Downregulation of MicroRNA-200 in EBV-Associated Gastric Carcinoma
|
|
|
- Solomon Snow
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Tumor and Stem Cell Biology Downregulation of MicroRNA-200 in EBV-Associated Gastric Carcinoma Cancer Research Aya Shinozaki 1, Takashi Sakatani 1, Tetsuo Ushiku 1, Rumi Hino 1, Maya Isogai 1, Shunpei Ishikawa 1, Hiroshi Uozaki 1, Kenzo Takada 2, and Masashi Fukayama 1 Abstract EBV-associated gastric carcinoma is a distinct gastric carcinoma subtype with characteristic morphologic features similar to those of cells that undergo epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. The effect of microrna abnormalities in carcinogenesis was investigated by measuring the expression of the epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition related micrornas, mir-200a and mir-200b, in 36 surgically resected gastric carcinomas using quantitative reverse transcription-pcr analysis. MiR-200 family expression was decreased in EBV-associated gastric carcinoma, as compared with that in EBV-negative carcinoma. Downregulation of the mir-200 family was found in gastric carcinoma cell lines infected with recombinant EBV (MKN74-EBV, MKN7-EBV, and NUGC3-EBV), accompanied by the loss of cell adhesion, reduction of E-cadherin expression, and upregulation of ZEB1 and ZEB2. E-cadherin expression was partially restored by transfection of EBV-infected cells with mir- 200 family precursors. Reverse transcription-pcr analysis of primary precursors of mir-200 (pri-mir-200) revealed that the transcription of pri-mir-200 was decreased in EBV-infected cells. Transfection of MKN74 cells with BARF0, EBNA1, andlmp2a resulted in a decrease of pri-mir-200, whereas transfection with EBV-encoded small RNA (EBER) did not. These four latent genes contributed to the downregulation of the mature mir-200 family and the subsequent upregulation of ZEB1/ZEB2, resulting in the reduction of E-cadherin expression. These findings indicate that all the latency type I genes have a synergetic effect on the downregulation of the mir-200 family that leads to reduced E-cadherin expression, which is a crucial step in the carcinogenesis of EBVassociated gastric carcinoma. Cancer Res; 70(11); AACR. Introduction Gastric carcinoma is one of the most common malignancies worldwide and ranks second in terms of global carcinoma-related mortality (1). Effective therapy depends on the identification of distinct gastric carcinoma subgroups and the clarification of their pathologic features and molecular mechanisms. EBV-associated gastric carcinoma is a distinct subtype comprising 8% to 11% of all gastric carcinomas (2). Monoclonal EBV is present in nearly all neoplastic cells, strongly suggesting a causal role in gastric carcinogenesis. EBV-associated gastric carcinoma displays characteristic clinicopathologic features, including male predominance, proximal localization within the stomach, and a relatively better prognosis than EBV-negative gastric carcinoma. EBV-associated gastric carcinoma is identified by its unique Authors' Affiliations: 1 Department of Pathology, Graduate School of Medicine, The University of Tokyo, Tokyo, Japan and 2 Department of Tumor Virology, Institute for Genetic Medicine, Hokkaido University, Sapporo, Japan Note: A. Shinozaki and T. Sakatani contributed equally to this work. Corresponding Author: Masashi Fukayama, Department of Pathology, Graduate School of Medicine, The University of Tokyo, Hongo 7-3-1, Bunkyo-ku, Tokyo , Japan. Phone: ; Fax: ; mfukayama-tky@umin.net. doi: / CAN American Association for Cancer morphology. It is generally referred to as a lymphoepitheliomalike carcinoma, which consists of poorly differentiated tumor cell nests intermingled with dense lymphocytic infiltration. These characteristic features reflect specific interactions between infective organisms and infected host cells, i.e., EBV and gastric epithelial cells. Viruses represent one of the major factors that could cause excessive proliferation, migration, and prolonged survival of normal cells. EBV, originally isolated from Burkitt's lymphoma, is associated with various malignancies including Hodgkin's lymphoma, lymphoproliferative disorders in immunosuppressed patients, nasopharyngeal carcinoma, and gastric carcinoma (3 5). Several studies have investigated the role of EBV in carcinogenesis, and attempted to show that EBV gene transcripts, such as EBNA2 or latent membrane protein-1 (LMP1), disturb signal transduction in host cells, and cause immortalization or transformation (6). However, the pathologic role of latent genes in EBV latency type I neoplasms, such as EBV-associated gastric carcinoma, in which only a few viral latent genes are expressed (BARF0, EBER, EBNA1, and LMP2A), has not been fully explained. Recently, a novel class of small, noncoding RNA molecules referred to as micrornas (mirna) have been identified as important posttranscriptional regulators of gene expression. MiRNAs play an important role in a wide variety of complex biological processes, including cellular development and differentiation, but investigations have only begun to clarify
2 Shinozaki et al. their significance in viral infection and carcinogenesis. In a preliminary experiment, we found that mir-200a and mir-200b were downregulated in a gastric carcinoma cell line infected with EBV. Both mirnas belong to the mir- 200 family, the downregulation of which induces epithelialto-mesenchymal transition (EMT) in normal and neoplastic cells via dysregulation of the E-cadherin transcription repressors, ZEB1 and ZEB2. ZEB1 and ZEB2, also known as TCF8 and SIP1, respectively, are possible targets of the mir-200 family, and they were found to repress E-cadherin expression in vitro in the previous reports (7 10). In the present study, we first confirmed that mir-200a and mir-200b were downregulated in surgically resected gastric carcinoma tissue, and assessed the associations between mir-200a and mir-200b downregulation and E-cadherin expression. We then verified that the mir-200 family was downregulated in vitro using established EBV-infected cell lines as models of EBV-associated gastric carcinoma and studied the EBV-latent gene underlying the downregulation of mir-200a and mir-200b. Our results identified a new role for mirnas in the carcinogenesis of EBV-associated gastric carcinoma. Materials and Methods Tissue samples Thirty-six cases of primary gastric carcinoma were used to investigate mir-200a and mir-200b expression in EBVassociated gastric carcinoma tissue. The cases were taken from the archives of the Department of Pathology at the University of Tokyo Hospital. The study included 18 EBVassociated gastric carcinoma cases and 18 EBV-negative gastric carcinoma cases. All aspects of the study were approved by the University of Tokyo Ethics Committee. The H&Estained slides of the cases were reviewed. All cases of gastric carcinoma were histologically evaluated according to Lauren's classification (11). We used the tumor-node-metastasis classification of the International Union Against Cancer for tumor staging (12). EBER in situ hybridization and immunohistochemistry The presence of EBV in tumor cells was confirmed using in situ hybridization targeting EBV-encoded small RNA with EBER1-RNA oligonucleotide probes as previously described (13). Immunohistochemical staining with E-cadherin (clone NCH-38, dilution 1:100; Dako), LMP1 (clone cs1-4, dilution 1:200; Dako), and EBNA2 (clone PE2, dilution 1:25; Dako) in surgically resected specimens was performed using the Ventana BenchMark automated immunostainer with the labeled streptavidin-biotin peroxidase method and visualized using 3,3 -diaminobenzidine with the appropriate positive and negative controls. The immunohistochemical results were blinded and independently evaluated by two pathologists (A. Shinozaki and T. Sakatani). The proportion of E- cadherin positive tumor cells did not differ significantly among the cases, and E-cadherin expression was evaluated according to the staining pattern and intensity. E-cadherin expression was considered preserved when more than 50% of the positively stained tumor cells showed a strong and membranous staining pattern. Expression was defined as decreased when more than 50% of the positively stained tumor cells had a weak, discontinuous, and punctate cell membrane staining pattern. The expressions of LMP1 and EBNA2 were evaluated according to the number of cells which stained positively. Cell culture and treatment The gastric carcinoma cell lines used in the study were MKN7, MKN74, NUGC3, SNU719, and Raji. The former three were originally derived from gastric carcinoma with histologic features of well, moderately, and poorly differentiated adenocarcinoma without EBV infection, respectively. MKN7 and MKN74 were obtained from Riken BioResource Center Cell Bank (Tsukuba, Japan) and NUGC3 was from the Japanese Cancer Research Resource Bank (Osaka, Japan). SNU719 was derived from EBV-associated gastric carcinoma and was obtained from the Korean Cell Line Bank (Seoul, Korea). Raji was derived from Burkitt's lymphoma, and was obtained from The Global Bioresource Center, American Type Culture Collection. The cell lines were authenticated by the cell banks using short tandem repeat PCR. The cell lines were cultured in RPMI 1640 (Nacalai Tesque) supplemented with 10% FCS (MP Biomedicals), penicillin (40 units/ml), and streptomycin (50 μg/ml) at 37 C in a 5% CO 2 incubator. EBV infection MKN7, MKN74, and NUGC3 were infected with recombinant EBV using the cell-to-cell contact method (14). A Burkitt's lymphoma cell line, Akata, was modified to produce recombinant EBV, in which the neomycin-resistant gene is inserted into BXLF1, and was used as a source of the virus in the present study. EBV-infected cells were obtained after bulk selection with G418 (700 μg/ml; Sigma- Aldrich). EBV infection establishment was confirmed using EBER in situ hybridization applied to the cells grown on plastic slides after fixation with 10% formalin. The expression of EBV latent genes (BARF0, EBER, EBNA1, EBNA2, LMP1, and LMP2A) was evaluated using reverse transcription-pcr (RT-PCR) as previously described (15). EBV-infected cells were maintained in bulk in RPMI 1640 supplemented with 10% FCS and G418 (50 μg/ml), but G418 was removed from the medium 24 hours before the experiments. RNA extraction and quantitative RT-PCR Total RNA, including mirna, was extracted from the paraffin-embedded tissue of surgically resected samples with a RecoverAll Total Nucleic Acid Isolation Kit for FFPE Tissues (Ambion). Two representative sections were selected from each case: one from gastric carcinoma tissue and the other from nonneoplastic gastric tissue. Extraction of total RNA from cultured cells was performed using the mirvana mirna Isolation Kit (Ambion). For mirna analysis, mature mirnas were reverse transcribed and quantitative PCR was performed using TaqMan 4720 Cancer Res; 70(11) June 1, 2010 Cancer Research
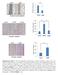
3 Downregulation of mir-200 in EBV-Associated Gastric Carcinoma MiRNA assays (Applied Biosystems) according to the protocols of the manufacturer. The mir-200a and mir-200b expression data were normalized to the reference RNA, RNU6B expression, and then the expression levels relative to those of SNU719 were calculated. For the mrna analysis of E-cadherin, ZEB1, and ZEB2, total RNA was reverse transcribed using the SuperScript II First-Strand Synthesis system (Invitrogen) with random primers. Quantitative PCR was performed using TaqMan Gene Expression assays (Applied Biosystems) according to the protocols of the manufacturer. The data were normalized to glyceraldehyde- 3-phosphate dehydrogenase expression. All quantitative PCR analyses were performed using the 7300 Real-time PCR System (Applied Biosystems). The mir-200 family primary precursor transcript (pri-mir- 200) expression was evaluated using RT-PCR analysis, and total RNA was extracted with TRI REAGENT (Sigma-Aldrich) and subjected to reverse transcription using the Quantitect reverse transcription kit (Qiagen) according to the protocols of the manufacturer. The RT-PCR analysis was performed using primers that targeted the predicted transcript start site of mir-200b 200a 429 clusters as previously described (8). Western blotting Whole cell extracts were prepared using lysis buffer [10 mmol/l Tris-HCl (ph 7.4), 150 mmol/l NaCl, 5 mmol/l EDTA, 1.0% Triton X-100, 1.0% sodium deoxycholate, 0.1% SDS, and 1 mmol/l of phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride with protease inhibitor cocktail] and 10 μg of protein per lane was loaded and fractionated on an 8% SDS polyacrylamide gel. After transfer onto a polyvinylidene difluoride membrane, probing was carried out with anti-human E-cadherin antibody (clone NCH-38, 1:100; Dako). The membranes were visualized using the ECL Plus Western Blotting Detection System (GE Healthcare) according to the protocols of the manufacturer. Transfection with mirna precursors EBV-infected MKN74 cells (MKN74-EBV) were seeded at cells per well in six-well plates and transfected with synthetic precursors of mirnas (pre-mir mirna Precursor Molecules; Ambion) using siport NeoFX Transfection Agent (Ambion). The final concentration of each pre-mir was 20 nmol/l (pre-mir-200a), 20 nmol/l (pre-mir-200b), and 40 nmol/l (20 nmol/l pre-mir-200a and 20 nmol/l premir-200b). Total RNA was collected for assay 3 days posttransfection. Cells transfected with pre-mir mirna Precursor Negative Control no. 1 (Ambion) at a final concentration of 20 nmol/l were used as a negative control. Transfection with EBV-latent genes Each EBV-latent gene, BARF0, EBER (EBER1 and EBER2), EBNA1, and LMP2A (gifts from Dr. Paul J Farrell) was cloned into a pcdna3 vector containing FLAG-tag. MKN74 cells were transfected with each expression vector using FuGENE6 Transfection Reagent (Roche). The expression of each gene was confirmed using RT-PCR analysis as previously described (15, 16). Statistical analyses Statistical differences between clinicopathologic variables and E-cadherin expression were determined using Fisher's exact test, Student's t test, or the Mann-Whitney U test. Associations between mirna expression levels and clinicopathologic variables were analyzed using Student's t test, and ANOVA followed up with Fisher's Protected Least Significant Difference, Pearson's correlation coefficient, or Spearman's rank correlation. All analyses were performed using StatView statistical software (version 5.0, SAS Institute, Inc.). P < 0.05 was considered to be statistically significant. Results Downregulation of the mir-200 family in surgically resected EBV-associated gastric carcinoma MiR-200a and mir-200b expression levels in the surgically resected gastric tissue are shown in Fig. 1A. Expression of both mir-200a and mir-200b was decreased in EBVassociated gastric carcinoma compared with that in EBV-negative gastric carcinoma (P = and 0.002, respectively; ANOVA, Fisher's Protected Least Significant Difference follow-up), and compared with that in nonneoplastic gastric tissue obtained from EBV-associated gastric carcinoma patients (P = and , respectively). No statistically significant differences in mir-200a or mir-200b expression were observed between the nonneoplastic tissue and tumor tissue from EBV-negative gastric carcinoma patients or between nonneoplastic tissues obtained from EBV-associated gastric carcinoma patients and those from EBV-negative gastric carcinoma patients. No statistically significant differences were observed between mir-200 family expression and age, sex, tumor size, tumor histology, stage, venous or lymphatic invasion, and lymph node metastasis. Association between mir-200 family expression and clinicopathologic variables E-cadherin expression was evaluated using immunohistochemistry. The typical decreased/preserved staining patterns of E-cadherin are shown in Fig. 1B. Nine out of 18 EBVassociated gastric carcinoma cases showed decreased E- cadherin expression patterns, whereas only 1 out of 18 EBV-negative cases showed decreased E-cadherin expression, and the difference was statistically significant (Fisher's exact test, P = ). Tumors with decreased E-cadherin expression had lower levels of mir-200a and mir-200b than tumors with preserved E-cadherin expression, and the differences were statistically significant (P = and , respectively, Student's t test; Fig. 1C). Downregulation of the mir-200 family and E-cadherin in EBV-infected cell lines The effect of EBV infection on downregulation of the mir- 200 family and E-cadherin was further investigated in vitro in EBV-infected gastric carcinoma cell lines (MKN74-EBV, MKN7-EBV, and NUGC3-EBV). Western blot analysis revealed that E-cadherin expression was decreased in all three Cancer Res; 70(11) June 1,
4 Shinozaki et al. Figure 1. The expression of mir-200a, mir-200b, and E-cadherin in surgically resected gastric tissues. A, quantitative RT-PCR analysis of mir-200a and mir-200b in normal gastric mucosa and carcinoma tissue from EBV-associated and EBV-negative gastric carcinoma cases. B, decreased E-cadherin expression in EBV-associated gastric carcinoma and EBV-negative gastric carcinoma showing preserved E-cadherin expression (bar, 100 μm). C, associations between mir-200 family expression and E-cadherin expression. P < 0.05 were considered to be statistically significant. EBV-infected cell lines, as compared with their original cell lines (Fig. 2A). Furthermore, mir-200a and mir-200b expression were downregulated in these EBV-infected cell lines (Fig. 2B). Quantitative RT-PCR analysis showed ZEB1 upregulation in all EBV-infected cell lines and ZEB2 upregulation in the MKN74-EBV and NUGC3-EBV cell lines (Fig. 2B). EBV infection produced a dramatic morphologic change in the MKN74-EBV cell line (Fig. 2C). It showed significant loss of cell-to-cell adhesion, as compared with its original cell line, MKN74, which formed colonies with a cobblestone arrangement of mutually cohesive cells. The effect of transfection with mir-200 family precursors on E-cadherin expression The effect of transfection with mir-200 family precursors on E-cadherin expression in cells with low endogenous mir- 200 family expression was investigated. We found that transfection of MKN74-EBV with mir-200a and mir-200b precursors alone or together resulted in the downregulation of ZEB1, and transfection with mir-200a resulted in the downregulation of ZEB2, as compared with their levels in MKN74-EBV transfected with negative controls (Fig. 3). Subsequently, an increase in E-cadherin at the transcriptional level was observed in MKN74-EBV cells transfected with the mir-200 family (Fig. 3). Downregulation of pri-mir-200 in EBV-infected gastric cell lines To investigate how EBV infection regulates mir-200a and mir-200b levels, we performed RT-PCR analysis of their primary precursor, pri-mir-200 in EBV-infected cell lines. PrimiR-200 transcripts were detected in MKN74, MKN7, and NUGC3 cells; however, a decrease in pri-mir-200 was apparent in all of the three cell lines infected with EBV (Fig. 4A). The effect of EBV latent gene expression on downregulation of the mir-200 family and E-cadherin To further elucidate which viral factor underlies the downregulation of the mir-200 family, we established MKN74 cells transfected with four different EBV latent genes, BARF0, 4722 Cancer Res; 70(11) June 1, 2010 Cancer Research
5 Downregulation of mir-200 in EBV-Associated Gastric Carcinoma EBERs, EBNA1, andlmp2a, that are expressed in EBVassociated gastric carcinoma. RT-PCR analysis confirmed the expression of these four latent genes and the absence of LMP1 and EBNA2 expression in MKN74-EBV (Fig. 4B). The lack of LMP1 and EBNA2 expression in EBV-associated gastric carcinoma was also confirmed immunohistochemically in surgically resected tissues, which defined these tumors as latency type I, as has been described previously. RT-PCR analysis showed a decrease in pri-mir-200 transcripts in MKN74 cells transfected with BARF0, EBNA1, and LMP2A, compared with MKN74 and MKN74-Flag (Fig. 4C), although the degree of reduction of pri-mir-200 was not as prominent as in MKN74-EBV cells. In contrast, transfection of EBERs did not downregulate pir-mir-200. To further evaluate the downstream effects of EBV-latent genes, the expression of mir-200a, mir-200b, ZEB1, ZEB2, and E-cadherin was investigated in MKN74 transfected with BARF0, EBERs, EBNA1, andlmp2a (Fig. 5). MKN74-BARF0, MKN74-EBERs, and MKN74-EBNA1 cells showed downregulation of mature mir-200a and mir-200b compared with MKN74 and MKN74-Flag, and MKN74-LMP2A showed downregulation of mature mir-200b compared with MKN74-Flag. Quantitative RT-PCR analyses revealed the upregulation of ZEB1 in MKN74-BARF0, MKN74-EBERs, and MKN74-LMP2A (Fig. 5A). Subsequent downregulation of E-cadherin expression was observed in all cells transfected with EBV latent genes at the transcriptional level, among which only MKN74-EBERs showed a prominent decrease in E-cadherin expression in Western blotting (Fig. 5B), together with a slight change in cell morphology and the loss of cell-to-cell adhesion (Fig. 5C). Discussion The role that cellular mirna abnormalities play in the genesis of diseases such as cancer has been intensely Figure 2. The expression of E-cadherin, the mir-200 family, ZEB1, and ZEB2 in the EBV-associated gastric carcinoma cell line models. A, Western blot analysis of E-cadherin in gastric carcinoma cell lines. Cells with EBV infection (MKN74-EBV, MKN7-EBV, and NUGC3-EBV) show decreased E-cadherin expression compared with their original cell lines. B, quantitative RT-PCR analysis of the mir-200 family, ZEB1, and ZEB2 in EBV-infected cell lines. Columns, averages of measurements done in triplicate; bars, SD (P < 0.05 was considered to be statistically significant). C, a significant loss of cell-to-cell adhesion observed in EBV-infected MKN74 cells. Immunohistochemical staining shows decreased E-cadherin expression in MKN74-EBV cells. Cancer Res; 70(11) June 1,
6 Shinozaki et al. Figure 3. Transfection of MKN74-EBV cells with mir-200 family precursors. Quantitative RT-PCR analysis of ZEB1, ZEB2, and E-cadherin 3 d posttransfection. Columns, average values from experiments done in triplicate; bars, SD (P < 0.05 were considered to be statistically significant). investigated. In EBV-related tumors, the EBV-latent membrane protein, LMP1, was recently found to activate several mirnas, including mir-146a and mir-155, through NF-κB pathways, and this mechanism might underlie the development of B-cell malignancies (17, 18). However, the role of mirnas in carcinogenesis has not been investigated in EBV-associated gastric carcinoma. The abnormal expression of several mirnas in gastric carcinoma has been reported in vitro and in vivo. Zhang and colleagues reported that mir-21 was overexpressed in gastric cancer and that it accelerated cell proliferation and had antiapoptotic effects (19). Recently, Du and colleagues showed that mir-141, a member of the mir-200 family, had an inhibitory effect on cell proliferation and was downregulated in 80% of gastric carcinomas; however, the authors did not investigate the association between mir-141 and E-cadherin or epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in their study (20). Abnormal E-cadherin expression plays a key role in gastric carcinogenesis. In our previous study, hypermethylation of the E-cadherin gene promoter was more frequent in EBVassociated gastric carcinoma than in EBV-negative gastric carcinoma. This finding is consistent with the abnormal expression of E-cadherin in cancer tissues (21). In the present study, we observed that the mir-200 family was specifically downregulated in surgically resected EBV-associated gastric carcinoma tissue, leading to the reduction of E-cadherin expression. This phenomenon was also confirmed in vitro in the EBV-infected gastric cancer cell lines; EBV infection induced downregulation of the mir-200 family and the subsequent upregulation of ZEB1 and ZEB2, resulting in the inhibition of E-cadherin expression and the corresponding morphologic change, especially in MKN74 cells. These results are consistent with previous studies that showed a role for the mir-200 family in the induction of 4724 Cancer Res; 70(11) June 1, 2010 Cancer Research
7 Downregulation of mir-200 in EBV-Associated Gastric Carcinoma epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in normal cells and various cancer cells (7 10). It is noteworthy that EBVassociated gastric carcinoma has a unique expression profile among other cell adhesion molecules, including major tight junction proteins such as claudins (22). E-cadherin dysregulation induced by EBV infection further contributes to the disruption of cell-to-cell adhesion and promotion of cell migration. These abnormalities might be closely associated with the development, progression, and unique histologic features of EBV-associated gastric carcinoma. The results of the present study showed that EBV infection downregulates pri-mir-200 at the transcriptional level. Considering that MKN74-EBV showed the most prominent morphologic change that well reflected the marked loss of E-cadherin expression, we selected MKN74-EBV as the most suitable model of EBV-associated gastric carcinoma for further experimentation to investigate which EBV latent gene contributed to the regulation of pri-mir-200. Among various kinds of EBV-associated malignancies, EBV-associated gastric carcinoma is distinctive owing to the limited number of EBV latent genes expressed in tumor cells. It is classified as latency type I; expressed latent genes are restricted to BARF0, EBERs, EBNA1, andlmp2a, excludinglmp1 or EBNA2 which have been considered to be essential for transforming ability (3, 5, 6). We recently revealed that LMP2A plays an important role in the dysregulation of intracellular signaling pathways, such as phosphorylation of signal transducers and activators of transcription 3, leading to the promotion of DNMT1-mediated CpG island methylation (16). In contrast, Iwakiri and colleagues showed that EBERs upregulate insulin-like growth factor I to function as an autocrine growth factor (23, 24). In the present study, transfection of MKN74 with BARF0, EBNA1, and LMP2A downregulated the pri-mir-200 transcript, whereas transfection of EBERs did not. However, all four of these genes played a role in the downregulation of mature mir- 200 and the subsequent decrease in E-cadherin expression. The results of our study revealed that all the latency type I genes have a synergetic effect on the downregulation of mir-200 family in EBV-associated gastric carcinoma; the repression of pri-mir-200 transcription by BARF0, EBNA1, and LMP2A, and the inhibition of mature mir-200 at the posttranscriptional step by EBERs. The subsequent decrease in E-cadherin expression was attributed to the upregulation of ZEB1 and/or ZEB2 in most of the cell lines transfected with EBV latent genes, whereas MKN74-EBNA1 was not associated with the upregulation of ZEB1 or ZEB2. This implies the presence of some other mechanisms which do not involve ZEB1 or ZEB2. Recently, Tryndyak and colleagues showed in their study that mir-200 family mediated transcriptional upregulation of E-cadherin was associated indirectly with increased Figure 4. The effect of EBV and its latent genes on downregulation of primary precursor of mir-200 (pri-mir-200). A, RT-PCR analysis of pri-mir-200 in gastric carcinoma cell lines. B, transfection of MKN74 cells with EBV latent genes. RT-PCR analysis of EBV latent genes in MKN74-EBV cells and MKN74 cells transfected with vectors containing each latent gene or Flag tag (Flag). SNU719 was used as a positive control for latency type I genes BARF0, EBERs, EBNA1, and LMP2A, and Raji was used as a positive control for EBNA2 and LMP1. C, RT-PCR analysis of pri-mir-200 in MKN74 cells transfected with EBV latency type I genes. Cancer Res; 70(11) June 1,
8 Shinozaki et al. Figure 5. The effect of EBV latent genes on downregulation of mir-200 family, ZEB1/ZEB2, and E-cadherin. A, quantitative RT-PCR analysis of the mir-200 family, ZEB1, and ZEB2 in MKN74 cells transfected with EBV latency type I genes. Columns, average values of measurements done in triplicate; bars, SD (**, P < 0.05, statistically significant compared with MKN74 and MKN74-Flag; *, P < 0.05, statistically significant compared with MKN74-Flag). B, quantitative RT-PCR analysis and Western blot analysis of E-cadherin expression in MKN74 cells transfected with EBV latent genes. Columns, average values of quantitative RT-PCR analyses done in triplicate; bars, SD (**, P < 0.05, statistically significant compared with MKN74 and MKN74-Flag). C, morphologic changes observed in MKN74-EBER cells with a slight decrease in cell-to-cell adhesion. acetylation of histone H3 at the E-cadherin promoter, the mechanism independent of the expression level of ZEB1 (25). The effect of histone acetylation status should be investigated in future studies to clarify the role of mir-200 family in theregulationofe-cadherinexpressioninebv-associated gastric carcinoma. In mammalian mirna biogenesis, pri-mirnas are cleaved into pre-mirnas by the nuclear RNase III Drosha and further processed into mature mirnas by cytosolic Dicer. The decrease in mature mirnas in human cancers may be caused by genomic or epigenetic alterations, as well as by the impairment of mirna processing steps (26). The exact mechanisms of how BARF0, EBNA1, and LMP2A repress pri-mir-200 transcription remain to be elucidated in future studies, and how EBERs reduce mature mir-200 family expression must be clarified as well. One possible explanation might be the hypermethylation of promoter regions of these mirna genes, an interaction between viral and cellular noncoding RNAs, or a decrease in the half-life of mature forms of the mir-200 family; however, these hypotheses need further elucidation (27). In conclusion, the present study showed that EBV infection of epithelial cells causes downregulation of the mir- 200 family by repressing transcription of pri-mirnas and by posttranscriptional dysregulation of the mirna, and all the latency type I genes have a synergetic effect on these processes. Downregulation of the mir-200 family causes a reduction in E-cadherin expression through the upregulation of the E-cadherin repressors, ZEB1 and ZEB2. The loss of cellto-cell adhesion is essential for tumor progression, and our findings provide some clues for clarifying viral carcinogenesis in EBV-associated gastric carcinoma Cancer Res; 70(11) June 1, 2010 Cancer Research
9 Downregulation of mir-200 in EBV-Associated Gastric Carcinoma Disclosure of Potential Conflicts of Interest No potential conflicts of interest were disclosed. Acknowledgments We thank Dr. Paul J. Farrell (Tumor Virology, Division of Investigative Science, Imperial College, London, United Kingdom) for supplying the LMP2A cdna. Grant Support Grants-in Aid for Scientific Research (T. Sakatani) and (M. Fukayama). The costs of publication of this article were defrayed in part by the payment of page charges. This article must therefore be hereby marked advertisement in accordance with 18 U.S.C. Section 1734 solely to indicate this fact. Received 12/19/2009; revised 03/22/2010; accepted 04/01/2010; published OnlineFirst 05/18/2010. References 1. Ohgaki H, Matsukura N. Stomach cancer. In: Stewart BW, Kleihues P, editors. World Cancer Report. Lyon: IARC Press; 2003, p Fukayama M, Hino R, Uozaki H. Epstein-Barr virus and gastric carcinoma: virus-host interactions leading to carcinoma. Cancer Sci 2008;99: Kutok JL, Wang F. Spectrum of Epstein-Barr virus-associated diseases. Annu Rev Pathol 2006;1: Fukayama M, Ibuka T, Hayashi Y, Ooba T, Koike M, Mizutani S. Epstein-Barr virus in pyothorax-associated pleural lymphoma. Am J Pathol 1993;143: Young LS, Rickinson AB. Epstein-Barr virus: 40 years on. Nat Rev Cancer 2004;4: Young LS, Murray PG. Epstein-Barr virus and oncogenesis: from latent genes to tumours. Oncogene 2003;22: Korpal M, Lee ES, Hu G, Kang Y. The mir-200 family inhibits epithelial-mesenchymal transition and cancer cell migration by direct targeting of E-cadherin transcriptional repressors ZEB1 and ZEB2. J Biol Chem 2008;283: Bracken CP, Gregory PA, Kolesnikoff N, et al. A double-negative feedback loop between ZEB1-1 and the microrna-200 family regulates epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Cancer Res 2008; 68: Gregory PA, Bert AG, Paterson EL, et al. The mir-200 family and mir-205 regulate epithelial to mesenchymal transition by targeting ZEB1 and SIP1. Nat Cell Biol 2008;10: ParkSM,GaurAB,LengyelE,PeterME.ThemiR-200family determines the epithelial phenotype of cancer cells by targeting the E-cadherin repressors ZEB1 and ZEB2. Genes Dev 2008; 22: Lauren P. The two histological main types of gastric carcinoma: diffuse and so-called intestinal-type carcinoma. An attempt at a histo-clinical classification. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand 1965; 64: Sobin L, Wittekind C. TNM classification of malignant tumours. 6th ed. New Jersey: John Wiley & Sons; Fukayama M, Hayashi Y, Iwasaki Y, et al. Epstein-Barr virusassociated gastric carcinoma and Epstein-Barr virus infection of the stomach. Lab Invest 1994;71: Imai S, Nishikawa J, Takada K. Cell-to-cell contact as an efficient mode of Epstein-Barr virus infection of diverse human epithelial cells. J Virol 1998;72: Iwasaki Y, Chong JM, Hayashi Y, et al. Establishment and characterization of a human Epstein-Barr virus-associated gastric carcinoma in SCID mice. J Virol 1998;72: Hino R, Uozaki H, Murakami N, et al. Activation of DNA methyltransferase 1 by EBV latent membrane protein 2A leads to promoter hypermethylation of PTEN gene in gastric carcinoma. Cancer Res 2009;69: Cameron JE, Yin Q, Fewell C, et al. Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein 1 induces cellular microrna mir-146a, a modulator of lymphocyte signaling pathways. J Virol 2008;82: Gatto G, Rossi A, Rossi D, Kroening S, Bonatti S, Mallardo M. Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein 1 trans-activates mir- 155 transcription through the NF-κB pathway. Nucleic Acids Res 2008;36: Zhang Z, Li Z, Gao C, et al. mir-21 plays a pivotal role in gastric cancer pathogenesis and progression. Lab Invest 2008;88: Du Y, Xu Y, Ding L, et al. Down-regulation of mir-141 in gastric cancer and its involvement in cell growth. J Gastroenterol 2009; 44: Sudo M, Chong JM, Sakuma K, et al. Promoter hypermethylation of E-cadherin and its abnormal expression in Epstein-Barr virusassociated gastric carcinoma. Int J Cancer 2004;109: Shinozaki A, Ushiku T, Morikawa T, et al. Epstein-Barr virusassociated gastric carcinoma: a distinct carcinoma of gastric phenotype by claudin expression profiling. J Histochem Cytochem 2009;57: Iwakiri D, Eizuru Y, Tokunaga M, Takada K. Autocrine growth of Epstein-Barr virus-positive gastric carcinoma cells mediated by an Epstein-Barr virus-encoded small RNA. Cancer Res 2003;63: Nanbo A, Yoshiyama H, Takada K. Epstein-Barr virus-encoded poly (A)- RNA confers resistance to apoptosis mediated through Fas by blocking the PKR pathway in human epithelial intestine 407 cells. J Virol 2005;79: Tryndyak VP, Beland FA, Pogribny IP. E-cadherin transcriptional down-regulation by epigenetic and microrna-200 family alterations is related to mesenchymal and drug-resistant phenotypes in human breast cancer cells. Int J Cancer 2010;126: Suzuki HI, Yamagata K, Sugimoto K, Iwamoto T, Kato S, Miyazono K. Modulation of microrna processing by p53. Nature 2009;460: Swaminathan S. Noncoding RNAs produced by oncogenic human herpesviruses. J Cell Physiol 2008;216: Cancer Res; 70(11) June 1,
10 Downregulation of MicroRNA-200 in EBV-Associated Gastric Carcinoma Aya Shinozaki, Takashi Sakatani, Tetsuo Ushiku, et al. Cancer Res 2010;70: Published OnlineFirst May 18, Updated version Access the most recent version of this article at: doi: / can Cited articles Citing articles This article cites 25 articles, 9 of which you can access for free at: This article has been cited by 9 HighWire-hosted articles. Access the articles at: alerts Sign up to receive free -alerts related to this article or journal. Reprints and Subscriptions Permissions To order reprints of this article or to subscribe to the journal, contact the AACR Publications Department at pubs@aacr.org. To request permission to re-use all or part of this article, use this link Click on "Request Permissions" which will take you to the Copyright Clearance Center's (CCC) Rightslink site.
mirna Dr. S Hosseini-Asl
 mirna Dr. S Hosseini-Asl 1 2 MicroRNAs (mirnas) are small noncoding RNAs which enhance the cleavage or translational repression of specific mrna with recognition site(s) in the 3 - untranslated region
mirna Dr. S Hosseini-Asl 1 2 MicroRNAs (mirnas) are small noncoding RNAs which enhance the cleavage or translational repression of specific mrna with recognition site(s) in the 3 - untranslated region
Epstein-Barr virus driven promoter hypermethylated genes in gastric cancer
 RESEARCH FUND FOR THE CONTROL OF INFECTIOUS DISEASES Epstein-Barr virus driven promoter hypermethylated genes in gastric cancer J Yu *, KF To, QY Liang K e y M e s s a g e s 1. Somatostatin receptor 1
RESEARCH FUND FOR THE CONTROL OF INFECTIOUS DISEASES Epstein-Barr virus driven promoter hypermethylated genes in gastric cancer J Yu *, KF To, QY Liang K e y M e s s a g e s 1. Somatostatin receptor 1
Gastric Carcinoma with Lymphoid Stroma: Association with Epstein Virus Genome demonstrated by PCR
 Gastric Carcinoma with Lymphoid Stroma: Association with Epstein Virus Genome demonstrated by PCR Pages with reference to book, From 305 To 307 Irshad N. Soomro,Samina Noorali,Syed Abdul Aziz,Suhail Muzaffar,Shahid
Gastric Carcinoma with Lymphoid Stroma: Association with Epstein Virus Genome demonstrated by PCR Pages with reference to book, From 305 To 307 Irshad N. Soomro,Samina Noorali,Syed Abdul Aziz,Suhail Muzaffar,Shahid
Survival Advantage of EBV-Associated Gastric Carcinoma: Survivin Up-regulation by Viral Latent Membrane Protein 2A
 Survival Advantage of EBV-Associated Gastric Carcinoma: Survivin Up-regulation by Viral Latent Membrane Protein 2A Rumi Hino, 1 Hiroshi Uozaki, 1 Yoko Inoue, 1 Yukako Shintani, 1 Tetsuo Ushiku, 1 Takashi
Survival Advantage of EBV-Associated Gastric Carcinoma: Survivin Up-regulation by Viral Latent Membrane Protein 2A Rumi Hino, 1 Hiroshi Uozaki, 1 Yoko Inoue, 1 Yukako Shintani, 1 Tetsuo Ushiku, 1 Takashi
microrna Presented for: Presented by: Date:
 microrna Presented for: Presented by: Date: 2 micrornas Non protein coding, endogenous RNAs of 21-22nt length Evolutionarily conserved Regulate gene expression by binding complementary regions at 3 regions
microrna Presented for: Presented by: Date: 2 micrornas Non protein coding, endogenous RNAs of 21-22nt length Evolutionarily conserved Regulate gene expression by binding complementary regions at 3 regions
Activation of DNA Methyltransferase 1 by EBV Latent Membrane Protein 2A Leads to Promoter Hypermethylation of PTEN Gene in Gastric Carcinoma
 Research Article Activation of DNA Methyltransferase 1 by EBV Latent Membrane Protein 2A Leads to Promoter Hypermethylation of PTEN Gene in Gastric Carcinoma Rumi Hino, 1 Hiroshi Uozaki, 1 Noriko Murakami,
Research Article Activation of DNA Methyltransferase 1 by EBV Latent Membrane Protein 2A Leads to Promoter Hypermethylation of PTEN Gene in Gastric Carcinoma Rumi Hino, 1 Hiroshi Uozaki, 1 Noriko Murakami,
W orldwide, gastric carcinoma is one of the leading
 487 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Epstein-Barr virus in gastric carcinomas and gastric stump carcinomas: a late event in gastric carcinogenesis A zur Hausen, B P van Rees, J van Beek, M E Craanen, E Bloemena, G J A
487 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Epstein-Barr virus in gastric carcinomas and gastric stump carcinomas: a late event in gastric carcinogenesis A zur Hausen, B P van Rees, J van Beek, M E Craanen, E Bloemena, G J A
EBV infection B cells and lymphomagenesis. Sridhar Chaganti
 EBV infection B cells and lymphomagenesis Sridhar Chaganti How EBV infects B-cells How viral genes influence the infected B cell Differences and similarities between in vitro and in vivo infection How
EBV infection B cells and lymphomagenesis Sridhar Chaganti How EBV infects B-cells How viral genes influence the infected B cell Differences and similarities between in vitro and in vivo infection How
JVI Accepts, published online ahead of print on 19 May 2010 J. Virol. doi: /jvi
 JVI Accepts, published online ahead of print on 19 May 2010 J. Virol. doi:10.1128/jvi.00379-10 Copyright 2010, American Society for Microbiology and/or the Listed Authors/Institutions. All Rights Reserved.
JVI Accepts, published online ahead of print on 19 May 2010 J. Virol. doi:10.1128/jvi.00379-10 Copyright 2010, American Society for Microbiology and/or the Listed Authors/Institutions. All Rights Reserved.
Bmi-1 regulates stem cell-like properties of gastric cancer cells via modulating mirnas
 Wang et al. Journal of Hematology & Oncology (2016) 9:90 DOI 10.1186/s13045-016-0323-9 RESEARCH Bmi-1 regulates stem cell-like properties of gastric cancer cells via modulating mirnas Open Access Xiaofeng
Wang et al. Journal of Hematology & Oncology (2016) 9:90 DOI 10.1186/s13045-016-0323-9 RESEARCH Bmi-1 regulates stem cell-like properties of gastric cancer cells via modulating mirnas Open Access Xiaofeng
(A) RT-PCR for components of the Shh/Gli pathway in normal fetus cell (MRC-5) and a
 Supplementary figure legends Supplementary Figure 1. Expression of Shh signaling components in a panel of gastric cancer. (A) RT-PCR for components of the Shh/Gli pathway in normal fetus cell (MRC-5) and
Supplementary figure legends Supplementary Figure 1. Expression of Shh signaling components in a panel of gastric cancer. (A) RT-PCR for components of the Shh/Gli pathway in normal fetus cell (MRC-5) and
Molecular Probes Introducing 14 new probes
 Molecular Probes Introducing 14 new probes Gene and Chromosome Probes Dual Colour ISH INFORM HER2 Dual ISH DNA Probe Cocktail Assay Product Part Number INFORM HER2 Dual ISH DNA Probe Cocktail 800-4422
Molecular Probes Introducing 14 new probes Gene and Chromosome Probes Dual Colour ISH INFORM HER2 Dual ISH DNA Probe Cocktail Assay Product Part Number INFORM HER2 Dual ISH DNA Probe Cocktail 800-4422
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb2607 Figure S1 Elf5 loss promotes EMT in mammary epithelium while Elf5 overexpression inhibits TGFβ induced EMT. (a, c) Different confocal slices through the Z stack image. (b, d) 3D rendering
DOI: 10.1038/ncb2607 Figure S1 Elf5 loss promotes EMT in mammary epithelium while Elf5 overexpression inhibits TGFβ induced EMT. (a, c) Different confocal slices through the Z stack image. (b, d) 3D rendering
Correlation between expression and significance of δ-catenin, CD31, and VEGF of non-small cell lung cancer
 Correlation between expression and significance of δ-catenin, CD31, and VEGF of non-small cell lung cancer X.L. Liu 1, L.D. Liu 2, S.G. Zhang 1, S.D. Dai 3, W.Y. Li 1 and L. Zhang 1 1 Thoracic Surgery,
Correlation between expression and significance of δ-catenin, CD31, and VEGF of non-small cell lung cancer X.L. Liu 1, L.D. Liu 2, S.G. Zhang 1, S.D. Dai 3, W.Y. Li 1 and L. Zhang 1 1 Thoracic Surgery,
Profiles of gene expression & diagnosis/prognosis of cancer. MCs in Advanced Genetics Ainoa Planas Riverola
 Profiles of gene expression & diagnosis/prognosis of cancer MCs in Advanced Genetics Ainoa Planas Riverola Gene expression profiles Gene expression profiling Used in molecular biology, it measures the
Profiles of gene expression & diagnosis/prognosis of cancer MCs in Advanced Genetics Ainoa Planas Riverola Gene expression profiles Gene expression profiling Used in molecular biology, it measures the
mir-509-5p and mir-1243 increase the sensitivity to gemcitabine by inhibiting
 mir-509-5p and mir-1243 increase the sensitivity to gemcitabine by inhibiting epithelial-mesenchymal transition in pancreatic cancer Hidekazu Hiramoto, M.D. 1,3, Tomoki Muramatsu, Ph.D. 1, Daisuke Ichikawa,
mir-509-5p and mir-1243 increase the sensitivity to gemcitabine by inhibiting epithelial-mesenchymal transition in pancreatic cancer Hidekazu Hiramoto, M.D. 1,3, Tomoki Muramatsu, Ph.D. 1, Daisuke Ichikawa,
MicroRNA dysregulation in cancer. Systems Plant Microbiology Hyun-Hee Lee
 MicroRNA dysregulation in cancer Systems Plant Microbiology Hyun-Hee Lee Contents 1 What is MicroRNA? 2 mirna dysregulation in cancer 3 Summary What is MicroRNA? What is MicroRNA? MicroRNAs (mirnas) -
MicroRNA dysregulation in cancer Systems Plant Microbiology Hyun-Hee Lee Contents 1 What is MicroRNA? 2 mirna dysregulation in cancer 3 Summary What is MicroRNA? What is MicroRNA? MicroRNAs (mirnas) -
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION FOR Liver X Receptor α mediates hepatic triglyceride accumulation through upregulation of G0/G1 Switch Gene 2 (G0S2) expression I: SUPPLEMENTARY METHODS II: SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION FOR Liver X Receptor α mediates hepatic triglyceride accumulation through upregulation of G0/G1 Switch Gene 2 (G0S2) expression I: SUPPLEMENTARY METHODS II: SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES
Downregulation of serum mir-17 and mir-106b levels in gastric cancer and benign gastric diseases
 Brief Communication Downregulation of serum mir-17 and mir-106b levels in gastric cancer and benign gastric diseases Qinghai Zeng 1 *, Cuihong Jin 2 *, Wenhang Chen 2, Fang Xia 3, Qi Wang 3, Fan Fan 4,
Brief Communication Downregulation of serum mir-17 and mir-106b levels in gastric cancer and benign gastric diseases Qinghai Zeng 1 *, Cuihong Jin 2 *, Wenhang Chen 2, Fang Xia 3, Qi Wang 3, Fan Fan 4,
(A) PCR primers (arrows) designed to distinguish wild type (P1+P2), targeted (P1+P2) and excised (P1+P3)14-
 1 Supplemental Figure Legends Figure S1. Mammary tumors of ErbB2 KI mice with 14-3-3σ ablation have elevated ErbB2 transcript levels and cell proliferation (A) PCR primers (arrows) designed to distinguish
1 Supplemental Figure Legends Figure S1. Mammary tumors of ErbB2 KI mice with 14-3-3σ ablation have elevated ErbB2 transcript levels and cell proliferation (A) PCR primers (arrows) designed to distinguish
Yamaguchi University School of Medicine, Kogushi, Ube, Yamaguchi. growth in low serum, anchorage-independent growth in soft
 JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, Sept. 1994, p. 6069-6073 Vol. 68, No. 9 0022-538X/94/$04.00+0 Copyright 1994, American Society for Microbiology Isolation of Epstein-Barr Virus (EBV)-Negative Cell Clones from the
JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, Sept. 1994, p. 6069-6073 Vol. 68, No. 9 0022-538X/94/$04.00+0 Copyright 1994, American Society for Microbiology Isolation of Epstein-Barr Virus (EBV)-Negative Cell Clones from the
Supplementary Figure 1. HOPX is hypermethylated in NPC. (a) Methylation levels of HOPX in Normal (n = 24) and NPC (n = 24) tissues from the
 Supplementary Figure 1. HOPX is hypermethylated in NPC. (a) Methylation levels of HOPX in Normal (n = 24) and NPC (n = 24) tissues from the genome-wide methylation microarray data. Mean ± s.d.; Student
Supplementary Figure 1. HOPX is hypermethylated in NPC. (a) Methylation levels of HOPX in Normal (n = 24) and NPC (n = 24) tissues from the genome-wide methylation microarray data. Mean ± s.d.; Student
RNA extraction, RT-PCR and real-time PCR. Total RNA were extracted using
 Supplementary Information Materials and Methods RNA extraction, RT-PCR and real-time PCR. Total RNA were extracted using Trizol reagent (Invitrogen,Carlsbad, CA) according to the manufacturer's instructions.
Supplementary Information Materials and Methods RNA extraction, RT-PCR and real-time PCR. Total RNA were extracted using Trizol reagent (Invitrogen,Carlsbad, CA) according to the manufacturer's instructions.
Determination of the temporal pattern and importance of BALF1 expression in Epstein-Barr viral infection
 Determination of the temporal pattern and importance of BALF1 expression in Epstein-Barr viral infection Melissa Mihelidakis May 6, 2004 7.340 Research Proposal Introduction Apoptosis, or programmed cell
Determination of the temporal pattern and importance of BALF1 expression in Epstein-Barr viral infection Melissa Mihelidakis May 6, 2004 7.340 Research Proposal Introduction Apoptosis, or programmed cell
MicroRNA sponges: competitive inhibitors of small RNAs in mammalian cells
 MicroRNA sponges: competitive inhibitors of small RNAs in mammalian cells Margaret S Ebert, Joel R Neilson & Phillip A Sharp Supplementary figures and text: Supplementary Figure 1. Effect of sponges on
MicroRNA sponges: competitive inhibitors of small RNAs in mammalian cells Margaret S Ebert, Joel R Neilson & Phillip A Sharp Supplementary figures and text: Supplementary Figure 1. Effect of sponges on
Cell Culture. The human thyroid follicular carcinoma cell lines FTC-238, FTC-236 and FTC-
 Supplemental material and methods Reagents. Hydralazine was purchased from Sigma-Aldrich. Cell Culture. The human thyroid follicular carcinoma cell lines FTC-238, FTC-236 and FTC- 133, human thyroid medullary
Supplemental material and methods Reagents. Hydralazine was purchased from Sigma-Aldrich. Cell Culture. The human thyroid follicular carcinoma cell lines FTC-238, FTC-236 and FTC- 133, human thyroid medullary
Functional characterisation of hepatitis B viral X protein/microrna-21 interaction in HBVassociated hepatocellular carcinoma
 RESEARCH FUND FOR THE CONTROL OF INFECTIOUS DISEASES Functional characterisation of hepatitis B viral X protein/microrna-21 interaction in HBVassociated hepatocellular carcinoma CH Li, SC Chow, DL Yin,
RESEARCH FUND FOR THE CONTROL OF INFECTIOUS DISEASES Functional characterisation of hepatitis B viral X protein/microrna-21 interaction in HBVassociated hepatocellular carcinoma CH Li, SC Chow, DL Yin,
Review Article Effect of mir-200b on metastasis of gastric cancer
 Am J Digest Dis 2017;4(1):1-5 www.ajdd.us /ISSN:2329-6992/AJDD0040112 Review Article Effect of mir-200b on metastasis of gastric cancer Leyu Chiu 1, Brock Humphries 2,3 1 College of Human Medicine, 2 Department
Am J Digest Dis 2017;4(1):1-5 www.ajdd.us /ISSN:2329-6992/AJDD0040112 Review Article Effect of mir-200b on metastasis of gastric cancer Leyu Chiu 1, Brock Humphries 2,3 1 College of Human Medicine, 2 Department
An epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition-inducing potential of. granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor in colon. cancer
 An epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition-inducing potential of granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor in colon cancer Yaqiong Chen, Zhi Zhao, Yu Chen, Zhonglin Lv, Xin Ding, Renxi Wang, He Xiao,
An epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition-inducing potential of granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor in colon cancer Yaqiong Chen, Zhi Zhao, Yu Chen, Zhonglin Lv, Xin Ding, Renxi Wang, He Xiao,
Supplementary Figure 1. The CagA-dependent wound healing or transwell migration of gastric cancer cell. AGS cells transfected with vector control or
 Supplementary Figure 1. The CagA-dependent wound healing or transwell migration of gastric cancer cell. AGS cells transfected with vector control or 3xflag-CagA expression vector were wounded using a pipette
Supplementary Figure 1. The CagA-dependent wound healing or transwell migration of gastric cancer cell. AGS cells transfected with vector control or 3xflag-CagA expression vector were wounded using a pipette
Supplementary Figures
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Confirmation of Dnmt1 conditional knockout out mice. a, Representative images of sorted stem (Lin - CD49f high CD24 + ), luminal (Lin - CD49f low CD24 + )
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Confirmation of Dnmt1 conditional knockout out mice. a, Representative images of sorted stem (Lin - CD49f high CD24 + ), luminal (Lin - CD49f low CD24 + )
Analysis of small RNAs from Drosophila Schneider cells using the Small RNA assay on the Agilent 2100 bioanalyzer. Application Note
 Analysis of small RNAs from Drosophila Schneider cells using the Small RNA assay on the Agilent 2100 bioanalyzer Application Note Odile Sismeiro, Jean-Yves Coppée, Christophe Antoniewski, and Hélène Thomassin
Analysis of small RNAs from Drosophila Schneider cells using the Small RNA assay on the Agilent 2100 bioanalyzer Application Note Odile Sismeiro, Jean-Yves Coppée, Christophe Antoniewski, and Hélène Thomassin
RALYL Hypermethylation: A Potential Diagnostic Marker of Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma (ESCC) Junwei Liu, MD
 RALYL Hypermethylation: A Potential Diagnostic Marker of Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma (ESCC) Junwei Liu, MD Aurora Healthcare, Milwaukee, WI INTRODUCTION v Epigenetic aberration and genetic alteration
RALYL Hypermethylation: A Potential Diagnostic Marker of Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma (ESCC) Junwei Liu, MD Aurora Healthcare, Milwaukee, WI INTRODUCTION v Epigenetic aberration and genetic alteration
Title page. Title: MicroRNA-155 Controls Exosome Synthesis and Promotes Gemcitabine Resistance in
 Title page Title: MicroRNA- Controls Synthesis and Promotes Gemcitabine Resistance in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma Authors Manabu Mikamori, Daisaku Yamada, Hidetoshi Eguchi, Shinichiro Hasegawa, Tomoya
Title page Title: MicroRNA- Controls Synthesis and Promotes Gemcitabine Resistance in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma Authors Manabu Mikamori, Daisaku Yamada, Hidetoshi Eguchi, Shinichiro Hasegawa, Tomoya
Supplementary webappendix
 Supplementary webappendix This webappendix formed part of the original submission and has been peer reviewed. We post it as supplied by the authors. Supplement to: Ueda T, Volinia S, Okumura H, et al.
Supplementary webappendix This webappendix formed part of the original submission and has been peer reviewed. We post it as supplied by the authors. Supplement to: Ueda T, Volinia S, Okumura H, et al.
BIT 120. Copy of Cancer/HIV Lecture
 BIT 120 Copy of Cancer/HIV Lecture Cancer DEFINITION Any abnormal growth of cells that has malignant potential i.e.. Leukemia Uncontrolled mitosis in WBC Genetic disease caused by an accumulation of mutations
BIT 120 Copy of Cancer/HIV Lecture Cancer DEFINITION Any abnormal growth of cells that has malignant potential i.e.. Leukemia Uncontrolled mitosis in WBC Genetic disease caused by an accumulation of mutations
Epstein-Barr Virus BART MicroRNAs Are Produced from a Large Intron prior to Splicing
 JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, Sept. 2008, p. 9094 9106 Vol. 82, No. 18 0022-538X/08/$08.00 0 doi:10.1128/jvi.00785-08 Copyright 2008, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Epstein-Barr Virus BART
JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, Sept. 2008, p. 9094 9106 Vol. 82, No. 18 0022-538X/08/$08.00 0 doi:10.1128/jvi.00785-08 Copyright 2008, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Epstein-Barr Virus BART
Serum mir-200c expression level as a prognostic biomarker for gastric cancer
 Serum mir-200c expression level as a prognostic biomarker for gastric cancer H.-P. Zhang 1 *, F.-B. Sun 2 * and S.-J. Li 2 1 Department of Gastrointestinal Surgery, Yantai Yuhuangding Hospital, Yantai,
Serum mir-200c expression level as a prognostic biomarker for gastric cancer H.-P. Zhang 1 *, F.-B. Sun 2 * and S.-J. Li 2 1 Department of Gastrointestinal Surgery, Yantai Yuhuangding Hospital, Yantai,
Study on the expression of MMP-9 and NF-κB proteins in epithelial ovarian cancer tissue and their clinical value
 Study on the expression of MMP-9 and NF-κB proteins in epithelial ovarian cancer tissue and their clinical value Shen Wei 1,a, Chen Juan 2, Li Xiurong 1 and Yin Jie 1 1 Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology,
Study on the expression of MMP-9 and NF-κB proteins in epithelial ovarian cancer tissue and their clinical value Shen Wei 1,a, Chen Juan 2, Li Xiurong 1 and Yin Jie 1 1 Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology,
Lack of Association between EBV and Breast Carcinoma
 Lack of Association between EBV and Breast Carcinoma Cancer Epidemiology, Biomarkers & Prevention 809 Jacqueline G. Perrigoue, 1 Johan A. den Boon, 1,4 Andreas Friedl, 2 Michael A. Newton, 3 Paul Ahlquist,
Lack of Association between EBV and Breast Carcinoma Cancer Epidemiology, Biomarkers & Prevention 809 Jacqueline G. Perrigoue, 1 Johan A. den Boon, 1,4 Andreas Friedl, 2 Michael A. Newton, 3 Paul Ahlquist,
Lymphoepithelioma-like carcinoma of the stomach: a case report and review of the literature
 Bittar et al. Diagnostic Pathology 2013, 8:184 CASE REPORT Open Access Lymphoepithelioma-like carcinoma of the stomach: a case report and review of the literature Zeid Bittar *, Falko Fend and Leticia
Bittar et al. Diagnostic Pathology 2013, 8:184 CASE REPORT Open Access Lymphoepithelioma-like carcinoma of the stomach: a case report and review of the literature Zeid Bittar *, Falko Fend and Leticia
Supplementary Figures
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1 DOT1L regulates the expression of epithelial and mesenchymal markers. (a) The expression levels and cellular localizations of EMT markers were confirmed by
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1 DOT1L regulates the expression of epithelial and mesenchymal markers. (a) The expression levels and cellular localizations of EMT markers were confirmed by
Roles of transcriptional factor Snail and adhesion factor E-cadherin in clear cell renal cell carcinoma
 EXPERIMENTAL AND THERAPEUTIC MEDICINE 6: 1489-1493, 2013 Roles of transcriptional factor Snail and adhesion factor E-cadherin in clear cell renal cell carcinoma JINQUAN CAI Department of Urology, Fuzhou
EXPERIMENTAL AND THERAPEUTIC MEDICINE 6: 1489-1493, 2013 Roles of transcriptional factor Snail and adhesion factor E-cadherin in clear cell renal cell carcinoma JINQUAN CAI Department of Urology, Fuzhou
Serum Amyloid A3 Gene Expression in Adipocytes is an Indicator. of the Interaction with Macrophages
 Serum Amyloid A3 Gene Expression in Adipocytes is an Indicator of the Interaction with Macrophages Yohei Sanada, Takafumi Yamamoto, Rika Satake, Akiko Yamashita, Sumire Kanai, Norihisa Kato, Fons AJ van
Serum Amyloid A3 Gene Expression in Adipocytes is an Indicator of the Interaction with Macrophages Yohei Sanada, Takafumi Yamamoto, Rika Satake, Akiko Yamashita, Sumire Kanai, Norihisa Kato, Fons AJ van
mir-206 Expression Is Down-regulated in Estrogen Receptor A Positive Human Breast Cancer
 Priority Report mir-206 Expression Is Down-regulated in Estrogen Receptor A Positive Human Breast Cancer Naoto Kondo, Tatsuya Toyama, Hiroshi Sugiura, Yoshitaka Fujii, and Hiroko Yamashita Oncology, Immunology,
Priority Report mir-206 Expression Is Down-regulated in Estrogen Receptor A Positive Human Breast Cancer Naoto Kondo, Tatsuya Toyama, Hiroshi Sugiura, Yoshitaka Fujii, and Hiroko Yamashita Oncology, Immunology,
Purification and Fluorescent Labeling of Exosomes Asuka Nanbo 1*, Eri Kawanishi 2, Ryuji Yoshida 2 and Hironori Yoshiyama 3
 Purification and Fluorescent Labeling of Exosomes Asuka Nanbo 1*, Eri Kawanishi 2, Ryuji Yoshida 2 and Hironori Yoshiyama 3 1 Graduate School of Medicine, Hokkaido University, Sapporo, Japan; 2 Graduate
Purification and Fluorescent Labeling of Exosomes Asuka Nanbo 1*, Eri Kawanishi 2, Ryuji Yoshida 2 and Hironori Yoshiyama 3 1 Graduate School of Medicine, Hokkaido University, Sapporo, Japan; 2 Graduate
Product Datasheet. ZEB1 Antibody NBP Unit Size: 0.1 ml. Store at 4C. Do not freeze. Reviews: 6 Publications: 32
 Product Datasheet ZEB1 Antibody NBP1-05987 Unit Size: 0.1 ml Store at 4C. Do not freeze. Reviews: 6 Publications: 32 Protocols, Publications, Related Products, Reviews, Research Tools and Images at: www.novusbio.com/nbp1-05987
Product Datasheet ZEB1 Antibody NBP1-05987 Unit Size: 0.1 ml Store at 4C. Do not freeze. Reviews: 6 Publications: 32 Protocols, Publications, Related Products, Reviews, Research Tools and Images at: www.novusbio.com/nbp1-05987
Synchronous squamous cell carcinoma of the breast. and invasive lobular carcinoma
 Sentani K et al. 1 Letter to the editor Synchronous squamous cell carcinoma of the breast and invasive lobular carcinoma Kazuhiro Sentani, 1 Takashi Tashiro, 2 Naohide Oue, 1 Wataru Yasui 1 1 Department
Sentani K et al. 1 Letter to the editor Synchronous squamous cell carcinoma of the breast and invasive lobular carcinoma Kazuhiro Sentani, 1 Takashi Tashiro, 2 Naohide Oue, 1 Wataru Yasui 1 1 Department
Construction of a hepatocellular carcinoma cell line that stably expresses stathmin with a Ser25 phosphorylation site mutation
 Construction of a hepatocellular carcinoma cell line that stably expresses stathmin with a Ser25 phosphorylation site mutation J. Du 1, Z.H. Tao 2, J. Li 2, Y.K. Liu 3 and L. Gan 2 1 Department of Chemistry,
Construction of a hepatocellular carcinoma cell line that stably expresses stathmin with a Ser25 phosphorylation site mutation J. Du 1, Z.H. Tao 2, J. Li 2, Y.K. Liu 3 and L. Gan 2 1 Department of Chemistry,
Type of file: PDF Size of file: 0 KB Title of file for HTML: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures
 Type of file: PDF Size of file: 0 KB Title of file for HTML: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1 mir-128-3p is highly expressed in chemoresistant, metastatic
Type of file: PDF Size of file: 0 KB Title of file for HTML: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1 mir-128-3p is highly expressed in chemoresistant, metastatic
(a) Significant biological processes (upper panel) and disease biomarkers (lower panel)
 Supplementary Figure 1. Functional enrichment analyses of secretomic proteins. (a) Significant biological processes (upper panel) and disease biomarkers (lower panel) 2 involved by hrab37-mediated secretory
Supplementary Figure 1. Functional enrichment analyses of secretomic proteins. (a) Significant biological processes (upper panel) and disease biomarkers (lower panel) 2 involved by hrab37-mediated secretory
Herpesviruses. Virion. Genome. Genes and proteins. Viruses and hosts. Diseases. Distinctive characteristics
 Herpesviruses Virion Genome Genes and proteins Viruses and hosts Diseases Distinctive characteristics Virion Enveloped icosahedral capsid (T=16), diameter 125 nm Diameter of enveloped virion 200 nm Capsid
Herpesviruses Virion Genome Genes and proteins Viruses and hosts Diseases Distinctive characteristics Virion Enveloped icosahedral capsid (T=16), diameter 125 nm Diameter of enveloped virion 200 nm Capsid
Regulation of Gene Expression in Eukaryotes
 Ch. 19 Regulation of Gene Expression in Eukaryotes BIOL 222 Differential Gene Expression in Eukaryotes Signal Cells in a multicellular eukaryotic organism genetically identical differential gene expression
Ch. 19 Regulation of Gene Expression in Eukaryotes BIOL 222 Differential Gene Expression in Eukaryotes Signal Cells in a multicellular eukaryotic organism genetically identical differential gene expression
An Epstein-Barr virus-encoded microrna targets PUMA to promote host cell survival
 An Epstein-Barr virus-encoded microrna targets to promote host cell survival The Journal of Experimental Medicine 205(11): 2551-2560, 2008. 1 Elizabeth Yee-Wai Choy, Kam-Leung Siu, Kin-Hang Kok, Raymond
An Epstein-Barr virus-encoded microrna targets to promote host cell survival The Journal of Experimental Medicine 205(11): 2551-2560, 2008. 1 Elizabeth Yee-Wai Choy, Kam-Leung Siu, Kin-Hang Kok, Raymond
Ch. 18 Regulation of Gene Expression
 Ch. 18 Regulation of Gene Expression 1 Human genome has around 23,688 genes (Scientific American 2/2006) Essential Questions: How is transcription regulated? How are genes expressed? 2 Bacteria regulate
Ch. 18 Regulation of Gene Expression 1 Human genome has around 23,688 genes (Scientific American 2/2006) Essential Questions: How is transcription regulated? How are genes expressed? 2 Bacteria regulate
Expression of ERas Oncogene in Gastric Carcinoma
 Expression of ERas Oncogene in Gastric Carcinoma RYOJI KAIZAKI 1, MASAKAZU YASHIRO 1,2, OSAMU SHINTO 1, KOICHI YASUDA 1, TARO MATSUZAKI 1, TETSUJI SAWADA 1 and KOSEI HIRAKAWA 1 1 Department of Surgical
Expression of ERas Oncogene in Gastric Carcinoma RYOJI KAIZAKI 1, MASAKAZU YASHIRO 1,2, OSAMU SHINTO 1, KOICHI YASUDA 1, TARO MATSUZAKI 1, TETSUJI SAWADA 1 and KOSEI HIRAKAWA 1 1 Department of Surgical
High expression of fibroblast activation protein is an adverse prognosticator in gastric cancer.
 Biomedical Research 2017; 28 (18): 7779-7783 ISSN 0970-938X www.biomedres.info High expression of fibroblast activation protein is an adverse prognosticator in gastric cancer. Hu Song 1, Qi-yu Liu 2, Zhi-wei
Biomedical Research 2017; 28 (18): 7779-7783 ISSN 0970-938X www.biomedres.info High expression of fibroblast activation protein is an adverse prognosticator in gastric cancer. Hu Song 1, Qi-yu Liu 2, Zhi-wei
MicroRNA and Male Infertility: A Potential for Diagnosis
 Review Article MicroRNA and Male Infertility: A Potential for Diagnosis * Abstract MicroRNAs (mirnas) are small non-coding single stranded RNA molecules that are physiologically produced in eukaryotic
Review Article MicroRNA and Male Infertility: A Potential for Diagnosis * Abstract MicroRNAs (mirnas) are small non-coding single stranded RNA molecules that are physiologically produced in eukaryotic
Supplementary Figure S1 Expression of mir-181b in EOC (A) Kaplan-Meier
 Supplementary Figure S1 Expression of mir-181b in EOC (A) Kaplan-Meier curves for progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) in a cohort of patients (N=52) with stage III primary ovarian
Supplementary Figure S1 Expression of mir-181b in EOC (A) Kaplan-Meier curves for progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) in a cohort of patients (N=52) with stage III primary ovarian
Update on Epstein-Barr virus and gastric cancer (Review)
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ONCOLOGY 46: 1421-1434, 2015 Update on Epstein-Barr virus and gastric cancer (Review) Aya Shinozaki-Ushiku, Akiko Kunita and Masashi Fukayama Department of Pathology, Graduate
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ONCOLOGY 46: 1421-1434, 2015 Update on Epstein-Barr virus and gastric cancer (Review) Aya Shinozaki-Ushiku, Akiko Kunita and Masashi Fukayama Department of Pathology, Graduate
Characterization and significance of MUC1 and c-myc expression in elderly patients with papillary thyroid carcinoma
 Characterization and significance of MUC1 and c-myc expression in elderly patients with papillary thyroid carcinoma Y.-J. Hu 1, X.-Y. Luo 2, Y. Yang 3, C.-Y. Chen 1, Z.-Y. Zhang 4 and X. Guo 1 1 Department
Characterization and significance of MUC1 and c-myc expression in elderly patients with papillary thyroid carcinoma Y.-J. Hu 1, X.-Y. Luo 2, Y. Yang 3, C.-Y. Chen 1, Z.-Y. Zhang 4 and X. Guo 1 1 Department
Supplementary Figure S1. Venn diagram analysis of mrna microarray data and mirna target analysis. (a) Western blot analysis of T lymphoblasts (CLS)
 Supplementary Figure S1. Venn diagram analysis of mrna microarray data and mirna target analysis. (a) Western blot analysis of T lymphoblasts (CLS) and their exosomes (EXO) in resting (REST) and activated
Supplementary Figure S1. Venn diagram analysis of mrna microarray data and mirna target analysis. (a) Western blot analysis of T lymphoblasts (CLS) and their exosomes (EXO) in resting (REST) and activated
DOCTORAL THESIS SUMMARY
 UNIVERSITY OF MEDICINE AND PHARMACY CRAIOVA DOCTORAL THESIS HISTOPATHOLOGICAL AND IMMUNOHISTOCHEMICAL STUDY OF GASTRIC CARCINOMAS SUMMARY Scientific Coordinator: Univ. Prof. Dr. SIMIONESCU CRISTIANA EUGENIA
UNIVERSITY OF MEDICINE AND PHARMACY CRAIOVA DOCTORAL THESIS HISTOPATHOLOGICAL AND IMMUNOHISTOCHEMICAL STUDY OF GASTRIC CARCINOMAS SUMMARY Scientific Coordinator: Univ. Prof. Dr. SIMIONESCU CRISTIANA EUGENIA
Research Article Stromal Expression of CD10 in Invasive Breast Carcinoma and Its Correlation with ER, PR, HER2-neu, and Ki67
 SAGE-Hindawi Access to Research International Breast Cancer Volume 20, Article ID 47957, 4 pages doi:0.406/20/47957 Research Article Stromal Expression of CD0 in Invasive Breast Carcinoma and Its Correlation
SAGE-Hindawi Access to Research International Breast Cancer Volume 20, Article ID 47957, 4 pages doi:0.406/20/47957 Research Article Stromal Expression of CD0 in Invasive Breast Carcinoma and Its Correlation
(a) Schematic diagram of the FS mutation of UVRAG in exon 8 containing the highly instable
 Supplementary Figure 1. Frameshift (FS) mutation in UVRAG. (a) Schematic diagram of the FS mutation of UVRAG in exon 8 containing the highly instable A 10 DNA repeat, generating a premature stop codon
Supplementary Figure 1. Frameshift (FS) mutation in UVRAG. (a) Schematic diagram of the FS mutation of UVRAG in exon 8 containing the highly instable A 10 DNA repeat, generating a premature stop codon
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Asymmetrical function of 5p and 3p arms of mir-181 and mir-30 families and mir-142 and mir-154. (a) Control experiments using mirna sensor vector and empty pri-mirna overexpression
Supplementary Figure 1 Asymmetrical function of 5p and 3p arms of mir-181 and mir-30 families and mir-142 and mir-154. (a) Control experiments using mirna sensor vector and empty pri-mirna overexpression
Soft Agar Assay. For each cell pool, 100,000 cells were resuspended in 0.35% (w/v)
 SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL AND METHODS Soft Agar Assay. For each cell pool, 100,000 cells were resuspended in 0.35% (w/v) top agar (LONZA, SeaKem LE Agarose cat.5004) and plated onto 0.5% (w/v) basal agar.
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL AND METHODS Soft Agar Assay. For each cell pool, 100,000 cells were resuspended in 0.35% (w/v) top agar (LONZA, SeaKem LE Agarose cat.5004) and plated onto 0.5% (w/v) basal agar.
Applications of IHC. Determination of the primary site in metastatic tumors of unknown origin
 Applications of IHC Determination of the primary site in metastatic tumors of unknown origin Classification of tumors that appear 'undifferentiated' by standard light microscopy Precise classification
Applications of IHC Determination of the primary site in metastatic tumors of unknown origin Classification of tumors that appear 'undifferentiated' by standard light microscopy Precise classification
TITLE: The Role of hcdc4 as a Tumor Suppressor Gene in Genomic Instability Underlying Prostate Cancer
 AD Award Number: TITLE: The Role of hcdc4 as a Tumor Suppressor Gene in Genomic Instability Underlying Prostate Cancer PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Audrey van Drogen, Ph.D. CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: Sidney
AD Award Number: TITLE: The Role of hcdc4 as a Tumor Suppressor Gene in Genomic Instability Underlying Prostate Cancer PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Audrey van Drogen, Ph.D. CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: Sidney
PD-L1 Analyte Control DR
 Quality in Control PD-L1 Analyte Control DR PD-L1_PI_v2 Product Codes: HCL019, HCL020 and HCL021 Contents PD-L1 Analyte Control DR 2 What is PD-L1? 3 The Role of PD-L1 in Cancer 3 PD-L1 Assessment 4 PD-L1
Quality in Control PD-L1 Analyte Control DR PD-L1_PI_v2 Product Codes: HCL019, HCL020 and HCL021 Contents PD-L1 Analyte Control DR 2 What is PD-L1? 3 The Role of PD-L1 in Cancer 3 PD-L1 Assessment 4 PD-L1
Dr. dr. Primariadewi R, SpPA(K)
 Curriculum Vitae Dr. dr. Primariadewi R, SpPA(K) Education : Medical Doctor from UKRIDA Doctoral Degree from Faculty of Medicine University of Indonesia Pathologist Specialist and Consultant from Faculty
Curriculum Vitae Dr. dr. Primariadewi R, SpPA(K) Education : Medical Doctor from UKRIDA Doctoral Degree from Faculty of Medicine University of Indonesia Pathologist Specialist and Consultant from Faculty
RCD24, B7-H4 and PCNA expression and clinical significance in ovarian cancer
 JBUON 2019; 24(2): 715-719 ISSN: 1107-0625, online ISSN: 2241-6293 www.jbuon.com E-mail: editorial_office@jbuon.com ORIGINAL ARTICLE RCD24, B7-H4 and PCNA expression and clinical significance in ovarian
JBUON 2019; 24(2): 715-719 ISSN: 1107-0625, online ISSN: 2241-6293 www.jbuon.com E-mail: editorial_office@jbuon.com ORIGINAL ARTICLE RCD24, B7-H4 and PCNA expression and clinical significance in ovarian
Original Article CREPT expression correlates with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma histological grade and clinical outcome
 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2017;10(2):2030-2035 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0009456 Original Article CREPT expression correlates with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma histological grade and clinical
Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2017;10(2):2030-2035 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0009456 Original Article CREPT expression correlates with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma histological grade and clinical
Does EMT Contribute to Radiation Resistance in Human Breast Cancer?
 AD Award Number: W81XWH-10-1-0592 TITLE: Does EMT Contribute to Radiation Resistance in Human Breast Cancer? PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Anupama Munshi, Ph.D CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: University of Oklahoma
AD Award Number: W81XWH-10-1-0592 TITLE: Does EMT Contribute to Radiation Resistance in Human Breast Cancer? PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Anupama Munshi, Ph.D CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: University of Oklahoma
Citation Acta Medica Nagasakiensia. 1992, 37
 NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) A Study on the Expression of EGFR a Content in the Stomach Cancer Tissu Nakazaki Takayuki Citation Acta Medica Nagasakiensia. 1992 37 Issue Date 1992-12-25
NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) A Study on the Expression of EGFR a Content in the Stomach Cancer Tissu Nakazaki Takayuki Citation Acta Medica Nagasakiensia. 1992 37 Issue Date 1992-12-25
Expression and clinical significance of ADAM17 protein in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
 Expression and clinical significance of ADAM17 protein in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma H.B. Liu, Y. Zhu, Q.C. Yang, Y. Shen, X.J. Zhang and H. Chen Department of Pathology First People s Hospital
Expression and clinical significance of ADAM17 protein in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma H.B. Liu, Y. Zhu, Q.C. Yang, Y. Shen, X.J. Zhang and H. Chen Department of Pathology First People s Hospital
supplementary information
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb1875 Figure S1 (a) The 79 surgical specimens from NSCLC patients were analysed by immunohistochemistry with an anti-p53 antibody and control serum (data not shown). The normal bronchi served
DOI: 10.1038/ncb1875 Figure S1 (a) The 79 surgical specimens from NSCLC patients were analysed by immunohistochemistry with an anti-p53 antibody and control serum (data not shown). The normal bronchi served
Supplementary data Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 2
 Supplementary data Supplementary Figure 1 SPHK1 sirna increases RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis in RAW264.7 cell culture. (A) RAW264.7 cells were transfected with oligocassettes containing SPHK1 sirna
Supplementary data Supplementary Figure 1 SPHK1 sirna increases RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis in RAW264.7 cell culture. (A) RAW264.7 cells were transfected with oligocassettes containing SPHK1 sirna
Evaluation of altered expression of mir-9 and mir-106a as an early diagnostic approach in gastric cancer
 Original Article Evaluation of altered expression of mir-9 and mir-106a as an early diagnostic approach in gastric cancer Khadije Shirmohammadi, Sareh Sohrabi, Zahra Jafarzadeh Samani, Hosein Effatpanah,
Original Article Evaluation of altered expression of mir-9 and mir-106a as an early diagnostic approach in gastric cancer Khadije Shirmohammadi, Sareh Sohrabi, Zahra Jafarzadeh Samani, Hosein Effatpanah,
Hepatitis B virus X gene in the development of hepatocellular carcinoma. Citation Hong Kong Medical Journal, 2011, v. 17 n. 6, suppl. 6, p.
 Title Hepatitis B virus X gene in the development of hepatocellular carcinoma Author(s) Ma, NF; Lau, SH; Hu, L; Dong, SS; Guan, XY Citation Hong Kong Medical Journal, 2011, v. 17 n. 6, suppl. 6, p. 44-47
Title Hepatitis B virus X gene in the development of hepatocellular carcinoma Author(s) Ma, NF; Lau, SH; Hu, L; Dong, SS; Guan, XY Citation Hong Kong Medical Journal, 2011, v. 17 n. 6, suppl. 6, p. 44-47
Epstein-Barr Virus: Stimulation By 5 '-Iododeoxy uridine or 5 '-Brom odeoxy uridine in Human Lymphoblastoid Cells F ro m a Rhabdom yosarcom a*
 A n n a ls o f C l i n i c a l L a b o r a t o r y S c i e n c e, Vol. 3, No. 6 Copyright 1973, Institute for Clinical Science Epstein-Barr Virus: Stimulation By 5 '-Iododeoxy uridine or 5 '-Brom odeoxy
A n n a ls o f C l i n i c a l L a b o r a t o r y S c i e n c e, Vol. 3, No. 6 Copyright 1973, Institute for Clinical Science Epstein-Barr Virus: Stimulation By 5 '-Iododeoxy uridine or 5 '-Brom odeoxy
Detection of Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase (ALK) gene in Non-Small Cell lung Cancer (NSCLC) By CISH Technique
 Cancer and Clinical Oncology; Vol. 7, No. 1; 2018 ISSN 1927-4858 E-ISSN 1927-4866 Published by Canadian Center of Science and Education Detection of Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase (ALK) gene in Non-Small Cell
Cancer and Clinical Oncology; Vol. 7, No. 1; 2018 ISSN 1927-4858 E-ISSN 1927-4866 Published by Canadian Center of Science and Education Detection of Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase (ALK) gene in Non-Small Cell
Online Data Supplement. Anti-aging Gene Klotho Enhances Glucose-induced Insulin Secretion by Upregulating Plasma Membrane Retention of TRPV2
 Online Data Supplement Anti-aging Gene Klotho Enhances Glucose-induced Insulin Secretion by Upregulating Plasma Membrane Retention of TRPV2 Yi Lin and Zhongjie Sun Department of physiology, college of
Online Data Supplement Anti-aging Gene Klotho Enhances Glucose-induced Insulin Secretion by Upregulating Plasma Membrane Retention of TRPV2 Yi Lin and Zhongjie Sun Department of physiology, college of
mir-218 tissue expression level is associated with aggressive progression of gastric cancer
 mir-218 tissue expression level is associated with aggressive progression of gastric cancer X.X. Wang 1, S.J. Ge 2, X.L. Wang 2, L.X. Jiang 1, M.F. Sheng 2 and J.J. Ma 2 1 Department of General Surgery,
mir-218 tissue expression level is associated with aggressive progression of gastric cancer X.X. Wang 1, S.J. Ge 2, X.L. Wang 2, L.X. Jiang 1, M.F. Sheng 2 and J.J. Ma 2 1 Department of General Surgery,
Low levels of serum mir-99a is a predictor of poor prognosis in breast cancer
 Low levels of serum mir-99a is a predictor of poor prognosis in breast cancer J. Li 1, Z.J. Song 2, Y.Y. Wang 1, Y. Yin 1, Y. Liu 1 and X. Nan 1 1 Tumor Research Department, Shaanxi Provincial Tumor Hospital,
Low levels of serum mir-99a is a predictor of poor prognosis in breast cancer J. Li 1, Z.J. Song 2, Y.Y. Wang 1, Y. Yin 1, Y. Liu 1 and X. Nan 1 1 Tumor Research Department, Shaanxi Provincial Tumor Hospital,
Acta Medica Okayama AUGUST A spectrum of clinical manifestations caused by host immune responses against Epstein-Barr virus infections.
 Acta Medica Okayama Volume 58, Issue 4 2004 Article 1 AUGUST 2004 A spectrum of clinical manifestations caused by host immune responses against Epstein-Barr virus infections. Keiji Iwatsuki Takenobu Yamamoto
Acta Medica Okayama Volume 58, Issue 4 2004 Article 1 AUGUST 2004 A spectrum of clinical manifestations caused by host immune responses against Epstein-Barr virus infections. Keiji Iwatsuki Takenobu Yamamoto
Oncolytic Adenovirus Complexes Coated with Lipids and Calcium Phosphate for Cancer Gene Therapy
 Oncolytic Adenovirus Complexes Coated with Lipids and Calcium Phosphate for Cancer Gene Therapy Jianhua Chen, Pei Gao, Sujing Yuan, Rongxin Li, Aimin Ni, Liang Chu, Li Ding, Ying Sun, Xin-Yuan Liu, Yourong
Oncolytic Adenovirus Complexes Coated with Lipids and Calcium Phosphate for Cancer Gene Therapy Jianhua Chen, Pei Gao, Sujing Yuan, Rongxin Li, Aimin Ni, Liang Chu, Li Ding, Ying Sun, Xin-Yuan Liu, Yourong
MicroRNA expression profiling and functional analysis in prostate cancer. Marco Folini s.c. Ricerca Traslazionale DOSL
 MicroRNA expression profiling and functional analysis in prostate cancer Marco Folini s.c. Ricerca Traslazionale DOSL What are micrornas? For almost three decades, the alteration of protein-coding genes
MicroRNA expression profiling and functional analysis in prostate cancer Marco Folini s.c. Ricerca Traslazionale DOSL What are micrornas? For almost three decades, the alteration of protein-coding genes
VIRUSES AND CANCER Michael Lea
 VIRUSES AND CANCER 2010 Michael Lea VIRAL ONCOLOGY - LECTURE OUTLINE 1. Historical Review 2. Viruses Associated with Cancer 3. RNA Tumor Viruses 4. DNA Tumor Viruses HISTORICAL REVIEW Historical Review
VIRUSES AND CANCER 2010 Michael Lea VIRAL ONCOLOGY - LECTURE OUTLINE 1. Historical Review 2. Viruses Associated with Cancer 3. RNA Tumor Viruses 4. DNA Tumor Viruses HISTORICAL REVIEW Historical Review
MicroRNA in Cancer Karen Dybkær 2013
 MicroRNA in Cancer Karen Dybkær RNA Ribonucleic acid Types -Coding: messenger RNA (mrna) coding for proteins -Non-coding regulating protein formation Ribosomal RNA (rrna) Transfer RNA (trna) Small nuclear
MicroRNA in Cancer Karen Dybkær RNA Ribonucleic acid Types -Coding: messenger RNA (mrna) coding for proteins -Non-coding regulating protein formation Ribosomal RNA (rrna) Transfer RNA (trna) Small nuclear
Original Article High serum mir-203 predicts the poor prognosis in patients with pancreatic cancer
 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2017;10(4):4688-4693 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0047128 Original Article High serum mir-203 predicts the poor prognosis in patients with pancreatic cancer Jun Ma, Xiaokun
Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2017;10(4):4688-4693 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0047128 Original Article High serum mir-203 predicts the poor prognosis in patients with pancreatic cancer Jun Ma, Xiaokun
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/7/310/ra11/dc1 Supplementary Materials for STAT3 Induction of mir-146b Forms a Feedback Loop to Inhibit the NF-κB to IL-6 Signaling Axis and STAT3-Driven Cancer
www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/7/310/ra11/dc1 Supplementary Materials for STAT3 Induction of mir-146b Forms a Feedback Loop to Inhibit the NF-κB to IL-6 Signaling Axis and STAT3-Driven Cancer
Corporate Medical Policy
 Corporate Medical Policy Microarray-based Gene Expression Testing for Cancers of Unknown File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: microarray-based_gene_expression_testing_for_cancers_of_unknown_primary
Corporate Medical Policy Microarray-based Gene Expression Testing for Cancers of Unknown File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: microarray-based_gene_expression_testing_for_cancers_of_unknown_primary
Cellular Physiology and Biochemistry
 Original Paper 2015 The Author(s). 2015 Published The Author(s) by S. Karger AG, Basel Published online: November 27, 2015 www.karger.com/cpb Published by S. Karger AG, Basel 2194 1421-9778/15/0376-2194$39.50/0
Original Paper 2015 The Author(s). 2015 Published The Author(s) by S. Karger AG, Basel Published online: November 27, 2015 www.karger.com/cpb Published by S. Karger AG, Basel 2194 1421-9778/15/0376-2194$39.50/0
Patnaik SK, et al. MicroRNAs to accurately histotype NSCLC biopsies
 Patnaik SK, et al. MicroRNAs to accurately histotype NSCLC biopsies. 2014. Supplemental Digital Content 1. Appendix 1. External data-sets used for associating microrna expression with lung squamous cell
Patnaik SK, et al. MicroRNAs to accurately histotype NSCLC biopsies. 2014. Supplemental Digital Content 1. Appendix 1. External data-sets used for associating microrna expression with lung squamous cell
MEDICAL POLICY Gene Expression Profiling for Cancers of Unknown Primary Site
 POLICY: PG0364 ORIGINAL EFFECTIVE: 04/22/16 LAST REVIEW: 07/26/18 MEDICAL POLICY Gene Expression Profiling for Cancers of Unknown Primary Site GUIDELINES This policy does not certify benefits or authorization
POLICY: PG0364 ORIGINAL EFFECTIVE: 04/22/16 LAST REVIEW: 07/26/18 MEDICAL POLICY Gene Expression Profiling for Cancers of Unknown Primary Site GUIDELINES This policy does not certify benefits or authorization
Supplementary information
 Supplementary information Human Cytomegalovirus MicroRNA mir-us4-1 Inhibits CD8 + T Cell Response by Targeting ERAP1 Sungchul Kim, Sanghyun Lee, Jinwook Shin, Youngkyun Kim, Irini Evnouchidou, Donghyun
Supplementary information Human Cytomegalovirus MicroRNA mir-us4-1 Inhibits CD8 + T Cell Response by Targeting ERAP1 Sungchul Kim, Sanghyun Lee, Jinwook Shin, Youngkyun Kim, Irini Evnouchidou, Donghyun
microrna-200b and microrna-200c promote colorectal cancer cell proliferation via
 Supplementary Materials microrna-200b and microrna-200c promote colorectal cancer cell proliferation via targeting the reversion-inducing cysteine-rich protein with Kazal motifs Supplementary Table 1.
Supplementary Materials microrna-200b and microrna-200c promote colorectal cancer cell proliferation via targeting the reversion-inducing cysteine-rich protein with Kazal motifs Supplementary Table 1.
Supplementary Figure 1.TRIM33 binds β-catenin in the nucleus. a & b, Co-IP of endogenous TRIM33 with β-catenin in HT-29 cells (a) and HEK 293T cells
 Supplementary Figure 1.TRIM33 binds β-catenin in the nucleus. a & b, Co-IP of endogenous TRIM33 with β-catenin in HT-29 cells (a) and HEK 293T cells (b). TRIM33 was immunoprecipitated, and the amount of
Supplementary Figure 1.TRIM33 binds β-catenin in the nucleus. a & b, Co-IP of endogenous TRIM33 with β-catenin in HT-29 cells (a) and HEK 293T cells (b). TRIM33 was immunoprecipitated, and the amount of
Alan G. Casson FRCSC Professor of Surgery & VP Integrated Health Services University of Saskatchewan & Saskatoon Health Region
 Identification and Characterization of Stem-like Cells in Human Esophageal Adenocarcinoma and Normal Epithelial Cell Lines No disclosures / conflict of interest Alan G. Casson FRCSC Professor of Surgery
Identification and Characterization of Stem-like Cells in Human Esophageal Adenocarcinoma and Normal Epithelial Cell Lines No disclosures / conflict of interest Alan G. Casson FRCSC Professor of Surgery
