1.1 The structure and functions of the musculo-skeletal system Learning objectives
|
|
|
- Norah York
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 1.1 The structure and functions of the musculo-skeletal system Learning objectives To be able to describe the functions of the skeleton. To understand different bone classifications and functioning. To be able to recognise and label a skeleton. To be able to define different joint classifications. To be able to describe and analyse different types of joint movements and how they are used during sporting movements. To be able to describe the difference between cartilage, tendons and ligaments.
2 Functions of the skeleton The skeleton performs many functions in the body: Support The skeleton supports the muscles. Protection The skeleton protects delicate parts of the body like the brain. Muscle Attachment/Movement Muscles are attached to the bones and move them creating levers. Blood cell production blood cells are made in the bone marrow.
3 Support The skeleton acts as a framework. It gives the body support, enabling us to stand. The bones of the body are held together by ligaments. The skeleton provides a framework for the muscles, which are attached to bones by tendons.
4 Protection Some of our body parts, such as the brain, are very delicate and need protection. Bones can protect body parts from impact and injuries. 1. What vital organ does the Cranium protect? Answer: 2. What vital organ does the Rib Cage protect? Answer:
5 Muscle Attachment/Movement Muscles are firmly attached to bones forming levers which create sporting movements.
6 Blood cell production Long bones and other bones including the ribs, humerus, femur and vertebrae bones, contain red bone marrow. This is where red blood cells are produced which carry oxygen. Other functions include: White blood cells to combat illness and disease Platelets for clotting and healing. Storage of Calcium and Phosphorus
7 Skeletal System Without your skeleton you would be a shapeless sack of flesh. The adult skeleton has 206 bones. How many bones can you name?
8 Skeletal System Structure Clavicle Ribs Pelvis Patella (knee cap) Fibula Tibia Cranium Sternum Humerus Radius Ulna Femur
9 Skeletal System Structure Hand Foot Scapula Vertebral column Carpals Metacarpals Phalanges Tarsals Metatarsals Phalanges
10 The vertebral column It is made up of irregularly shaped bones called vertebrae. Between each vertebra there is a pad of cartilage which allows movement and prevents friction. The vertebrae protects the spinal cord. The vertebral column is divided into 5 sections.
11 Classification of bones Bones are divided into a number of different categories which have different roles in the body. 1. Long bones Long bones have a long shaft and are responsible for different types of movement. Sporting actions are created by long bones through levers. Long bones can be any size; they include the femur, humerus, tibia, fibula, metatarsals, metacarpals and phalanges.
12 2. Flat bones Flat bones perform a number of functions. 1. Protection for delicate areas. i.e. the cranium protects the brain. 2. Provides a broad surface area for muscle attachment. i.e. muscles in the back attach to the pelvis.
13 3. Short bones Short bones are light, small and very strong. The primary function is to support the weight of the body. Carpals The carpals in the wrist and the tarsals in the foot are examples of short bones. How does this aid sportspeople in an event? Gymnasts use carpals to support a handstand.
14 4. Irregular bones Femur Irregular bones are specially shaped to perform a particular function. Patella These functions include: 1. Protection 2. Muscle attachment Examples include the patella and the vertebrae. Tibia Fibula
15 Classification of Joints DEFINITION: A joint is a place where two or more bones meet. Joints are responsible for the huge range of movement that the body can produce. There are several different types of joint classification.
16 Classification of Joints 1. Ball and socket joint - the rounded end of a bone fits inside a cup-shaped end. Hip Ball and socket joints allow movement in all directions. These are the most mobile joints in the body. Examples found in the body: Shoulders and hips. Why are these joints important for sport? Most sporting movements require movement by the shoulder and hip joints e.g. tennis serve
17 Classification of Joints 2. Hinge joints - only allow forwards and backwards movement like the hinge on a door. Examples found in the body: The knee and elbow. Why are these joints important for sport? These joints are extremely powerful and in conjunction with surrounding muscles can produce power and speed e.g. Knee drive during a 100m sprint
18 Classification of Joints 3. The Pivot joint has a ring of bone that fits over a pivoting bone. Pivot joints allow rotation only. Neck Examples found in the body: The joint between the atlas and axis in the neck allows turning and nodding of the head. Why are these joints important for sport? This joint allows for small movements that assist a larger sporting action e.g. breathing during a swimming stroke
19 Classification of Joints 4. Condyloid joints have an oval-shaped bone which fits into a similar shaped bone. They allow small movements in all directions. Examples found in the body: Found between the carpals and metacarpals in the wrist. Why are these joints important for sport? These joints are extremely useful when a sport involves gripping a ball. e.g. handball throw
20 Apply it! What has stuck with you? What synovial joints are used in these sporting examples?
21 Apply it! What has stuck with you? What are the 4 functions of the skeletal system? Explain why we have flat, short, long and irregular bones. Can you give examples of each? Musculoskeletal system Highlight on your body as many bones as you can! Name the 4 joint classifications?
22 Practice it! Exam questions 1. List three major types of bones, found in the human skeleton. (3) (i) Irregular (ii) (iii) (iv) 2. Except for the femur, provide the names of two other bones in the leg that are classified as long bones. (2) a) b)
23 Practice it! Exam questions 3. The humerus is a long bone. Which of the following statements correctly identifies a function of the humerus and its associated advantage to the performer in the statement? (1) A B C D a hockey player can reach further to hit the ball as the humerus is a long bone a footballer can kick the ball harder due to the length of the humerus the humerus acts as a lever so a hockey player can apply more force to the ball the humerus protects the footballer from injury.
24 Practice it! Exam Questions: 4.Name the bones of the upper and lower arm? (3) 5.Name the anatomical name for the following bones (5) a) Skull b) Knee cap c) Collar Bone d) Shoulder blade e) Wrist
25 Practice it! Exam Questions: 6. The following are regions or bones of the vertebral column. Thoracic Sacral Atlas Lumbar Cervical Axis Place these regions of the vertebral column in the order they appear after the bones Atlas and Axis. (4) Atlas Axis
26 Practice it! Marks Scheme: 1. Short, Long, Flat 2. Tibia, Fibula 3. C 4. Humerus, Radius, Ulna 5. a) Cranium b) Patella c) Clavicle d) Scapula e) Carpals 6. Cervical, Thoracic, Lumbar, Sacral
27 1.1 The structure and functions of the musculo-skeletal system Learning objectives To understand the three muscle types and their functions To be able to label the voluntary muscles in our body To explain the term antagonist pair and provide examples To understand the characteristics of fast and slow twitch muscle fibres
28 Connective tissues There are 3 types of connective tissue: Tendons connect muscles to bones. Ligaments are tough, elastic fibres that link bones to bones. Cartilage prevents the ends of bones rubbing together at joints.
29 Joint Movements 1. Flexion and Extension FLEXION Decreasing the angle at a joint. (Bending the joint) EXTENSION - Increasing the angle at a joint. (Straightening the joint)
30 Joint Movements 2. Abduction and Adduction Abduction and Adduction is determined from the MIDLINE of the body.
31 Joint Movements ADDUCTION Sideways moving limb towards midline of the body. REMEMBER: Adduction is to ADD towards the midline. ABDUCTION Sideways moving limb away from midline of the body REMEMBER: Abduction is to TAKE AWAY from the midline.
32 Joint Movements 3. Rotation/Circumduction The joint moves in a circular motion. e.g. Service action or bowling action.
33 Joint Movements 4. Planter-Flexion and Dorsi-Flexion Planter-flexion The action of pointing toes away from the body. Dorsi-flexion The action of pulling toes towards the body.
34 Apply it! What has stuck with you? What movements occur during these action?
35 Cyclist FLEXION at the RIGHT knee joint EXTENSION - at the LEFT knee joint FLEXION at the RIGHT hip joint as the leg raises FLEXION Slight Flexion at the elbows FLEXION Torso (body is bent forwards) Footballer EXTENSION at the knee joints FLEXION at the HIP JOINT of right leg ADDUCTION at the hip joint as the left leg is moving towards the central line of the body ADDUCTION Left arm FLEXION at left elbow Swimmer - Start ADDUCTION of the arms EXTENSION at the knee joints EXTENSION at the elbows Butterfly Stroke ROTATION at the shoulder joint EXTENSION at elbow joints ABDUCTION of the arms
36 Label as many joint movements as you can see. i.e. flexion at the knee
37 Classification and Characteristics of Muscles Muscles are used in everyday life all the time. Sportspeople are reliant on the power of muscles to compete. What do you know about muscles already?
38 Classification and Characteristics of Muscles Muscles are involved in every movement in your body. Muscle is a special type of tissue made up of fibres that contract (shorten) and relax (lengthen). There are three types of muscle fibre.
39 Classification and Characteristics of Muscles 1. Voluntary Muscles These are attached to bones and they work whenever we want them to. e.g. Biceps & Triceps. These muscles are under our conscious control.
40 Classification and Characteristics of Muscles 2. Involuntary muscle These are found on the walls of the internal organs and they contract in waves. Food travels through the digestive system and blood through the blood vessels in this way. It works without you consciously controlling it, or even being aware of it.
41 Classification and Characteristics of Muscles 3. Cardiac muscle This is a special type of muscle that forms the walls of the heart chambers. It is a type of involuntary muscle, as it contracts without conscious thought or effort. It works non-stop without ever tiring. When it contracts it pumps blood out of the heart and around the body.
42 Classification and Characteristics of Muscles All three types of muscle are important in physical activity: Voluntary muscles enable movement throughout the body. Involuntary muscles are essential in maintaining healthy body systems. Cardiac muscle is vital in sport because it makes the heart pump. Fitness training will strengthen cardiac muscle making the heart more efficient at pumping blood around the body.
43 Voluntary Muscles Pectorals Bicep External Obliques Abdominals Hip Flexors Quadriceps Triceps Deltoid Latissimus Dorsi Gluteus Maximus Hamstring Gastrocnemius Tibialis Anterior
44 Voluntary Muscles What happens when muscles contract? Muscles shorten when they contract and lengthen when they relax.
45 Voluntary Muscles When you contract your QUADRICEP what is the effect on the limb? When you contract your HAMSTRING what is the effect on the limb? When you contract your DELTOID what is the effect on the limb?
46 Now complete the grid below. What happens when each muscle contracts? Muscle 1 Deltoid 2 Biceps 3 Abdominals 4 Quadriceps 5 Pectorals 6 Latissimus Dorsi 7 External Obiliques 8 Triceps 9 Gulteus Maximus 10 Hamstring 11 Taibialis Anterior 12 Gastrocnemius 13 Hip Flexors Main Action (s)
47 Muscle 1 Deltoid 2 Biceps 3 Abdominals 4 Quadriceps 5 Pectorals 6 Latissimus Dorsi 7 External Obiliques 8 Triceps 9 Gulteus Maximus 10 Hamstring 11 Taibialis Anterior 12 Gastrocnemius 13 Hip Flexors Main Action (s) Raises arm sideways at the shoulder (abduction) Bends arm at the elbow (Flexion) Flexes trunk so you can bend forward Straighten leg at the knee (extension) Draws arm across chest Pulls arms backwards towards back Allows twisting and turning of the torso Straightens arm at the elbow joint (extension) Pull leg back at hip. Bends leg at the knee. (flexion) Flexes the ankle joint so you can pull toes towards the body Extends the ankle joint so you can stand on tiptoes Pulls upper leg towards the chest
48 Antagonistic muscle action The fixed or non-moving end is known as the origin. The insertion is known as the moving end. Muscles are arranged in antagonistic pairs. As one muscle contracts (shortens) its partner relaxes (lengthens). E.g. Bicep and Tricep.
49 Antagonistic muscle action Can you think of another antagonists pair in the body?
50 Antagonistic muscle action Gastrocnemius and Tibialis Anterior acting at the ankle joint Hamstring and Quadricep acting at the knee joint. Hip Flexors and Gluteus Maximus acting at the hip joint.
51 Muscle fibre types Muscle twitch fibres occur in different proportions in different people. This proportion is mainly to do with the genes you inherit but can be altered by training.
52 Muscle fibre types How can athletes do this? What do you know about muscle fibres already?
53 Muscle fibre types There are two main types of muscle fibres: 1. SLOW TWITCH MUSCLE FIBRES Small in size. These fibres take a relatively long time to contract. Have a good oxygen supply and is why they are deep red in colour. They contract slowly, but can work for long periods.
54 Muscle fibre types 2. FAST TWITCH MUSCLE FIBRES - Large in size. These fibres contract quickly and powerfully. Fast twitch fibres are paler in colour and have limited oxygen supply. They contract quickly and powerfully, but tire easily.
55 Muscle fibre types An average person possesses: 60% 40% Slow twitch Fast twitch fibres Elite endurance athletes possess a high percentage of slow twitch fibres. Elite explosive athletes possess a high percentage of fast twitch muscle fibres.
56 Apply it! What has stuck with you? What are the 3 classification of muscle types? Explain what is meant by an antagonistic pair and an example in the body? Musculoskeletal system Highlight and name as many muscle as you can! Explain the difference between fast and slow twitch muscle fibres.
57 Apply it! What has stuck with you? Will each of the athletes below require mostly fast twitch or slow twitch muscle fibres and why?
58 Practice it! Exam questions 1. Figure 4 shows a high board diver in flight. Complete the following statements about the diver. (i) The high diver has... his legs at the knee and folded his body by... at the... joint to allow him to bend forward. (3) (ii) The diver s arms are... at the elbow. The muscle that contracts to bring about this movement is the.... (2)
59 Practice it! Exam questions 1. Figure 4 shows a high board diver in flight. Complete the following statements about the diver. iii) Movement occurs at the joints. The hip and shoulder provide the greatest range of movement in the body. What type of joint are the hip and shoulder?... (1)
60 Practice it! Exam questions 2. Figure 5 is a diagram of a joint. A C B i) What is the name and type of joint shown in Figure 5? (2) Joint name... Joint type... (ii) Name the bones of the joint labelled A, B and C in Figure 5. (3) A... B... C...
61 Practice it! Exam question 3. Using examples to illustrate your answer, describe the differences between slow and fast twitch muscle fibres. (4) 4. What percentage of fast twitch and slow twitch muscle fibres would a midfield football player need and why? (3)
62 Practice it! Marks Scheme: 1. i) Extended/extension, Flexing/flexion, Hip ii) Flexed, Bicep iii) Ball and Socket 2. i) Knee, Hinge ii) Femur, Patella, Tibia 3. Endurance event slow twitch fibres (Marathon runner) Better oxygen content/delivery therefore allows athletes to continue to work without tiring. Power event fast twitch fibres (100m Sprinter) Not as dense oxygen supply but powerful contraction possible %/30% - slow/fast twitch fibres. Position requires endurance to cover all areas of the pitch both attack and defence. Powerful sprints required at times to make runs and track attacking players.
Y12 Transition Pack Sports Leadership
 Y12 Transition Pack Sports Leadership Name: Base School: Section 1: The Muscular System Read through the following information on the Muscular System Cardiac muscle is unique to the heart. It never tires.
Y12 Transition Pack Sports Leadership Name: Base School: Section 1: The Muscular System Read through the following information on the Muscular System Cardiac muscle is unique to the heart. It never tires.
VCE PHYSICAL EDUCATION WORKBOOK UNIT 1 BODIES IN MOTION NAME:
 VCE PHYSICAL EDUCATION WORKBOOK UNIT 1 BODIES IN MOTION NAME: SKELETAL SYSTEM List the 5 functions of the skeletal system and complete the following table. FUNCTION DESCRIPTION Label the following features
VCE PHYSICAL EDUCATION WORKBOOK UNIT 1 BODIES IN MOTION NAME: SKELETAL SYSTEM List the 5 functions of the skeletal system and complete the following table. FUNCTION DESCRIPTION Label the following features
VCE PHYSICAL EDUCATION WORKBOOK UNIT 1 BODIES IN MOTION NAME:
 VCE PHYSICAL EDUCATION WORKBOOK UNIT 1 BODIES IN MOTION NAME: SKELETAL SYSTEM List the 5 functions of the skeletal system and complete the following table. FUNCTION DESCRIPTION Label the following features
VCE PHYSICAL EDUCATION WORKBOOK UNIT 1 BODIES IN MOTION NAME: SKELETAL SYSTEM List the 5 functions of the skeletal system and complete the following table. FUNCTION DESCRIPTION Label the following features
1.1 The Structure and Functions of the Musculo- Skeletal System Teacher Answer Booklet
 GCSE EDEXCEL 1.1 1.1 The Structure and Functions of the Musculo- Skeletal System Teacher Answer Booklet GCSE EDEXCEL 1.1 WWW.THEPECLASSROOM.COM Topic Description from Specification Pupil comments How confident
GCSE EDEXCEL 1.1 1.1 The Structure and Functions of the Musculo- Skeletal System Teacher Answer Booklet GCSE EDEXCEL 1.1 WWW.THEPECLASSROOM.COM Topic Description from Specification Pupil comments How confident
Please do the following
 Please do the following 1. Read the Learners must know section (see below) 2. Watch the GCSE POD video 3. Attempt Exam Questions 4. Mark your answers 5. Reflect and repeat until you are successful and
Please do the following 1. Read the Learners must know section (see below) 2. Watch the GCSE POD video 3. Attempt Exam Questions 4. Mark your answers 5. Reflect and repeat until you are successful and
Skeletal System. Std. VIII
 Skeletal System Std. VIII The skeleton in our body serves following functions : 1. Support and shape : The skeleton provides a support or framework to all the soft parts and gives the body and its parts
Skeletal System Std. VIII The skeleton in our body serves following functions : 1. Support and shape : The skeleton provides a support or framework to all the soft parts and gives the body and its parts
REVISION BOOKLET. The Body Systems
 REVISION BOOKLET The Body Systems GCSE PE 2016 Skeletal System Functions of the skeleton Joints for movement Muscle attachment Protection of vital organs Red and white blood cell production platelets Storage
REVISION BOOKLET The Body Systems GCSE PE 2016 Skeletal System Functions of the skeleton Joints for movement Muscle attachment Protection of vital organs Red and white blood cell production platelets Storage
Applied Anatomy and Physiology
 Applied Anatomy and Physiology 1.1.a. The Structure and Function of the Skeletal System Cranium LEARNING OUTCOMES Phalanges Pelvis Phalanges By the end of this topic you should Know the name and location
Applied Anatomy and Physiology 1.1.a. The Structure and Function of the Skeletal System Cranium LEARNING OUTCOMES Phalanges Pelvis Phalanges By the end of this topic you should Know the name and location
Anatomy. Anatomy deals with the structure of the human body, and includes a precise language on body positions and relationships between body parts.
 Anatomy deals with the structure of the human body, and includes a precise language on body positions and relationships between body parts. Proper instruction on safe and efficient exercise technique requires
Anatomy deals with the structure of the human body, and includes a precise language on body positions and relationships between body parts. Proper instruction on safe and efficient exercise technique requires
SUPPORT, MOVEMENT AND LOCOMOTION
 SUPPORT, MOVEMENT AND LOCOMOTION Overview Bones Joints Antagonistic Muscles Forelimbs Bones Functions of the skeleton Locomotion The ability to move from place to place Support Holds the body off the ground
SUPPORT, MOVEMENT AND LOCOMOTION Overview Bones Joints Antagonistic Muscles Forelimbs Bones Functions of the skeleton Locomotion The ability to move from place to place Support Holds the body off the ground
1.1 a The structure and functin if the skeletal system Learning ibjectves
 1.1 a The structure and functin if the skeletal system Learning ibjectves To be able to describe the functons of the skeleton. To be able to recognise and label a skeleton. To understand the diferent joint
1.1 a The structure and functin if the skeletal system Learning ibjectves To be able to describe the functons of the skeleton. To be able to recognise and label a skeleton. To understand the diferent joint
YEAR 9 GCSE PE Learning Programme
 YEAR 9 GCSE PE Learning Programme Half Term/Term Learning objective Learning activity Differentiation and extension Bones. Knowledge of the bones at the following locations: head/neck cranium, vertebrae
YEAR 9 GCSE PE Learning Programme Half Term/Term Learning objective Learning activity Differentiation and extension Bones. Knowledge of the bones at the following locations: head/neck cranium, vertebrae
The Musculoskeletal system
 Level 3 BTEC Applied Science Summer Homework The Musculoskeletal system Student name:.. Tutor name: 1 Student Instructions This workbook incorporates elements of Unit 8 Learning Aim A: Understand the impact
Level 3 BTEC Applied Science Summer Homework The Musculoskeletal system Student name:.. Tutor name: 1 Student Instructions This workbook incorporates elements of Unit 8 Learning Aim A: Understand the impact
CHAPTER 1: 1.1 Muscular skeletal system. Question - text book page 16. Question - text book page 20 QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS. Answers
 QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS CHAPTER 1: 1.1 Muscular skeletal system Question - text book page 16 Using the information on pages 12 to 14 above, complete the table below. joint joint type articulating bones associated
QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS CHAPTER 1: 1.1 Muscular skeletal system Question - text book page 16 Using the information on pages 12 to 14 above, complete the table below. joint joint type articulating bones associated
Certified Personal Trainer Re-Certification Manual
 Certified Personal Trainer Re-Certification Manual Section II 1 Anatomy & Physiology Terms Anatomy and physiology are closely related fields of study: anatomy is the study of form, and physiology is the
Certified Personal Trainer Re-Certification Manual Section II 1 Anatomy & Physiology Terms Anatomy and physiology are closely related fields of study: anatomy is the study of form, and physiology is the
Topic Guide 1: Applied Anatomy and Physiology. GCSE (9-1) Physical Education
 Topic Guide 1: Applied Anatomy and Physiology GCSE (9-1) Physical Education Pearson Edexcel Level 1/Level 2 GCSE (9-1) in Physical Education (1PE0) Pearson Edexcel Level 1/Level 2 GCSE (9-1) in Physical
Topic Guide 1: Applied Anatomy and Physiology GCSE (9-1) Physical Education Pearson Edexcel Level 1/Level 2 GCSE (9-1) in Physical Education (1PE0) Pearson Edexcel Level 1/Level 2 GCSE (9-1) in Physical
36.3 The Integumentary System The Skin. KEY CONCEPT The integumentary system has many tissues that protect the body.
 36.3 The Integumentary System The Skin KEY CONCEPT The integumentary system has many tissues that protect the body. 36.3 The Integumentary System The Skin The integument is the body system that surrounds
36.3 The Integumentary System The Skin KEY CONCEPT The integumentary system has many tissues that protect the body. 36.3 The Integumentary System The Skin The integument is the body system that surrounds
Challenge Question: Prediction: (Wait for directions) Evidence: (Draw, color and label how your Clay model looked when it was complete)
 Activity #12 What s happening inside? Challenge Question: Prediction: (Wait for directions) Evidence: (Draw, color and label how your Clay model looked when it was complete) Act #12 pg 1 of 3 Analysis
Activity #12 What s happening inside? Challenge Question: Prediction: (Wait for directions) Evidence: (Draw, color and label how your Clay model looked when it was complete) Act #12 pg 1 of 3 Analysis
PRELIMINARY HSC PDHPE. CQ1 How do the musculoskeletal and cardiorespiratory systems of the body influence and respond to movement?
 PRELIMINARY HSC PDHPE CQ1 How do the musculoskeletal and cardiorespiratory systems of the body influence and respond to movement? How do the musculoskeletal and cardiorespiratory systems of the body influence
PRELIMINARY HSC PDHPE CQ1 How do the musculoskeletal and cardiorespiratory systems of the body influence and respond to movement? How do the musculoskeletal and cardiorespiratory systems of the body influence
Boardworks Ltd Types of Synovial Joint
 1 of 37 Types of Synovial Joint Definition: 2 of 37 3 of 37 3. Freely movable or synovial joints 90% of the joints in the body are synovial joints. They are freely movable. Synovial joints contain synovial
1 of 37 Types of Synovial Joint Definition: 2 of 37 3 of 37 3. Freely movable or synovial joints 90% of the joints in the body are synovial joints. They are freely movable. Synovial joints contain synovial
PRELIMINARY HSC PDHPE. CQ1 How do the musculoskeletal and cardiorespiratory systems of the body influence and respond to movement?
 PRELIMINARY HSC PDHPE CQ1 How do the musculoskeletal and cardiorespiratory systems of the body influence and respond to movement? How do the musculoskeletal and cardiorespiratory systems of the body influence
PRELIMINARY HSC PDHPE CQ1 How do the musculoskeletal and cardiorespiratory systems of the body influence and respond to movement? How do the musculoskeletal and cardiorespiratory systems of the body influence
CHAPTER 4: The musculo-skeletal system. Practice questions - text book pages QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS. Answers
 CHAPTER 4: The musculo-skeletal system Practice questions - text book pages 64-66 1) A prime mover of hip flexion is the: a. rectus femoris. b. Iliopsoas. c. vastus muscles. d. gluteus maximus. b. Key
CHAPTER 4: The musculo-skeletal system Practice questions - text book pages 64-66 1) A prime mover of hip flexion is the: a. rectus femoris. b. Iliopsoas. c. vastus muscles. d. gluteus maximus. b. Key
UNIT 4. BONES AND MUSCLES
 UNIT 4. BONES AND MUSCLES 1. Skeletal System 1. Functions of the Skeletal System The cervical vertebrae make up the neck. You have 7 of these and the top one is connected to the base of the skull. They
UNIT 4. BONES AND MUSCLES 1. Skeletal System 1. Functions of the Skeletal System The cervical vertebrae make up the neck. You have 7 of these and the top one is connected to the base of the skull. They
Lifting your toes up towards your tibia would be an example of what movement around the ankle joint?
 NAME: TEST 1 ANATOMY IN SPORT SCIENCE: SEMESTER 2, 2016 TOTAL MARKS = 72 Total: /72 marks Percentage: Grade: TERMINOLOGY: The structures that connect bone to bone are called: The hip joint is to the shoulder
NAME: TEST 1 ANATOMY IN SPORT SCIENCE: SEMESTER 2, 2016 TOTAL MARKS = 72 Total: /72 marks Percentage: Grade: TERMINOLOGY: The structures that connect bone to bone are called: The hip joint is to the shoulder
The Skeletal System in Action!! The Skeletal System in Action!
 Skeletal System The Skeletal System in Action!! The Skeletal System in Action! 5 Functions of the Skeletal System 1. Movement: Skeletal system provides points of attachment for muscles. Your legs and arms
Skeletal System The Skeletal System in Action!! The Skeletal System in Action! 5 Functions of the Skeletal System 1. Movement: Skeletal system provides points of attachment for muscles. Your legs and arms
inquiry question How do bones and joints assist movement in sprinting? UNCORRECTED PAGE PROOFS
 inquiry question How do bones and joints assist movement in sprinting? chapter 2 Structure and functions of the skeletal system The skeletal and muscular systems work together to produce movement in physical
inquiry question How do bones and joints assist movement in sprinting? chapter 2 Structure and functions of the skeletal system The skeletal and muscular systems work together to produce movement in physical
THe Skeletal System 1
 THe Skeletal System 1 What the Skeletal System DOes! Skeleton: works as the framework of your body and is made up of all of the bones in your body The number of bones in your skeleton depends on your age.
THe Skeletal System 1 What the Skeletal System DOes! Skeleton: works as the framework of your body and is made up of all of the bones in your body The number of bones in your skeleton depends on your age.
GCSE PERSONAL LEARNING CHECKLIST PHYSICAL EDUCATION
 GCSE PERSONAL LEARNING CHECKLIST PHYSICAL EDUCATION PLC KEY: COMPONENT 1: FITNESS AND BODY SYSTEMS 1.1-4.1 You have covered the concept in lesson by the teacher. You have extended the concept in your file
GCSE PERSONAL LEARNING CHECKLIST PHYSICAL EDUCATION PLC KEY: COMPONENT 1: FITNESS AND BODY SYSTEMS 1.1-4.1 You have covered the concept in lesson by the teacher. You have extended the concept in your file
The Musculoskeletal System
 The Musculoskeletal System Introduction The skeletal system and muscular system are often considered together because they are close in terms of structure and function. The two systems are referred to
The Musculoskeletal System Introduction The skeletal system and muscular system are often considered together because they are close in terms of structure and function. The two systems are referred to
Yoga Anatomy & Physiology
 Yoga Anatomy & Physiology Anatomy & Physiology Anatomy- One of the basic essential sciences of medicine that studies the structure of an organism. Physiology- The biological study of the functions of living
Yoga Anatomy & Physiology Anatomy & Physiology Anatomy- One of the basic essential sciences of medicine that studies the structure of an organism. Physiology- The biological study of the functions of living
The Skeletal System. Chapter 8
 The Skeletal System Chapter 8 1 Introduction Movement is essential for animals. This is done by moving muscles with the skeleton. 2 Functions of the skeleton 1. Gives shape and support to the body. The
The Skeletal System Chapter 8 1 Introduction Movement is essential for animals. This is done by moving muscles with the skeleton. 2 Functions of the skeleton 1. Gives shape and support to the body. The
2º ESO - PE Workbook - IES Joan Miró Physical Education Department THE MUSCULAR SYSTEM
 THE MUSCULAR SYSTEM The muscular system is one of 10 organ systems in the human body. The human body has more than 650 muscles, which make up half of a person's body weight. Without muscles, we would not
THE MUSCULAR SYSTEM The muscular system is one of 10 organ systems in the human body. The human body has more than 650 muscles, which make up half of a person's body weight. Without muscles, we would not
The Skeletal System. Functions of the Skeletal System
 11/15/17 The Skeletal System The Skeletal System 1 Functions of the Skeletal System Provide support and structure Protects vital internal organs Storage site for minerals Site for blood formation Bones
11/15/17 The Skeletal System The Skeletal System 1 Functions of the Skeletal System Provide support and structure Protects vital internal organs Storage site for minerals Site for blood formation Bones
Table of Contents. Introduction to the Teacher...1. Body Organization...2 Cells, tissues, organs, and systems
 Table of Contents Table of Contents Introduction to the Teacher...1 Body Organization...2 Cells, tissues, organs, and systems...3 Purpose and parts of the skeletal system, bones, joints, cartilage, etc....8
Table of Contents Table of Contents Introduction to the Teacher...1 Body Organization...2 Cells, tissues, organs, and systems...3 Purpose and parts of the skeletal system, bones, joints, cartilage, etc....8
The muscles in the body each fall into one of three groups:
 MUSCLES The muscles in the body each fall into one of three groups: 1. VOLUNTARY or SKELETAL MUSCLESthese muscles are under the control of our will. All these muscles are attached to the skeleton. These
MUSCLES The muscles in the body each fall into one of three groups: 1. VOLUNTARY or SKELETAL MUSCLESthese muscles are under the control of our will. All these muscles are attached to the skeleton. These
PiXL Independence: PE Answer Booklet KS4. Applied Anatomy and Physiology. Contents: Answers
 PiXL Independence: PE Answer Booklet KS4 Applied Anatomy and Physiology Contents: Answers 1 I. Quizzes Multiple Choice Quiz 1. Which one of the following statements is false? a. The scapula, cranium and
PiXL Independence: PE Answer Booklet KS4 Applied Anatomy and Physiology Contents: Answers 1 I. Quizzes Multiple Choice Quiz 1. Which one of the following statements is false? a. The scapula, cranium and
Lab-1. Miss. Lina Al-Onazy & samar Al-Wgeet =)
 Lab-1 Introduction The human skeleton is composed of 300 bones at birth and by the time adulthood is reached, some bones have fused together to give a total of 206 bones in the body. The human skeleton
Lab-1 Introduction The human skeleton is composed of 300 bones at birth and by the time adulthood is reached, some bones have fused together to give a total of 206 bones in the body. The human skeleton
L01:Name and locate the major bones within the skeletal system.
 L01:Name and locate the major bones within the skeletal system. All physical activity requires movement using bones and muscles. Name three major bones which are located in the leg. Bone 1 - Bone 2- Bone
L01:Name and locate the major bones within the skeletal system. All physical activity requires movement using bones and muscles. Name three major bones which are located in the leg. Bone 1 - Bone 2- Bone
Grade 10 Intro to Resistance Training
 Grade 10 Intro to Resistance Training Benefits to Training with Weights Hypertrophy - Increase in existing muscle fibers Strengthening of tendons and ligament tissues Improve posture Decrease the size
Grade 10 Intro to Resistance Training Benefits to Training with Weights Hypertrophy - Increase in existing muscle fibers Strengthening of tendons and ligament tissues Improve posture Decrease the size
The skeletal system is the framework for the muscular system to attach to so we can move.
 Skeletal System The skeletal system is the framework for the muscular system to attach to so we can move. BONE: A rigid connective tissue Helps to move & support the body Protect the organs (skull, ribs)
Skeletal System The skeletal system is the framework for the muscular system to attach to so we can move. BONE: A rigid connective tissue Helps to move & support the body Protect the organs (skull, ribs)
Applied Anatomy and Physiology
 Applied Anatomy and Physiology 1.1.b. The Structure and Function of the Muscular System Learning Outcomes BY THE END OF THIS TOPIC YOU SHOULD.. Know the name and location of major muscle groups Be able
Applied Anatomy and Physiology 1.1.b. The Structure and Function of the Muscular System Learning Outcomes BY THE END OF THIS TOPIC YOU SHOULD.. Know the name and location of major muscle groups Be able
Locomotion: The act or power of moving from place to place
 Locomotion Locomotion: The act or power of moving from place to place Vocabulary 1. Motile = The ability to move from place to place 2. Sessile = 3. Muscle contraction = 4. Exoskeleton = 5. Endoskeleton
Locomotion Locomotion: The act or power of moving from place to place Vocabulary 1. Motile = The ability to move from place to place 2. Sessile = 3. Muscle contraction = 4. Exoskeleton = 5. Endoskeleton
YEAR 8 REVISION BOOKLET 2018
 Name: PE Teacher YEAR 8 REVISION BOOKLET 2018 Year 8 End of Year Exam Revision - Physical Education Section 1: The Skeletal System, Types of Joint and the Functions of the Skeleton Cranium Scapula Clavicle
Name: PE Teacher YEAR 8 REVISION BOOKLET 2018 Year 8 End of Year Exam Revision - Physical Education Section 1: The Skeletal System, Types of Joint and the Functions of the Skeleton Cranium Scapula Clavicle
Human Skeletal System Glossary
 Acromegaly Apatite Acromegaly - is a condition which involves excessive growth of the jaw, hands, and feet. It results from overproduction of somatotropin in adults (after fusion of the ossification centres
Acromegaly Apatite Acromegaly - is a condition which involves excessive growth of the jaw, hands, and feet. It results from overproduction of somatotropin in adults (after fusion of the ossification centres
How can sportspeople train the body systems to ensure there are long term benefits? Excercise Physiology. Chapter 2. GCSE Physical Education
 How can sportspeople train the body systems to ensure there are long term benefits? Excercise Physiology GCSE Physical Education To answer the big question you will need to be able to complete the following
How can sportspeople train the body systems to ensure there are long term benefits? Excercise Physiology GCSE Physical Education To answer the big question you will need to be able to complete the following
Anatomy and physiology for sport
 Anatomy and physiology for sport UV21527 D/502/5474 Learner name: VRQ Learner number: VTCT is the specialist awarding body for the Hairdressing, Beauty Therapy, Complementary Therapy, Hospitality and Catering
Anatomy and physiology for sport UV21527 D/502/5474 Learner name: VRQ Learner number: VTCT is the specialist awarding body for the Hairdressing, Beauty Therapy, Complementary Therapy, Hospitality and Catering
Bones of Thorax (Rib Cage)
 Musculoskeletal System (Part A-2) Module 7 -Chapter 10 Overview Muscles Attachments Bones Bone types Surface features of bones Divisions of the skeletal system Joints or Articulations Susie Turner, M.D.
Musculoskeletal System (Part A-2) Module 7 -Chapter 10 Overview Muscles Attachments Bones Bone types Surface features of bones Divisions of the skeletal system Joints or Articulations Susie Turner, M.D.
KS4 Physical Education
 KS4 Physical Education Muscles and Muscle Action These icons indicate that teacher s notes or useful web addresses are available in the Notes Page. This icon indicates that the slide contains activities
KS4 Physical Education Muscles and Muscle Action These icons indicate that teacher s notes or useful web addresses are available in the Notes Page. This icon indicates that the slide contains activities
Bone Composition. Bone is very strong for its relatively light weight The major components of bone are:
 Human Bones Bone Composition Bone is very strong for its relatively light weight The major components of bone are: Calcium carbonate Calcium phosphate Collagen Water Cortical Bone Spongy Bone Medullary
Human Bones Bone Composition Bone is very strong for its relatively light weight The major components of bone are: Calcium carbonate Calcium phosphate Collagen Water Cortical Bone Spongy Bone Medullary
YOGA ANATOMY. Part Three - Bones. Yoga Teacher Training Robin Bennett 200 RYT
 YOGA ANATOMY Yoga Teacher Training Part Three - Bones 2015 Robin Bennett 200 RYT THE HUMAN SKELETON BONE COMPOSITION A femur head with a cortex of compact bone and medulla of trabecular (spongy) bone OSTEOBLASTS
YOGA ANATOMY Yoga Teacher Training Part Three - Bones 2015 Robin Bennett 200 RYT THE HUMAN SKELETON BONE COMPOSITION A femur head with a cortex of compact bone and medulla of trabecular (spongy) bone OSTEOBLASTS
IB SEHS Summer Assignment 2017
 IB SEHS Summer Assignment 2017 Seneca Valley High School Mrs. Meaghan Stuckey meaghan_s_stuckey@mcpsmd.org meaghan.s.stuckey@mcpsmd.net DUE: First Day of School, September 5, 2017 Welcome to IB Sports,
IB SEHS Summer Assignment 2017 Seneca Valley High School Mrs. Meaghan Stuckey meaghan_s_stuckey@mcpsmd.org meaghan.s.stuckey@mcpsmd.net DUE: First Day of School, September 5, 2017 Welcome to IB Sports,
Dr.Israa H. Mohsen. Lecture 5. The vertebral column
 Anatomy Lecture 5 Dr.Israa H. Mohsen The vertebral column The vertebral column a flexible structure consisting of 33 vertebrae holds the head and torso upright, serves as an attachment point for the legs,
Anatomy Lecture 5 Dr.Israa H. Mohsen The vertebral column The vertebral column a flexible structure consisting of 33 vertebrae holds the head and torso upright, serves as an attachment point for the legs,
Ch. 5 - Skeletal System
 Ch. 5 - Skeletal System Bones are living, ever-changing structures. This allows them grow and adapt to new situations that the body encounters. The functions of the skeletal system: 1) support bones are
Ch. 5 - Skeletal System Bones are living, ever-changing structures. This allows them grow and adapt to new situations that the body encounters. The functions of the skeletal system: 1) support bones are
S.A.F.E. Elements of Technique. S.A.F.E. is an acronym for strength, alignment, flexibility, and STRENGTH ALIGNMENT FLEXIBILITY ENDURANCE
 Elements of Technique S.A.F.E. S.A.F.E. is an acronym for strength, alignment, flexibility, and endurance. These are all elements that are innate in the study of dance. STRENGTH The amount of control and
Elements of Technique S.A.F.E. S.A.F.E. is an acronym for strength, alignment, flexibility, and endurance. These are all elements that are innate in the study of dance. STRENGTH The amount of control and
THE STRUCTURE OF OUR BODY
 THE STRUCTURE OF OUR BODY 1. INTRODUCTION This chapter will describe the basic anatomy of the human body, explaining the most important elements of the muscular and skeletal system. 2. THE MUSCULOSKELETAL
THE STRUCTURE OF OUR BODY 1. INTRODUCTION This chapter will describe the basic anatomy of the human body, explaining the most important elements of the muscular and skeletal system. 2. THE MUSCULOSKELETAL
1.2 Your healthy, active body
 1.2 Your healthy, active body 1.2.4 A healthy, active lifestyle and your muscular system Contents Worksheets Worksheet 1: Types of muscle, Level A 152 Worksheet 1: Types of muscle, Level B 153 Worksheet
1.2 Your healthy, active body 1.2.4 A healthy, active lifestyle and your muscular system Contents Worksheets Worksheet 1: Types of muscle, Level A 152 Worksheet 1: Types of muscle, Level B 153 Worksheet
Microanatomy, Physiology of Bone & Joints
 Microanatomy, Physiology of Bone & Joints The Skeleton There are 206 bones in the human body. The bones that are required in this syllabus are the cranium, mandible, clavicle, sternum, scapula, ribs, humerous,
Microanatomy, Physiology of Bone & Joints The Skeleton There are 206 bones in the human body. The bones that are required in this syllabus are the cranium, mandible, clavicle, sternum, scapula, ribs, humerous,
NHS Training for Physiotherapy Support Workers. Workbook 11 The articular system
 NHS Training for Physiotherapy Support Workers Workbook 11 The articular system Contents Workbook 11 The articular system 1 11.1 Aim 3 11.2 Learning outcomes 3 11.3 The articular system 4 11.4 Individual
NHS Training for Physiotherapy Support Workers Workbook 11 The articular system Contents Workbook 11 The articular system 1 11.1 Aim 3 11.2 Learning outcomes 3 11.3 The articular system 4 11.4 Individual
SIR MICHELANGELO REFALO
 SIR MICHELANGELO REFALO SIXTH FORM Half Yearly Exam 2014 Name: Subject: Physical Education Intermediate Time: 2 Hours Answer ALL questions Question 1: (The Skeleton) The human skeleton is made up of 206
SIR MICHELANGELO REFALO SIXTH FORM Half Yearly Exam 2014 Name: Subject: Physical Education Intermediate Time: 2 Hours Answer ALL questions Question 1: (The Skeleton) The human skeleton is made up of 206
Skeletal Considerations for Movement. Kinesiology RHS 341 Lecture 2 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa
 Skeletal Considerations for Movement Kinesiology RHS 341 Lecture 2 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa The Skeletal System Bones, cartilage, ligaments, & joints Consists of approximately 20% of total body weight Bone constitutes
Skeletal Considerations for Movement Kinesiology RHS 341 Lecture 2 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa The Skeletal System Bones, cartilage, ligaments, & joints Consists of approximately 20% of total body weight Bone constitutes
Skeletal System. Supplementary Information
 Skeletal System Supplementary Information COMMON ANATOMICAL TERMS Planes run through the body side to side and front to back eg. median plane Surfaces of the body are also named eg. anterior surface This
Skeletal System Supplementary Information COMMON ANATOMICAL TERMS Planes run through the body side to side and front to back eg. median plane Surfaces of the body are also named eg. anterior surface This
Structural Support and Movement. Chapter 33
 Structural Support and Movement Chapter 33 33.1 Skeletons and Muscles Most animals move when the force of muscle contraction is applied to skeletal elements Animal Skeletons Hydrostatic skeleton A confined
Structural Support and Movement Chapter 33 33.1 Skeletons and Muscles Most animals move when the force of muscle contraction is applied to skeletal elements Animal Skeletons Hydrostatic skeleton A confined
The skeleton supports the body. The skeleton protects soft body parts The skeleton produces blood cells. The skeleton stores minerals and fat.
 SKELETAL SYSTEM SKELETAL SYSTEM The skeleton supports the body. The bones of the legs support the entire body when we are standing, and the coxal bones of the pelvic girdle support the abdominal cavity.
SKELETAL SYSTEM SKELETAL SYSTEM The skeleton supports the body. The bones of the legs support the entire body when we are standing, and the coxal bones of the pelvic girdle support the abdominal cavity.
Prime movers provide the major force for producing a specific movement Antagonists oppose or reverse a particular movement Synergists
 Dr. Gary Mumaugh Prime movers provide the major force for producing a specific movement Antagonists oppose or reverse a particular movement Synergists Add force to a movement Reduce undesirable or unnecessary
Dr. Gary Mumaugh Prime movers provide the major force for producing a specific movement Antagonists oppose or reverse a particular movement Synergists Add force to a movement Reduce undesirable or unnecessary
CHAPTER 3 What Is Anatomy?
 CHAPTER 3 What Is Anatomy? Kinesiology Books Publisher 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS The Language of Anatomy Anatomical Position Directional Terms Body Planes Movements Musculoskeletal System Human Skeleton Types
CHAPTER 3 What Is Anatomy? Kinesiology Books Publisher 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS The Language of Anatomy Anatomical Position Directional Terms Body Planes Movements Musculoskeletal System Human Skeleton Types
Chapter 6 & 7 The Skeleton
 Chapter 6 & 7 The Skeleton Try this Make clockwise circles with your RIGHT foot, while doing this, draw the number 6 in the air with you RIGHT hand what happens to your foot???? Bony Background Adult body
Chapter 6 & 7 The Skeleton Try this Make clockwise circles with your RIGHT foot, while doing this, draw the number 6 in the air with you RIGHT hand what happens to your foot???? Bony Background Adult body
36 1 The Skeletal System Slide 1 of 40
 1 of 40 The Skeleton All organisms need structural support. Unicellular organisms have a cytoskeleton. Multicellular animals have either an exoskeleton (arthropods) or an endoskeleton (vertebrates). 2
1 of 40 The Skeleton All organisms need structural support. Unicellular organisms have a cytoskeleton. Multicellular animals have either an exoskeleton (arthropods) or an endoskeleton (vertebrates). 2
SUMMER WORK MRS KANSARA
 Name: A LEVEL PE Anatomy and Physiology SUMMER WORK MRS KANSARA Complete the following activities throughout the summer It is important that you understand and remember all the information included in
Name: A LEVEL PE Anatomy and Physiology SUMMER WORK MRS KANSARA Complete the following activities throughout the summer It is important that you understand and remember all the information included in
STD.6 (2015) MOVEMENT IN THE BODY. When an organism moves from one place to another, it is termed as locomotion. locomotion.
 STD.6 (2015) MOVEMENT IN THE BODY Q.1 Define Locomotion. When an organism moves from one place to another, it is termed as locomotion. Ex.A jump, hop, walk and swim. Q.2 Differentiate between movement
STD.6 (2015) MOVEMENT IN THE BODY Q.1 Define Locomotion. When an organism moves from one place to another, it is termed as locomotion. Ex.A jump, hop, walk and swim. Q.2 Differentiate between movement
The Skeletal System. Mosby items and derived items 2010, 2006, 2002, 1997, 1992 by Mosby, Inc., an affiliate of Elsevier Inc.
 The Skeletal System Functions of Skeletal System Provides internal framework that supports the body Protects internal organs Helps fight disease by producing white blood cells 2 Functions of Skeletal System
The Skeletal System Functions of Skeletal System Provides internal framework that supports the body Protects internal organs Helps fight disease by producing white blood cells 2 Functions of Skeletal System
WTC II Term 3 Notes & Assessments
 Term 3 Notes & Assessments Planes of Motion/Axes The body moves in a number of various ways and directions. In the past you have learned about the terminology for movements at specific joints, for example,
Term 3 Notes & Assessments Planes of Motion/Axes The body moves in a number of various ways and directions. In the past you have learned about the terminology for movements at specific joints, for example,
Level 2 Mock Paper Anatomy and Physiology For Exercise. Unit Accreditation Number H/600/9013
 MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION PAPER Paper number MPAPEH Please insert this reference number in the appropriate boxes on your candidate answer sheet Title Time allocation 60 minutes Level 2 Mock Paper Anatomy
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION PAPER Paper number MPAPEH Please insert this reference number in the appropriate boxes on your candidate answer sheet Title Time allocation 60 minutes Level 2 Mock Paper Anatomy
OBJECTIVES. Unit 7:5 PROPERTIES OR CHARACTERISTICS OF MUSCLES. Introduction. 3 Kinds of Muscles. 3 Kinds of Muscles 4/17/2018 MUSCULAR SYSTEM
 OBJECTIVES Unit 7:5 MUSCULAR SYSTEM Compare the three main kinds of muscles by describing the action of each Differentiate between voluntary and involuntary muscles List at least three functions of muscles
OBJECTIVES Unit 7:5 MUSCULAR SYSTEM Compare the three main kinds of muscles by describing the action of each Differentiate between voluntary and involuntary muscles List at least three functions of muscles
11/25/2012. Chapter 7 Part 2: Bones! Skeletal Organization. The Skull. Skull Bones to Know Cranium
 Chapter 7 Part 2: Bones! 5) Distinguish between the axial and appendicular skeletons and name the major parts of each 6) Locate and identify the bones and the major features of the bones that compose the
Chapter 7 Part 2: Bones! 5) Distinguish between the axial and appendicular skeletons and name the major parts of each 6) Locate and identify the bones and the major features of the bones that compose the
Major Functions of the Skeletal System
 Skeletal System Major Functions of the Skeletal System 1. Provide shape and support. 2. Enables you to move 3. Protects your organs 4. Produces blood cells 5. stores minerals and other materials until
Skeletal System Major Functions of the Skeletal System 1. Provide shape and support. 2. Enables you to move 3. Protects your organs 4. Produces blood cells 5. stores minerals and other materials until
PHYSICAL EDUCATION. 4º E.S.O. 2nd TERM. The skeletal and muscular systems.
 PHYSICAL EDUCATION 4º E.S.O. 2nd TERM. The skeletal and muscular systems. PARTS OF THE BODY Head Torso / Trunk Dorsal: Back Ventral: Thorax y Abdomen Extremities Superior: Arm Forearm Hand Joint: Shoulder
PHYSICAL EDUCATION 4º E.S.O. 2nd TERM. The skeletal and muscular systems. PARTS OF THE BODY Head Torso / Trunk Dorsal: Back Ventral: Thorax y Abdomen Extremities Superior: Arm Forearm Hand Joint: Shoulder
THE SKELETAL SYSTEM 7 TH GRADE SCIENCE
 THE SKELETAL SYSTEM 7 TH GRADE SCIENCE INTRODUCTION Skeletal system is made up of your bones, ligaments, and tendons. It determines : the shape and symmetry of the body acts as protection for your organs
THE SKELETAL SYSTEM 7 TH GRADE SCIENCE INTRODUCTION Skeletal system is made up of your bones, ligaments, and tendons. It determines : the shape and symmetry of the body acts as protection for your organs
Types of Body Movements
 Types of Body Movements Bởi: OpenStaxCollege Synovial joints allow the body a tremendous range of movements. Each movement at a synovial joint results from the contraction or relaxation of the muscles
Types of Body Movements Bởi: OpenStaxCollege Synovial joints allow the body a tremendous range of movements. Each movement at a synovial joint results from the contraction or relaxation of the muscles
In Activity 12, What s Happening Inside? you learned about the functions
 16 Support System: Bones, Joints and Muscles l a b o r at o ry In Activity 12, What s Happening Inside? you learned about the functions of the skeletal and muscular systems in supporting and moving your
16 Support System: Bones, Joints and Muscles l a b o r at o ry In Activity 12, What s Happening Inside? you learned about the functions of the skeletal and muscular systems in supporting and moving your
Human Body. Bones, Joints and Muscles
 Human Body Bones, Joints and Muscles 1 Bone cranium mandible clavicle sternum humerus ribs pelvis ulna femur patella phalanges phalanges vertebrae Also known as skull lower jaw collarbone breastplate upper
Human Body Bones, Joints and Muscles 1 Bone cranium mandible clavicle sternum humerus ribs pelvis ulna femur patella phalanges phalanges vertebrae Also known as skull lower jaw collarbone breastplate upper
LEVEL 3 DIPLOMA IN AROMATHERAPY MODULE 10 KNOWLEDGE OF ANATOMY, PHYSIOLOGY & PATHOLOGY FOR COMPLEMENTARY THERAPIES THE ARTICULAR SYSTEM COURSE MANUAL
 LEVEL 3 DIPLOMA IN AROMATHERAPY MODULE 10 KNOWLEDGE OF ANATOMY, PHYSIOLOGY & PATHOLOGY FOR COMPLEMENTARY THERAPIES THE ARTICULAR SYSTEM COURSE MANUAL CHRISTINA LYNE christina@aromalyne.com 1 THE ARTICULAR
LEVEL 3 DIPLOMA IN AROMATHERAPY MODULE 10 KNOWLEDGE OF ANATOMY, PHYSIOLOGY & PATHOLOGY FOR COMPLEMENTARY THERAPIES THE ARTICULAR SYSTEM COURSE MANUAL CHRISTINA LYNE christina@aromalyne.com 1 THE ARTICULAR
The Skeletal System THE APPENDICULAR SKELETON
 The Skeletal System THE APPENDICULAR SKELETON The appendicular skeleton consists of the girdles and the skeleton of the limbs. The upper (anterior) limbs are attached to the pectoral (shoulder) girdle
The Skeletal System THE APPENDICULAR SKELETON The appendicular skeleton consists of the girdles and the skeleton of the limbs. The upper (anterior) limbs are attached to the pectoral (shoulder) girdle
Vocabulary Crossword - Ch22 Body Systems
 Name Date Vocabulary Crossword - Ch22 Body Systems 1 2 Per. 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 13 14 12 16 17 18 15 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52
Name Date Vocabulary Crossword - Ch22 Body Systems 1 2 Per. 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 13 14 12 16 17 18 15 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52
The Human Body. Lesson Goal. Lesson Objectives 9/10/2012. Provide a brief overview of body systems, anatomy, physiology, and topographic anatomy
 The Human Body Lesson Goal Provide a brief overview of body systems, anatomy, physiology, and topographic anatomy Medial Lateral Proximal Distal Superior Inferior Anterior Lesson Objectives Explain the
The Human Body Lesson Goal Provide a brief overview of body systems, anatomy, physiology, and topographic anatomy Medial Lateral Proximal Distal Superior Inferior Anterior Lesson Objectives Explain the
Biology v2 Describe the functioning of human digestive & skeletomuscular systems. Skeletomuscular system cards
 Biology 90166 v2 Describe the functioning of human digestive & skeletomuscular systems Skeletomuscular system cards Test yourself / test me cards Cover answer bottom 1/3; Read question / notes / diagram
Biology 90166 v2 Describe the functioning of human digestive & skeletomuscular systems Skeletomuscular system cards Test yourself / test me cards Cover answer bottom 1/3; Read question / notes / diagram
Contents. Section 1: Life s Building Blocks. Section 2: The Human Framework. Section 3: The Senses and the Respiratory System
 Contents Section 1: Life s Building Blocks 1. Cell Structure.... 2 2. Cell Functions.... 5 3. Cell Teamwork... 8 4. Quiz 1.... 12 Section 2: The Human Framework 5. Skeletal System.... 13 6. Muscular System....
Contents Section 1: Life s Building Blocks 1. Cell Structure.... 2 2. Cell Functions.... 5 3. Cell Teamwork... 8 4. Quiz 1.... 12 Section 2: The Human Framework 5. Skeletal System.... 13 6. Muscular System....
Lifting your toes up towards your tibia would be an example of what movement around the ankle joint?
 NAME: TEST 1 ANATOMY IN SPORT SCIENCE: SEMESTER 1, 2017 TOTAL MARKS = 58 Total: / 58 marks Percentage: Grade: TERMINOLOGY: The structures that connect bone to bone are called: The ankle joint is to the
NAME: TEST 1 ANATOMY IN SPORT SCIENCE: SEMESTER 1, 2017 TOTAL MARKS = 58 Total: / 58 marks Percentage: Grade: TERMINOLOGY: The structures that connect bone to bone are called: The ankle joint is to the
Skeletal System. Chapter 7.1. Objective- Read 7.1 and understand that bones are alive and multifunctional. Introduction:
 Chapter 7.1 Skeletal System Objective- Read 7.1 and understand that bones are alive and multifunctional. Introduction: A. Bones are very active tissues B. Each bone is made up of several types of tissues
Chapter 7.1 Skeletal System Objective- Read 7.1 and understand that bones are alive and multifunctional. Introduction: A. Bones are very active tissues B. Each bone is made up of several types of tissues
The Skeletal System. Chapter 7a. Skeletal System Introduction Functions of the skeleton Framework of bones The skeleton through life
 The Skeletal System Skeletal System Introduction Functions of the skeleton Framework of bones The skeleton through life Chapter 7a Support Protection Movement Storage areas Minerals Lipids Hemopoiesis
The Skeletal System Skeletal System Introduction Functions of the skeleton Framework of bones The skeleton through life Chapter 7a Support Protection Movement Storage areas Minerals Lipids Hemopoiesis
CHAPTER 2: Muscular skeletal system - Biomechanics. Exam style questions - pages QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS. Answers
 CHAPTER 2: Muscular skeletal system - Biomechanics Exam style questions - pages 32-35 1) A Level. Warm up is considered to be an essential element of a training programme. Explain how the muscular and
CHAPTER 2: Muscular skeletal system - Biomechanics Exam style questions - pages 32-35 1) A Level. Warm up is considered to be an essential element of a training programme. Explain how the muscular and
Skin. the largest organ of the body 1 mm to 2 mm thick almost 2 square meters 6% of a person s body weight
 Skin the largest organ of the body 1 mm to 2 mm thick almost 2 square meters 6% of a person s body weight Functions of the Skin protection disease-causing organisms dangerous chemicals blood loss fluid
Skin the largest organ of the body 1 mm to 2 mm thick almost 2 square meters 6% of a person s body weight Functions of the Skin protection disease-causing organisms dangerous chemicals blood loss fluid
Unit 7: Skeletal and muscular systems
 Unit 7: Skeletal and muscular systems 1. The locomotor system 2. The skeletal system 2.1. The human skeleton 2.2. Bones 2.3. Joints 2.4. Tendons and ligaments 3. The muscular system 3.1. Muscles of the
Unit 7: Skeletal and muscular systems 1. The locomotor system 2. The skeletal system 2.1. The human skeleton 2.2. Bones 2.3. Joints 2.4. Tendons and ligaments 3. The muscular system 3.1. Muscles of the
The effects of exercise and sports performance on the muscular system
 Assessment practice 1.1 1 Explain how the bones of the skeleton are used in movement for sport. (2 marks) 2 Jack has the first stages of osteoporosis. He has been advised to take part in exercise to help
Assessment practice 1.1 1 Explain how the bones of the skeleton are used in movement for sport. (2 marks) 2 Jack has the first stages of osteoporosis. He has been advised to take part in exercise to help
A Healthy, Active. Lifestyle and Your. Muscular System
 A Healthy, Active Lifestyle and Your Muscular System 1. Muscular System 2. Types of Muscle muscle - Smooth Muscle that works without consciousness. a. Arteries - The walls of the arteries contract and
A Healthy, Active Lifestyle and Your Muscular System 1. Muscular System 2. Types of Muscle muscle - Smooth Muscle that works without consciousness. a. Arteries - The walls of the arteries contract and
Bell Work. How does the muscular system relate to the following organ systems, Respiratory Circulatory Digestive
 Muscular System Bell Work How does the muscular system relate to the following organ systems, Respiratory Circulatory Digestive Exercise Science Standards 8) Review the gross and cellular anatomy and physiology
Muscular System Bell Work How does the muscular system relate to the following organ systems, Respiratory Circulatory Digestive Exercise Science Standards 8) Review the gross and cellular anatomy and physiology
Skeletal System Tour Lab. Station Label the bones on your answer sheet.
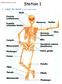 Station 1 1. Label the bones on your answer sheet. Station 2 2. Label the joints on your answer sheet. Fixed Pivot Hinge Hinge Gliding Ball and Socket Hinge Swivel Gliding Gliding Ball and Socket Types
Station 1 1. Label the bones on your answer sheet. Station 2 2. Label the joints on your answer sheet. Fixed Pivot Hinge Hinge Gliding Ball and Socket Hinge Swivel Gliding Gliding Ball and Socket Types
Musculoskeletal Anatomy. Chapter 1
 Musculoskeletal Anatomy Chapter 1 1 This Week Monday - Anatomy (classroom) Tuesday - Group Workout Wednesday - Movement skill analysis Thursday - Group Workout Friday - Anatomy (classroom) 2 Human Anatomy:
Musculoskeletal Anatomy Chapter 1 1 This Week Monday - Anatomy (classroom) Tuesday - Group Workout Wednesday - Movement skill analysis Thursday - Group Workout Friday - Anatomy (classroom) 2 Human Anatomy:
KULLEĠĠ SAN BENEDITTU Boys Secondary, Kirkop
 KULLEĠĠ SAN BENEDITTU Boys Secondary, Kirkop Mark HALF-YEARLY EXAMINATION 2012/2013 Track 3 FORM 3 PHYSICAL EDUCATION TIME: 1h 30min Instructions to students: Answer ALL questions. Read carefully each
KULLEĠĠ SAN BENEDITTU Boys Secondary, Kirkop Mark HALF-YEARLY EXAMINATION 2012/2013 Track 3 FORM 3 PHYSICAL EDUCATION TIME: 1h 30min Instructions to students: Answer ALL questions. Read carefully each
TRAINING LAB SKELETAL REMAINS: IDENTIFYING BONES NAME
 TRAINING LAB SKELETAL REMAINS: IDENTIFYING BONES NAME Background: Skeletal remains are important pieces of evidence. The flesh, muscle, and organs of a victim rapidly decompose; however, the victim s skeleton
TRAINING LAB SKELETAL REMAINS: IDENTIFYING BONES NAME Background: Skeletal remains are important pieces of evidence. The flesh, muscle, and organs of a victim rapidly decompose; however, the victim s skeleton
The Muscular System PART C. PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Muscular System 6 PART C Five Golden Rules of Skeletal Muscle Activity Table 6.2 Muscles and Body
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Muscular System 6 PART C Five Golden Rules of Skeletal Muscle Activity Table 6.2 Muscles and Body
