Figure S1. Molecular confirmation of the precise insertion of the AsMCRkh2 cargo into the kh w locus.
|
|
|
- Joseph Warren
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Supporting Information Appendix Table S1. Larval and adult phenotypes of G 2 progeny of lines 10.1 and 10.2 G 1 outcrosses to wild-type mosquitoes. Table S2. List of oligonucleotide primers. Table S3. G 3 larval phenotypes of line 10.1 G 2 outcrosses to wild-type mosquitoes. Table S4. G 3 larval phenotypes of line 10.2 G 2 outcrosses to wild-type mosquitoes. Table S5. G 3 adult phenotypes of line 10.1 G 2 outcrosses to wild-type mosquitoes. Table S6. G 3 adult phenotypes of line 10.2 G 2 outcrosses to wild-type mosquitoes. Table S7. G 4 larval phenotypes of line 10.1 G 3 outcrosses to wild-type mosquitoes. Table S8. G 4 larval phenotypes of line 10.2 G 3 outcrosses to wild-type mosquitoes. Table S9. G 4 larval phenotypes of lines 10.1 and 10.2 batch G 3 intercrosses. Table S10. G 4 adult phenotypes of line 10.1 G 3 outcrosses to wild-type mosquitoes. Table S11. G 4 adult phenotypes of line 10.2 G 3 outcrosses to wild-type mosquitoes. Figure S1. Molecular confirmation of the precise insertion of the AsMCRkh2 cargo into the kh w locus. Figure S2. Nucleotide sequences of the kh2 target sites in selected G 2 gene-drive phenotypes. Figure S3. Gene amplification of the kh2 target sites in selected G 3 founder mosquitoes. Supporting Materials and Methods References 1
2 Table S1. Larval and adult phenotypes of G 2 progeny of lines 10.1 and 10.2 G 1 outcrosses to wild-type mosquitoes. G 1 Larval phenotypes * Adult phenotypes* Males Females Founder DsRed + /kh w+ DsRed + /kh w- DsRed/kh w+ DsRed - /kh w- DsRed + /kh w+ DsRed + /kh w- DsRed - /kh w+ DsRed - /kh w- DsRed + /kh w+ DsRed + /kh w- DsRed -/ kh w+ DsRed/kh w * Shaded cells are G 2 progeny positive for DsRed (DsRed + ). 2
3 Table S2. List of oligonucleotide primers. * Primer Sequence (5-3 ) Reference Vg451 GTACGCGTATCGATAAGCTTtaaGATACATTGATGAGTTTGG This study Vg452 TAGGCCGGCCGATCTCGGATCTGACAATG This study Vg453 GCTTATCGATACGCGTACGCATCTGCATCCTGGTACCACAGTCTTATTGG This study Vg454 GTACTTCTTATCCATCTTCCTAGATCGATTTTAAGCACGCCGC This study Vg455 CTAGGAAGATGGATAAGAAGTACTCGATCGGTCTGGATATCGG This study Vg456 CTCTCGTTACACCTTGCGCTTCTTCTTCGGCG This study Vg457 GCAAGGTGTAACGAGAGTTCGGTGCGAATCTCTCTCTTGATTTTTCCC This study Vg458 AGATCGGCCGGCCTAACCAAGGCCAGCCTGTTGAGC This study Vg464 AAGCTTATCGATACGCGTACCTCAACTGCCGACGAGTTGCTCG This study Vg465 ATCCGAGATCGGCCGGCCTACGTTCTGCGTGGCTGTTGTAAGGTTCC This study Vg494 GGTATCAGCTCACTCAAAGGCGGTAATACGG This study Vg495 GAAAGGGCCTCGTGATACGCCTATTTTTATAGG This study Vg498 CCTTTGAGTGAGCTGATACCCCCAAAAATTGACCTCAGATCTCTCAAGAAGCG This study Vg499 GCGTATCACGAGGCCCTTTCGCATCTGAACGAGGTGCTGCTAAATGG This study Vg500 GTTTTAGAGCTAGAAATAGCAAGTTAAAATAAGGCTAGTCCGTTATCAACTTGAAAAAGTGGCAC CGAGTCGGTGCTTTTTTTGTGGAAATTTGATTCACTTGTTTTAGG This study Vg501 AGGTCTTCTCGAAGACCCCAAGGGAGGGGGCAAATGGGTTGG This study Vg505 GTCCACTAACGAAAGAGGTCAAGAGC This study Vg507 CGATCGTTTAGTGACGAGATCACGC This study Vg537 CTTGATGGTTCCGTTCTACGGGC This study Vg538 AAACGCCCGTAGAACGGAACCAT This study Vg543 CATGTACATTTCCTTTTACGttaattaaCGTAGAACGGAACCATCGCGTGC This study Vg544 ATGGTTCCGTTCTACGttaattaaCGTAAAAGGAAATGTACATGGTAAAGCAATCTGACG This study Vg546 CCGGGCGAGCTCGactcgagcCTGGTACCACAGTCTTATTGGCGTGATGG This study Vg551 CAATAAGACTGTGGTACCAGgctcgagTTGTTTGATCGCACGGTTCCCACAATGG This study Vg552 CCTTACAACAGCCACGCAGAACGggatccGGCAGGGCATGAACGCGGGCTTTGAAGAC This study Vg553 GCCCGCGTTCATGCCCTGCCggatccCGTTCTGCGTGGCTGTTGTAAGGTTTCG This study Vg554 GCTCAACAGGCTGGCCTTGGTActcgagCTCAACTGCCGACGAGTTGCTCG This study Vg555 CAACTCGTCGGCAGTTGAGctcgagTACCAAGGCCAGCCTGTTGAGCAGCTTGC This study Vg557 CGATCGTTTAGTGACGAGATCACGC This study dscas9 1 F TAATACGACTCACTATAGTGCCATCCTGCTGTCGGATA This study dscas9 1 R TAATACGACTCACTATAGCTTCGGCAGCACCTTCTCGT This study dsku70 F TAATACGACTCACTATAGCTACGGCATTGGGTTTGTCT This study dsku70 R TAATACGACTCACTATAGGCTTAGCTTGTAGCCGGATG This study G1F2 CGTATGCTGCACGACGTTAAC This study 3
4 G2R1 CTGGACATCTGCTTCTGAG This study G2R2 GCAATAGCTGACTCCTG This study Km1F1 CGATGCGATCGAGCTAATTG This study Km2R1 GTGACGAGATCACGCATCTG This study Vg5 R1 CGTTTGGTGCTCAGCTCAGAC This study Vg5 R2 GTCGTAGGTGGTGGTATGCTAAC This study U6F1 CTACCTGTACGATGGCTTAAG This study m2a10 FOR GAGACGGTGAAGATCTCGTGCAAGG 1 m2a10 REV GCTTCGTACCACCACCGAACACGTA 1 m1c3 FOR AAGGGCTCGCTGAAACTGT 1 m1c3 REV ACAGAAGTACACCGCCAGGT 1 AsVg1 for CAACATCATGTCCAAGTCGGAGGTGA 2 AsVg1 rev CTTGAAGCTTTCGTGCTCTTCCTCCG 2 AsCPAFOR CTTTACGGAAACGCTCGAAG 3 AsCPAREV CCATAGCAGAATGGACCGTAA-3 3 Asrib26Sfor AATCCTTCCCGAAGGACATGAACCG 4 Asrib26Srev TACGAAACAAATCCCATCCTAATCGAAGC 4 * Lowercase letters are introduced restriction endonuclease cleavage sites. 4
5 Table S3. G 3 larval phenotypes of line 10.1 G 2 outcrosses to wild-type mosquitoes. Founder Cross DsRed + Larval phenotypes * DsRed Subtotal Subtotal Total * Shaded cells are G 3 progeny positive for DsRed (DsRed + ). Progeny of single G 2 male or female out-crossed to wild-types of the opposite sex. Χ 2 analyses show significant differences (p<<0.0001) in DsRed + :DsRed - ratios from random segregation. Table S4. G 3 larval phenotypes of line 10.2 G 2 outcrosses to wild-type mosquitoes. Founder Cross Larval phenotypes * DsRed + DsRed - DsRed - /kh w Subtotal Batch Total * Shaded cells are G 3 progeny positive for DsRed (DsRed + ). Progeny of single G 2 female out-crossed to wild-type males. 27 G 2 males out-crossed to 270 wild-type females. Χ 2 analyses show significant differences (p<<0.0001) in DsRed + :DsRed - ratios from random segregation. 5
6 Table S5. G 3 adult phenotypes of line 10.1 G 2 outcrosses to wild-type mosquitoes. Adult phenotypes * Founder Males Cross DsRed + /kh w+ DsRed + /kh w- DsRed + / mosaic Females DsRed -/ kh w+ DsRed - /kh w- DsRed + /kh w+ DsRed + /kh w- DsRed + / mosaic Total Total * Shaded cells are G 3 progeny positive for DsRed (DsRed + ). Progeny of single G 2 male or female out-crossed to wild-types of the opposite sex. Χ 2 analyses show significant differences (p<<0.0001) in DsRed + :DsRed - ratios from random segregation. DsRed -/ kh w+ DsRed - /kh w- 6
7 Table S6. G 3 adult phenotypes of line 10.2 G 2 outcrosses to wild-type mosquitoes. Adult phenotypes * Founde Cross Males r DsRed + /kh w+ DsRed + /kh w- DsRed + / mosaic DsRed -/ kh w+ Females DsRed - /kh w- DsRed + /kh w+ DsRed + /kh w- DsRed + / mosaic DsRed -/ kh w ND 44 ND ND 61 ND ND 32 3 ND ND 33 ND ND 51 ND Total DsRed - /kh w- Batch * Shaded cells are G 3 progeny positive for DsRed (DsRed + ). Progeny of single G 2 female out-crossed to wild-type males. 27 G 2 males out-crossed to 270 wild-type females. The first column numbers are those mosquitoes with mosaicism in the eye. The second column numbers are mosquitoes with the colored eye phenotypes consistent with mosaicism in the rest of the body. ND, not determined. Χ 2 analyses show significant differences (p<<0.0001) in DsRed + :DsRed - ratios from random segregation. 7
8 Table S7. G 4 larval phenotypes of line 10.1 G 3 outcrosses to wild-type mosquitoes. (Cross)Transgenic parent (n) * Larval phenotypes DsRed + DsRed - (1) DsRed + /kh w- (26) (2) DsRed + /kh w- (32) (5) DsRed + /kh w+ (40) (6) DsRed + /kh w+ (40) * Progeny of batch-mated G 3 males or females out-crossed to wild-types of the opposite sex. (n) is the number of transgenic founder parents. Shaded cells are G 4 progeny positive for DsRed (DsRed + ). Χ 2 analyses show significant differences (p<<0.0001) in DsRed + :DsRed - ratios from random segregation. Table S8. G 4 larval phenotypes of line 10.2 G 3 outcrosses to wild-type mosquitoes. (Cross)Transgenic parent (n) * Larval phenotypes DsRed + DsRed - (3) DsRed + /kh w- (43) (4) DsRed + /kh w- (25) (7) DsRed + /kh w+ (50) (8) DsRed + /kh w+ (50) * Progeny of batch-mated G 3 males or females out-crossed to wild-types of the opposite sex. (n) is the number of transgenic founder parents. Shaded cells are G 4 progeny positive for DsRed (DsRed + ). Χ 2 analyses show significant differences (p<<0.0001) in DsRed + :DsRed - ratios from random segregation. Table S9. Table S9. G 4 larval phenotypes of lines 10.1 and 10.2 batch G 3 intercrosses. 1 Larval phenotypes Cross DsRed + /kh w- DsRed - /kh w- Line Line G 3 DsRed-positive (DsRed + ) males and females were intercrossed as a single batch for each line. Shaded cells are G 4 progeny positive for DsRed (DsRed + ). 8
9 Table S10. G 4 adult phenotypes of line 10.1 G 3 outcrosses to wild-type mosquitoes. Adult phenotypes 1 Line (Cross) Founder DsRed + / DsRed + / G 4 males DsRed + / DsRed -/ DsRed - / DsRed + / DsRed + / G 4 females DsRed + / DsRed -/ DsRed - / kh w+ kh w- mosaic kh w+ kh w- kh w+ kh w- mosaic kh w+ kh w- (1) DsRed + /kh w (2) DsRed + /kh w (5) DsRed + /kh w (6) DsRed + /kh w * Shaded cells are G 4 progeny positive for DsRed (DsRed + ). The first column numbers are those mosquitoes with mosaicism in the eye. The second column numbers are mosquitoes with the colored eye phenotypes consistent with mosaicism in the rest of the body. Χ 2 analyses show significant differences (p=0.0137) in DsRed + :DsRed - ratios from random segregation. Χ 2 analyses show significant differences (p<<0.0001) in DsRed + :DsRed - ratios from random segregation. 9
10 Table S11. G 4 adult phenotypes of line 10.2 G 3 outcrosses to wild-type mosquitoes. Adult phenotypes * Line (Cross) Founder DsRed + / DsRed + / G 4 males DsRed + / DsRed -/ DsRed - / DsRed + / DsRed + / G 4 females DsRed + / DsRed -/ DsRed - / kh w+ kh w- mosaic kh w+ kh w- kh w+ kh w- mosaic kh w+ kh w- (3) DsRed + /kh w (4) DsRed + /kh w (7) DsRed + /kh w (8) DsRed + /kh w * Shaded cells are G 4 progeny positive for DsRed (DsRed + ). The first column numbers are those mosquitoes with mosaicism in the eye. The second column numbers are mosquitoes with the colored eye phenotypes consistent with mosaicism in the rest of the body. Χ 2 analyses show significant differences (p<0.0001) in DsRed + :DsRed - ratios from random segregation. Χ 2 analyses show significant differences (p=0.0011) in DsRed + :DsRed - ratios from random segregation. Χ 2 analyses show significant differences (p<<0.0001) in DsRed + :DsRed - ratios from random segregation. 10
11 Figure S1. Molecular confirmation of the precise insertions of the AsMCRkh2 cargo into the kh w locus. Sequencing of the 5'- and 3 -end G1F2-vg5'1 and U6F1-G2R2 junction amplification fragments (left and right, respectively) amplified from the G 1 founder male mosquitoes 10.1 and 10.2 (lower sequencing traces) revealed a perfect match to the sequences from Cas9-mediated cleavage at the kh2 target site and precise integration of the ASMCRkh2 cargo (Figure 1) into that site. Positions of the kh2 homology arms (maroon boxes), guide RNA targeting sequences (blue boxes), PAM site (red arrowhead) and the PCR primers Vg-5prime (orange box) and U6A3'Seq (red box) are shown. Genomic nucleotides depicted in lower case letters indicate restriction endonuclease enzyme recognition sites used in the construction of the AsMCRkh2 cargo. 11
12 Figure S2. Mutated sequences at the kh2 target site in selected G2 transgenic mosquitoes. The top sequence is the wild-type reference sequence at the kh2 target site from a control mosquito. The PAM sequence is shaded in peach, the 20 nt targeting sequence is shaded in purple, indels are shaded in pink, and the grna directed cleavage site by a thin vertical white line. NHEJ events were detected in three different white-eyed DsRed- mosquitoes. Different sequences were isolated by cloning PCR products generated from the khw locus in lines and , supporting the conclusion that these mosquitoes are mosaics carrying at least two distinct NHEJ-directed mutations. Isolate is derived from a direct sequencing reaction of an amplification product confirming that this transgenic mosquito had only a single NHEJ event. In contrast to the other two cases, this mutation maintains the translation frame but nonetheless results in a white-eye phenotype supporting the conclusion that the deletion of a single amino acid (Y328) and substitution of its neighbor (G329W) eliminates or greatly reduces kynurenine hydroxylase enzymatic activity. 12
13 Females Males C M ~754 bp ~754 bp Figure S3. Gene amplification of the kh2 target sites in selected G 3 founder mosquitoes. Genomic DNA prepared from individual male and female G 3 founder mosquitoes positive for DsRed and with white eyes (DsRed + /kh w- ; crosses 1-4, Tables S10 and S11) was used with the gene-specific primers, vg505 and vg557 (Table S2) to amplify a portion of the kh w gene. The diagnostic fragment at 754 base-pairs indicates at least one of the chromosomes had a kh w gene without the large ~17 kb transgene cargo insert. These alleles must be mutant because the eye phenotype of each mosquito from which the DNA was derived is white (kh w- ). C is a control sample of DNA from a wild-type mosquito. M are the molecular-weight markers. 13
14 Supporting Materials and Methods. Construction of the vasa-cas9 cassette. The Drosophila melanogaster vasa gene and its Anopheles gambiae ortholog AGAP (5) were used as BLAST search queries to identify the ASTE gene as the putative unique Anopheles stephensi ortholog. A 4009 bp genomic fragment comprising the Anopheles stephensi vasa promoter and regulatory sequences preceding the predicted translational start site was amplified using oligonucleotides vg453/vg454. Four DNA fragments were then joined in the following order: 1) the An. stephensi vasa regulatory fragment; 2) a recoded Cas9 gene codon-optimized for translation in Anopheles stephensi (puc57kan-t7-ascas9 (amplified with the oligonucleotides vg455/vg456); 3) a 1014bp fragment following the translational stop codon (TAA) of the ASTE (amplified using the oligonucleotides vg457/458), 4) the backbone of the pbacdsred plasmid (amplified using the oligonucleotides vg451/vg452). These four amplicons were purified, treated with the restriction enzyme DpnI to remove methylated DNA and joined in a Gibson assembly (New England Biolabs, #E5510S) reaction to obtain the plasmid pvg160 (pvg160_pbacdsred-attb_aste-vasa-cas9). Construction of the U6A-kh-gRNA cassette. A 923bp fragment spanning the annotated Anopheles stephensi U6-snRNA gene ASTE was amplified using the oligonucleotides vg464/vg465, and the amplification product was cloned into pcr2.1-topo using a TA Topoisomerase Cloning Kit (Invitrogen, #450641). The resulting plasmid was used as a template for site-directed mutagenesis using the oligonucleotides vg500/vg501 thereby substituting the U6 transcript with a 2xBbsI restriction site linker followed by the grna core sequence. The resulting plasmid (pvg145) serves as vector for one-step insertion of 20 bp grna guide sequences to generate complete grnas under the control of the An. stephensi U6 RNA polymerase-iii promoter. pvg145 was cut with the restriction enzyme BbsI and a linker generated by annealing the oligonucleotides vg537/vg538 was ligated to close the gap, the resulting plasmid (pvg163) expresses a grna targeting cleavage of the kynurenine hydroxylase-white (kh w ) coding sequence at the sequence GATGGTTCCGTTCTACG/GGCAGG ; the bolded GGG corresponds to the encoded glycine 329 of the kh w gene product. Construction of the homology arms backbone (pvg159). To minimize the final vector size, a minimal 1943 bp backbone fragment of puc19 was amplified using vg494/vg495 and fused to a 2.4kb genomic fragment from the An. stephensi kh w locus (amplified with vg498/vg499), using Gibson assembly, to yield the plasmid pvg159. Construction of the pasmcrkh construct. The final construct, pasmcrkh, was assembled using restriction cloning in two steps. First, a three-way fusion was generated comprising: 1) a fragment containing the puc19 plasmid backbone and the kh w homology arms was amplified from pvg159 using vg543/vg552, which added PacI and BamHI restriction enzyme cut sites at the ends; 2) a 6.6kb DNA fragment including the 3xP3-DsRed eye marker and a dual-single chain (scfv) antibody cassette expressing m1c3 and m2a10 (1,3) and amplified with vg544/vg551, which added PacI and PspXI sites at the ends); and 3) the U6A-kh2-gRNA cassette (amplified from pvg163 using vg553/vg554, which added PspXI and BamHI sites at the ends). Each of the three fragments was cut with the respective restriction enzymes followed by treatment with DpnI to remove the methylated templates, and ligated together to obtain the intermediate plasmid pvg165. In the second step, the two above fragments were joined. The vasa-cas9 cassette was amplified from pvg160 (using vg546/vg555, which added PspXI sites at both ends) and the obtained amplicon was cut with PspXI and DpnI, and then ligated to pvg165 linearized with PspXI (and treated with calf intestinal alkaline phosphatase to obtain the final construct. Reagents: all amplification steps were performed using Phusion High-Fidelity DNA Polymerase (for fragments <6kb, New England Biolabs, Cat.#M0530S) or Q5 High-Fidelity DNA Polymerase (for fragments >6kb, New England Biolabs, Cat.#M0491S). The enzymes mentioned were purchased from New England Biolabs: BamHI- 14
15 HF (R3136S), BbsI (R0539S), DpnI (R0176S), PacI (R0547S), PspXI (R0656S), calf intestinal alkaline phosphatase (M0290S). References 1. Isaacs, A.T., Li, F., Jasinskiene, N., Chen, X., Nirmala, X., Marinotti, O., Vinetz, J.M. and James, A.A. (2011) Engineered resistance to Plasmodium falciparum development in transgenic Anopheles stephensi. PLoS Pathogens 7(4): PMID: , PMCID: PMC Nirmala, X., Marinotti, O., Sandoval, J.M., Phin, S., Gakhar, S., Jasinskiene. N. and James, A.A. (2006) Functional characterization of the promoter of the vitellogenin gene, AsVg1, of the malaria vector, Anopheles stephensi. Insect. Biochem. Molec. Biol., 36, PMID: Isaacs, A.T., Jasinskiene, N., Tretiakov, M., Thiery, I., Zettor, A., Bourgouin, C. and James, A.A. (2012) Transgenic Anopheles stephensi co-expressing single-chain antibodies resist Plasmodium falciparum development. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 109, E1922-E1930. PMID: PNAS PLUS, 109, Chen, X., Marinotti, O., Whitman, L., Jasinskiene N., Romans, P and James A.A. (2007) The Anopheles gambiae vitellogenin gene (VGT2) promoter directs persistent accumulation of a reporter gene product in transgenic Anopheles stephensi following multiple blood meals. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hygiene 76, PMID Papathanos, P.A., Windbichler, N., Menichelli, M., Burt A. and Crisanti, A. (2009) The vasa regulatory region mediates germline expression and maternal transmission of proteins in the malaria mosquito Anopheles gambiae: a versatile tool for genetic control strategies. BMC Mol Biol Jul 2;10:65. doi: / PMID:
Construction of a hepatocellular carcinoma cell line that stably expresses stathmin with a Ser25 phosphorylation site mutation
 Construction of a hepatocellular carcinoma cell line that stably expresses stathmin with a Ser25 phosphorylation site mutation J. Du 1, Z.H. Tao 2, J. Li 2, Y.K. Liu 3 and L. Gan 2 1 Department of Chemistry,
Construction of a hepatocellular carcinoma cell line that stably expresses stathmin with a Ser25 phosphorylation site mutation J. Du 1, Z.H. Tao 2, J. Li 2, Y.K. Liu 3 and L. Gan 2 1 Department of Chemistry,
Genome-editing via Oviductal Nucleic Acids Delivery (GONAD) system: a novel microinjection-independent genome engineering method in mice
 Supplementary Information Genome-editing via Oviductal Nucleic Acids Delivery (GONAD) system: a novel microinjection-independent genome engineering method in mice Gou Takahashi, Channabasavaiah B Gurumurthy,
Supplementary Information Genome-editing via Oviductal Nucleic Acids Delivery (GONAD) system: a novel microinjection-independent genome engineering method in mice Gou Takahashi, Channabasavaiah B Gurumurthy,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature10643 Supplementary Table 1. Identification of hecw-1 coding polymorphisms at amino acid positions 322 and 325 in 162 strains of C. elegans. WWW.NATURE.COM/NATURE 1 Supplementary Figure
doi:10.1038/nature10643 Supplementary Table 1. Identification of hecw-1 coding polymorphisms at amino acid positions 322 and 325 in 162 strains of C. elegans. WWW.NATURE.COM/NATURE 1 Supplementary Figure
Supplementary Appendix
 Supplementary Appendix This appendix has been provided by the authors to give readers additional information about their work. Supplement to: Choi YL, Soda M, Yamashita Y, et al. EML4-ALK mutations in
Supplementary Appendix This appendix has been provided by the authors to give readers additional information about their work. Supplement to: Choi YL, Soda M, Yamashita Y, et al. EML4-ALK mutations in
Supplemental Materials and Methods Plasmids and viruses Quantitative Reverse Transcription PCR Generation of molecular standard for quantitative PCR
 Supplemental Materials and Methods Plasmids and viruses To generate pseudotyped viruses, the previously described recombinant plasmids pnl4-3-δnef-gfp or pnl4-3-δ6-drgfp and a vector expressing HIV-1 X4
Supplemental Materials and Methods Plasmids and viruses To generate pseudotyped viruses, the previously described recombinant plasmids pnl4-3-δnef-gfp or pnl4-3-δ6-drgfp and a vector expressing HIV-1 X4
WKH$F02( (R539T( 957( 005( 24# 17# 32# 26# 30# 21# 21# 9# 14# 18# 9# 13# 21# 14# 14# 2# 42# 17#
 20 KH$C(( WT( WKH$F02( (R539T( WKH$F04( (Y493H( WKH$F03( C580Y( 18 027( 004( 010( 967( 005( 0.94 957( 0.96 887( 818$2( 0.98 829( 1.00 1.02 1.04 16 14 12 10 8 6 4 2 0 n 113 142 170 140 158 143 244 217 78
20 KH$C(( WT( WKH$F02( (R539T( WKH$F04( (Y493H( WKH$F03( C580Y( 18 027( 004( 010( 967( 005( 0.94 957( 0.96 887( 818$2( 0.98 829( 1.00 1.02 1.04 16 14 12 10 8 6 4 2 0 n 113 142 170 140 158 143 244 217 78
Alternative RNA processing: Two examples of complex eukaryotic transcription units and the effect of mutations on expression of the encoded proteins.
 Alternative RNA processing: Two examples of complex eukaryotic transcription units and the effect of mutations on expression of the encoded proteins. The RNA transcribed from a complex transcription unit
Alternative RNA processing: Two examples of complex eukaryotic transcription units and the effect of mutations on expression of the encoded proteins. The RNA transcribed from a complex transcription unit
Supplementary Information. Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure 1 1 Supplementary Figure 1. Functional assay of the hcas9-2a-mcherry construct (a) Gene correction of a mutant EGFP reporter cell line mediated by hcas9 or
Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure 1 1 Supplementary Figure 1. Functional assay of the hcas9-2a-mcherry construct (a) Gene correction of a mutant EGFP reporter cell line mediated by hcas9 or
Hands-On Ten The BRCA1 Gene and Protein
 Hands-On Ten The BRCA1 Gene and Protein Objective: To review transcription, translation, reading frames, mutations, and reading files from GenBank, and to review some of the bioinformatics tools, such
Hands-On Ten The BRCA1 Gene and Protein Objective: To review transcription, translation, reading frames, mutations, and reading files from GenBank, and to review some of the bioinformatics tools, such
Iso-Seq Method Updates and Target Enrichment Without Amplification for SMRT Sequencing
 Iso-Seq Method Updates and Target Enrichment Without Amplification for SMRT Sequencing PacBio Americas User Group Meeting Sample Prep Workshop June.27.2017 Tyson Clark, Ph.D. For Research Use Only. Not
Iso-Seq Method Updates and Target Enrichment Without Amplification for SMRT Sequencing PacBio Americas User Group Meeting Sample Prep Workshop June.27.2017 Tyson Clark, Ph.D. For Research Use Only. Not
Genomic structural variation
 Genomic structural variation Mario Cáceres The new genomic variation DNA sequence differs across individuals much more than researchers had suspected through structural changes A huge amount of structural
Genomic structural variation Mario Cáceres The new genomic variation DNA sequence differs across individuals much more than researchers had suspected through structural changes A huge amount of structural
Host Double Strand Break Repair Generates HIV-1 Strains Resistant to CRISPR/Cas9
 Host Double Strand Break Repair Generates HIV-1 Strains Resistant to CRISPR/Cas9 Kristine E. Yoder, a * and Ralf Bundschuh b a Department of Molecular Virology, Immunology and Medical Genetics, Center
Host Double Strand Break Repair Generates HIV-1 Strains Resistant to CRISPR/Cas9 Kristine E. Yoder, a * and Ralf Bundschuh b a Department of Molecular Virology, Immunology and Medical Genetics, Center
MRC-Holland MLPA. Description version 08; 30 March 2015
 SALSA MLPA probemix P351-C1 / P352-D1 PKD1-PKD2 P351-C1 lot C1-0914: as compared to the previous version B2 lot B2-0511 one target probe has been removed and three reference probes have been replaced.
SALSA MLPA probemix P351-C1 / P352-D1 PKD1-PKD2 P351-C1 lot C1-0914: as compared to the previous version B2 lot B2-0511 one target probe has been removed and three reference probes have been replaced.
Overview of the Expressway Cell-Free Expression Systems. Expressway Mini Cell-Free Expression System
 Overview of the Expressway Cell-Free Expression Systems The Expressway Cell-Free Expression Systems use an efficient coupled transcription and translation reaction to produce up to milligram quantities
Overview of the Expressway Cell-Free Expression Systems The Expressway Cell-Free Expression Systems use an efficient coupled transcription and translation reaction to produce up to milligram quantities
1) DNA unzips - hydrogen bonds between base pairs are broken by special enzymes.
 Biology 12 Cell Cycle To divide, a cell must complete several important tasks: it must grow, during which it performs protein synthesis (G1 phase) replicate its genetic material /DNA (S phase), and physically
Biology 12 Cell Cycle To divide, a cell must complete several important tasks: it must grow, during which it performs protein synthesis (G1 phase) replicate its genetic material /DNA (S phase), and physically
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi: 1.138/nature8645 Physical coverage (x haploid genomes) 11 6.4 4.9 6.9 6.7 4.4 5.9 9.1 7.6 125 Neither end mapped One end mapped Chimaeras Correct Reads (million ns) 1 75 5 25 HCC1187 HCC1395 HCC1599
doi: 1.138/nature8645 Physical coverage (x haploid genomes) 11 6.4 4.9 6.9 6.7 4.4 5.9 9.1 7.6 125 Neither end mapped One end mapped Chimaeras Correct Reads (million ns) 1 75 5 25 HCC1187 HCC1395 HCC1599
100 mm Sucrose. +Berberine +Quinine
 8 mm Sucrose Probability (%) 7 6 5 4 3 Wild-type Gr32a / 2 +Caffeine +Berberine +Quinine +Denatonium Supplementary Figure 1: Detection of sucrose and bitter compounds is not affected in Gr32a / flies.
8 mm Sucrose Probability (%) 7 6 5 4 3 Wild-type Gr32a / 2 +Caffeine +Berberine +Quinine +Denatonium Supplementary Figure 1: Detection of sucrose and bitter compounds is not affected in Gr32a / flies.
Problem Set 5 KEY
 2006 7.012 Problem Set 5 KEY ** Due before 5 PM on THURSDAY, November 9, 2006. ** Turn answers in to the box outside of 68-120. PLEASE WRITE YOUR ANSWERS ON THIS PRINTOUT. 1. You are studying the development
2006 7.012 Problem Set 5 KEY ** Due before 5 PM on THURSDAY, November 9, 2006. ** Turn answers in to the box outside of 68-120. PLEASE WRITE YOUR ANSWERS ON THIS PRINTOUT. 1. You are studying the development
Identification of Mutation(s) in. Associated with Neutralization Resistance. Miah Blomquist
 Identification of Mutation(s) in the HIV 1 gp41 Subunit Associated with Neutralization Resistance Miah Blomquist What is HIV 1? HIV-1 is an epidemic that affects over 34 million people worldwide. HIV-1
Identification of Mutation(s) in the HIV 1 gp41 Subunit Associated with Neutralization Resistance Miah Blomquist What is HIV 1? HIV-1 is an epidemic that affects over 34 million people worldwide. HIV-1
Class XII Chapter 5 Principles of Inheritance and Variation Biology
 Question 1: Mention the advantages of selecting pea plant for experiment by Mendel. Mendel selected pea plants to carry out his study on the inheritance of characters from parents to offspring. He selected
Question 1: Mention the advantages of selecting pea plant for experiment by Mendel. Mendel selected pea plants to carry out his study on the inheritance of characters from parents to offspring. He selected
SALSA MLPA probemix P241-D2 MODY mix 1 Lot D As compared to version D1 (lot D1-0911), one reference probe has been replaced.
 mix P241-D2 MODY mix 1 Lot D2-0413. As compared to version D1 (lot D1-0911), one reference has been replaced. Maturity-Onset Diabetes of the Young (MODY) is a distinct form of non insulin-dependent diabetes
mix P241-D2 MODY mix 1 Lot D2-0413. As compared to version D1 (lot D1-0911), one reference has been replaced. Maturity-Onset Diabetes of the Young (MODY) is a distinct form of non insulin-dependent diabetes
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION. Divergent TLR7/9 signaling and type I interferon production distinguish
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFOATION Divergent TLR7/9 signaling and type I interferon production distinguish pathogenic and non-pathogenic AIDS-virus infections Judith N. Mandl, Ashley P. Barry, Thomas H. Vanderford,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFOATION Divergent TLR7/9 signaling and type I interferon production distinguish pathogenic and non-pathogenic AIDS-virus infections Judith N. Mandl, Ashley P. Barry, Thomas H. Vanderford,
SALSA MLPA probemix P169-C2 HIRSCHSPRUNG-1 Lot C As compared to version C1 (lot C1-0612), the length of one probe has been adjusted.
 mix P169-C2 HIRSCHSPRUNG-1 Lot C2-0915. As compared to version C1 (lot C1-0612), the length of one has been adjusted. Hirschsprung disease (HSCR), or aganglionic megacolon, is a congenital disorder characterised
mix P169-C2 HIRSCHSPRUNG-1 Lot C2-0915. As compared to version C1 (lot C1-0612), the length of one has been adjusted. Hirschsprung disease (HSCR), or aganglionic megacolon, is a congenital disorder characterised
MRC-Holland MLPA. Description version 29;
 SALSA MLPA KIT P003-B1 MLH1/MSH2 Lot 1209, 0109. As compared to the previous lots 0307 and 1006, one MLH1 probe (exon 19) and four MSH2 probes have been replaced. In addition, one extra MSH2 exon 1 probe,
SALSA MLPA KIT P003-B1 MLH1/MSH2 Lot 1209, 0109. As compared to the previous lots 0307 and 1006, one MLH1 probe (exon 19) and four MSH2 probes have been replaced. In addition, one extra MSH2 exon 1 probe,
Soft Agar Assay. For each cell pool, 100,000 cells were resuspended in 0.35% (w/v)
 SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL AND METHODS Soft Agar Assay. For each cell pool, 100,000 cells were resuspended in 0.35% (w/v) top agar (LONZA, SeaKem LE Agarose cat.5004) and plated onto 0.5% (w/v) basal agar.
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL AND METHODS Soft Agar Assay. For each cell pool, 100,000 cells were resuspended in 0.35% (w/v) top agar (LONZA, SeaKem LE Agarose cat.5004) and plated onto 0.5% (w/v) basal agar.
Chromosomes, Mapping, and the Meiosis-Inheritance Connection. Chapter 13
 Chromosomes, Mapping, and the Meiosis-Inheritance Connection Chapter 13 Chromosome Theory Chromosomal theory of inheritance - developed in 1902 by Walter Sutton - proposed that genes are present on chromosomes
Chromosomes, Mapping, and the Meiosis-Inheritance Connection Chapter 13 Chromosome Theory Chromosomal theory of inheritance - developed in 1902 by Walter Sutton - proposed that genes are present on chromosomes
RNA Processing in Eukaryotes *
 OpenStax-CNX module: m44532 1 RNA Processing in Eukaryotes * OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this section, you
OpenStax-CNX module: m44532 1 RNA Processing in Eukaryotes * OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this section, you
RECAP (1)! In eukaryotes, large primary transcripts are processed to smaller, mature mrnas.! What was first evidence for this precursorproduct
 RECAP (1) In eukaryotes, large primary transcripts are processed to smaller, mature mrnas. What was first evidence for this precursorproduct relationship? DNA Observation: Nuclear RNA pool consists of
RECAP (1) In eukaryotes, large primary transcripts are processed to smaller, mature mrnas. What was first evidence for this precursorproduct relationship? DNA Observation: Nuclear RNA pool consists of
Studying The Role Of DNA Mismatch Repair In Brain Cancer Malignancy
 Kavya Puchhalapalli CALS Honors Project Report Spring 2017 Studying The Role Of DNA Mismatch Repair In Brain Cancer Malignancy Abstract Malignant brain tumors including medulloblastomas and primitive neuroectodermal
Kavya Puchhalapalli CALS Honors Project Report Spring 2017 Studying The Role Of DNA Mismatch Repair In Brain Cancer Malignancy Abstract Malignant brain tumors including medulloblastomas and primitive neuroectodermal
MRC-Holland MLPA. Description version 29; 31 July 2015
 SALSA MLPA probemix P081-C1/P082-C1 NF1 P081 Lot C1-0114. As compared to the previous B2 version (lot 0813 and 0912), 11 target probes are replaced or added, and 10 new reference probes are included. P082
SALSA MLPA probemix P081-C1/P082-C1 NF1 P081 Lot C1-0114. As compared to the previous B2 version (lot 0813 and 0912), 11 target probes are replaced or added, and 10 new reference probes are included. P082
Supporting Online Material for
 www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/1171320/dc1 Supporting Online Material for A Frazzled/DCC-Dependent Transcriptional Switch Regulates Midline Axon Guidance Long Yang, David S. Garbe, Greg J. Bashaw*
www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/1171320/dc1 Supporting Online Material for A Frazzled/DCC-Dependent Transcriptional Switch Regulates Midline Axon Guidance Long Yang, David S. Garbe, Greg J. Bashaw*
by Micah Johnson, Michael Turner, Elena Poiata, Stephanie Vadasz, Nathan Yardley, and Maria Moreno
 MCDB 201L: Molecular Biology Laboratory Professor: Maria Moreno By submitting this essay, I attest that it is my own work, completed in accordance with University regulations. Micah Johnson Abstract Cloning
MCDB 201L: Molecular Biology Laboratory Professor: Maria Moreno By submitting this essay, I attest that it is my own work, completed in accordance with University regulations. Micah Johnson Abstract Cloning
Analysis of Massively Parallel Sequencing Data Application of Illumina Sequencing to the Genetics of Human Cancers
 Analysis of Massively Parallel Sequencing Data Application of Illumina Sequencing to the Genetics of Human Cancers Gordon Blackshields Senior Bioinformatician Source BioScience 1 To Cancer Genetics Studies
Analysis of Massively Parallel Sequencing Data Application of Illumina Sequencing to the Genetics of Human Cancers Gordon Blackshields Senior Bioinformatician Source BioScience 1 To Cancer Genetics Studies
Template for Reporting Results of Monitoring Tests for Patients With Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia (BCR-ABL1+)
 Template for Reporting Results of Monitoring Tests for Patients With Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia (BCR-ABL1+) Version: CMLBiomarkers 1.0.0.2 Protocol Posting Date: June 2017 This biomarker template is
Template for Reporting Results of Monitoring Tests for Patients With Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia (BCR-ABL1+) Version: CMLBiomarkers 1.0.0.2 Protocol Posting Date: June 2017 This biomarker template is
Annotation of Drosophila mojavensis fosmid 8 Priya Srikanth Bio 434W
 Annotation of Drosophila mojavensis fosmid 8 Priya Srikanth Bio 434W 5.1.2007 Overview High-quality finished sequence is much more useful for research once it is annotated. Annotation is a fundamental
Annotation of Drosophila mojavensis fosmid 8 Priya Srikanth Bio 434W 5.1.2007 Overview High-quality finished sequence is much more useful for research once it is annotated. Annotation is a fundamental
Example: Distance in M.U. % Crossing Over Why? Double crossovers
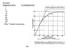 Example: Distance in M.U. % Crossing Over 1 5 10 15 50 80 100 107 Why? Double crossovers 232 .. A B. a b. 1. A fully heterozygous gray-bodied (b+), normal winged (vg+) female F 1 fruit fly crossed with
Example: Distance in M.U. % Crossing Over 1 5 10 15 50 80 100 107 Why? Double crossovers 232 .. A B. a b. 1. A fully heterozygous gray-bodied (b+), normal winged (vg+) female F 1 fruit fly crossed with
Phenylketonuria (PKU) the Biochemical Basis. Biol 405 Molecular Medicine
 Phenylketonuria (PKU) the Biochemical Basis Biol 405 Molecular Medicine PKU a history In 1934 Følling identified a clinical condition - imbecillitas phenylpyruvica. Mental retardation associated with this
Phenylketonuria (PKU) the Biochemical Basis Biol 405 Molecular Medicine PKU a history In 1934 Følling identified a clinical condition - imbecillitas phenylpyruvica. Mental retardation associated with this
Laboratory. Mendelian Genetics
 Laboratory 9 Mendelian Genetics Biology 171L FA17 Lab 9: Mendelian Genetics Student Learning Outcomes 1. Predict the phenotypic and genotypic ratios of a monohybrid cross. 2. Determine whether a gene is
Laboratory 9 Mendelian Genetics Biology 171L FA17 Lab 9: Mendelian Genetics Student Learning Outcomes 1. Predict the phenotypic and genotypic ratios of a monohybrid cross. 2. Determine whether a gene is
Conditional and reversible disruption of essential herpesvirus protein functions
 nature methods Conditional and reversible disruption of essential herpesvirus protein functions Mandy Glaß, Andreas Busche, Karen Wagner, Martin Messerle & Eva Maria Borst Supplementary figures and text:
nature methods Conditional and reversible disruption of essential herpesvirus protein functions Mandy Glaß, Andreas Busche, Karen Wagner, Martin Messerle & Eva Maria Borst Supplementary figures and text:
MODULE 4: SPLICING. Removal of introns from messenger RNA by splicing
 Last update: 05/10/2017 MODULE 4: SPLICING Lesson Plan: Title MEG LAAKSO Removal of introns from messenger RNA by splicing Objectives Identify splice donor and acceptor sites that are best supported by
Last update: 05/10/2017 MODULE 4: SPLICING Lesson Plan: Title MEG LAAKSO Removal of introns from messenger RNA by splicing Objectives Identify splice donor and acceptor sites that are best supported by
Genetic Variation Junior Science
 2018 Version Genetic Variation Junior Science http://img.publishthis.com/images/bookmarkimages/2015/05/d/5/c/d5cf017fb4f7e46e1c21b874472ea7d1_bookmarkimage_620x480_xlarge_original_1.jpg Sexual Reproduction
2018 Version Genetic Variation Junior Science http://img.publishthis.com/images/bookmarkimages/2015/05/d/5/c/d5cf017fb4f7e46e1c21b874472ea7d1_bookmarkimage_620x480_xlarge_original_1.jpg Sexual Reproduction
Lab 5: Testing Hypotheses about Patterns of Inheritance
 Lab 5: Testing Hypotheses about Patterns of Inheritance How do we talk about genetic information? Each cell in living organisms contains DNA. DNA is made of nucleotide subunits arranged in very long strands.
Lab 5: Testing Hypotheses about Patterns of Inheritance How do we talk about genetic information? Each cell in living organisms contains DNA. DNA is made of nucleotide subunits arranged in very long strands.
Supplementary Figure 1. SC35M polymerase activity in the presence of Bat or SC35M NP encoded from the phw2000 rescue plasmid.
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 Supplementary Figure 1. SC35M polymerase activity in the presence of Bat or SC35M NP encoded from the phw2000 rescue plasmid. HEK293T
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 Supplementary Figure 1. SC35M polymerase activity in the presence of Bat or SC35M NP encoded from the phw2000 rescue plasmid. HEK293T
CRISPR/Cas9 Enrichment and Long-read WGS for Structural Variant Discovery
 CRISPR/Cas9 Enrichment and Long-read WGS for Structural Variant Discovery PacBio CoLab Session October 20, 2017 For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostics procedures. Copyright 2017 by Pacific Biosciences
CRISPR/Cas9 Enrichment and Long-read WGS for Structural Variant Discovery PacBio CoLab Session October 20, 2017 For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostics procedures. Copyright 2017 by Pacific Biosciences
Mutations in the Caenorhabditis elegans U2AF Large Subunit UAF-1 Al= of a 3' Splice Site In Vivo
 Mutations in the Caenorhabditis elegans U2AF Large Subunit UAF-1 Al= of a 3' Splice Site In Vivo The MIT Faculty has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your
Mutations in the Caenorhabditis elegans U2AF Large Subunit UAF-1 Al= of a 3' Splice Site In Vivo The MIT Faculty has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your
Non-Mendelian inheritance
 Non-Mendelian inheritance Focus on Human Disorders Peter K. Rogan, Ph.D. Laboratory of Human Molecular Genetics Children s Mercy Hospital Schools of Medicine & Computer Science and Engineering University
Non-Mendelian inheritance Focus on Human Disorders Peter K. Rogan, Ph.D. Laboratory of Human Molecular Genetics Children s Mercy Hospital Schools of Medicine & Computer Science and Engineering University
MRC-Holland MLPA. Description version 07; 26 November 2015
 SALSA MLPA probemix P266-B1 CLCNKB Lot B1-0415, B1-0911. As compared to version A1 (lot A1-0908), one target probe for CLCNKB (exon 11) has been replaced. In addition, one reference probe has been replaced
SALSA MLPA probemix P266-B1 CLCNKB Lot B1-0415, B1-0911. As compared to version A1 (lot A1-0908), one target probe for CLCNKB (exon 11) has been replaced. In addition, one reference probe has been replaced
Structural Variation and Medical Genomics
 Structural Variation and Medical Genomics Andrew King Department of Biomedical Informatics July 8, 2014 You already know about small scale genetic mutations Single nucleotide polymorphism (SNPs) Deletions,
Structural Variation and Medical Genomics Andrew King Department of Biomedical Informatics July 8, 2014 You already know about small scale genetic mutations Single nucleotide polymorphism (SNPs) Deletions,
Polyomaviridae. Spring
 Polyomaviridae Spring 2002 331 Antibody Prevalence for BK & JC Viruses Spring 2002 332 Polyoma Viruses General characteristics Papovaviridae: PA - papilloma; PO - polyoma; VA - vacuolating agent a. 45nm
Polyomaviridae Spring 2002 331 Antibody Prevalence for BK & JC Viruses Spring 2002 332 Polyoma Viruses General characteristics Papovaviridae: PA - papilloma; PO - polyoma; VA - vacuolating agent a. 45nm
Ch 8 Practice Questions
 Ch 8 Practice Questions Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. What fraction of offspring of the cross Aa Aa is homozygous for the dominant allele?
Ch 8 Practice Questions Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. What fraction of offspring of the cross Aa Aa is homozygous for the dominant allele?
The Modern Genetics View
 Inheritance Mendelian Genetics The Modern Genetics View Alleles are versions of a gene Gene for flower color Alleles for purple or white flowers Two alleles per trait 2 chromosomes, each with 1 gene The
Inheritance Mendelian Genetics The Modern Genetics View Alleles are versions of a gene Gene for flower color Alleles for purple or white flowers Two alleles per trait 2 chromosomes, each with 1 gene The
Lecture 3-4. Identification of Positive Regulators downstream of SA
 Lecture 3-4 Identification of Positive Regulators downstream of SA Positive regulators between SA and resistance/pr Systemic resistance PR gene expression? SA Local infection Necrosis SA What could they
Lecture 3-4 Identification of Positive Regulators downstream of SA Positive regulators between SA and resistance/pr Systemic resistance PR gene expression? SA Local infection Necrosis SA What could they
MRC-Holland MLPA. Description version 30; 06 June 2017
 SALSA MLPA probemix P081-C1/P082-C1 NF1 P081 Lot C1-0517, C1-0114. As compared to the previous B2 version (lot B2-0813, B2-0912), 11 target probes are replaced or added, and 10 new reference probes are
SALSA MLPA probemix P081-C1/P082-C1 NF1 P081 Lot C1-0517, C1-0114. As compared to the previous B2 version (lot B2-0813, B2-0912), 11 target probes are replaced or added, and 10 new reference probes are
Principles of Inheritance and Variation
 Principles of Inheritance and Variation Question 1: Mention the advantages of selecting pea plant for experiment by Mendel. Answer Mendel selected pea plants to carry out his study on the inheritance of
Principles of Inheritance and Variation Question 1: Mention the advantages of selecting pea plant for experiment by Mendel. Answer Mendel selected pea plants to carry out his study on the inheritance of
Molecular Biology (BIOL 4320) Exam #2 May 3, 2004
 Molecular Biology (BIOL 4320) Exam #2 May 3, 2004 Name SS# This exam is worth a total of 100 points. The number of points each question is worth is shown in parentheses after the question number. Good
Molecular Biology (BIOL 4320) Exam #2 May 3, 2004 Name SS# This exam is worth a total of 100 points. The number of points each question is worth is shown in parentheses after the question number. Good
Introduction 1/3. The protagonist of our story: the prokaryotic ribosome
 Introduction 1/3 The protagonist of our story: the prokaryotic ribosome Introduction 2/3 The core functional domains of the ribosome (the peptidyl trasferase center and the decoding center) are composed
Introduction 1/3 The protagonist of our story: the prokaryotic ribosome Introduction 2/3 The core functional domains of the ribosome (the peptidyl trasferase center and the decoding center) are composed
Generating Spontaneous Copy Number Variants (CNVs) Jennifer Freeman Assistant Professor of Toxicology School of Health Sciences Purdue University
 Role of Chemical lexposure in Generating Spontaneous Copy Number Variants (CNVs) Jennifer Freeman Assistant Professor of Toxicology School of Health Sciences Purdue University CNV Discovery Reference Genetic
Role of Chemical lexposure in Generating Spontaneous Copy Number Variants (CNVs) Jennifer Freeman Assistant Professor of Toxicology School of Health Sciences Purdue University CNV Discovery Reference Genetic
Introduction retroposon
 17.1 - Introduction A retrovirus is an RNA virus able to convert its sequence into DNA by reverse transcription A retroposon (retrotransposon) is a transposon that mobilizes via an RNA form; the DNA element
17.1 - Introduction A retrovirus is an RNA virus able to convert its sequence into DNA by reverse transcription A retroposon (retrotransposon) is a transposon that mobilizes via an RNA form; the DNA element
a) SSR with core motif > 2 and repeats number >3. b) MNR with repeats number>5.
 1 2 APPENDIX Legends to figures 3 4 5 Figure A1: Distribution of perfect SSR along chromosome 1 of V. cholerae (El-Tor N191). a) SSR with core motif > 2 and repeats number >3. b) MNR with repeats number>5.
1 2 APPENDIX Legends to figures 3 4 5 Figure A1: Distribution of perfect SSR along chromosome 1 of V. cholerae (El-Tor N191). a) SSR with core motif > 2 and repeats number >3. b) MNR with repeats number>5.
iplex genotyping IDH1 and IDH2 assays utilized the following primer sets (forward and reverse primers along with extension primers).
 Supplementary Materials Supplementary Methods iplex genotyping IDH1 and IDH2 assays utilized the following primer sets (forward and reverse primers along with extension primers). IDH1 R132H and R132L Forward:
Supplementary Materials Supplementary Methods iplex genotyping IDH1 and IDH2 assays utilized the following primer sets (forward and reverse primers along with extension primers). IDH1 R132H and R132L Forward:
Supplementary Information. Transforming Insect Population Control with Precision Guided Sterile Males
 Supplementary Information Transforming Insect Population Control with Precision Guided Sterile Males Authors Affiliation Nikolay P. Kandul 1, Junru Liu 1, Hector M. Sanchez C. 2, Sean L. Wu 2, John M.
Supplementary Information Transforming Insect Population Control with Precision Guided Sterile Males Authors Affiliation Nikolay P. Kandul 1, Junru Liu 1, Hector M. Sanchez C. 2, Sean L. Wu 2, John M.
Muscular Dystrophy. Biol 405 Molecular Medicine
 Muscular Dystrophy Biol 405 Molecular Medicine Duchenne muscular dystrophy Duchenne muscular dystrophy is a neuromuscular disease that occurs in ~ 1/3,500 male births. The disease causes developmental
Muscular Dystrophy Biol 405 Molecular Medicine Duchenne muscular dystrophy Duchenne muscular dystrophy is a neuromuscular disease that occurs in ~ 1/3,500 male births. The disease causes developmental
Materials and Methods , The two-hybrid principle.
 The enzymatic activity of an unknown protein which cleaves the phosphodiester bond between the tyrosine residue of a viral protein and the 5 terminus of the picornavirus RNA Introduction Every day there
The enzymatic activity of an unknown protein which cleaves the phosphodiester bond between the tyrosine residue of a viral protein and the 5 terminus of the picornavirus RNA Introduction Every day there
SALSA MLPA probemix P315-B1 EGFR
 SALSA MLPA probemix P315-B1 EGFR Lot B1-0215 and B1-0112. As compared to the previous A1 version (lot 0208), two mutation-specific probes for the EGFR mutations L858R and T709M as well as one additional
SALSA MLPA probemix P315-B1 EGFR Lot B1-0215 and B1-0112. As compared to the previous A1 version (lot 0208), two mutation-specific probes for the EGFR mutations L858R and T709M as well as one additional
Insulin mrna to Protein Kit
 Insulin mrna to Protein Kit A 3DMD Paper BioInformatics and Mini-Toober Folding Activity Student Handout www.3dmoleculardesigns.com Insulin mrna to Protein Kit Contents Becoming Familiar with the Data...
Insulin mrna to Protein Kit A 3DMD Paper BioInformatics and Mini-Toober Folding Activity Student Handout www.3dmoleculardesigns.com Insulin mrna to Protein Kit Contents Becoming Familiar with the Data...
MRC-Holland MLPA. Description version 18; 09 September 2015
 SALSA MLPA probemix P090-A4 BRCA2 Lot A4-0715, A4-0714, A4-0314, A4-0813, A4-0712: Compared to lot A3-0710, the 88 and 96 nt control fragments have been replaced (QDX2). This product is identical to the
SALSA MLPA probemix P090-A4 BRCA2 Lot A4-0715, A4-0714, A4-0314, A4-0813, A4-0712: Compared to lot A3-0710, the 88 and 96 nt control fragments have been replaced (QDX2). This product is identical to the
The functional investigation of the interaction between TATA-associated factor 3 (TAF3) and p53 protein
 THESIS BOOK The functional investigation of the interaction between TATA-associated factor 3 (TAF3) and p53 protein Orsolya Buzás-Bereczki Supervisors: Dr. Éva Bálint Dr. Imre Miklós Boros University of
THESIS BOOK The functional investigation of the interaction between TATA-associated factor 3 (TAF3) and p53 protein Orsolya Buzás-Bereczki Supervisors: Dr. Éva Bálint Dr. Imre Miklós Boros University of
Computational Identification and Prediction of Tissue-Specific Alternative Splicing in H. Sapiens. Eric Van Nostrand CS229 Final Project
 Computational Identification and Prediction of Tissue-Specific Alternative Splicing in H. Sapiens. Eric Van Nostrand CS229 Final Project Introduction RNA splicing is a critical step in eukaryotic gene
Computational Identification and Prediction of Tissue-Specific Alternative Splicing in H. Sapiens. Eric Van Nostrand CS229 Final Project Introduction RNA splicing is a critical step in eukaryotic gene
Received 26 January 1996/Returned for modification 28 February 1996/Accepted 15 March 1996
 MOLECULAR AND CELLULAR BIOLOGY, June 1996, p. 3012 3022 Vol. 16, No. 6 0270-7306/96/$04.00 0 Copyright 1996, American Society for Microbiology Base Pairing at the 5 Splice Site with U1 Small Nuclear RNA
MOLECULAR AND CELLULAR BIOLOGY, June 1996, p. 3012 3022 Vol. 16, No. 6 0270-7306/96/$04.00 0 Copyright 1996, American Society for Microbiology Base Pairing at the 5 Splice Site with U1 Small Nuclear RNA
Analysis of individual differences in radiosensitivity using genome editing
 3 rd International Symposium on the System of Radiological Protection ICRP2015 Analysis of individual differences in radiosensitivity using genome editing Shinya Matsuura Department of Genetics and Cell
3 rd International Symposium on the System of Radiological Protection ICRP2015 Analysis of individual differences in radiosensitivity using genome editing Shinya Matsuura Department of Genetics and Cell
TITLE: A Mouse Model to Investigate the Role of DBC2 in Breast Cancer
 AD Award Number: W81XWH-04-1-0325 TITLE: A Mouse Model to Investigate the Role of DBC2 in Breast Cancer PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Valerie Boka CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: University of Texas Health Science
AD Award Number: W81XWH-04-1-0325 TITLE: A Mouse Model to Investigate the Role of DBC2 in Breast Cancer PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Valerie Boka CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: University of Texas Health Science
Abstract. Optimization strategy of Copy Number Variant calling using Multiplicom solutions APPLICATION NOTE. Introduction
 Optimization strategy of Copy Number Variant calling using Multiplicom solutions Michael Vyverman, PhD; Laura Standaert, PhD and Wouter Bossuyt, PhD Abstract Copy number variations (CNVs) represent a significant
Optimization strategy of Copy Number Variant calling using Multiplicom solutions Michael Vyverman, PhD; Laura Standaert, PhD and Wouter Bossuyt, PhD Abstract Copy number variations (CNVs) represent a significant
New: P077 BRCA2. This new probemix can be used to confirm results obtained with P045 BRCA2 probemix.
 SALSA MLPA KIT P045-B2 BRCA2/CHEK2 Lot 0410, 0609. As compared to version B1, four reference probes have been replaced and extra control fragments at 100 and 105 nt (X/Y specific) have been included. New:
SALSA MLPA KIT P045-B2 BRCA2/CHEK2 Lot 0410, 0609. As compared to version B1, four reference probes have been replaced and extra control fragments at 100 and 105 nt (X/Y specific) have been included. New:
Deep-Sequencing of HIV-1
 Deep-Sequencing of HIV-1 The quest for true variants Alexander Thielen, Martin Däumer 09.05.2015 Limitations of drug resistance testing by standard-sequencing Blood plasma RNA extraction RNA Reverse Transcription/
Deep-Sequencing of HIV-1 The quest for true variants Alexander Thielen, Martin Däumer 09.05.2015 Limitations of drug resistance testing by standard-sequencing Blood plasma RNA extraction RNA Reverse Transcription/
Figure S1. Generation of inducible PTEN deficient mice and the BMMCs (A) B6.129 Pten loxp/loxp mice were mated with B6.
 Figure S1. Generation of inducible PTEN deficient mice and the BMMCs (A) B6.129 Pten loxp/loxp mice were mated with B6.129-Gt(ROSA)26Sor tm1(cre/ert2)tyj /J mice. To induce deletion of the Pten locus,
Figure S1. Generation of inducible PTEN deficient mice and the BMMCs (A) B6.129 Pten loxp/loxp mice were mated with B6.129-Gt(ROSA)26Sor tm1(cre/ert2)tyj /J mice. To induce deletion of the Pten locus,
Supplementary Figure 1. Spitzoid Melanoma with PPFIBP1-MET fusion. (a) Histopathology (4x) shows a domed papule with melanocytes extending into the
 Supplementary Figure 1. Spitzoid Melanoma with PPFIBP1-MET fusion. (a) Histopathology (4x) shows a domed papule with melanocytes extending into the deep dermis. (b) The melanocytes demonstrate abundant
Supplementary Figure 1. Spitzoid Melanoma with PPFIBP1-MET fusion. (a) Histopathology (4x) shows a domed papule with melanocytes extending into the deep dermis. (b) The melanocytes demonstrate abundant
Section Chapter 14. Go to Section:
 Section 12-3 Chapter 14 Go to Section: Content Objectives Write these Down! I will be able to identify: The origin of genetic differences among organisms. The possible kinds of different mutations. The
Section 12-3 Chapter 14 Go to Section: Content Objectives Write these Down! I will be able to identify: The origin of genetic differences among organisms. The possible kinds of different mutations. The
Mutation Detection and CNV Analysis for Illumina Sequencing data from HaloPlex Target Enrichment Panels using NextGENe Software for Clinical Research
 Mutation Detection and CNV Analysis for Illumina Sequencing data from HaloPlex Target Enrichment Panels using NextGENe Software for Clinical Research Application Note Authors John McGuigan, Megan Manion,
Mutation Detection and CNV Analysis for Illumina Sequencing data from HaloPlex Target Enrichment Panels using NextGENe Software for Clinical Research Application Note Authors John McGuigan, Megan Manion,
DATA SHEET. Provided: 500 µl of 5.6 mm Tris HCl, 4.4 mm Tris base, 0.05% sodium azide 0.1 mm EDTA, 5 mg/liter calf thymus DNA.
 Viral Load DNA >> Standard PCR standard 0 Copies Catalog Number: 1122 Lot Number: 150298 Release Category: A Provided: 500 µl of 5.6 mm Tris HCl, 4.4 mm Tris base, 0.05% sodium azide 0.1 mm EDTA, 5 mg/liter
Viral Load DNA >> Standard PCR standard 0 Copies Catalog Number: 1122 Lot Number: 150298 Release Category: A Provided: 500 µl of 5.6 mm Tris HCl, 4.4 mm Tris base, 0.05% sodium azide 0.1 mm EDTA, 5 mg/liter
II. The effect of strain and IGF-1 gene transfer using SMGT techniques on some semen characteristics:-
 The experimental work of this study was carried out in poultry farm of the Department of Animal Production, Faculty of Agriculture, Benha University, Egypt with cooperation of Genetic Engineering and Biotechnology
The experimental work of this study was carried out in poultry farm of the Department of Animal Production, Faculty of Agriculture, Benha University, Egypt with cooperation of Genetic Engineering and Biotechnology
MODULE NO.14: Y-Chromosome Testing
 SUBJECT Paper No. and Title Module No. and Title Module Tag FORENSIC SIENCE PAPER No.13: DNA Forensics MODULE No.21: Y-Chromosome Testing FSC_P13_M21 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. Learning Outcome 2. Introduction:
SUBJECT Paper No. and Title Module No. and Title Module Tag FORENSIC SIENCE PAPER No.13: DNA Forensics MODULE No.21: Y-Chromosome Testing FSC_P13_M21 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. Learning Outcome 2. Introduction:
Introduction to Genetics
 Introduction to Genetics Table of contents Chromosome DNA Protein synthesis Mutation Genetic disorder Relationship between genes and cancer Genetic testing Technical concern 2 All living organisms consist
Introduction to Genetics Table of contents Chromosome DNA Protein synthesis Mutation Genetic disorder Relationship between genes and cancer Genetic testing Technical concern 2 All living organisms consist
Computational Systems Biology: Biology X
 Bud Mishra Room 1002, 715 Broadway, Courant Institute, NYU, New York, USA L#4:(October-0-4-2010) Cancer and Signals 1 2 1 2 Evidence in Favor Somatic mutations, Aneuploidy, Copy-number changes and LOH
Bud Mishra Room 1002, 715 Broadway, Courant Institute, NYU, New York, USA L#4:(October-0-4-2010) Cancer and Signals 1 2 1 2 Evidence in Favor Somatic mutations, Aneuploidy, Copy-number changes and LOH
SALSA MLPA probemix P241-D2 MODY mix 1 Lot D2-0716, D As compared to version D1 (lot D1-0911), one reference probe has been replaced.
 mix P241-D2 MODY mix 1 Lot D2-0716, D2-0413. As compared to version D1 (lot D1-0911), one reference has been replaced. Maturity-Onset Diabetes of the Young (MODY) is a distinct form of non insulin-dependent
mix P241-D2 MODY mix 1 Lot D2-0716, D2-0413. As compared to version D1 (lot D1-0911), one reference has been replaced. Maturity-Onset Diabetes of the Young (MODY) is a distinct form of non insulin-dependent
8 Suppression Analysis
 Genetic Techniques for Biological Research Corinne A. Michels Copyright q 2002 John Wiley & Sons, Ltd ISBNs: 0-471-89921-6 (Hardback); 0-470-84662-3 (Electronic) 8 Suppression Analysis OVERVIEW Suppression
Genetic Techniques for Biological Research Corinne A. Michels Copyright q 2002 John Wiley & Sons, Ltd ISBNs: 0-471-89921-6 (Hardback); 0-470-84662-3 (Electronic) 8 Suppression Analysis OVERVIEW Suppression
Bio 111 Study Guide Chapter 17 From Gene to Protein
 Bio 111 Study Guide Chapter 17 From Gene to Protein BEFORE CLASS: Reading: Read the introduction on p. 333, skip the beginning of Concept 17.1 from p. 334 to the bottom of the first column on p. 336, and
Bio 111 Study Guide Chapter 17 From Gene to Protein BEFORE CLASS: Reading: Read the introduction on p. 333, skip the beginning of Concept 17.1 from p. 334 to the bottom of the first column on p. 336, and
Course Title Form Hours subject
 Course Title Form Hours subject Types, and structure of chromosomes L 1 Histology Karyotyping and staining of human chromosomes L 2 Histology Chromosomal anomalies L 2 Histology Sex chromosomes L 1 Histology
Course Title Form Hours subject Types, and structure of chromosomes L 1 Histology Karyotyping and staining of human chromosomes L 2 Histology Chromosomal anomalies L 2 Histology Sex chromosomes L 1 Histology
Supplemental Data: Detailed Characteristics of Patients with MKRN3. Patient 1 was born after an uneventful pregnancy. She presented in our
 1 2 Supplemental Data: Detailed Characteristics of Patients with MKRN3 Mutations 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 Patient 1 was born after an uneventful pregnancy. She presented
1 2 Supplemental Data: Detailed Characteristics of Patients with MKRN3 Mutations 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 Patient 1 was born after an uneventful pregnancy. She presented
SALSA MLPA probemix P185-C2 Intersex Lot C2-1015: As compared to the previous version C1 (lot C1-0611), the lengths of four probes have been adjusted.
 mix P185-C2 Intersex Lot C2-1015: As compared to the previous version C1 (lot C1-0611), the lengths of four s have been adjusted. The sex-determining region on chromosome Y (SRY) is the most important
mix P185-C2 Intersex Lot C2-1015: As compared to the previous version C1 (lot C1-0611), the lengths of four s have been adjusted. The sex-determining region on chromosome Y (SRY) is the most important
Annotation of Chimp Chunk 2-10 Jerome M Molleston 5/4/2009
 Annotation of Chimp Chunk 2-10 Jerome M Molleston 5/4/2009 1 Abstract A stretch of chimpanzee DNA was annotated using tools including BLAST, BLAT, and Genscan. Analysis of Genscan predicted genes revealed
Annotation of Chimp Chunk 2-10 Jerome M Molleston 5/4/2009 1 Abstract A stretch of chimpanzee DNA was annotated using tools including BLAST, BLAT, and Genscan. Analysis of Genscan predicted genes revealed
Variations in Chromosome Structure & Function. Ch. 8
 Variations in Chromosome Structure & Function Ch. 8 1 INTRODUCTION! Genetic variation refers to differences between members of the same species or those of different species Allelic variations are due
Variations in Chromosome Structure & Function Ch. 8 1 INTRODUCTION! Genetic variation refers to differences between members of the same species or those of different species Allelic variations are due
Eukaryotic transcription (III)
 Eukaryotic transcription (III) 1. Chromosome and chromatin structure Chromatin, chromatid, and chromosome chromatin Genomes exist as chromatins before or after cell division (interphase) but as chromatids
Eukaryotic transcription (III) 1. Chromosome and chromatin structure Chromatin, chromatid, and chromosome chromatin Genomes exist as chromatins before or after cell division (interphase) but as chromatids
Figure 1: Transmission of Wing Shape & Body Color Alleles: F0 Mating. Figure 1.1: Transmission of Wing Shape & Body Color Alleles: Expected F1 Outcome
 I. Chromosomal Theory of Inheritance As early cytologists worked out the mechanism of cell division in the late 1800 s, they began to notice similarities in the behavior of BOTH chromosomes & Mendel s
I. Chromosomal Theory of Inheritance As early cytologists worked out the mechanism of cell division in the late 1800 s, they began to notice similarities in the behavior of BOTH chromosomes & Mendel s
Supplemental Figure 1. Genes showing ectopic H3K9 dimethylation in this study are DNA hypermethylated in Lister et al. study.
 mc mc mc mc SUP mc mc Supplemental Figure. Genes showing ectopic HK9 dimethylation in this study are DNA hypermethylated in Lister et al. study. Representative views of genes that gain HK9m marks in their
mc mc mc mc SUP mc mc Supplemental Figure. Genes showing ectopic HK9 dimethylation in this study are DNA hypermethylated in Lister et al. study. Representative views of genes that gain HK9m marks in their
Two. The Power of. Special offers on Thermo Scientific products:
 The Power of Two Special offers on Thermo Scientific products: Phusion High-Fidelity DNA Polymerases Phire Hot Start II DNA Polymerase Direct PCR Kits dntp Solutions PCR Cloning Kits FastRuler DNA Ladders
The Power of Two Special offers on Thermo Scientific products: Phusion High-Fidelity DNA Polymerases Phire Hot Start II DNA Polymerase Direct PCR Kits dntp Solutions PCR Cloning Kits FastRuler DNA Ladders
SALSA MLPA KIT P050-B2 CAH
 SALSA MLPA KIT P050-B2 CAH Lot 0510, 0909, 0408: Compared to lot 0107, extra control fragments have been added at 88, 96, 100 and 105 nt. The 274 nt probe gives a higher signal in lot 0510 compared to
SALSA MLPA KIT P050-B2 CAH Lot 0510, 0909, 0408: Compared to lot 0107, extra control fragments have been added at 88, 96, 100 and 105 nt. The 274 nt probe gives a higher signal in lot 0510 compared to
Primer DNA sequence (5 to 3 )
 Supplemental Table 1 Oligonucleotide primers used in the study Primer DNA sequence (5 to 3 ) Plasmodium falciparum 18s forward Plasmodium falciparum 18s reverse Plasmodium falciparum MSP1 forward Plasmodium
Supplemental Table 1 Oligonucleotide primers used in the study Primer DNA sequence (5 to 3 ) Plasmodium falciparum 18s forward Plasmodium falciparum 18s reverse Plasmodium falciparum MSP1 forward Plasmodium
Fine Mapping of a cis-acting Sequence Element in Yellow Fever Virus RNA That Is Required for RNA Replication and Cyclization
 JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, Feb. 2003, p. 2265 2270 Vol. 77, No. 3 0022-538X/03/$08.00 0 DOI: 10.1128/JVI.77.3.2265 2270.2003 Copyright 2003, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Fine Mapping
JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, Feb. 2003, p. 2265 2270 Vol. 77, No. 3 0022-538X/03/$08.00 0 DOI: 10.1128/JVI.77.3.2265 2270.2003 Copyright 2003, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Fine Mapping
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature10495 WWW.NATURE.COM/NATURE 1 2 WWW.NATURE.COM/NATURE WWW.NATURE.COM/NATURE 3 4 WWW.NATURE.COM/NATURE WWW.NATURE.COM/NATURE 5 6 WWW.NATURE.COM/NATURE WWW.NATURE.COM/NATURE 7 8 WWW.NATURE.COM/NATURE
doi:10.1038/nature10495 WWW.NATURE.COM/NATURE 1 2 WWW.NATURE.COM/NATURE WWW.NATURE.COM/NATURE 3 4 WWW.NATURE.COM/NATURE WWW.NATURE.COM/NATURE 5 6 WWW.NATURE.COM/NATURE WWW.NATURE.COM/NATURE 7 8 WWW.NATURE.COM/NATURE
MODULE 3: TRANSCRIPTION PART II
 MODULE 3: TRANSCRIPTION PART II Lesson Plan: Title S. CATHERINE SILVER KEY, CHIYEDZA SMALL Transcription Part II: What happens to the initial (premrna) transcript made by RNA pol II? Objectives Explain
MODULE 3: TRANSCRIPTION PART II Lesson Plan: Title S. CATHERINE SILVER KEY, CHIYEDZA SMALL Transcription Part II: What happens to the initial (premrna) transcript made by RNA pol II? Objectives Explain
