Unit 1 Word Building: Glossary, Pronunciation, & Construction. Word Pronunciation Definition and deconstruction
|
|
|
- Belinda Briggs
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Unit 1 Word Building: Glossary, Pronunciation, & Construction Word Pronunciation Definition and deconstruction Construction is seen differently in different texts, e.g.: logy > study of > may be seen as -log/y or -logy logist > person who studies > may be seen as -log/ist or logist ostomy > to cut a new opening > may be seen as ostomy or os/tomy ectomy > to surgically remove > may be seen as ectomy or ec/tomy Abbreviations > a-bree-vee-ay-shuns > Short form of a word or phrase Acidosis > as-i-doe-sis > Abnormal condition of blood acid level, increased H + ions. Acid/osis Acronyms > ak-row-nims > first letter of each word in a phrase is used as short-hand like CDC, MRSA, RUQ, RBC Amenorrhea > a-men-or-ree-ah > absence of the discharge of menses (monthly period in women). a/men/o/rrhea Anaerobic > an-a-roe-bik > Pertaining to an organism living without air. An/aer/o/bic 1
2 Anatomy > a-nah-toe-me > All the pieces and part of a structure such as the human body. It is the form or shape or make up of a structure. Literally: to cut into the body (dissection) Anemia > a-knee-me-a > A relative lack of blood due to injury, diet, or illness. Literally, without (an) blood (emia) an/emia Antibiotic > an-tea-buy-ot-ik > This is the general term for the medication group fighting against bacterial infections. Literally, it means against life. Anti/bi/o/tic Antidote > an-tea-dote > A substance (medication), neutralizes or counteracts poisons. Anti/dote Antipyretic > an-tea-pie-ret-ik > A medication, lowers or reduces fever. Anti/pyr/etic Aplasia > a-play-ze-ah > The absence of development of an organ or cell type. A/plas/ia Arteriogram > ahr-tier-ee-oh-gram > Imaging: A radiologic study of the arteries of the human body looking for blockage, tears, or enlargements. Arteri/o/gram Arteritis > ahr-tier-eye-tis > Inflammation of the arteries. Arter/itis Arthritis > are-thri-tis > Inflammation of the joints. Arthr/itis 2
3 Bacteria (plural), Bacterium (singular) > bak-tier-ee-ah or bak-tier-ee-um > One-celled organism found in and on the human body. Some are helpful, others are pathogens, and others are opportunistic. Bacter/ia or Bacter/i/um Cardiac > kar-dee-ak > Pertaining (-ac) to the heart. Cardi/ac Cardiocentesis > kar-dee-oh-sen-tea-sis > Procedure: Removal of fluid from the heart. Cardi/o/centesis Cardiologist > kar-dee-ol-oh-jist > Specialist of who studies and treats heart disease. Cardi/o/logist or Cardi/o/log/ist Cardiomegaly > kar-dee-oh-meg-a-lee > Enlargement of the heart. Cardi/o/megaly Cardiomyopathy > kar-dee-oh-my-op-ath-ee > Disease of the heart muscle. Cardi/o/my/o/pathy Cellulitis > sell-u-lie-tis > Inflammation, infection of the skin cells. Cellul/itis Cerebrovascular > ser-eh-bro-vas-q-lar > Pertaining to the brain s blood vessels. Cerebr/o/vascul/ar Chondromyalgia > kon-dro-ma-lay-sah > Pain of the cartilage and muscle. Chondr/o/my/algia Colostomy > ko-los-toe-me > Surgical: Surgery to create a new opening in the colon. Col/ostomy or Col/os/tomy Craniostomy > kray-knee-os-toe-me > Surgical: to cut a new opening in the skull (cranium) 3
4 Craniotomy > kray-knee-ot-oh-me > Surgical: To cut into the skull. Crani/o/tomy Dermatitis > dur-ma-tie-tis > Inflammation of the skin. Dermat/itis Dermatologist > dur-ma-tol-oh-jist > Specialist of who studies and treats skin diseases. Dermat/o/logist or Dermat/o/log/ist Dermatome > dur-ma-tohm > An instrument to cut or slice the skin. Dermat/ome Dermatosis > dur-ma-toe-sis > Abnormal condition of the skin. Dermat/osis Diagnosis (Dx) > die-ag-no-sis > Discernment through knowledge, this is the disease or injury the person is believed to have after taking a history and doing a physical exam/laboratory. Dia/gno/sis Dyspnea > dis-knee-ya > Difficult breathing. Dys/pnea Eccentric > ek-sen-trik > Moving away from the center, abnormal behavior. Ectopic > ek-top-ik > Something is out of place, a pregnancy or organ. Ec/topic Electronic Health Record (EHR) > e-lek-tron-ik health wrek-ord > Methodical collection of the electronic health information produced by visits and events pertaining to a specific individual. Also called Electronic Medical Record (EMR) 4
5 Embolectomy > em-bow-lek-toe-me > Surgical: Removal of a plug, an embolism. Embol/ectomy or embol/ec/tomy Encephalitis > en-sef-ah-lie-tis > Inflammation inside the head, used specifically for the brain. En/cephal/itis Endocarditis > en-doe-kar-die-tis > Inflammation of the inner lining of the heart. Endo/cardi/tis Endocrine > en-doe-krin > hormones, travel inside the blood stream. Endo/crine Endocytosis > en-doe-sigh-toe-sis > Condition inside of the cell or cells. Endo/cyt/osis Endomyocarditis > en-doe-my-oh-kar-die-tis > Inflammation of the inside lining of the heart muscle. Endo/my/o/cardi/tis Enterology > en-ter-ol-oh-gee > The process of studying the small intestines: duodenum, jejunum, and ileum. Enter/o/logy Enterostomy > en-ter-os-toe-me > Surgical: Surgery to create a new opening into the small intestines. Enter/ostomy or enter/os/tomy Epidemiologist > ep-ee-dee-me-ol-oh-jist > Specialist who studies the patterns, causes, and effects of health and disease conditions in defined populations. Epi/demi/o/logist or epi/demi/o/log/ist Eponyms > ep-oh-nims > Names of the people who discovered or described a particular structure or set of symptoms. 5
6 Esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD) > eh-sof-a-go-gas-tro-due-oh-deh-nos-ko-pee > Procedure: The process of using a scope to look at the esophagus, stomach, and small intestine (duodenum portion), an EGD. Esophag/o/gastr/o/duoden/o/scopy Exogenous > eks-oh-je-us > Produced or originating from outside the organism or cell. Exo/gen/ous Exposure > eks-poe-zur > Contact with an element from the outside, the environment. Gastrectomy > gas-trek-toe-me > Surgical: Surgery to remove the stomach. Gastr/ectomy or gastr/ec/tomy Gastroduodenostomy > gas-tro-due-oh-de-nos-toe-me > Surgical: Surgery to create a new opening between the stomach and duodenum. Gastr/o/duoden/ostomy or gastr/o/duoden/os/tomy Gastroenterology > gas-tro-en-ter-ol-oh-gee > Inflammation of the stomach and small intestines. Gastr/o/enter/o/logy Hepatic > hep-at-ik > Pertaining (-ic) to the liver. Hepat/ic History (Hx) > hiss-tor-ee > The systematic medical record of past events, current symptoms, medication, allergies, and more relating to an individual. Hypothyroidism > hi-poe-thigh-roid-ism > Condition of the thyroid, not producing sufficient thyroid hormone to maintain homeostasis. A collection of symptoms. Hypo/thyroid/ism 6
7 Incision > in-si-zhun > To cut into. Infection > in-fek-shun > An organism, gets into the body. Injection > in-jek-shun > This medication delivered via a needle (most common), or a medication pushed into rectum or vagina or taken orally by mouth. Literally, to push inside. Internist > in-tur-nist > Specialist who studies and treats diseases of the internal organs. Intern/ist Intraorbital > in-tra-or-bit-al > Inside the orbit of the eye. Intra/orbit/al Laparotomy > lap-ar-ot-toe-me > Surgical: A surgical incision over the abdomen, usually vertically. Lapar/o/tomy Lymphoma > lim-foe-mah > Tumor of the lymph tissue. Lymph/oma Microscope > mike-row-scope > An instrument, looks at really small things. Micro/scope Morbidity > mor-bid-it-ee > Disease state, it is used as a ratio of sick or injured people versus well people. It tracks disease, injury, and medical efforts to correct these by CDC and other agencies. 7
8 Mortality > mor-tal-it-ee > The state of being mortal, the ability to die. It is used to track the number of deaths, age, and cause as a report of the CDC and other agencies. Myospasm > my-oh-spazm > The involuntary contraction of the muscle(s). My/o/spasm Nasopharynx > nay-zo-fair-inks > The nose and throat. Nas/o/pharynx Objective > ob-jek-tiv > This is the facts, they are seen, touched, heard or perceived by a provider during an exam. It is the findings which can be measured and analyzed. Ophthalmoscope > of-thal-moe-scope > An instrument to look at the eyes. Ophthalm/o/scope. Alternate: op-thal-moe-scope Orthopedist > or-tho-pee-dist > Specialist who studies and treats disease and injury of the bones, including surgery. Orth/o/ped/ist Osteitis > os-tea-eye-tis > Inflammation of the bone. Oste/itis Osteoarthritis > os-tea-oh-are-thri-tis > Inflammation of the bone and joint. Usually used as a term describing the wear and tear on joints. Oste/o/arthr/itis Osteotome > os-tea-oh-tohm > An instrument, cuts bone. Oste/o/tome 8
9 Parksonism (an eponym) > parh-kin-son-izm > A collection of symptoms associated a progressive disorder of the nervous system. Pharyngitis > fair-in-jie-tis > Inflammation of the back of the throat (pharynx). Pharyng/itis Physical Exam (PE) > fiz-zi-kal x-am > A set of procedures performed on or with the patient to define the body s status and function for health exam, illness, or injury. Pneumonia > new-mow-knee-ah > An infection, inflames the air sacs (alveoli) of the lungs. There are many different types and causes. Pneumon/ia Prognosis > prog-no-sis > Condition of predicting knowledge, a forecast of outcome. Pro/gno/sis Rheumatology > roo-mah-tol-oh-gee > Specialist who studies and treats diseases of the joints. Rheumat/o/logy Rhinitis > rye-nigh-tis > Inflammation of the nose. Rhin/itis Rhinoplasty > rye-no-plas-tee > Surgical: surgery to repair of the nose. Rhin/o/plasty Rhinorrhea > rye-no-ree-ya > Discharge or flow from the nose (runny nose). Rhin/o/rrhea Rhinoscopy > rye-nos-kop-ee > Procedure: The process of using an instrument to look in or at the nose. Rhin/o/scopy 9
10 Sclerosis > sklar-oh-sis > Abnormal condition of hardening. Scler/osis Splenectomy > sple-nek-toe-me > Surgical: Surgery to remove the spleen. Splen/ectomy or splen/ec/tomy Stethoscope > steth-oh-scope > An instrument to listen to body sounds from the Greek for chest. Steth/o/scope Subjective > sub-jek-tiv > This is the concern of the patient, in their own words, with their own descriptions of events as it related to illness or injury. It is the given history. Terminology > tur-min-ol-oh-gee > The process of studying the vocabulary or words of a specific language. Termin/o/logy Tomogram > toe-moe-gram> Imaging: A radiographic procedure, takes a series of x-rays in slices or cuts. Tom/o/gram Tonsillitis > tohn-si-lie-tis > Inflammation of the tonsils, lymphatic tissue found at the back of the throat. Tonsill/itis Tracheotomy> trake-ee-ot-oh-me > Surgical: surgery to cut into the trachea (windpipe). Trache/o/tomy Treatment (Tx) > treet-ment > The medical, surgical, dental, or psychiatric management of a patient s illness or injury. It can also include preventive medicine to avoid illness and injury. It is part of the plan in the acronym SOAP. Urostomy > your-os-toe-me > Surgical: Surgery to create a new opening into the ureter to drain urine. Ur/ostomy or ur/os/tomy 10
11 11
Unit 11 Cardiovascular: Glossary, Pronunciation, & Construction. Word Pronunciation Definition and Construction
 Unit 11 Cardiovascular: Glossary, Pronunciation, & Construction Word Pronunciation Definition and Construction Aneurysm > an-yur-izm > localized weakening of an arterial wall that enlarges over time. Angina
Unit 11 Cardiovascular: Glossary, Pronunciation, & Construction Word Pronunciation Definition and Construction Aneurysm > an-yur-izm > localized weakening of an arterial wall that enlarges over time. Angina
FAQ: Foundations of Medical Terminology
 Question 1: What is the purpose of a root? A root in a medical term is the basic meaning of the term. Roots refer to body parts or systems of the body. Body systems include skin, muscular, digestive, nervous,
Question 1: What is the purpose of a root? A root in a medical term is the basic meaning of the term. Roots refer to body parts or systems of the body. Body systems include skin, muscular, digestive, nervous,
Chapter 5 Medical Terminology Health Care Science Technology
 Chapter 5 Medical Terminology Health Care Science Technology Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Objectives 2 Identify the 4 medical technology word parts. Build and break apart medical terms to
Chapter 5 Medical Terminology Health Care Science Technology Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Objectives 2 Identify the 4 medical technology word parts. Build and break apart medical terms to
Cell Specialization Vocabulary. Zaria Herriman
 Cell Specialization Vocabulary Zaria Herriman Antibiotic Pronunciation: (Ahn-tie-by-ah-tic) Definition: A medicine that can block the growth and reproduction of bacteria. Sentence: The doctor gave me an
Cell Specialization Vocabulary Zaria Herriman Antibiotic Pronunciation: (Ahn-tie-by-ah-tic) Definition: A medicine that can block the growth and reproduction of bacteria. Sentence: The doctor gave me an
Homework Packet. The branch of biological science that studies and describes how body parts. The study of the shape and structure of body parts
 Anatomy & Physiology Chap. 1: The Human Body Name Block: P/W Homework Packet ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY DISTINCTIONS 1. Match the term on the right to the appropriate description on the left. Enter the correct
Anatomy & Physiology Chap. 1: The Human Body Name Block: P/W Homework Packet ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY DISTINCTIONS 1. Match the term on the right to the appropriate description on the left. Enter the correct
Cardiovascular and Lymphatic Systems
 10 Cardiovascular and atic Systems Cardiology The medical specialty of cardiology encompasses the treatment of heart disease. Generally, three types of cardiology specialists provide medical care: the
10 Cardiovascular and atic Systems Cardiology The medical specialty of cardiology encompasses the treatment of heart disease. Generally, three types of cardiology specialists provide medical care: the
Spelling & Pronunciation
 Spelling & Pronunciation Question 1: What are examples of medical terms with silent and differently pronounced letters? Examples of silent and differently pronounced letters (Leonard, 2000): pneumonia
Spelling & Pronunciation Question 1: What are examples of medical terms with silent and differently pronounced letters? Examples of silent and differently pronounced letters (Leonard, 2000): pneumonia
Medical Terms of Cardiovascular System and Respiratory System. Dr. Sarmed Nabhan Yaseen BSc., MPharm, PhD, RPh
 Medical Terms of Cardiovascular System and Respiratory System Dr. Sarmed Nabhan Yaseen BSc., MPharm, PhD, RPh sarmednabhan@ibnsina.edu.iq Outlines Terms Cardiovascular System (CVS) Respiratory System
Medical Terms of Cardiovascular System and Respiratory System Dr. Sarmed Nabhan Yaseen BSc., MPharm, PhD, RPh sarmednabhan@ibnsina.edu.iq Outlines Terms Cardiovascular System (CVS) Respiratory System
Respiratory System. Anatomy and Physiology Overview. Pulmonology
 Respiratory System 9 Pulmonology The medical specialty of pulmonology, also called pulmonary medicine, is the branch of medicine concerned with the diagnosis and treatment of diseases involving the structures
Respiratory System 9 Pulmonology The medical specialty of pulmonology, also called pulmonary medicine, is the branch of medicine concerned with the diagnosis and treatment of diseases involving the structures
Pneumonia. Trachea , The Patient Education Institute, Inc. id Last reviewed: 11/11/2017 1
 Pneumonia Introduction Pneumonia is an inflammation and infection of the lungs. Pneumonia causes millions of deaths every year. It can affect anybody, but is more dangerous to older adults, babies and
Pneumonia Introduction Pneumonia is an inflammation and infection of the lungs. Pneumonia causes millions of deaths every year. It can affect anybody, but is more dangerous to older adults, babies and
Human Anatomy & Physiology
 Human Anatomy & Physiology Hey I thought those were the same thing! Nope they ain t Anatomy-Where everything is and to what it is connected. Physiology-How all that stuff works to keep you alive! Morphology-How
Human Anatomy & Physiology Hey I thought those were the same thing! Nope they ain t Anatomy-Where everything is and to what it is connected. Physiology-How all that stuff works to keep you alive! Morphology-How
Cells Tissues Organs Organ Systems Organism. Cells: the smallest unit of life.
 Cells Tissues Organs Organ Systems Organism Cells: the smallest unit of life. The Circulatory Systems brings oxygen, nutrients and hormones to cells; fights infections; removes cell wastes; regulates
Cells Tissues Organs Organ Systems Organism Cells: the smallest unit of life. The Circulatory Systems brings oxygen, nutrients and hormones to cells; fights infections; removes cell wastes; regulates
Colon Cancer Surgery
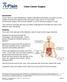 Colon Cancer Surgery Introduction Colon cancer is a life-threatening condition that affects thousands of people. Doctors usually recommend surgery for the removal of colon cancer. If your doctor recommends
Colon Cancer Surgery Introduction Colon cancer is a life-threatening condition that affects thousands of people. Doctors usually recommend surgery for the removal of colon cancer. If your doctor recommends
C H A P T E R 5 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM
 C H A P T E R 5 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Learning Objectives Upon completion of this chapter, you will be able to Identify and define the combining forms and suffixes introduced in this chapter. Correctly
C H A P T E R 5 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Learning Objectives Upon completion of this chapter, you will be able to Identify and define the combining forms and suffixes introduced in this chapter. Correctly
ESSENTIALS OF A&P FOR EMERGENCY CARE. Learning Objectives. Pronunciation Guide Click on the megaphone icon before each item to hear the pronunciation.
 ESSENTIALS OF A&P FOR EMERGENCY CARE CHAPTER 14 The Respiratory System: It s a Gas Learning Objectives List and state the basic functions of the components of the respiratory system. Differentiate between
ESSENTIALS OF A&P FOR EMERGENCY CARE CHAPTER 14 The Respiratory System: It s a Gas Learning Objectives List and state the basic functions of the components of the respiratory system. Differentiate between
Human Anatomy Key Points Unit 1/ Study Guide
 Human Anatomy Key Points Unit 1/ Study Guide I. Anatomy and Physiology a. Anatomy 1. Means cutting apart (dissection) 2. Study of the body and the relationships of its parts to each other. 3. Dissection
Human Anatomy Key Points Unit 1/ Study Guide I. Anatomy and Physiology a. Anatomy 1. Means cutting apart (dissection) 2. Study of the body and the relationships of its parts to each other. 3. Dissection
If You Have Head or Neck Cancer
 EASY READING If You Have Head or Neck Cancer What is head and neck cancer? Cancer can start any place in the body. Cancer that starts in the head and neck can have many names. It depends on where the cancer
EASY READING If You Have Head or Neck Cancer What is head and neck cancer? Cancer can start any place in the body. Cancer that starts in the head and neck can have many names. It depends on where the cancer
Human Anatomy and Body Systems
 Human Anatomy and Body Systems Levels of Organization The human body is organized in several levels, from the simplest to the most complex... Cells the basic unit of life Tissues clusters of cells performing
Human Anatomy and Body Systems Levels of Organization The human body is organized in several levels, from the simplest to the most complex... Cells the basic unit of life Tissues clusters of cells performing
Chapter 22. Body Organization & Structure
 Chapter 22 Body Organization & Structure Start-Up Activity Too Cold for Comfort Hold a few pieces of ice in one hand. Hold the ice until the cold is uncomfortable. Then release the ice into the dish. Compare
Chapter 22 Body Organization & Structure Start-Up Activity Too Cold for Comfort Hold a few pieces of ice in one hand. Hold the ice until the cold is uncomfortable. Then release the ice into the dish. Compare
Nervous System. Functions Controls all body s functions Senses and recognizes information from inside and outside of the body
 Human Body Systems Nervous System Functions Controls all body s functions Senses and recognizes information from inside and outside of the body Nervous System Main Parts Brain Nerves Spinal cord What it
Human Body Systems Nervous System Functions Controls all body s functions Senses and recognizes information from inside and outside of the body Nervous System Main Parts Brain Nerves Spinal cord What it
BELLWORK DAY 1 RESEARCH THE DIFFERENCE BETWEEN INTERNAL AND EXTERNAL RESPIRATION. COPY BOTH OF THE STATE STANDARDS ENTIRELY ON THE NEXT SLIDE.
 BELLWORK DAY 1 RESEARCH THE DIFFERENCE BETWEEN INTERNAL AND EXTERNAL RESPIRATION. COPY BOTH OF THE STATE STANDARDS ENTIRELY ON THE NEXT SLIDE. STANDARDS 42) Review case studies that involve persons with
BELLWORK DAY 1 RESEARCH THE DIFFERENCE BETWEEN INTERNAL AND EXTERNAL RESPIRATION. COPY BOTH OF THE STATE STANDARDS ENTIRELY ON THE NEXT SLIDE. STANDARDS 42) Review case studies that involve persons with
Growing bones. Baby s s bones are made from cartilage Babies have 300 bones Adults have 206. bones
 Body Systems Objectives Students should be able to list the different body systems Students should be able to give a general function of each of the body systems Students should be able to tell the differences
Body Systems Objectives Students should be able to list the different body systems Students should be able to give a general function of each of the body systems Students should be able to tell the differences
Chapter 16. Vocabulary. Name Class Date
 Chapter 16 Vocabulary plasma congenital larynx hemoglobin anemia bronchitis arteries leukemia pneumonia capillaries Hodgkin s disease pleurisy veins respiration asthma platelets diaphragm sinusitis lymph
Chapter 16 Vocabulary plasma congenital larynx hemoglobin anemia bronchitis arteries leukemia pneumonia capillaries Hodgkin s disease pleurisy veins respiration asthma platelets diaphragm sinusitis lymph
Human Body Systems. Transport and Defense
 CHAPTER 12 Human Body Systems LESSON 1 Transport and Defense What do you think? Read the two statements below and decide whether you agree or disagree with them. Place an A in the Before column if you
CHAPTER 12 Human Body Systems LESSON 1 Transport and Defense What do you think? Read the two statements below and decide whether you agree or disagree with them. Place an A in the Before column if you
Nervous System. Skeletal System. Muscular System. Reproductive System. Circulatory System. Endocrine System. Respiratory System. Integumentary System
 The Human Body Skeletal System Muscular System Circulatory System Respiratory System Digestive System Nervous System Reproductive System Endocrine System Integumentary System Excretory System Lymphatic/Immune
The Human Body Skeletal System Muscular System Circulatory System Respiratory System Digestive System Nervous System Reproductive System Endocrine System Integumentary System Excretory System Lymphatic/Immune
Unit 4 Circulatory, Respiratory and Excretory System
 Unit 4 Circulatory, Respiratory and Excretory System Test Date Project Due Lesson 1 The Cardiovascular System Homework: read pages 176-179 and take notes Warm up 1. 2. 3. 4. Finding Target Heart rate (220
Unit 4 Circulatory, Respiratory and Excretory System Test Date Project Due Lesson 1 The Cardiovascular System Homework: read pages 176-179 and take notes Warm up 1. 2. 3. 4. Finding Target Heart rate (220
UNIT 2. THE VITAL FUNCTIONS OF HUMAN BEINGS. PRIMARY 3 / Natural Science Pedro Antonio López Hernández
 UNIT 2. THE VITAL FUNCTIONS OF HUMAN BEINGS PRIMARY 3 / Natural Science Pedro Antonio López Hernández VITAL FUNCTIONS Nutrition It is the process of transforming NUTRIENTS into ENERGY. When we eat, we
UNIT 2. THE VITAL FUNCTIONS OF HUMAN BEINGS PRIMARY 3 / Natural Science Pedro Antonio López Hernández VITAL FUNCTIONS Nutrition It is the process of transforming NUTRIENTS into ENERGY. When we eat, we
9 Review. Labeling Exercise. Blood high in oxygen. Blood low in oxygen. Chapter 9 Circulation: The Cardiovascular and Lymphatic Systems 195
 Chapter 9 Circulation: The Cardiovascular and Lymphatic Systems 195 Chapter 9 Review Labeling Exercise THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Write the name of each numbered part on the corresponding line of the answer
Chapter 9 Circulation: The Cardiovascular and Lymphatic Systems 195 Chapter 9 Review Labeling Exercise THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Write the name of each numbered part on the corresponding line of the answer
Bile > acts as a detergent to break up fats like dish soap. It is produced by the liver.
 Unit 13 Gastrointestinal: Glossary, Pronunciation, & Construction Word Pronunciation Definition and Construction Achalasia > ak-ah-lay-zee-ah > when a sphincter fails to relax, in the case of the LES,
Unit 13 Gastrointestinal: Glossary, Pronunciation, & Construction Word Pronunciation Definition and Construction Achalasia > ak-ah-lay-zee-ah > when a sphincter fails to relax, in the case of the LES,
Dissection on Demand: Fetal Pig
 TEACHER GUIDE Dissection on Demand: Fetal Pig 60-Minute Health & Life Science Lesson Interactive Video Conferencing Grades: 6-12 Dissection on Demand: Fetal Pig Description Observe the dissection of a
TEACHER GUIDE Dissection on Demand: Fetal Pig 60-Minute Health & Life Science Lesson Interactive Video Conferencing Grades: 6-12 Dissection on Demand: Fetal Pig Description Observe the dissection of a
ORGANS OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
 ORGANS OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM OBJECTIVES: 1. List and describe the major activities of the digestive system. 2. Identify and give the functions of the organs in and along the digestive tract. MAJOR ACTIVITIES
ORGANS OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM OBJECTIVES: 1. List and describe the major activities of the digestive system. 2. Identify and give the functions of the organs in and along the digestive tract. MAJOR ACTIVITIES
Warm Up Where in a flower would you find xylem and phloem? 2. Where in a flower would you find palisade cells?
 Body Systems Warm Up 4-4-16 1. Where in a flower would you find xylem and phloem? 2. Where in a flower would you find palisade cells? 3. Where in a flower would you find root hair cells? 4. What organelle
Body Systems Warm Up 4-4-16 1. Where in a flower would you find xylem and phloem? 2. Where in a flower would you find palisade cells? 3. Where in a flower would you find root hair cells? 4. What organelle
Respiratory Diseases and Disorders
 Chapter 9 Respiratory Diseases and Disorders Anatomy and Physiology Chest, lungs, and conducting airways Two parts: Upper respiratory system consists of nose, mouth, sinuses, pharynx, and larynx Lower
Chapter 9 Respiratory Diseases and Disorders Anatomy and Physiology Chest, lungs, and conducting airways Two parts: Upper respiratory system consists of nose, mouth, sinuses, pharynx, and larynx Lower
System Name: INTEGUMENTARY (cell wall) (Lysosomes) Main Organs: Main Organs: SKIN HAIR NAILS KIDNEYS URETERS BLADDER URETHRA
 URINARY System Name: (Lysosomes) KIDNEYS URETERS BLADDER URETHRA LUNGS SKIN EXCRETORY System Name: INTEGUMENTARY (cell wall) SKIN HAIR NAILS Skin is the largest Organ. The excretory system collects and
URINARY System Name: (Lysosomes) KIDNEYS URETERS BLADDER URETHRA LUNGS SKIN EXCRETORY System Name: INTEGUMENTARY (cell wall) SKIN HAIR NAILS Skin is the largest Organ. The excretory system collects and
The Human Body: Circulatory and Respiratory Systems
 The Human Body: Circulatory and Respiratory Systems Lesson 1: What is a Body System? Cells - smallest parts - billions in the body - can have special jobs Tissues - similar cells grouped together - muscle
The Human Body: Circulatory and Respiratory Systems Lesson 1: What is a Body System? Cells - smallest parts - billions in the body - can have special jobs Tissues - similar cells grouped together - muscle
Anatomy & Physiology Lymphatic System and Immunity
 Anatomy & Physiology Lymphatic System and Immunity BELL WORK: DEFINE THE TERMS USING YOUR NEW BOOKS (PAGES 335-336): LYMPHOCYTE PHAGOCYTE PATHOGEN A NTIGEN A NTIBODIES A&P State Standards 33) Describe
Anatomy & Physiology Lymphatic System and Immunity BELL WORK: DEFINE THE TERMS USING YOUR NEW BOOKS (PAGES 335-336): LYMPHOCYTE PHAGOCYTE PATHOGEN A NTIGEN A NTIBODIES A&P State Standards 33) Describe
Dissection Lab Manuals: Required Content
 Dissection Lab Manuals: Required Content 1. Introduction a. Basic terminology (directions) b. External features of the cat c. Adaptations to predatory niche d. How to skin a cat e. How to make the incisions
Dissection Lab Manuals: Required Content 1. Introduction a. Basic terminology (directions) b. External features of the cat c. Adaptations to predatory niche d. How to skin a cat e. How to make the incisions
Drug information. Secukinumab SECUKINUMAB. is used to treat psoriatic arthritis and ankylosing spondylitis. Helpline
 Drug information Secukinumab SECUKINUMAB is used to treat psoriatic arthritis and ankylosing spondylitis Helpline 0800 5200 520 1 Introduction Secukinumab is a drug that can help prevent your condition
Drug information Secukinumab SECUKINUMAB is used to treat psoriatic arthritis and ankylosing spondylitis Helpline 0800 5200 520 1 Introduction Secukinumab is a drug that can help prevent your condition
Colon Cancer , The Patient Education Institute, Inc. oc Last reviewed: 05/17/2017 1
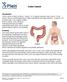 Colon Cancer Introduction Colon cancer is fairly common. About 1 in 15 people develop colon cancer. Colon cancer can be a life threatening condition that affects the large intestine. However, if it is
Colon Cancer Introduction Colon cancer is fairly common. About 1 in 15 people develop colon cancer. Colon cancer can be a life threatening condition that affects the large intestine. However, if it is
Geography of Pulmo Park: Landmarks. Cards 1A
 Geography of Pulmo Park: Landmarks Cards 1A Directions: Cut out the cards, fold and laminate and then hand out to students (one each). If you have more cards than students, some students will have more
Geography of Pulmo Park: Landmarks Cards 1A Directions: Cut out the cards, fold and laminate and then hand out to students (one each). If you have more cards than students, some students will have more
Name Score. The Neck Bone s Connected to the Head Bone
 Name Score The Neck Bone s Connected to the Head Bone The Function and Interdependence of Organs and Tissues Main Idea 1. We are made of cells. Supporting Information 1. A group of specialized cells form
Name Score The Neck Bone s Connected to the Head Bone The Function and Interdependence of Organs and Tissues Main Idea 1. We are made of cells. Supporting Information 1. A group of specialized cells form
The Human Body. Lesson Goal. Lesson Objectives 9/10/2012. Provide a brief overview of body systems, anatomy, physiology, and topographic anatomy
 The Human Body Lesson Goal Provide a brief overview of body systems, anatomy, physiology, and topographic anatomy Medial Lateral Proximal Distal Superior Inferior Anterior Lesson Objectives Explain the
The Human Body Lesson Goal Provide a brief overview of body systems, anatomy, physiology, and topographic anatomy Medial Lateral Proximal Distal Superior Inferior Anterior Lesson Objectives Explain the
Tracheoesophageal Fistula and Esophageal Atresia
 Patient and Family Education Tracheoesophageal Fistula and Esophageal Atresia What is tracheoesophageal fistula? The word fistula means abnormal connection. Tracheoesophageal fistula (TEF) is a condition
Patient and Family Education Tracheoesophageal Fistula and Esophageal Atresia What is tracheoesophageal fistula? The word fistula means abnormal connection. Tracheoesophageal fistula (TEF) is a condition
Heal a th t y h y B o B dy d Systems
 Chapter 16 Healthy Body Systems The Cell The smallest unit of structure in a living organism Robert Hooke Identified & coined the term Cell when he saw cork under the microscope He used a compound microscope
Chapter 16 Healthy Body Systems The Cell The smallest unit of structure in a living organism Robert Hooke Identified & coined the term Cell when he saw cork under the microscope He used a compound microscope
The Digestive System: to convert food particles into simpler micro molecules that can be absorbed into the bloodstream and used by the body
 Body Systems The Digestive System: to convert food particles into simpler micro molecules that can be absorbed into the bloodstream and used by the body Major Organs and their Functions: Mouth to chew
Body Systems The Digestive System: to convert food particles into simpler micro molecules that can be absorbed into the bloodstream and used by the body Major Organs and their Functions: Mouth to chew
Bronchitis. Anatomy of the Lungs The lungs allow us to fill our blood with oxygen. The oxygen we breathe is absorbed into our blood in the lungs.
 Bronchitis Introduction Bronchitis is an inflammation of the bronchial tubes, the airways that carry air to the lungs. It causes shortness of breath, wheezing and chest tightness as well as a cough that
Bronchitis Introduction Bronchitis is an inflammation of the bronchial tubes, the airways that carry air to the lungs. It causes shortness of breath, wheezing and chest tightness as well as a cough that
Dissection on Demand: Fetal Pig
 TEACHER GUIDE DISSECTION ON DEMAND: FETAL PIG 60 Minute Health and Life Science Lesson Science-to-Go! Program Grades: 6-12 Dissection on Demand: Fetal Pig Description Students will perform a dissection
TEACHER GUIDE DISSECTION ON DEMAND: FETAL PIG 60 Minute Health and Life Science Lesson Science-to-Go! Program Grades: 6-12 Dissection on Demand: Fetal Pig Description Students will perform a dissection
The Circulatory System
 The Circulatory System Single-celled organisms do not need a circulatory system. They are in direct contact with their environment, so transport of materials occurs by diffusion and osmosis. Larger organisms
The Circulatory System Single-celled organisms do not need a circulatory system. They are in direct contact with their environment, so transport of materials occurs by diffusion and osmosis. Larger organisms
What Is an Endoscopic Ultrasound (EUS)?
 ENDOSCOPIC ULTRASOUND (EUS) What Is an Endoscopic Ultrasound (EUS)? An endoscopic ultrasound (EUS) is a specialized procedure that blends: Endoscopy use of a scope to look at the inside lining of the gastrointestinal
ENDOSCOPIC ULTRASOUND (EUS) What Is an Endoscopic Ultrasound (EUS)? An endoscopic ultrasound (EUS) is a specialized procedure that blends: Endoscopy use of a scope to look at the inside lining of the gastrointestinal
Lesson Overview The Digestive System
 30.3 THINK ABOUT IT The only system in the body that food actually enters is the digestive system. So how does food get to the rest of the body after the process of digestion? Functions of the Digestive
30.3 THINK ABOUT IT The only system in the body that food actually enters is the digestive system. So how does food get to the rest of the body after the process of digestion? Functions of the Digestive
Biomedical Terminology. Cardiovascular and Lymphatic System
 Biomedical Terminology Cardiovascular and Lymphatic System Cardiovascular System Cardiovascular system is composed of the Heart (cardi/o) Blood vessels (angi/o) Arteries (arteri/o) blood vessels which
Biomedical Terminology Cardiovascular and Lymphatic System Cardiovascular System Cardiovascular system is composed of the Heart (cardi/o) Blood vessels (angi/o) Arteries (arteri/o) blood vessels which
CHAPTER 1 MEDICAL TERMINOLOGY BUILDING BLOCKS
 CHAPTER 1 MEDICAL TERMINOLOGY BUILDING BLOCKS COMPLETION 1. An enlarged stomach is known as. gastromegaly 2. Inflammation of the joints is known as. arthritis 3. Pertaining to the stomach is known as.
CHAPTER 1 MEDICAL TERMINOLOGY BUILDING BLOCKS COMPLETION 1. An enlarged stomach is known as. gastromegaly 2. Inflammation of the joints is known as. arthritis 3. Pertaining to the stomach is known as.
Colonic (Large Intestine) Manometry
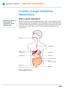 Patient and Family Education Colonic (Large Intestine) Manometry Manometry measures the pressure of contractions of the digestive tract. What is colonic manometry? The colon (also known as the large intestine)
Patient and Family Education Colonic (Large Intestine) Manometry Manometry measures the pressure of contractions of the digestive tract. What is colonic manometry? The colon (also known as the large intestine)
CAYUGA COMMUNITY COLLEGE Division of Computer Science, Mechanical Technology, Electrical Technology, GIS, Math, Nursing, Science
 CAYUGA COMMUNITY COLLEGE Division of Computer Science, Mechanical Technology, Electrical Technology, GIS, Math, Nursing, Science Anatomy and Physiology II - Biology 204 4 Credit Hours CATALOG DESCRIPTION
CAYUGA COMMUNITY COLLEGE Division of Computer Science, Mechanical Technology, Electrical Technology, GIS, Math, Nursing, Science Anatomy and Physiology II - Biology 204 4 Credit Hours CATALOG DESCRIPTION
Organ Systems (ch21-26) Practice Questions. Name:
 1. Which one of the following types of tissue stores fat in the body? A) blood B) cartilage C) bone D) adipose tissue E) fibrous connective tissue 2. Which of the following tissues does not match its function?
1. Which one of the following types of tissue stores fat in the body? A) blood B) cartilage C) bone D) adipose tissue E) fibrous connective tissue 2. Which of the following tissues does not match its function?
What is the function of the urinary system? How do the kidneys filter the blood? What are common problems with the urinary system?
 CHAPTER 24 2 The Urinary System SECTION The Digestive and Urinary Systems BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is the function of the urinary
CHAPTER 24 2 The Urinary System SECTION The Digestive and Urinary Systems BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is the function of the urinary
BIO 116 Anatomy & Physiology II Practice Assignment 3 - The Lymphatic, Immune and Digestive Systems This is not a required assignment
 BIO 116 Anatomy & Physiology II Practice Assignment 3 - The Lymphatic, Immune and Digestive Systems This is not a required assignment 1. Which are components of the lymphatic system? a: Thyroid gland b:
BIO 116 Anatomy & Physiology II Practice Assignment 3 - The Lymphatic, Immune and Digestive Systems This is not a required assignment 1. Which are components of the lymphatic system? a: Thyroid gland b:
Human Organ Systems. Circulatory, Respiratory, Digestive
 Human Organ Systems Circulatory, Respiratory, Digestive The Circulatory System The circulatory system picks up and transports nutrients and oxygen to all the cells in the body, and carries wastes to the
Human Organ Systems Circulatory, Respiratory, Digestive The Circulatory System The circulatory system picks up and transports nutrients and oxygen to all the cells in the body, and carries wastes to the
amygdala (ah MIG da la) a region of the brain involved in emotional memory, such as fear (SRB)
 FOSS Human Systems Interactions, Next Generation Edition Glossary abnormal different from what is usual (SRB) aerobic cellular respiration the process by which a cell releases energy using chemical reactions
FOSS Human Systems Interactions, Next Generation Edition Glossary abnormal different from what is usual (SRB) aerobic cellular respiration the process by which a cell releases energy using chemical reactions
Unit 1: Human body: combination I - IV
 Unit 1: Human body: combination I - IV Study online at quizlet.com/_1kzmm2 1. alveoli 6. bronchioles microscopic air sacs in the lung where diffusion of the respiratory gases, oxygen and carbon dioxide
Unit 1: Human body: combination I - IV Study online at quizlet.com/_1kzmm2 1. alveoli 6. bronchioles microscopic air sacs in the lung where diffusion of the respiratory gases, oxygen and carbon dioxide
Body Systems Notes. Nervous, Integumentary, Immune/Lymphatic, Circulatory, Skeletal, Respiratory, Digestive, Excretory, Endocrine, Reproductive
 Body Systems Notes Nervous, Integumentary, Immune/Lymphatic, Circulatory, Skeletal, Respiratory, Digestive, Excretory, Endocrine, Reproductive Homeostasis: maintaining a balance. Examples: temperature,
Body Systems Notes Nervous, Integumentary, Immune/Lymphatic, Circulatory, Skeletal, Respiratory, Digestive, Excretory, Endocrine, Reproductive Homeostasis: maintaining a balance. Examples: temperature,
Overview of Anatomy & Physiology
 Overview of Anatomy & Physiology Anatomy the study of the structure of body parts and their relationships to one another Gross or macroscopic Microscopic Developmental Physiology the study of the function
Overview of Anatomy & Physiology Anatomy the study of the structure of body parts and their relationships to one another Gross or macroscopic Microscopic Developmental Physiology the study of the function
Body Systems Overview
 Body Systems Overview Body Systems work together: If you damage one system, you may damage several for example, smoking irritates the lungs and destroys the cells of the immune system Levels of Organization
Body Systems Overview Body Systems work together: If you damage one system, you may damage several for example, smoking irritates the lungs and destroys the cells of the immune system Levels of Organization
Lung Cancer. This reference summary will help you better understand lung cancer and the treatment options that are available.
 Lung Cancer Introduction Lung cancer is the number one cancer killer of men and women. Over 165,000 people die of lung cancer every year in the United States. Most cases of lung cancer are related to cigarette
Lung Cancer Introduction Lung cancer is the number one cancer killer of men and women. Over 165,000 people die of lung cancer every year in the United States. Most cases of lung cancer are related to cigarette
Premium Specialty: Pediatrics
 Premium Specialty: Pediatrics Credentialed Specialties include: Adolescent Medicine, Pediatric Adolescent, and Pediatrics This document is designed to be used in conjunction with the UnitedHealth Premium
Premium Specialty: Pediatrics Credentialed Specialties include: Adolescent Medicine, Pediatric Adolescent, and Pediatrics This document is designed to be used in conjunction with the UnitedHealth Premium
Medical Terminology EMED1201/ Mid- Term Exam. PART I: Multiple Choice Questions - Select the one best answer:
 Question One: Medical Terminology EMED1201/ Mid- Term Exam PART I: Multiple Choice Questions - Select the one best answer: 1. The main part of a medical term is the A. prefix B. combining form. C. root.
Question One: Medical Terminology EMED1201/ Mid- Term Exam PART I: Multiple Choice Questions - Select the one best answer: 1. The main part of a medical term is the A. prefix B. combining form. C. root.
Biology Anatomy and Physiology I. Learn and Understand. What is Biology? bios = life -ology = study of
 Biology 2331 Anatomy and Physiology I "If you want something you've never had, then you've got to do something you've never done." Learn and Understand A new language At this stage, science drives the
Biology 2331 Anatomy and Physiology I "If you want something you've never had, then you've got to do something you've never done." Learn and Understand A new language At this stage, science drives the
Digestive System 7/15/2015. Outline Digestive System. Digestive System
 Digestive System Biology 105 Lecture 18 Chapter 15 Outline Digestive System I. Functions II. Layers of the GI tract III. Major parts: mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine,
Digestive System Biology 105 Lecture 18 Chapter 15 Outline Digestive System I. Functions II. Layers of the GI tract III. Major parts: mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine,
Human Body Systems. Human Body Project Notes
 Human Body Systems Human Body Project Notes Human Body Organ Systems for the Project Big Idea: Organ systems are composed of organs that are made of more than one type of tissue. Tissues are made of one
Human Body Systems Human Body Project Notes Human Body Organ Systems for the Project Big Idea: Organ systems are composed of organs that are made of more than one type of tissue. Tissues are made of one
INTEREST GRABBER NOTEBOOK #1
 INTEREST GRABBER NOTEBOOK #1 AN IMPORTANT PROCESS While walking along a dusty path, you begin to cough. As you continue your walk, a small insect comes flying toward you. You blink and then duck so that
INTEREST GRABBER NOTEBOOK #1 AN IMPORTANT PROCESS While walking along a dusty path, you begin to cough. As you continue your walk, a small insect comes flying toward you. You blink and then duck so that
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY II
 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY II THE BODY SYSTEMS Anatomy & Physiology II The Body Systems Michelle Cochrane 2014 All rights reserved. This material is subject to copyright and may not be reprinted or reproduced
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY II THE BODY SYSTEMS Anatomy & Physiology II The Body Systems Michelle Cochrane 2014 All rights reserved. This material is subject to copyright and may not be reprinted or reproduced
Digestive System. How your body obtains nutrients. Wednesday, March 2, 16
 Digestive System How your body obtains nutrients Vocabulary Ingestion: food enters the system Physical and enzymatic breakdown begins Digestion: Further breakdown Chemical/enzymatic Vocabulary Absorption:
Digestive System How your body obtains nutrients Vocabulary Ingestion: food enters the system Physical and enzymatic breakdown begins Digestion: Further breakdown Chemical/enzymatic Vocabulary Absorption:
The Circulatory. Systems. and Respiratory. How do the circulatory and respiratory systems work? Lesson ESSENTIAL QUESTION
 Lesson 3 The Circulatory and Respiratory Systems ESSENTIAL QUESTION How do the circulatory and respiratory systems work? By the end of this lesson, you should be able to relate the structures of the circulatory
Lesson 3 The Circulatory and Respiratory Systems ESSENTIAL QUESTION How do the circulatory and respiratory systems work? By the end of this lesson, you should be able to relate the structures of the circulatory
NEO 111 Melanie Jorgenson, RN, BSN
 NEO 111 Melanie Jorgenson, RN, BSN Inspection: performing deliberate, purposeful observations in a systematic manner Palpation: using the sense of touch Percussion: striking one object against another
NEO 111 Melanie Jorgenson, RN, BSN Inspection: performing deliberate, purposeful observations in a systematic manner Palpation: using the sense of touch Percussion: striking one object against another
This system consists of the heart (cardi/o) and blood vessels (vascular). It is this system
 SECTION 8 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM This system consists of the heart (cardi/o) and blood vessels (vascular). It is this system that allows blood to travel through the body. The heart works as a pump to keep
SECTION 8 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM This system consists of the heart (cardi/o) and blood vessels (vascular). It is this system that allows blood to travel through the body. The heart works as a pump to keep
Chapter 8. Bellringer. Write as many words or phrases that describe the circulatory system as you can. Lesson 5 The Circulatory System
 Lesson 5 The Circulatory System Bellringer Write as many words or phrases that describe the circulatory system as you can. Lesson 5 The Circulatory System Objectives Trace the path of blood through the
Lesson 5 The Circulatory System Bellringer Write as many words or phrases that describe the circulatory system as you can. Lesson 5 The Circulatory System Objectives Trace the path of blood through the
Name Class Date. Complete each of the following sentences by choosing the correct term from the word bank.
 Skills Worksheet Chapter Review USING KEY TERMS Complete each of the following sentences by choosing the correct term from the word bank. red blood cells veins white blood cells arteries lymphatic system
Skills Worksheet Chapter Review USING KEY TERMS Complete each of the following sentences by choosing the correct term from the word bank. red blood cells veins white blood cells arteries lymphatic system
Pre- Assessment. Prompt. Advance. 1. Duplicate assessment for each student
 Pre- Assessment Concepts Assessed Living things are organized structurally from microscopic cells to tissues, organs, and organ systems; within each of these levels, living things demonstrate a structure
Pre- Assessment Concepts Assessed Living things are organized structurally from microscopic cells to tissues, organs, and organ systems; within each of these levels, living things demonstrate a structure
UNDERSTANDING & MANAGING
 UNDERSTANDING & MANAGING YOUR CHRONIC OBSTRUCTIVE PULMONARY DISEASE (COPD)* *Includes chronic bronchitis, emphysema, or both Boehringer Ingelheim Pharmaceuticals, Inc. has no ownership interest in any
UNDERSTANDING & MANAGING YOUR CHRONIC OBSTRUCTIVE PULMONARY DISEASE (COPD)* *Includes chronic bronchitis, emphysema, or both Boehringer Ingelheim Pharmaceuticals, Inc. has no ownership interest in any
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Composed of two parts: 1. 2. There are 4 main parts of digestion: 1. Ingestion: 2. Digestion: a. Mechanical Digestion: Example: b. Chemical Digestion: Example: 3. Absorption: 4. Egestion:
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Composed of two parts: 1. 2. There are 4 main parts of digestion: 1. Ingestion: 2. Digestion: a. Mechanical Digestion: Example: b. Chemical Digestion: Example: 3. Absorption: 4. Egestion:
Chapter One Study Guide Answers
 Chapter One Study Guide Answers I. Aids to Understanding Words Append to hang something Cardi heart Cran helmet pertaining to the part of the skull that surrounds the brain. Dors back Homeo same -logy
Chapter One Study Guide Answers I. Aids to Understanding Words Append to hang something Cardi heart Cran helmet pertaining to the part of the skull that surrounds the brain. Dors back Homeo same -logy
ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY SESSION 12 THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY SESSION 12 THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM The Respiratory system is made up of organs that allow us to breathe. The primary function of the respiratory system is to supply oxygen to the
ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY SESSION 12 THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM The Respiratory system is made up of organs that allow us to breathe. The primary function of the respiratory system is to supply oxygen to the
A patient educational resource provided by Boehringer Ingelheim Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
 Boehringer Ingelheim Pharmaceuticals, Inc. has no ownership interest in any other organization that advertises or markets its disease management products and services. A patient educational resource provided
Boehringer Ingelheim Pharmaceuticals, Inc. has no ownership interest in any other organization that advertises or markets its disease management products and services. A patient educational resource provided
Peptic Ulcers. What I need to know about. hvordan man vælger en børnelæge med speciale i astma. National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse
 What I need to know about Peptic Ulcers U.S. Department NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH of Health and hvordan man vælger en børnelæge med speciale i astma National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse
What I need to know about Peptic Ulcers U.S. Department NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH of Health and hvordan man vælger en børnelæge med speciale i astma National Digestive Diseases Information Clearinghouse
UNIT 5 MAINTENANCE SYSTEMS Digestive System Test Bank
 UNIT 5 MAINTENANCE SYSTEMS Digestive System Test Bank Objective 5.01 Describe the basic functions of the digestive system. 1. What is the main function of the digestive system? a. Hold and receive food
UNIT 5 MAINTENANCE SYSTEMS Digestive System Test Bank Objective 5.01 Describe the basic functions of the digestive system. 1. What is the main function of the digestive system? a. Hold and receive food
Karen Storey. Multiple Choice: Draw a Complete Circle around the ONE BEST answer.
 Human Body Systems Test Review Karen Storey 7th Grade Science Multiple Choice: Draw a Complete Circle around the ONE BEST answer. 1. Which organ system makes blood cells? a. nervous system b. circulatory
Human Body Systems Test Review Karen Storey 7th Grade Science Multiple Choice: Draw a Complete Circle around the ONE BEST answer. 1. Which organ system makes blood cells? a. nervous system b. circulatory
Respiration. Chapter 35
 Respiration Chapter 35 Respiration Respiration is the exchange of gasses between an organism and its environment Gas exchange occurs between the environment and blood at the lungs, and the blood and cells
Respiration Chapter 35 Respiration Respiration is the exchange of gasses between an organism and its environment Gas exchange occurs between the environment and blood at the lungs, and the blood and cells
A Student Book on Tobacco Prevention
 A Student Book on Tobacco Prevention A Vocational and Rehabilitation Research Insitute (VRRI) partnership with The Alberta Alcohol and Drug Comission (AADAC) Tobacco Free Too Student book Contents Unit
A Student Book on Tobacco Prevention A Vocational and Rehabilitation Research Insitute (VRRI) partnership with The Alberta Alcohol and Drug Comission (AADAC) Tobacco Free Too Student book Contents Unit
How is an organism made up? (Use the levels or organization and explain their relationship to each other.)
 Unit 11 Test Review Chapter 28 a. List and describe the systems of the body and their functions (Respiratory, circulatory, digestive, immune, reproductive, excretory, nervous, integumentary, muscular,
Unit 11 Test Review Chapter 28 a. List and describe the systems of the body and their functions (Respiratory, circulatory, digestive, immune, reproductive, excretory, nervous, integumentary, muscular,
HASPI Medical Biology Lab 03
 Patient 1001 is a 42-year-old female that is experiencing severe heartburn, abdominal pain, bloating, nausea, and vomiting. Ulcers Bleeding sores in the stomach or intestine Gallbladder Disease Gallstones
Patient 1001 is a 42-year-old female that is experiencing severe heartburn, abdominal pain, bloating, nausea, and vomiting. Ulcers Bleeding sores in the stomach or intestine Gallbladder Disease Gallstones
Human Body. The student knows that the human body is made of systems with structure and functions that are related.
 Human Body The student knows that the human body is made of systems with structure and functions that are related. Cells Cells are the smallest living structures. All living things are made up of one or
Human Body The student knows that the human body is made of systems with structure and functions that are related. Cells Cells are the smallest living structures. All living things are made up of one or
Digestion: An Absorbing Tale
 8 r Digestion: An Absorbing Tale e a d i n g W hen melia s mom was diagnosed with an ulcer, her doctor thought it was caused by pain medication she had been taking for a knee injury. Almost half of all
8 r Digestion: An Absorbing Tale e a d i n g W hen melia s mom was diagnosed with an ulcer, her doctor thought it was caused by pain medication she had been taking for a knee injury. Almost half of all
X-Plain Muscles Reference Summary
 X-Plain Reference Summary Introduction are very important elements of the human body. They account for about half of a person s weight. Understanding how muscles work and how they can be injured is necessary
X-Plain Reference Summary Introduction are very important elements of the human body. They account for about half of a person s weight. Understanding how muscles work and how they can be injured is necessary
Organs and Systems Organ: System:
 3.2 Organ Systems Organs and Systems Organ: a combination of several types of tissues working together to perform a specific function System: a group of tissues and organs that perform specific functions
3.2 Organ Systems Organs and Systems Organ: a combination of several types of tissues working together to perform a specific function System: a group of tissues and organs that perform specific functions
The Body s Organization
 Chapter 4 The Body s Organization CHAPTER CONTENTS Introduction The Major Body Cavities The Anatomic Position and Directional Terms Body Systems Exercises Pre-Quiz Checklist Chapter Quiz 28 CHAPTER 4 THE
Chapter 4 The Body s Organization CHAPTER CONTENTS Introduction The Major Body Cavities The Anatomic Position and Directional Terms Body Systems Exercises Pre-Quiz Checklist Chapter Quiz 28 CHAPTER 4 THE
Science 8 Chapter 12 Section 1
 Science 8 Chapter 12 Section 1 How Body Systems are Connected (pp. 436-445) System Coordination Cellular Respiration There are 4 different body systems that all play a part in the process of cellular respiration:
Science 8 Chapter 12 Section 1 How Body Systems are Connected (pp. 436-445) System Coordination Cellular Respiration There are 4 different body systems that all play a part in the process of cellular respiration:
The primary function of the respiratory system is to supply the blood with oxygen in order for the blood to deliver oxygen to all parts of the body.
 Respiratory System The primary function of the respiratory system is to supply the blood with oxygen in order for the blood to deliver oxygen to all parts of the body. The respiratory system does this
Respiratory System The primary function of the respiratory system is to supply the blood with oxygen in order for the blood to deliver oxygen to all parts of the body. The respiratory system does this
Human Body Systems. Long narrow tube mixes enzymes with food Small nutrient molecules diffuse into blood
 Human Body Systems Living Environment AIS Mr. DuRoss Digestive System : Break down large food molecules into smaller parts that the body can use Mouth Esophagus Stomach Small intestine Large intestine
Human Body Systems Living Environment AIS Mr. DuRoss Digestive System : Break down large food molecules into smaller parts that the body can use Mouth Esophagus Stomach Small intestine Large intestine
Anatomy & Physiology Student Edition. 1. Which list shows different levels or organization within a population ordered from least to most complex?
 Name: Date: 1. Which list shows different levels or organization within a population ordered from least to most complex? A. organ systems, organs, organelles, organisms B. organelles, organs, organ systems,
Name: Date: 1. Which list shows different levels or organization within a population ordered from least to most complex? A. organ systems, organs, organelles, organisms B. organelles, organs, organ systems,
