A LEVEL PE PRE COURSE TASK READ EVERYTHING IN BLACK DO EVERYTHING IN RED
|
|
|
- Randell Craig
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 A LEVEL PE PRE COURSE TASK READ EVERYTHING IN BLACK DO EVERYTHING IN RED
2
3 1.1.2 CLASSIFICATION OF BONES: LONG (LEVERAGE); SHORT (WEIGHT BEARING); FLAT (PROTECTION, BROAD SURFACE FOR MUSCLE ATTACHMENT); IRREGULAR (PROTECTION AND MUSCLE ATTACHMENT) APPLIED TO PERFORMANCE IN PHYSICAL ACTIVITIES AND SPORT PRINT A SKELETON AND COLOUR IN THE DIFFERENT BONE CLASSIFICATIONS LONG (LEVERAGE); CLAVICLE, HUMERUS, ULNA, RADIUS, FEMUR, FIBULA, METACARPALS, PHALANGES, METATARSALS. ALL USED FOR MOVEMENT. KNOW WHAT BODY PART THEY MOVE AND NAME A SPORTING EXAMPLE. SHORT (WEIGHT BEARING); CARPALS, TARSALS. KNOW WHAT BODY PART THEY MOVE AND NAME A SPORTING EXAMPLE. FLAT (PROTECTION, BROAD SURFACE FOR MUSCLE ATTACHMENT); CRANIUM, STERNUM, SCAPULA, PELVIS. KNOW WHAT BODY PART THEY MOVE AND NAME A SPORTING EXAMPLE. IRREGULAR (PROTECTION AND MUSCLE ATTACHMENT) VERTEBRAE. LEARN THE 5 AREAS APPLIED TO PERFORMANCE IN PHYSICAL ACTIVITIES AND SPORT
4
5 STRUCTURE OF THE HEART: ATRIA (LEFT AND RIGHT ATRIA) VENTRICLES (LEFT AND RIGHT VENTRICLES). THE ORDER OF THE CARDIAC CYCLE, INCLUDING DIASTOLE (FILLING) AND SYSTOLE (EJECTION) OF THE CHAMBERS. THIS STARTS FROM A SPECIFIED CHAMBER OF THE HEART, EG THE CARDIAC CYCLE STARTING AT THE RIGHT VENTRICLE.
6 PATHWAY OF THE BLOOD: DEOXYGENATED BLOOD INTO RIGHT ATRIUM THEN INTO THE RIGHT VENTRICLE THE PULMONARY ARTERY THEN TRANSPORTS DEOXYGENATED BLOOD TO THE LUNGS GAS EXCHANGE OCCURS (BLOOD IS OXYGENATED) PULMONARY VEIN TRANSPORTS OXYGENATED BLOOD BACK TO THE LEFT ATRIUM THEN INTO THE LEFT VENTRICLE BEFORE OXYGENATED BLOOD IS EJECTED AND TRANSPORTED TO THE BODY VIA THE AORTA. WATCH THESE! VALVE NAMES ARE NOT REQUIRED BUT STUDENTS SHOULD BE TAUGHT THAT VALVES OPEN DUE TO PRESSURE AND CLOSE TO PREVENT BACKFLOW.
7 CARDIAC OUTPUT, STROKE VOLUME AND HEART RATE, AND THE RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN THEM. WHY AND HOW DOES THIS CHANGE WHEN YOU EXERCISE? CARDIAC OUTPUT (Q) = STROKE VOLUME X HEART RATE. SV= AMOUNT OF BLOOD PUMPED OUT OF THE HEART PER BEAT. HR= AMOUNT OF BEATS PER MINUTE Q= VOLUME OF BLOOD PUMPED OUT OF THE HEART PER MINUTE
8 1.2.5 FUNCTION AND IMPORTANCE OF RED AND WHITE BLOOD CELLS, PLATELETS AND PLASMA FOR PHYSICAL ACTIVITY AND SPORT RED BLOOD CELLS CARRY O2 WHICH CAN BE USED TO RELEASE ENERGY TO THE MUSCLES WHITE BLOOD CELLS FIGHT AGAINST DISEASE PLATELETS HELP BLOOD TO CLOT AT WOUNDS TO PREVENT INFECTION PLASMA CARRIES EVERYTHING IN THE BLOOD STREAM (BLOOD CELLS, GLUCOSE, CO2)
9 IDENTIFICATION OF THE FOLLOWING VOLUMES ON A SPIROMETER TRACE. HOW MAY THESE CHANGE FROM REST TO EXERCISE? TIDAL VOLUME FREQUENCY VITAL CAPACITY MINUTE VENTILATION(MV, MEASURED IN LITRES) DEFINE THESE TERMS Frequency Amount of air in and out in 1 breath (normal breathing) Most amount of air you could breath in after breathing out the most you can.
10 INTERPRETATION AND EXPLANATION OF A SPIROMETER TRACE (AND CONTINUE A TRACE ON PAPER) TO REFLECT THE DIFFERENCE IN A TRACE BETWEEN REST AND THE ONSET OF EXERCISE. HOW DOES IT CHANGE??
11 1.2.9 STRUCTURE OF ALVEOLI TO ENABLE GAS EXCHANGE AND THE PROCESS OF GAS EXCHANGE. HOW DOES IT MEET THE DEMANDS OF VARYING INTENSITIES OF EXERCISE (AEROBIC AND ANAEROBIC) Alveoli have a large surface area and thin walls. Exchange of gases happens through diffusion, gases move down the concentration gradient (from high concentration to lower concentration).
12 DEFINITION OF THE TERMS: AEROBIC EXERCISE ANAEROBIC EXERCISE. SUMMARY OF AEROBIC EXERCISE (GLUCOSE + OXYGEN ENERGY + CARBON DIOXIDE + WATER). SUMMARY OF ANAEROBIC EXERCISE (GLUCOSE ENERGY + LACTIC ACID). WHAT DO THE TERMS ABOVE MEAN? WHAT ARE THE MAIN ATTRIBUTES OF THESE DIFFERENT SYSTEMS (DIFFERENCES) WHAT SPORTS USE EACH TYPE OF ENERGY
13 DEFINITION OF THE TERM EPOC (OXYGEN DEBT). AN UNDERSTANDING THAT EPOC (OXYGEN DEBT) IS CAUSED BY ANAEROBIC EXERCISE (PRODUCING LACTIC ACID) AND REQUIRES THE PERFORMER TO MAINTAIN INCREASED BREATHING RATE AFTER EXERCISE TO REPAY THE DEBT. EXCESS POST-EXERCISE OXYGEN CONSUMPTION (EPOC)= OXYGEN DEBT WHEN EXERCISING, IF THE BODY IS UNABLE TO KEEP UP WITH DEMAND IT WILL RESPIRE ANAEROBICALLY. THIS IN TURN RESULTS IS LACTIC ACID BUILD UP. WHEN EXERCISE IS FINISHED DEEP GASPING BREATHS CONTINUE TO ALLOW O2 IN TO OXIDISE LACTIC ACID TO CO2 AND WATER SO THEY CAN BE REMOVED FROM THE BODY. OXYGEN DEBT IS REPAID DURING RECOVERY AFTER EXERCISE AND HELPS TO GET RID OF WASTE PRODUCTS. NAME A SPORTING EXAMPLE WHERE THIS OCCURS
14 IDENTIFICATION OF FIRST, SECOND AND THIRD CLASS LEVER SYSTEMS. BASIC DRAWINGS OF THE THREE CLASSES OF LEVER TO ILLUSTRATE THE POSITIONING OF: FULCRUM LOAD (RESISTANCE) EFFORT
15 DRAW LINEAR VERSIONS OF A LEVER, SHOWING THE POSITIONING OF THE FULCRUM, LOAD/RESISTANCE AND EFFORT. STUDENTS DO NOT NEED TO BE TAUGHT TO DRAW ANATOMICAL BODY PARTS BUT MUST BE ABLE TO LINK THE CORRECT LEVER TO A SPORTING MOVEMENT OR ACTION. INTERPRETATION OF SPORTING MOVEMENTS OR ACTIONS WHICH INVOLVE FLEXION OR EXTENSION OF THE ELBOW AND/OR KNEE, AND PLANTAR OR DORSI- FLEXION AT THE ANKLE. IDENTIFY SPORTING EXAMPLES FOR EACH LEVER
16 LABEL THE EFFORT ARM AND LOAD/RESISTANCE ARM ON THE THREE CLASSES OF LEVER. MECHANICAL ADVANTAGE = EFFORT ARM WEIGHT (RESISTANCE) ARM. LABELLING OF THE EFFORT ARM AND RESISTANCE ARM ON LEVER DRAWINGS, AND INTERPRETATION OF THE MECHANICAL ADVANTAGE OF THAT LEVER. CAN YOU DRAW THEM YOURSELF? WHAT ARE THE ADVANTAGES OF EACH? WHAT LEVERS ARE THESE?
17 PLANES (FRONTAL, TRANSVERSE, SAGITTAL) AND AXES (LONGITUDINAL, TRANSVERSE, SAGITTAL) SHOULD BE RELATED TO SPORTING ACTIONS.
18 TEACHING OF THESE PLANES/AXES SHOULD INCLUDE BUT NOT BE LIMITED TO THE FOLLOWING SPORTING ACTIONS: FRONT SOMERSAULT/FORWARD ROLL/RUNNING ACTION 360 TWIST (ICE SKATING SPIN)/DISCUS THROWER ROTATING IN CIRCLE EFFORT CARTWHEEL. WHICH PLANE/AXIS DO THE ABOVE SPORTING ACTIONS RELATE TO? FROM SOMERSAULT FWRD ROLL RUNNING 360 TWIST DISCUS THROW (SPIN TECHNIQUE) CARTWHEEL
19 UNDERSTANDING OF HOW TEST SCORES ARE MEASURED/RECORDED (EG IN SECONDS, LEVELS, CENTIMETERS, NUMBERS). DEFINITIONS OF THE TERMS QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE, IN RELATION TO THE COLLECTION OF FITNESS TESTING DATA. UNDERSTANDING THAT THE QUANTITATIVE DATA COLLECTED DURING FITNESS TESTING CAN BE COMPARED TO NATIONAL AVERAGES. FOLLOW THIS LINK AND HAVE A READ ABOUT FITNESS TESTING FOLLOW THIS LINK AND FIND THE NORMATIVE DATA FOR YOU ON THIS TEST QUANTITATIVE DATA DEALS WITH NUMBERS USUALLY CLOSED QUESTIONS, METHODS FOR COLLECTING QUANTITATIVE DATA: QUESTIONNAIRES SURVEYS. DATA CAN BE PRESENTED IN TABLE, GRAPH OR PIE CHART. QUALITATIVE DATA DEALS WITH DESCRIPTIONS USUALLY OPEN QUESTIONS, UNSTRUCTURED QUESTIONS ASKING ABOUT HOW A PERSON FEELS, THINKS AND BEHAVES. HARDER TO PRESENT, INTERPRET AND ANALYSE AND OFTEN LOOK FOR TRENDS. METHODS FOR COLLECTING QUALITATIVE DATA: INTERVIEWS OBSERVATIONS. THIS ALLOWS YOU TO PREDICT WHAT PEOPLE WHO DID NOT COMPLETE THE QUESTIONS MAY FEEL/THINK/BEHAVE.
20 DEFINITION OF TRAINING THRESHOLD. CALCULATE THE AEROBIC/ANAEROBIC TRAINING ZONE: CALCULATE MAXIMUM HEART RATE (220 MINUS AGE) CALCULATE AEROBIC TRAINING ZONE (60 80% OF MAXIMAL HEART RATE). FOR CIRCUIT TRAINING, ALTERING THE TIME/REST/CONTENT OF THE CIRCUIT WILL DETERMINE THE FITNESS AIM MAKE SURE YOU KNOW HOW THIS WORKS CALCULATION OF MAXIMUM HEART RATE THE EASIEST AND BEST KNOWN METHOD TO CALCULATE YOUR MAXIMUM HEART RATE (HR MAX ) IS TO USE THE FORMULA HR MAX = AGE
21
22
23 . HOW TO CALCULATE ONE REPETITION MAXIMUM (ONE REP MAX) AS PART OF WEIGHT TRAINING AND HOW TO MAKE USE OF ONE REP MAX. RESEARCH HOW TO WORK OUT A ONE REPETITION MAXIMUM FOR WEIGHT TRAINING. STRENGTH/POWER TRAINING (HIGH WEIGHT/LOW REPS ABOVE 70% OF ONE REP MAX, APPROXIMATELY THREE SETS OF 4 8 REPS) MUSCULAR ENDURANCE (LOW WEIGHT/HIGH REPS BELOW 70% OF ONE REP MAX APPROXIMATELY THREE SETS OF REPS).
24 HOW TO PLOT BASIC: BAR CHARTS LINE GRAPHS. HOW TO LABEL X AND Y AXES ON BAR CHARTS AND LINE GRAPHS. INTERPRETATION OF DATA PRESENTED IN BASIC: TABLES BAR CHARTS LINE GRAPHS PIE CHARTS LOOK AT SOME FITNESS DATA PRESENTED IN CHARTS AND GRAPHS AND TRY TO INTERPRET IT, WHAT DOES IT SHOW, HOW DOES IT CHANGE WITH EXERCISE?
25
Year 11 Revision checklist
 Year 11 Revision checklist Below shows what you need to revise for Paper 1. Use your coursework to help you revise components of fitness, SPORT, FITT, SMART targets Paper 2 is everything you have completed
Year 11 Revision checklist Below shows what you need to revise for Paper 1. Use your coursework to help you revise components of fitness, SPORT, FITT, SMART targets Paper 2 is everything you have completed
RAG rating your knowledge
 RAG rating your knowledge Bones Structure of the skeleton Functions of the skeleton Muscles of the body Structure of a synovial joint Types of freely movable joints that allow different movements How joints
RAG rating your knowledge Bones Structure of the skeleton Functions of the skeleton Muscles of the body Structure of a synovial joint Types of freely movable joints that allow different movements How joints
GCSE PERSONAL LEARNING CHECKLIST PHYSICAL EDUCATION
 GCSE PERSONAL LEARNING CHECKLIST PHYSICAL EDUCATION PLC KEY: COMPONENT 1: FITNESS AND BODY SYSTEMS 1.1-4.1 You have covered the concept in lesson by the teacher. You have extended the concept in your file
GCSE PERSONAL LEARNING CHECKLIST PHYSICAL EDUCATION PLC KEY: COMPONENT 1: FITNESS AND BODY SYSTEMS 1.1-4.1 You have covered the concept in lesson by the teacher. You have extended the concept in your file
PiXL Independence: PE Answer Booklet KS4. Applied Anatomy and Physiology. Contents: Answers
 PiXL Independence: PE Answer Booklet KS4 Applied Anatomy and Physiology Contents: Answers 1 I. Quizzes Multiple Choice Quiz 1. Which one of the following statements is false? a. The scapula, cranium and
PiXL Independence: PE Answer Booklet KS4 Applied Anatomy and Physiology Contents: Answers 1 I. Quizzes Multiple Choice Quiz 1. Which one of the following statements is false? a. The scapula, cranium and
1. Describe the main functions of the skeletal system that keep the body healthy and active. [4]
![1. Describe the main functions of the skeletal system that keep the body healthy and active. [4] 1. Describe the main functions of the skeletal system that keep the body healthy and active. [4]](/thumbs/79/80173575.jpg) GCSE PE Structured questions 1a Applied anatomy and physiology Understand the structure and functions of the skeleton 1. Describe the main functions of the skeletal system that keep the body healthy and
GCSE PE Structured questions 1a Applied anatomy and physiology Understand the structure and functions of the skeleton 1. Describe the main functions of the skeletal system that keep the body healthy and
Topic Guide 1: Applied Anatomy and Physiology. GCSE (9-1) Physical Education
 Topic Guide 1: Applied Anatomy and Physiology GCSE (9-1) Physical Education Pearson Edexcel Level 1/Level 2 GCSE (9-1) in Physical Education (1PE0) Pearson Edexcel Level 1/Level 2 GCSE (9-1) in Physical
Topic Guide 1: Applied Anatomy and Physiology GCSE (9-1) Physical Education Pearson Edexcel Level 1/Level 2 GCSE (9-1) in Physical Education (1PE0) Pearson Edexcel Level 1/Level 2 GCSE (9-1) in Physical
Applied anatomy and physiology: definitions of key terms
 Applied anatomy and physiology: definitions of key terms See pages 5 46 These are the key terms from Chapter 1. Try cutting them out and then matching the key terms with their definitions, or asking friends
Applied anatomy and physiology: definitions of key terms See pages 5 46 These are the key terms from Chapter 1. Try cutting them out and then matching the key terms with their definitions, or asking friends
How can sportspeople train the body systems to ensure there are long term benefits? Excercise Physiology. Chapter 2. GCSE Physical Education
 How can sportspeople train the body systems to ensure there are long term benefits? Excercise Physiology GCSE Physical Education To answer the big question you will need to be able to complete the following
How can sportspeople train the body systems to ensure there are long term benefits? Excercise Physiology GCSE Physical Education To answer the big question you will need to be able to complete the following
Year 10 GCSE Revision - Physical Education Paper 1 Fitness and Body Systems Topic Areas for Revision Key questions
 Year 10 GCSE Revision - Physical Education Paper 1 Fitness and Body Systems Topic Areas for Revision Key questions 1.1 The structure and functions of the musculoskeletal s Functions of the Skeleton for
Year 10 GCSE Revision - Physical Education Paper 1 Fitness and Body Systems Topic Areas for Revision Key questions 1.1 The structure and functions of the musculoskeletal s Functions of the Skeleton for
YEAR 8 REVISION BOOKLET 2018
 Name: PE Teacher YEAR 8 REVISION BOOKLET 2018 Year 8 End of Year Exam Revision - Physical Education Section 1: The Skeletal System, Types of Joint and the Functions of the Skeleton Cranium Scapula Clavicle
Name: PE Teacher YEAR 8 REVISION BOOKLET 2018 Year 8 End of Year Exam Revision - Physical Education Section 1: The Skeletal System, Types of Joint and the Functions of the Skeleton Cranium Scapula Clavicle
Anatomy and physiology for sport
 Anatomy and physiology for sport UV21527 D/502/5474 Learner name: VRQ Learner number: VTCT is the specialist awarding body for the Hairdressing, Beauty Therapy, Complementary Therapy, Hospitality and Catering
Anatomy and physiology for sport UV21527 D/502/5474 Learner name: VRQ Learner number: VTCT is the specialist awarding body for the Hairdressing, Beauty Therapy, Complementary Therapy, Hospitality and Catering
HASTINGS HIGH SCHOOL GCSE PHYSICAL EDUCATION OCR 9-1 ELEVATE
 HASTINGS HIGH SCHOOL GCSE PHYSICAL EDUCATION OCR 9-1 ELEVATE HASTINGS HIGH SCHOOL EXAMINATION GUIDE 2017-19 Subject Course code Website address Provisional examination dates Computer Science Computer Science
HASTINGS HIGH SCHOOL GCSE PHYSICAL EDUCATION OCR 9-1 ELEVATE HASTINGS HIGH SCHOOL EXAMINATION GUIDE 2017-19 Subject Course code Website address Provisional examination dates Computer Science Computer Science
PERSONALISED LEARNING CHECKLISTS
 Component 1 Fitness and body systems 1. 2. 3. 4. Applied anatomy and physiology Movement analysis Physical training Use of data Component 2 - Health and Performance 1. 2. 3. 4. Health, fitness and well-being
Component 1 Fitness and body systems 1. 2. 3. 4. Applied anatomy and physiology Movement analysis Physical training Use of data Component 2 - Health and Performance 1. 2. 3. 4. Health, fitness and well-being
Level 2 Anatomy and Physiology Bite size revision. Respiratory System. The order of the passage of oxygen into the body (inhalation/inspiration) is: -
 Respiratory System Function of the respiratory system The lungs are located in the chest cavity and their function is to intake oxygen and remove carbon dioxide from the body. Structure of the respiratory
Respiratory System Function of the respiratory system The lungs are located in the chest cavity and their function is to intake oxygen and remove carbon dioxide from the body. Structure of the respiratory
Understand the Body and the Supporting Technology for Sport and Activity
 COMPONENT 01 Understand the Body and the Supporting Technology for Sport and ctivity In this component, you will explore the cardiorespiratory and musculoskeletal systems and how they allow us to take
COMPONENT 01 Understand the Body and the Supporting Technology for Sport and ctivity In this component, you will explore the cardiorespiratory and musculoskeletal systems and how they allow us to take
Learning Objectives; 1. Identify the key features of the cardiovascular system. 2. Describe the function of the cardiovascular system.
 Learning Objectives; 1. Identify the key features of the cardiovascular system. 2. Describe the function of the cardiovascular system. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=yaxna8lmoiy The Circulatory System
Learning Objectives; 1. Identify the key features of the cardiovascular system. 2. Describe the function of the cardiovascular system. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=yaxna8lmoiy The Circulatory System
Level 2 Mock Paper Anatomy and Physiology For Exercise. Unit Accreditation Number H/600/9013
 MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION PAPER Paper number MPAPEH Please insert this reference number in the appropriate boxes on your candidate answer sheet Title Time allocation 60 minutes Level 2 Mock Paper Anatomy
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION PAPER Paper number MPAPEH Please insert this reference number in the appropriate boxes on your candidate answer sheet Title Time allocation 60 minutes Level 2 Mock Paper Anatomy
KS3 - PE THEORY REVISION GUIDE Y9
 KS3 - PE THEORY REVISION GUIDE Y9 Theory Knowledge Checklist Topic Tick off I can explain why physical activity is essential to a healthy lifestyle I can identify different types of movement using the
KS3 - PE THEORY REVISION GUIDE Y9 Theory Knowledge Checklist Topic Tick off I can explain why physical activity is essential to a healthy lifestyle I can identify different types of movement using the
. Know the definition of mechanical advantage.
 Please do the following 1. Read the Learners must know section (see below) 2. Watch the GCSE POD video 3. Attempt Exam Questions 4. Mark your answers 5. Reflect and repeat until you are successful and
Please do the following 1. Read the Learners must know section (see below) 2. Watch the GCSE POD video 3. Attempt Exam Questions 4. Mark your answers 5. Reflect and repeat until you are successful and
The Human Body. Lesson Goal. Lesson Objectives 9/10/2012. Provide a brief overview of body systems, anatomy, physiology, and topographic anatomy
 The Human Body Lesson Goal Provide a brief overview of body systems, anatomy, physiology, and topographic anatomy Medial Lateral Proximal Distal Superior Inferior Anterior Lesson Objectives Explain the
The Human Body Lesson Goal Provide a brief overview of body systems, anatomy, physiology, and topographic anatomy Medial Lateral Proximal Distal Superior Inferior Anterior Lesson Objectives Explain the
The cardiovascular and respiratory system
 The cardiovascular and respiratory system For this unit you need to be able to... Learning Outcomes: Covered? Confident? Understand and be able to give sporting examples of when each respiratory system
The cardiovascular and respiratory system For this unit you need to be able to... Learning Outcomes: Covered? Confident? Understand and be able to give sporting examples of when each respiratory system
Planes and axes of movement. Movement patterns and the bodies planes and axes
 Planes and axes of movement Movement patterns and the bodies planes and axes Learning Outcomes Be able to name the three planes of movement and the three axes of rotation. Be aware of sporting movements
Planes and axes of movement Movement patterns and the bodies planes and axes Learning Outcomes Be able to name the three planes of movement and the three axes of rotation. Be aware of sporting movements
Cardiovascular Learners MUST KNOW R A G. Know the double- circulatory system (systemic and pulmonary)
 Please do the following 1. Read the Learners must know section (see below) 2. Watch the GCSE POD video 3. Attempt Exam Questions 4. Mark your answers 5. Reflect and repeat until you are successful and
Please do the following 1. Read the Learners must know section (see below) 2. Watch the GCSE POD video 3. Attempt Exam Questions 4. Mark your answers 5. Reflect and repeat until you are successful and
Unit 1: Human body: combination I - IV
 Unit 1: Human body: combination I - IV Study online at quizlet.com/_1kzmm2 1. alveoli 6. bronchioles microscopic air sacs in the lung where diffusion of the respiratory gases, oxygen and carbon dioxide
Unit 1: Human body: combination I - IV Study online at quizlet.com/_1kzmm2 1. alveoli 6. bronchioles microscopic air sacs in the lung where diffusion of the respiratory gases, oxygen and carbon dioxide
Please do the following
 Please do the following 1. Read the Learners must know section (see below) 2. Watch the GCSE POD video 3. Attempt Exam Questions 4. Mark your answers 5. Reflect and repeat until you are successful and
Please do the following 1. Read the Learners must know section (see below) 2. Watch the GCSE POD video 3. Attempt Exam Questions 4. Mark your answers 5. Reflect and repeat until you are successful and
Level 2 Anatomy and Physiology Internal Practice Paper
 Level 2 Anatomy and Physiology Internal Practice Paper Time allocated: 60 minutes. 30 questions, multiple choice answers. Select A,B,C or D only select one answer. You are required to achieve 22 correct
Level 2 Anatomy and Physiology Internal Practice Paper Time allocated: 60 minutes. 30 questions, multiple choice answers. Select A,B,C or D only select one answer. You are required to achieve 22 correct
Year 11 Physical Education LC3 Medium Term Plan
 Year 11 Physical Education LC3 Medium Term Plan Overarching challenge question Exam board links Line of enquiry s Home learning Do all elite athletes have the responsibility to inspire and influence others?
Year 11 Physical Education LC3 Medium Term Plan Overarching challenge question Exam board links Line of enquiry s Home learning Do all elite athletes have the responsibility to inspire and influence others?
GCSE PE CORE KNOWLEDGE QUIZ BOOKLET QUESTIONS
 GCSE PE CORE KNOWLEDGE QUIZ BOOKLET 2018-19 QUESTIONS Sections to revise: Exam Topic 1 Fitness and Body Systems 1hr 45mins 90 Marks Wednesday 15 th May 2019 AM Functions of the musculo-skeletal system
GCSE PE CORE KNOWLEDGE QUIZ BOOKLET 2018-19 QUESTIONS Sections to revise: Exam Topic 1 Fitness and Body Systems 1hr 45mins 90 Marks Wednesday 15 th May 2019 AM Functions of the musculo-skeletal system
Blood flows away from the heart in arteries, to the capillaries and back to the heart in the veins
 Cardiovascular System Summary Notes The cardiovascular system includes: The heart, a muscular pump The blood, a fluid connective tissue The blood vessels, arteries, veins and capillaries Blood flows away
Cardiovascular System Summary Notes The cardiovascular system includes: The heart, a muscular pump The blood, a fluid connective tissue The blood vessels, arteries, veins and capillaries Blood flows away
ANYTHING THAT IT IS CARRYING)
 1) A rigid structure (BONE) Levers in our body are formed from Bones, Joints and Muscles. A lever consists of 2) A force acting upon it (MUSCLE) to produce a turning movement (ANGULAR MOTION) 3) A fulcrum
1) A rigid structure (BONE) Levers in our body are formed from Bones, Joints and Muscles. A lever consists of 2) A force acting upon it (MUSCLE) to produce a turning movement (ANGULAR MOTION) 3) A fulcrum
VCERT PE Final Test Revision
 VCERT PE Final Test Revision Skeletal System This one is known as the Condyloid Joint Definition: The point at which two or more bones meet to produce movement. Slightly Moveable Joints- spine Fix Joints-
VCERT PE Final Test Revision Skeletal System This one is known as the Condyloid Joint Definition: The point at which two or more bones meet to produce movement. Slightly Moveable Joints- spine Fix Joints-
Level 2 Cambridge Technical in Sport and Physical Activity
 Level 2 Cambridge Technical in Sport and Physical Activity Unit 1: Physical activity, health & wellbeing Sample Assessment Material Date Morning/Afternoon Time Allowed: 45 minutes This test is a computer
Level 2 Cambridge Technical in Sport and Physical Activity Unit 1: Physical activity, health & wellbeing Sample Assessment Material Date Morning/Afternoon Time Allowed: 45 minutes This test is a computer
THE HEART. Unit 3: Transportation and Respiration
 THE HEART Unit 3: Transportation and Respiration The Circulatory System Also called the Cardiovascular System Circulates blood in the body Transports nutrients, oxygen, carbon dioxide, hormones, and blood
THE HEART Unit 3: Transportation and Respiration The Circulatory System Also called the Cardiovascular System Circulates blood in the body Transports nutrients, oxygen, carbon dioxide, hormones, and blood
Sports, exercise and health science Standard level Paper 1
 M17/4/SPEXS/SPM/ENG/TZ0/XX Sports, exercise and health science Standard level Paper 1 Monday 15 May 2017 (afternoon) 45 minutes Instructions to candidates y Do not open this examination paper until instructed
M17/4/SPEXS/SPM/ENG/TZ0/XX Sports, exercise and health science Standard level Paper 1 Monday 15 May 2017 (afternoon) 45 minutes Instructions to candidates y Do not open this examination paper until instructed
Anatomy. Anatomy deals with the structure of the human body, and includes a precise language on body positions and relationships between body parts.
 Anatomy deals with the structure of the human body, and includes a precise language on body positions and relationships between body parts. Proper instruction on safe and efficient exercise technique requires
Anatomy deals with the structure of the human body, and includes a precise language on body positions and relationships between body parts. Proper instruction on safe and efficient exercise technique requires
TOPIC 6: HUMAN HEALTH AND PHYSIOLOGY
 TOPIC 6: HUMAN HEALTH AND PHYSIOLOGY 6.2 Transport System/Circulatory Draw and label a diagram of the heart showing the four chambers, associated blood vessels, valves and the route of blood through the
TOPIC 6: HUMAN HEALTH AND PHYSIOLOGY 6.2 Transport System/Circulatory Draw and label a diagram of the heart showing the four chambers, associated blood vessels, valves and the route of blood through the
REVISION BOOKLET. The Body Systems
 REVISION BOOKLET The Body Systems GCSE PE 2016 Skeletal System Functions of the skeleton Joints for movement Muscle attachment Protection of vital organs Red and white blood cell production platelets Storage
REVISION BOOKLET The Body Systems GCSE PE 2016 Skeletal System Functions of the skeleton Joints for movement Muscle attachment Protection of vital organs Red and white blood cell production platelets Storage
KS4 Physical Education
 KS4 Physical Education The Circulatory System These icons indicate that teacher s notes or useful web addresses are available in the Notes Page. This icon indicates that the slide contains activities created
KS4 Physical Education The Circulatory System These icons indicate that teacher s notes or useful web addresses are available in the Notes Page. This icon indicates that the slide contains activities created
Challenge Question: Prediction: (Wait for directions) Evidence: (Draw, color and label how your Clay model looked when it was complete)
 Activity #12 What s happening inside? Challenge Question: Prediction: (Wait for directions) Evidence: (Draw, color and label how your Clay model looked when it was complete) Act #12 pg 1 of 3 Analysis
Activity #12 What s happening inside? Challenge Question: Prediction: (Wait for directions) Evidence: (Draw, color and label how your Clay model looked when it was complete) Act #12 pg 1 of 3 Analysis
KS4 Physical Education
 KS4 Physical Education The Effects of Exercise These icons indicate that teacher s notes or useful web addresses are available in the Notes Page. This icon indicates that the slide contains activities
KS4 Physical Education The Effects of Exercise These icons indicate that teacher s notes or useful web addresses are available in the Notes Page. This icon indicates that the slide contains activities
Human Circulation and Respiration Chapter 38
 Human Circulation and Respiration Chapter 38 Goals: 1. Compare closed and open circulatory systems. 2. Label the parts of the human heart. 3. Explain how blood travels through the heart; identify chambers
Human Circulation and Respiration Chapter 38 Goals: 1. Compare closed and open circulatory systems. 2. Label the parts of the human heart. 3. Explain how blood travels through the heart; identify chambers
YEAR 9 GCSE PE Learning Programme
 YEAR 9 GCSE PE Learning Programme Half Term/Term Learning objective Learning activity Differentiation and extension Bones. Knowledge of the bones at the following locations: head/neck cranium, vertebrae
YEAR 9 GCSE PE Learning Programme Half Term/Term Learning objective Learning activity Differentiation and extension Bones. Knowledge of the bones at the following locations: head/neck cranium, vertebrae
 Questions Q1. Cell transport mechanisms (a) Substances in the soil are taken up by plant root hair cells. The diagram shows the direction of movement of two substances A and B across the cell membrane
Questions Q1. Cell transport mechanisms (a) Substances in the soil are taken up by plant root hair cells. The diagram shows the direction of movement of two substances A and B across the cell membrane
GCSE Physical Education (Short Course) 2016: Content Mapping Edexcel
 GCSE Physical Education (Short Course) 2016: Content Mapping Edexcel Contents Introduction 2 Comparing the 2012 Edexcel GCSE Physical Education (Short Course) specification with the new 2016 Edexcel Physical
GCSE Physical Education (Short Course) 2016: Content Mapping Edexcel Contents Introduction 2 Comparing the 2012 Edexcel GCSE Physical Education (Short Course) specification with the new 2016 Edexcel Physical
Bone Classification *
 OpenStax-CNX module: m46282 1 Bone Classification * OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this section, you will be
OpenStax-CNX module: m46282 1 Bone Classification * OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this section, you will be
1.1 The structure and functions of the musculo-skeletal system Learning objectives
 1.1 The structure and functions of the musculo-skeletal system Learning objectives To be able to describe the functions of the skeleton. To understand different bone classifications and functioning. To
1.1 The structure and functions of the musculo-skeletal system Learning objectives To be able to describe the functions of the skeleton. To understand different bone classifications and functioning. To
Multicellular Organisms. Sub-Topic 2.6 Transport Systems in Animals
 Multicellular Organisms Sub-Topic 2.6 Transport Systems in Animals On completion of this sub-topic I will be able to state that: In mammals a transport system is required to deliver essential substances
Multicellular Organisms Sub-Topic 2.6 Transport Systems in Animals On completion of this sub-topic I will be able to state that: In mammals a transport system is required to deliver essential substances
Today s objectives:! - Learn BASICS of circulatory system (Heart, different veins and arteries)! - Appreciate effects and treatment for
 Today s objectives:! - Learn BASICS of circulatory system (Heart, different veins and arteries)! - Appreciate effects and treatment for hyperlipidemia! Agenda! - Review objectives for 6.2! - Video of circulatory
Today s objectives:! - Learn BASICS of circulatory system (Heart, different veins and arteries)! - Appreciate effects and treatment for hyperlipidemia! Agenda! - Review objectives for 6.2! - Video of circulatory
Identify and describe the circulation system that is missing from the organizer above.
 Lesson 15.1 NOTES: The Circulatory System (Unlock) Essential Question: -What are the structures and functions of the circulatory system? Learning Target(s): -I can identify structures and explain functions
Lesson 15.1 NOTES: The Circulatory System (Unlock) Essential Question: -What are the structures and functions of the circulatory system? Learning Target(s): -I can identify structures and explain functions
Applied anatomy and physiology
 1 Applied anatomy and physiology When you have worked through this chapter, you will have developed knowledge and understanding of: the structure and functions of the musculo-skeletal system the structure
1 Applied anatomy and physiology When you have worked through this chapter, you will have developed knowledge and understanding of: the structure and functions of the musculo-skeletal system the structure
HAYESFIELD SCHOOL YEAR 1 A LEVEL PE REVISION BOOKLET APPLIED ANATOMY
 HAYESFIELD SCHOOL YEAR 1 A LEVEL PE REVISION BOOKLET APPLIED ANATOMY TOP TIPS FOR EXAMS: Read the question carefully! Check you have included enough marks for the questions. Don t leave any gaps attempt
HAYESFIELD SCHOOL YEAR 1 A LEVEL PE REVISION BOOKLET APPLIED ANATOMY TOP TIPS FOR EXAMS: Read the question carefully! Check you have included enough marks for the questions. Don t leave any gaps attempt
Mock Paper Level 2 Anatomy and Physiology for Exercise. Unit Reference Number H/600/9013
 MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION PAPER Paper number MPAPEH2.01 Please insert this reference number in the appropriate boxes on your candidate answer sheet Title Time allocation 60 minutes Mock Paper Level 2 Anatomy
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION PAPER Paper number MPAPEH2.01 Please insert this reference number in the appropriate boxes on your candidate answer sheet Title Time allocation 60 minutes Mock Paper Level 2 Anatomy
Year 12 Physical Education LC2 Medium Term Plan
 Year 12 Physical Education LC2 Medium Term Plan Physiological factors (Miss Brett) Overarching challenge question Exam board links Line of enquiry s Home learning Independent study How does the nervous
Year 12 Physical Education LC2 Medium Term Plan Physiological factors (Miss Brett) Overarching challenge question Exam board links Line of enquiry s Home learning Independent study How does the nervous
3. Which one of the following is NOT a function of the skeleton? A. Stores fat B. Allows movement C. Gives shape D.
 GSE P.E. questions and mark schemes 1 a pplied natomy and Physiology 1. Which of one of the following is NOT a function of the skeleton?. llows movement at a joint. Gives the body shape. Pulls tendons.
GSE P.E. questions and mark schemes 1 a pplied natomy and Physiology 1. Which of one of the following is NOT a function of the skeleton?. llows movement at a joint. Gives the body shape. Pulls tendons.
1. Which of the following blood vessels has a thin elastic layer? A. Aorta. B. Pulmonary artery. C. Posterior vena cava. D. Mesenteric capillary.
 CIRCULATORY SYSTEM 1. Which of the following blood vessels has a thin elastic layer? A. Aorta. B. Pulmonary artery. C. Posterior vena cava. D. Mesenteric capillary. 2. Capillary beds are equipped with
CIRCULATORY SYSTEM 1. Which of the following blood vessels has a thin elastic layer? A. Aorta. B. Pulmonary artery. C. Posterior vena cava. D. Mesenteric capillary. 2. Capillary beds are equipped with
L01:Name and locate the major bones within the skeletal system.
 L01:Name and locate the major bones within the skeletal system. All physical activity requires movement using bones and muscles. Name three major bones which are located in the leg. Bone 1 - Bone 2- Bone
L01:Name and locate the major bones within the skeletal system. All physical activity requires movement using bones and muscles. Name three major bones which are located in the leg. Bone 1 - Bone 2- Bone
Performance Enhancement. Cardiovascular/Respiratory Systems and Athletic Performance
 Performance Enhancement Cardiovascular/Respiratory Systems and Athletic Performance Functions of the Cardiovascular System Deliver oxygen & nutrients to body tissues Carry wastes from the cells Anatomy
Performance Enhancement Cardiovascular/Respiratory Systems and Athletic Performance Functions of the Cardiovascular System Deliver oxygen & nutrients to body tissues Carry wastes from the cells Anatomy
It s Totally Tubular, Dude!
 It s Totally Tubular, Dude! Objective: To learn the structure and function of the Cardiovascular and Lymphatic Systems Bell Work: For the following, place the items in order from most simple to most complex:
It s Totally Tubular, Dude! Objective: To learn the structure and function of the Cardiovascular and Lymphatic Systems Bell Work: For the following, place the items in order from most simple to most complex:
The circulatory system transports blood to deliver important substances, such as oxygen, to cells and to remove wastes, such as carbon dioxide.
 Section 1: The circulatory system transports blood to deliver important substances, such as oxygen, to cells and to remove wastes, such as carbon dioxide. K What I Know W What I Want to Find Out L What
Section 1: The circulatory system transports blood to deliver important substances, such as oxygen, to cells and to remove wastes, such as carbon dioxide. K What I Know W What I Want to Find Out L What
Examination Scope: PHYSICAL EDUCATION. Year: 11. Mock EXAM
 Examination Scope: PHYSICAL EDUCATION Year: 11 Mock EXAM Preparation: The topics that will be in your mock exam are listed below. It is essential that you build on your knowledge and success by following
Examination Scope: PHYSICAL EDUCATION Year: 11 Mock EXAM Preparation: The topics that will be in your mock exam are listed below. It is essential that you build on your knowledge and success by following
The Circulatory System
 The Circulatory System Science Matters Chapter 8 Introduction Living things need a transport system to carry things around the body. In humans its called The Circulatory system. The parts of the system
The Circulatory System Science Matters Chapter 8 Introduction Living things need a transport system to carry things around the body. In humans its called The Circulatory system. The parts of the system
LAB 9: Metabolic Rates
 LAB 9: Metabolic Rates Introduction: The cardiovascular (circulatory) system functions to deliver oxygen and nutrients to tissues for growth and metabolism, and to remove metabolic wastes. The heart pumps
LAB 9: Metabolic Rates Introduction: The cardiovascular (circulatory) system functions to deliver oxygen and nutrients to tissues for growth and metabolism, and to remove metabolic wastes. The heart pumps
Cardiovascular System
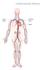 Cardiovascular System Cardiovascular System - Function The cardiovascular system transports, from one part of the body to another: nutrients, oxygen, ions, proteins, hormones and other signaling molecules,
Cardiovascular System Cardiovascular System - Function The cardiovascular system transports, from one part of the body to another: nutrients, oxygen, ions, proteins, hormones and other signaling molecules,
Level 1/2 Technical Award in Health and Fitness (603/2650/5) Unit 01 Introduction to body systems and principles of training in health and fitness
 Level /2 Technical Award in Health and Fitness (603/2650/5) Sample 207 Unit 0 Introduction to body systems and principles of training in health and fitness Mark Scheme v0. All the material in this publication
Level /2 Technical Award in Health and Fitness (603/2650/5) Sample 207 Unit 0 Introduction to body systems and principles of training in health and fitness Mark Scheme v0. All the material in this publication
Monday 14 th May The Body Anatomy and Physiology Lesson 10 Cardio-Respiratory System
 Monday 14 th May 2018 The Body Anatomy and Physiology Lesson 10 Cardio-Respiratory System Homework 1. What is the function of the cardiovascular system? 2. List the main components of blood and describe
Monday 14 th May 2018 The Body Anatomy and Physiology Lesson 10 Cardio-Respiratory System Homework 1. What is the function of the cardiovascular system? 2. List the main components of blood and describe
The Circulatory System:
 The Circulatory System: The Body s Transport System The Circulatory System! What is the CIRCULATORY SYSTEM? A HIGHWAY NETWORK that LINKS all parts of your body. Consists of the HEART, BLOOD VESSELS, and
The Circulatory System: The Body s Transport System The Circulatory System! What is the CIRCULATORY SYSTEM? A HIGHWAY NETWORK that LINKS all parts of your body. Consists of the HEART, BLOOD VESSELS, and
Physical Education GCSE 1PE0/01. Component 1: Fitness and Body Systems. Time: 1 hour and 45 minutes. You will need a calculator.
 Write your name here Surname Other names GCSE Physical Education Component 1: Fitness and Body Systems Time: 1 hour and 45 minutes Paper Reference 1PE0/01 You will need a calculator. Total Marks Instructions
Write your name here Surname Other names GCSE Physical Education Component 1: Fitness and Body Systems Time: 1 hour and 45 minutes Paper Reference 1PE0/01 You will need a calculator. Total Marks Instructions
Introduction to Human Body Systems
 The Human Organism: Introduction to Human Body Systems By Deanne Erdmann, MS Levels of Organization in the Body Cells Tissues Epithelial, connective, muscular, nervous Organs Examples include stomach,
The Human Organism: Introduction to Human Body Systems By Deanne Erdmann, MS Levels of Organization in the Body Cells Tissues Epithelial, connective, muscular, nervous Organs Examples include stomach,
Functions of the Circulatory System
 Functions of the Circulatory System Carry oxygen from lungs to tissues Carry carbon dioxide from tissues to lungs thereby aiding in the exchange of gases Helps carry nutrients to cells Helps to fight against
Functions of the Circulatory System Carry oxygen from lungs to tissues Carry carbon dioxide from tissues to lungs thereby aiding in the exchange of gases Helps carry nutrients to cells Helps to fight against
PAPER 1 GCSE PE REVISION GUIDE MR MARGOLAN Applied Anatomy and Physiology Structure and function of the musculoskeletal system
 PAPER 1 GCSE PE REVISION GUIDE MR MARGOLAN 3.1.1 Applied Anatomy and Physiology 3.1.1.1 Structure and function of the musculoskeletal system The Skeletal System There are 206 bones in the human body -
PAPER 1 GCSE PE REVISION GUIDE MR MARGOLAN 3.1.1 Applied Anatomy and Physiology 3.1.1.1 Structure and function of the musculoskeletal system The Skeletal System There are 206 bones in the human body -
IB Sports, Exercise and Health Science. Learning Outcomes
 IB Sports, Exercise and Health Science Learning Outcomes 1 TOPIC 1: ANATOMY 1.1. THE SKELETAL SYSTEM 1.1.1 Distinguish anatomically between the axial and appendicular skeleton. 1.1.2 Distinguish between
IB Sports, Exercise and Health Science Learning Outcomes 1 TOPIC 1: ANATOMY 1.1. THE SKELETAL SYSTEM 1.1.1 Distinguish anatomically between the axial and appendicular skeleton. 1.1.2 Distinguish between
Lecture 2. Statics & Dynamics of Rigid Bodies: Human body 30 August 2018
 Lecture 2. Statics & Dynamics of Rigid Bodies: Human body 30 August 2018 Wannapong Triampo, Ph.D. Static forces of Human Body Equilibrium and Stability Stability of bodies. Equilibrium and Stability Fulcrum
Lecture 2. Statics & Dynamics of Rigid Bodies: Human body 30 August 2018 Wannapong Triampo, Ph.D. Static forces of Human Body Equilibrium and Stability Stability of bodies. Equilibrium and Stability Fulcrum
The teacher guide contains: ü Additional activities. ü Suggested answers for selected student workbook activities. ü Practical lab activities
 HOW TO USE YOUR TEACHER RESOURCE As your students progress through the IVET Sport & Recreation YEAR 2 Core Competencies Student Workbook, some of the pages will have the following symbol: üt1.0 The (T)
HOW TO USE YOUR TEACHER RESOURCE As your students progress through the IVET Sport & Recreation YEAR 2 Core Competencies Student Workbook, some of the pages will have the following symbol: üt1.0 The (T)
How does the Circulatory System maintain
 How does the Circulatory System maintain -It supplies cells throughout the body with oxygen and nutrients while also ridding them of wastes. Transports materials such as: (to cells) (to attack foreign
How does the Circulatory System maintain -It supplies cells throughout the body with oxygen and nutrients while also ridding them of wastes. Transports materials such as: (to cells) (to attack foreign
CARDIORESPIRATORY DEVELOPMENT
 CARDIORESPIRATORY DEVELOPMENT Fahey/Insel/Roth, Fit & Well: Core Concepts and Labs in Physical Fitness and Wellness, Chapter 3 ANATOMY OF THE HEART O The heart is divided into right and left hand side
CARDIORESPIRATORY DEVELOPMENT Fahey/Insel/Roth, Fit & Well: Core Concepts and Labs in Physical Fitness and Wellness, Chapter 3 ANATOMY OF THE HEART O The heart is divided into right and left hand side
name F septum ; D bicuspid / mitral / atrioventricular, valve ; aorta pulmonary artery K semilunar valve ; right atrium right ventricle ; [6]
![name F septum ; D bicuspid / mitral / atrioventricular, valve ; aorta pulmonary artery K semilunar valve ; right atrium right ventricle ; [6] name F septum ; D bicuspid / mitral / atrioventricular, valve ; aorta pulmonary artery K semilunar valve ; right atrium right ventricle ; [6]](/thumbs/79/79061016.jpg) Question Mark Guidance 1 (a) function letter on Fig. 1.1 name structure that separates oxygenated and deoxygenated blood structure that prevents backflow of blood from ventricle to atrium F septum ; D
Question Mark Guidance 1 (a) function letter on Fig. 1.1 name structure that separates oxygenated and deoxygenated blood structure that prevents backflow of blood from ventricle to atrium F septum ; D
The Digestive System: to convert food particles into simpler micro molecules that can be absorbed into the bloodstream and used by the body
 Body Systems The Digestive System: to convert food particles into simpler micro molecules that can be absorbed into the bloodstream and used by the body Major Organs and their Functions: Mouth to chew
Body Systems The Digestive System: to convert food particles into simpler micro molecules that can be absorbed into the bloodstream and used by the body Major Organs and their Functions: Mouth to chew
Unit 6.1 Test Review THE NERVOUS, INTEGUMENTARY, CIRCULATORY, AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEMS
 Name: Period: Due Date: Unit 6.1 Test Review THE NERVOUS, INTEGUMENTARY, CIRCULATORY, AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEMS The Nervous System: 1. Name the 3 parts of a neuron and their function: a. b. c. 2. What is
Name: Period: Due Date: Unit 6.1 Test Review THE NERVOUS, INTEGUMENTARY, CIRCULATORY, AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEMS The Nervous System: 1. Name the 3 parts of a neuron and their function: a. b. c. 2. What is
Lesson 10 Circulatory System (Nelson p.88-93)
 Name: Date: Lesson 10 Circulatory System (Nelson p.88-93) Learning Goals: A. I can explain the primary functions of the circulatory system in animals. B. I can identify and explain all the parts of the
Name: Date: Lesson 10 Circulatory System (Nelson p.88-93) Learning Goals: A. I can explain the primary functions of the circulatory system in animals. B. I can identify and explain all the parts of the
30.1 Respiratory and Circulatory Functions. KEY CONCEPT The respiratory and circulatory systems bring oxygen and nutrients to the cells.
 30.1 Respiratory and Circulatory Functions KEY CONCEPT The respiratory and circulatory systems bring oxygen and nutrients to the cells. 30.1 Respiratory and Circulatory Functions The respiratory and circulatory
30.1 Respiratory and Circulatory Functions KEY CONCEPT The respiratory and circulatory systems bring oxygen and nutrients to the cells. 30.1 Respiratory and Circulatory Functions The respiratory and circulatory
Aerobic and Anaerobic Respiration Revision 2
 Aerobic and Anaerobic Respiration Revision 2 65 minutes 65 marks Page of 23 Q. A person did five different activities in turn. These activities needed increasing amounts of energy. For each activity two
Aerobic and Anaerobic Respiration Revision 2 65 minutes 65 marks Page of 23 Q. A person did five different activities in turn. These activities needed increasing amounts of energy. For each activity two
Stonelaw High School Science Faculty. S2 Science Body Systems Homework Booklet
 Stonelaw High School Science Faculty S2 Science Body Systems Homework Booklet Name: Class: Success Criteria I am confident that I understand this and can apply this to problems? I have some understanding
Stonelaw High School Science Faculty S2 Science Body Systems Homework Booklet Name: Class: Success Criteria I am confident that I understand this and can apply this to problems? I have some understanding
d) Cardiovascular System Higher Human Biology
 d) Cardiovascular System Higher Human Biology What can your remember about the heart and blood vessels? What is the Cardiovascular System? The cardiovascular system, also known as the circulatory system,
d) Cardiovascular System Higher Human Biology What can your remember about the heart and blood vessels? What is the Cardiovascular System? The cardiovascular system, also known as the circulatory system,
Circulation: Chapter 25. Cardiac Output. The Mammalian Heart Fig Right side of the heart
 Circulation: Chapter 25 1. Limits of Diffusion A. Small organisms use diffusion B. rapid over small distances 2. Most animals have circulatory systems A. Blood B. Pump (Heart) or propulsive structures
Circulation: Chapter 25 1. Limits of Diffusion A. Small organisms use diffusion B. rapid over small distances 2. Most animals have circulatory systems A. Blood B. Pump (Heart) or propulsive structures
Separate information into components and identify their characteristics. Finish a task by adding to given information.
 Exam technique GCSE PE Command Words Analyse Apply Calculate Compare Complete Consider Define Describe Discuss Evaluate Explain Identify Illustrate Interpret Justify Outline Suggest State Separate information
Exam technique GCSE PE Command Words Analyse Apply Calculate Compare Complete Consider Define Describe Discuss Evaluate Explain Identify Illustrate Interpret Justify Outline Suggest State Separate information
Lab 16. The Cardiovascular System Heart and Blood Vessels. Laboratory Objectives
 Lab 16 The Cardiovascular System Heart and Blood Vessels Laboratory Objectives Describe the anatomical structures of the heart to include the pericardium, chambers, valves, and major vessels. Describe
Lab 16 The Cardiovascular System Heart and Blood Vessels Laboratory Objectives Describe the anatomical structures of the heart to include the pericardium, chambers, valves, and major vessels. Describe
GCSE Physical Education
 GCSE Physical Education GCSE year 10 2017 You Should Know Guide 1.1 Healthy Active Lifestyle and How it Could Benefit You What is a healthy active lifestyle? A lifestyle that contributes positively to
GCSE Physical Education GCSE year 10 2017 You Should Know Guide 1.1 Healthy Active Lifestyle and How it Could Benefit You What is a healthy active lifestyle? A lifestyle that contributes positively to
CIRCULATION & GAS EXCHANGE
 AP BIOLOGY ACTIVITY2.13 Text:Campbell,v.8,chapter42 NAME DATE HOUR CIRCULATION & GAS EXCHANGE 1. In general, what is the function of transport systems? 2. What method/structure do most invertebrates use
AP BIOLOGY ACTIVITY2.13 Text:Campbell,v.8,chapter42 NAME DATE HOUR CIRCULATION & GAS EXCHANGE 1. In general, what is the function of transport systems? 2. What method/structure do most invertebrates use
Foundations of physical activity
 1 Foundations of physical activity 1 Body systems and energy for physical activity In this chapter a student: 1.1 discusses factors that limit and enhance the capacity to move and perform 1.2 analyses
1 Foundations of physical activity 1 Body systems and energy for physical activity In this chapter a student: 1.1 discusses factors that limit and enhance the capacity to move and perform 1.2 analyses
4. Which one of the following correctly identifies the part of the skeleton that produces red blood cells?
 GSE P.E. questions and mark schemes 1 a pplied natomy and Physiology 1. Which of one of the following is NOT a function of the skeleton? 2. Which one of the following is NOT a function of the skeleton?
GSE P.E. questions and mark schemes 1 a pplied natomy and Physiology 1. Which of one of the following is NOT a function of the skeleton? 2. Which one of the following is NOT a function of the skeleton?
The Cardiovascular System home study course
 The Cardiovascular System home study course harmony house holistic therapy treatment centre and training academy www.harmony-house.org 1 Copyright 2010 by Mark and Katy Rogers All rights reserved. No part
The Cardiovascular System home study course harmony house holistic therapy treatment centre and training academy www.harmony-house.org 1 Copyright 2010 by Mark and Katy Rogers All rights reserved. No part
Human Body System Lab Packet
 Human Body System Lab Packet Name 1 Circulatory System Lab Introduction An average-sized adult has about 5.5 liters of blood in their body, which the heart circulates about three times every minute. Your
Human Body System Lab Packet Name 1 Circulatory System Lab Introduction An average-sized adult has about 5.5 liters of blood in their body, which the heart circulates about three times every minute. Your
Hierarchy of Biological Organization
 Hierarchy of Biological Organization Transport & Exchange (Circulation & Respiration) Cardiovascular System - transports materials What materials? Components of Blood Read about The Components of the Blood
Hierarchy of Biological Organization Transport & Exchange (Circulation & Respiration) Cardiovascular System - transports materials What materials? Components of Blood Read about The Components of the Blood
Introduction. Every organism must exchange materials and energy with its environment, and this exchange ultimately occurs at the cellular level.
 Introduction Every organism must exchange materials and energy with its environment, and this exchange ultimately occurs at the cellular level. Cells live in aqueous environments. The resources that they
Introduction Every organism must exchange materials and energy with its environment, and this exchange ultimately occurs at the cellular level. Cells live in aqueous environments. The resources that they
Paper 1 Final Revision
 Paper 1 Final Revision Physical Factors affecting Performance - Body Systems Location of major bones Functions of the skeleton Types of Synovial Joints Types of Movements at Hine and Ball & Socket Joint
Paper 1 Final Revision Physical Factors affecting Performance - Body Systems Location of major bones Functions of the skeleton Types of Synovial Joints Types of Movements at Hine and Ball & Socket Joint
Circulatory, Respiratory, and Excretory Systems
 34 Circulatory, Respiratory, and Excretory Systems section 1 Circulatory System Before You Read Press the tips of two fingers to the inside of your wrist, at a point just below your thumb. Can you feel
34 Circulatory, Respiratory, and Excretory Systems section 1 Circulatory System Before You Read Press the tips of two fingers to the inside of your wrist, at a point just below your thumb. Can you feel
Biology Unit 3 The Human Heart P
 Biology 2201 Unit 3 The Human Heart P 314-321 Structure and Function of the Human Heart Structure of the Human Heart Has four Chambers (2 Atria and 2 Ventricles) Made of Cardiac Muscle Found in Chest Cavity
Biology 2201 Unit 3 The Human Heart P 314-321 Structure and Function of the Human Heart Structure of the Human Heart Has four Chambers (2 Atria and 2 Ventricles) Made of Cardiac Muscle Found in Chest Cavity
The Cardiovascular System
 11 PART A The Cardiovascular System PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB The Cardiovascular
11 PART A The Cardiovascular System PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB The Cardiovascular
 Caledonia Science the system that circulates blood and lymph through the body, consisting of the heart, blood vessels, The is the muscle that moves the blood throughout the highway system of vessles. The
Caledonia Science the system that circulates blood and lymph through the body, consisting of the heart, blood vessels, The is the muscle that moves the blood throughout the highway system of vessles. The
Circulation and Respiration
 Lesson 10 Circulation and Respiration Introduction to Life Processes - SCI 102 1 Circulatory System: Features and Functions All circulatory systems have three major parts The heart: a pump that keeps blood
Lesson 10 Circulation and Respiration Introduction to Life Processes - SCI 102 1 Circulatory System: Features and Functions All circulatory systems have three major parts The heart: a pump that keeps blood
