BONES JOINTS MUSCLES OF THE LOWER LIMB
|
|
|
- Alfred Edwards
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 BONES JOINTS MUSCLES OF THE LOWER LIMB
2 LOWER LIMB: BONES LOWER LIMB GLUTEAL REGION consists of 6 major segments: FEMORAL REGION (THIGH) KNEE REGION LEG REGION TALOCRURAL REGION (ANKLE) FOOT REGION
3 LOWER LIMB: BONES THE POSTERIOR FEMORAL REGION (THIGH) is between the gluteal fold and the knee joint. THE KNEE REGION includes: the prominences (condyles) of the distal femur and proximal tibia the head of the fibula the patella (knee cap) THE LEG REGION is between the knee and ankle joint. IN ANATOMY: THE LEG THE LOWER LIMB THE TALOCRURAL REGION (THE ANKLE) includes: the medial prominence the lateral prominence that flank the ankle. THE FOOT REGION the distal part containing: the tarsus the metatarsus the phalanges
4 LOWER LIMB: BONES THE SKELETON OF THE LOWER LIMB HIP BONE ILIUM ISCHIUM PUBIS FEMUR TIBIA AND FIBULA FOOT BONES TARSUS METATARSUS PHALANGES
5 LOWER LIMB: BONES THE PELVIC GIRDLE: attaches the free lower limb to the axial skeleton bony ring composed of the sacrum and right and left hip bones, jointed anteriorly at the pubic symphysis THE HIP BONE is formed by fusion of the: ILIUM ISCHIUM PUBIS THE HIP BONE At birth, the three bones are joined by hyaline cartilage. The bones begin to fuse between years of age.
6 LOWER LIMB: BONES RELATIONSHIP TO OTHER REGIONS there are 4 major entry and exit points between the lower limb and the abdomen, pelvis, and perineum These are: the gap between the inguinal ligament and pelvic bone, the greater sciatic foramen, the obturator canal (at the top of the obturator foramen), and the lesser sciatic foramen. THE HIP BONE: THE ILIUM Body fused to ischium and pubis, all meeting in the acetabulum (socket for articulation with femoral head) Ala of ilium (wing): weak spot of ilium! ASIS and PSIS
7 LOWER LIMB: BONES THE HIP BONE: THE ILIUM Neurovascular structures from within the pelvic girdle pass through the greater and lesser sciatic foramen to the gluteal region THE HIP BONE: THE PUBIS Body fused with other two bones Ramus fused with ischium Medially, the symphysial surface articulates with contralateral pubis by means of the pubic symphysis THE HIP BONE: THE ISCHIUM Body fused with other two bones Ramus fused with pubis The body s weight rests on the large ischial tuberosity when sitting ( sitting bone ) it provides attachment of posterior thigh muscles
8 LOWER LIMB: BONES THE OBTURATOR FORAMEN large opening in the hip bone it s bounded by: rami of the pubis and ischium is inferior to the acetabulum most of it is closed by a membrane of flat connective tissue, the obturator membrane THE ACETABULUM a cup-shaped depression where the head of the femur articulates with the pelvic girdle all three primary bones contribute to the formation of the acetabulum
9 LOWER LIMB: BONES THE FEMUR the longest and heaviest bone in the body consists of: shaft (body) and two ends THE FEMUR the proximal (superior) consists of the head, neck and two trochanters: lesser and greater THE FEMUR the head the fovea for the ligament of the head in the early life, the ligament gives passage to an artery supplying the epiphysis of the head THE FEMUR The angle of inclination is greatest at the birth and becomes more acute the adult angle is (averaging ) is less in females
10 LOWER LIMB: BONES THE FEMUR The neck common fracture site! THE FEMUR The body is slightly convex anteriorly smooth on anterior side posteriorly rough line the linea apsera, attachment for adductors of the thigh the greater trochanter - point of the hip; attachment site for several gluteal muscles THE FEMUR The distal end its major weight-bearing articulation is with the tibia, but it also articulates anteriorly with the patella (knee cap) the patella is the largest sesamoid bone in the body the medial and lateral femoral condyles articulate with menisci and tibial condyles to form the knee joint
11 LOWER LIMB: BONES THE TIBIA MEDIAL SIDE The weight-bearing bone of the leg and is therefore much larger than the fibula It takes part in the formation of the knee joint and below it forms the medial malleolus and most of the bony surface for articulation of the leg with the foot at the ankle joint THE FIBULA LATERAL SIDE Smaller than the tibia and is on the lateral side of the leg. It articulates superiorly with the inferior aspect of the lateral condyle of the proximal tibia. THE FIBULA LATERAL SIDE Does not take part in formation of the knee joint. The distal end forms the lateral malleolus of the ankle joint. THE TIBIA AND THE FIBULA tibial tuberosity - anterior soleal line - posterior head of fibula - proximal lateral malleolus - distal
12 LOWER LIMB: BONES THE BONES OF THE FOOT Tarsal bones: talus, calcaneus, cuboid, navicular and three cuneiforms Metatarsals I-V Phalanges I-V digits THE BONES OF THE FOOT THE TARSUS consists of 7 bones: talus calcaneus, cuboid navicular three cuneiforms
13 LOWER LIMB: BONES THE BONES OF THE FOOT THE TALUS the most superior bone of the foot sits on top of and is supported by the calcaneus it articulates above with the tibia and fibula to form the ankle joint projects forward to articulate with the intermediate tarsal bone (navicular) on the medial side of the foot THE BONES OF THE FOOT THE TALUS the most superior bone of the foot sits on top of and is supported by the calcaneus it articulates above with the tibia and fibula to form the ankle joint projects forward to articulate with the intermediate tarsal bone (navicular) on the medial side of the foot
14 LOWER LIMB: BONES THE BONES OF THE FOOT - THE CALCANEUS sits under and supports the talus box-shaped bone with its long axis generally oriented along the midline of the foot the calcaneal tendon (Achilles tendon) attaches to the calcaneal tuberosity THE BONES OF THE FOOT - THE NAVICULAR the intermediate tarsal bone on the medial side of the foot articulates behind with the talus and articulates in front and on the lateral side with the distal group of tarsal The navicular bone is located between head of the talus posteriorly and the three cuneiforms anteriorly
15 LOWER LIMB: BONES THE BONES OF THE FOOT THE CUBOID articulates posteriorly with the calcaneus medially with the lateral cuneiform anteriorly with the bases of the lateral two metatarsals THE BONES OF THE FOOT - THE 3 CUNEIFORMS the lateral, intermediate and medial cuneiform bones articulate posteriorly with the navicular bone anteriorly with the bases of the medial three metatarsals articulating with each others THE BONES OF THE FOOT Tarsal bones: talus, calcaneus, cuboid, navicular and three cuneiforms Metatarsals I-V Phalanges I-V digits (the 1-st digit has only two phalanges)
16 THE JOINTS LOWER LIMB: JOINTS OF THE LOWER LIMB HIP JOINT KNEE JOINT TIBIOFIBULAR JOINTS ANKLE JOINT (talocrural articulation) FOOT JOINTS
17 LOWER LIMB: JOINTS THE HIP JOINT multiaxial ball and socket type of synovial joint articulation between the head of the femur and the acetabulum of the pelvic bone THE HIP JOINT The articular surfaces of the hip joint are: the spherical head of the femur and the lunate surface of the acetabulum of the pelvic bone THE HIP JOINT Movements at the joint include: flexion, extension abduction, adduction (and abduction of pelvis) internal and external rotation and circumduction THE HIP JOINT The acetabulum: almost encompasses the head of the femur contributes substantially to joint stability The lunate surface is covered by hyaline cartilage The lunate surface of the acetabulum is created by the acetabular notch and fossa
18 LOWER LIMB: JOINTS THE HIP JOINT Except for the fovea, the head of the femur is also covered by hyaline cartilage. THE HIP JOINT The labrum bridges across the acetabular notch as the transverse acetabular ligament and converts the notch into a foramen. THE HIP JOINT The ligament of the head of the femur is a flat band of connective tissue that attaches: at one end to the fovea on the head of the femur and at the other end to: the acetabular fossa, transverse acetabular ligament, and margins of the acetabular notch
19 LOWER LIMB: JOINTS THE HIP JOINT The ligament of the head of the femur carries a small branch of the obturator artery (the acetabular branch), which contributes to the blood supply of the head of the femur (the artery to the head of the femur). THE HIP JOINT Three ligaments reinforce the external surface of the fibrous membrane and stabilize the joint: the iliofemoral, the pubofemoral, the ischiofemoral ligaments THE HIP JOINT CLINICAL NOTE Fractures (through the neck of the femur) are more common than hip dislocations. THE HIP JOINT CLINICAL NOTE Because the branches are often compromised in a fractured hip (common in elderly women due to osteoporosis), the femoral head commonly undergoes avascular necrosis. In cases of avascular necrosis, the femoral head is removed and a prosthetic hip joint is surgically implanted.
20 LOWER LIMB: JOINTS The hip joint is supported by the following ligaments: The largest ligament, which reinforces the hip joint anteriorly is the iliofemoral ligament (Y-shaped) The ligament which reinforces the hip joint inferiorly is the pubofemoral ligament. The thinnest ligament, which reinforces the hip joint posteriorly is the Ischiofemoral ligament. The ligament which plays only a minor role in stability but carries the artery to the head of the femur the ligamentum (teres) of the head of the femur.
21 LOWER LIMB: JOINTS THE KNEE JOINT the knee joint is the largest and most superficial joint in the body. it is a hinge type od synovial joint. The knee joint consists of: the articulation between the femur and tibia, and the articulation between the patella and the femur Two fibrocartilaginous menisci, one on each side, between the femoral condyles and tibia accommodate changes in the shape of the articular surfaces during joint movements. The medial meniscus is attached around its margin to the capsule of the joint and to the tibial collateral ligament, whereas the lateral meniscus is unattached to the capsule. Therefore, the lateral meniscus is more mobile than the medial meniscus.
22 LOWER LIMB: JOINTS THE KNEE JOINT THE SYNOVIAL MEMBRANE The synovial membrane of the knee joint attaches to: the margins of the articular surfaces and to the superior and inferior outer margins of the menisci The major ligaments associated with the knee joint are: the patellar ligament the tibial (medial) TCL and fibular (lateral) FCL collateral ligaments the anterolateral ligament ALL the anterior and posterior cruciate ligaments The patellar ligament is basically the continuation of the quadriceps femoris tendon inferior to the patella. It is attached above to the margins and apex of the patella and below to the tibial tuberosity.
23 LOWER LIMB: JOINTS THE KNEE JOINT THE LIGAMENTS The fibular collateral ligament (FCL) (lateral collateral ligament) is attached superiorly to the lateral femoral epicondyle. Inferiorly, it is attached to a depression on the lateral surface of the fibular head. The anterolateral ligament (ALL) is a ligament on the lateral aspect of the knee, anterior to the fibular collateral ligament NEW KNEE LIGAMENT! The tibial collateral ligament (TCL) (medial collateral ligament) is attached superiorly to the medial femoral epicondyle and descends anteriorly to attach to the medial margin and medial surface of the tibia.
24 LOWER LIMB: JOINTS THE KNEE JOINT THE LIGAMENTS The two cruciate ligaments: (ACL) anterior cruciate ligament and (PCL) posterior cruciate ligament The cruciate ligaments lie inside the knee joint, but outside the articular cavity.
25 LOWER LIMB: JOINTS THE KNEE JOINT THE LIGAMENTS ACL - the anterior cruciate ligament the weaker of the two cruciate ligaments arises from the anterior intercondylar area of the tibia ACL extends: superiorly, posteriorly and laterally to posterior part of the medial side of the lateral condyle of the femur ACL - the anterior cruciate ligament ACL limits posterior rolling of the femoral condyles during flexion ACL prevents posterior displacement of the femur on the tibia ACL prevents hyperextension of the knee joint ACL - the anterior cruciate ligament ACL taut during extension ACL is lax during flexion ACL MAY BE TORN WHEN THE KNEE IS HYPEREXTENDED
26 LOWER LIMB: JOINTS THE KNEE JOINT THE LIGAMENTS PCL - the posterior cruciate ligament the stronger of the two cruciate ligaments arises from the posterior intercondylar area of the tibia PCL extends: superiorly, anteriorly on the medial side of ACL to attach to the anterior part of the lateral side of the medial condyle of the femur PCL - the posterior cruciate ligament PCL taut during flexion PCL is lax during extension PCL - the posterior cruciate ligament PCL prevents backward sliding of the tibia on the femur PCL limits hyperflexion of the knee joint
27 LOWER LIMB: JOINTS THE KNEE JOINT THE LIGAMENTS THE EXTRACAPSULAR LIGAMENTS OF KNEE JOINT: The joint capsule is strengthened by five extracapsular or capsular (intrinsic) ligaments: patellar ligament fibular collateral ligament tibial collateral ligament oblique popliteal ligament, and arcuate popliteal ligament THE INTRA-ARTICULAR LIGAMENTS OF KNEE JOINT: The intra-articular ligaments within the knee joint consist of the cruciate ligaments and menisci: anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) posterior cruciate ligament (PCL) coronary ligaments transverse ligament of the knee posterior meniscofemoral ligament
28 LOWER LIMB: JOINTS THE KNEE JOINT THE LIGAMENTS PCL - the posterior cruciate ligament PCL is taut during flexion PCL lax during extension 50% of the classical cause of isolated PCL injury is the DASHBOARD INJURY PCL MAY BE TORN WHEN THE KNEE IS HYPERFLEXTED
29 LOWER LIMB: JOINTS THE TIBIOFIBULAR JOINT The small proximal tibiofibular joint is synovial in type and allows very little movement. The interosseous membrane of leg is a tough fibrous sheet of connective tissue that spans the distance between facing interosseous borders of the tibial and fibular shafts. The membrane provides an increased surface area for muscle attachment. The inferior tibiofibular syndesmosis is a compound fibrous joint type and allows very slight movement.
30 LOWER LIMB: JOINTS THE ANKLE JOINT The ankle joint (talocrural articulation) is synovial in type and involves the talus of the foot and the tibia and fibula of the leg The fibula and tibia create a socket for the upper expanded part of the body of the talus: the roof of the socket is formed by the inferior surface of the distal end of the tibia the medial side of the socket is formed by the medial malleolus of the tibia the longer lateral side of the socket is formed by the lateral malleolus of the fibula The articular surfaces are covered by hyaline cartilage The ankle joint is stabilized by: the medial (deltoid) ligaments and the lateral ligaments
31 LOWER LIMB: JOINTS THE ANKLE JOINT THE MEDIAL LIGAMENT THE DELTOID LIGAMENT MEDIAL LIGAMENT (DELTOID LIGAMENT) The medial (deltoid) ligament is large, strong and triangular shape. The medial ligament is subdivided into four parts based on the inferior points of attachment: tibionavicular part tibiocalcaneal part posterior tibiotalar part anterior tibiotalar part THE ANKLE JOINT THE LATERAL LIGAMENT The lateral ligament of the ankle is composed of three separate ligaments: the anterior talofibular ligament the posterior talofibular ligament, and the calcaneofibular ligament
32 LOWER LIMB: JOINTS THE FOOT JOINTS THE INTERTARSAL JOINTS The numerous synovial joints between the individual tarsal bones mainly invert, evert, supinate, and pronate the foot. The major joints include: the subtalar, the talocalcaneonavicular, the calcaneocuboid joints THE SUBTALAR JOINT The subtalar joint is between: the large posterior calcaneal facet on the inferior surface of the talus, and the corresponding posterior talar facet on the superior surface of the calcaneus. THE SUBTALAR JOINT The anatomical subtalar joint is a single synovial joint between the slightly concave posterior calcaneal articular surface of the talus and the convex posterior articular facet of the calcaneus. Orthopaedic surgeons use the term subtalar joint for the compound functional joint consisting of the anatomical subtalar joint plus the talocalcaneal part of the talocalcaneonavicular joint.
33 LOWER LIMB: JOINTS THE FOOT JOINTS The transverse tarsal joint is a compound joint formed by two separate joints aligned transversely: the talonavicular part of the talocalcaneonavicular joint and the calcaneocuboid joint. THE TALOCALCANEONAVICULAR JOINT It is a complex joint in which the head of the talus articulates with: the calcaneus plantar calcaneonavicular ligament below, and the navicular in front THE CALCANEOCUBOID JOINT It is a synovial joint between: the facet on the anterior surface of the calcaneus, and the corresponding facet on the posterior surface of the cuboid. THE TARSOMETATARSAL JOINTS are between the metatarsal bones and tarsal bones. There are plane joints and allow limited sliding movements.
34 LOWER LIMB: JOINTS THE FOOT JOINTS THE METATARSOPHALANGEAL JOINTS are ellipsoid synovial joints between the sphere-shaped heads of the metatarsals and the corresponding bases of the proximal phalanges of the digits. THE INTERPHALANGEAL JOINTS The interphalangeal joints are hinge joints that allow mainly flexion and extension. They are reinforced by medial and lateral collateral ligaments and by plantar ligaments
35 LOWER LIMB: TIGH MUSCLES THE TIGH MUSCLES THE ANTERIOR TIGH MUSCLES pectineus iliopsoas sartorius quadriceps femoris THE ADDUCTOR (MEDIAL) THIGH MUSCLES the adductor longus adductor brevis adductor magnus gracilis obturator externus THE POSTERIOR THIGH MUSCLES The hamstring muscles are: semitendinosus semimembranosus biceps femoris (long head)
36 LOWER LIMB: TIGH MUSCLES THE PECTINEUS MUSCLE The pectineus is a flat quadrangular muscle located in the anterior part of the superomedial aspect of the thigh. The pectineus is innervated by two different nerves: femoral nerve (L2, L3); may receive a branch from obturator nerve. THE ILIOPSOAS MUSCLE The iliopsoas is the chief flexor of the thigh, the most powerful of the hip flexors with the longest range. Its mass located in the posterior wall of the abdomen and greater pelvis. Its broad lateral part, the iliacus, and its long medial part, the psoas major. FLEXOR OF THE HIP JOINT
37 LOWER LIMB: TIGH MUSCLES THE SARTORIUS MUSCLE the tailor s muscle is long and ribbon-like the longest muscle in the body It descends inferiorly as far as the medial side of the knee None of the actions of the sartorius is strong THE QUADRICEPS FEMORIS MUSCLE It covers almost all the anterior aspect and sides of the femur Consists of 4 parts: rectus femoris vastus lateralis vastus intermedius vastus medialis The quadriceps is the great extensor of the leg FLEXOR OF THE HIP JOINT
38 LOWER LIMB: TIGH MUSCLES THE QUADRICEPS FEMORIS MUSCLE The quadriceps is the great extensor of the leg Extends the knee against gravity The tendons of the four parts of the quadriceps unite in the distal portion of the thigh to form a single, strong, broad quadriceps tendon. The patellar ligament, attached to the tibial tuberosity, is the continuation of the quadriceps tendon EXTENSOR OF KNEE THE PECTINEUS: Femoral nerve (L2, L3); may receive a branch from obturator nerve THE PSOAS MAJOR: anterior rami of lumbar nerves (L1, L2, L3) THE ILIACUS: femoral nerve (L2, L3) THE SARTORIUS: femoral nerve (L2, L3) THE QUADRICEPS FEMORIS: femoral nerve (L2, L3, L4)
39 LOWER LIMB: TIGH MUSCLES THE MUSCLES OF THE MEDIAL COMPARTMENT THE ADDUCTOR GROUP OF MUSCLES consisting of the adductor longus adductor brevis adductor magnus gracilis obturator externus All five muscles cross the hip joint, but only gracilis reaches beyond the knee. They attach proximally to the anteroinferior external surface of the pelvis and adjacent obturator membrane, and distally to the linea aspera of the femur. Most of the adductor muscles are supplied by the obturator nerve
40 LOWER LIMB: TIGH MUSCLES THE ADDUCTOR LONGUS The adductor longus is a large, fan-shaped muscle and is the most anteriorly placed of the adductor group THE ADDUCTOR BREVIS The adductor brevis, the short adductor, lies deep to the pectineus and adductor longus THE ADDUCTOR MAGNUS The adductor magnus is the largest, most powerful, and most posterior muscle in the adductor group THE ADDUCTOR HIATUS
41 LOWER LIMB: TIGH MUSCLES THE GRACILIS It is the only one of the group to cross the knee joint as well as the hip joint. Gracilis is sometimes transplanted to replace damaged muscles elsewhere in the body. THE OBTURATOR EXTERNUS The obturator externus is a flat, relatively small muscle that is deeply placed in the superomedial part of the thigh. All adductor muscles, except the hamstring part of the adductor magnus and part of the pectineus are supplied by the obturator nerve (L2 L4). The hamstring part of the adductor magnus is supplied by the tibial part of the sciatic nerve (L4). The gracilis, sartorius and semitendinosus muscles have a common tendinous insertion, the pes anserinus, into the superior part of the medial surface of the tibia. THE ADDUCTOR MAGNUS: Adductor part: obturator nerve (L2, L3, L4), branches of posterior division. Hamstring part: tibial part of sciatic nerve (L4). THE ADDUCTOR LONGUS THE ADDUCTOR BREVIS OBTURATOR NERVE THE GRACILIS THE OBTURATOR EXTERNUS
42 LOWER LIMB: TIGH MUSCLES THE POSTERIOR TIGH MUSCLES The hamstring muscles are: semitendinosus semimembranosus biceps femoris (long head)
43 LOWER LIMB: TIGH MUSCLES THE POSTERIOR TIGH MUSCLES The hamstring muscles ( hamstrings for short) share common features: Proximal attachment to the ischial tuberosity deep to the gluteus maximus Distal attachment to the bones of the leg Thus they span and act on two joints, producing extension at the hip joint and flexion at the knee joint Innervation by the tibial division of the sciatic nerve. THE SEMITENDINOSUS AND SEMIMEMBRANOSUS: Tibial division of sciatic nerve part of tibia THE BICEPS FEMORIS Long head: tibial division of sciatic nerve Short head: common fibular division of sciatic nerve Distally, the tendon attaches to the medial surface of the superior part of the tibia as part of the pes anserinus formation in conjunction with the tendinous insertions of the sartorius and gracilis.
The Dance Hall by Vincent van Gogh,1888
 The Dance Hall by Vincent van Gogh,1888 Articulations of the pelvic girdle Lumbosacral joints, sacroiliac joints & pubic symphysis The remaining joints of the lower limb Hip joint Knee joint Tibiofibular
The Dance Hall by Vincent van Gogh,1888 Articulations of the pelvic girdle Lumbosacral joints, sacroiliac joints & pubic symphysis The remaining joints of the lower limb Hip joint Knee joint Tibiofibular
Bones of Lower Limb. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology
 Bones of Lower Limb Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Bones of the lower limb Hip Bone Made up of 3 bones: 1) Ilium (flat), superior in position 2) Ischium (L), postero-inferior
Bones of Lower Limb Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Bones of the lower limb Hip Bone Made up of 3 bones: 1) Ilium (flat), superior in position 2) Ischium (L), postero-inferior
Copyright 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings. Dr. Nabil Khouri MD, MSc, Ph.D
 Dr. Nabil Khouri MD, MSc, Ph.D Pelvic Girdle (Hip) Organization of the Lower Limb It is divided into: The Gluteal region The thigh The knee The leg The ankle The foot The thigh and the leg have compartments
Dr. Nabil Khouri MD, MSc, Ph.D Pelvic Girdle (Hip) Organization of the Lower Limb It is divided into: The Gluteal region The thigh The knee The leg The ankle The foot The thigh and the leg have compartments
The Hip (Iliofemoral) Joint. Presented by: Rob, Rachel, Alina and Lisa
 The Hip (Iliofemoral) Joint Presented by: Rob, Rachel, Alina and Lisa Surface Anatomy: Posterior Surface Anatomy: Anterior Bones: Os Coxae Consists of 3 Portions: Ilium Ischium Pubis Bones: Pubis Portion
The Hip (Iliofemoral) Joint Presented by: Rob, Rachel, Alina and Lisa Surface Anatomy: Posterior Surface Anatomy: Anterior Bones: Os Coxae Consists of 3 Portions: Ilium Ischium Pubis Bones: Pubis Portion
The Lower Limb II. Anatomy RHS 241 Lecture 3 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa
 The Lower Limb II Anatomy RHS 241 Lecture 3 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa Tibia The larger & medial bone of the leg Functions: Attachment of muscles Transfer of weight from femur to skeleton of the foot Articulations
The Lower Limb II Anatomy RHS 241 Lecture 3 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa Tibia The larger & medial bone of the leg Functions: Attachment of muscles Transfer of weight from femur to skeleton of the foot Articulations
The thigh. Prof. Oluwadiya KS
 The thigh Prof. Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.com The Thigh: Boundaries The thigh is the region of the lower limb that is approximately between the hip and knee joints Anteriorly, it is separated from the
The thigh Prof. Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.com The Thigh: Boundaries The thigh is the region of the lower limb that is approximately between the hip and knee joints Anteriorly, it is separated from the
Anatomy of the lower limb
 Anatomy of the lower limb 1. Bones of the lower limb Pelvis Hip bone/coxal bone Acetabulum o Acetabular margin o Acetabular fossa o Acetabular notch o Lunate surface Ischiopubic ramus Obturator foramen
Anatomy of the lower limb 1. Bones of the lower limb Pelvis Hip bone/coxal bone Acetabulum o Acetabular margin o Acetabular fossa o Acetabular notch o Lunate surface Ischiopubic ramus Obturator foramen
Topic 7: Hip and pelvis. Parts of the hip. Parts of the femur
 Topic 7: Hip and pelvis Parts of the hip Parts of the femur Classifying the hip joint Ball and socket Synovial Multiaxial Movements of the hip: Abduction/adduction Flexion/extension Medial/lateral rotation
Topic 7: Hip and pelvis Parts of the hip Parts of the femur Classifying the hip joint Ball and socket Synovial Multiaxial Movements of the hip: Abduction/adduction Flexion/extension Medial/lateral rotation
Pelvic Girdle
 ARTICULATIONS OF LOWER EXTREMITY Pages 429-437 Pelvic Girdle formed by connection of the hip bones and the sacrum Sacroiliac Joints compound joints synovial joint - anterior, between the auricular surfaces
ARTICULATIONS OF LOWER EXTREMITY Pages 429-437 Pelvic Girdle formed by connection of the hip bones and the sacrum Sacroiliac Joints compound joints synovial joint - anterior, between the auricular surfaces
It is formed by fusion of 3 bones: I. Ilium (superior bone). II. Pubis (antero-inferior bone). III. Ischium (postero-inferior bone).
 It is formed by fusion of 3 bones: I. Ilium (superior bone). II. Pubis (antero-inferior bone). III. Ischium (postero-inferior bone). Pubis Acetabulum Ana (242 ) The three constituent of bones of the hip
It is formed by fusion of 3 bones: I. Ilium (superior bone). II. Pubis (antero-inferior bone). III. Ischium (postero-inferior bone). Pubis Acetabulum Ana (242 ) The three constituent of bones of the hip
Bones of the Lower Limb Bone Structure Description Notes. border of the superior ramus. inferolaterally from the pubic symphysis
 Bones of the Lower Limb Bone Structure Description Notes pubis an angulated bone the forms the anterior part of the pelvis one of three bones that form the os coxae: ilium, ischium, pubis; its forms 1/5
Bones of the Lower Limb Bone Structure Description Notes pubis an angulated bone the forms the anterior part of the pelvis one of three bones that form the os coxae: ilium, ischium, pubis; its forms 1/5
Anatomy & Physiology. Muscles of the Lower Limbs.
 Anatomy & Physiology Muscles of the Lower Limbs http://www.ishapeup.com/musclecharts.html Muscles of the Lower Limbs Among the strongest muscles in the body. Because pelvic girdle is composed of heavy,
Anatomy & Physiology Muscles of the Lower Limbs http://www.ishapeup.com/musclecharts.html Muscles of the Lower Limbs Among the strongest muscles in the body. Because pelvic girdle is composed of heavy,
Anatomage Table Instructors Guide- Lower Limb
 The Lower Limb Anatomage Table Instructors Guide- Lower Limb Table of Contents Lower Limb 1- The Skeletal System...3 1: Hip Bone...3 2: Hip Joint and Femur...4 3: Patella and Knee Joint...7 4: Tibia, Fibula,
The Lower Limb Anatomage Table Instructors Guide- Lower Limb Table of Contents Lower Limb 1- The Skeletal System...3 1: Hip Bone...3 2: Hip Joint and Femur...4 3: Patella and Knee Joint...7 4: Tibia, Fibula,
Joints of the Lower Limb II
 Joints of the Lower Limb II Lecture Objectives Describe the components of the knee and ankle joint. List the ligaments associated with these joints and their attachments. List the muscles acting on these
Joints of the Lower Limb II Lecture Objectives Describe the components of the knee and ankle joint. List the ligaments associated with these joints and their attachments. List the muscles acting on these
Muscles of the lower extremities. Dr. Nabil khouri MD, MSc, Ph.D
 Muscles of the lower extremities Dr. Nabil khouri MD, MSc, Ph.D Posterior leg Popliteal fossa Boundaries Biceps femoris (superior-lateral) Semitendinosis and semimembranosis (superior-medial) Gastrocnemius
Muscles of the lower extremities Dr. Nabil khouri MD, MSc, Ph.D Posterior leg Popliteal fossa Boundaries Biceps femoris (superior-lateral) Semitendinosis and semimembranosis (superior-medial) Gastrocnemius
Muscles of Lesson Five. Muscular Nomenclature and Kinesiology - Two. Muscles of Lesson Five, cont. Chapter 16
 Chapter 16 Muscular Nomenclature and Kinesiology - Two Lessons 5-6 Muscles of Lesson Five Iliopsoas (psoas major, iliacus) Hip outward rotators (piriformis, gemellus superior, gemellus inferior, obturator
Chapter 16 Muscular Nomenclature and Kinesiology - Two Lessons 5-6 Muscles of Lesson Five Iliopsoas (psoas major, iliacus) Hip outward rotators (piriformis, gemellus superior, gemellus inferior, obturator
Hip joint Type: Articulating bones:
 Ana (242 ) Hip joint Type: Synovial, ball & socket Articulating bones: Formed between head of femur and lunate surface of acetabulum of hip bone. Capsule: it is a strong fibrous sleeve connecting the articulating
Ana (242 ) Hip joint Type: Synovial, ball & socket Articulating bones: Formed between head of femur and lunate surface of acetabulum of hip bone. Capsule: it is a strong fibrous sleeve connecting the articulating
To describe he knee joint, ligaments, structure & To list the main features of other lower limb joints
 To describe he knee joint, ligaments, structure & neurovascular supply To demonstrate the ankle joint anatomy To list the main features of other lower limb joints To list main groups of lymph nodes in
To describe he knee joint, ligaments, structure & neurovascular supply To demonstrate the ankle joint anatomy To list the main features of other lower limb joints To list main groups of lymph nodes in
The Lower Limb. Anatomy RHS 241 Lecture 2 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa
 The Lower Limb Anatomy RHS 241 Lecture 2 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa The bony pelvis Protective osseofibrous ring for the pelvic viscera Transfer of forces to: acetabulum & head of femur (when standing) ischial
The Lower Limb Anatomy RHS 241 Lecture 2 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa The bony pelvis Protective osseofibrous ring for the pelvic viscera Transfer of forces to: acetabulum & head of femur (when standing) ischial
Lower limb summary. Anterior compartment of the thigh. Done By: Laith Qashou. Doctor_2016
 Lower limb summary Done By: Laith Qashou Doctor_2016 Anterior compartment of the thigh Sartorius Anterior superior iliac spine Upper medial surface of shaft of tibia 1. Flexes, abducts, laterally rotates
Lower limb summary Done By: Laith Qashou Doctor_2016 Anterior compartment of the thigh Sartorius Anterior superior iliac spine Upper medial surface of shaft of tibia 1. Flexes, abducts, laterally rotates
Figure 7: Bones of the lower limb
 BONES OF THE APPENDICULAR SKELETON The appendicular skeleton is composed of the 126 bones of the appendages and the pectoral and pelvic girdles, which attach the limbs to the axial skeleton. Although the
BONES OF THE APPENDICULAR SKELETON The appendicular skeleton is composed of the 126 bones of the appendages and the pectoral and pelvic girdles, which attach the limbs to the axial skeleton. Although the
rotation of the hip Flexion of the knee Iliac fossa of iliac Lesser trochanter Femoral nerve Flexion of the thigh at the hip shaft of tibia
 Anatomy of the lower limb Anterior & medial compartments of the thigh Dr. Hayder The fascia lata encloses the entire thigh like a sleeve/stocking. Three intramuscular fascial septa (lateral, medial, and
Anatomy of the lower limb Anterior & medial compartments of the thigh Dr. Hayder The fascia lata encloses the entire thigh like a sleeve/stocking. Three intramuscular fascial septa (lateral, medial, and
lesser trochanter of femur lesser trochanter of femur iliotibial tract (connective tissue) medial surface of proximal tibia
 LOWER LIMB MUSCLES OF THE APPENDICULAR SKELETON The muscles that act on the lower limb fall into three groups: those that move the thigh, those that move the lower leg, and those that move the ankle, foot,
LOWER LIMB MUSCLES OF THE APPENDICULAR SKELETON The muscles that act on the lower limb fall into three groups: those that move the thigh, those that move the lower leg, and those that move the ankle, foot,
The Appendicular Skeleton
 8 The Appendicular Skeleton PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris 8-1 The Pectoral Girdle The Pectoral Girdle Also called shoulder girdle Connects the
8 The Appendicular Skeleton PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris 8-1 The Pectoral Girdle The Pectoral Girdle Also called shoulder girdle Connects the
Main Menu. Joint and Pelvic Girdle click here. The Power is in Your Hands
 1 Hip Joint and Pelvic Girdle click here Main Menu K.6 http://www.handsonlineeducation.com/classes//k6entry.htm[3/23/18, 2:01:12 PM] Hip Joint (acetabular femoral) Relatively stable due to : Bony architecture
1 Hip Joint and Pelvic Girdle click here Main Menu K.6 http://www.handsonlineeducation.com/classes//k6entry.htm[3/23/18, 2:01:12 PM] Hip Joint (acetabular femoral) Relatively stable due to : Bony architecture
Pelvic cavity. Gross anatomy of the lower limb. Walking. Sándor Katz M.D.,Ph.D.
 Pelvic cavity. Gross anatomy of the lower limb. Walking. Sándor Katz M.D.,Ph.D. Lower limb Pelvic girdle Free lower extremity Hip bone Definitive fusion of the Y- shaped growth plate occurs 16th -18th
Pelvic cavity. Gross anatomy of the lower limb. Walking. Sándor Katz M.D.,Ph.D. Lower limb Pelvic girdle Free lower extremity Hip bone Definitive fusion of the Y- shaped growth plate occurs 16th -18th
Human Anatomy Biology 351
 Human Anatomy Biology 351 Lower Limb Please place your name on the back of the last page of this exam. You must answer all questions on this exam. Because statistics demonstrate that, on average, between
Human Anatomy Biology 351 Lower Limb Please place your name on the back of the last page of this exam. You must answer all questions on this exam. Because statistics demonstrate that, on average, between
Muscles of the Thigh. 6.1 Identify, describe the attachments of and deduce the actions of the muscles of the thigh: Anterior group
 Muscles of the Thigh 6.1 Identify, describe the attachments of and deduce the actions of the muscles of the thigh: Anterior group Sartorius: This is a long strap like muscle with flattened tendons at each
Muscles of the Thigh 6.1 Identify, describe the attachments of and deduce the actions of the muscles of the thigh: Anterior group Sartorius: This is a long strap like muscle with flattened tendons at each
CHAPTER 8: THE BIOMECHANICS OF THE HUMAN LOWER EXTREMITY
 CHAPTER 8: THE BIOMECHANICS OF THE HUMAN LOWER EXTREMITY _ 1. The hip joint is the articulation between the and the. A. femur, acetabulum B. femur, spine C. femur, tibia _ 2. Which of the following is
CHAPTER 8: THE BIOMECHANICS OF THE HUMAN LOWER EXTREMITY _ 1. The hip joint is the articulation between the and the. A. femur, acetabulum B. femur, spine C. femur, tibia _ 2. Which of the following is
Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D. 1 SCCC BIO130 Lab 7 Appendicular Skeleton & Articulations
 The Skeletal System II: Appendicular Skeleton and Articulations Exercises 11, 13 (begins: page 145 in 9 th and 10 th editions) Exercises 10, 11 (begins: page 147 in 11 th edition, page 149 in 12 th edition)
The Skeletal System II: Appendicular Skeleton and Articulations Exercises 11, 13 (begins: page 145 in 9 th and 10 th editions) Exercises 10, 11 (begins: page 147 in 11 th edition, page 149 in 12 th edition)
The Hip Joint. Shenequia Howard David Rivera
 The Hip Joint Shenequia Howard David Rivera Topics Of Discussion Movement Bony Anatomy Ligamentous Anatomy Muscular Anatomy Origin/Insertion/Action/Innervation Common Injuries MOVEMENT Flexion Extension
The Hip Joint Shenequia Howard David Rivera Topics Of Discussion Movement Bony Anatomy Ligamentous Anatomy Muscular Anatomy Origin/Insertion/Action/Innervation Common Injuries MOVEMENT Flexion Extension
Muscles of the Hip 1. Tensor Fasciae Latae O: iliac crest I: lateral femoral condyle Action: abducts the thigh Nerve: gluteal nerve
 Muscles of the Hip 1. Tensor Fasciae Latae O: iliac crest I: lateral femoral condyle Action: abducts the thigh Nerve: gluteal nerve 2. Gluteus Maximus O: ilium I: femur Action: abduct the thigh Nerve:
Muscles of the Hip 1. Tensor Fasciae Latae O: iliac crest I: lateral femoral condyle Action: abducts the thigh Nerve: gluteal nerve 2. Gluteus Maximus O: ilium I: femur Action: abduct the thigh Nerve:
To classify the joints relative to structure & shape
 To classify the joints relative to structure & shape To describe the anatomy of the hip joint To describe the ankle joint To memorize their blood & nerve supply JOINTS: Joints are sites where skeletal
To classify the joints relative to structure & shape To describe the anatomy of the hip joint To describe the ankle joint To memorize their blood & nerve supply JOINTS: Joints are sites where skeletal
Joints of the lower limb
 Joints of the lower limb 1-Type: Hip joint Synovial ball-and-socket joint 2-Articular surfaces: a- head of femur b- lunate surface of acetabulum Which is deepened by the fibrocartilaginous labrum acetabulare
Joints of the lower limb 1-Type: Hip joint Synovial ball-and-socket joint 2-Articular surfaces: a- head of femur b- lunate surface of acetabulum Which is deepened by the fibrocartilaginous labrum acetabulare
Anterior and Medial compartments of the thigh. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology
 Anterior and Medial compartments of the thigh Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Terms Related to Movements Movement Flexion Extension Abduction Adduction Medial (internal)
Anterior and Medial compartments of the thigh Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Terms Related to Movements Movement Flexion Extension Abduction Adduction Medial (internal)
Identify the muscles associated with the medial compartment of the thigh. Identify the attachment points of the medial thigh muscles.
 L 8 A B O R A T O R Y Thigh MEDIAL THIGH Identify the muscles associated with the medial compartment of the thigh. Identify the attachment points of the medial thigh muscles. Identify the actions of these
L 8 A B O R A T O R Y Thigh MEDIAL THIGH Identify the muscles associated with the medial compartment of the thigh. Identify the attachment points of the medial thigh muscles. Identify the actions of these
Lectures of Human Anatomy
 Lectures of Human Anatomy Lower Limb Gluteal Region and Hip Joint By DR. ABDEL-MONEM AWAD HEGAZY M.B. with honor 1983, Dipl."Gynecology and Obstetrics "1989, Master "Anatomy and Embryology" 1994, M.D.
Lectures of Human Anatomy Lower Limb Gluteal Region and Hip Joint By DR. ABDEL-MONEM AWAD HEGAZY M.B. with honor 1983, Dipl."Gynecology and Obstetrics "1989, Master "Anatomy and Embryology" 1994, M.D.
First practical session. Bones of the gluteal region
 First practical session 2017 Bones of the gluteal region The Hip bone The hip bone is made of: 1 The ilium: superior in position 2 The ischium:postero-inferior in position 3 The pubis: antero-inferior
First practical session 2017 Bones of the gluteal region The Hip bone The hip bone is made of: 1 The ilium: superior in position 2 The ischium:postero-inferior in position 3 The pubis: antero-inferior
The Lower Limb. Sevda LAFCI FAHRİOĞLU, MD.PhD.
 The Lower Limb Sevda LAFCI FAHRİOĞLU, MD.PhD. The Lower Limb The bones of the lower limb form the inferior part of the appendicular skeleton the organ of locomotion for bearing the weight of body stronger
The Lower Limb Sevda LAFCI FAHRİOĞLU, MD.PhD. The Lower Limb The bones of the lower limb form the inferior part of the appendicular skeleton the organ of locomotion for bearing the weight of body stronger
Lab Activity 9. Appendicular Skeleton Martini Chapter 8. Portland Community College BI 231
 Lab Activity 9 Appendicular Skeleton Martini Chapter 8 Portland Community College BI 231 Appendicular Skeleton Upper & Lower extremities Shoulder Girdle Pelvic Girdle 2 Humerus 3 Humerus: Proximal End
Lab Activity 9 Appendicular Skeleton Martini Chapter 8 Portland Community College BI 231 Appendicular Skeleton Upper & Lower extremities Shoulder Girdle Pelvic Girdle 2 Humerus 3 Humerus: Proximal End
Lesson 24. A & P Hip
 Lesson 24 A & P Hip 1 Aims of the Session This session will allow candidates to have an understanding of the bony prominences and soft tissues of the hip 2 Learning Outcomes By the end of the lesson the
Lesson 24 A & P Hip 1 Aims of the Session This session will allow candidates to have an understanding of the bony prominences and soft tissues of the hip 2 Learning Outcomes By the end of the lesson the
Clarification of Terms
 Clarification of Terms The plantar aspect of the foot refers to the role or its bottom The dorsal aspect refers to the top or its superior portion The ankle and foot perform three main functions: 1. shock
Clarification of Terms The plantar aspect of the foot refers to the role or its bottom The dorsal aspect refers to the top or its superior portion The ankle and foot perform three main functions: 1. shock
Human Anatomy Biology 351
 Human Anatomy Biology 351 Lower Limb Please place your name on the back of the last page of this exam. You must answer all questions on this exam. Because statistics demonstrate that, on average, between
Human Anatomy Biology 351 Lower Limb Please place your name on the back of the last page of this exam. You must answer all questions on this exam. Because statistics demonstrate that, on average, between
Hip joint and pelvic girdle. Lower Extremity. Pelvic Girdle 6/5/2017
 Hip joint and pelvic girdle Lower Extremity The relationship between the pelvic girdle and hip is similar to that between the shoulder girdle and shoulder joint. The lower limbs are attached to the axial
Hip joint and pelvic girdle Lower Extremity The relationship between the pelvic girdle and hip is similar to that between the shoulder girdle and shoulder joint. The lower limbs are attached to the axial
ANATYOMY OF The thigh
 ANATYOMY OF The thigh 1- Lateral cutaneous nerve of the thigh Ι) Skin of the thigh Anterior view 2- Femoral branch of the genitofemoral nerve 5- Intermediate cutaneous nerve of the thigh 1, 2 and 3 are
ANATYOMY OF The thigh 1- Lateral cutaneous nerve of the thigh Ι) Skin of the thigh Anterior view 2- Femoral branch of the genitofemoral nerve 5- Intermediate cutaneous nerve of the thigh 1, 2 and 3 are
The Hay is in the Barn
 Anatomy 1 Practical 1 Review Made by Forrest Allen (nerd) Edited by TJ Williamson (not nerd) The Hay is in the Barn 2019 Thunderbringers Too much to handle https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=glii-kaza d8
Anatomy 1 Practical 1 Review Made by Forrest Allen (nerd) Edited by TJ Williamson (not nerd) The Hay is in the Barn 2019 Thunderbringers Too much to handle https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=glii-kaza d8
Baraa Ayed حسام أبو عوض. Ahmad Salman. 1 P a g e
 4 Baraa Ayed حسام أبو عوض Ahmad Salman 1 P a g e Today we are going to cover these concepts: Iliotibial tract Anterior compartment of the thigh and the hip Medial compartment of the thigh Femoral triangle
4 Baraa Ayed حسام أبو عوض Ahmad Salman 1 P a g e Today we are going to cover these concepts: Iliotibial tract Anterior compartment of the thigh and the hip Medial compartment of the thigh Femoral triangle
LOWER LIMB. As we know the bony part of the body is divided into Axial and Appendicular (upper and lower Limbs)
 LOWER LIMB As we know the bony part of the body is divided into Axial and Appendicular (upper and lower Limbs) Bones of the Lower limb: 1-Pelvic Girdle: composed of: 1. Right hip bone : is formed by 3
LOWER LIMB As we know the bony part of the body is divided into Axial and Appendicular (upper and lower Limbs) Bones of the Lower limb: 1-Pelvic Girdle: composed of: 1. Right hip bone : is formed by 3
The Knee. Clarification of Terms. Osteology of the Knee 7/28/2013. The knee consists of: The tibiofemoral joint Patellofemoral joint
 The Knee Clarification of Terms The knee consists of: The tibiofemoral joint Patellofemoral joint Mansfield, p273 Osteology of the Knee Distal Femur Proximal tibia and fibula Patella 1 Osteology of the
The Knee Clarification of Terms The knee consists of: The tibiofemoral joint Patellofemoral joint Mansfield, p273 Osteology of the Knee Distal Femur Proximal tibia and fibula Patella 1 Osteology of the
LAB Notes#1. Ahmad Ar'ar. Eslam
 LAB Notes#1 Ahmad Ar'ar Eslam 1 P a g e Anatomy lab Notes Lower limb bones :- Pelvic girdle: It's the connection between the axial skeleton and the lower limb; it's made up of one bone called the HIP BONE
LAB Notes#1 Ahmad Ar'ar Eslam 1 P a g e Anatomy lab Notes Lower limb bones :- Pelvic girdle: It's the connection between the axial skeleton and the lower limb; it's made up of one bone called the HIP BONE
Lecture 08 THIGH MUSCLES ANTERIOR COMPARTMENT. Dr Farooq Khan Aurakzai. Dated:
 Lecture 08 THIGH MUSCLES ANTERIOR COMPARTMENT BY Dr Farooq Khan Aurakzai Dated: 11.02.2017 INTRODUCTION to the thigh Muscles. The musculature of the thigh can be split into three sections by intermuscular
Lecture 08 THIGH MUSCLES ANTERIOR COMPARTMENT BY Dr Farooq Khan Aurakzai Dated: 11.02.2017 INTRODUCTION to the thigh Muscles. The musculature of the thigh can be split into three sections by intermuscular
The Knee. Prof. Oluwadiya Kehinde
 The Knee Prof. Oluwadiya Kehinde www.oluwadiya.sitesled.com The Knee: Introduction 3 bones: femur, tibia and patella 2 separate joints: tibiofemoral and patellofemoral. Function: i. Primarily a hinge joint,
The Knee Prof. Oluwadiya Kehinde www.oluwadiya.sitesled.com The Knee: Introduction 3 bones: femur, tibia and patella 2 separate joints: tibiofemoral and patellofemoral. Function: i. Primarily a hinge joint,
Chapter 8. The Appendicular Skeleton. Lecture Presentation by Lee Ann Frederick University of Texas at Arlington Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 8 The Appendicular Skeleton Lecture Presentation by Lee Ann Frederick University of Texas at Arlington An Introduction to the Appendicular Skeleton The Appendicular Skeleton 126 bones Allows us
Chapter 8 The Appendicular Skeleton Lecture Presentation by Lee Ann Frederick University of Texas at Arlington An Introduction to the Appendicular Skeleton The Appendicular Skeleton 126 bones Allows us
The psoas minor is medial to the psoas major. The iliacus is a fan-shaped muscle that when contracted helps bring the swinging leg forward in walking
 1 p.177 2 3 The psoas minor is medial to the psoas major. The iliacus is a fan-shaped muscle that when contracted helps bring the swinging leg forward in walking and running. The iliopsoas and adductor
1 p.177 2 3 The psoas minor is medial to the psoas major. The iliacus is a fan-shaped muscle that when contracted helps bring the swinging leg forward in walking and running. The iliopsoas and adductor
Acland's DVD Atlas of Human Anatomy. Transcript for Volume Robert D Acland
 Acland's DVD Atlas of Human Anatomy Transcript for Volume 2 2007 Robert D Acland This free downloadable pdf file is to be used for individual study only. It is not to be reproduced in any form without
Acland's DVD Atlas of Human Anatomy Transcript for Volume 2 2007 Robert D Acland This free downloadable pdf file is to be used for individual study only. It is not to be reproduced in any form without
The Muscular System. Chapter 10 Part D. PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Karen Dunbar Kareiva Ivy Tech Community College
 Chapter 10 Part D The Muscular System Annie Leibovitz/Contact Press Images PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Karen Dunbar Kareiva Ivy Tech Community College Table 10.14: Muscles Crossing the Hip and
Chapter 10 Part D The Muscular System Annie Leibovitz/Contact Press Images PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Karen Dunbar Kareiva Ivy Tech Community College Table 10.14: Muscles Crossing the Hip and
Pectoral (Shoulder) Girdle
 Chapter 8 Skeletal System: Appendicular Skeleton Pectoral girdle Pelvic girdle Upper limbs Lower limbs 8-1 Pectoral (Shoulder) Girdle Consists of scapula and clavicle Clavicle articulates with sternum
Chapter 8 Skeletal System: Appendicular Skeleton Pectoral girdle Pelvic girdle Upper limbs Lower limbs 8-1 Pectoral (Shoulder) Girdle Consists of scapula and clavicle Clavicle articulates with sternum
Biology 218 Human Anatomy. Adapted from Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 7 The Skeletal System Appendicular Division
 Adapted from Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 7 The Skeletal System Appendicular Division Introduction The appendicular skeleton includes: Pectoral girdle Shoulder bones Upper limbs Pelvic girdle
Adapted from Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 7 The Skeletal System Appendicular Division Introduction The appendicular skeleton includes: Pectoral girdle Shoulder bones Upper limbs Pelvic girdle
Human Anatomy Biology 255
 Human Anatomy Biology 255 Exam #4 Please place your name and I.D. number on the back of the last page of this exam. You must answer all questions on this exam. Because statistics demonstrate that, on average,
Human Anatomy Biology 255 Exam #4 Please place your name and I.D. number on the back of the last page of this exam. You must answer all questions on this exam. Because statistics demonstrate that, on average,
Understanding Leg Anatomy and Function THE UPPER LEG
 Understanding Leg Anatomy and Function THE UPPER LEG The long thigh bone is the femur. It connects to the pelvis to form the hip joint and then extends down to meet the tibia (shin bone) at the knee joint.
Understanding Leg Anatomy and Function THE UPPER LEG The long thigh bone is the femur. It connects to the pelvis to form the hip joint and then extends down to meet the tibia (shin bone) at the knee joint.
In-Depth Foundations: Anatomy Terms to Know
 Be familiar with / able to identify and define all the following parts. The Spine Cranium Vertebrae Cervical, Thoracic, Lumbar Sacrum Coccyx Bones of Upper Body Cranium Mastoid process; Occipital condyle,
Be familiar with / able to identify and define all the following parts. The Spine Cranium Vertebrae Cervical, Thoracic, Lumbar Sacrum Coccyx Bones of Upper Body Cranium Mastoid process; Occipital condyle,
Gluteal region DR. GITANJALI KHORWAL
 Gluteal region DR. GITANJALI KHORWAL Gluteal region The transitional area between the trunk and the lower extremity. The gluteal region includes the rounded, posterior buttocks and the laterally placed
Gluteal region DR. GITANJALI KHORWAL Gluteal region The transitional area between the trunk and the lower extremity. The gluteal region includes the rounded, posterior buttocks and the laterally placed
Myology of the Knee. PTA 105 Kinesiology
 Myology of the Knee PTA 105 Kinesiology Objectives Describe the planes of motion and axes of rotation of the knee joint Visualize the origins and insertions of the muscles about the knee List the innervations
Myology of the Knee PTA 105 Kinesiology Objectives Describe the planes of motion and axes of rotation of the knee joint Visualize the origins and insertions of the muscles about the knee List the innervations
5.1 Identify, describe the attachments of and deduce the actions of the muscles of the thigh:
 5.1 Identify, describe the attachments of and deduce the actions of the muscles of the thigh: Anterior group Proximal attachment Distal attachment Sartorius ASIS» Upper part of shaft tibia (middle surface)»
5.1 Identify, describe the attachments of and deduce the actions of the muscles of the thigh: Anterior group Proximal attachment Distal attachment Sartorius ASIS» Upper part of shaft tibia (middle surface)»
Figure 1 - Hip and Pelvis
 Hip Figure 1 - Hip and Pelvis The terms hip and pelvis are frequently used interchangeably, but strictly speaking, the pelvis is a girdle of bones and the hip is a joint. The pelvis consists of The sacrum
Hip Figure 1 - Hip and Pelvis The terms hip and pelvis are frequently used interchangeably, but strictly speaking, the pelvis is a girdle of bones and the hip is a joint. The pelvis consists of The sacrum
Introduction. The primary function of the ankle and foot is to absorb shock and impart thrust to the body during walking.
 The ankle 1 Introduction The primary function of the ankle and foot is to absorb shock and impart thrust to the body during walking. OSTEOLOGRY The term ankle refers primarily to the talocrural joint,
The ankle 1 Introduction The primary function of the ankle and foot is to absorb shock and impart thrust to the body during walking. OSTEOLOGRY The term ankle refers primarily to the talocrural joint,
MUSCLES OF THE LOWER LIMBS
 MUSCLES OF THE LOWER LIMBS Naming, location and general function Dr. Nabil khouri ROLES THAT SHOULD NOT BE FORGOTTEN Most anterior compartment muscles of the hip and thigh Flexor of the femur at the hip
MUSCLES OF THE LOWER LIMBS Naming, location and general function Dr. Nabil khouri ROLES THAT SHOULD NOT BE FORGOTTEN Most anterior compartment muscles of the hip and thigh Flexor of the femur at the hip
and K n e e J o i n t Is the most complicated joint in the body!!!!
 K n e e J o i n t K n e e J o i n t Is the most complicated joint in the body!!!! 1-Consists of two condylar joints between: A-The medial and lateral condyles of the femur and The condyles of the tibia
K n e e J o i n t K n e e J o i n t Is the most complicated joint in the body!!!! 1-Consists of two condylar joints between: A-The medial and lateral condyles of the femur and The condyles of the tibia
Bony Anatomy. Femur. Femoral Head Femoral Neck Greater Trochanter Lesser Trochanter Intertrochanteric Crest Intertrochanteric Line Gluteal Tuberosity
 Hip Anatomy Bony Anatomy Femur Femoral Head Femoral Neck Greater Trochanter Lesser Trochanter Intertrochanteric Crest Intertrochanteric Line Gluteal Tuberosity Bony Anatomy Pelvic Girdle Acetabulum 3 bones
Hip Anatomy Bony Anatomy Femur Femoral Head Femoral Neck Greater Trochanter Lesser Trochanter Intertrochanteric Crest Intertrochanteric Line Gluteal Tuberosity Bony Anatomy Pelvic Girdle Acetabulum 3 bones
UNIT 7 JOINTS. Knee and Ankle Joints DR. ABDEL-MONEM A. HEGAZY
 UNIT 7 JOINTS Knee and Ankle Joints BY DR. ABDEL-MONEM A. HEGAZY (Degree in Bachelor of Medicine and Surgery with honor 1983, Dipl."Gynaecology and Obstetrics "1989, Master "Anatomy and Embryology "1994,
UNIT 7 JOINTS Knee and Ankle Joints BY DR. ABDEL-MONEM A. HEGAZY (Degree in Bachelor of Medicine and Surgery with honor 1983, Dipl."Gynaecology and Obstetrics "1989, Master "Anatomy and Embryology "1994,
Lower Limb Dr. Robin Paudel
 Lower Limb n What is a limb? n Skeleton n Joints n Pelvis or limb girdle n Hip/Hip Muscles n Lumber and sacral plexus getting spinal nerves out onto limb n Muscles anterior and posterior compartments n
Lower Limb n What is a limb? n Skeleton n Joints n Pelvis or limb girdle n Hip/Hip Muscles n Lumber and sacral plexus getting spinal nerves out onto limb n Muscles anterior and posterior compartments n
Practical 1 Worksheet
 Practical 1 Worksheet ANATOMICAL TERMS 1. Use the word bank to fill in the missing words. reference side stand body arms palms anatomical forward All anatomical terms have a(n) point which is called the
Practical 1 Worksheet ANATOMICAL TERMS 1. Use the word bank to fill in the missing words. reference side stand body arms palms anatomical forward All anatomical terms have a(n) point which is called the
Contents of the Posterior Fascial Compartment of the Thigh
 Contents of the Posterior Fascial Compartment of the Thigh 1-Muscles: B i c e p s f e m o r i s S e m i t e n d i n o s u s S e m i m e m b r a n o s u s a small part of the adductor magnus (h a m s t
Contents of the Posterior Fascial Compartment of the Thigh 1-Muscles: B i c e p s f e m o r i s S e m i t e n d i n o s u s S e m i m e m b r a n o s u s a small part of the adductor magnus (h a m s t
Exercise 13. Articulations and Body Movements
 Exercise 13 Articulations and Body Movements Articulations Articulations, or joints, are points where a bone is connected to one or more other bones. Articulations hold the skeleton together. Articulations
Exercise 13 Articulations and Body Movements Articulations Articulations, or joints, are points where a bone is connected to one or more other bones. Articulations hold the skeleton together. Articulations
Chapter 8B. The Skeletal System: Appendicular Skeleton. The Appendicular Skeleton. Clavicle. Pectoral (Shoulder) Girdle
 The Appendicular Skeleton Chapter 8B The Skeletal System: Appendicular Skeleton 126 bones Pectoral (shoulder) girdle Pelvic (hip) girdle Upper limbs Lower limbs Functions primarily to facilitate movement
The Appendicular Skeleton Chapter 8B The Skeletal System: Appendicular Skeleton 126 bones Pectoral (shoulder) girdle Pelvic (hip) girdle Upper limbs Lower limbs Functions primarily to facilitate movement
ANATYOMY OF The thigh
 ANATYOMY OF The thigh 1- Lateral cutaneous nerve of the thigh Ι) Skin of the thigh Anterior view 2- Femoral branch of the genitofemoral nerve 5- Intermediate cutaneous nerve of the thigh 1, 2 and 3 are
ANATYOMY OF The thigh 1- Lateral cutaneous nerve of the thigh Ι) Skin of the thigh Anterior view 2- Femoral branch of the genitofemoral nerve 5- Intermediate cutaneous nerve of the thigh 1, 2 and 3 are
DISSECTION SCHEDULE. Session I - Hip (Front) & Thigh (Superficial)
 DISSECTION SCHEDULE Session I - Hip (Front) & Thigh (Superficial) Surface anatomy Inguinal region Gluteal region Thigh Leg Foot bones Hip bone Femur Superficial fascia Great saphenous vein Superficial
DISSECTION SCHEDULE Session I - Hip (Front) & Thigh (Superficial) Surface anatomy Inguinal region Gluteal region Thigh Leg Foot bones Hip bone Femur Superficial fascia Great saphenous vein Superficial
ANATYOMY OF The thigh
 ANATYOMY OF The thigh 1- Lateral cutaneous nerve of the thigh Ι) Skin of the thigh Anterior view 2- Femoral branch of the genitofemoral nerve 1, 2 and 3 are From the lumber plexus 5- Intermediate cutaneous
ANATYOMY OF The thigh 1- Lateral cutaneous nerve of the thigh Ι) Skin of the thigh Anterior view 2- Femoral branch of the genitofemoral nerve 1, 2 and 3 are From the lumber plexus 5- Intermediate cutaneous
Knee Joint Anatomy 101
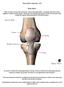 Knee Joint Anatomy 101 Bone Basics There are three bones at the knee joint femur, tibia and patella commonly referred to as the thighbone, shinbone and kneecap. The fibula is not typically associated with
Knee Joint Anatomy 101 Bone Basics There are three bones at the knee joint femur, tibia and patella commonly referred to as the thighbone, shinbone and kneecap. The fibula is not typically associated with
MUSCULOSKELETAL LOWER LIMB
 MUSCULOSKELETAL LOWER LIMB Spinal Cord Lumbar and Sacral Regions Spinal cord Dorsal root ganglion Conus medullaris Cauda equina Dorsal root ganglion of the fifth lumbar nerve End of subarachnoid space
MUSCULOSKELETAL LOWER LIMB Spinal Cord Lumbar and Sacral Regions Spinal cord Dorsal root ganglion Conus medullaris Cauda equina Dorsal root ganglion of the fifth lumbar nerve End of subarachnoid space
The Lower Limb VII: The Ankle & Foot. Anatomy RHS 241 Lecture 7 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa
 The Lower Limb VII: The Ankle & Foot Anatomy RHS 241 Lecture 7 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa Ankle joint Synovial, hinge joint Allow movement of the foot in the sagittal plane only (1 degree of freedom): dorsiflexion:
The Lower Limb VII: The Ankle & Foot Anatomy RHS 241 Lecture 7 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa Ankle joint Synovial, hinge joint Allow movement of the foot in the sagittal plane only (1 degree of freedom): dorsiflexion:
The Knee Joint By Prof. Dr. Muhammad Imran Qureshi
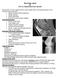 The Knee Joint By Prof. Dr. Muhammad Imran Qureshi Structurally, it is the Largest and the most complex joint in the body because of the functions that it performs: Allows mobility (flexion/extension)
The Knee Joint By Prof. Dr. Muhammad Imran Qureshi Structurally, it is the Largest and the most complex joint in the body because of the functions that it performs: Allows mobility (flexion/extension)
Balanced Body Movement Principles
 Balanced Body Movement Principles How the Body Works and How to Train it. Module 3: Lower Body Strength and Power Developing Strength, Endurance and Power The lower body is our primary source of strength,
Balanced Body Movement Principles How the Body Works and How to Train it. Module 3: Lower Body Strength and Power Developing Strength, Endurance and Power The lower body is our primary source of strength,
Sports Medicine 15. Unit I: Anatomy. The knee, Thigh, Hip and Groin. Part 4 Anatomies of the Lower Limbs
 Sports Medicine 15 Unit I: Anatomy Part 4 Anatomies of the Lower Limbs The knee, Thigh, Hip and Groin Anatomy of the lower limbs In Part 3 of this section we focused upon 11 of the 12 extrinsic muscles
Sports Medicine 15 Unit I: Anatomy Part 4 Anatomies of the Lower Limbs The knee, Thigh, Hip and Groin Anatomy of the lower limbs In Part 3 of this section we focused upon 11 of the 12 extrinsic muscles
lower limb Anterior Compartment: lecture 3 The deep fascia ( fascia lata) divides the thigh into 3 compartments:
 lower limb lecture 3 The deep fascia ( fascia lata) divides the thigh into 3 compartments: 1. Anterior Extensor compartment 2. Medial Adductor compartment 3. Posterior Flexor compartment Anterior Compartment:
lower limb lecture 3 The deep fascia ( fascia lata) divides the thigh into 3 compartments: 1. Anterior Extensor compartment 2. Medial Adductor compartment 3. Posterior Flexor compartment Anterior Compartment:
The Appendicular Skeleton
 8 The Appendicular Skeleton PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris An Introduction to the Appendicular Skeleton Learning Outcomes 8-1 Identify the bones
8 The Appendicular Skeleton PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris An Introduction to the Appendicular Skeleton Learning Outcomes 8-1 Identify the bones
HUMAN BODY COURSE LOWER LIMB NERVES AND VESSELS
 HUMAN BODY COURSE LOWER LIMB NERVES AND VESSELS October 22, 2010 D. LOWER LIMB MUSCLES 2. Lower limb compartments ANTERIOR THIGH COMPARTMENT General lfunction: Hip flexion, knee extension, other motions
HUMAN BODY COURSE LOWER LIMB NERVES AND VESSELS October 22, 2010 D. LOWER LIMB MUSCLES 2. Lower limb compartments ANTERIOR THIGH COMPARTMENT General lfunction: Hip flexion, knee extension, other motions
Muscle Testing of Knee Extensors. Yasser Moh. Aneis, PhD, MSc., PT. Lecturer of Physical Therapy Basic Sciences Department
 Muscle Testing of Knee Extensors Yasser Moh. Aneis, PhD, MSc., PT. Lecturer of Physical Therapy Basic Sciences Department Muscle Testing of Knee Extensors othe Primary muscle Quadriceps Femoris -Rectus
Muscle Testing of Knee Extensors Yasser Moh. Aneis, PhD, MSc., PT. Lecturer of Physical Therapy Basic Sciences Department Muscle Testing of Knee Extensors othe Primary muscle Quadriceps Femoris -Rectus
Biology 325 Fall 2003
 Name: pre-lab exercise due at beginning of your lab session Matching a. fibrous joints b. cartilaginous joints c. synovial joints 1. exhibit a joint cavity 2. types are sutures and syndesmoses 3. bones
Name: pre-lab exercise due at beginning of your lab session Matching a. fibrous joints b. cartilaginous joints c. synovial joints 1. exhibit a joint cavity 2. types are sutures and syndesmoses 3. bones
Muscles to know. Lab 21. Muscles of the Pelvis and Lower Limbs. Muscles that Position the Lower Limbs. Generally. Muscles that Move the Thigh
 Muscles to know Lab 21 Muscles of the Pelvis, Leg and Foot psoas major iliacus gluteus maximus gluteus medius sartorius quadriceps femoris (4) gracilus adductor longus biceps femoris semitendinosis semimembranosus
Muscles to know Lab 21 Muscles of the Pelvis, Leg and Foot psoas major iliacus gluteus maximus gluteus medius sartorius quadriceps femoris (4) gracilus adductor longus biceps femoris semitendinosis semimembranosus
C. Bones of the Pelvic Girdle
 C. Bones of the Pelvic Girdle 1. 2 coxal bones (a.k.a hip bones): -bony pelvis is made up of hip bones, sacrum, & coccyx -pelvic bones are large & heavy & attach to the axial skeleton via sacrum/coccyx
C. Bones of the Pelvic Girdle 1. 2 coxal bones (a.k.a hip bones): -bony pelvis is made up of hip bones, sacrum, & coccyx -pelvic bones are large & heavy & attach to the axial skeleton via sacrum/coccyx
Copyright 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings. Dr. Nabil khouri
 Dr. Nabil khouri Appendicular Skeleton The appendicular skeleton is made up of the bones of the upper and lower limbs and their girdles Two girdles: Pectoral girdles attach the upper limbs to the body
Dr. Nabil khouri Appendicular Skeleton The appendicular skeleton is made up of the bones of the upper and lower limbs and their girdles Two girdles: Pectoral girdles attach the upper limbs to the body
Biology 218 Human Anatomy
 Chapter 8 Adapted from Tortora 10 th ed. LECTURE OUTLINE A. Introduction (p. 203) 1. The appendicular skeleton contains 126 bones that form: i. two pectoral (shoulder) girdles two upper limbs i one pelvic
Chapter 8 Adapted from Tortora 10 th ed. LECTURE OUTLINE A. Introduction (p. 203) 1. The appendicular skeleton contains 126 bones that form: i. two pectoral (shoulder) girdles two upper limbs i one pelvic
Applied anatomy of the hip and buttock
 CHAPTER CONTENTS The hip joint e9 Capsule and ligaments e9 s e0 Flexor muscles................... e0 Extensor muscles.................. e Abductor muscles.................. e Adductor muscles..................
CHAPTER CONTENTS The hip joint e9 Capsule and ligaments e9 s e0 Flexor muscles................... e0 Extensor muscles.................. e Abductor muscles.................. e Adductor muscles..................
Scapula Spine Lateral edge of clavicle. Medial border Scapula. Medial border of Scapula, between superior angle and root of spine. Scapula.
 Muscle attachments and actions answer sheet Muscle Origins insertions Movements Joints crossed Trapezius Base of skull Spinous process of C7 Thoracic Spine Lateral edge of clavicle Elevation Retraction
Muscle attachments and actions answer sheet Muscle Origins insertions Movements Joints crossed Trapezius Base of skull Spinous process of C7 Thoracic Spine Lateral edge of clavicle Elevation Retraction
Appendicular Skeleton. Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi
 Appendicular Skeleton Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi a.alnuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk abdulameerh@yahoo.com Hi Prof, It is great to hear from you, I really enjoyed your teaching last year. You taught me the hardest
Appendicular Skeleton Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi a.alnuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk abdulameerh@yahoo.com Hi Prof, It is great to hear from you, I really enjoyed your teaching last year. You taught me the hardest
Organization of the Lower Limb
 Organization of the Lower Limb Most illustrations from: Thieme Atlas of Anatomy: Musculoskeletal System. M Schuenke, et al, 2006. Anatomy: A Regional Atlas of the Human Body. Carmine Clemente, 4th edition.
Organization of the Lower Limb Most illustrations from: Thieme Atlas of Anatomy: Musculoskeletal System. M Schuenke, et al, 2006. Anatomy: A Regional Atlas of the Human Body. Carmine Clemente, 4th edition.
SKELETAL SYSTEM 206. AXIAL SKELETON 80 APPENDICULAR SKELETON 126 (see Figure 6.1) Clavicle. Clavicle. Pectoral girdles. Scapula. Scapula.
 SKELETAL SYSTEM 206 AXIAL SKELETON 80 APPENDICULAR SKELETON 126 (see Figure 6.1) Pectoral girdles 4 Clavicle Scapula 2 2 Clavicle Scapula Humerus 2 Humerus Upper limbs 60 Radius 2 Ulna Carpal bones Metacarpal
SKELETAL SYSTEM 206 AXIAL SKELETON 80 APPENDICULAR SKELETON 126 (see Figure 6.1) Pectoral girdles 4 Clavicle Scapula 2 2 Clavicle Scapula Humerus 2 Humerus Upper limbs 60 Radius 2 Ulna Carpal bones Metacarpal
Lumbar Plexus. Ventral rami L1 L4 Supplies: Major nerves.. Abdominal wall External genitalia Anteromedial thigh
 Lower Limb Nerves Lectures Objectives Describe the structure and relationships of the plexuses of the lower limb. Describe the course, relationships and structures supplied for the major nerves of the
Lower Limb Nerves Lectures Objectives Describe the structure and relationships of the plexuses of the lower limb. Describe the course, relationships and structures supplied for the major nerves of the
Chapter 8 Outline. Pectoral Girdle Upper Limb Pelvic Girdle Lower Limb Aging of the Appendicular Skeleton Development of the Appendicular Skeleton
 Chapter 8 Outline Pectoral Girdle Upper Limb Pelvic Girdle Lower Limb Aging of the Appendicular Skeleton Development of the Appendicular Skeleton Figure 8.1 Appendicular Skeleton Pectoral Girdle Clavicle
Chapter 8 Outline Pectoral Girdle Upper Limb Pelvic Girdle Lower Limb Aging of the Appendicular Skeleton Development of the Appendicular Skeleton Figure 8.1 Appendicular Skeleton Pectoral Girdle Clavicle
