CONTENTS NEURAL SIGNALING 23. CHAPTER 1 Studying the Nervous System 1. CHAPTER 3 Voltage-Dependent Membrane Permeability 41
|
|
|
- Lucinda Cooper
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 CONTENTS CHAPTER 1 Studying the Nervous System 1 Overview 1 Genetics, Genomics, and the Brain 1 BOX MODEL ORGANISMS NEUROSCIENCE 2 The Cellular Components of the Nervous System 4 Neurons 6 Glial Cells 7 Cellular Diversity in the Nervous System 10 Neural Circuits 10 The Organization of the Human Nervous System 13 Neural Systems 15 Structural Analysis of Neural Systems 15 Functional Analysis of Neural Systems 16 BOX BRAIN IMAGING TECHNIQUES Analyzing Complex Behavior 21 Summary 21 Additional Reading 21 NEURAL SIGNALING 23 Summary 40 Additional Reading 40 CHAPTER 2 Electrical Signals of Nerve Cells 25 Overview 25 Electrical Signals of Nerve Cells 25 Long-Distance Transmission of Electrical Signals 27 How Ion Movements Produce Electrical Signals 29 BOX 2A PASSIVE MEMBRANE PROPERTIES 30 Forces That Create Membrane Potentials 33 Electrochemical Equilibrium in an Environment with More Than One Permeant Ion 34 The Ionic Basis of the Resting Membrane Potential 35 BOX 2B THE REMARKABLE GIANT NERVE CELLS OF SQUID 36 The Ionic Basis of Action Potentials 37 BOX 2C ACTION POTENTIAL FORM AND NOMENCLATURE 39 CHAPTER 3 Voltage-Dependent Membrane Permeability 41 Overview 41 Ionic Currents across Nerve Cell Membranes 41 BOX 3A THE VOLTAGE CLAMP METHOD 42 Two Types of Voltage-Dependent Ionic Currents 43 Two Voltage-Dependent Membrane Conductances 45 Reconstruction of the Action Potential 47 BOX 3B THRESHOLD 49 Long-Distance Signaling by Means of Action Potentials 51 Increased Conduction Velocity as a Result of Myelination 51 Summary 53 BOX 3C MULTIPLE SCLEROSIS 54 Additional Reading 55
2 VIII CONTENTS CHAPTER 4 Ion Channels and Transporters 57 Overview 57 Ion Channels Underlying Action Potentials 57 BOX 4A THE PATCH CLAMP METHOD 59 BOX 4B TOXINS THAT POISON ION CHANNELS 62 The Diversity of Ion Channels 63 BOX 4C EXPRESSION OF OOCYTES 63 CHANNELS XENOPUS Voltage-Gated Ion Channels 64 Ligand-Gated Ion Channels 66 Stretch- and Channels 66 The Molecular Structure of Ion Channels 66 Active Transporters Create and Maintain Ion Gradients 69 BOX 4D DISEASES CAUSED BY ALTERED ION CHANNELS 70 Functional Properties of the Pump 72 The Molecular Structure of ATPase Pumps 72 Summary 74 Additional Reading 75 CHAPTER 5 Synaptic Transmission 77 Overview 77 Electrical Synapses 78 Signal Transmission at Chemical Synapses 80 Properties of Neurotransmitters 81 BOX 5A CRITERIA THAT DEFINE A NEUROTRANSMITTER 84 Quantal Release of Neurotransmitters 84 Release of Transmitters from Synaptic Vesicles 86 Local Recycling of Synaptic Vesicles 86 The Role of Calcium in Transmitter Secretion 88 Molecular Mechanisms of Synaptic Vesicle Cycling 90 BOX SB DISEASES THAT AFFECT THE PRESYNAPTIC TERMINAL 93 Neurotransmitter Receptors 96 Postsynaptic Membrane Permeability Changes during Synaptic Transmission 97 Excitatory and Inhibitory Postsynaptic Potentials 101 Summation of Synaptic Potentials 102 BOX 5C THE 'TRIPARTITE SYNAPSE" Summary 105 Additional Reading 106 CHAPTER 6 Neurotransmitters and Their Receptors Overview 109 Categories of Neurotransmitters 109 Acetylcholine BOX 6A NEUROTOXINS THAT ACT ON POSTSYNAPTIC RECEPTORS Glutamate 116 BOX 6B MYASTHENIA GRAVIS: AN AUTOIMMUNE DISEASE OF NEUROMUSCULAR SYNAPSES BOX 6C EXCITOTOXICITY FOLLOWING ACUTE BRAIN INJURY 121 GABA and Glycine 122 BOX 6D EXCITATORY ACTIONS OF GABA IN THE DEVELOPING BRAIN 124 The Biogenic Amines 125 BOX 6E BIOGENIC AMINE NEUROTRANSMITTERS AND PSYCHIATRIC DISORDERS 126 ADDICTION 128 ATP and Other Purines 131 Peptide Neurotransmitters 132 Unconventional Neurotransmitters 135 MARIJUANA AND THE BRAIN 137 Summary 139 Additional Reading 139 CHAPTER 7 Molecular Signaling within Neurons 141 Overview 141 Strategies of Molecular Signaling 141 The Activation of Signaling Pathways 143 Receptor Types 144 G-Proteins and Their Molecular Targets 145 Second Messengers 147 BOX 7A DYNAMIC IMAGING OF INTRACELLULAR SIGNALING 149 Second Messenger Targets: Protein Kinases and Phosphatases 151 Nuclear Signaling 153 DENDRITIC SPINES 154 Examples of Neuronal Signal Transduction 157 Summary 159 Additional Reading 160
3 CHAPTER 8 Synaptic Plasticity Overview 163 Short-Term Synaptic Plasticity 163 Long-Term Synaptic Plasticity Underlies Behavioral Modification in 166 Long-Term Potentiation at a Hippocampal Synapse 169 BOX 8A GENETICS OF LEARNING AND MEMORY IN THE FRUIT FLY 170 Mechanisms Underlying LTP SILENT SYNAPSES Mechanisms Underlying LTD Spike-Timing Dependent Plasticity 181 BOX 8C EPILEPSY: THE EFFECT OF PATHOLOGICAL ACTIVITY ON NEURAL CIRCUITRY Summary 183 Additional Reading 184 UNIT II SENSATION AND SENSORY PROCESSING 187 Beyond SI: Corticocortical and Descending Pathways 205 Plasticity in the Adult Cerebral Cortex 206 Summary 207 Additional Reading 207 CHAPTER 9 The Somatic Sensory System: Touch and Proprioception Overview 189 Afferent Fibers Convey Somatic Sensory Information to the Central Nervous System 189 Somatic Sensory Afferents Exhibit Distinct Functional Properties 191 DERMATOMES 191 Mechanoreceptors Specialized to Receive Tactile Information 194 Mechanoreceptors Specialized for Proprioception 196 Central Pathways Conveying Tactile Information from the Body: The Dorsal Column-Medial System 198 Central Pathways Conveying Tactile Information from the Face: The Trigeminothalamic System 200 Central Pathways Conveying Proprioceptive Information Body 200 Central Pathways Conveying Proprioceptive Information from the Face 201 The Somatic Sensory Components of the Thalamus 201 Primary Somatic Sensory Cortex 202 BOX 9B PATTERNS OF ORGANIZATION WITHIN THE SENSORY CORTICES: BRAIN MODULES 203 CHAPTER Pain 209 Overview 209 Nociceptors 209 Transduction and Transmission of Nociceptive Signals 211 CAPSAICIN 212 Central Pain Pathways Are Distinct from Mechanosensory Pathways 213 BOX OB REFERRED PAIN BOX A DORSAL COLUMN PATHWAY FOR VISCERAL PAIN 215 Parallel Pain Pathways 217 Pain and Temperature Pathways for the Face 218 Other Modalities Mediated by the Anterolateral System 220 Sensitization 220 Descending Control of Pain Perception 223 BOX PHANTOM LIMBS AND PHANTOM PAIN 222 The Placebo Effect 223 The Physiological Basis of Pain Modulation 224 Summary 226 Additional Reading 226
4 CHAPTER 11 Vision: The Eye 229 Overview 229 Anatomy of the Eye 229 The Formation of Images on the Retina 230 BOX MYOPIA AND OTHER REFRACTIVE ERRORS 231 The Surface of the Retina 233 Retinal Circuitry 233 BOX THE BLIND SPOT 234 BOX 11C MACULAR DEGENERATION 235 BOX RETINITIS PIGMENTOSA 237 Retinal Pigment Epithelium 238 Phototransduction 238 Functional Specialization of the Rod and Cone Systems 242 Anatomical Distribution of Rods and Cones 244 Cones and Color Vision 245 BOX HE THE IMPORTANCE OF CONTEXT IN COLOR PERCEPTION 246 Retinal Circuits for Detecting Luminance Change 249 BOX THE PERCEPTION OF LIGHT INTENSITY 250 Contribution of Retinal Circuits to Light Adaptation 253 Summary 255 Additional Reading 256 CHAPTER 12 Central Visual Pathways 257 Overview 257 Central Projections of Retinal Ganglion Cells 257 The Representation of the Visual Field 259 Visual Field Deficits 261 Spatiotemporal Tuning Properties of Neurons in Primary Visual Cortex 263 Primary Visual Cortex Architecture 265 Combining Inputs from Two Eyes 267 Division of Labor within the Primary Visual Pathway 269 BOX RANDOM DOT STEREOGRAMS AND RELATED AMUSEMENTS 270 The Functional Organization of Extrastriate Visual Areas 272 Summary 274 Additional Reading 275 CHAPTER 13 The Auditory System 277 Overview 277 Sound 277 The Audible Spectrum 278 A Synopsis of Auditory Function 279 BOX 13A FOUR CAUSES OF ACQUIRED HEARING LOSS 279 BOX 13B MUSIC 280 The External Ear 281 The Middle Ear 282 BOX 13C SENSORINEURAL HEARING LOSS AND COCHLEAR IMPLANTS 283 The Inner Ear 284 Hair Cells and the Mechanoelectrical Transduction of 287 The Ionic Basis of in Hair Cells 290 The Cochlear Amplifier 291 Tuning and Timing in the Auditory Nerve 291 BOX THE SWEET SOUND OF DISTORTION 292 How Information from the Cochlea Reaches Targets in the Brainstem 293 Integrating Information from the Two Ears 294 Monaural Pathways from the Cochlear Nucleus to the Nuclei of the Lateral Lemniscus 297 Integration in the Inferior Colliculus 297 The Auditory Thalamus 297 The Auditory Cortex 298 BOX 13E REPRESENTING COMPLEX SOUNDS IN THE BRAINS OF BATS AND HUMANS 299 Summary 301 Additional Reading 301 CHAPTER The Vestibular System 303 Overview 303 The Vestibular Labyrinth 303 BOX 14A A PRIMER ON TERMINOLOGY 304 Vestibular Hair Cells 305 BOX 14B ADAPTATION AND TUNING OF VESTIBULAR HAIR CELLS 306 The Otolith Organs: The Utricle and Saccule 307 How Otolith Neurons Sense Tilts and Linear Accelerations of the Head 309 The Semicircular Canals 310 How Semicircular Canal Neurons Sense Angular Accelerations 312
5 Central Pathways for Stabilizing Gaze, Head, and Posture 312 BOX 14C CLINICAL EVALUATION OF THE VESTIBULAR SYSTEM 314 BOX 14D MAUTHNER CELLS FISH Vestibular Pathways to the Thalamus and Cortex 318 Spatial Orientation Perception and Multisensory Integration 318 Summary 319 Additional Reading 320 CHAPTER 15 The Chemical Senses 321 Overview 321 The Organization of the Olfactory System 321 Olfactory Perception in Humans 323 Assessing Olfactory Function in the Laboratory or Clinic 324 BOX 15A YOU ONLY GET ONE NOSE 326 Physiological and Behavioral Responses to Odorants 327 BOX PHEROMONES, REPRODUCTION, AND THE VOMERONASAL SYSTEM 328 Olfactory Epithelium and Olfactory Receptor Neurons 329 Odor Transduction and Odorant Receptor Proteins 332 BOX 15C THE "DOGTOR" IS IN 333 Physiological Mechanisms of Odor Transduction 334 The Olfactory Bulb 336 Cortical Processing of Information Relayed from the Olfactory Bulb 340 The Organization of the Taste System 341 Taste Perception in Humans 343 Taste Receptor Proteins and Transduction 345 Neural Coding in the Taste System 347 Trigeminal Chemoreception 349 Summary 349 Additional Reading 350 UNIT III MOVEMENT AND ITS CENTRAL CONTROL CHAPTER 16 Lower Motor Neuron Circuits and Motor Control 353 Overview 353 Neural Centers Responsible for Movement 353 Motor Neuron-Muscle Relationships 355 The Motor Unit 357 The Regulation of Muscle Force 358 BOX 16A MOTOR UNIT PLASTICITY 359 The Spinal Cord Circuitry Underlying Muscle Stretch Reflexes 362 The Influence of Sensory Activity on Motor Behavior 364 Other Sensory Feedback Affecting Motor Performance 365 Flexion Reflex Pathways 367 BOX LOCOMOTION IN THE LEECH AND THE LAMPREY 368 Spinal Cord Circuitry and Locomotion 369 BOX 16C THE AUTONOMY OF CENTRAL PATTERN GENERATORS: EVIDENCE FROM THE LOBSTER STOMATOGASTRIC GANGLION 370 The Lower Motor Neuron Syndrome 372 BOX AMYOTROPHIC LATERAL SCLEROSIS 373 Summary 373 Additional Reading 374 CHAPTER 17 Upper Motor Neuron Control of the Brainstem and Spinal Cord 375 Overview 375 Organization of Descending Motor Control 375 The Corticospinal and Corticobulbar Tracts 377 BOX PATTERNS OF FACIAL WEAKNESS AND THEIR IMPORTANCE FOR LOCALIZING NEUROLOGICAL INJURY 379 Functional Organization of the Primary Motor Cortex 380
6 BOX 17B WHAT DO MOTOR MAPS REPRESENT? 381 BOX SENSORY MOTOR TALENTS AND CORTICAL SPACE 384 The Cortex 387 Motor Control Centers in the Brainstem: Upper Motor Neurons that Maintain Balance, Govern Posture, and Orient Gaze 389 BOX 17D THE RETICULAR FORMATION 391 Damage to Descending Motor Pathways: The Upper Motor Neuron Syndrome 395 BOX 17E MUSCLE TONE 397 Summary 397 Additional Reading 398 CHAPTER Modulation of Movement by the Basal Ganglia 399 Overview 399 Projections to the Basal Ganglia 399 Projections from the Basal Ganglia to Other Brain Regions 402 Evidence Studies of Eye Movements 404 Circuits within the Basal Ganglia System 405 Dopamine Modulates Basal Ganglia Circuits 407 Hypokinetic and Hyperkinetic Movement Disorders 408 BOX 18A PARKINSON'S DISEASE: AN OPPORTUNITY FOR NOVEL THERAPEUTIC APPROACHES 410 BOX 18B HUNTINGTON'S DISEASE BOX 18C DEEP BRAIN STIMULATION BOX BRAIN FUNCTIONS Summary 416 Additional Reading 416 BASAL GANGLIA LOOPS AND NON-MOTOR CHAPTER 19 Modulation of Movement by the Cerebellum Overview 417 Organization of the Cerebellum 417 Projections to the Cerebellum 419 Projections from the Cerebellum 421 Circuits within the Cerebellum 423 Cerebellar Circuitry and the Coordination of Ongoing Movement 426 BOX 19A PRION DISEASES 427 Further Consequences of Cerebellar Lesions 429 BOX GENETIC ANALYSIS OF CEREBELLAR FUNCTION 431 Summary 433 Additional Reading 433 CHAPTER 20 Eye Movements and Sensory Motor Integration 435 Overview 435 What Eye Movements Accomplish 435 The Actions and Innervation of Extraocular Muscles 436 BOX 20A THE PERCEPTION OF STABILIZED RETINAL IMAGES 437 Types of Eye Movements and Their Functions 438 Neural Control of Saccadic Eye Movements 440 BOX 20B SENSORY MOTOR INTEGRATION IN THE SUPERIOR COLLICULUS 443 BOX 20C FROM PLACE CODES TO RATE CODES 445 Neural Control of Smooth Pursuit Movements 449 Neural Control of Vergence Movements 449 Summary 450 Additional Reading 450 CHAPTER 21 The Visceral Motor System 451 Overview 451 Early Studies of the Visceral Motor System 454 Distinctive Features of the Visceral Motor System 454 The Sympathetic Division of the Visceral Motor System 456 BOX 21A THE HYPOTHALAMUS 456 The Parasympathetic Division of the Visceral Motor System 460 The Enteric Nervous System 461 Sensory Components of the Visceral Motor System 462 Central Control of Visceral Motor Functions 464 HORNER'S SYNDROME 465 Neurotransmission in the Visceral Motor System 466 BOX OBESITY AND THE BRAIN 466 Autonomic Regulation of Cardiovascular Function 468 Autonomic Regulation of the Bladder 470 Autonomic Regulation of Sexual Function 472 Summary 473 Additional Reading 474
7 UNIT IV THE CHANGING BRAIN 475 CHAPTER 22 Early Brain Development 477 Overview 477 Formation of the Nervous System: Neurulation 477 BOX 22A STEM CELLS: PROMISE AND PERIL 479 Formation of the Major Brain Subdivisions 481 BOX 22B RHOMBOMERES 484 The Molecular Basis of Neural Induction 485 and BOX 22C RETINOIC ACID: TERATOGEN AND INDUCTIVE SIGNAL 488 Integrated Inductive Signals Establish Neuron Identity 489 The Initial Differentiation of Neurons and 489 BOX 22D NEUROGENESIS: WHERE, WHEN, AND WHAT 492 Molecular Regulation of Neurogenesis 493 The Generation of Neuronal Diversity 495 Molecular and Genetic Disruptions of Early Neural Development 496 BOX 22E TRIPLE JEOPARDY: DISEASES ASSOCIATED WITH SONIC HEDGEHOG 497 Neuronal Migration in the Peripheral Nervous System 499 BOX 22F MIXING IT UP: LONG-DISTANCE NEURONAL MIGRATION 501 Neuronal Migration in the Central Nervous System 502 Molecular Mechanisms of Neuronal Migration and Cortical Migration Disorders 503 Summary 503 Additional Reading 505 CHAPTER 23 Construction of Neural Circuits 507 Overview 507 Neuronal Polarization: The First Step in Neural Circuit Formation 507 The Axon Growth Cone 509 The Molecular Basis of Growth Cone Motility 510 BOX 23A CHOOSING SIDES: AXON GUIDANCE AT THE OPTIC CHIASM 512 Non-Diffusible Signals for Axon Guidance 513 HUMAN AXON GUIDANCE DISORDERS Chemoattraction and Chemorepulsion 517 The Formation of Topographic Maps 519 Selective Synapse Formation 521 Regulation of Neuronal Connections by Trophic Interactions 523 Competitive Interactions and the Formation of Neuronal Connections 525 BOX 23C WHY DO NEURONS HAVE DENDRITES? 528 The Molecular Basis of Trophic Interactions 529 BOX 23D THE DISCOVERY OF BDNF AND THE NEURO- TROPHIN FAMILY 530 Neurotrophin Signaling 533 Summary 535 Additional Reading 535 CHAPTER 24 Modification of Neural Circuits as a Result of Experience 537 Overview 537 Neural Activity and Brain Development 537 Critical Periods 538 BOX 24A BUILT-IN BEHAVIORS 540 BIRDSONG 541 Cellular and Molecular Correlates of Activity-Dependent Plasticity during Critical Periods 542 Critical Periods in Visual System Development 543 BOX 24C TRANSNEURONAL LABELING WITH ACTIVE AMINO ACIDS 544 Effects of Visual Deprivation on Ocular Dominance 545 BOX 24D CORRELATION AS CAUSATION: LESSONS FROM A THREE-EYED FROG 549 Manipulating Competition 550 Amblyopia, Strabismus, and Critical Periods for Human Vision 551 Evidence for Critical Periods in Other Sensory Systems 552
8 The Development of Language: A Critical Period for a Distinctly Human Behavior 553 Human Brain Development, Activity-Dependent Plasticity, and Critical Periods 554 Summary 556 Additional Reading 557 CHAPTER 25 Repair and Regeneration in the Nervous System 559 Overview 559 The Damaged Brain 559 Functional Reorganization without Repair 560 Three Types of Neuronal Repair 561 Peripheral Nerve Regeneration 563 The Cellular and Molecular Basis of Peripheral Nerve Repair 564 Regeneration of Peripheral Synapses 567 BOX 25A SPECIFIC REGENERATION OF SYNAPTIC CONNECTIONS IN AUTONOMIC GANGLIA 568 Regeneration after Damage to the Central Nervous System 570 Cellular and Molecular Responses to Injury 570 CASUALTIES OF WAR AND SPORTS Axon Growth after Brain Injury 574 Neurogenesis in the Mature Central Nervous System 575 Adult Neurogenesis in Non-Mammalian Vertebrates 576 Neurogenesis in the Adult Mammalian Brain 577 Cellular and Molecular Mechanisms of Adult Neurogenesis 578 Adult Neurogenesis, Stem Cells, and Brain Repair in Humans 580 NUCLEAR WEAPONS AND NEUROGENESIS 581 Summary 583 Additional Reading 583 COMPLEX BRAIN FUNCTIONS "Planning Neurons" in the Monkey Frontal Cortex 603 Summary 605 Additional Reading 605 CHAPTER 26 Association Cortex and Cognition 587 Overview 587 The Association Cortices 587 An Overview of Cortical Structure 588 Unique Features of the Association Cortices 589 BOX 26A CORTICAL LAMINATION 590 The Parietal Association Cortex Mediates Attention 591 "Attention Neurons" in the Monkey Parietal Cortex 594 The Temporal Association Cortex Mediates Recognition 596 "Recognition Neurons" in the Monkey Temporal Cortex 598 The Frontal Association Cortex Mediates Planning and Decision Making 599 BOX 26B NEUROPSYCHOLOGICAL TESTING 600 BOX 26C PSYCHOSURGERY 602 CHAPTER 27 Speech and Language 607 Overview 607 Language Is Localized and Lateralized in the Brain 607 BOX 27A THE GENERATION OF SPEECH 608 Aphasias 610 BOX 27B DO OTHER ANIMALS HAVE LANGUAGE? BOX 27C WORDS AND MEANING Confirmation of Language Lateralization and Other Insights 615 LANGUAGE AND HANDEDNESS 617 The Search Anatomical Differences between the Right and Left Hemispheres 618 Mapping Language Functions 619 The Role of the Right Hemisphere 622 Sign Language 622 Summary 623 Additional Reading 623
9 CHAPTER 28 Sleep and Wakefulness 625 Overview 625 Why Do Humans (and Many Other Animals) Sleep? 625 BOX 28A THE SLEEP STYLES OF DIFFERENT SPECIES 627 The Circadian Cycle of Sleep and Wakefulness 628 BOX 28B MOLECULAR MECHANISMS OF BIOLOGICAL CLOCKS 629 Stages of Sleep 631 BOX 28C ELECTROENCEPHALOGRAPHY 632 Physiological Changes in Sleep States 635 Other Possible Functions of Sleep and Dreaming 636 Neural Circuits Governing Sleep 637 BOX 28D CONSCIOUSNESS 638 Thalamocortical Interactions in Sleep 641 BOX 28E DRUGS AND SLEEP 641 Sleep Disorders 643 BOX 28F CHRONIC FATIGUE SYNDROME 644 Summary 645 Additional Reading 645 CHAPTER 29 Emotions 647 Overview 647 Physiological Changes Associated with Emotion 647 BOX 29A FACIAL EXPRESSIONS: PYRAMIDAL AND EXTRA PYRAMIDAL CONTRIBUTIONS 648 The Integration of Emotional Behavior 650 The Limbic System 652 The Importance of the Amygdala 653 BOX 29B THE ANATOMY OF THE AMYGDALA 654 BOX 29C THE REASONING BEHIND AN IMPORTANT DISCOVERY 655 BOX 29D FEAR AND THE HUMAN AMYGDALA: A CASE STUDY 657 BOX 29E AFFECTIVE DISORDERS 659 The Relationship between Neocortex and Amygdala 660 Cortical Lateralization of Emotional Functions 661 Emotion, Reason, and Social Behavior 662 Emotional Reinforcement and Addiction 663 Summary 666 Additional Reading 667 CHAPTER 30 Sexuality, and the Brain 669 Overview 669 Sexual Dimorphisms and Sexually Dimorphic Behaviors 669 Sex, Gonads, Bodies, and Brains 671 BOX 30A THE SCIENCE OF LOVE (OR, LOVE IS A DRUG) 672 Hormonal Influences on Sexual Dimorphism 674 Primary Sexual Dimorphisms in the Brain 676 Brain Dimorphisms and the Control of Reproductive Behaviors 678 Structural and Functional Dimorphisms for Pregnancy and Parenting 680 BOX 30B THE GOOD MOTHER 683 Cellular and Molecular Basis of Sexually Dimorphic Structures and Behaviors 684 Steroid Receptors and Responses in the Adult Brain 686 Human Genetic Disorders of Genotypic and Sex 687 Sexual Orientation and the Brain: Molecular and Genetic Analysis 688 Sexual Orientation and Human Brain Structure 690 Sex-Based Differences in Cognitive Functions 691 Summary 693 Additional Reading 693 CHAPTER 31 Memory 695 Overview 695 Qualitative Categories of Human Memory 695 Temporal Categories of Memory 696 BOX PHYLOGENETIC MEMORY 697 Memory Consolidation and Priming 698 The Importance of Association in Information Storage 698 Conditioned Learning 699 SAVANT SYNDROME 700 Forgetting 702 Brain Systems Underlying Declarative Memory Acquisition and Storage 703 BOX CLINICAL CASES REVEAL AN ANATOMICAL SUB STRATE FOR DECLARATIVE MEMORIES 703 Brain Systems Underlying Nondeclarative Memory Acquisition and Storage 711 Memory and Aging 712 ALZHEIMER'S DISEASE 713 Summary 714 Additional Reading 715
10 APPENDIX Survey of Human Neuroanatomy Overview 717 Neuroanatomical Terminology 717 Basic Subdivisions of the Central Nervous System 718 External Anatomy of the Spinal Cord 720 Internal Anatomy of the Spinal Cord 721 Brainstem and Cranial Nerves 722 Lateral Surface of the Brain 728 Dorsal and Ventral Surfaces of the Brain 729 Midsagittal Surface of the Brain 730 Internal Anatomy of the Forebrain 731 BOX A THALAMUS AND THALAMOCORTICAL RELATIONS 732 Blood Supply of the Brain and Spinal Cord 735 BOX B STROKE 735 The Blood-Brain Barrier 741 The Meninges 742 The Ventricular System 742 References 744 ATLAS The Human Central Nervous System 745 Plate 1: Brain Surface 746 Plate 2: Coronal MR 748 Plate 3: Axial MR 750 Plate 4: Sagittal MR 754 Plate 5: Brainstem 756 Plate 6: Spinal Cord 758 GLOSSARY ILLUSTRATION CREDITS INDEX
Module H NERVOUS SYSTEM
 Module H NERVOUS SYSTEM Topic from General functions of the nervous system Organization of the nervous system from both anatomical & functional perspectives Gross & microscopic anatomy of nervous tissue
Module H NERVOUS SYSTEM Topic from General functions of the nervous system Organization of the nervous system from both anatomical & functional perspectives Gross & microscopic anatomy of nervous tissue
THE CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTE M
 THE CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTE M Structure and Functio n THIRD EDITIO N PER BRODAL A Brief Survey, x i Studying the Structures and Function of the Nervous System, xii i Animal Experiments Crucial for Progress,
THE CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTE M Structure and Functio n THIRD EDITIO N PER BRODAL A Brief Survey, x i Studying the Structures and Function of the Nervous System, xii i Animal Experiments Crucial for Progress,
Course Calendar
 Clinical Neuroscience BMS 6706C Charles, Ph.D., Course Director charles.ouimet@med.fsu.edu (850) 644-2271 2004 2005 Course Calendar Click here to return to the syllabus Meeting Hours for entire semester:
Clinical Neuroscience BMS 6706C Charles, Ph.D., Course Director charles.ouimet@med.fsu.edu (850) 644-2271 2004 2005 Course Calendar Click here to return to the syllabus Meeting Hours for entire semester:
Course Calendar - Neuroscience
 2006-2007 Course Calendar - Neuroscience Meeting Hours for entire semester: Monday - Friday 1:00-2:20 p.m. Room 1200, COM August 28 August 29 August 30 August 31 September 1 Course introduction, Neurocytology:
2006-2007 Course Calendar - Neuroscience Meeting Hours for entire semester: Monday - Friday 1:00-2:20 p.m. Room 1200, COM August 28 August 29 August 30 August 31 September 1 Course introduction, Neurocytology:
Page 1. Neurons Transmit Signal via Action Potentials: neuron At rest, neurons maintain an electrical difference across
 Chapter 33: The Nervous System and the Senses Neurons: Specialized excitable cells that allow for communication throughout the body via electrical impulses Neuron Anatomy / Function: 1) Dendrites: Receive
Chapter 33: The Nervous System and the Senses Neurons: Specialized excitable cells that allow for communication throughout the body via electrical impulses Neuron Anatomy / Function: 1) Dendrites: Receive
Physiology Unit 2 SENSORY PHYSIOLOGY
 Physiology Unit 2 SENSORY PHYSIOLOGY In Physiology Today Sensory System Sensory information Conscious sensations Unconscious sensations Sensory processing Transferring stimulus energy into a graded potential
Physiology Unit 2 SENSORY PHYSIOLOGY In Physiology Today Sensory System Sensory information Conscious sensations Unconscious sensations Sensory processing Transferring stimulus energy into a graded potential
biological psychology, p. 40 The study of the nervous system, especially the brain. neuroscience, p. 40
 biological psychology, p. 40 The specialized branch of psychology that studies the relationship between behavior and bodily processes and system; also called biopsychology or psychobiology. neuroscience,
biological psychology, p. 40 The specialized branch of psychology that studies the relationship between behavior and bodily processes and system; also called biopsychology or psychobiology. neuroscience,
Lesson 14. The Nervous System. Introduction to Life Processes - SCI 102 1
 Lesson 14 The Nervous System Introduction to Life Processes - SCI 102 1 Structures and Functions of Nerve Cells The nervous system has two principal cell types: Neurons (nerve cells) Glia The functions
Lesson 14 The Nervous System Introduction to Life Processes - SCI 102 1 Structures and Functions of Nerve Cells The nervous system has two principal cell types: Neurons (nerve cells) Glia The functions
Neural Communication. Central Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System. Communication in the Nervous System. 4 Common Components of a Neuron
 Neural Communication Overview of CNS / PNS Electrical Signaling Chemical Signaling Central Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System Somatic = sensory & motor Autonomic = arousal state Parasympathetic =
Neural Communication Overview of CNS / PNS Electrical Signaling Chemical Signaling Central Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System Somatic = sensory & motor Autonomic = arousal state Parasympathetic =
Shift 1, 8 July 2018, 09:30-13:00
 Shift 1, 8 July 2018, 09:30-13:00 CNS patterning A001-A014 Stem cells: basic biology and postnatal neurogenesis - part I Development of neural systems: Molecular and genetic characterisationa Epigenetic
Shift 1, 8 July 2018, 09:30-13:00 CNS patterning A001-A014 Stem cells: basic biology and postnatal neurogenesis - part I Development of neural systems: Molecular and genetic characterisationa Epigenetic
Chapter 17. Nervous System Nervous systems receive sensory input, interpret it, and send out appropriate commands. !
 Chapter 17 Sensory receptor Sensory input Integration Nervous System Motor output Brain and spinal cord Effector cells Peripheral nervous system (PNS) Central nervous system (CNS) 28.1 Nervous systems
Chapter 17 Sensory receptor Sensory input Integration Nervous System Motor output Brain and spinal cord Effector cells Peripheral nervous system (PNS) Central nervous system (CNS) 28.1 Nervous systems
Neural Basis of Motor Control
 Neural Basis of Motor Control Central Nervous System Skeletal muscles are controlled by the CNS which consists of the brain and spinal cord. Determines which muscles will contract When How fast To what
Neural Basis of Motor Control Central Nervous System Skeletal muscles are controlled by the CNS which consists of the brain and spinal cord. Determines which muscles will contract When How fast To what
REVIEW QUESTIONS AND SAMPLE MIDTERM QUESTIONS FOR THE MIDTERM EXAM
 REVIEW QUESTIONS AND SAMPLE MIDTERM QUESTIONS FOR THE MIDTERM EXAM REVIEW QUESTIONS Chapter 1 / Lecture 1 1. Diagram a neuron and label its components. In what ways are neurons specialized for communication?
REVIEW QUESTIONS AND SAMPLE MIDTERM QUESTIONS FOR THE MIDTERM EXAM REVIEW QUESTIONS Chapter 1 / Lecture 1 1. Diagram a neuron and label its components. In what ways are neurons specialized for communication?
CHAPTER 48: NERVOUS SYSTEMS
 CHAPTER 48: NERVOUS SYSTEMS Name I. AN OVERVIEW OF NERVOUS SYSTEMS A. Nervous systems perform the three overlapping functions of sensory input, integration, and motor output B. Networks of neurons with
CHAPTER 48: NERVOUS SYSTEMS Name I. AN OVERVIEW OF NERVOUS SYSTEMS A. Nervous systems perform the three overlapping functions of sensory input, integration, and motor output B. Networks of neurons with
Cephalization. Nervous Systems Chapter 49 11/10/2013. Nervous systems consist of circuits of neurons and supporting cells
 Nervous Systems Chapter 49 Cephalization Nervous systems consist of circuits of neurons and supporting cells Nervous system organization usually correlates with lifestyle Organization of the vertebrate
Nervous Systems Chapter 49 Cephalization Nervous systems consist of circuits of neurons and supporting cells Nervous system organization usually correlates with lifestyle Organization of the vertebrate
Chapter 11 Introduction to the Nervous System and Nervous Tissue Chapter Outline
 Chapter 11 Introduction to the Nervous System and Nervous Tissue Chapter Outline Module 11.1 Overview of the Nervous System (Figures 11.1-11.3) A. The nervous system controls our perception and experience
Chapter 11 Introduction to the Nervous System and Nervous Tissue Chapter Outline Module 11.1 Overview of the Nervous System (Figures 11.1-11.3) A. The nervous system controls our perception and experience
Auditory and Vestibular Systems
 Auditory and Vestibular Systems Objective To learn the functional organization of the auditory and vestibular systems To understand how one can use changes in auditory function following injury to localize
Auditory and Vestibular Systems Objective To learn the functional organization of the auditory and vestibular systems To understand how one can use changes in auditory function following injury to localize
Psychophysical laws. Legge di Fechner: I=K*log(S/S 0 )
 Psychophysical laws Legge di Weber: ΔS=K*S Legge di Fechner: I=K*log(S/S 0 ) Sensory receptors Vision Smell Taste Touch Thermal senses Pain Hearing Balance Proprioception Sensory receptors Table 21-1 Classification
Psychophysical laws Legge di Weber: ΔS=K*S Legge di Fechner: I=K*log(S/S 0 ) Sensory receptors Vision Smell Taste Touch Thermal senses Pain Hearing Balance Proprioception Sensory receptors Table 21-1 Classification
CHAPTER 16 LECTURE OUTLINE
 CHAPTER 16 LECTURE OUTLINE I. INTRODUCTION A. The components of the brain interact to receive sensory input, integrate and store the information, and transmit motor responses. B. To accomplish the primary
CHAPTER 16 LECTURE OUTLINE I. INTRODUCTION A. The components of the brain interact to receive sensory input, integrate and store the information, and transmit motor responses. B. To accomplish the primary
Lecture 22: A little Neurobiology
 BIO 5099: Molecular Biology for Computer Scientists (et al) Lecture 22: A little Neurobiology http://compbio.uchsc.edu/hunter/bio5099 Larry.Hunter@uchsc.edu Nervous system development Part of the ectoderm
BIO 5099: Molecular Biology for Computer Scientists (et al) Lecture 22: A little Neurobiology http://compbio.uchsc.edu/hunter/bio5099 Larry.Hunter@uchsc.edu Nervous system development Part of the ectoderm
NERVOUS SYSTEM C H A P T E R 2 8
 NERVOUS SYSTEM C H A P T E R 2 8 CAN AN INJURED SPINAL CORD BE FIXED? Injuries to the spinal cord disrupt communication between the central nervous system (brain and spinal cord) and the rest of the body
NERVOUS SYSTEM C H A P T E R 2 8 CAN AN INJURED SPINAL CORD BE FIXED? Injuries to the spinal cord disrupt communication between the central nervous system (brain and spinal cord) and the rest of the body
Primary Functions. Monitor changes. Integrate input. Initiate a response. External / internal. Process, interpret, make decisions, store information
 NERVOUS SYSTEM Monitor changes External / internal Integrate input Primary Functions Process, interpret, make decisions, store information Initiate a response E.g., movement, hormone release, stimulate/inhibit
NERVOUS SYSTEM Monitor changes External / internal Integrate input Primary Functions Process, interpret, make decisions, store information Initiate a response E.g., movement, hormone release, stimulate/inhibit
COGNITIVE SCIENCE 107A. Sensory Physiology and the Thalamus. Jaime A. Pineda, Ph.D.
 COGNITIVE SCIENCE 107A Sensory Physiology and the Thalamus Jaime A. Pineda, Ph.D. Sensory Physiology Energies (light, sound, sensation, smell, taste) Pre neural apparatus (collects, filters, amplifies)
COGNITIVE SCIENCE 107A Sensory Physiology and the Thalamus Jaime A. Pineda, Ph.D. Sensory Physiology Energies (light, sound, sensation, smell, taste) Pre neural apparatus (collects, filters, amplifies)
The Nervous System. Overview. Phylogenetic Development
 The Nervous System Juliana Paz Bio 490 Dr. Smith May 20, 2010 Overview Irritability: The capacity of cells and the whole organism to respond in a characteristic fashion to stimuli. Specific responses for
The Nervous System Juliana Paz Bio 490 Dr. Smith May 20, 2010 Overview Irritability: The capacity of cells and the whole organism to respond in a characteristic fashion to stimuli. Specific responses for
Nervous System, Neuroanatomy, Neurotransmitters
 Nervous System, Neuroanatomy, Neurotransmitters Neurons Structure of neurons Soma Dendrites Spines Axon Myelin Nodes of Ranvier Neurons Structure of neurons Axon collaterals 1 Neurons Structure of neurons
Nervous System, Neuroanatomy, Neurotransmitters Neurons Structure of neurons Soma Dendrites Spines Axon Myelin Nodes of Ranvier Neurons Structure of neurons Axon collaterals 1 Neurons Structure of neurons
Nsci 2100: Human Neuroanatomy 2017 Examination 3
 Name KEY Lab Section Nsci 2100: Human Neuroanatomy 2017 Examination 3 On this page, write your name and lab section. On your bubble answer sheet, enter your name (last name, space, first name), internet
Name KEY Lab Section Nsci 2100: Human Neuroanatomy 2017 Examination 3 On this page, write your name and lab section. On your bubble answer sheet, enter your name (last name, space, first name), internet
Chapter 7. The Nervous System: Structure and Control of Movement
 Chapter 7 The Nervous System: Structure and Control of Movement Objectives Discuss the general organization of the nervous system Describe the structure & function of a nerve Draw and label the pathways
Chapter 7 The Nervous System: Structure and Control of Movement Objectives Discuss the general organization of the nervous system Describe the structure & function of a nerve Draw and label the pathways
The neurvous system senses, interprets, and responds to changes in the environment. Two types of cells makes this possible:
 NERVOUS SYSTEM The neurvous system senses, interprets, and responds to changes in the environment. Two types of cells makes this possible: the neuron and the supporting cells ("glial cells"). Neuron Neurons
NERVOUS SYSTEM The neurvous system senses, interprets, and responds to changes in the environment. Two types of cells makes this possible: the neuron and the supporting cells ("glial cells"). Neuron Neurons
Chapter 7. Objectives
 Chapter 7 The Nervous System: Structure and Control of Movement Objectives Discuss the general organization of the nervous system Describe the structure & function of a nerve Draw and label the pathways
Chapter 7 The Nervous System: Structure and Control of Movement Objectives Discuss the general organization of the nervous system Describe the structure & function of a nerve Draw and label the pathways
The Nervous System: Sensory and Motor Tracts of the Spinal Cord
 15 The Nervous System: Sensory and Motor Tracts of the Spinal Cord PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Steven Bassett Southeast Community College Lincoln, Nebraska Introduction Millions of sensory
15 The Nervous System: Sensory and Motor Tracts of the Spinal Cord PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Steven Bassett Southeast Community College Lincoln, Nebraska Introduction Millions of sensory
CISC 3250 Systems Neuroscience
 CISC 3250 Systems Neuroscience Levels of organization Central Nervous System 1m 10 11 neurons Neural systems and neuroanatomy Systems 10cm Networks 1mm Neurons 100μm 10 8 neurons Professor Daniel Leeds
CISC 3250 Systems Neuroscience Levels of organization Central Nervous System 1m 10 11 neurons Neural systems and neuroanatomy Systems 10cm Networks 1mm Neurons 100μm 10 8 neurons Professor Daniel Leeds
Medical Neuroscience Tutorial
 Pain Pathways Medical Neuroscience Tutorial Pain Pathways MAP TO NEUROSCIENCE CORE CONCEPTS 1 NCC1. The brain is the body's most complex organ. NCC3. Genetically determined circuits are the foundation
Pain Pathways Medical Neuroscience Tutorial Pain Pathways MAP TO NEUROSCIENCE CORE CONCEPTS 1 NCC1. The brain is the body's most complex organ. NCC3. Genetically determined circuits are the foundation
All questions below pertain to mandatory material: all slides, and mandatory homework (if any).
 ECOL 182 Spring 2008 Dr. Ferriere s lectures Lecture 6: Nervous system and brain Quiz Book reference: LIFE-The Science of Biology, 8 th Edition. http://bcs.whfreeman.com/thelifewire8e/ All questions below
ECOL 182 Spring 2008 Dr. Ferriere s lectures Lecture 6: Nervous system and brain Quiz Book reference: LIFE-The Science of Biology, 8 th Edition. http://bcs.whfreeman.com/thelifewire8e/ All questions below
Modules 4 & 6. The Biology of Mind
 Modules 4 & 6 The Biology of Mind 1 Neuron - 100 Billion - Communication System Glial cells Cell body (nucleus) Dendrites Axon Axon Terminals (terminal buttons) Synaptic cleft 3 4 Communication Within
Modules 4 & 6 The Biology of Mind 1 Neuron - 100 Billion - Communication System Glial cells Cell body (nucleus) Dendrites Axon Axon Terminals (terminal buttons) Synaptic cleft 3 4 Communication Within
Visualizing Psychology
 Visualizing Psychology by Siri Carpenter & Karen Huffman PowerPoint Lecture Notes Presentation Chapter 2: Neuroscience and Biological Foundations Siri Carpenter, Yale University Karen Huffman, Palomar
Visualizing Psychology by Siri Carpenter & Karen Huffman PowerPoint Lecture Notes Presentation Chapter 2: Neuroscience and Biological Foundations Siri Carpenter, Yale University Karen Huffman, Palomar
Function of the Nervous System
 Nervous System Function of the Nervous System Receive sensory information, interpret it, and send out appropriate commands to form a response Composed of neurons (functional unit of the nervous system)
Nervous System Function of the Nervous System Receive sensory information, interpret it, and send out appropriate commands to form a response Composed of neurons (functional unit of the nervous system)
TABLE OF CONTINENTS. PSYC1002 Notes. Neuroscience.2. Cognitive Processes Learning and Motivation. 37. Perception Mental Abilities..
 TABLE OF CONTINENTS Neuroscience.2 Cognitive Processes...21 Learning and Motivation. 37 Perception.....54 Mental Abilities.. 83 Abnormal Psychology....103 1 Topic 1: Neuroscience Outline 1. Gross anatomy
TABLE OF CONTINENTS Neuroscience.2 Cognitive Processes...21 Learning and Motivation. 37 Perception.....54 Mental Abilities.. 83 Abnormal Psychology....103 1 Topic 1: Neuroscience Outline 1. Gross anatomy
Chapter 14: Integration of Nervous System Functions I. Sensation.
 Chapter 14: Integration of Nervous System Functions I. Sensation A. General Organization 1. General senses have receptors a. The somatic senses provide information about & 1. Somatic senses include: a.
Chapter 14: Integration of Nervous System Functions I. Sensation A. General Organization 1. General senses have receptors a. The somatic senses provide information about & 1. Somatic senses include: a.
The Nervous System. Divisions of the Nervous System. Branches of the Autonomic Nervous System. Central versus Peripheral
 The Nervous System Divisions of the Nervous System Central versus Peripheral Central Brain and spinal cord Peripheral Everything else Somatic versus Autonomic Somatic Nerves serving conscious sensations
The Nervous System Divisions of the Nervous System Central versus Peripheral Central Brain and spinal cord Peripheral Everything else Somatic versus Autonomic Somatic Nerves serving conscious sensations
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY: ( Division B) Boyceville Invite Dec. 3, 2016 (50pts.)
 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY: ( Division B) Boyceville Invite Dec. 3, 2016 (50pts.) Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following statements
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY: ( Division B) Boyceville Invite Dec. 3, 2016 (50pts.) Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following statements
Chapter 3. Biological Processes
 Biological Processes Psychology, Fifth Edition, James S. Nairne What s It For? Biological Solutions Communicating internally Initiating and coordinating behavior Regulating growth and other internal functions
Biological Processes Psychology, Fifth Edition, James S. Nairne What s It For? Biological Solutions Communicating internally Initiating and coordinating behavior Regulating growth and other internal functions
Name: Period: Chapter 2 Reading Guide The Biology of Mind
 Name: Period: Chapter 2 Reading Guide The Biology of Mind The Nervous System (pp. 55-58) 1. What are nerves? 2. Complete the diagram below with definitions of each part of the nervous system. Nervous System
Name: Period: Chapter 2 Reading Guide The Biology of Mind The Nervous System (pp. 55-58) 1. What are nerves? 2. Complete the diagram below with definitions of each part of the nervous system. Nervous System
Vision II. Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota
 Vision II Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Ganglion Cells The axons of the retinal ganglion cells form the optic nerve and carry visual information into the brain. 2 Optic
Vision II Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Ganglion Cells The axons of the retinal ganglion cells form the optic nerve and carry visual information into the brain. 2 Optic
Psychology in Your Life
 Sarah Grison Todd Heatherton Michael Gazzaniga Psychology in Your Life SECOND EDITION Chapter 2 The Role of Biology in Psychology 1 2016 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. 2.1 How Do Our Nervous Systems Affect
Sarah Grison Todd Heatherton Michael Gazzaniga Psychology in Your Life SECOND EDITION Chapter 2 The Role of Biology in Psychology 1 2016 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. 2.1 How Do Our Nervous Systems Affect
Bio11 schedule. Chapter 13 and 14. The Nervous System. The Nervous System. Organization of Nervous Systems. Nerves. Nervous and Sensory Systems
 Bio11 schedule Lecture Nervous system and senses Lab Current events reports (10 pts) Urinalysis Lecture exam 2 Thursday Feb 24 Same format as before Study guide will be posted Your total points so far
Bio11 schedule Lecture Nervous system and senses Lab Current events reports (10 pts) Urinalysis Lecture exam 2 Thursday Feb 24 Same format as before Study guide will be posted Your total points so far
Neural Integration I: Sensory Pathways and the Somatic Nervous System
 15 Neural Integration I: Sensory Pathways and the Somatic Nervous System PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris An Introduction to Sensory Pathways and
15 Neural Integration I: Sensory Pathways and the Somatic Nervous System PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris An Introduction to Sensory Pathways and
Fig Copyright 2002 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings
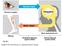 Fig. 48.1 Fig. 48.2 Axon endings are called synaptic terminals. They contain neurotransmitters which conduct a signal across a synapse. A synapse is the junction between a presynaptic and postsynaptic
Fig. 48.1 Fig. 48.2 Axon endings are called synaptic terminals. They contain neurotransmitters which conduct a signal across a synapse. A synapse is the junction between a presynaptic and postsynaptic
Chapter 16: Sensory, Motor, and Integrative Systems. Copyright 2009, John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
 Chapter 16: Sensory, Motor, and Integrative Systems Sensation n Conscious and subconscious awareness of changes in the external or internal environment. n Components of sensation: Stimulation of the sensory
Chapter 16: Sensory, Motor, and Integrative Systems Sensation n Conscious and subconscious awareness of changes in the external or internal environment. n Components of sensation: Stimulation of the sensory
Nervous System. 1. What N.S. division controls skeletal muscles? 3. What kind of neuroglia myelinates axons in the PNS?
 . What N.S. division controls skeletal muscles? Nervous System SRS Review %. Central nervous system %. Peripheral nervous system %. Afferent division %. Somatic division %. Autonomic division %. Sympathetic
. What N.S. division controls skeletal muscles? Nervous System SRS Review %. Central nervous system %. Peripheral nervous system %. Afferent division %. Somatic division %. Autonomic division %. Sympathetic
Warm-Up. Label the parts of the neuron below.
 Warm-Up Label the parts of the neuron below. A B C D E F G Warm-Up 1. One neuron transmits a nerve impulse at 40 m/s. Another conducts at the rate of 1 m/s. Which neuron has a myelinated axon? 2. List
Warm-Up Label the parts of the neuron below. A B C D E F G Warm-Up 1. One neuron transmits a nerve impulse at 40 m/s. Another conducts at the rate of 1 m/s. Which neuron has a myelinated axon? 2. List
E) A, B, and C Answer: D Topic: Concept 49.1 Skill: Knowledge/Comprehension
 Chapter 49 Nervous Systems Multiple-Choice Questions 1) Which of the following is (are) characteristic of a simple nervous system? A) a nerve net such as is found in cnidarians B) nerve cell ganglia C)
Chapter 49 Nervous Systems Multiple-Choice Questions 1) Which of the following is (are) characteristic of a simple nervous system? A) a nerve net such as is found in cnidarians B) nerve cell ganglia C)
[CHAPTER 12: THE NERVOUS SYSTEM] [ANSWER KEY]
![[CHAPTER 12: THE NERVOUS SYSTEM] [ANSWER KEY] [CHAPTER 12: THE NERVOUS SYSTEM] [ANSWER KEY]](/thumbs/71/65616244.jpg) WORDBANK: Cholinesterase Dopamine Axon Choroid layer Cochlea Incus Action Potential Cataract Cornea Astigmatism Dendrite Malleus Alzheimer s Disease Central Excitatory Response Fovea Centralis Acetylcholine
WORDBANK: Cholinesterase Dopamine Axon Choroid layer Cochlea Incus Action Potential Cataract Cornea Astigmatism Dendrite Malleus Alzheimer s Disease Central Excitatory Response Fovea Centralis Acetylcholine
PSYC& 100: Biological Psychology (Lilienfeld Chap 3) 1
 PSYC& 100: Biological Psychology (Lilienfeld Chap 3) 1 1 What is a neuron? 2 Name and describe the functions of the three main parts of the neuron. 3 What do glial cells do? 4 Describe the three basic
PSYC& 100: Biological Psychology (Lilienfeld Chap 3) 1 1 What is a neuron? 2 Name and describe the functions of the three main parts of the neuron. 3 What do glial cells do? 4 Describe the three basic
Overview of Brain Structures
 First Overview of Brain Structures Psychology 470 Introduction to Chemical Additions Steven E. Meier, Ph.D. All parts are interrelated. You need all parts to function normally. Neurons = Nerve cells Listen
First Overview of Brain Structures Psychology 470 Introduction to Chemical Additions Steven E. Meier, Ph.D. All parts are interrelated. You need all parts to function normally. Neurons = Nerve cells Listen
P215 Basic Human Physiology Summer 2003 Lecture Exam #2
 PLEASE BE AWARE CONTENT COVERED ON EXAMS VARIES FROM ONE SEMESTER TO ANOTHER. THIS EXAM MAY NOT CONTAIN MATERIAL THAT WILL BE ON YOUR EXAM THIS SEMESTER, AND/OR MAY CONTAIN MATERIAL THAT WILL NOT BE COVERED
PLEASE BE AWARE CONTENT COVERED ON EXAMS VARIES FROM ONE SEMESTER TO ANOTHER. THIS EXAM MAY NOT CONTAIN MATERIAL THAT WILL BE ON YOUR EXAM THIS SEMESTER, AND/OR MAY CONTAIN MATERIAL THAT WILL NOT BE COVERED
Cranial Nerves. Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota
 Cranial Nerves Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Course News Change in Lab Sequence Week of Oct 2 Lab 5 Week of Oct 9 Lab 4 2 Sensory and Motor Systems Sensory Systems:
Cranial Nerves Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Course News Change in Lab Sequence Week of Oct 2 Lab 5 Week of Oct 9 Lab 4 2 Sensory and Motor Systems Sensory Systems:
Biology. A Guide to the Natural World. Chapter 27 Lecture Outline Communication and Control 1: The Nervous System. Fifth Edition.
 Biology A Guide to the Natural World Chapter 27 Lecture Outline Communication and Control 1: The Nervous System Fifth Edition David Krogh The Nervous System Nervous tissue is composed of two kinds of cells:
Biology A Guide to the Natural World Chapter 27 Lecture Outline Communication and Control 1: The Nervous System Fifth Edition David Krogh The Nervous System Nervous tissue is composed of two kinds of cells:
Guide to Draw It to Know It Neuroanatomy (relative to Medical Neuro, UI-COM Urbana)
 Guide to Draw It to Know It Neuroanatomy (relative to Medical Neuro, UI-COM Urbana) Note: Sometimes DITKI goes into far more detail than is necessary for the course, and in other cases not enough. As helpful
Guide to Draw It to Know It Neuroanatomy (relative to Medical Neuro, UI-COM Urbana) Note: Sometimes DITKI goes into far more detail than is necessary for the course, and in other cases not enough. As helpful
Neural Basis of Motor Control. Chapter 4
 Neural Basis of Motor Control Chapter 4 Neurological Perspective A basic understanding of the physiology underlying the control of voluntary movement establishes a more comprehensive appreciation and awareness
Neural Basis of Motor Control Chapter 4 Neurological Perspective A basic understanding of the physiology underlying the control of voluntary movement establishes a more comprehensive appreciation and awareness
Sensory Systems Vision, Audition, Somatosensation, Gustation, & Olfaction
 Sensory Systems Vision, Audition, Somatosensation, Gustation, & Olfaction Sarah L. Chollar University of California, Riverside sarah.chollar@gmail.com Sensory Systems How the brain allows us to see, hear,
Sensory Systems Vision, Audition, Somatosensation, Gustation, & Olfaction Sarah L. Chollar University of California, Riverside sarah.chollar@gmail.com Sensory Systems How the brain allows us to see, hear,
Nervous System. Chapter Structure of the Nervous System. Neurons
 33.1 Structure of the Neurons Neurons are specialized nerve cells that help you gather information about your environment, interpret the information, and react to it. Neurons consist of three main regions:
33.1 Structure of the Neurons Neurons are specialized nerve cells that help you gather information about your environment, interpret the information, and react to it. Neurons consist of three main regions:
16. which is not synthesised in postganglionic sympathetic neurons a. L-dopa b. DA c. NA d. A e. ACh
 NERVOUS SYSTEM 1. Visual pathways a. Have P cells that are associated with colour b. Utilize the primary colours, red, yellow and blue c. Have simple cells which respond to all light stimuli d. Pass through
NERVOUS SYSTEM 1. Visual pathways a. Have P cells that are associated with colour b. Utilize the primary colours, red, yellow and blue c. Have simple cells which respond to all light stimuli d. Pass through
Okami Study Guide: Chapter 2 1
 Okami Study Guide: Chapter 2 1 Chapter Test 1. A cell that receives information and transmits it to other cells via an electrochemical process is called a(n) a. neuron b. hormone c. glia d. endorphin Answer:
Okami Study Guide: Chapter 2 1 Chapter Test 1. A cell that receives information and transmits it to other cells via an electrochemical process is called a(n) a. neuron b. hormone c. glia d. endorphin Answer:
Basic Neuroscience. Sally Curtis
 The Physiology of Pain Basic Neuroscience Sally Curtis sac3@soton.ac.uk The behaviour of humans is a result of the actions of nerves. Nerves form the basis of Thoughts, sensations and actions both reflex
The Physiology of Pain Basic Neuroscience Sally Curtis sac3@soton.ac.uk The behaviour of humans is a result of the actions of nerves. Nerves form the basis of Thoughts, sensations and actions both reflex
PART I. Neural Foundations of Behavior: The Basic Equipment
 Detailed Contents Preface xiii About the Author xvi chapter 1. What Is Biopsychology? 1 The Origins of Biopsychology 3 Prescientific Psychology and the Mind-Brain Problem 4 Descartes and the Physical Model
Detailed Contents Preface xiii About the Author xvi chapter 1. What Is Biopsychology? 1 The Origins of Biopsychology 3 Prescientific Psychology and the Mind-Brain Problem 4 Descartes and the Physical Model
Receptors and Neurotransmitters: It Sounds Greek to Me. Agenda. What We Know About Pain 9/7/2012
 Receptors and Neurotransmitters: It Sounds Greek to Me Cathy Carlson, PhD, RN Northern Illinois University Agenda We will be going through this lecture on basic pain physiology using analogies, mnemonics,
Receptors and Neurotransmitters: It Sounds Greek to Me Cathy Carlson, PhD, RN Northern Illinois University Agenda We will be going through this lecture on basic pain physiology using analogies, mnemonics,
What is the effect on the hair cell if the stereocilia are bent away from the kinocilium?
 CASE 44 A 53-year-old man presents to his primary care physician with complaints of feeling like the room is spinning, dizziness, decreased hearing, ringing in the ears, and fullness in both ears. He states
CASE 44 A 53-year-old man presents to his primary care physician with complaints of feeling like the room is spinning, dizziness, decreased hearing, ringing in the ears, and fullness in both ears. He states
Neurons, Synapses and Signaling. Chapter 48
 Neurons, Synapses and Signaling Chapter 48 Warm Up Exercise What types of cells can receive a nerve signal? Nervous Organization Neurons- nerve cells. Brain- organized into clusters of neurons, called
Neurons, Synapses and Signaling Chapter 48 Warm Up Exercise What types of cells can receive a nerve signal? Nervous Organization Neurons- nerve cells. Brain- organized into clusters of neurons, called
The Nervous System. Chapter 35: Biology II
 The Nervous System Chapter 35: Biology II Anatomy and Physiology Anatomy: the study of structure Physiology: The study of how living organisms function, including such processes as nutrition, movement,
The Nervous System Chapter 35: Biology II Anatomy and Physiology Anatomy: the study of structure Physiology: The study of how living organisms function, including such processes as nutrition, movement,
CSE 599E Lecture 2: Basic Neuroscience
 CSE 599E Lecture 2: Basic Neuroscience 1 Today s Roadmap The neuron doctrine (or dogma) Neuronal signaling The electrochemical dance of ions Action Potentials (= spikes) Synapses and Synaptic Plasticity
CSE 599E Lecture 2: Basic Neuroscience 1 Today s Roadmap The neuron doctrine (or dogma) Neuronal signaling The electrochemical dance of ions Action Potentials (= spikes) Synapses and Synaptic Plasticity
1. Processes nutrients and provides energy for the neuron to function; contains the cell's nucleus; also called the soma.
 1. Base of brainstem; controls heartbeat and breathing 2. tissue destruction; a brain lesion is a naturally or experimentally caused destruction of brain tissue 3. A thick band of axons that connects the
1. Base of brainstem; controls heartbeat and breathing 2. tissue destruction; a brain lesion is a naturally or experimentally caused destruction of brain tissue 3. A thick band of axons that connects the
The Nervous System. Anatomy of a Neuron
 The Nervous System Chapter 38.1-38.5 Anatomy of a Neuron I. Dendrites II. Cell Body III. Axon Synaptic terminal 1 Neuron Connections dendrites cell body terminal cell body cell body terminals dendrites
The Nervous System Chapter 38.1-38.5 Anatomy of a Neuron I. Dendrites II. Cell Body III. Axon Synaptic terminal 1 Neuron Connections dendrites cell body terminal cell body cell body terminals dendrites
Okami Study Guide: Chapter 2 1
 Okami Study Guide: Chapter 2 1 Chapter in Review 1. The human nervous system is a complex biological system designed for nearly instantaneous communication among billions of neurons throughout the body.
Okami Study Guide: Chapter 2 1 Chapter in Review 1. The human nervous system is a complex biological system designed for nearly instantaneous communication among billions of neurons throughout the body.
THE CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM. The Brain & Spinal Cord
 THE CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM The Brain & Spinal Cord Review: Nervous System Parallel Distributed Processing Composition of the CNS Nuclei: Clusters of neurons in the CNS ( neighborhoods ) Fiber Tracts/Pathways:
THE CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM The Brain & Spinal Cord Review: Nervous System Parallel Distributed Processing Composition of the CNS Nuclei: Clusters of neurons in the CNS ( neighborhoods ) Fiber Tracts/Pathways:
Organization of the nervous system. [See Fig. 48.1]
![Organization of the nervous system. [See Fig. 48.1] Organization of the nervous system. [See Fig. 48.1]](/thumbs/90/103926552.jpg) Nervous System [Note: This is the text version of this lecture file. To make the lecture notes downloadable over a slow connection (e.g. modem) the figures have been replaced with figure numbers as found
Nervous System [Note: This is the text version of this lecture file. To make the lecture notes downloadable over a slow connection (e.g. modem) the figures have been replaced with figure numbers as found
NEURAL TISSUE (NEUROPHYSIOLOGY) PART I (A): NEURONS & NEUROGLIA
 PART I (A): NEURONS & NEUROGLIA Neural Tissue Contains 2 kinds of cells: neurons: cells that send and receive signals neuroglia (glial cells): cells that support and protect neurons Neuron Types Sensory
PART I (A): NEURONS & NEUROGLIA Neural Tissue Contains 2 kinds of cells: neurons: cells that send and receive signals neuroglia (glial cells): cells that support and protect neurons Neuron Types Sensory
Biology 105 Midterm Exam 3 Review Sheet
 Biology 105 Midterm Exam 3 Review Sheet The third midterm exam will cover the following lecture material (lectures 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, and 13): Skeletal System (from chapter 5 in the textbook), Nervous System
Biology 105 Midterm Exam 3 Review Sheet The third midterm exam will cover the following lecture material (lectures 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, and 13): Skeletal System (from chapter 5 in the textbook), Nervous System
The Central Nervous System I. Chapter 12
 The Central Nervous System I Chapter 12 The Central Nervous System The Brain and Spinal Cord Contained within the Axial Skeleton Brain Regions and Organization Medical Scheme (4 regions) 1. Cerebral Hemispheres
The Central Nervous System I Chapter 12 The Central Nervous System The Brain and Spinal Cord Contained within the Axial Skeleton Brain Regions and Organization Medical Scheme (4 regions) 1. Cerebral Hemispheres
The Nervous System. Biological School. Neuroanatomy. How does a Neuron fire? Acetylcholine (ACH) TYPES OF NEUROTRANSMITTERS
 Biological School The Nervous System It is all about the body!!!! It starts with an individual nerve cell called a NEURON. Synapse Neuroanatomy Neurotransmitters (chemicals held in terminal buttons that
Biological School The Nervous System It is all about the body!!!! It starts with an individual nerve cell called a NEURON. Synapse Neuroanatomy Neurotransmitters (chemicals held in terminal buttons that
Chapter 28 Nervous Systems
 Chapter 28 Nervous Systems PowerPoint Lectures for Biology: Concepts & Connections, Sixth Edition Campbell, Reece, Taylor, Simon, and Dickey Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Lecture by Edward J.
Chapter 28 Nervous Systems PowerPoint Lectures for Biology: Concepts & Connections, Sixth Edition Campbell, Reece, Taylor, Simon, and Dickey Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Lecture by Edward J.
Nervous System C H A P T E R 2
 Nervous System C H A P T E R 2 Input Output Neuron 3 Nerve cell Allows information to travel throughout the body to various destinations Receptive Segment Cell Body Dendrites: receive message Myelin sheath
Nervous System C H A P T E R 2 Input Output Neuron 3 Nerve cell Allows information to travel throughout the body to various destinations Receptive Segment Cell Body Dendrites: receive message Myelin sheath
Biology 3201 The Nervous System Test
 Biology 3201 The Nervous System Test 1. The central nervous system consists of: a. Nerves and neurons c. spinal chord and nerves b. brain and neurons d. brain and spinal chord 2. This part of the brain
Biology 3201 The Nervous System Test 1. The central nervous system consists of: a. Nerves and neurons c. spinal chord and nerves b. brain and neurons d. brain and spinal chord 2. This part of the brain
NERVOUS SYSTEM MODULE. Academic Year Study Guide
 NERVOUS SYSTEM MODULE Academic Year 2004-2005 Study Guide CNS Objectives At the end of this course, students should recognize the followings: 1. Histological structure of the brain meninges and the supporting
NERVOUS SYSTEM MODULE Academic Year 2004-2005 Study Guide CNS Objectives At the end of this course, students should recognize the followings: 1. Histological structure of the brain meninges and the supporting
Nervous System - PNS and CNS. Bio 105
 Nervous System - PNS and CNS Bio 105 Outline I. Central Nervous System vs Peripheral Nervous System II. Peripheral Nervous System A. Autonomic Nervous Systems B. Somatic Nervous Systems III. Autonomic
Nervous System - PNS and CNS Bio 105 Outline I. Central Nervous System vs Peripheral Nervous System II. Peripheral Nervous System A. Autonomic Nervous Systems B. Somatic Nervous Systems III. Autonomic
PSYCH 260 Exam 2. March 2, Answer the questions using the Scantron form. Name:
 PSYCH 260 Exam 2 March 2, 2017 Answer the questions using the Scantron form. Name: 1 1 Main Please put in their proper order the steps that lead to synaptic communication between neurons. Begin with the
PSYCH 260 Exam 2 March 2, 2017 Answer the questions using the Scantron form. Name: 1 1 Main Please put in their proper order the steps that lead to synaptic communication between neurons. Begin with the
3/15/17. Outline. Nervous System - PNS and CNS. Two Parts of the Nervous System
 Nervous System - PNS and CNS Bio 105 Outline I. Central Nervous System vs Peripheral Nervous System II. Peripheral Nervous System A. Autonomic Nervous Systems B. Somatic Nervous Systems III. Autonomic
Nervous System - PNS and CNS Bio 105 Outline I. Central Nervous System vs Peripheral Nervous System II. Peripheral Nervous System A. Autonomic Nervous Systems B. Somatic Nervous Systems III. Autonomic
Chapter 6. Gathering information; the sensory systems
 Chapter 6 Gathering information; the sensory systems Gathering information the sensory systems The parts of the nervous system that receive and process information are termed sensory systems. There are
Chapter 6 Gathering information; the sensory systems Gathering information the sensory systems The parts of the nervous system that receive and process information are termed sensory systems. There are
Chapter 2 The Brain or Bio Psychology
 Chapter 2 The Brain or Bio Psychology 1 2 3 1 Glial Cells Surround neurons and hold them in place Make Myelin (covering for neurons) Manufacture nutrient chemicals neurons need Absorb toxins and waste
Chapter 2 The Brain or Bio Psychology 1 2 3 1 Glial Cells Surround neurons and hold them in place Make Myelin (covering for neurons) Manufacture nutrient chemicals neurons need Absorb toxins and waste
2. When a neuron receives signals, an abrupt, temporary the inside becomes more positive in the polarity is generated (an action potential).
 Chapter 34 Integration and Control: Nervous Systems I. Neurons The Communication Specialists A. Functional Zones of a Neuron 1. The contains the nucleus and metabolic machinery for protein synthesis. 2.
Chapter 34 Integration and Control: Nervous Systems I. Neurons The Communication Specialists A. Functional Zones of a Neuron 1. The contains the nucleus and metabolic machinery for protein synthesis. 2.
CNS MCQ 2 nd term. Select the best answer:
 Select the best answer: CNS MCQ 2 nd term 1) Vestibular apparatus: a) Represent the auditory part of the labyrinth. b) May help in initiating the voluntary movements. c) Contains receptors concerned with
Select the best answer: CNS MCQ 2 nd term 1) Vestibular apparatus: a) Represent the auditory part of the labyrinth. b) May help in initiating the voluntary movements. c) Contains receptors concerned with
CNS composed of: Grey matter Unmyelinated axons Dendrites and cell bodies White matter Myelinated axon tracts
 CNS composed of: Grey matter Unmyelinated axons Dendrites and cell bodies White matter Myelinated axon tracts The Brain: A Quick Tour Frontal Lobe Control of skeletal muscles Personality Concentration
CNS composed of: Grey matter Unmyelinated axons Dendrites and cell bodies White matter Myelinated axon tracts The Brain: A Quick Tour Frontal Lobe Control of skeletal muscles Personality Concentration
Biology 218 Human Anatomy
 Chapter 17 Adapted form Tortora 10 th ed. LECTURE OUTLINE A. Overview of the Nervous System (p. 537) 1. The nervous system and the endocrine system are the body s major control and integrating centers.
Chapter 17 Adapted form Tortora 10 th ed. LECTURE OUTLINE A. Overview of the Nervous System (p. 537) 1. The nervous system and the endocrine system are the body s major control and integrating centers.
ACTIVITY2.15 Text:Campbell,v.8,chapter48 DATE HOUR NERVOUS SYSTEMS NEURON
 AP BIOLOGY ACTIVITY2.15 Text:Campbell,v.8,chapter48 NAME DATE HOUR NERVOUS SYSTEMS NEURON SIMPLE REFLEX RESTING POTENTIAL ACTION POTENTIAL ACTION POTENTIAL GRAPH TRANSMISSION ACROSS A SYNAPSE QUESTIONS:
AP BIOLOGY ACTIVITY2.15 Text:Campbell,v.8,chapter48 NAME DATE HOUR NERVOUS SYSTEMS NEURON SIMPLE REFLEX RESTING POTENTIAL ACTION POTENTIAL ACTION POTENTIAL GRAPH TRANSMISSION ACROSS A SYNAPSE QUESTIONS:
Chapter 9. Nervous System
 Chapter 9 Nervous System Central Nervous System (CNS) vs. Peripheral Nervous System(PNS) CNS Brain Spinal cord PNS Peripheral nerves connecting CNS to the body Cranial nerves Spinal nerves Neurons transmit
Chapter 9 Nervous System Central Nervous System (CNS) vs. Peripheral Nervous System(PNS) CNS Brain Spinal cord PNS Peripheral nerves connecting CNS to the body Cranial nerves Spinal nerves Neurons transmit
Guided Reading Activities
 Name Period Chapter 28: Nervous Systems Guided Reading Activities Big idea: Nervous system structure and function Answer the following questions as you read modules 28.1 28.2: 1. Your taste receptors for
Name Period Chapter 28: Nervous Systems Guided Reading Activities Big idea: Nervous system structure and function Answer the following questions as you read modules 28.1 28.2: 1. Your taste receptors for
Acetylcholine (ACh) Action potential. Agonists. Drugs that enhance the actions of neurotransmitters.
 Acetylcholine (ACh) The neurotransmitter responsible for motor control at the junction between nerves and muscles; also involved in mental processes such as learning, memory, sleeping, and dreaming. (See
Acetylcholine (ACh) The neurotransmitter responsible for motor control at the junction between nerves and muscles; also involved in mental processes such as learning, memory, sleeping, and dreaming. (See
Nervous System. Master controlling and communicating system of the body. Secrete chemicals called neurotransmitters
 Nervous System Master controlling and communicating system of the body Interacts with the endocrine system to control and coordinate the body s responses to changes in its environment, as well as growth,
Nervous System Master controlling and communicating system of the body Interacts with the endocrine system to control and coordinate the body s responses to changes in its environment, as well as growth,
BIOLOGICAL PSYCHOLOGY I (2012) MIDTERM EXAM 2
 BIOLOGICAL PSYCHOLOGY I (2012) MIDTERM EXAM 2 Mark the ONE BEST letter choice (either A, B, C, D, or E) on the computer-graded sheet in NUMBER TWO PENCIL. If you need to erase, do so completely! You MUST
BIOLOGICAL PSYCHOLOGY I (2012) MIDTERM EXAM 2 Mark the ONE BEST letter choice (either A, B, C, D, or E) on the computer-graded sheet in NUMBER TWO PENCIL. If you need to erase, do so completely! You MUST
3) Most of the organelles in a neuron are located in the A) dendritic region. B) axon hillock. C) axon. D) cell body. E) axon terminals.
 Chapter 48 Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling Multiple-Choice Questions 1) A simple nervous system A) must include chemical senses, mechanoreception, and vision. B) includes a minimum of 12 ganglia. C) has
Chapter 48 Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling Multiple-Choice Questions 1) A simple nervous system A) must include chemical senses, mechanoreception, and vision. B) includes a minimum of 12 ganglia. C) has
Systems Neuroscience Dan Kiper. Today: Wolfger von der Behrens
 Systems Neuroscience Dan Kiper Today: Wolfger von der Behrens wolfger@ini.ethz.ch 18.9.2018 Neurons Pyramidal neuron by Santiago Ramón y Cajal (1852-1934, Nobel prize with Camillo Golgi in 1906) Neurons
Systems Neuroscience Dan Kiper Today: Wolfger von der Behrens wolfger@ini.ethz.ch 18.9.2018 Neurons Pyramidal neuron by Santiago Ramón y Cajal (1852-1934, Nobel prize with Camillo Golgi in 1906) Neurons
