Cluster Dendrogram. dist(cor(na.omit(tss.exprs.chip[, c(1:10, 24, 27, 30, 48:50, dist(cor(na.omit(tss.exprs.chip[, c(1:99, 103, 104, 109, 110,
|
|
|
- Brendan Jennings
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 A Transcriptome (RNA-seq) Transcriptome (RNA-seq) Cluster Dendrogram RS_ES3.2 RS_ES3. RS_SHS5.2 RS_SHS5. PS_SHS5.2 PS_SHS5. RS_LJ3 PS_LJ3..4 _SHS5.2 _SHS _LA3.2. _E3d5_LJ3.2 _E3d5_LJ3. _E3d5_LJ3.3 _E2d5_LJ3.3 _E2d5_LJ3.2 _E4d5_LJ3.3 _E4d5_LJ3. _E4d5_LJ3.2 _E2d5_LJ3. _SY2.2 _SY2. HSC. RS_ES3_2 RS_ES3_ RS_SHS5_2 RS_SHS5_ PS_SHS5_2 PS_SHS5_ RS_LJ3 PS_LJ3 _6 _OG _VG _OG2 GS_SHS5_2 GS_SHS5 VG8 _VG5 _Rosa5 _29mix _Rosa3 4 _OG _LA3 _OG2 _OG _E3d5_LJ3_2 _E3d5_LJ3 E3d5_LJ3_3 _E2d5_LJ3_3 _E2d5_LJ3_2 _E4d5_LJ3_3 _E4d5_LJ3 E4d5_LJ3_2 _E2d5_LJ3 SY2_2 _SY2_ HSC_2 HSC_ dist(cor(na.omit(tss.exprs.chip[, c(:, 24, 27, 3, 48:5, hclust 56:4)]))) (*, "complete") Cluster Dendrogram RS_ES3.2 RS_ES3. RS_SHS5.2 RS_SHS5. PS_SHS5.2 PS_SHS5. RS_LJ3 PS_LJ _E2d5_LJ3.3 _E2d5_LJ3.2 _E3d5_LJ3.2 _E3d5_LJ3. _E3d5_LJ3.3 _E4d5_LJ3.3 _E4d5_LJ3. _E4d5_LJ3.2 _E2d5_LJ3. HSC. RS_ES3_2 RS_ES3_ RS_SHS5_2 RS_SHS5_ PS_SHS5_2 PS_SHS5_ RS_LJ3 PS_LJ3 _OG2 _OG _OG 4 _VG8 _VG5 _Rosa5 _29mix _Rosa3 _VG _OG2 _6 _OG _E2d5_LJ3_3 _E2d5_LJ3_2 _E3d5_LJ3_2 _E3d5_LJ3 E3d5_LJ3_3 _E4d5_LJ3_3 _E4d5_LJ3 E4d5_LJ3_2 _E2d5_LJ3_ HSC_2 HSC_ dist(cor(na.omit(tss.exprs.chip[, c(:, 3, 24:27, 3, 32, hclust 33, 48:5, (*, "complete") 56:4)]))) Epigenome at Promoters (PRIM) Epigenome at Promoters (PRIM) Cluster Dendrogram P_MCV8_MTS8 P_MCV6_MTS8 _MTS8 _MTS7 _SHS5. _LA3 _WJA2 _MTS7 _MCV8_MTS RS_ES3 PS_LJ3 RS_LJ3 Sperm_ES3 RS_SHS5 PS_SHS5 _HSS4 HSC. LSK_AM ahfsc_lwh qhfsc_lwh HFTAC_LWH _E4d5_LJ3 _E3d5_LJ3 _E2d5_LJ3. P_MCV8_MTS8.prim P_MCV6_MTS8.prim _MTS8.prim _MTS7.prim _H3d3OSKM_D.prim GS_SHS5.prim _OG.prim _VG.prim _6.prim 4_H3d3OSKM.prim _H3d3HA_LA3.prim _WJA2.prim _MTS7.prim _MCV8_MTS8.prim _Rosa.prim _OG_3.prim _OG 2.prim RS_ES3.prim PS_LJ3.prim RS_LJ3.prim Sperm_ES3.prim RS_SHS5.prim PS_SHS5.prim _HSS4.prim HSC_2.prim HSC_.prim MAC.prim LSK_AM.prim ahfsc.prim qhfsc.prim HFTAC.prim _E4d5_LJ3.prim _E3d5_LJ3.prim _E2d5_LJ3.prim _H3d3OSKM.prim dist(cor(na.omit(tss.exprs.chip[, c(:99, 3, 4, 9,, hclust 28, (*, 32, "complete") 4)]))) Cluster Dendrogram P_MCV8_MTS8 P_MCV6_MTS8. _LA3 _WJA2 _MTS RS_ES3 PS_LJ3 RS_LJ3 Sperm_ES3 RS_SHS5 PS_SHS5 HSC. LSK_AM ahfsc_lwh qhfsc_lwh HFTAC_LWH _HSS4 _E4d5_LJ3 _E3d5_LJ3 _E2d5_LJ3. P_MCV8_MTS8.prim P_MCV6_MTS8.prim _H3d3OSKM_D.prim _VG.prim _6.prim _OG.prim 4_H3d3OSKM.prim _H3d3HA_LA3.prim _WJA2.prim _MTS7.prim _Rosa.prim _OG_3.prim _OG 2.prim RS_ES3.prim PS_LJ3.prim RS_LJ3.prim Sperm_ES3.prim RS_SHS5.prim PS_SHS5.prim HSC_2.prim HSC_.prim MAC.prim LSK_AM.prim ahfsc.prim qhfsc.prim HFTAC.prim _HSS4.prim _E4d5_LJ3.prim _E3d5_LJ3.prim _E2d5_LJ3.prim _H3d3OSKM.prim dist(cor(na.omit(tss.exprs.chip[, c(:99, 3, 4, 9,, 7:9, hclust 28, (*, "complete") 32, 34, 4)]))) Supplementary Figure. Dendrogram based on (A) expression or () PRIMs of all protein-coding and noncoding genes. Different cell types are distinguished by colors as in Figure. Left, dendrograms include all cell lines. Right, dendrograms without published data on s, Cs, and s. In-house data are highlighed in gray.
2 A Transcriptome (RNA-seq) PC3 Epigenome at Promoters (PRIM) PC /2/4..2.3/4/5/ _LA3.3 P_MCV6 P_MCV8.2 _MTS7 _WJA PC HSC. PC2 PC2 HSC.. P - HSC Pluripotent P Germ q/a HFSC, Cells HFTAC Somatic Cells / Multipotent Cells HSC, LSK P Pachytene PS Spermatocyte q/a HFSC, q/a-hfsc, HFTAC Round RS Spermatid Spermatozoon HSC Pachytene Spermatocyte q/a HFSC, HFTAC Round Spermatid Sperm Pachytene Spermatocyte Supplementary Figure 2. Round 3D Spermatid PCA plot based on (A) expression or () PRIMs of all Sperm protein-coding and noncoding genes. For s, Cs, and s, only in-house data were analyzed. Different cell types are distinguished by colors as in Figure PC
3 A. _LA _SHS5.2 _SHS Gene Expression (RNA-seq) Pearson Correlation _SHS5. _SHS _LA PRIM=log2(H3/H3) P_MCV8_MTS8 P_MCV6_MTS8 _MCV8_MTS8. _LA3 _WJA2 _MTS _SHS Pearson Correlation _SHS _MTS7 _WJA2 _LA _MCV8_MTS8 P_MCV6_MTS8 P_MCV8_MTS8 Supplementary Figure 3. Correlation coefficients between in-house and published cell lines. (A) Expression of all protein-coding and noncoding genes. () PRIMs of all protein-coding and noncoding gene promoters with and/or modification. lack boxes denote data produced in-house.
4 A Pluri-/Multipotent Germline Soma % Total Promoter % 8% 6% 4% 2% Only + Only No Modification % Enrichment 5-5 Depletion (3) (3) (2) (4) E2.5 E3.5 E4.5 PS (2) RS (3) E2.5 E3.5 E4.5 PS RS Sperm LSK HSC qhfsc ahfsc HFTAC Sperm (3) LSK HSC (2) qhfsc ahfsc HFTAC Cell fate commitment, GO:4565 Heart morphogenesis, GO:37 Pancreas GO:36 Eye morphogenesis, GO:48592 Embryonic placenta GO:892 Regulation of organ formation, GO:356 Mesenchymal to epithelial transition, GO:623 Regulation of kidney GO:983 one morphogenesis, GO:6349 Epithelial cell morphogenesis, GO:3382 Development of primary male sexual characteristics, GO:46546 Mammary gland morphogenesis, GO:6443 Gut morphogenesis, GO:48547 Neuron fate specification, GO:48665 Hemopoiesis, GO:397 Cell-cell signaling involved in cell fate commitment, GO:4568 Embryonic skeletal system GO:4876 Ear GO:43583 Lung GO:3324 Anterior/posterior pattern formation, GO:9952 Mesenchyme GO:6485 Vasculature GO:944 Limb GO:673 Supplementary Figure 4. Genes grouped by promoter histone modifications. (A) Using peak detection results at promoters, all 32,58 protein-coding and noncoding genes were assigned to each of four different categories: only (green), only marked by modification; only (red), only marked by modification; + (yellow), marked by both and modifications; and no modification (grey), no significant or modification detected. For each cell type with at least three biological repeats from different cell lines or resources (Supplementary Table S), results are presented as mean values and standard deviations. Number in brackets, sample size. () GO enrichment in bivalent genes identified from different cell types. Red, over representation. lue, under representation.
5 (522) 5 Depletion Depletion (25) Expression of ivalent Promoters D 8 % Selected Genes p-value =. 6 X7 X6 X5 Expression Change in % 4 Development of primary sexual characteristics, GO:4537 Development of primary sexual characteristics, GO:4537 Heart GO:757 Development of primary sexual characteristics, GO:4537 Heart GO:757 Lung GO:3324 Lung GO:3324 Endocrine system GO:3527 rain GO:742 rain GO:742 Morphogenesis of an epithelium, GO:29 GO:43583 EarEar GO:43583 Gland GO:48732 Gland GO:48732 Gland GO:48732 Ear GO:43583 GO:654 EyeEye GO:654 Lung GO:3324 Urogenital system Urogenital system GO:655 GO:655 Eye GO:654 Kidney GO:822 Kidney GO:822 Urogenital system GO:655 Vasculature GO:944 Vasculature GO:944 Endocrine system GO:3527 Heart GO:757 Endocrine system GO:3527 Skeletal system GO:5 Skeletal system GO:5 rain GO:742 Pattern specification process, GO:7389 process, GO:7389 Pattern specification Vasculature GO:944 Embryonic organ GO:48568 GO:48568 Embryonic organ Kidney GO:822 Morphogenesis of an epithelium, GO:29 Morphogenesis of an epithelium, GO:29 Pattern specification process, GO:7389 Embryonic organ GO:48568 Skeletal system GO:5 2 C (867) X4 X X3 X5 X2X6 X3 X XX4 Enrichment Enrichment X ivalent Promoter X A X Figure S3 Increase Decrease 8% 6% 4% 2 2% % ivalent Genes Univalent & Unmodified Genes Supplementary Figure 5. -like bivalent promoter modification is incompletely established in. (A) Overlap of bivalent genes identified by peak detection in s, s, and cells. () GO enrichment in bivalent genes shared or unique in s, s, and cells. Presence and absence of promoter bivalency in certain cell types is denoted by + and -, respectively. Red, over representation. lue, under representation. (C) Comparison of global gene expression profiles between s and cells. lack dots, bivalent genes identified by peak detection. dashed line, cut-off of twofold (log2) expression differences between s and cells. (D) Percentage of genes with expression increases (black) or decreases (grey) in cells. bivalent genes,,867 genes with both and modifications at promoters. univalent & unmodified genes, 3,74 genes modified with either,, or neither of the two modifications at promoters. p-value =. by Fisher s exact test (one-sided).
6 K27 7 A % Total Promoter % Total Promoter C % Total Promoter % 8% 6% 4% 2% % % 8% 6% 4% 2% % % 8% 6% 4% 2% % (MTS7) Only + Only No Modification Only + Only No Modification Only + Only No Modification Density Density Density (R) (A) Promoter with Peak Only + Only 2.7 PRIM low PRIM high PRIM (R) (A) 2.2 PRIM low PRIM high PRIM (R) (A) PRIM low 2.2 PRIM PRIM high Gene Expression (log2 FPKM) Gene Expression (log2 FPKM) Gene Expression (log2 FPKM) Chromatin State Chromatin State Chromatin State Gene Expression (PRIM low ) (PRIM high ) Gene Expression (PRIM low ) (PRIM high ) Gene Expression (PRIM low ) (PRIM high ) D % Total Promoter E % Total Promoter % Only + 8% Only No Modification 6% 4% 2% % (MTS7) % Only + 8% Only No Modification 6% 4% 2% % _MCV8 (MTS8) Density Density (R) (A) PRIM low 2. PRIM (R) (A) PRIM low 2. PRIM PRIM high PRIM high Gene Expression (log2 FPKM) Gene Expression (log2 FPKM) Chromatin State Chromatin State Gene Expression (PRIM low ) (PRIM high ) Gene Expression (PRIM low ) (PRIM high ) Supplementary Figure 6. Distinguishing active and repressive promoter chromatin states by PRIMs in (A) s, () s, (C) s, (D) s, and (E). ased on peak detection results at promoters, all genes were assigned to each of four histone modification categories as in Figure S4A (left). Probability density distribution of PRIMs was made for each of the three categories, only (green Figure line), S4 + (yellow line), and only (red line), and cut-off value between and + or groups was selected by the crossover between and + plot (dashed line). X-axis, PRIMs. Y-axis, probability density. Cut-off value, =2.7, =2.2, =2.2, =2., =2. (middle). Expression of genes in promoter chromatin states delineated by active (above PRIM cutoff) and repressive (at or below PRIM cut-off) marks is shown in boxplot (Right). The bottom and top of the boxes indicate the 25 th and 75 th percentiles, the central bars indicate medians and whiskers indicate non-outlier extremes. Dashed line, median expression value of all genes.
7 A (PRIM) No r =.86 No C Class I Promoters (PRIM) - R N R M A A N Enrichment 5-5 Depletion () (Modified) (Stable I) A M R N A R N..5 Regulation 2. of cell cycle, 2.5 GO: Regulation of fibroblast proliferation, GO:4845 Pattern specification process, GO:7389 Neuron fate commitment, GO:48663 Venous blood vessel morphogenesis, GO:48845 Embryonic organ GO:48568 Cell fate commitment, GO:4565 Vasculature GO:944 Stem cell maintenance, GO:9827 Heart morphogenesis, GO:37 Primary neural tube formation, GO:42 Morphogenesis of an epithelium, GO:29 in utero embryonic GO:7 Placenta GO:89 Lung morphogenesis, GO:6425 Genes Gene Expression [log2 FPKM] * Genes Modified Genes Stable I Genes All Class I Genes * *._avg _avg.5 _avg 2._avg _avg 2.5 _avg 3. Type (a) Promoters Type (b) Promoters Type (a) Promoters Genes Type (c) Stable Promoters I Genes Type (b) Modified Promoters Genes All Class I I Genes Promoters Type (c) Promoters All Class I Promoters Figure S7 Supplementary Figure 7. Promoter chromatin states, transcriptional activities, and biological functions of genes activated during reprogramming of s (Class I). (A) Comparison of chromatin states (PRIMs) between s and s for all class I promoters (grey dots). X-axis, PRIMs from s. Y-axis, PRIMs from s. lack dots, class I example genes displayed in Figure 3A. Dashed black line, cut-off between active and repressive chromatin states. Dark grey line, optimal curve fits to all class I promoters. r, correlation coefficient with all class I promoter PRIMs. () Transcriptional activities of selected gene subsets. Genes are grouped by promoter PRIMs as in Figure 4A. The bottom and top of the boxes indicate the 25 th and 75 th percentiles, the central bars indicate medians and whiskers indicate non-outlier extremes. p-values were calculated using Wilcoxon tests., p-value <.. *, p- value <.5. Dashed line, median expression value of all genes. (C) GO enrichment in all Class I genes. Genes are grouped by promoter PRIMs as in Figure 4A. A, chromatin state. R, chromatin state. M, Histone modification ( or ) identifiable. N, Histone modification ( or ) unidentifiable. ottom, number of genes in each group.
8 A (PRIM) No r =.9 No C Class II Promoters (PRIM) R - A () (Unmodified) (Stable II) N R M A A N M R N A R N Regulation of gene expression, epigenetic, GO:429 DNA methylation involved in gamete generation, GO:4346 Spermatogenesis, GO:7283 pirna metabolic process, GO:34587 Meiosis, GO:726 Sexual reproduction, GO:9953 Morphogenesis of an epithelium, GO:29 Pattern specification process, GO:7389 Skeletal system GO:5 Stem cell division, GO:745 Somatic stem cell division, GO:483 Germ cell GO:728 Genes Gene Expression [log2 FPKM] Repress Genes No Modified Genes Stable II Genes All Class II Genes *._avg _avg.5 _avg 2._avg _avg 2.5 _avg 3. Type (a) Promoters Type (b) Promoters Type (a) Promoters Genes Type (c) Stable Promoters II Genes Type (b) Unmodified Promoters Genes All All Class II II Genes Promoters Type (c) Promoters All Class II Promoters Figure S8 Supplementary Figure 8. Promoter chromatin states, transcriptional activities, and biological functions of gene repressed during reprogramming of s (Class II). (A) Comparison of chromatin states (PRIMs) between s and s for all class II promoters (grey dots). X-axis, PRIMs from s. Y-axis, PRIMs from s. lack dots, Class II example genes displayed in Figure 3A. Dashed black line, cut-off between active and repressive chromatin states. Dark grey line, optimal curve fits to all class II promoters. r, correlation coefficient with all class II promoter PRIMs. () Transcription activities of selected gene subsets. Genes are grouped by promoter PRIMs as in Figure 4C. The bottom and top of the boxes indicate the 25 th and 75 th percentiles, the central bars indicate medians and whiskers indicate non-outlier extremes. p-values were calculated using Wilcoxon tests., p-value <.. *, p- value <.5. Dashed line, median expression value of all genes. (C) GO enrichment in all Class II genes. Genes are grouped by promoter PRIMs as in Figure 4C. A, active chromatin state. R, repressive chromatin state. M, histone modification ( or ) is identifiable. N, histone modification ( or ) is unidentifiable. ottom, number of genes in each group.
9 A C Suz2 Zfx Nr5a2 Nanog Sox2 Pou5f Klf4 Esrrb Tfcp2l ME ME SME ME ME ME ME SME ME S S S Zic3 Nanog Zbtb6 kb Supplementary Figure 9. K27ac modification in different cell types (blue) and transcription factor enrichment in s (black) at selected genes. (A) Zic3 (Class I, ). () Nanog (Class I, Modified ). (C) Zbtb6 (Class II, ). Core pluripotency regulators (Pou5f, Sox2, Nanog) are highlighted in red. Pink region, Promoter. lue bar at bottom, enhancer. ME, enhancers active in both s and s. SME, enhancers active in, s and s. S, enhancers active only in s. K27ac and transcription factor track range,.
10 ivalent Promoters (PRIM) in Different Cell Types./2 PC Epigenome at Promoters - (PRIM).3 PC _LA _MTS7 _WJA P_MCV6 P_MCV8 Supplementary Figure Pachytene. Spermatocyte 3D PCA plot based on PRIMs of all promoters with Round Spermatid + bivalent Sperm histone modifications in s. For s, Cs, and s, only in-house data were analyzed. Different cell types are distinguished by colors as in Figure.. PC2.3 PC2 HSC PC P HSC Pluripotent P Germ q/a HFSC, Cells HFTAC Somatic Cells / Multipotent Cells HSC, LSK P Pachytene PS Spermatocyte q/a HFSC, q/a-hfsc, HFTAC Round RS Spermatid Spermatozoon HSC Pachytene Spermatocyte q/a HFSC, HFTAC Round Spermatid Sperm PC
11 A C E2.5 E3.5 E4.5 PS RS Sperm kb Sox2 Cdx2 Gata6 Supplementary Figure. Histone modifications at selected genes in different types of germ cells. Green, modification. Red, modification. track range,. track range,.5.
12 Specific antibody Control immunoglobulin a6-integrin CD9 Thy- c-kit 83.4% 89.4% 23.7% Count Supplementary Figure 2. Analysis of cell surface marks by flow cytometry.
Nature Genetics: doi: /ng Supplementary Figure 1. Assessment of sample purity and quality.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Assessment of sample purity and quality. (a) Hematoxylin and eosin staining of formaldehyde-fixed, paraffin-embedded sections from a human testis biopsy collected concurrently with
Supplementary Figure 1 Assessment of sample purity and quality. (a) Hematoxylin and eosin staining of formaldehyde-fixed, paraffin-embedded sections from a human testis biopsy collected concurrently with
Supplementary Figure 1. Metabolic landscape of cancer discovery pipeline. RNAseq raw counts data of cancer and healthy tissue samples were downloaded
 Supplementary Figure 1. Metabolic landscape of cancer discovery pipeline. RNAseq raw counts data of cancer and healthy tissue samples were downloaded from TCGA and differentially expressed metabolic genes
Supplementary Figure 1. Metabolic landscape of cancer discovery pipeline. RNAseq raw counts data of cancer and healthy tissue samples were downloaded from TCGA and differentially expressed metabolic genes
Broad H3K4me3 is associated with increased transcription elongation and enhancer activity at tumor suppressor genes
 Broad H3K4me3 is associated with increased transcription elongation and enhancer activity at tumor suppressor genes Kaifu Chen 1,2,3,4,5,10, Zhong Chen 6,10, Dayong Wu 6, Lili Zhang 7, Xueqiu Lin 1,2,8,
Broad H3K4me3 is associated with increased transcription elongation and enhancer activity at tumor suppressor genes Kaifu Chen 1,2,3,4,5,10, Zhong Chen 6,10, Dayong Wu 6, Lili Zhang 7, Xueqiu Lin 1,2,8,
Nature Immunology: doi: /ni Supplementary Figure 1. Characteristics of SEs in T reg and T conv cells.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Characteristics of SEs in T reg and T conv cells. (a) Patterns of indicated transcription factor-binding at SEs and surrounding regions in T reg and T conv cells. Average normalized
Supplementary Figure 1 Characteristics of SEs in T reg and T conv cells. (a) Patterns of indicated transcription factor-binding at SEs and surrounding regions in T reg and T conv cells. Average normalized
Single-cell RNA-Seq profiling of human pre-implantation embryos and embryonic stem cells
 Single-cell RNA-Seq profiling of human pre-implantation embryos and embryonic stem cells Liying Yan,2,5, Mingyu Yang,5, Hongshan Guo, Lu Yang, Jun Wu, Rong Li,2, Ping Liu, Ying Lian, Xiaoying Zheng, Jie
Single-cell RNA-Seq profiling of human pre-implantation embryos and embryonic stem cells Liying Yan,2,5, Mingyu Yang,5, Hongshan Guo, Lu Yang, Jun Wu, Rong Li,2, Ping Liu, Ying Lian, Xiaoying Zheng, Jie
Transcriptome profiling of the developing male germ line identifies the mir-29 family as a global regulator during meiosis
 RNA BIOLOGY 2017, VOL. 14, NO. 2, 219 235 http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/15476286.2016.1270002 RESEARCH PAPER Transcriptome profiling of the developing male germ line identifies the mir-29 family as a global
RNA BIOLOGY 2017, VOL. 14, NO. 2, 219 235 http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/15476286.2016.1270002 RESEARCH PAPER Transcriptome profiling of the developing male germ line identifies the mir-29 family as a global
Computational Analysis of UHT Sequences Histone modifications, CAGE, RNA-Seq
 Computational Analysis of UHT Sequences Histone modifications, CAGE, RNA-Seq Philipp Bucher Wednesday January 21, 2009 SIB graduate school course EPFL, Lausanne ChIP-seq against histone variants: Biological
Computational Analysis of UHT Sequences Histone modifications, CAGE, RNA-Seq Philipp Bucher Wednesday January 21, 2009 SIB graduate school course EPFL, Lausanne ChIP-seq against histone variants: Biological
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology: doi: /nsmb.2419
 Supplementary Figure 1 Mapped sequence reads and nucleosome occupancies. (a) Distribution of sequencing reads on the mouse reference genome for chromosome 14 as an example. The number of reads in a 1 Mb
Supplementary Figure 1 Mapped sequence reads and nucleosome occupancies. (a) Distribution of sequencing reads on the mouse reference genome for chromosome 14 as an example. The number of reads in a 1 Mb
7SK ChIRP-seq is specifically RNA dependent and conserved between mice and humans.
 Supplementary Figure 1 7SK ChIRP-seq is specifically RNA dependent and conserved between mice and humans. Regions targeted by the Even and Odd ChIRP probes mapped to a secondary structure model 56 of the
Supplementary Figure 1 7SK ChIRP-seq is specifically RNA dependent and conserved between mice and humans. Regions targeted by the Even and Odd ChIRP probes mapped to a secondary structure model 56 of the
Chromatin marks identify critical cell-types for fine-mapping complex trait variants
 Chromatin marks identify critical cell-types for fine-mapping complex trait variants Gosia Trynka 1-4 *, Cynthia Sandor 1-4 *, Buhm Han 1-4, Han Xu 5, Barbara E Stranger 1,4#, X Shirley Liu 5, and Soumya
Chromatin marks identify critical cell-types for fine-mapping complex trait variants Gosia Trynka 1-4 *, Cynthia Sandor 1-4 *, Buhm Han 1-4, Han Xu 5, Barbara E Stranger 1,4#, X Shirley Liu 5, and Soumya
Expanded View Figures
 EMO Molecular Medicine Proteomic map of squamous cell carcinomas Hanibal ohnenberger et al Expanded View Figures Figure EV1. Technical reproducibility. Pearson s correlation analysis of normalised SILC
EMO Molecular Medicine Proteomic map of squamous cell carcinomas Hanibal ohnenberger et al Expanded View Figures Figure EV1. Technical reproducibility. Pearson s correlation analysis of normalised SILC
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature10866 a b 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Match No Match 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Turcan et al. Supplementary Fig.1 Concepts mapping H3K27 targets in EF CBX8 targets in EF H3K27 targets in ES SUZ12 targets in ES
doi:10.1038/nature10866 a b 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Match No Match 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Turcan et al. Supplementary Fig.1 Concepts mapping H3K27 targets in EF CBX8 targets in EF H3K27 targets in ES SUZ12 targets in ES
Supplementary Figures
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Heatmap of GO terms for differentially expressed genes. The terms were hierarchically clustered using the GO term enrichment beta. Darker red, higher positive
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Heatmap of GO terms for differentially expressed genes. The terms were hierarchically clustered using the GO term enrichment beta. Darker red, higher positive
Strategic delivery: Setting standards Increasing and. Details: Output: Demonstrating efficiency. informing choice.
 Strategic delivery: Setting standards Increasing and informing choice Demonstrating efficiency economy and value Details: Meeting Scientific and Clinical Advances Advisory Committee Agenda item 6 Paper
Strategic delivery: Setting standards Increasing and informing choice Demonstrating efficiency economy and value Details: Meeting Scientific and Clinical Advances Advisory Committee Agenda item 6 Paper
Supplementary. properties of. network types. randomly sampled. subsets (75%
 Supplementary Information Gene co-expression network analysis reveals common system-level prognostic genes across cancer types properties of Supplementary Figure 1 The robustness and overlap of prognostic
Supplementary Information Gene co-expression network analysis reveals common system-level prognostic genes across cancer types properties of Supplementary Figure 1 The robustness and overlap of prognostic
Testicular stem cells
 Testicular stem cells Dirk G. de Rooij Department of Endocrinology Faculty of Biology, Utrecht University 1. Knowledge on the development of the spermatogenic stem cell lineage 2. Principals of the nature
Testicular stem cells Dirk G. de Rooij Department of Endocrinology Faculty of Biology, Utrecht University 1. Knowledge on the development of the spermatogenic stem cell lineage 2. Principals of the nature
Comparison of open chromatin regions between dentate granule cells and other tissues and neural cell types.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Comparison of open chromatin regions between dentate granule cells and other tissues and neural cell types. (a) Pearson correlation heatmap among open chromatin profiles of different
Supplementary Figure 1 Comparison of open chromatin regions between dentate granule cells and other tissues and neural cell types. (a) Pearson correlation heatmap among open chromatin profiles of different
Nature Genetics: doi: /ng Supplementary Figure 1. SEER data for male and female cancer incidence from
 Supplementary Figure 1 SEER data for male and female cancer incidence from 1975 2013. (a,b) Incidence rates of oral cavity and pharynx cancer (a) and leukemia (b) are plotted, grouped by males (blue),
Supplementary Figure 1 SEER data for male and female cancer incidence from 1975 2013. (a,b) Incidence rates of oral cavity and pharynx cancer (a) and leukemia (b) are plotted, grouped by males (blue),
Supplementary Figure 1 Information on transgenic mouse models and their recording and optogenetic equipment. (a) 108 (b-c) (d) (e) (f) (g)
 Supplementary Figure 1 Information on transgenic mouse models and their recording and optogenetic equipment. (a) In four mice, cre-dependent expression of the hyperpolarizing opsin Arch in pyramidal cells
Supplementary Figure 1 Information on transgenic mouse models and their recording and optogenetic equipment. (a) In four mice, cre-dependent expression of the hyperpolarizing opsin Arch in pyramidal cells
Stem Cell Epigenetics
 Stem Cell Epigenetics Philippe Collas University of Oslo Institute of Basic Medical Sciences Norwegian Center for Stem Cell Research www.collaslab.com Source of stem cells in the body Somatic ( adult )
Stem Cell Epigenetics Philippe Collas University of Oslo Institute of Basic Medical Sciences Norwegian Center for Stem Cell Research www.collaslab.com Source of stem cells in the body Somatic ( adult )
Large conserved domains of low DNA methylation maintained by Dnmt3a
 Supplementary information Large conserved domains of low DNA methylation maintained by Dnmt3a Mira Jeong# 1, Deqiang Sun # 2, Min Luo# 1, Yun Huang 3, Grant A. Challen %1, Benjamin Rodriguez 2, Xiaotian
Supplementary information Large conserved domains of low DNA methylation maintained by Dnmt3a Mira Jeong# 1, Deqiang Sun # 2, Min Luo# 1, Yun Huang 3, Grant A. Challen %1, Benjamin Rodriguez 2, Xiaotian
Supplementary Figure 1. Efficiency of Mll4 deletion and its effect on T cell populations in the periphery. Nature Immunology: doi: /ni.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Efficiency of Mll4 deletion and its effect on T cell populations in the periphery. Expression of Mll4 floxed alleles (16-19) in naive CD4 + T cells isolated from lymph nodes and
Supplementary Figure 1 Efficiency of Mll4 deletion and its effect on T cell populations in the periphery. Expression of Mll4 floxed alleles (16-19) in naive CD4 + T cells isolated from lymph nodes and
Nature Methods: doi: /nmeth.3115
 Supplementary Figure 1 Analysis of DNA methylation in a cancer cohort based on Infinium 450K data. RnBeads was used to rediscover a clinically distinct subgroup of glioblastoma patients characterized by
Supplementary Figure 1 Analysis of DNA methylation in a cancer cohort based on Infinium 450K data. RnBeads was used to rediscover a clinically distinct subgroup of glioblastoma patients characterized by
Supplemental Information. Derivation of Human Trophoblast Stem Cells
 Cell Stem Cell, Volume 22 Supplemental Information Derivation of Human Trophoblast Stem Cells Hiroaki Okae, Hidehiro Toh, Tetsuya Sato, Hitoshi Hiura, Sota Takahashi, Kenjiro Shirane, Yuka Kabayama, Mikita
Cell Stem Cell, Volume 22 Supplemental Information Derivation of Human Trophoblast Stem Cells Hiroaki Okae, Hidehiro Toh, Tetsuya Sato, Hitoshi Hiura, Sota Takahashi, Kenjiro Shirane, Yuka Kabayama, Mikita
Relationship between genomic features and distributions of RS1 and RS3 rearrangements in breast cancer genomes.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Relationship between genomic features and distributions of RS1 and RS3 rearrangements in breast cancer genomes. (a,b) Values of coefficients associated with genomic features, separately
Supplementary Figure 1 Relationship between genomic features and distributions of RS1 and RS3 rearrangements in breast cancer genomes. (a,b) Values of coefficients associated with genomic features, separately
Nature Genetics: doi: /ng Supplementary Figure 1. Phenotypic characterization of MES- and ADRN-type cells.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Phenotypic characterization of MES- and ADRN-type cells. (a) Bright-field images showing cellular morphology of MES-type (691-MES, 700-MES, 717-MES) and ADRN-type (691-ADRN, 700-
Supplementary Figure 1 Phenotypic characterization of MES- and ADRN-type cells. (a) Bright-field images showing cellular morphology of MES-type (691-MES, 700-MES, 717-MES) and ADRN-type (691-ADRN, 700-
Nature Immunology: doi: /ni Supplementary Figure 1. Transcriptional program of the TE and MP CD8 + T cell subsets.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Transcriptional program of the TE and MP CD8 + T cell subsets. (a) Comparison of gene expression of TE and MP CD8 + T cell subsets by microarray. Genes that are 1.5-fold upregulated
Supplementary Figure 1 Transcriptional program of the TE and MP CD8 + T cell subsets. (a) Comparison of gene expression of TE and MP CD8 + T cell subsets by microarray. Genes that are 1.5-fold upregulated
PhD THESIS Epigenetic mechanisms involved in stem cell differentiation
 Romanian Academy Institute of Cellular Biology and Pathology "Nicolae Simionescu" PhD THESIS Epigenetic mechanisms involved in stem cell differentiation Coordinator: Acad. Maya Simionescu PhD Student:
Romanian Academy Institute of Cellular Biology and Pathology "Nicolae Simionescu" PhD THESIS Epigenetic mechanisms involved in stem cell differentiation Coordinator: Acad. Maya Simionescu PhD Student:
An epigenetic approach to understanding (and predicting?) environmental effects on gene expression
 www.collaslab.com An epigenetic approach to understanding (and predicting?) environmental effects on gene expression Philippe Collas University of Oslo Institute of Basic Medical Sciences Stem Cell Epigenetics
www.collaslab.com An epigenetic approach to understanding (and predicting?) environmental effects on gene expression Philippe Collas University of Oslo Institute of Basic Medical Sciences Stem Cell Epigenetics
Epigenetics: The Future of Psychology & Neuroscience. Richard E. Brown Psychology Department Dalhousie University Halifax, NS, B3H 4J1
 Epigenetics: The Future of Psychology & Neuroscience Richard E. Brown Psychology Department Dalhousie University Halifax, NS, B3H 4J1 Nature versus Nurture Despite the belief that the Nature vs. Nurture
Epigenetics: The Future of Psychology & Neuroscience Richard E. Brown Psychology Department Dalhousie University Halifax, NS, B3H 4J1 Nature versus Nurture Despite the belief that the Nature vs. Nurture
Fragile X Syndrome. Genetics, Epigenetics & the Role of Unprogrammed Events in the expression of a Phenotype
 Fragile X Syndrome Genetics, Epigenetics & the Role of Unprogrammed Events in the expression of a Phenotype A loss of function of the FMR-1 gene results in severe learning problems, intellectual disability
Fragile X Syndrome Genetics, Epigenetics & the Role of Unprogrammed Events in the expression of a Phenotype A loss of function of the FMR-1 gene results in severe learning problems, intellectual disability
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/8/375/ra41/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Actin cytoskeletal remodeling with protrusion formation is essential for heart regeneration in Hippo-deficient mice
www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/8/375/ra41/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Actin cytoskeletal remodeling with protrusion formation is essential for heart regeneration in Hippo-deficient mice
fl/+ KRas;Atg5 fl/+ KRas;Atg5 fl/fl KRas;Atg5 fl/fl KRas;Atg5 Supplementary Figure 1. Gene set enrichment analyses. (a) (b)
 KRas;At KRas;At KRas;At KRas;At a b Supplementary Figure 1. Gene set enrichment analyses. (a) GO gene sets (MSigDB v3. c5) enriched in KRas;Atg5 fl/+ as compared to KRas;Atg5 fl/fl tumors using gene set
KRas;At KRas;At KRas;At KRas;At a b Supplementary Figure 1. Gene set enrichment analyses. (a) GO gene sets (MSigDB v3. c5) enriched in KRas;Atg5 fl/+ as compared to KRas;Atg5 fl/fl tumors using gene set
Nature Immunology: doi: /ni Supplementary Figure 1. RNA-Seq analysis of CD8 + TILs and N-TILs.
 Supplementary Figure 1 RNA-Seq analysis of CD8 + TILs and N-TILs. (a) Schematic representation of the tumor and cell types used for the study. HNSCC, head and neck squamous cell cancer; NSCLC, non-small
Supplementary Figure 1 RNA-Seq analysis of CD8 + TILs and N-TILs. (a) Schematic representation of the tumor and cell types used for the study. HNSCC, head and neck squamous cell cancer; NSCLC, non-small
Supplementary Figure S1. Gene expression analysis of epidermal marker genes and TP63.
 Supplementary Figure Legends Supplementary Figure S1. Gene expression analysis of epidermal marker genes and TP63. A. Screenshot of the UCSC genome browser from normalized RNAPII and RNA-seq ChIP-seq data
Supplementary Figure Legends Supplementary Figure S1. Gene expression analysis of epidermal marker genes and TP63. A. Screenshot of the UCSC genome browser from normalized RNAPII and RNA-seq ChIP-seq data
The Biology and Genetics of Cells and Organisms The Biology of Cancer
 The Biology and Genetics of Cells and Organisms The Biology of Cancer Mendel and Genetics How many distinct genes are present in the genomes of mammals? - 21,000 for human. - Genetic information is carried
The Biology and Genetics of Cells and Organisms The Biology of Cancer Mendel and Genetics How many distinct genes are present in the genomes of mammals? - 21,000 for human. - Genetic information is carried
MicroRNAs control mrna fate by compartmentalization based on 3 UTR length in male germ cells
 Zhang et al. Genome Biology (2017) 18:105 DOI 10.1186/s13059-017-1243-x RESEARCH MicroRNAs control mrna fate by compartmentalization based on 3 UTR length in male germ cells Ying Zhang 1, Chong Tang 1,
Zhang et al. Genome Biology (2017) 18:105 DOI 10.1186/s13059-017-1243-x RESEARCH MicroRNAs control mrna fate by compartmentalization based on 3 UTR length in male germ cells Ying Zhang 1, Chong Tang 1,
Nature Getetics: doi: /ng.3471
 Supplementary Figure 1 Summary of exome sequencing data. ( a ) Exome tumor normal sample sizes for bladder cancer (BLCA), breast cancer (BRCA), carcinoid (CARC), chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLLX), colorectal
Supplementary Figure 1 Summary of exome sequencing data. ( a ) Exome tumor normal sample sizes for bladder cancer (BLCA), breast cancer (BRCA), carcinoid (CARC), chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLLX), colorectal
Supplemental Figure S1. Tertiles of FKBP5 promoter methylation and internal regulatory region
 Supplemental Figure S1. Tertiles of FKBP5 promoter methylation and internal regulatory region methylation in relation to PSS and fetal coupling. A, PSS values for participants whose placentas showed low,
Supplemental Figure S1. Tertiles of FKBP5 promoter methylation and internal regulatory region methylation in relation to PSS and fetal coupling. A, PSS values for participants whose placentas showed low,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature19360 Supplementary Tables Supplementary Table 1. Number of monoclonal reads in each sample Sample Number of cells Total reads Aligned reads Monoclonal reads
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature19360 Supplementary Tables Supplementary Table 1. Number of monoclonal reads in each sample Sample Number of cells Total reads Aligned reads Monoclonal reads
ChromHMM Tutorial. Jason Ernst Assistant Professor University of California, Los Angeles
 ChromHMM Tutorial Jason Ernst Assistant Professor University of California, Los Angeles Talk Outline Chromatin states analysis and ChromHMM Accessing chromatin state annotations for ENCODE2 and Roadmap
ChromHMM Tutorial Jason Ernst Assistant Professor University of California, Los Angeles Talk Outline Chromatin states analysis and ChromHMM Accessing chromatin state annotations for ENCODE2 and Roadmap
Jayanti Tokas 1, Puneet Tokas 2, Shailini Jain 3 and Hariom Yadav 3
 Jayanti Tokas 1, Puneet Tokas 2, Shailini Jain 3 and Hariom Yadav 3 1 Department of Biotechnology, JMIT, Radaur, Haryana, India 2 KITM, Kurukshetra, Haryana, India 3 NIDDK, National Institute of Health,
Jayanti Tokas 1, Puneet Tokas 2, Shailini Jain 3 and Hariom Yadav 3 1 Department of Biotechnology, JMIT, Radaur, Haryana, India 2 KITM, Kurukshetra, Haryana, India 3 NIDDK, National Institute of Health,
Table S1. Total and mapped reads produced for each ChIP-seq sample
 Tale S1. Total and mapped reads produced for each ChIP-seq sample Sample Total Reads Mapped Reads Col- H3K27me3 rep1 125662 1334323 (85.76%) Col- H3K27me3 rep2 9176437 7986731 (87.4%) atmi1a//c H3K27m3
Tale S1. Total and mapped reads produced for each ChIP-seq sample Sample Total Reads Mapped Reads Col- H3K27me3 rep1 125662 1334323 (85.76%) Col- H3K27me3 rep2 9176437 7986731 (87.4%) atmi1a//c H3K27m3
Lung Met 1 Lung Met 2 Lung Met Lung Met H3K4me1. Lung Met H3K27ac Primary H3K4me1
 a Gained Met-VELs 1.5 1.5 -.5 Lung Met 1 Lung Met Lung Met 3 1. Lung Met H3K4me1 Lung Met H3K4me1 1 Lung Met H3K4me1 Lung Met H3K7ac 1.5 Lung Met H3K7ac Lung Met H3K7ac.8 Primary H3K4me1 Primary H3K7ac
a Gained Met-VELs 1.5 1.5 -.5 Lung Met 1 Lung Met Lung Met 3 1. Lung Met H3K4me1 Lung Met H3K4me1 1 Lung Met H3K4me1 Lung Met H3K7ac 1.5 Lung Met H3K7ac Lung Met H3K7ac.8 Primary H3K4me1 Primary H3K7ac
Dynamics of mono, di and tri-methylated histone H3 lysine 4 during male meiotic prophase I. Nuclei were co-stained for H3.1/H3.2. Progressing stages
 Dynamics of mono, di and tri-methylated histone H3 lysine 4 during male meiotic prophase I. Nuclei were co-stained for H3.1/H3.2. Progressing stages of spermatogenesis are shown from left to right. Arrows/dotted
Dynamics of mono, di and tri-methylated histone H3 lysine 4 during male meiotic prophase I. Nuclei were co-stained for H3.1/H3.2. Progressing stages of spermatogenesis are shown from left to right. Arrows/dotted
a) List of KMTs targeted in the shrna screen. The official symbol, KMT designation,
 Supplementary Information Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. a) List of KMTs targeted in the shrna screen. The official symbol, KMT designation, gene ID and specifities are provided. Those highlighted
Supplementary Information Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. a) List of KMTs targeted in the shrna screen. The official symbol, KMT designation, gene ID and specifities are provided. Those highlighted
Ductal pancreatic cancer modeling and drug screening using human pluripotent stem cell and patient-derived tumor organoids
 Ductal pancreatic cancer modeling and drug screening using human pluripotent stem cell and patient-derived tumor organoids Ling Huang 1, Audrey Holtzinger 1,2,11, Ishaan Jagan 1,11, Michael BeGora 1, Ines
Ductal pancreatic cancer modeling and drug screening using human pluripotent stem cell and patient-derived tumor organoids Ling Huang 1, Audrey Holtzinger 1,2,11, Ishaan Jagan 1,11, Michael BeGora 1, Ines
SSM signature genes are highly expressed in residual scar tissues after preoperative radiotherapy of rectal cancer.
 Supplementary Figure 1 SSM signature genes are highly expressed in residual scar tissues after preoperative radiotherapy of rectal cancer. Scatter plots comparing expression profiles of matched pretreatment
Supplementary Figure 1 SSM signature genes are highly expressed in residual scar tissues after preoperative radiotherapy of rectal cancer. Scatter plots comparing expression profiles of matched pretreatment
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1. Behavioral training.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Behavioral training. a, Mazes used for behavioral training. Asterisks indicate reward location. Only some example mazes are shown (for example, right choice and not left choice maze
Supplementary Figure 1 Behavioral training. a, Mazes used for behavioral training. Asterisks indicate reward location. Only some example mazes are shown (for example, right choice and not left choice maze
Genome Control in Cell Identity and Disease! Development and cell identity Loss of cell identity and disease New diagnostics and therapeutics
 Genome Control in Cell Identity and Disease! Development and cell identity Loss of cell identity and disease New diagnostics and therapeutics Development and cell identity! 30,000,000,000 cells!! Control
Genome Control in Cell Identity and Disease! Development and cell identity Loss of cell identity and disease New diagnostics and therapeutics Development and cell identity! 30,000,000,000 cells!! Control
RNA-Seq Preparation Comparision Summary: Lexogen, Standard, NEB
 RNA-Seq Preparation Comparision Summary: Lexogen, Standard, NEB CSF-NGS January 22, 214 Contents 1 Introduction 1 2 Experimental Details 1 3 Results And Discussion 1 3.1 ERCC spike ins............................................
RNA-Seq Preparation Comparision Summary: Lexogen, Standard, NEB CSF-NGS January 22, 214 Contents 1 Introduction 1 2 Experimental Details 1 3 Results And Discussion 1 3.1 ERCC spike ins............................................
Biology 4361 Developmental Biology. October 11, Multiple choice (one point each)
 Biology 4361 Developmental Biology Exam 1 October 11, 2005 Name: ID#: Multiple choice (one point each) 1. Sertoli cells a. surround spermatocytes b. are the structural components of the seminiferous tubules
Biology 4361 Developmental Biology Exam 1 October 11, 2005 Name: ID#: Multiple choice (one point each) 1. Sertoli cells a. surround spermatocytes b. are the structural components of the seminiferous tubules
The Pathology of Germ Cell Tumours of the Ovary
 The Pathology of Germ Cell Tumours of the Ovary Professor Mike Wells University of Sheffield Amman, Jordan November 2013 Professor Francisco Paco Nogales I. Primitive germ cell tumors A. Dysgerminoma
The Pathology of Germ Cell Tumours of the Ovary Professor Mike Wells University of Sheffield Amman, Jordan November 2013 Professor Francisco Paco Nogales I. Primitive germ cell tumors A. Dysgerminoma
The Avatar System TM Yields Biologically Relevant Results
 Application Note The Avatar System TM Yields Biologically Relevant Results Liquid biopsies stand to revolutionize the cancer field, enabling early detection and noninvasive monitoring of tumors. In the
Application Note The Avatar System TM Yields Biologically Relevant Results Liquid biopsies stand to revolutionize the cancer field, enabling early detection and noninvasive monitoring of tumors. In the
Transient β-hairpin Formation in α-synuclein Monomer Revealed by Coarse-grained Molecular Dynamics Simulation
 Transient β-hairpin Formation in α-synuclein Monomer Revealed by Coarse-grained Molecular Dynamics Simulation Hang Yu, 1, 2, a) Wei Han, 1, 3, b) Wen Ma, 1, 2 1, 2, 3, c) and Klaus Schulten 1) Beckman
Transient β-hairpin Formation in α-synuclein Monomer Revealed by Coarse-grained Molecular Dynamics Simulation Hang Yu, 1, 2, a) Wei Han, 1, 3, b) Wen Ma, 1, 2 1, 2, 3, c) and Klaus Schulten 1) Beckman
Chromatin and Transcription Transitions of Mammalian Adult Germline Stem Cells and Spermatogenesis
 Resource Chromatin and Transcription Transitions of Mammalian Adult Germline Stem Cells and Spermatogenesis Saher Sue Hammoud,,4 Diana H.P. Low,, Chongil Yi, Douglas T. Carrell, 4 Ernesto Guccione,,, *
Resource Chromatin and Transcription Transitions of Mammalian Adult Germline Stem Cells and Spermatogenesis Saher Sue Hammoud,,4 Diana H.P. Low,, Chongil Yi, Douglas T. Carrell, 4 Ernesto Guccione,,, *
Supplementary Fig.S1. MeDIP RPKM distribution of 5kb windows. Relative expression of DNMT. Percentage of genome. (fold change)
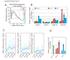 Supplementary Fig.S1 Percentage of genome 10% 8% 6% 4% 2% 0 MeDIP RPKM distribution of 5kb windows 0 0. 0.5 0.75 >1 MeDIP RPKM value EC Relative expression of DNMT (fold change) 12 6 4 3 2 1 EC DNMT1 DNMT2
Supplementary Fig.S1 Percentage of genome 10% 8% 6% 4% 2% 0 MeDIP RPKM distribution of 5kb windows 0 0. 0.5 0.75 >1 MeDIP RPKM value EC Relative expression of DNMT (fold change) 12 6 4 3 2 1 EC DNMT1 DNMT2
Supplemental Information. Genomic Characterization of Murine. Monocytes Reveals C/EBPb Transcription. Factor Dependence of Ly6C Cells
 Immunity, Volume 46 Supplemental Information Genomic Characterization of Murine Monocytes Reveals C/EBPb Transcription Factor Dependence of Ly6C Cells Alexander Mildner, Jörg Schönheit, Amir Giladi, Eyal
Immunity, Volume 46 Supplemental Information Genomic Characterization of Murine Monocytes Reveals C/EBPb Transcription Factor Dependence of Ly6C Cells Alexander Mildner, Jörg Schönheit, Amir Giladi, Eyal
MIR retrotransposon sequences provide insulators to the human genome
 Supplementary Information: MIR retrotransposon sequences provide insulators to the human genome Jianrong Wang, Cristina Vicente-García, Davide Seruggia, Eduardo Moltó, Ana Fernandez- Miñán, Ana Neto, Elbert
Supplementary Information: MIR retrotransposon sequences provide insulators to the human genome Jianrong Wang, Cristina Vicente-García, Davide Seruggia, Eduardo Moltó, Ana Fernandez- Miñán, Ana Neto, Elbert
SUPPLEMENTAL INFORMATION FOR. PAX7 expression defines germline stem cells in the adult testis
 SUPPLEMENTAL INFORMATION FOR PAX7 expression defines germline stem cells in the adult testis Gina M. Aloisio, Yuji Nakada, Hatice D. Saatcioglu, Christopher G. Peña, Michael D. Baker, Edward D. Tarnawa,
SUPPLEMENTAL INFORMATION FOR PAX7 expression defines germline stem cells in the adult testis Gina M. Aloisio, Yuji Nakada, Hatice D. Saatcioglu, Christopher G. Peña, Michael D. Baker, Edward D. Tarnawa,
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/10/487/eaag2476/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Gene expression profiles of brain endothelial cells during embryonic development at bulk and single-cell levels
www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/10/487/eaag2476/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Gene expression profiles of brain endothelial cells during embryonic development at bulk and single-cell levels
Sirt1 Hmg20b Gm (0.17) 24 (17.3) 877 (857)
 3 (0.17) 24 (17.3) Sirt1 Hmg20 Gm4763 877 (857) c d Suppl. Figure 1. Screen validation for top candidate antagonists of Dot1L (a) Numer of genes with one (gray), two (cyan) or three (red) shrna scored
3 (0.17) 24 (17.3) Sirt1 Hmg20 Gm4763 877 (857) c d Suppl. Figure 1. Screen validation for top candidate antagonists of Dot1L (a) Numer of genes with one (gray), two (cyan) or three (red) shrna scored
Supplementary Information. Gauge size. midline. arcuate 10 < n < 15 5 < n < 10 1 < n < < n < 15 5 < n < 10 1 < n < 5. principal principal
 Supplementary Information set set = Reward = Reward Gauge size Gauge size 3 Numer of correct trials 3 Numer of correct trials Supplementary Fig.. Principle of the Gauge increase. The gauge size (y axis)
Supplementary Information set set = Reward = Reward Gauge size Gauge size 3 Numer of correct trials 3 Numer of correct trials Supplementary Fig.. Principle of the Gauge increase. The gauge size (y axis)
Measuring DNA Methylation with the MinION. Winston Timp Department of Biomedical Engineering Johns Hopkins University 12/1/16
 Measuring DNA Methylation with the MinION Winston Timp Department of Biomedical Engineering Johns Hopkins University 12/1/16 Epigenetics: Modern Modern Definition of epigenetics involves heritable changes
Measuring DNA Methylation with the MinION Winston Timp Department of Biomedical Engineering Johns Hopkins University 12/1/16 Epigenetics: Modern Modern Definition of epigenetics involves heritable changes
Nature Medicine: doi: /nm.3967
 Supplementary Figure 1. Network clustering. (a) Clustering performance as a function of inflation factor. The grey curve shows the median weighted Silhouette widths for varying inflation factors (f [1.6,
Supplementary Figure 1. Network clustering. (a) Clustering performance as a function of inflation factor. The grey curve shows the median weighted Silhouette widths for varying inflation factors (f [1.6,
Use Case 9: Coordinated Changes of Epigenomic Marks Across Tissue Types. Epigenome Informatics Workshop Bioinformatics Research Laboratory
 Use Case 9: Coordinated Changes of Epigenomic Marks Across Tissue Types Epigenome Informatics Workshop Bioinformatics Research Laboratory 1 Introduction Active or inactive states of transcription factor
Use Case 9: Coordinated Changes of Epigenomic Marks Across Tissue Types Epigenome Informatics Workshop Bioinformatics Research Laboratory 1 Introduction Active or inactive states of transcription factor
Profiling of the Exosomal Cargo of Bovine Milk Reveals the Presence of Immune- and Growthmodulatory Non-coding RNAs (ncrna)
 Animal Industry Report AS 664 ASL R3235 2018 Profiling of the Exosomal Cargo of Bovine Milk Reveals the Presence of Immune- and Growthmodulatory Non-coding RNAs (ncrna) Eric D. Testroet Washington State
Animal Industry Report AS 664 ASL R3235 2018 Profiling of the Exosomal Cargo of Bovine Milk Reveals the Presence of Immune- and Growthmodulatory Non-coding RNAs (ncrna) Eric D. Testroet Washington State
Accessing and Using ENCODE Data Dr. Peggy J. Farnham
 1 William M Keck Professor of Biochemistry Keck School of Medicine University of Southern California How many human genes are encoded in our 3x10 9 bp? C. elegans (worm) 959 cells and 1x10 8 bp 20,000
1 William M Keck Professor of Biochemistry Keck School of Medicine University of Southern California How many human genes are encoded in our 3x10 9 bp? C. elegans (worm) 959 cells and 1x10 8 bp 20,000
Epigenetics. Lyle Armstrong. UJ Taylor & Francis Group. f'ci Garland Science NEW YORK AND LONDON
 ... Epigenetics Lyle Armstrong f'ci Garland Science UJ Taylor & Francis Group NEW YORK AND LONDON Contents CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION TO 3.2 CHROMATIN ARCHITECTURE 21 THE STUDY OF EPIGENETICS 1.1 THE CORE
... Epigenetics Lyle Armstrong f'ci Garland Science UJ Taylor & Francis Group NEW YORK AND LONDON Contents CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION TO 3.2 CHROMATIN ARCHITECTURE 21 THE STUDY OF EPIGENETICS 1.1 THE CORE
Epigenetics DNA methylation. Biosciences 741: Genomics Fall, 2013 Week 13. DNA Methylation
 Epigenetics DNA methylation Biosciences 741: Genomics Fall, 2013 Week 13 DNA Methylation Most methylated cytosines are found in the dinucleotide sequence CG, denoted mcpg. The restriction enzyme HpaII
Epigenetics DNA methylation Biosciences 741: Genomics Fall, 2013 Week 13 DNA Methylation Most methylated cytosines are found in the dinucleotide sequence CG, denoted mcpg. The restriction enzyme HpaII
Allelic reprogramming of the histone modification H3K4me3 in early mammalian development
 Allelic reprogramming of the histone modification H3K4me3 in early mammalian development 张戈 Method and material STAR ChIP seq (small-scale TELP-assisted rapid ChIP seq) 200 mouse embryonic stem cells PWK/PhJ
Allelic reprogramming of the histone modification H3K4me3 in early mammalian development 张戈 Method and material STAR ChIP seq (small-scale TELP-assisted rapid ChIP seq) 200 mouse embryonic stem cells PWK/PhJ
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology: doi: /nsmb Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Frequency of alternative-cassette-exon engagement with the ribosome is consistent across data from multiple human cell types and from mouse stem cells. Box plots showing AS frequency
Supplementary Figure 1 Frequency of alternative-cassette-exon engagement with the ribosome is consistent across data from multiple human cell types and from mouse stem cells. Box plots showing AS frequency
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Illustration of the working of network-based SVM to confidently predict a new (and now confirmed) ASD gene. Gene CTNND2 s brain network neighborhood that enabled its prediction by
Supplementary Figure 1 Illustration of the working of network-based SVM to confidently predict a new (and now confirmed) ASD gene. Gene CTNND2 s brain network neighborhood that enabled its prediction by
SUPPLEMENTARY APPENDIX
 SUPPLEMENTARY APPENDIX 1) Supplemental Figure 1. Histopathologic Characteristics of the Tumors in the Discovery Cohort 2) Supplemental Figure 2. Incorporation of Normal Epidermal Melanocytic Signature
SUPPLEMENTARY APPENDIX 1) Supplemental Figure 1. Histopathologic Characteristics of the Tumors in the Discovery Cohort 2) Supplemental Figure 2. Incorporation of Normal Epidermal Melanocytic Signature
Supplementary Figure 1: Attenuation of association signals after conditioning for the lead SNP. a) attenuation of association signal at the 9p22.
 Supplementary Figure 1: Attenuation of association signals after conditioning for the lead SNP. a) attenuation of association signal at the 9p22.32 PCOS locus after conditioning for the lead SNP rs10993397;
Supplementary Figure 1: Attenuation of association signals after conditioning for the lead SNP. a) attenuation of association signal at the 9p22.32 PCOS locus after conditioning for the lead SNP rs10993397;
Transgenerational epigenetics in the germline cycle of Caenorhabditis elegans
 Transgenerational epigenetics in the germline cycle of Caenorhabditis elegans William G Kelly, Emory University Journal Title: Epigenetics and Chromatin Volume: Volume 7, Number 6 Publisher: BioMed Central
Transgenerational epigenetics in the germline cycle of Caenorhabditis elegans William G Kelly, Emory University Journal Title: Epigenetics and Chromatin Volume: Volume 7, Number 6 Publisher: BioMed Central
Transcription factor p63 bookmarks and regulates dynamic enhancers during epidermal differentiation
 Published online: June 1, 15 Article Transcription factor p63 bookmarks and regulates dynamic enhancers during epidermal differentiation Evelyn N Kouwenhoven 1,, Martin Oti, Hanna Niehues 3, Simon J van
Published online: June 1, 15 Article Transcription factor p63 bookmarks and regulates dynamic enhancers during epidermal differentiation Evelyn N Kouwenhoven 1,, Martin Oti, Hanna Niehues 3, Simon J van
Supplementary Figure S1 Expression of mir-181b in EOC (A) Kaplan-Meier
 Supplementary Figure S1 Expression of mir-181b in EOC (A) Kaplan-Meier curves for progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) in a cohort of patients (N=52) with stage III primary ovarian
Supplementary Figure S1 Expression of mir-181b in EOC (A) Kaplan-Meier curves for progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) in a cohort of patients (N=52) with stage III primary ovarian
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:1.138/nature1139 a d Whisker angle (deg) Whisking repeatability Control Muscimol.4.3.2.1 -.1 8 4-4 1 2 3 4 Performance (d') Pole 8 4-4 1 2 3 4 5 Time (s) b Mean protraction angle (deg) e Hit rate (p
doi:1.138/nature1139 a d Whisker angle (deg) Whisking repeatability Control Muscimol.4.3.2.1 -.1 8 4-4 1 2 3 4 Performance (d') Pole 8 4-4 1 2 3 4 5 Time (s) b Mean protraction angle (deg) e Hit rate (p
Reviewers' Comments: Reviewer #1 (Remarks to the Author)
 Reviewers' Comments: Reviewer #1 (Remarks to the Author) The manuscript "MicroRNAs shape gene co-regulation within cells and transcriptional heterogeneity across cells" by Gennaro Gambardella et al performed
Reviewers' Comments: Reviewer #1 (Remarks to the Author) The manuscript "MicroRNAs shape gene co-regulation within cells and transcriptional heterogeneity across cells" by Gennaro Gambardella et al performed
Theta sequences are essential for internally generated hippocampal firing fields.
 Theta sequences are essential for internally generated hippocampal firing fields. Yingxue Wang, Sandro Romani, Brian Lustig, Anthony Leonardo, Eva Pastalkova Supplementary Materials Supplementary Modeling
Theta sequences are essential for internally generated hippocampal firing fields. Yingxue Wang, Sandro Romani, Brian Lustig, Anthony Leonardo, Eva Pastalkova Supplementary Materials Supplementary Modeling
APPLICATION NOTE. Highly reproducible and Comprehensive Proteome Profiling of Formalin-Fixed Paraffin-Embedded (FFPE) Tissues Slices
 APPLICATION NOTE Highly reproducible and Comprehensive Proteome Profiling of Formalin-Fixed Paraffin-Embedded (FFPE) Tissues Slices INTRODUCTION Preservation of tissue biopsies is a critical step to This
APPLICATION NOTE Highly reproducible and Comprehensive Proteome Profiling of Formalin-Fixed Paraffin-Embedded (FFPE) Tissues Slices INTRODUCTION Preservation of tissue biopsies is a critical step to This
Measuring DNA Methylation with the MinION
 Measuring DNA Methylation with the MinION Winston Timp Department of Biomedical Engineering Johns Hopkins University Epigenetics: Modern Modern Definition of epigenetics involves heritable changes other
Measuring DNA Methylation with the MinION Winston Timp Department of Biomedical Engineering Johns Hopkins University Epigenetics: Modern Modern Definition of epigenetics involves heritable changes other
Are you the way you are because of the
 EPIGENETICS Are you the way you are because of the It s my fault!! Nurture Genes you inherited from your parents? Nature Experiences during your life? Similar DNA Asthma, Autism, TWINS Bipolar Disorders
EPIGENETICS Are you the way you are because of the It s my fault!! Nurture Genes you inherited from your parents? Nature Experiences during your life? Similar DNA Asthma, Autism, TWINS Bipolar Disorders
Supplementary Figures
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Pan-cancer analysis of global and local DNA methylation variation a) Variations in global DNA methylation are shown as measured by averaging the genome-wide
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Pan-cancer analysis of global and local DNA methylation variation a) Variations in global DNA methylation are shown as measured by averaging the genome-wide
Supplementary Figures
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Confirmation of Dnmt1 conditional knockout out mice. a, Representative images of sorted stem (Lin - CD49f high CD24 + ), luminal (Lin - CD49f low CD24 + )
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Confirmation of Dnmt1 conditional knockout out mice. a, Representative images of sorted stem (Lin - CD49f high CD24 + ), luminal (Lin - CD49f low CD24 + )
Effects of UBL5 knockdown on cell cycle distribution and sister chromatid cohesion
 Supplementary Figure S1. Effects of UBL5 knockdown on cell cycle distribution and sister chromatid cohesion A. Representative examples of flow cytometry profiles of HeLa cells transfected with indicated
Supplementary Figure S1. Effects of UBL5 knockdown on cell cycle distribution and sister chromatid cohesion A. Representative examples of flow cytometry profiles of HeLa cells transfected with indicated
Expression and epigenomic landscape of the sex chromosomes in mouse post meiotic male germ cells
 DOI 10.1186/s13072-016-0099-8 Epigenetics & Chromatin RESEARCH Open Access Expression and epigenomic landscape of the sex chromosomes in mouse post meiotic male germ cells Charlotte Moretti 1,2,3, Daniel
DOI 10.1186/s13072-016-0099-8 Epigenetics & Chromatin RESEARCH Open Access Expression and epigenomic landscape of the sex chromosomes in mouse post meiotic male germ cells Charlotte Moretti 1,2,3, Daniel
Supplemental Figure 1
 Supplemental Figure 1 1a 1c PD-1 MFI fold change 6 5 4 3 2 1 IL-1α IL-2 IL-4 IL-6 IL-1 IL-12 IL-13 IL-15 IL-17 IL-18 IL-21 IL-23 IFN-α Mut Human PD-1 promoter SBE-D 5 -GTCTG- -1.2kb SBE-P -CAGAC- -1.kb
Supplemental Figure 1 1a 1c PD-1 MFI fold change 6 5 4 3 2 1 IL-1α IL-2 IL-4 IL-6 IL-1 IL-12 IL-13 IL-15 IL-17 IL-18 IL-21 IL-23 IFN-α Mut Human PD-1 promoter SBE-D 5 -GTCTG- -1.2kb SBE-P -CAGAC- -1.kb
Heintzman, ND, Stuart, RK, Hon, G, Fu, Y, Ching, CW, Hawkins, RD, Barrera, LO, Van Calcar, S, Qu, C, Ching, KA, Wang, W, Weng, Z, Green, RD,
 Heintzman, ND, Stuart, RK, Hon, G, Fu, Y, Ching, CW, Hawkins, RD, Barrera, LO, Van Calcar, S, Qu, C, Ching, KA, Wang, W, Weng, Z, Green, RD, Crawford, GE, Ren, B (2007) Distinct and predictive chromatin
Heintzman, ND, Stuart, RK, Hon, G, Fu, Y, Ching, CW, Hawkins, RD, Barrera, LO, Van Calcar, S, Qu, C, Ching, KA, Wang, W, Weng, Z, Green, RD, Crawford, GE, Ren, B (2007) Distinct and predictive chromatin
Supplementary Figure 1. ALVAC-protein vaccines and macaque immunization. (A) Maximum likelihood
 Supplementary Figure 1. ALVAC-protein vaccines and macaque immunization. (A) Maximum likelihood tree illustrating CRF01_AE gp120 protein sequence relationships between 107 Envs sampled in the RV144 trial
Supplementary Figure 1. ALVAC-protein vaccines and macaque immunization. (A) Maximum likelihood tree illustrating CRF01_AE gp120 protein sequence relationships between 107 Envs sampled in the RV144 trial
EPIGENOMICS PROFILING SERVICES
 EPIGENOMICS PROFILING SERVICES Chromatin analysis DNA methylation analysis RNA-seq analysis Diagenode helps you uncover the mysteries of epigenetics PAGE 3 Integrative epigenomics analysis DNA methylation
EPIGENOMICS PROFILING SERVICES Chromatin analysis DNA methylation analysis RNA-seq analysis Diagenode helps you uncover the mysteries of epigenetics PAGE 3 Integrative epigenomics analysis DNA methylation
Online Appendix Material and Methods: Pancreatic RNA isolation and quantitative real-time (q)rt-pcr. Mice were fasted overnight and killed 1 hour (h)
 Online Appendix Material and Methods: Pancreatic RNA isolation and quantitative real-time (q)rt-pcr. Mice were fasted overnight and killed 1 hour (h) after feeding. A small slice (~5-1 mm 3 ) was taken
Online Appendix Material and Methods: Pancreatic RNA isolation and quantitative real-time (q)rt-pcr. Mice were fasted overnight and killed 1 hour (h) after feeding. A small slice (~5-1 mm 3 ) was taken
Polycomb Repressive Complex 2 Regulates Lineage Fidelity during Embryonic Stem Cell Differentiation
 Polycomb Repressive Complex 2 Regulates Lineage Fidelity during Embryonic Stem Cell Differentiation The MIT Faculty has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your
Polycomb Repressive Complex 2 Regulates Lineage Fidelity during Embryonic Stem Cell Differentiation The MIT Faculty has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your
Mohammad Sha ban. Basheq Jehad. Hamzah Nakhleh
 11 Mohammad Sha ban Basheq Jehad Hamzah Nakhleh Physiology of the reproductive system In physiology, we are concerned with the mechanisms in which the system functions, and how the system responds to different
11 Mohammad Sha ban Basheq Jehad Hamzah Nakhleh Physiology of the reproductive system In physiology, we are concerned with the mechanisms in which the system functions, and how the system responds to different
CS 6824: Tissue-Based Map of the Human Proteome
 CS 6824: Tissue-Based Map of the Human Proteome T. M. Murali November 17, 2016 Human Protein Atlas Measure protein and gene expression using tissue microarrays and deep sequencing, respectively. Alternative
CS 6824: Tissue-Based Map of the Human Proteome T. M. Murali November 17, 2016 Human Protein Atlas Measure protein and gene expression using tissue microarrays and deep sequencing, respectively. Alternative
Supplementary Figure 1. Genotyping strategies for Mcm3 +/+, Mcm3 +/Lox and Mcm3 +/- mice and luciferase activity in Mcm3 +/Lox mice. A.
 Supplementary Figure 1. Genotyping strategies for Mcm3 +/+, Mcm3 +/Lox and Mcm3 +/- mice and luciferase activity in Mcm3 +/Lox mice. A. Upper part, three-primer PCR strategy at the Mcm3 locus yielding
Supplementary Figure 1. Genotyping strategies for Mcm3 +/+, Mcm3 +/Lox and Mcm3 +/- mice and luciferase activity in Mcm3 +/Lox mice. A. Upper part, three-primer PCR strategy at the Mcm3 locus yielding
Epigenetic Patterns Maintained in Early Caenorhabditis elegans Embryos Can Be Established by Gene Activity in the Parental Germ Cells
 Epigenetic Patterns Maintained in Early Caenorhabditis elegans Embryos Can Be Established by Gene Activity in the Parental Germ Cells Jackelyn K. Arico, Emory University David J Katz, Emory University
Epigenetic Patterns Maintained in Early Caenorhabditis elegans Embryos Can Be Established by Gene Activity in the Parental Germ Cells Jackelyn K. Arico, Emory University David J Katz, Emory University
Supplementary Figure 1: High-throughput profiling of survival after exposure to - radiation. (a) Cells were plated in at least 7 wells in a 384-well
 Supplementary Figure 1: High-throughput profiling of survival after exposure to - radiation. (a) Cells were plated in at least 7 wells in a 384-well plate at cell densities ranging from 25-225 cells in
Supplementary Figure 1: High-throughput profiling of survival after exposure to - radiation. (a) Cells were plated in at least 7 wells in a 384-well plate at cell densities ranging from 25-225 cells in
Author(s) Park, Sung-kyu Robin; Yates, John R. the original author and source are
 NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) The Specification and Global Reprog during Gamete Formation and Early E Samson, Mark; Jow, Margaret M.; Won Colin; Aslanian, Aaron; Saucedo, Is Park, Sung-kyu
NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) The Specification and Global Reprog during Gamete Formation and Early E Samson, Mark; Jow, Margaret M.; Won Colin; Aslanian, Aaron; Saucedo, Is Park, Sung-kyu
