Effect of DHU001, a Polyherbal Formula on Formalin-induced Paw Chronic Inflammation of Mice
|
|
|
- Morris Henry
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Toxicol. Res. Vol. 27, No. 2, pp (2011) Open Access DOI: /TR Perspectives - Minireview Effect of DHU001, a Polyherbal Formula on Formalin-induced Paw Chronic Inflammation of Mice Yoon-Hee Cho 1, In-Kwon Chung 2, Woo-Hyun Cheon 2, Hyeung-Sik Lee 1 and Sae-Kwang Ku 2 1 Department of Clinical Laboratory Science, College of Health and Therapy 2 College of Oriental Medicine, Daegu Haany University, Gyeongsan , Korea (Received May 1, 2011; Revised May 7, 2011; Accepted May 13, 2011) The effect of DHU001, a mixed herbal formula consisted of 7 types aqueous extrts for various respiratory disorders were evaluated on the formalin-induced paw chronic inflammation in mice after oral administration. Mice were subaponeurotically injected in the left hind paw with 0.02 ml of 3.75% formalin, then subjected to 500, 250 and 125 mg/kg of DHU001 oral administration, once a day for 10 days during which then the hind-paw thickness and volume were measured daily. The paw wet-weight, histological profiles, histomorphometrical analyses and paw tumor necrosis ftor (TNF)-α contents were conducted at termination. After two formalin treatments, a marked increase in the paw thickness and volume was detected in the formalin-injected control as compared with that in the intt control, plus at the time of srifice the paw wet-weights, paw TNF-α contents were also dramatically increased with severe chronic inflammation signs at histopathological observations. However, these formalin-induced chronic inflammatory changes were dramatically decreased by treatment of dexamethasone and all three different dosages of DHU001. DHU001 has favorable effects on formalin-induced chronic inflammation mediated by TNF-α suppression, and DHU001 may represent an alternative approh for the treatment of chronic inflammatory diseases. Key words: DHU001, Polyherbal Formula, Chronic Inflammation, Mouse, Tumor Necrosis Ftor INTRODUCTION Correspondence to: Sae-Kwang Ku, Department of Anatomy and Histology, College of Oriental Medicine, Daegu Haany University, 290, Yugok-dong, Gyeongsan-si, Gyeongsangbuk-do, , Korea gucci200@hanmail.net Inflammation is an essential protective process alerting organisms to physical, chemical and infective insults. However, the inflammatory response to several insults frequently leads to damage to normal tissues (Habashy et al. 2005). Chronic inflammation is an inflammatory response of prolonged duration, weeks, months, or even indefinitely, where the extended time course is provoked by the persistence of the causative stimulus of inflammation in the tissue (Kim et al., 2006, 2007). Formalin-injected hind-paw chronic inflammatory mice have generally been used as a classic method to detect the efficy of anti-inflammatory drugs, because marked chronic inflammation is evoked by aponeurotic formalin injection (Akindele and Adeyemi, 2007; Kim et al., 2010). Recently, evidence has been provided of a widespread role of tumor necrosis ftor-α (TNF-α) in mediating hyperalgesia at different levels (Schäfers et al., 2003), both filitating neuronal excitability and triggering the release of other proinflammatory substances (Watkins and Maier, 2002). Therefore, TNF-α is treated as one of the key pro-inflammatory cytokines in ute and chronic inflammation models (Bianchi et al., 2004). Steroids have been a popular choice for treating various inflammatory disorders; however, the potential for significant local and systemic adverse events, like skin atrophy and hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis suppression, has limited their use (Gupta and Chow, 2004). Dexamethasone is a well-known glucocorticoid, and it is the most widely used anti-inflammatory control drug in the development of new anti-inflammatory drugs (Kim et al., 2006). DHU001 is a mixed herbal formula consisted of 7 types aqueous extrts; Ficis fructus, Liriopis tuber, Platycodi radix, Schisandrae fructus, Glycyrrhizae radix, Zingiberis rhizome and Menthae herba and being developed for various respiratory disorders (Lee et al., 2010). Most of seven herbal components of DHU001 have been used for treating or ameliorating various respiratory symptoms based on the anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects (Sun and Pan, 2006; Aimbire et al., 2007; Minghetti et al., 2007; Lee et al., 2010). Recently, 95
2 96 Y.-H. Cho et al. anti-inflammatory effects of DHU001 itself, was also demonstrated on the xylene-induced ute inflammation (Bk et al., 2008) and dinitrofluorobenzene-induced contt dermatitis (Lee et al., 2010) with single mouse oral dose toxicity (Roh and Ku, 2010) and micronucleus test (Roh et al., 2009). An immunomodulatory agent can reduce the inflammation previously observed (Ramprasath et al., 2006). For example, nitric oxide (NO) plays an important role in inflammation, and NO synthase inhibitors can reverse several classic inflammatory symptoms (Amin et al., 1995) as related to anti-oxidative effects (Kim et al., 2006). Therefore, it can be postulated that DHU001 will have a favorable effect on reducing or speeding-up the recovery from local chronic inflammation induced by irritants. Accordingly, in the present study, the effects of the DHU001 on formalin-induced chronic inflammation were investigated and compared with mice intraperitoneally injected with 15 mg/kg dexamethasone. MATERIALS AND METHODS Experimental animals. Forty-eight male ICR mice (6- wks-old upon receipt; SLC, Japan) were used after climatization for 7 days. The three or four animals were allocated to polycarbonate cages in a temperature (20~25 o C) and humidity (40~45%) controlled room. The light - dark cycle was 12 h : 12 h, while food (Samyang, Korea) and water were supplied ad libitum. The animals were fasted overnight before the start of DHU001 administration and before being srificed (about 18 h; water not restricted). This study was carried out with prior approval of the Animal Ethical Committee, The University of Daegu Haany University (Gyeongsan, Korea). Preparation of DHU001. The herbal compositions of DHU001 were listed in Table 1. Eh herbal component was purchased from Cho-Heung Pharmeutical Ind. Co. (Daegu, Korea) after confirmation of the morphology under microscopy. Approximated amounts of eh herbal component was mixed (317.5 g) and boiled in 2 l of distilled water for 2 hours and then filtrated. The filtrate was decompressed using a rotary vuum evaporator (Lab. Camp, Daejeon, Korea) and lyophilized in a programmable freezedryer (IlShin Lab., Daejeon, Korea). Total quired lyophilized extrts were g (yield 11%). Powders of extrts were stored in a desiccator to protect against light and moisture. It was well dissolved up to 30 mg/ml concentration levels and appeared to be a deep brown solution. Administration of drugs. The animals were allocated to six groups with 8 mice per group: vehicle control, formalin control, 500, 250 and 125 mg/kg with the DHU001 administered groups, 15 mg/kg of dexamethasone-water soluble (Sigma, MO, USA)-treated groups. Three different dosages of DHU001 were selected based on the results on the xylene-induced ute inflammation (Bk et al., 2008), and 15 mg/kg of intraperitoneal treatment of dexamethasone was also selected from previous report (Kim et al., 2007). DHU001 aqueous extrts were orally administered once a day for 10 days, while the dexamethasone dissolved in saline were intraperitoneally administered at a volume of 10 ml/kg. In formalin-treated control and vehicle control, distilled water was orally administered instead of DHU001 as same methods. Induction of chronic inflammation. One hour before DHU001 administration or dexamethasone injection, a subaponeurotic injection of 0.02 ml of 3.75% formalin (Sigma, MO, USA) was administered to the left hind paw (Planta pedis) on the first and third days of the experiment. In the case of the vehicle control, the same volume of saline as that used in the other dosing groups, including the formalin control, was administered in the same region using the same method as described previously (Kim et al., 2010). Changes in body weights. Daily body weights of all experimental animals used in this study were measured from 1 day before the start of the experimental period to 10 days of treatment with an automatic electronic balance (Precisa Instrument, Switzland). Paw thickness and volume measurements. The thicknesses of the left hind paws were measured using an elec- Table 1. Herbal composition of DHU001 used in this study Herbs Scientific name Amounts (g) Ficis fructus Ficus carica Linn Liriopis tuber Liriope spicata Lour. 45. Platycodi radix Platycodon grandiflorum Jq. 60. Schisandrae fructus Schisandra chinensis Baill Glycyrrhizae radix Glycyrrhiza uralensis Fisch 15. Zingiberis rhizoma recens Zingiber officinale Roscoe 15. Menthae Herba Mentha arvensis Linne var piperascens 20. Total 7 types All herbs were purchase from from Cho-Heung Pharmeutical Ind. Co. (Daegu, Korea) and yield 11% aqueous extrts were quired.
3 DHU001 Ameliorated Chronic Inflammation 97 tronic digital caliper (Mytutoyo, Japan) and recorded once a day for 10 days at 1 h before the first formalin injection, at 1 h before the second formalin injection or 2 h before DHU001 treatment. The lengths of the long axis (longitudinal; excluding dtyl region) and short axis of the left hind paws were measured using an electronic digital caliper and recorded once a day for 10 days. The paw volume was calculated as described in a previous report (Kim et al., 2010): paw volume (mm 3 ) = 1/2(length of long axis length of short axis thickness of paw). Paw weight measurements. At srifice, the wet-weight of the left hind paws was measured, and to reduce any errors due to individual body weight differences, the relative weight (%) was calculated using the body weight at srifice and absolute weight: Relative paw weight (% of body weight) = (Absolute weight/body weight at srifice) 100. Paw TNF-α content measurement. After wet-weight measurements of paws, for TNF-α evaluation, skin samples of the left hind paws were homogenized in 3 ml of phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) containing 10 mm EDTA and 20 KIU/ml aprotinin (Sigma, MO, USA). After centrifugation at 10,000 g, the supernatant was frozen at 70 o C for TNF-α assay as described in a previous report (Bianchi et al., 2004). The levels of TNF-α in paw supernatants were measured by means of an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) kit specific for mouse TNF-α (Santa Cruz Biotechnology, CA, USA). Histopathology. The dorsum pedis (including the subcutaneous regions) skin was separated from the hind paw, and longitudinally trimmed, then were fixed in 10% neutral buffered formalin. In addition, the metatarsal region including the second metatarsal bones was cross-trimmed, and fixed in 10% neutral buffered formalin, then decalcified using decalcifying solution [24.4% formic id, and 0.5 N sodium hydroxide] for 5 days (mixed decalcifying solution was exchanged once a day for 5 days). After that, the prepared dorsum pedis skin and the metatarsal region were embedded in paraffin, sectioned (3~4 µm) and stained with hematoxylin and eosin (H&E). The histological profiles of the hind paws were compared with those of the vehicle control. Histomorphometry: To detect more detailed changes, the thicknesses from the epidermis to the hypodermis of the dorsum pedis and dorsum digit skin and the numbers of infiltrating inflammatory cells in the dorsum pedis and dorsum digit skin were measured as described previously (Kim et al., 2010) with some modifications. The histopathologist was blinded to group distribution when this analysis was made. Statistical analyses. All data are expressed as the mean ± standard deviation (SD) of seven mice, and multiple comparison tests for different dose groups were conducted. Variance homogeneity was examined using the Levene test. If the Levene test indicated no significant deviations from variance homogeneity, the data were analyzed with one way ANOVA followed by a least-significant differences multi-comparison test to determine which pairs of group comparison were significantly different. In cases of significant deviation from variance homogeneity as indicated by the Levene test, a non-parametric comparison test, the Kruskal-Wallis H test, was conducted. When a significant difference was observed with the Kruskal-Wallis H test, the Mann-Whitney U test was conducted to determine the specific pairs of groups which were significantly different. Statistical analyses were conducted using SPSS for Windows (Release 14.0K, SPSS Inc., USA). RESULTS Changes on the body weights. No meaningful changes in body weights were detected between the formalin control and the vehicle control throughout the 10-day experimental period. However, dexamethasone-treated mice showed significant (p < 0.01 or p < 0.05) decreases in body weight, Fig. 1. Body weights detected during 10 days of continuous oral treatment periods of DHU001 in formalin-induced chronic inflammation mice. No meaningful changes on the body weights were detected in all administrated groups as compared with intt or formalin controls, respectively except for dexamethasone-treated mice in which significant decreases on the body weights were detected from 5 days after administration as compared with intt and formalin control. Values are expressed mean ± S.D. of eight mice. Before means 1 day before first formalin treatment or start of test material administration. Subaponeurotic injection of formalin was conducted at Day 0 and Day 3, respectively (arrows). All animals were overnight fasted at Day 0 and srifice. a p < 0.01 and b p < 0.05 as compared with intt control; c p < 0.01 and d p < 0.05 as compared with Formalin control.
4 98 Y.-H. Cho et al. which were detected from 5 days after administration as compared with the vehicle or formalin control. No meaningful changes in body weights were detected in any of the three DHU001 treatment groups in a comparison with the vehicle and formalin controls throughout the 10-day experimental period (Fig. 1). Table 2. Changes in paw thicknesses of the mice Group Paw thicknesses At start of treatment At srifice Differences [% changes*] Controls Vehicle 2.45 ± ± ± 0.19 Formalin 2.46 ± 0.16 a4.21 ± 0.26 a 1.75 ± 0.41 a Dexamethasone 2.47 ± 0.12 b 2.67 ± 0.20 b 0.21 ± 0.20 b [ 88.27] DHU001 treatment 500 mg/kg 2.45 ± 0.11 ab 3.26 ± 0.28 ab 0.81 ± 0.31 ab [ 53.75] 250 mg/kg 2.45 ± 0.19 ab 3.45 ± 0.35 ab 1.00 ± 0.43 ab [ 42.99] 125 mg/kg 2.45 ± 0.13 ab 3.78 ± 0.17 ab 1.33 ± 0.19 [ 23.82] Values are expressed as Mean ± SD of eight mice, mm. Differences = paw thicknesses at srifice paw thicknesses at srifice at start of treatment. * % changes between formalin control and treated group. a p < 0.01 as compared with vehicle control. b p<0.01 and c p < 0.05 as compared with formalin control. Table 3. Changes in paw volumes of the mice Group Paw thicknesses At start of treatment At srifice Differences [% changes*] Controls Vehicle ± ± ± 6.41 Formalin ± ± a ± a Dexamethasone ± ± b ± b [ 88.89] DHU001 treatment 500 mg/kg ± ± 9.16 ab ± ab [ 70.83] 250 mg/kg ± ± ab ± ab [ 56.94] 125 mg/kg ± ± ± ab [ 30.56] Values are expressed as Mean ± SD of eight mice, mm 3. Paw volume = 1/2(length of long axis length of short axis thickness of paw). Differences = paw volumes at srifice paw volumes at srifice at start of treatment. * % changes between formalin control and treated group. a p < 0.01 as compared with vehicle control. b p<0.01 and c p < 0.05 as compared with formalin control. Table 4. Changes in paw weights and TNF-α contents of the mice Group Paw thicknesses Paw TNF-α contents At start of treatment At srifice (ng/g paw) [% changes*] Controls Vehicle ± ± ± 1.56 Formalin a0.347 ± a a ± a ± a Dexamethasone bc ± bc ± ± 4.26 [ 76.46] DHU001 treatment 500 mg/kg ± ± ± 6.42 [ 61.97] 250 mg/kg ± ± ± 7.45 [ 49.58] 125 mg/kg ± ± ± 6.66 ad [ 30.10] Values are expressed as Mean ± SD of eight mice. Relative paw weights (% of body weight) = (Absolute weight/body weight at srifice) 100. * % changes between formalin control and treated group. a p<0.01 and b p < 0.05 as compared with vehicle control. c p<0.01 and d p < 0.05 as compared with formalin control.
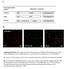
5 DHU001 Ameliorated Chronic Inflammation Changes on the paw thicknesses. A significant (p < 0.01) increase of left hind paw thickness was detected in the formalin control compared with that of vehicle control from 1 day after formalin injection. Consequently the increases of paw thickness during the 10-day experimental period were also significant (p < 0.01). However, left hind paw thicknesses were significantly (p < 0.01 or p < 0.05) decreased compared with the formalin control from 1 day after the start of dexamethasone treatment, from 2 days after the start of DHU mg/kg treatment, and from 3 days after the start of DHU and 125 mg/kg treatment. The changes of paw thickness during the 10-day experimental period were also significant (p < 0.01 or p < 0.05) for dexamethasone and all three different dosages of DHU001 compared with the formalin-injected control (Table 2). 99 skins of the formalin control. In the dexamethasone- and DHU001-treated groups, these histopathological changes were dramatically decreased compared with the formalin control (Fig. 1 and 2). Significant (p < 0.01) increases in the thickness and the numbers of infiltrating inflammatory cells in the dorsum pedis and dorsum digit skin were detected in the formalin control compared with the vehicle control. However, these increases of skin thickness and infiltrating inflammatory cells were significantly (p < 0.01) decreased in the dexamethasone- and DHU001-treated groups when compared with the formalin control (Table 5). Changes on the paw volumes. A significant (p < 0.01) increase of left hind paw volume was detected in the formalin-injected control compared with the vehicle control from 1 day after formalin injection. Consequently, the increases of paw volume during the 10-day experimental period were also significant (p < 0.01). However, paw volumes were significantly (p < 0.01 or p < 0.05) decreased compared with the formalin-injected control from 2 days after the start of dexamethasone, DHU and 250 mg/kg administration, and from 3 days after start of DHU mg/kg treatment. The decreases of volume during the 10-day experimental period were also significant (p < 0.01) for dexamethasone and all three different dosages of DHU001 as compared with the formalin control (Table 3). Changes on the paw weights. Significant (p < 0.01) increases of left hind paw absolute and relative weights were detected in the formalin control compared with the vehicle control. However, the paw weights were significantly (p < 0.01) decreased in the dexamethasone- and DHU001-treated groups compared with the formalin control (Table 4). Changes on the paw TNF-α contents. A significant (p < 0.01) increase of left hind paw TNF-α contents was detected in the formalin control compared with the vehicle control. However, the paw TNF-α contents were significantly (p < 0.01) decreased in the dexamethasone- and DHU001-treated groups compared with formalin control (Table 4). Histopathological changes. Histopathological changes related to chronic inflammation, such as severe fibrosis, the formation of necrotic debris, and infiltration of inflammatory cells, leading to the hypertrophy of subcutaneous regions were observed in both the dorsum pedis and dorsum digit Fig. 2. The representative histological profiles of dorsum pedis skin: observed in vehicle control (A, B), formalin-injected control (C, D), and dexamethasone (E, F), DHU (G, H), 250 (I, J), and 125 (K, L) mg/kg treated groups. Note that histopathological changes related to chronic inflammation, such as severe fibrosis, the formation of necrotic debris, and infiltration of inflammatory cells, were observed in the dorsum pedis skins of the formalin-injected control, leading to the hypertrophy of subcutaneous regions. However these histopathological changes were dramatically decreased by treatment with dexamethasone and at all three different dosages of DHU001 as compared with the formalin-injected control. The arrow indicates the thickness of dorsum pedis skin. Ep, epithelium keratinized stratified squamous epithelium; Se, sebeous gland; H&E stain; Scale bars = 160 µm.
6 100 Y.-H. Cho et al. Fig. 3. The representative histological profiles of dorsum digit skin: observed in vehicle control (A, B), formalin-injected control (C, D), and dexamethasone (E, F), DHU (G, H), 250 (I, J), and 125 (K, L) mg/kg treated groups. Note that histopathological changes related to chronic inflammation, such as severe fibrosis, the formation of necrotic debris, and infiltration of inflammatory cells, were observed in the dorsum digit skins of the formalin-injected control, leading to the hypertrophy of subcutaneous regions. However these histopathological changes were dramatically decreased by treatment with dexamethasone and at all three different dosages of DHU001 as compared with the formalin-injected control. The arrow indicates the thickness of dorsum digit skin. Bo, metatarsal bones; Ep, epithelium keratinized stratified squamous epithelium; H&E stain; Scale bars = 160 µm. DISCUSSION In the present study, the anti-inflammatory effects of DHU001, a polyherbal formula were evaluated using formalin-induced chronic inflammation in mice paws, one of the simplest animal models for detecting chronic inflammation (Kim et al., 2006; Akindele and Adeyemi, 2007), and compared with those of 15 mg/kg dexamethasone intraperitoneally injected. After two subaponeurotic formalin treatments, marked increases in the paw thickness and volume were detected in the formalin-injected control as compared with the vehicle control. In addition, at the time of srifice, the paw wet-weights and paw TNF-α contents had also dramatically increased. In histopathological observations, severe chronic inflammation signs such as severe fibrosis, the formation of necrotic debris, and infiltration of inflammatory cells, were detected in the formalin-injected control, and marked increases in the thickness of the skin of the dorsum pedis and of the dorsum digit were induced with increases in infiltrating inflammatory cells in the dorsum pedis and dorsum digits skin. However, these formalin-induced chronic inflammatory changes were dramatically decreased by treatment with dexamethasone or one of the three dosages of DHU001. Therefore, these results are considered as direct evidence that DHU001 treatment improves the chronic inflammatory response induced by formalin, and correspond well with the anti-inflammatory effects of DHU001 in the other inflammatory animal experiments (Bk et al., 2008; Lee et al., 2010). The body weight decreases detected in the dexamethasone-treated group were considered to be due to the direct toxicity of glucocorticoid. Steroids have been a popular choice for treating various cutaneous disorders; however, the potential for significant local and systemic adverse events, like skin atrophy and HPA axis suppression, has limited their use (Gupta and Chow, 2004). No meaningful changes in body weight or body weight gains were detected at any dosage of DHU001 as compared with the formalin control in this study. After a local injection of formalin, marked increases in the paw thickness, volume, and weight are detected as a general chronic inflammation response, and these increases are used as valuable markers for testing anti-inflammatory effects (Pillai et al., 2003). In the present study, the increased paw thickness, volume, and weights were markedly inhibited by treatment with DHU001 at eh of the three different dosages. Consequently, these inhibitions were considered to be direct evidence that DHU001 treatment has a favorable effect on reducing the chronic inflammatory response. TNF-α, a 17-kDa protein, which was first identified as a product of tivated mrophages, is a well-known proinflammatory cytokine (Whittle et al., 2008) and it is involved in various inflammations (Schottelius et al., 2010). Recently, evidence has been provided of the widespread role of TNFα in mediating hyperalgesia at different levels (Schäfers et al., 2003), both filitating neuronal excitability and triggering the release of other pro-inflammatory substances (Watkins and Maier, 2002). In the present study, DHU001 treatment dose-dependently inhibited the elevations of TNF-α induced in mouse paws by subaponeurotic injection of formalin. Therefore, we consider that DHU001 showed favorable anti-inflammatory effects on chronic inflammations mediated by cytokine TNF-α suppression. However, we should not excluded the possibility that the previously reported antioxidative effects and immune stimulation of treatment DHU001 components (Sun and Pan, 2006; Aimbire et al., 2007; Minghetti et al., 2007; Lee et al., 2010) may also have been
7 DHU001 Ameliorated Chronic Inflammation 101 Table 5. Changes in histomorphometry analyses of the mice Group Thicknesses of skin (mm) Number of inflammatory cells (cells/mm 2 ) Dorsum pedis (mm) Dorsum digitalis Infiltrating dorsum pedis Infiltrating dorsum digit Controls Vehicle 0.91 ± ± ± ± Formalin a 2.85 ± 0.29 a a 2.62 ± 0.43 a a ± a 0 a ± a Dexamethasone 1.23 ± ± 0.23 bc ± ± DHU001 treatment 500 mg/kg 1.60 ± ± ± ± mg/kg 1.77 ± ± ± ± mg/kg 2.10 ± ± ± ± Values are expressed as Mean ± SD of eight mice. Thickness of skin = the thicknesses from epidermis to hypodermis> a p<0.01 and p < 0.05 as compared with vehicle control. c p < 0.01 as compared with formalin control. involved in the anti-inflammatory tivity observed in the present study, because NO synthase inhibitors can reverse several classic inflammatory symptoms (Ramprasath et al., 2006) and immunomodulatory agents can reduce inflammation (Amin et al., 1995). Histopathologically, severe fibrosis, the formation of necrotic debris, infiltration of inflammatory cells (mainly lymphocytes) and hypertrophy of the subcutaneous regions are used as signs of chronic inflammation after a local injection of formalin (Kenjo et al., 2002). Infiltration of inflammatory cells also results in a marked increase in the thickness of the skin (including hypodermis) (Kim et al., 2006, 2010). However, in the present study, these histopathological changes were markedly and dose-dependently inhibited after treatment with DHU001 at eh of the three different dosages. These inhibitions were considered as direct evidence that DHU001 has a relatively favorable effect on reducing the chronic inflammatory response. Accordingly, based on the current results, we conclude that DHU001 treatment had a favorable effect, mediated by TNF-α suppression, on reducing the chronic inflammatory response induced in mouse paws by formalin injection. Although the anti-inflammatory efficies were low compared with dexamethasone, DHU001 may present an alternative approh for the treatment of chronic inflammatory diseases with relatively fewer side effects. ACKNOWLEDGMENT This study was supported by a grant from the Korea Healthcare Technology R&D Project, Ministry for Health, Welfare & Family Affairs, Republic of Korea (A ). REFERENCES Aimbire, F., Penna, S.C., Rodrigues, M., Rodrigues, K.C., Lopes- Martins, R.A. and Sertié, J.A. (2007). Effect of hydroalcoholic extrt of Zingiber officinalis rhizomes on LPS-induced rat airway hyperretivity and lung inflammation. Prostaglandins Leukot. Essent. Fatty Acids, 77, Akindele, A.J. and Adeyemi, O.O. (2007). Antiinflammatory tivity of the aqueous leaf extrt of Byrsocarpus coccineus. Fitoterapia, 78, Amin, A.R., Vyas, P., Attur, M., Leszczynska-Piziak, J., Patel, I.R., Weissmann, G. and Abramson, S.B. (1995). The mode of tion of aspirin-like drugs: effect on inducible nitric oxide synthase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A., 92, Bk, Y.D., Lee, H.S. and Ku, S.K. (2008). Effects of DHU001, a mixed herbal formula on ute inflammation in mice. Toxicol. Res., 24, Bianchi, M., Martucci, C., Biella, G., Ferrario, P. and Serdote, P. (2004). Increased substance P and tumor necrosis ftor-alpha level in the paws following formalin injection in rat tail. Brain Res., 1019, Gupta, A.K. and Chow, M. (2004). Prednicarbate (Dermatop): profile of a corticosteroid. J. Cutan. Med. Surg., 8, Habashy, R.R., Abdel-Naim, A.B., Khalifa, A.E. and Al-Azizi, M.M. (2005). Anti-inflammatory effects of jojoba liquid wax in experimental models. Pharmol. Res., 51, Kenjo, T., Kikuchi, S. and Konno, S. (2002). Cooling decreases fos-immunoretivity in the rat after formalin injection. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res., 394, Kim, H.D., Cho, H.R., Moon, S.B., Shin, H.D., Yang, K.J., Park, B.R., Jang, H.J., Lim, L.S., Lee, H.S. and Ku, S.K. (2006). Effect of exopolymers from Aureobasidum pullulans on formalin-induced chronic paw inflammation in mice. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol., 16, Kim, H.D., Cho, H.R., Moon, S.B., Shin, H.D., Yang, K.J., Park, B.R., Jang, H.J., Lim, L.S., Lee, H.S. and Ku, S.K. (2007). Effects of β-glucan from Aureobasidum pullulans on ute inflammation in mice. Arch. Pharm. Res., 30, Kim, H.D., Cho, K.H., Lee, B.W., Kwon, Y.S., Lee, H.S., Choi, S.H. and Ku, S.K. (2010). Effects of magnetic infrared laser on formalin-induced chronic Paw inflammation of mice. J. Phys. Ther. Sci., 22, Lee, H.S., Lee, B.C. and Ku, S.K. (2010). Effect of DHU001, a
8 102 Y.-H. Cho et al. polyherbal formula, on dinitrofluorobenzene-induced contt dermatitis (Type I allergy). Toxicol. Res., 26, Minghetti, P., Sosa, S., Cilurzo, F., Casiraghi, A., Alberti, E., Tubaro, A., Loggia, R.D. and Montanari, L. (2007). Evaluation of the topical anti-inflammatory tivity of ginger dry extrts from solutions and plasters. Planta Med., 73, Pillai, A.D., Pathod, P.D., P, X.F., Patel, M., Nivsarkar, M., Vasu, K.K., Padh, H. and Sudarsanam, V. (2003). Novel drug designing approh for dual inhibitors as anti-inflammatory agents: implication of pyridine template. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 301, Ramprasath, V.R., Shanthi, P. and Shdanandam, P. (2006). Immunomodulatory and anti-inflammatory effects of Semecarpus anardium LINN. Nut milk extrt in experimental inflammatory conditions. Biol. Pharm. Bull., 29, Roh, S.S. and Ku, S.K. (2010). Mouse single oral dose toxicity study of DHU001, a polyherbal formula. Toxicol. Res., 26, Roh, S.S., Lee, H.S. and Ku, S.K. (2009). Micronucleus test of DHU001, a polyherbal formula, in bone marrow cells of male ICR mice. Toxicol. Res., 25, Schäfers, M., Lee, D.H., Brors, D., Yaksh, T.L. and Sorkin, L.S. (2003). Increased sensitivity of injured and adjent uninjured rat primary sensory neurons to exogenous tumor necrosis ftor-alpha after spinal nerve ligation. J. Neurosci., 23, Schottelius, A.J., Zügel, U., Döcke, W.D., Zollner, T.M., Röse, L., Mengel, A., Buchmann, B., Becker, A., Grütz, G., Naundorf, S., Friedrich, A., Gaestel, M. and Asadullah, K. (2010). The role of mitogen-tivated protein kinase-tivated protein kinase 2 in the p38/tnf-alpha pathway of systemic and cutaneous inflammation. J. Invest. Dermatol., 130, Sun, H.X. and Pan, H.J. (2006). Immunological adjuvant effect of Glycyrrhiza uralensis saponins on the immune responses to ovalbumin in mice. Vcine, 24, Watkins, L.R. and Maier, S.F. (2002). Beyond neurons: evidence that immune and glial cells contribute to pathological pain states. Physiol. Rev., 82, Whittle, B.J., Varga, C., Berko, A., Horvath, K., Posa, A., Riley, J.P., Lundeen, K.A., Fourie, A.M. and Dunford, P.J. (2008). Attenuation of inflammation and cytokine production in rat colitis by a novel selective inhibitor of leukotriene A4 hydrolase. Br. J. Pharmol., 153,
Effect of DHU001, a Polyherbal Formula, on Dinitrofluorobenzene-induced Contact Dermatitis (Type I allergy)
 Toxicol. Res. Vol. 26, No. 2, pp. 123-130 (2010) Perspectives - Minireview Effect of DHU001, a Polyherbal Formula, on Dinitrofluorobenzene-induced Contact Dermatitis (Type I allergy) Hyeung-Sik Lee 1,
Toxicol. Res. Vol. 26, No. 2, pp. 123-130 (2010) Perspectives - Minireview Effect of DHU001, a Polyherbal Formula, on Dinitrofluorobenzene-induced Contact Dermatitis (Type I allergy) Hyeung-Sik Lee 1,
Effect of Picrorrhiza Rhizoma on Dinitrofluorobenzene-induced Contact Dermatitis (Type I allergy)
 Biomolecules & Therapeutics, 16, 237-242(2008) Effect of Picrorrhiza Rhizoma on Dinitrofluorobenzene-induced Contact Dermatitis (Type I allergy) Ji-Ha PARK 1, Sang-Nam LEE 1, and Sae-Kwang KU 1,2,* 1 College
Biomolecules & Therapeutics, 16, 237-242(2008) Effect of Picrorrhiza Rhizoma on Dinitrofluorobenzene-induced Contact Dermatitis (Type I allergy) Ji-Ha PARK 1, Sang-Nam LEE 1, and Sae-Kwang KU 1,2,* 1 College
Micronucleus Test of Picrorrhiza Rhizoma Aqueous Extract in Bone Marrow Cells of Male ICR Mice
 Toxicol. Res. Vol. 27, No. 2, pp. 119-123 (2011) Open Access DOI:10.5487/TR.2011.27.2.119 Perspectives - Minireview Micronucleus Test of Picrorrhiza Rhizoma Aqueous Extract in Bone Marrow Cells of Male
Toxicol. Res. Vol. 27, No. 2, pp. 119-123 (2011) Open Access DOI:10.5487/TR.2011.27.2.119 Perspectives - Minireview Micronucleus Test of Picrorrhiza Rhizoma Aqueous Extract in Bone Marrow Cells of Male
Mouse Single Oral Dose Toxicity Test of Lactobacillus-fermented Araliae Continentalis Radix Aqueous Extracts (facr)
 Journal of Life Science 2016 Vol. 26. No. 2. 204~211 ISSN (Print) 1225-9918 ISSN (Online) 2287-3406 DOI : http://dx.doi.org/10.5352/jls.2016.26.2.204 Mouse Single Oral Dose Toxicity Test of Lactobacillus-fermented
Journal of Life Science 2016 Vol. 26. No. 2. 204~211 ISSN (Print) 1225-9918 ISSN (Online) 2287-3406 DOI : http://dx.doi.org/10.5352/jls.2016.26.2.204 Mouse Single Oral Dose Toxicity Test of Lactobacillus-fermented
APPENDIX 1 ETHICAL CLEARANCE
 APPENDIX 1 ETHICAL CLEARANCE 75 APPENDIX 2 76 PROCEDURE FOR PREPARING OF LIVER HISTOLOGY SLIDES Overview: Histology involves the use of a set of techniques to examine the morphology, architecture and composition
APPENDIX 1 ETHICAL CLEARANCE 75 APPENDIX 2 76 PROCEDURE FOR PREPARING OF LIVER HISTOLOGY SLIDES Overview: Histology involves the use of a set of techniques to examine the morphology, architecture and composition
Expression of acid base transporters in the kidney collecting duct in Slc2a7 -/-
 Supplemental Material Results. Expression of acid base transporters in the kidney collecting duct in Slc2a7 -/- and Slc2a7 -/- mice. The expression of AE1 in the kidney was examined in Slc26a7 KO mice.
Supplemental Material Results. Expression of acid base transporters in the kidney collecting duct in Slc2a7 -/- and Slc2a7 -/- mice. The expression of AE1 in the kidney was examined in Slc26a7 KO mice.
Supplementary Figure S1. Flow cytometric analysis of the expression of Thy1 in NH cells. Flow cytometric analysis of the expression of T1/ST2 and
 Supplementary Figure S1. Flow cytometric analysis of the expression of Thy1 in NH cells. Flow cytometric analysis of the expression of T1/ST2 and Thy1 in NH cells derived from the lungs of naïve mice.
Supplementary Figure S1. Flow cytometric analysis of the expression of Thy1 in NH cells. Flow cytometric analysis of the expression of T1/ST2 and Thy1 in NH cells derived from the lungs of naïve mice.
Hypothalamic TLR2 triggers sickness behavior via a microglia-neuronal axis
 Hypothalamic TLR triggers sickness behavior via a microglia-neuronal axis Sungho Jin, *, Jae Geun Kim,, *, Jeong Woo Park, Marco Koch,, Tamas L. Horvath and Byung Ju Lee Department of Biological Sciences,
Hypothalamic TLR triggers sickness behavior via a microglia-neuronal axis Sungho Jin, *, Jae Geun Kim,, *, Jeong Woo Park, Marco Koch,, Tamas L. Horvath and Byung Ju Lee Department of Biological Sciences,
Stability Study for Herbal Drug According to Storage Conditions and Periods
 J Korean Oriental Med 2009;30(2):127-132 Original Article 손진영 신장우 손창규 대전대학교한의과대학간장면역학교실 Stability Study for Herbal Drug According to Storage Conditions and Periods Jin-Young Son Jang-Woo Shin Chang-Gue
J Korean Oriental Med 2009;30(2):127-132 Original Article 손진영 신장우 손창규 대전대학교한의과대학간장면역학교실 Stability Study for Herbal Drug According to Storage Conditions and Periods Jin-Young Son Jang-Woo Shin Chang-Gue
Appendix 1. A. Procedure for preparing histopathology slides. The liver removed and stored immediately in buffered formalin 10 % for
 Appendix 1 A. Procedure for preparing histopathology slides. The liver removed and stored immediately in buffered formalin 10 % for histopathological examination. The tissue fixed for at least 48 hours
Appendix 1 A. Procedure for preparing histopathology slides. The liver removed and stored immediately in buffered formalin 10 % for histopathological examination. The tissue fixed for at least 48 hours
Standard Operating Procedure
 1.0 Purpose: 1.1 Relaxation, dissection, weighing and fixation of heart for histological analysis. Changes in heart weight and wall thickness are linked to cardiovascular phenotypes. This protocol describes
1.0 Purpose: 1.1 Relaxation, dissection, weighing and fixation of heart for histological analysis. Changes in heart weight and wall thickness are linked to cardiovascular phenotypes. This protocol describes
Summary of Inhalation Carcinogenicity Study. of Isopropyl Acetate. in F344 Rats
 Summary of Inhalation Carcinogenicity Study of Isopropyl Acetate in F344 Rats March 2009 Japan Bioassay Research Center Japan Industrial Safety and Health Association PREFACE The tests were contracted
Summary of Inhalation Carcinogenicity Study of Isopropyl Acetate in F344 Rats March 2009 Japan Bioassay Research Center Japan Industrial Safety and Health Association PREFACE The tests were contracted
Leptin deficiency suppresses progression of atherosclerosis in apoe-deficient mice
 Leptin deficiency suppresses progression of atherosclerosis in apoe-deficient mice Atherosclerosis, 2007 Chiba T, Shinozaki S, Nakazawa T, et al. Present by Sudaporn Pummoung Apolipoprotein E (apoe( apoe)
Leptin deficiency suppresses progression of atherosclerosis in apoe-deficient mice Atherosclerosis, 2007 Chiba T, Shinozaki S, Nakazawa T, et al. Present by Sudaporn Pummoung Apolipoprotein E (apoe( apoe)
Entrainment of the mouse circadian clock by sub-acute physical and psychological
 Supplementary Information Entrainment of the mouse circadian clock by sub-acute physical and psychological Yu Tahara 1, Takuya Shiraishi 1, Yosuke Kikuchi 1, Atsushi Haraguchi 1, Daisuke Kuriki 1, Hiroyuki
Supplementary Information Entrainment of the mouse circadian clock by sub-acute physical and psychological Yu Tahara 1, Takuya Shiraishi 1, Yosuke Kikuchi 1, Atsushi Haraguchi 1, Daisuke Kuriki 1, Hiroyuki
IMO-8400, a novel TLR7, TLR8 and TLR9 antagonist, psoriasis
 IMO-8400, a novel TLR7, TLR8 and TLR9 antagonist, inhibits disease development in mouse models of psoriasis Weiwen e Ja Jiang, Fu-Gang Zhu, Dong Yu, Ekambar R. Kandimalla, a a, Nicola La Monica, and Sudhir
IMO-8400, a novel TLR7, TLR8 and TLR9 antagonist, inhibits disease development in mouse models of psoriasis Weiwen e Ja Jiang, Fu-Gang Zhu, Dong Yu, Ekambar R. Kandimalla, a a, Nicola La Monica, and Sudhir
Nature Medicine: doi: /nm.3922
 Title: Glucocorticoid-induced tumor necrosis factor receptor-related protein co-stimulation facilitates tumor regression by inducing IL-9-producing helper T cells Authors: Il-Kyu Kim, Byung-Seok Kim, Choong-Hyun
Title: Glucocorticoid-induced tumor necrosis factor receptor-related protein co-stimulation facilitates tumor regression by inducing IL-9-producing helper T cells Authors: Il-Kyu Kim, Byung-Seok Kim, Choong-Hyun
COPD lungs show an attached stratified mucus layer that separate. bacteria from the epithelial cells resembling the protective colonic
 COPD lungs show an attached stratified mucus layer that separate bacteria from the epithelial cells resembling the protective colonic mucus SUPPLEMENTARY TABLES AND FIGURES Tables S1 S8, page 1 and separate
COPD lungs show an attached stratified mucus layer that separate bacteria from the epithelial cells resembling the protective colonic mucus SUPPLEMENTARY TABLES AND FIGURES Tables S1 S8, page 1 and separate
Sunghyen Lee 1, Youngmin Lee 2, Sungjoon Lee 3, Haejeung Lee 4, Hyun Lillehoj 5
 Dec 8, 2015 Sunghyen Lee 1, Youngmin Lee 2, Sungjoon Lee 3, Haejeung Lee 4, Hyun Lillehoj 5 1 Functional Food & Nutrition Division, National Institute of Agricultural Science, 2 Seoul Women s Univ, 3 Eulji
Dec 8, 2015 Sunghyen Lee 1, Youngmin Lee 2, Sungjoon Lee 3, Haejeung Lee 4, Hyun Lillehoj 5 1 Functional Food & Nutrition Division, National Institute of Agricultural Science, 2 Seoul Women s Univ, 3 Eulji
Programmed necrosis, not apoptosis, is a key mediator of cell loss and DAMP-mediated inflammation in dsrna-induced retinal degeneration
 Programmed necrosis, not apoptosis, is a key mediator of cell loss and DAMP-mediated inflammation in dsrna-induced retinal degeneration The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please
Programmed necrosis, not apoptosis, is a key mediator of cell loss and DAMP-mediated inflammation in dsrna-induced retinal degeneration The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please
Green tea extract Its potential protective effect on bleomycin induced lung injuries in rats
 Green tea extract Its potential protective effect on bleomycin induced lung injuries in rats Azza H. EL-Medany, Jamila EL-Medany The interest in the use of plant extracts in the treatment of several diseases
Green tea extract Its potential protective effect on bleomycin induced lung injuries in rats Azza H. EL-Medany, Jamila EL-Medany The interest in the use of plant extracts in the treatment of several diseases
VEGFR2-Mediated Vascular Dilation as a Mechanism of VEGF-Induced Anemia and Bone Marrow Cell Mobilization
 Cell Reports, Volume 9 Supplemental Information VEGFR2-Mediated Vascular Dilation as a Mechanism of VEGF-Induced Anemia and Bone Marrow Cell Mobilization Sharon Lim, Yin Zhang, Danfang Zhang, Fang Chen,
Cell Reports, Volume 9 Supplemental Information VEGFR2-Mediated Vascular Dilation as a Mechanism of VEGF-Induced Anemia and Bone Marrow Cell Mobilization Sharon Lim, Yin Zhang, Danfang Zhang, Fang Chen,
Supporting Information
 Notes Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 2013, Vol. 34, No. 1 1 http://dx.doi.org/10.5012/bkcs.2013.34.1.xxx Supporting Information Chemical Constituents of Ficus drupacea Leaves and their α-glucosidase Inhibitory
Notes Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 2013, Vol. 34, No. 1 1 http://dx.doi.org/10.5012/bkcs.2013.34.1.xxx Supporting Information Chemical Constituents of Ficus drupacea Leaves and their α-glucosidase Inhibitory
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Pang et al. 10.1073/pnas.1322009111 SI Materials and Methods ELISAs. These assays were performed as previously described (1). ELISA plates (MaxiSorp Nunc; Thermo Fisher Scientific)
Supporting Information Pang et al. 10.1073/pnas.1322009111 SI Materials and Methods ELISAs. These assays were performed as previously described (1). ELISA plates (MaxiSorp Nunc; Thermo Fisher Scientific)
: Ajou University College of Medicine, Suwon, Korea; Ajou University College of Medicine, Graduate
 CURRICULUM VITAE NAME Hyun Woo Lee, M.D. EDUCATION 1991.3.-2001.2 : Ajou University College of Medicine, Suwon, Korea; Doctor of Medicine 2004.3-2006.2 Ajou University College of Medicine, Graduate School,
CURRICULUM VITAE NAME Hyun Woo Lee, M.D. EDUCATION 1991.3.-2001.2 : Ajou University College of Medicine, Suwon, Korea; Doctor of Medicine 2004.3-2006.2 Ajou University College of Medicine, Graduate School,
EXPANSION RESEARCH FOR DEVELOPMENT OF LOCAL ANESTHETIC HAVING ANTI INFLAMMATORY ACTION
 No. 137 EXPANSION RESEARCH FOR DEVELOPMENT OF LOCAL ANESTHETIC HAVING ANTI INFLAMMATORY ACTION Takuya MIYAWAKI Professor Graduate School of Medicine, Dentistry and Pharmaceutical Sciences Okayama University
No. 137 EXPANSION RESEARCH FOR DEVELOPMENT OF LOCAL ANESTHETIC HAVING ANTI INFLAMMATORY ACTION Takuya MIYAWAKI Professor Graduate School of Medicine, Dentistry and Pharmaceutical Sciences Okayama University
DermaPep A530. Multifunctional anti-inflammatory peptide for irritated and sensitive skin. Experience The Magic of Science
 Experience The Magic of Science DermaPep A53 Multifunctional anti-inflammatory peptide for irritated and sensitive skin DermaP ep Experience the magic of science Anti-aging DermaPep A35 DermaPep A42 DermaPep
Experience The Magic of Science DermaPep A53 Multifunctional anti-inflammatory peptide for irritated and sensitive skin DermaP ep Experience the magic of science Anti-aging DermaPep A35 DermaPep A42 DermaPep
Anti-inflammatory properties of SM04690, a small molecule inhibitor of the Wnt pathway as a potential treatment for knee osteoarthritis
 Anti-inflammatory properties of SM04690, a small molecule inhibitor of the Wnt pathway as a potential treatment for knee osteoarthritis V. Deshmukh 1, T. Seo 1, C. Swearingen 1, Y. Yazici 1 1 Samumed,
Anti-inflammatory properties of SM04690, a small molecule inhibitor of the Wnt pathway as a potential treatment for knee osteoarthritis V. Deshmukh 1, T. Seo 1, C. Swearingen 1, Y. Yazici 1 1 Samumed,
Combined Rho-kinase inhibition and immunogenic cell death triggers and propagates immunity against cancer
 Supplementary Information Combined Rho-kinase inhibition and immunogenic cell death triggers and propagates immunity against cancer Gi-Hoon Nam, Eun-Jung Lee, Yoon Kyoung Kim, Yeonsun Hong, Yoonjeong Choi,
Supplementary Information Combined Rho-kinase inhibition and immunogenic cell death triggers and propagates immunity against cancer Gi-Hoon Nam, Eun-Jung Lee, Yoon Kyoung Kim, Yeonsun Hong, Yoonjeong Choi,
Metabolic classification of herb plants by NMR-based metabolomics
 Journal of the Korean Magnetic Resonance Society 2012, 16, 91-102 Metabolic classification of herb plants by NMR-based metabolomics Hee-Eun Kim, 1,a Ye Hun Choi, 2,a Kwang-Ho Choi, 1,a Ji Su Park, 2 Hyeon
Journal of the Korean Magnetic Resonance Society 2012, 16, 91-102 Metabolic classification of herb plants by NMR-based metabolomics Hee-Eun Kim, 1,a Ye Hun Choi, 2,a Kwang-Ho Choi, 1,a Ji Su Park, 2 Hyeon
SCIENCE CHAGA MUSHROOM
 SCIENCE 2 CHAGA mushroom INONOTUS OBLIQUUS Basiodiomycota fungus comprise a vast and yet largely untapped source of powerful new pharmaceutical products. In particular, and most importantly for modern
SCIENCE 2 CHAGA mushroom INONOTUS OBLIQUUS Basiodiomycota fungus comprise a vast and yet largely untapped source of powerful new pharmaceutical products. In particular, and most importantly for modern
- Final Report - Animal Testing Report for Safety and Efficacy of Ultraskin. October 31, 2012
 - Final Report - Animal Testing Report for Safety and Efficacy of Ultraskin October 31, 2012 CHUNGANG University Industry- Academic Cooperation Foundation 1 / 15 - Contents - 1. Test Overview... 3 2. Test
- Final Report - Animal Testing Report for Safety and Efficacy of Ultraskin October 31, 2012 CHUNGANG University Industry- Academic Cooperation Foundation 1 / 15 - Contents - 1. Test Overview... 3 2. Test
Mountain Ginseng Pharmacopuncture Treatment on Three Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis Patients -Case Report-
 3 119 DOI : 10.3831/KPI.2010.13.4.119 3 Received : 10. 11. 06 Revised : 10. 11. 18 Accepted : 10. 11. 26 Key Words: Mountain Ginseng Pharmacopuncture(MG P), Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis(ALS), Amyotrophic
3 119 DOI : 10.3831/KPI.2010.13.4.119 3 Received : 10. 11. 06 Revised : 10. 11. 18 Accepted : 10. 11. 26 Key Words: Mountain Ginseng Pharmacopuncture(MG P), Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis(ALS), Amyotrophic
Novan Provides Update on SB414 Inflammatory Skin Disease Development Program
 Novan Provides Update on SB414 Inflammatory Skin Disease Development Program SB414 Nitric Oxide-Releasing Cream Safe and Well-Tolerated in Psoriasis Phase 1b Trial Preclinical Data with SB414 Targeting
Novan Provides Update on SB414 Inflammatory Skin Disease Development Program SB414 Nitric Oxide-Releasing Cream Safe and Well-Tolerated in Psoriasis Phase 1b Trial Preclinical Data with SB414 Targeting
Summary of Feed Carcinogenicity Study. of Diphenylamine. in F344 Rats
 Summary of Feed Carcinogenicity Study of Diphenylamine in F344 Rats August 2011 Japan Bioassay Research Center Japan Industrial Safety and Health Association PREFACE The tests were contracted and supported
Summary of Feed Carcinogenicity Study of Diphenylamine in F344 Rats August 2011 Japan Bioassay Research Center Japan Industrial Safety and Health Association PREFACE The tests were contracted and supported
Repeated intra-articular injections of acidic saline produce long-lasting joint pain and. widespread hyperalgesia
 Repeated intra-articular injections of acidic saline produce long-lasting joint pain and widespread hyperalgesia N. Sugimura 1, M. Ikeuchi 1 *, M. Izumi 1, T. Kawano 2, K. Aso 1, T. Kato 1, T. Ushida 3,
Repeated intra-articular injections of acidic saline produce long-lasting joint pain and widespread hyperalgesia N. Sugimura 1, M. Ikeuchi 1 *, M. Izumi 1, T. Kawano 2, K. Aso 1, T. Kato 1, T. Ushida 3,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION. Involvement of IL-21 in the epidermal hyperplasia of psoriasis
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Involvement of IL-21 in the epidermal hyperplasia of psoriasis Roberta Caruso 1, Elisabetta Botti 2, Massimiliano Sarra 1, Maria Esposito 2, Carmine Stolfi 1, Laura Diluvio 2,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Involvement of IL-21 in the epidermal hyperplasia of psoriasis Roberta Caruso 1, Elisabetta Botti 2, Massimiliano Sarra 1, Maria Esposito 2, Carmine Stolfi 1, Laura Diluvio 2,
Chemical Chaperones Mitigate Experimental Asthma By Attenuating Endoplasmic
 Chemical Chaperones Mitigate Experimental Asthma By Attenuating Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress Lokesh Makhija, BE, Veda Krishnan, MSc, Rakhshinda Rehman, MTech, Samarpana Chakraborty, MSc, Shuvadeep Maity,
Chemical Chaperones Mitigate Experimental Asthma By Attenuating Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress Lokesh Makhija, BE, Veda Krishnan, MSc, Rakhshinda Rehman, MTech, Samarpana Chakraborty, MSc, Shuvadeep Maity,
Title proteinase-activated receptor 2 ago. Published by Elsevier Ireland Ltd.
 NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) Olopatadine hydrochloride inhibits proteinase-activated receptor 2 ago Yoshizaki, Ayumi; Sato, Shinichi Citation Journal of dermatological science, Issue
NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) Olopatadine hydrochloride inhibits proteinase-activated receptor 2 ago Yoshizaki, Ayumi; Sato, Shinichi Citation Journal of dermatological science, Issue
C57BL/6 Mice are More Appropriate. than BALB/C Mice in Inducing Dilated Cardiomyopathy with Short-Term Doxorubicin Treatment
 Original Article C57BL/6 Mice are More Appropriate Acta Cardiol Sin 2012;28:236 240 Heart Failure & Cardiomyopathy C57BL/6 Mice are More Appropriate than BALB/C Mice in Inducing Dilated Cardiomyopathy
Original Article C57BL/6 Mice are More Appropriate Acta Cardiol Sin 2012;28:236 240 Heart Failure & Cardiomyopathy C57BL/6 Mice are More Appropriate than BALB/C Mice in Inducing Dilated Cardiomyopathy
SUPPLEMENTARY METHODS
 SUPPLEMENTARY METHODS Histological analysis. Colonic tissues were collected from 5 parts of the middle colon on day 7 after the start of DSS treatment, and then were cut into segments, fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde,
SUPPLEMENTARY METHODS Histological analysis. Colonic tissues were collected from 5 parts of the middle colon on day 7 after the start of DSS treatment, and then were cut into segments, fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde,
The Role of Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase- Activated Protein Kinase 2 in the p38/tnf-a Pathway of Systemic and Cutaneous Inflammation
 See related commentary on pg 342 ORIGINAL ARTICLE The Role of Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase- Activated Protein Kinase 2 in the p38/tnf-a Pathway of Systemic and Cutaneous Inflammation Arndt J. Schottelius,
See related commentary on pg 342 ORIGINAL ARTICLE The Role of Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase- Activated Protein Kinase 2 in the p38/tnf-a Pathway of Systemic and Cutaneous Inflammation Arndt J. Schottelius,
Figure S1 Genetic or pharmacologic COX-2 inhibition led to increased kidney
 SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE LEGENDS Figure S1 Genetic or pharmacologic COX-2 inhibition led to increased kidney macrophage infiltration. Wild type or COX-2 -/- mice (2 months old, C57/Bl6 background) were treated
SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE LEGENDS Figure S1 Genetic or pharmacologic COX-2 inhibition led to increased kidney macrophage infiltration. Wild type or COX-2 -/- mice (2 months old, C57/Bl6 background) were treated
of 3-Aminophenol in B6D2F1 Mice
 Summary of Drinking Water Carcinogenicity Study of 3-Aminophenol in B6D2F1 Mice July 2012 Japan Bioassay Research Center Japan Industrial Safety and Health Association PREFACE The tests were contracted
Summary of Drinking Water Carcinogenicity Study of 3-Aminophenol in B6D2F1 Mice July 2012 Japan Bioassay Research Center Japan Industrial Safety and Health Association PREFACE The tests were contracted
Ozonated Olive Oil Enhances the Growth of Granulation Tissue in a Mouse Model of Pressure Ulcer
 Ozone: Science and Engineering, 29: 503 507 Copyright # 2007 International Ozone Association ISSN: 0191-9512 print / 1547-6545 online DOI: 10.1080/01919510701618205 Ozonated Olive Oil Enhances the Growth
Ozone: Science and Engineering, 29: 503 507 Copyright # 2007 International Ozone Association ISSN: 0191-9512 print / 1547-6545 online DOI: 10.1080/01919510701618205 Ozonated Olive Oil Enhances the Growth
감초 (Glycyrrhiza uralensis Fisch, GLU) 가천식모델생쥐의 BALF 내면역세포및 Cytokine 에미치는효과
 감초 (Glycyrrhiza uralensis Fisch, GLU) 가천식모델생쥐의 BALF 내면역세포및 Cytokine 에미치는효과 Effects of Glycyrrhiza uralensis Fisch on Immunocyte and Cytokine Production in Asthma Model Mouse Young-Joo Han, Yang-Chun Park
감초 (Glycyrrhiza uralensis Fisch, GLU) 가천식모델생쥐의 BALF 내면역세포및 Cytokine 에미치는효과 Effects of Glycyrrhiza uralensis Fisch on Immunocyte and Cytokine Production in Asthma Model Mouse Young-Joo Han, Yang-Chun Park
PUBLICATIONS. cells. J. Physiol. (London) 517P:91P (Manchester, England, UK).
 277 PUBLICATIONS Abstracts Haddad JJ, Land SC (1999). Differential activation of oxygen-responsive transcription factors over fetal-to-neonatal alveolar oxygen tensions in rat fetal distal lung epithelial
277 PUBLICATIONS Abstracts Haddad JJ, Land SC (1999). Differential activation of oxygen-responsive transcription factors over fetal-to-neonatal alveolar oxygen tensions in rat fetal distal lung epithelial
FOR OPTIMAL GUT HEALTH KEMIN.COM/GUTHEALTH
 FOR OPTIMAL GUT HEALTH KEMIN.COM/GUTHEALTH ALETA A SOURCE OF 1,3-BETA GLUCANS Aleta is highly bioavailable, offering a concentration greater than 5% of 1,3-beta glucans. Aleta provides a consistent response
FOR OPTIMAL GUT HEALTH KEMIN.COM/GUTHEALTH ALETA A SOURCE OF 1,3-BETA GLUCANS Aleta is highly bioavailable, offering a concentration greater than 5% of 1,3-beta glucans. Aleta provides a consistent response
Serum mirna signature diagnoses and discriminates murine colitis subtypes and predicts ulcerative colitis in humans
 Serum mirna signature diagnoses and discriminates murine colitis subtypes and predicts ulcerative colitis in humans Emilie Viennois 1*, Yuan Zhao 1, 2, Moon Kwon Han 1, Bo Xiao 1, 3, Mingzhen Zhang 1,
Serum mirna signature diagnoses and discriminates murine colitis subtypes and predicts ulcerative colitis in humans Emilie Viennois 1*, Yuan Zhao 1, 2, Moon Kwon Han 1, Bo Xiao 1, 3, Mingzhen Zhang 1,
GMI-1070: A Novel Potential Study Treatment During Sickle Cell Crisis. September 17, 2011
 GMI-1070: A Novel Potential Study Treatment During Sickle Cell Crisis September 17, 2011 Current Available Treatment for Vaso-Occlusive Crisis (VOC) VOC results in life-threatening complications and reduced
GMI-1070: A Novel Potential Study Treatment During Sickle Cell Crisis September 17, 2011 Current Available Treatment for Vaso-Occlusive Crisis (VOC) VOC results in life-threatening complications and reduced
Supplementary Material for
 Supplementary Material for Parathyroid Hormone Signaling through Low-density-lipoprotein-related Protein 6 Mei Wan, Chaozhe Yang, Jun Li, Xiangwei Wu, Hongling Yuan, Hairong Ma, Xi He, Shuyi Nie, Chenbei
Supplementary Material for Parathyroid Hormone Signaling through Low-density-lipoprotein-related Protein 6 Mei Wan, Chaozhe Yang, Jun Li, Xiangwei Wu, Hongling Yuan, Hairong Ma, Xi He, Shuyi Nie, Chenbei
Reviewers' comments: Reviewer #1 Expert in EAE and IL-17a (Remarks to the Author):
 Reviewers' comments: Reviewer #1 Expert in EAE and IL-17a (Remarks to the Author): This study shows that the inducible camp early repressor (ICER) is involved in development of Th17 cells that are pathogenic
Reviewers' comments: Reviewer #1 Expert in EAE and IL-17a (Remarks to the Author): This study shows that the inducible camp early repressor (ICER) is involved in development of Th17 cells that are pathogenic
Human TNFα Transgenic Mouse Model of Spontaneous Arthritis
 Human TNFα Transgenic Mouse Model of Spontaneous Arthritis HEIDELBERG PHARMA AT A GLANCE CRO situated in Ladenburg, near Heidelberg, Germany 45 employees, 2000 m 2 of lab space Core competence: pre-clinical
Human TNFα Transgenic Mouse Model of Spontaneous Arthritis HEIDELBERG PHARMA AT A GLANCE CRO situated in Ladenburg, near Heidelberg, Germany 45 employees, 2000 m 2 of lab space Core competence: pre-clinical
Biodegradable Zwitterionic Nanogels with Long. Circulation for Antitumor Drug Delivery
 Supporting Information Biodegradable Zwitterionic Nanogels with Long Circulation for Antitumor Drug Delivery Yongzhi Men, Shaojun Peng, Peng Yang, Qin Jiang, Yanhui Zhang, Bin Shen, Pin Dong, *, Zhiqing
Supporting Information Biodegradable Zwitterionic Nanogels with Long Circulation for Antitumor Drug Delivery Yongzhi Men, Shaojun Peng, Peng Yang, Qin Jiang, Yanhui Zhang, Bin Shen, Pin Dong, *, Zhiqing
Supplementary Information. Glycogen shortage during fasting triggers liver-brain-adipose. neurocircuitry to facilitate fat utilization
 Supplementary Information Glycogen shortage during fasting triggers liver-brain-adipose neurocircuitry to facilitate fat utilization Supplementary Figure S1. Liver-Brain-Adipose neurocircuitry Starvation
Supplementary Information Glycogen shortage during fasting triggers liver-brain-adipose neurocircuitry to facilitate fat utilization Supplementary Figure S1. Liver-Brain-Adipose neurocircuitry Starvation
Part-I: Screening. 3.1 Assessment of non-toxic concentration of test compounds in RAW cells. Results
 Part-I: Screening Our strategy was to look for compounds which can inhibit HMGB1 (high mobility group box 1) release in activated macrophages and check effect of screened compound on endotoxemic mice.
Part-I: Screening Our strategy was to look for compounds which can inhibit HMGB1 (high mobility group box 1) release in activated macrophages and check effect of screened compound on endotoxemic mice.
Supplemental Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Food & Function. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Supplemental Information Supplementary Materials and Methods Materials Assay kits of total
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Food & Function. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Supplemental Information Supplementary Materials and Methods Materials Assay kits of total
Expression constructs
 Gene expressed in bebe3 ZmBEa Expression constructs 35S ZmBEa Pnos:Hygromycin r 35S Pnos:Hygromycin r 35S ctp YFP Pnos:Hygromycin r B -1 Chl YFP- Merge Supplemental Figure S1: Constructs Used for the Expression
Gene expressed in bebe3 ZmBEa Expression constructs 35S ZmBEa Pnos:Hygromycin r 35S Pnos:Hygromycin r 35S ctp YFP Pnos:Hygromycin r B -1 Chl YFP- Merge Supplemental Figure S1: Constructs Used for the Expression
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Notch deficiency decreases hepatic lipid accumulation by induction of fatty acid oxidation No-Joon Song,#, Ui Jeong Yun,#, Sunghee Yang, Chunyan Wu, Cho-Rong Seo, A-Ryeong Gwon,,
Supplementary Information Notch deficiency decreases hepatic lipid accumulation by induction of fatty acid oxidation No-Joon Song,#, Ui Jeong Yun,#, Sunghee Yang, Chunyan Wu, Cho-Rong Seo, A-Ryeong Gwon,,
Supplementary Figure 1. H-PGDS deficiency does not affect GI tract functions and anaphylactic reaction. (a) Representative pictures of H&E-stained
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 Supplementary Figure 1. H-PGDS deficiency does not affect GI tract functions and anaphylactic reaction. (a) Representative pictures of H&E-stained jejunum sections ( 200 magnification;
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 Supplementary Figure 1. H-PGDS deficiency does not affect GI tract functions and anaphylactic reaction. (a) Representative pictures of H&E-stained jejunum sections ( 200 magnification;
Blocking antibodies and peptides. Rat anti-mouse PD-1 (29F.1A12, rat IgG2a, k), PD-
 Supplementary Methods Blocking antibodies and peptides. Rat anti-mouse PD-1 (29F.1A12, rat IgG2a, k), PD- L1 (10F.9G2, rat IgG2b, k), and PD-L2 (3.2, mouse IgG1) have been described (24). Anti-CTLA-4 (clone
Supplementary Methods Blocking antibodies and peptides. Rat anti-mouse PD-1 (29F.1A12, rat IgG2a, k), PD- L1 (10F.9G2, rat IgG2b, k), and PD-L2 (3.2, mouse IgG1) have been described (24). Anti-CTLA-4 (clone
SOME ASPECTS OF ANTI-INFLAMMATORY ACTION OF IMMUNOSUPPRESSIVE DRUGS
 SOME ASPECTS OF ANTI-INFLAMMATORY ACTION OF IMMUNOSUPPRESSIVE DRUGS Wataru TSUKADA, Takeshi AKIMOTO and Yutaka MIZUSHIMA* Laboratory of Pharmacology, Research Institute, Daiiclri Seiyaku Co., Ltd., Edogawa-ku,
SOME ASPECTS OF ANTI-INFLAMMATORY ACTION OF IMMUNOSUPPRESSIVE DRUGS Wataru TSUKADA, Takeshi AKIMOTO and Yutaka MIZUSHIMA* Laboratory of Pharmacology, Research Institute, Daiiclri Seiyaku Co., Ltd., Edogawa-ku,
IKKα Causes Chromatin Modification on Pro-Inflammatory Genes by Cigarette Smoke in Mouse Lung
 IKKα Causes Chromatin Modification on Pro-Inflammatory Genes by Cigarette Smoke in Mouse Lung Se-Ran Yang, Samantha Valvo, Hongwei Yao, Aruna Kode, Saravanan Rajendrasozhan, Indika Edirisinghe, Samuel
IKKα Causes Chromatin Modification on Pro-Inflammatory Genes by Cigarette Smoke in Mouse Lung Se-Ran Yang, Samantha Valvo, Hongwei Yao, Aruna Kode, Saravanan Rajendrasozhan, Indika Edirisinghe, Samuel
Curriculum Vitae. Wan-Seob Cho, D.V.M., Ph.D
 Curriculum Vitae Wan-Seob Cho, D.V.M., Ph.D Department of Toxicologic Pathology, National Institute of Toxicological Research, Korea Food and Drug Administration #5, Nokbundong, Eunpyung-gu, Seoul, 122-704,
Curriculum Vitae Wan-Seob Cho, D.V.M., Ph.D Department of Toxicologic Pathology, National Institute of Toxicological Research, Korea Food and Drug Administration #5, Nokbundong, Eunpyung-gu, Seoul, 122-704,
Supplementary Figure 1. Expression of CUGBP1 in non-parenchymal liver cells treated with TGF-β
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Expression of CUGBP1 in non-parenchymal liver cells treated with TGF-β and LPS. Non-parenchymal liver cells were isolated and treated with or without TGF-β
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Expression of CUGBP1 in non-parenchymal liver cells treated with TGF-β and LPS. Non-parenchymal liver cells were isolated and treated with or without TGF-β
Mass Histology Service
 Mass Histology Service A complete anatomical pathology laboratory www.masshistology.com Telephone: (877) 286-6004 Report on Pathology A Time Course Study of the Local Effects of Intramuscular XXXXXXX Injection
Mass Histology Service A complete anatomical pathology laboratory www.masshistology.com Telephone: (877) 286-6004 Report on Pathology A Time Course Study of the Local Effects of Intramuscular XXXXXXX Injection
Role of the Brain-Lung Axis in Fatigue
 Role of the Brain-Lung Axis in Fatigue Y.S. Prakash, M.D., Ph.D. Professor of Anesthesiology and Physiology Chair, Department of Physiology & BME Mayo Clinic Rochester, Minnesota, USA Fatigue in Chronic
Role of the Brain-Lung Axis in Fatigue Y.S. Prakash, M.D., Ph.D. Professor of Anesthesiology and Physiology Chair, Department of Physiology & BME Mayo Clinic Rochester, Minnesota, USA Fatigue in Chronic
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 The average sigmoid parametric curves of capillary dilation time courses and average time to 50% peak capillary diameter dilation computed from individual capillary responses averaged
Supplementary Figure 1 The average sigmoid parametric curves of capillary dilation time courses and average time to 50% peak capillary diameter dilation computed from individual capillary responses averaged
7. NOOTROPIC AND ANTIOXIDANT ACTIVITY. 7.1 Introduction
 268 7. NOOTROPIC AND ANTIOXIDANT ACTIVITY 7.1 Introduction Alzheimer s disease is a neurodegenerative disorder, which according to World Health Organization (WHO) affects 22 million people world wide,
268 7. NOOTROPIC AND ANTIOXIDANT ACTIVITY 7.1 Introduction Alzheimer s disease is a neurodegenerative disorder, which according to World Health Organization (WHO) affects 22 million people world wide,
Tissues. Tissues - Overview. Bio 101 Laboratory 3. Epithelial Tissues and Integument
 Bio 101 Laboratory 3 Epithelial Tissues and Integument 1 Tissues Tissues to be examined under the microscope Epithelial Tissue Integument Connective Tissue **We will be doing muscle and nervous tissues
Bio 101 Laboratory 3 Epithelial Tissues and Integument 1 Tissues Tissues to be examined under the microscope Epithelial Tissue Integument Connective Tissue **We will be doing muscle and nervous tissues
c Ischemia (30 min) Reperfusion (8 w) Supplementary Figure bp 300 bp Ischemia (30 min) Reperfusion (4 h) Dox 20 mg/kg i.p.
 a Marker Ripk3 +/ 5 bp 3 bp b Ischemia (3 min) Reperfusion (4 h) d 2 mg/kg i.p. 1 w 5 w Sacrifice for IF size A subset for echocardiography and morphological analysis c Ischemia (3 min) Reperfusion (8
a Marker Ripk3 +/ 5 bp 3 bp b Ischemia (3 min) Reperfusion (4 h) d 2 mg/kg i.p. 1 w 5 w Sacrifice for IF size A subset for echocardiography and morphological analysis c Ischemia (3 min) Reperfusion (8
Introduction. Acute sodium overload produces renal tubulointerstitial inflammation in normal rats
 Acute sodium overload produces renal tubulointerstitial inflammation in normal rats MI Roson, et al. Kidney International (2006) Introduction Present by Kanya Bunnan and Wiraporn paebua Tubular sodium
Acute sodium overload produces renal tubulointerstitial inflammation in normal rats MI Roson, et al. Kidney International (2006) Introduction Present by Kanya Bunnan and Wiraporn paebua Tubular sodium
Role of Tyk-2 in Th9 and Th17 cells in allergic asthma
 Supplementary File Role of Tyk-2 in Th9 and Th17 cells in allergic asthma Caroline Übel 1*, Anna Graser 1*, Sonja Koch 1, Ralf J. Rieker 2, Hans A. Lehr 3, Mathias Müller 4 and Susetta Finotto 1** 1 Laboratory
Supplementary File Role of Tyk-2 in Th9 and Th17 cells in allergic asthma Caroline Übel 1*, Anna Graser 1*, Sonja Koch 1, Ralf J. Rieker 2, Hans A. Lehr 3, Mathias Müller 4 and Susetta Finotto 1** 1 Laboratory
BUT ONLY MINIMALLY AFFECTS OTHER INDICATORS OF COLONIC INTEGRITY IN A RAT MODEL OF
 EMU OIL INCREASES CRYPT DEPTH BUT ONLY MINIMALLY AFFECTS OTHER INDICATORS OF COLONIC INTEGRITY IN A RAT MODEL OF COLITIS SUZANNE MASHTOUB Discipline of Physiology, School of Molecular & Biomedical Science,
EMU OIL INCREASES CRYPT DEPTH BUT ONLY MINIMALLY AFFECTS OTHER INDICATORS OF COLONIC INTEGRITY IN A RAT MODEL OF COLITIS SUZANNE MASHTOUB Discipline of Physiology, School of Molecular & Biomedical Science,
Cathepsin S Inhibitors for the Treatment of Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Therapeutic Area Partnerships Presentation.
 Inhibitors for the Treatment of Inflammatory Bowel Disease Therapeutic Area Partnerships Presentation November 29, 2012 Cathepsin Cysteine Proteinases Fibrosis Cathepsin O Cathepsin B Cathepsin C Cathepsin
Inhibitors for the Treatment of Inflammatory Bowel Disease Therapeutic Area Partnerships Presentation November 29, 2012 Cathepsin Cysteine Proteinases Fibrosis Cathepsin O Cathepsin B Cathepsin C Cathepsin
AQP0 Low Lens eyeball Cataract
 Topics Kampo Medicine Water-Metabolism Regulatory Action of Chinese Herbal Medicine Yoichiro Isohama Field of Drug Activities, Bioscience Research Div. Graduate School of Kumamoto University 1. Introduction
Topics Kampo Medicine Water-Metabolism Regulatory Action of Chinese Herbal Medicine Yoichiro Isohama Field of Drug Activities, Bioscience Research Div. Graduate School of Kumamoto University 1. Introduction
Data Sheet TIGIT / NFAT Reporter - Jurkat Cell Line Catalog #60538
 Data Sheet TIGIT / NFAT Reporter - Jurkat Cell Line Catalog #60538 Background: TIGIT is a co-inhibitory receptor that is highly expressed in Natural Killer (NK) cells, activated CD4+, CD8+ and regulatory
Data Sheet TIGIT / NFAT Reporter - Jurkat Cell Line Catalog #60538 Background: TIGIT is a co-inhibitory receptor that is highly expressed in Natural Killer (NK) cells, activated CD4+, CD8+ and regulatory
Canqiu Yu 1, Jinwei Chen 2, Li Huang 3*
 A STUDY ON THE ANTITUMOUR EFFECT OF TOTAL FLAVONOIDS FROM PTERIS MULTIFIDA POIR IN H22 TUMOUR-BEARING MICE 459 Canqiu Yu 1, Jinwei Chen 2, Li Huang 3* 1 Department of General Surgery, The Second Xiangya
A STUDY ON THE ANTITUMOUR EFFECT OF TOTAL FLAVONOIDS FROM PTERIS MULTIFIDA POIR IN H22 TUMOUR-BEARING MICE 459 Canqiu Yu 1, Jinwei Chen 2, Li Huang 3* 1 Department of General Surgery, The Second Xiangya
CYLD Negatively Regulates Transforming Growth Factor-β Signaling via Deubiquitinating Akt
 Supplementary Information CYLD Negatively Regulates Transforming Growth Factor-β Signaling via Deubiquitinating Akt Jae Hyang Lim, Hirofumi Jono, Kensei Komatsu, Chang-Hoon Woo, Jiyun Lee, Masanori Miyata,
Supplementary Information CYLD Negatively Regulates Transforming Growth Factor-β Signaling via Deubiquitinating Akt Jae Hyang Lim, Hirofumi Jono, Kensei Komatsu, Chang-Hoon Woo, Jiyun Lee, Masanori Miyata,
-26- MATERIALS AND METHODS
 -26- MATERIALS AND METHODS The pollutant : Sevin (1-naphthyl N-methyl carbamate) was used at a concentrations of 0.5 and 1.0 mg/l. At these concentrations, the insecticide was completely soluble in water.
-26- MATERIALS AND METHODS The pollutant : Sevin (1-naphthyl N-methyl carbamate) was used at a concentrations of 0.5 and 1.0 mg/l. At these concentrations, the insecticide was completely soluble in water.
Recent Trend in the Incidence of Premalignant and Malignant Skin Lesions in Korea between 1991 and 2006
 J Korean Med Sci 2010; 25: 924-9 ISSN 1011-8934 DOI: 10.3346/jkms.2010.25.6.924 Recent Trend in the Incidence of Premalignant and Malignant Skin Lesions in Korea between 1991 and 2006 We evaluated the
J Korean Med Sci 2010; 25: 924-9 ISSN 1011-8934 DOI: 10.3346/jkms.2010.25.6.924 Recent Trend in the Incidence of Premalignant and Malignant Skin Lesions in Korea between 1991 and 2006 We evaluated the
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL. Sample preparation for light microscopy
 SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL Sample preparation for light microscopy To characterize the granulocytes and melanomacrophage centers, cross sections were prepared for light microscopy, as described in Material
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL Sample preparation for light microscopy To characterize the granulocytes and melanomacrophage centers, cross sections were prepared for light microscopy, as described in Material
Citation The Journal of dermatology, 37(1), available at
 NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) Case of localized scleroderma assoc Muroi, Eiji; Ogawa, Fumihide; Yamao Sato, Shinichi Citation The Journal of dermatology, 37(1), Issue Date 2010-01 URL
NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) Case of localized scleroderma assoc Muroi, Eiji; Ogawa, Fumihide; Yamao Sato, Shinichi Citation The Journal of dermatology, 37(1), Issue Date 2010-01 URL
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Desnues et al. 10.1073/pnas.1314121111 SI Materials and Methods Mice. Toll-like receptor (TLR)8 / and TLR9 / mice were generated as described previously (1, 2). TLR9 / mice were
Supporting Information Desnues et al. 10.1073/pnas.1314121111 SI Materials and Methods Mice. Toll-like receptor (TLR)8 / and TLR9 / mice were generated as described previously (1, 2). TLR9 / mice were
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 AAV-GFP injection in the MEC of the mouse brain C57Bl/6 mice at 4 months of age were injected with AAV-GFP into the MEC and sacrificed at 7 days post injection (dpi). (a) Brains
Supplementary Figure 1 AAV-GFP injection in the MEC of the mouse brain C57Bl/6 mice at 4 months of age were injected with AAV-GFP into the MEC and sacrificed at 7 days post injection (dpi). (a) Brains
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information M1 macrophage-derived nanovesicles potentiate the anticancer efficacy of immune checkpoint inhibitors Yeon Woong Choo, 1, Mikyung Kang, 2, Han Young Kim, 1 Jin Han, 1 Seokyung Kang,
Supporting Information M1 macrophage-derived nanovesicles potentiate the anticancer efficacy of immune checkpoint inhibitors Yeon Woong Choo, 1, Mikyung Kang, 2, Han Young Kim, 1 Jin Han, 1 Seokyung Kang,
Changes in the seroprevalence of IgG anti-hepatitis A virus between 2001 and 2013: experience at a single center in Korea
 pissn 2287-2728 eissn 2287-285X Original Article Clinical and Molecular Hepatology 214;2:162-167 Changes in the seroprevalence of IgG anti-hepatitis A virus between 21 and 213: experience at a single center
pissn 2287-2728 eissn 2287-285X Original Article Clinical and Molecular Hepatology 214;2:162-167 Changes in the seroprevalence of IgG anti-hepatitis A virus between 21 and 213: experience at a single center
Pharmacological and histopathological study of cyclophosphamide-induced hemorrhagic cystitis - comparison of the effects of dexamethasone and Mesna
 Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research (1999) 32: 1211-1215 ISSN 0100-879X Short Communication 1211 Pharmacological and histopathological study of cyclophosphamide-induced hemorrhagic cystitis
Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research (1999) 32: 1211-1215 ISSN 0100-879X Short Communication 1211 Pharmacological and histopathological study of cyclophosphamide-induced hemorrhagic cystitis
INDUCTION OF OVULATION IN URETHANE-TREATED RATS
 5 INDUCTION OF OVULATION IN URETHANE-TREATED RATS Ronald D. Johnson* and Barbara Shirley Faculty of Natural Sciences, University of Tulsa, Tulsa, Oklahoma 74104 Subcutaneous injection of urethane (1 g/kg
5 INDUCTION OF OVULATION IN URETHANE-TREATED RATS Ronald D. Johnson* and Barbara Shirley Faculty of Natural Sciences, University of Tulsa, Tulsa, Oklahoma 74104 Subcutaneous injection of urethane (1 g/kg
Evaluation of the Protective Effect of Plant Extracts Against Pheophorbide a-induced Photosensitive Damage
 Trace Nutrients Research 26 : 88 92 (2009) Evaluation of the Protective Effect of Plant Extracts Against Pheophorbide a-induced Photosensitive Damage Amy TOMITA, Tomoyo KAJIURA and Shuichi KIMURA Showa
Trace Nutrients Research 26 : 88 92 (2009) Evaluation of the Protective Effect of Plant Extracts Against Pheophorbide a-induced Photosensitive Damage Amy TOMITA, Tomoyo KAJIURA and Shuichi KIMURA Showa
Serum Amyloid A3 Gene Expression in Adipocytes is an Indicator. of the Interaction with Macrophages
 Serum Amyloid A3 Gene Expression in Adipocytes is an Indicator of the Interaction with Macrophages Yohei Sanada, Takafumi Yamamoto, Rika Satake, Akiko Yamashita, Sumire Kanai, Norihisa Kato, Fons AJ van
Serum Amyloid A3 Gene Expression in Adipocytes is an Indicator of the Interaction with Macrophages Yohei Sanada, Takafumi Yamamoto, Rika Satake, Akiko Yamashita, Sumire Kanai, Norihisa Kato, Fons AJ van
Corticosteroids. Veterinary Pharmacology Endocrine System. University of Tehran Faculty of Veterinary Medicine Academic Year
 Veterinary Pharmacology Endocrine System Corticosteroids University of Tehran Faculty of Veterinary Medicine Academic Year 2008-9 Goudarz Sadeghi, DVM, PhD, DSc Associate Professor of Pharmacology Introduction
Veterinary Pharmacology Endocrine System Corticosteroids University of Tehran Faculty of Veterinary Medicine Academic Year 2008-9 Goudarz Sadeghi, DVM, PhD, DSc Associate Professor of Pharmacology Introduction
Development of Supercritical Fluid Extraction of Glabridin from Glycyrrhiza glabra
 Development of Supercritical Fluid Extraction of Glabridin from Glycyrrhiza glabra On-line Number 939 Yun-Kyoung Cho, 1 Sang-Yun Lee, 1,2 Hyun-Seok Kim, 3 Jong-Hoon Ryu, 1 and Gio-Bin Lim 1 1 Department
Development of Supercritical Fluid Extraction of Glabridin from Glycyrrhiza glabra On-line Number 939 Yun-Kyoung Cho, 1 Sang-Yun Lee, 1,2 Hyun-Seok Kim, 3 Jong-Hoon Ryu, 1 and Gio-Bin Lim 1 1 Department
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Memory-type ST2 + CD + T cells participate in the steroid-resistant pathology of eosinophilic pneumonia Naoko Mato 1, 2, Kiyoshi Hirahara 2, Tomomi Ichikawa 2, Jin Kumagai 2,
Supplementary Information Memory-type ST2 + CD + T cells participate in the steroid-resistant pathology of eosinophilic pneumonia Naoko Mato 1, 2, Kiyoshi Hirahara 2, Tomomi Ichikawa 2, Jin Kumagai 2,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION FOR Liver X Receptor α mediates hepatic triglyceride accumulation through upregulation of G0/G1 Switch Gene 2 (G0S2) expression I: SUPPLEMENTARY METHODS II: SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION FOR Liver X Receptor α mediates hepatic triglyceride accumulation through upregulation of G0/G1 Switch Gene 2 (G0S2) expression I: SUPPLEMENTARY METHODS II: SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES
Experience The Magic of Science. DermaPep UL. Multi-functional whitening active. Experience the magic of science
 Experience The Magic of Science Multi-functional whitening active DermaP ep Experience the magic of science Anti-aging DermaPep A35 DermaPep A42 DermaPep A44 DermaPep A53 Whitening DermaPep A35 DermaPep
Experience The Magic of Science Multi-functional whitening active DermaP ep Experience the magic of science Anti-aging DermaPep A35 DermaPep A42 DermaPep A44 DermaPep A53 Whitening DermaPep A35 DermaPep
Supplementary Figure 1: Kv7 currents in neonatal CA1 neurons measured with the classic M- current voltage-clamp protocol.
 Supplementary Figures 1-11 Supplementary Figure 1: Kv7 currents in neonatal CA1 neurons measured with the classic M- current voltage-clamp protocol. (a), Voltage-clamp recordings from CA1 pyramidal neurons
Supplementary Figures 1-11 Supplementary Figure 1: Kv7 currents in neonatal CA1 neurons measured with the classic M- current voltage-clamp protocol. (a), Voltage-clamp recordings from CA1 pyramidal neurons
University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul 05505, Republic of Korea.
 Nanoparticle-Assisted Transcutaneous Delivery of a Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription 3-Inhibiting Peptide Ameliorates Psoriasis-like Skin Inflammation Jin Yong Kim 1,5, Jinhyo Ahn 3,4, Jinjoo
Nanoparticle-Assisted Transcutaneous Delivery of a Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription 3-Inhibiting Peptide Ameliorates Psoriasis-like Skin Inflammation Jin Yong Kim 1,5, Jinhyo Ahn 3,4, Jinjoo
Supplementary Figure 1. Characterization of basophils after reconstitution of SCID mice
 Supplementary figure legends Supplementary Figure 1. Characterization of after reconstitution of SCID mice with CD4 + CD62L + T cells. (A-C) SCID mice (n = 6 / group) were reconstituted with 2 x 1 6 CD4
Supplementary figure legends Supplementary Figure 1. Characterization of after reconstitution of SCID mice with CD4 + CD62L + T cells. (A-C) SCID mice (n = 6 / group) were reconstituted with 2 x 1 6 CD4
Over-expression of MKP-3 and knockdown of MKP-3 and FOXO1 in primary rat. day, cells were transduced with adenoviruses expressing GFP, MKP-3 or shgfp,
 SUPPLEMENTAL METHODS Over-expression of MKP-3 and knockdown of MKP-3 and FOXO1 in primary rat hepatocytes Primary rat hepatocytes were seeded as described in experimental procedures. The next day, cells
SUPPLEMENTAL METHODS Over-expression of MKP-3 and knockdown of MKP-3 and FOXO1 in primary rat hepatocytes Primary rat hepatocytes were seeded as described in experimental procedures. The next day, cells
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information A novel pyrazole derivative protects from ovariectomy-induced osteoporosis through the inhibition of NADPH oxidase Jung Hee Joo 1*, Jeong-Eun Huh 1*,JeeHyunLee 1,DooRiPark 1,
Supplementary Information A novel pyrazole derivative protects from ovariectomy-induced osteoporosis through the inhibition of NADPH oxidase Jung Hee Joo 1*, Jeong-Eun Huh 1*,JeeHyunLee 1,DooRiPark 1,
