E2F1 stability is regulated by a novel-pkc/p38b MAP kinase signaling pathway during keratinocyte differentiation
|
|
|
- Harold Dean
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 (2006) 25, & 2006 Nture Pulishing Group All rights reserved /06 $ ORGINAL ARTICLE stility is regulted y novel-pkc/p38 MAP kinse signling pthwy during kertinoyte differentition IA Ivnov 1, SJA D Souz 1 nd L Dgnino 1,2 1 Deprtment of Physiology nd Phrmology, University of Western Ontrio, London, Ontrio, Cnd nd 2 Deprtment of Peditris, University of Western Ontrio, London, Ontrio, Cnd E2F trnsription ftors regulte prolifertion, differentition, DNA repir nd poptosis. Tight E2F regultion is ruil for epiderml formtion nd regenertion. However, virtully nothing is known out the moleulr events modulting E2F during epiderml kertinoyte differentition. Eluidtion of these events is essentil to understnd epiderml morphogenesis, trnsformtion nd repir. Here we show tht, in differentiting kertinoytes, C 2 þ -indued protein kinse C (PKC) tivtion downregultes protein levels. Further, we hve identified PKC d nd g s those isoforms speifilly involved in indution of protesoml degrdtion. We lso demonstrte tht downregultion y novel PKC isozymes requires tivtion of p38 mitogentivted protein kinse (MAPK). This is the first exmple of regultion in the E2F trnsription ftor fmily y tivtion of PKC nd MAPK in the ontext of iologilly signifint differentition stimuli in epitheli. (2006) 25, doi: /sj.on ; pulished online 22 August 2005 Keywords: kertinoyte; E2F; differentition Introdution The E2F fmily of trnsription ftors is wellestlished regultor of mny ell responses, suh s ell yle progression, differentition, poptosis nd DNA repir (Cm nd Dynlht, 2003; Bell nd Ryn, 2004). However, key issue tht remins poorly understood is, how externl stimuli tht indue hnges in prolifertion or differentition re trnsmitted intrellulrly to regulte E2F. Further, lthough it hs een estlished tht E2F proteinsn e regulted trnsriptionlly nd post-trnsltionlly, the identifition of the physiologil stimuli governing suh regultion is in its infny. E2F proteinsre differentilly modulted in epiderml kertinoytes., -2 nd -3 re undnt in Correspondene: Dr L Dgnino, Deprtment of Physiology & Phrmology, University of Western Ontrio, London, Ontrio, Cnd N6A 5C1. E-mil: ldgnino@uwo. Reeived 12 April 2005; revised 8 July 2005; epted 8 July 2005; pulished online 22 August 2005 undifferentited kertinoytes. Differentition triggers downregultion of these E2F forms nd upregultion of E2F5 (D Souz et l., 2001). The iologil importne of funtion nd regultion in epiderml homeostsis hs een mply demonstrted. For exmple, is essentil to mintin norml prolifertion in undifferentited kertinoytes, nd intivtion of the E2f1 gene in mie yieldsepiderml ellswith douling times out seven-fold longer thn wild-type ells, nd whih exhiit severely redued ility to re-epithelilize the skin during utneous regenertion (D Souz et l., 2002). Conversely, downregultion is neessry for proper kertinoyte differentition, sexogenous expression in differentiting ultured kertinoytes prevents exit from the ell yle, uses poptosis nd interfereswith expression of differentition mrkers, suh s trnsglutminse 1 nd kertin 10 (Diker et l., 2000; D Souz et l., 2001). Further, norml expression in the squmous epitheli of trnsgeni mie indueshyperprolifertion, hyperplsi nd poptosis in vivo, oth in interfolliulr nd folliulr epidermis(piere et l., 1998, 1999). In the epidermis, n extrellulr C 2 þ grdient is present from the undifferentited sl to the terminlly differentited ornified lyer. Indeed, n importnt mehnism for kertinoyte indution of terminl differentition involvesc 2 þ signling (reviewed in Koster nd Roop, 2004). In ulture, primry mouse kertinoytesn e mintined sn undifferentited ell popultion, nd n e indued to differentite y elevting the extrellulr C 2 þ onentrtion to mm (Dotto, 1999). Clium tretment of these ells tivtes protein kinse C (PKC), tyrosine kinses nd phosphtidyl inositol-3 (PI-3) kinse, mimiking epiderml differentition proesses, inluding entry into quiesene nd expression of differentition mrkers. Centrl in kertinoyte withdrwl from the ell yle is the E2F/ network (Ruiz et l., 2004). However, severl key issues remin to e resolved: Wht re the pthwystht onvey extrellulr differentition signls to downstrem E2F proteins? To whih extent do these pthwys onverge in the regultion of other differentition trgets? Wht re the mehnisms of E2F regultion in differentiting kertinoytes? We hve egun to ddress those questions, nd demonstrte tht C 2 þ -indued tivtion of PKC in differentiting kertinoytesresultsin
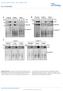
2 protein destiliztion through mehnisms tht lso involve p38 tivtion. Together, these results point to PKC- nd p38-medited turnover s ritil omponent of differentition responses in epithelil ells. PKC regultion of turnover Antiody: E2F5 E2F5 431 F Results Protein kinse C tivtion modultes E2F in differentiting epiderml mouse kertinoytes In primry murine kertinoytes, indution of differentition y ulture in medium ontining 1.0 mm C 2 þ ledsto downregultion of, -2 nd -3, upregultion of E2F5, nd hngesin DNA-inding omplexes (D Souz et l., 2001). In greement with previous reports(d Souz et l., 2001), nlysis of E2F DNAinding omplexesy eletrophoreti moility shift ssys (EMSA) using lystes from undifferentited kertinoytesultured in low C 2 þ (0.05 mm) medium reveled the ontriution of, nd, s evidened y the formtion of supershifted speies in the presene of ntiodies ginst those proteins (Figure 1). In ontrst, no hnges in nding pttern were deteted in the presene of ntiodies ginst or E2F5, inditing tht these proteins my e minor onstituents of E2F DNA-inding omplexes in these ells(figure 1). Indution of differentition y ulture in high C 2 þ (1.0 mm) medium resulted in the formtion of omplexesminly omposed of nd (Figure 1). E2F5-ontining DNA inding speies were lso deteted in differentited kertinoytes (Figure 1). To identify the eventstivted y C 2 þ upstrem from E2F, we first investigted the involvement of kinse signling sdes known to e involved in primry kertinoyte differentition in the formtion of E2F/ nd E2F/ omplexes using EMSA. These signling sdes inlude PKC, tyrosine kinses nd phosphoinositide-3 kinse (Dotto, 1999). Tretment of undifferentited kertinoyteswith the PKC tivtor 12-O-tetrdenoylphorol-13-ette () mimiked the C 2 þ -indued formtion of E2F5-, - nd -ontining omplexes(figure 1). Conversely, tretment with the PKC inhiitorshelerythrine or Ro interfered with the indution of those omplexesy C 2 þ (Figure 1). In ontrst, the presene of the tyrosine kinse inhiitors genistein nd herimyin, or the phosphoinositide-3 kinse inhiitor wortmnnin did not interfere with C 2 þ -indution of the E2F/ nd E2F/ DNA-inding speies ssoited with differentition (Figure 1). Although nd the PKC inhiitorsmy individully modulte ellulr pthwys other thn PKC, tken together, our results re onsistent with the onept tht PKC is involved in regultion of E2F DNA-inding omplex formtion in differentiting kertinoytes. Ativtion of PKC y lso mimis the redution in nd inrese in E2F5 protein levels indued y C 2 þ in differentited ells(figure 2), ut doesnot F Unt Low C 2+ Ro Chel High C Antiody Low C 2+ High C 2+ High C 2+ Antiody: E2F5 lter levelsof E2F2 or E2F3 (Figure 2). Finlly, the C 2 þ -indued derese ws olished in the presene of the PKC inhiitor Ro3179, further evidening the involvement of PKC sn upstrem regultor (Figure 2). Importntly, it hseen shown tht long-term (>18 h) tretment of kertinoytesdoesnot result in downregultion of ll PKC tivity. Speifilly, lthough these onditions result in downregultion of the nd e isoforms, PKC d, Z nd z remin tive (Reynold et l., 1994; Efimov et l., 1998). Unt Inhiitor Her+Genis Wort High C Figure 1 Formtion of differentition-speifi E2F DNA-inding omplexesrequirespkc tivtion. () Primry murine kertinoyteswere isolted nd ultured in low C 2 þ medium (0.05 mm) or high C 2 þ medium (1.0 mm) for 24 h. Kertinoyte lystes were prepred nd DNA-inding retionswere onduted using n oligonuleotide proe ontining the E2F element in the DHFR promoter. DNA-inding retionswere onduted in the presene of the indited ntiodiesfor 45 min prior to seprtion y nondenturing gel eletrophoresis. Supershifted nds in the presene of the ntiodies re indited with. Undifferentited ellsultured in low C 2 þ show multiple nds orresponding to free E2F/DP omplexes(f), nd lower moility omplexes ontining nd. () Kertinoyteswere ultured for 24 h in high C 2 þ ( þ ) or low C 2 þ ( ) medium in the presene of ( nm), helerythrine (Chel, 1 mm), or Ro (Ro, 1 mm), sindited. E2F DNA-inding retionswere onduted in the presene of the indited ntiodies, nd nlyzed y EMSA. () The formtion of nd omplexesin ellsindued to differentite y ulture in medium ontining 1.0 mm C 2 þ isnot ffeted y the presene in ulture medi of the protein tyrosine kinse inhiitors herimyin A (Her, 1 mm) nd genistein (Genis, 300 mm), or to the PI-3 kinse inhiitor wortmnnin (Wort, 50 nm).
3 PKC regultion of turnover 432 Low C 2+ High C 2+ γ-tuulin 110 CHX h 94 E2F5 + CHX h Low C 2+ High C 2+ Post-trnsriptionl regultion of y PKC in differentiting kertinoytes We next foused on the mehnisms of downregultion in response to PKC tivtion. First, we ddressed the effet of on mrna levels nd found no signifint differenes etween treted nd untreted ells (dt not shown). We lso mesured -indued protein dey y exmining hnges in levelsin ellstreted with yloheximide (CHX) (Figure 3, ). The hlf-life of in the presene of E2F2 E2F3 Ro Figure 2 Regultion of E2F protein levelsduring C 2 þ - or indued kertinoyte differentition. () Kertinoyteswere ultured for 24 h in medium ontining 0.05 mm C 2 þ without dditives(low C 2 þ ), in the presene of (0.1%, finl) or ( nm, finl), or in medium ontining 1.0 mm C 2 þ (High C 2 þ ). Whole-ell lystes were prepred, resolved y SDS PAGE nd nlysed with the indited nti-e2f ntiodies. () Primry kertinoyteswere ultured for 24 h in medium ontining 0.05 mm C 2 þ nd (0.1%) or ( nm), sindited. Whole-ell lystes were prepred, resolved y SDS PAGE nd nlysed with the indited nti-e2f ntiodies. () Cellswere ultured for 24 h in medium ontining 0.05 mm C 2 þ or 1.0 mm C 2 þ (High C 2 þ ) with (0.1%, finl) or Ro3179 (1 mm, finl), sindited. Whole-ell lystes were prepred nd nlyzed for expression y immunolot. undne (% t=0) d Time (h) MG132 High C 2+ γ-tuulin CHX CHX/ Figure 3 Inresed turnover vi protesoml tivity in differentiting kertinoytes. (, ) Primry kertinoytesultured in medium ontining 0.05 mm C 2 þ were treted with CHX mg/ml 30 min prior to ddition of, used to indue differentition ( nm). Cell lystes were prepred t the indited timesfollowing ddition of, resolved y SDS PAGE nd nlyzed y immunolotting with the indited ntiodies. () Densitometri quntifition of protein levels in kertinoytestreted with CHX or CHX þ, sdesried ove. Densitometri vues were normlized to g -tuulin. The results re expressed s men þ s.d. (n ¼ 3). indites Po0.01 (Student s t-test). (d) Kertinoyte ultureswere inuted in high C 2 þ medium for 8 h prior to the ddition of MG132. Cell lystes were prepred 16 h fter MG132 tretment, nd nlysed y imunolot, sdesried in (). CHX wsout 11.5 h, nd wsredued to out 6.5 h when ws lso present (Figure 3), inditing tht PKC tivtion inreses turnover in kertinoytes. Although the CHX tretment preludes mesurement of hlf-life in epiderml ellsunder norml growth onditions, these experiments indite tht PKC
4 tivtion is suffiient to inrese turnover, independent of de novo protein synthesis. The retinolstom protein () n ssoite with nd stilize (Hofmnn et l., 1996). Hene, we investigted if the derese in stility ws ssoited with dispperne of. We exmined levelss funtion of time nd found moderte inrese fter 10 h of inution in the presene of CHX. Inution of ellsin the presene of oth CHX nd deresed levels y out 50% fter 10 h. prb hs een shown to e sustrte for PKC (Suzum et l., 2002), nd inresed phosphoryltion n derese the stility of this protein (Pen uels et l., 2003). Whether PKC-indued phosphoryltion of used the oserved dereses in levels remins to e estlished. Nevertheless, it is noteworthy tht is still highly expressed in -treted kertinoytes t time when 90% of hslredy een degrded (Figure 3), suggesting the possiility tht modifitions in nd/or my prelude the ltter from proteting from degrdtion. turnover involvesuiquitintion followed y protesoml degrdtion (Hteoer et l., 1996; Cmpnero nd Flemington, 1997). To determine if C 2 þ -indued degrdtion oursthrough protesoml tivity, we treted differentiting kertinoyte ultureswith high C 2 þ in the presene or sene of the protesoml inhiitor MG132. The presene of MG132 in kertinoytesultured rogted downregultion indued y high C 2 þ (Figure 3d), inditing tht differentition triggers sde of ellulr eventstht ulminte in inresed rtes of protesoml degrdtion. Ativtion of PKCd nd PKCZ medites downregultion in differentiting kertinoytes Five PKC isozymes re expressed in the epidermis (, d, e, Z, z ) (Denning, 2004). Of these, tivtion of the, d nd Z forms hs een ssoited with vrious kertinoyte differentition responses, inluding involurin upregultion, tivtion of Fyn tyrosine kinse, nd withdrwl from the ell yle (Oh et l., 1998; Codi et l., 2000; Alt et l., 2001; Ekert et l., 2004). To identify the PKC form(s) involved in regultion, we mesured levels in ells exogenously expressing eh isozyme using reominnt denoviruses, or ontrol -gl-enoding virus(figure 4). High levels of exogenously expressed PKC isoforms re suffiient to inrese PKC tivity sustntilly, even in the sene of or other stimuli, in vrious ell types, inluding epiderml kertinoytes (Oh et l., 1998; Li et l., 1999). Exogenous expression of PKCd or Z, ut not of or e, indued mrked derese in protein levels24 nd 48 h fter denovirl infetion (Figure 4), with no signifint hnges in mrna undne (dt not shown). Expression of PKC z inonsistently hd smll effets on protein undne. To onfirm tht PKCd nd Z re indeed upstrem regultors, we lso expressed dominnt-negtive PKC regultion of turnover Adenovirus PKC α PKC δ PKC ε PKC η PKC ζ MX17 PKCα PKCδ PKCε PKCη PKCζ β gl E2F-1 (dn) formsof these enzymesvi reominnt denoviruses (Figure 5). We then mesured levels in ells infeted with denoviruses enoding these PKC forms. We lso used severl denoviruses s ontrols, inluding the nonreominnt denovirusmx17 (whih is ontrol for the PKCd viruses), s well s n denovirusenoding -gl (whih is ontrol for PKCZ nd PKCe). We then treted ll ultureswith, nd oserved tht expression of either dn PKCd or Z, ut not of -gl or dn PKCe, rogted -indued -downregultion (Figure 5). These dt suggest tht C 2 þ tretment of kertinoytes triggers differentition signling sde tht tivtes PKC d nd Z, whih, in turn, regultes protein turnover. 40 Adenovirus Figure 4 Regultion of levelsy novel PKC forms. () Protein lystes (50 mg) from kertinoytesinfeted with reominnt denovirusenoding the indited PKC formswere prepred 48 h postinfetion. The smples were nlysed y SDS PAGE nd immunolotting. () Cellswere ultured in medium ontining 0.05 mm C 2 þ nd were infeted with the indited denoviruses. Cell lystes were prepred 48 h postinfetion nd mg were nlysed s desried for pnel. p38 MAP kinse tivtion medites downregultion in differentiting kertinoytes We next investigted the identity of PKC downstrem effetorstht medite turnover. In primry epiderml kertinoytes, PKCZ tivtesfyn tyrosine kinse nd dereses ylin E/dk2 (Codi et l., 2000; Kshiwgi et l., 2000). In these ells, tivtion of PKCd results in sequentil tivtion of rs, MEKK1, MEK3 nd p38 (Ekert et l., 2004). Thispthwy is very importnt for differentition, sit promotes expression of the differentition mrkers involurin nd trnsglutminse 1 (Oh et l., 1998; Codi 433
5 PKC regultion of turnover MX17 wt dn PKCδ wt dn PKCη dn PKCε MX17 wt PKCδ dn PKCδ wt PKCη dn PKCη wt PKCε dn PKCε Figure 5 PKC d nd Z medite -indued downregultion. () Protein lystes (50 mg) from kertinoytesinfeted with reominnt denovirusenoding wild-type (wt) or dominnt-negtive (dn) PKC d, Z or e, sindited, were prepred 48 h postinfetion. The smples were nlysed y SDS PAGE nd immunolotting with ntiodies ginst the indited PKC forms. () Kertinoyteswere infeted with the indited reominnt denovirusnd ultured in 0.05 mm C 2 þ for 24 h prior to the ddition of ( nm). Cell lystes were prepred 24 h lter, nd nlysed for expression y SDS PAGE nd immunolotting. et l., 2000; Kshiwgi et l., 2000). Given tht tyrosine kinse inhiitors did not ffet C 2 þ -indued hngesin E2F DNA-inding omplexes, we first turned our ttention to the mitogen-tivted protein kinse (MAPK) sde nd p38. Kertinoytes express p38, nd d (Dshti et l., 2001). We resoned tht inhiition of p38 tivity would rogte PKC-indued downregultion if p38 tsdownstrem of PKC. Thus, we expressed PKCd, nd oserved tht downregultion ws olished in the presene of the p38 inhiitorssb or SB202190, ut not in the presene of the intive nlogue SB (Figure 6). We otined similr results when we expressed PKCZ in the presene of those sme drugs (Figure 6), wheres the inhiitorsy themselveshd no effet on levels (Figure 6). At the onentrtionsused (10 mm), these p38 inhiitorsre seletive for p38 nd p38, nd do not ffet p38d (Kumr et l., 2003). Hene, p38d plys little, if ny, role in differentition-indued hnges. To determine whether p38 or p38 medite turnover, we infeted -treted kertinoyteswith reominnt denoviruses enoding dn p38 mutnts. Expression of dn p38, ut not of dn p38, interfered with the redution in protein levelsindued y (Figure 7). Thus, we hve defined hitherto unidentified pthwy in differentiting kertinoytesin whih C 2 þ tivtespkcd nd PKCZ, whih results in tivtion of p38 nd inresed protein turnover. We lso ttempted to knokdown p38 nd p38 using sirna pprohes. Although we oserved derese in p38 mrna, thisdid not trnslte into p38 protein loss even fter severl dys of sirna tretments (dt not shown). However, the results we otined y omining phrmologil nd geneti pprohesto inhiit p38 re onsistent with the notion tht this MAPK pthwy isinvolved in regultion in kertinoytes. Although the ext mehnism of p38 modultion of reminsto e eluidted, the tivtion of this pthwy isruil for norml epiderml morphogenesis PKCδ SB PKCη SB SB SB SB SB SB SB MX17 SB Figure 6 p38 inhiition interfereswith PKC-indued downregultion. Primry kertinoyteswere ultured in 0.05 mm C 2 þ nd infeted with the indited denovirusin the presene of ( nm), or p38 inhiitors(10 mm). After 24 h, ell lystes were prepred nd nlysed for expression y immunolot. nd funtion, given tht is essentil for epiderml kertinoyte prolifertion nd epiderml regenertion (D Souz et l., 2002), nd itsdownregultion is neessry for norml expression of differentition
6 mrkersnd entry into quiesene (Diker et l., 2000; D Souz et l., 2001). Disussion dn p38 40 α 40 β dn p dn p38β dn p38α Figure 7 Expression of dn p38 interfereswith -indued downregultion. Kertinoyteswere infeted with the indited denovirusnd ultured in 0.05 mm C 2 þ for 24 h prior to ddition of. Cell lystes were prepred 24 h lter, nd nlysed for expression y immunolot. E2F trnsription ftors re fundmentl regultors of ell yle progression, differentition, DNA repir nd poptosis. During epiderml development nd kertinoyte differentition, E2F formsre modulted t multiple levels, inluding mrna nd protein undne, intertionswith fmily proteinsnd suellulr distriution (D Souz et l., 2001; Apostolov et l., 2002). E2F tivity is essentil for proper epiderml morphogenesis nd kertinoyte prolifertion, s evidened y the perturtions in these proesses used y exogenous expression of dn DP-1 mutnt in primry ultured kertinoytesnd emryoni etoderml explnts(chng et l., 2004). Further, fulfills essentil, nonredundnt funtions in epiderml kertinoytes. Intivtion of the E2f1 gene ledsto redued kertinoyte prolifertion, migrtion nd tthment to the extrellulr mtrix in ulture, swell simpired epiderml regenertion fter injury in vivo (D Souz et l., 2002). In spite of the demonstrted importne of in epiderml formtion nd homeostsis, entrl question to e ddressed is how differentition signls re trnsmitted. We estlished tht indution of differentition in epiderml kertinoytesis physiologil stimulus tht negtively modultes protein stility. Seond, we demonstrte signling pthwy linking C 2 þ -indued kertinoyte differentition with regultion, whih involvestivtion of PKCd PKC regultion of turnover nd Z, nd of p38 MAP kinse. Other differentition responses, suh s ell yle exit nd involurin expression, re indued y those two PKC enzymes (Efimov et l., 1998; Oh et l., 1998), nd PKCZ is indispensle for epiderml homeostsis in vivo (Chid et l., 2003). The mehnisti reltionship etween tivtion of PKCd nd Z reminsto e defined. One possiility is tht they modulte eh other, similr to the regultion of PKCd y PKC in lymphom ells (Romnov et l., 1998). Alterntively, these PKC isozymes my t on ommon downstrem trget(s). protein undne isprtly determined y degrdtion vi uiquitin-dependent proteolysis nd stiliztion through ssoition with, whih interfereswith uiquitintion (Hteoer et l., 1996). Importntly, degrdtion in differentiting kertinoytesinvolvesprotesoml tivity, nd oursin spite of the ontinuous presene of. Murine kertinoyte differentition is ssoited with loss of E2F/ DNA-inding omplexes(d Souz et l., 2001), nd we hve een unle to detet / omplexesin differentited ells(ia Ivnov nd L Dgnino, unpulished oservtions). The mehnisms tht medite PKC-indued dissoition of from remin to e eluidted. However, the inility of to omplex with my ontriute to its degrdtion. Regionsin outside its-interting C- terminus n lso regulte post-trnsltionl modifitions nd stility. For exmple, phosphoryltion on S403 nd T433 uses degrdtion (Vndel nd Kouzrides, 1999). Notly, these two residues re within sequenes tht orrespond to oth dk nd MAPK onsensus sites, nd re phosphorylted y dk7 nd other, syet unidentified, kinses. We hve deteted in tivted-p38 immunopreipittesfrom differentited kertinoytes(ia Ivnov nd L Dgnino, unpulished oservtions), whih leds us to speulte tht p38 my modify, thusregulting itsstility. The inresed turnover in kertinoytes ontrsts with itsstiliztion during myogeni differentition in C2/C12 myolsts, whih involves intertions with (Mrtelli et l., 2001). downregultion my e requisite for proper differentition of vrious ell types, s exogenous expression prevents terminl differentition in hondroytes(sheijen et l., 2003), predipoytes(porse et l., 2001), nd HCt ells, humn kertinoyte ell line (Prmio et l., 2000). PKCd nd Z re tivted during C 2 þ - or indued kertinoyte differentition, resulting in sequentil tivtion of rs, MEKK1, MEK3 nd p38 (Ekert et l., 2004). Thispthwy promotesexpression of the differentition mrkersinvolurin nd trnsglutminse 1 (Oh et l., 1998; Codi et l., 2000; Kshiwgi et l., 2000). In these ells, tretment ledsto p38 tivtion oserved y 2 h. Mximum p38 tivity ismintined etween 6 nd 24 h post- (Efimov et l., 2002). levelsegin to derese 2 4 h fter tretment, nd reh their minimum y 10 h. Importntly, the kinetis of loss suggest tht 435
7 436 this event ours just downstrem from or in ssoition with p38 tivtion. It islso noteworthy tht, wherestrnsriptionl tivtion of the involurin gene minly involvesp38d (Efimov et l., 2002), downregultion oursthrough p38. Although p38 nd p38 re involved in differentition of some ell types(figle et l., 2004; Qi et l., 2004), thisis, to our knowledge, the first report of inhiition E2F trnsription ftor stility y differentition-indued tivtion of MAP kinses. Vrioussignling eventsmodulte the E2F/ growth regultory network. A well-defined signling sde involves tivtion of phosphoinositide-3 kinse nd Akt/PKB, whih results in upregultion of Cylin D, followed y phosphoryltion nd relese of E2F, indiretly tivting itstrnsriptionl tivity (Brennn et l., 1997). Our studies show novel mehnism for regultion vi PKC-MAPK pthwysduring epiderml differentition, thusdding dditionl lyersof omplexity to the pthwystht modulte the E2F/ growth regultory network. Mterils nd methods PKC regultion of turnover Regents nd ntiodies The ntiodies nd their soures were s follows: PKC (610107), PKCd (610397) nd PKCe (610397) from BD Trnsdution Lortories; E2F5 (SC-999) from Snt Cruz Biotehnologies; (MS880) from Neomrkers; AU1 (MMS-130R) from Covne; PKCz from BIOMOL; glyerldehyde-3-phosphte dehydrogense (; Ct. No, ) from Biogenesis nd g-tuulin (T67) from Sigm. The p38 inhiitorssb203580, SB nd SB202474, MG132, nd the PKC inhiitorsro3179 nd Ro were from Cliohem. All other regentswere from Sigm. Adenoviruses Reominnt denovirusenoding wild type (wt) PKC, wt nd dn PKCdK 376R, nd wt nd dn PKCe (Crpenter et l., 2001; Czzoli et l., 2002) were giftsof Dr T Biden. The PKCzenoding denovirusws gift from G King (Suzum et l., 2002). The dn PKCZ DNA ontins K384A muttion (Oh et l., 1998), nd wsgenerted y polymerse hin retion. Both PKCd K376R nd PKCZ K384A mutntslk kinse tivity nd exhiit isozyme-speifi dn properties (Oh et l., 1998; Crpenter et l., 2001). Plsmids enoding mouse dn p38 nd humn dn p38 DNAs(Jing et l., 1996; Engelmn et l., 1998) were gifts, respetively, from P Sherer nd J Hn. Mutnt PKCZ, p38 or p38 DNA wsloned into pshuttlecmv (gift of B Vogelstein), whih ws used to generte reominnt denoviruses using the Ad-Esy system (He et l., 1998). The virusontrolsused to ount for the two different denovirl vetor koneswere Ad-MX17 (for PKC, nd wt nd dn PKCd) nd Ad-LZ, whih enodes -gltosidse (-gl; ontrol for PKCe, wt nd dn PKCZ, PKCz, dn p38 nd dn p38). Adenoviruses were purified on CsCl grdients nd titered prior to use. Cell ulture Primry kertinoytesisolted from 1 2-dy-old CD-1 mie were ultured in C 2 þ -free Egle s minimum essentil medium supplemented with 8% Chelex-treted fetl ovine serum nd indued to differentite y elevting the C 2 þ onentrtion to 1mM (D Souz et l., 2001). Kertinoyteswere inuted in serum-free medium with virus for 5 h. The multipliities of infetion used for the viruses resulted in 90 % effiieny, nd were: PKC, 10; wt PKCd, dnpkcd, wt nd dn PKCe, nd PKCz, 50; ll other viruses, 75. These onditions ensured tht X90% of ells were infeted, nd tht expression of exogenousenzymeswssix- to nine-fold greter thn the orresponding endogenous enzyme, s mesured y immunolot. In kertinoytes, these levels of exogenous PKC expression result in three- to five-fold inreses in PKC tivity (Oh et l., 1998; Luowei et l., 1999). Inutions nd finl drug onentrtionswere:, nm, 24h; helerythrine or Ro 3179, 1 mm; genistein, 300 mm, herimyin A, 1 mm; nd wortmnnin, 50 nm; ll dded 3 4 h prior to dding 1 mm CCl 2. For turnover experiments, yloheximide (CHX; mg/ml) wsdded 30 min prior to ddition of. In experiments using protesoml inhiitors, primry kertinoyteswere inuted with MG132 (10 mm, finl) MG132 (10 mm, finl), dded to the ulture medium 8 h following djustment of C 2 þ to 1mm. The ellswere ultured in high C 2 þ medium for 24 h prior to hrvesting nd lyste preprtion. In these experiments, ws not used in onjuntion with MG132 due to ytotoxiity of the drug omintion over the inution periodsrequired. For p38 experiments, ells infeted with denovirus-enoding PKCd or PKCZ were immeditely ultured in the presene of dimethylsulfoxide () vehile or 10 mm SB203580, SB or SB Fresh medium ontining the inhiitor ws dded to the ellsevery 12 h. Cell lystes nd immunolotting Cell lystes were prepred nd nlyzed for EMSA or immunolot sdesried (D Souz et l., 2001). Frtions ontining 50 mg protein were resolved y denturing polyrylmide gel eletrophoresis (SDS PAGE), nd trnsferred to polyvinylidene difluoride or nitroellulose memrnes. Immunolots were proed with the pproprite ntiodies. or g-tuulin wsused to normlize for protein loding. All results shown re representtive of t lest three experiments. Aknowledgements We thnk DrsF Beier, S Li nd D Lithfield for helpful ommentson the mnusript, nd H Dupuisfor tehnil ssistne. This work ws supported y grnts to LD from the Ntionl Siene nd Engineering Reserh Counil of Cnd, nd the Ntionl Cner Institute of Cnd (NCIC) with fundsfrom the Cndin Cner Soiety nd the Terry Fox Foundtion, rised through the Terry Fox Run. IAI is Reserh student of the Terry Fox Foundtion, through n wrd from NCIC. SJAD is CIHR New Investigtor. During the development of thiswork, LD ws CIHR/Cner Reserh Soiety In. New Investigtor. Referenes Alt A, Oh M, Li L, Grtsein M, Belnger A, Denning MF et l. (2001). Cner Res 61: Apostolov MD, Ivnov IA, Dgnino C, D Souz SJA, Dgnino L. (2002). J Biol Chem 277:
8 Bell LA, Ryn KM. (2004). Cell Deth Differ 11: Brennn P, Bge JW, Burgering BM, Groner B, Reif K, Cntrell DA. (1997). Immunity 7: Codi S, Clutti E, Tlor C, Kuroki T, Stein PL, Dotto GP. (2000). Mol Cell 6: Cm H, Dynlht BD. (2003). Cner Cell 3: Cmpnero MR, Flemington EK. (1997). Pro Ntl Ad Si USA 94: Crpenter L, Cordery D, Biden TJ. (2001). J Biol Chem 276: Czzoli R, Crig DL, Biden TJ, Smitz-Pfeiffer C. (2002). Am J Physiol 282: Chng WY, Brye DM, D Souz SJA, Dgnino L. (2004). J Biol Chem 279: Chid K, Hr T, Hiri T, Konishi C, Nkmur K, Nko K et l. (2003). Cner Res 63: D Souz SJA, Pjk A, Blzsi K, Dgnino L. (2001). J Biol Chem 276: D Souz SJA, Vesp A, Murkherjee S, Mher A, Pjk S, Dgnino L. (2002). J Biol Chem 277: Dshti SR, Efimov T, Ekert RL. (2001). J Biol Chem 276: Denning MF. (2004). Int J Biohem Cell Biol 36: Diker AJ, Pop C, Dhler AL, Serewko MM, Hildith- Mguire PA, Frzer IH et l. (2000). 19: Dotto GP. (1999). Crit Rev Orl Biol Med 10: Ekert RL, Crish JF, Efimov T, Dshti SR, Deuher A, Bone F et l. (2004). J Invest Dermtol 123: Efimov T, Deuher A, Kuroki T, Oh M, Ekert RL. (2002). J Biol Chem 277: Efimov T, L Cell P, Welter JF, Ekert RL. (1998). J Biol Chem 38: Engelmn JA, Lisnti MP, Sherer PE. (1998). J Biol Chem 273: Figle R, Brederlu A, Elmi M, Arvidsson Y, Hmzki TS, Urmoto H et l. (2004). Mol Cell Biol 24: Hteoer G, Kerkhoven RM, ShvrtsA, BernrdsR, Beijersergen RL. (1996). Genes Dev 10: He TC, Zhou S, d Cost LT, Yu J, Kinzler KW, Vogelstein B. (1998). Pro Ntl Ad Si USA 95: PKC regultion of turnover Hofmnn F, Mrtelli F, Livingston DM, Wng Z. (1996). Genes Dev 10: Jing Y, Chen C, Li Z, Guo W, Gegner JA, LinsS et l. (1996). J Biol Chem 271: Kshiwgi M, Oh M, Wtne H, Ishino K, Kshr K, Sni Y et l. (2000). 19: Koster MI, Roop DR. (2004). Eur J Cell Biol 83: Kumr S, Boehm J, Lee JC. (2003). Nt Rev Drug Disov 2: Li L, Lorenzo PS, Bogi K, Blumerg PM, Yusp SH. (1999). Mol Cell Biol 19: Luowei LI, Lorenzo PS, Bogi K, Blumerg PM, Yusp SA. (1999). Mol Cell Biol 19: Mrtelli F, Hmilton T, Silver DP, Shrpless NE, Brdeesy N, RoksM et l. (2001). Pro Ntl Ad Si USA 98: Oh M, Ishino K, Kshiwgi M, Kwe S, Chid K, Huh NH et l. (1998). Mol Cell Biol 18: Prmio JM, SegrellesC, Csnov ML, Jorno JL. (2000). J Biol Chem 275: Pen uelss, Alemny C, Noe V, Ciudd CJ. (2003). Eur J Biohem 270: Piere AM, Fisher SM, Conti CJ, Johnson DG. (1998). 16: Piere AM, Shneider-Broussrd R, Gimenez-Conti IB, Russell JL, Conti CJ, Johnson DG. (1999). Mol Cell Biol 19: Porse BT, Pedersen TA, Xu X, Linderg B, Wewer UM, Friis-Hnsen L et l. (2001). Cell 107: Qi X, Li TG, Hu J, Wng J, SimmonsH, Miur S et l. (2004). Pro Ntl Ad Si USA 101: Reynold NJ, Bldssre JJ, Henderson PA, Shuler JL, BllsLM, BurnsDJ et l. (1994). J Invest Dermtol 103: Romnov LY, Alexndrov IA, Nordn RP, Blgosklonny MV, Mushinski JF. (1998). Biohem 37: Ruiz S, SntosM, SegrellesC, LeisH, Jorno JL, BernsA et l. (2004). Development 131: Sheijen B, Bronk M, vn der Meer T, BernrdsR. (2003). Mol Cell Biol 23: Suzum K, Tkhr N, Suzum I, Isshiki K, Ueki K, Leitges M et l. (2002). Pro Ntl Ad Si USA 99: Vndel L, KouzridesT. (1999). EMBO J 18:
TNF-a Downregulates Filaggrin and Loricrin through c-jun N-terminal Kinase: Role for TNF-a Antagonists to Improve Skin Barrier
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE TNF- Downregultes Filggrin nd Loririn through -Jun N-terminl Kinse: Role for TNF- Antgonists to Improve Skin Brrier Byung Eui Kim, Mihel D. Howell,, Emm Guttmn,, Ptrii M. Gilleudeu, Irm
ORIGINAL ARTICLE TNF- Downregultes Filggrin nd Loririn through -Jun N-terminl Kinse: Role for TNF- Antgonists to Improve Skin Brrier Byung Eui Kim, Mihel D. Howell,, Emm Guttmn,, Ptrii M. Gilleudeu, Irm
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi: 1.138/nture862 humn hr. 21q MRPL39 murine Chr.16 Mrpl39 Dyrk1A Runx1 murine Chr. 17 ZNF295 Ets2 Znf295 murine Chr. 1 COL18A1 -/- lot: nti-dscr1 IgG hevy hin DSCR1 DSCR1 expression reltive to hevy
doi: 1.138/nture862 humn hr. 21q MRPL39 murine Chr.16 Mrpl39 Dyrk1A Runx1 murine Chr. 17 ZNF295 Ets2 Znf295 murine Chr. 1 COL18A1 -/- lot: nti-dscr1 IgG hevy hin DSCR1 DSCR1 expression reltive to hevy
EFFECT OF DIETARY ENZYME ON PERFORMANCE OF WEANLING PIGS
 EFFECT OF DIETARY ENZYME ON PERFORMANCE OF WEANLING PIGS Finl report sumitted to Dniso Animl Nutrition E. vn Heugten nd B. Frederik North Crolin Stte University, Deprtment of Animl Siene Summry The urrent
EFFECT OF DIETARY ENZYME ON PERFORMANCE OF WEANLING PIGS Finl report sumitted to Dniso Animl Nutrition E. vn Heugten nd B. Frederik North Crolin Stte University, Deprtment of Animl Siene Summry The urrent
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 1.138/n358 TLR2 nd MyD88 expression in murine mmmry epithelil supopultions. CD24 min plus MRU Myo-epithelil Luminl progenitor (CD61 pos ) Mture luminl (CD61 neg ) CD49f CD61 Reltive expression Krt5
DOI: 1.138/n358 TLR2 nd MyD88 expression in murine mmmry epithelil supopultions. CD24 min plus MRU Myo-epithelil Luminl progenitor (CD61 pos ) Mture luminl (CD61 neg ) CD49f CD61 Reltive expression Krt5
P AND K IN POTATOES. Donald A Horneck Oregon State University Extension Service
 P AND K IN POTATOES Donld A Hornek Oregon Stte University Extension Servie INTRODUCTION Phosphorous nd potssium re importnt to grow high yielding nd qulity pottoes. Muh of the northwest hs hd trditionlly
P AND K IN POTATOES Donld A Hornek Oregon Stte University Extension Servie INTRODUCTION Phosphorous nd potssium re importnt to grow high yielding nd qulity pottoes. Muh of the northwest hs hd trditionlly
The GCN5-CITED2-PKA signalling module controls hepatic glucose metabolism through a camp-induced substrate switch
 Reeived 6 Apr 216 Aepted 8 Sep 216 Pulished 22 Nov 216 DOI: 1.138/nomms13147 OPEN The GCN5-CITED2-PKA signlling module ontrols hepti gluose metolism through AMP-indued sustrte swith Mshito Ski 1, Tomoko
Reeived 6 Apr 216 Aepted 8 Sep 216 Pulished 22 Nov 216 DOI: 1.138/nomms13147 OPEN The GCN5-CITED2-PKA signlling module ontrols hepti gluose metolism through AMP-indued sustrte swith Mshito Ski 1, Tomoko
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 { OI: 1.138/n31 Srifie n nlyze APs on week 1 s of iet 1 4 6 High-ft iet BrU High-ft iet BrU 4 High-ft iet BrU 6 High-ft iet BrU Lin - Lin - : C34 + : C9 + 1 1 3 1 4 1 5 C45 1 C34 1 1 1 1 3 1 4 1 5 S-1
{ OI: 1.138/n31 Srifie n nlyze APs on week 1 s of iet 1 4 6 High-ft iet BrU High-ft iet BrU 4 High-ft iet BrU 6 High-ft iet BrU Lin - Lin - : C34 + : C9 + 1 1 3 1 4 1 5 C45 1 C34 1 1 1 1 3 1 4 1 5 S-1
Supplementary Figure S1
 Supplementry Figure S1 - UTR m - 3HA - 2-1 hgh - 1 Uiquitin *! *! lk distl promoter m K3R/ K121R-3HA UTR hgh founder lines - HA - - founder lines TG- E1 L A2 B1 F9 G6 H4 H6 B C D2 G1 H3 J2 L - 7 IP: lk
Supplementry Figure S1 - UTR m - 3HA - 2-1 hgh - 1 Uiquitin *! *! lk distl promoter m K3R/ K121R-3HA UTR hgh founder lines - HA - - founder lines TG- E1 L A2 B1 F9 G6 H4 H6 B C D2 G1 H3 J2 L - 7 IP: lk
YAP transcriptionally regulates COX-2 expression and GCCSysm-4 (G-4), a dual YAP/COX-2 inhibitor, overcomes drug resistance in colorectal cancer
 Li et l. Journl of Experimentl & Clinil Cner Reserh (7) 36:44 DOI.86/s346-7-6-3 RESEARCH Open Aess trnsriptionlly regultes expression nd GCCSysm-4 (G-4), dul / inhiitor, overomes drug resistne in oloretl
Li et l. Journl of Experimentl & Clinil Cner Reserh (7) 36:44 DOI.86/s346-7-6-3 RESEARCH Open Aess trnsriptionlly regultes expression nd GCCSysm-4 (G-4), dul / inhiitor, overomes drug resistne in oloretl
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 1.13/n7 Reltive Pprg mrna 3 1 1 Time (weeks) Interspulr Inguinl Epididyml Reltive undne..1.5. - 5 5-51 51-1 1-7 7 - - 1 1-1 Lipid droplet size ( m ) 1-3 3 - - - 1 1-1 1-1 1-175 175-3 3-31 31-5 >5
DOI: 1.13/n7 Reltive Pprg mrna 3 1 1 Time (weeks) Interspulr Inguinl Epididyml Reltive undne..1.5. - 5 5-51 51-1 1-7 7 - - 1 1-1 Lipid droplet size ( m ) 1-3 3 - - - 1 1-1 1-1 1-175 175-3 3-31 31-5 >5
The Hippo/YAP pathway interacts with EGFR signaling and HPV oncoproteins to regulate cervical cancer progression
 Reserh Artile The Hippo/ pthwy interts with EGFR signling nd HPV onoproteins to regulte ervil ner progression Chuno He 1,, Dgn Mo 1,3, Guohu Hu 1,, Xingmin Lv 1, Xingheng Chen, Peter C Angeletti 5, Jixin
Reserh Artile The Hippo/ pthwy interts with EGFR signling nd HPV onoproteins to regulte ervil ner progression Chuno He 1,, Dgn Mo 1,3, Guohu Hu 1,, Xingmin Lv 1, Xingheng Chen, Peter C Angeletti 5, Jixin
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:.8/nture98 : hr NEMO :5 hr IKK IKK NF-κB p65 p5 p65/-rel NF-κB p65 p5 p65/-rel Cytoplsm Cytoplsm p65/p5 Nuleus Nuleus NEMO IKK IKK d : hr > : hr p65/-rel NF- p65 p5 Cytoplsm Cytoplsm p65/p5 p65/-rel
doi:.8/nture98 : hr NEMO :5 hr IKK IKK NF-κB p65 p5 p65/-rel NF-κB p65 p5 p65/-rel Cytoplsm Cytoplsm p65/p5 Nuleus Nuleus NEMO IKK IKK d : hr > : hr p65/-rel NF- p65 p5 Cytoplsm Cytoplsm p65/p5 p65/-rel
Interplay of LRRK2 with chaperone-mediated autophagy
 Interply of with hperone-medited utophgy Smnth J Orenstein,, Sheng-Hn Kuo,, Inmuld Tsset,,, Espernz Aris,, Hiroshi Kog,, Irene Fernndez-Crs, Etty Cortes,5, Lwrene S Honig,5, Willim Duer 6, Antonell Consiglio,7,
Interply of with hperone-medited utophgy Smnth J Orenstein,, Sheng-Hn Kuo,, Inmuld Tsset,,, Espernz Aris,, Hiroshi Kog,, Irene Fernndez-Crs, Etty Cortes,5, Lwrene S Honig,5, Willim Duer 6, Antonell Consiglio,7,
Protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B deficiency or inhibition delays ErbB2-induced mammary tumorigenesis and protects from lung metastasis
 Protein tyrosine phosphtse 1B defiieny or inhiition delys ErB2-indued mmmry tumorigenesis nd protets from lung metstsis Sofi G Julien 1,5, Ndi Dué 1,6, Mihelle Red 1, Jnie Penney 1, Mrilene Pquet 2, Yongxin
Protein tyrosine phosphtse 1B defiieny or inhiition delys ErB2-indued mmmry tumorigenesis nd protets from lung metstsis Sofi G Julien 1,5, Ndi Dué 1,6, Mihelle Red 1, Jnie Penney 1, Mrilene Pquet 2, Yongxin
Roles of the PI-3K and MEK pathways in Ras-mediated chemoresistance in breast cancer cells
 ritish Journl of Cner (23) 89, 18 191 & 23 Cner Reserh UK All rights reserved 7 92/3 $2. www.jner.om Roles of the PI-3K nd MEK pthwys in Rs-medited hemoresistne in rest ner ells W Jin 1,LWu 1, K Ling 1,
ritish Journl of Cner (23) 89, 18 191 & 23 Cner Reserh UK All rights reserved 7 92/3 $2. www.jner.om Roles of the PI-3K nd MEK pthwys in Rs-medited hemoresistne in rest ner ells W Jin 1,LWu 1, K Ling 1,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 % ells with ili (mrke y A-Tu) Reltive Luiferse % ells with ili (mrke y Arl13) % ells with ili DOI: 1.138/n2259 A-Tuulin Hoehst % Cilite Non-ilite -Serum 9% 8% 7% 1 6% % 4% +Serum 1 3% 2% 1% % Serum: -
% ells with ili (mrke y A-Tu) Reltive Luiferse % ells with ili (mrke y Arl13) % ells with ili DOI: 1.138/n2259 A-Tuulin Hoehst % Cilite Non-ilite -Serum 9% 8% 7% 1 6% % 4% +Serum 1 3% 2% 1% % Serum: -
Cos7 (3TP) (K): TGFβ1(h): (K)
 IP#2: IP#1: Totl Lystes luiferse tivity (K): 6-4 - (K): luiferse tivity luiferse tivity (K): 2 1 RL-: - + + + + + Sm4-3F: + - + + + + MYC-Sm3: - - - - + + TβRI-HA(T204D): - - - + - + α-ha Luiferse Ativity
IP#2: IP#1: Totl Lystes luiferse tivity (K): 6-4 - (K): luiferse tivity luiferse tivity (K): 2 1 RL-: - + + + + + Sm4-3F: + - + + + + MYC-Sm3: - - - - + + TβRI-HA(T204D): - - - + - + α-ha Luiferse Ativity
The microrna mir-31 inhibits CD8 + T cell function in chronic viral infection
 A rt i l e s The mirorna mir-3 inhiits CD8 + T ell funtion in hroni virl infetion Howell F Moffett, Adm N R Crtwright, Hye-Jung Kim, Jernej Gode, Json Pyrdol, Trmo Äijö 3, Gustvo J Mrtinez,6, Anjn Ro,
A rt i l e s The mirorna mir-3 inhiits CD8 + T ell funtion in hroni virl infetion Howell F Moffett, Adm N R Crtwright, Hye-Jung Kim, Jernej Gode, Json Pyrdol, Trmo Äijö 3, Gustvo J Mrtinez,6, Anjn Ro,
AUTHOR COPY ONLY. Glycogen synthase kinase 3b mediates high glucose-induced ubiquitination and proteasome degradation of insulin receptor substrate 1
 Glyogen synthse kinse 3 medites high gluose-indued uiquitintion nd protesome degrdtion of insulin reeptor sustrte 1 171 Snhu Leng, Wenshuo Zhng, Ynin Zheng, Ziv Liermn 1, Christopher J Rhodes, Hgit Eldr-Finkelmn
Glyogen synthse kinse 3 medites high gluose-indued uiquitintion nd protesome degrdtion of insulin reeptor sustrte 1 171 Snhu Leng, Wenshuo Zhng, Ynin Zheng, Ziv Liermn 1, Christopher J Rhodes, Hgit Eldr-Finkelmn
Tankyrase inhibition stabilizes axin and antagonizes Wnt signalling
 Vol 461 1 Otoer 29 doi:1.138/nture8356 Tnkyrse inhiition stilizes xin nd ntgonizes Wnt signlling Shih-Min A. Hung 1, Yuji M. Mishin 1, Shnming Liu 1, Atwood Cheung 1, rnk Stegmeier 1, Gregory A. Mihud
Vol 461 1 Otoer 29 doi:1.138/nture8356 Tnkyrse inhiition stilizes xin nd ntgonizes Wnt signlling Shih-Min A. Hung 1, Yuji M. Mishin 1, Shnming Liu 1, Atwood Cheung 1, rnk Stegmeier 1, Gregory A. Mihud
Rapamycin toxicity in MIN6 cells and rat and human islets is mediated by the inhibition of mtor complex 2 (mtorc2)
 Dietologi (212) 55:1355 1365 DOI 1.17/s125-12-2475-7 ARTICLE myin toxiity in MIN6 ells nd rt nd humn islets is medited y the inhiition of mtor omplex 2 (mtorc2) A. D. Brlow & J. Xie & C. E. Moore & S.
Dietologi (212) 55:1355 1365 DOI 1.17/s125-12-2475-7 ARTICLE myin toxiity in MIN6 ells nd rt nd humn islets is medited y the inhiition of mtor omplex 2 (mtorc2) A. D. Brlow & J. Xie & C. E. Moore & S.
The soy isoflavone genistein promotes apoptosis in mammary epithelial cells by inducing the tumor suppressor PTEN
 Crinogenesis vol. no.1 pp.1793 183, 5 doi:1.193/rin/gi131 dvne ess pulition My 19, 5 The soy isoflvone genistein promotes poptosis in mmmry epithelil ells y induing the tumor suppressor huvnesh Dve 1,,
Crinogenesis vol. no.1 pp.1793 183, 5 doi:1.193/rin/gi131 dvne ess pulition My 19, 5 The soy isoflvone genistein promotes poptosis in mmmry epithelil ells y induing the tumor suppressor huvnesh Dve 1,,
Fates-shifted is an F box protein that targets Bicoid for degradation and regulates developmental fate determination in Drosophila embryos
 ARTICLES Ftes-shifted is n F ox protein tht trgets Bioid for degrdtion nd regultes developmentl fte determintion in Drosophil emryos Juno Liu 1 nd Jun M 1,2,3 Bioid (Bd) is morphogeneti protein tht instruts
ARTICLES Ftes-shifted is n F ox protein tht trgets Bioid for degrdtion nd regultes developmentl fte determintion in Drosophil emryos Juno Liu 1 nd Jun M 1,2,3 Bioid (Bd) is morphogeneti protein tht instruts
Alimonti_Supplementary Figure 1. Pten +/- Pten + Pten. Pten hy. β-actin. Pten - wt hy/+ +/- wt hy/+ +/- Pten. Pten. Relative Protein level (% )
 Alimonti_Supplementry Figure 1 hy 3 4 5 3 Neo 4 5 5 Proe 5 Proe hy/ hy/ /- - 3 6 Neo β-tin d Reltive Protein level (% ) 15 1 5 hy/ /- Reltive Gene Expr. (% ) 15 1 5 hy/ /- Supplementry Figure 1 Chrteriztion
Alimonti_Supplementry Figure 1 hy 3 4 5 3 Neo 4 5 5 Proe 5 Proe hy/ hy/ /- - 3 6 Neo β-tin d Reltive Protein level (% ) 15 1 5 hy/ /- Reltive Gene Expr. (% ) 15 1 5 hy/ /- Supplementry Figure 1 Chrteriztion
RNAi Targeting CXCR4 Inhibits Tumor Growth Through Inducing Cell Cycle Arrest and Apoptosis
 originl rtile RNAi Trgeting CXCR4 Inhiits Tumor Growth Through Induing Cell Cyle Arrest nd Apoptosis To Yu 1,2, Yingying Wu 2, Yi Hung 1,2, Chorn Yn 1, Ying Liu 1, Zongsheng Wng 3, Xioyi Wng 1, Yuming
originl rtile RNAi Trgeting CXCR4 Inhiits Tumor Growth Through Induing Cell Cyle Arrest nd Apoptosis To Yu 1,2, Yingying Wu 2, Yi Hung 1,2, Chorn Yn 1, Ying Liu 1, Zongsheng Wng 3, Xioyi Wng 1, Yuming
Inhibitory effect of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase inhibitors on cytokine release from human macrophages
 British Journl of Phrmology (26) 149, 393 44 & 26 Nture Pulishing Group All rights reserved 7 1188/6 $3. www.rjphrmol.org RESEARCH PAPER Inhiitory effet of p38 mitogen-tivted protein kinse inhiitors on
British Journl of Phrmology (26) 149, 393 44 & 26 Nture Pulishing Group All rights reserved 7 1188/6 $3. www.rjphrmol.org RESEARCH PAPER Inhiitory effet of p38 mitogen-tivted protein kinse inhiitors on
Involvement of thioredoxin-interacting protein (TXNIP) in glucocorticoid-mediated beta cell death
 Dietologi (12) 55:148 157 DOI 1.7/s125-11-2422-z ARTICLE Involvement of thioredoxin-interting protein (TXNIP) in gluoortioid-medited et ell deth E. Reih & A. Tmry & R. Vogt Sionov & D. Melloul Reeived:
Dietologi (12) 55:148 157 DOI 1.7/s125-11-2422-z ARTICLE Involvement of thioredoxin-interting protein (TXNIP) in gluoortioid-medited et ell deth E. Reih & A. Tmry & R. Vogt Sionov & D. Melloul Reeived:
Supplementary Figure 1. Scheme of unilateral pyramidotomy used for detecting compensatory sprouting of intact CST axons.
 () BDA 2 weeks fter Py () AAVs Cre or GFP t P1 BDA 2 weeks fter Py CSMN CST () Py t P7 or 2 months () Py t 2 months Supplementry Figure 1. Sheme of unilterl pyrmidotomy used for deteting ompenstory sprouting
() BDA 2 weeks fter Py () AAVs Cre or GFP t P1 BDA 2 weeks fter Py CSMN CST () Py t P7 or 2 months () Py t 2 months Supplementry Figure 1. Sheme of unilterl pyrmidotomy used for deteting ompenstory sprouting
a3 Chains of type V collagen regulate breast tumour growth via glypican-1
 Reeive 5 Aug 16 Aepte De 16 Pulishe 19 Jn 17 3 Chins of type V ollgen regulte rest tumour growth vi glypin-1 Guorui Hung 1, Goxing Ge 1,w, Vlerio Izzi & Dniel S. Greenspn 1 DOI: 1.138/nomms1351 OPEN Periellulr
Reeive 5 Aug 16 Aepte De 16 Pulishe 19 Jn 17 3 Chins of type V ollgen regulte rest tumour growth vi glypin-1 Guorui Hung 1, Goxing Ge 1,w, Vlerio Izzi & Dniel S. Greenspn 1 DOI: 1.138/nomms1351 OPEN Periellulr
Thioredoxin-interacting protein links oxidative stress to inflammasome activation
 A rt i l e s Thioredoxin-interting protein links oxidtive stress to inflmmsome tivtion Rongin Zhou 1, Aury Trdivel 1, Bernrd Thorens 2, Inpyo Choi 3 & Jürg Tshopp 1 29 Nture Ameri, In. All rights reserved.
A rt i l e s Thioredoxin-interting protein links oxidtive stress to inflmmsome tivtion Rongin Zhou 1, Aury Trdivel 1, Bernrd Thorens 2, Inpyo Choi 3 & Jürg Tshopp 1 29 Nture Ameri, In. All rights reserved.
ARTICLE. I. Chopra & H. F. Li & H. Wang & K. A. Webster
 Dietologi (212) 55:783 794 DOI 1.17/s125-11-247-y ARTICLE Phosphoryltion of the insulin reeptor y AMP-tivted protein kinse (AMPK) promotes lignd-independent tivtion of the insulin signlling pthwy in rodent
Dietologi (212) 55:783 794 DOI 1.17/s125-11-247-y ARTICLE Phosphoryltion of the insulin reeptor y AMP-tivted protein kinse (AMPK) promotes lignd-independent tivtion of the insulin signlling pthwy in rodent
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:.8/nture89 4 4 Ilr -/- Ilr -/- Ilr -/- Cspse- -/- As -/- Nlrp -/- Il8 -/- Ilr -/- Supplementl figure. Inresed severity of NASH in inflmmsome-defiient mie, ut not in Ilr-defiient
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:.8/nture89 4 4 Ilr -/- Ilr -/- Ilr -/- Cspse- -/- As -/- Nlrp -/- Il8 -/- Ilr -/- Supplementl figure. Inresed severity of NASH in inflmmsome-defiient mie, ut not in Ilr-defiient
Title of Experiment: Author, Institute and address:
 Title of Experiment: Trsfetion of murine mrophge RAW264.7 ells with METAFECTENE PRO. Author, Institute n ress: Ptrizi Pellegtti n Frneso Di Virgilio. Deprtment of Experimentl n Dignosti Meiine, Setion
Title of Experiment: Trsfetion of murine mrophge RAW264.7 ells with METAFECTENE PRO. Author, Institute n ress: Ptrizi Pellegtti n Frneso Di Virgilio. Deprtment of Experimentl n Dignosti Meiine, Setion
GSK-3 is a master regulator of neural progenitor homeostasis
 GSK-3 is mster regultor of neurl progenitor homeostsis Woo-Yng Kim 1, Xinshuo Wng 1, Yohong Wu 1, Brdley W Dole 2, Stish Ptel 3, Jmes R Woodgett 3 & Willim D Snider 1 The development of the rin requires
GSK-3 is mster regultor of neurl progenitor homeostsis Woo-Yng Kim 1, Xinshuo Wng 1, Yohong Wu 1, Brdley W Dole 2, Stish Ptel 3, Jmes R Woodgett 3 & Willim D Snider 1 The development of the rin requires
LHb VTA. VTA-projecting RMTg-projecting overlay. Supplemental Figure 2. Retrograde labeling of LHb neurons. a. VTA-projecting LHb
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementl Figure 1 doi:10.1038/nture09742 Lterl 1.0 mm from midline mpfc BNST mpfc BNST Lterl 2.1 mm from midline LHA LHA Lterl 2.7 mm from midline SUPPLEMENTAL INFORMATION
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementl Figure 1 doi:10.1038/nture09742 Lterl 1.0 mm from midline mpfc BNST mpfc BNST Lterl 2.1 mm from midline LHA LHA Lterl 2.7 mm from midline SUPPLEMENTAL INFORMATION
LETTERS. Chfr is required for tumor suppression and Aurora A regulation
 25 Nture Pulishing Group http://www.nture.om/nturegenetis Chfr is required for tumor suppression nd Auror A regultion Xiohun Yu 1, Ktherine Minter-Dykhouse 1, Liviu Mlurenu 2, Wei-Meng Zho 3, Dongwei Zhng
25 Nture Pulishing Group http://www.nture.om/nturegenetis Chfr is required for tumor suppression nd Auror A regultion Xiohun Yu 1, Ktherine Minter-Dykhouse 1, Liviu Mlurenu 2, Wei-Meng Zho 3, Dongwei Zhng
FAK integrates growth-factor and integrin signals to promote cell migration
 integrtes growth-ftor nd integrin signls to promote ell migrtion rtiles Dvid J. Sieg*, Christof R. Huk*, Dusko Ili, Cndie K. Klingeil*, Erik Shefer, Croline H. Dmsky nd Dvid D. Shlepfer* *Deprtment of
integrtes growth-ftor nd integrin signls to promote ell migrtion rtiles Dvid J. Sieg*, Christof R. Huk*, Dusko Ili, Cndie K. Klingeil*, Erik Shefer, Croline H. Dmsky nd Dvid D. Shlepfer* *Deprtment of
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 1.138/n2977 Numer of ells per field 6 4 2 P =.1 Orthotopi eum Normlized ventrl photon flux 1E7 1E6 1E5 1E4 1E3 1E2 n=8 n=9 1 2 3 4 5 6 Dys Dy54 1.5E5 2.4E7 d Mie with lymph node metstsis (%) 1 8 6
DOI: 1.138/n2977 Numer of ells per field 6 4 2 P =.1 Orthotopi eum Normlized ventrl photon flux 1E7 1E6 1E5 1E4 1E3 1E2 n=8 n=9 1 2 3 4 5 6 Dys Dy54 1.5E5 2.4E7 d Mie with lymph node metstsis (%) 1 8 6
Differential expression of cyclin G2, cyclin dependent kinase inhibitor 2C and peripheral myelin protein 22 genes during adipogenesis..
 The Ohio Stte University From the SeletedWorks of Jiin Zhng Summer My 5, 214 Differentil expression of ylin G2, ylin dependent kinse inhiitor 2C nd peripherl myelin protein 22 genes during dipogenesis..pdf
The Ohio Stte University From the SeletedWorks of Jiin Zhng Summer My 5, 214 Differentil expression of ylin G2, ylin dependent kinse inhiitor 2C nd peripherl myelin protein 22 genes during dipogenesis..pdf
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:1.138/nture1794 BR EPFs BRI1? ERECTA TMM BSKs YDA PP2A BSU1 BIN2 pbzr1/2 BZR1/2 MKK4/5/7/9 MPK3/6 SPCH Cell growth Stomtl production Supplementry Figure 1. The model of BR nd stomtl signling pthwys.
doi:1.138/nture1794 BR EPFs BRI1? ERECTA TMM BSKs YDA PP2A BSU1 BIN2 pbzr1/2 BZR1/2 MKK4/5/7/9 MPK3/6 SPCH Cell growth Stomtl production Supplementry Figure 1. The model of BR nd stomtl signling pthwys.
Osteoblasts secrete Cxcl9 to regulate angiogenesis in bone
 Reeived 2 De 215 Aepted 9 Nov 216 Pulished 14 De 216 DOI: 1.138/nomms13885 OPEN Osteolsts serete to regulte ngiogenesis in one Bin Hung 1,, Wenho Wng 1,, Qinghu Li 1,, Zhenyu Wng 1,BoYn 1, Zhongmin Zhng
Reeived 2 De 215 Aepted 9 Nov 216 Pulished 14 De 216 DOI: 1.138/nomms13885 OPEN Osteolsts serete to regulte ngiogenesis in one Bin Hung 1,, Wenho Wng 1,, Qinghu Li 1,, Zhenyu Wng 1,BoYn 1, Zhongmin Zhng
TNF-α (pg/ml) IL-6 (ng/ml)
 Xio, et l., Supplementry Figure 1 IL-6 (ng/ml) TNF-α (pg/ml) 16 12 8 4 1,4 1,2 1, 8 6 4 2 med Cl / Pm3CSK4 zymosn curdln Poly (I:C) LPS flgelin MALP-2 imiquimod R848 CpG TNF-α (pg/ml) IL-6 (ng/ml) 2 1.6
Xio, et l., Supplementry Figure 1 IL-6 (ng/ml) TNF-α (pg/ml) 16 12 8 4 1,4 1,2 1, 8 6 4 2 med Cl / Pm3CSK4 zymosn curdln Poly (I:C) LPS flgelin MALP-2 imiquimod R848 CpG TNF-α (pg/ml) IL-6 (ng/ml) 2 1.6
Insulin-like Growth Factor-binding Protein-7 (IGFBP7): A Promising Gene Therapeutic for Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC)
 originl rtile The Amerin Soiety of Gene & Cell Therpy Insulin-like Growth Ftor-inding Protein-7 (IGFBP7): A Promising Gene Therpeuti for Heptoellulr Crinom (HCC) Dong Chen 1, Ayesh Siddiq 2, Luni Emdd
originl rtile The Amerin Soiety of Gene & Cell Therpy Insulin-like Growth Ftor-inding Protein-7 (IGFBP7): A Promising Gene Therpeuti for Heptoellulr Crinom (HCC) Dong Chen 1, Ayesh Siddiq 2, Luni Emdd
Oocytes determine cumulus cell lineage in mouse ovarian follicles
 133 Reserh tile Ooytes determine umulus ell linege in mouse ovrin folliles Frniso J. Diz, Kren Wigglesworth nd John J. Eppig* The Jkson Lortory, 6 Min Street, Br Hror, ME 469, USA *Author for orrespondene
133 Reserh tile Ooytes determine umulus ell linege in mouse ovrin folliles Frniso J. Diz, Kren Wigglesworth nd John J. Eppig* The Jkson Lortory, 6 Min Street, Br Hror, ME 469, USA *Author for orrespondene
AJ PUTT. Hematology. Chemistry. Species: Canine Gender: Female Year of Birth: 2013 Client: PUTT
 Speies: Cnine Gender: Femle Yer of Birth: 2013 Client: PUTT Requisition #: 9034-12 Aession #: W2152816 Aount Code: 72364 Veterinrin: CARTER Pnel/Profile: Tik Pnel Add-on Senior Profile with L 4Dx Plus
Speies: Cnine Gender: Femle Yer of Birth: 2013 Client: PUTT Requisition #: 9034-12 Aession #: W2152816 Aount Code: 72364 Veterinrin: CARTER Pnel/Profile: Tik Pnel Add-on Senior Profile with L 4Dx Plus
Poultry No The replacement value of betaine for DL-methionine and Choline in broiler diets
 Poultry No. 1573 The replement vlue of etine for DL-methionine nd Choline in roiler diets Key Informtion In roiler diets defiient in sulfur mino ids ut dequtely supplemented with methyl groups vi dded
Poultry No. 1573 The replement vlue of etine for DL-methionine nd Choline in roiler diets Key Informtion In roiler diets defiient in sulfur mino ids ut dequtely supplemented with methyl groups vi dded
A p75 NTR and Nogo receptor complex mediates repulsive signaling by myelin-associated glycoprotein
 A p75 NTR nd Nogo reeptor omplex medites repulsive signling y myelin-ssoited glyoprotein Sott T. Wong 1, John R. Henley 1, Kevin C. Knning 2, Kuo-hu Hung 1, Mrk Bothwell 2 nd Mu-ming Poo 1 1 Division of
A p75 NTR nd Nogo reeptor omplex medites repulsive signling y myelin-ssoited glyoprotein Sott T. Wong 1, John R. Henley 1, Kevin C. Knning 2, Kuo-hu Hung 1, Mrk Bothwell 2 nd Mu-ming Poo 1 1 Division of
Ulk λ PPase. 32 P-Ulk1 32 P-GST-TSC2. Ulk1 GST (TSC2) : Ha-Ulk1 : AMPK. WB: Ha (Ulk1) : Glu. h CON - Glu - A.A WB: LC3 AMPK-WT AMPK-DKO
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb2152 C.C + - + - : Glu b Ulk1 - - + λ PPse c AMPK + - + + : ATP P-GST-TSC2 WB: Flg (Ulk1) WB Ulk1 WB: H (Ulk1) GST (TSC2) C.C d e WT K46R - + - + : H-Ulk1 : AMPK - + - + + + AMPK H-Ulk1
DOI: 10.1038/ncb2152 C.C + - + - : Glu b Ulk1 - - + λ PPse c AMPK + - + + : ATP P-GST-TSC2 WB: Flg (Ulk1) WB Ulk1 WB: H (Ulk1) GST (TSC2) C.C d e WT K46R - + - + : H-Ulk1 : AMPK - + - + + + AMPK H-Ulk1
Inhibiting Stat3 signaling in the hematopoietic system elicits multicomponent antitumor immunity
 2 Nture Pulishing Group http://www.nture.om/nturemediine Inhiiting Stt3 signling in the hemtopoieti system eliits multiomponent ntitumor immunity Mrin Kortylewski 1,4, Miej Kujwski 1,4, Tinhong Wng 2,
2 Nture Pulishing Group http://www.nture.om/nturemediine Inhiiting Stt3 signling in the hemtopoieti system eliits multiomponent ntitumor immunity Mrin Kortylewski 1,4, Miej Kujwski 1,4, Tinhong Wng 2,
Activation of Akt as a Mechanism for Tumor Immune Evasion
 The Amerin Soiety of Gene Therpy originl rtile Ativtion of Akt s Mehnism for Tumor Immune Evsion Kyung Hee Noh 1, Te Heung Kng 1, Jin Hee Kim 1, Sr I Pi 2, Ken Y Lin 3, Chien-Fu Hung 4, T-C Wu 4 7 nd Te
The Amerin Soiety of Gene Therpy originl rtile Ativtion of Akt s Mehnism for Tumor Immune Evsion Kyung Hee Noh 1, Te Heung Kng 1, Jin Hee Kim 1, Sr I Pi 2, Ken Y Lin 3, Chien-Fu Hung 4, T-C Wu 4 7 nd Te
Raina Devi Ramnath, Jia Sun, and Madhav Bhatia. Department of Pharmacology, National University of Singapore, Singapore
 -3565/9/39-48 48$. THE JOURNAL OF PHARMACOLOGY AND EXPERIMENTAL THERAPEUTICS Vol. 39, No. Copyright 9 y The Amerin Soiety for Phrmology nd Experimentl s 48684/346663 JPET 39:48 48, 9 Printed in U.S.A.
-3565/9/39-48 48$. THE JOURNAL OF PHARMACOLOGY AND EXPERIMENTAL THERAPEUTICS Vol. 39, No. Copyright 9 y The Amerin Soiety for Phrmology nd Experimentl s 48684/346663 JPET 39:48 48, 9 Printed in U.S.A.
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Prentl doi:.8/nture57 Figure S HPMECs LM Cells Cell lines VEGF (ng/ml) Prentl 7. +/-. LM 7. +/-.99 LM 7. +/-.99 Fold COX induction 5 VEGF: - + + + Bevcizum: - - 5 (µg/ml) Reltive MMP LM mock COX MMP LM+
Prentl doi:.8/nture57 Figure S HPMECs LM Cells Cell lines VEGF (ng/ml) Prentl 7. +/-. LM 7. +/-.99 LM 7. +/-.99 Fold COX induction 5 VEGF: - + + + Bevcizum: - - 5 (µg/ml) Reltive MMP LM mock COX MMP LM+
Research Article TNF-α and IFN-s-Dependent Muscle Decay Is Linked to NF-κB- and STAT-1α-Stimulated Atrogin1 and MuRF1 Genes in C2C12 Myotubes
 Hindwi Pulishing Corportion Meditors of Inflmmtion Volume 213, Artile ID 171437, 18 pges http://dx.doi.org/1.1155/213/171437 Reserh Artile nd IFN-s-Dependent Musle Dey Is Linked to NF-κB- nd STAT-1α-Stimulted
Hindwi Pulishing Corportion Meditors of Inflmmtion Volume 213, Artile ID 171437, 18 pges http://dx.doi.org/1.1155/213/171437 Reserh Artile nd IFN-s-Dependent Musle Dey Is Linked to NF-κB- nd STAT-1α-Stimulted
Ayman Hyder 1, Sabrina Ehnert 2, Hebke Hinz 1, Andreas K Nüssler 2, Fred Fändrich 1 and Hendrik Ungefroren 1,3*
 Hyder et l. Cell Communition nd Signling 212, 1:23 http://www.biosignling.om/ontent/1/1/23 RESEARCH Open Aess EGF nd HB-EGF enhne the prolifertion of progrmmble ells of monoyti origin (PCMO) through tivtion
Hyder et l. Cell Communition nd Signling 212, 1:23 http://www.biosignling.om/ontent/1/1/23 RESEARCH Open Aess EGF nd HB-EGF enhne the prolifertion of progrmmble ells of monoyti origin (PCMO) through tivtion
(% of adherent cells) *** PBL firm adhesion. Frequency (% ) 4 1 L 2 CXCR3 DP-2
 Chemotxis (% of dded ells) PBL totl dhesion (N ells/mm 2 /1.1 6 PBL) Frequeny (% ) PBL firm dhesion Supplementry Figure 1 4 4 3 3 2 2 1.1-4 1-3 1.1.2. 1 1 8 6 4 2 Adiponetin ( g/ml) - + Adiponetin ( g/ml)
Chemotxis (% of dded ells) PBL totl dhesion (N ells/mm 2 /1.1 6 PBL) Frequeny (% ) PBL firm dhesion Supplementry Figure 1 4 4 3 3 2 2 1.1-4 1-3 1.1.2. 1 1 8 6 4 2 Adiponetin ( g/ml) - + Adiponetin ( g/ml)
Supplementary figure 1
 Supplementry figure 1 Dy 8 post LCMV infection Vsculr Assoc. Prenchym Dy 3 post LCMV infection 1 5 6.7.29 1 4 1 3 1 2 88.9 4.16 1 2 1 3 1 4 1 5 1 5 1.59 5.97 1 4 1 3 1 2 21.4 71 1 2 1 3 1 4 1 5 1 5.59.22
Supplementry figure 1 Dy 8 post LCMV infection Vsculr Assoc. Prenchym Dy 3 post LCMV infection 1 5 6.7.29 1 4 1 3 1 2 88.9 4.16 1 2 1 3 1 4 1 5 1 5 1.59 5.97 1 4 1 3 1 2 21.4 71 1 2 1 3 1 4 1 5 1 5.59.22
Erucin Exerts Anti-Inflammatory Properties in Murine Macrophages and Mouse Skin: Possible Mediation through the Inhibition of NFκB Signaling
 Int. J. Mol. Si. 213, 14, 2564-2577; doi:1.339/ijms1412564 Artile OPEN ACCESS Interntionl Journl of Moleulr Sienes ISSN 1422-67 www.mdpi.om/journl/ijms Eruin Exerts Anti-Inflmmtory Properties in Murine
Int. J. Mol. Si. 213, 14, 2564-2577; doi:1.339/ijms1412564 Artile OPEN ACCESS Interntionl Journl of Moleulr Sienes ISSN 1422-67 www.mdpi.om/journl/ijms Eruin Exerts Anti-Inflmmtory Properties in Murine
Autocrine IL-2 is required for secondary population expansion of CD8 + memory T cells
 Autorine IL-2 is required for seondry popultion expnsion of CD8 + memory T ells Soni Feu, Rmon Arens,2, Susn Togher & Stephen P Shoenerger 2 Nture Ameri, In. All rights reserved. Two ompeting theories
Autorine IL-2 is required for seondry popultion expnsion of CD8 + memory T ells Soni Feu, Rmon Arens,2, Susn Togher & Stephen P Shoenerger 2 Nture Ameri, In. All rights reserved. Two ompeting theories
Research Article The Protection of Hepatocyte Cells from the Effects of Oxidative Stress by Treatment with Vitamin E in Conjunction with DTT
 Hindwi Pulishing Corportion Journl of Biomediine nd Biotehnology Volume 21, Artile ID 486267, 7 pges doi:1.1155/21/486267 Reserh Artile The Protetion of Heptoyte Cells from the Effets of Oxidtive Stress
Hindwi Pulishing Corportion Journl of Biomediine nd Biotehnology Volume 21, Artile ID 486267, 7 pges doi:1.1155/21/486267 Reserh Artile The Protetion of Heptoyte Cells from the Effets of Oxidtive Stress
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 . Norml Physiologicl Conditions. SIRT1 Loss-of-Function S1. Model for the role of SIRT1 in the regultion of memory nd plsticity. () Our findings suggest tht SIRT1 normlly functions in coopertion with YY1,
. Norml Physiologicl Conditions. SIRT1 Loss-of-Function S1. Model for the role of SIRT1 in the regultion of memory nd plsticity. () Our findings suggest tht SIRT1 normlly functions in coopertion with YY1,
ARTICLE. Keywords ACE-2. Akita mice. Angiotensinogen. Diabetes. Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein F. Hypertension. Renal fibrosis.
 Dietologi (5) 58:44 454 DOI.7/s5-5-7-y ARTICLE Overexpression of heterogeneous nuler rionuleoprotein F stimultes renl Ae- gene expression nd prevents TGF-β-indued kidney injury in mouse model of dietes
Dietologi (5) 58:44 454 DOI.7/s5-5-7-y ARTICLE Overexpression of heterogeneous nuler rionuleoprotein F stimultes renl Ae- gene expression nd prevents TGF-β-indued kidney injury in mouse model of dietes
Endothelial Cells Promote Pigmentation through Endothelin Receptor B Activation
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Endothelil Cells Promote Pigmenttion through Endothelin Reeptor B Ativtion Clire Regzzetti, Gin Mro De Dontis, Houd Hmmmi Ghorel 2, Nthlie Crdot-Lei 3, Dmien Amrosetti 3, Philippe Bhdorn
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Endothelil Cells Promote Pigmenttion through Endothelin Reeptor B Ativtion Clire Regzzetti, Gin Mro De Dontis, Houd Hmmmi Ghorel 2, Nthlie Crdot-Lei 3, Dmien Amrosetti 3, Philippe Bhdorn
Braf V600E cooperates with Pten loss to induce metastatic melanoma
 Brf V6E oopertes with Pten loss to indue metstti melnom Dvid Dnkort 1,5,6, Dvid P Curley 2,6, Roert A Crtlidge 1, Betsy Nelson 2, Anthony N Krnezis 3, Willim E Dmsky, Jr 2, Mingjin J You 4,5, Ronld A DePinho
Brf V6E oopertes with Pten loss to indue metstti melnom Dvid Dnkort 1,5,6, Dvid P Curley 2,6, Roert A Crtlidge 1, Betsy Nelson 2, Anthony N Krnezis 3, Willim E Dmsky, Jr 2, Mingjin J You 4,5, Ronld A DePinho
Supplementary Figure 1
 Roles of endoplsmic reticulum stress-medited poptosis in -polrized mcrophges during mycocteril infections Supplementry informtion Yun-Ji Lim, Min-Hee Yi, Ji-Ae Choi, Jung-hwn Lee, Ji-Ye Hn, Sung-Hee Jo,
Roles of endoplsmic reticulum stress-medited poptosis in -polrized mcrophges during mycocteril infections Supplementry informtion Yun-Ji Lim, Min-Hee Yi, Ji-Ae Choi, Jung-hwn Lee, Ji-Ye Hn, Sung-Hee Jo,
DHRS3, a retinal reductase, is differentially regulated by retinoic acid and lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation in THP-1 cells and rat liver
 Am J Physiol Gstrointest Liver Physiol 33: G78 G88, 212. First pulished July 12, 212; doi:1.112/jpgi.23.212. DHRS3, retinl redutse, is differentilly regulted y retinoi id nd lipopolyshride-indued inflmmtion
Am J Physiol Gstrointest Liver Physiol 33: G78 G88, 212. First pulished July 12, 212; doi:1.112/jpgi.23.212. DHRS3, retinl redutse, is differentilly regulted y retinoi id nd lipopolyshride-indued inflmmtion
BTLA is a lymphocyte inhibitory receptor with similarities to CTLA-4 and PD-1
 BTLA is lymphoyte inhiitory reeptor with similrities to CTLA-4 nd PD-1 Norihiko Wtne 1,5, My Gvrieli 1, John R Sedy 1, Jinfei Yng 1,5, Frnes Fllrino 2, Susn K Loftin 1, Mihelle A Hurhl 1, Ntlie Zimmermn
BTLA is lymphoyte inhiitory reeptor with similrities to CTLA-4 nd PD-1 Norihiko Wtne 1,5, My Gvrieli 1, John R Sedy 1, Jinfei Yng 1,5, Frnes Fllrino 2, Susn K Loftin 1, Mihelle A Hurhl 1, Ntlie Zimmermn
BRAF Inhibition Generates a Host Tumor Niche that Mediates Therapeutic Escape
 See relted ommentry on pg 9 ORIGINAL ARTICLE BRAF Inhiition Genertes Host Tumor Nihe tht edites Therpeuti Espe Inn V. Fedorenko 1, Jennifer A. Wrgo, Keith T. Flherty, Jne L. essin nd Keirn S.. Smlley 1,
See relted ommentry on pg 9 ORIGINAL ARTICLE BRAF Inhiition Genertes Host Tumor Nihe tht edites Therpeuti Espe Inn V. Fedorenko 1, Jennifer A. Wrgo, Keith T. Flherty, Jne L. essin nd Keirn S.. Smlley 1,
regulates stem cells through Wnt/β-catenin signalling
 LETTERS O regultes stem ells through Wnt/β-tenin signlling Jolly Mzumdr,,7, W. Timothy O Brien, Rndll S. Johnson, Joseph C. LMnn, Jun C. Chvez 5, Peter S. Klein nd M. Celeste Simon,, Stem ells reside in
LETTERS O regultes stem ells through Wnt/β-tenin signlling Jolly Mzumdr,,7, W. Timothy O Brien, Rndll S. Johnson, Joseph C. LMnn, Jun C. Chvez 5, Peter S. Klein nd M. Celeste Simon,, Stem ells reside in
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI:.3/n95 Thymus Kiney (kd) TA T7 T TA T7 T Hert TA T7 T: +Dox Cylin B (kd) Thymus Kiney Hert TA T5 T TA T5 T TA T5 T: +Dox Cylin B Poneu S Poneu S CnB T7 CnB T Thymus (kd) + Liver Colon + + (kd) Thymus
DOI:.3/n95 Thymus Kiney (kd) TA T7 T TA T7 T Hert TA T7 T: +Dox Cylin B (kd) Thymus Kiney Hert TA T5 T TA T5 T TA T5 T: +Dox Cylin B Poneu S Poneu S CnB T7 CnB T Thymus (kd) + Liver Colon + + (kd) Thymus
Progestin effects on cell proliferation pathways in the postmenopausal mammary gland
 Wood et l. Brest Cner Reserh 213, 15:R62 http://rest-ner-reserh.om/ontent/15/4/r62 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Aess Progestin effets on ell prolifertion pthwys in the postmenopusl mmmry glnd Chrles E Wood 1,
Wood et l. Brest Cner Reserh 213, 15:R62 http://rest-ner-reserh.om/ontent/15/4/r62 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Aess Progestin effets on ell prolifertion pthwys in the postmenopusl mmmry glnd Chrles E Wood 1,
Effects of Plant Sphingolipids on Inflammatory Stress in Differentiated Caco-2 Cells
 Journl of Oleo Siene Copyright 2017 y Jpn Oil Chemists Soiety doi : 10.5650/jos.ess17171 J. Oleo Si. 66, (12) 1337-1342 (2017) NOTE Effets of Plnt Sphingolipids on Inflmmtory Stress in Differentited Co-2
Journl of Oleo Siene Copyright 2017 y Jpn Oil Chemists Soiety doi : 10.5650/jos.ess17171 J. Oleo Si. 66, (12) 1337-1342 (2017) NOTE Effets of Plnt Sphingolipids on Inflmmtory Stress in Differentited Co-2
Introduction to Study Designs II
 Introdution to Study Designs II Commonly used study designs in publi helth & epidemiologi reserh Benjmin Rihrd H. Muthmbi, DrPH, MPH Stte HIV Epidemiologist HIV Epidemiology Investigtion Setion PA Deprtment
Introdution to Study Designs II Commonly used study designs in publi helth & epidemiologi reserh Benjmin Rihrd H. Muthmbi, DrPH, MPH Stte HIV Epidemiologist HIV Epidemiology Investigtion Setion PA Deprtment
RESEARCH ARTICLE Transport of selenium across the plasma membrane of primary hepatocytes and enterocytes of rainbow trout
 191 The Journl of Experimentl iology 15, 191-151 1. Pulished y The ompny of iologists Ltd doi:1.1/je.37 RESERH RTILE Trnsport of selenium ross the plsm memrne of primry heptoytes nd enteroytes of rinow
191 The Journl of Experimentl iology 15, 191-151 1. Pulished y The ompny of iologists Ltd doi:1.1/je.37 RESERH RTILE Trnsport of selenium ross the plsm memrne of primry heptoytes nd enteroytes of rinow
Upregulation of tissue inhibitor of matrix metalloproteinases-1 confers the anti-invasive action of cisplatin on human cancer cells
 (27) 26, 5822 5827 & 27 Nture Pulishing Group All rights reserved 95-9232/7 $3. SHORT COMMUNICATION Upregultion of tissue inhiitor of mtrix metlloproteinses-1 onfers the nti-invve tion of ispltin on humn
(27) 26, 5822 5827 & 27 Nture Pulishing Group All rights reserved 95-9232/7 $3. SHORT COMMUNICATION Upregultion of tissue inhiitor of mtrix metlloproteinses-1 onfers the nti-invve tion of ispltin on humn
Supplementary Figure S1
 Supplementry Figure S Connexin4 TroponinI Merge Plsm memrne Met Intrcellulr Met Supplementry Figure S H9c rt crdiomyolsts cell line. () Immunofluorescence of crdic mrkers: Connexin4 (green) nd TroponinI
Supplementry Figure S Connexin4 TroponinI Merge Plsm memrne Met Intrcellulr Met Supplementry Figure S H9c rt crdiomyolsts cell line. () Immunofluorescence of crdic mrkers: Connexin4 (green) nd TroponinI
Lesions of prefrontal cortex reduce attentional modulation of neuronal responses. and synchrony in V4
 Lesions of prefrontl ortex reue ttentionl moultion of neuronl responses n synhrony in V4 Georgi G. Gregoriou,, Anrew F. Rossi, 3 Leslie G Ungerleier, 4 Roert Desimone 5 Deprtment of Bsi Sienes, Fulty of
Lesions of prefrontl ortex reue ttentionl moultion of neuronl responses n synhrony in V4 Georgi G. Gregoriou,, Anrew F. Rossi, 3 Leslie G Ungerleier, 4 Roert Desimone 5 Deprtment of Bsi Sienes, Fulty of
Tbp. Per Relative mrna levels Circadian Time. Liver weight/ body weight (%) n.s. Pernull
 Liver weight/ ody weight (%) Dy Body weight (g) Reltive mrna levels Reltive mrna levels Reltive mrna levels Reltive mrna levels Dy Per1 Per2 Per3 Tp 8 2 8 2. 6 2 8 12162 Cirdin Time 3 2 1 2 1 1 8 12162
Liver weight/ ody weight (%) Dy Body weight (g) Reltive mrna levels Reltive mrna levels Reltive mrna levels Reltive mrna levels Dy Per1 Per2 Per3 Tp 8 2 8 2. 6 2 8 12162 Cirdin Time 3 2 1 2 1 1 8 12162
Supplementary Information
 Supplementry Informtion Non-nonil prevents skeletl ging n inflmmtion y inhiiting NF-κB Bo Yu, Ji Chng, Yunsong Liu, Jiong Li, Kreen Kevork, Khli Al Hezimi, Dn T. Grves, No-Hee Prk, Cun-Yu Wng Supplementry
Supplementry Informtion Non-nonil prevents skeletl ging n inflmmtion y inhiiting NF-κB Bo Yu, Ji Chng, Yunsong Liu, Jiong Li, Kreen Kevork, Khli Al Hezimi, Dn T. Grves, No-Hee Prk, Cun-Yu Wng Supplementry
13-cis Retinoic Acid Induces Apoptosis and Cell Cycle Arrest in Human SEB-1 Sebocytes
 ORIGINAL ARTILE See relted ommentry on pge 15 13-is Retinoi Aid Indues Apoptosis nd ell yle Arrest in Humn SEB-1 Seoytes Amnd M. Nelson 1, Kthryn L. Gillilnd 1, Zhoyun ong 1 nd Dine M. Thioutot 1, Isotretinoin
ORIGINAL ARTILE See relted ommentry on pge 15 13-is Retinoi Aid Indues Apoptosis nd ell yle Arrest in Humn SEB-1 Seoytes Amnd M. Nelson 1, Kthryn L. Gillilnd 1, Zhoyun ong 1 nd Dine M. Thioutot 1, Isotretinoin
A1/Bfl-1 expression is restricted to TCR engagement in T lymphocytes
 (3) 1, 19 17 & 3 Nture Pulishing Group All rights reserved 13-97/3 $. www.nture.om/dd /Bfl-1 expression is restrited to TCR enggement in T lymphoytes C Vershelde 1, T Wlzer, P Gli 1, M-C Biémont 1, L Quemeneur
(3) 1, 19 17 & 3 Nture Pulishing Group All rights reserved 13-97/3 $. www.nture.om/dd /Bfl-1 expression is restrited to TCR enggement in T lymphoytes C Vershelde 1, T Wlzer, P Gli 1, M-C Biémont 1, L Quemeneur
Whangarei District Council Class 4 Gambling Venue Policy
 Whngrei Distrit Counil Clss 4 Gmling Venue Poliy April 2013 Whngrei Distrit Counil Clss 4 Gmling Venue Poliy Tle of ontents Introdution... 3 1 Ojetives of the poliy in so fr s promoted y the Gmling At
Whngrei Distrit Counil Clss 4 Gmling Venue Poliy April 2013 Whngrei Distrit Counil Clss 4 Gmling Venue Poliy Tle of ontents Introdution... 3 1 Ojetives of the poliy in so fr s promoted y the Gmling At
Plant Physiology Preview. Published on February 21, 2017, as DOI: /pp
 Plnt Physiology Preview. Pulished on Ferury 21, 217, s DOI:1.114/pp.16.1928 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 1 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 Running title: Spliing regultor STA1 in het stress dpttion Corresponding Author:
Plnt Physiology Preview. Pulished on Ferury 21, 217, s DOI:1.114/pp.16.1928 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 1 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 Running title: Spliing regultor STA1 in het stress dpttion Corresponding Author:
Maintenance of protein synthesis reading frame by EF-P and m 1 G37-tRNA
 Reeived 23 Nov 214 Aepted 2 Apr 215 Pulished 26 My 215 DOI: 1.138/nomms8226 Mintenne of protein synthesis reding frme y EF-P nd m 1 G37-tRNA Howrd B. Gmper 1, *, Iso Msud 1, *, Miln Frenkel-Morgenstern
Reeived 23 Nov 214 Aepted 2 Apr 215 Pulished 26 My 215 DOI: 1.138/nomms8226 Mintenne of protein synthesis reding frme y EF-P nd m 1 G37-tRNA Howrd B. Gmper 1, *, Iso Msud 1, *, Miln Frenkel-Morgenstern
MiR-29a Assists in Preventing the Activation of Human Stellate Cells and Promotes Recovery From Liver Fibrosis in Mice
 originl rtile The Amerin Soiety of Gene & Cell Therpy MiR-9 Assists in Preventing the Ativtion of Humn Stellte Cells nd Promotes Reovery From Liver Firosis in Mie Yoshinri Mtsumoto,,3, Sori Itmi, Mshiko
originl rtile The Amerin Soiety of Gene & Cell Therpy MiR-9 Assists in Preventing the Ativtion of Humn Stellte Cells nd Promotes Reovery From Liver Firosis in Mie Yoshinri Mtsumoto,,3, Sori Itmi, Mshiko
Gibberellins regulate iron deficiency-response by influencing iron transport and translocation in rice seedlings (Oryza sativa)
 nnls of otny 119: 95 956, 17 doi:1.19/o/mw5, ville online t www.o.oxfordjournls.org Gierellins regulte iron defiieny-response y influening iron trnsport nd trnslotion in rie seedlings (Oryz stiv) oln Wng
nnls of otny 119: 95 956, 17 doi:1.19/o/mw5, ville online t www.o.oxfordjournls.org Gierellins regulte iron defiieny-response y influening iron trnsport nd trnslotion in rie seedlings (Oryz stiv) oln Wng
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION CD169 + MACROPHAGES PRESENT LIPID ANTIGENS TO MEDIATE EARLY ACTIVATION OF INVARIANT NKT CELLS IN LYMPH NODES Ptrii Brrl, Polo Polzell, Andres Brukuer, Nio vn Rooijen, Gurdyl S.
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION CD169 + MACROPHAGES PRESENT LIPID ANTIGENS TO MEDIATE EARLY ACTIVATION OF INVARIANT NKT CELLS IN LYMPH NODES Ptrii Brrl, Polo Polzell, Andres Brukuer, Nio vn Rooijen, Gurdyl S.
Targeting BIG3 PHB2 interaction to overcome tamoxifen resistance in breast cancer cells
 Reeive Fe 13 Aepte 15 Aug 13 Pulishe Sep 13 DOI: 1.13/nomms33 OPEN Trgeting intertion to overome tmoxifen resistne in rest ner ells Tetsuro Yoshimru 1, Msto Komtsu 1, Tisuke Mtsuo 1, Yi-An Chen, Yoihi
Reeive Fe 13 Aepte 15 Aug 13 Pulishe Sep 13 DOI: 1.13/nomms33 OPEN Trgeting intertion to overome tmoxifen resistne in rest ner ells Tetsuro Yoshimru 1, Msto Komtsu 1, Tisuke Mtsuo 1, Yi-An Chen, Yoihi
WNK1 kinase balances T cell adhesion versus migration in vivo
 WNK1 kinse lnes T ell dhesion versus migrtion in vivo Roert Köhl 1, Flvin Thelen, Lesley Vnes 1, Tigo F Brzão 1, Kthryn Fountin 1, Jin Xie 3, Chou-Long Hung 3, Ruth Lyk, Jens V Stein & Vitor L J Tyulewiz
WNK1 kinse lnes T ell dhesion versus migrtion in vivo Roert Köhl 1, Flvin Thelen, Lesley Vnes 1, Tigo F Brzão 1, Kthryn Fountin 1, Jin Xie 3, Chou-Long Hung 3, Ruth Lyk, Jens V Stein & Vitor L J Tyulewiz
LETTERS. Novel mutant-selective EGFR kinase inhibitors against EGFR T790M
 Vol 462 24/31 Deemer 29 doi:1.138/nture8622 ovel mutnt-seletive kinse inhiitors ginst T79M Wenjun Zhou 1,2 *, Dli Ern 3,4 *, Ling Chen 3,4 *, Ci-Hong Yun 1,2 *, Dnn Li 3,4, Mrzi Cpelletti 3,4, Alexis B.
Vol 462 24/31 Deemer 29 doi:1.138/nture8622 ovel mutnt-seletive kinse inhiitors ginst T79M Wenjun Zhou 1,2 *, Dli Ern 3,4 *, Ling Chen 3,4 *, Ci-Hong Yun 1,2 *, Dnn Li 3,4, Mrzi Cpelletti 3,4, Alexis B.
Expression of Three Cell Cycle Inhibitors during Development of Adipose Tissue
 Expression of Three Cell Cycle Inhiitors during Development of Adipose Tissue Jiin Zhng Deprtment of Animl Sciences Advisor: Michel E. Dvis Co-dvisor: Kichoon Lee Development of niml dipose tissue Hypertrophy
Expression of Three Cell Cycle Inhiitors during Development of Adipose Tissue Jiin Zhng Deprtment of Animl Sciences Advisor: Michel E. Dvis Co-dvisor: Kichoon Lee Development of niml dipose tissue Hypertrophy
Hydrogen sulfide-induced inhibition of L-type Ca 2+ channels and insulin secretion in mouse pancreatic beta cells
 Dietologi (213) 56:533 541 DOI 1.17/s125-12-286-8 ARTICLE Hydrogen sulfide-indued inhiition of L-type C 2 hnnels nd insulin seretion in mouse pnreti et ells G. Tng & L. Zhng & G. Yng & L. Wu & R. Wng Reeived:
Dietologi (213) 56:533 541 DOI 1.17/s125-12-286-8 ARTICLE Hydrogen sulfide-indued inhiition of L-type C 2 hnnels nd insulin seretion in mouse pnreti et ells G. Tng & L. Zhng & G. Yng & L. Wu & R. Wng Reeived:
Stimulation of the insulin/mtor pathway delays cone death in a mouse model of retinitis pigmentosa
 Stimultion of the insulin/mtor pthwy delys one deth in mouse model of retinitis pigmentos Cludio Punzo 1, Krl Kornker 2 & Constne L Cepko 1,3 Retinitis pigmentos is n inurle retinl disese tht leds to lindness.
Stimultion of the insulin/mtor pthwy delys one deth in mouse model of retinitis pigmentos Cludio Punzo 1, Krl Kornker 2 & Constne L Cepko 1,3 Retinitis pigmentos is n inurle retinl disese tht leds to lindness.
CAUSES OF DIARRHEA, PNEUMONIA, AND ABORTION IN 1991 CATTLE SUBMISSIONS TO THE KSU VETERINARY DIAGNOSTIC LABORATORY
 CAUSES OF DIARRHEA, PNEUMONIA, AND ABORTION IN 1991 CATTLE SUBMISSIONS TO THE KSU VETERINARY DIAGNOSTIC LABORATORY 1 1 2 R. K. Frnk, M. W. Vorhies, nd M. M. Chengpp Summry Cuses of dirrhe, pneumoni, nd
CAUSES OF DIARRHEA, PNEUMONIA, AND ABORTION IN 1991 CATTLE SUBMISSIONS TO THE KSU VETERINARY DIAGNOSTIC LABORATORY 1 1 2 R. K. Frnk, M. W. Vorhies, nd M. M. Chengpp Summry Cuses of dirrhe, pneumoni, nd
BATF regulates collagen-induced arthritis by regulating T helper cell differentiation
 Prk et l. Arthritis Reserh & Therpy (218) 2:161 https://doi.org/1.1186/s1375-18-1658- RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Aess BATF regultes ollgen-indued rthritis y regulting T helper ell differentition Sng-Heon Prk
Prk et l. Arthritis Reserh & Therpy (218) 2:161 https://doi.org/1.1186/s1375-18-1658- RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Aess BATF regultes ollgen-indued rthritis y regulting T helper ell differentition Sng-Heon Prk
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 2 weeks high holesterol diet 2 weeks high holesterol diet 2 weeks high holesterol diet 2 μm Mrophges Crystls Hoehst μm Mrophges Crystls Hoehst Hoehst Crystls Mrophges 2 μm 2 μm Supplementry Fig. 1: Erly
2 weeks high holesterol diet 2 weeks high holesterol diet 2 weeks high holesterol diet 2 μm Mrophges Crystls Hoehst μm Mrophges Crystls Hoehst Hoehst Crystls Mrophges 2 μm 2 μm Supplementry Fig. 1: Erly
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 1.138/nc286 Figure S1 e f Medium DMSO AktVIII PP242 Rp S6K1-I Gr1 + + + + + + Strvtion + + + + + IB: Akt-pT38 IB: Akt K-pT389 K IB: Rptor Gr1 shs6k1-a shs6k1-b shs6k1-c shrictor shrptor Gr1 c IB:
DOI: 1.138/nc286 Figure S1 e f Medium DMSO AktVIII PP242 Rp S6K1-I Gr1 + + + + + + Strvtion + + + + + IB: Akt-pT38 IB: Akt K-pT389 K IB: Rptor Gr1 shs6k1-a shs6k1-b shs6k1-c shrictor shrptor Gr1 c IB:
MicroRNA 125b promotes tumor metastasis through targeting tumor protein 53 induced nuclear protein 1 in patients with non small cell lung cancer
 Li et l. Cner Cell Int (15) 15:8 DOI 1.118/s1935-15-33-x PRIMARY RESEARCH MiroRNA 15 promotes tumor metstsis through trgeting tumor protein 53 indued nuler protein 1 in ptients with non smll ell lung ner
Li et l. Cner Cell Int (15) 15:8 DOI 1.118/s1935-15-33-x PRIMARY RESEARCH MiroRNA 15 promotes tumor metstsis through trgeting tumor protein 53 indued nuler protein 1 in ptients with non smll ell lung ner
Acute and gradual increases in BDNF concentration elicit distinct signaling and functions in neurons
 nd grdul increses in BDNF concentrtion elicit distinct signling nd functions in neurons Yunyun Ji,, Yun Lu, Feng Yng, Wnhu Shen, Tin Tze-Tsng Tng,, Linyin Feng, Shumin Dun, nd Bi Lu,.. - Grdul (normlized
nd grdul increses in BDNF concentrtion elicit distinct signling nd functions in neurons Yunyun Ji,, Yun Lu, Feng Yng, Wnhu Shen, Tin Tze-Tsng Tng,, Linyin Feng, Shumin Dun, nd Bi Lu,.. - Grdul (normlized
Multisite phosphorylation of a CDK inhibitor sets a threshold for the onset of DNA replication
 Multisite phosphoryltion of CDK inhiitor sets threshold for the onset of DNA replition iers Nsh*², iojing Tng*², Stephen Orliky*, Qinghu Chen³, Frnk B. Gertler, Mihel D. Mendenhll³, Frnk Siheri*k, Tony
Multisite phosphoryltion of CDK inhiitor sets threshold for the onset of DNA replition iers Nsh*², iojing Tng*², Stephen Orliky*, Qinghu Chen³, Frnk B. Gertler, Mihel D. Mendenhll³, Frnk Siheri*k, Tony
Pathogenesis of NSAID-induced gastric damage: Importance of cyclooxygenase inhibition and gastric hypermotility
 Online Submissions: http://www.wjgnet.om/7-9327offie wjg@wjgnet.om doi:.3748/wjg.v18.i18.2147 World J Gstroenterol 12 My 14; 18(18): 2147-21 ISSN 7-9327 (print) ISSN 2219-28 (online) 12 Bishideng. All
Online Submissions: http://www.wjgnet.om/7-9327offie wjg@wjgnet.om doi:.3748/wjg.v18.i18.2147 World J Gstroenterol 12 My 14; 18(18): 2147-21 ISSN 7-9327 (print) ISSN 2219-28 (online) 12 Bishideng. All
