1.1.c Movement analysis
|
|
|
- Alison Floyd
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 1.1.c Movement analysis Learning objectves To understand the 3 diferent lever class systems To be able to describe the components of each lever system. To be able to explain the mechanical advantage of each of the lever and related movements. To understand the diferent planes of the body To understand the movement possible at each of the bodies planes and axes.
2 Lever systems Watch m e How does the body use levers to bring about movement?
3 Levers The joints of our skeleton not only allow movement, they also act as LEVERS. The functon of levers are to increase the speed at which a body can move.
4 Levers The human body is a system of levers and pulleys which enables us to move. The joint itself is the fulcrum (Pivot). This fulcrum 'takes the strain' of pulling one near, or away from another bone.
5 Levers The levers rotate around a series of joints. The force is provided by the muscles atached to the bone (think of the muscles actng as pulleys). The resistance comes from body weight and any implement used for sport (e.g. a bat or racquet).
6 Levers Levers consist of three components: 1. Fulcrum (F) - the fxed point or pivot 2. Efort (E) point where the force/efort is applied 3. Load (L) - point where the weight/resistance is coming from
7 Class of lever Levers can be classifed as: First class Second class Third class
8 Class of lever First Class This is a lever where the Fulcrum (pivot) occurs between the efort and load. Efort Load Lever Arm Fulcrum
9 Class of lever First Class The head is a good example of the acton of a frst-order lever in the body when the head and neck are being fexed and extended, as in nodding. Muscles in neck contractng Weight of head Neck joint First class levers can increase both efects of efort and the speed of a body.
10 Class of lever Second Class This lever occurs when the load is between the efort and the fulcrum. Load Lever Arm Efort Fulcrum
11 Class of lever Second Class When you raise up on to your toes you are using a second order lever. Weight of body and gravity Muscle working Ankle joint Second class levers tend to increase the efect of the efort force.
12 Class of lever Third Class This lever occurs when the efort lies between the fulcrum and load. This is very common in human movement Load Lever Arm Fulcrum Efort
13 Class of lever Third Class In terms of applying force this is a very inefcient lever, but it allows speed and range of movement. An example within the body is a bicep curl during fexion. The weight Arm Elbow Bicep muscle Third class levers can be used to increase the speed of a body.
14 Mechanical Advantage The relatve efciency of each of the lever systems is called the mechanical advantage. Use the following equipment to explore how high you can propel the eraser. Efort Load Lever Arm Fulcrum How can the 1st class lever below be adjusted to increase or change how high the load can be propelled?
15 Mechanical Advantage The body s levers can be made even more efectve by using rackets, oars, paddles, stcks and bats.
16 Mechanical Advantage These pieces of equipment increase the length of the resistance arm of the lever. This in turn increases the speed at the end of the lever.
17 Efects of a lever on the human body The extent to which a lever can increase speed depends upon the relatve lengths of the resistance arm (RA) and efort arm (EA). Efort Load Lever Arm RA - Part of the lever between the fulcrum & the load Fulcrum Resistance Arm (RA) Efort Arm (EA) EA - Part of the lever between the fulcrum & the efort
18 Resistance arm The resistance arm (RA) is the part of the lever between the fulcrum and the resistance. The longer the resistance arm, the greater speed can be generated. Efort Load Lever Arm Fulcrum Resistance Arm (RA)
19 Efort arm The efort arm (EA) is the distance between the fulcrum and the efort; the longer the efort arm Sportng implements are ofen used such as rackets or bats to increase the length of the efort arm which will increase the force that an object such as a ball is struck. Efort Load Lever Arm Fulcrum Efort Arm (EA)
20 Efort arm However the optmal length of an implement should be determined by the strength of the person handling. e.g. junior tennis rackets have been designed for this purpose.
21 Mechanical Disadvantage Most levers in the body are third class levers where the resistance arm is always greater than the efort arm (mechanical disadvantage). The longer the resistance arm of the lever, the greater the speed at the end of it. So when bowling or passing a ball the performers arm should be fully extended to generate the most force and with the greatest speed.
22 Planes and axes of movement Watch m e Movement paterns and the bodies planes and axes
23 Planes and axes of movement To help explain movement, the body can be viewed as having a series of imaginary slices/glass panes running through it. These are referred to as planes of movement
24 Planes 1. The sagital plane is a vertical plane that divides the body into right and lef sides.
25 Planes 2. The frontal plane is also a vertcal plane but this divides the body into front and back.
26 Planes 3. The transverse plane is a horizontal plane that divides the body into upper and lower halves.
27 Axes of the body Axes are like invisible skewers running through the body. All movements rotate around one of the axes. Longitudinal axis Transverse axis Frontal axis
28 Axes of the body Longitudinal axis runs through the body vertcally from the top to botom.
29 Axes of the body Transverse axis runs through the body horizontally from the lef to right.
30 Axes of the body Frontal axis runs through the body horizontally from the back to front.
31 Planes & Axes of the body combined Movement in the sagital plane about the transverse axis allows for front somersaults/forward roll. TRANSVERSE AXIS SAGITTAL PLANE
32 Planes & Axes of the body combined Movement in the frontal plane about the frontal axis allows for cartwheels. FRONTAL AXIS FRONTAL PLANE
33 Planes & Axes of the body combined Movement in the transverse plane about the longitudinal axis allows for a 360 degree twist. LONGITUDINAL AXIS TRANSVERSE PLANE
34 Apply it! What has stuck with you?
35 Apply it! What has stuck with you?
36 Practce it! Exam questons 1.Which one of the following describes a second class lever system? A B C D (1) The load is at the right-hand end of the lever The fulcrum is in the middle of the lever The load is in the middle of the lever The load and the fulcrum are at the same point on the lever 2. Label the lever system below (4) Lever class =
37 Practce it! Exam questons 3. Which one of these shows how to calculate the mechanical advantage of a lever? (1) A B C D Efort arm x weight (resistance) arm Efort arm weight (resistance) arm Efort arm + weight (resistance) arm Efort arm - weight (resistance) arm
38 Practce it! Exam questons 4. Analyse how the following parts of the lever system allow the weight trainer in Figure 5 to lif the weight. (i) Fulcrum (2) (ii) Efort (2)
39 Practce it! Exam questons 5. Figure 4 shows a basketball player jumping to execute a shot. Draw the lever system which operates at the ankle joint in the space below. Label the fulcrum, efort and load. (1)
40 Practce it! Marks Scheme: Load Efort Fulcrum C i) Third class lever B One mark for linking bone or muscle to component of lever system and one mark for linking this to its use in the biceps curl to lif the weight. For example: Fulcrum elbow is the fulcrum (1) which allows the arm to bend/fex (1) Efort biceps muscle provide the efort (1) which allows the weight lifer to lif the weight (1)
41 Practce it! Marks Scheme: 5. Award one mark for labelling the efort, load / resistance and fulcrum in the correct order.
42 Practce it! Exam questons 1. Figure 1 shows one plane and one axis of the human body. The plane is represented by the square. The axis is represented by the doted line. (1) Identfy the plane and axis shown in Figure 1. A B C D Sagital plane and transverse axis Frontal plane and longitudinal axis Transverse plane and transverse axis Transverse plane and longitudinal axis
43 Practce it! Exam questons 2. Which one of the following statements is false? (1) (A)The movement at the elbow joint during a biceps curl is an example of fexion and extension. (B) The deltoid at the shoulder joint during a biceps curl is an example of a fxator. (C) Most of the lever systems that provide movement in sport are examples of third class levers. (D) An example of a second class lever is a tennis player using their elbow joint during a forehand shot.
44 Practce it! Exam questons 3. The dancer in the picture below has performed a movement that has passed through the frontal plane. (1) Is this statement true or false?
45 Practce it! Marks Scheme: 1. D 2. (D) An example of a second class lever is a tennis player using their elbow joint during a forehand shot 3. False
2.1 Lever systems, examples of their use and the mechanical advantages they provide
 2.1 Lever systems, examples of their use and the mechanical advantages they provide Learning objectives To understand the 3 different lever class systems To be able to describe the components of each lever
2.1 Lever systems, examples of their use and the mechanical advantages they provide Learning objectives To understand the 3 different lever class systems To be able to describe the components of each lever
Planes and axes of movement. Movement patterns and the bodies planes and axes
 Planes and axes of movement Movement patterns and the bodies planes and axes Learning Outcomes Be able to name the three planes of movement and the three axes of rotation. Be aware of sporting movements
Planes and axes of movement Movement patterns and the bodies planes and axes Learning Outcomes Be able to name the three planes of movement and the three axes of rotation. Be aware of sporting movements
3.1.2 MOVEMENT ANALYSIS
 3.1.2 MOVEMENT ANALYSIS 3.1.1.1 Levers Mechanical Advantage starter 1. Stick in your Assessment Grids from last lesson. NOT FOLDED 2. Fill out the score underneath the start of the lesson Start = % End
3.1.2 MOVEMENT ANALYSIS 3.1.1.1 Levers Mechanical Advantage starter 1. Stick in your Assessment Grids from last lesson. NOT FOLDED 2. Fill out the score underneath the start of the lesson Start = % End
ANYTHING THAT IT IS CARRYING)
 1) A rigid structure (BONE) Levers in our body are formed from Bones, Joints and Muscles. A lever consists of 2) A force acting upon it (MUSCLE) to produce a turning movement (ANGULAR MOTION) 3) A fulcrum
1) A rigid structure (BONE) Levers in our body are formed from Bones, Joints and Muscles. A lever consists of 2) A force acting upon it (MUSCLE) to produce a turning movement (ANGULAR MOTION) 3) A fulcrum
2.1. Lever Systems 2.2 Planes and Axes of Movement Teacher Answer Booklet
 GCSE EDEXCEL 2.1/2.2 2.1. Lever Systems 2.2 Planes and Axes of Movement Teacher Answer Booklet GCSE EDEXCEL 2.1/2.2 WWW.MYPECLASSROOM.COM Topic Description from Specification Pupil comments How confident
GCSE EDEXCEL 2.1/2.2 2.1. Lever Systems 2.2 Planes and Axes of Movement Teacher Answer Booklet GCSE EDEXCEL 2.1/2.2 WWW.MYPECLASSROOM.COM Topic Description from Specification Pupil comments How confident
2.1. Lever Systems 2.2 Planes and Axes of Movement. Name. Class
 GCSE EDEXCEL 2.1/2.2 2.1. Lever Systems 2.2 Planes and Axes of Movement Name Class GCSE EDEXCEL 2.1/2.2 WWW.MYPECLASSROOM.COM Topic Description from Specification Pupil comments How confident do you feel
GCSE EDEXCEL 2.1/2.2 2.1. Lever Systems 2.2 Planes and Axes of Movement Name Class GCSE EDEXCEL 2.1/2.2 WWW.MYPECLASSROOM.COM Topic Description from Specification Pupil comments How confident do you feel
. Know the definition of mechanical advantage.
 Please do the following 1. Read the Learners must know section (see below) 2. Watch the GCSE POD video 3. Attempt Exam Questions 4. Mark your answers 5. Reflect and repeat until you are successful and
Please do the following 1. Read the Learners must know section (see below) 2. Watch the GCSE POD video 3. Attempt Exam Questions 4. Mark your answers 5. Reflect and repeat until you are successful and
3 Movement analysis. Muscle contractions: isotonic and isometric. Exam practice. Now test yourself
 3 Movement analysis Muscle contractions: isotonic and isometric There are two types of muscle contraction: isotonic isometric. An isotonic contraction occurs when the muscle changes length as it contracts
3 Movement analysis Muscle contractions: isotonic and isometric There are two types of muscle contraction: isotonic isometric. An isotonic contraction occurs when the muscle changes length as it contracts
Movement Analysis UNDERSTANDING MOVEMENT AND FORCE
 Movement Analysis UNDERSTANDING MOVEMENT AND FORCE Learning objectives for this topic After completing this chapter you should have knowledge and understanding of 1. First, second and third class levers
Movement Analysis UNDERSTANDING MOVEMENT AND FORCE Learning objectives for this topic After completing this chapter you should have knowledge and understanding of 1. First, second and third class levers
CHAPTER 4: The musculo-skeletal system. Practice questions - text book pages QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS. Answers
 CHAPTER 4: The musculo-skeletal system Practice questions - text book pages 64-66 1) A prime mover of hip flexion is the: a. rectus femoris. b. Iliopsoas. c. vastus muscles. d. gluteus maximus. b. Key
CHAPTER 4: The musculo-skeletal system Practice questions - text book pages 64-66 1) A prime mover of hip flexion is the: a. rectus femoris. b. Iliopsoas. c. vastus muscles. d. gluteus maximus. b. Key
1.1 a The structure and functin if the skeletal system Learning ibjectves
 1.1 a The structure and functin if the skeletal system Learning ibjectves To be able to describe the functons of the skeleton. To be able to recognise and label a skeleton. To understand the diferent joint
1.1 a The structure and functin if the skeletal system Learning ibjectves To be able to describe the functons of the skeleton. To be able to recognise and label a skeleton. To understand the diferent joint
SPORT AND PHYSICAL ACTIVITY
 2016 Suite Cambridge TECHNICALS LEVEL 3 SPORT AND PHYSICAL ACTIVITY Unit 10 Biomechanics and movement analysis L/507/4461 Guided learning hours: 60 Version 4 - revised September 2018 *changes indicated
2016 Suite Cambridge TECHNICALS LEVEL 3 SPORT AND PHYSICAL ACTIVITY Unit 10 Biomechanics and movement analysis L/507/4461 Guided learning hours: 60 Version 4 - revised September 2018 *changes indicated
The big question : How does the coach make Gareth Bale a better player? Movement analysis. Chapter 3. GCSE Physical Education
 The big question : How does the coach make Gareth Bale a better player? Movement analysis GCSE Physical Education To answer the big question you will need to be able to complete the following tasks: 1.
The big question : How does the coach make Gareth Bale a better player? Movement analysis GCSE Physical Education To answer the big question you will need to be able to complete the following tasks: 1.
 a) Maximum Strength:- It is the ability to overcome or to act against resistance. It is the maximum force which is applied by the muscles to perform any certain activity. For developing maximum strength
a) Maximum Strength:- It is the ability to overcome or to act against resistance. It is the maximum force which is applied by the muscles to perform any certain activity. For developing maximum strength
PiXL Independence: PE Answer Booklet KS4. Applied Anatomy and Physiology. Contents: Answers
 PiXL Independence: PE Answer Booklet KS4 Applied Anatomy and Physiology Contents: Answers 1 I. Quizzes Multiple Choice Quiz 1. Which one of the following statements is false? a. The scapula, cranium and
PiXL Independence: PE Answer Booklet KS4 Applied Anatomy and Physiology Contents: Answers 1 I. Quizzes Multiple Choice Quiz 1. Which one of the following statements is false? a. The scapula, cranium and
WTC II Term 3 Notes & Assessments
 Term 3 Notes & Assessments Planes of Motion/Axes The body moves in a number of various ways and directions. In the past you have learned about the terminology for movements at specific joints, for example,
Term 3 Notes & Assessments Planes of Motion/Axes The body moves in a number of various ways and directions. In the past you have learned about the terminology for movements at specific joints, for example,
Revision Booklet Paper 1
 OCR GCSE Physical Education Paper 1 Revision Booklet Revision Booklet Paper 1 Name.. Tutor. Teacher.. 1 OCR GCSE Physical Education Paper 1 Revision Booklet Paper 1 Anatomy & Physiology About the Paper:
OCR GCSE Physical Education Paper 1 Revision Booklet Revision Booklet Paper 1 Name.. Tutor. Teacher.. 1 OCR GCSE Physical Education Paper 1 Revision Booklet Paper 1 Anatomy & Physiology About the Paper:
1. Describe the main functions of the skeletal system that keep the body healthy and active. [4]
![1. Describe the main functions of the skeletal system that keep the body healthy and active. [4] 1. Describe the main functions of the skeletal system that keep the body healthy and active. [4]](/thumbs/79/80173575.jpg) GCSE PE Structured questions 1a Applied anatomy and physiology Understand the structure and functions of the skeleton 1. Describe the main functions of the skeletal system that keep the body healthy and
GCSE PE Structured questions 1a Applied anatomy and physiology Understand the structure and functions of the skeleton 1. Describe the main functions of the skeletal system that keep the body healthy and
KS3 - PE THEORY REVISION GUIDE Y9
 KS3 - PE THEORY REVISION GUIDE Y9 Theory Knowledge Checklist Topic Tick off I can explain why physical activity is essential to a healthy lifestyle I can identify different types of movement using the
KS3 - PE THEORY REVISION GUIDE Y9 Theory Knowledge Checklist Topic Tick off I can explain why physical activity is essential to a healthy lifestyle I can identify different types of movement using the
CHAPTER 2: Muscular skeletal system - Biomechanics. Exam style questions - pages QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS. Answers
 CHAPTER 2: Muscular skeletal system - Biomechanics Exam style questions - pages 32-35 1) A Level. Warm up is considered to be an essential element of a training programme. Explain how the muscular and
CHAPTER 2: Muscular skeletal system - Biomechanics Exam style questions - pages 32-35 1) A Level. Warm up is considered to be an essential element of a training programme. Explain how the muscular and
CHAPTER 3 What Is Anatomy?
 CHAPTER 3 What Is Anatomy? Kinesiology Books Publisher 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS The Language of Anatomy Anatomical Position Directional Terms Body Planes Movements Musculoskeletal System Human Skeleton Types
CHAPTER 3 What Is Anatomy? Kinesiology Books Publisher 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS The Language of Anatomy Anatomical Position Directional Terms Body Planes Movements Musculoskeletal System Human Skeleton Types
Lever system. Rigid bar. Fulcrum. Force (effort) Resistance (load)
 Lever system lever is any elongated, rigid (bar) object that move or rotates around a fixed point called the fulcrum when force is applied to overcome resistance. Force (effort) Resistance (load) R Rigid
Lever system lever is any elongated, rigid (bar) object that move or rotates around a fixed point called the fulcrum when force is applied to overcome resistance. Force (effort) Resistance (load) R Rigid
Weight Loss Interval (Beginner)
 Program for BP Fitness Center Introduction Weight Loss Interval (Beginner) This is a full body interval workout. Keep your heart rate up to safe levels by not resting between exercises. Please workout
Program for BP Fitness Center Introduction Weight Loss Interval (Beginner) This is a full body interval workout. Keep your heart rate up to safe levels by not resting between exercises. Please workout
Please do the following
 Please do the following 1. Read the Learners must know section (see below) 2. Watch the GCSE POD video 3. Attempt Exam Questions 4. Mark your answers 5. Reflect and repeat until you are successful and
Please do the following 1. Read the Learners must know section (see below) 2. Watch the GCSE POD video 3. Attempt Exam Questions 4. Mark your answers 5. Reflect and repeat until you are successful and
Technical Progression Workshop. Throws Shot Put, Discus and Javelin
 Technical Progression Workshop Throws Shot Put, Discus and Javelin Position & Context of Workshop Position Sits after Athletics Coach and Coaching in Running Fitness You will hopefully have attended the
Technical Progression Workshop Throws Shot Put, Discus and Javelin Position & Context of Workshop Position Sits after Athletics Coach and Coaching in Running Fitness You will hopefully have attended the
6.4 The Ankle. Body Divided into Planes. Health Services: Unit 6 Arms and Legs. Body Movement Vocabulary
 6.4 The Ankle Body Movement Vocabulary When fitness professionals refer to movement of the body, the pattern of movement is described from the anatomical position This position can best be described as
6.4 The Ankle Body Movement Vocabulary When fitness professionals refer to movement of the body, the pattern of movement is described from the anatomical position This position can best be described as
Introduction to Biomechanics
 Module Five: Introduction to Biomechanics INTRODUCTION In Level One you learnt to divide a skill into meaningful phases, identify the key elements within each phase, and develop an observation plan to
Module Five: Introduction to Biomechanics INTRODUCTION In Level One you learnt to divide a skill into meaningful phases, identify the key elements within each phase, and develop an observation plan to
Exercises Guide. Standing Exercises. Dead Lift. Exercise Muscles Targeted
 s Guide. Standing s Dead Lift Dead Lift Hamstrings, glutes Instructions Stand on the footplates and hold the bar horizontally in both hands at shoulder distance apart with palms facing inwards at hip level.
s Guide. Standing s Dead Lift Dead Lift Hamstrings, glutes Instructions Stand on the footplates and hold the bar horizontally in both hands at shoulder distance apart with palms facing inwards at hip level.
When training an athlete s core, the training should mimic real life FEATURE ARTICLE HOW TO TRAIN THE CORE: SPECIFIC TO SPORTS MOVEMENTS
 SPECIFIC TO SPORTS MOVEMENTS TRAVIS BROWN, MS, CSCS,*D When training an athlete s core, the training should mimic real life sport movements. The core should be trained in multiplanar and multidirectional
SPECIFIC TO SPORTS MOVEMENTS TRAVIS BROWN, MS, CSCS,*D When training an athlete s core, the training should mimic real life sport movements. The core should be trained in multiplanar and multidirectional
Stability Ball Band & Free Weight Work-out
 Stability Ball Band & Free Weight Work-out High Mountain Personal Training Michael Martin Cell Phone: 970-946-6398 1. Chest Do 2 sets of 1 exercise Or Do 1 set of 2 different exercises Start position End
Stability Ball Band & Free Weight Work-out High Mountain Personal Training Michael Martin Cell Phone: 970-946-6398 1. Chest Do 2 sets of 1 exercise Or Do 1 set of 2 different exercises Start position End
The Human Machine: Biomechanics in Daily Life.
 The Human Machine: Biomechanics in Daily Life www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz Biomechanics The study or application of mechanics to biological systems. The study of the forces that act on the body and their
The Human Machine: Biomechanics in Daily Life www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz Biomechanics The study or application of mechanics to biological systems. The study of the forces that act on the body and their
Lifting your toes up towards your tibia would be an example of what movement around the ankle joint?
 NAME: TEST 1 ANATOMY IN SPORT SCIENCE: SEMESTER 2, 2016 TOTAL MARKS = 72 Total: /72 marks Percentage: Grade: TERMINOLOGY: The structures that connect bone to bone are called: The hip joint is to the shoulder
NAME: TEST 1 ANATOMY IN SPORT SCIENCE: SEMESTER 2, 2016 TOTAL MARKS = 72 Total: /72 marks Percentage: Grade: TERMINOLOGY: The structures that connect bone to bone are called: The hip joint is to the shoulder
Grade Level Outcomes for Elementary School (4 5)
 Grade Level Outcomes for Elementary School (4 5) (Standard #. Critical Element #. Grade Level Outcome) Standard #1 : The physically literate individual demonstrates competency in a variety of motor skills
Grade Level Outcomes for Elementary School (4 5) (Standard #. Critical Element #. Grade Level Outcome) Standard #1 : The physically literate individual demonstrates competency in a variety of motor skills
Functional Strength Exercise Guide
 Functional Strength Exercise Guide Fast, convenient weight training that helps you look better, feel better and perform better during everyday activities. Welcome to Functional Strength Training from Horizon
Functional Strength Exercise Guide Fast, convenient weight training that helps you look better, feel better and perform better during everyday activities. Welcome to Functional Strength Training from Horizon
Diarthrosis Joints - Freely Moveable Joints
 Reprinted with permission from the Aquatic Exercise Association (AEA) www.aeawave.com Anatomy Gets Real By June M Chewning BS, MS For fitness professionals, anatomy is the never-ending learning challenge.
Reprinted with permission from the Aquatic Exercise Association (AEA) www.aeawave.com Anatomy Gets Real By June M Chewning BS, MS For fitness professionals, anatomy is the never-ending learning challenge.
What is Kinesiology? Basic Biomechanics. Mechanics
 What is Kinesiology? The study of movement, but this definition is too broad Brings together anatomy, physiology, physics, geometry and relates them to human movement Lippert pg 3 Basic Biomechanics the
What is Kinesiology? The study of movement, but this definition is too broad Brings together anatomy, physiology, physics, geometry and relates them to human movement Lippert pg 3 Basic Biomechanics the
BIOMECHANICS. Biomechanics - the application of mechanical laws to living structures, specifically to the locomotor system of the human body.
 1 BIOMECHANICS Biomechanics - the application of mechanical laws to living structures, specifically to the locomotor system of the human body. I. Uses of Biomechanical Analyses Improvement of sports skill
1 BIOMECHANICS Biomechanics - the application of mechanical laws to living structures, specifically to the locomotor system of the human body. I. Uses of Biomechanical Analyses Improvement of sports skill
GCSE PHYSICAL EDUCATION - Course Summary
 Subject Overview Curriculum pathway GCSE PHYSICAL EDUCATION - Course Summary Unit / Module Course: GCSE Edexcel Physical Education Overall Summary Exam / Controlled % of course UMS allocation Marks available
Subject Overview Curriculum pathway GCSE PHYSICAL EDUCATION - Course Summary Unit / Module Course: GCSE Edexcel Physical Education Overall Summary Exam / Controlled % of course UMS allocation Marks available
SAMPLE ASSESSMENT TASKS PHYSICAL EDUCATION STUDIES GENERAL YEAR 12
 SAMPLE ASSESSMENT TASKS PHYSICAL EDUCATION STUDIES GENERAL YEAR 12 Copyright School Curriculum and Standards Authority, 2015 This document apart from any third party copyright material contained in it
SAMPLE ASSESSMENT TASKS PHYSICAL EDUCATION STUDIES GENERAL YEAR 12 Copyright School Curriculum and Standards Authority, 2015 This document apart from any third party copyright material contained in it
Physical Education GCSE 1PE0/01. Component 1: Fitness and Body Systems. Time: 1 hour and 45 minutes. You will need a calculator.
 Write your name here Surname Other names GCSE Physical Education Component 1: Fitness and Body Systems Time: 1 hour and 45 minutes Paper Reference 1PE0/01 You will need a calculator. Total Marks Instructions
Write your name here Surname Other names GCSE Physical Education Component 1: Fitness and Body Systems Time: 1 hour and 45 minutes Paper Reference 1PE0/01 You will need a calculator. Total Marks Instructions
CHAPTER 1: 1.1 Muscular skeletal system. Question - text book page 16. Question - text book page 20 QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS. Answers
 QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS CHAPTER 1: 1.1 Muscular skeletal system Question - text book page 16 Using the information on pages 12 to 14 above, complete the table below. joint joint type articulating bones associated
QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS CHAPTER 1: 1.1 Muscular skeletal system Question - text book page 16 Using the information on pages 12 to 14 above, complete the table below. joint joint type articulating bones associated
Dumbarton Academy. Physical Education. Standard Grade Course. Skills and Techniques Booklet
 Dumbarton Academy Physical Education Standard Grade Course Skills and Techniques Booklet DUMBARTON ACADEMY Name.. Teacher.. 1 Dumbarton Academy Physical Education Department Skills and Techniques You must
Dumbarton Academy Physical Education Standard Grade Course Skills and Techniques Booklet DUMBARTON ACADEMY Name.. Teacher.. 1 Dumbarton Academy Physical Education Department Skills and Techniques You must
Introduction to Biomechanical Analysis
 Introduction to Biomechanical Analysis LEARNING OBJECTIVES: At the end of this laboratory exercise the student will be able to: Identify forces used during activities Identify moments used during activities
Introduction to Biomechanical Analysis LEARNING OBJECTIVES: At the end of this laboratory exercise the student will be able to: Identify forces used during activities Identify moments used during activities
Assignment 2: Human Anatomy
 Assignment 2: Human Anatomy Chapter 2 Quiz: How Much Do You Know About Anatomy? 1. Which of the following is not a feature of the anatomical position: A) The body stands erect. B) The body is facing forward.
Assignment 2: Human Anatomy Chapter 2 Quiz: How Much Do You Know About Anatomy? 1. Which of the following is not a feature of the anatomical position: A) The body stands erect. B) The body is facing forward.
1.1 The structure and functions of the musculo-skeletal system Learning objectives
 1.1 The structure and functions of the musculo-skeletal system Learning objectives To be able to describe the functions of the skeleton. To understand different bone classifications and functioning. To
1.1 The structure and functions of the musculo-skeletal system Learning objectives To be able to describe the functions of the skeleton. To understand different bone classifications and functioning. To
4. Which one of the following correctly identifies the part of the skeleton that produces red blood cells?
 GSE P.E. questions and mark schemes 1 a pplied natomy and Physiology 1. Which of one of the following is NOT a function of the skeleton? 2. Which one of the following is NOT a function of the skeleton?
GSE P.E. questions and mark schemes 1 a pplied natomy and Physiology 1. Which of one of the following is NOT a function of the skeleton? 2. Which one of the following is NOT a function of the skeleton?
Body Bar FLEX. Stretching and Strengthening Exercises. Organized by Muscle Groups Exercised. by Gordon L. Brown, Jr. for Body Bar, Inc.
 Body Bar FLEX Stretching and Strengthening Exercises Organized by Muscle Groups Exercised by Gordon L. Brown, Jr. for Body Bar, Inc. 1 Stretching and Strengthening Exercises This presentation features
Body Bar FLEX Stretching and Strengthening Exercises Organized by Muscle Groups Exercised by Gordon L. Brown, Jr. for Body Bar, Inc. 1 Stretching and Strengthening Exercises This presentation features
TORUS HOME GYM EXERCISE GUIDE
 TORUS HOME GYM EXERCISE GUIDE Get more from your strength training routine with the Horizon Torus Home Gym. This Training Guide includes set-up instructions and illustrates more than 40 exercises you can
TORUS HOME GYM EXERCISE GUIDE Get more from your strength training routine with the Horizon Torus Home Gym. This Training Guide includes set-up instructions and illustrates more than 40 exercises you can
RESISTANCE STRENGTH TRAINING EXERCISE
 RESISTANCE STRENGTH TRAINING EXERCISE Alternating Dumbbell Chest Press Lie supine on a flat bench with dumbbells in each hand with a pronated grip. Extend your arms, holding the dumbbells in line with
RESISTANCE STRENGTH TRAINING EXERCISE Alternating Dumbbell Chest Press Lie supine on a flat bench with dumbbells in each hand with a pronated grip. Extend your arms, holding the dumbbells in line with
Monster Walk Stand with your feet slightly closer than shoulder-width apart in an athletic stance. Loop an elastic band around your ankles.
 Off-season Lower-Body Tennis Exercises Research conducted on elite tennis players shows that lower-body strength is the same on both the left and right sides. Therefore, lower-body training for tennis
Off-season Lower-Body Tennis Exercises Research conducted on elite tennis players shows that lower-body strength is the same on both the left and right sides. Therefore, lower-body training for tennis
As a former college football player, I can remember the
 A DIFFERENT APPROACH TO TACKLE FOOTBALL TRAINING TRAVIS BROWN, MS, CSCS,*D As a former college football player, I can remember the countless hours and days of Olympic-style lifts and power lifts that we
A DIFFERENT APPROACH TO TACKLE FOOTBALL TRAINING TRAVIS BROWN, MS, CSCS,*D As a former college football player, I can remember the countless hours and days of Olympic-style lifts and power lifts that we
Standards align with California State Standards
 Standards align with California State Standards Kindergarten: A. Movement a. Travel within a large group, without bumping into others or falling, while using locomotor skills. b. Travel forward and sideways
Standards align with California State Standards Kindergarten: A. Movement a. Travel within a large group, without bumping into others or falling, while using locomotor skills. b. Travel forward and sideways
Year 10 GCSE Revision - Physical Education Paper 1 Fitness and Body Systems Topic Areas for Revision Key questions
 Year 10 GCSE Revision - Physical Education Paper 1 Fitness and Body Systems Topic Areas for Revision Key questions 1.1 The structure and functions of the musculoskeletal s Functions of the Skeleton for
Year 10 GCSE Revision - Physical Education Paper 1 Fitness and Body Systems Topic Areas for Revision Key questions 1.1 The structure and functions of the musculoskeletal s Functions of the Skeleton for
BLUE SKY SCHOOL OF PROFESSIONAL MASSAGE AND THERAPEUTIC BODYWORK. Musculoskeletal Anatomy & Kinesiology MUSCLES, MOVEMENTS & BIOMECHANICS
 BLUE SKY SCHOOL OF PROFESSIONAL MASSAGE AND THERAPEUTIC BODYWORK Musculoskeletal Anatomy & Kinesiology MUSCLES, MOVEMENTS & BIOMECHANICS MSAK101-I Session 7 Learning Objectives: 1. List the three types
BLUE SKY SCHOOL OF PROFESSIONAL MASSAGE AND THERAPEUTIC BODYWORK Musculoskeletal Anatomy & Kinesiology MUSCLES, MOVEMENTS & BIOMECHANICS MSAK101-I Session 7 Learning Objectives: 1. List the three types
return to sports after injury IMPROVING STRENGTH, POWER, AND AGILITY
 return to sports after injury IMPROVING STRENGTH, POWER, AND AGILITY This booklet is designed for people recovering from a knee or leg injury who participate in recreational or competitive sports such
return to sports after injury IMPROVING STRENGTH, POWER, AND AGILITY This booklet is designed for people recovering from a knee or leg injury who participate in recreational or competitive sports such
High Voltage Circuitry is designed to provide high voltage STIMULATION for:
 HIGH VOLTAGE CIRCUITRY (HVC) Presented by Michael Steel, Greg Sellar and the HQH Total Gym Team PROGRAM DESCRIPTION This dynamic circuit workout is designed to build the musculoskeletal system through
HIGH VOLTAGE CIRCUITRY (HVC) Presented by Michael Steel, Greg Sellar and the HQH Total Gym Team PROGRAM DESCRIPTION This dynamic circuit workout is designed to build the musculoskeletal system through
Exercises Guide. Standing Exercises. Dead Lift. Exercise Muscles Targeted
 s Guide. Standing s Dead Lift Dead Lift Hamstrings, glutes inwards at hip level Hinge from the hips and maintain a tall torso as you fold the body forward and glide the hands to knee level eturn to standing
s Guide. Standing s Dead Lift Dead Lift Hamstrings, glutes inwards at hip level Hinge from the hips and maintain a tall torso as you fold the body forward and glide the hands to knee level eturn to standing
Y12 Transition Pack Sports Leadership
 Y12 Transition Pack Sports Leadership Name: Base School: Section 1: The Muscular System Read through the following information on the Muscular System Cardiac muscle is unique to the heart. It never tires.
Y12 Transition Pack Sports Leadership Name: Base School: Section 1: The Muscular System Read through the following information on the Muscular System Cardiac muscle is unique to the heart. It never tires.
GCSE PE 1-9 SPEC. 9 Mark Questions
 GCSE PE 1-9 SPEC 9 Mark Questions Example Question: At the end of both your exams there is a 9 mark essay question It should be 2 sides of A4 and only take 15-20 mins It is marked in bands: Half term 1
GCSE PE 1-9 SPEC 9 Mark Questions Example Question: At the end of both your exams there is a 9 mark essay question It should be 2 sides of A4 and only take 15-20 mins It is marked in bands: Half term 1
The Language of Anatomy. (Anatomical Terminology)
 The Language of Anatomy (Anatomical Terminology) Terms of Position The anatomical position is a fixed position of the body (cadaver) taken as if the body is standing (erect) looking forward with the upper
The Language of Anatomy (Anatomical Terminology) Terms of Position The anatomical position is a fixed position of the body (cadaver) taken as if the body is standing (erect) looking forward with the upper
DVRT Certification: Level 1 Written Exam
 DVRT Certification: Level 1 Written Exam 1. What is NOT a concept or training principle of the DVRT System? A. Addressing specific needs of the client. B. Mixing simplicity with complexity. C. Progressive
DVRT Certification: Level 1 Written Exam 1. What is NOT a concept or training principle of the DVRT System? A. Addressing specific needs of the client. B. Mixing simplicity with complexity. C. Progressive
CKSS 2012 Exercise Science Section 1: The Anatomical Position An Introduction to Health and Physical Education
 CKSS 2012 Exercise Science Section 1: The Anatomical Position An Introduction to Health and Physical Education Ted Temertzoglou Paul Challen ISBN 1-55077-132-9 Text Books, Work Book and Reading List Introductions
CKSS 2012 Exercise Science Section 1: The Anatomical Position An Introduction to Health and Physical Education Ted Temertzoglou Paul Challen ISBN 1-55077-132-9 Text Books, Work Book and Reading List Introductions
The Golf Swing Speed Challenge (103) - First 3 Weeks
 103 The Golf Swing Speed Challenge (103) - First 3 Weeks In the first three weeks of this elite program you're going to be predominantly doing two things 1. Improving your flexibility through a range of
103 The Golf Swing Speed Challenge (103) - First 3 Weeks In the first three weeks of this elite program you're going to be predominantly doing two things 1. Improving your flexibility through a range of
2/4/2017. The Anatomical Position. Body Movement. Anatomical Terminology, Position, and Movement
 Anatomical Terminology, Position, and Movement PSK 4U North Grenville DHS S. Kelly The Anatomical Position The starting point for describing ALL anatomical and physiological features Upright, standing
Anatomical Terminology, Position, and Movement PSK 4U North Grenville DHS S. Kelly The Anatomical Position The starting point for describing ALL anatomical and physiological features Upright, standing
9/26/2012. Osteokinematics (how the bones move) & Arthrokinematics (how the joints move) Planes & Axes. Planes & Axes continued
 Osteokinematics (how the bones move) & (how the joints move) Planes & Axes Planes of Action = Three fixed lines of reference along which the body is divided. Each plane is at right angles (or perpendicular)
Osteokinematics (how the bones move) & (how the joints move) Planes & Axes Planes of Action = Three fixed lines of reference along which the body is divided. Each plane is at right angles (or perpendicular)
Fitness Friends: Aqua Favorites
 Fitness Friends: Aqua Favorites Stephanie Thielen: Tri-Core Segment Course Description: To build a strong core you need to train a variety of muscles from your hips to your shoulders. Through a series
Fitness Friends: Aqua Favorites Stephanie Thielen: Tri-Core Segment Course Description: To build a strong core you need to train a variety of muscles from your hips to your shoulders. Through a series
Body Bar FLEX. Strengthening Exercises for GOLF. Organized by Muscle Groups Exercised. by Gordon L. Brown, Jr. for Body Bar, Inc.
 Body Bar FLEX Strengthening Exercises for GOLF Organized by Muscle Groups Exercised by Gordon L. Brown, Jr. for Body Bar, Inc. 1 Introduction This presentation features strengthening exercises for golfers,
Body Bar FLEX Strengthening Exercises for GOLF Organized by Muscle Groups Exercised by Gordon L. Brown, Jr. for Body Bar, Inc. 1 Introduction This presentation features strengthening exercises for golfers,
Aquatic Fitness Professional Practical & Skill Applications Course Outline Please bring this handout to the course for reference.
 Aquatic Fitness Professional Practical & Skill Applications Course Outline Please bring this handout to the course for reference. The Aquatic Fitness Professional (AFP) Practical & Skill Applications Course
Aquatic Fitness Professional Practical & Skill Applications Course Outline Please bring this handout to the course for reference. The Aquatic Fitness Professional (AFP) Practical & Skill Applications Course
GCSE PERSONAL LEARNING CHECKLIST PHYSICAL EDUCATION
 GCSE PERSONAL LEARNING CHECKLIST PHYSICAL EDUCATION PLC KEY: COMPONENT 1: FITNESS AND BODY SYSTEMS 1.1-4.1 You have covered the concept in lesson by the teacher. You have extended the concept in your file
GCSE PERSONAL LEARNING CHECKLIST PHYSICAL EDUCATION PLC KEY: COMPONENT 1: FITNESS AND BODY SYSTEMS 1.1-4.1 You have covered the concept in lesson by the teacher. You have extended the concept in your file
A LEVEL PE PRE COURSE TASK READ EVERYTHING IN BLACK DO EVERYTHING IN RED
 A LEVEL PE PRE COURSE TASK READ EVERYTHING IN BLACK DO EVERYTHING IN RED 1.1.2 CLASSIFICATION OF BONES: LONG (LEVERAGE); SHORT (WEIGHT BEARING); FLAT (PROTECTION, BROAD SURFACE FOR MUSCLE ATTACHMENT);
A LEVEL PE PRE COURSE TASK READ EVERYTHING IN BLACK DO EVERYTHING IN RED 1.1.2 CLASSIFICATION OF BONES: LONG (LEVERAGE); SHORT (WEIGHT BEARING); FLAT (PROTECTION, BROAD SURFACE FOR MUSCLE ATTACHMENT);
Overview of the Human Arm Anatomy
 Senior MESA Day Overview of the Human Arm Anatomy Bones, Joints, Muscles Review Arm Motion Kinematics: types of motion, location of motion, direction of motion, magnitude of motion, and degrees of freedom
Senior MESA Day Overview of the Human Arm Anatomy Bones, Joints, Muscles Review Arm Motion Kinematics: types of motion, location of motion, direction of motion, magnitude of motion, and degrees of freedom
Full Body. Strengthening Routine
 Full Body Strengthening Routine Full Body Strengthening Routine Strengthening activities are recommended 2 to 4 days a week to help improve strength, reduce body fat, risk of osteoporosis, stress, and
Full Body Strengthening Routine Full Body Strengthening Routine Strengthening activities are recommended 2 to 4 days a week to help improve strength, reduce body fat, risk of osteoporosis, stress, and
Basic Biomechanical Factors & Concepts
 Basic Biomechanical Factors & Concepts 2007 McGraw-Hill Higher Education. All rights reserved 3-1 Biomechanics Biomechanics - study of the mechanics as it relates to the functional and anatomical analysis
Basic Biomechanical Factors & Concepts 2007 McGraw-Hill Higher Education. All rights reserved 3-1 Biomechanics Biomechanics - study of the mechanics as it relates to the functional and anatomical analysis
State of equilibrium is when the sum (or net effect) of forces acting on a body equals zero
 Kinesiology is the science of, or study of, human motion. It brings together the fields of anatomy,physiology, biomechanics, physics and geometry relating them to human movement. Bio - refers to living
Kinesiology is the science of, or study of, human motion. It brings together the fields of anatomy,physiology, biomechanics, physics and geometry relating them to human movement. Bio - refers to living
University of Cyprus Biomedical Imaging and Applied Optics. ECE 370 Introduction to Biomedical Engineering. Principles of Biomechanics
 University of Cyprus Biomedical Imaging and Applied Optics ECE 370 Introduction to Biomedical Engineering Principles of Biomechanics Introduction What is Biomechanics? The study of internal and external
University of Cyprus Biomedical Imaging and Applied Optics ECE 370 Introduction to Biomedical Engineering Principles of Biomechanics Introduction What is Biomechanics? The study of internal and external
BIOMECHANICAL INFLUENCES ON THE SOCCER PLAYER. Planes of Lumbar Pelvic Femoral (Back, Pelvic, Hip) Muscle Function
 BIOMECHANICAL INFLUENCES ON THE SOCCER PLAYER Functional performance of the soccer player reflects functional capability of certain specific muscle and muscle groups of the back, pelvis and hip to work
BIOMECHANICAL INFLUENCES ON THE SOCCER PLAYER Functional performance of the soccer player reflects functional capability of certain specific muscle and muscle groups of the back, pelvis and hip to work
1.1.e Efects of exercise on body systems Learning objecties
 1.1.e Efects of exercise on body systems Learning objecties To understand the short term efect of exercise. To be able to evaluate the long term efects of exercise on the body systems. To be able to interpret
1.1.e Efects of exercise on body systems Learning objecties To understand the short term efect of exercise. To be able to evaluate the long term efects of exercise on the body systems. To be able to interpret
At-Home Dryland Training Program
 At-Home Dryland Training Program Name of Player Team Name Program start date Player's Information Session 1 (Weeks 1-5) Age Exercises Reps Wts (Lb) Weeks Sets Rest Gender Squats 15 5 2 0 Height (Feet)
At-Home Dryland Training Program Name of Player Team Name Program start date Player's Information Session 1 (Weeks 1-5) Age Exercises Reps Wts (Lb) Weeks Sets Rest Gender Squats 15 5 2 0 Height (Feet)
Chapter 3 Basic Biomechanical Factors & Concepts
 Biomechanics Chapter 3 Basic Biomechanical Factors & Concepts Biomechanics - study of the mechanics as it relates to the functional and anatomical analysis of biological systems and especially humans Necessary
Biomechanics Chapter 3 Basic Biomechanical Factors & Concepts Biomechanics - study of the mechanics as it relates to the functional and anatomical analysis of biological systems and especially humans Necessary
VIPR and Power plate EXERCISE - 1 EXERCISE Fitness Professionals Ltd 2011 Job No. 2968
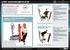 FIT FOR DAILY LIFE To be fit for daily life includes many movement abilities. Dynamic stability, co-ordination, balance, motor control, mobility and efficiency are all vital (including basic strength and
FIT FOR DAILY LIFE To be fit for daily life includes many movement abilities. Dynamic stability, co-ordination, balance, motor control, mobility and efficiency are all vital (including basic strength and
The Human Trainer Full Body Express Workout
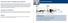 The Human Trainer Full Body Express Workout The Human Trainer Full Body Express workout is designed to be performed nearly anywhere. This is a full body workout designed with functional exercises to increase
The Human Trainer Full Body Express Workout The Human Trainer Full Body Express workout is designed to be performed nearly anywhere. This is a full body workout designed with functional exercises to increase
Year 7 PE Module 2 theory Content: Movement Analysis
 Year 7 PE Module 2 theory Content: Movement Analysis Assessment objective: To understand the different types of movements we make around an axis or movement plane the three types of axes/movement planes
Year 7 PE Module 2 theory Content: Movement Analysis Assessment objective: To understand the different types of movements we make around an axis or movement plane the three types of axes/movement planes
SUMMER WORK MRS KANSARA
 Name: A LEVEL PE Anatomy and Physiology SUMMER WORK MRS KANSARA Complete the following activities throughout the summer It is important that you understand and remember all the information included in
Name: A LEVEL PE Anatomy and Physiology SUMMER WORK MRS KANSARA Complete the following activities throughout the summer It is important that you understand and remember all the information included in
Table of Contents BASIC. Preface... i
 BASIC Table of Contents Preface... i Section 1 Section 2 Section 3 Section 4 FIVE COMPONENTS OF FITNESS Five for Life Five for Life... 1.1 Cardiorespiratory Endurance Heart Health K-3... 1.14 Heart Health...
BASIC Table of Contents Preface... i Section 1 Section 2 Section 3 Section 4 FIVE COMPONENTS OF FITNESS Five for Life Five for Life... 1.1 Cardiorespiratory Endurance Heart Health K-3... 1.14 Heart Health...
ADULT - PHASE 6. ACTIVATEye PART A PART B SMALL SIDED GAMES SNAKE RUNS KNEE TO ELBOW STATIC BEAR CRAWL 5 TO 10 MINUTES
 PART A SMALL SIDED GAMES For the first 5 to 10 minutes of training, while players arrive, use small-sided games to get players moving, to keep them warm and to act as a pulse raiser exercise. Groups should
PART A SMALL SIDED GAMES For the first 5 to 10 minutes of training, while players arrive, use small-sided games to get players moving, to keep them warm and to act as a pulse raiser exercise. Groups should
Separate information into components and identify their characteristics. Finish a task by adding to given information.
 Exam technique GCSE PE Command Words Analyse Apply Calculate Compare Complete Consider Define Describe Discuss Evaluate Explain Identify Illustrate Interpret Justify Outline Suggest State Separate information
Exam technique GCSE PE Command Words Analyse Apply Calculate Compare Complete Consider Define Describe Discuss Evaluate Explain Identify Illustrate Interpret Justify Outline Suggest State Separate information
PE Long Term Planning Overview
 PE Long Term Overview NURSERY AUTUMN SPRING SUMMER 22-36 months Moving and Handling Runs safely on whole foot Squats with steadiness to rest or play with objects on the ground, and rises to feet without
PE Long Term Overview NURSERY AUTUMN SPRING SUMMER 22-36 months Moving and Handling Runs safely on whole foot Squats with steadiness to rest or play with objects on the ground, and rises to feet without
Certified Personal Trainer Re-Certification Manual
 Certified Personal Trainer Re-Certification Manual Section II 1 Anatomy & Physiology Terms Anatomy and physiology are closely related fields of study: anatomy is the study of form, and physiology is the
Certified Personal Trainer Re-Certification Manual Section II 1 Anatomy & Physiology Terms Anatomy and physiology are closely related fields of study: anatomy is the study of form, and physiology is the
Taking Your Resistance Band to a New Level!
 How Many Reps? The guide instructs you to start with 5 repetitions, but if you would like to know more about building muscular strength versus muscular endurance, below are some guidelines: Muscular Strength
How Many Reps? The guide instructs you to start with 5 repetitions, but if you would like to know more about building muscular strength versus muscular endurance, below are some guidelines: Muscular Strength
Physical Education 8 th Grade Scope and Sequence (Year At a Glance) Physical Education First Semester
 Physical Education 8 th Grade Scope and Sequence (Year At a Glance) Physical Education First Semester Three Weeks 1 st 3 weeks 2 nd 3 weeks 3 rd 3 weeks 4 th 3 weeks 5 th 3 weeks 6 th 3 weeks Topics/ Concepts
Physical Education 8 th Grade Scope and Sequence (Year At a Glance) Physical Education First Semester Three Weeks 1 st 3 weeks 2 nd 3 weeks 3 rd 3 weeks 4 th 3 weeks 5 th 3 weeks 6 th 3 weeks Topics/ Concepts
Basketball Jump-Shot. Since basketball was created in 1891, the game has evolved tremendously in many
 Brittani Bush and Collin Grogan Structural Anatomy Project Paper Biomechanics of the Jump-Shot May 13, 2011 Basketball Jump-Shot Since basketball was created in 1891, the game has evolved tremendously
Brittani Bush and Collin Grogan Structural Anatomy Project Paper Biomechanics of the Jump-Shot May 13, 2011 Basketball Jump-Shot Since basketball was created in 1891, the game has evolved tremendously
The study of the internal workings of the human body and how it moves. A user s guide
 DEFINITION The study of the internal workings of the human body and how it moves. A user s guide OUR FOCUS Bones: structure, protection, levers Joints: allow for movement Muscles: cause movement Anatomical
DEFINITION The study of the internal workings of the human body and how it moves. A user s guide OUR FOCUS Bones: structure, protection, levers Joints: allow for movement Muscles: cause movement Anatomical
Day 5. Leg Raises. Throw downs. Side Crunches. Core/Abdominals
 Day 5 Tips: Total control of the torso is necessary to get the most benefit out of these exercises. Slow and controlled motion is required on all exercises. You are not looking for speed. On applicable
Day 5 Tips: Total control of the torso is necessary to get the most benefit out of these exercises. Slow and controlled motion is required on all exercises. You are not looking for speed. On applicable
Support, Movement and Locomotion
 Support, Movement and Locomotion Question Paper Level Subject Exam oard Topic Sub Topic ooklet O Level iology ambridge International Examinations Support, Movement and Locomotion Question Paper Time llowed:
Support, Movement and Locomotion Question Paper Level Subject Exam oard Topic Sub Topic ooklet O Level iology ambridge International Examinations Support, Movement and Locomotion Question Paper Time llowed:
Great Balls of Fire Revision Game
 Great Balls of Fire Revision Game Task: - The class needs to be divided in to teams (4/5 per team) - The students are positioned at the back of the class, each team with a bean bag (the colour denoting
Great Balls of Fire Revision Game Task: - The class needs to be divided in to teams (4/5 per team) - The students are positioned at the back of the class, each team with a bean bag (the colour denoting
Pilates for Brachialis Tendonitis (Tennis Elbow)
 Pilates for Brachialis Tendonitis (Tennis Elbow) Sally Dunford September 2017 Wimbledon, UK Abstract Tennis Elbow is a term used to describe a painful condition in which the tendons of the elbow are overloaded
Pilates for Brachialis Tendonitis (Tennis Elbow) Sally Dunford September 2017 Wimbledon, UK Abstract Tennis Elbow is a term used to describe a painful condition in which the tendons of the elbow are overloaded
Training the Shoulder for Racquet Sports Michael Barnes, MEd, CSCS
 Training the Shoulder for Racquet Sports Michael Barnes, MEd, CSCS Many sport movements involve accelerating an implement, such as a ball, bat or racquet, or transferring force from the ground to the hands.
Training the Shoulder for Racquet Sports Michael Barnes, MEd, CSCS Many sport movements involve accelerating an implement, such as a ball, bat or racquet, or transferring force from the ground to the hands.
Plyometrics. Ankle Bounces. Bounding. Butt Kuck
 Plyometrics Plyometric exercises are good for power, speed and strength. These exercises are not easy so you need to be in good shape before doing them. Check with your coach and/or trainer before adding
Plyometrics Plyometric exercises are good for power, speed and strength. These exercises are not easy so you need to be in good shape before doing them. Check with your coach and/or trainer before adding
EXO Chair A DETAILED GUIDE FOR PRACTICING PILATES
 EXO Chair A DETAILED GUIDE FOR PRACTICING PILATES TABLE OF CONTENTS 1 Balanced Body Education 2 What is Pilates? 4 Pilates Principles 6 Introduction to the EXO Chair 10 Hamstring Stretch 1 12 Hamstring
EXO Chair A DETAILED GUIDE FOR PRACTICING PILATES TABLE OF CONTENTS 1 Balanced Body Education 2 What is Pilates? 4 Pilates Principles 6 Introduction to the EXO Chair 10 Hamstring Stretch 1 12 Hamstring
Lab no 1 Structural organization of the human body
 Physiology Lab Manual Page 1 of 6 Lab no 1 Structural organization of the human body Physiology is the science which deals with functions of the body parts, and how they work. Since function cannot be
Physiology Lab Manual Page 1 of 6 Lab no 1 Structural organization of the human body Physiology is the science which deals with functions of the body parts, and how they work. Since function cannot be
