Supplemental Information. Derivation of Human Trophoblast Stem Cells
|
|
|
- Joanna Conley
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Cell Stem Cell, Volume 22 Supplemental Information Derivation of Human Trophoblast Stem Cells Hiroaki Okae, Hidehiro Toh, Tetsuya Sato, Hitoshi Hiura, Sota Takahashi, Kenjiro Shirane, Yuka Kabayama, Mikita Suyama, Hiroyuki Sasaki, and Takahiro Arima
2
3 Figure S1. Related to Figure 1 (A) Flow cytometry histogram of ITGA6 expression on CT cells isolated from a first trimester placenta. The proportion of ITGA6-positive cells typically exceeded 95% after immunomagnetic enrichment. (B) Flow cytometry histogram of HLA-G expression on EVT cells isolated from a first trimester placenta. The proportion of HLA-G-positive cells typically exceeded 95% after immunomagnetic enrichment. (C) Oblique illumination image of ST cells isolated from a first trimester placenta (top). Note that almost all cells are >40 m in diameter. Immunostaining of the ST marker protein SDC1 on ST cells (bottom). Nuclei were stained with Hoechst The percentage of SDC1-positive cells was typically >80%. (D) Phase-contrast images of CT cells cultured in various conditions as described in Figure 1B. The cells cultured in Condition-1, -7, -8, and -9 were highly proliferative and morphologically indistinguishable. Cell proliferation was significantly suppressed in Condition-3, -4, and -5. (E) Phase-contrast and immunofluorescence images of CT cells cultured in Condition-2 (see Figure 1B) for nine days. These cells expressed the EVT marker HLA-G and were unable to propagate. Nuclei were stained with Hoechst (F) Effects of EGF and inhibitors on the long-term maintenance of proliferative CT cells. Proliferative CT cells were established in the presence of VPA, CHIR99021, A83-01, SB431542, EGF, and Y27632, and were then maintained in the absence of VPA, CHIR99021, A83-01 and SB431542, or EGF. CHIR99021, EGF, and TGF- inhibitors were essential and VPA was important for the long-term maintenance of proliferative CT cells. Data are presented as mean ± SD (n = 3). (G) Phase-contrast images of proliferative CT cells established using TSA or SAHA. CT cells were cultured for about three weeks in the TS medium where VPA was replaced by TSA or SAHA. (H) Phase-contrast images of proliferative CT cells established using either A83-01 or SB CT cells were cultured for about three weeks in the TS medium containing either A83-01 (0.5 M) or SB (10 M). A83-01 was more potent than SB (see Table S2). (I) Chromosome analysis of TS CT cells. Both TS CT #1 and #2 were karyotypically normal after 30 passages. 1
4 The scale bars indicate 100 m. 2
5
6 Figure S2. Related to Figure 2 (A) Phase-contrast and immunofluorescence images of TS CT cells cultured in the TS medium without EGF, CHIR99021, A83-01, SB431542, and VPA. The cells were analyzed at day 4. Some cells were SDC1-negative and remained mononucleated (arrows). The medium did not support the survival of the differentiated cells and most of them died within 5 days. Similar results were obtained with two independent cell lines. (B) Phase-contrast and immunofluorescence images of CT cells treated with the indicated concentrations of A83-01 or SB for nine days. A83-01 or SB was added to the TS medium without CHIR99021, A83-01, SB431542, and VPA. A83-01 increased the number of HLA-G-expressing cells with a mesenchymal-like morphology in a dose-dependent manner. This experiment was repeated three times with similar results. (C) Serial phase-contrast images of TS CT cells differentiating into EVT-TS CT cells. TS CT cells transiently proliferated and differentiated into EVT-like cells with a mesenchymal-like morphology. (D) Effects of A83-01, NRG1 and Matrigel on the differentiation of TS CT cells into EVT-TS CT cells. TS CT cells were cultured in the EVT medium (see Methods for details) without A83-01, NRG1, or Matrigel for five days. Few EVT-like cells emerged in the absence of A NRG1 enhanced the transient proliferation of the differentiating cells. Both EVT- and ST-like cells emerged in the absence of Matrigel. (E) Serial phase-contrast images of TS CT cells differentiating into ST(2D)-TS CT cells. The cells indicated by arrows aggregated and fused to form a large syncytium. (F) Effects of forskolin and EGF on the differentiation of TS CT cells into ST(3D)-TS CT cells. Forskolin and EGF synergistically enhanced the formation of large cyst-like structures. This experiment was repeated three times with similar results. (G) Quantitative real-time PCR analysis of ST markers in ST(2D)-TS CT and ST(3D)-TS CT cells. The expression levels of CGB, CSH1/2, and SDC1 were higher in ST(3D)-TS CT cells than in ST(2D)-TS CT cells. The data were normalized to GAPDH expression. The error bars indicate SD (n = 3). (H) Phase-contrast and immunofluorescence images of EVT-TS CT cells. TS CT cells maintained their ability to differentiate into EVT-TS CT cells after 50 passages. Similar results were obtained with two independent cell lines. (I) Immunostaining of CGB and SDC1 in ST(3D)-TS CT cells. TS CT cells maintained 3
7 their ability to differentiate into ST(3D)-TS CT cells after 53 passages. Similar results were obtained with two independent cell lines. The scale bars indicate 100 m. 4
8
9 Figure S3. Related to Figure 3 (A) Chromosome analysis of TS blast cells. Both TS blast #1 and #2 were karyotypically normal after 30 passages. (B) Representative flow cytometry histogram of HLA-ABC expression on TS blast cells. HLA-ABC expression was low in the cells. Similar results were obtained with two independent cell lines. (C) Phase-contrast images of EVT-like cells derived from TS blast #4 and #7. These lines differentiated into spindle-shaped cells less efficiently than the other TS blast lines. (D) Quantitative real-time PCR analysis of all TS lines derived in this study. We analyzed TP63 and TEAD4 (CT markers), CGB and SDC1 (ST markers), and HLA-G and MMP2 (EVT markers). The data were normalized to GAPDH expression. Although EVT-TS blast #4 and #7 expressed high levels of EVT markers, their TP63 expression levels were comparable to some undifferentiated TS lines (e.g., TS CT #4 and TS blast #1). (E) Phase-contrast and immunofluorescence images of EVT-TS blast cells. TS blast cells maintained their ability to differentiate into EVT-TS blast cells after 55 passages. Similar results were obtained with two independent cell lines. (F) Immunostaining of CGB and SDC1 in ST(3D)-TS blast cells. TS blast cells maintained their ability to differentiate into ST(3D)-TS blast cells after 55 passages. Similar results were obtained with two independent cell lines. The scale bars indicate 100 m. 5
10
11 Figure S4. Related to Figure 4 (A) Heat scatter plots and Pearson correlation coefficients for comparison of gene expression patterns between ST, ST(2D)-TS CT, and ST(3D)-TS CT cells. All genes were considered. Although ST(2D)- and ST(3D)-TS CT cells had very similar transcriptome profiles, ST(3D)-TS CT cells were a little more similar to ST cells than ST(2D)-TS CT cells. (B) Gene set enrichment analysis (GSEA) comparison between primary and TS-derive cells. The data from TS CT and TS blast cells were combined. Genes were ranked based on DESeq2 log2 fold changes. The top five enriched and depleted gene ontology (GO) terms are shown. GO terms with positive and negative normalized enrichment scores (NES) were enriched among genes upregulated in TS-derived and primary cells, respectively. (C) GSEA comparison between EVT and TS-derived EVT-like cells. Genes associated with DNA replication were downregulated in TS-derived EVT-like cells. (D) Gene expression patterns at the CYP19A1, EDNRB, IL2RB, and PTN loci. The placenta-specific promoters of these genes were active in ST(3D)-TS CT and ST(3D)-TS blast cells. CYP19A1 has at least 10 promoters and only the placenta-specific promoter is shown. The vertical axis indicates the number of uniquely mapped reads. (E) Sashimi plots of the alternative splicing events of FGFR2. The numbers of reads spanning exon-exon junctions are indicated. Of the two major isoforms of FGFR2 (FGFR2b and FGFR2c), FGFR2b was almost exclusively expressed in CT, TS CT, and TS blast cells. 6
12
13 Figure S5. Related to Figure 5 (A) Density scatterplots of gene body methylation levels and gene expression levels in CT, TS CT, and TS blast cells. Only autosomal genes longer than 5 kb were analyzed. Most repressed regions (FPKM <1) had intermediate methylation levels (30-60%) in CT cells. However, a substantial number of repressed regions were hypomethylated (<20%) in TS CT and TS blast cells. (B) DNA methylation levels of the DSCR4, ELF5, and ZNF750 promoters in all TS lines derived in this study. The DNA methylation levels were analyzed by combined bisulfite restriction analysis (COBRA). Cord blood cells were analyzed for comparison. (C) DNA methylation levels of placenta-specific gdmrs in TS CT and TS blast cells. WGBS data of CT, TS CT, TS blast, human ES, and cord blood cells were analyzed. All of the gdmrs maintained 30-70% methylation levels in TS blast cells except for the ZC3H12C DMR. Publicly available data are used for CT cells (Hamada et al., 2016), human ES cells (Lister et al., 2011) and cord blood cells (Okae et al., 2014). (D) Allelic expression patterns of ZFAT, KLHDC10, PROSER2-AS1, and AIM1. The proportion of maternal and paternal reads is shown. The allelic expression data for CT cells were obtained in our previous study (Hamada et al., 2016). NA, not analyzed due to the lack of informative SNPs. (E) Scatter plots for comparison of expression levels of X-linked genes. The expression levels are shown as log 2 (FPKM + 1). The expression levels of X-linked genes were comparable between male and female TS cells, and XIST (shown in red) was expressed only in female TS cells. (F) Heat map representation of Pearson correlation coefficients for mirna. Publicly available data were used for human ES cells (GEO: GSM438362) and IMR90 cells (GEO: GSM438364). Autosomal mirnas detected in at least one sample (n = 819) were analyzed. 7
14 Table S2. Culture Conditions Tested for the Derivation of Proliferative CT Cells, Related to Figure 1 Reagents Y27632 CHIR99021 A83-01 SB VPA TSA SAHA EGF FGF10 HGF NOG Outcome Note 5 mm 2 mm 0.5 mm 1 mm 0.8 mm ng/ml 50 ng/ml 50 ng/ml 20 ng/ml +++ Condition-1 in Fig. 1B 5 mm mm 1 mm 0.8 mm ng/ml 50 ng/ml 50 ng/ml 20 ng/ml ND Condition-2 in Fig. 1B 5 mm 2 mm 0.5 mm 1 mm 0.8 mm ng/ml 50 ng/ml 20 ng/ml + Condition-3 in Fig. 1B 5 mm 2 mm mm ng/ml 50 ng/ml 50 ng/ml 20 ng/ml + Condition-4 in Fig. 1B 5 mm 2 mm 0.5 mm 1 mm ng/ml 50 ng/ml 50 ng/ml 20 ng/ml + Condition-5 in Fig. 1B - 2 mm 0.5 mm 1 mm 0.8 mm ng/ml 50 ng/ml 50 ng/ml 20 ng/ml ND Condition-6 in Fig. 1B 5 mm 2 mm 0.5 mm 1 mm 0.8 mm ng/ml - 50 ng/ml 20 ng/ml +++ Condition-7 in Fig. 1B 5 mm 2 mm 0.5 mm 1 mm 0.8 mm ng/ml 50 ng/ml - 20 ng/ml +++ Condition-8 in Fig. 1B 5 mm 2 mm 0.5 mm 1 mm 0.8 mm ng/ml 50 ng/ml 50 ng/ml Condition-9 in Fig. 1B 5 mm 2 mm mm ng/ml 50 ng/ml 20 ng/ml ND 5 mm mm 1 mm 0.8 mm ng/ml 50 ng/ml 20 ng/ml ND 5 mm 2 mm 0.5 mm 1 mm 0.8 mm ng/ml TS medium 5 mm 2 mm 0.5 mm mm ng/ml Fig. S1H 5 mm 2 mm - 1 mm 0.8 mm ng/ml mm 2 mm - 10 mm 0.8 mm ng/ml Fig. S1H 5 mm 2 mm 0.5 mm 1 mm - 10 nm - 50 ng/ml Fig. S1G 5 mm 2 mm 0.5 mm 1 mm nm 50 ng/ml Fig. S1G - 2 mm ng/ml ND 5 mm 2 mm ng/ml ND +++, doubling time of hours; ++, doubling time of hours, + doubling time of >36 hours; ND, not derived.
15 Table S3. Summary of TS CT and TS blast Cell Derivation, Related to Figures 1 and 3 TS line Source (Gestational age) Karyotype (Passage number) Doubling time (Passage number) TS CT #1 CT cells (6 weeks) 46, XX (P30) 24.0±1.7 hours (P13) TS CT #2 CT cells (7 weeks) 46, XY (P30) 23.2±3.9 hours (P17) TS CT #3 CT cells (7 weeks) 46, XX (P30) 19.4±1.6 hours (P17) TS CT #4 CT cells (7 weeks) 46, XX (P30) NA TS CT #5 CT cells (7 weeks) 46, XY (P13) NA TS CT #6 CT cells (9 weeks) NA NA TS CT #7 CT cells (6 weeks) NA NA TS CT #8 CT cells (8 weeks) NA NA TS blast #1 Blastocyst 46, XY (P30) 21.7±3.0 hours (P18) TS blast #2 Blastocyst 46, XX (P30) 22.6±2.5 hours (P11) TS blast #3 Blastocyst 46, XY (P13) 23.7±2.6 hours (P11) TS blast #4 Blastocyst 46, XY (P14) NA TS blast #5 Blastocyst 46, XY (P15) NA TS blast #6 Blastocyst 46, XX (P12) NA TS blast #7 Blastocyst NA NA TS blast #8 Blastocyst NA NA Karyotype and population doubling time were analyzed at the indicated passage numbers. NA, not analyzed.
16 Methods S1. Primer Sequences, Related to STAR Methods Description Forward Reverse DSCR4_COBRA TTTGTGGAGAGGAGAAGTTGAGG CCATCTTCTCTTTTTACCACCCATA ELF5_COBRA TGGGGAAAGGAATTTAGTTAGGG TCCATCTCCAACTCCAAAACC ZNF750_COBRA TGGGAGGGATTTAAGTGTAGGA CCACAAATCCTCAAAAACCTCA CGB_real-time CAGCATCCTATCACCTCCTGGT CTGGAACATCTCCATCCTTGGT SDC1_real-time CTATTCCCACGTCTCCAGAACC GGACTACAGCCTCTCCCTCCTT CSH1/2_real-time CATGACTCCCAGACCTCCTTCT ATTTCTGTTGCGTTTCCTCCAT TP63_real-time AGAAACGAAGATCCCCAGATGA CTGTTGCTGTTGCCTGTACGTT TEAD4_real-time CAGGTGGTGGAGAAAGTTGAGA GTGCTTGAGCTTGTGGATGAAG HLA-G_real-time CCACCACCCTGTCTTTGACTAT ACGTCCTGGGTCTGGTCCT MMP2_real-time TGGCACCCATTTACACCTACAC ATGTCAGGAGAGGCCCCATAGA GAPDH_real-time CCTCAACGACCACTTTGTCAAG TCTTCCTCTTGTGCTCTTGCTG
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb2607 Figure S1 Elf5 loss promotes EMT in mammary epithelium while Elf5 overexpression inhibits TGFβ induced EMT. (a, c) Different confocal slices through the Z stack image. (b, d) 3D rendering
DOI: 10.1038/ncb2607 Figure S1 Elf5 loss promotes EMT in mammary epithelium while Elf5 overexpression inhibits TGFβ induced EMT. (a, c) Different confocal slices through the Z stack image. (b, d) 3D rendering
Lentiviral Delivery of Combinatorial mirna Expression Constructs Provides Efficient Target Gene Repression.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Lentiviral Delivery of Combinatorial mirna Expression Constructs Provides Efficient Target Gene Repression. a, Design for lentiviral combinatorial mirna expression and sensor constructs.
Supplementary Figure 1 Lentiviral Delivery of Combinatorial mirna Expression Constructs Provides Efficient Target Gene Repression. a, Design for lentiviral combinatorial mirna expression and sensor constructs.
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/8/375/ra41/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Actin cytoskeletal remodeling with protrusion formation is essential for heart regeneration in Hippo-deficient mice
www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/8/375/ra41/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Actin cytoskeletal remodeling with protrusion formation is essential for heart regeneration in Hippo-deficient mice
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb2638 Figure S1 Morphological characteristics of fetal testes and ovaries from 6.5-20 developmental weeks. Representative images of Hematoxylin and Eosin staining of testes and ovaries over
DOI: 10.1038/ncb2638 Figure S1 Morphological characteristics of fetal testes and ovaries from 6.5-20 developmental weeks. Representative images of Hematoxylin and Eosin staining of testes and ovaries over
Supplemental Data. Integrating omics and alternative splicing i reveals insights i into grape response to high temperature
 Supplemental Data Integrating omics and alternative splicing i reveals insights i into grape response to high temperature Jianfu Jiang 1, Xinna Liu 1, Guotian Liu, Chonghuih Liu*, Shaohuah Li*, and Lijun
Supplemental Data Integrating omics and alternative splicing i reveals insights i into grape response to high temperature Jianfu Jiang 1, Xinna Liu 1, Guotian Liu, Chonghuih Liu*, Shaohuah Li*, and Lijun
Effects of UBL5 knockdown on cell cycle distribution and sister chromatid cohesion
 Supplementary Figure S1. Effects of UBL5 knockdown on cell cycle distribution and sister chromatid cohesion A. Representative examples of flow cytometry profiles of HeLa cells transfected with indicated
Supplementary Figure S1. Effects of UBL5 knockdown on cell cycle distribution and sister chromatid cohesion A. Representative examples of flow cytometry profiles of HeLa cells transfected with indicated
Today. Genomic Imprinting & X-Inactivation
 Today 1. Quiz (~12 min) 2. Genomic imprinting in mammals 3. X-chromosome inactivation in mammals Note that readings on Dosage Compensation and Genomic Imprinting in Mammals are on our web site. Genomic
Today 1. Quiz (~12 min) 2. Genomic imprinting in mammals 3. X-chromosome inactivation in mammals Note that readings on Dosage Compensation and Genomic Imprinting in Mammals are on our web site. Genomic
Transcriptional repression of Xi
 Transcriptional repression of Xi Xist Transcription of Xist Xist RNA Spreading of Xist Recruitment of repression factors. Stable repression Translocated Xic cannot efficiently silence autosome regions.
Transcriptional repression of Xi Xist Transcription of Xist Xist RNA Spreading of Xist Recruitment of repression factors. Stable repression Translocated Xic cannot efficiently silence autosome regions.
Nature Genetics: doi: /ng Supplementary Figure 1. Assessment of sample purity and quality.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Assessment of sample purity and quality. (a) Hematoxylin and eosin staining of formaldehyde-fixed, paraffin-embedded sections from a human testis biopsy collected concurrently with
Supplementary Figure 1 Assessment of sample purity and quality. (a) Hematoxylin and eosin staining of formaldehyde-fixed, paraffin-embedded sections from a human testis biopsy collected concurrently with
Supplementary Figure 1. Metabolic landscape of cancer discovery pipeline. RNAseq raw counts data of cancer and healthy tissue samples were downloaded
 Supplementary Figure 1. Metabolic landscape of cancer discovery pipeline. RNAseq raw counts data of cancer and healthy tissue samples were downloaded from TCGA and differentially expressed metabolic genes
Supplementary Figure 1. Metabolic landscape of cancer discovery pipeline. RNAseq raw counts data of cancer and healthy tissue samples were downloaded from TCGA and differentially expressed metabolic genes
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI:.38/ncb3399 a b c d FSP DAPI 5mm mm 5mm 5mm e Correspond to melanoma in-situ Figure a DCT FSP- f MITF mm mm MlanaA melanoma in-situ DCT 5mm FSP- mm mm mm mm mm g melanoma in-situ MITF MlanaA mm mm
DOI:.38/ncb3399 a b c d FSP DAPI 5mm mm 5mm 5mm e Correspond to melanoma in-situ Figure a DCT FSP- f MITF mm mm MlanaA melanoma in-situ DCT 5mm FSP- mm mm mm mm mm g melanoma in-situ MITF MlanaA mm mm
Supplementary Figure S1. Gene expression analysis of epidermal marker genes and TP63.
 Supplementary Figure Legends Supplementary Figure S1. Gene expression analysis of epidermal marker genes and TP63. A. Screenshot of the UCSC genome browser from normalized RNAPII and RNA-seq ChIP-seq data
Supplementary Figure Legends Supplementary Figure S1. Gene expression analysis of epidermal marker genes and TP63. A. Screenshot of the UCSC genome browser from normalized RNAPII and RNA-seq ChIP-seq data
Cluster Dendrogram. dist(cor(na.omit(tss.exprs.chip[, c(1:10, 24, 27, 30, 48:50, dist(cor(na.omit(tss.exprs.chip[, c(1:99, 103, 104, 109, 110,
 A Transcriptome (RNA-seq) Transcriptome (RNA-seq) 3. 2.5 2..5..5...5..5 2. 2.5 3. 2.5 2..5..5...5..5 2. 2.5 Cluster Dendrogram RS_ES3.2 RS_ES3. RS_SHS5.2 RS_SHS5. PS_SHS5.2 PS_SHS5. RS_LJ3 PS_LJ3..4 _SHS5.2
A Transcriptome (RNA-seq) Transcriptome (RNA-seq) 3. 2.5 2..5..5...5..5 2. 2.5 3. 2.5 2..5..5...5..5 2. 2.5 Cluster Dendrogram RS_ES3.2 RS_ES3. RS_SHS5.2 RS_SHS5. PS_SHS5.2 PS_SHS5. RS_LJ3 PS_LJ3..4 _SHS5.2
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology: doi: /nsmb Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Effect of HSP90 inhibition on expression of endogenous retroviruses. (a) Inducible shrna-mediated Hsp90 silencing in mouse ESCs. Immunoblots of total cell extract expressing the
Supplementary Figure 1 Effect of HSP90 inhibition on expression of endogenous retroviruses. (a) Inducible shrna-mediated Hsp90 silencing in mouse ESCs. Immunoblots of total cell extract expressing the
(A) Cells grown in monolayer were fixed and stained for surfactant protein-c (SPC,
 Supplemental Figure Legends Figure S1. Cell line characterization (A) Cells grown in monolayer were fixed and stained for surfactant protein-c (SPC, green) and co-stained with DAPI to visualize the nuclei.
Supplemental Figure Legends Figure S1. Cell line characterization (A) Cells grown in monolayer were fixed and stained for surfactant protein-c (SPC, green) and co-stained with DAPI to visualize the nuclei.
a) List of KMTs targeted in the shrna screen. The official symbol, KMT designation,
 Supplementary Information Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. a) List of KMTs targeted in the shrna screen. The official symbol, KMT designation, gene ID and specifities are provided. Those highlighted
Supplementary Information Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. a) List of KMTs targeted in the shrna screen. The official symbol, KMT designation, gene ID and specifities are provided. Those highlighted
Supplementary Figures
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Heatmap of GO terms for differentially expressed genes. The terms were hierarchically clustered using the GO term enrichment beta. Darker red, higher positive
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Heatmap of GO terms for differentially expressed genes. The terms were hierarchically clustered using the GO term enrichment beta. Darker red, higher positive
Supplementary Figure 1: Neuregulin 1 increases the growth of mammary organoids compared to EGF. (a) Mammary epithelial cells were freshly isolated,
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Supplementary Figure 1: Neuregulin 1 increases the growth of mammary organoids compared to EGF. (a) Mammary epithelial cells were freshly isolated, embedded in matrigel and exposed
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Supplementary Figure 1: Neuregulin 1 increases the growth of mammary organoids compared to EGF. (a) Mammary epithelial cells were freshly isolated, embedded in matrigel and exposed
Supplementary Figure 1. Identification of tumorous sphere-forming CSCs and CAF feeder cells. The LEAP (Laser-Enabled Analysis and Processing)
 Supplementary Figure 1. Identification of tumorous sphere-forming CSCs and CAF feeder cells. The LEAP (Laser-Enabled Analysis and Processing) platform with laser manipulation to efficiently purify lung
Supplementary Figure 1. Identification of tumorous sphere-forming CSCs and CAF feeder cells. The LEAP (Laser-Enabled Analysis and Processing) platform with laser manipulation to efficiently purify lung
Supplementary Figure S1 Expression of mir-181b in EOC (A) Kaplan-Meier
 Supplementary Figure S1 Expression of mir-181b in EOC (A) Kaplan-Meier curves for progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) in a cohort of patients (N=52) with stage III primary ovarian
Supplementary Figure S1 Expression of mir-181b in EOC (A) Kaplan-Meier curves for progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) in a cohort of patients (N=52) with stage III primary ovarian
Nature Genetics: doi: /ng Supplementary Figure 1. Somatic coding mutations identified by WES/WGS for 83 ATL cases.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Somatic coding mutations identified by WES/WGS for 83 ATL cases. (a) The percentage of targeted bases covered by at least 2, 10, 20 and 30 sequencing reads (top) and average read
Supplementary Figure 1 Somatic coding mutations identified by WES/WGS for 83 ATL cases. (a) The percentage of targeted bases covered by at least 2, 10, 20 and 30 sequencing reads (top) and average read
Supplementary Figures
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1 Characterization of stable expression of GlucB and sshbira in the CT26 cell line (a) Live cell imaging of stable CT26 cells expressing green fluorescent protein
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1 Characterization of stable expression of GlucB and sshbira in the CT26 cell line (a) Live cell imaging of stable CT26 cells expressing green fluorescent protein
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature10866 a b 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Match No Match 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Turcan et al. Supplementary Fig.1 Concepts mapping H3K27 targets in EF CBX8 targets in EF H3K27 targets in ES SUZ12 targets in ES
doi:10.1038/nature10866 a b 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Match No Match 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Turcan et al. Supplementary Fig.1 Concepts mapping H3K27 targets in EF CBX8 targets in EF H3K27 targets in ES SUZ12 targets in ES
Nature Genetics: doi: /ng.3731
 Supplementary Figure 1 Circadian profiles of Adarb1 transcript and ADARB1 protein in mouse tissues. (a) Overlap of rhythmic transcripts identified in the previous transcriptome analyses. The mouse liver
Supplementary Figure 1 Circadian profiles of Adarb1 transcript and ADARB1 protein in mouse tissues. (a) Overlap of rhythmic transcripts identified in the previous transcriptome analyses. The mouse liver
Nature Immunology: doi: /ni Supplementary Figure 1. Gene expression profile of CD4 + T cells and CTL responses in Bcl6-deficient mice.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Gene expression profile of CD4 + T cells and CTL responses in Bcl6-deficient mice. (a) Gene expression profile in the resting CD4 + T cells were analyzed by an Affymetrix microarray
Supplementary Figure 1 Gene expression profile of CD4 + T cells and CTL responses in Bcl6-deficient mice. (a) Gene expression profile in the resting CD4 + T cells were analyzed by an Affymetrix microarray
Supplementary Figures
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Confirmation of Dnmt1 conditional knockout out mice. a, Representative images of sorted stem (Lin - CD49f high CD24 + ), luminal (Lin - CD49f low CD24 + )
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Confirmation of Dnmt1 conditional knockout out mice. a, Representative images of sorted stem (Lin - CD49f high CD24 + ), luminal (Lin - CD49f low CD24 + )
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary Figure 1. Generation of a conditional allele of the Kindlin-2 gene. (A) A restriction map of the relevant genomic region of Kindlin-2 (top), the targeting construct
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary Figure 1. Generation of a conditional allele of the Kindlin-2 gene. (A) A restriction map of the relevant genomic region of Kindlin-2 (top), the targeting construct
NOD-like receptor signaling and inflammasome-related pathways are highlighted in psoriatic epidermis
 Supplementary Information NOD-like receptor signaling and inflammasome-related pathways are highlighted in psoriatic epidermis Mari H. Tervaniemi, Shintaro Katayama, Tiina Skoog, H. Annika Siitonen, Jyrki
Supplementary Information NOD-like receptor signaling and inflammasome-related pathways are highlighted in psoriatic epidermis Mari H. Tervaniemi, Shintaro Katayama, Tiina Skoog, H. Annika Siitonen, Jyrki
genomics for systems biology / ISB2020 RNA sequencing (RNA-seq)
 RNA sequencing (RNA-seq) Module Outline MO 13-Mar-2017 RNA sequencing: Introduction 1 WE 15-Mar-2017 RNA sequencing: Introduction 2 MO 20-Mar-2017 Paper: PMID 25954002: Human genomics. The human transcriptome
RNA sequencing (RNA-seq) Module Outline MO 13-Mar-2017 RNA sequencing: Introduction 1 WE 15-Mar-2017 RNA sequencing: Introduction 2 MO 20-Mar-2017 Paper: PMID 25954002: Human genomics. The human transcriptome
EPIGENETIC RE-EXPRESSION OF HIF-2α SUPPRESSES SOFT TISSUE SARCOMA GROWTH
 EPIGENETIC RE-EXPRESSION OF HIF-2α SUPPRESSES SOFT TISSUE SARCOMA GROWTH Supplementary Figure 1. Supplementary Figure 1. Characterization of KP and KPH2 autochthonous UPS tumors. a) Genotyping of KPH2
EPIGENETIC RE-EXPRESSION OF HIF-2α SUPPRESSES SOFT TISSUE SARCOMA GROWTH Supplementary Figure 1. Supplementary Figure 1. Characterization of KP and KPH2 autochthonous UPS tumors. a) Genotyping of KPH2
SOPten flox/flox (KO) Pten flox/flox (WT) flox allele 6.0 kb. Pten. Actin. ! allele 2.3 kb. Supplementary Figure S1. Yanagi, et al.
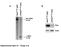 s1 A Pten flox/flox () SOPten flox/flox () flox allele 6. kb B Pten flox/flox () SOPten flox/flox () Pten Actin! allele 2.3 kb Supplementary Figure S1. Yanagi, et al. A B BrdU BrdU positive cells ( ) 3
s1 A Pten flox/flox () SOPten flox/flox () flox allele 6. kb B Pten flox/flox () SOPten flox/flox () Pten Actin! allele 2.3 kb Supplementary Figure S1. Yanagi, et al. A B BrdU BrdU positive cells ( ) 3
Supplementary Information and Figure legends
 Supplementary Information and Figure legends Table S1. Primers for quantitative RT-PCR Target Sequence (5 -> 3 ) Target Sequence (5 -> 3 ) DAB2IP F:TGGACGATGTGCTCTATGCC R:GGATGGTGATGGTTTGGTAG Snail F:CCTCCCTGTCAGATGAGGAC
Supplementary Information and Figure legends Table S1. Primers for quantitative RT-PCR Target Sequence (5 -> 3 ) Target Sequence (5 -> 3 ) DAB2IP F:TGGACGATGTGCTCTATGCC R:GGATGGTGATGGTTTGGTAG Snail F:CCTCCCTGTCAGATGAGGAC
Analysis of Massively Parallel Sequencing Data Application of Illumina Sequencing to the Genetics of Human Cancers
 Analysis of Massively Parallel Sequencing Data Application of Illumina Sequencing to the Genetics of Human Cancers Gordon Blackshields Senior Bioinformatician Source BioScience 1 To Cancer Genetics Studies
Analysis of Massively Parallel Sequencing Data Application of Illumina Sequencing to the Genetics of Human Cancers Gordon Blackshields Senior Bioinformatician Source BioScience 1 To Cancer Genetics Studies
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 1.138/ncb3355 a S1A8 + cells/ total.1.8.6.4.2 b S1A8/?-Actin c % T-cell proliferation 3 25 2 15 1 5 T cells Supplementary Figure 1 Inter-tumoral heterogeneity of MDSC accumulation in mammary tumor
DOI: 1.138/ncb3355 a S1A8 + cells/ total.1.8.6.4.2 b S1A8/?-Actin c % T-cell proliferation 3 25 2 15 1 5 T cells Supplementary Figure 1 Inter-tumoral heterogeneity of MDSC accumulation in mammary tumor
Supplemental Figure S1. RANK expression on human lung cancer cells.
 Supplemental Figure S1. RANK expression on human lung cancer cells. (A) Incidence and H-Scores of RANK expression determined from IHC in the indicated primary lung cancer subgroups. The overall expression
Supplemental Figure S1. RANK expression on human lung cancer cells. (A) Incidence and H-Scores of RANK expression determined from IHC in the indicated primary lung cancer subgroups. The overall expression
Supplementary Figure 1. Repression of hepcidin expression in the liver of mice treated with
 Supplementary Figure 1. Repression of hepcidin expression in the liver of mice treated with DMN Immunohistochemistry for hepcidin and H&E staining (left). qrt-pcr assays for hepcidin in the liver (right).
Supplementary Figure 1. Repression of hepcidin expression in the liver of mice treated with DMN Immunohistochemistry for hepcidin and H&E staining (left). qrt-pcr assays for hepcidin in the liver (right).
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES
 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES 1 Supplementary Figure 1, Adult hippocampal QNPs and TAPs uniformly express REST a-b) Confocal images of adult hippocampal mouse sections showing GFAP (green), Sox2 (red), and REST
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES 1 Supplementary Figure 1, Adult hippocampal QNPs and TAPs uniformly express REST a-b) Confocal images of adult hippocampal mouse sections showing GFAP (green), Sox2 (red), and REST
Supplemental Figure 1. (A) The localization of Cre DNA recombinase in the testis of Cyp19a1-Cre mice was detected by immunohistchemical analyses
 Supplemental Figure 1. (A) The localization of Cre DNA recombinase in the testis of Cyp19a1-Cre mice was detected by immunohistchemical analyses using an anti-cre antibody; testes at 1 week (left panel),
Supplemental Figure 1. (A) The localization of Cre DNA recombinase in the testis of Cyp19a1-Cre mice was detected by immunohistchemical analyses using an anti-cre antibody; testes at 1 week (left panel),
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb3200 Supplementary Figure 1 Expression analysis of stomach markers in gutlike structure. (a) Differentiation scheme of gut-like structure formation from embryonic stem cells. (b) RT-PCR
DOI: 10.1038/ncb3200 Supplementary Figure 1 Expression analysis of stomach markers in gutlike structure. (a) Differentiation scheme of gut-like structure formation from embryonic stem cells. (b) RT-PCR
oocytes were pooled for RT-PCR analysis. The number of PCR cycles was 35. Two
 Supplementary Fig. 1 a Kdm3a Kdm4b β-actin Oocyte Testis Oocyte Testis Oocyte Testis b 1.8 Relative expression.6.4.2 Kdm3a Kdm4b RT-PCR analysis of Kdm3a and Kdm4b expression in oocytes and testes. Twenty
Supplementary Fig. 1 a Kdm3a Kdm4b β-actin Oocyte Testis Oocyte Testis Oocyte Testis b 1.8 Relative expression.6.4.2 Kdm3a Kdm4b RT-PCR analysis of Kdm3a and Kdm4b expression in oocytes and testes. Twenty
Supplementary Figure 1. HOPX is hypermethylated in NPC. (a) Methylation levels of HOPX in Normal (n = 24) and NPC (n = 24) tissues from the
 Supplementary Figure 1. HOPX is hypermethylated in NPC. (a) Methylation levels of HOPX in Normal (n = 24) and NPC (n = 24) tissues from the genome-wide methylation microarray data. Mean ± s.d.; Student
Supplementary Figure 1. HOPX is hypermethylated in NPC. (a) Methylation levels of HOPX in Normal (n = 24) and NPC (n = 24) tissues from the genome-wide methylation microarray data. Mean ± s.d.; Student
Mesenchymal Stem Cells Reshape and Provoke Proliferation of Articular. State Key Laboratory of Bioreactor Engineering, East China University of
 Mesenchymal Stem Cells Reshape and Provoke Proliferation of Articular Chondrocytes by Paracrine Secretion Lei Xu, Yuxi Wu, Zhimiao Xiong, Yan Zhou, Zhaoyang Ye *, Wen-Song Tan * State Key Laboratory of
Mesenchymal Stem Cells Reshape and Provoke Proliferation of Articular Chondrocytes by Paracrine Secretion Lei Xu, Yuxi Wu, Zhimiao Xiong, Yan Zhou, Zhaoyang Ye *, Wen-Song Tan * State Key Laboratory of
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Asymmetrical function of 5p and 3p arms of mir-181 and mir-30 families and mir-142 and mir-154. (a) Control experiments using mirna sensor vector and empty pri-mirna overexpression
Supplementary Figure 1 Asymmetrical function of 5p and 3p arms of mir-181 and mir-30 families and mir-142 and mir-154. (a) Control experiments using mirna sensor vector and empty pri-mirna overexpression
7SK ChIRP-seq is specifically RNA dependent and conserved between mice and humans.
 Supplementary Figure 1 7SK ChIRP-seq is specifically RNA dependent and conserved between mice and humans. Regions targeted by the Even and Odd ChIRP probes mapped to a secondary structure model 56 of the
Supplementary Figure 1 7SK ChIRP-seq is specifically RNA dependent and conserved between mice and humans. Regions targeted by the Even and Odd ChIRP probes mapped to a secondary structure model 56 of the
<10. IL-1β IL-6 TNF + _ TGF-β + IL-23
 3 ns 25 ns 2 IL-17 (pg/ml) 15 1 ns ns 5 IL-1β IL-6 TNF
3 ns 25 ns 2 IL-17 (pg/ml) 15 1 ns ns 5 IL-1β IL-6 TNF
Type of file: PDF Size of file: 0 KB Title of file for HTML: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures
 Type of file: PDF Size of file: 0 KB Title of file for HTML: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1 mir-128-3p is highly expressed in chemoresistant, metastatic
Type of file: PDF Size of file: 0 KB Title of file for HTML: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1 mir-128-3p is highly expressed in chemoresistant, metastatic
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature19360 Supplementary Tables Supplementary Table 1. Number of monoclonal reads in each sample Sample Number of cells Total reads Aligned reads Monoclonal reads
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature19360 Supplementary Tables Supplementary Table 1. Number of monoclonal reads in each sample Sample Number of cells Total reads Aligned reads Monoclonal reads
Supplementary Figure 1. Using DNA barcode-labeled MHC multimers to generate TCR fingerprints
 Supplementary Figure 1 Using DNA barcode-labeled MHC multimers to generate TCR fingerprints (a) Schematic overview of the workflow behind a TCR fingerprint. Each peptide position of the original peptide
Supplementary Figure 1 Using DNA barcode-labeled MHC multimers to generate TCR fingerprints (a) Schematic overview of the workflow behind a TCR fingerprint. Each peptide position of the original peptide
Supplementary information
 Supplementary information High fat diet-induced changes of mouse hepatic transcription and enhancer activity can be reversed by subsequent weight loss Majken Siersbæk, Lyuba Varticovski, Shutong Yang,
Supplementary information High fat diet-induced changes of mouse hepatic transcription and enhancer activity can be reversed by subsequent weight loss Majken Siersbæk, Lyuba Varticovski, Shutong Yang,
Nature Medicine: doi: /nm.4078
 Supplementary Figure 1. Cetuximab induces ER stress response in DiFi cells. (a) Scheme of SILAC proteome. (b) MS-base read out of SILAC experiment. The histogram of log 2 -transformed normalized H/L ratios
Supplementary Figure 1. Cetuximab induces ER stress response in DiFi cells. (a) Scheme of SILAC proteome. (b) MS-base read out of SILAC experiment. The histogram of log 2 -transformed normalized H/L ratios
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure 1. Short-term coreceptor and costimulation blockade induces tolerance to pluripotent human ESCs. (A) Schematic diagram showing experimental approaches and
Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure 1. Short-term coreceptor and costimulation blockade induces tolerance to pluripotent human ESCs. (A) Schematic diagram showing experimental approaches and
EPIGENOMICS PROFILING SERVICES
 EPIGENOMICS PROFILING SERVICES Chromatin analysis DNA methylation analysis RNA-seq analysis Diagenode helps you uncover the mysteries of epigenetics PAGE 3 Integrative epigenomics analysis DNA methylation
EPIGENOMICS PROFILING SERVICES Chromatin analysis DNA methylation analysis RNA-seq analysis Diagenode helps you uncover the mysteries of epigenetics PAGE 3 Integrative epigenomics analysis DNA methylation
Nature Immunology: doi: /ni Supplementary Figure 1. DNA-methylation machinery is essential for silencing of Cd4 in cytotoxic T cells.
 Supplementary Figure 1 DNA-methylation machinery is essential for silencing of Cd4 in cytotoxic T cells. (a) Scheme for the retroviral shrna screen. (b) Histogram showing CD4 expression (MFI) in WT cytotoxic
Supplementary Figure 1 DNA-methylation machinery is essential for silencing of Cd4 in cytotoxic T cells. (a) Scheme for the retroviral shrna screen. (b) Histogram showing CD4 expression (MFI) in WT cytotoxic
Development Supplementary information. Supplementary Figures * * +/+ +/- -/- +/+ +/- -/-
 Development 144: doi:1.1242/dev.1473: Supplementary information Supplementary Figures A (f) FRT LoxP 2 3 4 B All Males Females I Ovary 1 (+) 77 bps (f) 78 bps (-) >13 bps (-) 2 4 (-) 424 bps M +/f +/-
Development 144: doi:1.1242/dev.1473: Supplementary information Supplementary Figures A (f) FRT LoxP 2 3 4 B All Males Females I Ovary 1 (+) 77 bps (f) 78 bps (-) >13 bps (-) 2 4 (-) 424 bps M +/f +/-
Supplemental Information. Metabolic Maturation during Muscle Stem Cell. Differentiation Is Achieved by mir-1/133a-mediated
 Cell Metabolism, Volume 27 Supplemental Information Metabolic Maturation during Muscle Stem Cell Differentiation Is Achieved by mir-1/133a-mediated Inhibition of the Dlk1-Dio3 Mega Gene Cluster Stas Wüst,
Cell Metabolism, Volume 27 Supplemental Information Metabolic Maturation during Muscle Stem Cell Differentiation Is Achieved by mir-1/133a-mediated Inhibition of the Dlk1-Dio3 Mega Gene Cluster Stas Wüst,
SUPPLEMENTARY LEGENDS...
 TABLE OF CONTENTS SUPPLEMENTARY LEGENDS... 2 11 MOVIE S1... 2 FIGURE S1 LEGEND... 3 FIGURE S2 LEGEND... 4 FIGURE S3 LEGEND... 5 FIGURE S4 LEGEND... 6 FIGURE S5 LEGEND... 7 FIGURE S6 LEGEND... 8 FIGURE
TABLE OF CONTENTS SUPPLEMENTARY LEGENDS... 2 11 MOVIE S1... 2 FIGURE S1 LEGEND... 3 FIGURE S2 LEGEND... 4 FIGURE S3 LEGEND... 5 FIGURE S4 LEGEND... 6 FIGURE S5 LEGEND... 7 FIGURE S6 LEGEND... 8 FIGURE
Supplemental Figure 1: Leydig cells are reduced at multiple stages in both male sterile mutants
 SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE LEGENDS: Supplemental Figure 1: Leydig cells are reduced at multiple stages in both male sterile mutants (Sgpl1 -/- and Plekha1 -/- ). Using an antibody against CYP11a1 to label Leydig
SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE LEGENDS: Supplemental Figure 1: Leydig cells are reduced at multiple stages in both male sterile mutants (Sgpl1 -/- and Plekha1 -/- ). Using an antibody against CYP11a1 to label Leydig
Supplemental Information. Myocardial Polyploidization Creates a Barrier. to Heart Regeneration in Zebrafish
 Developmental Cell, Volume 44 Supplemental Information Myocardial Polyploidization Creates a Barrier to Heart Regeneration in Zebrafish Juan Manuel González-Rosa, Michka Sharpe, Dorothy Field, Mark H.
Developmental Cell, Volume 44 Supplemental Information Myocardial Polyploidization Creates a Barrier to Heart Regeneration in Zebrafish Juan Manuel González-Rosa, Michka Sharpe, Dorothy Field, Mark H.
Neocortex Zbtb20 / NFIA / Sox9
 Neocortex / NFIA / Sox9 Supplementary Figure 1. Expression of, NFIA, and Sox9 in the mouse neocortex at. The lower panels are higher magnification views of the oxed area. Arrowheads indicate triple-positive
Neocortex / NFIA / Sox9 Supplementary Figure 1. Expression of, NFIA, and Sox9 in the mouse neocortex at. The lower panels are higher magnification views of the oxed area. Arrowheads indicate triple-positive
The autoimmune disease-associated PTPN22 variant promotes calpain-mediated Lyp/Pep
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION The autoimmune disease-associated PTPN22 variant promotes calpain-mediated Lyp/Pep degradation associated with lymphocyte and dendritic cell hyperresponsiveness Jinyi Zhang, Naima
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION The autoimmune disease-associated PTPN22 variant promotes calpain-mediated Lyp/Pep degradation associated with lymphocyte and dendritic cell hyperresponsiveness Jinyi Zhang, Naima
SSM signature genes are highly expressed in residual scar tissues after preoperative radiotherapy of rectal cancer.
 Supplementary Figure 1 SSM signature genes are highly expressed in residual scar tissues after preoperative radiotherapy of rectal cancer. Scatter plots comparing expression profiles of matched pretreatment
Supplementary Figure 1 SSM signature genes are highly expressed in residual scar tissues after preoperative radiotherapy of rectal cancer. Scatter plots comparing expression profiles of matched pretreatment
Soft Agar Assay. For each cell pool, 100,000 cells were resuspended in 0.35% (w/v)
 SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL AND METHODS Soft Agar Assay. For each cell pool, 100,000 cells were resuspended in 0.35% (w/v) top agar (LONZA, SeaKem LE Agarose cat.5004) and plated onto 0.5% (w/v) basal agar.
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL AND METHODS Soft Agar Assay. For each cell pool, 100,000 cells were resuspended in 0.35% (w/v) top agar (LONZA, SeaKem LE Agarose cat.5004) and plated onto 0.5% (w/v) basal agar.
mir-509-5p and mir-1243 increase the sensitivity to gemcitabine by inhibiting
 mir-509-5p and mir-1243 increase the sensitivity to gemcitabine by inhibiting epithelial-mesenchymal transition in pancreatic cancer Hidekazu Hiramoto, M.D. 1,3, Tomoki Muramatsu, Ph.D. 1, Daisuke Ichikawa,
mir-509-5p and mir-1243 increase the sensitivity to gemcitabine by inhibiting epithelial-mesenchymal transition in pancreatic cancer Hidekazu Hiramoto, M.D. 1,3, Tomoki Muramatsu, Ph.D. 1, Daisuke Ichikawa,
MII. Supplement Figure 1. CapZ β2. Merge. 250ng. 500ng DIC. Merge. Journal of Cell Science Supplementary Material. GFP-CapZ β2 DNA
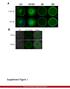 A GV GVBD MI DNA CapZ β2 CapZ β2 Merge B DIC GFP-CapZ β2 Merge CapZ β2-gfp 250ng 500ng Supplement Figure 1. MII A early MI late MI Control RNAi CapZαβ DNA Actin Tubulin B Phalloidin Intensity(A.U.) n=10
A GV GVBD MI DNA CapZ β2 CapZ β2 Merge B DIC GFP-CapZ β2 Merge CapZ β2-gfp 250ng 500ng Supplement Figure 1. MII A early MI late MI Control RNAi CapZαβ DNA Actin Tubulin B Phalloidin Intensity(A.U.) n=10
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information M1 macrophage-derived nanovesicles potentiate the anticancer efficacy of immune checkpoint inhibitors Yeon Woong Choo, 1, Mikyung Kang, 2, Han Young Kim, 1 Jin Han, 1 Seokyung Kang,
Supporting Information M1 macrophage-derived nanovesicles potentiate the anticancer efficacy of immune checkpoint inhibitors Yeon Woong Choo, 1, Mikyung Kang, 2, Han Young Kim, 1 Jin Han, 1 Seokyung Kang,
RNA SEQUENCING AND DATA ANALYSIS
 RNA SEQUENCING AND DATA ANALYSIS Length of mrna transcripts in the human genome 5,000 5,000 4,000 3,000 2,000 4,000 1,000 0 0 200 400 600 800 3,000 2,000 1,000 0 0 2,000 4,000 6,000 8,000 10,000 Length
RNA SEQUENCING AND DATA ANALYSIS Length of mrna transcripts in the human genome 5,000 5,000 4,000 3,000 2,000 4,000 1,000 0 0 200 400 600 800 3,000 2,000 1,000 0 0 2,000 4,000 6,000 8,000 10,000 Length
An Unexpected Function of the Prader-Willi Syndrome Imprinting Center in Maternal Imprinting in Mice
 An Unexpected Function of the Prader-Willi Syndrome Imprinting Center in Maternal Imprinting in Mice Mei-Yi Wu 1 *, Ming Jiang 1, Xiaodong Zhai 2, Arthur L. Beaudet 2, Ray-Chang Wu 1 * 1 Department of
An Unexpected Function of the Prader-Willi Syndrome Imprinting Center in Maternal Imprinting in Mice Mei-Yi Wu 1 *, Ming Jiang 1, Xiaodong Zhai 2, Arthur L. Beaudet 2, Ray-Chang Wu 1 * 1 Department of
Supplementary Figure S1. Monolayer differentiation of mouse ESCs into telencephalic neural precursors. (a) Schematic representation of the protocols
 Supplementary Figure S1. Monolayer differentiation of mouse ESCs into telencephalic neural precursors. (a) Schematic representation of the protocols used to differentiate mouse ESCs. (b) Representative
Supplementary Figure S1. Monolayer differentiation of mouse ESCs into telencephalic neural precursors. (a) Schematic representation of the protocols used to differentiate mouse ESCs. (b) Representative
Total genomic DNA was extracted from either 6 DBS punches (3mm), or 0.1ml of peripheral or
 Material and methods Measurement of telomere length (TL) Total genomic DNA was extracted from either 6 DBS punches (3mm), or 0.1ml of peripheral or cord blood using QIAamp DNA Mini Kit and a Qiacube (Qiagen).
Material and methods Measurement of telomere length (TL) Total genomic DNA was extracted from either 6 DBS punches (3mm), or 0.1ml of peripheral or cord blood using QIAamp DNA Mini Kit and a Qiacube (Qiagen).
p = formed with HCI-001 p = Relative # of blood vessels that formed with HCI-002 Control Bevacizumab + 17AAG Bevacizumab 17AAG
 A.. Relative # of ECs associated with HCI-001 1.4 1.2 1.0 0.8 0.6 0.4 0.2 0.0 ol b p < 0.001 Relative # of blood vessels that formed with HCI-001 1.4 1.2 1.0 0.8 0.6 0.4 0.2 0.0 l b p = 0.002 Control IHC:
A.. Relative # of ECs associated with HCI-001 1.4 1.2 1.0 0.8 0.6 0.4 0.2 0.0 ol b p < 0.001 Relative # of blood vessels that formed with HCI-001 1.4 1.2 1.0 0.8 0.6 0.4 0.2 0.0 l b p = 0.002 Control IHC:
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information 5-hydroxymethylcytosine-mediated epigenetic dynamics during postnatal neurodevelopment and aging By Keith E. Szulwach 1,8, Xuekun Li 1,8, Yujing Li 1, Chun-Xiao Song 2, Hao Wu
Supplementary Information 5-hydroxymethylcytosine-mediated epigenetic dynamics during postnatal neurodevelopment and aging By Keith E. Szulwach 1,8, Xuekun Li 1,8, Yujing Li 1, Chun-Xiao Song 2, Hao Wu
Single-cell RNA-Seq profiling of human pre-implantation embryos and embryonic stem cells
 Single-cell RNA-Seq profiling of human pre-implantation embryos and embryonic stem cells Liying Yan,2,5, Mingyu Yang,5, Hongshan Guo, Lu Yang, Jun Wu, Rong Li,2, Ping Liu, Ying Lian, Xiaoying Zheng, Jie
Single-cell RNA-Seq profiling of human pre-implantation embryos and embryonic stem cells Liying Yan,2,5, Mingyu Yang,5, Hongshan Guo, Lu Yang, Jun Wu, Rong Li,2, Ping Liu, Ying Lian, Xiaoying Zheng, Jie
Supplementary Figure 1 ITGB1 and ITGA11 increase with evidence for heterodimers following HSC activation. (a) Time course of rat HSC activation
 Supplementary Figure 1 ITGB1 and ITGA11 increase with evidence for heterodimers following HSC activation. (a) Time course of rat HSC activation indicated by the detection of -SMA and COL1 (log scale).
Supplementary Figure 1 ITGB1 and ITGA11 increase with evidence for heterodimers following HSC activation. (a) Time course of rat HSC activation indicated by the detection of -SMA and COL1 (log scale).
Nature Methods: doi: /nmeth.3115
 Supplementary Figure 1 Analysis of DNA methylation in a cancer cohort based on Infinium 450K data. RnBeads was used to rediscover a clinically distinct subgroup of glioblastoma patients characterized by
Supplementary Figure 1 Analysis of DNA methylation in a cancer cohort based on Infinium 450K data. RnBeads was used to rediscover a clinically distinct subgroup of glioblastoma patients characterized by
Nature Genetics: doi: /ng Supplementary Figure 1. SEER data for male and female cancer incidence from
 Supplementary Figure 1 SEER data for male and female cancer incidence from 1975 2013. (a,b) Incidence rates of oral cavity and pharynx cancer (a) and leukemia (b) are plotted, grouped by males (blue),
Supplementary Figure 1 SEER data for male and female cancer incidence from 1975 2013. (a,b) Incidence rates of oral cavity and pharynx cancer (a) and leukemia (b) are plotted, grouped by males (blue),
Supplementary Table S1. List of PTPRK-RSPO3 gene fusions in TCGA's colon cancer cohort. Chr. # of Gene 2. Chr. # of Gene 1
 Supplementary Tale S1. List of PTPRK-RSPO3 gene fusions in TCGA's colon cancer cohort TCGA Case ID Gene-1 Gene-2 Chr. # of Gene 1 Chr. # of Gene 2 Genomic coordiante of Gene 1 at fusion junction Genomic
Supplementary Tale S1. List of PTPRK-RSPO3 gene fusions in TCGA's colon cancer cohort TCGA Case ID Gene-1 Gene-2 Chr. # of Gene 1 Chr. # of Gene 2 Genomic coordiante of Gene 1 at fusion junction Genomic
Nature Immunology: doi: /ni Supplementary Figure 1. Characteristics of SEs in T reg and T conv cells.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Characteristics of SEs in T reg and T conv cells. (a) Patterns of indicated transcription factor-binding at SEs and surrounding regions in T reg and T conv cells. Average normalized
Supplementary Figure 1 Characteristics of SEs in T reg and T conv cells. (a) Patterns of indicated transcription factor-binding at SEs and surrounding regions in T reg and T conv cells. Average normalized
SUPPLEMENTARY DATA. Supplementary Table 2. Antibodies used for Immunofluoresence. Supplementary Table 3. Real-time PCR primer sequences.
 Supplementary Table 2. Antibodies used for Immunofluoresence. Antibody Dilution Source Goat anti-pdx1 1:100 R&D Systems Rabbit anti-hnf6 1:100 Santa Cruz Biotechnology Mouse anti-nkx6.1 1:200 Developmental
Supplementary Table 2. Antibodies used for Immunofluoresence. Antibody Dilution Source Goat anti-pdx1 1:100 R&D Systems Rabbit anti-hnf6 1:100 Santa Cruz Biotechnology Mouse anti-nkx6.1 1:200 Developmental
Nature Genetics: doi: /ng Supplementary Figure 1. Country distribution of GME samples and designation of geographical subregions.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Country distribution of GME samples and designation of geographical subregions. GME samples collected across 20 countries and territories from the GME. Pie size corresponds to the
Supplementary Figure 1 Country distribution of GME samples and designation of geographical subregions. GME samples collected across 20 countries and territories from the GME. Pie size corresponds to the
Supplementary figure 1
 Supplementary figure 1 Nature Medicine: doi:1.138/nm.275 CLUSTER BY SELF-ORGANIZING MAPS SELECTED PATHWAY ANALISYS TERMS Cluster : up-regulated genes in acute patients Cell cycle/dna repair Fatty acid
Supplementary figure 1 Nature Medicine: doi:1.138/nm.275 CLUSTER BY SELF-ORGANIZING MAPS SELECTED PATHWAY ANALISYS TERMS Cluster : up-regulated genes in acute patients Cell cycle/dna repair Fatty acid
Supplemental Information. CD4 + CD25 + Foxp3 + Regulatory T Cells Promote. Th17 Cells In Vitro and Enhance Host Resistance
 Immunity, Volume 34 Supplemental Information D4 + D25 + + Regulatory T ells Promote Th17 ells In Vitro and Enhance Host Resistance in Mouse andida albicans Th17 ell Infection Model Pushpa Pandiyan, Heather
Immunity, Volume 34 Supplemental Information D4 + D25 + + Regulatory T ells Promote Th17 ells In Vitro and Enhance Host Resistance in Mouse andida albicans Th17 ell Infection Model Pushpa Pandiyan, Heather
Supplementary Figure 1: Tissue of Origin analysis on 152 cell lines. (a) Heatmap representation of the 30 Tissue scores for the 152 cell lines.
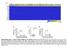 Supplementary Figure 1: Tissue of Origin analysis on 152 cell lines. (a) Heatmap representation of the 30 Tissue scores for the 152 cell lines. The scores summarize the global expression of the tissue
Supplementary Figure 1: Tissue of Origin analysis on 152 cell lines. (a) Heatmap representation of the 30 Tissue scores for the 152 cell lines. The scores summarize the global expression of the tissue
BIOL2005 WORKSHEET 2008
 BIOL2005 WORKSHEET 2008 Answer all 6 questions in the space provided using additional sheets where necessary. Hand your completed answers in to the Biology office by 3 p.m. Friday 8th February. 1. Your
BIOL2005 WORKSHEET 2008 Answer all 6 questions in the space provided using additional sheets where necessary. Hand your completed answers in to the Biology office by 3 p.m. Friday 8th February. 1. Your
Relationship between genomic features and distributions of RS1 and RS3 rearrangements in breast cancer genomes.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Relationship between genomic features and distributions of RS1 and RS3 rearrangements in breast cancer genomes. (a,b) Values of coefficients associated with genomic features, separately
Supplementary Figure 1 Relationship between genomic features and distributions of RS1 and RS3 rearrangements in breast cancer genomes. (a,b) Values of coefficients associated with genomic features, separately
Neoplasia 18 lecture 6. Dr Heyam Awad MD, FRCPath
 Neoplasia 18 lecture 6 Dr Heyam Awad MD, FRCPath ILOS 1. understand the role of TGF beta, contact inhibition and APC in tumorigenesis. 2. implement the above knowledge in understanding histopathology reports.
Neoplasia 18 lecture 6 Dr Heyam Awad MD, FRCPath ILOS 1. understand the role of TGF beta, contact inhibition and APC in tumorigenesis. 2. implement the above knowledge in understanding histopathology reports.
Supplementary Figure 1 (Related with Figure 4). Molecular consequences of Eed deletion. (a) ChIP analysis identifies 3925 genes that are associated
 Supplementary Figure 1 (Related with Figure 4). Molecular consequences of Eed deletion. (a) ChIP analysis identifies 3925 genes that are associated with the H3K27me3 mark in chondrocytes (see Table S1,
Supplementary Figure 1 (Related with Figure 4). Molecular consequences of Eed deletion. (a) ChIP analysis identifies 3925 genes that are associated with the H3K27me3 mark in chondrocytes (see Table S1,
GENDER James Bier
 GENDER 2005-2008 James Bier Objectives 1. State the method of determining gender in several genetic systems. 2. List the three regions of the Y chromosome. 3. Describe the events that promote sexual development
GENDER 2005-2008 James Bier Objectives 1. State the method of determining gender in several genetic systems. 2. List the three regions of the Y chromosome. 3. Describe the events that promote sexual development
Gene Ontology 2 Function/Pathway Enrichment. Biol4559 Thurs, April 12, 2018 Bill Pearson Pinn 6-057
 Gene Ontology 2 Function/Pathway Enrichment Biol4559 Thurs, April 12, 2018 Bill Pearson wrp@virginia.edu 4-2818 Pinn 6-057 Function/Pathway enrichment analysis do sets (subsets) of differentially expressed
Gene Ontology 2 Function/Pathway Enrichment Biol4559 Thurs, April 12, 2018 Bill Pearson wrp@virginia.edu 4-2818 Pinn 6-057 Function/Pathway enrichment analysis do sets (subsets) of differentially expressed
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology: doi: /nsmb Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 U1 inhibition causes a shift of RNA-seq reads from exons to introns. (a) Evidence for the high purity of 4-shU-labeled RNAs used for RNA-seq. HeLa cells transfected with control
Supplementary Figure 1 U1 inhibition causes a shift of RNA-seq reads from exons to introns. (a) Evidence for the high purity of 4-shU-labeled RNAs used for RNA-seq. HeLa cells transfected with control
Metabolic ER stress and inflammation in white adipose tissue (WAT) of mice with dietary obesity.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Metabolic ER stress and inflammation in white adipose tissue (WAT) of mice with dietary obesity. Male C57BL/6J mice were fed a normal chow (NC, 10% fat) or a high-fat diet (HFD,
Supplementary Figure 1 Metabolic ER stress and inflammation in white adipose tissue (WAT) of mice with dietary obesity. Male C57BL/6J mice were fed a normal chow (NC, 10% fat) or a high-fat diet (HFD,
Supplementary Figure 1.TRIM33 binds β-catenin in the nucleus. a & b, Co-IP of endogenous TRIM33 with β-catenin in HT-29 cells (a) and HEK 293T cells
 Supplementary Figure 1.TRIM33 binds β-catenin in the nucleus. a & b, Co-IP of endogenous TRIM33 with β-catenin in HT-29 cells (a) and HEK 293T cells (b). TRIM33 was immunoprecipitated, and the amount of
Supplementary Figure 1.TRIM33 binds β-catenin in the nucleus. a & b, Co-IP of endogenous TRIM33 with β-catenin in HT-29 cells (a) and HEK 293T cells (b). TRIM33 was immunoprecipitated, and the amount of
Color Key PCA. mir- 15a let-7c 106b let-7b let-7a 16 10b 99a 26a 20b 374b 19b 135b 125b a-5p 199b-5p 93 92b MES PN.
 1123 83 528 816 84 2 17 718 Comp3 3 2 1 1 2 3 4 Comp2 a b Color Key MES PN PCA 3 2 1 1 2 3 4 Comp1 1 2 3 1 2 3 4-2 -1 1 2 mi- 15a let-7c 16b let-7b let-7a 16 1b 99a 26a 2b 374b 19b 135b 125b 9 34 125a-5p
1123 83 528 816 84 2 17 718 Comp3 3 2 1 1 2 3 4 Comp2 a b Color Key MES PN PCA 3 2 1 1 2 3 4 Comp1 1 2 3 1 2 3 4-2 -1 1 2 mi- 15a let-7c 16b let-7b let-7a 16 1b 99a 26a 2b 374b 19b 135b 125b 9 34 125a-5p
Therapy-related acute myeloid leukemia with germline TP53 mutation (Li-Fraumeni syndrome) SH Chelsey Deel MD Teresa Scordino MD
 Therapy-related acute myeloid leukemia with germline TP53 mutation (Li-Fraumeni syndrome) SH2017-167 Chelsey Deel MD Teresa Scordino MD Clinical History HPI: 44 year old Caucasian female referred for evaluation
Therapy-related acute myeloid leukemia with germline TP53 mutation (Li-Fraumeni syndrome) SH2017-167 Chelsey Deel MD Teresa Scordino MD Clinical History HPI: 44 year old Caucasian female referred for evaluation
TMA-VARESE COHORT-1 TMA-BERN COHORT-2
 Supplementary Figure 1 TMA-VARESE COHORT-1 TOTAL SAMPLES #5 GLEASON SCORE Number Percentage 6 16 32% = 7 17 34% >7 17 34% TUMOR STAGE T2C 28 56% T3A- 21 42% T3C-T4 1 2% NODE STATUS N 42 84% N1 8 16% PSA
Supplementary Figure 1 TMA-VARESE COHORT-1 TOTAL SAMPLES #5 GLEASON SCORE Number Percentage 6 16 32% = 7 17 34% >7 17 34% TUMOR STAGE T2C 28 56% T3A- 21 42% T3C-T4 1 2% NODE STATUS N 42 84% N1 8 16% PSA
Genome-Wide Analysis of DNA Methylation Dynamics during Early Human Development
 Genome-Wide Analysis of DNA Methylation Dynamics during Early Human Development Hiroaki Okae 1,2, Hatsune Chiba 1,2, Hitoshi Hiura 1,2, Hirotaka Hamada 1,2, Akiko Sato 1,3, Takafumi Utsunomiya 3, Hiroyuki
Genome-Wide Analysis of DNA Methylation Dynamics during Early Human Development Hiroaki Okae 1,2, Hatsune Chiba 1,2, Hitoshi Hiura 1,2, Hirotaka Hamada 1,2, Akiko Sato 1,3, Takafumi Utsunomiya 3, Hiroyuki
Figure S1. In vitro drug combinations Growth inhibition assays performed on BE(2)-C neuroblastoma cell line using Alamar Blue after 72 h incubation
 Figure S1. In vitro drug combinations Growth inhibition assays performed on BE(2)-C neuroblastoma cell line using Alamar Blue after 72 h incubation with a range of concentrations of chemotherapy agents
Figure S1. In vitro drug combinations Growth inhibition assays performed on BE(2)-C neuroblastoma cell line using Alamar Blue after 72 h incubation with a range of concentrations of chemotherapy agents
SUPPLEMENTAL INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTAL INFORMATION GO term analysis of differentially methylated SUMIs. GO term analysis of the 458 SUMIs with the largest differential methylation between human and chimp shows that they are more
SUPPLEMENTAL INFORMATION GO term analysis of differentially methylated SUMIs. GO term analysis of the 458 SUMIs with the largest differential methylation between human and chimp shows that they are more
Supplementary Figure 1. Linkage analysis of Family 7. Red arrow, position of SRRM2 gene in chromosome16.
 A germline mutation in SRRM2, a splicing factor gene, is implicated in papillary thyroid carcinoma predisposition Jerneja Tomsic 1, Huiling He 1, Keiko Akagi 1, Sandya Liyanarachchi 1, Qun Pan 2, Blake
A germline mutation in SRRM2, a splicing factor gene, is implicated in papillary thyroid carcinoma predisposition Jerneja Tomsic 1, Huiling He 1, Keiko Akagi 1, Sandya Liyanarachchi 1, Qun Pan 2, Blake
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature12652 Supplementary Figure 1. PRDM16 interacts with endogenous EHMT1 in brown adipocytes. Immunoprecipitation of PRDM16 complex by flag antibody (M2) followed by Western blot analysis
doi:10.1038/nature12652 Supplementary Figure 1. PRDM16 interacts with endogenous EHMT1 in brown adipocytes. Immunoprecipitation of PRDM16 complex by flag antibody (M2) followed by Western blot analysis
m 6 A mrna methylation regulates AKT activity to promote the proliferation and tumorigenicity of endometrial cancer
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Articles https://doi.org/10.1038/s41556-018-0174-4 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. m 6 A mrna methylation regulates AKT activity to promote the proliferation
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Articles https://doi.org/10.1038/s41556-018-0174-4 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. m 6 A mrna methylation regulates AKT activity to promote the proliferation
