EFFECTS OF PAK KINASE INHIBITION ON EMERGENCE OF VEMURAFENIB RESISTANCE IN MELANOMA
|
|
|
- Agnes Marsh
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 University of Iowa Honors Theses University of Iowa Honors Program Spring 2018 EFFECTS OF PAK KINASE INHIBITION ON EMERGENCE OF VEMURAFENIB RESISTANCE IN MELANOMA Brooke Jennings Follow this and additional works at: Part of the Other Chemicals and Drugs Commons, Skin and Connective Tissue Diseases Commons, and the Therapeutics Commons Copyright 2018 Brooke Jennings Hosted by Iowa Research Online. For more information please contact:
2 EFFECTS OF PAK KINASE INHIBITION ON EMERGENCE OF VEMURAFENIB RESISTANCE IN MELANOMA by Brooke Jennings A thesis submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for graduation with Honors in the Biology Christopher Stipp Thesis Mentor Spring 2018 All requirements for graduation with Honors in the Biology have been completed. Lori C. Adams Biology Honors Advisor This honors thesis is available at Iowa Research Online:
3
4 Abstract Melanoma is considered the most dangerous form of skin cancer, and the number of cases of melanoma per year has doubled in 30 years. Mutations in the B-RAF gene account for approximately 50% of genetic driver mutations in skin melanoma. Patients with B-RAF mutant melanoma are typically treated with a chemotherapy drug called vemurafenib. However, patients can stop responding to this treatment in as little as six months. The main purpose of this study was to determine if inhibiting PAK, a kinase-signaling molecule, in combination with vemurafenib could prevent the treatment-resistance in melanoma. PAK signaling plays an important role in the Hippo tumor suppressor pathway, which is important in cell proliferation and growth. In order to evaluate the effects of PAK kinase inhibition, we utilized a drug called FRAX-486, which is a type of PAK kinase inhibitor in combination with vemurafenib to treat melanoma cells in cell growth experiments. The main findings suggest that PAK inhibition with vemurafenib prevents cell proliferation in the cancer cells. Therefore, these results support the conclusion that PAK kinase inhibition in combination with vemurafenib can prevent emergence of treatment resistant melanoma. This new combination treatment could have the potential to prevent or delay the emergence of treatment-resistant melanoma and prolong the patient s life.
5 Acknowledgements First and foremost, I would like to give my sincerest thanks to my thesis mentor, Dr. Christopher Stipp, for his patience during training, immense knowledge, and enthusiasm for my project. His support was essential for the successful completion of my project, and expansion of my knowledge on not only metastasis and cellular pathways, but also in research as a whole. I would also like to thank Afshin Varzavand, for always being patient while I asked him questions for the second, third, or fourth time. I would also like to express my gratitude for him taking the time to train me on the various protocols. I would like to thank all the lab members as a whole for providing me with an extremely welcoming atmosphere in which to grow and learn. Finally, I would like to thank the biology department and biology honors advisor, Dr. Lori Adams, for their support, advice, and encouragement through the entire process. ii
6 TABLE OF CONTENTS INTRODUCTION. 1 PAGE MATERIALS AND METHODS.. 5 Reagents Cell culture 5 Drug resistance assay 5 Cell viability assay 6 Antibodies. 6 Western blot... 7 RESULTS PAK Inhibition Prevents Resistance in Melanoma... 8 Short-Term Biochemical Assay PAK Inhibitor Concentration Levels.. 10 DISCUSSION LITERATURE CITED iii
7 Introduction Melanoma is a type of cancer arising from melanocytes, the cell type that produces the pigment in skin. Melanoma is considered the most dangerous form of skin cancer (MacGill, 2018). The number of cases of melanoma per year has doubled from 1982 to In 2011, in the United States alone, there were over 65,000 cases of melanoma, and over 9,000 deaths caused by melanoma (Guy et al., 2015). Mutations in the B-RAF gene account for approximately 50% of genetic mutations in melanoma, and have been found in about 7-15% of cancers (Dhomen & Marais, 2007) (Curtin et al., 2005). Inhibition of the B-RAF kinase is a common target for treatment of melanoma because it is a commonly seen mutation found in the oncogenic cells. Vemurafenib is used to treat metastatic melanoma containing the B-RAF V600 mutations. Vemurafenib is an orally administered drug that inhibits the oncogenic B-RAF kinase. There are 3 primary highly conserved RAF serine-threonine protein kinase genes (A-RAF, B- RAF, C-RAF) that function in the RAS-RAF-MEK-ERK pathway. The RAS-RAF-MEK-ERK pathway is a kinase cascade that is responsible for transmitting signals from extracellular growth factors, which play a role in many processes such as cell cycle progression, differentiation, survival, and migration (Molina Jr., 2006). This treatment is effective, with a report of a response rate as high as 84% in B-RAF V600 melanoma treated with the B-RAF-targeted therapy (Chapman, 2011). However, the cancer cells can develop resistance to vemurafenib in as short as 6 months (Chapman, 2011). The resistant cells display an increase in actin stress fiber formation, indicating resistance involves actin cytoskeletal remodeling (Kim, et al., 2016). Monomeric GTPases regulate cystoskeletal rearrangements. PAK kinase signaling downstream of Rac1 (GTPase) results in increased actin polymerization. PAK kinase also has the potential to activate YAP and TAZ, proto-oncogenic 1
8 transcriptional co-activators. B-RAF inhibitor resistant cells are shown to have an increase in actin stress fiber formation, and increased accumulation of YAP and TAZ in the nucleus. Overexpression of constitutively active YAP has also shown to cause resistance (Kim, et al., 2016). It has been concluded that YAP/TAZ activation in cancer cells is oncogenic and stimulates resistance to anti-cancer drug therapies (Kim et al., 2016). PAK is a possible contributor to the emergence of vemurafenib resistance because of its potential to activate YAP and TAZ. PAK, also known as p21-activated kinase, is a member of a family of enzymes that serve as targets for small GTP binding proteins. PAK is a possible contributor to vemurafenib resistance because of its potential to activate YAP and TAZ, the proto-oncogenic transcriptional co-activators that are the targets of the Hippo tumor suppressor pathway. Typically, this signaling pathway plays key roles in the biological processes of organ size control, cell proliferation and apoptosis, stem cell homeostasis, and cellular differentiation (Kim et al., 2016). PAK signaling downstream of Rac1 is a possible activator of YAP and TAZ (Fig 1). Rac1 stimulates the PAK kinase proteins, which in turn activates LIMK. LIMK is an actinbinding kinase that subsequently phosphorylates and inactivates the actin-severing protein cofilin, which in turn favors actin polymerization and F-actin accumulation. Subsequently, F- actin is binding AMOT, dislodging YAP, which then goes to the nucleus to initiation gene expression leading to abnormal cell growth (Feng, 2014). This potential pathway could explain the upregulation of YAP and TAZ as well as actin remodeling seen in resistant cells (Fig 1). It is known that YAP/TAZ activation of the Hippo pathway and actin remodeling result in emergence of treatment-resistant melanoma, however the role of upstream signaling by PAK kinases in resistance remains largely unexplored (Kim et al., 2016). Successful long term 2
9 outcomes of the research presented here may include the ability to shut down this pathway through a PAK kinase inhibitor to prevent the development of vemurafenib-resistant cells. Here we report the effects of PAK kinase inhibition on emergence of vemurafenib resistance and on some of the signaling proteins that lie downstream of PAK that might contribute to drug resistance. PAK Figure 1: Schematic representation of Hippo-dependent and Hippo-independent pathways resulting in YAP activation (Feng, 2014). 3
10 In order to evaluate the effects of PAK kinase inhibition, we utilized a drug called FRAX-486, which is a type of PAK (p21-activated kinase 1) kinase inhibitor (Chow et al., 2012). To test the effects of PAK kinase inhibition on vemurafenib resistance, we completed a population doubling versus time experiment. Cells were treated with four different conditions: a negative control, vemurafenib alone, FRAX-486 alone, and a combination of FRAX-486 and vemurafenib. The cell populations doubling over time were examined to determine how the conditions affected cell growth and proliferation. Western blots were completed with to examine the effect of FRAX-486 treatment on signaling proteins in the treated cells. Proteins associated with the predicted path of resistance, as well as up and downstream components of PAK kinase signaling were examined. Overall based on the in vitro studies, PAK inhibition seems to be an ideal potential target for preventing treatment-resistance in patients. In future research, the PAK inhibition coupled with vemurafenib should be tested with small animal trials to evaluate results and possible side effects in an in vivo model. 4
11 Materials and Methods Reagents Vemurafenib was purchased from LC Laboratories, and FRAX-486 was purchased from Selleckchem. Vemurafenib was used at 3 μm and FRAX-486 was used at 50 nm. These were each dissolved in dimethyl sulfoxide. Cell Culture A375 cells were purchased from ATCC. Prior to this study, the cells had been transduced with firefly luciferase to enable bioluminescence imaging of viable cells. Growth media was prepared with DMEM 1X media, 50 ml 10% Fetal Bovine Serum, 5 ml Penicillin (100 U/mL) /Streptomycin (100 μg/ml) solution, 5 ml MEM Non-Essential Amino Acids, and 2 ml L- glutamine. Cells were plated at 300,000 cells in a six well plate to begin the experiment. The cells were grown under four primary conditions: a negative control (no drug treatment), vemurafenib alone, FRAX-486 alone, and vemurafenib and FRAX-486 in combination. Drug Resistance Assay Growth media was replaced every 4 days. Cells were harvested, counted, and replated as tolerated during the growth experiment. Cell culture was terminated when treated cells either died out or developed resistance to the drug treatment. Cell populations were deemed resistant once they had achieved 10 population doublings under continuous drug treatment. The data was subsequently graphed and analyzed by GraphPad Prism software. 5
12 Cell viability assay For FRAX-486 dose response analysis, luciferase-expressing cells were treated with variable doses of FRAX-486 in a 96-well plate and incubated for 24 h after plating. For each condition (0 nm, 50 nm, 100 nm, 200 nm, 500 nm, 1000 nm, 5000 nm, 10,000 nm) six wells were plated with 5,0000 cells each. A bioluminescence imager quantified viable cells. Data was analyzed by using GraphPad Prism software. Antibodies Primary antibodies used for western blot experiments are shown in Table 1 below. Table 1: Antibodies utilized in Western Blot Experiments Name Dilution Isotype Purchasing Company Catalog number AKT 1000X Mouse BD Transduction Phospho-AKT 2000X Rabbit Phospho-ERK 1000X Rabbit MEK 1000X Mouse Phospho-MEK 1000X Rabbit PAK 1/2/3 1000X Rabbit Cell Signaling Technology Cell Signaling Technology Cell Signaling Technology Cell Signaling Technology Cell Signaling Technology 4060S 9101S 2352S 98105S 2604 Tubulin 1000X Rabbit DSHB 12G10 Secondary antibodies were goat HRP-conjugated anti-mouse IgG and anti-rabbit igg purchased from Jackson ImmunoResearch. 6
13 Western Blot To prepare protein lysates, cells were seeded in 60 mm dishes and treated and grown for the indicated time points at 37 C in full growth media. Cells were transferred to ice, washed with ice-cold HBSM buffer (20 mm Hepes, ph 7, 150 mm NaCl, 2 mm CaCl2, 5 mm MgCl2 dissolved in H2O), and lysed by Triton X-100 lysis buffer with 2 mm phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride (PMSF). Protein concentration of each lysate was measured using a Red 660 assay kit (G-Biosciences). Lysates were loaded at equal protein amounts of 20 µg per lane into a 9% SDS page gel, and subsequently transferred to a nitrocellulose membrane. After blocking with Aquablock (EastCoast Bio), membranes were incubated with primary antibodies diluted 1:1,000 in Aquablock with 0.1% Tween 20. The primary antibody was stained overnight in at 4 o C. The secondary antibody was diluted 1:1,000 in Aquablock with 1% Tween 20, and stained at room temperature for 1 hour. Membranes were scanned on an Odyssey CLx scanner (Licor) with 700 and 800 nm channels set to membrane and normal or low resolution. Protein levels were quantified with the Image Studio software, by utilizing the built-in quantification tool that corrects for background noise. 7
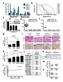
14 Results PAK Inhibition Prevents Resistance in Melanoma In order to examine the effects of the PAK kinase inhibitor FRAX-486 on cell viability we completed a dose response curve with the following concentrations (in nm): 0, 50, 100, 200, 500, 1000, 5000, (Fig 2.A). This graph fits the expected logarithmic form. Concentrations towards the right end of the graph indicate highly toxic amounts of the drug that result in cell death. To limit cytotoxicity, 50 nm, a concentration similar to the IC20 as calculated from the dose-response curve, was chosen for subsequent assays. This concentration was chosen with the expectation that there would be little to no effect alone, but could be successful when used in combination with vemurafenib. Subsequent cell culture assays were completed in two independent experiments in order to examine the effects of vemurafenib and FRAX-486 in combination, in comparison to a DMSO vehicle control, FRAX-486 alone, and vemurafenib alone. The second experiment included 3 biological replicates run in parallel. The cumulative population doubling is plotted on the y-axis, while time in days is plotted on the x-axis. In both experiments, cells under vemurafenib + FRAX treatment died out around days (Fig 2.B & 2.C). The control treatment (DMSO) and FRAX alone reached 10 population doublings in as little as less than 15 days (Fig 2.B). The vemurafenib treated cells reached 10 population doublings at an average of 69 days, while increased growth can be noted on average around 35 days indicating vemurafenib treatment alone did not prevent development of drug-resistance in the cells. Short-Term Biochemical Assay Shows Inconclusive Results of VEM+FRAX Treatment In order to assess the potentially involved proteins and pathways for blockage of resistance by PAK kinase inhibition, lysates were generated and immunoblotted for various 8
15 Figure 2. PAK Kinase Inhibition Prevents Resistance in Melanoma Cell Line A Dose response curve for PAK Kinase Inhibitor (FRAX-486). Bars indicate the standard error of the mean of the six wells per condition. The x-axis indicates the log concentration of FRAX-486, while the y-axis indicates the percentage of viable cells. B Population doublings vs. time graph evaluated the effects of treatment. This represents a single trial of a cell assay. Cells were re-fed with corresponding treatment every 4-5 days. DMSO and FRAX alone treatments reached 10 population doublings within 15 days. Vemurafenib treatment reached 10 population doublings around 81 days. The VEM- FRAX combination treatment cells died off by day 60. C Population doublings vs. time graph evaluated the effects of treatment. This graph represents three trials run simultaneously. Cells were re-fed with corresponding treatment every 4-5 days. Vemurafenib treatment reached 10 population doublings on average by 65 days. The VEM-FRAX combination treatment cells died off by around day 55. 9
16 potential proteins (see Figure 1) involved in vemurafenib resistance. Proteins involved in the MAP-kinase pathway targeted for treatment with vemurafenib were also tested. Tubulin served as the loading control for equal amounts of protein sample loading. When comparing the cells under vemurafenib (VEM) treatment and the vemurafenib and FRAX-486 combination (VEM+FRAX) treatment we expected to see a down-regulation of TAZ, perk, and pakt and/or AKT in the VEM+FRAX cells because these proteins are associated with resistance in melanoma. We also expected to see a down-regulation of phosphorylation of MEK at position 298 in the VEM+FRAX cells because this position on MEK is phosphorylated by activated PAK. Overall, there were no dramatic changes in any of the signaling protein levels when comparing the vemurafenib treated cells with the VEM+FRAX combination (Fig 3). The protein levels of TAZ, pmek, pakt, and perk are all highest in the DMSO and FRAX treated cells, while they are significantly lower in both the VEM treated and VEM+FRAX treated cells. The protein levels of TAZ and pmek moderately decrease with time in both the VEM treated and VEM+FRAX treated cells. Interestingly, the protein levels of perk was significantly diminished by day 2 of treatment and then moderately increased by day 7 in both the VEM treated and VEM+FRAX treated cells. These results indicated either the mechanism by which PAK inhibition blocks drug resistance has not been identified, or that the PAK inhibition mechanism is functioning at sub-detectible levels during the beginning of treatment. PAK Inhibitor Concentration Levels in Relation to pmek S298 Signal Inhibition In order to assess the relationship of FRAX 486 concentration and the inhibition of the downstream target of PAK, lysates were generated from cells treated with the following 10
17 Figure 3. Protein involvement in resistance prevention via VEM+FRAX is inconclusive Immunoblotting for the indicated proteins, quantification for relative intensity of the band can be seen underneath each lane. The protein levels of TAZ, pmek, pakt, and perk are all highest in the DMSO and FRAX treated cells, while they are significantly lower in both the VEM treated and VEM+FRAX treated cells. The protein levels of TAZ and pmek moderately decrease with time in both the VEM treated and VEM+FRAX treated cells. The protein levels of perk was significantly diminished by day 2 of treatment and then moderately increased by day 7 in both the VEM treated and VEM+FRAX treated cells. Tubulin served as the positive loading control. 11
18 concentrations of FRAX 486 (in nm): 0, 50, 100, 200, 500, They were subsequently blotted for total MEK and pmek S298, the target site for PAK signaling. Tubulin served as the loading control for equal amounts of protein sample loading. The relative amount of pmek S298 and total MEK decreased with increasing concentrations of FRAX 486 (Fig 4.A). A dose response curve was created to visualize the percentage of target inhibition. From this graph, the IC50 was calculated to be 540 nm (Fig 4.B). The IC50 for target inhibition corresponds to the concentration of FRAX 486 that inhibits 50% of the amount of pmek S298 in untreated cells. 12
19 A B IC50 = 540 nm Figure 4. Dose Response Curve for FRAX 486 Target Inhibition. A Immunoblotting for the indicated proteins at varying levels of PAK inhibitor concentrations; quantification for relative intensity of the band can be seen underneath each lane. PAK inhibition results in a decreased level of phosphorylated MEK and total MEK. Tubulin served as the loading control. B Dose response curve for PAK Kinase Inhibitor (FRAX-486). The x-axis indicates the log concentration of FRAX-486, while the y-axis indicates the percentage of the pmek signal inhibited by FRAX
20 Discussion This study aimed to evaluate the effects of PAK kinase inhibition on emergence of vemurafenib resistance and potentially related biochemical signaling pathways. Our results strongly indicate that combining PAK kinase inhibition via FRAX-486 with vemurafenib treatment can prevent development of resistance in melanoma cells. In the cell culture assays, cells under vemurafenib treatment alone began to show signs of resistance by day 35 on average. However, cells under VEM-FRAX combination treatment eventually died out between days 55-60, and resistance was never developed. Treatment with FRAX alone showed no effect on cell growth in comparison to the DMSO control. This provides evidence that the FRAX treatment at the 50 nm dose we chose may not result in cytotoxicity in normal cells; there may be minimal to no effects. Furthermore, these results indicate that PAK kinases are playing an important role in the development of resistance in melanoma cells. According to the short-term biochemical assay, there were no significant differences in the levels of selected signaling proteins within the first seven days of treatment. However, there are several possible explanations for this observation. Phosphorylation of MEK at the 298 position is associated with activation by PAK. One possible way the treatment of PAK kinase inhibition is effective is through deactivation of PAK and subsequent effects on cell proliferation occurring at sub-detectible levels at the beginning of treatment. The protein levels of perk are highest in the DMSO and FRAX treated cells. The protein levels of perk are extremely diminished in the VEM and VEM+FRAX treated cells. There was a two fold increase from day 2 to day 7 in perk in the VEM and VEM+FRAX treated cells. It is possible the cells begin to combat the vemurafenib treatment by attempting to reactivate the ERK protein by 14
21 phosphorylation. Although not tested in this study, PAK kinase inhibition may work to prevent resistance by having a slow build up over time of cumulative inhibition of ERK phosphorylation. The inconclusive results of the short-term biochemical assay are further rationalized by the results of the FRAX 486 concentration vs. pmek S298. These concentration lysates were used to determine the signaling IC50 of 540 nm for the FRAX 486 drug. For the drug resistance experiments we chose a FRAX 486 concentration close to the IC20, 50 nm. This value is significantly lower, which leads us to believe that the blockage of resistance is taking place at a sub-detectible level in the short term. This study faced constraints mostly due to time. The results from the short-term biochemical assays were difficult to draw conclusions from. Moving forward, biochemical assays on long-term lysates need to be assessed. In the drug-resistance assays differences between cell treatment growths weren t seen until around days Ideally, when making the new lysates, they should be from cells grown under the treatment conditions until at least day 30. Previous studies have shown increased PAK-1 expression in cancers of the bladder, breast, lung, and T cell lymphomas (Ong et al., 2011)(Field and Ye, 2015)(Pandolfi et al., 2015)(Gan et al., 2016). However, the role of PAK in metastasis with relation to the Hippo pathway was not explored. As discussed in previous literature, PAK seems to play an essential role cancer metastasis. Developing a potential treatment to target PAK would be beneficial in a large number of cancers. Previous research has also linked PAK signaling directly to resistance in B-RAF mutant melanomas like studied here (Lu et al., 2017). However, the major focus in Lu et al. was on the MAP Kinase pathway. The potential role of the Hippo pathway was not explored despite the evidence of cytoskeletal rearrangement in drug-resistant melanoma. Furthermore, the effects of 15
22 PAK inhibition with the common B-RAF inhibitor was only studied after the cells developed resistance to the B-RAF inhibitor treatment. The avenue of potential preventative treatment was not investigated (Lu et al., 2017). Another future avenue for this project involves evaluating the role of Src/PAK signaling in vemurafenib resistant melanoma. It has been shown that oncogenic Src results in cancerous cellular transformation through activation of Rac1 (Servitja, et al., 2003). It is possible that vemurafenib resistance is developed through a pathway involving Src signaling through Rac1, and subsequent downstream signaling through PAK. In conclusion, PAK appears to play an important role of development of resistance in vemurafenib treated B-RAF melanoma. This means PAK kinase inhibition could be an extremely important therapeutic target moving forward. Further investigation into the mechanism will provide insight to the cancer community, as it is possible PAK kinase is an important factor in a variety of cancers. Subsequent animal trials will allow evaluation of the potential treatment in an in vivo setting. 16
23 Literature Cited Chapman, P. B., A. Hauschild, C. Robert, J. B. Haanen, P. Ascierto, J. Larkin, R. Dummer, C. Garbe, A. Testori, M. Maio, D. Hogg, P. Lorigan, C. Lebbe, T. Jouary, D. Schadendorf, A. Ribas, S. J. O'Day, J. A. Sosman, J. M. Kirkwood, A. M. Eggermont, B. Dreno, K. Nolop, J. Li, B. Nelson, J. Hou, R. J. Lee, K. T. Flaherty, G. A. McArthur, and G. R. BRIM-3. (2011) Improved survival with vemurafenib in melanoma with BRAF V600E mutation. The New England journal of medicine, 364(26), Curtin JA, Fridlyand J, Kageshita T, et al. (2005) Distinct sets of genetic alterations in melanoma. The New England journal of medicine, 353(20), Dhomen N, Marais R. New insight into BRAF mutations in cancer. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2007;17(1):31 9. FDA Approval for Vemurafenib. (Rev. 2013). Retrieved February 24, 2018, from Feng, X., Degese, M., Iglesias-Bartolome, R., Vaque, J., Molinolo, A., Rodrigues, M.,... Gutkind, J. (2014). Hippo-Independent Activation of YAP by the GNAQ Uveal Melanoma Oncogene through a Trio-Regulated Rho GTPase Signaling Circuitry. Cancer Cell, 25(6), Field, J., Ye, D.Z. PAK signaling in cancer, Cell. Logist. 2 (2) (2012) Gan, J., et al. Growth hormone-releasing hormone receptor antagonists inhibit human gastric cancer through downregulation of PAK1-STAT3/NF-kappaB signaling, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 113 (51) (2016) Guy, Gery P., Jr., Cheryll C. Thomas, Trevor Thompson, Meg Watson, Greta M. Massetti, and Lisa C. Richardson. "Vital Signs: Melanoma Incidence and Mortality Trends and Projections United States, " Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report (2015): Kim, M. H., Kim, J., Hong, H., Lee, S., Lee, J., Jung, E., & Kim, J. (2015). Actin remodeling confers BRAF inhibitor resistance to melanoma cells through YAP/TAZ activation. The EMBO Journal, 35(5), Lu, H., Liu, S., Zhang, G., Wu, B., Zhu, Y., Frederick, D. T.,... Guo, W. (2017). PAK signalling drives acquired drug resistance to MAPK inhibitors in BRAF-mutant melanomas. MacGill, M. (2018, January 25). What You Should Know About Melanoma. Medical News Today: Health News. Retrieved from 17
24 Molina JR, Adjei AA. The Ras/Raf/MAPK pathway. J Thorac Oncol. 2006;1(1):7 9. Ong, C., et al. Targeting p21-activated kinase 1 (PAK1) to induce apoptosis of tumor cells, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 108 (17) (2011) Pandolfi, A., et al. PAK1 is a therapeutic target in acute myeloid leukemia and myelodysplastic syndrome, Blood 126 (9) (2015) Servitja, J., et al. (2003). Rac1 Function Is Required for Src-induced Transformation. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 278(36),
MTC-TT and TPC-1 cell lines were cultured in RPMI medium (Gibco, Breda, The Netherlands)
 Supplemental data Materials and Methods Cell culture MTC-TT and TPC-1 cell lines were cultured in RPMI medium (Gibco, Breda, The Netherlands) supplemented with 15% or 10% (for TPC-1) fetal bovine serum
Supplemental data Materials and Methods Cell culture MTC-TT and TPC-1 cell lines were cultured in RPMI medium (Gibco, Breda, The Netherlands) supplemented with 15% or 10% (for TPC-1) fetal bovine serum
a b G75 G60 Sw-2 Sw-1 Supplementary Figure 1. Structure predictions by I-TASSER Server.
 a b G75 2 2 G60 Sw-2 Sw-1 Supplementary Figure 1. Structure predictions by I-TASSER Server. a. Overlay of top 10 models generated by I-TASSER illustrates the potential effect of 7 amino acid insertion
a b G75 2 2 G60 Sw-2 Sw-1 Supplementary Figure 1. Structure predictions by I-TASSER Server. a. Overlay of top 10 models generated by I-TASSER illustrates the potential effect of 7 amino acid insertion
Part-4. Cell cycle regulatory protein 5 (Cdk5) A novel target of ERK in Carb induced cell death
 Part-4 Cell cycle regulatory protein 5 (Cdk5) A novel target of ERK in Carb induced cell death 95 1. Introduction The process of replicating DNA and dividing cells can be described as a series of coordinated
Part-4 Cell cycle regulatory protein 5 (Cdk5) A novel target of ERK in Carb induced cell death 95 1. Introduction The process of replicating DNA and dividing cells can be described as a series of coordinated
Understanding Signaling Pathways by Modifying Sensitivity to PLX4720 in B-RAF V600E Melanoma
 Understanding Signaling Pathways by Modifying Sensitivity to PLX4720 in B-RAF V600E Melanoma Muska Hassan NCI-ICBP Summer Fellow Broad Institute of MIT and Harvard: Cancer Program Mentor: Cory Johannessen,
Understanding Signaling Pathways by Modifying Sensitivity to PLX4720 in B-RAF V600E Melanoma Muska Hassan NCI-ICBP Summer Fellow Broad Institute of MIT and Harvard: Cancer Program Mentor: Cory Johannessen,
Supplementary Figure 1. BMS enhances human T cell activation in vitro in a
 Supplementary Figure 1. BMS98662 enhances human T cell activation in vitro in a concentration-dependent manner. Jurkat T cells were activated with anti-cd3 and anti-cd28 antibody in the presence of titrated
Supplementary Figure 1. BMS98662 enhances human T cell activation in vitro in a concentration-dependent manner. Jurkat T cells were activated with anti-cd3 and anti-cd28 antibody in the presence of titrated
Electrical Stimulation Control Nerve Regeneration via the p38 Mitogen-activated Protein Kinase and CREB
 Electrical Stimulation Control Nerve Regeneration via the p38 Mitogen-activated Protein Kinase and CREB Kenji Kawamura, Yoshio Kano. Kibi International University, Takahashi-city, Japan. Disclosures: K.
Electrical Stimulation Control Nerve Regeneration via the p38 Mitogen-activated Protein Kinase and CREB Kenji Kawamura, Yoshio Kano. Kibi International University, Takahashi-city, Japan. Disclosures: K.
Supplementary data Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 2
 Supplementary data Supplementary Figure 1 SPHK1 sirna increases RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis in RAW264.7 cell culture. (A) RAW264.7 cells were transfected with oligocassettes containing SPHK1 sirna
Supplementary data Supplementary Figure 1 SPHK1 sirna increases RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis in RAW264.7 cell culture. (A) RAW264.7 cells were transfected with oligocassettes containing SPHK1 sirna
Growth and Differentiation Phosphorylation Sampler Kit
 Growth and Differentiation Phosphorylation Sampler Kit E 0 5 1 0 1 4 Kits Includes Cat. Quantity Application Reactivity Source Akt (Phospho-Ser473) E011054-1 50μg/50μl IHC, WB Human, Mouse, Rat Rabbit
Growth and Differentiation Phosphorylation Sampler Kit E 0 5 1 0 1 4 Kits Includes Cat. Quantity Application Reactivity Source Akt (Phospho-Ser473) E011054-1 50μg/50μl IHC, WB Human, Mouse, Rat Rabbit
HCC1937 is the HCC1937-pcDNA3 cell line, which was derived from a breast cancer with a mutation
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Materials and Methods Human cell lines and culture conditions HCC1937 is the HCC1937-pcDNA3 cell line, which was derived from a breast cancer with a mutation in exon 20 of BRCA1
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Materials and Methods Human cell lines and culture conditions HCC1937 is the HCC1937-pcDNA3 cell line, which was derived from a breast cancer with a mutation in exon 20 of BRCA1
Normal RAS-RAF (MAPK) pathway signaling
 BRAF-Mutations in Melanomas L. Mazzucchelli Istituto Cantonale di Patologia, Locarno 77. Annual Meeting Swiss Society of Pathology, Lucerne 2011 Sponsored by Roche Pharma Switzerland Melanoma has increased
BRAF-Mutations in Melanomas L. Mazzucchelli Istituto Cantonale di Patologia, Locarno 77. Annual Meeting Swiss Society of Pathology, Lucerne 2011 Sponsored by Roche Pharma Switzerland Melanoma has increased
RayBio KinaseSTAR TM Akt Activity Assay Kit
 Activity Assay Kit User Manual Version 1.0 March 13, 2015 RayBio KinaseSTAR TM Akt Activity Kit Protocol (Cat#: 68AT-Akt-S40) RayBiotech, Inc. We Provide You With Excellent Support And Service Tel:(Toll
Activity Assay Kit User Manual Version 1.0 March 13, 2015 RayBio KinaseSTAR TM Akt Activity Kit Protocol (Cat#: 68AT-Akt-S40) RayBiotech, Inc. We Provide You With Excellent Support And Service Tel:(Toll
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 EGFR inhibition activates signaling pathways (a-b) EGFR inhibition activates signaling pathways (a) U251EGFR cells were treated with erlotinib (1µM) for the indicated times followed
Supplementary Figure 1 EGFR inhibition activates signaling pathways (a-b) EGFR inhibition activates signaling pathways (a) U251EGFR cells were treated with erlotinib (1µM) for the indicated times followed
supplementary information
 Figure S1 Nucleotide binding status of RagA mutants. Wild type and mutant forms of MycRagA was transfected into HEK293 cells and the transfected cells were labeled with 32 Pphosphate. MycRagA was immunoprecipitated
Figure S1 Nucleotide binding status of RagA mutants. Wild type and mutant forms of MycRagA was transfected into HEK293 cells and the transfected cells were labeled with 32 Pphosphate. MycRagA was immunoprecipitated
Supplementary Information Supplementary Fig. 1. Elevated Usp9x in melanoma and NRAS mutant melanoma cells are dependent on NRAS for 3D growth.
 Supplementary Information Supplementary Fig. 1. Elevated Usp9x in melanoma and NRAS mutant melanoma cells are dependent on NRAS for 3D growth. a. Immunoblot for Usp9x protein in NRAS mutant melanoma cells
Supplementary Information Supplementary Fig. 1. Elevated Usp9x in melanoma and NRAS mutant melanoma cells are dependent on NRAS for 3D growth. a. Immunoblot for Usp9x protein in NRAS mutant melanoma cells
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure S1. Binding of full-length OGT and deletion mutants to PIP strips (Echelon Biosciences). Supplementary Figure S2. Binding of the OGT (919-1036) fragments with
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure S1. Binding of full-length OGT and deletion mutants to PIP strips (Echelon Biosciences). Supplementary Figure S2. Binding of the OGT (919-1036) fragments with
Validation & Assay Performance Summary
 Validation & Assay Performance Summary LanthaScreen IGF-1R GripTite Cells Cat. no. K1834 Modification Detected: Phosphorylation of Multiple Tyr Residues on IGF-1R LanthaScreen Cellular Assay Validation
Validation & Assay Performance Summary LanthaScreen IGF-1R GripTite Cells Cat. no. K1834 Modification Detected: Phosphorylation of Multiple Tyr Residues on IGF-1R LanthaScreen Cellular Assay Validation
Enzyme-coupled Receptors. Cell-surface receptors 1. Ion-channel-coupled receptors 2. G-protein-coupled receptors 3. Enzyme-coupled receptors
 Enzyme-coupled Receptors Cell-surface receptors 1. Ion-channel-coupled receptors 2. G-protein-coupled receptors 3. Enzyme-coupled receptors Cell-surface receptors allow a flow of ions across the plasma
Enzyme-coupled Receptors Cell-surface receptors 1. Ion-channel-coupled receptors 2. G-protein-coupled receptors 3. Enzyme-coupled receptors Cell-surface receptors allow a flow of ions across the plasma
Human Urokinase / PLAU / UPA ELISA Pair Set
 Human Urokinase / PLAU / UPA ELISA Pair Set Catalog Number : SEK10815 To achieve the best assay results, this manual must be read carefully before using this product and the assay is run as summarized
Human Urokinase / PLAU / UPA ELISA Pair Set Catalog Number : SEK10815 To achieve the best assay results, this manual must be read carefully before using this product and the assay is run as summarized
Supplementary Materials
 Supplementary Materials Figure S1. MTT Cell viability assay. To measure the cytotoxic potential of the oxidative treatment, the MTT [3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol- 2-yl)-2,5-diphenyl tetrazolium bromide] assay
Supplementary Materials Figure S1. MTT Cell viability assay. To measure the cytotoxic potential of the oxidative treatment, the MTT [3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol- 2-yl)-2,5-diphenyl tetrazolium bromide] assay
Supplementary Figure 1: Digitoxin induces apoptosis in primary human melanoma cells but not in normal melanocytes, which express lower levels of the
 Supplementary Figure 1: Digitoxin induces apoptosis in primary human melanoma cells but not in normal melanocytes, which express lower levels of the cardiac glycoside target, ATP1A1. (a) The percentage
Supplementary Figure 1: Digitoxin induces apoptosis in primary human melanoma cells but not in normal melanocytes, which express lower levels of the cardiac glycoside target, ATP1A1. (a) The percentage
Update on Targeted Therapy in Melanoma
 Update on Targeted Therapy in Melanoma Seville June 2013 James Larkin FRCP PhD London UK Overview What are the targets in melanoma? BRAF / KIT / NRAS / GNAQ / MEK DNA / microtubules CTLA4 / PD1 / PDL1
Update on Targeted Therapy in Melanoma Seville June 2013 James Larkin FRCP PhD London UK Overview What are the targets in melanoma? BRAF / KIT / NRAS / GNAQ / MEK DNA / microtubules CTLA4 / PD1 / PDL1
Supplementary Figure 1: si-craf but not si-braf sensitizes tumor cells to radiation.
 Supplementary Figure 1: si-craf but not si-braf sensitizes tumor cells to radiation. (a) Embryonic fibroblasts isolated from wildtype (WT), BRAF -/-, or CRAF -/- mice were irradiated (6 Gy) and DNA damage
Supplementary Figure 1: si-craf but not si-braf sensitizes tumor cells to radiation. (a) Embryonic fibroblasts isolated from wildtype (WT), BRAF -/-, or CRAF -/- mice were irradiated (6 Gy) and DNA damage
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES AND TABLES
 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES AND TABLES Supplementary Figure S1: CaSR expression in neuroblastoma models. A. Proteins were isolated from three neuroblastoma cell lines and from the liver metastasis of a MYCN-non
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES AND TABLES Supplementary Figure S1: CaSR expression in neuroblastoma models. A. Proteins were isolated from three neuroblastoma cell lines and from the liver metastasis of a MYCN-non
TFEB-mediated increase in peripheral lysosomes regulates. Store Operated Calcium Entry
 TFEB-mediated increase in peripheral lysosomes regulates Store Operated Calcium Entry Luigi Sbano, Massimo Bonora, Saverio Marchi, Federica Baldassari, Diego L. Medina, Andrea Ballabio, Carlotta Giorgi
TFEB-mediated increase in peripheral lysosomes regulates Store Operated Calcium Entry Luigi Sbano, Massimo Bonora, Saverio Marchi, Federica Baldassari, Diego L. Medina, Andrea Ballabio, Carlotta Giorgi
Supplemental Data. TGF-β-mediated mir-181a expression promotes breast cancer metastasis by targeting Bim.
 Supplemental Data TGF-β-mediated mir-181a expression promotes breast cancer metastasis by targeting Bim. Molly A. Taylor 1, Khalid Sossey-Alaoui 2, Cheryl L. Thompson 3, David Danielpour 4, and William
Supplemental Data TGF-β-mediated mir-181a expression promotes breast cancer metastasis by targeting Bim. Molly A. Taylor 1, Khalid Sossey-Alaoui 2, Cheryl L. Thompson 3, David Danielpour 4, and William
Notch Signaling Pathway Notch CSL Reporter HEK293 Cell line Catalog #: 60652
 Notch Signaling Pathway Notch CSL Reporter HEK293 Cell line Catalog #: 60652 Background The Notch signaling pathway controls cell fate decisions in vertebrate and invertebrate tissues. Notch signaling
Notch Signaling Pathway Notch CSL Reporter HEK293 Cell line Catalog #: 60652 Background The Notch signaling pathway controls cell fate decisions in vertebrate and invertebrate tissues. Notch signaling
Figures S1-S5, Figure Legends, Table S1 List of primers used in the study
 Insulin receptor alternative splicing is regulated by insulin signaling and modulates beta cell survival Pushkar Malakar,4, Lital Chartarifsky,4, Ayat Hija, Gil Leibowitz 3, Benjamin Glaser 3, Yuval Dor,
Insulin receptor alternative splicing is regulated by insulin signaling and modulates beta cell survival Pushkar Malakar,4, Lital Chartarifsky,4, Ayat Hija, Gil Leibowitz 3, Benjamin Glaser 3, Yuval Dor,
Supplemental Information. Inhibition of the Proteasome b2 Site Sensitizes. Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Cells
 Cell Chemical Biology, Volume 24 Supplemental Information Inhibition of the Proteasome b2 Site Sensitizes Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Cells to b5 Inhibitors and Suppresses Nrf1 Activation Emily S. Weyburne,
Cell Chemical Biology, Volume 24 Supplemental Information Inhibition of the Proteasome b2 Site Sensitizes Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Cells to b5 Inhibitors and Suppresses Nrf1 Activation Emily S. Weyburne,
RAS Genes. The ras superfamily of genes encodes small GTP binding proteins that are responsible for the regulation of many cellular processes.
 ۱ RAS Genes The ras superfamily of genes encodes small GTP binding proteins that are responsible for the regulation of many cellular processes. Oncogenic ras genes in human cells include H ras, N ras,
۱ RAS Genes The ras superfamily of genes encodes small GTP binding proteins that are responsible for the regulation of many cellular processes. Oncogenic ras genes in human cells include H ras, N ras,
Anti-Lamin B1/LMNB1 Picoband Antibody
 Anti-Lamin B1/LMNB1 Picoband Antibody Catalog Number:PB9611 About LMNB1 Lamin-B1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the LMNB1 gene. The nuclear lamina consists of a two-dimensional matrix of proteins
Anti-Lamin B1/LMNB1 Picoband Antibody Catalog Number:PB9611 About LMNB1 Lamin-B1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the LMNB1 gene. The nuclear lamina consists of a two-dimensional matrix of proteins
Essential Medium, containing 10% fetal bovine serum, 100 U/ml penicillin and 100 µg/ml streptomycin. Huvec were cultured in
 Supplemental data Methods Cell culture media formulations A-431 and U-87 MG cells were maintained in Dulbecco s Modified Eagle s Medium. FaDu cells were cultured in Eagle's Minimum Essential Medium, containing
Supplemental data Methods Cell culture media formulations A-431 and U-87 MG cells were maintained in Dulbecco s Modified Eagle s Medium. FaDu cells were cultured in Eagle's Minimum Essential Medium, containing
Overexpression of Mcl-1 confers resistance to BRAFV600E inhibitors alone and in combination with MEK1/2 inhibitors in melanoma
 Overexpression of Mcl-1 confers resistance to BRAFV600E inhibitors alone and in combination with MEK1/2 inhibitors in melanoma The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share
Overexpression of Mcl-1 confers resistance to BRAFV600E inhibitors alone and in combination with MEK1/2 inhibitors in melanoma The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 1. Neither the activation nor suppression of the MAPK pathway affects the ASK1/Vif interaction. (a, b) HEK293 cells were cotransfected with plasmids encoding
Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 1. Neither the activation nor suppression of the MAPK pathway affects the ASK1/Vif interaction. (a, b) HEK293 cells were cotransfected with plasmids encoding
A549 and A549-fLuc cells were maintained in high glucose Dulbecco modified
 Cell culture and animal model A549 and A549-fLuc cells were maintained in high glucose Dulbecco modified Eagle medium supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum at 37 C in humidified atmosphere containing
Cell culture and animal model A549 and A549-fLuc cells were maintained in high glucose Dulbecco modified Eagle medium supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum at 37 C in humidified atmosphere containing
A novel bfgf antagonist peptide inhibits breast cancer cell growth
 210 A novel bfgf antagonist peptide inhibits breast cancer cell growth QUCHOU LI 1, SUSU GAO 1, YONGLIN YU 1, WENHUI WANG 1, XILEI CHEN 1, RUIXUE WANG 1, TAO LI 1, CONG WANG 1, XIAOKUN LI 1,2 and XIAOPING
210 A novel bfgf antagonist peptide inhibits breast cancer cell growth QUCHOU LI 1, SUSU GAO 1, YONGLIN YU 1, WENHUI WANG 1, XILEI CHEN 1, RUIXUE WANG 1, TAO LI 1, CONG WANG 1, XIAOKUN LI 1,2 and XIAOPING
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 6 HE-50 HE-116 E-1 HE-108 Supplementary Figure 1. Targeted drug response curves of endometrial cancer cells. Endometrial cancer cell lines were incubated with serial dilutions of
Supplementary Figure 1 6 HE-50 HE-116 E-1 HE-108 Supplementary Figure 1. Targeted drug response curves of endometrial cancer cells. Endometrial cancer cell lines were incubated with serial dilutions of
Protocol for Gene Transfection & Western Blotting
 The schedule and the manual of basic techniques for cell culture Advanced Protocol for Gene Transfection & Western Blotting Schedule Day 1 26/07/2008 Transfection Day 3 28/07/2008 Cell lysis Immunoprecipitation
The schedule and the manual of basic techniques for cell culture Advanced Protocol for Gene Transfection & Western Blotting Schedule Day 1 26/07/2008 Transfection Day 3 28/07/2008 Cell lysis Immunoprecipitation
Evaluation of the Small Molecular Weight G-Protein Ras in the Interaction of Growth Hormone and Epidermal Growth Factor Signaling
 Evaluation of the Small Molecular Weight G-Protein Ras in the Interaction of Growth Hormone and Epidermal Growth Factor Signaling Danielle Mollet TVI Community College & University of New Mexico Dr. Paul
Evaluation of the Small Molecular Weight G-Protein Ras in the Interaction of Growth Hormone and Epidermal Growth Factor Signaling Danielle Mollet TVI Community College & University of New Mexico Dr. Paul
p47 negatively regulates IKK activation by inducing the lysosomal degradation of polyubiquitinated NEMO
 Supplementary Information p47 negatively regulates IKK activation by inducing the lysosomal degradation of polyubiquitinated NEMO Yuri Shibata, Masaaki Oyama, Hiroko Kozuka-Hata, Xiao Han, Yuetsu Tanaka,
Supplementary Information p47 negatively regulates IKK activation by inducing the lysosomal degradation of polyubiquitinated NEMO Yuri Shibata, Masaaki Oyama, Hiroko Kozuka-Hata, Xiao Han, Yuetsu Tanaka,
Supplemental Materials. STK16 regulates actin dynamics to control Golgi organization and cell cycle
 Supplemental Materials STK16 regulates actin dynamics to control Golgi organization and cell cycle Juanjuan Liu 1,2,3, Xingxing Yang 1,3, Binhua Li 1, Junjun Wang 1,2, Wenchao Wang 1, Jing Liu 1, Qingsong
Supplemental Materials STK16 regulates actin dynamics to control Golgi organization and cell cycle Juanjuan Liu 1,2,3, Xingxing Yang 1,3, Binhua Li 1, Junjun Wang 1,2, Wenchao Wang 1, Jing Liu 1, Qingsong
Supplementary Figure 1. a. b. Relative cell viability. Nature Genetics: doi: /ng SCR shyap1-1 shyap
 Supplementary Figure 1. a. b. p-value for depletion in vehicle (DMSO) 1e-05 1e-03 1e-01 1 0 1000 2000 3000 4000 5000 Genes log2 normalized shrna counts in T0 0 2 4 6 8 sh1 shluc 0 2 4 6 8 log2 normalized
Supplementary Figure 1. a. b. p-value for depletion in vehicle (DMSO) 1e-05 1e-03 1e-01 1 0 1000 2000 3000 4000 5000 Genes log2 normalized shrna counts in T0 0 2 4 6 8 sh1 shluc 0 2 4 6 8 log2 normalized
Supplemental Figure 1. Western blot analysis indicated that MIF was detected in the fractions of
 Supplemental Figure Legends Supplemental Figure 1. Western blot analysis indicated that was detected in the fractions of plasma membrane and cytosol but not in nuclear fraction isolated from Pkd1 null
Supplemental Figure Legends Supplemental Figure 1. Western blot analysis indicated that was detected in the fractions of plasma membrane and cytosol but not in nuclear fraction isolated from Pkd1 null
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/7/322/ra38/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Dynamic Reprogramming of Signaling Upon Met Inhibition Reveals a Mechanism of Drug Resistance in Gastric Cancer Andrea
www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/7/322/ra38/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Dynamic Reprogramming of Signaling Upon Met Inhibition Reveals a Mechanism of Drug Resistance in Gastric Cancer Andrea
HOMEWORK RUBRICS MECHANOTRANSDUCTION UNIT: HOMEWORK #1 (20 pts towards your grade)
 HOMEWORK RUBRICS MECHANOTRANSDUCTION UNIT: HOMEWORK #1 (20 pts towards your grade) 1. Mesenchymal stem cells (MSC) cultured on extracellular matrices with different stiffness exhibit diverse lineage commitment
HOMEWORK RUBRICS MECHANOTRANSDUCTION UNIT: HOMEWORK #1 (20 pts towards your grade) 1. Mesenchymal stem cells (MSC) cultured on extracellular matrices with different stiffness exhibit diverse lineage commitment
CytoSelect Tumor Transendothelial Migration Assay
 Product Manual CytoSelect Tumor Transendothelial Migration Assay Catalog Number CBA-216 24 assays FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY Not for use in diagnostic procedures Introduction Cancer metastasis comprises several
Product Manual CytoSelect Tumor Transendothelial Migration Assay Catalog Number CBA-216 24 assays FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY Not for use in diagnostic procedures Introduction Cancer metastasis comprises several
MEK1 Assay Kit 1 Catalog # Lot # 16875
 MEK1 Assay Kit 1 Kit Components Assay Dilution Buffer (ADB), Catalog # 20-108. Three vials, each containing 1.0ml of assay dilution buffer (20mM MOPS, ph 7.2, 25mM ß-glycerol phosphate, 5mM EGTA, 1mM sodium
MEK1 Assay Kit 1 Kit Components Assay Dilution Buffer (ADB), Catalog # 20-108. Three vials, each containing 1.0ml of assay dilution buffer (20mM MOPS, ph 7.2, 25mM ß-glycerol phosphate, 5mM EGTA, 1mM sodium
Supplementary Figure 1. Basal level EGFR across a panel of ESCC lines. Immunoblots demonstrate the expression of phosphorylated and total EGFR as
 Supplementary Figure 1. Basal level EGFR across a panel of ESCC lines. Immunoblots demonstrate the expression of phosphorylated and total EGFR as well as their downstream effectors across a panel of ESCC
Supplementary Figure 1. Basal level EGFR across a panel of ESCC lines. Immunoblots demonstrate the expression of phosphorylated and total EGFR as well as their downstream effectors across a panel of ESCC
ISOGENIC CELL LINES. ATCC No. Designation Mutation Parental Cell Line Disease Cancer Model
 THE ESSENTILS OF LIFE SCIENCE RESERCH GLOLLY DELIVERED ISOGENIC CELL LINES TCC CRISPR/CS9 GENE-EDITED ISOGENIC CELL LINES Clinically relevant cell models are critical for studies of molecular and cellular
THE ESSENTILS OF LIFE SCIENCE RESERCH GLOLLY DELIVERED ISOGENIC CELL LINES TCC CRISPR/CS9 GENE-EDITED ISOGENIC CELL LINES Clinically relevant cell models are critical for studies of molecular and cellular
(A) Dose response curves of HMLE_shGFP (blue circle), HMLE_shEcad (red square),
 Supplementary Figures and Tables Figure S1. Validation of EMT-selective small molecules (A) Dose response curves of HMLE_shGFP (blue circle), HMLE_shEcad (red square), and HMLE_Twist (black diamond) cells
Supplementary Figures and Tables Figure S1. Validation of EMT-selective small molecules (A) Dose response curves of HMLE_shGFP (blue circle), HMLE_shEcad (red square), and HMLE_Twist (black diamond) cells
2,6,9-Triazabicyclo[3.3.1]nonanes as overlooked. amino-modification products by acrolein
![2,6,9-Triazabicyclo[3.3.1]nonanes as overlooked. amino-modification products by acrolein 2,6,9-Triazabicyclo[3.3.1]nonanes as overlooked. amino-modification products by acrolein](/thumbs/86/94743397.jpg) Supplementary Information 2,6,9-Triazabicyclo[3.3.1]nonanes as overlooked amino-modification products by acrolein Ayumi Tsutsui and Katsunori Tanaka* Biofunctional Synthetic Chemistry Laboratory, RIKEN
Supplementary Information 2,6,9-Triazabicyclo[3.3.1]nonanes as overlooked amino-modification products by acrolein Ayumi Tsutsui and Katsunori Tanaka* Biofunctional Synthetic Chemistry Laboratory, RIKEN
KEY CONCEPT QUESTIONS IN SIGNAL TRANSDUCTION
 Signal Transduction - Part 2 Key Concepts - Receptor tyrosine kinases control cell metabolism and proliferation Growth factor signaling through Ras Mutated cell signaling genes in cancer cells are called
Signal Transduction - Part 2 Key Concepts - Receptor tyrosine kinases control cell metabolism and proliferation Growth factor signaling through Ras Mutated cell signaling genes in cancer cells are called
Phospho-AKT Sampler Kit
 Phospho-AKT Sampler Kit E 0 5 1 0 0 3 Kits Includes Cat. Quantity Application Reactivity Source Akt (Ab-473) Antibody E021054-1 50μg/50μl IHC, WB Human, Mouse, Rat Rabbit Akt (Phospho-Ser473) Antibody
Phospho-AKT Sampler Kit E 0 5 1 0 0 3 Kits Includes Cat. Quantity Application Reactivity Source Akt (Ab-473) Antibody E021054-1 50μg/50μl IHC, WB Human, Mouse, Rat Rabbit Akt (Phospho-Ser473) Antibody
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION. Supplementary Figures S1-S9. Supplementary Methods
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION SUMO1 modification of PTEN regulates tumorigenesis by controlling its association with the plasma membrane Jian Huang 1,2#, Jie Yan 1,2#, Jian Zhang 3#, Shiguo Zhu 1, Yanli Wang
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION SUMO1 modification of PTEN regulates tumorigenesis by controlling its association with the plasma membrane Jian Huang 1,2#, Jie Yan 1,2#, Jian Zhang 3#, Shiguo Zhu 1, Yanli Wang
Signaling. Dr. Sujata Persad Katz Group Centre for Pharmacy & Health research
 Signaling Dr. Sujata Persad 3-020 Katz Group Centre for Pharmacy & Health research E-mail:sujata.persad@ualberta.ca 1 Growth Factor Receptors and Other Signaling Pathways What we will cover today: How
Signaling Dr. Sujata Persad 3-020 Katz Group Centre for Pharmacy & Health research E-mail:sujata.persad@ualberta.ca 1 Growth Factor Receptors and Other Signaling Pathways What we will cover today: How
Data Sheet. PCSK9[Biotinylated]-LDLR Binding Assay Kit Catalog # 72002
![Data Sheet. PCSK9[Biotinylated]-LDLR Binding Assay Kit Catalog # 72002 Data Sheet. PCSK9[Biotinylated]-LDLR Binding Assay Kit Catalog # 72002](/thumbs/79/80181612.jpg) Data Sheet PCSK9[Biotinylated]-LDLR Binding Assay Kit Catalog # 72002 DESCRIPTION: The PCSK9[Biotinylated]-LDLR Binding Assay Kit is designed for screening and profiling purposes. PCSK9 is known to function
Data Sheet PCSK9[Biotinylated]-LDLR Binding Assay Kit Catalog # 72002 DESCRIPTION: The PCSK9[Biotinylated]-LDLR Binding Assay Kit is designed for screening and profiling purposes. PCSK9 is known to function
TSH Receptor Monoclonal Antibody (49) Catalog Number MA3-218 Product data sheet
 Website: thermofisher.com Customer Service (US): 1 800 955 6288 ext. 1 Technical Support (US): 1 800 955 6288 ext. 441 TSH Receptor Monoclonal Antibody (49) Catalog Number MA3-218 Product data sheet Details
Website: thermofisher.com Customer Service (US): 1 800 955 6288 ext. 1 Technical Support (US): 1 800 955 6288 ext. 441 TSH Receptor Monoclonal Antibody (49) Catalog Number MA3-218 Product data sheet Details
Berberine Sensitizes Human Ovarian Cancer Cells to Cisplatin Through mir-93/ PTEN/Akt Signaling Pathway
 Chen Accepted: et al.: February Berberine 24, Sensitizes 2015 Ovarian Cancer Cells to Cisplatin www.karger.com/cpb 956 1421-9778/15/0363-0956$39.50/0 Original Paper This is an Open Access article licensed
Chen Accepted: et al.: February Berberine 24, Sensitizes 2015 Ovarian Cancer Cells to Cisplatin www.karger.com/cpb 956 1421-9778/15/0363-0956$39.50/0 Original Paper This is an Open Access article licensed
Supplementary Table; Supplementary Figures and legends S1-S21; Supplementary Materials and Methods
 Silva et al. PTEN posttranslational inactivation and hyperactivation of the PI3K/Akt pathway sustain primary T cell leukemia viability Supplementary Table; Supplementary Figures and legends S1-S21; Supplementary
Silva et al. PTEN posttranslational inactivation and hyperactivation of the PI3K/Akt pathway sustain primary T cell leukemia viability Supplementary Table; Supplementary Figures and legends S1-S21; Supplementary
HEK293FT cells were transiently transfected with reporters, N3-ICD construct and
 Supplementary Information Luciferase reporter assay HEK293FT cells were transiently transfected with reporters, N3-ICD construct and increased amounts of wild type or kinase inactive EGFR. Transfections
Supplementary Information Luciferase reporter assay HEK293FT cells were transiently transfected with reporters, N3-ICD construct and increased amounts of wild type or kinase inactive EGFR. Transfections
Introduction: 年 Fas signal-mediated apoptosis. PI3K/Akt
 Fas-ligand (CD95-L; Fas-L) Fas (CD95) Fas (apoptosis) 年 了 不 度 Fas Fas-L 力 不 Fas/Fas-L T IL-10Fas/Fas-L 不 年 Fas signal-mediated apoptosis 度降 不 不 力 U-118, HeLa, A549, Huh-7 MCF-7, HepG2. PI3K/Akt FasPI3K/Akt
Fas-ligand (CD95-L; Fas-L) Fas (CD95) Fas (apoptosis) 年 了 不 度 Fas Fas-L 力 不 Fas/Fas-L T IL-10Fas/Fas-L 不 年 Fas signal-mediated apoptosis 度降 不 不 力 U-118, HeLa, A549, Huh-7 MCF-7, HepG2. PI3K/Akt FasPI3K/Akt
4.2 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
 phosphorylated proteins on treatment with Erlotinib.This chapter describes the finding of the SILAC experiment. 4.2 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION This is the first global report of its kind using dual strategies
phosphorylated proteins on treatment with Erlotinib.This chapter describes the finding of the SILAC experiment. 4.2 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION This is the first global report of its kind using dual strategies
Determination Differentiation. determinated precursor specialized cell
 Biology of Cancer -Developmental Biology: Determination and Differentiation -Cell Cycle Regulation -Tumor genes: Proto-Oncogenes, Tumor supressor genes -Tumor-Progression -Example for Tumor-Progression:
Biology of Cancer -Developmental Biology: Determination and Differentiation -Cell Cycle Regulation -Tumor genes: Proto-Oncogenes, Tumor supressor genes -Tumor-Progression -Example for Tumor-Progression:
Signal Transduction Pathways. Part 2
 Signal Transduction Pathways Part 2 GPCRs G-protein coupled receptors > 700 GPCRs in humans Mediate responses to senses taste, smell, sight ~ 1000 GPCRs mediate sense of smell in mouse Half of all known
Signal Transduction Pathways Part 2 GPCRs G-protein coupled receptors > 700 GPCRs in humans Mediate responses to senses taste, smell, sight ~ 1000 GPCRs mediate sense of smell in mouse Half of all known
Antitumor activity of the ERK inhibitor SCH against BRAF mutant, NRAS mutant and wild-type melanoma
 Wong et al. Molecular Cancer 2014, 13:194 RESEARCH Open Access Antitumor activity of the ERK inhibitor SCH722984 against BRAF mutant, NRAS mutant and wild-type melanoma Deborah JL Wong 1, Lidia Robert
Wong et al. Molecular Cancer 2014, 13:194 RESEARCH Open Access Antitumor activity of the ERK inhibitor SCH722984 against BRAF mutant, NRAS mutant and wild-type melanoma Deborah JL Wong 1, Lidia Robert
Protocol. G-LISA Rac1 Activation Assay Biochem Kit : 24 Assays (Absorbance Based) Cat. # BK128-S. cytoskeleton.com. Cytoskeleton, Inc.
 The Protein Experts Protocol Cytoskeleton, Inc. V 8.1 G-LISA Rac1 Activation Assay Biochem Kit : 24 Assays (Absorbance Based) Cat. # BK128-S cytoskeleton.com Phone: (303) 322.2254 Fax: (303) 322.2257 Customer
The Protein Experts Protocol Cytoskeleton, Inc. V 8.1 G-LISA Rac1 Activation Assay Biochem Kit : 24 Assays (Absorbance Based) Cat. # BK128-S cytoskeleton.com Phone: (303) 322.2254 Fax: (303) 322.2257 Customer
Proteomic profiling of small-molecule inhibitors reveals dispensability of MTH1 for cancer cell survival
 Supplementary Information for Proteomic profiling of small-molecule inhibitors reveals dispensability of MTH1 for cancer cell survival Tatsuro Kawamura 1, Makoto Kawatani 1, Makoto Muroi, Yasumitsu Kondoh,
Supplementary Information for Proteomic profiling of small-molecule inhibitors reveals dispensability of MTH1 for cancer cell survival Tatsuro Kawamura 1, Makoto Kawatani 1, Makoto Muroi, Yasumitsu Kondoh,
Focus Application. Compound-Induced Cytotoxicity
 xcelligence System Real-Time Cell Analyzer Focus Application Compound-Induced Cytotoxicity Featured Study: Using the Time Resolving Function of the xcelligence System to Optimize Endpoint Viability and
xcelligence System Real-Time Cell Analyzer Focus Application Compound-Induced Cytotoxicity Featured Study: Using the Time Resolving Function of the xcelligence System to Optimize Endpoint Viability and
IMMP8-1. Different Mechanisms of Androg and IPAD on Apoptosis Induction in Cervical Cancer Cells
 IMMP8-1 Different Mechanisms of Androg and IPAD on Apoptosis Induction in Cervical Cancer Cells Assanan Dokmaikaew* Tipaya Ekalaksananan** Dr.Chamsai Pientong** ABSTRACT Androg and IPAD are recently known
IMMP8-1 Different Mechanisms of Androg and IPAD on Apoptosis Induction in Cervical Cancer Cells Assanan Dokmaikaew* Tipaya Ekalaksananan** Dr.Chamsai Pientong** ABSTRACT Androg and IPAD are recently known
Pre-clinical PK/PD modelling of combination therapies in oncology: abemaciclib and vemurafenib
 Pre-clinical PK/PD modelling of combination therapies in oncology: abemaciclib and vemurafenib Combination Therapies in Oncology Combination therapies in oncology have been explored and used for many decades
Pre-clinical PK/PD modelling of combination therapies in oncology: abemaciclib and vemurafenib Combination Therapies in Oncology Combination therapies in oncology have been explored and used for many decades
The Schedule and the Manual of Basic Techniques for Cell Culture
 The Schedule and the Manual of Basic Techniques for Cell Culture 1 Materials Calcium Phosphate Transfection Kit: Invitrogen Cat.No.K2780-01 Falcon tube (Cat No.35-2054:12 x 75 mm, 5 ml tube) Cell: 293
The Schedule and the Manual of Basic Techniques for Cell Culture 1 Materials Calcium Phosphate Transfection Kit: Invitrogen Cat.No.K2780-01 Falcon tube (Cat No.35-2054:12 x 75 mm, 5 ml tube) Cell: 293
Figure S1. ERBB3 mrna levels are elevated in Luminal A breast cancers harboring ERBB3
 Supplemental Figure Legends. Figure S1. ERBB3 mrna levels are elevated in Luminal A breast cancers harboring ERBB3 ErbB3 gene copy number gain. Supplemental Figure S1. ERBB3 mrna levels are elevated in
Supplemental Figure Legends. Figure S1. ERBB3 mrna levels are elevated in Luminal A breast cancers harboring ERBB3 ErbB3 gene copy number gain. Supplemental Figure S1. ERBB3 mrna levels are elevated in
Utilizing AlphaLISA Technology to Screen for Inhibitors of the CTLA-4 Immune Checkpoint
 APPLICATION NOTE AlphaLISA Technology Authors: Matthew Marunde Stephen Hurt PerkinElmer, Inc. Hopkinton, MA Utilizing AlphaLISA Technology to Screen for Inhibitors of the CTLA-4 Immune Checkpoint Introduction
APPLICATION NOTE AlphaLISA Technology Authors: Matthew Marunde Stephen Hurt PerkinElmer, Inc. Hopkinton, MA Utilizing AlphaLISA Technology to Screen for Inhibitors of the CTLA-4 Immune Checkpoint Introduction
Figure S1. PMVs from THP-1 cells expose phosphatidylserine and carry actin. A) Flow
 SUPPLEMENTARY DATA Supplementary Figure Legends Figure S1. PMVs from THP-1 cells expose phosphatidylserine and carry actin. A) Flow cytometry analysis of PMVs labelled with annexin-v-pe (Guava technologies)
SUPPLEMENTARY DATA Supplementary Figure Legends Figure S1. PMVs from THP-1 cells expose phosphatidylserine and carry actin. A) Flow cytometry analysis of PMVs labelled with annexin-v-pe (Guava technologies)
hexahistidine tagged GRP78 devoid of the KDEL motif (GRP78-His) on SDS-PAGE. This
 SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE LEGEND Fig. S1. Generation and characterization of. (A) Coomassie staining of soluble hexahistidine tagged GRP78 devoid of the KDEL motif (GRP78-His) on SDS-PAGE. This protein was expressed
SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE LEGEND Fig. S1. Generation and characterization of. (A) Coomassie staining of soluble hexahistidine tagged GRP78 devoid of the KDEL motif (GRP78-His) on SDS-PAGE. This protein was expressed
Islet viability assay and Glucose Stimulated Insulin Secretion assay RT-PCR and Western Blot
 Islet viability assay and Glucose Stimulated Insulin Secretion assay Islet cell viability was determined by colorimetric (3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5- diphenyltetrazolium bromide assay using CellTiter
Islet viability assay and Glucose Stimulated Insulin Secretion assay Islet cell viability was determined by colorimetric (3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5- diphenyltetrazolium bromide assay using CellTiter
A View to the Future: The Development of Targeted Therapy for Melanoma. Michael Davies, M.D., Ph.D.
 A View to the Future: Science to Survivorship Symposium September 26, 2009 The Development of Targeted Therapy for Melanoma Michael Davies, M.D., Ph.D. Assistant Professor, Melanoma Medical Oncology How
A View to the Future: Science to Survivorship Symposium September 26, 2009 The Development of Targeted Therapy for Melanoma Michael Davies, M.D., Ph.D. Assistant Professor, Melanoma Medical Oncology How
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 14 12 SEM4C PLXN2 8 SEM4C C 3 Cancer Cell Non Cancer Cell Expression 1 8 6 6 4 log2 ratio Expression 2 1 4 2 2 p value.1 D Supplementary Figure 1. Expression of Sema4C and Plexin2
Supplementary Figure 1 14 12 SEM4C PLXN2 8 SEM4C C 3 Cancer Cell Non Cancer Cell Expression 1 8 6 6 4 log2 ratio Expression 2 1 4 2 2 p value.1 D Supplementary Figure 1. Expression of Sema4C and Plexin2
BRaf V600E cooperates with Pten silencing to elicit metastatic melanoma (Nature Genetics Supplementary Information)
 BRaf V600E cooperates with Pten silencing to elicit metastatic melanoma (Nature Genetics Supplementary Information) David Dankort, David P. Curley, Robert A. Cartlidge, Betsy Nelson, Anthony N. Karnezis,
BRaf V600E cooperates with Pten silencing to elicit metastatic melanoma (Nature Genetics Supplementary Information) David Dankort, David P. Curley, Robert A. Cartlidge, Betsy Nelson, Anthony N. Karnezis,
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Identification of Novel ROS Inducers: Quinone Derivatives Tethered to Long Hydrocarbon Chains Yeonsun Hong,, Sandip Sengupta,, Wooyoung Hur, *, Taebo Sim,, * KU-KIST Graduate School
Supporting Information Identification of Novel ROS Inducers: Quinone Derivatives Tethered to Long Hydrocarbon Chains Yeonsun Hong,, Sandip Sengupta,, Wooyoung Hur, *, Taebo Sim,, * KU-KIST Graduate School
supplementary information
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb2133 Figure S1 Actomyosin organisation in human squamous cell carcinoma. (a) Three examples of actomyosin organisation around the edges of squamous cell carcinoma biopsies are shown. Myosin
DOI: 10.1038/ncb2133 Figure S1 Actomyosin organisation in human squamous cell carcinoma. (a) Three examples of actomyosin organisation around the edges of squamous cell carcinoma biopsies are shown. Myosin
New paradigms for treating metastatic melanoma
 New paradigms for treating metastatic melanoma Paul B. Chapman, MD Melanoma Clinical Director Melanoma and Immunotherapeutics Service Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, New York 20 th Century Overall
New paradigms for treating metastatic melanoma Paul B. Chapman, MD Melanoma Clinical Director Melanoma and Immunotherapeutics Service Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, New York 20 th Century Overall
Validation & Assay Performance Summary
 Validation & Assay Performance Summary CellSensor DBE-bla MDA-MB-468 Cell Line Cat. no. K1814 Pathway Description The phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase (PI3K) signaling cascade is essential for cell growth
Validation & Assay Performance Summary CellSensor DBE-bla MDA-MB-468 Cell Line Cat. no. K1814 Pathway Description The phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase (PI3K) signaling cascade is essential for cell growth
Protocol for A-549 VIM RFP (ATCC CCL-185EMT) TGFβ1 EMT Induction and Drug Screening
 Protocol for A-549 VIM RFP (ATCC CCL-185EMT) TGFβ1 EMT Induction and Drug Screening Introduction: Vimentin (VIM) intermediate filament (IF) proteins are associated with EMT in lung cancer and its metastatic
Protocol for A-549 VIM RFP (ATCC CCL-185EMT) TGFβ1 EMT Induction and Drug Screening Introduction: Vimentin (VIM) intermediate filament (IF) proteins are associated with EMT in lung cancer and its metastatic
Serum Amyloid A3 Gene Expression in Adipocytes is an Indicator. of the Interaction with Macrophages
 Serum Amyloid A3 Gene Expression in Adipocytes is an Indicator of the Interaction with Macrophages Yohei Sanada, Takafumi Yamamoto, Rika Satake, Akiko Yamashita, Sumire Kanai, Norihisa Kato, Fons AJ van
Serum Amyloid A3 Gene Expression in Adipocytes is an Indicator of the Interaction with Macrophages Yohei Sanada, Takafumi Yamamoto, Rika Satake, Akiko Yamashita, Sumire Kanai, Norihisa Kato, Fons AJ van
HIV-1 p24 ELISA Pair Set Cat#: orb54951 (ELISA Manual)
 HIV-1 p24 ELISA Pair Set Cat#: orb54951 (ELISA Manual) BACKGROUND Human Immunodeficiency Virus ( HIV ) can be divided into two major types, HIV type 1 (HIV-1) and HIV type 2 (HIV-2). HIV-1 is related to
HIV-1 p24 ELISA Pair Set Cat#: orb54951 (ELISA Manual) BACKGROUND Human Immunodeficiency Virus ( HIV ) can be divided into two major types, HIV type 1 (HIV-1) and HIV type 2 (HIV-2). HIV-1 is related to
General Laboratory methods Plasma analysis: Gene Expression Analysis: Immunoblot analysis: Immunohistochemistry:
 General Laboratory methods Plasma analysis: Plasma insulin (Mercodia, Sweden), leptin (duoset, R&D Systems Europe, Abingdon, United Kingdom), IL-6, TNFα and adiponectin levels (Quantikine kits, R&D Systems
General Laboratory methods Plasma analysis: Plasma insulin (Mercodia, Sweden), leptin (duoset, R&D Systems Europe, Abingdon, United Kingdom), IL-6, TNFα and adiponectin levels (Quantikine kits, R&D Systems
CHAPTER 3: EGFR ACTIVATION IMPACTS ON FAK PROTEIN EXPRESSION AND PHOSPHORYLATION STATUS IN HOSCC CELL LINES
 CHAPTER 3: EGFR ACTIVATION IMPACTS ON FAK PROTEIN EXPRESSION AND PHOSPHORYLATION STATUS IN HOSCC CELL LINES 3.1 Introduction Developmental processes such as cell migration depend on signals from both the
CHAPTER 3: EGFR ACTIVATION IMPACTS ON FAK PROTEIN EXPRESSION AND PHOSPHORYLATION STATUS IN HOSCC CELL LINES 3.1 Introduction Developmental processes such as cell migration depend on signals from both the
FOXO Reporter Kit PI3K/AKT Pathway Cat. #60643
 Data Sheet FOXO Reporter Kit PI3K/AKT Pathway Cat. #60643 Background The PI3K/AKT signaling pathway is essential for cell growth and survival. Disruption of this pathway or its regulation has been linked
Data Sheet FOXO Reporter Kit PI3K/AKT Pathway Cat. #60643 Background The PI3K/AKT signaling pathway is essential for cell growth and survival. Disruption of this pathway or its regulation has been linked
Predictive PP1Ca binding region in BIG3 : 1,228 1,232aa (-KAVSF-) HEK293T cells *** *** *** KPL-3C cells - E E2 treatment time (h)
 Relative expression ERE-luciferase activity activity (pmole/min) activity (pmole/min) activity (pmole/min) activity (pmole/min) MCF-7 KPL-3C ZR--1 BT-474 T47D HCC15 KPL-1 HBC4 activity (pmole/min) a d
Relative expression ERE-luciferase activity activity (pmole/min) activity (pmole/min) activity (pmole/min) activity (pmole/min) MCF-7 KPL-3C ZR--1 BT-474 T47D HCC15 KPL-1 HBC4 activity (pmole/min) a d
Problem Set 8 Key 1 of 8
 7.06 2003 Problem Set 8 Key 1 of 8 7.06 2003 Problem Set 8 Key 1. As a bright MD/PhD, you are interested in questions about the control of cell number in the body. Recently, you've seen three patients
7.06 2003 Problem Set 8 Key 1 of 8 7.06 2003 Problem Set 8 Key 1. As a bright MD/PhD, you are interested in questions about the control of cell number in the body. Recently, you've seen three patients
Karyotype analysis reveals transloction of chromosome 22 to 9 in CML chronic myelogenous leukemia has fusion protein Bcr-Abl
 Chapt. 18 Cancer Molecular Biology of Cancer Student Learning Outcomes: Describe cancer diseases in which cells no longer respond Describe how cancers come from genomic mutations (inherited or somatic)
Chapt. 18 Cancer Molecular Biology of Cancer Student Learning Outcomes: Describe cancer diseases in which cells no longer respond Describe how cancers come from genomic mutations (inherited or somatic)
Scavenger receptor class B type I regulates cellular cholesterol metabolism and cell signaling associated with breast cancer development.
 Thomas Jefferson University Jefferson Digital Commons Department of Stem Cell Biology and Regenerative Medicine Papers & Presentations Department of Stem Cell Biology and Regenerative Medicine 9-24-2013
Thomas Jefferson University Jefferson Digital Commons Department of Stem Cell Biology and Regenerative Medicine Papers & Presentations Department of Stem Cell Biology and Regenerative Medicine 9-24-2013
Rationale and results from. BRAFi and immunotherapy
 Rationale and results from emerging combinations of BRAFi and immunotherapy Antoni Ribas, M.D. rofessor of Medicine rofessor of Surgery rofessor of Molecular and Medical harmacology Director, Tumor Immunology
Rationale and results from emerging combinations of BRAFi and immunotherapy Antoni Ribas, M.D. rofessor of Medicine rofessor of Surgery rofessor of Molecular and Medical harmacology Director, Tumor Immunology
Total Histone H3 Acetylation Detection Fast Kit (Colorimetric)
 Total Histone H3 Acetylation Detection Fast Kit (Colorimetric) Catalog Number KA1538 48 assays Version: 02 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Intended Use...
Total Histone H3 Acetylation Detection Fast Kit (Colorimetric) Catalog Number KA1538 48 assays Version: 02 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Intended Use...
7/6/2015. Cancer Related Deaths: United States. Management of NSCLC TODAY. Emerging mutations as predictive biomarkers in lung cancer: Overview
 Emerging mutations as predictive biomarkers in lung cancer: Overview Kirtee Raparia, MD Assistant Professor of Pathology Cancer Related Deaths: United States Men Lung and bronchus 28% Prostate 10% Colon
Emerging mutations as predictive biomarkers in lung cancer: Overview Kirtee Raparia, MD Assistant Professor of Pathology Cancer Related Deaths: United States Men Lung and bronchus 28% Prostate 10% Colon
Human Immunodeficiency Virus type 1 (HIV-1) gp120 / Glycoprotein 120 ELISA Pair Set
 Human Immunodeficiency Virus type 1 (HIV-1) gp120 / Glycoprotein 120 ELISA Pair Set Catalog Number : SEK11233 To achieve the best assay results, this manual must be read carefully before using this product
Human Immunodeficiency Virus type 1 (HIV-1) gp120 / Glycoprotein 120 ELISA Pair Set Catalog Number : SEK11233 To achieve the best assay results, this manual must be read carefully before using this product
AN ABSTRACT OF THE THESIS OF
 AN ABSTRACT OF THE THESIS OF Hui Qian for the Master of Science. in Biology presented on July 19, 2017. Title: Development of a Cocktail Therapy against Human Malignant Melanoma by Combining Autophagy
AN ABSTRACT OF THE THESIS OF Hui Qian for the Master of Science. in Biology presented on July 19, 2017. Title: Development of a Cocktail Therapy against Human Malignant Melanoma by Combining Autophagy
ORIGINAL PAPER DISRUPTION OF CELL SPREADING BY THE ACTIVATION OF MEK/ERK PATHWAY IS DEPENDENT ON AP-1 ACTIVITY
 Nagoya J. Med. Sci. 72. 139 ~ 144, 1 ORIGINAL PAPER DISRUPTION OF CELL SPREADING BY THE ACTIVATION OF MEK/ERK PATHWAY IS DEPENDENT ON AP-1 ACTIVITY FENG XU, SATOKO ITO, MICHINARI HAMAGUCHI and TAKESHI
Nagoya J. Med. Sci. 72. 139 ~ 144, 1 ORIGINAL PAPER DISRUPTION OF CELL SPREADING BY THE ACTIVATION OF MEK/ERK PATHWAY IS DEPENDENT ON AP-1 ACTIVITY FENG XU, SATOKO ITO, MICHINARI HAMAGUCHI and TAKESHI
SUPPLEMENT. Materials and methods
 SUPPLEMENT Materials and methods Cell culture and reagents Cell media and reagents were from Invitrogen unless otherwise indicated. Antibiotics and Tet-certified serum were from Clontech. In experiments
SUPPLEMENT Materials and methods Cell culture and reagents Cell media and reagents were from Invitrogen unless otherwise indicated. Antibiotics and Tet-certified serum were from Clontech. In experiments
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL. Supplementary Methods
 SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL Supplementary Methods Culture of cardiomyocytes, fibroblasts and cardiac microvascular endothelial cells The isolation and culturing of neonatal rat ventricular cardiomyocytes was
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL Supplementary Methods Culture of cardiomyocytes, fibroblasts and cardiac microvascular endothelial cells The isolation and culturing of neonatal rat ventricular cardiomyocytes was
