Maintenance of protein synthesis reading frame by EF-P and m 1 G37-tRNA
|
|
|
- Joella Hines
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Reeived 23 Nov 214 Aepted 2 Apr 215 Pulished 26 My 215 DOI: 1.138/nomms8226 Mintenne of protein synthesis reding frme y EF-P nd m 1 G37-tRNA Howrd B. Gmper 1, *, Iso Msud 1, *, Miln Frenkel-Morgenstern 2 & Y-Ming Hou 1 Mintining the trnsltionl reding frme poses diffiulty for the riosome. Slippery mrna sequenes suh s CC[C/U]-[C/U], red y isoeptors of trna Pro, re highly prone to þ 1 frmeshift ( þ 1FS) errors. Here we show tht þ 1FS errors our y two mehnisms, slow mehnism when trna Pro is stlled in the P-site next to n empty A-site nd fst mehnism during trnslotion of trna Pro into the P-site. Suppression of þ 1FS errors requires the m 1 G37 methyltion of trna Pro on the 3 side of the ntiodon nd the trnsltion ftor EF-P. Importntly, oth m 1 G37 nd EF-P show the strongest suppression effet when CC[C/U]-[C/U] re pled t the seond odon of reding frme. This work demonstrtes tht mintining the reding frme immeditely fter the initition of trnsltion y the riosome is n essentil spet of protein synthesis. 1 Deprtment of Biohemistry nd Moleulr Biology, Thoms Jefferson University, 233 South 1th Street, Phildelphi, Pennsylvni 1917, USA. 2 Fulty of Mediine, Br-Iln University, Henriett Szold 8, Sfed , Isrel. * These uthors ontriuted eqully to this work. Correspondene nd requests for mterils should e ddressed to Y.-M.H. (emil: y-ming.hou@jefferson.edu). NATURE COMMUNICATIONS 6:7226 DOI: 1.138/nomms
2 NATURE COMMUNICATIONS DOI: 1.138/nomms8226 Mintenne of the trnsltionl reding frme is n importnt open question in iology. Loss of the reding frme due to spontneous þ 1 frmeshift ( þ 1FS) errors is deleterious, resulting in premture termintion of gene expression. However, despite the dynmi movement of suessive trna moleules nd ssoited mrna from the A-site to the P-site nd to the E-site, eh riosome mnges to sty in the orret reding frme (-frme) through hundreds of odons. At rpid rte of inorporting 1 2 mino ids per seond into the nsent hin, n E. oli riosome mkes less thn one þ 1FS error per 3, mino ids 1, frequeny t lest tenfold lower reltive to other types of trnsltion errors. How is the reding frme mintined so fithfully? Although erly geneti work suggested model of trna shifting y qudruplet se piring, susequent isoltion of non-trna suppressors invlidted this model 2,3. More reent work fvoured model of trna slippge from stlled P-site 2,3, lthough the mehnism tht drives the slippge remins unknown. Here we provide moleulr-level insights into the speed, frequeny nd timing of þ 1-frmeshifting nd the ellulr ftors tht suppress suh errors. Protein synthesis in teri egins with the ssemly of the lrge nd smll riosoml suunits (5S nd 3S) into 7S initition omplex (7SIC) tht ples the inititor fmettrna fmet t the AUG strt odon t the P-site. Upon ommodtion of the in-frme minoyl-trna t the A-site, the 7SIC synthesizes the first peptide ond nd moves the newly synthesized peptidyl-trna from the A- to the P-site in the first round of trnslotion to enter into the elongtion phse. Mintining the reding frme during elongtion is most hllenging for the riosome t slippery mrna sequenes. Sequenes suh s CC[C/U]-[C/U] re prtiulrly slippery 4, euse the odon ntiodon intertion with the ognte GGG isoeptor trna Pro, for exmple, is identil in the - nd þ 1-frme, inditing minimum energeti penlty for the trna to shift to the þ 1-frme. Among totl E. oli sense odons, CC[C/U]-[C/U] our B2,3 times, the mjority of whih re within the first 1 odons of protein-oding genes (Supplementry Tle 1). Some of these sequenes re diretly djent to the strt odon, wheres others re within short distne from the strt (Supplementry Fig. 1,). Notly, the CC[C/U]-[C/U] sequenes re red y the GGG nd UGG isoeptors of trna Pro, oth of whih hve on the 3 side of the ntiodon n m 1 G37, where the N 1 of the G37 se is methylted. Although m 1 G37 is known to suppress þ 1FS errors 5, the mehnism is unresolved, euse the methyltion does not interfere with the ntiodon odon se piring intertion. Between the two isoeptors of trna Pro, the UGG isoeptor is of high interest, euse it is essentil for ell growth 6 nd it is ple of reding ll Pro odons, inluding the CC[C/U]-[C/U], through the use of n dditionl modifition mo 5 t the wole se U34. The ritil rrier to understnding the mehnism of produing nd suppressing þ 1FS errors is the lk of quntittive ssys to monitor errors. We thus developed quntittive ssys to mesure intrellulr trnsltion of lz ontining the CCC-C sequene s n exmple of the slippery motif. We found tht erly rounds of peptide synthesis re more prone to þ 1FS errors thn lter rounds, with trnsltion t the seond odon eing the most shift-prone. We then developed kineti ssys to mesure the formtion of þ 1FS errors in vitro, with view towrds eluidting the riosome retion steps tht re shift-prone. We identified two shift-prone mehnisms: slow mehnism during trna Pro stlling t the P-site next to n empty A-site nd fst mehnism during trna Pro trnslotion into the P-site. Although the slow mehnism ws implited y geneti studies 2,7 9 nd is relevnt in nutrient strvtion, the fst mehnism is thret to ells in the norml growth ondition. We found tht, mong nturl post-trnsriptionl modifitions in trna Pro,m 1 G37 is the mjor determinnt to suppress þ 1FS errors; however, lthough it is dominnt in UGG trna Pro,it requires the ssistne of the trnsltion ftor EF-P to suppress errors of GGG trna Pro. This ltter finding expnds the iologil sope of EF-P, est known for relieving riosomes from stlling t poly-pro sequenes 1,11. The tion of oth m 1 G37 nd EF-P is strongest when CC[C/U]-[C/U] our t the seond odon, emphsizing the importne of sfegurding the riosome for the first round of protein synthesis efore it moves downstrem. Together, this work highlights the prevlent nd dynmi nture of trna shifting nd the importne of m 1 G37 nd EF-P to suppress shifts. Results The seond odon is prone to þ 1FS errors in vivo. To determine whether the plement of CCC-C reltive to the strt odon ffets the propensity of þ 1FS errors inside E. oli ells, we reted severl onstruts of the reporter lz, eh with only one CCC-C in the entire reding frme. In the ORF2 onstrut, the CCC-C ws inserted to the seond odon, wheres in the ORF5, ORF1, ORF2, ORF6 nd ORF124 onstruts, it ws inserted to odon 5, 1, 2, 6 nd 124, respetively (Fig. 1). In eh onstrut, the CCC triplet ws followed y modertely undnt odon; for exmple, the CCC t position 124 ws followed y the odon CAC nturlly present in lz. With eh insertion, restortion of the reding frme nd synthesis of n tive -gltosidse (-gl) required þ 1FS event t the insertion site. We defined the frequeny of the þ 1FS event y mesuring the -gl tivity produed from ells expressing the CCC-C onstrut reltive to ells expressing n in-frme insertion of CCC. To test how the þ 1FS event is influened y odon ontext, we reted two dditionl onstruts ORF124CGG nd ORF124UGG, where the CCC t position 124 ws followed in the -frme y rre odons CGG nd UGG, respetively. To evlute the role of m 1 G37 in suppressing the þ 1FS event, we reted n E. oli trmd-ko (knokout) strin, where the trmd gene for the enzymti synthesis of m 1 G37 ws disrupted, nd euse of the growth-essentility of the gene 12 we mintined ell viility y expressing the humn ounterprt trm5 gene 13 from n rinose promoter. Upon removl of rinose, the trmd-ko strin lost the ility to synthesize m 1 G37, lthough the pre-existing m 1 G37 kept ells live for 5 6 h. During this time window, the þ 1FS frequeny ws mesured in ells without synthesis of m 1 G37 reltive to ells with synthesis. Trnsltion of the CCC-C involved oth GGG nd UGG trna Pro, so the þ 1FS frequeny refleted the effet of oth. Unexpetedly, even when m 1 G37 synthesis ws tive, the þ 1FS frequeny ws lredy twofold higher t the seond odon reltive to lter odons in onstruts where the CCC-C ws followed y modertely undnt odon (Fig. 1 nd Supplementry Tle 2). When m 1 G37 synthesis ws intivted, the þ 1FS frequeny inresed drmtilly y eightfold for ORF2 ut only y two- to fourfold for other onstruts, inditing speifi role of m 1 G37 in suppressing þ 1FS errors t the seond odon. For onstruts where the CCC-C ws followed y rre odon, the sl level of þ 1FS errors ws higher reltive to n undnt odon nd error suppression y m 1 G37 ws dependent on the nture of the odon: intivtion of m 1 G37 synthesis inresed errors y 1.5-fold for ORF124CGG ut y 4-fold for ORF124UGG. Thus, regrdless of where the CCC-C ppers reltive to the strt odon, m 1 G37 is importnt for suppressing þ 1FS errors, lthough its strongest effet ws t the seond odon. 2 NATURE COMMUNICATIONS 6:7226 DOI: 1.138/nomms8226
3 NATURE COMMUNICATIONS DOI: 1.138/nomms8226 ARTICLE IZ ORF , AUGCCCCACCAUCAU ACGUCGUGA CAAAAAUAA - 3 () M P H H H T S * (+1) T I I H K * ,32 IZ 5 - AUGACC GUUCCCCACCGA CACAUUUAA CAAAAAUAA - 3 ORF124 () M T V P H R H I * (+1) T E H K * d +1FS (%) +1FS (%) +1FS (%) ORF ORF ORF 8.x CGG 3.x x x 1.6x 4.6x WT K34A 2.4x 1.7x e efp + efp 4.4x 1.9x m 1 G37+ m 1 G CGG trmd wt ts wt ts 2.5x EF-P+ EF-P- 124 UGG 124 UGG 3 C 44 C (Permissive) (Non-permissive) x 1.3x 1.3x x 2.4x 4.x 3.6x Figure 1 Suppression of ellulr þ 1FS errors y m 1 G37 nd EF-P. () Suppression of þ 1FS errors ws monitored using lz reporter genes ontining the CCC-C frmeshift site (in red) djent to the AUG strt odon or further downstrem. Exmples re shown for the Open Reding Frme (ORF) 2 onstrut with the CCC-C t the 2nd odon position nd the ORF124 onstrut with the CCC-C t the 124th odon position. Norml trnsltion t eh CCC-C site would result in premture termintion of -gl synthesis (indited y the symol *) unless þ 1FS event ourred with trna Pro. The þ 1FS frequeny is expressed s the rtio of -gl of the þ 1-frme reporter with the CCC-C sequene over the in-frme reporter with the CCC sequene. () Mesurement of þ 1FS frequeny of eh reporter in n E. oli trmd-ko strin with nd without the synthesis of m 1 G37. This trmd-ko strin ws mintined vile y expressing the humn ounterprt trm5 on n rinose-ontrolled expression plsmid. The m 1 G37 þ ondition ws hieved with.2% (w/v) rinose, wheres the m 1 G37- ondition ws hieved without rinose. () Mesurement of þ 1FS frequeny of eh reporter onstrut in n isogeni pir of E. oli efp þ versus efp strins. (d) Mesurement of þ 1FS frequeny of ORF2 nd ORF1 in the E. oli efp strin omplemented y WT or K34A mutnt of EF-P o-expressed with yjea nd yjek. In d, eh þ 1FS frequeny is the verge of t lest three independent mesurements, with the errors showing s.d. (stndrd devition). The vlue of fold-inrese in þ 1FS frequeny is shown for eh onstrut. (e) Syntheti lethlity of trmd nd efp. S. typhimurium strins rrying efp þ or efp nd/or temperture-sensitive (ts) llele of trmd 17 were grown t 3 or 44 C, the permissive or the non-permissive temperture, respetively. Trnsltion of the seond odon requires stle positioning of the inititor fmet-trna fmet, whih in teri is enfored y EF-P, the trnsltion ftor tht stimultes the first peptide ond formtion 1. Beuse elimintion of EF-P in teri does not use ell deth, we ompred n E. oli efp strin with the isogeni efp þ strin to determine its role in reding-frme mintenne (Fig. 1 nd Supplementry Tle 2). In efp þ ells, the þ 1FS frequeny in our lz ssy ws the highest when the CCC-C ws pled t the seond odon, ut it grdully deresed s the CCC-C moved downstrem. In efp ells, the þ 1FS frequeny inresed most drmtilly t the seond odon, ut only modertely t lter odons. When the þ 1FS frequeny ws elevted due to the plement of CCC efore rre odon, the removl of EF-P further inresed errors t oth ORF124CGG nd ORF124UGG. Notly, E. oli EF-P ontins K34 tht is hydroxylted nd -lysylted This modified K34 ws importnt for the shift-suppression tivity; the þ 1FS frequeny rose y 3.8-fold t the seond odon nd y 4.6-fold t the tenth odon in ells expressing the K34A mutnt of EF-P (Fig. 1d nd Supplementry Tle 2). Colletively, these dt reveled previously unreognized role of EF-P in suppressing þ 1FS errors, showing tht it hs the strongest error-suppression effet t the seond odon. In m 1 G37 þ or EF-P þ ells, the þ 1FS frequeny of.4 1.% when the CCC-C ws pled t the seond odon ws high reltive to the verge frequeny of.3% in teri 1. This points to the propensity of the riosome to þ 1-frmeshifting t the seond odon nd it my explin why E. oli hs only four genes with CCC-C t the seond odon, inluding one growthessentil gene lolb (for loliztion of lipoproteins to outermemrne) nd three non-essentil genes pna (niotinmide demidse, Supplementry Fig. 1), ygp (for nti-termintor regultion) nd ptra (for zin metlloprotese). Our result suggests tht trnsltion of eh of these genes requires oth m 1 G37 nd EF-P to minimize þ 1FS errors. This is supported y nlysis of the protein produt of pna, showing tht the enzyme tivity in ell lystes ws redued y 2.5-fold upon elimintion of m 1 G37 nd y 2.3-fold upon elimintion of EF-P. A similr redution upon intivtion of m 1 G37 synthesis ws lso oserved in trmd TS (temperture sensitive) 17 strin (Supplementry Fig. 1). The importne of oth m 1 G37 nd EF-P for reding frme mintenne is further emphsized y the syntheti lethlity of doule mutnt hrouring the trmd TS nd efp lleles (Fig. 1e). The high þ 1FS frequeny upon intivtion of m 1 G37 (t 8.3%) my thus indite threshold for ell survivl. Kineti nlysis of þ 1FS errors. To determine the kinetis of þ 1-frmeshifting nd its speed reltive to peptide ond formtion, we developed ssys for monitoring shift errors using purified riosoml omponents. Both GGG nd UGG trna Pro were exmined in three sttes: (i) the trnsript, lking ny post-trnsriptionl modifitions, (ii) the m 1 trnsript, ontining only the TrmD-introdued modifition nd (iii) the ntive-stte isolted from ells ontining ll nturl modifitions (Supplementry Fig. 2). Stoihiometri levels of m 1 G37 in the m 1 G37- nd ntive-stte of oth trnas were onfirmed y RNse T1 nlysis (Supplementry Fig. 3). Two dditionl sttes of UGG trna Pro were lso exmined: (iv) the nd (v) the ho 5 U34-stte (the preursor of the mo 5 U34 stte) 18 in n otherwise ntive trna. These two sttes were isolted from E. oli ells defiient in the synthesis of m 1 G37 nd in the onversion of ho 5 U34 to mo 5 U34, respetively. To study the high propensity of þ 1FS errors t the seond odon, we progrmmed n E. oli 7SIC with n mrna strting NATURE COMMUNICATIONS 6:7226 DOI: 1.138/nomms
4 NATURE COMMUNICATIONS DOI: 1.138/nomms8226 with the sequene AUG-CCC-CGU-U, where the CCC-C ws pled t the seond odon. Using GGG trna Pro s n exmple, the post-trnslotion omplex fter one round of peptide ond formtion ontined deylted trna fmet in the E-site, fmet-pro (fmp)-trna Pro in the P-site nd n empty A-site (Fig. 2). Piring of trna Pro/GGG in the -frme would position the Arg CGU odon in the A-site, wheres piring in the þ d F (fmp fmpv, fmpr) P site deoding In-frme triplet +1 frme triplet 7SIC + EF-G Pro/GGG 1 Post M P m 1 G 5 UAC GGG AUG CCC CGU M P m 1 G 5 UAC GGG AUG CCCC GUU Arg + Vl fmpr () 27 s R 3 V 3 5 GC I + EF-Tu + GTP 5 CAU* + EF-Tu + GTP 37 C k os = (7. ± 1.) 1 3 s 1 fmp Pre M PR 3 3' m 1 G 5 5 GGG GC I AUG CCC CGU M PV 3 3 m 1 G 5 5 GGG CAU* AUG CCCC GUU Tripeptide produt fmpr fmpv fm Puse time (s) fmpr () M Origin fmp Figure 2 Assys for þ 1FS errors of GGG trna Pro t the seond odon. () Digrm of two possile piring sttes of fmp-trna Pro/GGG t the P-site of stlled post-trnslotion omplex nd the orresponding pretrnslotion omplexes fter one round of peptide ond formtion on n E. oli 7SIC progrmmed with the mrna AUG-CCC-CGU-U. Eh trna is shown in the L shpe with the ntiodon speified. The letter I in the ntiodon of trna Arg denotes inosine nd the letter U* in the ntiodon of trna Vl denotes mo 5 U; oth re ple of piring with U. While in-frme triplet piring of trna Pro in the P-site would diret formtion of fmpr, þ 1-frme piring would diret formtion of fmpv. Oupny of the E site y the deylted trna fmet is proly short-lived. () An fmp-posttrnslotion omplex ws formed vi rpid mixing of 7SIC with the ternry omplex of trna Pro/GGG in the presene of EF-G. Over time ourse to llow trna Pro/GGG to shift into the þ 1-frme, liquots were mixed with ternry omplexes of trna Arg (Arg) nd trna Vl (Vl) to support tripeptide synthesis, followed y quenhing with. () Eletrophoreti TLC of quenhed retions, showing onversion of fmp to fmpr (the -frme produt) nd fmpv (the þ 1-frme produt). Remining sustrtes fm nd M re indited. (d) Plots of the frtionl onversion of fmp to fmpr nd to fmpv over time. The F in the y xis is the frtionl synthesis of fmpr or fmpv from totl fmp moleules, inluding retive nd non-retive fmp moleules. Plese note tht dt here were olleted t 37 C, wheres dt in the rest of the experiments in this work were olleted t room temperture (2 C). At equilirium t 37 C, the perentge of the trna Pro in the þ 1-frme ws 67%, wheres t 2 C it ws 26% (Fig. 4). This effet indites tht trna slippge is fvored y higher temperture. Error rnge of urve fitting is denoted for fmpv formtion. 1-frme would position the Vl GUU odon in the A-site. By inuting the stlled omplex over time to llow trna Pro/GGG to shift into the þ 1-frme, we determined the stte of shifting y simultneously dding ternry omplexes (TCs) of trna Arg nd trna Vl to llow for seond round of peptide ond formtion (Fig. 2). The -frme piring of trna Pro/GGG would generte fmet-pro-arg (fmpr), wheres the þ 1-frme piring would generte fmet-pro-vl (fmpv). Anlysis of the two produts y eletrophoreti thin-lyer hromtogrphy (TLC; Fig. 2) showed slow ut stedy inrese of the þ 1-frme produt fmpv nd onomitnt redution of the -frme produt fmpr (Fig. 2d). This result, together with toeprint nlysis (Supplementry Fig. 3), supports time-dependent shift of trna Pro/GGG into the þ 1-frme. Although the rte of synthesis of the þ 1-frme produt fmpv ws slow ( s 1 ), it ws still B1-fold fster reltive to mis-inorportion of Vl due to trna Vl mispiring t the Arg CGU odon or out-of-frme piring t the Vl GUU odon 19 (Supplementry Fig. 4). Thus, the synthesis of fmpv from fmp ws ttriuted to the peptide ond formtion fter trna Pro/GGG shifted into the þ 1-frme, rther thn the mis-oding y trna Vl. Additionl dt vlidted the iologil relevne of these kineti ssys. First, C31A muttion in the trna Pro/GGG elevted the mplitude of the shift to 5% (Supplementry Fig. 5), onsistent with geneti study 2 showing tht disrupting the se pir of trna Pro inresed þ 1FS errors. Seond, the þ 1-shift of trna Pro/GGG in stlled post-omplex lso ourred with other mrnas, suh s the AUG-CCC-CUU sequene (Supplementry Fig. 6). Third, these ssys reveled speifi shifting fetures of eh trna Pro. For GGG trna Pro, the se identity following the CCC triplet ws strong determinnt of the shift, wheres for UGG trna Pro, its propensity of shifting ws independent of the se identity following the CCC triplet (Supplementry Fig. 7). Riosome tive for tlyzing peptidyl trnsfer on þ 1-frme. We found tht with the trna Pro/GGG, despite its shift to the þ 1-frme, the riosome ws fully tive for the next peptide ond formtion. Speifilly, fter the shift rehed equilirium, ddition of TCs of oth trna Arg nd trna Vl showed fster synthesis of the þ 1-frme fmpv produt reltive to the -frme fmpr produt (Fig. 3,), inditing tht peptidyl trnsfer ws not pertured y the shift. In ddition, the peptide on the shifted trna ws not removed y the riosome or relese ftors (Supplementry Fig. 8), inditing tht þ 1FS errors were not sujet to the riosome post-peptidyl-trnsfer qulity ontrol tht removes mis-inorportion errors 21. The fster synthesis of fmpv my reflet more fvourle event for peptidyl trnsfer to Vl 22 nd/or for the se-piring ontext of the odon ntiodon intertion. Importntly, the fster synthesis of fmpv ws lso oserved with the m 1 G37- or the ntive-stte of the trna (Fig. 3), inditing tht it ws independent of the stte of trna modifition. Insted, the mplitude of the shift deresed from 23% with the to 11% nd 9% with the m 1 G37- nd ntive-stte, respetively. Beuse the m 1 G37- nd the ntive-stte exhiited virtully identil error redution, the single m 1 G37 modifition is the mjor determinnt nd its tion lone is s effetive s the sum of ll modifitions. The effet of m 1 G37 in the UGG isoeptor trna Pro (trna Pro/UGG ) is most remrkle. Although the riosome ws tive with ll three sttes of the trna for synthesis of fmpv, the frtionl synthesis deresed mrkedly from 22% with the to 4% with the m 1 G37- nd to 2% with the ntive-stte (Fig. 3), eh ompnied y more thn 1-fold redution in 4 NATURE COMMUNICATIONS 6:7226 DOI: 1.138/nomms8226
5 NATURE COMMUNICATIONS DOI: 1.138/nomms8226 ARTICLE fmp-post Arg + Vl F (fmp fmpv, fmpr) F (fmp fmpv, fmpr) k =.31 ±.1 s 1.8 m 1.7 fmpr () fmpr () fmpr () k os = 1.4 ±.1 s 1 k os =.9 ±.1 s 1 k os = 1.8 ±.1 s k os = 6. ±.7 s 1.3 k os = 2.4 ±.3 s 1 k os = 2.3 ±.2 s m 1 fmpr ().25 k os =.14 ±.1 s k fmpr () os =.55 ±.7 s 1 k os =.1 ±.1 s 1.1 fmpr () os k os =.6 ±.1 s 1.5 k os =.18 ±.1 s Figure 3 Peptide ond formtion y post-trnslotion omplex with GGG or UGG trna Pro stlled t the P-site. () Kineti sheme for mesurement of k os of peptide ond formtion upon rpid mixing of exess ternry omplexes of trna Arg nd trna Vl (molr rtio of 1:1) with stlled post-initition omplex rrying fmp-trna Pro/GGG or fmp-trna Pro/UGG in the P-site. The oding mrna sequene ws AUG-CCC-CGU-U. () Mesurement of the frtionl onversion F of totl fmp moleules to the in-frme fmpr produt (lue) nd to the þ 1-frme fmpv produt (red) over time for G37- (left), m 1 G37- (middle) nd ntive-stte (right) trna Pro/GGG, showing the rte onstnt of onversion (k os ) for eh. Yields of the respetive tripeptides did not hnge when the molr rtio of trna Arg to trna Vl ws vried from 1:5 to 5:1 or when eh inoming trna ternry omplex ws dded seprtely to limiting mount of the post-trnslotion omplex. () Similr nlysis onduted with trna Pro/UGG (ntiodon presented 5 to 3 ) in the P-site of the post-trnslotion omplex. Error rnge of the urve fitting is denoted. kinetis of þ 1 frmeshifting (see Fig. 5). Thus, the single m 1 G37 is the mjor determinnt to suppress þ 1FS errors, suggesting tht ll other modifitions in the ntive-stte, inluding the mo 5 U34, hve little effet. Indeed, sustitution of mo 5 U34 with ho 5 U34 in n otherwise ntive-stte hd no effet on the mplitude of the shift, wheres sustitution of m 1 G37 with G37 in the ntive-stte gretly inresed the mplitude (Supplementry Fig. 9). Error suppression t the seond odon. Beuse the seond odon is most shift-prone, we determined the tion of m 1 G37 nd EF-P t this position. To determine the m 1 G37 effet, we ompred the kinetis of trna Pro shifting into the þ 1-frme in the G37- stte nd in the m 1 G37-ontining ntive-stte. In riosome omplex on the mrna AUG-CCC-C sequene with GGG trna Pro stlled in the P-site, we showed tht the trna shifting into the þ 1-frme ws slow (k os ¼ s 1,Fig.4,) reltive to peptide ond formtion (B1s 1 ; Supplementry Fig. 1), inditing tht suh shifts re rre during tive protein synthesis ut re indued when the A-site is empty. A slow shift ws lso oserved with the ntive-stte, inditing tht m 1 G37 does not suppress the kinetis of shift of this trna. In ft, the k os of shift of the ntive-stte GGG trna Pro ws generlly fster reltive to the, inditing tht the full omplement of nturl modifitions in the ntive-stte rendered the trna kinetilly more ompetent on the riosome. Importntly, lthough m 1 G37 did not redue the kinetis of shift, it redued the mplitude, from 26% with the to 8.1% with the ntive stte. The mplitude t 26% of the GGG trna Pro is notle, inditing tht one-qurter of the post omplexes t the seond odon CCC-C oupy the þ 1-frme t equilirium. Even with the mplitude redued to 8.1% y m 1 G37, the level is still high (lmost the level tht hllenges ell survivl). We showed tht the ddition of EF-P effetively suppressed the mplitude to the kground nd redued the kinetis y more thn 1-fold from to 1 5 s 1 (Fig. 4). This error suppression y EF-P ws dependent on the -lysyl K34; n EF-P produed from ells o-expressing the -lysyltion tivity 23 ws effetive in suppressing the shift, wheres the K34A mutnt (Supplementry Fig. 11) nd the protein without the -lysyl modifition of K34 were less effetive. Notly, -lysyl EF-P redued the kinetis of shift y 4-fold for the nd y 2-fold for the ntive-stte (Fig. 4,), showing stronger effet on the m 1 G37-ontining ntive-stte. We sought to determine whether there existed other trnsltionl steps tht would permit fster shift reltive to the shift from the P-site. In onerted ssy tht monitored suessive NATURE COMMUNICATIONS 6:7226 DOI: 1.138/nomms
6 NATURE COMMUNICATIONS DOI: 1.138/nomms8226 7SIC ± EF-P Pro/GGG + EF-G 27 s Arg + Vl F (fmp fmpv).2 EF-P.15 k os = (2. ±.3) 1 3 s 1 mp = (26 ± 2)%.1.5 k os = (1.3 ±.1) 1 2 s 1 mp = (8.1 ±.2)% EF-P k os = (5.3 ±.1) 1 5 s 1 k os = (6.3 ±.1) 1 5 s d 7SIC ± EF-P Pro/GGG + Vl + EF-G e F (fmp fmpv) EF-P k os1 =.14 ±.2 s 1 mp 1 = (1.2 ±.1)% k os2 = (6.1 ±.1) 1 4 s 1 f + EF-P k os1 =.5 ±.1 s 1 k mp 1 = (.6 ±.1)% os1 =.29 ±.6 s 1 mp = (.9 ±.1)% k os2 = (7.3 ±.1) 1 4 s 1 k os2 = (2.8 ±.1) 1 4 s k os1 =.21 ±.4 s 1 mp 1 = (.9 ±.1)% k os2 = (3.3 ±.1) 1 4 s Figure 4 Formtion of þ 1FS errors y GGG trna Pro t the seond odon. () The kineti sheme to mesure the rte of þ 1FS formtion y fmp-trna Pro/GGG stlled t the P-site of post-trnslotion omplex on the templte AUG-CCC-CGU-U. A 7SIC ws mixed with Pro-tRNA Pro/GGG nd EF-G to form stlled post-trnslotion omplex, whih ws smpled over time y mixing with exess ternry omplexes of trna Arg nd trna Vl (molr rtio of 1:1). After 27 s of peptide synthesis, eh seondry retion ws quenhed nd the peptides nlysed. () Time ourse of the frtionl onversion F from totl fmp moleules to fmpv moleules, showing the kinetis of þ 1-frmeshifting y the G37- (lk) nd ntive-stte (red) of trna Pro/GGG t 2 C. () Anlysis s in ut in the presene of EF-P (1 mm). (d) The kineti sheme to mesure the rte of þ 1FS formtion y fmp-trna Pro/GGG when 7SIC ws rpidly mixed with ternry omplexes of trna Pro nd trna Vl in the presene of EF-G. (e) Biphsi kinetis were oserved for þ 1FS y oth the G37- (lk) nd ntive-stte (red) trna Pro/GGG.(f) Anlysis s in e ut in the presene of EF-P (1 mm). The k os nd mplitude of eh shift re indited, eh s the verge of t lest three independent mesurements. Error rs denote s.d. tivities of GGG trna Pro from deoding t the A-site to trnslotion into the P-site, we oserved iphsi shift kinetis (Fig. 4d,e). Both the G37- nd ntive-stte displyed similr kinetis, with fst k os1 followed y slow k os2. Beuse the slow k os2 ( s 1 ) ws omprle to the rte of trna shifting from the P-site, we ttriuted the fst k os1 (.1.2 s 1 ) to the trna shifting efore rrivl t the P-site. This ssignment ws supported y the oservtion tht oupny of the -frme trna Arg t the A-site suppressed the slow shift ut not the fst shift (Supplementry Fig. 12). Given the lk of shifting in the A-site 24,25 nd the lk of roust peptide ond formtion when deoding n out-of-frme triplet (Supplementry Fig. 4), we suggest tht the fst k os1 reports on the trna shifting during trnslotion into the P-site. Both m 1 G37 nd EF-P hd smll effets in reduing the mplitude of the fst shift (Fig. 4e,f). This shift is of interest, euse its k os1 is omprle to the rte of peptide ond formtion nd thus it n ffet reding frme ury during tive protein synthesis. Also, its ssoition with trna trnslotion hs prllel to tht found in progrmmed 1 frmeshifting 26,27. UGG trna Pro differs from its GGG ounterprt in oth the slow nd fst shift. The slow shift of UGG trna rehed higher level, ut m 1 G37 lone redued it to kground nd deresed the kinetis from 1 3 to 1 5 s 1 (Fig. 5,). This dul role of m 1 G37 in UGG trna is in ontrst to its single role in reduing the mplitude in GGG trna. EF-P hd little effet on the slow 6 NATURE COMMUNICATIONS 6:7226 DOI: 1.138/nomms8226
7 NATURE COMMUNICATIONS DOI: 1.138/nomms8226 ARTICLE 7SIC ± EF-P Pro/UGG + EF-G 27 s Arg + Vl F (fmp fmpv) F (fmp fmpv) e EF-P k os = (4.8 ±.2) 1 3 s 1 mp = (38 ± 1)% k os = (2 ± 1) 1 5 s 1 m 1 k os = (4.7 ±.5) 1 5 s d fmpv k os =.6 ±.1 s 1 mp = (5.9 ±.3)% 7SIC + EF-G Pro/UGG + Arg + Vl f + EF-P k os = (2.9 ±.3) 1 3 s 1 mp = (24 ± 1)% m 1 k os = (6.7 ±.3) 1 5 s 1 k os = (2 ± 1) 1 5 s 1 m 1 fmpv k os = (.3 ±.6) s 1 mp = (3. ±.6)% Figure 5 Formtion of þ 1FS errors y UGG trna Pro t the seond odon. () Kineti sheme to mesure the rte of þ 1FS formtion y fmp-trna Pro/UGG stlled t the P-site of post-trnslotion omplex on the templte AUG-CCC-CGU-U. Smpling ws the sme s in Fig. 4. () Time ourse of the frtionl onversion F from totl fmp moleules to fmpv moleules, showing the kinetis of þ 1FS y the G37- (red), m 1 G37- (lue) nd ntive-stte (lk) of trna Pro/UGG.() Anlysis s in ut in the presene of EF-P (1 mm). (d) Kineti sheme to mesure the rte of þ 1FS formtion y fmp-trna Pro/UGG when 7SIC ws rpidly mixed with ternry omplexes of trna Pro nd trna Vl in the presene of EF-G. (e) Kinetis of þ 1FS formtion y the trna Pro/UGG.(f) Kinetis of þ 1FS formtion y the m 1 trna Pro/UGG. The k os nd mplitude of eh shift re indited, eh s the verge of t lest three independent mesurements. Error rs denote s.d. shift of UGG trna in ll three sttes (Fig. 5), in ontrst to its strong effets on GGG trna. Conversely, the fst shift of UGG trna lso rehed higher level reltive to GGG trna (Fig. 5d,e), inditing tht UGG trna n hve stronger impt during tive protein synthesis. Both m 1 G37 nd EF-P hd smll effets on the mplitude of the fst shift (Fig. 5,f). Error suppression t the third odon. We evluted the effet of m 1 G37 nd EF-P t the third odon s representtive of lter odons. In stlled riosome omplex on n mrna strting with AUG-UAU-CCC-CGU-U, the of GGG trna Pro exhiited slow shift into the þ 1-frme (Fig. 6,), lthough with k os fster nd n mplitude higher reltive to its plement t the seond odon. Although m 1 G37 hd no effet on the kinetis or mplitude of the shift, -lysyl EF-P hd smll effet on oth, reduing the kinetis from to s 1 nd the mplitude from 43 to 34% (Fig. 6). These re smller effets reltive to those t the seond odon. In the onerted ssy with oth trna Arg nd trna Vl present, we oserved no evidene of fst shift. When the sme retion ws onduted with only trna Vl present, we oserved single-phse NATURE COMMUNICATIONS 6:7226 DOI: 1.138/nomms
8 NATURE COMMUNICATIONS DOI: 1.138/nomms8226 7SIC ± EF-P Pro/GGG + Tyr +EF-G 27 s Arg + Vl F (fmyp fmypv) EF-P k os = (1.9 ±.2) 1 2 s 1 mp = (43 ± 1)% k os = (2. ±.2) 1 2 s 1 mp = (4 ± 1)% EF-P k os = (7. ± 1) 1 3 s 1 mp = (34 ± 2)% k os = (8. ± 1) 1 3 s 1 mp = (33 ± 1)% d 7SIC + EF-G ± EF-P Pro/GGG + Tyr + Vl e 1.6 EF-P f + EF-P F (fmyp fmypv) k os = (1.3 ±.3) 1 2 s 1 k os = (2. ±.1) 1 2 s 1 k os = (1.6 ±.1) 1 3 s 1 k os = (2.18 ±.1) 1 3 s Figure 6 Formtion of þ 1FS errors y GGG trna Pro t the third odon. () Kineti sheme to mesure the rte of þ 1FS formtion y fmyp-trna Pro/GGG stlled t the P-site of post-trnslotion omplex on the templte AUG-UAU-CCC-CGU-U. A 7SIC ws mixed with ternry omplexes of trna Tyr nd trna Pro/GGG in the presene of EF-G to form stlled post omplex, whih ws smpled over time y mixing with exess ternry omplexes of trna Arg nd trna Vl (molr rtio of 1:1). After 27 s of peptide synthesis, eh retion ws quenhed nd the peptides were nlysed. () Time ourse of the frtionl onversion F from totl fmyp moleules to fmypv moleules, showing the kinetis of þ 1FS y the G37- (lk) nd ntive-stte (red) of trna Pro/GGG.() Anlysis s in ut in the presene of EF-P (1 mm). (d) The kineti sheme to mesure the rte of þ 1FS formtion y fmyp-trna Pro/GGG when 7SIC ws rpidly mixed with ternry omplexes of trna Tyr, trna Pro/GGG nd trna Vl in the presene of EF-G. (e) Kinetis of þ 1FS formtion y G37- (lk) nd ntive-stte (red) trna Pro/GGG were determined. (f) Anlysis s in e ut in the presene of EF-P (1 mm). The k os nd mplitude of eh shift re indited, eh s the verge of t lest three independent mesurements. Error rs denote s.d. kinetis with k os of the shift similr to tht of the slow shift (Fig. 6d f). Here, m 1 G37 hd no effet on the kinetis, wheres EF-P hd smll effet on oth the kinetis nd mplitude, onsistent with the nture of slow shift from the P-site. In ontrst, the of UGG trna Pro is sujet to oth slow nd fst shifts t the third odon (Supplementry Fig. 13). In the slow shift, m 1 G37 redued the mplitude of the shift y smll effet, ut EF-P hd no effet, wheres in the fst shift, neither hd n effet. Importntly, the detetion of fst shifts with UGG trna is in ontrst to the sene of fst shifts of GGG trna. This indites tht UGG trna is responsile for fst shifts t the third nd lter odons, onsistent with its mjor role in driving shifts in geneti nlysis 2. Disussion Cell viility depends on lne etween rpid protein synthesis nd urte reding-frme mintenne. Here we provide insight into this lne y eluidting the moleulr mehnisms governing þ 1-frmeshifting of GGG nd UGG trna Pro t the CCC-C sequene (Supplementry Tle 3). We hve identified two mehnisms: the fst shift during trna trnslotion into the P-site nd the slow shift during trna stlling next to n empty A-site (Fig. 7). With the exeption of the first round of elongtion, the fst shift mehnism is restrited to UGG trna. In ontrst, the slow shift mehnism is essile to either trna t ny round of elongtion. EF-P nd m 1 G37 re seletive inhiitors of þ 1-frmeshifting. Although neither ftor 8 NATURE COMMUNICATIONS 6:7226 DOI: 1.138/nomms8226
9 NATURE COMMUNICATIONS DOI: 1.138/nomms8226 ARTICLE Seond odon position Slow shift: t P-site GGG UGG Frequeny 3% 4% EF-P m 1 G37 m 1 G37 EF-P Third odon position Slow shift: t P-site GGG UGG Frequeny 4% 2% EF-P m 1 G37 m 1 G37 EF-P Fst shift: trnslotionn into P-site GGG UGGG Frequeny 1 2% 5% m 1 G37 EF-P EF-P m 1 G37 d Fst shift: trnslotion into P-site GGG UGGG Frequeny % 5% m 1 G37 EF-P EF-P m 1 G37 Figure 7 A model of þ 1FS on CCC-C y GGG nd UGG trna Pro. Frequenies of þ 1FS on CCC-C re shown for GGG or UGG trna Pro sed on kineti dt for the of eh. () In the post-trnslotion omplex where CCC-C is pled t the seond odon position, the high frequenies of slow shifts, due to trna Pro shifting from stlled P-site, re suppressed primrily y m 1 G37 for the UGG trna nd y EF-P for the GGG trna. () The low frequenies of fst shifts t the seond odon, due to trna Pro shifting en route to the P-site, re suppressed y oth m 1 G37 nd EF-P for eh trna. () When CCC-C is pled t the third odon position, the high frequenies of slow shifts re suppressed y m 1 G37 for the UGG trna nd y EF-P for the GGG trna. (d) The low frequenies of fst shifts in the erly elongtion phse re not effetively suppressed y m 1 G37 or EF-P. Open rrows indite suppression of error frequenies, wheres oxed rrows indite suppression of oth frequenies nd kinetis of error formtion. One rrow indites redution of 2- to 3-fold, two rrows indite 3- to 3-fold, three rrows indite greter thn 3-fold nd indites less thn 2-fold effets. Perent frequenies re rounded up to the losest pproximtion. hs strong effet on the fst shift mehnism, oth exert strong ut differentil effet on suppressing the slow shift. EF-P inhiits slow shifts of GGG trna, wheres m 1 G37 inhiits slow shifts of UGG trna. These dt form the sis for n importnt oneptul dvne for understnding how þ 1FS errors re formed nd suppressed in ells. In the sene of stress, ells expressing oth m 1 G37 nd EF-P hve low levels of þ 1-frmeshifting t CCC-C sequene, primrily due to fst shifts of UGG trna during trnslotion. The one exeption is t the seond odon, where oth UGG nd GGG trnas n slip, thus ounting for the notiely high levels of endogenous frmeshifting t this odon in our lz ssys. However, in times of nutrient strvtion, the slow shift eomes more relevnt nd ells lking m 1 G37 or EF-P show elevted þ 1FS errors in eh round of protein synthesis. The seond odon is unique for its high suseptiility to fst shifts of oth UGG nd GGG trnas. This my e due to its ssoition with the first trnslotion event, whih hs severl unique fetures. One is the sene of n E-site trna, whih n promote reding-frme errors 28,29 ; the seond is the ssoition of the riosome omplex with the Shine-Dlgrno (SD) sequene, whih n hmper the first trnslotion nd promote trna shifting 3 ; nd the third is the involvement of the struturlly distint inititor trna fmet in moving from the P- to E-site. Owing to the lk of norml first se pir in the eptor stem, trna fmet is preferentilly stilized in the lssil stte, rther thn the hyrid stte, rendering the first trnslotion struturlly nd dynmilly unfvourle 31. In ontrst, trnslotion in lter yles hs stedy oupny of the E-site, is dissoited from the SD sequene, nd engges only elongtor trnas with onformtionl flexiility tht is lking in trna fmet. This onformtionl flexiility enles eh elongtor trna to redily dopt intermedite strutures in the hyrid stte to mintin tight ontts with the rtheting riosome 32,33. In ddition, upon moving wy from the strt odon, eh trnslting riosome nrrows down the mrna entrne hnnel 34 to filitte the intertion of two stritly onserved ses in the 16S rrna with the mrna ses. The tion of these two ses, representing pwls of the trnslotion rthet, my prevent slippge of the reding frme 33. The seond odon is lso highly suseptile to slow shifts. The CCC triplet itself is rre odon prone to induing riosome stlling 35 nd when it is followed y nother rre odon, the sequene ontext inreses the trnsltionl þ 1FS frequeny (Fig. 1,). Protein-oding sequenes often ontin lusters of rre odons within the first 25 positions 36,37. This is n evolutionrily onserved feture tht should sensitize slippery sequenes suh s CCC to slow shifts, whenever shortge of minoyl-trnas ours. Our dt emphsize the importne of m 1 G37 nd EF-P for suppressing þ 1FS errors. Although dditionl ftors ontriuting to reding-frme mintenne re possile, the strong effet of m 1 G37 nd EF-P nd the growth rrest upon their onurrent removl suggests tht they re the mjor determinnts to orretly position trnslting riosome throughout protein synthesis. Intriguingly, suppression of shifts y m 1 G37 nd EF-P is lned etween the GGG nd UGG isoeptors. This lne is most striking for suppression of slow shifts t the seond odon (Fig. 7), where m 1 G37 ontrols UGG trna, wheres EF-P ontrols GGG trna, oth y ting on the frequeny nd the kinetis of shifts. In ft, the seond odon is the only ple where m 1 G37 nd EF-P hve drmti effet on the kinetis of shifts, wheres in ll other instnes they primrily t on the frequeny of shifts. For suppressing fst shifts, the two ftors t similrly with either trna (Fig. 7). At the third odon, the two ftors gin divide their responsiility etween the two trnas to suppress slow shifts (Fig. 7), leit with weker effet reltive to the seond odon, nd neither ftor suppresses fst shifts (Fig. 7d). Thus, in the overll lndspe of error redution, m 1 G37 is minly responsile for reduing slow shifts of UGG trna Pro, wheres EF-P is the ounterprt for GGG trna Pro. If the riosome stlling time t the CCC-C is long reltive to peptide ond formtion, then the high levels of errors t the seond odon upon elimintion of m 1 G37 re primrily due to slow shifts of UGG trna Pro, wheres they rise from slow shifts of GGG trna Pro upon elimintion of EF-P. NATURE COMMUNICATIONS 6:7226 DOI: 1.138/nomms
10 NATURE COMMUNICATIONS DOI: 1.138/nomms8226 The preferene of m 1 G37 for UGG trna Pro is likely onsequene of the wek ntiodon piring to the CCC odon. Beuse the mo 5 modifition t U34 plys little role in suppressing shifts, this trna must ommodte the imperfet piring of U34, ho 5 U34 or mo 5 U34 with C, regrdless in the - or þ 1-frme. How m 1 G37 restrits the piring to the -frme is therefore intriguing. We suggest tht m 1 G37 enhnes the qulity of the imperfet U-C piring in the -frme y preorgnizing the ntiodon loop nd y promoting new intertions with the riosome. A reent rystl struture of CGG trna Pro supports the onept of pre-orgniztion, showing tht m 1 G37 enles U32 nd A38 to form new se pir in the ntiodon loop 24. An exmple of promoting new intertions with the riosome is found in the struture of the ms 2 i 6 modifition of A37 (2-methyl thio-n6 isopentenyl denosine) in trna Phe, whih prevents P-site trna from shifting y strengthening the odon ntiodon intertion in ll three inding sites nd y mking new ontts with the riosome etween the P- nd E-sites 34. Understnding how m 1 G37 prevents UGG trna Pro from slow shifts will require new rystl strutures of the trna in omplex with riosome. In ontrst, GGG trna Pro reds the CCC-C using three stle G-C se pirs regrdless of the - or þ 1-frme. In this se, m 1 G37 lone is unlikely to influene the piring frme. Insted, the trna reruits EF-P, whih inds to the P-site trna on the riosome next to the E-site 38, with extensive intertions tht n prevent slow shifts of the P-site trna in wy distint from m 1 G37. This EF-P stiliztion my e prtiulrly importnt for GGG trna, euse the trna hs rre A32-U38 se pir in the ntiodon loop known to use riosome mis-oding 39 nd it hs n unpired U3-U4 tht n destilize the ntiodon stem. In eh se, the struturl wekness of the trna my e reognized nd strengthened y EF-P. Both m 1 G37 nd EF-P lso suppress fst shifts in trna-independent mnner during the first trnslotion (Fig. 7). Beuse our ssys for fst shifts enompss suessive trna movements from the A- to P-site, nd euse there is no evidene of shifting in the A-site 24, fst shifts most likely our t lte stge of trnslotion efore trna rrivl t the P-site. Here m 1 G37 n redue fst shifts y pre-orgnizing the ntiodon loop, wheres EF-P n help to position trna orretly upon entering the P-site. Although EF-P is est known for relesing stlled riosomes from poly-pro sequenes 1,11, its suppression of trna shifting is likely y different mehnism, ting t single Pro odon. The m 1 G37 methyltion is onserved in ll isoeptors of trna Pro nd in CAG trna Leu nd CCG trna Arg. The propensity of eh trna to shift t slippery sequenes is high nd m 1 G37 is expeted to redue suh shifts nd promote protein synthesis. Similrly, EF-P is onserved in teri nd is orthologous to the rhel nd eukryoti initition ftor 5A (/eif-5a) 4. Similr to the -lysyltion of EF-P, eif-5a hs hypusine modifition tht is importnt for the ftor to ind to the riosome nd to promote protein synthesis 41. Bsed on our results here tht the -lysyltion of EF-P is importnt for redingfrme ury, the hypusine modifition is likely to hve similr role. This work emphsizes the importne of the posttrnsriptionl modifition of trna y m 1 G37 nd the posttrnsltionl modifition of EF-P or eif-5a y -lysyltion or hypusine for reding-frme mintenne. Indeed, oth m 1 G37 nd eif-5a re essentil to ell survivl, wheres EF-P is vitl for roust growth of most teri 17,41,42. The enggement of these two ftors fter the first peptide synthesis emphsizes tht strting off riosome on the orret reding frme is n essentil spet of trnsltion. Methods Regents. mrnas were trnsried with T7 RNA polymerse nd purified y denturing gel eletrophoresis. Eh mrna ontined onsensus SD sequene (underlined) followed y n AUG strt odon (itliized). Most studies utilized mrna1 or mrna2 with CCC-C sequene (in old fe) t the seond or third odon position. mrna1: 5 -GGGAAGGAGGUAAAAAUGCCCCGUUCUAAG(CAC) 7 mrna2: 5 -GGGAAGGAGGUAAAAAUGUAUCCCCGUUCUAAG-(CAC) 6 Tight-oupled 7S riosomes were isolted from E. oli MRE6 ells nd overexpressed His-tgged E. oli initition nd elongtion ftors were purified on nikel-nitrilotrieti id olumns 43. These regents were liquoted efore storge t 7 C. Reominnt His-tgged E. oli EF-P ering -lysyl-k34 or the K34A mutnt ws expressed nd purified from ells 23 o-expressing efp, yjea nd yjek nd stored t 2 C. Kineti mesurements of þ 1FS. Peptide ond formtion ws mesured with reonstituted E. oli riosome, using purified omponents 44,45.The þ 1 slippge of or ntive-stte fmp-trna Pro in the P-site of stlled post-trnslotion omplex ws monitored using two-step retion sheme in whih 7SIC (ering 35 S-fMet-tRNA fmet ) ws mixed with the TC of Pro-tRNA Pro in the presene of EF-G. Aliquots were removed over time nd supplemented with TCs of Vl-tRNA Vl nd Arg-tRNA Arg. After fixed period (27 s) these seondry retions were quenhed with nd lelled peptides were resolved on eletrophoreti TLC. The þ 1 slippge during trnslotion ws monitored in Kintek hemil quenh pprtus y mixing 7SIC with TCs of Pro-tRNA Pro, Vl-tRNA Vl nd Arg-tRNA Arg.The þ 1 slippge ttriutle to oth trnslotion nd P-site stlling ws monitored y hemil quenh in the sene of Arg-tRNA Arg. Regent onentrtions long with more detiled protool re presented elow. Determintion of þ 1FS frequenies. Using the first round of elongtion s n exmple, the totl frequeny of þ 1FS ws determined y inuting 7SIC (templted with mrna1) with the TC of trna Pro in the presene of EF-G for 5 s followed y dditionl 27 s inution with exess TCs of trna Arg nd trna Vl. The perent of fmp onverted to fmpv refleted totl þ 1FS. The frequeny of þ 1FS ssoited with trnslotion ws determined y inuting 7SIC with TCs of trna Pro, trna Arg nd trna Vl in the presene of EF-G. The perent of fmp onverted to fmpv upon ompletion of the retion refleted the frequeny of þ 1FS due to the fst mehnism. Sutrtion of this frequeny from the totl frequeny yielded the frequeny of þ 1FS in the P-site. Chrged trnas. All of the ntive trnas used in this study were overexpressed in E. oli nd ffinity purified from totl trna using iotinylted oligonuleotide proes immoilized to streptvidin sephrose 46. In vitro trnsried trna Pro ws prepred using T7 RNA polymerse nd ws purified y eletrophoresis in 12% denturing polyrylmide gel. For speifi experiments, trna Pro trnsript ws onverted to the m 1 using TrmD in the presene of AdoMet 47. Eh trna ws enzymtilly hrged with its ognte mino id using the respetive minoyl-trna synthetse nd then stored in 25 mm ette uffer (ph 5.) t 2 C until use. Formyltion of Met-tRNA fmet ws rried out during the hrging retion y inluding methionyl-trna formyl trnsferse nd the methyl donor 1-formyltetrhydrofolte (derived from folini id t neutrl ph) 44.The effiieny of hrging ws determined y doping eh retion with smll mount of rdiolelled mino id nd determining oth A 26 nd rdiotive ounts of produt trna fter removl of free mino id, ATP nd protein y phenol extrtion, gel filtrtion through spin olumn nd ethnol preipittion. This methodology indited hrging effiienies of 4% for trna fmet, 52% for ntive trna Pro/GGG, 17% for trnsript trna Pro/GGG, 6% for ntive trna Pro/UGG,18% for trnsript trna Pro/UGG, 67% for ntive trna Arg, 48% for ntive trna Vl nd 25% for ntive trna Tyr. Preprtion of trna for kineti mesurements. The ws synthesized y in vitro trnsription, the m 1 ws synthesized y treting the trna trnsript with E. oli TrmD in the presene of AdoMet 48 nd the ntive-stte ws isolted from n E. oli overexpression strin. The UGG trna Pro ws prepred in two dditionl sttes: the (G37) ntive stte ws prepred y isolting the ntivestte trna from the temperture-sensitive ts-trmd-s88l strin 17 grown t 44 C for 24 h to intivte m 1 G37 synthesis, nd the (ho 5 U34) ntive stte ws prepred y isolting the ntive-stte trna from n mob-defiient E. oli strin 18 unle to onvert ho 5 U34 to mo 5 U34 (otined from Yle E. oli Stok Center). RNse T1 digestion. Methyltion of G37 in ntive trna Pro/GGG nd in trnsript trna Pro/GGG nd trna Pro/UGG tht hd een treted with TrmD in the presene of AdoMet ws onfirmed y RNAse T1 digestion followed y polyrylmide gel eletrophoresis (PAGE) nlysis (Supplementry Fig. 3). Eh trna ws 3 -end lelled y Billus sterothermophilus CCA-dding enzyme 49 in the presene of [- 32 P]ATP t 6 C nd digested y RNse T1 for 2 min t 5 C in2mm sodium itrte (ph 5.5) nd 1 mm EDTA 5. The RNA frgments generted from 1 NATURE COMMUNICATIONS 6:7226 DOI: 1.138/nomms8226
11 NATURE COMMUNICATIONS DOI: 1.138/nomms8226 ARTICLE levge were seprted y denturing 7 M ure/12% PAGE nd nlyzed y phosphorimging. Toeprint of riosoml omplexes. Unlelled initition nd post-trnslotion omplexes were formed on three 96-mer mrnas tht hd een prepred y in vitro trnsription. The initil oding sequenes of these mrnas were (i) AUG-CCC-CGU, (ii) AUG-CCC-AGU nd (iii) AUG-CCA-CGU in n otherwise identil sequene. Before nlysis, post-trnslotion omplexes were inuted 4 min t 37 C to promote þ 1FS. Reverse trnsription ws initited from 5 -end lelled DNA primer omplementry to the 3 -end of eh mrna, resulting in primer extension produts of pproximtely 6 nuleotides long. Primer extension ws rried out t 37 C for 15 min in the presene of.6 U ml 1 of AMV-RT,.6 mm eh dntp, 1.2 mm ATP, 1 mm Mg(OA) 2 nd 1 mm dithiothreitol. Retions were extrted with phenol hloroform isomyl lohol, ethnol preipitted in the presene of glyogen rrier, nd nlyzed on 4-m-long 9% PAGE/7 M ure gel. Peptide ond formtion. In vitro trnsltion retions were monitored for peptide ond formtion y mixing 7SIC or post-trnslotion omplex with one or more inoming TCs in Kintek RQF-3 hemil quenh flow pprtus (single inution retions) or on the enh (single or doule inution retions). As pproprite, EF-G nd EF-P were inluded in the retions. Assys were performed in Buffer A (5 mm Tris-HCl, ph 7.5, 7 mm NH 4 Cl, 3 mm KCl, 3.5 mm MgCl 2, 1 mm dithiothreitol,.5 mm spermidine) t 2 C unless otherwise indited. Before eh retion, TCs were freshly prepred y inuting EF-Tu with 1 mm GTP in Buffer A for 15 min t 37 C, followed y dding one or more hrged elongtor trnas to the solution in n ie th nd inuting for n dditionl 15 min (molr rtio of EF-Tu to hrged trna ws 1.5 to 1.). The 7SIC ws formed y inuting E. oli 7S riosome, IF1, IF2, IF3, mrna nd 35 S-fMet-tRNA fmet (t molr rtios of 1.5, 2., 2., 2., 2. nd 1., respetively) in Buffer A supplemented with 1 mm GTP for 25 min t 37 C. Post-trnslotion omplexes were formed y inuting the 7SIC with requisite TCs nd EF-G t 37 C for 2 min. Before monitoring retion kinetis, preformed TC, 7SIC nd post-trnslotion omplex were stored in ie. Unless otherwise speified, fter ddition of ll omponents the finl onentrtions were.375 mm 7S riosome,.5 mm eh initition ftor 1, 2 nd 3,.25 mm 35 S-fMet-tRNA fmet,.5 mm mrna,.5 mm eh hrged elongtor trna,.75 mm EF-Tu per eh trna, 2 mm EF-G, 1 mm GTP nd where indited 1 mm EF-P. Retions were onduted t 2 C unless otherwise speified, nd were quenhed y dding onentrted to.5 M. After rief inution t 37 C, liquots of.65 ml were spotted onto ellulose-ked plsti TLC sheet nd eletrophoresed t 1, V in PYRAC uffer (62 mm pyridine, 3.48 M eti id, ph 2.7) until the mrker dye romophenol lue rehed the wter oil interfe t the node 51. The position of the origin ws djusted to mximize seprtion of the expeted oligopeptide produts. Spots were visulized y phosphorimging nd quntified using ImgeQunt (GE Helthre) nd kineti plots were fitted using Kleidgrph (Synergy softwre). Relese ftor ssy. E. oli strins overexpressing relese ftors (RFs) 2 nd 3 were kindly provided y Dr Tkuy Ued t the University of Tokyo. The His-tgged proteins were purified using metl ffinity nd DEAE-sephrose CL6B (Phrmi) olumns nd inuted with GTP t 37 C just efore use. Post-trnslotion omplexes with 35 S-fMP-tRNA Pro/GGG were prepred in Buffer C 21. The mrna-oding region sequene ws either AUG-CCC-CGU (for fmpr) or AUG-CCC-UGA (for fmp-stop). Post-trnslotion omplexes were inuted t 37 C for 1 min to filitte þ 1FS nd then treted with (i) 3 mm RF2 nd 3 mm RF3, (ii) 3 mm RF2, (iii).8 M or (iv) retion uffer C. Retions with relese ftors were inuted t 37 C for 1 min nd then quenhed with 5% formi id. All other retions were quenhed with. Aliquots of 1 ml were sujeted to eletrophoreti TLC nd the rdiotivity signl ws nlysed s desried for the kineti ssys. two overnights to intivte the ts-replition origin of the plsmid. An ttempt to onstrut trmd-ko strin with mintenne plsmid expressing trmd ws unsuessful. -Gltosidse (-gl) ssy. We utilized the -gl ssy to study þ 1FS in vivo. First, to speifilly study þ 1FS t the position of interest, we hnged ll pre-existing CCC-C or CCC-U motifs in the lz gene of pjc27 plsmid 53 into CCG-[C/U] to rete sequene tht mintined the ntive mino-id sequene ut lked CCC-[C/U] sequenes y site-direted mutgenesis. To rule out the possiility of lterntive initition, we mutted the AUG t the third odon position of the originl lz gene into AUC, resulting in lz gene without ny in-frme AUG in the first 1 odons exept for the inititing odon. The modified lz gene ws trnsferred to pkk223-3 nd CCC-C (or CCC s ontrol) ws inserted to odon position 5, 1, 2, 6 or 124 in the sme CCC-C-ACC (or CCC-ACC for ontrol) ontext (Fig. 1). In ll ses, the orret lz produt ws synthesized only when trna Pro exhiited þ 1FS movement t the CCC-C sequene. Note tht the CAC odon following the CCC-C run in the -frme nd the ACC odon following the CCC-C run in the þ 1-frme hve frequenies of 1.1% nd 2.4%, respetively, inditing similr supply levels of the orresponding trnas for expression of these lterntive reding frmes. To test the effet of rre odon t the A-site, we mde dditionl onstruts where CCC t odon 124 ws followed y in-frme CGG or UGG, the odon frequeny of whih ws.5% nd 1.4%, respetively. In these ses, the þ 1-frme odon is GGU with usge frequeny of 2.8%. Eh CCC-C onstrut, s well s the ontrol CCC onstrut, ws introdued into the trmd-ko strin. A single olony ws piked from n rinose-ontining Luri-Bertni (LB) plte nd ws grown in 3 ml LB without rinose t 3 C to OD 6 of.1 (B3 h) to deplete pre-existing Trm5 in ells. Cultures were then inoulted into fresh LB with or without.2% (w/v) rinose t 5-fold dilution. The ultures with rinose were hrvested t OD 6 ¼.4.6, wheres the ultures without rinose were grown until they were slightly turid. Cells were resuspended in Z uffer (1 mm KCl, 1 mm MgSO 4,5mM-merptoethnol, 6 mm N 2 HPO 4,4mMNH 2 PO 4, ph 7.), permeilized with.5% SDS nd 1% hloroform, nd the -gl tivity ws mesured 54. The þ 1FS frequeny ws lulted s the rtio of the CCC-C reporter tivity over the CCC reporter tivity. Similr -gl mesurements for eh CCC-C reporter versus the ontrol CCC reporter were performed for E. oli efp nd efp þ strins (JW417-1 nd BW25113 of the Yle E. oli Stok) grown nd ssyed t 3 C. To omplement the efp strin, we introdued n EF-P-expressing plsmid y isolting the NsiI- SpeI frgment (whih o-expressed efp-yjea-yjek under the ontrol of the T7 promoter) from the pst39 plsmid 23 nd inserting it into pacyc184 t the PstI nd XI sites (whih were reted y mutgenesis), respetively. Expression of efpyjea-yjek from the T7 promoter ws enled y lysogeniztion of E. oli efp strin with lde3 (Merk Millipore). The lysogenized ells hrouring lz reporter onstrut were grown t 3 CtoOD¼.1.2, then 4 5 h in the presene of.1 mm IPTG to tivte expression of the efp-yjea-yjek genes. Cells were then hrvested nd ell lystes ssyed for -gl t 3 C. Growth ssy for syntheti lethl phenotype. To tke dvntge of previously isolted isogeni pir of S. typhimurium wt-trmd nd ts-trmd-s88l strins (GT7496 nd GT7497, respetively, mde y Dr G. Bjork), we introdued the efp-ko onstrut into this pir of strins. To do this, knmyin ssette ws mplified from pkd4 y PCR with primers enompssing flnking regions of the efp gene: forwrd primer, 5 -GCGCCATTTTGTGGCTTAGCTACCAGTTAACA ATTTCAGAGTGTAGGCTGGAGCTGCTTC-3 nd reverse primer, 5 -GGCGCA GCATACGCTGCACCATTTTTCCCGATAACGTAAAATGGGAATTAGCC ATGGTCC-3. Using the l Red gene disruption method 52, the PCR produts were introdued into S. typhimurium wt-trmd nd ts-trmd-s88l strins to otin efp þ nd efp strins in eh. Cells from eh strin were grown overnight t 3 C in LB with hlormpheniol nd knmyin, nd spotted y seril dilutions on LB pltes with the sme ntiiotis nd tested for growth t 3 or 44 C. An E. oli trmd-knokout (trmd-ko) strin. Beuse trmd is essentil for teril growth, mintenne plsmid expressing the humn ounterprt trm5 ws mde first. For this purpose, the humn ounterprt trm5 gene ws loned downstrem from the rinose-ontrolled PrB promoter in pkd46 nd the entire rinose operon onsisting of the rc repressor, the P promoter nd the PrB-ontrolled trm5 ws trnsferred to the pacycduet-1 (Novgen). E. oli BL21(DE3) ells hrouring the mintenne plsmid were sujeted to l Red reomintion 52 to disrupt trmd. To do this, the knmyin gene ssette ws mplified from pkd4 y PCR using the forwrd primer 5 -CCACCGGATAAA CGGTAAAAGACGGCGCTGTGTAGGCTGGAGCTGCTTC-3 nd the reverse primer 5 -ATCCTGGGTAAACTGATATCTCGGGGGCATGGGAATTAGCCA TGGTCCATATG-3 with extensions homologous to flnking regions of the E. oli hromosoml trmd gene. The purified PCR frgment ws eletroported into ompetent ells expressing trm5 from the mintenne plsmid nd survivl olonies with trmd-ko were reovered in the sene of.2% (w/v) rinose. The gene replement ws onfirmed y PCR using primers flnking trmd. To ure the pkd46 plsmid from the trmd-ko strin, ells were inuted t 37 C for one or Pyrzinmidse ssy. The produt of the pna gene is niotimidsepyrzinmidse (PZse), whih tlyzes oxidtion of pyrzinmide (PZA) into pyrzinoi id (POA). Anlysis of the enzymti tivity of PZse 55 ws performed on ell lystes from the efp þ nd efp strins, nd the trmd-ko strin grown with or without.2% (w/v) rinose. Cells were grown overnight in 2 ml LB medi supplemented with ntiiotis nd 8 mm PZA t 3 C. The ells were hrvested nd wshed twie with 1 mm glyine, ph ¼ 6.. Cells were then resuspended in 2 ml of glyine uffer, sonited on ie nd ell lystes olleted y entrifugtion t 16,g for 3 min t 4 C. Protein onentrtion of the lered lystes ws determined y Brdford method. A lyste of 142 ml of eh smple ws mixed with 8 ml of 15 mm PZA (8 mm finl) to strt the retion nd liquots were removed fter inution for, 5, 15, 3 nd 6 t 37 C. The removed liquots, whih ontined the produt POA, were spun t 16,g for 5 min nd portion of the superntnt ws mixed with 25 mm Fe(NH 4 ) 2 (SO 4 ) 2 to form red-oloured omplex for whih OD 45 ws mesured. A stndrd urve ws mde y mesuring OD 45 of mixture of 25 mm Fe(NH 4 ) 2 (SO 4 ) 2 with inresing onentrtions of POA. Speifi tivity ws lulted t eh time point s nmol NATURE COMMUNICATIONS 6:7226 DOI: 1.138/nomms
EFFECT OF DIETARY ENZYME ON PERFORMANCE OF WEANLING PIGS
 EFFECT OF DIETARY ENZYME ON PERFORMANCE OF WEANLING PIGS Finl report sumitted to Dniso Animl Nutrition E. vn Heugten nd B. Frederik North Crolin Stte University, Deprtment of Animl Siene Summry The urrent
EFFECT OF DIETARY ENZYME ON PERFORMANCE OF WEANLING PIGS Finl report sumitted to Dniso Animl Nutrition E. vn Heugten nd B. Frederik North Crolin Stte University, Deprtment of Animl Siene Summry The urrent
Supplementary Figure 1.
 Supplementary Figure 1. Supplementary Figure 1. Translation of naturally occurring CC[C/U]-[C/U] sequences in E. coli. a. The frequency of occurrence of CC[C/U]-[C/U] in E. coli K12 protein coding genes.
Supplementary Figure 1. Supplementary Figure 1. Translation of naturally occurring CC[C/U]-[C/U] sequences in E. coli. a. The frequency of occurrence of CC[C/U]-[C/U] in E. coli K12 protein coding genes.
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi: 1.138/nture862 humn hr. 21q MRPL39 murine Chr.16 Mrpl39 Dyrk1A Runx1 murine Chr. 17 ZNF295 Ets2 Znf295 murine Chr. 1 COL18A1 -/- lot: nti-dscr1 IgG hevy hin DSCR1 DSCR1 expression reltive to hevy
doi: 1.138/nture862 humn hr. 21q MRPL39 murine Chr.16 Mrpl39 Dyrk1A Runx1 murine Chr. 17 ZNF295 Ets2 Znf295 murine Chr. 1 COL18A1 -/- lot: nti-dscr1 IgG hevy hin DSCR1 DSCR1 expression reltive to hevy
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 1.138/n358 TLR2 nd MyD88 expression in murine mmmry epithelil supopultions. CD24 min plus MRU Myo-epithelil Luminl progenitor (CD61 pos ) Mture luminl (CD61 neg ) CD49f CD61 Reltive expression Krt5
DOI: 1.138/n358 TLR2 nd MyD88 expression in murine mmmry epithelil supopultions. CD24 min plus MRU Myo-epithelil Luminl progenitor (CD61 pos ) Mture luminl (CD61 neg ) CD49f CD61 Reltive expression Krt5
Title of Experiment: Author, Institute and address:
 Title of Experiment: Trsfetion of murine mrophge RAW264.7 ells with METAFECTENE PRO. Author, Institute n ress: Ptrizi Pellegtti n Frneso Di Virgilio. Deprtment of Experimentl n Dignosti Meiine, Setion
Title of Experiment: Trsfetion of murine mrophge RAW264.7 ells with METAFECTENE PRO. Author, Institute n ress: Ptrizi Pellegtti n Frneso Di Virgilio. Deprtment of Experimentl n Dignosti Meiine, Setion
P AND K IN POTATOES. Donald A Horneck Oregon State University Extension Service
 P AND K IN POTATOES Donld A Hornek Oregon Stte University Extension Servie INTRODUCTION Phosphorous nd potssium re importnt to grow high yielding nd qulity pottoes. Muh of the northwest hs hd trditionlly
P AND K IN POTATOES Donld A Hornek Oregon Stte University Extension Servie INTRODUCTION Phosphorous nd potssium re importnt to grow high yielding nd qulity pottoes. Muh of the northwest hs hd trditionlly
Alimonti_Supplementary Figure 1. Pten +/- Pten + Pten. Pten hy. β-actin. Pten - wt hy/+ +/- wt hy/+ +/- Pten. Pten. Relative Protein level (% )
 Alimonti_Supplementry Figure 1 hy 3 4 5 3 Neo 4 5 5 Proe 5 Proe hy/ hy/ /- - 3 6 Neo β-tin d Reltive Protein level (% ) 15 1 5 hy/ /- Reltive Gene Expr. (% ) 15 1 5 hy/ /- Supplementry Figure 1 Chrteriztion
Alimonti_Supplementry Figure 1 hy 3 4 5 3 Neo 4 5 5 Proe 5 Proe hy/ hy/ /- - 3 6 Neo β-tin d Reltive Protein level (% ) 15 1 5 hy/ /- Reltive Gene Expr. (% ) 15 1 5 hy/ /- Supplementry Figure 1 Chrteriztion
Cos7 (3TP) (K): TGFβ1(h): (K)
 IP#2: IP#1: Totl Lystes luiferse tivity (K): 6-4 - (K): luiferse tivity luiferse tivity (K): 2 1 RL-: - + + + + + Sm4-3F: + - + + + + MYC-Sm3: - - - - + + TβRI-HA(T204D): - - - + - + α-ha Luiferse Ativity
IP#2: IP#1: Totl Lystes luiferse tivity (K): 6-4 - (K): luiferse tivity luiferse tivity (K): 2 1 RL-: - + + + + + Sm4-3F: + - + + + + MYC-Sm3: - - - - + + TβRI-HA(T204D): - - - + - + α-ha Luiferse Ativity
Using Paclobutrazol to Suppress Inflorescence Height of Potted Phalaenopsis Orchids
 Using Pcloutrzol to Suppress Inflorescence Height of Potted Phlenopsis Orchids A REPORT SUBMITTED TO FINE AMERICAS Linsey Newton nd Erik Runkle Deprtment of Horticulture Spring 28 Using Pcloutrzol to Suppress
Using Pcloutrzol to Suppress Inflorescence Height of Potted Phlenopsis Orchids A REPORT SUBMITTED TO FINE AMERICAS Linsey Newton nd Erik Runkle Deprtment of Horticulture Spring 28 Using Pcloutrzol to Suppress
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:.8/nture98 : hr NEMO :5 hr IKK IKK NF-κB p65 p5 p65/-rel NF-κB p65 p5 p65/-rel Cytoplsm Cytoplsm p65/p5 Nuleus Nuleus NEMO IKK IKK d : hr > : hr p65/-rel NF- p65 p5 Cytoplsm Cytoplsm p65/p5 p65/-rel
doi:.8/nture98 : hr NEMO :5 hr IKK IKK NF-κB p65 p5 p65/-rel NF-κB p65 p5 p65/-rel Cytoplsm Cytoplsm p65/p5 Nuleus Nuleus NEMO IKK IKK d : hr > : hr p65/-rel NF- p65 p5 Cytoplsm Cytoplsm p65/p5 p65/-rel
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 1.13/n7 Reltive Pprg mrna 3 1 1 Time (weeks) Interspulr Inguinl Epididyml Reltive undne..1.5. - 5 5-51 51-1 1-7 7 - - 1 1-1 Lipid droplet size ( m ) 1-3 3 - - - 1 1-1 1-1 1-175 175-3 3-31 31-5 >5
DOI: 1.13/n7 Reltive Pprg mrna 3 1 1 Time (weeks) Interspulr Inguinl Epididyml Reltive undne..1.5. - 5 5-51 51-1 1-7 7 - - 1 1-1 Lipid droplet size ( m ) 1-3 3 - - - 1 1-1 1-1 1-175 175-3 3-31 31-5 >5
Supplementary Figure S1
 Supplementry Figure S1 - UTR m - 3HA - 2-1 hgh - 1 Uiquitin *! *! lk distl promoter m K3R/ K121R-3HA UTR hgh founder lines - HA - - founder lines TG- E1 L A2 B1 F9 G6 H4 H6 B C D2 G1 H3 J2 L - 7 IP: lk
Supplementry Figure S1 - UTR m - 3HA - 2-1 hgh - 1 Uiquitin *! *! lk distl promoter m K3R/ K121R-3HA UTR hgh founder lines - HA - - founder lines TG- E1 L A2 B1 F9 G6 H4 H6 B C D2 G1 H3 J2 L - 7 IP: lk
LHb VTA. VTA-projecting RMTg-projecting overlay. Supplemental Figure 2. Retrograde labeling of LHb neurons. a. VTA-projecting LHb
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementl Figure 1 doi:10.1038/nture09742 Lterl 1.0 mm from midline mpfc BNST mpfc BNST Lterl 2.1 mm from midline LHA LHA Lterl 2.7 mm from midline SUPPLEMENTAL INFORMATION
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementl Figure 1 doi:10.1038/nture09742 Lterl 1.0 mm from midline mpfc BNST mpfc BNST Lterl 2.1 mm from midline LHA LHA Lterl 2.7 mm from midline SUPPLEMENTAL INFORMATION
FRAMEstar. 2-Component PCR Plates
 FRAMEstr -Component Pltes FrmeStr two-omponent tehnology redues evportion from pltes, improving results nd llowing for volume redutions to sve on expensive regents. FrmeStr pltes mximise therml stility
FRAMEstr -Component Pltes FrmeStr two-omponent tehnology redues evportion from pltes, improving results nd llowing for volume redutions to sve on expensive regents. FrmeStr pltes mximise therml stility
Nucleosome positioning as a determinant of exon recognition
 Nuleosome positioning s determinnt of exon reognition Hgen Tilgner 1,3, Christoforos Nikolou 1,3, Sonj Althmmer 1, Mihel Smmeth 1, Miguel Beto 1, Jun Vlárel 1,2 & Roderi Guigó 1 200 Nture Ameri, In. All
Nuleosome positioning s determinnt of exon reognition Hgen Tilgner 1,3, Christoforos Nikolou 1,3, Sonj Althmmer 1, Mihel Smmeth 1, Miguel Beto 1, Jun Vlárel 1,2 & Roderi Guigó 1 200 Nture Ameri, In. All
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 % ells with ili (mrke y A-Tu) Reltive Luiferse % ells with ili (mrke y Arl13) % ells with ili DOI: 1.138/n2259 A-Tuulin Hoehst % Cilite Non-ilite -Serum 9% 8% 7% 1 6% % 4% +Serum 1 3% 2% 1% % Serum: -
% ells with ili (mrke y A-Tu) Reltive Luiferse % ells with ili (mrke y Arl13) % ells with ili DOI: 1.138/n2259 A-Tuulin Hoehst % Cilite Non-ilite -Serum 9% 8% 7% 1 6% % 4% +Serum 1 3% 2% 1% % Serum: -
Chloride Nutrition Regulates Water Balance in Plants
 XII Portuguese-Spnish Symposium on Plnt Wter Reltions Chloride Nutrition Regultes Wter Blne in Plnts Frno-Nvrro JD 1, Brumós J, Rosles MA 1, Vázquez-Rodríguez A 1, Sñudo BJ 1, Díz- Rued P 1, Rivero C 1,
XII Portuguese-Spnish Symposium on Plnt Wter Reltions Chloride Nutrition Regultes Wter Blne in Plnts Frno-Nvrro JD 1, Brumós J, Rosles MA 1, Vázquez-Rodríguez A 1, Sñudo BJ 1, Díz- Rued P 1, Rivero C 1,
Chow KD CR HFD. Fed Fast Refed
 Supplementry Figure 1 Control d/d Chow KD CR Fed Fst Refed Supplementry Figure 1: Liver expression in diet nd disese models. () expression in the livers of ontrol nd d/d mie. () expression in the livers
Supplementry Figure 1 Control d/d Chow KD CR Fed Fst Refed Supplementry Figure 1: Liver expression in diet nd disese models. () expression in the livers of ontrol nd d/d mie. () expression in the livers
The GCN5-CITED2-PKA signalling module controls hepatic glucose metabolism through a camp-induced substrate switch
 Reeived 6 Apr 216 Aepted 8 Sep 216 Pulished 22 Nov 216 DOI: 1.138/nomms13147 OPEN The GCN5-CITED2-PKA signlling module ontrols hepti gluose metolism through AMP-indued sustrte swith Mshito Ski 1, Tomoko
Reeived 6 Apr 216 Aepted 8 Sep 216 Pulished 22 Nov 216 DOI: 1.138/nomms13147 OPEN The GCN5-CITED2-PKA signlling module ontrols hepti gluose metolism through AMP-indued sustrte swith Mshito Ski 1, Tomoko
EFFECT OF SOYBEAN CYST NEMATODE ON GROWTH OF DRY BEAN. Research Report to Northarvest Bean Growers, January 19, 2009
 EFFECT OF SOYBEAN CYST NEMATODE ON GROWTH OF DRY BEAN Reserh Report to Northrvest Ben Growers, Jnury 19, 29 Berlin D. Nelson, Susilo Poromrto, n Ruell Goswmi, Dept. Plnt Pthology, NDSU Ojetive: Determine
EFFECT OF SOYBEAN CYST NEMATODE ON GROWTH OF DRY BEAN Reserh Report to Northrvest Ben Growers, Jnury 19, 29 Berlin D. Nelson, Susilo Poromrto, n Ruell Goswmi, Dept. Plnt Pthology, NDSU Ojetive: Determine
Interplay of LRRK2 with chaperone-mediated autophagy
 Interply of with hperone-medited utophgy Smnth J Orenstein,, Sheng-Hn Kuo,, Inmuld Tsset,,, Espernz Aris,, Hiroshi Kog,, Irene Fernndez-Crs, Etty Cortes,5, Lwrene S Honig,5, Willim Duer 6, Antonell Consiglio,7,
Interply of with hperone-medited utophgy Smnth J Orenstein,, Sheng-Hn Kuo,, Inmuld Tsset,,, Espernz Aris,, Hiroshi Kog,, Irene Fernndez-Crs, Etty Cortes,5, Lwrene S Honig,5, Willim Duer 6, Antonell Consiglio,7,
Trans-dominant inhibition of RNA viral replication can slow growth of drug-resistant viruses
 25 Nture Pulishing Group http://www.nture.om/nturegenetis Trns-dominnt inhiition of RNA virl replition n slow growth of drug-resistnt viruses Sott Crowder & Krl Kirkegrd The high error rtes of virl RNA-dependent
25 Nture Pulishing Group http://www.nture.om/nturegenetis Trns-dominnt inhiition of RNA virl replition n slow growth of drug-resistnt viruses Sott Crowder & Krl Kirkegrd The high error rtes of virl RNA-dependent
(% of adherent cells) *** PBL firm adhesion. Frequency (% ) 4 1 L 2 CXCR3 DP-2
 Chemotxis (% of dded ells) PBL totl dhesion (N ells/mm 2 /1.1 6 PBL) Frequeny (% ) PBL firm dhesion Supplementry Figure 1 4 4 3 3 2 2 1.1-4 1-3 1.1.2. 1 1 8 6 4 2 Adiponetin ( g/ml) - + Adiponetin ( g/ml)
Chemotxis (% of dded ells) PBL totl dhesion (N ells/mm 2 /1.1 6 PBL) Frequeny (% ) PBL firm dhesion Supplementry Figure 1 4 4 3 3 2 2 1.1-4 1-3 1.1.2. 1 1 8 6 4 2 Adiponetin ( g/ml) - + Adiponetin ( g/ml)
Inhibitory effect of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase inhibitors on cytokine release from human macrophages
 British Journl of Phrmology (26) 149, 393 44 & 26 Nture Pulishing Group All rights reserved 7 1188/6 $3. www.rjphrmol.org RESEARCH PAPER Inhiitory effet of p38 mitogen-tivted protein kinse inhiitors on
British Journl of Phrmology (26) 149, 393 44 & 26 Nture Pulishing Group All rights reserved 7 1188/6 $3. www.rjphrmol.org RESEARCH PAPER Inhiitory effet of p38 mitogen-tivted protein kinse inhiitors on
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 { OI: 1.138/n31 Srifie n nlyze APs on week 1 s of iet 1 4 6 High-ft iet BrU High-ft iet BrU 4 High-ft iet BrU 6 High-ft iet BrU Lin - Lin - : C34 + : C9 + 1 1 3 1 4 1 5 C45 1 C34 1 1 1 1 3 1 4 1 5 S-1
{ OI: 1.138/n31 Srifie n nlyze APs on week 1 s of iet 1 4 6 High-ft iet BrU High-ft iet BrU 4 High-ft iet BrU 6 High-ft iet BrU Lin - Lin - : C34 + : C9 + 1 1 3 1 4 1 5 C45 1 C34 1 1 1 1 3 1 4 1 5 S-1
Plant Physiology Preview. Published on February 21, 2017, as DOI: /pp
 Plnt Physiology Preview. Pulished on Ferury 21, 217, s DOI:1.114/pp.16.1928 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 1 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 Running title: Spliing regultor STA1 in het stress dpttion Corresponding Author:
Plnt Physiology Preview. Pulished on Ferury 21, 217, s DOI:1.114/pp.16.1928 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 1 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 Running title: Spliing regultor STA1 in het stress dpttion Corresponding Author:
Introduction to Study Designs II
 Introdution to Study Designs II Commonly used study designs in publi helth & epidemiologi reserh Benjmin Rihrd H. Muthmbi, DrPH, MPH Stte HIV Epidemiologist HIV Epidemiology Investigtion Setion PA Deprtment
Introdution to Study Designs II Commonly used study designs in publi helth & epidemiologi reserh Benjmin Rihrd H. Muthmbi, DrPH, MPH Stte HIV Epidemiologist HIV Epidemiology Investigtion Setion PA Deprtment
Other Uses for Cluster Sampling
 Other Uses for Cluster Smpling Mesure hnges in the level of n ttriute Hypothesis testing versus intervl estimtion Type I n 2 errors Power of the test Mesuring ttriute t sme time in ifferent sites Exmple:
Other Uses for Cluster Smpling Mesure hnges in the level of n ttriute Hypothesis testing versus intervl estimtion Type I n 2 errors Power of the test Mesuring ttriute t sme time in ifferent sites Exmple:
Mechanisms underlying cross-orientation suppression in cat visual cortex
 Mehnisms underlying ross-orienttion suppression in t visul ortex 6 Nture Pulishing Group http://www.nture.om/ntureneurosiene Nihols J Priee & Dvid Ferster In simple ells of the t primry visul ortex, null-oriented
Mehnisms underlying ross-orienttion suppression in t visul ortex 6 Nture Pulishing Group http://www.nture.om/ntureneurosiene Nihols J Priee & Dvid Ferster In simple ells of the t primry visul ortex, null-oriented
Lesions of prefrontal cortex reduce attentional modulation of neuronal responses. and synchrony in V4
 Lesions of prefrontl ortex reue ttentionl moultion of neuronl responses n synhrony in V4 Georgi G. Gregoriou,, Anrew F. Rossi, 3 Leslie G Ungerleier, 4 Roert Desimone 5 Deprtment of Bsi Sienes, Fulty of
Lesions of prefrontl ortex reue ttentionl moultion of neuronl responses n synhrony in V4 Georgi G. Gregoriou,, Anrew F. Rossi, 3 Leslie G Ungerleier, 4 Roert Desimone 5 Deprtment of Bsi Sienes, Fulty of
Fates-shifted is an F box protein that targets Bicoid for degradation and regulates developmental fate determination in Drosophila embryos
 ARTICLES Ftes-shifted is n F ox protein tht trgets Bioid for degrdtion nd regultes developmentl fte determintion in Drosophil emryos Juno Liu 1 nd Jun M 1,2,3 Bioid (Bd) is morphogeneti protein tht instruts
ARTICLES Ftes-shifted is n F ox protein tht trgets Bioid for degrdtion nd regultes developmentl fte determintion in Drosophil emryos Juno Liu 1 nd Jun M 1,2,3 Bioid (Bd) is morphogeneti protein tht instruts
Genome-wide nucleosome positioning during embryonic stem cell development
 Genome-wide nuleosome positioning during emryoni stem ell development Vldimir B Teif 1,2, Yevhen Vinshtein 2,3, Mïwen Cudron-Herger 1,2, Jn-Philipp Mllm 1,2, Croline Mrth 1,2, Thoms Höfer 2,3 & Krsten
Genome-wide nuleosome positioning during emryoni stem ell development Vldimir B Teif 1,2, Yevhen Vinshtein 2,3, Mïwen Cudron-Herger 1,2, Jn-Philipp Mllm 1,2, Croline Mrth 1,2, Thoms Höfer 2,3 & Krsten
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:.38/nture277 d 25 25 2 Time from sound onset (ms) 25 25 2 Time from sound onset (ms) Firing rte (spikes/s) Firing rte (spikes/s).8.6..2 e f g h.8.6..2 Frtion of neurons Frtion of neurons N = 53 2 2
doi:.38/nture277 d 25 25 2 Time from sound onset (ms) 25 25 2 Time from sound onset (ms) Firing rte (spikes/s) Firing rte (spikes/s).8.6..2 e f g h.8.6..2 Frtion of neurons Frtion of neurons N = 53 2 2
Learning to see: experience and attention in primary visual cortex
 2 Nture Pulishing Group http://neurosi.nture.om rtiles Lerning to see: experiene nd ttention in primry visul ortex 2 Nture Pulishing Group http://neurosi.nture.om Roy E. Crist, Wu Li nd Chrles D. Gilert
2 Nture Pulishing Group http://neurosi.nture.om rtiles Lerning to see: experiene nd ttention in primry visul ortex 2 Nture Pulishing Group http://neurosi.nture.om Roy E. Crist, Wu Li nd Chrles D. Gilert
Whangarei District Council Class 4 Gambling Venue Policy
 Whngrei Distrit Counil Clss 4 Gmling Venue Poliy April 2013 Whngrei Distrit Counil Clss 4 Gmling Venue Poliy Tle of ontents Introdution... 3 1 Ojetives of the poliy in so fr s promoted y the Gmling At
Whngrei Distrit Counil Clss 4 Gmling Venue Poliy April 2013 Whngrei Distrit Counil Clss 4 Gmling Venue Poliy Tle of ontents Introdution... 3 1 Ojetives of the poliy in so fr s promoted y the Gmling At
Objectives. R/S determination. R/S determination. Epoxidation. Last lecture Chirality
 Lst leture hirlity This leture enntiomers distereomers / nottion hirlity jetives optil & iologil properties hirl moleules ontining more thn one hirlity enter. retions tht rete stereoisomers 1 Dr. Ky nderg
Lst leture hirlity This leture enntiomers distereomers / nottion hirlity jetives optil & iologil properties hirl moleules ontining more thn one hirlity enter. retions tht rete stereoisomers 1 Dr. Ky nderg
WesternBright Quantum
 WesternBright Quntum Quntify hemiluminesent Western lots over wie ynmi rnge WesternBright Quntum is new hemiluminesent regent speilly formulte for CCD imging. This novel Horserish peroxise (HRP) sustrte
WesternBright Quntum Quntify hemiluminesent Western lots over wie ynmi rnge WesternBright Quntum is new hemiluminesent regent speilly formulte for CCD imging. This novel Horserish peroxise (HRP) sustrte
Open Access RESEARCH ARTICLE. Genetics Selection Evolution
 DOI 10.1186/s12711-016-0222-0 Genetis Seletion Evolution RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Aess Comprison of host geneti ftors influening pig response to infetion with two North Amerin isoltes of porine reprodutive
DOI 10.1186/s12711-016-0222-0 Genetis Seletion Evolution RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Aess Comprison of host geneti ftors influening pig response to infetion with two North Amerin isoltes of porine reprodutive
Lipid Composition of Egg Yolk and Serum in Laying Hens Fed Diets Containing Black Cumin (Nigella sativa)
 Interntionl Journl of Poultry Siene 5 (6): 574-578, 2006 ISSN 682-8356 Asin Network for Sientifi Informtion, 2006 Lipid Composition of Egg Yolk nd Serum in Lying Hens Fed Diets Contining Blk Cumin (Nigell
Interntionl Journl of Poultry Siene 5 (6): 574-578, 2006 ISSN 682-8356 Asin Network for Sientifi Informtion, 2006 Lipid Composition of Egg Yolk nd Serum in Lying Hens Fed Diets Contining Blk Cumin (Nigell
Poultry No The replacement value of betaine for DL-methionine and Choline in broiler diets
 Poultry No. 1573 The replement vlue of etine for DL-methionine nd Choline in roiler diets Key Informtion In roiler diets defiient in sulfur mino ids ut dequtely supplemented with methyl groups vi dded
Poultry No. 1573 The replement vlue of etine for DL-methionine nd Choline in roiler diets Key Informtion In roiler diets defiient in sulfur mino ids ut dequtely supplemented with methyl groups vi dded
Autocrine IL-2 is required for secondary population expansion of CD8 + memory T cells
 Autorine IL-2 is required for seondry popultion expnsion of CD8 + memory T ells Soni Feu, Rmon Arens,2, Susn Togher & Stephen P Shoenerger 2 Nture Ameri, In. All rights reserved. Two ompeting theories
Autorine IL-2 is required for seondry popultion expnsion of CD8 + memory T ells Soni Feu, Rmon Arens,2, Susn Togher & Stephen P Shoenerger 2 Nture Ameri, In. All rights reserved. Two ompeting theories
The Hippo/YAP pathway interacts with EGFR signaling and HPV oncoproteins to regulate cervical cancer progression
 Reserh Artile The Hippo/ pthwy interts with EGFR signling nd HPV onoproteins to regulte ervil ner progression Chuno He 1,, Dgn Mo 1,3, Guohu Hu 1,, Xingmin Lv 1, Xingheng Chen, Peter C Angeletti 5, Jixin
Reserh Artile The Hippo/ pthwy interts with EGFR signling nd HPV onoproteins to regulte ervil ner progression Chuno He 1,, Dgn Mo 1,3, Guohu Hu 1,, Xingmin Lv 1, Xingheng Chen, Peter C Angeletti 5, Jixin
Ulk λ PPase. 32 P-Ulk1 32 P-GST-TSC2. Ulk1 GST (TSC2) : Ha-Ulk1 : AMPK. WB: Ha (Ulk1) : Glu. h CON - Glu - A.A WB: LC3 AMPK-WT AMPK-DKO
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb2152 C.C + - + - : Glu b Ulk1 - - + λ PPse c AMPK + - + + : ATP P-GST-TSC2 WB: Flg (Ulk1) WB Ulk1 WB: H (Ulk1) GST (TSC2) C.C d e WT K46R - + - + : H-Ulk1 : AMPK - + - + + + AMPK H-Ulk1
DOI: 10.1038/ncb2152 C.C + - + - : Glu b Ulk1 - - + λ PPse c AMPK + - + + : ATP P-GST-TSC2 WB: Flg (Ulk1) WB Ulk1 WB: H (Ulk1) GST (TSC2) C.C d e WT K46R - + - + : H-Ulk1 : AMPK - + - + + + AMPK H-Ulk1
EFFECTS OF AN ACUTE ENTERIC DISEASE CHALLENGE ON IGF-1 AND IGFBP-3 GENE EXPRESSION IN PORCINE SKELETAL MUSCLE
 Swine Dy 22 Contents EFFECTS OF AN ACUTE ENTERIC DISEASE CHALLENGE ON IGF-1 AND IGFBP-3 GENE EXPRESSION IN PORCINE SKELETAL MUSCLE B. J. Johnson, J. P. Kyser, J. D. Dunn, A. T. Wyln, S. S. Dritz 1, J.
Swine Dy 22 Contents EFFECTS OF AN ACUTE ENTERIC DISEASE CHALLENGE ON IGF-1 AND IGFBP-3 GENE EXPRESSION IN PORCINE SKELETAL MUSCLE B. J. Johnson, J. P. Kyser, J. D. Dunn, A. T. Wyln, S. S. Dritz 1, J.
YAP transcriptionally regulates COX-2 expression and GCCSysm-4 (G-4), a dual YAP/COX-2 inhibitor, overcomes drug resistance in colorectal cancer
 Li et l. Journl of Experimentl & Clinil Cner Reserh (7) 36:44 DOI.86/s346-7-6-3 RESEARCH Open Aess trnsriptionlly regultes expression nd GCCSysm-4 (G-4), dul / inhiitor, overomes drug resistne in oloretl
Li et l. Journl of Experimentl & Clinil Cner Reserh (7) 36:44 DOI.86/s346-7-6-3 RESEARCH Open Aess trnsriptionlly regultes expression nd GCCSysm-4 (G-4), dul / inhiitor, overomes drug resistne in oloretl
Supplementary Figure 1. Scheme of unilateral pyramidotomy used for detecting compensatory sprouting of intact CST axons.
 () BDA 2 weeks fter Py () AAVs Cre or GFP t P1 BDA 2 weeks fter Py CSMN CST () Py t P7 or 2 months () Py t 2 months Supplementry Figure 1. Sheme of unilterl pyrmidotomy used for deteting ompenstory sprouting
() BDA 2 weeks fter Py () AAVs Cre or GFP t P1 BDA 2 weeks fter Py CSMN CST () Py t P7 or 2 months () Py t 2 months Supplementry Figure 1. Sheme of unilterl pyrmidotomy used for deteting ompenstory sprouting
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Prentl doi:.8/nture57 Figure S HPMECs LM Cells Cell lines VEGF (ng/ml) Prentl 7. +/-. LM 7. +/-.99 LM 7. +/-.99 Fold COX induction 5 VEGF: - + + + Bevcizum: - - 5 (µg/ml) Reltive MMP LM mock COX MMP LM+
Prentl doi:.8/nture57 Figure S HPMECs LM Cells Cell lines VEGF (ng/ml) Prentl 7. +/-. LM 7. +/-.99 LM 7. +/-.99 Fold COX induction 5 VEGF: - + + + Bevcizum: - - 5 (µg/ml) Reltive MMP LM mock COX MMP LM+
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementry Figure 1 c d Wistr SHR Wistr AF-353 SHR AF-353 n = 6 n = 6 n = 28 n = 3 n = 12 n = 12 Supplementry Figure 1 Neurophysiologicl properties of petrosl chemoreceptive neurones in Wistr nd SH rts.
Supplementry Figure 1 c d Wistr SHR Wistr AF-353 SHR AF-353 n = 6 n = 6 n = 28 n = 3 n = 12 n = 12 Supplementry Figure 1 Neurophysiologicl properties of petrosl chemoreceptive neurones in Wistr nd SH rts.
supplementary information
 DOI:.38/n83 k Mouse Ch8 lous 8 9 Stop CHD8L 75 CHD8L Chromoomins Helise/ATPse omin DNA ining omin 5 kd NIH 3T3 MEF 93T HeL HCT UOS SOS.. CHD8L IB: CHD8 8 5 L S Reltive mrna mount 3... Reltive mrna mount.8.
DOI:.38/n83 k Mouse Ch8 lous 8 9 Stop CHD8L 75 CHD8L Chromoomins Helise/ATPse omin DNA ining omin 5 kd NIH 3T3 MEF 93T HeL HCT UOS SOS.. CHD8L IB: CHD8 8 5 L S Reltive mrna mount 3... Reltive mrna mount.8.
static principle: output determined by a connection with strong node dynamic principle: output (sometimes) determined by a weak (floating) node
 stti n ynmi priniple pmos network nmos network v out stti priniple: output etermine y onnetion with strong noe ynmi priniple: output (sometimes) etermine y wek (floting) noe hrging: C s is eing hrge up
stti n ynmi priniple pmos network nmos network v out stti priniple: output etermine y onnetion with strong noe ynmi priniple: output (sometimes) etermine y wek (floting) noe hrging: C s is eing hrge up
BTLA is a lymphocyte inhibitory receptor with similarities to CTLA-4 and PD-1
 BTLA is lymphoyte inhiitory reeptor with similrities to CTLA-4 nd PD-1 Norihiko Wtne 1,5, My Gvrieli 1, John R Sedy 1, Jinfei Yng 1,5, Frnes Fllrino 2, Susn K Loftin 1, Mihelle A Hurhl 1, Ntlie Zimmermn
BTLA is lymphoyte inhiitory reeptor with similrities to CTLA-4 nd PD-1 Norihiko Wtne 1,5, My Gvrieli 1, John R Sedy 1, Jinfei Yng 1,5, Frnes Fllrino 2, Susn K Loftin 1, Mihelle A Hurhl 1, Ntlie Zimmermn
Check your understanding 3
 1 Wht is the difference etween pssive trnsport nd ctive trnsport? Pssive trnsport is the movement of prticles not requiring energy. Movement of prticles in ctive trnsport uses energy. 2 A gs tp in the
1 Wht is the difference etween pssive trnsport nd ctive trnsport? Pssive trnsport is the movement of prticles not requiring energy. Movement of prticles in ctive trnsport uses energy. 2 A gs tp in the
Chapter 7. Control and Coordination
 Chpter 7 Control n Coorintion 1 Whih of the following sttements is orret out reeptors? Gusttory reeptors etet tste while olftory reeptors etet smell Both gusttory n olftory reeptors etet smell Auitory
Chpter 7 Control n Coorintion 1 Whih of the following sttements is orret out reeptors? Gusttory reeptors etet tste while olftory reeptors etet smell Both gusttory n olftory reeptors etet smell Auitory
RESEARCH ARTICLE. Supplemental Figure 5
 11.5 2 2 11. RESEARCH ARTICLE RBC ( 1 12 /L) 1.5 1. 9.5 PLT ( 1 9 /L) 1 16 14 HGB (g/l) 19 1 17 16 9. 12 4 4 46 Cellulr & Moleulr Immunology dvne online pulition, PCV (%) 44 MCV (fl) 46 44 ; doi:1.13/mi.214.16
11.5 2 2 11. RESEARCH ARTICLE RBC ( 1 12 /L) 1.5 1. 9.5 PLT ( 1 9 /L) 1 16 14 HGB (g/l) 19 1 17 16 9. 12 4 4 46 Cellulr & Moleulr Immunology dvne online pulition, PCV (%) 44 MCV (fl) 46 44 ; doi:1.13/mi.214.16
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:.8/nture89 4 4 Ilr -/- Ilr -/- Ilr -/- Cspse- -/- As -/- Nlrp -/- Il8 -/- Ilr -/- Supplementl figure. Inresed severity of NASH in inflmmsome-defiient mie, ut not in Ilr-defiient
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:.8/nture89 4 4 Ilr -/- Ilr -/- Ilr -/- Cspse- -/- As -/- Nlrp -/- Il8 -/- Ilr -/- Supplementl figure. Inresed severity of NASH in inflmmsome-defiient mie, ut not in Ilr-defiient
REVIEW Study of the Formation of trans Fatty Acids in Model Oils (triacylglycerols) and Edible Oils during the Heating Process
 JARQ 46 (3), 215 220 (2012) http://www.jirs.ffr.go.jp REVIEW Study of the Formtion of trns Ftty Aids in Model Oils (triylglyerols) nd Edible Oils during the Heting Proess Wkko TSUZUKI* Food Resoure Division,
JARQ 46 (3), 215 220 (2012) http://www.jirs.ffr.go.jp REVIEW Study of the Formtion of trns Ftty Aids in Model Oils (triylglyerols) nd Edible Oils during the Heting Proess Wkko TSUZUKI* Food Resoure Division,
larvi 2013 Epigenetic regulation of muscle development and growth in Senegalese sole larvae Catarina Campos
 lrvi 213 6th fish & shellfish lrviulture symposium Epigeneti regultion of musle development nd growth in Seneglese sole lrve Ctrin Cmpos ghent university, elgium, 2-5 septemer 213 EPIGENETIC REGULATION
lrvi 213 6th fish & shellfish lrviulture symposium Epigeneti regultion of musle development nd growth in Seneglese sole lrve Ctrin Cmpos ghent university, elgium, 2-5 septemer 213 EPIGENETIC REGULATION
Multisite phosphorylation of a CDK inhibitor sets a threshold for the onset of DNA replication
 Multisite phosphoryltion of CDK inhiitor sets threshold for the onset of DNA replition iers Nsh*², iojing Tng*², Stephen Orliky*, Qinghu Chen³, Frnk B. Gertler, Mihel D. Mendenhll³, Frnk Siheri*k, Tony
Multisite phosphoryltion of CDK inhiitor sets threshold for the onset of DNA replition iers Nsh*², iojing Tng*², Stephen Orliky*, Qinghu Chen³, Frnk B. Gertler, Mihel D. Mendenhll³, Frnk Siheri*k, Tony
FAK integrates growth-factor and integrin signals to promote cell migration
 integrtes growth-ftor nd integrin signls to promote ell migrtion rtiles Dvid J. Sieg*, Christof R. Huk*, Dusko Ili, Cndie K. Klingeil*, Erik Shefer, Croline H. Dmsky nd Dvid D. Shlepfer* *Deprtment of
integrtes growth-ftor nd integrin signls to promote ell migrtion rtiles Dvid J. Sieg*, Christof R. Huk*, Dusko Ili, Cndie K. Klingeil*, Erik Shefer, Croline H. Dmsky nd Dvid D. Shlepfer* *Deprtment of
A AOAC Official Method Fat (Total, Saturated, Unsaturated, and Monounsaturated) in Cereal Products
 32.2.02A AOAC Offiil Method 996.01 Ft (Totl, Sturted, Unsturted, nd Monounsturted) in Cerel Produts Aid Hydrolysis Cpillry Gs Chromtogrphi Method First Ation 1996 (Applile for determintion of ft in erel
32.2.02A AOAC Offiil Method 996.01 Ft (Totl, Sturted, Unsturted, nd Monounsturted) in Cerel Produts Aid Hydrolysis Cpillry Gs Chromtogrphi Method First Ation 1996 (Applile for determintion of ft in erel
a3 Chains of type V collagen regulate breast tumour growth via glypican-1
 Reeive 5 Aug 16 Aepte De 16 Pulishe 19 Jn 17 3 Chins of type V ollgen regulte rest tumour growth vi glypin-1 Guorui Hung 1, Goxing Ge 1,w, Vlerio Izzi & Dniel S. Greenspn 1 DOI: 1.138/nomms1351 OPEN Periellulr
Reeive 5 Aug 16 Aepte De 16 Pulishe 19 Jn 17 3 Chins of type V ollgen regulte rest tumour growth vi glypin-1 Guorui Hung 1, Goxing Ge 1,w, Vlerio Izzi & Dniel S. Greenspn 1 DOI: 1.138/nomms1351 OPEN Periellulr
LETTERS. Disulphide-isomerase-enabled shedding of tumour-associated NKG2D ligands
 Vol 447 24 My 2007 doi:10.1038/nture05768 LETTERS Disulphide-isomerse-enled shedding of tumour-ssoited NKG2D lignds Brett K. Kiser 1 *, Desong Yim 1 *, I-Ting Chow 1 *, Segundo Gonzlez 1 {, Zhenpeng Di
Vol 447 24 My 2007 doi:10.1038/nture05768 LETTERS Disulphide-isomerse-enled shedding of tumour-ssoited NKG2D lignds Brett K. Kiser 1 *, Desong Yim 1 *, I-Ting Chow 1 *, Segundo Gonzlez 1 {, Zhenpeng Di
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:1.138/nture1794 BR EPFs BRI1? ERECTA TMM BSKs YDA PP2A BSU1 BIN2 pbzr1/2 BZR1/2 MKK4/5/7/9 MPK3/6 SPCH Cell growth Stomtl production Supplementry Figure 1. The model of BR nd stomtl signling pthwys.
doi:1.138/nture1794 BR EPFs BRI1? ERECTA TMM BSKs YDA PP2A BSU1 BIN2 pbzr1/2 BZR1/2 MKK4/5/7/9 MPK3/6 SPCH Cell growth Stomtl production Supplementry Figure 1. The model of BR nd stomtl signling pthwys.
Toxicity effects of seven Cu compounds/nps in Lettuce (Lactuca sativa) and Alfalfa (Medicago sativa)
 Toxiity effets of seven Cu ompounds/nps in Lettue (Ltu stiv) nd Alflf (Medigo stiv) Jie Hong, Lijun Zho, Cyren Rio, Jose R Perlt-Vide, Jorge Grde-Torresdey The University of Texs t El Pso UC-CEIN Theme
Toxiity effets of seven Cu ompounds/nps in Lettue (Ltu stiv) nd Alflf (Medigo stiv) Jie Hong, Lijun Zho, Cyren Rio, Jose R Perlt-Vide, Jorge Grde-Torresdey The University of Texs t El Pso UC-CEIN Theme
CAUSES OF DIARRHEA, PNEUMONIA, AND ABORTION IN 1991 CATTLE SUBMISSIONS TO THE KSU VETERINARY DIAGNOSTIC LABORATORY
 CAUSES OF DIARRHEA, PNEUMONIA, AND ABORTION IN 1991 CATTLE SUBMISSIONS TO THE KSU VETERINARY DIAGNOSTIC LABORATORY 1 1 2 R. K. Frnk, M. W. Vorhies, nd M. M. Chengpp Summry Cuses of dirrhe, pneumoni, nd
CAUSES OF DIARRHEA, PNEUMONIA, AND ABORTION IN 1991 CATTLE SUBMISSIONS TO THE KSU VETERINARY DIAGNOSTIC LABORATORY 1 1 2 R. K. Frnk, M. W. Vorhies, nd M. M. Chengpp Summry Cuses of dirrhe, pneumoni, nd
ARTICLE. I. Chopra & H. F. Li & H. Wang & K. A. Webster
 Dietologi (212) 55:783 794 DOI 1.17/s125-11-247-y ARTICLE Phosphoryltion of the insulin reeptor y AMP-tivted protein kinse (AMPK) promotes lignd-independent tivtion of the insulin signlling pthwy in rodent
Dietologi (212) 55:783 794 DOI 1.17/s125-11-247-y ARTICLE Phosphoryltion of the insulin reeptor y AMP-tivted protein kinse (AMPK) promotes lignd-independent tivtion of the insulin signlling pthwy in rodent
Supplementary figure 1
 Supplementry figure 1 Dy 8 post LCMV infection Vsculr Assoc. Prenchym Dy 3 post LCMV infection 1 5 6.7.29 1 4 1 3 1 2 88.9 4.16 1 2 1 3 1 4 1 5 1 5 1.59 5.97 1 4 1 3 1 2 21.4 71 1 2 1 3 1 4 1 5 1 5.59.22
Supplementry figure 1 Dy 8 post LCMV infection Vsculr Assoc. Prenchym Dy 3 post LCMV infection 1 5 6.7.29 1 4 1 3 1 2 88.9 4.16 1 2 1 3 1 4 1 5 1 5 1.59 5.97 1 4 1 3 1 2 21.4 71 1 2 1 3 1 4 1 5 1 5.59.22
AJ PUTT. Hematology. Chemistry. Species: Canine Gender: Female Year of Birth: 2013 Client: PUTT
 Speies: Cnine Gender: Femle Yer of Birth: 2013 Client: PUTT Requisition #: 9034-12 Aession #: W2152816 Aount Code: 72364 Veterinrin: CARTER Pnel/Profile: Tik Pnel Add-on Senior Profile with L 4Dx Plus
Speies: Cnine Gender: Femle Yer of Birth: 2013 Client: PUTT Requisition #: 9034-12 Aession #: W2152816 Aount Code: 72364 Veterinrin: CARTER Pnel/Profile: Tik Pnel Add-on Senior Profile with L 4Dx Plus
Copy Number ID2 MYCN ID2 MYCN. Copy Number MYCN DDX1 ID2 KIDINS220 MBOAT2 ID2
 Copy Numer Copy Numer Copy Numer Copy Numer DIPG38 DIPG49 ID2 MYCN ID2 MYCN c DIPG01 d DIPG29 ID2 MYCN ID2 MYCN e STNG2 f MYCN DIPG01 Chr. 2 DIPG29 Chr. 1 MYCN DDX1 Chr. 2 ID2 KIDINS220 MBOAT2 ID2 Supplementry
Copy Numer Copy Numer Copy Numer Copy Numer DIPG38 DIPG49 ID2 MYCN ID2 MYCN c DIPG01 d DIPG29 ID2 MYCN ID2 MYCN e STNG2 f MYCN DIPG01 Chr. 2 DIPG29 Chr. 1 MYCN DDX1 Chr. 2 ID2 KIDINS220 MBOAT2 ID2 Supplementry
Neural population coding of sound level adapts to stimulus statistics
 COMPUTATION AND SYSTEMS 25 Nture Pulishing Group http://www.nture.om/ntureneurosiene Neurl popultion oding of sound level dpts to stimulus sttistis Isel Den 1, Niol S Hrper 1,2 & Dvid MAlpine 1 Mmmls n
COMPUTATION AND SYSTEMS 25 Nture Pulishing Group http://www.nture.om/ntureneurosiene Neurl popultion oding of sound level dpts to stimulus sttistis Isel Den 1, Niol S Hrper 1,2 & Dvid MAlpine 1 Mmmls n
Intestine specific MTP deficiency with global ACAT2 gene ablation lowers acute cholesterol absorption with chylomicrons and high density lipoproteins
 Intestine speifi MTP defiieny with glol ACAT2 gene ltion lowers ute holesterol sorption with hylomirons nd high density lipoproteins 1,2 Jhngir Iql, 1,2 Mohmed Boutjdir, 3 Lwrene L. Rudel, 1,2 M. Mhmood
Intestine speifi MTP defiieny with glol ACAT2 gene ltion lowers ute holesterol sorption with hylomirons nd high density lipoproteins 1,2 Jhngir Iql, 1,2 Mohmed Boutjdir, 3 Lwrene L. Rudel, 1,2 M. Mhmood
RESEARCH ARTICLE Transport of selenium across the plasma membrane of primary hepatocytes and enterocytes of rainbow trout
 191 The Journl of Experimentl iology 15, 191-151 1. Pulished y The ompny of iologists Ltd doi:1.1/je.37 RESERH RTILE Trnsport of selenium ross the plsm memrne of primry heptoytes nd enteroytes of rinow
191 The Journl of Experimentl iology 15, 191-151 1. Pulished y The ompny of iologists Ltd doi:1.1/je.37 RESERH RTILE Trnsport of selenium ross the plsm memrne of primry heptoytes nd enteroytes of rinow
A AOAC Official Method Fructans in Food Products
 45.4.06A AOAC Offiil Method 997.08 Frutns in Food Produts Ion Exhnge Chromtogrphi Method First Ation 1997 Finl Ation 1999 (Applile to the determintion of dded frutns in proessed foods.) See Tle 997.08A
45.4.06A AOAC Offiil Method 997.08 Frutns in Food Produts Ion Exhnge Chromtogrphi Method First Ation 1997 Finl Ation 1999 (Applile to the determintion of dded frutns in proessed foods.) See Tle 997.08A
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
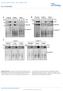 DOI:.3/n95 Thymus Kiney (kd) TA T7 T TA T7 T Hert TA T7 T: +Dox Cylin B (kd) Thymus Kiney Hert TA T5 T TA T5 T TA T5 T: +Dox Cylin B Poneu S Poneu S CnB T7 CnB T Thymus (kd) + Liver Colon + + (kd) Thymus
DOI:.3/n95 Thymus Kiney (kd) TA T7 T TA T7 T Hert TA T7 T: +Dox Cylin B (kd) Thymus Kiney Hert TA T5 T TA T5 T TA T5 T: +Dox Cylin B Poneu S Poneu S CnB T7 CnB T Thymus (kd) + Liver Colon + + (kd) Thymus
Estrogens and androgens affect human luteal cell function
 Estrogens nd ndrogens ffet humn lutel ell funtion Ann Trope, M.D., Antonio Lnzone, M.D., Federi Tieri, B.S., Federi Romni, M.D., Stefni tino, M.L.T., nd Rosnn Ap, M.D. ttedr di Fisioptologi dell Riproduzione
Estrogens nd ndrogens ffet humn lutel ell funtion Ann Trope, M.D., Antonio Lnzone, M.D., Federi Tieri, B.S., Federi Romni, M.D., Stefni tino, M.L.T., nd Rosnn Ap, M.D. ttedr di Fisioptologi dell Riproduzione
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION CD169 + MACROPHAGES PRESENT LIPID ANTIGENS TO MEDIATE EARLY ACTIVATION OF INVARIANT NKT CELLS IN LYMPH NODES Ptrii Brrl, Polo Polzell, Andres Brukuer, Nio vn Rooijen, Gurdyl S.
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION CD169 + MACROPHAGES PRESENT LIPID ANTIGENS TO MEDIATE EARLY ACTIVATION OF INVARIANT NKT CELLS IN LYMPH NODES Ptrii Brrl, Polo Polzell, Andres Brukuer, Nio vn Rooijen, Gurdyl S.
Tankyrase inhibition stabilizes axin and antagonizes Wnt signalling
 Vol 461 1 Otoer 29 doi:1.138/nture8356 Tnkyrse inhiition stilizes xin nd ntgonizes Wnt signlling Shih-Min A. Hung 1, Yuji M. Mishin 1, Shnming Liu 1, Atwood Cheung 1, rnk Stegmeier 1, Gregory A. Mihud
Vol 461 1 Otoer 29 doi:1.138/nture8356 Tnkyrse inhiition stilizes xin nd ntgonizes Wnt signlling Shih-Min A. Hung 1, Yuji M. Mishin 1, Shnming Liu 1, Atwood Cheung 1, rnk Stegmeier 1, Gregory A. Mihud
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 TM TM tip link horizontl top connectors 1 leucine-rich (21 %) otoncorin-like 1809 ntigenic peptides B D signl peptide hydrophoic segment proline/threonine-rich (79 %) Supplementry Figure 1. () The outer
TM TM tip link horizontl top connectors 1 leucine-rich (21 %) otoncorin-like 1809 ntigenic peptides B D signl peptide hydrophoic segment proline/threonine-rich (79 %) Supplementry Figure 1. () The outer
A maternal junk food diet in pregnancy and lactation promotes an exacerbated taste for junk food and a greater propensity for obesity in rat offspring
 British Journl of Nutrition (27), pge 1 of 9 q The uthors 27 doi: 1.117/S7114781237 mternl junk food diet in pregnny nd lttion promotes n exerted tste for junk food nd greter propensity for oesity in rt
British Journl of Nutrition (27), pge 1 of 9 q The uthors 27 doi: 1.117/S7114781237 mternl junk food diet in pregnny nd lttion promotes n exerted tste for junk food nd greter propensity for oesity in rt
SOME MECHANISTIC CONCEPTS IN ELECTROPHILIC ADDITION REACTIONS TO C=C BONDS
 SM MANISTI NPTS IN LTPILI AITIN ATINS T = BNS The = ond is considered to e wek se/nucleophile. The high concentrtion of electron density mkes the pi ond Lewis se, ut in order to donte electrons the pi
SM MANISTI NPTS IN LTPILI AITIN ATINS T = BNS The = ond is considered to e wek se/nucleophile. The high concentrtion of electron density mkes the pi ond Lewis se, ut in order to donte electrons the pi
Operating Systems Principles. Page Replacement Algorithms
 Operting Systems Priniples Pge Replement Algorithms Steve Gor gor@se.unl.eu http://www.se.unl.eu/~gor/courses/csce45 Virtul Memory Mngement Funmentl issues Plement strtegy Replement strtegies Lo ontrol
Operting Systems Priniples Pge Replement Algorithms Steve Gor gor@se.unl.eu http://www.se.unl.eu/~gor/courses/csce45 Virtul Memory Mngement Funmentl issues Plement strtegy Replement strtegies Lo ontrol
Provide a Buffet and Carvery Service
 CU926 Provide Buffet nd Crvery Servie Unit summry This unit is out prepring the rvery or uffet disply y rrnging items suh s rokery, utlery nd npkins. It lso overs serving ustomers t the rvery or uffet
CU926 Provide Buffet nd Crvery Servie Unit summry This unit is out prepring the rvery or uffet disply y rrnging items suh s rokery, utlery nd npkins. It lso overs serving ustomers t the rvery or uffet
Not for Citation or Publication Without Consent of the Author
 Not for Cittion or Puliction Without Consent of the Author AN AUTOMATED SEX PHEROMONE TRAP FOR MONITORING ADULT CM AND OFM AND THE INFLUENCE OF TRAP COLOR ON MOTH AND NON-TARGET CAPTURES Brin L. Lehmn
Not for Cittion or Puliction Without Consent of the Author AN AUTOMATED SEX PHEROMONE TRAP FOR MONITORING ADULT CM AND OFM AND THE INFLUENCE OF TRAP COLOR ON MOTH AND NON-TARGET CAPTURES Brin L. Lehmn
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 . Norml Physiologicl Conditions. SIRT1 Loss-of-Function S1. Model for the role of SIRT1 in the regultion of memory nd plsticity. () Our findings suggest tht SIRT1 normlly functions in coopertion with YY1,
. Norml Physiologicl Conditions. SIRT1 Loss-of-Function S1. Model for the role of SIRT1 in the regultion of memory nd plsticity. () Our findings suggest tht SIRT1 normlly functions in coopertion with YY1,
A critical assessment of different transmethylation procedures commonly employed in the fatty acid analysis of aquatic organisms
 LIMNOLOGY nd OCEANOGRAPHY: METHODS Limnol. Oenogr.: Methods 6, 2008, 523 531 2008, y the Amerin Soiety of Limnology nd Oenogrphy, In. A ritil ssessment of different trnsmethyltion proedures ommonly employed
LIMNOLOGY nd OCEANOGRAPHY: METHODS Limnol. Oenogr.: Methods 6, 2008, 523 531 2008, y the Amerin Soiety of Limnology nd Oenogrphy, In. A ritil ssessment of different trnsmethyltion proedures ommonly employed
The soy isoflavone genistein promotes apoptosis in mammary epithelial cells by inducing the tumor suppressor PTEN
 Crinogenesis vol. no.1 pp.1793 183, 5 doi:1.193/rin/gi131 dvne ess pulition My 19, 5 The soy isoflvone genistein promotes poptosis in mmmry epithelil ells y induing the tumor suppressor huvnesh Dve 1,,
Crinogenesis vol. no.1 pp.1793 183, 5 doi:1.193/rin/gi131 dvne ess pulition My 19, 5 The soy isoflvone genistein promotes poptosis in mmmry epithelil ells y induing the tumor suppressor huvnesh Dve 1,,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:1.138/nture17 Men tumour dimeter (mm) 2 Rg2-/- 2 1 2 2 1 Control IgG!-CD8!-CD4 1 2 3 1 2 3 c Men tumour dimeter (mm) 2 2 1 d Ifnr1-/- Rg2-/- 2 2 1 Ifngr1-/- d42m1!ic 1 2 3 Dys post trnsplnt 1 2 3 Supplementry
doi:1.138/nture17 Men tumour dimeter (mm) 2 Rg2-/- 2 1 2 2 1 Control IgG!-CD8!-CD4 1 2 3 1 2 3 c Men tumour dimeter (mm) 2 2 1 d Ifnr1-/- Rg2-/- 2 2 1 Ifngr1-/- d42m1!ic 1 2 3 Dys post trnsplnt 1 2 3 Supplementry
Rapamycin toxicity in MIN6 cells and rat and human islets is mediated by the inhibition of mtor complex 2 (mtorc2)
 Dietologi (212) 55:1355 1365 DOI 1.17/s125-12-2475-7 ARTICLE myin toxiity in MIN6 ells nd rt nd humn islets is medited y the inhiition of mtor omplex 2 (mtorc2) A. D. Brlow & J. Xie & C. E. Moore & S.
Dietologi (212) 55:1355 1365 DOI 1.17/s125-12-2475-7 ARTICLE myin toxiity in MIN6 ells nd rt nd humn islets is medited y the inhiition of mtor omplex 2 (mtorc2) A. D. Brlow & J. Xie & C. E. Moore & S.
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 oi:1.138/nture1134 CS+ CS- MCH 3 OCT OCT 3 MCH CS- CS+ OCT MCH 3 MCH OCT 3 OCT vs MCH OCT vs MCH ppetitive memory (PI) A 1-1 Unpire onitioning DDC-GAL4/UAS-Trp UAS-Trp/+ -2 MCH OCT OCT MCH sugr OCT MCH
oi:1.138/nture1134 CS+ CS- MCH 3 OCT OCT 3 MCH CS- CS+ OCT MCH 3 MCH OCT 3 OCT vs MCH OCT vs MCH ppetitive memory (PI) A 1-1 Unpire onitioning DDC-GAL4/UAS-Trp UAS-Trp/+ -2 MCH OCT OCT MCH sugr OCT MCH
Supplementary Information
 Supplementry Informtion A new lss of plnt lipid is essentil for protetion ginst phosphorus depletion Yozo Okzki 1, Hitomi Otsuki 1, Tomoko Nrisw 1, Mkoto Koyshi 1, Storu Swi 2, Yukiko Kmide 1, Miyko Kusno
Supplementry Informtion A new lss of plnt lipid is essentil for protetion ginst phosphorus depletion Yozo Okzki 1, Hitomi Otsuki 1, Tomoko Nrisw 1, Mkoto Koyshi 1, Storu Swi 2, Yukiko Kmide 1, Miyko Kusno
Shear behaviour of regular and irregular rock joints under cyclic conditions
 Pper No. 69 ISMS 2016 Sher ehviour of regulr n irregulr rok joints uner yli onitions S. M. Mhi Niktr, *, K. Seshgiri Ro, Amit Kumr Shrivstv Deprtment of Civil Engineering, Inin Institute of Tehnology Delhi,
Pper No. 69 ISMS 2016 Sher ehviour of regulr n irregulr rok joints uner yli onitions S. M. Mhi Niktr, *, K. Seshgiri Ro, Amit Kumr Shrivstv Deprtment of Civil Engineering, Inin Institute of Tehnology Delhi,
Meat and Food Safety. B.A. Crow, M.E. Dikeman, L.C. Hollis, R.A. Phebus, A.N. Ray, T.A. Houser, and J.P. Grobbel
 Met nd Food Sfety Needle-Free Injection Enhncement of Beef Strip Loins with Phosphte nd Slt Hs Potentil to Improve Yield, Tenderness, nd Juiciness ut Hrm Texture nd Flvor B.A. Crow, M.E. Dikemn, L.C. Hollis,
Met nd Food Sfety Needle-Free Injection Enhncement of Beef Strip Loins with Phosphte nd Slt Hs Potentil to Improve Yield, Tenderness, nd Juiciness ut Hrm Texture nd Flvor B.A. Crow, M.E. Dikemn, L.C. Hollis,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:1.18/nture129 ontrol-dna -DNA CD49 Blood Lung e.98 +/-.9.71 +/-.2.29+/-.1 2.9 +/-.6 Bsophils (x1 )/ml 4 Bsophils ( x1 ) d f 45. 22.5 15 75 ontrol-dna ontrol-dna -DNA -DNA
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:1.18/nture129 ontrol-dna -DNA CD49 Blood Lung e.98 +/-.9.71 +/-.2.29+/-.1 2.9 +/-.6 Bsophils (x1 )/ml 4 Bsophils ( x1 ) d f 45. 22.5 15 75 ontrol-dna ontrol-dna -DNA -DNA
Osteoblasts secrete Cxcl9 to regulate angiogenesis in bone
 Reeived 2 De 215 Aepted 9 Nov 216 Pulished 14 De 216 DOI: 1.138/nomms13885 OPEN Osteolsts serete to regulte ngiogenesis in one Bin Hung 1,, Wenho Wng 1,, Qinghu Li 1,, Zhenyu Wng 1,BoYn 1, Zhongmin Zhng
Reeived 2 De 215 Aepted 9 Nov 216 Pulished 14 De 216 DOI: 1.138/nomms13885 OPEN Osteolsts serete to regulte ngiogenesis in one Bin Hung 1,, Wenho Wng 1,, Qinghu Li 1,, Zhenyu Wng 1,BoYn 1, Zhongmin Zhng
Minimum effective dose of chenic acid for gallstone patients: reduction with bedtime administration and
 Gut, 1982, 23, 28-284 Minimum effetive dose of heni id for gllstone ptients: redution with bedtime dministrtion nd low holesterol diet D P MUDGL, R M KUPFER, ND T C NORTHFIELD* From the Normn Tnner Gstroenterology
Gut, 1982, 23, 28-284 Minimum effetive dose of heni id for gllstone ptients: redution with bedtime dministrtion nd low holesterol diet D P MUDGL, R M KUPFER, ND T C NORTHFIELD* From the Normn Tnner Gstroenterology
The Role of Background Statistics in Face Adaptation
 The Journl of Neurosiene, Septemer 3, 29 29(39):235 244 235 Behviorl/Systems/Cognitive The Role of Bkground Sttistis in Fe Adpttion Jinhu Wu, * Hong Xu, * Peter Dyn, 2 nd Ning Qin Deprtments of Neurosiene
The Journl of Neurosiene, Septemer 3, 29 29(39):235 244 235 Behviorl/Systems/Cognitive The Role of Bkground Sttistis in Fe Adpttion Jinhu Wu, * Hong Xu, * Peter Dyn, 2 nd Ning Qin Deprtments of Neurosiene
Research Article The Protection of Hepatocyte Cells from the Effects of Oxidative Stress by Treatment with Vitamin E in Conjunction with DTT
 Hindwi Pulishing Corportion Journl of Biomediine nd Biotehnology Volume 21, Artile ID 486267, 7 pges doi:1.1155/21/486267 Reserh Artile The Protetion of Heptoyte Cells from the Effets of Oxidtive Stress
Hindwi Pulishing Corportion Journl of Biomediine nd Biotehnology Volume 21, Artile ID 486267, 7 pges doi:1.1155/21/486267 Reserh Artile The Protetion of Heptoyte Cells from the Effets of Oxidtive Stress
EFFECTS OF DIETARY CALCIUM LEVELS ON GROWTH-PERFORMANCE AND DIGESTIVE FUNCTION IN CATTLE FED A HIGH-FAT FINISHING DIET
 EFFECTS OF DIETARY CALCIUM LEVELS ON GROWTH-PERFORMANCE AND DIGESTIVE FUNCTION IN CATTLE FED A HIGH-FAT FINISHING DIET R. A. Zinn, Y. Shen, R. Brjs, M. Montño, E. Alvrez, nd E. Rmirez Desert Reserh nd
EFFECTS OF DIETARY CALCIUM LEVELS ON GROWTH-PERFORMANCE AND DIGESTIVE FUNCTION IN CATTLE FED A HIGH-FAT FINISHING DIET R. A. Zinn, Y. Shen, R. Brjs, M. Montño, E. Alvrez, nd E. Rmirez Desert Reserh nd
Adiabatic CMOS Circuit Design: Principles and Examples
 Aditi CMOS Ciruit Design: Priniples nd Exmples X.Wu,G.Hng,ndM.Pedrm Astrt: In view of hnging the type of energy onversion in CMOS iruits nd therey hieving ultr-low-power design, this pper investigtes diti
Aditi CMOS Ciruit Design: Priniples nd Exmples X.Wu,G.Hng,ndM.Pedrm Astrt: In view of hnging the type of energy onversion in CMOS iruits nd therey hieving ultr-low-power design, this pper investigtes diti
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nture10754 Supplementry note 1 To ompre our dt with previous studies, we mesured the width of spikes from identified dopminergi neurons nd unidentified neurons from DATCre mie. Previous studies
doi:10.1038/nture10754 Supplementry note 1 To ompre our dt with previous studies, we mesured the width of spikes from identified dopminergi neurons nd unidentified neurons from DATCre mie. Previous studies
