END OF SEM ANATOMY MASTER REVISION
|
|
|
- Gwenda Morton
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 CONTENTS: END OF SEM ANATOMY MASTER REVISION 1. KNEE & LEGS 2. ANKLE & FOOT 3. VERTEBRAL COLUMN 4. CERVICAL SPINE 5. THORACOLUMBAR SPINE & PELVIS 6. DIAPHRAGM, PELVIC FLOOR & ABDOMINALS KNEE KNEE JOINT COMPLEX TIBIOFEMORAL Joint (femoral condyles + tibial plateau) Hinge Joint = Predominantly Uniaxial (limited rotation) Great Stability in E w/ Screw Home Mechanism F/E along Sagittal Plane on Coronal Axis Mobility in F (allow foot clearance & optimal orientation of foot) Poor degree of interlocking joint surfaces (dependent on active & passive structures such as ligaments, menisci & muscles) Large Lever Arms (therefore, predisposed to injury due to long bones) Femoral Articular Surface > Tibial Articular Surface (due to differences in condyle size) *5 o of HE is critically important for knee function *Can t rotate tibia & fibula voluntarily *Recurvatum = hyperextension of kneecap Knee Alignment Q Angle (between axis of tibia & femur): Measured along ASIS Patella (centre)/ Tibial Tuberosity 14 o = Men 17 o = Women 5 o Genu Valgus: Tibia is laterally inclined in relation to femur; medial fem condyle extends slightly more distally. Alignment of the femoral condyles on the transverse plane determine the orientation of the F/ E axis of Knee Mechanical Axis of Lower Limb = 2-3 o Varus (tibial midline HOF) Shortens width of Base of Support to for better weight-bearing & gait Knee Tendon Attachment Semimembranosus Tendon attaches posteriorly to Tibial Medial Condyle, superior to Popliteus Sartorius, Gracilis & Semitendinosus (Medial Lateral) Oblique Popliteal Ligament blends in with Posterior Capsule Synovial Membrane Synovial surfaces surround all articular areas, capsule surrounds the entirety of joint An intracapsular extrasynovial space exists between menisci 1
2 Actively supported by: 1) Quad attachments 2) laterally by ITB 3) medially by Tibial Collateral Ligament 4) posteriorly reinforced by Oblique Popliteal ligament (restricts HE) 5) posterolaterally (pierced by popliteus) Tibial Meniscal Discs Circular fibrocartilage pieces that articular contact & congruency, compression stress & protect articular cartilage After total meniscectomy, contact areas ~75% & peak local contact stress ~235% Medial Menisci (MM) AP length w/ thicker posterior horn (as the primary coverage over tibial plateau, it bears a large portion of the articular stress). Thus, the Screw Home Mechanism IR to the MM during Knee E for weight-bearing LM are narrower, more mobile compared to MM which is anchored to TCL SCREW HOME Mechanism Tibiofemoral Joint initiates screw home mechanism by slightly rotates during a primary action to tighten its ligaments (especially ACL & PCL) for stability, a contact area w/ MM Flexion + LR Extension + MR 20 o F 0 o E In terminal extension, this mechanism locks up the knee for greater stability, apart from tightening ligaments, interlocking between the joints If tibia is not fixed on the floor, it will LR for the screw home mechanism, if foot is fixed on the ground it will then femur will MR after posteriorly sliding Popliteus locks TFJ w/ femur IR, to unlock the extended leg it must ER femur during F Femoral/Tibial Gliding During movement, the kneecap has two directions of movement, sliding (AP) & rolling (of either the tibia or femur), both directions will not happen purely but in conjunction *ACL/PCL tightens during flexion or gliding, pulling femur back into a slide backwards or forwards For tibial extension, tibia will slide & roll anteriorly For femoral extension, it will slide backwards but still roll anteriorly To prevent excessive knee F, the ACL will tighten, forcing the femur into an anterior slide PATELLOFEMORAL Joint Patellar glides upon Patella Groove on the Femur Leverage of Quads by altering its LOA & distance from axis (thus moment arm). Net pull towards HOF (in a slightly valgus direction) Provides protection to the exposed cartilage of femoral condyles in Knee F Distributes forces & pressure placed on the femur Friction of Quads Tendon as it will rub upon the fem condyles w/o Patella Patella is most inclined to dislocate laterally even w/ the VMO s medial pull resistance and the greater height of the lateral portion of the Patella Groove Patellectomy = Quads Moment Arm, Knee ROM, Anterior Instability & Loss of Trochlea Protection Patella glides distally permitted by the unfolding of the Suprapatellar Pouch Translations Glides distally on femur during Knee F 2
3 Glides medially during 0-30 o F then lateral during o F Rotations Laterally tilts during flexion Contact Area w/ increasing knee flexion, the patella moves proximally to contact area Patella Bursae & Spaces Bursae Suprapatellar Subcutaneous Prepatellar Subcutaneous Infrapatellar Deep Infrapatellar Infrapatellar Fat Semimembranosus Subsartorial (pes anserinus) Location Above patellar, deep to the patellar tendon Superficial to patellar Superficial to patellar tendon, below patellar Inferior to patellar, deep to patellar tendon Deep to Infrapatellar bursae Behind femorotibial joint On medial side of the tibia Fat Pad separates Quads Tendon from Femur ( moment arm) Articular Genus pulls Suprapatellar Bursae back from being pinched during Knee E Bursae promotes frictionless Knee movement, but pain sensitive and susceptible to inflammation Knee Movement Range Motion Range o Gait: o o Stairs: >110 o o Sitting: 93 o o Shoe Tying: 106 o Loading o Level Ground: 3x BW o Stairs: 4.25x BW Movement Range Flexion 140 o Hyperextension 5 o Accessory Movements AP Glide Medial/ Lateral Rotation Medial/ Lateral (Transverse) Glide ABD/ADD Superior Tibiofibular Joint Arthrodial (Plane) Joint 3
4 KNEE MUSCLE COMPLEMENT Action Muscles Extension Quads Flexion Hamstrings (weak contribution from gastro, soleus & sartorius) Internal Rotation Semitendinosus, Semimembranosus, Popliteus, Gracilis & Sartorius External Rotation Biceps Femoris & TFL *popliteus unlocks knee from screw mechanism as well as assisting the PCL w/ resisting anterior gliding Muscle Origin Insertion Innervation Function Anterior Compartment (Knee E) Rectus Femoris (deep to satorius) Vastus Medialis Vastus Intermedius (deep to RF) Vastus Lateralis AIIS Medial Lip of Linea Aspera & Intertrochanteric Line Anterior surface of femur Greater Trochanter & Lateral Lip of Linea Aspera Patellar via Quadriceps Tendon Femoral N (L2-4) Sartorius ASIS Pes Anserinus Femoral N (L2-3) Medial Compartment (Adduction) Adductor Longus (anterior) Adductor Brevis (superior) Adductor Magnus (posterior, largest) Gracilis Pectineus Superior Ramus of Pubis Pectineal Line & Inferior Pubic Ramus Inferior Ramus & Ischiopubic Ramus & Ischial Tuberosity Inferior Pubic Ramus & Pubic Symphysis Pecten Pubis (like superior pubic ramus) Posterior Compartment (Knee Flexion) Biceps Femoris *Long Head (left) *Short Head (right) Semitendinosus (lateral, more posterior to semimembranosus) Semimembranosus Long: Ischial Tuberosity Short: Lateral Lip of Linea Aspera Ischial Tuberosity *posterior thigh muscles are biarticular (crosses two joints) KNEE LIGAMENT STRUCTURES Linea Aspera Linea Aspera & Adductor Tubercle Obturator N (L2-4) Obturator N (L2-4) & Tibial N (L4) Knee E Hip F Knee E Hip F, ADD & LR Knee MR Hip ADD & F (Hip E 90 o F) Pes Anserinus Obturator N (L2-3) Hip ADD Pectineal Line Head of Fibula & Lateral Condyle of Tibia Pes Anserinus Medial Condyle of Tibia Femoral N (L2-3) & Obturator N (L3-4) Tibial N (L5-S2) Hip ADD, F & MR Knee F & LR Hip E (long head only) *Tibial ER Knee F & MR Hip E *Tibial IR Ligament Attachments Resists Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) Anterior Tibial Head Posteriorly Posterolateral Band (PLB): largest, tightest in E below Lateral Menisci Anteromedial Band (AMB): tightens in F Posterior Cruciate Ligament Posterior Tibial Head > Anteriorly (PCL) below Medial Menisci Anterior Gliding (during Tibial/ Femoral E) Medial Femoral Condyle Midline of Superficial (longer): Valgus Force (throughout Tibial (medial) Collateral Ligament Medial Tibia F) (TCL) Medial Femoral Condyle Posterior Edge of Medial Tibial Condyle Deep (shorter): Anterior Displacement of Tibia Anterolateral Ligament (ALL) Posterior Edge of Lateral Condyle Lateral Head of Tibia Tibial 30 o F + Anterolateral Stability Fibular (lateral) Collateral Ligament Posterior Edge of Lateral Condyle (FCL) Head of Fibula Varus Force 4
5 Posterior Tibiofibular Ligament (PTL) Inferior Posterior Tibia Fibula Stability of TFJ Oblique Popliteal Ligament (OPL) Lateral Femoral Epicondyle Medial Tibial Condyle Knee HE Transverse Ligament Connects Anterior Lateral & Medial Menisci Coronary Ligaments Inferior edges of LM & MM Knee Capsule Posterior Meniscofemoral Posterior Horn of LM Femur??? *TCL tends to be part of capsule while the FCL is more prominently outside the capsule Anterior Gliding of Anterior Menisci Horns (as they are somewhat mobile & being pinched by the femur OR tibia) Anchors four points onto the tibia ANTERIOR CRUCIATE LIGAMENT Resists anterior translation of tibia on femur Resists posterior translation of femur on tibia rotation stability Resists valgus forces terminal E (but not main restraint) 10 o IR & 30 o ER Injury Large valgus moment that creates excessive knee ABD & tibial ER Commonly caused by pivoting sports w/ females being 3-5x more likely to suffer from this injury ACL Deficiency Test: Lachman s Test 15 o knee F) & Anterior Drawer Test (@ 90 o knee F) done by gliding the tibia in an AP manner, lack of resistance = compromised ACL POSTERIOR CRUCIATE LIGAMENT Resists posterior translation of tibia on femur Resists anterior translation of femur on tibia Injury Throw against dashboard during car crash Hyperflexion or HE PCL Deficiency Test: Sag Test by placing the 90 o F, if there is a deficiency than the knee should have a slight backwards bend to it (meaning that the tibia is gliding posteriorly & the femur is anterior translating) 5
6 ANKLE ANKLE JOINT COMPLEX Stability & Mobility Demands Support of Entire Body Weight Control of Leg & Stabilisation over Foot Adjustment over irregular surfaces Elevation of Body Shock Absorption *function is dependent upon 3 intrinsic foot arches, ligament support & dynamic muscle contractions 3 Axes of Movement Dorsiflexion (30 0 )/ Plantarflexion ( ) only talocrucial joint (sagittal plane) ABD/ADD forefoot (transverse plane) Inversion/Eversion (40 o total ROM, may be more on one side than other) happens at subtalar joint (on coronal plane) Pronation (DF + Eversion + ABD)/ Supination (PF + Inversion + ADD) (triplanar movement, requires all three joints) Close-Packed Positions Ankle DF (end feel is firm) Tarsal Joints full inversion Metatarsophalangeal (MTP) extension Interphalangeal (IP) extension Force Transfer Largest distally & proximally, force transfer thru tibia Anterior Tibia under tension forces Posterior Tibia under compression forces 90% of Tibial Stress Fractures is located posteromedial o External Tibial Torsion Navicular Stress Fractures the central zone of force between the medial & intermediate cuneiform whereupon medial & lateral compressive forces are directed thru 1 st & 2 nd Ray, this can cause hypovascularity (lack of blood supply) FIBULA Muscle Attachment Talocrural Joint Stability Ligament Attachment *not a structural bone, only for the attachments of important active structures Regions of Foot Rearfoot (talus & calcaneal) Midfoot (navicular, cuboid, lateral, intermediate & medial cuneiform) Forefoot (phalanges) 1 st, 2 nd & 3 rd Ray: corresponding cuneiform w/ phalange 4 th & 5 th Ray: just 4 th & 5 th phalange *2 nd ray is least mobile while 1 st ray provides stable medial side for push-off during gait 6
7 Tendons 2 sesamoid bones in tendons of FHB under 1 st MTP prevents weightbearing from compressing the tendon & aligns tendon fibularis tendon sulcus on lateral calcaneus facilitates passing of the fibularis tendons DISTAL TIBIOFIBULAR Joint (DTFJ) Fibrous Syndesmosis Joint Stability of Distal Tibiofibular Joint is crucial for the stability of the Talocrural Joint Consists of: o Anterior Tibiofibular Ligament (ATL) o Posterior Tibiofibular Ligament (PTL) o Interosseous Membrane (IOM) TALOCRUCAL Joint Synovial Hinge Widest part of the talus firmly fits into the mortise (inverted cup formed by the tibia & fibular) in DF, if ER of the foot is experienced the talus s widest side is angled & jammed into the mortise, possibly causing separation of the distal fibula & tibia OR tearing anterior tibiofibular ligament OR fractures fibula OR fractures at the corners of the talar dome DF is the close-packed position of the talocrural joint, providing most stability In PF, the talus s narrow part is moved into the mortise SUBTALAR (Talocalcaneal) Joint (STJ) 3 articular facets between talus & calcaneus, vital for supination & pronation Translates movements of the foot to the leg, i.e. foot pronation = tibial IR Inclined ~45 o anterior to posterior, slightly medial to the long axis of the foot Transverse Tarsal Joint = Talonavicular & Calcaneocuboid forms joint between rearfoot & midfoot Calcaneocuboid Saddle Joint (Convex Debate between function Talonavicular Concave)/ Plane Joint of joint & its actual range Talocalcaneonavicular Ball & Socket Joint *rest are plane joint* Arches of the Foot - Medial Longitudinal Arch (stabilised by fibularis longus, abductor hallucis, TA & TP) - Lateral Longitudinal Arch (stabilised by fibularis brevis) - Transverse Arch *arches serve as shock absorbers & energy returners (during gait) *arches protect the blood vessels, neural & musculoskeletal structures underneath the foot during weight-bearing *the medial arch can be tested w/ the Navicular Drop Test, comparing the differences in height between the arch and the floor when load is placed on the foot Arch Medial Arch Lateral Arch Transverse Arch Muscular Support - TA, TP, FHL, FDL & Fibularis Longus, - Fibularis Longus & Brevis, FDL - Fibularis Longus, TP & Adductor Hallucis Plantar Aponeurosis, Long & Short Plantar Ligament + Spring Ligament (for medial arch) ANKLE MUSCLE COMPLEMENT Action Muscles Inversion TA/ TA Eversion FB & FL Dorsiflexion TA/ EHL & ED Plantarflexion Triceps Surae (Gastro, Soleus, Popliteus, Plantaris) 7
8 Muscle Origin Insertion Innervation Action Anterior Compartment (DF & Inversion) Tibialis Anterior Extensor Hallucis Longus Extensor Digitorum Longus Lateral Tibia Condyle Fibula & Interosseous Membrane Lateral Tibia Condyle + Interosseous Membrane Posterior Compartment (PF & Knee Flexion) Medial Cuneiform & 1 st MT Base of Distal Phalanx of 1 th Digit Distal Phalanges of 2 nd -5 th Digit Deep Fibular N (L4-5) Deep Fibular N (L5-S1) DF (agonist) Midfoot Inversion (contributes) Popliteus Lateral Femoral Condyle Posterior Tibia Tibial N (L4-S1) Knee MR & F Tibialis Posterior Gastrocnemius Soleus (deep to plantaris) Plantaris (deep to Gastrocnemius) Flexor Digitorum Longus Flexor Hallucis Longus Lateral Compartment (Eversion) Fibularis Brevis Fibularis Longus Intrinsic Foot (supports arches) Extensor Hallucis Brevis (medial to EDB) Extensor Digitorum Brevis Flexor Digitorum Brevis Flexor Hallucis Brevis Flexor Digiti Minimi Brevis Abductor Hallucis Adductor Hallucis Flexor Digiti Minimi Abductor Digiti Minimi (lateral to FDB) Lumbricals Posterior Interosseous Membrane Lateral & Medial Femoral Condyles Posterior Head of Fibula Posterior Lateral Femoral Condyle Posterior Tibia Interosseous Membrane & Posterior of Fibula Lateral Fibula Superolateral surface of Calcaneus Navicular Tuberosity, All Cuneiforms & 2 nd -4 th MT Calcaneal Tendon (Archimedes tendon) Plantar 2 nd -5 th DP Base of Distal 1 st Phalanx 5 th MT Tuberosity Base of 1 st MT (wraps underneath foot) Dorsal 1 st MTP Dorsal 2 nd -4 th PIP Tibial N (L4-5) Tibial N (S1-2) Tibial N (S2-3) Superficial Fibular N (L5-S2) Deep Fibular N (L5-S1) PF Inversion (agonist) & PF (slight contribution) PF (agonist) & Inversion (small contribution as it is aligned medially) (Knee F only for Gastro) PF (agonist) Eversion (agonists) PF (small contribution) 1 st Ray E 2 nd -4 th Ray E Calcaneal Tuberosity & Plantar Aponeurosis Plantar 2 nd -4 th MP 2 nd -5 th Ray F Plantar Cuboid, Lateral Cuneiform & medial 1st Plantar 1 st PP 1 Medial Plantar N Ray F MTT (S2-3) Base of 5 th MT 5 th PP 5 th Ray F Medial Calcaneal Tuberosity Oblique: Base of MT Transverse: 2 nd -4 th MTP Plantar 5th MMT Calcaneal Tuberosity & Plantar Aponeurosis Medial side of FDL Tendons Dorsal 1 st MTP Lateral Base of 1 st PP Plantar 5th MTP Medial side of MTP Lateral Plantar N (S2-3) Medial & Lateral Plantar N (S3) 1 st Ray ABD 1 st Ray ADD 5th Ray F 5th Ray ABD IP E while MTP F Assists FDL w/ F (also Calcaneal Tuberosity & Quadratus Plantae Tendon of FDL realigns angle of FDP Long Plantar Ligament pull) Lateral Plantar N Plantar Interossei Medial side of 3 rd -5 th MT Medial Side of 3 rd -5 th PP ADD 2 (S2-3) nd 4 th Ray Dorsal Interossei Between all MT Both sides of 2 nd PP, but only on lateral side of 3 rd & 4 th PP ABD 2 nd 4 th Ray 8
9 9
10 ANKLE LIGAMENT STRUCTURES Ligament Attachments Resists Fibular Ligaments Anterior Tibiofibular Ligament (ATL) Distal Anterior Tibia Distal Anterior Fibula (consists of 2 separate superior & inferior bands) Separation & Stability of TFJ Distal Posterior Tibia Distal Posterior Posterior Tibiofibular Ligament (PTL) Fibula Interosseous Membrane (IOM) Within the Tibiofibular Joint Anterior Talofibular Ligament (ATFL) Lateral Posterior Lateral Talus Posterior Distal Fibula Posterior Talofibular Ligament (PTFL) Lateral Anterior Talus Anterior Distal TCJ Stability & Excessive Inversion Fibula Calcaneofibular Ligament (CFL) Lateral Calcaneus Apex of Fibula Intrinsic Ligaments Flexor Retinaculum Medial Malleolus Calcaneus Creates the Tarsal Tunnel, anchors flexor & TP tendons Talocalcaneal Interosseous Lateral Anterior Calcaneus Lateral Anterior Talus (w/ sinus tarsi) Talar Calcaneal Stability Dorsal Calcaneonavicular Dorsal Calcaneus Posterior Lateral Bifurcated Ligaments Navicular Calcaneus Navicular Stability Dorsal Calcaneocuboid Dorsal Calcaneus Cuboid (x3 bands) Calcaneus Cuboid Stability Cervical Ligament Calcaneus Talus (much like CFL but Resists Inversion & Stability of Calcaneus/ anterior) Talus Long Plantar Ligament Base of 4 th & 5 th MT Plantar Calcaneus Short Plantar Ligament Plantar Lateral Cuneiform Plantar Maintains Lateral Arch Calcaneus Plantar Calcaneonavicular (Spring) Ligament Plantar MTP Capsules Plantar Calcaneus (medial side) Stores energy during gait & releases energy as a spring during push-off phase 2x tensile strength of plantar ligaments, Plantar Fascia Plantar PIP Plantar Medial Calcaneal rich in proprioceptors, maintains rigid foot Tuberosity during step-off in gait (during MTP HE & PF pushes calcaneal tuberosity posteriorly Tibial Ligaments (Deltoid Ligaments) Anterior Tibiotalar Ligament (ATTL) Anterior Distal Tibia Anterior Talar Posterior Tibiotalar Ligament (PTTL) Posterior Distal Tibia Posterior Talar Tibiocalcaneal (& Tibiospring) Excessive Inversion Medial Distal Tibia Medial Calcaneal Ligament Tibionavicular Ligament Distal Tibia Dorsal Navicular 10
11 Ankle Osteology Subtalar joint is formed by posterior, lateral & anterior talar articular surfaces between the calcaneus & talus Sustentaculum Tali is a shelf between the lateral & posterior articular surfaces Tarsi Sinus is the cavity created between the calcaneus & talus 11
Clarification of Terms
 Clarification of Terms The plantar aspect of the foot refers to the role or its bottom The dorsal aspect refers to the top or its superior portion The ankle and foot perform three main functions: 1. shock
Clarification of Terms The plantar aspect of the foot refers to the role or its bottom The dorsal aspect refers to the top or its superior portion The ankle and foot perform three main functions: 1. shock
The Dance Hall by Vincent van Gogh,1888
 The Dance Hall by Vincent van Gogh,1888 Articulations of the pelvic girdle Lumbosacral joints, sacroiliac joints & pubic symphysis The remaining joints of the lower limb Hip joint Knee joint Tibiofibular
The Dance Hall by Vincent van Gogh,1888 Articulations of the pelvic girdle Lumbosacral joints, sacroiliac joints & pubic symphysis The remaining joints of the lower limb Hip joint Knee joint Tibiofibular
5.1 Identify, describe the attachments of and deduce the actions of the muscles of the thigh:
 5.1 Identify, describe the attachments of and deduce the actions of the muscles of the thigh: Anterior group Proximal attachment Distal attachment Sartorius ASIS» Upper part of shaft tibia (middle surface)»
5.1 Identify, describe the attachments of and deduce the actions of the muscles of the thigh: Anterior group Proximal attachment Distal attachment Sartorius ASIS» Upper part of shaft tibia (middle surface)»
Pelvic cavity. Gross anatomy of the lower limb. Walking. Sándor Katz M.D.,Ph.D.
 Pelvic cavity. Gross anatomy of the lower limb. Walking. Sándor Katz M.D.,Ph.D. Lower limb Pelvic girdle Free lower extremity Hip bone Definitive fusion of the Y- shaped growth plate occurs 16th -18th
Pelvic cavity. Gross anatomy of the lower limb. Walking. Sándor Katz M.D.,Ph.D. Lower limb Pelvic girdle Free lower extremity Hip bone Definitive fusion of the Y- shaped growth plate occurs 16th -18th
Joints of the Lower Limb II
 Joints of the Lower Limb II Lecture Objectives Describe the components of the knee and ankle joint. List the ligaments associated with these joints and their attachments. List the muscles acting on these
Joints of the Lower Limb II Lecture Objectives Describe the components of the knee and ankle joint. List the ligaments associated with these joints and their attachments. List the muscles acting on these
Topic 7: Hip and pelvis. Parts of the hip. Parts of the femur
 Topic 7: Hip and pelvis Parts of the hip Parts of the femur Classifying the hip joint Ball and socket Synovial Multiaxial Movements of the hip: Abduction/adduction Flexion/extension Medial/lateral rotation
Topic 7: Hip and pelvis Parts of the hip Parts of the femur Classifying the hip joint Ball and socket Synovial Multiaxial Movements of the hip: Abduction/adduction Flexion/extension Medial/lateral rotation
Anatomy of the lower limb
 Anatomy of the lower limb 1. Bones of the lower limb Pelvis Hip bone/coxal bone Acetabulum o Acetabular margin o Acetabular fossa o Acetabular notch o Lunate surface Ischiopubic ramus Obturator foramen
Anatomy of the lower limb 1. Bones of the lower limb Pelvis Hip bone/coxal bone Acetabulum o Acetabular margin o Acetabular fossa o Acetabular notch o Lunate surface Ischiopubic ramus Obturator foramen
CHAPTER 8: THE BIOMECHANICS OF THE HUMAN LOWER EXTREMITY
 CHAPTER 8: THE BIOMECHANICS OF THE HUMAN LOWER EXTREMITY _ 1. The hip joint is the articulation between the and the. A. femur, acetabulum B. femur, spine C. femur, tibia _ 2. Which of the following is
CHAPTER 8: THE BIOMECHANICS OF THE HUMAN LOWER EXTREMITY _ 1. The hip joint is the articulation between the and the. A. femur, acetabulum B. femur, spine C. femur, tibia _ 2. Which of the following is
The Lower Limb VII: The Ankle & Foot. Anatomy RHS 241 Lecture 7 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa
 The Lower Limb VII: The Ankle & Foot Anatomy RHS 241 Lecture 7 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa Ankle joint Synovial, hinge joint Allow movement of the foot in the sagittal plane only (1 degree of freedom): dorsiflexion:
The Lower Limb VII: The Ankle & Foot Anatomy RHS 241 Lecture 7 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa Ankle joint Synovial, hinge joint Allow movement of the foot in the sagittal plane only (1 degree of freedom): dorsiflexion:
BONES JOINTS MUSCLES OF THE LOWER LIMB
 BONES JOINTS MUSCLES OF THE LOWER LIMB LOWER LIMB: BONES LOWER LIMB GLUTEAL REGION consists of 6 major segments: FEMORAL REGION (THIGH) KNEE REGION LEG REGION TALOCRURAL REGION (ANKLE) FOOT REGION LOWER
BONES JOINTS MUSCLES OF THE LOWER LIMB LOWER LIMB: BONES LOWER LIMB GLUTEAL REGION consists of 6 major segments: FEMORAL REGION (THIGH) KNEE REGION LEG REGION TALOCRURAL REGION (ANKLE) FOOT REGION LOWER
Copyright 2004, Yoshiyuki Shiratori. All right reserved.
 Ankle and Leg Evaluation 1. History Chief Complaint: A. What happened? B. Is it a sharp or dull pain? C. How long have you had the pain? D. Can you pinpoint the pain? E. Do you have any numbness or tingling?
Ankle and Leg Evaluation 1. History Chief Complaint: A. What happened? B. Is it a sharp or dull pain? C. How long have you had the pain? D. Can you pinpoint the pain? E. Do you have any numbness or tingling?
To describe he knee joint, ligaments, structure & To list the main features of other lower limb joints
 To describe he knee joint, ligaments, structure & neurovascular supply To demonstrate the ankle joint anatomy To list the main features of other lower limb joints To list main groups of lymph nodes in
To describe he knee joint, ligaments, structure & neurovascular supply To demonstrate the ankle joint anatomy To list the main features of other lower limb joints To list main groups of lymph nodes in
Anatomy of Foot and Ankle
 Anatomy of Foot and Ankle Surface anatomy of the ankle & foot Surface anatomy of the ankle & foot Medial orientation point medial malleous sustentaculum tali tuberosity of navicular TA muscle TP muscle
Anatomy of Foot and Ankle Surface anatomy of the ankle & foot Surface anatomy of the ankle & foot Medial orientation point medial malleous sustentaculum tali tuberosity of navicular TA muscle TP muscle
Muscles of Lesson Five. Muscular Nomenclature and Kinesiology - Two. Muscles of Lesson Five, cont. Chapter 16
 Chapter 16 Muscular Nomenclature and Kinesiology - Two Lessons 5-6 Muscles of Lesson Five Iliopsoas (psoas major, iliacus) Hip outward rotators (piriformis, gemellus superior, gemellus inferior, obturator
Chapter 16 Muscular Nomenclature and Kinesiology - Two Lessons 5-6 Muscles of Lesson Five Iliopsoas (psoas major, iliacus) Hip outward rotators (piriformis, gemellus superior, gemellus inferior, obturator
Main Menu. Ankle and Foot Joints click here. The Power is in Your Hands
 1 The Ankle and Foot Joints click here Main Menu Copyright HandsOn Therapy Schools 2009 K.8 http://www.handsonlineeducation.com/classes/k8/k8entry.htm[3/27/18, 1:40:03 PM] Ankle and Foot Joint 26 bones
1 The Ankle and Foot Joints click here Main Menu Copyright HandsOn Therapy Schools 2009 K.8 http://www.handsonlineeducation.com/classes/k8/k8entry.htm[3/27/18, 1:40:03 PM] Ankle and Foot Joint 26 bones
The Muscular System. Chapter 10 Part D. PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Karen Dunbar Kareiva Ivy Tech Community College
 Chapter 10 Part D The Muscular System Annie Leibovitz/Contact Press Images PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Karen Dunbar Kareiva Ivy Tech Community College Table 10.14: Muscles Crossing the Hip and
Chapter 10 Part D The Muscular System Annie Leibovitz/Contact Press Images PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Karen Dunbar Kareiva Ivy Tech Community College Table 10.14: Muscles Crossing the Hip and
Anatomage Table Instructors Guide- Lower Limb
 The Lower Limb Anatomage Table Instructors Guide- Lower Limb Table of Contents Lower Limb 1- The Skeletal System...3 1: Hip Bone...3 2: Hip Joint and Femur...4 3: Patella and Knee Joint...7 4: Tibia, Fibula,
The Lower Limb Anatomage Table Instructors Guide- Lower Limb Table of Contents Lower Limb 1- The Skeletal System...3 1: Hip Bone...3 2: Hip Joint and Femur...4 3: Patella and Knee Joint...7 4: Tibia, Fibula,
Myology of the Knee. PTA 105 Kinesiology
 Myology of the Knee PTA 105 Kinesiology Objectives Describe the planes of motion and axes of rotation of the knee joint Visualize the origins and insertions of the muscles about the knee List the innervations
Myology of the Knee PTA 105 Kinesiology Objectives Describe the planes of motion and axes of rotation of the knee joint Visualize the origins and insertions of the muscles about the knee List the innervations
The Knee. Clarification of Terms. Osteology of the Knee 7/28/2013. The knee consists of: The tibiofemoral joint Patellofemoral joint
 The Knee Clarification of Terms The knee consists of: The tibiofemoral joint Patellofemoral joint Mansfield, p273 Osteology of the Knee Distal Femur Proximal tibia and fibula Patella 1 Osteology of the
The Knee Clarification of Terms The knee consists of: The tibiofemoral joint Patellofemoral joint Mansfield, p273 Osteology of the Knee Distal Femur Proximal tibia and fibula Patella 1 Osteology of the
The Knee. Prof. Oluwadiya Kehinde
 The Knee Prof. Oluwadiya Kehinde www.oluwadiya.sitesled.com The Knee: Introduction 3 bones: femur, tibia and patella 2 separate joints: tibiofemoral and patellofemoral. Function: i. Primarily a hinge joint,
The Knee Prof. Oluwadiya Kehinde www.oluwadiya.sitesled.com The Knee: Introduction 3 bones: femur, tibia and patella 2 separate joints: tibiofemoral and patellofemoral. Function: i. Primarily a hinge joint,
Pelvic Girdle
 ARTICULATIONS OF LOWER EXTREMITY Pages 429-437 Pelvic Girdle formed by connection of the hip bones and the sacrum Sacroiliac Joints compound joints synovial joint - anterior, between the auricular surfaces
ARTICULATIONS OF LOWER EXTREMITY Pages 429-437 Pelvic Girdle formed by connection of the hip bones and the sacrum Sacroiliac Joints compound joints synovial joint - anterior, between the auricular surfaces
Human Anatomy Biology 351
 Human Anatomy Biology 351 Lower Limb Please place your name on the back of the last page of this exam. You must answer all questions on this exam. Because statistics demonstrate that, on average, between
Human Anatomy Biology 351 Lower Limb Please place your name on the back of the last page of this exam. You must answer all questions on this exam. Because statistics demonstrate that, on average, between
lesser trochanter of femur lesser trochanter of femur iliotibial tract (connective tissue) medial surface of proximal tibia
 LOWER LIMB MUSCLES OF THE APPENDICULAR SKELETON The muscles that act on the lower limb fall into three groups: those that move the thigh, those that move the lower leg, and those that move the ankle, foot,
LOWER LIMB MUSCLES OF THE APPENDICULAR SKELETON The muscles that act on the lower limb fall into three groups: those that move the thigh, those that move the lower leg, and those that move the ankle, foot,
The Knee. Tibio-Femoral
 The Knee Tibio-Femoral Osteology Distal Femur with Proximal Tibia Largest Joint Cavity in the Body A modified hinge joint with significant passive rotation Technically, one degree of freedom (Flexion/Extension)
The Knee Tibio-Femoral Osteology Distal Femur with Proximal Tibia Largest Joint Cavity in the Body A modified hinge joint with significant passive rotation Technically, one degree of freedom (Flexion/Extension)
Joints and muscles of the foot. Architecture of the foot. Sándor Katz M.D.,Ph.D.
 Joints and muscles of the foot. Architecture of the foot. Sándor Katz M.D.,Ph.D. Ankle (talocrural) joint type: hinge Talocrural joint - medial collateral ligament Medial collateral = deltoid ligament
Joints and muscles of the foot. Architecture of the foot. Sándor Katz M.D.,Ph.D. Ankle (talocrural) joint type: hinge Talocrural joint - medial collateral ligament Medial collateral = deltoid ligament
The Hay is in the Barn
 Anatomy 1 Practical 1 Review Made by Forrest Allen (nerd) Edited by TJ Williamson (not nerd) The Hay is in the Barn 2019 Thunderbringers Too much to handle https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=glii-kaza d8
Anatomy 1 Practical 1 Review Made by Forrest Allen (nerd) Edited by TJ Williamson (not nerd) The Hay is in the Barn 2019 Thunderbringers Too much to handle https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=glii-kaza d8
Introduction. The primary function of the ankle and foot is to absorb shock and impart thrust to the body during walking.
 The ankle 1 Introduction The primary function of the ankle and foot is to absorb shock and impart thrust to the body during walking. OSTEOLOGRY The term ankle refers primarily to the talocrural joint,
The ankle 1 Introduction The primary function of the ankle and foot is to absorb shock and impart thrust to the body during walking. OSTEOLOGRY The term ankle refers primarily to the talocrural joint,
The Lower Limb II. Anatomy RHS 241 Lecture 3 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa
 The Lower Limb II Anatomy RHS 241 Lecture 3 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa Tibia The larger & medial bone of the leg Functions: Attachment of muscles Transfer of weight from femur to skeleton of the foot Articulations
The Lower Limb II Anatomy RHS 241 Lecture 3 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa Tibia The larger & medial bone of the leg Functions: Attachment of muscles Transfer of weight from femur to skeleton of the foot Articulations
BLUE SKY SCHOOL OF PROFESSIONAL MASSAGE AND THERAPEUTIC BODYWORK Musculoskeletal Anatomy & Kinesiology KNEE & ANKLE MUSCLES
 BLUE SKY SCHOOL OF PROFESSIONAL MASSAGE AND THERAPEUTIC BODYWORK Musculoskeletal Anatomy & Kinesiology KNEE & ANKLE MUSCLES MSAK201-I Session 3 1) REVIEW a) THIGH, LEG, ANKLE & FOOT i) Tibia Medial Malleolus
BLUE SKY SCHOOL OF PROFESSIONAL MASSAGE AND THERAPEUTIC BODYWORK Musculoskeletal Anatomy & Kinesiology KNEE & ANKLE MUSCLES MSAK201-I Session 3 1) REVIEW a) THIGH, LEG, ANKLE & FOOT i) Tibia Medial Malleolus
DISSECTION SCHEDULE. Session I - Hip (Front) & Thigh (Superficial)
 DISSECTION SCHEDULE Session I - Hip (Front) & Thigh (Superficial) Surface anatomy Inguinal region Gluteal region Thigh Leg Foot bones Hip bone Femur Superficial fascia Great saphenous vein Superficial
DISSECTION SCHEDULE Session I - Hip (Front) & Thigh (Superficial) Surface anatomy Inguinal region Gluteal region Thigh Leg Foot bones Hip bone Femur Superficial fascia Great saphenous vein Superficial
Anatomy & Physiology. Muscles of the Lower Limbs.
 Anatomy & Physiology Muscles of the Lower Limbs http://www.ishapeup.com/musclecharts.html Muscles of the Lower Limbs Among the strongest muscles in the body. Because pelvic girdle is composed of heavy,
Anatomy & Physiology Muscles of the Lower Limbs http://www.ishapeup.com/musclecharts.html Muscles of the Lower Limbs Among the strongest muscles in the body. Because pelvic girdle is composed of heavy,
Muscles of the lower extremities. Dr. Nabil khouri MD, MSc, Ph.D
 Muscles of the lower extremities Dr. Nabil khouri MD, MSc, Ph.D Posterior leg Popliteal fossa Boundaries Biceps femoris (superior-lateral) Semitendinosis and semimembranosis (superior-medial) Gastrocnemius
Muscles of the lower extremities Dr. Nabil khouri MD, MSc, Ph.D Posterior leg Popliteal fossa Boundaries Biceps femoris (superior-lateral) Semitendinosis and semimembranosis (superior-medial) Gastrocnemius
Lower limb summary. Anterior compartment of the thigh. Done By: Laith Qashou. Doctor_2016
 Lower limb summary Done By: Laith Qashou Doctor_2016 Anterior compartment of the thigh Sartorius Anterior superior iliac spine Upper medial surface of shaft of tibia 1. Flexes, abducts, laterally rotates
Lower limb summary Done By: Laith Qashou Doctor_2016 Anterior compartment of the thigh Sartorius Anterior superior iliac spine Upper medial surface of shaft of tibia 1. Flexes, abducts, laterally rotates
MUSCLES OF THE LOWER LIMBS
 MUSCLES OF THE LOWER LIMBS Naming, location and general function Dr. Nabil khouri ROLES THAT SHOULD NOT BE FORGOTTEN Most anterior compartment muscles of the hip and thigh Flexor of the femur at the hip
MUSCLES OF THE LOWER LIMBS Naming, location and general function Dr. Nabil khouri ROLES THAT SHOULD NOT BE FORGOTTEN Most anterior compartment muscles of the hip and thigh Flexor of the femur at the hip
Hip joint Type: Articulating bones:
 Ana (242 ) Hip joint Type: Synovial, ball & socket Articulating bones: Formed between head of femur and lunate surface of acetabulum of hip bone. Capsule: it is a strong fibrous sleeve connecting the articulating
Ana (242 ) Hip joint Type: Synovial, ball & socket Articulating bones: Formed between head of femur and lunate surface of acetabulum of hip bone. Capsule: it is a strong fibrous sleeve connecting the articulating
Balanced Body Movement Principles
 Balanced Body Movement Principles How the Body Works and How to Train it. Module 3: Lower Body Strength and Power Developing Strength, Endurance and Power The lower body is our primary source of strength,
Balanced Body Movement Principles How the Body Works and How to Train it. Module 3: Lower Body Strength and Power Developing Strength, Endurance and Power The lower body is our primary source of strength,
Human Anatomy Biology 351
 Human Anatomy Biology 351 Lower Limb Please place your name on the back of the last page of this exam. You must answer all questions on this exam. Because statistics demonstrate that, on average, between
Human Anatomy Biology 351 Lower Limb Please place your name on the back of the last page of this exam. You must answer all questions on this exam. Because statistics demonstrate that, on average, between
Leg. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology
 Leg Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Skin of the Leg Cutaneous Nerves Medially: The saphenous nerve, a branch of the femoral nerve supplies the skin on the medial surface
Leg Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Skin of the Leg Cutaneous Nerves Medially: The saphenous nerve, a branch of the femoral nerve supplies the skin on the medial surface
The thigh. Prof. Oluwadiya KS
 The thigh Prof. Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.com The Thigh: Boundaries The thigh is the region of the lower limb that is approximately between the hip and knee joints Anteriorly, it is separated from the
The thigh Prof. Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.com The Thigh: Boundaries The thigh is the region of the lower limb that is approximately between the hip and knee joints Anteriorly, it is separated from the
بسم هللا الرحمن الرحيم
 بسم هللا الرحمن الرحيم Laboratory RHS 221 Manual Muscle Testing Theory 1 hour practical 2 hours Dr. Ali Aldali, MS, PT Department of Physical Therapy King Saud University Talocrural and Subtalar Joint
بسم هللا الرحمن الرحيم Laboratory RHS 221 Manual Muscle Testing Theory 1 hour practical 2 hours Dr. Ali Aldali, MS, PT Department of Physical Therapy King Saud University Talocrural and Subtalar Joint
Muscles of the Gluteal Region
 Muscles of the Gluteal Region 1 Some of the most powerful in the body Extend the thigh during forceful extension Stabilize the iliotibial band and thoracolumbar fascia Related to shoulders and arms because
Muscles of the Gluteal Region 1 Some of the most powerful in the body Extend the thigh during forceful extension Stabilize the iliotibial band and thoracolumbar fascia Related to shoulders and arms because
Anatomy of Ankle & Foot. Chang-Hyung Lee, M.D., Ph.D. Physical Medicine & Rehabilitation Samsung Medical Center
 Anatomy of Ankle & Foot Chang-Hyung Lee, M.D., Ph.D. Physical Medicine & Rehabilitation Samsung Medical Center Ankle Introduction Most frequently injured major joint 3 main articulation: distal tibiofibular
Anatomy of Ankle & Foot Chang-Hyung Lee, M.D., Ph.D. Physical Medicine & Rehabilitation Samsung Medical Center Ankle Introduction Most frequently injured major joint 3 main articulation: distal tibiofibular
Muscles of the Thigh. 6.1 Identify, describe the attachments of and deduce the actions of the muscles of the thigh: Anterior group
 Muscles of the Thigh 6.1 Identify, describe the attachments of and deduce the actions of the muscles of the thigh: Anterior group Sartorius: This is a long strap like muscle with flattened tendons at each
Muscles of the Thigh 6.1 Identify, describe the attachments of and deduce the actions of the muscles of the thigh: Anterior group Sartorius: This is a long strap like muscle with flattened tendons at each
THE LOWER EXTREMITY EXAM FOR THE FAMILY PRACTITIONER
 THE LOWER EXTREMITY EXAM FOR THE FAMILY PRACTITIONER Melinda A. Scott, D.O. Orthopedic Associates of Dayton Board Certified in Primary Care Sports Medicine GOALS Identify landmarks necessary for exam of
THE LOWER EXTREMITY EXAM FOR THE FAMILY PRACTITIONER Melinda A. Scott, D.O. Orthopedic Associates of Dayton Board Certified in Primary Care Sports Medicine GOALS Identify landmarks necessary for exam of
Muscles of the Hip 1. Tensor Fasciae Latae O: iliac crest I: lateral femoral condyle Action: abducts the thigh Nerve: gluteal nerve
 Muscles of the Hip 1. Tensor Fasciae Latae O: iliac crest I: lateral femoral condyle Action: abducts the thigh Nerve: gluteal nerve 2. Gluteus Maximus O: ilium I: femur Action: abduct the thigh Nerve:
Muscles of the Hip 1. Tensor Fasciae Latae O: iliac crest I: lateral femoral condyle Action: abducts the thigh Nerve: gluteal nerve 2. Gluteus Maximus O: ilium I: femur Action: abduct the thigh Nerve:
HUMAN BODY COURSE LOWER LIMB NERVES AND VESSELS
 HUMAN BODY COURSE LOWER LIMB NERVES AND VESSELS October 22, 2010 D. LOWER LIMB MUSCLES 2. Lower limb compartments ANTERIOR THIGH COMPARTMENT General lfunction: Hip flexion, knee extension, other motions
HUMAN BODY COURSE LOWER LIMB NERVES AND VESSELS October 22, 2010 D. LOWER LIMB MUSCLES 2. Lower limb compartments ANTERIOR THIGH COMPARTMENT General lfunction: Hip flexion, knee extension, other motions
The Leg. Prof. Oluwadiya KS
 The Leg Prof. Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.sitesled.com Compartments of the leg 4 Four Compartments: 1. Anterior compartment Deep fibular nerve Dorsiflexes the foot and toes 2. Lateral Compartment Superficial
The Leg Prof. Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.sitesled.com Compartments of the leg 4 Four Compartments: 1. Anterior compartment Deep fibular nerve Dorsiflexes the foot and toes 2. Lateral Compartment Superficial
The Hip (Iliofemoral) Joint. Presented by: Rob, Rachel, Alina and Lisa
 The Hip (Iliofemoral) Joint Presented by: Rob, Rachel, Alina and Lisa Surface Anatomy: Posterior Surface Anatomy: Anterior Bones: Os Coxae Consists of 3 Portions: Ilium Ischium Pubis Bones: Pubis Portion
The Hip (Iliofemoral) Joint Presented by: Rob, Rachel, Alina and Lisa Surface Anatomy: Posterior Surface Anatomy: Anterior Bones: Os Coxae Consists of 3 Portions: Ilium Ischium Pubis Bones: Pubis Portion
Contents of the Posterior Fascial Compartment of the Thigh
 Contents of the Posterior Fascial Compartment of the Thigh 1-Muscles: B i c e p s f e m o r i s S e m i t e n d i n o s u s S e m i m e m b r a n o s u s a small part of the adductor magnus (h a m s t
Contents of the Posterior Fascial Compartment of the Thigh 1-Muscles: B i c e p s f e m o r i s S e m i t e n d i n o s u s S e m i m e m b r a n o s u s a small part of the adductor magnus (h a m s t
Recognizing common injuries to the lower extremity
 Recognizing common injuries to the lower extremity Bones Femur Patella Tibia Tibial Tuberosity Medial Malleolus Fibula Lateral Malleolus Bones Tarsals Talus Calcaneus Metatarsals Phalanges Joints - Knee
Recognizing common injuries to the lower extremity Bones Femur Patella Tibia Tibial Tuberosity Medial Malleolus Fibula Lateral Malleolus Bones Tarsals Talus Calcaneus Metatarsals Phalanges Joints - Knee
From Childhood to Adulthood OMT for LOWER EXTREMITY Hip, Knee, Ankle, Foot. Objectives
 From Childhood to Adulthood OMT for LOWER EXTREMITY Hip, Knee, Ankle, Foot Jan Hendryx, DO, FAAO Peek n Peak CME March 1, 2019 Objectives 1. Demonstrate knowledge of the anatomy of the lower extremity-
From Childhood to Adulthood OMT for LOWER EXTREMITY Hip, Knee, Ankle, Foot Jan Hendryx, DO, FAAO Peek n Peak CME March 1, 2019 Objectives 1. Demonstrate knowledge of the anatomy of the lower extremity-
Understanding Leg Anatomy and Function THE UPPER LEG
 Understanding Leg Anatomy and Function THE UPPER LEG The long thigh bone is the femur. It connects to the pelvis to form the hip joint and then extends down to meet the tibia (shin bone) at the knee joint.
Understanding Leg Anatomy and Function THE UPPER LEG The long thigh bone is the femur. It connects to the pelvis to form the hip joint and then extends down to meet the tibia (shin bone) at the knee joint.
The Knee Joint By Prof. Dr. Muhammad Imran Qureshi
 The Knee Joint By Prof. Dr. Muhammad Imran Qureshi Structurally, it is the Largest and the most complex joint in the body because of the functions that it performs: Allows mobility (flexion/extension)
The Knee Joint By Prof. Dr. Muhammad Imran Qureshi Structurally, it is the Largest and the most complex joint in the body because of the functions that it performs: Allows mobility (flexion/extension)
Knee Joint Anatomy 101
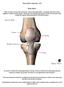 Knee Joint Anatomy 101 Bone Basics There are three bones at the knee joint femur, tibia and patella commonly referred to as the thighbone, shinbone and kneecap. The fibula is not typically associated with
Knee Joint Anatomy 101 Bone Basics There are three bones at the knee joint femur, tibia and patella commonly referred to as the thighbone, shinbone and kneecap. The fibula is not typically associated with
In the name of god. Knee. By: Tofigh Bahraminia Graduate Student of the Pathology Sports and corrective actions. Heat: Dr. Babakhani. Nov.
 In the name of god Knee By: Tofigh Bahraminia Graduate Student of the Pathology Sports and corrective actions Heat: Dr. Babakhani Nov. 2014 1 Anatomy-Bones Bones Femur Medial/lateral femoral condyles articulate
In the name of god Knee By: Tofigh Bahraminia Graduate Student of the Pathology Sports and corrective actions Heat: Dr. Babakhani Nov. 2014 1 Anatomy-Bones Bones Femur Medial/lateral femoral condyles articulate
First & second layers of muscles of the sole
 The FOOT First & second layers of muscles of the sole introduction The muscles acting on the foot can be divided into two distinct groups; extrinsic and intrinsic muscles. The extrinsic muscles arise from
The FOOT First & second layers of muscles of the sole introduction The muscles acting on the foot can be divided into two distinct groups; extrinsic and intrinsic muscles. The extrinsic muscles arise from
and K n e e J o i n t Is the most complicated joint in the body!!!!
 K n e e J o i n t K n e e J o i n t Is the most complicated joint in the body!!!! 1-Consists of two condylar joints between: A-The medial and lateral condyles of the femur and The condyles of the tibia
K n e e J o i n t K n e e J o i n t Is the most complicated joint in the body!!!! 1-Consists of two condylar joints between: A-The medial and lateral condyles of the femur and The condyles of the tibia
this makes sense, however this is lower order thinking and does not solve the lower leg
 Functional Knee Valgus in a Barbell Squat 1 One of the most common lower leg dysfunction we see in athletes, particularly general population is functional knee valgus, or better referred to as the knees
Functional Knee Valgus in a Barbell Squat 1 One of the most common lower leg dysfunction we see in athletes, particularly general population is functional knee valgus, or better referred to as the knees
Copyright 2012 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. McGraw-Hill/Irwin
 CHAPTER 8: THE LOWER EXTREMITY: KNEE, ANKLE, AND FOOT KINESIOLOGY Scientific Basis of Human Motion, 12 th edition Hamilton, Weimar & Luttgens Presentation Created by TK Koesterer, Ph.D., ATC Humboldt State
CHAPTER 8: THE LOWER EXTREMITY: KNEE, ANKLE, AND FOOT KINESIOLOGY Scientific Basis of Human Motion, 12 th edition Hamilton, Weimar & Luttgens Presentation Created by TK Koesterer, Ph.D., ATC Humboldt State
Human Anatomy Biology 255
 Human Anatomy Biology 255 Exam #4 Please place your name and I.D. number on the back of the last page of this exam. You must answer all questions on this exam. Because statistics demonstrate that, on average,
Human Anatomy Biology 255 Exam #4 Please place your name and I.D. number on the back of the last page of this exam. You must answer all questions on this exam. Because statistics demonstrate that, on average,
RN(EC) ENC(C) GNC(C) MN ACNP *** MECHANISM OF INJURY.. MOST IMPORTANT *** - Useful in determining mechanism of injury / overuse
 HISTORY *** MECHANISM OF INJURY.. MOST IMPORTANT *** Age of patient Sport / Occupation - Certain conditions are more prevalent in particular age groups (Osgood Schlaters in youth / Degenerative Joint Disease
HISTORY *** MECHANISM OF INJURY.. MOST IMPORTANT *** Age of patient Sport / Occupation - Certain conditions are more prevalent in particular age groups (Osgood Schlaters in youth / Degenerative Joint Disease
Bones of Lower Limb. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology
 Bones of Lower Limb Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Bones of the lower limb Hip Bone Made up of 3 bones: 1) Ilium (flat), superior in position 2) Ischium (L), postero-inferior
Bones of Lower Limb Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Bones of the lower limb Hip Bone Made up of 3 bones: 1) Ilium (flat), superior in position 2) Ischium (L), postero-inferior
UNIT 7 JOINTS. Knee and Ankle Joints DR. ABDEL-MONEM A. HEGAZY
 UNIT 7 JOINTS Knee and Ankle Joints BY DR. ABDEL-MONEM A. HEGAZY (Degree in Bachelor of Medicine and Surgery with honor 1983, Dipl."Gynaecology and Obstetrics "1989, Master "Anatomy and Embryology "1994,
UNIT 7 JOINTS Knee and Ankle Joints BY DR. ABDEL-MONEM A. HEGAZY (Degree in Bachelor of Medicine and Surgery with honor 1983, Dipl."Gynaecology and Obstetrics "1989, Master "Anatomy and Embryology "1994,
ChiroCredit.com Presents Biomechanics: Focus on
 ChiroCredit.com Presents Biomechanics: Focus on the Knee Presented by: Ivo Waerlop, DC Shawn Allen, DC 1 Focus on The Knee 2 Pertinent Anatomy Femur Tibia Fibula Patella Prepatellar bursa Infrapatellar
ChiroCredit.com Presents Biomechanics: Focus on the Knee Presented by: Ivo Waerlop, DC Shawn Allen, DC 1 Focus on The Knee 2 Pertinent Anatomy Femur Tibia Fibula Patella Prepatellar bursa Infrapatellar
Section Three: The Leg, Ankle, and Foot Lecture: Review of Clinical Anatomy, Patterns of Dysfunction and Injury, and
 Section Three: The Leg, Ankle, and Foot Lecture: Review of Clinical Anatomy, Patterns of Dysfunction and Injury, and Treatment Implications for the Leg, Ankle, and Foot Levels I and II Demonstration and
Section Three: The Leg, Ankle, and Foot Lecture: Review of Clinical Anatomy, Patterns of Dysfunction and Injury, and Treatment Implications for the Leg, Ankle, and Foot Levels I and II Demonstration and
Ligamentous and Meniscal Injuries: Diagnosis and Management
 Ligamentous and Meniscal Injuries: Diagnosis and Management Daniel K Williams, MD Franciscan Physician Network Orthopedic Specialists September 29, 2017 No Financial Disclosures INTRODUCTION Overview of
Ligamentous and Meniscal Injuries: Diagnosis and Management Daniel K Williams, MD Franciscan Physician Network Orthopedic Specialists September 29, 2017 No Financial Disclosures INTRODUCTION Overview of
Practical 1 Worksheet
 Practical 1 Worksheet ANATOMICAL TERMS 1. Use the word bank to fill in the missing words. reference side stand body arms palms anatomical forward All anatomical terms have a(n) point which is called the
Practical 1 Worksheet ANATOMICAL TERMS 1. Use the word bank to fill in the missing words. reference side stand body arms palms anatomical forward All anatomical terms have a(n) point which is called the
The Knee. Two Joints: Tibiofemoral. Patellofemoral
 Evaluating the Knee The Knee Two Joints: Tibiofemoral Patellofemoral HISTORY Remember the questions from lecture #2? Girth OBSERVATION TibioFemoral Alignment What are the consequences of faulty alignment?
Evaluating the Knee The Knee Two Joints: Tibiofemoral Patellofemoral HISTORY Remember the questions from lecture #2? Girth OBSERVATION TibioFemoral Alignment What are the consequences of faulty alignment?
rotation of the hip Flexion of the knee Iliac fossa of iliac Lesser trochanter Femoral nerve Flexion of the thigh at the hip shaft of tibia
 Anatomy of the lower limb Anterior & medial compartments of the thigh Dr. Hayder The fascia lata encloses the entire thigh like a sleeve/stocking. Three intramuscular fascial septa (lateral, medial, and
Anatomy of the lower limb Anterior & medial compartments of the thigh Dr. Hayder The fascia lata encloses the entire thigh like a sleeve/stocking. Three intramuscular fascial septa (lateral, medial, and
CLASSIFICATION OF JOINTS STRUCTURAL VS FUNCTIONAL
 CHAPTER 8 JOINTS CLASSIFICATION OF JOINTS STRUCTURAL VS FUNCTIONAL The most moveable type of joint is a 1) Synarthrosis 2) Amphiarthrosis 3) Diarthrosis FIBROUS JOINTS Figure 8.1 Fibrous joints. (a) Suture
CHAPTER 8 JOINTS CLASSIFICATION OF JOINTS STRUCTURAL VS FUNCTIONAL The most moveable type of joint is a 1) Synarthrosis 2) Amphiarthrosis 3) Diarthrosis FIBROUS JOINTS Figure 8.1 Fibrous joints. (a) Suture
musculoskeletal system anatomy muscles of foot sheet done by: dina sawadha & mohammad abukabeer
 musculoskeletal system anatomy muscles of foot sheet done by: dina sawadha & mohammad abukabeer Extensor retinaculum : A- superior extensor retinaculum (SER) : originates from the distal ends of the tibia
musculoskeletal system anatomy muscles of foot sheet done by: dina sawadha & mohammad abukabeer Extensor retinaculum : A- superior extensor retinaculum (SER) : originates from the distal ends of the tibia
Therapeutic Foot Care Certificate Program Part I: Online Home Study Program
 Therapeutic Foot Care Certificate Program Part I: Online Home Study Program 1 Anatomy And Terminology Of The Lower Extremity Joan E. Edelstein, MA, PT, FISPO Associate Professor of Clinical Physical Therapy
Therapeutic Foot Care Certificate Program Part I: Online Home Study Program 1 Anatomy And Terminology Of The Lower Extremity Joan E. Edelstein, MA, PT, FISPO Associate Professor of Clinical Physical Therapy
Biology 325 Fall 2003
 Name: pre-lab exercise due at beginning of your lab session Matching a. fibrous joints b. cartilaginous joints c. synovial joints 1. exhibit a joint cavity 2. types are sutures and syndesmoses 3. bones
Name: pre-lab exercise due at beginning of your lab session Matching a. fibrous joints b. cartilaginous joints c. synovial joints 1. exhibit a joint cavity 2. types are sutures and syndesmoses 3. bones
Bones of the Lower Limb Bone Structure Description Notes. border of the superior ramus. inferolaterally from the pubic symphysis
 Bones of the Lower Limb Bone Structure Description Notes pubis an angulated bone the forms the anterior part of the pelvis one of three bones that form the os coxae: ilium, ischium, pubis; its forms 1/5
Bones of the Lower Limb Bone Structure Description Notes pubis an angulated bone the forms the anterior part of the pelvis one of three bones that form the os coxae: ilium, ischium, pubis; its forms 1/5
It is formed by fusion of 3 bones: I. Ilium (superior bone). II. Pubis (antero-inferior bone). III. Ischium (postero-inferior bone).
 It is formed by fusion of 3 bones: I. Ilium (superior bone). II. Pubis (antero-inferior bone). III. Ischium (postero-inferior bone). Pubis Acetabulum Ana (242 ) The three constituent of bones of the hip
It is formed by fusion of 3 bones: I. Ilium (superior bone). II. Pubis (antero-inferior bone). III. Ischium (postero-inferior bone). Pubis Acetabulum Ana (242 ) The three constituent of bones of the hip
Muscle Testing of Knee Extensors. Yasser Moh. Aneis, PhD, MSc., PT. Lecturer of Physical Therapy Basic Sciences Department
 Muscle Testing of Knee Extensors Yasser Moh. Aneis, PhD, MSc., PT. Lecturer of Physical Therapy Basic Sciences Department Muscle Testing of Knee Extensors othe Primary muscle Quadriceps Femoris -Rectus
Muscle Testing of Knee Extensors Yasser Moh. Aneis, PhD, MSc., PT. Lecturer of Physical Therapy Basic Sciences Department Muscle Testing of Knee Extensors othe Primary muscle Quadriceps Femoris -Rectus
Main Menu. Joint and Pelvic Girdle click here. The Power is in Your Hands
 1 Hip Joint and Pelvic Girdle click here Main Menu K.6 http://www.handsonlineeducation.com/classes//k6entry.htm[3/23/18, 2:01:12 PM] Hip Joint (acetabular femoral) Relatively stable due to : Bony architecture
1 Hip Joint and Pelvic Girdle click here Main Menu K.6 http://www.handsonlineeducation.com/classes//k6entry.htm[3/23/18, 2:01:12 PM] Hip Joint (acetabular femoral) Relatively stable due to : Bony architecture
EDL EHL. Extensor Hallucis Longus L5 Extensor Digitorum longus L5,1 Peroneus Tertius L5 1 Extensor Digitorum Brevis S1,2 [like intrinsic muscle]
![EDL EHL. Extensor Hallucis Longus L5 Extensor Digitorum longus L5,1 Peroneus Tertius L5 1 Extensor Digitorum Brevis S1,2 [like intrinsic muscle] EDL EHL. Extensor Hallucis Longus L5 Extensor Digitorum longus L5,1 Peroneus Tertius L5 1 Extensor Digitorum Brevis S1,2 [like intrinsic muscle]](/thumbs/78/77875930.jpg) ANATOMY OF ANKLE AND FOOT Lateral aspect: [Dorsal medial to lateral= dorsal under extensor retinaculum] Tibialis Anterior EHL Artery [Dorsal pedal A] and Anterior tibial N EDL Peroneus Tertius Behind the
ANATOMY OF ANKLE AND FOOT Lateral aspect: [Dorsal medial to lateral= dorsal under extensor retinaculum] Tibialis Anterior EHL Artery [Dorsal pedal A] and Anterior tibial N EDL Peroneus Tertius Behind the
Ch. 2 - Therapeutic Relations Ch Hydrotherapy Ch. 13 Foot Reflexology Ch. 16 energy-based Work Ch. 15 Muscles of Knee Joint
 WEEKEND TWO HOMEWORK READING ASSIGNMENTS Salvo Massage Therapy Principles and Practice 4 th Edition Muscolino The Muscular System Manual Ch. 2 - Therapeutic Relations Ch. 12 - Hydrotherapy Ch. 13 Foot
WEEKEND TWO HOMEWORK READING ASSIGNMENTS Salvo Massage Therapy Principles and Practice 4 th Edition Muscolino The Muscular System Manual Ch. 2 - Therapeutic Relations Ch. 12 - Hydrotherapy Ch. 13 Foot
Knee Joint Assessment and General View
 Knee Joint Assessment and General View Done by; Mshari S. Alghadier BSc Physical Therapy RHPT 366 m.alghadier@sau.edu.sa http://faculty.sau.edu.sa/m.alghadier/ Functional anatomy The knee is the largest
Knee Joint Assessment and General View Done by; Mshari S. Alghadier BSc Physical Therapy RHPT 366 m.alghadier@sau.edu.sa http://faculty.sau.edu.sa/m.alghadier/ Functional anatomy The knee is the largest
The University Of Jordan Faculty Of Medicine FOOT. Dr.Ahmed Salman Assistant Prof. of Anatomy. The University Of Jordan
 The University Of Jordan Faculty Of Medicine FOOT Dr.Ahmed Salman Assistant Prof. of Anatomy. The University Of Jordan Tarsal Tunnel Syndrome Due to compression of Tibial nerve as it travels through the
The University Of Jordan Faculty Of Medicine FOOT Dr.Ahmed Salman Assistant Prof. of Anatomy. The University Of Jordan Tarsal Tunnel Syndrome Due to compression of Tibial nerve as it travels through the
~, /' ~::'~ EXTENSOR HALLUCIS LONGUS. Leg-anterolateral :.:~ / ~\,
 TIBIALIS ANTERIOR Lateral condyle of tibia, upper half of lateral surface of tibia, interosseous membrane Medial side and plantar surface of medial cuneiform bone, and base of first metatarsal bone Dorsiflexes
TIBIALIS ANTERIOR Lateral condyle of tibia, upper half of lateral surface of tibia, interosseous membrane Medial side and plantar surface of medial cuneiform bone, and base of first metatarsal bone Dorsiflexes
CHAPTER 80 BASIC CONSIDERATIONS
 Página 1 de 32 Copyright 2001 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins Loeser, John D. Bonica's Management of Pain, 3rd Edition CHAPTER 80 BASIC CONSIDERATIONS Part of "CHAPTER 80 - Pain in the Leg, Ankle, and Foot"
Página 1 de 32 Copyright 2001 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins Loeser, John D. Bonica's Management of Pain, 3rd Edition CHAPTER 80 BASIC CONSIDERATIONS Part of "CHAPTER 80 - Pain in the Leg, Ankle, and Foot"
ANKLE PLANTAR FLEXION
 ANKLE PLANTAR FLEXION Evaluation and Measurements By Isabelle Devreux 1 Ankle Plantar Flexion: Gastrocnemius and Soleus ROM: 0 to 40-45 A. Soleus: Origin: Posterior of head of fibula and proximal1/3 of
ANKLE PLANTAR FLEXION Evaluation and Measurements By Isabelle Devreux 1 Ankle Plantar Flexion: Gastrocnemius and Soleus ROM: 0 to 40-45 A. Soleus: Origin: Posterior of head of fibula and proximal1/3 of
The Foot. Dr. Wegdan Moh.Mustafa Medicine Faculty Assistant Professor Mob:
 The Foot Dr. Wegdan Moh.Mustafa Medicine Faculty Assistant Professor Mob: 0127155717 The skeleton of the foot Cutaneous innervations Sole of foot layers of muscles First layer -Abductor hallucis -Flexor
The Foot Dr. Wegdan Moh.Mustafa Medicine Faculty Assistant Professor Mob: 0127155717 The skeleton of the foot Cutaneous innervations Sole of foot layers of muscles First layer -Abductor hallucis -Flexor
Foot. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology
 Foot Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Dorsum of the Foot Sole of the Foot Plantar aponeurosis It is a triangular thickening of deep fascia in the sole of the foot Attachments:
Foot Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Dorsum of the Foot Sole of the Foot Plantar aponeurosis It is a triangular thickening of deep fascia in the sole of the foot Attachments:
Sports Medicine 15. Unit I: Anatomy. The knee, Thigh, Hip and Groin. Part 4 Anatomies of the Lower Limbs
 Sports Medicine 15 Unit I: Anatomy Part 4 Anatomies of the Lower Limbs The knee, Thigh, Hip and Groin Anatomy of the lower limbs In Part 3 of this section we focused upon 11 of the 12 extrinsic muscles
Sports Medicine 15 Unit I: Anatomy Part 4 Anatomies of the Lower Limbs The knee, Thigh, Hip and Groin Anatomy of the lower limbs In Part 3 of this section we focused upon 11 of the 12 extrinsic muscles
Anatomy of the lower limb
 Anatomy of the lower limb Arches & sole of the foot Dr. Hayder ARCHES OF THE FOOT The foot as a mechanical unit performs two major functions: - It acts as a pliable platform to support the body weigh during
Anatomy of the lower limb Arches & sole of the foot Dr. Hayder ARCHES OF THE FOOT The foot as a mechanical unit performs two major functions: - It acts as a pliable platform to support the body weigh during
Prevention and Treatment of Injuries. Anatomy. Anatomy. Chapter 20 The Knee Westfield High School Houston, Texas
 Prevention and Treatment of Injuries Chapter 20 The Knee Westfield High School Houston, Texas Anatomy MCL, Medial Collateral Ligament LCL, Lateral Collateral Ligament PCL, Posterior Cruciate Ligament ACL,
Prevention and Treatment of Injuries Chapter 20 The Knee Westfield High School Houston, Texas Anatomy MCL, Medial Collateral Ligament LCL, Lateral Collateral Ligament PCL, Posterior Cruciate Ligament ACL,
1. A worker falls from a height and lands on his feet. Radiographs reveal a fracture of the sustentaculum tali. The muscle passing immediately
 1. A worker falls from a height and lands on his feet. Radiographs reveal a fracture of the sustentaculum tali. The muscle passing immediately beneath it that would be adversely affected is the: fibularis
1. A worker falls from a height and lands on his feet. Radiographs reveal a fracture of the sustentaculum tali. The muscle passing immediately beneath it that would be adversely affected is the: fibularis
Copyright 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings. Dr. Nabil Khouri MD, MSc, Ph.D
 Dr. Nabil Khouri MD, MSc, Ph.D Pelvic Girdle (Hip) Organization of the Lower Limb It is divided into: The Gluteal region The thigh The knee The leg The ankle The foot The thigh and the leg have compartments
Dr. Nabil Khouri MD, MSc, Ph.D Pelvic Girdle (Hip) Organization of the Lower Limb It is divided into: The Gluteal region The thigh The knee The leg The ankle The foot The thigh and the leg have compartments
Articulations. Articulation. Joint between bones. Does not mean movement! Some joints are immovable; sutures.
 Articulations Joint between bones Articulation Does not mean movement Some joints are immovable; sutures. Classification of joints Two questions about joints: 1- How does it move? - functional 2- How is
Articulations Joint between bones Articulation Does not mean movement Some joints are immovable; sutures. Classification of joints Two questions about joints: 1- How does it move? - functional 2- How is
Exercise Science Section 4: Joint Mechanics and Joint Injuries
 Exercise Science Section 4: Joint Mechanics and Joint Injuries An Introduction to Health and Physical Education Ted Temertzoglou Paul Challen ISBN 1-55077-132-9 Types of Joints Fibrous joint Cartilaginous
Exercise Science Section 4: Joint Mechanics and Joint Injuries An Introduction to Health and Physical Education Ted Temertzoglou Paul Challen ISBN 1-55077-132-9 Types of Joints Fibrous joint Cartilaginous
حسام أبو عوض. - Ahmad. 1 P a g e
 - 9 حسام أبو عوض - - Ahmad 1 P a g e In the last lecture, we finished discussing the superficial part of the posterior compartment and the popliteus muscle of the deep layer[reminder: The entire posterior
- 9 حسام أبو عوض - - Ahmad 1 P a g e In the last lecture, we finished discussing the superficial part of the posterior compartment and the popliteus muscle of the deep layer[reminder: The entire posterior
The Hip Joint. Shenequia Howard David Rivera
 The Hip Joint Shenequia Howard David Rivera Topics Of Discussion Movement Bony Anatomy Ligamentous Anatomy Muscular Anatomy Origin/Insertion/Action/Innervation Common Injuries MOVEMENT Flexion Extension
The Hip Joint Shenequia Howard David Rivera Topics Of Discussion Movement Bony Anatomy Ligamentous Anatomy Muscular Anatomy Origin/Insertion/Action/Innervation Common Injuries MOVEMENT Flexion Extension
Knee Injury Assessment
 Knee Injury Assessment Clinical Anatomy p. 186 Femur Medial condyle Lateral condyle Femoral trochlea Tibia Intercondylar notch Tibial tuberosity Tibial plateau Fibula Fibular head Patella Clinical Anatomy
Knee Injury Assessment Clinical Anatomy p. 186 Femur Medial condyle Lateral condyle Femoral trochlea Tibia Intercondylar notch Tibial tuberosity Tibial plateau Fibula Fibular head Patella Clinical Anatomy
Musculoskeletal Ultrasound Technical Guidelines. VI. Ankle
 European Society of MusculoSkeletal Radiology Musculoskeletal Ultrasound Technical Guidelines VI. Ankle Ian Beggs, UK Stefano Bianchi, Switzerland Angel Bueno, Spain Michel Cohen, France Michel Court-Payen,
European Society of MusculoSkeletal Radiology Musculoskeletal Ultrasound Technical Guidelines VI. Ankle Ian Beggs, UK Stefano Bianchi, Switzerland Angel Bueno, Spain Michel Cohen, France Michel Court-Payen,
OTM Lecture Gait and Somatic Dysfunction of the Lower Extremity
 OTM Lecture Gait and Somatic Dysfunction of the Lower Extremity Somatic Dysfunction Tenderness Asymmetry Range of Motion Tissue Texture Changes Any one of which must be present to diagnosis somatic dysfunction.
OTM Lecture Gait and Somatic Dysfunction of the Lower Extremity Somatic Dysfunction Tenderness Asymmetry Range of Motion Tissue Texture Changes Any one of which must be present to diagnosis somatic dysfunction.
BIOMECHANICS OF ANKLE FRACTURES
 BIOMECHANICS OF ANKLE FRACTURES William R Reinus, MD MBA FACR Significance of Ankle Fractures Most common weight-bearing Fx 70% of all Fxs Incidence is increasing Bimodal distribution Men 15-24 Women over
BIOMECHANICS OF ANKLE FRACTURES William R Reinus, MD MBA FACR Significance of Ankle Fractures Most common weight-bearing Fx 70% of all Fxs Incidence is increasing Bimodal distribution Men 15-24 Women over
Anatomy MCQs Week 13
 Anatomy MCQs Week 13 1. Posterior to the medial malleolus of the ankle: The neurovascular bundle lies between Tibialis Posterior and Flexor Digitorum Longus The tendon of Tibialis Posterior inserts into
Anatomy MCQs Week 13 1. Posterior to the medial malleolus of the ankle: The neurovascular bundle lies between Tibialis Posterior and Flexor Digitorum Longus The tendon of Tibialis Posterior inserts into
