Molecular Mechanisms in Inflammasome Signalling: From NLRP1 to Pyroptosis. Sebastian Hiller
|
|
|
- Jonah Hopkins
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Molecular Mechanisms in Inflammasome Signalling: From NLRP1 to Pyroptosis Sebastian Hiller
2 How do host cells detect pathogens?
3 The inflammasome: a caspase-1 activation platform
4 Inflammasome receptors: modular sensors
5 Latz et al. Nat Rev Immunol 2013, Broz and Dixit Nat Rev Immunol 2016 Canonical Inflammasomes
6 Inflammasomes in health and disease Host defense Genetic disorders Sterile inflammation Bacteria, viruses, fungi, parasites Gain-of-function mutations in NLRP3, NLRC4, PYRIN,.. Gout, Infl. Bowel disease, Asbestosis, Type-II-diabetes,.. Inflammasomes Inflammasomes Beneficial Inflammation (Auto)-inflammatory disease Understanding the basic mechanisms of inflammasome signaling can have an impact on the development of therapies for both infectious as well as (auto)-inflammatory diseases
7 High-resolution methods in structural biology NMR spectroscopy X-ray crystallography cryo-electron microscopy atomic force microscopy
8 Atomic structure of the ASC inflammasome filament
9 Structures of death domains human NLRP1 PYD: human full-length ASC: Hiller et al., Structure 11, 1199 (2003) De Alba, JBC 284, (2009)
10 The ASC-PYD is sufficient to form filaments in cells ATP DNA (AIM2) Scale bars: 10 µm Dick et al., Nat. Comm. (2016)
11 Solid-state NMR spectroscopy of ASC filaments
12 ASC-PYD filament: Sequence-specific resonance assignments Ravotti et al., Biomol. NMR Assign. (2015)
13 Cryo-Electron microscopy of ASC-PYD filament Recorded on Titan Krios with direct electron detector C3 symmetry with 53 right-handed rotation and 14 Å rise
14 Protocol for hybrid structure determination cryo-em solid state NMR alternative protocols: Lange, Sgourakis, Habeck et al.
15 Structure of the mouse ASC PYD filament Sborgi et al., PNAS 112, (2015)
16 Helical filaments in immune signalling MyD88 MAVS CARD Lin et al., Nature 2010; Qiao et al., Mol Cell 2013 Xu et al., elife 2014 solid-state NMR structure: He et al., PNAS 2016 human ASC-PYD mouse (blue) vs. human (green) ASC-PYD Lu et al., Cell 2014
17 Chemical shift differences validate interfaces
18 Structure of the ASC PYD filament
19 Structure-based mutagenesis I N PYD PYD Y59A PYD K21A PYD E80R 0.2 PYD PYD Y59A PYD E80R PYD K21A t [min.]
20 Solid-state NMR: ASC-CARD is flexibly unfolded INEPT INEPT
21 Model for inflammasome assembly
22 Molecular mechanism of a genetic skin disease
23 MSPC and FKLC: Genetic skin diseases MSPC-TN-1 IV:11 MSPC-TN-1 IV:15 MSPC-TN-1 IV:20 MSPC-TN-1 IV:2 MSPC-FR-1 III:2 MSPC-TN-1 IV:20 FKLC-EG-1 V:3 MSPC-RO-1 III:3 MSPC-FR-1 III:2 FKLC-EG-1 V:5 FKLC-EG-1 V:3 MSPC: multiple self-healing palmoplantar carcinoma FKLC: familial keratosis lichenoides chronica Zhong et al. Cell 2016
24 MSPC and FKLC are heritable MSPC-TN-1 I:1 I:2 II:1 II:2 II:3 II:4 II:5 II:6 II:7 II:8 II:9 II:10 II:11 III:1 III:2 III:3 III:4 III:5 III:6 III:7 III:8 III:9 III:10 III:11 III:12 III:13 III:14 III:15 III:16 IV:1 IV:2 IV:3 IV:4 IV:5 IV:6 IV:7 IV:8 IV:9IV:10 IV:11IV:12 IV:13 IV:14 IV:15 IV:16IV:17 IV:18 IV:19 IV:20 IV:21 V:1 V:2 V:3 V:4 V:5 MSPC-RO-1 MSPC-FR-1 FKLC-EG-1 I:1 I:2 I:1 I:2 I:3 I:4 I:1 I:2 II:1 II:2 II:3 II:4 II:5 II:6 II:7 II:1 II:2 II:1 II:2 II:3 II:4 III:1 III:2 III:3 III:4 III:5 III:6 III:7 III:8 III:9 III:10 III:11 III:12 III:13 III:1 III:2 III:1 III:2 III:3 III:4 III:5 III:6 III:8 IV:1 IV:1 IV:2 IV:3 IV:4 IV:5 IV:6 V:1 V:2 V:3 V:4 V:5 V:6 V:7 MSPC: multiple self-healing palmoplantar carcinoma FKLC: familial keratosis lichenoides chronica
25 MSPC and FKLC locate to NLRP1 Chr.17p13.2: 5,417,438-5,487,832 NLRP1 Exon NLRP1 1 PYD NACHT LRR FIIND CARD 1474 p.f787_r843del FKLC-EG-1 Human 1-MAGGAWGRLACYLEFLKKEELKEFQLLLANKAHSRSSSGETPAQPEKTSGMEVASYLVAQYGEQRAWDLALHTWEQMGLRSLCAQAQEGAGH RA W QM G -92 Chimpanzee 1-MAGGAWGRLACYLEFLKKEELKEFQLLLANKAHSRSSSGETPAQPEKTSGMEVASYLVAQYGEQRAWDLALHTWEQMGLRSLCTQAQEGAGH RA W QM G -92 Macaque 1-MAGGAWGRLACYLELLKKEELKEFQLLFASKVHSSGSSGETPARPEKTSGMEVASYLVAQYGEQRAWDLALRTWEQMGLWSLCTQAREGAGY VA RA W QM G -92 Marmoset 1-MAGGAWGRLACYLELLEKEELKKFQFLLTNKVHSRGSSGETPAQPEKTSGMQVASHLVAQYGEQQAWDLAIHIWEQMGLRSLCAQAQEEAGH VA QA W QM G -92 Gibbon 1-MAGGAWGRLACYLEFLKKEELKEFQLLLANKAHSRSSSGETPTQPEKTSGMEVASYLVAQYGEQRAWDLALHTWEQMGLRSLCAQAQEGAGH RA W QM G -92 Horse 1-MAGGAELQWPWYLESREKKEPKEFQLRLPD-AHSRHSPGETVAQV-EASGPEVASRLVALYGQRQAWDLALLTQRRMDLSRVSIQAHREAAS V QA W RM D -90 Dog 1-MACRVQWQLAWYLEMMGKEELKEFQLRLLEQQFWGDPPHALRAQLGKARGLEVASRLVAQYGEQQAWVLALRTWEEMGLSRLCAQSRAEAGL VA QA W EMG -92 conservation **. : *** *:* *:**: :.. :: :: * :*** *****:::** **:.. * * :. *:: *. p.a54t MSPC-TN-1 p.a66v MSPC-RO-1 p.m77t MSPC-FR-1 MSPC: multiple self-healing palmoplantar carcinoma FKLC: familial keratosis lichenoides chronica
26 NLRP1 is the predominant NLR in human skin **** NLRP1 NLRP3 RNAscope: dapb RNAscope: NLRP1 FKPM AIM2 NLRC4 MEFV hair-bearing skin IHC: no primary Ab IHC: NLRP1 Skin Bone marrow Spleen NLRP1 NLRP3 MEFV AIM2 NLRC4 fibroblasts melanocytes keratinocytes PBMCs Primary human cells Inflammasome sensors CASP1 ASC IL1B IL18 KRT14 GAPDH fibroblasts melanocytes keratinocytes PBMCs Inflammasome effectors and substrates plantar skin IHC: no primary Ab IHC: NLRP1 50 μm
27 MSPC mutations increase NLRP1 activity 293T-ASC-GFP 80 ** DAPI ASC-GFP DAPI ASC-GFP 60 NLRP1 mutants (this study) vector NLRP1 WT NLRP1 A54T NLRP1 M77T NLRP1 A66V NLRP1 F787_R843del 20 μm % cells with ASC specks ** Vector WT R8H n.s NLRP1 SNPs (1000 Genome) N30D A32V R35G S36R T41A P42T A43T T48M S49G S55L E63K Q64H A84T A86T E88K A54T M77T A66V F787_R843del
28 MSPC mutations unfold PYD domain of NLRP1 NLRP1 PYD domain Unfolded PYD leads to Nlrp1 activation Nlrp1 PYD plays inhibitory function Zhong et al. Cell 2016
29 NLRP1 signals via its CARD domain Zhong et al. Cell 2016
30 Human NLRP1: Model of autoinhibition Zhong et al. Cell 2016
31 Molecular mechanism of pyroptotic cell death
32 Gasdermin-D is essential for pyroptosis induction GSDMD is required for both caspase-1- and caspase-11-induced pyroptosis Caspase-mediated processing of GSDMD into a N- and C-terminal fragment is essential The N-terminal domain harbors the cytotoxic activity Salmonella infection (NLRC4 inflammasome) Kayagaki et al. Nature (2015), Shi et al. Nature (2015)
33 The GSDMD protein family N 30 kda C 53 kda protein, consisting of two domains (GSDMD Nterm and GSDMD Cterm ) Expressed in the gastrointestinal tract and the dermis Belongs to the ill-characterized gasdermin protein family (6 human / 10 murine members) All members share a similar N-terminal domain GSDMD CTERM mouse human mouse GSDMA3 Ding et al. Nature (2016)
34 GSDMD Nterm targets cellular membranes GSDMD VDAC (mitochondria) HDAC (nucleus) Na+K+ ATPase (plasma membrane) GAPDH (cytosol) Subcellular fractionation of macrophages left uninfected (NS) or infected with S. typhimurium Sborgi et al. EMBO J. 2016
35 GSDMD Nterm targets liposomes in vitro GSDMD Nterm targets liposomes after in vitro cleavage GSDMD FL GSDMD Nterm GSDMD Cterm Sborgi et al. EMBO J. 2016
36 GSDMD Nterm lyses liposomes in vitro GSDMD Nterm induces dye release from liposomes (6-carboxifluorescein, self-quenching) nm GSDMD + 5 nm Casp1 Sborgi et al. EMBO J. 2016
37 Cryo-Electron Microscopy of GSDMD pores in liposomes untreated GSDMD GSDMD + Casp1 (0 ) GSDMD + Casp1 (30 ) GSDMD + Casp1 (60 ) Sborgi et al. EMBO J. 2016
38 Atomic force microscopy analysis of GSDMD pores Pore formation by GSDMD Nterm is the effector mechanism of pyroptosis Sborgi et al. EMBO J. 2016
39 Mechanism of pyroptotic cell death
40 Acknowledgements Lorenzo Sborgi Adam Mazur Joka Pipercevic Petr Broz Mathias Dick Sebastian Rühl Henning Stahlberg Venkat Dandey Timm Maier Daniel Müller Estefania Mulvihill Beat Meier Francesco Ravotti Anja Böckmann Bruno Reversade Franklin Zhong Ed Egelman Chris Farady
Type of file: PDF Title of file for HTML: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures
 Type of file: PDF Title of file for HTML: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures Type of file: MOV Title of file for HTML: Supplementary Movie 1 Description: NLRP3 is moving along
Type of file: PDF Title of file for HTML: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures Type of file: MOV Title of file for HTML: Supplementary Movie 1 Description: NLRP3 is moving along
Innate immunity. Abul K. Abbas University of California San Francisco. FOCiS
 1 Innate immunity Abul K. Abbas University of California San Francisco FOCiS 2 Lecture outline Components of innate immunity Recognition of microbes and dead cells Toll Like Receptors NOD Like Receptors/Inflammasome
1 Innate immunity Abul K. Abbas University of California San Francisco FOCiS 2 Lecture outline Components of innate immunity Recognition of microbes and dead cells Toll Like Receptors NOD Like Receptors/Inflammasome
A Yersinia-Secreted Effector Protein Promotes Virulence by Preventing Inflammasome Recognition of the Type III Secretion System
 Cell Host & Microbe, Volume 7 Supplemental Information A Yersinia-Secreted Effector Protein Promotes Virulence by Preventing Inflammasome Recognition of the Type III Secretion System Igor E. Brodsky, Noah
Cell Host & Microbe, Volume 7 Supplemental Information A Yersinia-Secreted Effector Protein Promotes Virulence by Preventing Inflammasome Recognition of the Type III Secretion System Igor E. Brodsky, Noah
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature11429 S1a 6 7 8 9 Nlrc4 allele S1b Nlrc4 +/+ Nlrc4 +/F Nlrc4 F/F 9 Targeting construct 422 bp 273 bp FRT-neo-gb-PGK-FRT 3x.STOP S1c Nlrc4 +/+ Nlrc4 F/F casp1
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature11429 S1a 6 7 8 9 Nlrc4 allele S1b Nlrc4 +/+ Nlrc4 +/F Nlrc4 F/F 9 Targeting construct 422 bp 273 bp FRT-neo-gb-PGK-FRT 3x.STOP S1c Nlrc4 +/+ Nlrc4 F/F casp1
Journal club. Lama Nazzal
 Journal club Lama Nazzal Background Kidney stone disease affects about 12% of men and 5% of women during their lifetimes in the United States Intrarenal nephrocalcinosis is often asymptomatic, but can
Journal club Lama Nazzal Background Kidney stone disease affects about 12% of men and 5% of women during their lifetimes in the United States Intrarenal nephrocalcinosis is often asymptomatic, but can
2. Innate immunity 2013
 1 Innate Immune Responses 3 Innate immunity Abul K. Abbas University of California San Francisco The initial responses to: 1. Microbes: essential early mechanisms to prevent, control, or eliminate infection;
1 Innate Immune Responses 3 Innate immunity Abul K. Abbas University of California San Francisco The initial responses to: 1. Microbes: essential early mechanisms to prevent, control, or eliminate infection;
Understanding the Role of the Inflammasome in Inflammation
 Understanding the Role of the Inflammasome in Inflammation Martha O Brien, Ph.D. Assay Design Group 215 Innate Immune Response in Inflammation LPS flagellin TLR-1/2/6 TLR-4 TLR-5 Adaptor proteins PAMPs,
Understanding the Role of the Inflammasome in Inflammation Martha O Brien, Ph.D. Assay Design Group 215 Innate Immune Response in Inflammation LPS flagellin TLR-1/2/6 TLR-4 TLR-5 Adaptor proteins PAMPs,
The oxidized phospholipid oxpapc protects from septic shock by targeting the non-canonical inflammasome in macrophages
 ARTICLE DOI: 1.138/s41467-18-39-3 OPEN The oxidized phospholipid protects from septic shock by targeting the non-canonical inflammasome in macrophages Lan H. Chu 1,2, Mohanalaxmi Indramohan 1, Rojo A.
ARTICLE DOI: 1.138/s41467-18-39-3 OPEN The oxidized phospholipid protects from septic shock by targeting the non-canonical inflammasome in macrophages Lan H. Chu 1,2, Mohanalaxmi Indramohan 1, Rojo A.
Gout and Nucleic Acid Metabolism Vol.33 No
 Gout and Nucleic Acid Metabolism Vol.33 No.1 2009 1 1 2 3 in vitro 14 IgM 1 IgM IgM 1 PAMPs Pattern recognition receptors PRRs PRRs PRRs PAMPs Toll Toll-like receptor TLR PAMPs Nod Nod-like receptor NLR
Gout and Nucleic Acid Metabolism Vol.33 No.1 2009 1 1 2 3 in vitro 14 IgM 1 IgM IgM 1 PAMPs Pattern recognition receptors PRRs PRRs PRRs PAMPs Toll Toll-like receptor TLR PAMPs Nod Nod-like receptor NLR
3rd International Conference on Neurology & Therapeutics.
 3rd International Conference on Neurology & Therapeutics www.neuroimmunology.ca Multiple sclerosis is a devastating disease The first description of the disease was mentioned in 14th century In 1838 Dr.
3rd International Conference on Neurology & Therapeutics www.neuroimmunology.ca Multiple sclerosis is a devastating disease The first description of the disease was mentioned in 14th century In 1838 Dr.
Integrated Innate Immunity Combining Activation and Effector Functions
 Section 4 Integrated Innate Immunity Combining Activation and Effector Functions 4.1 THE DETECTION OF BACTERIAL LIPOPOLYSACCHARIDE LPS is one of the most potent immune stimuli known. It is found in the
Section 4 Integrated Innate Immunity Combining Activation and Effector Functions 4.1 THE DETECTION OF BACTERIAL LIPOPOLYSACCHARIDE LPS is one of the most potent immune stimuli known. It is found in the
Role of Innate Immunity in Control of Adaptive Immunity
 Role of Innate Immunity in Control of Adaptive Immunity Innate Immunity The burden of pathogen sensing is placed on the innate immune system Danger hypothesis Missing Self Based on the detection of molecular
Role of Innate Immunity in Control of Adaptive Immunity Innate Immunity The burden of pathogen sensing is placed on the innate immune system Danger hypothesis Missing Self Based on the detection of molecular
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Bauer et al. 10.1073/pnas.1610421113 SI Materials and Methods Immunofluorescence experiments were performed as described (8). Briefly, NUGC-3 cells were treated with 25 μm PK11007
Supporting Information Bauer et al. 10.1073/pnas.1610421113 SI Materials and Methods Immunofluorescence experiments were performed as described (8). Briefly, NUGC-3 cells were treated with 25 μm PK11007
Structure-function analysis of Nlrp1b reveals a link. between metabolism and inflammation: energy stress. triggers inflammasome activation
 Structure-function analysis of Nlrp1b reveals a link between metabolism and inflammation: energy stress triggers inflammasome activation by Kuo-Chieh Liao A thesis submitted in conformity with the requirements
Structure-function analysis of Nlrp1b reveals a link between metabolism and inflammation: energy stress triggers inflammasome activation by Kuo-Chieh Liao A thesis submitted in conformity with the requirements
Innate Immunity: (I) Molecules & (II) Cells
 Innate Immunity: (I) Molecules & (II) Cells Stephanie Eisenbarth, M.D., Ph.D. FOCIS Advanced Course 2/19/18 Department of Laboratory Medicine Yale School of Medicine Department of Immunobiology Yale School
Innate Immunity: (I) Molecules & (II) Cells Stephanie Eisenbarth, M.D., Ph.D. FOCIS Advanced Course 2/19/18 Department of Laboratory Medicine Yale School of Medicine Department of Immunobiology Yale School
Diabetes and Inflammasomes in the Bladder
 Diabetes and Inflammasomes in the Bladder J Todd Purves MD, PhD Duke University Medical Center Division of Urology Disclosures: None Introduction Diabetic Bladder Dysfunction (DBD) is the most common
Diabetes and Inflammasomes in the Bladder J Todd Purves MD, PhD Duke University Medical Center Division of Urology Disclosures: None Introduction Diabetic Bladder Dysfunction (DBD) is the most common
modified dye uptake assay including formazan test EC 90 not tested plaque reduction assay
 Sauerbrei A, Bohn-Wippert K, Kaspar M, Krumbholz A, Karrasch M, Zell R. 2015. Database on natural polymorphisms and resistance-related non-synonymous mutations in thymidine kinase and DNA polymerase genes
Sauerbrei A, Bohn-Wippert K, Kaspar M, Krumbholz A, Karrasch M, Zell R. 2015. Database on natural polymorphisms and resistance-related non-synonymous mutations in thymidine kinase and DNA polymerase genes
Lecture on Innate Immunity and Inflammation
 Lecture on Innate Immunity and Inflammation Evolutionary View Epithelial barriers to infection Four main types of innate recognition molecules:tlrs, CLRs, NLRs, RLRs NF-κB, the master transcriptional regulator
Lecture on Innate Immunity and Inflammation Evolutionary View Epithelial barriers to infection Four main types of innate recognition molecules:tlrs, CLRs, NLRs, RLRs NF-κB, the master transcriptional regulator
Innate Immunity & Inflammation
 Innate Immunity & Inflammation The innate immune system is an evolutionally conserved mechanism that provides an early and effective response against invading microbial pathogens. It relies on a limited
Innate Immunity & Inflammation The innate immune system is an evolutionally conserved mechanism that provides an early and effective response against invading microbial pathogens. It relies on a limited
Caspase-11 Activation in Response to Bacterial Secretion Systems That Access the Host Cytosol
 University of Pennsylvania ScholarlyCommons Department of Microbiology Perelman School of Medicine 6-6-2013 Caspase-11 Activation in Response to Bacterial Secretion Systems That Access the Host Cytosol
University of Pennsylvania ScholarlyCommons Department of Microbiology Perelman School of Medicine 6-6-2013 Caspase-11 Activation in Response to Bacterial Secretion Systems That Access the Host Cytosol
NOD-like Receptors (NLRs) and Inflammasomes
 International Edition NOD-like Receptors (NLRs) and Inflammasomes In mammals, germ-line encoded pattern recognition receptors (PRRs) detect the presence of pathogens through recognition of pathogen-associated
International Edition NOD-like Receptors (NLRs) and Inflammasomes In mammals, germ-line encoded pattern recognition receptors (PRRs) detect the presence of pathogens through recognition of pathogen-associated
Supplementary Appendix
 Supplementary Appendix This appendix has been provided by the authors to give readers additional information about their work. Supplement to: Goldbach-Mansky R, Dailey NJ, Canna SW, et al. Neonatal-onset
Supplementary Appendix This appendix has been provided by the authors to give readers additional information about their work. Supplement to: Goldbach-Mansky R, Dailey NJ, Canna SW, et al. Neonatal-onset
Supplementary Figure 1. Prevalence of U539C and G540A nucleotide and E172K amino acid substitutions among H9N2 viruses. Full-length H9N2 NS
 Supplementary Figure 1. Prevalence of U539C and G540A nucleotide and E172K amino acid substitutions among H9N2 viruses. Full-length H9N2 NS nucleotide sequences (a, b) or amino acid sequences (c) from
Supplementary Figure 1. Prevalence of U539C and G540A nucleotide and E172K amino acid substitutions among H9N2 viruses. Full-length H9N2 NS nucleotide sequences (a, b) or amino acid sequences (c) from
T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y
 T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Supplemental material Krenn et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201110013/dc1 Figure S1. Levels of expressed proteins and demonstration that C-terminal
T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Supplemental material Krenn et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201110013/dc1 Figure S1. Levels of expressed proteins and demonstration that C-terminal
Mechanism of membrane pore formation by human gasdermin-d
 Article Mechanism of membrane pore formation by human gasdermin-d Estefania Mulvihill 1, Lorenzo Sborgi 2, Stefania A Mari 1, Moritz Pfreundschuh 1, Sebastian Hiller 2 & Daniel J Müller 1,* Abstract Gasdermin-D
Article Mechanism of membrane pore formation by human gasdermin-d Estefania Mulvihill 1, Lorenzo Sborgi 2, Stefania A Mari 1, Moritz Pfreundschuh 1, Sebastian Hiller 2 & Daniel J Müller 1,* Abstract Gasdermin-D
WDR62 is associated with the spindle pole and mutated in human microcephaly
 WDR62 is associated with the spindle pole and mutated in human microcephaly Adeline K. Nicholas, Maryam Khurshid, Julie Désir, Ofélia P. Carvalho, James J. Cox, Gemma Thornton, Rizwana Kausar, Muhammad
WDR62 is associated with the spindle pole and mutated in human microcephaly Adeline K. Nicholas, Maryam Khurshid, Julie Désir, Ofélia P. Carvalho, James J. Cox, Gemma Thornton, Rizwana Kausar, Muhammad
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 AAV-GFP injection in the MEC of the mouse brain C57Bl/6 mice at 4 months of age were injected with AAV-GFP into the MEC and sacrificed at 7 days post injection (dpi). (a) Brains
Supplementary Figure 1 AAV-GFP injection in the MEC of the mouse brain C57Bl/6 mice at 4 months of age were injected with AAV-GFP into the MEC and sacrificed at 7 days post injection (dpi). (a) Brains
NALP12, a gene responsible for periodic fever syndromes. Isabelle Jéru INSERM U.654, Paris, FRANCE
 NALP12, a gene responsible for periodic fever syndromes Isabelle Jéru INSERM U.654, Paris, FRANCE Hereditary periodic fever syndromes (HPFs) Phenotype 6 clinical entities Fever episodes Abdominal pain
NALP12, a gene responsible for periodic fever syndromes Isabelle Jéru INSERM U.654, Paris, FRANCE Hereditary periodic fever syndromes (HPFs) Phenotype 6 clinical entities Fever episodes Abdominal pain
Innate immune regulation of T-helper (Th) cell homeostasis in the intestine
 Innate immune regulation of T-helper (Th) cell homeostasis in the intestine Masayuki Fukata, MD, Ph.D. Research Scientist II Division of Gastroenterology, Department of Medicine, F. Widjaja Foundation,
Innate immune regulation of T-helper (Th) cell homeostasis in the intestine Masayuki Fukata, MD, Ph.D. Research Scientist II Division of Gastroenterology, Department of Medicine, F. Widjaja Foundation,
Nature Immunology doi: /ni.3268
 Supplementary Figure 1 Loss of Mst1 and Mst2 increases susceptibility to bacterial sepsis. (a) H&E staining of colon and kidney sections from wild type and Mst1 -/- Mst2 fl/fl Vav-Cre mice. Scale bar,
Supplementary Figure 1 Loss of Mst1 and Mst2 increases susceptibility to bacterial sepsis. (a) H&E staining of colon and kidney sections from wild type and Mst1 -/- Mst2 fl/fl Vav-Cre mice. Scale bar,
Supplementary Figure 1 Induction of cellular senescence and isolation of exosome. a to c, Pre-senescent primary normal human diploid fibroblasts
 Supplementary Figure 1 Induction of cellular senescence and isolation of exosome. a to c, Pre-senescent primary normal human diploid fibroblasts (TIG-3 cells) were rendered senescent by either serial passage
Supplementary Figure 1 Induction of cellular senescence and isolation of exosome. a to c, Pre-senescent primary normal human diploid fibroblasts (TIG-3 cells) were rendered senescent by either serial passage
Supplementary Material
 Supplementary Material Summary: The supplementary information includes 1 table (Table S1) and 4 figures (Figure S1 to S4). Supplementary Figure Legends Figure S1 RTL-bearing nude mouse model. (A) Tumor
Supplementary Material Summary: The supplementary information includes 1 table (Table S1) and 4 figures (Figure S1 to S4). Supplementary Figure Legends Figure S1 RTL-bearing nude mouse model. (A) Tumor
Immunology Part II. Innate Immunity. 18. April 2018, Ruhr-Universität Bochum Marcus Peters,
 Immunology Part II Innate Immunity 18. April 2018, Ruhr-Universität Bochum Marcus Peters, marcus.peters@rub.de Conserved structures of pathogens PAMPs are detected by Pattern Recognition Receptors PRRs
Immunology Part II Innate Immunity 18. April 2018, Ruhr-Universität Bochum Marcus Peters, marcus.peters@rub.de Conserved structures of pathogens PAMPs are detected by Pattern Recognition Receptors PRRs
ERK1/2/MAPK pathway-dependent regulation of the telomeric factor TRF2
 ERK1/2/MAPK pathway-dependent regulation of the telomeric factor TRF2 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES AND TABLE Supplementary Figure S1: Conservation of the D domain throughout evolution. Alignment of TRF2 sequences
ERK1/2/MAPK pathway-dependent regulation of the telomeric factor TRF2 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES AND TABLE Supplementary Figure S1: Conservation of the D domain throughout evolution. Alignment of TRF2 sequences
Inflammasome activation causes dual recruitment of NLRC4 and NLRP3 to the same macro-molecular complex
 Inflammasome activation causes dual recruitment of NLRC4 and NLRP3 to the same macro-molecular complex Si Ming Man, 1 Lee J. Hopkins, 1 Eileen Nugent, 2 Susan Cox, 3 Ivo M. Glück, 1 Panagiotis Tourlomousis,
Inflammasome activation causes dual recruitment of NLRC4 and NLRP3 to the same macro-molecular complex Si Ming Man, 1 Lee J. Hopkins, 1 Eileen Nugent, 2 Susan Cox, 3 Ivo M. Glück, 1 Panagiotis Tourlomousis,
LPS LPS P6 - + Supplementary Fig. 1.
 P6 LPS - - - + + + - LPS + + - - P6 + Supplementary Fig. 1. Pharmacological inhibition of the JAK/STAT blocks LPS-induced HMGB1 nuclear translocation. RAW 267.4 cells were stimulated with LPS in the absence
P6 LPS - - - + + + - LPS + + - - P6 + Supplementary Fig. 1. Pharmacological inhibition of the JAK/STAT blocks LPS-induced HMGB1 nuclear translocation. RAW 267.4 cells were stimulated with LPS in the absence
Inflammation: How to Cool the Fire Inside your Gut? REINVENTING DIAGNOSTICS
 Inflammation: How to Cool the Fire Inside your Gut? REINVENTING DIAGNOSTICS Future of Healthcare REINVENTING DIAGNOSTICS Inflammation Gut Inflammation Basis of a Healthy
Inflammation: How to Cool the Fire Inside your Gut? REINVENTING DIAGNOSTICS Future of Healthcare REINVENTING DIAGNOSTICS Inflammation Gut Inflammation Basis of a Healthy
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
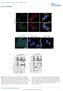 DOI:.38/ncb2822 a MTC02 FAO cells EEA1 b +/+ MEFs /DAPI -/- MEFs /DAPI -/- MEFs //DAPI c HEK 293 cells WCE N M C P AKT TBC1D7 Lamin A/C EEA1 VDAC d HeLa cells WCE N M C P AKT Lamin A/C EEA1 VDAC Figure
DOI:.38/ncb2822 a MTC02 FAO cells EEA1 b +/+ MEFs /DAPI -/- MEFs /DAPI -/- MEFs //DAPI c HEK 293 cells WCE N M C P AKT TBC1D7 Lamin A/C EEA1 VDAC d HeLa cells WCE N M C P AKT Lamin A/C EEA1 VDAC Figure
RECAP FROM MONDAY AND TUESDAY LECTURES
 RECAP FROM MONDAY AND TUESDAY LECTURES Nucleo-cytoplasmic transport factors: interact with the target macromolecule (signal recognition) interact with the NPC (nucleoporin Phe - Gly repeats) NPC cytoplasmic
RECAP FROM MONDAY AND TUESDAY LECTURES Nucleo-cytoplasmic transport factors: interact with the target macromolecule (signal recognition) interact with the NPC (nucleoporin Phe - Gly repeats) NPC cytoplasmic
Introduction to pathology lecture 5/ Cell injury apoptosis. Dr H Awad 2017/18
 Introduction to pathology lecture 5/ Cell injury apoptosis Dr H Awad 2017/18 Apoptosis = programmed cell death = cell suicide= individual cell death Apoptosis cell death induced by a tightly regulated
Introduction to pathology lecture 5/ Cell injury apoptosis Dr H Awad 2017/18 Apoptosis = programmed cell death = cell suicide= individual cell death Apoptosis cell death induced by a tightly regulated
New virulence strategy of P. aeruginosa clonal outliers
 New virulence strategy of P. aeruginosa clonal outliers Ina Attrée Bacterial Pathogenesis and Cellular Responses CNRS, CEA Grenoble University Grenoble-Alpes Grenoble, France Pseudomonas aeruginosa virulence
New virulence strategy of P. aeruginosa clonal outliers Ina Attrée Bacterial Pathogenesis and Cellular Responses CNRS, CEA Grenoble University Grenoble-Alpes Grenoble, France Pseudomonas aeruginosa virulence
Newly Recognized Components of the Innate Immune System
 Newly Recognized Components of the Innate Immune System NOD Proteins: Intracellular Peptidoglycan Sensors NOD-1 NOD-2 Nod Protein LRR; Ligand Recognition CARD RICK I-κB p50 p65 NF-κB Polymorphisms in Nod-2
Newly Recognized Components of the Innate Immune System NOD Proteins: Intracellular Peptidoglycan Sensors NOD-1 NOD-2 Nod Protein LRR; Ligand Recognition CARD RICK I-κB p50 p65 NF-κB Polymorphisms in Nod-2
Alcoholic hepatitis is a drug-induced disorder
 Alcoholic hepatitis is a drug-induced disorder Gyongyi Szabo, MD, PhD Professor of Medicine University of Massachusetts Medical School Source: 2 Sobernation.com Clinical Progression of ALD Mortality Acute
Alcoholic hepatitis is a drug-induced disorder Gyongyi Szabo, MD, PhD Professor of Medicine University of Massachusetts Medical School Source: 2 Sobernation.com Clinical Progression of ALD Mortality Acute
WT Xid (h) poly(da:dt) Alum. Poly(dA:dT) 0.05
 IL1 (ng/ml) (1 x 1 3 cells) DMSO LFMA13 R46 IL1 (ng/ml) Control shrna TNFa (ng/ml) Alum Nigericin ATP IL1 (ng/ml) IL1 (ng/ml) IL1 (ng/ml) a c f 3 2 1 1 8 6 4 2 Sup 1 8 6 4 DMSO Alum/DMSO Alum/LFMA13 ***
IL1 (ng/ml) (1 x 1 3 cells) DMSO LFMA13 R46 IL1 (ng/ml) Control shrna TNFa (ng/ml) Alum Nigericin ATP IL1 (ng/ml) IL1 (ng/ml) IL1 (ng/ml) a c f 3 2 1 1 8 6 4 2 Sup 1 8 6 4 DMSO Alum/DMSO Alum/LFMA13 ***
NOD-like receptor signaling and inflammasome-related pathways are highlighted in psoriatic epidermis
 Supplementary Information NOD-like receptor signaling and inflammasome-related pathways are highlighted in psoriatic epidermis Mari H. Tervaniemi, Shintaro Katayama, Tiina Skoog, H. Annika Siitonen, Jyrki
Supplementary Information NOD-like receptor signaling and inflammasome-related pathways are highlighted in psoriatic epidermis Mari H. Tervaniemi, Shintaro Katayama, Tiina Skoog, H. Annika Siitonen, Jyrki
Differentiation-induced Changes of Mediterranean Fever Gene (MEFV) Expression in HL-60 Cell
 Differentiation-induced Changes of Mediterranean Fever Gene (MEFV) Expression in HL-60 Cell Wenxin Li Department of Biological Sciences Fordham University Abstract MEFV is a human gene that codes for an
Differentiation-induced Changes of Mediterranean Fever Gene (MEFV) Expression in HL-60 Cell Wenxin Li Department of Biological Sciences Fordham University Abstract MEFV is a human gene that codes for an
Supplementary Figure 1. SC35M polymerase activity in the presence of Bat or SC35M NP encoded from the phw2000 rescue plasmid.
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 Supplementary Figure 1. SC35M polymerase activity in the presence of Bat or SC35M NP encoded from the phw2000 rescue plasmid. HEK293T
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 Supplementary Figure 1. SC35M polymerase activity in the presence of Bat or SC35M NP encoded from the phw2000 rescue plasmid. HEK293T
Prolonged mitotic arrest induces a caspase-dependent DNA damage
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Prolonged mitotic arrest induces a caspase-dependent DNA damage response at telomeres that determines cell survival Karolina O. Hain, Didier J. Colin, Shubhra Rastogi, Lindsey
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Prolonged mitotic arrest induces a caspase-dependent DNA damage response at telomeres that determines cell survival Karolina O. Hain, Didier J. Colin, Shubhra Rastogi, Lindsey
INFLAMMASOME IN INTESTINAL INFLAMMATION AND CANCER. Laura Stronati ENEA - Roma
 INFLAMMASOME IN INTESTINAL INFLAMMATION AND CANCER Laura Stronati ENEA - Roma Inflammasome: definition, components and activation TLRs NODs RLRs CLRs PRRs LPS, Flagellin, DNA, RNA, etc) PAMPs DAMPs ATP,
INFLAMMASOME IN INTESTINAL INFLAMMATION AND CANCER Laura Stronati ENEA - Roma Inflammasome: definition, components and activation TLRs NODs RLRs CLRs PRRs LPS, Flagellin, DNA, RNA, etc) PAMPs DAMPs ATP,
A. Generation and characterization of Ras-expressing autophagycompetent
 Supplemental Material Supplemental Figure Legends Fig. S1 A. Generation and characterization of Ras-expressing autophagycompetent and -deficient cell lines. HA-tagged H-ras V12 was stably expressed in
Supplemental Material Supplemental Figure Legends Fig. S1 A. Generation and characterization of Ras-expressing autophagycompetent and -deficient cell lines. HA-tagged H-ras V12 was stably expressed in
Toll-like Receptors (TLRs): Biology, Pathology and Therapeutics
 Toll-like Receptors (TLRs): Biology, Pathology and Therapeutics Dr Sarah Sasson SydPATH Registrar 23 rd June 2014 TLRs: Introduction Discovered in 1990s Recognise conserved structures in pathogens Rely
Toll-like Receptors (TLRs): Biology, Pathology and Therapeutics Dr Sarah Sasson SydPATH Registrar 23 rd June 2014 TLRs: Introduction Discovered in 1990s Recognise conserved structures in pathogens Rely
Chapter 2 Inflammasomes and Obesity
 Chapter 2 Inflammasomes and Obesity Tuo Deng, Jun Cui, Christopher J. Lyon, Nan Zhang, Helen Y. Wang, Rong-fu Wang, and Willa A. Hsueh Abstract Inflammasomes are a family of protein complexes that recognize
Chapter 2 Inflammasomes and Obesity Tuo Deng, Jun Cui, Christopher J. Lyon, Nan Zhang, Helen Y. Wang, Rong-fu Wang, and Willa A. Hsueh Abstract Inflammasomes are a family of protein complexes that recognize
Scott Abrams, Ph.D. Professor of Oncology, x4375 Kuby Immunology SEVENTH EDITION
 Scott Abrams, Ph.D. Professor of Oncology, x4375 scott.abrams@roswellpark.org Kuby Immunology SEVENTH EDITION CHAPTER 13 Effector Responses: Cell- and Antibody-Mediated Immunity Copyright 2013 by W. H.
Scott Abrams, Ph.D. Professor of Oncology, x4375 scott.abrams@roswellpark.org Kuby Immunology SEVENTH EDITION CHAPTER 13 Effector Responses: Cell- and Antibody-Mediated Immunity Copyright 2013 by W. H.
Primer sequences Target Sequence F Sequence R TNF-α (Tnfa) TCAGCCGATTTGCTATCTCAT A
 Supplementary Table 1. Q- and RT-PR primers used in this study. Primer sequences Target Sequence F Sequence R TNF-α (Tnfa) TGGTTTGTTTT GTTTGGGGTTG T hemokine (- motif) ligand 5 (cl5) GTGTTTGTTT TGGTGGTG
Supplementary Table 1. Q- and RT-PR primers used in this study. Primer sequences Target Sequence F Sequence R TNF-α (Tnfa) TGGTTTGTTTT GTTTGGGGTTG T hemokine (- motif) ligand 5 (cl5) GTGTTTGTTT TGGTGGTG
Identification of Host Cytosolic Sensors and Bacterial Factors Regulating the Type I Interferon Response to Legionella pneumophila
 Identification of Host Cytosolic Sensors and Bacterial Factors Regulating the Type I Interferon Response to Legionella pneumophila Kathryn M. Monroe, Sarah M. McWhirter, Russell E. Vance* Division of Immunology
Identification of Host Cytosolic Sensors and Bacterial Factors Regulating the Type I Interferon Response to Legionella pneumophila Kathryn M. Monroe, Sarah M. McWhirter, Russell E. Vance* Division of Immunology
PERSPECTIVES. SMOCs: supramolecular organizing centres that control innate immunity
 Nature Reviews Immunology AOP, published online 31 October 2014; doi:10.1038/nri3757 PERSPECTIVES OPINION SMOCs: supramolecular organizing centres that control innate immunity Jonathan C. Kagan, Venkat
Nature Reviews Immunology AOP, published online 31 October 2014; doi:10.1038/nri3757 PERSPECTIVES OPINION SMOCs: supramolecular organizing centres that control innate immunity Jonathan C. Kagan, Venkat
Within the gastrointestinal (GI) tract, innate immune REVIEWS IN BASIC AND CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY
 GASTROENTEROLOGY 2011;141:1986 1999 IN BASIC CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY HEPATOLOGY Robert F. Schwabe and John W. Wiley, Section Editors Inflammasomes in Intestinal Inflammation and Cancer GRACE Y. CHEN*
GASTROENTEROLOGY 2011;141:1986 1999 IN BASIC CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY HEPATOLOGY Robert F. Schwabe and John W. Wiley, Section Editors Inflammasomes in Intestinal Inflammation and Cancer GRACE Y. CHEN*
Your Body's Defenses
 Your Body's Defenses For follow up on these notes read: Holt: pages 710 720 MSLS: pages 410 420 Blue writing indicates a video is linked to the picture. Click the pictures! Links to Videos are listed on
Your Body's Defenses For follow up on these notes read: Holt: pages 710 720 MSLS: pages 410 420 Blue writing indicates a video is linked to the picture. Click the pictures! Links to Videos are listed on
I. Lines of Defense Pathogen: Table 1: Types of Immune Mechanisms. Table 2: Innate Immunity: First Lines of Defense
 I. Lines of Defense Pathogen: Table 1: Types of Immune Mechanisms Table 2: Innate Immunity: First Lines of Defense Innate Immunity involves nonspecific physical & chemical barriers that are adapted for
I. Lines of Defense Pathogen: Table 1: Types of Immune Mechanisms Table 2: Innate Immunity: First Lines of Defense Innate Immunity involves nonspecific physical & chemical barriers that are adapted for
The death receptors: signaling and modulation
 The death receptors: signaling and modulation 1 1 The extrinsic cell death pathway 2 Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2008 Dec;7(12):1001-12. 2 Death receptors Belong to the tumor necrosis factor (TNF) receptor gene
The death receptors: signaling and modulation 1 1 The extrinsic cell death pathway 2 Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2008 Dec;7(12):1001-12. 2 Death receptors Belong to the tumor necrosis factor (TNF) receptor gene
Inflammation - Molecular events
 Academic lectures for students of medical schools 3rd Year updated 2004-2015 GENERAL PATHOPHYSIOLOGY Inflammation - Molecular events R. A. Benacka, MD, PhD Department of Pathophysiology Medical faculty
Academic lectures for students of medical schools 3rd Year updated 2004-2015 GENERAL PATHOPHYSIOLOGY Inflammation - Molecular events R. A. Benacka, MD, PhD Department of Pathophysiology Medical faculty
TLR2/MyD88/NF-kB Pathway, Reactive Oxygen Species, Potassium Efflux Activates NLRP3/ASC Inflammasome during Respiratory Syncytial Virus Infection
 TLR2/MyD88/NF-kB Pathway, Reactive Oxygen Species, Potassium Efflux Activates NLRP3/ASC Inflammasome during Respiratory Syncytial Virus Infection Jesus Segovia 1., Ahmed Sabbah 1., Victoria Mgbemena 1,
TLR2/MyD88/NF-kB Pathway, Reactive Oxygen Species, Potassium Efflux Activates NLRP3/ASC Inflammasome during Respiratory Syncytial Virus Infection Jesus Segovia 1., Ahmed Sabbah 1., Victoria Mgbemena 1,
Irf1 fold changes (D) 24h 48h. p-p65. t-p65. p-irf3. t-irf3. β-actin SKO TKO 100% 80% 60% 40% 20%
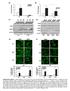 Irf7 Fold changes 3 1 Irf1 fold changes 3 1 8h h 8h 8h h 8h p-p6 p-p6 t-p6 p-irf3 β-actin p-irf3 t-irf3 β-actin TKO TKO STKO (E) (F) TKO TKO % of p6 nuclear translocation % % 1% 1% % % p6 TKO % of IRF3
Irf7 Fold changes 3 1 Irf1 fold changes 3 1 8h h 8h 8h h 8h p-p6 p-p6 t-p6 p-irf3 β-actin p-irf3 t-irf3 β-actin TKO TKO STKO (E) (F) TKO TKO % of p6 nuclear translocation % % 1% 1% % % p6 TKO % of IRF3
CHAPTER 4. Tryptophan fluorescence quenching by brominated lipids
 CHAPTER 4 Tryptophan fluorescence quenching by brominated lipids 102 4.1 INTRODUCTION The structure and dynamics of biological macromolecules have been widely studied with fluorescence quenching. The accessibility
CHAPTER 4 Tryptophan fluorescence quenching by brominated lipids 102 4.1 INTRODUCTION The structure and dynamics of biological macromolecules have been widely studied with fluorescence quenching. The accessibility
Pyroptosis and Apoptosis Pathways Engage in Bidirectional Crosstalk in Monocytes and Macrophages
 Article Pyroptosis and Apoptosis Pathways Engage in Bidirectional Crosstalk in Monocytes and Macrophages Graphical Abstract Authors Cornelius Y. Taabazuing, Marian C. Okondo, Daniel A. Bachovchin Correspondence
Article Pyroptosis and Apoptosis Pathways Engage in Bidirectional Crosstalk in Monocytes and Macrophages Graphical Abstract Authors Cornelius Y. Taabazuing, Marian C. Okondo, Daniel A. Bachovchin Correspondence
Lecture on Innate Immunity and Inflammation. Innate Immunity: An Evolutionary View
 Lecture on Innate Immunity and Inflammation Evolutionary View Epithelial barriers to infection Four main types of innate recognition molecules:tlrs, CLRs, NLRs, RLRs NF-κB, the master transcriptional regulator
Lecture on Innate Immunity and Inflammation Evolutionary View Epithelial barriers to infection Four main types of innate recognition molecules:tlrs, CLRs, NLRs, RLRs NF-κB, the master transcriptional regulator
Tel: ; Fax: ;
 Tel.: +98 216 696 9291; Fax: +98 216 696 9291; E-mail: mrasadeghi@pasteur.ac.ir Tel: +98 916 113 7679; Fax: +98 613 333 6380; E-mail: abakhshi_e@ajums.ac.ir A Soluble Chromatin-bound MOI 0 1 5 0 1 5 HDAC2
Tel.: +98 216 696 9291; Fax: +98 216 696 9291; E-mail: mrasadeghi@pasteur.ac.ir Tel: +98 916 113 7679; Fax: +98 613 333 6380; E-mail: abakhshi_e@ajums.ac.ir A Soluble Chromatin-bound MOI 0 1 5 0 1 5 HDAC2
TRAF6 ubiquitinates TGFβ type I receptor to promote its cleavage and nuclear translocation in cancer
 Supplementary Information TRAF6 ubiquitinates TGFβ type I receptor to promote its cleavage and nuclear translocation in cancer Yabing Mu, Reshma Sundar, Noopur Thakur, Maria Ekman, Shyam Kumar Gudey, Mariya
Supplementary Information TRAF6 ubiquitinates TGFβ type I receptor to promote its cleavage and nuclear translocation in cancer Yabing Mu, Reshma Sundar, Noopur Thakur, Maria Ekman, Shyam Kumar Gudey, Mariya
Kidney. Heart. Lung. Sirt1. Gapdh. Mouse IgG DAPI. Rabbit IgG DAPI
 a e Na V 1.5 Ad-LacZ Ad- 110KD b Scn5a/ (relative to Ad-LacZ) f 150 100 50 0 p = 0.65 Ad-LacZ Ad- c Heart Lung Kidney Spleen 110KD d fl/fl c -/- DAPI 20 µm Na v 1.5 250KD fl/fl Rabbit IgG DAPI fl/fl Mouse
a e Na V 1.5 Ad-LacZ Ad- 110KD b Scn5a/ (relative to Ad-LacZ) f 150 100 50 0 p = 0.65 Ad-LacZ Ad- c Heart Lung Kidney Spleen 110KD d fl/fl c -/- DAPI 20 µm Na v 1.5 250KD fl/fl Rabbit IgG DAPI fl/fl Mouse
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Asymmetrical function of 5p and 3p arms of mir-181 and mir-30 families and mir-142 and mir-154. (a) Control experiments using mirna sensor vector and empty pri-mirna overexpression
Supplementary Figure 1 Asymmetrical function of 5p and 3p arms of mir-181 and mir-30 families and mir-142 and mir-154. (a) Control experiments using mirna sensor vector and empty pri-mirna overexpression
Of inflammasomes and pathogens sensing of microbes by the inflammasome
 Series Host pathogen interactions OPEN ACCESS sensing of microbes by the inflammasome Franz Bauernfeind 1,2, Veit Hornung 1 * Keywords: caspase-1; inflammasome; ; NLRP3; pathogens DOI 10.1002/emmm.201201771
Series Host pathogen interactions OPEN ACCESS sensing of microbes by the inflammasome Franz Bauernfeind 1,2, Veit Hornung 1 * Keywords: caspase-1; inflammasome; ; NLRP3; pathogens DOI 10.1002/emmm.201201771
Structural vs. nonstructural proteins
 Why would you want to study proteins associated with viruses or virus infection? Receptors Mechanism of uncoating How is gene expression carried out, exclusively by viral enzymes? Gene expression phases?
Why would you want to study proteins associated with viruses or virus infection? Receptors Mechanism of uncoating How is gene expression carried out, exclusively by viral enzymes? Gene expression phases?
Felix Yarovinsky. Department of Immunology, UT Southwestern Medical Center. Innate immune defense to Toxoplasma gondii
 Felix Yarovinsky Department of Immunology, UT Southwestern Medical Center Innate immune defense to Toxoplasma gondii Pathogen recognition by innate immune cells Pathogen Parasites Viruses Bacteria Initiator
Felix Yarovinsky Department of Immunology, UT Southwestern Medical Center Innate immune defense to Toxoplasma gondii Pathogen recognition by innate immune cells Pathogen Parasites Viruses Bacteria Initiator
Electron Microscopy Imaging Reveals Unique Higher Order Structures of Adalimumab-TNFα and Infliximab-TNFα Complexes
 Electron Microscopy Imaging Reveals Unique Higher Order Structures of Adalimumab-TNFα and Infliximab-TNFα Complexes Siew Leong Chan Protein Analytics, AbbVie Bioresearch Center Worcester MA Acknowledgement
Electron Microscopy Imaging Reveals Unique Higher Order Structures of Adalimumab-TNFα and Infliximab-TNFα Complexes Siew Leong Chan Protein Analytics, AbbVie Bioresearch Center Worcester MA Acknowledgement
General information. Cell mediated immunity. 455 LSA, Tuesday 11 to noon. Anytime after class.
 General information Cell mediated immunity 455 LSA, Tuesday 11 to noon Anytime after class T-cell precursors Thymus Naive T-cells (CD8 or CD4) email: lcoscoy@berkeley.edu edu Use MCB150 as subject line
General information Cell mediated immunity 455 LSA, Tuesday 11 to noon Anytime after class T-cell precursors Thymus Naive T-cells (CD8 or CD4) email: lcoscoy@berkeley.edu edu Use MCB150 as subject line
New drugs on the horizon for heart failure: CaMK antagonists
 New drugs on the horizon for heart failure: CaMK antagonists (Lars S. Maier) Gerd Hasenfuss Disclosure Information: No relationship exists related to this presentation Dept. of Cardiology and Pneumology,
New drugs on the horizon for heart failure: CaMK antagonists (Lars S. Maier) Gerd Hasenfuss Disclosure Information: No relationship exists related to this presentation Dept. of Cardiology and Pneumology,
Figure S1. PMVs from THP-1 cells expose phosphatidylserine and carry actin. A) Flow
 SUPPLEMENTARY DATA Supplementary Figure Legends Figure S1. PMVs from THP-1 cells expose phosphatidylserine and carry actin. A) Flow cytometry analysis of PMVs labelled with annexin-v-pe (Guava technologies)
SUPPLEMENTARY DATA Supplementary Figure Legends Figure S1. PMVs from THP-1 cells expose phosphatidylserine and carry actin. A) Flow cytometry analysis of PMVs labelled with annexin-v-pe (Guava technologies)
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/science.aal4326/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Structure of a eukaryotic voltage-gated sodium channel at near-atomic resolution Huaizong Shen, Qiang Zhou, Xiaojing
www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/science.aal4326/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Structure of a eukaryotic voltage-gated sodium channel at near-atomic resolution Huaizong Shen, Qiang Zhou, Xiaojing
Thioredoxin(TRX) oxidation mediated by mitochondrial ROS is a key event in NLRP3 Inflammasome activation
 Thioredoxin(TRX) oxidation mediated by mitochondrial ROS is a key event in NLRP3 Inflammasome activation TRX-(SH) 2 TRX-S 2 A review on the role of mitochondria and redox reactions in NLRP3 inflammasome
Thioredoxin(TRX) oxidation mediated by mitochondrial ROS is a key event in NLRP3 Inflammasome activation TRX-(SH) 2 TRX-S 2 A review on the role of mitochondria and redox reactions in NLRP3 inflammasome
Nature Immunology: doi: /ni eee Supplementary Figure 1
 eee Supplementary Figure 1 Hyphae induce NET release, but yeast do not. (a) NET release by human peripheral neutrophils stimulated with a hgc1 yeast-locked C. albicans mutant (yeast) or pre-formed WT C.
eee Supplementary Figure 1 Hyphae induce NET release, but yeast do not. (a) NET release by human peripheral neutrophils stimulated with a hgc1 yeast-locked C. albicans mutant (yeast) or pre-formed WT C.
STRUCTURAL STUDIES OF THE HIV-1 PRE-INTEGRATION COMPLEX IN/LEDGF INTERACTION INHIBITORS
 STRUCTURAL STUDIES OF THE HIV-1 PRE-INTEGRATION COMPLEX IN/LEDGF INTERACTION INHIBITORS Marc Ruff Laboratory of Integrated structural biology IGBMC, Illkirch, France ruff@igbmc.fr Schematic diagram of
STRUCTURAL STUDIES OF THE HIV-1 PRE-INTEGRATION COMPLEX IN/LEDGF INTERACTION INHIBITORS Marc Ruff Laboratory of Integrated structural biology IGBMC, Illkirch, France ruff@igbmc.fr Schematic diagram of
Supplementary Materials for
 advances.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/3/2/e1602038/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Mitochondrial metabolic regulation by GRP78 Manoj Prasad, Kevin J. Pawlak, William E. Burak, Elizabeth E. Perry, Brendan
advances.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/3/2/e1602038/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Mitochondrial metabolic regulation by GRP78 Manoj Prasad, Kevin J. Pawlak, William E. Burak, Elizabeth E. Perry, Brendan
Microbial recognition and the immune response Dr. Dana Philpott
 Microbial Recognition and the Immune Response Dept. of Immunology University of Toronto 1 Outline of talk Introduction into innate immunity Function of TLRs and NLRs Role of NLRs in microbial detection
Microbial Recognition and the Immune Response Dept. of Immunology University of Toronto 1 Outline of talk Introduction into innate immunity Function of TLRs and NLRs Role of NLRs in microbial detection
Apoptosis Chapter 9. Neelu Yadav PhD
 Apoptosis Chapter 9 Neelu Yadav PhD Neelu.Yadav@Roswellpark.org 1 Apoptosis: Lecture outline Apoptosis a programmed cell death pathway in normal homeostasis Core Apoptosis cascade is conserved Compare
Apoptosis Chapter 9 Neelu Yadav PhD Neelu.Yadav@Roswellpark.org 1 Apoptosis: Lecture outline Apoptosis a programmed cell death pathway in normal homeostasis Core Apoptosis cascade is conserved Compare
Nature Medicine: doi: /nm.4322
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 Supplementary Figure 1. Predicted RNA structure of 3 UTR and sequence alignment of deleted nucleotides. (a) Predicted RNA secondary structure of ZIKV 3 UTR. The stem-loop structure
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 Supplementary Figure 1. Predicted RNA structure of 3 UTR and sequence alignment of deleted nucleotides. (a) Predicted RNA secondary structure of ZIKV 3 UTR. The stem-loop structure
Intrinsic cellular defenses against virus infection
 Intrinsic cellular defenses against virus infection Detection of virus infection Host cell response to virus infection Interferons: structure and synthesis Induction of antiviral activity Viral defenses
Intrinsic cellular defenses against virus infection Detection of virus infection Host cell response to virus infection Interferons: structure and synthesis Induction of antiviral activity Viral defenses
Identification of Microbes
 Identification of Microbes Recognition by PRR (pattern recognition receptors) Recognize conserved molecular patterns on microbes called pathogen associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) which are not present
Identification of Microbes Recognition by PRR (pattern recognition receptors) Recognize conserved molecular patterns on microbes called pathogen associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) which are not present
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI:.38/ncb3399 a b c d FSP DAPI 5mm mm 5mm 5mm e Correspond to melanoma in-situ Figure a DCT FSP- f MITF mm mm MlanaA melanoma in-situ DCT 5mm FSP- mm mm mm mm mm g melanoma in-situ MITF MlanaA mm mm
DOI:.38/ncb3399 a b c d FSP DAPI 5mm mm 5mm 5mm e Correspond to melanoma in-situ Figure a DCT FSP- f MITF mm mm MlanaA melanoma in-situ DCT 5mm FSP- mm mm mm mm mm g melanoma in-situ MITF MlanaA mm mm
John Bell Centre for Innovative Cancer Therapeutics
 Enhancing Oncolytic Virus Activity by Engineering of Artificial micrornas John Bell Centre for Innovative Cancer Therapeutics Affiliated with Affilié à 1 Oncolytic Viruses: A Therapy for Metastatic Cancers?
Enhancing Oncolytic Virus Activity by Engineering of Artificial micrornas John Bell Centre for Innovative Cancer Therapeutics Affiliated with Affilié à 1 Oncolytic Viruses: A Therapy for Metastatic Cancers?
#19 Apoptosis Chapter 9. Neelu Yadav PhD
 #19 Apoptosis Chapter 9 Neelu Yadav PhD Neelu.Yadav@Roswellpark.org Why cells decide to die? - Stress, harmful, not needed - Completed its life span Death stimulation or Stress Cell Survival Death Functions
#19 Apoptosis Chapter 9 Neelu Yadav PhD Neelu.Yadav@Roswellpark.org Why cells decide to die? - Stress, harmful, not needed - Completed its life span Death stimulation or Stress Cell Survival Death Functions
Supplementary Figure 1.TRIM33 binds β-catenin in the nucleus. a & b, Co-IP of endogenous TRIM33 with β-catenin in HT-29 cells (a) and HEK 293T cells
 Supplementary Figure 1.TRIM33 binds β-catenin in the nucleus. a & b, Co-IP of endogenous TRIM33 with β-catenin in HT-29 cells (a) and HEK 293T cells (b). TRIM33 was immunoprecipitated, and the amount of
Supplementary Figure 1.TRIM33 binds β-catenin in the nucleus. a & b, Co-IP of endogenous TRIM33 with β-catenin in HT-29 cells (a) and HEK 293T cells (b). TRIM33 was immunoprecipitated, and the amount of
Bioluminescence Resonance Energy Transfer (BRET)-based studies of receptor dynamics in living cells with Berthold s Mithras
 Bioluminescence Resonance Energy Transfer (BRET)-based studies of receptor dynamics in living cells with Berthold s Mithras Tarik Issad, Ralf Jockers and Stefano Marullo 1 Because they play a pivotal role
Bioluminescence Resonance Energy Transfer (BRET)-based studies of receptor dynamics in living cells with Berthold s Mithras Tarik Issad, Ralf Jockers and Stefano Marullo 1 Because they play a pivotal role
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Horwitz et al. 73/pnas.35295 A Copies ml - C 3NC7 7 697 698 7 7 73 76-2 2 Days Gp2 residue G458D G459D T278A 7/36 N28 K D 28 459 A28T ID# 697 ID# 698 ID# 7 ID# 7 ID# 73 ID# 76 ID#
Supporting Information Horwitz et al. 73/pnas.35295 A Copies ml - C 3NC7 7 697 698 7 7 73 76-2 2 Days Gp2 residue G458D G459D T278A 7/36 N28 K D 28 459 A28T ID# 697 ID# 698 ID# 7 ID# 7 ID# 73 ID# 76 ID#
To test the possible source of the HBV infection outside the study family, we searched the Genbank
 Supplementary Discussion The source of hepatitis B virus infection To test the possible source of the HBV infection outside the study family, we searched the Genbank and HBV Database (http://hbvdb.ibcp.fr),
Supplementary Discussion The source of hepatitis B virus infection To test the possible source of the HBV infection outside the study family, we searched the Genbank and HBV Database (http://hbvdb.ibcp.fr),
Immunology Lecture- 1
 Immunology Lecture- 1 Immunology and Immune System Immunology: Study of the components and function of the immune system Immune System a network collected from cells, tissues organs and soluble factors
Immunology Lecture- 1 Immunology and Immune System Immunology: Study of the components and function of the immune system Immune System a network collected from cells, tissues organs and soluble factors
Research programs in my laboratory
 Research programs in my laboratory Qiu-Xing Jiang Laboratory for Molecular Physiology and Biophysics Department of Microbiology and Cell Science qxjiang@ufl.edu ; phone: 352-8460953 Overall summary: My
Research programs in my laboratory Qiu-Xing Jiang Laboratory for Molecular Physiology and Biophysics Department of Microbiology and Cell Science qxjiang@ufl.edu ; phone: 352-8460953 Overall summary: My
Cross-talk between Two Partners Regulates the Gating of the K ATP Channel Pore
 International Conference on Metabolic Syndromes Cross-talk between Two Partners Regulates the Gating of the K ATP Channel Pore Dr Hussein N Rubaiy h.rubaiy@leeds.ac.uk School of Medicine, University of
International Conference on Metabolic Syndromes Cross-talk between Two Partners Regulates the Gating of the K ATP Channel Pore Dr Hussein N Rubaiy h.rubaiy@leeds.ac.uk School of Medicine, University of
Asc and Ipaf Inflammasomes Direct Distinct Pathways for Caspase-1 Activation in Response to Legionella pneumophila
 INFECTION AND IMMUNITY, May 2009, p. 1981 1991 Vol. 77, No. 5 0019-9567/09/$08.00 0 doi:10.1128/iai.01382-08 Copyright 2009, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Asc and Ipaf Inflammasomes
INFECTION AND IMMUNITY, May 2009, p. 1981 1991 Vol. 77, No. 5 0019-9567/09/$08.00 0 doi:10.1128/iai.01382-08 Copyright 2009, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Asc and Ipaf Inflammasomes
Sensing and reacting to microbes through the inflammasomes
 The inflammasome Sensing and reacting to microbes through the inflammasomes Luigi Franchi, Raul Muñoz-Planillo & Gabriel Núñez Inflammasomes are multiprotein complexes that activate caspase-1, which leads
The inflammasome Sensing and reacting to microbes through the inflammasomes Luigi Franchi, Raul Muñoz-Planillo & Gabriel Núñez Inflammasomes are multiprotein complexes that activate caspase-1, which leads
FOR OPTIMAL GUT HEALTH KEMIN.COM/GUTHEALTH
 FOR OPTIMAL GUT HEALTH KEMIN.COM/GUTHEALTH ALETA A SOURCE OF 1,3-BETA GLUCANS Aleta is highly bioavailable, offering a concentration greater than 5% of 1,3-beta glucans. Aleta provides a consistent response
FOR OPTIMAL GUT HEALTH KEMIN.COM/GUTHEALTH ALETA A SOURCE OF 1,3-BETA GLUCANS Aleta is highly bioavailable, offering a concentration greater than 5% of 1,3-beta glucans. Aleta provides a consistent response
