The GCN5-CITED2-PKA signalling module controls hepatic glucose metabolism through a camp-induced substrate switch
|
|
|
- Basil Spencer
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Reeived 6 Apr 216 Aepted 8 Sep 216 Pulished 22 Nov 216 DOI: 1.138/nomms13147 OPEN The GCN5-CITED2-PKA signlling module ontrols hepti gluose metolism through AMP-indued sustrte swith Mshito Ski 1, Tomoko Tujimur-Hykw 1, Tkshi Ygi 1,2, Hiroyuki Yno 1,2, Msru Mitsushim 1, Hiroyuki Unoki-Kuot 3, Ysushi Kurgi 3, Hiroshi Inoue 4, Yoshiki Kido 5,6, Msto Ksug 7 & Mihihiro Mtsumoto 1 Hepti gluoneogenesis during fsting results from gluoneogeni gene tivtion vi the glugonampprotein kinse A (PKA) pthwy, proess whose dysregultion underlies fsting hyperglyemi in dietes. Suh trnsriptionl tivtion requires epigeneti hnges t promoters y mehnisms tht hve remined unler. Here we show tht GCN5 funtions oth s histone etyltrnsferse (HAT) to tivte fsting gluoneogenesis nd s n etyltrnsferse for the trnsriptionl o-tivtor PGC-1 to inhiit gluoneogenesis in the fed stte. During fsting, PKA phosphoryltes GCN5 in mnner dependent on the trnsriptionl oregultor CITED2, therey inresing its etyltrnsferse tivity for histone nd ttenuting tht for PGC-1. This sustrte swith onomitntly promotes oth epigeneti hnges ssoited with trnsriptionl tivtion nd PGC-1medited otivtion, therey triggering gluoneogenesis. The GCN5-CITED2-PKA signlling module nd ssoited GCN5 sustrte swith thus serve s key driver of gluoneogenesis. Disruption of this module meliortes hyperglyemi in oese dieti nimls, offering potentil therpeuti strtegy for suh onditions. 1 Deprtment of Moleulr Metoli Regultion, Dietes Reserh Center, Reserh Institute, Ntionl Center for Glol Helth nd Mediine, Toym, Shinjuku-ku, Tokyo , Jpn. 2 Deprtment of Bioregultion, Nippon Medil Shool, Kosugi-mhi, Nkhr-ku, Kwski , Jpn. 3 Deprtment of Dieti Complitions, Dietes Reserh Center, Reserh Institute, Ntionl Center for Glol Helth nd Mediine, Toym, Shinjuku-ku, Tokyo , Jpn. 4 Metolism nd Nutrition Reserh Unit, Innovtive Integrted Bio-reserh Core, Institute for Frontier Siene Inititive, Knzw University, 13-1 Tkr-mhi, Knzw , Jpn. 5 Division of Medil Chemistry, Deprtment of Metolism nd Disese, Koe University Grdute Shool of Helth Sienes, Tomogok, Sum-ku, Koe , Jpn. 6 Division of Dietes nd Endorinology, Deprtment of Internl Mediine, Koe University Grdute Shool of Mediine, Kusunoki-ho, Chuo-ku, Koe 65-17, Jpn. 7 Ntionl Center for Glol Helth nd Mediine, Toym, Shinjuku-ku, Tokyo , Jpn. Correspondene nd requests for mterils should e ddressed to M.M. (emil: mmtsumoto@ri.ngm.go.jp). NATURE COMMUNICATIONS 7:13147 DOI: 1.138/nomms
2 NATURE COMMUNICATIONS DOI: 1.138/nomms13147 Hepti gluoneogenesis is indued y pnreti glugon during fsting to mintin gluose homeostsis 1, proess whose dysregultion in dietes results in fsting hyperglyemi 2,3. The glugonampprotein kinse A (PKA) pthwy tivtes hepti gluoneogenesis y induing expression of the gluoneogeni genes G6p (enoding the tlyti suunit of gluose-6-phosphtse) nd Pk1 (phosphoenolpyruvte roxykinse) 4. Suh indution is thought to e medited through orhestrtion of hormone-dependent epigeneti hnges 5 nd ssemly of trnsriptionl mhinery 3,613 t the gene promoters. A key omponent of this mhinery is the CREB (AMP response element-inding protein)crtc2 (CREB-regulted trnsriptionl o-tivtor 2) omplex, whose ssemly is triggered y PKA-dependent phosphoryltion of CREB nd the dephosphoryltion of CRTC2 nd whih promotes reruitment of the histone etyltrnsferse (HAT) CBP (CREB-inding protein, lso known s Kt3) nd therey tivtes peroxisome prolifertortivted reeptor g o-tivtor1 (PGC-1) gene trnsription 6. PGC-1 then funtions with the trnsription ftors forkhed ox O1 (FoxO1) 8 nd heptoyte nuler ftor4 (HNF-4) 7,9 to medite synergisti tivtion of the gluoneogeni progrm; however, how glugon signlling triggers epigeneti hnges for effiient trnsription of gluoneogeni genes hs een unler 5. Generl ontrol non-repressed protein 5 (GCN5, lso known s Kt2) funtions not only s HAT tht links histone etyltion nd trnsriptionl tivtion 14 ut it lso possesses etyltrnsferse tivity for non-histone sustrtes 15,16. GCN5 thus etyltes nd intivtes PGC-1 nd therey inhiits PGC-1dependent gluoneogenesis This funtion of GCN5 is inhiited during fsting y CBP- nd p3-interting trnstivtor with glutmi id nd sprti idrih COOH-terminl domin 2 (CITED2), fsting-induile trnsriptionl oregultor tht inds to GCN5 nd disrupts the GCN5PGC-1 intertion, resulting in deetyltion nd tivtion of PGC-1 (ref. 2); however, the preise role of GCN5 ssoited with CITED2 in the regultion of hepti gluoneogenesis y the glugon-amp-pka xis hs remined unknown. We now show tht GCN5 serves dul funtion in the feedingto-fsting trnsition: s HAT to tivte gluoneogenesis in the fsted stte nd s PGC-1 etyltrnsferse to inhiit it in the fed stte. This dul funtion of GCN5 is reiprolly regulted y glugon-dependent sustrte swith t the feeding-to-fsting trnsition. The fsting-indued GCN5-CITED2-PKA omplex serves s speifi module for PKA-dependent phosphoryltion of GCN5 t Ser 275, whih drives the sustrte swith from PGC-1 to histone H3. This swith integrtes epigeneti hnges nd the o-tivtor tivity of PGC-1, leding to full indution of the gluoneogeni progrm. Disruption of the GCN5-CITED2- PKA signlling module meliortes hyperglyemi in oese dieti nimls nd is therefore potentil strtegy for the tretment of suh onditions. Results Hepti GCN5 expression is regulted y AMP-PKA signlling. We first investigted hepti expression of GCN5 s well s of CBP, its prlog p3 (lso known s Kt3), nd the GCN5 prlog p3/cbp-ssoited ftor (PCAF, lso known s Kt2) in mie. Among these HATs, we found tht the expression of GCN5 ws seletively inresed in the liver of two mouse models of oesity-ssoited type 2 dietes norml mie fed high-ft diet (HFD) (Fig. 1) nd d/d mie (Fig. 1,) ompred with ontrol mie. The mount of GCN5 in primry ultured mouse heptoytes ws lso inresed y tretment with ell-permele nlogue of AMP (pcpt-amp) in PKA-dependent mnner (Fig. 1d), suggesting tht glugon-amp-pka signlling inreses the hepti of GCN5 s well s tht of CITED2 (ref. 2). These findings prompted us to exmine whether GCN5 regultes gluoneogenesis through histone etyltion in ollortion with CITED2. GCN5 depletion ttenutes gluoneogenesis in vivo nd in vitro. In len mie, depletion of hepti GCN5 with short hirpin RNA (shrna) redued the level of gluoneogeni gene expression pprent fter food deprivtion for 24 h s well s the lood gluose onentrtion either fter fsting for 6 h (Fig. 2 nd Supplementry Fig. 1) or fter dministrtion of pyruvte (Fig. 2) despite the ssoited mrked ttenution of PGC-1 etyltion (Fig. 2). Knokdown of hepti GCN5 in d/d mie lso redued fsting gluoneogeni gene expression nd glyemi (Supplementry Fig. 1). In primry mouse heptoytes, GCN5 knokdown ttenuted gluoneogeni gene expression s well s gluose prodution indued y pcpt-amp (Fig. 2d nd Supplementry Fig. 1) despite the oserved downregultion of PGC-1 etyltion (Fig. 2e). These results thus suggested tht GCN5 ontriutes in mnner independent of its PGC-1 etyltrnsferse funtion to gluoneogeni gene indution vi the glugon-amp pthwy. In heptoytes, fored expression of CITED2 enhnes gluoneogeni gene expression indued y AMP (Fig. 2f nd Supplementry Fig. 1d) or y PGC-1 overexpression in the sene of AMP 2 (Fig. 2g nd Supplementry Fig. 1e). The PGC-1 etyltrnsferse tivity of GCN5 is suppressed y intertion with CITED2 under these onditions 2. We therefore exmined whether GCN5 tht interts with CITED2 might funtion other thn s PGC-1 etyltrnsferse in the regultion of gluoneogenesis y dopting loss- nd gin-of-funtion pprohes in this setting. Loss of GCN5 ttenuted the CITED2-dependent enhnement of gluoneogeni gene expression indued y AMP (Fig. 2f nd Supplementry Fig. 1d) or y PGC-1 overexpression (Fig. 2g nd Supplementry Fig. 1e) despite the downregultion of PGC-1 etyltion indued y GCN5 knokdown (Fig. 2e). GCN5 promotes gluoneogenesis in onert with CITED2. Overexpression of wild-type (WT) GCN5 suppressed gluoneogeni gene indution y AMP in primry heptoytes (Fig. 3), onsistent with the previously oserved suppression of PGC-1indued gluoneogeni gene expression y GCN5 overexpression in Fo heptom ells 17. This effet ws lso oserved with mutnt (DAT) of GCN5 tht lks etyltrnsferse tivity 21 towrd oth histone H3 nd PGC-1 (Fig. 3 nd Supplementry Fig. 2,), however, inditing tht GCN5 suppresses gluoneogeni gene expression independently of its enzymti tivity in this setting. In ontrst, oexpression of GCN5(WT), ut not tht of GCN5(DAT), with CITED2 enhned AMP-indued gluoneogeni gene expression (Fig. 3 nd Supplementry Fig. 2). We lso exmined the effets of overexpression of GCN5, CITED2, nd oth proteins in the liver of C57BL/6J mie on gluoneogenesis. As previously shown 2, mie overexpressing CITED2 in the liver mnifested inresed fsting glyemi (Fig. 3) nd hepti expression of G6p nd Pk1 (Fig. 3d nd Supplementry Fig. 2d) ompred with ontrol mie. Hepti overexpression of GCN5 lone redued oth fsting glyemi (Fig. 3) nd hepti expression of gluoneogeni genes (Fig. 3d nd Supplementry Fig. 2d), onsistent with our in vitro results (Fig. 3) s well s previous oservtions 17. Agin onsistent with our in vitro findings (Fig. 3), oexpression of GCN5 with 2 NATURE COMMUNICATIONS 7:13147 DOI: 1.138/nomms
3 NATURE COMMUNICATIONS DOI: 1.138/nomms13147 ARTICLE Reltive Gn5 mrna NC HFD NC HFD IB: Histone H1 Reltive Gn5 mrna d/m d/d IB: Histone H1 d/m d/d d/m d/d IB: PCAF d IP: GCN5 IB: CBP IB: PCAF IB: p3 3 h 6 h 6 h Reltive GCN5/H1 rtio d/m d/d Reltive PCAF/H1 rtio 1..5 Reltive CBP/H1 rtio 1..5 Reltive p3/h1 rtio 1..5 H89: Figure 1 Hepti expression of GCN5 is upregulted in oese dieti mie vi AMP-PKA signlling. (,) qrt-pcr nlysis of Gn5 mrna nd immunolot (IB) nlysis of nuler GCN5 in the liver of C57BL/6J mie mintined on norml how (NC) or HFD ()orofd/d or d/m (ontrol) mie () fter deprivtion of food for 16 h. RTPCR dt re mens±s.e.m. (n ¼ 7() or6()). Histone H1 ws exmined s loding ontrol for immunolot nlysis. () Immunolot nlysis of GCN5, PCAF, CBP nd p3 in the liver of d/d or d/m mie deprived of food for 16 h. Quntittive dt re mens±s.e.m. (n ¼ 3). (d) Primry mouse heptoytes were inuted in the sene or presene of 1 mm pcpt-amp or the PKA inhiitor H89 (2 mm) for the indited times. Cell lystes were then sujeted to immunolot nlysis of PCAF or to IP followed y immunolot nlysis with ntiodies to GCN5. Dt re representtive of t lest three independent experiments. Sttistil nlysis ws performed with the unpired Student s t-test (). Po.5 versus NC () or d/m mie (,). RTPCR, PCR with reverse trnsription. CITED2 in the liver of C57BL/6J mie inresed oth fsting glyemi (Fig. 3) nd hepti gluoneogeni gene expression (Fig. 3d nd Supplementry Fig. 2d) ompred with those pprent with CITED2 expression lone. To evlute the effets of suh ltered gluoneogeni gene expression, we performed pyruvte hllenge test. Gluose levels fter pyruvte dministrtion were signifintly higher in mie with hepti CITED2 overexpression ut were lower in those with hepti GCN5 overexpression ompred with ontrol mie (Fig. 3e). Mie with hepti oexpression of CITED2 nd GCN5 showed lood gluose onentrtions fter pyruvte dministrtion tht were higher thn those in mie with CITED2 overexpression lone (Fig. 3e). Together, these in vitro nd in vivo results suggested tht GCN5 might funtion s AMP-responsive, CITED2-dependent HAT in the regultion of gluoneogenesis. GCN5 is ruil HAT for initition of gluoneogenesis. To test this hypothesis, we exmined the moleulr signtures of gluoneogeni gene promoters y hromtin immunopreipittion (ChIP) nd quntittive PCR nlysis in primry heptoytes depleted of GCN5, CITED2 or PGC-1. The oupny of suh promoters with GCN5 nd CBP ws inresed fter exposure of ontrol heptoytes to pcpt-amp for 16 h (Fig. 4, nd Supplementry Fig. 3). The mounts of histone H3 etylted t Lys 9 (H3K9) or Lys 22 (H3K27) whih re generted predominntly y GCN5 nd CBP, respetively 22 s well s tht of trimethylted H3K4 (H3K4me3) (ref. 23), ll three of whih mrks re ssoited with tive gene trnsription 24, were lso inresed t these promoters in ells treted with pcpt-amp (Fig. 4 nd Supplementry Fig. 3). Consistent with the ssoited downregultion of gluoneogeni gene trnsription 2 (Fig. 2d), these AMP-indued inreses in the mounts of H3K9, H3K27 nd H3K4me3 were lunted y depletion of either GCN5 (Fig. 4 nd Supplementry Fig. 3,e), CITED2 (Fig. 4 nd Supplementry Fig. 3,e) or PGC-1 (Fig. 4 nd Supplementry Fig. 3,e). The AMP-indued reruitment of GCN5 nd CBP ws lso ttenuted y NATURE COMMUNICATIONS 7:13147 DOI: 1.138/nomms
4 NATURE COMMUNICATIONS DOI: 1.138/nomms GCN5 KD 1..5 Gluose (mg dl 1 ) Gluose (mg dl 1 ) 15 GCN5 KD Fed Fsted Fsted 6 h 24 h GCN5 KD Time (min) GCN5 shrna: IP: PGC-1α IB: PGC-1α IP: PGC-1α IB: ALys d GCN5 shrna: 3,5 3, 2,5 2, 1,5 1, 5 Gluose prodution (AU) e FLAG- PGC-1α: GCN5 shrna: IB: PGC-1α IB: ALys IP: GCN5 f CITED2: GCN5 shrna: CITED2: GCN5 shrna: PGC-1α: g Figure 2 GCN5 depletion suppresses hepti gluoneogenesis in vivo nd in vitro. (,) Effets of shrna-medited knokdown (KD) of GCN5 in the liver of C57BL/6J mie on hepti gluoneogeni gene expression under the fsted (24 h) ondition () or on plsm glyemi either under fsted (6 or 24 h) or fed onditions () or fter pyruvte dministrtion (). () IP nd immunolot nlysis of etylted (A) PGC-1 in the liver of C57BL/6J mie injeted with n denovirus for GCN5 shrna nd deprived of food for 24 h. (d) Effets of shrna-medited depletion of GCN5 on gluoneogeni gene expression nd gluose prodution in primry mouse heptoytes exposed (or not) to pcpt-amp for 16 h. (e) IP nd immunolot nlysis of etylted PGC-1 in primry heptoytes expressing FLAGPGC-1 with or without GCN5 depletion nd inuted in the sene or presene of pcpt-amp for 6 h. (f) Effets of GCN5 depletion on CITED2-dependent enhnement of gluoneogeni gene expression indued y pcpt-amp (1 mm, 6 h) in primry heptoytes. (g) Effets of GCN5 knokdown on PGC-1-indued gluoneogeni gene expression with or without CITED2 overexpression in primry heptoytes. All quntittive dt re mens±s.e.m. (n ¼ 7(,) or 3(d,f,g)). Sttistil nlysis ws performed with the unpired Student s t-test () or ANOVA followed y Bonferroni s post ho test (,d,f,g). Po.5, Po.1 ompred with ontrol or s indited. Dt in,e re representtive of t lest three independent experiments. Adenovirl vetors enoding GCN5 shrna, FLAGPGC-1 or CITED2 were used for these experiments. ANOVA, nlysis of vrine. depletion of either CITED2 (Fig. 4, nd Supplementry Fig. 3,e) or PGC-1 (Fig. 4 nd Supplementry Fig. 3,e). In ddition, the AMP-indued reruitment of CBP to gluoneogeni gene promoters ws impired y GCN5 depletion (Fig. 4 nd Supplementry Fig. 3,e), inditing tht GCN5 is required for the reruitment of CBP. On the other hnd, wheres the inresed oupny of gluoneogeni gene promoters with PGC-1 or FoxO1 oserved in immortlized murine heptoytes treted with forskolin nd dexmethsone 8 or in primry mouse heptoytes exposed to glugon for 1 h (ref. 11), respetively, ws not pprent in primry ultured mouse heptoytes fter exposure to pcpt-amp for 6 h, promoter oupny with PGC-1, FoxO1, or HNF-4 ws lso dysregulted y depletion of GCN5, CITED2 or PGC-1 lthough we did not identify unifying defet in the inding of these regultors tht might ount for the impired indution of gluoneogeni genes (Fig. 4d nd Supplementry Fig. 3,e). To lrify whether epigeneti hnges indued y GCN5 depletion re restrited to gluoneogeni gene promoters or re more widespred, we exmined the effets of GCN5 knokdown on the epigeneti sttus of the promoters of two nongluoneogeni genes: Gpdh (enoding glyerldehyde-3- phosphte dehydrogense) nd Hmgr (hydroxymethylglutrteoenzyme A redutse). Depletion of GCN5 ffeted neither etyltion of H3K9 or H3K27 or trimethyltion of H3K4 t these promoters nor the orresponding mrna (Supplementry Fig. 3d), inditing tht the epigeneti hnges ssoited with GCN5 knokdown our seletively t gluoneogeni gene promoters. We lso investigted whether these epigeneti hnges indued y GCN5 depletion re oserved in mouse liver. Consistent with our in vitro results, the fsting levels of H3K9 nd H3K27 etyltion (ut not tht of H3K4 trimethyltion) t the gluoneogeni gene promoters were redued y GCN5 depletion (Supplementry Fig. 3f). The differene in the effet of GCN5 depletion on H3K4 trimethyltion sttus etween the in vivo nd in vitro results my reflet non-ell-utonomous response to ompenste for the impirment of gluoneogeni gene expression indued y 4 NATURE COMMUNICATIONS 7:13147 DOI: 1.138/nomms
5 NATURE COMMUNICATIONS DOI: 1.138/nomms13147 ARTICLE GCN5 (WT): GCN5 (ΔAT): 5, 4, 3, 2, 1, Reltive Gn5 mrna , 1,5 1, 5 5 CITED2: GCN5 (WT): GCN5 (ΔAT): Gluose (mg dl 1 ) GCN5 CITED2 CITED2GCN5 d GCN5 CITED2 CITED2GCN e Gluose (mg dl 1 ) GCN5 CITED2 CITED2GCN Time (min) Figure 3 GCN5 promotes gluoneogenesis in n etyltrnsferse- nd CITED2-dependent mnner. () Quntittive RT-PCR nlysis of Gn5 nd gluoneogeni gene expression in primry heptoytes infeted with denoviruses for WT or DAT mutnt forms of GCN5 nd exposed to pcpt-amp for 6h. () Effets of fored expression of WT or DAT forms of GCN5 together with CITED2 on pcpt-amp-indued gluoneogeni gene expression in primry heptoytes. (e) Effets of GCN5 overexpression with or without tht of CITED2 in the liver of C57BL/6J mie on glyemi under the fsted (6 h) ondition () or fter pyruvte dministrtion (e) s well s on hepti gluoneogeni gene expression under the fsted (24 h) ondition (d). All dt re mens±s.e.m. (n ¼ 3(,), 1 () or 8(d,e)). Sttistil nlysis ws performed with ANOVA followed y Bonferroni s post ho test. Po.5, Po.1 ompred with ontrol or s indited; wpo.5, wwpo.1 versus CITED2. Adenovirl vetors enoding GCN5(WT), GCN5(DAT) or CITED2 were used for these experiments. ANOVA, nlysis of vrine; RTPCR, PCR with reverse trnsription. hepti depletion of GCN5. Colletively, these dt indited tht GCN5 is ruil HAT for the initition of AMP-indued gluoneogeni gene trnsription in onert with CITED2. AMP nd CITED2 promote GCN5 sustrte swith. Given tht glugon-indued GCN5-CITED2 intertion is medited y the AMP-PKA pthwy 2, we tested whether GCN5 tivity is regulted y AMP, CITED2 or oth in heptoytes. The HAT tivity of GCN5 mesured in vitro with histone H3 s sustrte ws inresed y tretment of AML12 ells with pcpt-amp, nd this effet ws enhned y CITED2 overexpression in n dditive mnner (Fig. 5). These dt thus indited tht the HAT tivity of GCN5 ws inresed in the presene of AMP nd CITED2. We next exmined the effet of CITED2 on the lne etween the HAT nd PGC-1 etyltrnsferse tivities of GCN5 mesured in vitro with histone H3 nd n NH 2 -terminl frgment of PGC-1 s sustrtes. In this setting, GCN5 tivity ws reiprolly regulted y CITED2: HAT tivity ws inresed, wheres PGC-1 etyltrnsferse tivity nd utoetyltion tivity were deresed (Fig. 5). These results indited tht CITED2 inds to GCN5 nd promotes sustrte swith from PGC-1 to histone H3 s mesured in vitro. To exmine whether this swith lso ours in heptoytes, we investigted the intertion of GCN5 with PGC-1 or histone H3 in the nuleus with n in situ proximity ligtion ssy (PLA) 25. Exposure of primry heptoytes to pcpt-amp disrupted GCN5PGC-1 intertion nd promoted GCN5histone H3 intertion (Fig. 5). Together with our results showing tht GCN5 reruitment to nd H3K9 mrking of gluoneogeni gene promoters re dependent on AMP nd CITED2 (Fig. 4, nd Supplementry Fig. 3), these findings supported the notion tht AMP- nd CITED2-dependent sustrte swith of GCN5 integrtes epigeneti hnges nd o-tivtor tivity in gluoneogeni gene indution. PKA phosphoryltes GCN5 within module hroring CITED2. Given tht reominnt CITED2 interted with, ut did not enhne the HAT tivity of, GCN5 immunopreipitted from NATURE COMMUNICATIONS 7:13147 DOI: 1.138/nomms
6 NATURE COMMUNICATIONS DOI: 1.138/nomms13147 CITED2 KD GCN5 ChIP G6p promoter GCN5 ChIP Pk1 promoter Time (h) Time (h) GCN5 KD CITED2 KD CBP ChIP G6p promoter Time (h) Time (h) H3K9 ChIP H3K27 ChIP H3K4me3 ChIP G6p promoter G6p promoter G6p promoter Time (h) Time (h) AMP () AMP () GCN5 ChIP G6p promoter PGC-1α KD CBP ChIP G6p promoter.1 PGC-1α KD H3K9 ChIP G6p promoter PGC-1α KD H3K27 ChIP G6p promoter PGC-1α KD H3K4me3 ChIP G6p promoter PGC-1α KD d AMP () AMP () FLAG-PGC-1α ChIP HNF-4α ChIP FLAG-FoxO1 ChIP G6p promoter G6p promoter G6p promoter GCN5 CITED2 GCN5 CITED2 PGC-1α KD KD KD KD KD.1 GCN5 KD CITED2 KD PGC-1α KD Figure 4 GCN5 reruitment to gluoneogeni gene promoters is regulted y AMP in CITED2- nd PGC-1-dependent mnner in primry heptoytes. () ChIP-qPCR nlysis of the oupny of G6p nd Pk1 promoters with GCN5 in ells depleted of CITED2 nd exposed to pcpt-amp for the indited times. () ChIP-qPCR nlysis of the oupny of the G6p promoter with CBP or epigenomi mrks in ells depleted of GCN5 or CITED2 nd exposed to pcpt-amp for the indited times. () ChIP-qPCR nlysis of the oupny of the G6p promoter with GCN5, CBP or epigenomi modifitions in ells depleted of PGC-1 nd exposed to pcpt-amp for 6 h. (d) ChIP-qPCR nlysis of the oupny of the G6p promoter with FLAG-tgged PGC-1, HNF-4 or FLAG-FoxO1 in ells depleted of GCN5, CITED2 or PGC-1 nd exposed to pcpt-amp for 6 h. All dt re mens±s.e.m. (n ¼ 3). Po.5, Po.1 versus ontrol or s indited (ANOVA with Bonferroni s post ho test). Adenovirl vetors enoding GCN5, CITED2 or PGC-1 shrnas, FLAGPGC-1 or FLAG-FoxO1 were used for these experiments. ANOVA, nlysis of vrine; qpcr, quntittive PCR. 6 NATURE COMMUNICATIONS 7:13147 DOI: 1.138/nomms
7 NATURE COMMUNICATIONS DOI: 1.138/nomms13147 ARTICLE My-GCN5: FLAG-CITED2: IP: My IB: My IB: H3K9 IB: H3 IB: ALys IB: His 6 (PGC-1α(N-term)) IB: ALys (A-PGC-1α(N-term)) IB: H3K9 IB: H3 AMP() PLA AMP() FLAG-GCN5: His 6 -PGC-1α (N-term): HA-CITED2: GCN5PGC-1α intertion AMP() AMP() GCN5Histone H3 intertion Figure 5 GCN5 swithes sustrte in AMP- nd CITED2-dependent mnner. () Immunolot nlysis of the effets of FLAG-CITED2 expression or pcpt-amp tretment (for 1 h) in AML12 ells on the HAT tivity of immunopreipitted My epitope-tgged GCN5 ssyed in vitro with histone H3 s sustrte. () Effets of hemgglutinin epitope (HA)-tgged CITED2 expression in AML12 ells on the etyltrnsferse tivity of immunopreipitted FLAG-GCN5 ssyed in vitro with histone H3 nd His 6 -tgged NH 2 -terminl frgment of PGC-1 s sustrtes. () Intertion of GCN5 with PGC-1 or histone H3 ws ssessed y PLA in primry heptoytes expressing either My-GCN5 with FLAGPGC-1 (top) or FLAG-GCN5 lone (ottom) nd exposed (or not) to pcpt-amp for 1 h. PLA signls (red dots) represent proximity (o4 nm) of GCN5 nd either PGC-1 (top) or histone H3 (ottom). Nulei re stined lue with 4,6-dimidino-2-phenylindole. Sle rs, 1 mm. All dt re representtive of t lest three independent experiments. Adenovirl vetors were used for these experiments. AML12 ells overexpressing GCN5 lone (Supplementry Fig. 4,), we onluded tht n dditionl ftor tht interts with CITED2 might e neessry for the sustrte swith. We found tht, in the sene of pcpt-amp, inhiition of PKA y H89 signifintly suppressed gluoneogeni gene indution y overexpression of PGC-1 lone or in omintion with CITED2 in primry heptoytes (Fig. 6 nd Supplementry Fig. 4), inditive of the requirement for PKA tivity in this setting. PKA tivted y glugon-amp signlling medites indution of gluoneogenesis nd remodelling of the tin ytoskeleton through phosphoryltion of CREB 26,27 nd the inositol 1,4,5- trisphosphte reeptor (IP3R) 12 nd through tht of vsodiltorstimulted phosphoprotein (VASP) 28, respetively. We then tested whether GCN5 tivity is regulted y PKA-medited phosphoryltion. With the use of ntiodies speifi for phosphorylted PKA sustrtes, we found tht GCN5 phosphoryltion ws indued y pcpt-amp in AML12 ells (Fig. 6) s well s y glugon in mouse liver (Supplementry Fig. 4d). This effet of pcpt-amp ws enhned y CITED2 overexpression (Fig. 6) nd suppressed y shrna-medited CITED2 knokdown (Fig. 6). In ontrst, CITED2 knokdown did not ffet either the phosphoryltion of other PKA sustrtes suh s CREB, IP3R, nd VASP or the dephosphoryltion of CRTC2 (s ssessed on the sis of the ssoited nd moility shift) indued y pcpt-amp (Fig. 6). These results suggested tht PKA seletively phosphoryltes GCN5 in CITED2- dependent mnner, prompting us to exmine whether PKA interts with the GCN5-CITED2 omplex. The PKA holoenzyme onsists of two tlyti (PKAC) nd two regultory (PKAR) suunits, the ltter of whih serve s reeptors for AMP. The inding of AMP to the regultory suunits triggers dissoition nd tivtion of the tlyti suunits 29. Co-IP nlysis of AML12 ells reveled CITED2-PKA intertion (Supplementry Fig. 4e) s well s CITED2-dependent GCN5-PKA intertion (Fig. 6d,e) t the level of endogenous or epitope-tgged proteins, inditive of formtion of GCN5-CITED2-PKA omplex. We lso tested whether PKAC lters the HAT tivity of GCN5. Knokdown of PKAC lmost ompletely ttenuted the CITED2-indued inrese in HAT tivity (Fig. 6f), wheres fored expression of PKAC lone upregulted this tivity (Fig. 6g). Together, these results indited tht GCN5, CITED2 nd PKA form omplex tht funtions s module for PKA-dependent upregultion of the HAT tivity of GCN5. Co-IP nlysis lso reveled tht the intertion of GCN5 with PKA or CITED2 (Supplementry Fig. 4f) s well s tht of CITED2 with PKA (Supplementry Fig. 4g) were disrupted y exposure of AML12 ells to pcpt-amp for 3 min. PKA-dependent phosphoryltion of GCN5 ws lso oserved onomitntly with these effets (Supplementry Fig. 4h), nd AMP-indued disruption of the CITED2-GCN5 intertion ws loked y PKA inhiition (Supplementry Fig. 4i). Together, these results suggested tht the GCN5-CITED2-PKA signlling module disssemles in response to phosphoryltion of GCN5 y AMP-tivted PKA. GCN5 phosphoryltion t Ser 275 drives the sustrte swith. We next explored further the role of PKA-dependent phosphoryltion in the regultion of GCN5 tion within the module. In silio nlysis identified five serine or threonine NATURE COMMUNICATIONS 7:13147 DOI: 1.138/nomms
8 NATURE COMMUNICATIONS DOI: 1.138/nomms13147 Reltive G6p mrna PGC-1α: H89: CITED2: FLAG-GCN5: Reltive Pk1 mrna IB: Phospho-PKA sustrte IB: Phospho-CREB IB: CREB IB: Phospho-IP3R IB: IP3R IB: Phospho-VASP IB: VASP IB: CRTC2 FLAG-GCN5: My-PKAC: HA-CITED2: FLAG-GCN5: HA-CITED2: 1 min 3 min 1 min 3 min d e CITED2 shrna: AMP (3 min): IB: β-tin f IB: PKAC IB: HA IB: H3K9 IB: H3 IB: PKAC IB: My IB: HA IB: PKAC g FLAG-GCN5: IB: Phospho-PKA sustrte FLAG-GCN5: CITED2 shrna: My-PKAC: IB: H3K9 IB: H3 IB: PKAC IB: PKAC FLAG-GCN5: HA-CITED2: PKAC sirna: Figure 6 GCN5 is phosphorylted y PKA within GCN5-CITED2-PKA signlling module. () Effets of PKA inhiition with H89 (2 mm, 6 h) on gluoneogeni gene expression indued y overexpression of PGC-1 with or without CITED2 in primry heptoytes. Dt re mens±s.e.m. (n ¼ 3). Po.1 (ANOVA with Bonferroni s post ho test). () Immunolot nlysis of the effets of HA-CITED2 expression or pcpt-amp tretment (1 or 3 min) on phosphoryltion of FLAG-GCN5 in AML12 ells s ssessed with ntiodies to phosphorylted PKA sustrtes. () Effets of CITED2 depletion on pcptamp-indued phosphoryltion of FLAG-GCN5 nd other PKA sustrtes s well s on the dephosphoryltion of CRTC2 in primry heptoytes. (d,e) IPnd immunolot nlysis of the intertion of FLAG-GCN5 with My-PKAC nd HA-CITED2 (d) s well s of the effet of CITED2 knokdown on the intertion of FLAG-GCN5 with PKAC (e) in AML12 ells. (f) Effet of sirna-medited PKAC depletion in AML12 ells on sl nd CITED2-indued HAT tivity of FLAG- GCN5 s ssessed y in vitro ssy. (g) Effet of PKAC overexpression in AML12 ells on HATtivity of FLAG-GCN5 mesured in vitro. A My-PKAC plsmid nd PKAC sirna were introdued into ells y trnsfetion, wheres denovirl vetors were used to introdue other exogenous proteins or shrnas in these experiments. Dt re representtive of t lest three independent experiments. ANOVA, nlysis of vrine; sirna; smll interfering RNA. residues onserved etween rodents nd humn s puttive PKA phosphoryltion sites in GCN5 (Supplementry Fig. 5). We therefore generted series of puttive phosphoryltion-defetive mutnts, in whih these residues re repled with lnine. Similr to PKA inhiition with H89, the S275A muttion olished sl nd AMP-indued phosphoryltion of GCN5 s ssessed with the ntiodies to phosphorylted PKA sustrtes (Fig. 7). The phosphoryltion signl intensity for GCN5(S275A) ws similr to tht for GCN5(WT) in ells exposed to oth AMP nd H89 nd my therefore e ttriutle to phosphoryltion t PKA-independent site detetle y these ntiodies. Immunolot nlysis of immunopreipittes prepred from primry heptoytes with ntiodies to the Ser 275 -phosphorylted form of GCN5 lso onfirmed tht pcpt-amp indued the phosphoryltion of GCN5 in PKA- nd CITED2-dependent mnner (Supplementry Fig. 5). In ddition, reominnt PKAC phosphorylted GCN5(WT), ut not GCN5(S275A), in vitro, suggesting tht PKA diretly phosphoryltes Ser 275 of GCN5 (Supplementry Fig. 5). Colletively, these results indited tht Ser 275 is the prinipl PKA phosphoryltion site in GCN5. We exmined whether phosphoryltion of GCN5 t Ser 275 regultes etyltrnsferse tivity with the use of the S275A mutnt nd the phosphoryltion-mimiking mutnt S275D. GCN5(S275A) mnifested redued HAT tivity (Fig. 7) nd similr PGC-1 etyltrnsferse tivity (Supplementry Fig. 5d) ompred with the WT protein, ut it ws resistnt to CITED2-indued suppression of PGC-1 etyltrnsferse tivity in AML12 ells (Fig. 7). In ontrst, GCN5(S275D) showed inresed HAT tivity, redued PGC-1 etyltrnsferse tivity, nd n ttenuted intertion with PGC-1 (Fig. 7d,e). These results suggested tht PKAdependent phosphoryltion of GCN5 t Ser 275 drives its sustrte swith. 8 NATURE COMMUNICATIONS 7:13147 DOI: 1.138/nomms
9 NATURE COMMUNICATIONS DOI: 1.138/nomms13147 ARTICLE IP: Phospho-PKA sustrte IB: FLAG IB: FLAG IB: H3K9 FLAG-GCN5(WT): FLAG-GCN5(S275A): H89: FLAG-GCN5(WT): FLAG-GCN5(S275A): IB: H3 FLAG-PGC-1α: GCN5(WT): IB: PGC-1α IB: ALys IB: PGC-1α d FLAG-GCN5(WT): FLAG-GCN5(S275D): IB: H3K9 IB: H3 FLAG-PGC-1α: GCN5(WT): GCN5(S275D): IB: PGC-1α IB: ALys GCN5(S275A): HA-CITED2: e FLAG-GCN5(WT): FLAG-GCN5(S275D): V5-PGC-1α: IB: FLAG IB: V5 IB: FLAG IB: V5 f FLAG-GCN5(WT): FLAG-GCN5(S275A): IB: FLAG IB: HA IB: FLAG IB: HA FLAG-GCN5(S275D): HA-CITED2: g FLAG-GCN5(WT): FLAG-GCN5(S275A): HA-CITED2: AMP (3 min): Figure 7 GCN5 phosphoryltion t Ser 275 drives its sustrte swith. () AML12 ells expressing FLAG-tgged GCN5(WT) or GCN5(S275A) were exposed to pcpt-amp with or without H89 for 3 min nd then sujeted to IP with ntiodies to phosphorylted PKA sustrtes followed y immunolot nlysis with ntiodies to FLAG. () Effet of the S275A muttion of FLAG-GCN5 on in vitro etyltion of histone H3 in AML12 ells treted with pcpt-amp (1 h). () Aetyltion of FLAGPGC-1 in AML12 ells expressing GCN5(WT) or GCN5(S275A) with or without HA-CITED2. (d) Effets of the S275D muttion of GCN5 on histone H3 nd PGC-1 etyltrnsferse tivities in AML12 ells. (e) Effet of the S275D muttion of FLAG-GCN5 on intertion with V5-tgged PGC-1 in AML12 ells. (f) Effets of the S275A nd S275D muttions of FLAG-GCN5 on intertion with HA-CITED2 in AML12 ells. (g) The S275A muttion of GCN5 loks the pcpt-amp-indued dissoition of HA-CITED2 from FLAG-GCN5 in AML12 ells. All dt re representtive of t lest three independent experiments. Adenovirl vetors were used for these experiments. We lso tested whether GCN5 phosphoryltion t Ser 275 ffets its intertion with CITED2. The mount of HA-tgged CITED2 tht o-immunopreipitted from AML12 ells with FLAG-tgged GCN5 ws redued for the S275D mutnt ompred with the WT or S275A forms (Fig. 7f). Exposure of ells to pcpt-amp lso redued the mount of HA-CITED2 tht o-immunopreipitted with GCN5(WT) ut not of tht o-immunopreipitting with GCN5(S275A) (Fig. 7g). Phosphoryltion of GCN5 t Ser 275 thus ppers to promote disssemly of the GCN5-CITED2-PKA signlling omplex, supporting role for this module in phosphoryltion of GCN5 t this site y PKA. NATURE COMMUNICATIONS 7:13147 DOI: 1.138/nomms
10 NATURE COMMUNICATIONS DOI: 1.138/nomms13147 Phosphoryltion of GCN5 t Ser 275 promotes gluoneogenesis. We next investigted the effets of these GCN5 mutnts on gluoneogenesis in vitro. In primry heptoytes overexpressing CITED2, pcpt-amp-indued gluoneogeni gene expression ws enhned to lesser extent y GCN5(S275A) thn y GCN5(WT) (Fig. 8 nd Supplementry Fig. 6). On the other hnd, expression of the S275D mutnt without CITED2 overexpression enhned AMP-indued gluoneogeni gene expression (Fig. 8 nd Supplementry Fig. 6) in ontrst to the effet of GCN5(WT) (Fig. 3) resulting in enhned gluose prodution (Fig. 8). The seletive gluoneogeni effet of GCN5(S275D) ws ssoited with enhned AMP-indued etyltion of H3K9 nd H3K27 t gluoneogeni gene promoters, ut not t Gpdh or Hmgr promoters (Supplementry Fig. 6). GCN5(S275D) lso resued, t lest in prt, the inhiition of gluoneogeni gene expression y CITED2 depletion in pcpt-amp-stimulted heptoytes (Fig. 8d nd Supplementry Fig. 6d), suggesting tht GCN5 phosphorylted t Ser 275 funtions s gluoneogeni HAT downstrem of CITED2. These results indited tht phosphoryltion of GCN5 t Ser 275 y PKA in the GCN5-CITED2-PKA signlling module drives the sustrte swith of GCN5 nd therey promotes gluoneogenesis in vitro. We lso ssessed the phosphoryltion level of hepti GCN5 t Ser 275 in physiologil setting in vivo. The phosphoryltion level of GCN5 t Ser 275 in the liver of len mie ws inresed in the fsted stte ompred with the fed stte (Supplementry Fig. 6e). To onfirm the physiologil relevne of this finding, we exmined the time ourses of GCN5 phosphoryltion, PGC-1 etyltion, GCN5-CITED2 intertion nd gluoneogeni gene expression in the liver of len mie expressing oth FLAG-GCN5 nd HA-CITED2 t ner physiologil levels (out twie the of the endogenous proteins) during fsting fter refeeding for 12 h susequent to previous overnight fst. The 1 5 GCN5(WT): GCN5(S275A): CITED2: e Gluose prodution (AU) GCN5(S275D): GCN5(S275D): CITED2 shrna: GCN5(S275D) ,5 1, 5 d Reltive Gn5 mrna GCN5(S275D): 1 5 2,5 8 2, 1,5 1, f Gluose (mg dl 1 ) GCN5(S275D) Figure 8 Phosphoryltion of GCN5 t Ser 275 promotes gluoneogenesis. () Effets of fored expression of GCN5(WT) or GCN5(S275A) together with CITED2 on gluoneogeni gene expression in primry heptoytes exposed (or not) to pcpt-amp (6 h). (,) Effets of fored expression of GCN5(S275D) on gluoneogeni gene expression () nd gluose prodution () in primry heptoytes exposed (or not) to pcpt-amp (16 h). (d) qrt-pcr nlysis of G6p nd Pk1 expression in primry mouse heptoytes infeted with denoviruses enoding CITED2 shrna or GCN5(S275D) nd exposed (or not) to pcpt-amp for 6 h. (e,f) Effets of GCN5(S275D) expression in the liver of C57BL/6J mie on gluoneogeni gene expression (e) nd plsm glyemi (f) under the fsted (24 h) ondition. All dt re mens±s.e.m. (n ¼ 3(d)or7(e,f)). Po.5, Po.1 versus ontrol or s indited (ANOVA with Bonferroni s post ho test (d) or unpired Student s t-test (e,f)). Adenovirl vetors were used for these experiments. RTPCR, PCR with reverse trnsription. ANOVA, nlysis of vrine. 1 NATURE COMMUNICATIONS 7:13147 DOI: 1.138/nomms
11 NATURE COMMUNICATIONS DOI: 1.138/nomms13147 ARTICLE initil inrese in GCN5-CITED2 intertion (ssessed on the sis of the mount of CITED2 o-immunopreipitted with GCN5) ws followed y inreses in the level of GCN5 phosphoryltion t Ser 275 nd in PGC-1 (Supplementry Fig. 6f). Furthermore, the inrese in the level of GCN5 phosphoryltion ourred onomitntly with redution in the level of PGC-1 etyltion nd with the mximl upregultion of gluoneogeni gene expression (Supplementry Fig. 6f). In ddition, expression of GCN5(S275D) in the liver of len mie inresed gluoneogeni gene expression (Fig. 8e) nd lood gluose levels (Fig. 8f) in the fsted ondition. These dt thus suggested tht phosphoryltion of GCN5 t Ser 275 within the GCN5-CITED2-PKA signlling module during fsting drives the sustrte swith of GCN5, resulting in tivtion of PGC-1 nd of the HAT funtion of GCN5 nd onsequent promotion of gluoneogenesis. the liver of len mie (Fig. 8e,f), nd they indite tht inhiition of GCN5 phosphoryltion t Ser 275 suppresses gluoneogenesis nd therefore meliortes hyperglyemi, wheres enhned phosphoryltion of GCN5 t Ser 275 promotes gluoneogenesis nd exertes hyperglyemi, in dieti nimls. We hve previously shown tht depletion of CITED2 in the liver of d/d mie suppresses gluoneogenesis through enhnement of GCN5-dependent etyltion nd the onsequent intivtion of PGC-1 nd therey meliortes dietes 2. In this setting, phosphoryltion of GCN5 t Ser 275 ws lso inhiited (Fig. 9d), inditing tht disruption of the GCN5-CITED2-PKA signlling module y CITED2 depletion ttenutes gluoneogenesis nd meliortes hyperglyemi through suppression of GCN5 phosphoryltion t Ser 275 nd onsequent enhned GCN5- dependent etyltion nd inhiition of PGC-1 s well s redued GCN5-dependent etyltion of histone H3K9. Suppression of GCN5 phosphoryltion meliortes dietes. We lso exmined the phosphoryltion level of GCN5 t Ser 275 in the liver of dieti mie. Phosphoryltion of GCN5 (Fig. 9) s well s the mount of GCN5 protein (Fig. 1) were inresed in the liver of d/d mie nd of C57BL/6J mie fed HFD. The expression of CITED2 (ref. 2), ut not tht of PKA (Supplementry Fig. 7), ws lso inresed in the liver of dieti mie. These hnges in GCN5 nd CITED2 re onsistent with enhnement of gluoneogenesis nd prompted us to ddress whether GCN5 phosphoryltion t Ser 275 ontriutes to hyperglyemi through promotion of hepti gluoneogenesis in these nimls. Hepti expression of GCN5(S275D) inresed, wheres tht of GCN5(S275A) or GCN5(WT) deresed, lood gluose levels nd gluoneogeni gene expression in the liver of fsted d/d mie (Fig. 9, nd Supplementry Fig. 7). These effets re onsistent with those oserved in heptoytes (Fig. 8) or in Disussion Our dt show tht, in the fsted stte, glugon-amp signlling inreses the expression of CITED2 (ref. 2) nd GCN5 s well s promotes the formtion of GCN5-CITED2-PKA signlling module. Within this module, PKA tivted y AMP phosphoryltes GCN5 t Ser 275 (with the phosphoryltion of other PKA sustrtes suh s CREB, VASP nd IP3R eing unffeted), resulting in swith in the sustrte preferene of GCN5 from PGC-1 to histone H3 nd onsequent inrese in H3K9 etyltion nd the deetyltion-medited tivtion of PGC-1 t gluoneogeni gene promoters. The inrese in the mount of H3K9 promotes further epigeneti hnges nd the reruitment of trnsriptionl regultors required for initition of gene trnsription, wheres the tivted PGC-1 funtions s o-tivtor for gluoneogeni trnsription ftors suh s FoxO1 nd HNF-4. These two effets t oopertively d/m NC d/d GCN5(WT) GCN5(S275A) GCN5(S275D) IP: Phospho-Ser 275 GCN5 IP: GCN5 HFD IP: Phospho-Ser 275 GCN5 IP: GCN Gluose (mg dl 1 ) d GCN5(WT) GCN5(S275A) GCN5(S275D) Fed Fsted CITED2 shrna: IP: Phospho-Ser 275 GCN5 IP: GCN5 IP: CITED2 Figure 9 Suppression of hepti GCN5 phosphoryltion t Ser 275 meliortes dietes. () Anlysis of GCN5 phosphorylted t Ser 275 in the liver of d/d or d/m (ontrol) mie or of C57BL/6J mie fed NC or HFD. All mie were deprived of food for 16 h efore nlysis. Liver extrts were sujeted to IP with ntiodies to Ser 275 -phosphorylted GCN5 followed y immunolot nlysis with ntiodies to GCN5. (,) Effets of expression of GCN5(WT), GCN5(S275A) or GCN5(S275D) in the liver of d/d mie on plsm gluose onentrtion under fed or fsted (24 h) onditions () s well s on hepti expression of G6p nd Pk1 under the fsted (24 h) ondition (). (d) Effet of CITED2 depletion on GCN5 phosphoryltion t Ser 275 in the liver of d/d mie deprived of food for 24 h. All quntittive dt re mens±s.e.m. (n ¼ 7(,)). Po.5, Po.1 (ANOVA with Bonferroni s post ho test). Dt in,d re representtive of t lest three independent experiments. Adenovirl vetors were used for these experiments. ANOVA, nlysis of vrine; NC, norml how. NATURE COMMUNICATIONS 7:13147 DOI: 1.138/nomms
12 NATURE COMMUNICATIONS DOI: 1.138/nomms13147 Feeding Glugon Fsting or dietes Glugon P P P FoxO1 AMP AMP R R C C CITED2 CITED2 CITED2 PKA R R R R C C CBP C C P GCN5 A PGC-1α etyltion Ser 275 P GCN5 CBP GCN5 PGC-1α PGC-1α etyltion PGC-1α PGC-1α PGC-1α PGC-1α HNF-4α OFF FoxO1 HNF-4α OFF FoxO1 HNF-4α A CBP H3K9 H3K27 H3K4me3 ON GCN5 HAT OFF PGC-1α AT ON HAT ON GCN5 PGC-1α AT OFF Figure 1 Model for regultion of hepti gluoneogenesis y the GCN5-CITED2-PKA signlling module through AMP-indued sustrte swith of GCN5. (left) In the fed stte, the GCN5-CITED2-PKA signlling module is not ssemled s result of the low level of CITED2 expression mintined in the sene of glugon signlling nd the insulin-indued inhiition of GCN5-CITED2 intertion. GCN5 is not phosphorylted t Ser 275 nd therefore etyltes PGC-1 rther thn histone H3, resulting in intivtion of PGC-1 nd onsequent suppression of gluoneogeni gene trnsription. (middle) In the fsted stte or dietes, glugon-amp signlling inreses the expression of CITED2 nd GCN5 nd therey promotes formtion of the GCN5-CITED2-PKA signlling module, within whih PKA tivted y AMP phosphoryltes GCN5 t Ser 275. (right) Phosphoryltion of GCN5 indues sustrte swith from PGC-1 to histone H3 nd onsequent inrese in H3K9 etyltion nd the deetyltion-medited tivtion of PGC-1 t gluoneogeni gene promoters. The inrese in the mount of H3K9 promotes further epigeneti hnges nd the reruitment of trnsriptionl regultors required for initition of gene trnsription, wheres tivted PGC-1 funtions s o-tivtor for gluoneogeni trnsription ftors suh s FoxO1 nd HNF-4. These two effets t oopertively to tivte the gluoneogeni progrm. AT, etyltrnsferse. to tivte the gluoneogeni progrm (Fig. 1). In the fed stte, ttenution of glugon signlling leds to downregultion of CITED2 nd GCN5 expression, wheres insulin signlling inhiits GCN5-CITED2 intertion 2, resulting in disruption of the GCN5-CITED2-PKA signlling module. In this ondition, phosphoryltion of GCN5 t Ser 275 is inhiited nd GCN5 therefore etyltes PGC-1 rther thn histone H3, resulting in intivtion of PGC-1 nd the onsequent suppression of gluoneogeni gene trnsription. A previous study showed tht GCN5 etyltes nd suppresses the otivtion tivity of PGC-1 (ref. 17). Overexpression of GCN5 in Fo ells thus suppressed gluoneogeni gene expression nd gluose prodution indued y overexpression of PGC-1 (ref. 17). Overexpression of GCN5 in the liver of mie lso redued hepti gluoneogeni gene expression in the fsted stte s well s glyemi fter fsting or pyruvte dministrtion 17 (Fig. 3e). In ddition, the PGC-1 etyltrnsferse funtion of GCN5 ws previously shown to e tivted y Sirt6 or the CDK4ylin D1 omplex, whose expression is downregulted y glugon-amp signlling or upregulted y insulingsk3 (glyogen synthse kinse 3) signlling, respetively 18,19. GCN5 hs therefore een thought to funtion s negtive regultor of PGC-1 nd, onsequently, of hepti gluoneogenesis (presumly in the fed stte) 182,3,31. On the other hnd, the role of GCN5 in gluoneogeni gene indution y glugonamp signlling during fsting nd its role s HAT hve remined to e eluidted. Given tht CITED2 forms omplex with GCN5 during fsting nd tivtes PGC-1 through inhiition of GCN5-dependent etyltion 2, we foused on the fsting-induile GCN5-CITED2 omplex. Our dt now provide evidene tht GCN5 funtions s HAT to tivte the gluoneogeni progrm in the fsted stte in ddition to s PGC-1 etyltrnsferse to inhiit it in the fed stte. This dul funtion of GCN5 is reiprolly regulted y glugon-dependent sustrte swith t the fed-to-fsting trnsition. The fsting-indued formtion of the GCN5- CITED2-PKA omplex llows the speifi PKA-dependent phosphoryltion of GCN5 t Ser 275, whih, in turn, drives the sustrte swith of GCN5. This newly unovered mehnism thus inorportes GCN5-medited repression of the trnsriptionl o-tivtor tivity of PGC-1 in the fed stte s well s AMP- nd CITED2-medited upregultion of suh tivity in the fsted stte, nd it therefore integrtes epigeneti hnges nd o-tivtor tivity, leding to full indution of gluoneogenesis. The GCN5-CITED2-PKA signlling module explins why the HAT tivity of GCN5 s well s oth CITED2 nd PKA re required for the gluoneogeni effet of GCN5 overexpression. However, the moleulr mehnism y whih expression of GCN5(WT) or GCN5(S275A) in the sene of CITED2 overexpression suppresses AMP- or fsting-indued gluoneogeni gene expression remins to e eluidted. It n e rgued tht hepti overexpression of GCN5(WT) lone should promote formtion of this signlling module with endogenous CITED2 nd PKA, the former of whih is upregulted during fsting, nd therey tivte gluoneogenesis (Fig. 3e). It should e noted, however, tht in this setting the of Gn5 mrna in the liver overexpressing GCN5 ws 3 times tht in the ontrol liver, wheres the mount of CITED2 protein in the liver of fsted mie showed n B2.5-fold inrese ompred with tht in refed mie 2. It is therefore likely tht the mount of endogenous CITED2 ws insuffiient to form the GCN5-CITED2-PKA signlling module with overexpressed GCN5. Given tht phosphoryltion of GCN5 y PKA is dependent on this module, the exess GCN5 would not e phosphorylted y PKA. As previously desried 17, the suppressive effet of overexpressed GCN5 in the sene of CITED2 overexpression on AMP- or fsting-indued gluoneogeni gene expression might e medited y PGC-1 intivtion through etyltion medited y the nonphosphorylted form of GCN5. However, we found tht expression of GCN5(DAT) lone lso inhiited AMP-indued gluoneogeni gene expression, suggesting tht overexpression of GCN5 suppresses gluoneogenesis through oth etyltrnsferse-dependent nd -independent mehnisms. We hve previously shown tht oexpression of CITED2 with 12 NATURE COMMUNICATIONS 7:13147 DOI: 1.138/nomms
13 NATURE COMMUNICATIONS DOI: 1.138/nomms13147 ARTICLE GCN5(WT) hnges the pttern of GCN5 loliztion in the nuleus from homogeneous to spekled 2. Overexpressed GCN5 tht fils to intert with CITED2 my thus disrupt or ffet the loliztion of the GCN5-CITED2-PKA signlling module independently of its etyltrnsferse tivity, resulting in suppression of gluoneogeni gene expression. Depletion of GCN5 or expression of the phosphoryltiondefetive mutnt GCN5(S275A) in the liver of mie with oesity nd type 2 dietes suppressed gluoneogenesis nd therey improved glyemi, suggesting tht inhiition of GCN5 expression or phosphoryltion t Ser 275 my meliorte dietes. Disruption of the GCN5-CITED2-PKA signlling module (suh s tht hieved y CITED2 depletion) lso suppressed gluoneogenesis nd meliorted dietes, suggesting tht this module is promising phrmologil trget for tretment of oesity nd type 2 dietes. Methods Mie. All mouse experiments were performed ording to proedures pproved y the Institutionl Animl Cre nd Use Committee of the Ntionl Center for Glol Helth nd Mediine (Tokyo). Len C57BL/6J mle mie (CLEA Jpn) s well s d/d (C57BLKS/J Ir þ Lepr d / þ Lepr d )ndd/m (C57BLKS/J Ir þ m d / þ Lepr d ) mle mie otined from Institute for Animl Reprodution were studied t 8 weeks of ge. Reominnt denoviruses were injeted into the til vein of mie s desried previously 32 t dose of or plque-forming units in totl volume of.25 ml for C57BL/6J nd d/d mie, respetively, nd experiments were performed 4 dys fter denovirus injetion. Blood gluose onentrtion ws mesured with the use of stndrd gluose sensor (Glutest Ae, Snw Kgku Kenkyusho). For the pyruvte hllenge test, mie deprived of food for 16 h were injeted intrperitonelly with pyruvte dissolved in sline (2 g kg 1 ) s desried previously 33. For experiments with mie fed HFD, C57BL/6J mie were mintined on how ontining 3% ft y weight (14% ovine ft, 14% porine ft, 2% soyen oil; Orientl Yest) from 4 to 24 weeks of ge. For exmintion of the effets of glugon, mie were deprived of food for 3 h nd then injeted intrperitonelly with the hormone t dose of 1 mgkg 1. Liver extrts were prepred 1 h fter glugon tretment. We lloted ges of mie to the experimentl groups y rndom drw. The investigtor ws not linded to the group llotion during experiments. Plsmids. GCN5, CITED2, PGC-1, PKAC nd PKARI DNAs were isolted from C57BL/6J mouse liver nd loned into the mmmlin expression vetors pdna3 or pdna3.1 (Life Tehnologies). The DNAs for GCN5(DAT) (GYG-AYA/582Y584), GCN5(S275A) nd GCN5(S275D) were generted with the use of KOD-plus Mutgenesis Kit (Toyoo). Adenoviruses. Reominnt denoviruses were onstruted with the use of n Adenovirus Dul Expression Kit (Tkr Bio). FLAG-GCN5, My-GCN5, FLAG-GCN5(DAT), FLAG-GCN5(S275A), FLAG-GCN5(S275D), FLAG- CITED2, HA-CITED2, FLAGPGC-1, FLAG-FoxO1 nd -gltosidse (ontrol) were expressed under the ontrol of CAG promoter (ytomeglovirus enhner, hiken -tin gene promoter, nd rit -gloin gene poly(a) signl), wheres shrnas were expressed under the ontrol of U6 promoter. The shrnas for GCN5, CITED2 nd PGC-1 were sed on the sequenes 5 -TGTCAGAGG ACGAGATTAA-3 ;5 -TGACGGACTTCGTGTGCA-3 ;nd5 -GTATCTGACC ACAAACGAT-3, respetively. A negtive ontrol shrna sequene ws otined from BD Biosienes. Primry heptoytes or AML12 ells were infeted with denoviruses 1 dy fter plting. Anlyses of gene nd protein expression s well s gluose prodution ssy were performed 2 dys fter infetion. Chemils nd ntiodies. Glugon, pcpt-amp, insulin, MG132, trihosttin A nd etyl-coa were otined from Sigm; H89 nd niotinmide were from Enzo Life Sienes nd Nli Tesque, respetively; reominnt histone H3.1 ws from New Englnd Biols; nd reominnt humn CITED2 ws from Am. Antiodies to My (#2276, 1:1, dilution; #2272, 1:1,), to histone H3 (#4499, 1:1,), to H3K9 (#9649, 1:1,), to etylted lysine (#9441, 1:1,), to Ser/Thrphosphorylted PKA sustrtes (#9621, 1:1,), to CREB (#9197, 1:1,), to Ser 133 -phosphorylted CREB (#9198, 1:1,), to IP3R1 (#8568, 1:1,), to Ser phosphorylted IP3R (#8548, 1:1,), to VASP (#3132, 1:1,), to Ser 157 -phosphorylted VASP (#3111, 1:1,), to PKAC (#5842, 1:1,) nd to PKARI (#5675, 1:1,) were otined from Cell Signling. Antiodies to GCN5 (s-2698, 1:5; s , 1:5), to PCAF (s-13124, 1:5), to CBP (s-51517, 1:5; s-369), to HNF-4 (s-8987), to PGC-1 (s-67285, 1:5) nd to histone H1 (s-186, 1:4) were otined from Snt Cruz Biotehnology. Antiodies to CITED2 (18345, 1:1,), to H3K9 (4441, 1:1,) nd to H3K27 (4729) were from Am; those to p3 (5-257, 1:1,), to CRTC2 (ST-199, 1:2,), nd to H3K4me3 (5-745R) were from Millipore; those to FLAG (F184, 1:1,) nd to -tin (A5441, 1:1,) were from Sigm; those to HA ( , 1:2,) nd to His 6 ( , 1:5) were from Rohe; nd those to V5 (R96, 1:2,), to FLAG (KO62, 1:2,), to DsRed (for mcherry; , 1:1,), nd to T7 (69522, 1:1,) were from Life Tehnologies, Trnsgeni, Clonteh, nd Novgen, respetively. Rit ntiodies to Ser 275 -phosphorylted GCN5 (1:4) were generted in response to phosphopeptide ontining mino ids 271 to 28 of mouse GCN5. Cell ulture. Primry heptoytes were isolted from 8- to 12-week-old mle C57BL/6J mie fed norml how diet s desried previously 32. In rief, mie were nesthetised y intrperitonel injetion of medetomidine (.75 mg kg 1 ), midzolm (4 mg kg 1 ) nd utorphnol (5 mg kg 1 ), nd the liver ws perfused t rte of 4.5 ml min 1 first for 35 min with oxygented Hnks lned slt solution ontining 1 mm Hepes-NOH (ph 7.4) nd then for 18 min with the sme solution ontining ollgense type I (332 mg per 1 ml, Worthington) nd Protese Inhiitor Coktil CompleteEDTA Free (one tlet per 5 ml, Rohe). The heptoytes were hrvested nd purified y density grdient entrifugtion with Peroll (Sigm), nd their viility ws ssessed on the sis of trypn lue exlusion. We studied only heptoyte preprtions with viility of 49%. The ells were plted on type I ollgenoted six-well pltes ( ells per well) in Medium 199 (Life Tehnologies) supplemented with 5% fetl ovine serum, nd were inuted overnight in serum-free Medium 199 (Life Tehnologies) efore the ddition of pcpt-amp (1 mm) (ref. 34). AML12 nd HEK293 ells were otined from Amerin Type Culture Colletion. AML12 ells were ultured in 1:1 (v/v) mixture of Duleo s modified Egle s medium (DMEM) nd Hm s F12 medium tht ws supplemented with insulin (5 mgml 1 ), trnsferrin (5 mgml 1 ), selenium (5 ng ml 1 ), dexmethsone (4 ng ml 1 ), nd 1% fetl ovine serum, wheres HEK293 ells were ultured in DMEM supplemented with 1% fetl ovine serum. Primry heptoytes nd AML12 ells were tested for gluoneogeni gene indution y pcpt-amp. Where indited, primry heptoytes or AML12 ells were exposed to 2 mm H89 for 3 min efore inution in the dditionl presene of 1 mm pcpt-amp for the indited times. The ell lines were regulrly tested for myoplsm ontmintion. Gene expression nlysis. Totl RNA ws isolted from ells or pulverized liver with the use of n RNesy Mini Kit nd RNse-Free DNse Set (Qigen). For quntittive RT-PCR nlysis, DNA ws synthesized from the totl RNA with the use of rndom primers nd High Cpity DNA Reverse Trnsription Kit (Life Tehnologies) nd PCR ws then performed in triplite with the use of StepOnePlus Rel-Time PCR System nd Power SYBR Green PCR Mster Mix (Life Tehnologies). Reltive mrna ws lulted y the stndrd urve method nd ws normlized y the orresponding mount of 18S rrna. Primer sequenes re listed in Supplementry Tle 1. Protein intertion nlysis. Protein-protein intertions in ells were exmined with o-ip ssys. Epitope-tgged proteins were expressed in AML12 ells or HEK293 ells y trnsfetion with the use of Nuleofetor Kit V (Amx) or y denovirl trnsdution. The ells were then lysed in lysis uffer ontining 2 mm Tris-HCl (ph 7.5), 15 mm NCl,.5% Nonidet P-4, 2 mm EDTA, 1% glyerol, 1 mm niotinmide, 1 mm trihosttin A, 1 mm MG132, nd protese nd phosphtse inhiitors (Rohe), nd the lystes were sujeted to IP with the indited ntiodies nd either protein G-Sephrose (GE Helthre) or Dyneds Protein G (VERITAS). The immunopreipittes were frtionted y SDSpolyrylmide gel eletrophoresis (PAGE) nd sujeted to immunolot nlysis with the indited ntiodies. Unropped imges of representtive immunolots re shown in Supplementry Fig. 8. Preprtion of nuler extrts from mouse liver. The liver ws removed, rinsed in ie-old phosphte-uffered sline (PBS), suspended in 5 ml of uffer A (1 mm Hepes-NOH (ph 7.9), 25 mm KCl, 1 mm EDTA, 2 M surose, 1% glyerol, 1 mm niotinmide, 1 mm trihosttin A, 1 mm MG132 nd protese nd phosphtse inhiitors (Rohe)), nd homogenized riefly with Polytron disruptor. The homogente (15 ml) ws pssed five times through 2 G needle nd then lyered on top of 2 ml of uffer A in entrifuge tue nd entrifuged t 1,g for 1 h t 4 C. The resulting nuler pellet ws wshed with 3 ml of solution ontining 1 mm Hepes-NOH (ph 7.9), 1 mm KCl, 2 mm MgCl 2, 1 mm EDTA nd 1% glyerol nd ws then digested with Enzymtil Shering Coktil in 2 ml of Complete Digestion Buffer (Nuler Complex Co-IP Kit, Ative Motif). The retion ws terminted y the ddition of 4 ml of.5 M EDTA, nd the mixture ws then entrifuged t 14,g for 1 min t 4 C. The resulting superntnt ws olleted s the nuler extrt for o-ip experiments. Gluose prodution ssy. Primry heptoytes were ultured in serum-free Medium 199 in the sene or presene of 1 mm pcpt-amp for 16 h s previously desried 34. They were then inuted for 6 h in gluose- nd phenol red-free DMEM (ph 7.4) supplemented with sodium ltte nd pyruvte efore NATURE COMMUNICATIONS 7:13147 DOI: 1.138/nomms
Cos7 (3TP) (K): TGFβ1(h): (K)
 IP#2: IP#1: Totl Lystes luiferse tivity (K): 6-4 - (K): luiferse tivity luiferse tivity (K): 2 1 RL-: - + + + + + Sm4-3F: + - + + + + MYC-Sm3: - - - - + + TβRI-HA(T204D): - - - + - + α-ha Luiferse Ativity
IP#2: IP#1: Totl Lystes luiferse tivity (K): 6-4 - (K): luiferse tivity luiferse tivity (K): 2 1 RL-: - + + + + + Sm4-3F: + - + + + + MYC-Sm3: - - - - + + TβRI-HA(T204D): - - - + - + α-ha Luiferse Ativity
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 1.138/n358 TLR2 nd MyD88 expression in murine mmmry epithelil supopultions. CD24 min plus MRU Myo-epithelil Luminl progenitor (CD61 pos ) Mture luminl (CD61 neg ) CD49f CD61 Reltive expression Krt5
DOI: 1.138/n358 TLR2 nd MyD88 expression in murine mmmry epithelil supopultions. CD24 min plus MRU Myo-epithelil Luminl progenitor (CD61 pos ) Mture luminl (CD61 neg ) CD49f CD61 Reltive expression Krt5
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi: 1.138/nture862 humn hr. 21q MRPL39 murine Chr.16 Mrpl39 Dyrk1A Runx1 murine Chr. 17 ZNF295 Ets2 Znf295 murine Chr. 1 COL18A1 -/- lot: nti-dscr1 IgG hevy hin DSCR1 DSCR1 expression reltive to hevy
doi: 1.138/nture862 humn hr. 21q MRPL39 murine Chr.16 Mrpl39 Dyrk1A Runx1 murine Chr. 17 ZNF295 Ets2 Znf295 murine Chr. 1 COL18A1 -/- lot: nti-dscr1 IgG hevy hin DSCR1 DSCR1 expression reltive to hevy
EFFECT OF DIETARY ENZYME ON PERFORMANCE OF WEANLING PIGS
 EFFECT OF DIETARY ENZYME ON PERFORMANCE OF WEANLING PIGS Finl report sumitted to Dniso Animl Nutrition E. vn Heugten nd B. Frederik North Crolin Stte University, Deprtment of Animl Siene Summry The urrent
EFFECT OF DIETARY ENZYME ON PERFORMANCE OF WEANLING PIGS Finl report sumitted to Dniso Animl Nutrition E. vn Heugten nd B. Frederik North Crolin Stte University, Deprtment of Animl Siene Summry The urrent
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:.8/nture89 4 4 Ilr -/- Ilr -/- Ilr -/- Cspse- -/- As -/- Nlrp -/- Il8 -/- Ilr -/- Supplementl figure. Inresed severity of NASH in inflmmsome-defiient mie, ut not in Ilr-defiient
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:.8/nture89 4 4 Ilr -/- Ilr -/- Ilr -/- Cspse- -/- As -/- Nlrp -/- Il8 -/- Ilr -/- Supplementl figure. Inresed severity of NASH in inflmmsome-defiient mie, ut not in Ilr-defiient
Chow KD CR HFD. Fed Fast Refed
 Supplementry Figure 1 Control d/d Chow KD CR Fed Fst Refed Supplementry Figure 1: Liver expression in diet nd disese models. () expression in the livers of ontrol nd d/d mie. () expression in the livers
Supplementry Figure 1 Control d/d Chow KD CR Fed Fst Refed Supplementry Figure 1: Liver expression in diet nd disese models. () expression in the livers of ontrol nd d/d mie. () expression in the livers
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 { OI: 1.138/n31 Srifie n nlyze APs on week 1 s of iet 1 4 6 High-ft iet BrU High-ft iet BrU 4 High-ft iet BrU 6 High-ft iet BrU Lin - Lin - : C34 + : C9 + 1 1 3 1 4 1 5 C45 1 C34 1 1 1 1 3 1 4 1 5 S-1
{ OI: 1.138/n31 Srifie n nlyze APs on week 1 s of iet 1 4 6 High-ft iet BrU High-ft iet BrU 4 High-ft iet BrU 6 High-ft iet BrU Lin - Lin - : C34 + : C9 + 1 1 3 1 4 1 5 C45 1 C34 1 1 1 1 3 1 4 1 5 S-1
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 1.13/n7 Reltive Pprg mrna 3 1 1 Time (weeks) Interspulr Inguinl Epididyml Reltive undne..1.5. - 5 5-51 51-1 1-7 7 - - 1 1-1 Lipid droplet size ( m ) 1-3 3 - - - 1 1-1 1-1 1-175 175-3 3-31 31-5 >5
DOI: 1.13/n7 Reltive Pprg mrna 3 1 1 Time (weeks) Interspulr Inguinl Epididyml Reltive undne..1.5. - 5 5-51 51-1 1-7 7 - - 1 1-1 Lipid droplet size ( m ) 1-3 3 - - - 1 1-1 1-1 1-175 175-3 3-31 31-5 >5
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 X p -lu c ct ivi ty doi:.8/nture8 S CsA - THA + DAPI Merge FSK THA TUN Supplementry Figure : A. Ad-Xp luc ctivity in primry heptocytes exposed to FSK, THA, or TUN s indicted. Luciferse ctivity normlized
X p -lu c ct ivi ty doi:.8/nture8 S CsA - THA + DAPI Merge FSK THA TUN Supplementry Figure : A. Ad-Xp luc ctivity in primry heptocytes exposed to FSK, THA, or TUN s indicted. Luciferse ctivity normlized
Supplementary Figure S1
 Supplementry Figure S1 - UTR m - 3HA - 2-1 hgh - 1 Uiquitin *! *! lk distl promoter m K3R/ K121R-3HA UTR hgh founder lines - HA - - founder lines TG- E1 L A2 B1 F9 G6 H4 H6 B C D2 G1 H3 J2 L - 7 IP: lk
Supplementry Figure S1 - UTR m - 3HA - 2-1 hgh - 1 Uiquitin *! *! lk distl promoter m K3R/ K121R-3HA UTR hgh founder lines - HA - - founder lines TG- E1 L A2 B1 F9 G6 H4 H6 B C D2 G1 H3 J2 L - 7 IP: lk
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:.8/nture98 : hr NEMO :5 hr IKK IKK NF-κB p65 p5 p65/-rel NF-κB p65 p5 p65/-rel Cytoplsm Cytoplsm p65/p5 Nuleus Nuleus NEMO IKK IKK d : hr > : hr p65/-rel NF- p65 p5 Cytoplsm Cytoplsm p65/p5 p65/-rel
doi:.8/nture98 : hr NEMO :5 hr IKK IKK NF-κB p65 p5 p65/-rel NF-κB p65 p5 p65/-rel Cytoplsm Cytoplsm p65/p5 Nuleus Nuleus NEMO IKK IKK d : hr > : hr p65/-rel NF- p65 p5 Cytoplsm Cytoplsm p65/p5 p65/-rel
ARTICLE. I. Chopra & H. F. Li & H. Wang & K. A. Webster
 Dietologi (212) 55:783 794 DOI 1.17/s125-11-247-y ARTICLE Phosphoryltion of the insulin reeptor y AMP-tivted protein kinse (AMPK) promotes lignd-independent tivtion of the insulin signlling pthwy in rodent
Dietologi (212) 55:783 794 DOI 1.17/s125-11-247-y ARTICLE Phosphoryltion of the insulin reeptor y AMP-tivted protein kinse (AMPK) promotes lignd-independent tivtion of the insulin signlling pthwy in rodent
AUTHOR COPY ONLY. Glycogen synthase kinase 3b mediates high glucose-induced ubiquitination and proteasome degradation of insulin receptor substrate 1
 Glyogen synthse kinse 3 medites high gluose-indued uiquitintion nd protesome degrdtion of insulin reeptor sustrte 1 171 Snhu Leng, Wenshuo Zhng, Ynin Zheng, Ziv Liermn 1, Christopher J Rhodes, Hgit Eldr-Finkelmn
Glyogen synthse kinse 3 medites high gluose-indued uiquitintion nd protesome degrdtion of insulin reeptor sustrte 1 171 Snhu Leng, Wenshuo Zhng, Ynin Zheng, Ziv Liermn 1, Christopher J Rhodes, Hgit Eldr-Finkelmn
Alimonti_Supplementary Figure 1. Pten +/- Pten + Pten. Pten hy. β-actin. Pten - wt hy/+ +/- wt hy/+ +/- Pten. Pten. Relative Protein level (% )
 Alimonti_Supplementry Figure 1 hy 3 4 5 3 Neo 4 5 5 Proe 5 Proe hy/ hy/ /- - 3 6 Neo β-tin d Reltive Protein level (% ) 15 1 5 hy/ /- Reltive Gene Expr. (% ) 15 1 5 hy/ /- Supplementry Figure 1 Chrteriztion
Alimonti_Supplementry Figure 1 hy 3 4 5 3 Neo 4 5 5 Proe 5 Proe hy/ hy/ /- - 3 6 Neo β-tin d Reltive Protein level (% ) 15 1 5 hy/ /- Reltive Gene Expr. (% ) 15 1 5 hy/ /- Supplementry Figure 1 Chrteriztion
TNF-a Downregulates Filaggrin and Loricrin through c-jun N-terminal Kinase: Role for TNF-a Antagonists to Improve Skin Barrier
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE TNF- Downregultes Filggrin nd Loririn through -Jun N-terminl Kinse: Role for TNF- Antgonists to Improve Skin Brrier Byung Eui Kim, Mihel D. Howell,, Emm Guttmn,, Ptrii M. Gilleudeu, Irm
ORIGINAL ARTICLE TNF- Downregultes Filggrin nd Loririn through -Jun N-terminl Kinse: Role for TNF- Antgonists to Improve Skin Brrier Byung Eui Kim, Mihel D. Howell,, Emm Guttmn,, Ptrii M. Gilleudeu, Irm
Title of Experiment: Author, Institute and address:
 Title of Experiment: Trsfetion of murine mrophge RAW264.7 ells with METAFECTENE PRO. Author, Institute n ress: Ptrizi Pellegtti n Frneso Di Virgilio. Deprtment of Experimentl n Dignosti Meiine, Setion
Title of Experiment: Trsfetion of murine mrophge RAW264.7 ells with METAFECTENE PRO. Author, Institute n ress: Ptrizi Pellegtti n Frneso Di Virgilio. Deprtment of Experimentl n Dignosti Meiine, Setion
YAP transcriptionally regulates COX-2 expression and GCCSysm-4 (G-4), a dual YAP/COX-2 inhibitor, overcomes drug resistance in colorectal cancer
 Li et l. Journl of Experimentl & Clinil Cner Reserh (7) 36:44 DOI.86/s346-7-6-3 RESEARCH Open Aess trnsriptionlly regultes expression nd GCCSysm-4 (G-4), dul / inhiitor, overomes drug resistne in oloretl
Li et l. Journl of Experimentl & Clinil Cner Reserh (7) 36:44 DOI.86/s346-7-6-3 RESEARCH Open Aess trnsriptionlly regultes expression nd GCCSysm-4 (G-4), dul / inhiitor, overomes drug resistne in oloretl
supplementary information
 DOI:.38/n83 k Mouse Ch8 lous 8 9 Stop CHD8L 75 CHD8L Chromoomins Helise/ATPse omin DNA ining omin 5 kd NIH 3T3 MEF 93T HeL HCT UOS SOS.. CHD8L IB: CHD8 8 5 L S Reltive mrna mount 3... Reltive mrna mount.8.
DOI:.38/n83 k Mouse Ch8 lous 8 9 Stop CHD8L 75 CHD8L Chromoomins Helise/ATPse omin DNA ining omin 5 kd NIH 3T3 MEF 93T HeL HCT UOS SOS.. CHD8L IB: CHD8 8 5 L S Reltive mrna mount 3... Reltive mrna mount.8.
The Hippo/YAP pathway interacts with EGFR signaling and HPV oncoproteins to regulate cervical cancer progression
 Reserh Artile The Hippo/ pthwy interts with EGFR signling nd HPV onoproteins to regulte ervil ner progression Chuno He 1,, Dgn Mo 1,3, Guohu Hu 1,, Xingmin Lv 1, Xingheng Chen, Peter C Angeletti 5, Jixin
Reserh Artile The Hippo/ pthwy interts with EGFR signling nd HPV onoproteins to regulte ervil ner progression Chuno He 1,, Dgn Mo 1,3, Guohu Hu 1,, Xingmin Lv 1, Xingheng Chen, Peter C Angeletti 5, Jixin
LHb VTA. VTA-projecting RMTg-projecting overlay. Supplemental Figure 2. Retrograde labeling of LHb neurons. a. VTA-projecting LHb
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementl Figure 1 doi:10.1038/nture09742 Lterl 1.0 mm from midline mpfc BNST mpfc BNST Lterl 2.1 mm from midline LHA LHA Lterl 2.7 mm from midline SUPPLEMENTAL INFORMATION
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementl Figure 1 doi:10.1038/nture09742 Lterl 1.0 mm from midline mpfc BNST mpfc BNST Lterl 2.1 mm from midline LHA LHA Lterl 2.7 mm from midline SUPPLEMENTAL INFORMATION
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 % ells with ili (mrke y A-Tu) Reltive Luiferse % ells with ili (mrke y Arl13) % ells with ili DOI: 1.138/n2259 A-Tuulin Hoehst % Cilite Non-ilite -Serum 9% 8% 7% 1 6% % 4% +Serum 1 3% 2% 1% % Serum: -
% ells with ili (mrke y A-Tu) Reltive Luiferse % ells with ili (mrke y Arl13) % ells with ili DOI: 1.138/n2259 A-Tuulin Hoehst % Cilite Non-ilite -Serum 9% 8% 7% 1 6% % 4% +Serum 1 3% 2% 1% % Serum: -
Thioredoxin-interacting protein links oxidative stress to inflammasome activation
 A rt i l e s Thioredoxin-interting protein links oxidtive stress to inflmmsome tivtion Rongin Zhou 1, Aury Trdivel 1, Bernrd Thorens 2, Inpyo Choi 3 & Jürg Tshopp 1 29 Nture Ameri, In. All rights reserved.
A rt i l e s Thioredoxin-interting protein links oxidtive stress to inflmmsome tivtion Rongin Zhou 1, Aury Trdivel 1, Bernrd Thorens 2, Inpyo Choi 3 & Jürg Tshopp 1 29 Nture Ameri, In. All rights reserved.
Effects of exercise training on hepatic steatosis in high fat diet-induced obese mice
 Effets of exerise trining on hepti stetosis in high ft diet-indued oese mie Hyunsik Kng, PhD Sungkyunkwn University Non-Aloholi Ftty Liver Disese (NAFLD) A reversile ondition tht is hrterized y hepti lipid
Effets of exerise trining on hepti stetosis in high ft diet-indued oese mie Hyunsik Kng, PhD Sungkyunkwn University Non-Aloholi Ftty Liver Disese (NAFLD) A reversile ondition tht is hrterized y hepti lipid
Rapamycin toxicity in MIN6 cells and rat and human islets is mediated by the inhibition of mtor complex 2 (mtorc2)
 Dietologi (212) 55:1355 1365 DOI 1.17/s125-12-2475-7 ARTICLE myin toxiity in MIN6 ells nd rt nd humn islets is medited y the inhiition of mtor omplex 2 (mtorc2) A. D. Brlow & J. Xie & C. E. Moore & S.
Dietologi (212) 55:1355 1365 DOI 1.17/s125-12-2475-7 ARTICLE myin toxiity in MIN6 ells nd rt nd humn islets is medited y the inhiition of mtor omplex 2 (mtorc2) A. D. Brlow & J. Xie & C. E. Moore & S.
Interplay of LRRK2 with chaperone-mediated autophagy
 Interply of with hperone-medited utophgy Smnth J Orenstein,, Sheng-Hn Kuo,, Inmuld Tsset,,, Espernz Aris,, Hiroshi Kog,, Irene Fernndez-Crs, Etty Cortes,5, Lwrene S Honig,5, Willim Duer 6, Antonell Consiglio,7,
Interply of with hperone-medited utophgy Smnth J Orenstein,, Sheng-Hn Kuo,, Inmuld Tsset,,, Espernz Aris,, Hiroshi Kog,, Irene Fernndez-Crs, Etty Cortes,5, Lwrene S Honig,5, Willim Duer 6, Antonell Consiglio,7,
The microrna mir-31 inhibits CD8 + T cell function in chronic viral infection
 A rt i l e s The mirorna mir-3 inhiits CD8 + T ell funtion in hroni virl infetion Howell F Moffett, Adm N R Crtwright, Hye-Jung Kim, Jernej Gode, Json Pyrdol, Trmo Äijö 3, Gustvo J Mrtinez,6, Anjn Ro,
A rt i l e s The mirorna mir-3 inhiits CD8 + T ell funtion in hroni virl infetion Howell F Moffett, Adm N R Crtwright, Hye-Jung Kim, Jernej Gode, Json Pyrdol, Trmo Äijö 3, Gustvo J Mrtinez,6, Anjn Ro,
Raina Devi Ramnath, Jia Sun, and Madhav Bhatia. Department of Pharmacology, National University of Singapore, Singapore
 -3565/9/39-48 48$. THE JOURNAL OF PHARMACOLOGY AND EXPERIMENTAL THERAPEUTICS Vol. 39, No. Copyright 9 y The Amerin Soiety for Phrmology nd Experimentl s 48684/346663 JPET 39:48 48, 9 Printed in U.S.A.
-3565/9/39-48 48$. THE JOURNAL OF PHARMACOLOGY AND EXPERIMENTAL THERAPEUTICS Vol. 39, No. Copyright 9 y The Amerin Soiety for Phrmology nd Experimentl s 48684/346663 JPET 39:48 48, 9 Printed in U.S.A.
FAK integrates growth-factor and integrin signals to promote cell migration
 integrtes growth-ftor nd integrin signls to promote ell migrtion rtiles Dvid J. Sieg*, Christof R. Huk*, Dusko Ili, Cndie K. Klingeil*, Erik Shefer, Croline H. Dmsky nd Dvid D. Shlepfer* *Deprtment of
integrtes growth-ftor nd integrin signls to promote ell migrtion rtiles Dvid J. Sieg*, Christof R. Huk*, Dusko Ili, Cndie K. Klingeil*, Erik Shefer, Croline H. Dmsky nd Dvid D. Shlepfer* *Deprtment of
A liver HIF-2α/IRS2 pathway sensitizes hepatic insulin signaling and is modulated by VEGF inhibition
 A liver HIF-2α/IRS2 pthwy sensitizes hepti insulin signling n is moulte y VEGF inhiition Kevin Wei1,1, Stephnie M. Pieewiz1,1, Lis M. MGinnis1,1, Cullen M. Tniguhi2, Stnley J. Wiegn3, Keith Anerson3, Crol
A liver HIF-2α/IRS2 pthwy sensitizes hepti insulin signling n is moulte y VEGF inhiition Kevin Wei1,1, Stephnie M. Pieewiz1,1, Lis M. MGinnis1,1, Cullen M. Tniguhi2, Stnley J. Wiegn3, Keith Anerson3, Crol
Inhibitory effect of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase inhibitors on cytokine release from human macrophages
 British Journl of Phrmology (26) 149, 393 44 & 26 Nture Pulishing Group All rights reserved 7 1188/6 $3. www.rjphrmol.org RESEARCH PAPER Inhiitory effet of p38 mitogen-tivted protein kinse inhiitors on
British Journl of Phrmology (26) 149, 393 44 & 26 Nture Pulishing Group All rights reserved 7 1188/6 $3. www.rjphrmol.org RESEARCH PAPER Inhiitory effet of p38 mitogen-tivted protein kinse inhiitors on
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 1.138/n2977 Numer of ells per field 6 4 2 P =.1 Orthotopi eum Normlized ventrl photon flux 1E7 1E6 1E5 1E4 1E3 1E2 n=8 n=9 1 2 3 4 5 6 Dys Dy54 1.5E5 2.4E7 d Mie with lymph node metstsis (%) 1 8 6
DOI: 1.138/n2977 Numer of ells per field 6 4 2 P =.1 Orthotopi eum Normlized ventrl photon flux 1E7 1E6 1E5 1E4 1E3 1E2 n=8 n=9 1 2 3 4 5 6 Dys Dy54 1.5E5 2.4E7 d Mie with lymph node metstsis (%) 1 8 6
Fates-shifted is an F box protein that targets Bicoid for degradation and regulates developmental fate determination in Drosophila embryos
 ARTICLES Ftes-shifted is n F ox protein tht trgets Bioid for degrdtion nd regultes developmentl fte determintion in Drosophil emryos Juno Liu 1 nd Jun M 1,2,3 Bioid (Bd) is morphogeneti protein tht instruts
ARTICLES Ftes-shifted is n F ox protein tht trgets Bioid for degrdtion nd regultes developmentl fte determintion in Drosophil emryos Juno Liu 1 nd Jun M 1,2,3 Bioid (Bd) is morphogeneti protein tht instruts
(% of adherent cells) *** PBL firm adhesion. Frequency (% ) 4 1 L 2 CXCR3 DP-2
 Chemotxis (% of dded ells) PBL totl dhesion (N ells/mm 2 /1.1 6 PBL) Frequeny (% ) PBL firm dhesion Supplementry Figure 1 4 4 3 3 2 2 1.1-4 1-3 1.1.2. 1 1 8 6 4 2 Adiponetin ( g/ml) - + Adiponetin ( g/ml)
Chemotxis (% of dded ells) PBL totl dhesion (N ells/mm 2 /1.1 6 PBL) Frequeny (% ) PBL firm dhesion Supplementry Figure 1 4 4 3 3 2 2 1.1-4 1-3 1.1.2. 1 1 8 6 4 2 Adiponetin ( g/ml) - + Adiponetin ( g/ml)
Supplementary Figure 1. Scheme of unilateral pyramidotomy used for detecting compensatory sprouting of intact CST axons.
 () BDA 2 weeks fter Py () AAVs Cre or GFP t P1 BDA 2 weeks fter Py CSMN CST () Py t P7 or 2 months () Py t 2 months Supplementry Figure 1. Sheme of unilterl pyrmidotomy used for deteting ompenstory sprouting
() BDA 2 weeks fter Py () AAVs Cre or GFP t P1 BDA 2 weeks fter Py CSMN CST () Py t P7 or 2 months () Py t 2 months Supplementry Figure 1. Sheme of unilterl pyrmidotomy used for deteting ompenstory sprouting
ARTICLE. Keywords ACE-2. Akita mice. Angiotensinogen. Diabetes. Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein F. Hypertension. Renal fibrosis.
 Dietologi (5) 58:44 454 DOI.7/s5-5-7-y ARTICLE Overexpression of heterogeneous nuler rionuleoprotein F stimultes renl Ae- gene expression nd prevents TGF-β-indued kidney injury in mouse model of dietes
Dietologi (5) 58:44 454 DOI.7/s5-5-7-y ARTICLE Overexpression of heterogeneous nuler rionuleoprotein F stimultes renl Ae- gene expression nd prevents TGF-β-indued kidney injury in mouse model of dietes
BTLA is a lymphocyte inhibitory receptor with similarities to CTLA-4 and PD-1
 BTLA is lymphoyte inhiitory reeptor with similrities to CTLA-4 nd PD-1 Norihiko Wtne 1,5, My Gvrieli 1, John R Sedy 1, Jinfei Yng 1,5, Frnes Fllrino 2, Susn K Loftin 1, Mihelle A Hurhl 1, Ntlie Zimmermn
BTLA is lymphoyte inhiitory reeptor with similrities to CTLA-4 nd PD-1 Norihiko Wtne 1,5, My Gvrieli 1, John R Sedy 1, Jinfei Yng 1,5, Frnes Fllrino 2, Susn K Loftin 1, Mihelle A Hurhl 1, Ntlie Zimmermn
Roles of the PI-3K and MEK pathways in Ras-mediated chemoresistance in breast cancer cells
 ritish Journl of Cner (23) 89, 18 191 & 23 Cner Reserh UK All rights reserved 7 92/3 $2. www.jner.om Roles of the PI-3K nd MEK pthwys in Rs-medited hemoresistne in rest ner ells W Jin 1,LWu 1, K Ling 1,
ritish Journl of Cner (23) 89, 18 191 & 23 Cner Reserh UK All rights reserved 7 92/3 $2. www.jner.om Roles of the PI-3K nd MEK pthwys in Rs-medited hemoresistne in rest ner ells W Jin 1,LWu 1, K Ling 1,
Ulk λ PPase. 32 P-Ulk1 32 P-GST-TSC2. Ulk1 GST (TSC2) : Ha-Ulk1 : AMPK. WB: Ha (Ulk1) : Glu. h CON - Glu - A.A WB: LC3 AMPK-WT AMPK-DKO
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb2152 C.C + - + - : Glu b Ulk1 - - + λ PPse c AMPK + - + + : ATP P-GST-TSC2 WB: Flg (Ulk1) WB Ulk1 WB: H (Ulk1) GST (TSC2) C.C d e WT K46R - + - + : H-Ulk1 : AMPK - + - + + + AMPK H-Ulk1
DOI: 10.1038/ncb2152 C.C + - + - : Glu b Ulk1 - - + λ PPse c AMPK + - + + : ATP P-GST-TSC2 WB: Flg (Ulk1) WB Ulk1 WB: H (Ulk1) GST (TSC2) C.C d e WT K46R - + - + : H-Ulk1 : AMPK - + - + + + AMPK H-Ulk1
a3 Chains of type V collagen regulate breast tumour growth via glypican-1
 Reeive 5 Aug 16 Aepte De 16 Pulishe 19 Jn 17 3 Chins of type V ollgen regulte rest tumour growth vi glypin-1 Guorui Hung 1, Goxing Ge 1,w, Vlerio Izzi & Dniel S. Greenspn 1 DOI: 1.138/nomms1351 OPEN Periellulr
Reeive 5 Aug 16 Aepte De 16 Pulishe 19 Jn 17 3 Chins of type V ollgen regulte rest tumour growth vi glypin-1 Guorui Hung 1, Goxing Ge 1,w, Vlerio Izzi & Dniel S. Greenspn 1 DOI: 1.138/nomms1351 OPEN Periellulr
AMP-activated protein kinase regulates glucagon secretion from mouse pancreatic alpha cells
 Dietologi (2) 54:25 34 DOI.7/s25--929-z ARTICLE AMP-tivted protein kinse regultes glugon seretion from mouse pnreti lph ells I. Leler & G. Sun & C. Morris & E. Fernndez-Milln & M. Nyirend & G. A. Rutter
Dietologi (2) 54:25 34 DOI.7/s25--929-z ARTICLE AMP-tivted protein kinse regultes glugon seretion from mouse pnreti lph ells I. Leler & G. Sun & C. Morris & E. Fernndez-Milln & M. Nyirend & G. A. Rutter
Osteoblasts secrete Cxcl9 to regulate angiogenesis in bone
 Reeived 2 De 215 Aepted 9 Nov 216 Pulished 14 De 216 DOI: 1.138/nomms13885 OPEN Osteolsts serete to regulte ngiogenesis in one Bin Hung 1,, Wenho Wng 1,, Qinghu Li 1,, Zhenyu Wng 1,BoYn 1, Zhongmin Zhng
Reeived 2 De 215 Aepted 9 Nov 216 Pulished 14 De 216 DOI: 1.138/nomms13885 OPEN Osteolsts serete to regulte ngiogenesis in one Bin Hung 1,, Wenho Wng 1,, Qinghu Li 1,, Zhenyu Wng 1,BoYn 1, Zhongmin Zhng
LETTERS. Chfr is required for tumor suppression and Aurora A regulation
 25 Nture Pulishing Group http://www.nture.om/nturegenetis Chfr is required for tumor suppression nd Auror A regultion Xiohun Yu 1, Ktherine Minter-Dykhouse 1, Liviu Mlurenu 2, Wei-Meng Zho 3, Dongwei Zhng
25 Nture Pulishing Group http://www.nture.om/nturegenetis Chfr is required for tumor suppression nd Auror A regultion Xiohun Yu 1, Ktherine Minter-Dykhouse 1, Liviu Mlurenu 2, Wei-Meng Zho 3, Dongwei Zhng
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Prentl doi:.8/nture57 Figure S HPMECs LM Cells Cell lines VEGF (ng/ml) Prentl 7. +/-. LM 7. +/-.99 LM 7. +/-.99 Fold COX induction 5 VEGF: - + + + Bevcizum: - - 5 (µg/ml) Reltive MMP LM mock COX MMP LM+
Prentl doi:.8/nture57 Figure S HPMECs LM Cells Cell lines VEGF (ng/ml) Prentl 7. +/-. LM 7. +/-.99 LM 7. +/-.99 Fold COX induction 5 VEGF: - + + + Bevcizum: - - 5 (µg/ml) Reltive MMP LM mock COX MMP LM+
TNF-α (pg/ml) IL-6 (ng/ml)
 Xio, et l., Supplementry Figure 1 IL-6 (ng/ml) TNF-α (pg/ml) 16 12 8 4 1,4 1,2 1, 8 6 4 2 med Cl / Pm3CSK4 zymosn curdln Poly (I:C) LPS flgelin MALP-2 imiquimod R848 CpG TNF-α (pg/ml) IL-6 (ng/ml) 2 1.6
Xio, et l., Supplementry Figure 1 IL-6 (ng/ml) TNF-α (pg/ml) 16 12 8 4 1,4 1,2 1, 8 6 4 2 med Cl / Pm3CSK4 zymosn curdln Poly (I:C) LPS flgelin MALP-2 imiquimod R848 CpG TNF-α (pg/ml) IL-6 (ng/ml) 2 1.6
Effects of Enzyme Inducers in Therapeutic Efficacy of Rosiglitazone: An Antidiabetic Drug in Albino Rats
 Asin J. Exp. Si., Vol. 21, No. 2, 2007, 00-00 Effets of Enzyme Inuers in Therpeuti Effiy of Rosiglitzone: An Antiieti Drug in Alino Rts Ann Chursi,#* P.K. Krr** A. S. Mnn* & M.D. Khry* * Deprtment of Phrmeutil
Asin J. Exp. Si., Vol. 21, No. 2, 2007, 00-00 Effets of Enzyme Inuers in Therpeuti Effiy of Rosiglitzone: An Antiieti Drug in Alino Rts Ann Chursi,#* P.K. Krr** A. S. Mnn* & M.D. Khry* * Deprtment of Phrmeutil
Involvement of thioredoxin-interacting protein (TXNIP) in glucocorticoid-mediated beta cell death
 Dietologi (12) 55:148 157 DOI 1.7/s125-11-2422-z ARTICLE Involvement of thioredoxin-interting protein (TXNIP) in gluoortioid-medited et ell deth E. Reih & A. Tmry & R. Vogt Sionov & D. Melloul Reeived:
Dietologi (12) 55:148 157 DOI 1.7/s125-11-2422-z ARTICLE Involvement of thioredoxin-interting protein (TXNIP) in gluoortioid-medited et ell deth E. Reih & A. Tmry & R. Vogt Sionov & D. Melloul Reeived:
Supplementary figure 1
 Supplementry figure 1 Dy 8 post LCMV infection Vsculr Assoc. Prenchym Dy 3 post LCMV infection 1 5 6.7.29 1 4 1 3 1 2 88.9 4.16 1 2 1 3 1 4 1 5 1 5 1.59 5.97 1 4 1 3 1 2 21.4 71 1 2 1 3 1 4 1 5 1 5.59.22
Supplementry figure 1 Dy 8 post LCMV infection Vsculr Assoc. Prenchym Dy 3 post LCMV infection 1 5 6.7.29 1 4 1 3 1 2 88.9 4.16 1 2 1 3 1 4 1 5 1 5 1.59 5.97 1 4 1 3 1 2 21.4 71 1 2 1 3 1 4 1 5 1 5.59.22
Protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B deficiency or inhibition delays ErbB2-induced mammary tumorigenesis and protects from lung metastasis
 Protein tyrosine phosphtse 1B defiieny or inhiition delys ErB2-indued mmmry tumorigenesis nd protets from lung metstsis Sofi G Julien 1,5, Ndi Dué 1,6, Mihelle Red 1, Jnie Penney 1, Mrilene Pquet 2, Yongxin
Protein tyrosine phosphtse 1B defiieny or inhiition delys ErB2-indued mmmry tumorigenesis nd protets from lung metstsis Sofi G Julien 1,5, Ndi Dué 1,6, Mihelle Red 1, Jnie Penney 1, Mrilene Pquet 2, Yongxin
Research Article A Comparison of Inflammatory and Oxidative Stress Markers in Adipose Tissue from Weight-Matched Obese Male and Female Mice
 Hindwi Pulishing Corportion Experimentl Dietes Reserh Volume 1, Artile ID 859395, 8 pges doi:1.1155/1/859395 Reserh Artile A Comprison of Inflmmtory nd Oxidtive Stress Mrkers in Adipose Tissue from Weight-Mthed
Hindwi Pulishing Corportion Experimentl Dietes Reserh Volume 1, Artile ID 859395, 8 pges doi:1.1155/1/859395 Reserh Artile A Comprison of Inflmmtory nd Oxidtive Stress Mrkers in Adipose Tissue from Weight-Mthed
* * * * * liver kidney ileum. Supplementary Fig.S1
 Supplementry Fig.S1 liver kidney ileum Fig.S1. Orlly delivered Fexrmine is intestinlly-restricted Mice received vehicle or Fexrmine (100mg/kg) vi per os (PO) or intrperitonel (IP) injection for 5 dys (n=3/group).
Supplementry Fig.S1 liver kidney ileum Fig.S1. Orlly delivered Fexrmine is intestinlly-restricted Mice received vehicle or Fexrmine (100mg/kg) vi per os (PO) or intrperitonel (IP) injection for 5 dys (n=3/group).
The histone H3K9 methyltransferase SUV39H links SIRT1 repression to myocardial infarction
 Reeived 8 Jun 6 Aepted Fe 7 Pulished Mr 7 DOI:.8/nomms9 OPEN The histone HK9 methyltrnsferse SUV9H links SIRT repression to myordil infrtion Gung Yng,, Xinyu Weng,,,, Yuho Zho, Xinjin Zhng, Yunping Hu,
Reeived 8 Jun 6 Aepted Fe 7 Pulished Mr 7 DOI:.8/nomms9 OPEN The histone HK9 methyltrnsferse SUV9H links SIRT repression to myordil infrtion Gung Yng,, Xinyu Weng,,,, Yuho Zho, Xinjin Zhng, Yunping Hu,
Research Article TNF-α and IFN-s-Dependent Muscle Decay Is Linked to NF-κB- and STAT-1α-Stimulated Atrogin1 and MuRF1 Genes in C2C12 Myotubes
 Hindwi Pulishing Corportion Meditors of Inflmmtion Volume 213, Artile ID 171437, 18 pges http://dx.doi.org/1.1155/213/171437 Reserh Artile nd IFN-s-Dependent Musle Dey Is Linked to NF-κB- nd STAT-1α-Stimulted
Hindwi Pulishing Corportion Meditors of Inflmmtion Volume 213, Artile ID 171437, 18 pges http://dx.doi.org/1.1155/213/171437 Reserh Artile nd IFN-s-Dependent Musle Dey Is Linked to NF-κB- nd STAT-1α-Stimulted
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:1.138/nture1794 BR EPFs BRI1? ERECTA TMM BSKs YDA PP2A BSU1 BIN2 pbzr1/2 BZR1/2 MKK4/5/7/9 MPK3/6 SPCH Cell growth Stomtl production Supplementry Figure 1. The model of BR nd stomtl signling pthwys.
doi:1.138/nture1794 BR EPFs BRI1? ERECTA TMM BSKs YDA PP2A BSU1 BIN2 pbzr1/2 BZR1/2 MKK4/5/7/9 MPK3/6 SPCH Cell growth Stomtl production Supplementry Figure 1. The model of BR nd stomtl signling pthwys.
P AND K IN POTATOES. Donald A Horneck Oregon State University Extension Service
 P AND K IN POTATOES Donld A Hornek Oregon Stte University Extension Servie INTRODUCTION Phosphorous nd potssium re importnt to grow high yielding nd qulity pottoes. Muh of the northwest hs hd trditionlly
P AND K IN POTATOES Donld A Hornek Oregon Stte University Extension Servie INTRODUCTION Phosphorous nd potssium re importnt to grow high yielding nd qulity pottoes. Muh of the northwest hs hd trditionlly
GLP-1 oestrogen attenuates hyperphagia and protects from beta cell failure in diabetes-prone New Zealand obese (NZO) mice
 Dietologi () 8:64 614 DOI.7/s1-14-3478-3 ARTICLE GLP-1 oestrogen ttenutes hyperphgi nd protets from et ell filure in dietes-prone New Zelnd oese (NZO) mie Roert W. Shwenk & Christin Bumeier & Brin Finn
Dietologi () 8:64 614 DOI.7/s1-14-3478-3 ARTICLE GLP-1 oestrogen ttenutes hyperphgi nd protets from et ell filure in dietes-prone New Zelnd oese (NZO) mie Roert W. Shwenk & Christin Bumeier & Brin Finn
Endogenous GIP ameliorates impairment of insulin secretion in proglucagon-deficient mice under moderate beta cell damage induced by streptozotocin
 Dietologi (216) 59:1533 1541 DOI 1.17/s125-16-3935-2 ARTICLE Endogenous GIP meliortes impirment of insulin seretion in proglugon-defiient mie under moderte et ell dmge indued y streptozotoin Atsushi Iid
Dietologi (216) 59:1533 1541 DOI 1.17/s125-16-3935-2 ARTICLE Endogenous GIP meliortes impirment of insulin seretion in proglugon-defiient mie under moderte et ell dmge indued y streptozotoin Atsushi Iid
Intervention with citrus flavonoids reverses obesity, and improves metabolic syndrome and
 Intervention with itrus flvonoids reverses oesity, nd improves metoli syndrome nd theroslerosis in oese Ldlr -/- mie Authors: Amy C. Burke 1,2, Brin G. Sutherlnd 1, Dwn E. Telford 1,3, Mris R. Morrow 1,
Intervention with itrus flvonoids reverses oesity, nd improves metoli syndrome nd theroslerosis in oese Ldlr -/- mie Authors: Amy C. Burke 1,2, Brin G. Sutherlnd 1, Dwn E. Telford 1,3, Mris R. Morrow 1,
The soy isoflavone genistein promotes apoptosis in mammary epithelial cells by inducing the tumor suppressor PTEN
 Crinogenesis vol. no.1 pp.1793 183, 5 doi:1.193/rin/gi131 dvne ess pulition My 19, 5 The soy isoflvone genistein promotes poptosis in mmmry epithelil ells y induing the tumor suppressor huvnesh Dve 1,,
Crinogenesis vol. no.1 pp.1793 183, 5 doi:1.193/rin/gi131 dvne ess pulition My 19, 5 The soy isoflvone genistein promotes poptosis in mmmry epithelil ells y induing the tumor suppressor huvnesh Dve 1,,
Poultry No The replacement value of betaine for DL-methionine and Choline in broiler diets
 Poultry No. 1573 The replement vlue of etine for DL-methionine nd Choline in roiler diets Key Informtion In roiler diets defiient in sulfur mino ids ut dequtely supplemented with methyl groups vi dded
Poultry No. 1573 The replement vlue of etine for DL-methionine nd Choline in roiler diets Key Informtion In roiler diets defiient in sulfur mino ids ut dequtely supplemented with methyl groups vi dded
AMPK maintains energy homeostasis and survival in cancer cells via. regulating p38/pgc-1α-mediated mitochondrial biogenesis
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION AMPK mintins energy homeostsis nd survivl in cncer cells vi regulting p38/pgc-1α-medited mitochondril iogenesis Blkrishn Chue 1, Prmnnd Mlvi 1, Shivendr Vikrm Singh 1, Noshd Mohmmd
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION AMPK mintins energy homeostsis nd survivl in cncer cells vi regulting p38/pgc-1α-medited mitochondril iogenesis Blkrishn Chue 1, Prmnnd Mlvi 1, Shivendr Vikrm Singh 1, Noshd Mohmmd
Adipose tissue NAPE-PLD controls fat mass development by altering the browning process and gut microbiota
 Reeived 11 Jul 1 Aepted Fe Pulished 11 Mr DOI: 1.138/nomms795 OPEN Adipose tissue NAPE-PLD ontrols ft mss development y ltering the rowning proess nd gut miroiot Luie Geurts 1, Amndine Everrd 1,, Mtthis
Reeived 11 Jul 1 Aepted Fe Pulished 11 Mr DOI: 1.138/nomms795 OPEN Adipose tissue NAPE-PLD ontrols ft mss development y ltering the rowning proess nd gut miroiot Luie Geurts 1, Amndine Everrd 1,, Mtthis
ARTICLE. E. O. List & A. J. Palmer & D. E. Berryman & B. Bower & B. Kelder & J. J. Kopchick
 Dietologi (2009) 52:1647 1655 DOI 10.1007/s00125-009-1402-z ARTICLE Growth hormone improves ody omposition, fsting lood gluose, gluose tolerne nd liver triylglyerol in mouse model of diet-indued oesity
Dietologi (2009) 52:1647 1655 DOI 10.1007/s00125-009-1402-z ARTICLE Growth hormone improves ody omposition, fsting lood gluose, gluose tolerne nd liver triylglyerol in mouse model of diet-indued oesity
Activation of Akt as a Mechanism for Tumor Immune Evasion
 The Amerin Soiety of Gene Therpy originl rtile Ativtion of Akt s Mehnism for Tumor Immune Evsion Kyung Hee Noh 1, Te Heung Kng 1, Jin Hee Kim 1, Sr I Pi 2, Ken Y Lin 3, Chien-Fu Hung 4, T-C Wu 4 7 nd Te
The Amerin Soiety of Gene Therpy originl rtile Ativtion of Akt s Mehnism for Tumor Immune Evsion Kyung Hee Noh 1, Te Heung Kng 1, Jin Hee Kim 1, Sr I Pi 2, Ken Y Lin 3, Chien-Fu Hung 4, T-C Wu 4 7 nd Te
Targeting TSLP With shrna Alleviates Airway Inflammation and Decreases Epithelial CCL17 in a Murine Model of Asthma
 Cittion: Moleulr Therpy Nulei Aids (216), e316; doi:1.138/mtn.216.29 Offiil journl of the Amerin Soiety of Gene & Cell Therpy www.nture.om/mtn Trgeting TSLP With shrna Allevites Airwy Inflmmtion nd Dereses
Cittion: Moleulr Therpy Nulei Aids (216), e316; doi:1.138/mtn.216.29 Offiil journl of the Amerin Soiety of Gene & Cell Therpy www.nture.om/mtn Trgeting TSLP With shrna Allevites Airwy Inflmmtion nd Dereses
 DOI: 10.1038/nc2331 PCre;Ros26R 12 h induction 48 h induction Vegfr3 i EC c d ib4 24 h induction VEGFR3 e Fold chnge 1.0 0.5 P < 0.05 Vegfr3 i EC Vegfr3 Figure S1 Cre ctivtion leds to genetic deletion
DOI: 10.1038/nc2331 PCre;Ros26R 12 h induction 48 h induction Vegfr3 i EC c d ib4 24 h induction VEGFR3 e Fold chnge 1.0 0.5 P < 0.05 Vegfr3 i EC Vegfr3 Figure S1 Cre ctivtion leds to genetic deletion
Transplantation of PC1/3-Expressing α-cells Improves Glucose Handling and Cold Tolerance in Leptin-resistant Mice
 The Amerin Soiety of Gene Therpy originl rtile Trnsplnttion of PC1/3-Expressing α-ells Improves Gluose Hndling nd Cold Tolerne in Leptin-resistnt Mie Rhond D Widemn 1, Srh L Gry 1, Sott D Covey 1, Gene
The Amerin Soiety of Gene Therpy originl rtile Trnsplnttion of PC1/3-Expressing α-ells Improves Gluose Hndling nd Cold Tolerne in Leptin-resistnt Mie Rhond D Widemn 1, Srh L Gry 1, Sott D Covey 1, Gene
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 2 weeks high holesterol diet 2 weeks high holesterol diet 2 weeks high holesterol diet 2 μm Mrophges Crystls Hoehst μm Mrophges Crystls Hoehst Hoehst Crystls Mrophges 2 μm 2 μm Supplementry Fig. 1: Erly
2 weeks high holesterol diet 2 weeks high holesterol diet 2 weeks high holesterol diet 2 μm Mrophges Crystls Hoehst μm Mrophges Crystls Hoehst Hoehst Crystls Mrophges 2 μm 2 μm Supplementry Fig. 1: Erly
Inhibition of mtor induces autophagy and reduces toxicity of polyglutamine expansions in fly and mouse models of Huntington disease
 Inhiition of mtor indues utophgy nd redues toxiity of polyglutmine expnsions in fly nd mouse models of Huntington disese Brind Rvikumr 1,6, Corlie Vher 1,6, Zdenek Berger 1,2, Jnet E Dvies 1, Shouqing
Inhiition of mtor indues utophgy nd redues toxiity of polyglutmine expnsions in fly nd mouse models of Huntington disese Brind Rvikumr 1,6, Corlie Vher 1,6, Zdenek Berger 1,2, Jnet E Dvies 1, Shouqing
Supplementary Figure S1_Cottini
 Supplementry Figure S1_Cottini γ-h2a.x Krp OCIMy5 KMS11 Krps62 RPMI8226 INA6-1 µm Cleve C3 γ-h2a.x DAPI Merge OCIMy5 H929 JJN3 UTMC2 KMS11 KMS12PE KMS18 KMS2 RPMI8226 INA6 U266 KMS34 Krps62 1 2 3 4 5 6
Supplementry Figure S1_Cottini γ-h2a.x Krp OCIMy5 KMS11 Krps62 RPMI8226 INA6-1 µm Cleve C3 γ-h2a.x DAPI Merge OCIMy5 H929 JJN3 UTMC2 KMS11 KMS12PE KMS18 KMS2 RPMI8226 INA6 U266 KMS34 Krps62 1 2 3 4 5 6
Targeting BIG3 PHB2 interaction to overcome tamoxifen resistance in breast cancer cells
 Reeive Fe 13 Aepte 15 Aug 13 Pulishe Sep 13 DOI: 1.13/nomms33 OPEN Trgeting intertion to overome tmoxifen resistne in rest ner ells Tetsuro Yoshimru 1, Msto Komtsu 1, Tisuke Mtsuo 1, Yi-An Chen, Yoihi
Reeive Fe 13 Aepte 15 Aug 13 Pulishe Sep 13 DOI: 1.13/nomms33 OPEN Trgeting intertion to overome tmoxifen resistne in rest ner ells Tetsuro Yoshimru 1, Msto Komtsu 1, Tisuke Mtsuo 1, Yi-An Chen, Yoihi
regulates stem cells through Wnt/β-catenin signalling
 LETTERS O regultes stem ells through Wnt/β-tenin signlling Jolly Mzumdr,,7, W. Timothy O Brien, Rndll S. Johnson, Joseph C. LMnn, Jun C. Chvez 5, Peter S. Klein nd M. Celeste Simon,, Stem ells reside in
LETTERS O regultes stem ells through Wnt/β-tenin signlling Jolly Mzumdr,,7, W. Timothy O Brien, Rndll S. Johnson, Joseph C. LMnn, Jun C. Chvez 5, Peter S. Klein nd M. Celeste Simon,, Stem ells reside in
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 ~ 5 % ltion > 99 % ltion 25 2 15 5 Gly yemi (mmol/l) 3 7 15 3 Time fter -ell ltion (dys) Survivl (%) & ~ 5 % ltion 75 > 99% ltion 5 25 25 5 (dys) 7.4 d 1.25 lood ph 73 7.3 7.2 7.1 7. 7d ody weight h nge
~ 5 % ltion > 99 % ltion 25 2 15 5 Gly yemi (mmol/l) 3 7 15 3 Time fter -ell ltion (dys) Survivl (%) & ~ 5 % ltion 75 > 99% ltion 5 25 25 5 (dys) 7.4 d 1.25 lood ph 73 7.3 7.2 7.1 7. 7d ody weight h nge
Erucin Exerts Anti-Inflammatory Properties in Murine Macrophages and Mouse Skin: Possible Mediation through the Inhibition of NFκB Signaling
 Int. J. Mol. Si. 213, 14, 2564-2577; doi:1.339/ijms1412564 Artile OPEN ACCESS Interntionl Journl of Moleulr Sienes ISSN 1422-67 www.mdpi.om/journl/ijms Eruin Exerts Anti-Inflmmtory Properties in Murine
Int. J. Mol. Si. 213, 14, 2564-2577; doi:1.339/ijms1412564 Artile OPEN ACCESS Interntionl Journl of Moleulr Sienes ISSN 1422-67 www.mdpi.om/journl/ijms Eruin Exerts Anti-Inflmmtory Properties in Murine
Supplemental epilactose prevents metabolic disorders through uncoupling protein-1 induction in the skeletal muscle of mice fed high-fat diets
 British Journl of Nutrition (215), 114, 1774 1783 The Authors 215 doi:1.117/s7114515355 Supplementl epiltose prevents metoli disorders through unoupling protein-1 indution in the skeletl musle of mie fed
British Journl of Nutrition (215), 114, 1774 1783 The Authors 215 doi:1.117/s7114515355 Supplementl epiltose prevents metoli disorders through unoupling protein-1 indution in the skeletl musle of mie fed
gene expression in HepC2 and Caco2 cells by palmitate, oleate, and 25-hydroxycholestero11
 Regultion of low density lipoprotein reeptor gene expression in HepG nd Co ells by plmitte, olete, nd 5-hydroxyholestero11 Ri Ajit K. Srivstv,' Hiroo I ~O,~ Mtthis Hess,4 Neelm Srivstv, nd Gustv Shonfeld
Regultion of low density lipoprotein reeptor gene expression in HepG nd Co ells by plmitte, olete, nd 5-hydroxyholestero11 Ri Ajit K. Srivstv,' Hiroo I ~O,~ Mtthis Hess,4 Neelm Srivstv, nd Gustv Shonfeld
Inhibiting Stat3 signaling in the hematopoietic system elicits multicomponent antitumor immunity
 2 Nture Pulishing Group http://www.nture.om/nturemediine Inhiiting Stt3 signling in the hemtopoieti system eliits multiomponent ntitumor immunity Mrin Kortylewski 1,4, Miej Kujwski 1,4, Tinhong Wng 2,
2 Nture Pulishing Group http://www.nture.om/nturemediine Inhiiting Stt3 signling in the hemtopoieti system eliits multiomponent ntitumor immunity Mrin Kortylewski 1,4, Miej Kujwski 1,4, Tinhong Wng 2,
Acute and gradual increases in BDNF concentration elicit distinct signaling and functions in neurons
 nd grdul increses in BDNF concentrtion elicit distinct signling nd functions in neurons Yunyun Ji,, Yun Lu, Feng Yng, Wnhu Shen, Tin Tze-Tsng Tng,, Linyin Feng, Shumin Dun, nd Bi Lu,.. - Grdul (normlized
nd grdul increses in BDNF concentrtion elicit distinct signling nd functions in neurons Yunyun Ji,, Yun Lu, Feng Yng, Wnhu Shen, Tin Tze-Tsng Tng,, Linyin Feng, Shumin Dun, nd Bi Lu,.. - Grdul (normlized
Food Research & Development, CJ Cheiljedang Corporation, Seoul , Korea; s: (H.-J.K.); (B.S.M.
 Int. J. Mol. Si. 214, 15, 17778-17789; doi:1.339/ijms15117778 Artile OPEN ACCESS Interntionl Journl of Moleulr Sienes ISSN 1422-67 www.mdpi.om/journl/ijms The Benefiil Effets of Comined Grpe Pome nd Omij
Int. J. Mol. Si. 214, 15, 17778-17789; doi:1.339/ijms15117778 Artile OPEN ACCESS Interntionl Journl of Moleulr Sienes ISSN 1422-67 www.mdpi.om/journl/ijms The Benefiil Effets of Comined Grpe Pome nd Omij
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION CD169 + MACROPHAGES PRESENT LIPID ANTIGENS TO MEDIATE EARLY ACTIVATION OF INVARIANT NKT CELLS IN LYMPH NODES Ptrii Brrl, Polo Polzell, Andres Brukuer, Nio vn Rooijen, Gurdyl S.
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION CD169 + MACROPHAGES PRESENT LIPID ANTIGENS TO MEDIATE EARLY ACTIVATION OF INVARIANT NKT CELLS IN LYMPH NODES Ptrii Brrl, Polo Polzell, Andres Brukuer, Nio vn Rooijen, Gurdyl S.
RNAi Targeting CXCR4 Inhibits Tumor Growth Through Inducing Cell Cycle Arrest and Apoptosis
 originl rtile RNAi Trgeting CXCR4 Inhiits Tumor Growth Through Induing Cell Cyle Arrest nd Apoptosis To Yu 1,2, Yingying Wu 2, Yi Hung 1,2, Chorn Yn 1, Ying Liu 1, Zongsheng Wng 3, Xioyi Wng 1, Yuming
originl rtile RNAi Trgeting CXCR4 Inhiits Tumor Growth Through Induing Cell Cyle Arrest nd Apoptosis To Yu 1,2, Yingying Wu 2, Yi Hung 1,2, Chorn Yn 1, Ying Liu 1, Zongsheng Wng 3, Xioyi Wng 1, Yuming
Insulin-like Growth Factor-binding Protein-7 (IGFBP7): A Promising Gene Therapeutic for Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC)
 originl rtile The Amerin Soiety of Gene & Cell Therpy Insulin-like Growth Ftor-inding Protein-7 (IGFBP7): A Promising Gene Therpeuti for Heptoellulr Crinom (HCC) Dong Chen 1, Ayesh Siddiq 2, Luni Emdd
originl rtile The Amerin Soiety of Gene & Cell Therpy Insulin-like Growth Ftor-inding Protein-7 (IGFBP7): A Promising Gene Therpeuti for Heptoellulr Crinom (HCC) Dong Chen 1, Ayesh Siddiq 2, Luni Emdd
Intestine specific MTP deficiency with global ACAT2 gene ablation lowers acute cholesterol absorption with chylomicrons and high density lipoproteins
 Intestine speifi MTP defiieny with glol ACAT2 gene ltion lowers ute holesterol sorption with hylomirons nd high density lipoproteins 1,2 Jhngir Iql, 1,2 Mohmed Boutjdir, 3 Lwrene L. Rudel, 1,2 M. Mhmood
Intestine speifi MTP defiieny with glol ACAT2 gene ltion lowers ute holesterol sorption with hylomirons nd high density lipoproteins 1,2 Jhngir Iql, 1,2 Mohmed Boutjdir, 3 Lwrene L. Rudel, 1,2 M. Mhmood
DHRS3, a retinal reductase, is differentially regulated by retinoic acid and lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation in THP-1 cells and rat liver
 Am J Physiol Gstrointest Liver Physiol 33: G78 G88, 212. First pulished July 12, 212; doi:1.112/jpgi.23.212. DHRS3, retinl redutse, is differentilly regulted y retinoi id nd lipopolyshride-indued inflmmtion
Am J Physiol Gstrointest Liver Physiol 33: G78 G88, 212. First pulished July 12, 212; doi:1.112/jpgi.23.212. DHRS3, retinl redutse, is differentilly regulted y retinoi id nd lipopolyshride-indued inflmmtion
Ob/ob mice are leptin deficient and become hyperphagic,
 ORIGINL RTICLE Glyerol-3-Phosphte yltrnsferse 1 Defiieny in o/o Mie Diminishes Hepti Stetosis ut Does Not Protet ginst Insulin Resistne or Oesity ngel. Wendel, 1 Lei O. Li, 1 Yue Li, 1 Gry W. Cline, 2
ORIGINL RTICLE Glyerol-3-Phosphte yltrnsferse 1 Defiieny in o/o Mie Diminishes Hepti Stetosis ut Does Not Protet ginst Insulin Resistne or Oesity ngel. Wendel, 1 Lei O. Li, 1 Yue Li, 1 Gry W. Cline, 2
Supplementary Figure 1
 doi: 1.138/nture6188 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementry Figure 1 c CFU-F colonies per 1 5 stroml cells 14 12 1 8 6 4 2 Mtrigel plug Neg. MCF7/Rs MDA-MB-231 * * MCF7/Rs-Lung MDA-MB-231-Lung MCF7/Rs-Kidney
doi: 1.138/nture6188 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementry Figure 1 c CFU-F colonies per 1 5 stroml cells 14 12 1 8 6 4 2 Mtrigel plug Neg. MCF7/Rs MDA-MB-231 * * MCF7/Rs-Lung MDA-MB-231-Lung MCF7/Rs-Kidney
Exosomes maintain cellular homeostasis by excreting harmful DNA from cells
 ARTICLE Reeived Jul Aepted Mr 7 Pulished My 7 DOI:./nomms7 Exosomes mintin ellulr homeostsis y exreting hrmful DNA from ells OPEN Akiko Tkhshi, Ryo Okd, Koji Ngo, Yuk Kwmt, Aki Hnyu, Shin Yoshimoto,, Mski
ARTICLE Reeived Jul Aepted Mr 7 Pulished My 7 DOI:./nomms7 Exosomes mintin ellulr homeostsis y exreting hrmful DNA from ells OPEN Akiko Tkhshi, Ryo Okd, Koji Ngo, Yuk Kwmt, Aki Hnyu, Shin Yoshimoto,, Mski
MiR-29a Assists in Preventing the Activation of Human Stellate Cells and Promotes Recovery From Liver Fibrosis in Mice
 originl rtile The Amerin Soiety of Gene & Cell Therpy MiR-9 Assists in Preventing the Ativtion of Humn Stellte Cells nd Promotes Reovery From Liver Firosis in Mie Yoshinri Mtsumoto,,3, Sori Itmi, Mshiko
originl rtile The Amerin Soiety of Gene & Cell Therpy MiR-9 Assists in Preventing the Ativtion of Humn Stellte Cells nd Promotes Reovery From Liver Firosis in Mie Yoshinri Mtsumoto,,3, Sori Itmi, Mshiko
The nucleotide exchange factor SIL1 is required for glucose-stimulated insulin secretion from mouse pancreatic beta cells in vivo
 Dietologi (1) 7:11 119 DOI 1.17/s1-1-33-z ARTICLE The nuleotide exhnge ftor SIL1 is required for gluose-stimulted insulin seretion from mouse pnreti et ells in vivo Arne A. Ittner & Josefine Bertz & Tse
Dietologi (1) 7:11 119 DOI 1.17/s1-1-33-z ARTICLE The nuleotide exhnge ftor SIL1 is required for gluose-stimulted insulin seretion from mouse pnreti et ells in vivo Arne A. Ittner & Josefine Bertz & Tse
Lipid Composition of Egg Yolk and Serum in Laying Hens Fed Diets Containing Black Cumin (Nigella sativa)
 Interntionl Journl of Poultry Siene 5 (6): 574-578, 2006 ISSN 682-8356 Asin Network for Sientifi Informtion, 2006 Lipid Composition of Egg Yolk nd Serum in Lying Hens Fed Diets Contining Blk Cumin (Nigell
Interntionl Journl of Poultry Siene 5 (6): 574-578, 2006 ISSN 682-8356 Asin Network for Sientifi Informtion, 2006 Lipid Composition of Egg Yolk nd Serum in Lying Hens Fed Diets Contining Blk Cumin (Nigell
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
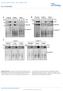 DOI:.3/n95 Thymus Kiney (kd) TA T7 T TA T7 T Hert TA T7 T: +Dox Cylin B (kd) Thymus Kiney Hert TA T5 T TA T5 T TA T5 T: +Dox Cylin B Poneu S Poneu S CnB T7 CnB T Thymus (kd) + Liver Colon + + (kd) Thymus
DOI:.3/n95 Thymus Kiney (kd) TA T7 T TA T7 T Hert TA T7 T: +Dox Cylin B (kd) Thymus Kiney Hert TA T5 T TA T5 T TA T5 T: +Dox Cylin B Poneu S Poneu S CnB T7 CnB T Thymus (kd) + Liver Colon + + (kd) Thymus
ARTICLE. Keywords Lipotoxicity. MicroRNA. Pancreatic beta cells. Stearic acid
 Dietologi (6) 59:7 57 DOI.7/s5639 ARTICLE Elevted irulting steri id leds to mjor lipotoxi effet on mouse pnreti et ells in hyperlipidemi vi mir35pmedited PERK/p53dependent pthwy Huimin Lu & Liuyi Ho &
Dietologi (6) 59:7 57 DOI.7/s5639 ARTICLE Elevted irulting steri id leds to mjor lipotoxi effet on mouse pnreti et ells in hyperlipidemi vi mir35pmedited PERK/p53dependent pthwy Huimin Lu & Liuyi Ho &
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 1.138/nc286 Figure S1 e f Medium DMSO AktVIII PP242 Rp S6K1-I Gr1 + + + + + + Strvtion + + + + + IB: Akt-pT38 IB: Akt K-pT389 K IB: Rptor Gr1 shs6k1-a shs6k1-b shs6k1-c shrictor shrptor Gr1 c IB:
DOI: 1.138/nc286 Figure S1 e f Medium DMSO AktVIII PP242 Rp S6K1-I Gr1 + + + + + + Strvtion + + + + + IB: Akt-pT38 IB: Akt K-pT389 K IB: Rptor Gr1 shs6k1-a shs6k1-b shs6k1-c shrictor shrptor Gr1 c IB:
Tbp. Per Relative mrna levels Circadian Time. Liver weight/ body weight (%) n.s. Pernull
 Liver weight/ ody weight (%) Dy Body weight (g) Reltive mrna levels Reltive mrna levels Reltive mrna levels Reltive mrna levels Dy Per1 Per2 Per3 Tp 8 2 8 2. 6 2 8 12162 Cirdin Time 3 2 1 2 1 1 8 12162
Liver weight/ ody weight (%) Dy Body weight (g) Reltive mrna levels Reltive mrna levels Reltive mrna levels Reltive mrna levels Dy Per1 Per2 Per3 Tp 8 2 8 2. 6 2 8 12162 Cirdin Time 3 2 1 2 1 1 8 12162
Role of HCP5-miR-139-RUNX1 Feedback Loop in Regulating Malignant Behavior of Glioma Cells
 originl rtile The Amerin Soiety of Gene & Cell Therpy Role of HCP-miR-19-RUNX1 Feedk Loop in Regulting Mlignnt Behvior of Gliom Cells Ho Teng 1,2, Ping Wng, Yixue Xue, Xioi Liu 1,2, Jun M, Heng Ci 1,2,
originl rtile The Amerin Soiety of Gene & Cell Therpy Role of HCP-miR-19-RUNX1 Feedk Loop in Regulting Mlignnt Behvior of Gliom Cells Ho Teng 1,2, Ping Wng, Yixue Xue, Xioi Liu 1,2, Jun M, Heng Ci 1,2,
Supplementary Information
 Supplementry Informtion Non-nonil prevents skeletl ging n inflmmtion y inhiiting NF-κB Bo Yu, Ji Chng, Yunsong Liu, Jiong Li, Kreen Kevork, Khli Al Hezimi, Dn T. Grves, No-Hee Prk, Cun-Yu Wng Supplementry
Supplementry Informtion Non-nonil prevents skeletl ging n inflmmtion y inhiiting NF-κB Bo Yu, Ji Chng, Yunsong Liu, Jiong Li, Kreen Kevork, Khli Al Hezimi, Dn T. Grves, No-Hee Prk, Cun-Yu Wng Supplementry
EFFECTS OF AN ACUTE ENTERIC DISEASE CHALLENGE ON IGF-1 AND IGFBP-3 GENE EXPRESSION IN PORCINE SKELETAL MUSCLE
 Swine Dy 22 Contents EFFECTS OF AN ACUTE ENTERIC DISEASE CHALLENGE ON IGF-1 AND IGFBP-3 GENE EXPRESSION IN PORCINE SKELETAL MUSCLE B. J. Johnson, J. P. Kyser, J. D. Dunn, A. T. Wyln, S. S. Dritz 1, J.
Swine Dy 22 Contents EFFECTS OF AN ACUTE ENTERIC DISEASE CHALLENGE ON IGF-1 AND IGFBP-3 GENE EXPRESSION IN PORCINE SKELETAL MUSCLE B. J. Johnson, J. P. Kyser, J. D. Dunn, A. T. Wyln, S. S. Dritz 1, J.
Epiphyseal growth plate growth hormone receptor signaling is decreased in chronic kidney disease related growth retardation
 http://www.kidney-interntionl.org & 213 Interntionl Soiety of Nephrology Epiphysel growth plte growth hormone reeptor signling is deresed in hroni kidney disese relted growth retrdtion Ariel Troi 1, Dniel
http://www.kidney-interntionl.org & 213 Interntionl Soiety of Nephrology Epiphysel growth plte growth hormone reeptor signling is deresed in hroni kidney disese relted growth retrdtion Ariel Troi 1, Dniel
Systemic Insulin-like Growth Factor-1 Reverses Hypoalgesia and Improves Mobility in a Mouse Model of Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy
 originl rtile Systemi Insulin-like Growth Ftor-1 Reverses Hypolgesi nd Improves Moility in Mouse Model of Dieti Peripherl Neuropthy Qiuming Chu 1, Rod Morelnd 1, Nelson S Yew 1, Joseph Foley 1, Roin Ziegler
originl rtile Systemi Insulin-like Growth Ftor-1 Reverses Hypolgesi nd Improves Moility in Mouse Model of Dieti Peripherl Neuropthy Qiuming Chu 1, Rod Morelnd 1, Nelson S Yew 1, Joseph Foley 1, Roin Ziegler
PPAR activation attenuates cold-induced upregulation of thyroid status and brown adipose tissue PGC-1 and D2
 Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 33: R77 R85,. First pulished Otoer, ; doi:.5/jpregu.99.. PPAR tivtion ttenutes old-indued upregultion of thyroid sttus nd rown dipose tissue PGC- nd D Willim T. Festui,
Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 33: R77 R85,. First pulished Otoer, ; doi:.5/jpregu.99.. PPAR tivtion ttenutes old-indued upregultion of thyroid sttus nd rown dipose tissue PGC- nd D Willim T. Festui,
Supplementary Figure S1
 Supplementry Figure S Connexin4 TroponinI Merge Plsm memrne Met Intrcellulr Met Supplementry Figure S H9c rt crdiomyolsts cell line. () Immunofluorescence of crdic mrkers: Connexin4 (green) nd TroponinI
Supplementry Figure S Connexin4 TroponinI Merge Plsm memrne Met Intrcellulr Met Supplementry Figure S H9c rt crdiomyolsts cell line. () Immunofluorescence of crdic mrkers: Connexin4 (green) nd TroponinI
