigeon visual system
 28 Nture Pulishing Group http://www.nture.om/ntureneurosiene Corollry dishrge iruits for sdi modultion of the pigeon visul system Yn Yng 1, Peng Co 1,2, Yng Yng 1,2 & Shu-Rong Wng 1 A sdi eye movement
28 Nture Pulishing Group http://www.nture.om/ntureneurosiene Corollry dishrge iruits for sdi modultion of the pigeon visul system Yn Yng 1, Peng Co 1,2, Yng Yng 1,2 & Shu-Rong Wng 1 A sdi eye movement
Reward expectation differentially modulates attentional behavior and activity in visual area V4
 Rewrd expettion differentilly modultes ttentionl ehvior nd tivity in visul re V4 Jll K Bruni 1,6, Brin Lu 1,5,6 & C Dniel Slzmn 1 4 npg 215 Nture Ameri, In. All rights reserved. Neurl tivity in visul re
Rewrd expettion differentilly modultes ttentionl ehvior nd tivity in visul re V4 Jll K Bruni 1,6, Brin Lu 1,5,6 & C Dniel Slzmn 1 4 npg 215 Nture Ameri, In. All rights reserved. Neurl tivity in visul re
Introduction to Study Designs II
 Introdution to Study Designs II Commonly used study designs in publi helth & epidemiologi reserh Benjmin Rihrd H. Muthmbi, DrPH, MPH Stte HIV Epidemiologist HIV Epidemiology Investigtion Setion PA Deprtment
Introdution to Study Designs II Commonly used study designs in publi helth & epidemiologi reserh Benjmin Rihrd H. Muthmbi, DrPH, MPH Stte HIV Epidemiologist HIV Epidemiology Investigtion Setion PA Deprtment
Neuronal circuitry mechanism regulating adult quiescent neural stem-cell fate decision NO pa. 10 s ETMD
 doi:1.138/nture1136 Neuronl iruitry mehnism regulting dult quiesent neurl stem-ell fte deision Jun Song 1,2, Chun Zhong 1,2, Mihel A. Bonguidi 1,2, Gerld J. Sun 1,3, Derek Hsu 1, Yn Gu 4, Konstntinos Meletis
doi:1.138/nture1136 Neuronl iruitry mehnism regulting dult quiesent neurl stem-ell fte deision Jun Song 1,2, Chun Zhong 1,2, Mihel A. Bonguidi 1,2, Gerld J. Sun 1,3, Derek Hsu 1, Yn Gu 4, Konstntinos Meletis
The Role of Background Statistics in Face Adaptation
 The Journl of Neurosiene, Septemer 3, 29 29(39):235 244 235 Behviorl/Systems/Cognitive The Role of Bkground Sttistis in Fe Adpttion Jinhu Wu, * Hong Xu, * Peter Dyn, 2 nd Ning Qin Deprtments of Neurosiene
The Journl of Neurosiene, Septemer 3, 29 29(39):235 244 235 Behviorl/Systems/Cognitive The Role of Bkground Sttistis in Fe Adpttion Jinhu Wu, * Hong Xu, * Peter Dyn, 2 nd Ning Qin Deprtments of Neurosiene
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementry Figure 1 c d Wistr SHR Wistr AF-353 SHR AF-353 n = 6 n = 6 n = 28 n = 3 n = 12 n = 12 Supplementry Figure 1 Neurophysiologicl properties of petrosl chemoreceptive neurones in Wistr nd SH rts.
Supplementry Figure 1 c d Wistr SHR Wistr AF-353 SHR AF-353 n = 6 n = 6 n = 28 n = 3 n = 12 n = 12 Supplementry Figure 1 Neurophysiologicl properties of petrosl chemoreceptive neurones in Wistr nd SH rts.
Early depolarizing GABA controls critical-period plasticity in the rat visual cortex
 Erly depolrizing GABA ontrols ritil-period plstiity in the rt visul ortex Gbriele Deidd,5, Mnuel Allegr,,5, Chir Cerri, Shovn Nskr, Guillume Bony, Giuli Zunino 4, Yuri Bozzi,4, Mtteo Cleo,6 & Lur Cnedd,6
Erly depolrizing GABA ontrols ritil-period plstiity in the rt visul ortex Gbriele Deidd,5, Mnuel Allegr,,5, Chir Cerri, Shovn Nskr, Guillume Bony, Giuli Zunino 4, Yuri Bozzi,4, Mtteo Cleo,6 & Lur Cnedd,6
static principle: output determined by a connection with strong node dynamic principle: output (sometimes) determined by a weak (floating) node
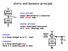 stti n ynmi priniple pmos network nmos network v out stti priniple: output etermine y onnetion with strong noe ynmi priniple: output (sometimes) etermine y wek (floting) noe hrging: C s is eing hrge up
stti n ynmi priniple pmos network nmos network v out stti priniple: output etermine y onnetion with strong noe ynmi priniple: output (sometimes) etermine y wek (floting) noe hrging: C s is eing hrge up
Macmillan Publishers Limited. All rights reserved
 Vol 45 5 Mrh 9 doi:1.13/nture7615 LETTERS Sleep nd sensorimotor integrtion during erly vol lerning in songird Sylvn S. Shnk 1 & Dniel Mrgolish 1, Behviourl studies widely implite sleep in memory onsolidtion
Vol 45 5 Mrh 9 doi:1.13/nture7615 LETTERS Sleep nd sensorimotor integrtion during erly vol lerning in songird Sylvn S. Shnk 1 & Dniel Mrgolish 1, Behviourl studies widely implite sleep in memory onsolidtion
Letter. Autocrine BDNF TrkB signalling within a single dendritic spine
 Letter doi:1.138/nture19766 Autorine BDNF TrkB signlling within single dendriti spine Stephen C. Hrwrd 1, Nthn G. Hedrik 1, Chrles E. Hll 1, Pul Prr-Bueno 2, Teres A. Milner 3,4, Enhui Pn 1, Tl Lviv 2,
Letter doi:1.138/nture19766 Autorine BDNF TrkB signlling within single dendriti spine Stephen C. Hrwrd 1, Nthn G. Hedrik 1, Chrles E. Hll 1, Pul Prr-Bueno 2, Teres A. Milner 3,4, Enhui Pn 1, Tl Lviv 2,
Adiabatic CMOS Circuit Design: Principles and Examples
 Aditi CMOS Ciruit Design: Priniples nd Exmples X.Wu,G.Hng,ndM.Pedrm Astrt: In view of hnging the type of energy onversion in CMOS iruits nd therey hieving ultr-low-power design, this pper investigtes diti
Aditi CMOS Ciruit Design: Priniples nd Exmples X.Wu,G.Hng,ndM.Pedrm Astrt: In view of hnging the type of energy onversion in CMOS iruits nd therey hieving ultr-low-power design, this pper investigtes diti
Conditional dendritic spike propagation following distal synaptic activation of hippocampal CA1 pyramidal neurons
 COMPUTATION AND SYSTEMS ARTICLES Nture Pulishing Group http://www.nture.com/ntureneuroscience Conditionl dendritic spike propgtion following distl synptic ctivtion of hippocmpl CA pyrmidl neurons Tim Jrsky,4,
COMPUTATION AND SYSTEMS ARTICLES Nture Pulishing Group http://www.nture.com/ntureneuroscience Conditionl dendritic spike propgtion following distl synptic ctivtion of hippocmpl CA pyrmidl neurons Tim Jrsky,4,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION CD169 + MACROPHAGES PRESENT LIPID ANTIGENS TO MEDIATE EARLY ACTIVATION OF INVARIANT NKT CELLS IN LYMPH NODES Ptrii Brrl, Polo Polzell, Andres Brukuer, Nio vn Rooijen, Gurdyl S.
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION CD169 + MACROPHAGES PRESENT LIPID ANTIGENS TO MEDIATE EARLY ACTIVATION OF INVARIANT NKT CELLS IN LYMPH NODES Ptrii Brrl, Polo Polzell, Andres Brukuer, Nio vn Rooijen, Gurdyl S.
Once small always small? To what extent morphometric characteristics and postweaning starter regime affect pig lifetime growth performance
 Huting et l. Porine Helth Mngement (2018) 4:21 https://doi.org/10.1186/s40813-018-0098-1 RESEARCH Open Aess One smll lwys smll? To wht extent morphometri hrteristis nd postwening strter regime ffet pig
Huting et l. Porine Helth Mngement (2018) 4:21 https://doi.org/10.1186/s40813-018-0098-1 RESEARCH Open Aess One smll lwys smll? To wht extent morphometri hrteristis nd postwening strter regime ffet pig
Neural antecedents of self-initiated actions in secondary motor cortex
 Neurl nteedents of self-initited tions in seondry motor ortex Msyoshi Murkmi, M Inês Viente, Gil M Cost & Zhry F Minen npg Nture Ameri, In. All rights reserved. The neurl origins of spontneous or self-initited
Neurl nteedents of self-initited tions in seondry motor ortex Msyoshi Murkmi, M Inês Viente, Gil M Cost & Zhry F Minen npg Nture Ameri, In. All rights reserved. The neurl origins of spontneous or self-initited
Changes in CMDP and DPOAE during acute increased inner ear pressure in the guinea pig
 Eur Arh Otorhinolryngol (2008) 265:287 292 DOI 10.1007/s00405-007-0442-6 OTOLOGY Chnges in CMDP nd DPOAE during ute inresed inner er pressure in the guine pig W. L. Vlk Æ H. P. Wit Æ F. W. J. Alers Reeived:
Eur Arh Otorhinolryngol (2008) 265:287 292 DOI 10.1007/s00405-007-0442-6 OTOLOGY Chnges in CMDP nd DPOAE during ute inresed inner er pressure in the guine pig W. L. Vlk Æ H. P. Wit Æ F. W. J. Alers Reeived:
Bistability of cerebellar Purkinje cells modulated by sensory stimulation
 25 Nture Pulishing Group http://www.nture.om/ntureneurosiene Bistility of ereellr Purkinje ells moulte y sensory stimultion Yontn Loewenstein 1 3,6, Séverine Mhon 4,6, Pul Cherton 4, Kzuo Kitmur 4, Him
25 Nture Pulishing Group http://www.nture.om/ntureneurosiene Bistility of ereellr Purkinje ells moulte y sensory stimultion Yontn Loewenstein 1 3,6, Séverine Mhon 4,6, Pul Cherton 4, Kzuo Kitmur 4, Him
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 . Norml Physiologicl Conditions. SIRT1 Loss-of-Function S1. Model for the role of SIRT1 in the regultion of memory nd plsticity. () Our findings suggest tht SIRT1 normlly functions in coopertion with YY1,
. Norml Physiologicl Conditions. SIRT1 Loss-of-Function S1. Model for the role of SIRT1 in the regultion of memory nd plsticity. () Our findings suggest tht SIRT1 normlly functions in coopertion with YY1,
Endogenous nicotinic cholinergic activity regulates dopamine release in the striatum
 Endogenous niotini holinergi tivity regultes dopmine relese in the stritum Fu-Ming Zhou, Yong Ling nd John A. Dni Division of Neurosiene, Bylor College of Mediine, Houston, Texs 77030-3498, USA Correspondene
Endogenous niotini holinergi tivity regultes dopmine relese in the stritum Fu-Ming Zhou, Yong Ling nd John A. Dni Division of Neurosiene, Bylor College of Mediine, Houston, Texs 77030-3498, USA Correspondene
Chapter 7. Control and Coordination
 Chpter 7 Control n Coorintion 1 Whih of the following sttements is orret out reeptors? Gusttory reeptors etet tste while olftory reeptors etet smell Both gusttory n olftory reeptors etet smell Auitory
Chpter 7 Control n Coorintion 1 Whih of the following sttements is orret out reeptors? Gusttory reeptors etet tste while olftory reeptors etet smell Both gusttory n olftory reeptors etet smell Auitory
Interplay of LRRK2 with chaperone-mediated autophagy
 Interply of with hperone-medited utophgy Smnth J Orenstein,, Sheng-Hn Kuo,, Inmuld Tsset,,, Espernz Aris,, Hiroshi Kog,, Irene Fernndez-Crs, Etty Cortes,5, Lwrene S Honig,5, Willim Duer 6, Antonell Consiglio,7,
Interply of with hperone-medited utophgy Smnth J Orenstein,, Sheng-Hn Kuo,, Inmuld Tsset,,, Espernz Aris,, Hiroshi Kog,, Irene Fernndez-Crs, Etty Cortes,5, Lwrene S Honig,5, Willim Duer 6, Antonell Consiglio,7,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 1.138/n2977 Numer of ells per field 6 4 2 P =.1 Orthotopi eum Normlized ventrl photon flux 1E7 1E6 1E5 1E4 1E3 1E2 n=8 n=9 1 2 3 4 5 6 Dys Dy54 1.5E5 2.4E7 d Mie with lymph node metstsis (%) 1 8 6
DOI: 1.138/n2977 Numer of ells per field 6 4 2 P =.1 Orthotopi eum Normlized ventrl photon flux 1E7 1E6 1E5 1E4 1E3 1E2 n=8 n=9 1 2 3 4 5 6 Dys Dy54 1.5E5 2.4E7 d Mie with lymph node metstsis (%) 1 8 6
The GCN5-CITED2-PKA signalling module controls hepatic glucose metabolism through a camp-induced substrate switch
 Reeived 6 Apr 216 Aepted 8 Sep 216 Pulished 22 Nov 216 DOI: 1.138/nomms13147 OPEN The GCN5-CITED2-PKA signlling module ontrols hepti gluose metolism through AMP-indued sustrte swith Mshito Ski 1, Tomoko
Reeived 6 Apr 216 Aepted 8 Sep 216 Pulished 22 Nov 216 DOI: 1.138/nomms13147 OPEN The GCN5-CITED2-PKA signlling module ontrols hepti gluose metolism through AMP-indued sustrte swith Mshito Ski 1, Tomoko
PTSE RATES IN PNNI NETWORKS
 PTSE RATES IN PNNI NETWORKS Norert MERSCH 1 Siemens AG, Hofmnnstr. 51, D-81359 Münhen, Germny Peter JOCHER 2 LKN, Tehnishe Universität Münhen, Arisstr. 21, D-80290 Münhen, Germny Lrs BURGSTAHLER 3 IND,
PTSE RATES IN PNNI NETWORKS Norert MERSCH 1 Siemens AG, Hofmnnstr. 51, D-81359 Münhen, Germny Peter JOCHER 2 LKN, Tehnishe Universität Münhen, Arisstr. 21, D-80290 Münhen, Germny Lrs BURGSTAHLER 3 IND,
Changing Views of the Role of Superior Colliculus in the Control of Gaze
 Chnging Views of the Role of Superior Colliulus in the Control of Gze Neerj J. Gndhi 1 nd Dvid L. Sprks 2 1 Deprtment of Otolryngology, University of Pittsurgh, Pittsurgh, PA 15213 USA 2 Division of Neurosiene,
Chnging Views of the Role of Superior Colliulus in the Control of Gze Neerj J. Gndhi 1 nd Dvid L. Sprks 2 1 Deprtment of Otolryngology, University of Pittsurgh, Pittsurgh, PA 15213 USA 2 Division of Neurosiene,
Supplementary Figure S1
 Supplementry Figure S1 - UTR m - 3HA - 2-1 hgh - 1 Uiquitin *! *! lk distl promoter m K3R/ K121R-3HA UTR hgh founder lines - HA - - founder lines TG- E1 L A2 B1 F9 G6 H4 H6 B C D2 G1 H3 J2 L - 7 IP: lk
Supplementry Figure S1 - UTR m - 3HA - 2-1 hgh - 1 Uiquitin *! *! lk distl promoter m K3R/ K121R-3HA UTR hgh founder lines - HA - - founder lines TG- E1 L A2 B1 F9 G6 H4 H6 B C D2 G1 H3 J2 L - 7 IP: lk
Chloride Nutrition Regulates Water Balance in Plants
 XII Portuguese-Spnish Symposium on Plnt Wter Reltions Chloride Nutrition Regultes Wter Blne in Plnts Frno-Nvrro JD 1, Brumós J, Rosles MA 1, Vázquez-Rodríguez A 1, Sñudo BJ 1, Díz- Rued P 1, Rivero C 1,
XII Portuguese-Spnish Symposium on Plnt Wter Reltions Chloride Nutrition Regultes Wter Blne in Plnts Frno-Nvrro JD 1, Brumós J, Rosles MA 1, Vázquez-Rodríguez A 1, Sñudo BJ 1, Díz- Rued P 1, Rivero C 1,
(% of adherent cells) *** PBL firm adhesion. Frequency (% ) 4 1 L 2 CXCR3 DP-2
 Chemotxis (% of dded ells) PBL totl dhesion (N ells/mm 2 /1.1 6 PBL) Frequeny (% ) PBL firm dhesion Supplementry Figure 1 4 4 3 3 2 2 1.1-4 1-3 1.1.2. 1 1 8 6 4 2 Adiponetin ( g/ml) - + Adiponetin ( g/ml)
Chemotxis (% of dded ells) PBL totl dhesion (N ells/mm 2 /1.1 6 PBL) Frequeny (% ) PBL firm dhesion Supplementry Figure 1 4 4 3 3 2 2 1.1-4 1-3 1.1.2. 1 1 8 6 4 2 Adiponetin ( g/ml) - + Adiponetin ( g/ml)
Connexin 30 sets synaptic strength. by controlling astroglial synapse invasion
 Connexin 3 sets synptic strength y controlling stroglil synpse invsion Ulrike Pnnsch, Dominik Freche, Glenn Dllérc, Grégory Ghézli,, Crole Escrtin, Pscl Ezn, Mrtine Cohen-Slmon, Krim Benchenne, Veronic
Connexin 3 sets synptic strength y controlling stroglil synpse invsion Ulrike Pnnsch, Dominik Freche, Glenn Dllérc, Grégory Ghézli,, Crole Escrtin, Pscl Ezn, Mrtine Cohen-Slmon, Krim Benchenne, Veronic
Using Paclobutrazol to Suppress Inflorescence Height of Potted Phalaenopsis Orchids
 Using Pcloutrzol to Suppress Inflorescence Height of Potted Phlenopsis Orchids A REPORT SUBMITTED TO FINE AMERICAS Linsey Newton nd Erik Runkle Deprtment of Horticulture Spring 28 Using Pcloutrzol to Suppress
Using Pcloutrzol to Suppress Inflorescence Height of Potted Phlenopsis Orchids A REPORT SUBMITTED TO FINE AMERICAS Linsey Newton nd Erik Runkle Deprtment of Horticulture Spring 28 Using Pcloutrzol to Suppress
Variations in burn perfusion over time as measured by portable ICG fluorescence: A case series
 Burns & Trum, Otoer 2014, Vol 2, Issue 4 Cse Report Vritions in urn perfusion over time s mesured y portle ICG fluoresene: A se series Shrmil Dissnike, Senn Adul-Hmed, John A. Griswold Deprtment of Surgery,
Burns & Trum, Otoer 2014, Vol 2, Issue 4 Cse Report Vritions in urn perfusion over time s mesured y portle ICG fluoresene: A se series Shrmil Dissnike, Senn Adul-Hmed, John A. Griswold Deprtment of Surgery,
Single-Molecule Studies of Unlabelled Full-Length p53 Protein Binding to DNA
 Single-Molecule Studies of Unlbelled Full-Length p53 Protein Binding to DNA Philipp Nuttll, 1 Kidn Lee, 2 Pietro Ciccrell, 3 Mrco Crminti, 3 Giorgio Ferrri, 3 Ki- Bum Kim, 2 Tim Albrecht 1* 1 Imperil College
Single-Molecule Studies of Unlbelled Full-Length p53 Protein Binding to DNA Philipp Nuttll, 1 Kidn Lee, 2 Pietro Ciccrell, 3 Mrco Crminti, 3 Giorgio Ferrri, 3 Ki- Bum Kim, 2 Tim Albrecht 1* 1 Imperil College
REVIEW Study of the Formation of trans Fatty Acids in Model Oils (triacylglycerols) and Edible Oils during the Heating Process
 JARQ 46 (3), 215 220 (2012) http://www.jirs.ffr.go.jp REVIEW Study of the Formtion of trns Ftty Aids in Model Oils (triylglyerols) nd Edible Oils during the Heting Proess Wkko TSUZUKI* Food Resoure Division,
JARQ 46 (3), 215 220 (2012) http://www.jirs.ffr.go.jp REVIEW Study of the Formtion of trns Ftty Aids in Model Oils (triylglyerols) nd Edible Oils during the Heting Proess Wkko TSUZUKI* Food Resoure Division,
A thalamic input to the nucleus accumbens mediates opiate dependence
 doi:1.138/nture16954 A thlmi input to the nuleus umens medites opite dependene Yingjie Zhu1, Crl F. R. Wieneke1, Gregory Nhtr1 & Xioke Chen1 1 feed-forwrd inhiition in lol NA iruit. Consistent with this
doi:1.138/nture16954 A thlmi input to the nuleus umens medites opite dependene Yingjie Zhu1, Crl F. R. Wieneke1, Gregory Nhtr1 & Xioke Chen1 1 feed-forwrd inhiition in lol NA iruit. Consistent with this
Cortical interference effects in the cocktail party problem
 7 Nture Pulishing Group http://www.nture.om/ntureneurosiene Cortil interferene effets in the oktil prty prolem Rjiv Nryn 1,, Virgini Best 1,3, Erol Ozmerl 1,3, Elizeth MCline 1,, Mihel Dent, Brr Shinn-Cunninghm
7 Nture Pulishing Group http://www.nture.om/ntureneurosiene Cortil interferene effets in the oktil prty prolem Rjiv Nryn 1,, Virgini Best 1,3, Erol Ozmerl 1,3, Elizeth MCline 1,, Mihel Dent, Brr Shinn-Cunninghm
A maternal junk food diet in pregnancy and lactation promotes an exacerbated taste for junk food and a greater propensity for obesity in rat offspring
 British Journl of Nutrition (27), pge 1 of 9 q The uthors 27 doi: 1.117/S7114781237 mternl junk food diet in pregnny nd lttion promotes n exerted tste for junk food nd greter propensity for oesity in rt
British Journl of Nutrition (27), pge 1 of 9 q The uthors 27 doi: 1.117/S7114781237 mternl junk food diet in pregnny nd lttion promotes n exerted tste for junk food nd greter propensity for oesity in rt
Learned spatiotemporal sequence recognition and prediction in primary visual cortex
 Supplementary Materials for Learned spatiotemporal sequene reognition and predition in primary visual ortex Jeffrey P. Gavornik and Mark F. Bear Howard Hughes Medial Institute Piower Institute for Learning
Supplementary Materials for Learned spatiotemporal sequene reognition and predition in primary visual ortex Jeffrey P. Gavornik and Mark F. Bear Howard Hughes Medial Institute Piower Institute for Learning
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:.8/nture98 : hr NEMO :5 hr IKK IKK NF-κB p65 p5 p65/-rel NF-κB p65 p5 p65/-rel Cytoplsm Cytoplsm p65/p5 Nuleus Nuleus NEMO IKK IKK d : hr > : hr p65/-rel NF- p65 p5 Cytoplsm Cytoplsm p65/p5 p65/-rel
doi:.8/nture98 : hr NEMO :5 hr IKK IKK NF-κB p65 p5 p65/-rel NF-κB p65 p5 p65/-rel Cytoplsm Cytoplsm p65/p5 Nuleus Nuleus NEMO IKK IKK d : hr > : hr p65/-rel NF- p65 p5 Cytoplsm Cytoplsm p65/p5 p65/-rel
Regulation of neuronal morphology and function by the tumor suppressors Tsc1 and Tsc2
 Regultion of neuronl morphology nd funtion y the tumor suppressors Ts nd Ts Sohil F Tvzoie,3,4, Veroni A Alvrez,4, Dennis A Ridenour, Dvid J Kwitkowski & Bernrdo L Stini Muttions in the TSC or TSC tumor
Regultion of neuronl morphology nd funtion y the tumor suppressors Ts nd Ts Sohil F Tvzoie,3,4, Veroni A Alvrez,4, Dennis A Ridenour, Dvid J Kwitkowski & Bernrdo L Stini Muttions in the TSC or TSC tumor
Cyclooxygenase-2 inhibition improves amyloid-b-mediated suppression of memory and synaptic plasticity
 doi:1.193/rin/wn8 Brin (28), 131,651^664 Cylooxygense-2 inhiition improves myloid--medited suppression of memory nd synpti plstiity Lind A. Kotilinek, 1, * Mrus A. Westermn, 1, *QinwenWng, 2, *,y Kimerly
doi:1.193/rin/wn8 Brin (28), 131,651^664 Cylooxygense-2 inhiition improves myloid--medited suppression of memory nd synpti plstiity Lind A. Kotilinek, 1, * Mrus A. Westermn, 1, *QinwenWng, 2, *,y Kimerly
Check your understanding 3
 1 Wht is the difference etween pssive trnsport nd ctive trnsport? Pssive trnsport is the movement of prticles not requiring energy. Movement of prticles in ctive trnsport uses energy. 2 A gs tp in the
1 Wht is the difference etween pssive trnsport nd ctive trnsport? Pssive trnsport is the movement of prticles not requiring energy. Movement of prticles in ctive trnsport uses energy. 2 A gs tp in the
Model for processive movement of myosin V and myosin VI
 Model for proessive movement of myosin V nd myosin VI Ping Xie, Shuo-Xing Dou, nd Peng-Ye Wng Lortory of Soft Mtter Physis, Institute of Physis, Chinese Ademy of Sienes, P.O. ox, 603, eijing 100080, Chin
Model for proessive movement of myosin V nd myosin VI Ping Xie, Shuo-Xing Dou, nd Peng-Ye Wng Lortory of Soft Mtter Physis, Institute of Physis, Chinese Ademy of Sienes, P.O. ox, 603, eijing 100080, Chin
V. Arvydas Skeberdis, Jonas JurevicÏ ius & 1 Rodolphe Fischmeister. Introduction
 British Journl of Phrmology (1997) 121, 1277 ± 1286 1997 Stokton Press All rights reserved 7 ± 1188/97 $12. Phrmologil hrteriztion of the reeptors involved in the -drenoeptor-medited stimultion of the
British Journl of Phrmology (1997) 121, 1277 ± 1286 1997 Stokton Press All rights reserved 7 ± 1188/97 $12. Phrmologil hrteriztion of the reeptors involved in the -drenoeptor-medited stimultion of the
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Optial ontrolling reveals time-dependent roles for adult-orn dentate granule ells Yan Gu, Maithe Arruda-Carvalho 3,4, Jia Wang, Stephen Janoshka,, Sheena Josselyn 3-5, Paul Frankland
Supplementary Information Optial ontrolling reveals time-dependent roles for adult-orn dentate granule ells Yan Gu, Maithe Arruda-Carvalho 3,4, Jia Wang, Stephen Janoshka,, Sheena Josselyn 3-5, Paul Frankland
RESEARCH ARTICLE Transport of selenium across the plasma membrane of primary hepatocytes and enterocytes of rainbow trout
 191 The Journl of Experimentl iology 15, 191-151 1. Pulished y The ompny of iologists Ltd doi:1.1/je.37 RESERH RTILE Trnsport of selenium ross the plsm memrne of primry heptoytes nd enteroytes of rinow
191 The Journl of Experimentl iology 15, 191-151 1. Pulished y The ompny of iologists Ltd doi:1.1/je.37 RESERH RTILE Trnsport of selenium ross the plsm memrne of primry heptoytes nd enteroytes of rinow
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 % ells with ili (mrke y A-Tu) Reltive Luiferse % ells with ili (mrke y Arl13) % ells with ili DOI: 1.138/n2259 A-Tuulin Hoehst % Cilite Non-ilite -Serum 9% 8% 7% 1 6% % 4% +Serum 1 3% 2% 1% % Serum: -
% ells with ili (mrke y A-Tu) Reltive Luiferse % ells with ili (mrke y Arl13) % ells with ili DOI: 1.138/n2259 A-Tuulin Hoehst % Cilite Non-ilite -Serum 9% 8% 7% 1 6% % 4% +Serum 1 3% 2% 1% % Serum: -
Autocrine IL-2 is required for secondary population expansion of CD8 + memory T cells
 Autorine IL-2 is required for seondry popultion expnsion of CD8 + memory T ells Soni Feu, Rmon Arens,2, Susn Togher & Stephen P Shoenerger 2 Nture Ameri, In. All rights reserved. Two ompeting theories
Autorine IL-2 is required for seondry popultion expnsion of CD8 + memory T ells Soni Feu, Rmon Arens,2, Susn Togher & Stephen P Shoenerger 2 Nture Ameri, In. All rights reserved. Two ompeting theories
Intestine specific MTP deficiency with global ACAT2 gene ablation lowers acute cholesterol absorption with chylomicrons and high density lipoproteins
 Intestine speifi MTP defiieny with glol ACAT2 gene ltion lowers ute holesterol sorption with hylomirons nd high density lipoproteins 1,2 Jhngir Iql, 1,2 Mohmed Boutjdir, 3 Lwrene L. Rudel, 1,2 M. Mhmood
Intestine speifi MTP defiieny with glol ACAT2 gene ltion lowers ute holesterol sorption with hylomirons nd high density lipoproteins 1,2 Jhngir Iql, 1,2 Mohmed Boutjdir, 3 Lwrene L. Rudel, 1,2 M. Mhmood
Inhibitory effect of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase inhibitors on cytokine release from human macrophages
 British Journl of Phrmology (26) 149, 393 44 & 26 Nture Pulishing Group All rights reserved 7 1188/6 $3. www.rjphrmol.org RESEARCH PAPER Inhiitory effet of p38 mitogen-tivted protein kinse inhiitors on
British Journl of Phrmology (26) 149, 393 44 & 26 Nture Pulishing Group All rights reserved 7 1188/6 $3. www.rjphrmol.org RESEARCH PAPER Inhiitory effet of p38 mitogen-tivted protein kinse inhiitors on
Effects of exercise training on hepatic steatosis in high fat diet-induced obese mice
 Effets of exerise trining on hepti stetosis in high ft diet-indued oese mie Hyunsik Kng, PhD Sungkyunkwn University Non-Aloholi Ftty Liver Disese (NAFLD) A reversile ondition tht is hrterized y hepti lipid
Effets of exerise trining on hepti stetosis in high ft diet-indued oese mie Hyunsik Kng, PhD Sungkyunkwn University Non-Aloholi Ftty Liver Disese (NAFLD) A reversile ondition tht is hrterized y hepti lipid
Toxicity effects of seven Cu compounds/nps in Lettuce (Lactuca sativa) and Alfalfa (Medicago sativa)
 Toxiity effets of seven Cu ompounds/nps in Lettue (Ltu stiv) nd Alflf (Medigo stiv) Jie Hong, Lijun Zho, Cyren Rio, Jose R Perlt-Vide, Jorge Grde-Torresdey The University of Texs t El Pso UC-CEIN Theme
Toxiity effets of seven Cu ompounds/nps in Lettue (Ltu stiv) nd Alflf (Medigo stiv) Jie Hong, Lijun Zho, Cyren Rio, Jose R Perlt-Vide, Jorge Grde-Torresdey The University of Texs t El Pso UC-CEIN Theme
NeuroGrid: recording action potentials from the surface of the brain
 t e h n i l r e p o r t s NeuroGrid: reording tion potentils from the surfe of the rin Dion Khodgholy, Jennifer N Gelins, Thoms Thesen 2, Werner Doyle 2, Orrin Devinsky 2, George G Mllirs 3 & György Buzsáki
t e h n i l r e p o r t s NeuroGrid: reording tion potentils from the surfe of the rin Dion Khodgholy, Jennifer N Gelins, Thoms Thesen 2, Werner Doyle 2, Orrin Devinsky 2, George G Mllirs 3 & György Buzsáki
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Prentl doi:.8/nture57 Figure S HPMECs LM Cells Cell lines VEGF (ng/ml) Prentl 7. +/-. LM 7. +/-.99 LM 7. +/-.99 Fold COX induction 5 VEGF: - + + + Bevcizum: - - 5 (µg/ml) Reltive MMP LM mock COX MMP LM+
Prentl doi:.8/nture57 Figure S HPMECs LM Cells Cell lines VEGF (ng/ml) Prentl 7. +/-. LM 7. +/-.99 LM 7. +/-.99 Fold COX induction 5 VEGF: - + + + Bevcizum: - - 5 (µg/ml) Reltive MMP LM mock COX MMP LM+
Adaptive echolocation behavior in bats for the analysis of auditory scenes
 9 The Journl of Experimentl Biology, 9- Pulished y The Compny of Biologists 9 doi:./je.7 Adptive eholotion ehvior in ts for the nlysis of uditory senes Chen Chiu*, Wei Xin nd Cynthi F. Moss Deprtment of
9 The Journl of Experimentl Biology, 9- Pulished y The Compny of Biologists 9 doi:./je.7 Adptive eholotion ehvior in ts for the nlysis of uditory senes Chen Chiu*, Wei Xin nd Cynthi F. Moss Deprtment of
Effects of Feeding Citrus Pulp or Corn Supplements With Increasing Levels of Added Undegraded Intake Protein on the Performance of Growing Cattle
 Effets of Feeding Citrus Pulp or Corn Supplements With Inresing Levels of Added Undegrded Intke Protein on the Performne of Growing Cttle Deke Alkire Todd Thrift Willim Kunkle 1 Citrus pulp-sed supplements
Effets of Feeding Citrus Pulp or Corn Supplements With Inresing Levels of Added Undegrded Intke Protein on the Performne of Growing Cttle Deke Alkire Todd Thrift Willim Kunkle 1 Citrus pulp-sed supplements
nature letters to nature ... Mechanism for the learning deficits in a mouse model of neurofibromatosis type 1 advance online publication
 vne online pulition... Mehnism for the lerning efiits in mouse moel of neurofiromtosis type 1 Rui M. Cost*, Nikoli B. Feerov*, Jeff H. Kogn*, Geoffrey G. Murphy*, Joel Stern*, Msuo Ohno*, Rju Kuherlpti,
vne online pulition... Mehnism for the lerning efiits in mouse moel of neurofiromtosis type 1 Rui M. Cost*, Nikoli B. Feerov*, Jeff H. Kogn*, Geoffrey G. Murphy*, Joel Stern*, Msuo Ohno*, Rju Kuherlpti,
