Upper Extremity Page Lower Extremity Special Cases
|
|
|
- Agnes Wilson
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 MSK MRI PROTOCOLS
2 Contents Upper Extremity Shoulder Elbow Wrist Finger Thumb Lower Extremity Hip Pelvis Thigh Knee Lower Extremity/Shin Ankle Foot Special Cases Soft Tissue Mass Metal Protocol Page
3 MSK CHEST
4 MR MSK Chest Indications: Pectoralis Major Indications: PecPec tear Sternum Sternum / SC joints Indications: Tumor, Tumor, infection, arthritis, trauma Chest Chest wall Indications: Trauma, Trauma, tumor
5 Use Use large FOV Pectoralis Major Medial-lateral: lateral: cover to midline chest Superior-inferior: inferior: cover down to mid-humeral shaft FOV
6 Pectoralis Major Seq. FOV Matrix/ Slice TR TE TI Flip ETL BW Nex T x / min FSTIR x 19 4/0.5 > T: T: T T: 70 - T FSE x 56 4/0.5 > Cor Obl FSTIR x 19 4/0.5 > T: T: T T: 70 - Sag Oblique T FSE Fat Sat x 19 >
7 Sternum Seq. FOV Matrix/ Slice TR TE TI Flip ETL BW Nex T x / min FSTIR 4 56 x 19 4/0.5 > T: T: T T: 70 - Sag T x 56 4/ min Sag FSTIR x 19 4/0.5 > T: T: T T: 70 - Cor oblique T FSE x 19 >
8 Coronal: Coronal: oblique along sternum Planned from sagittal images
9 Sternoclavicular joints Seq. FOV Matrix/ Slice TR TE TI Flip ETL BW Nex T x / min FSTIR x 19 4/0.5 > T: T: T T: 70 Sag T x 56 4/ min Sag FSTIR x 19 4/0.5 > T: T: T T: 70 Cor T FSE x 19 >
10 Smaller FOV for SC joints Otherwise protocol is similar to Sternum
11 MSK - Chest Wall
12 UPPER EXTREMITY
13 MR Shoulder Indications: Routine Shoulder Indications: Rotator Cuff Pathology/Evaluation MR Arthrogram Indications: Labrum Pathology/Tear Post Gadolinium Shoulder (Indirect MR Arthrogram) Indications: Labral Pathology/Instability without ability to do a direct arthrogram
14 Shoulder-Routine Seq. FOV Matrix/ Slice TR TE TI Flip ETL BW Nex PD FSE x 56 4/ Cor Oblique FSTIR x 19 4/0.5 > T: T: T T: 70 - Cor Oblique T1 SE Non x / minimum - - Sag Oblique T FSE Non Fat Sat x 19 1 >
15 MR Arthrogram Shoulder Seq. FOV Matrix/ Slice TR TE TI Flip ETL BW Nex T1 SE x 19 3/ minimum Cor Oblique T1 SE x 19 3/ minimum Cor Oblique PD FSE x 19 3/0.5 > Sag Oblique T1 SE Non x minimum ABER T1 SE Fat Sat x 19 3/ minimum
16 Shoulder-Post Gadolinium (Indirect MR Arthrogram) **Inject standard dose of IV contrast and wait 0 minutes before scanning** Seq. FOV Matrix/ Slice TR TE TI Flip ETL BW Nex T1 SE x 19 3/ minimum PD FSE x 19 3/ Cor Oblique T1 SE x 19 3/ minimum Sagittal PD FSE x Cor Oblique FSTIR x 19 4/0.5 > T: T: T T: 70 -
17 Shoulder- Imaging Plane Relevant Anatomy Imaging Plane Prescribe plane parallel to humeral shaft. Cover from top of AC joint through proximal humeral diaphysis. Clavicle Humeral Head AC Joint (Not shown on MR) Bony Glenoid
18 Shoulder-Coronal Imaging Plane Relevant Anatomy Coronal Imaging Plane Prescribe coronal plane off of axial images parallel to supraspinatus muscle Supraspinatus
19 Shoulder-Sagittal Sagittal Imaging Plane Relevant Anatomy Sagittal Imaging Plane Prescribe sagittal plane off axial images with line parallel to bony glenoid. Image from mid-scapula through deltoid muscle. Deltoid Muscle Cartilaginous Labrum Ant. and Post. Humeral Head Bony Glenoid Labrum
20 MR Elbow Indications: Routine Elbow Indications: Biceps/Triceps tear Medial/Lateral collateral ligament tear Common Flexor/Common extensor tendon pathology MR Arthrogram Elbow Indications: Intra articular body evaluation Medial/Lateral Collateral Ligament Evaluation Osteochondral defect (OCD) Post Gadolinium Elbow (Indirect MR arthrogram) Indications: IA body OCD
21 Elbow-Routine* Seq. FOV Matrix/ Slice TR TE TI Flip ETL BW Nex T x minimum FSTIR x 19 > T: T: T T: 70 Coronal T x / minimum Coronal PD FSE x 56 3/0.5 > Sag PD FSE x 56 3/ *for Biceps pathology perform FABS sequence; follow this link.
22 MR Arthrogram Elbow Seq. FOV Matrix/ Slice TR TE TI Flip ETL BW Nex T1 Non PD FSE x x >1500 minimum Coronal T x 56 3/ minimum Coronal PD FSE x 56 3/0.5 > Sag T1 SE x 56 3/ minimum
23 Elbow- Imaging Plane Relevant Anatomy Imaging Plane *Prescribe plane perpendicular to coronal plane ( ). Scan from humeral metaphysis through radial tuberosity. Lateral and Medial Humeral Condyles * Radial Tuberosity (bump on medial radius) Radius Ulna Radial tuberosity *
24 Elbow-Coronal Imaging Plane Relevant Anatomy Coronal Imaging Plane *Prescribe plane parallel to medial and lateral epicondyles. Lateral Epicondyle * Humerus Olecranon process of Ulna Medial Epicondyle *
25 Elbow-Sagittal Imaging Plane Relevant Anatomy Sagittal Imaging Plane *Prescribe plane perpendicular to coronal plane ( ). Scan through entire elbow. Lateral Humeral Condyle * Humerus Medial Humeral Condyle * Olecranon process of Ulna
26 For Biceps pathology FABS Sequence Acquire T1 and T FS
27 Wrist Indications: Routine Wrist Indications: TFCC, Lunotriquetral, Scapholunate tear Flexor Tendon/Carpal Tunnel/ Extensor Tendon Pathology Evaluation for Occult fracture MR Wrist Arthrogram Indications: TFCC/LT/SL ligament tears Dynamic Enhanced Wrist (Post Gad Images) Indications: Evaluation of Scaphoid Nonunion/Avascular Necrosis Exam: IMPORTANT: **Perform routine wrist PLUS Pre/Post Gadolinium images through carpal bones in coronal plane**
28 Wrist-Routine Seq. FOV Matrix/ Slice TR TE TI Flip ETL BW Nex Coronal T x / minimum Coronal PD FSE x 56 3/0.5 > Coronal D or 3D GRE x 19 1/0 60 minimum 0-40 PD FSE Fat Sat x 56 3/ Sag FSTIR x 19 3/1 > T: T: T T: 70
29 MR Arthrogram Wrist (direct or indirect) Seq. FOV Matrix/ Slice TR TE TI Flip ETL BW Nex Coronal T1 SE x 56 3/ minimum Coronal PD FSE x 56 3/0.5 > Coronal D or 3D GRE x 19 1/0 60 minimum PD FSE x 56 3/1 > T1 Non x / minimum Sag PD FSE /1 >
30 Wrist- Imaging Plane ***IMAGE WRIST IN PRONATED POSITION! SUPINATED PRONATED Relevant Anatomy Imaging Plane Prescribe plane parallel to distal radius. Scan from proximal metacarpals through distal radial/ulnar metaphysis. trapm trapz cap ham triq scaph lun Dist radius Distal ulna
31 Wrist-Coronal Imaging Plane Remember to pronate the wrist! Relevant Anatomy Coronal Imaging Plane *Prescribe plane parallel to line drawn from ulnar styloid through radial styloid. Scan through entire wrist. Ulnar Styloid Radial Styloid * *
32 Wrist-Sagittal Imaging Plane Relevant Anatomy Sagittal Imaging Plane *Prescribe plane perpendicular to coronal plane ( ). Scan through entire wrist. Ulnar Styloid Radial Styloid * *
33 Hint: if the ulnar styloid is poking out to the side, the wrist is in pronated position
34 Thumb Indications: Routine Routine Thumb Indications: Gamekeeper s s thumb (Ulnar( Collateral Ligament tear) Flexor/Extensor Tendon Tear R/O R/O Occult Fracture
35 Thumb Seq. FOV Matrix/ Slice TR TE TI Flip ETL BW Nex Coronal PD FSE x 56 3/0.3 > Coronal T FSE Fat Sat x 19 3/ Sag FSE STIR x 19 3/0.3 > T: T: T T: 70 T1 SE x / minimal T FSE Fat Sat x 19 3/
36 Thumb- Imaging Plane Relevant Anatomy Imaging Plane Prescribe plane perpendicular to midshaft of proximal 1 st phalanx. Scan from CMC joint through thumb. IP Joint Proximal Phalanx MCP Joint Metacarpal CMC Joint
37 Thumb-Coronal Imaging Plane Coronal Imaging Plane *Prescribe plane with line bisecting sesamoid bones. Scan through entire thumb. Relevant Anatomy * Sesamoids Thumb
38 Thumb-Sagittal Imaging Plane Relevant Anatomy Sagittal Imaging Plane *Prescribe plane perpendicular to coronal imaging plane ( ). Scan through entire thumb. Sesamoids * Thumb
39 Finger Indications: Routine Finger Indications: Pulley rupture/flexor or Extensor Tendon Injury Post Gadolinium Finger Indications: Mass **Perform routine finger plus and either Coronal or Sagittal (whichever plane mass best seen) pre/post gadolinium fast GRE or T1 SE images. See mass protocol and adjust FOV and other parameters as needed.
40 Finger-Routine Seq. FOV Matrix/ Slice TR TE TI Flip ETL BW Nex Sag T1 SE x / minimum Sag T FSE x 19 3/ T1 SE x 19 3/ minimum PD FSE x56 3/ Coronal STIR x56 3/0.3 > T: T: T T: 70
41 Finger- Imaging Plane Relevant Anatomy Distal Phalanx Mid Phalanx Proximal Phalanx Imaging Plane Prescribe best fit line. Scan from proximal metacarpal through entire finger. Metacarpal
42 Finger-Coronal Imaging Plane Relevant Anatomy Extensor Tendon Coronal Imaging Plane *Prescribe plane parallel to anterior metacarpal head. Scan through entire finger. Include adjacent fingers. * Thumb
43 Finger-Sagittal Imaging Plane Relevant Anatomy Extensor Tendon Sagittal Imaging Plane *Prescribe plane perpendicular to coronal plane ( ). Scan through entire finger. Include adjacent fingers. Thumb *
44 LOWER EXTREMITY
45 Bony pelvis Indication: AVN, Mets, transient osteoporosis, bursitis, arthritis, tis, tendonitis, hip pain over age 50 PA Torso Coil is 1 st choice Seq. FOV Matrix/ Slice TR TE TI Flip ETL BW Nex Coronal FSE-STIR STIR x19-3 > T FSE x 56 5/ Coronal T1 SE Non x Minimum Sag T FSE (Hip to Hip) 1-56 x /1 > Coronal in/out of phase T1 GRE
46 ER Hip (Hip fracture screening) Seq. FOV Matrix/ Slice TR TE TI Flip ETL BW Nex Coronal FSE-STIR STIR x19 > T: T: T T: 70 Coronal T1 SE Non x Minimum T FSE x 56 >
47 Direct arthrogram hip Indication: hip labrum tear, FAI or dysplasia, hip pain under age a 50 PA Torso coil is 1 st choice Prescribe obliques along femoral neck from coronal localizer Seq. FOV Matrix/ Slice TR TE TI Flip ETL BW Nex Coronal (PELVIS) T1 SE Non x Minimum Coronal (PELVIS) FSE-STIR STIR x19 > T: T: T T: 70 (PELVIS) T FSE x 56 > Ax oblique (HIP) T x 56 4/ Minimum Coronal (HIP) T x 56 4/ Minimum Sag (HIP) T x 56 4/ Minimum
48 Noncontrast hip Indication: Unilateral hip pain PA Torso coil is 1 st choice Prescribe ax obliques along femoral neck from coronal localizer Seq. FOV Matrix/ Slice TR TE TI Flip ETL BW Nex Coronal (PELVIS) T1 SE Non x Minimum Coronal (PELVIS) FSE-STIR STIR x19 > T: T: T T: 70 (PELVIS) T FSE x 56 > Ax oblique (HIP) PD FSE x 56 > Coronal (HIP) PD FSE x 56 > Sag (HIP) PD FSE x 56 >
49 MARS (Metal Artifact Reduction Sequences) Hip Exam Seq. FOV Matrix/ Slice TR TE TI Flip ETL BW Nex Coronal FSE-STIR STIR x19 > T: T: T T: Coronal T1 SE Non x Minimum 64 T FSE x 56 > (HIP) PD FSE x 56 > Coronal (HIP) PD FSE x 56 > Sag (HIP) PD FSE x 56 >
50 Hip- Imaging Plane Relevant Anatomy Imaging Plane Prescribe plane parallel line bisecting lesser trochanters and/or acetabular roofs. Scan from iliac crests through lesser trochanter. Ilium Acetabular Roof Greater Trochanter Lesser Trochanter
51 Hip-Coronal Imaging Plane Relevant Anatomy Coronal Imaging Plane *Prescribe plane parallel femoral heads. Scan from ischium through pubic symphyses. Femoral Neck Superior Pubic Ramus * Femoral Head Ischium Greater Trochanter
52 Hip-Sagittal Imaging Plane Relevant Anatomy Sagittal Imaging Plane *Prescribe plane perpendicular to coronal plane. Scan from acetabulum through greater trochanter. Femoral Neck Superior Pubic Ramus * Femoral Head Ischium Greater Trochanter
53 Oblique Imaging Plane (For Femoracetabular Impingement Patients Only) Relevant Anatomy Oblique Plane Prescribe plane parallel to femoral neck. Scan through entire femoral neck. Femoral Neck Femoral Head
54 TJUH Athletic Pubalgia MR Protocol Indication: Athletic Pubalgia, Sports Hernia, Sportsman s s Hernia, Adductor tear/strain, Rectus Abdominis Injury PA Torso coil is 1 st choice Prescribe obliques along anterior iliac crest from sagittal localizer Seq. FOV Matrix/NEX Slice TR TE TI ETL BW Coronal STIR Coronal T1 SE T FSE Fat Sat Obl PD FSE Nonfatsat Obl T FSE Fat Sat Sag T FSE Fat Sat Sag PD FSE Nonfatsat (optional) -36 (Both hips) (Both hips) (Both hips) x x x x x x x56-3 > minimum 5/1 > / (max) 4/.5 4/.5 4/.5 >000 >000 >
55 Oblique Imaging Plane (Adductor unfolding plane) Relevant Anatomy Oblique Imaging Plane *Prescribe plane to line paralleling anterior Iliac crest*. Be sure to scan across pubic symphysis at midline Iliac crest * Hip joint *
56 Oblique Imaging Plane (Adductor unfolding plane)
57 Post Gadolinium Pelvis Indications: Osteomylitis IMPORTANT: Bony Pelvis (Special Cases) *Follow Hip Planes* Same as Routine Hip Protocol but perform axial and coronal images on both sides. In addition, perform FMPSPGR fat saturated images pre/post in both axial and coronal planes. In/Out of Phase Pelvis Indications: Possible Bony Metastases IMPORTANT: Perform In/Out of Phase images in Coronal Plane
58 Bony Pelvis Osteo pre/post option Seq. FOV Matrix/ Slice TR TE TI Flip ETL BW Nex Coronal T1 Non Coronal STIR x x >000 minimal 0-40 T1 Non x minimal T FSE x Sag T FSE 0 56 x ? (60-70) /Cor FMPSPGR Pre/Post 1 56 x 19 3/
59 Coronal STIR Indications: Sacrum Sacroiliac joints Possible Sacroileitis (Septic/Rheumatoid or Rheumatoid Variant Seq. Arthritis) FOV Matrix/ Slice TR TE TI Flip ETL BW Nex x 19 > T FSE x 56 > Cor Oblique T1 SE Non 1-56 x 56 3/ minimal Cor Oblique T FSE 1-56 x 56 3/.5 > Sag T FSE 1-56 x 56 3/.5 > T1 SE Non 1-56 x 56 3/ minimal
60 Sacrum Sacroiliac joints Prescribing the coronal oblique plane: parallel the sacrum on a sagittal localizer
61 Routine Thigh (Follow Hip Imaging Planes) Routine Routine Thigh Indications: Polymyositis/Diabetic Myonecrosis
62 Thigh-Routine Seq. FOV Matrix/ Slice TR TE TI Flip ETL BW Nex Coronal T1 SE Non x minimal Coronal T FSE x 56 > Sag STIR 6 56 x 19 > SE T1 Non 6 56 x minimal T FSE 6 56 x 56 >
63 Knee Indications Routine Knee Indications: Meniscal Tear/Medial or Lateral Ligament Tear/ACL/PCL Direct Arthrogram Indications: Meniscal Re-tear Intra articular Body Post Gadolinium Knee Indications Meniscal Re-tear IMPORTANT: Image 0 minutes post gadolinium
64 Knee-Routine Seq. FOV Matrix/ Slice TR TE TI Flip ETL BW Nex Sag PD FSE Non x 56 4/ Sag T FSE x 56 4/ Cor T1 SE Non x / Minimal Coronal T FSE Fat Sat x 56 3/0.5 > T FSE x 56 3/0.5 >
65 MR Arthrogram Knee (dir or ind) Seq. FOV Matrix/ Slice TR TE TI Flip ETL BW Nex Sag T1 Se x Minimal Sag PD FSE Non x 56 4/ Coronal T FSE x 56 > Coronal T1 SE x Minimal T FSE x 56 > T1 SE x Minimal
66 Knee- Imaging Plane Relevant Anatomy Imaging Plane Image from distal quad tendon through patellar tendon insertion Distal Quadriceps tendon P A T Femur Patellar Tendon Insertion Tibia
67 Knee-Coronal Imaging Relevant Anatomy Coronal Imaging Plane Prescribe plane with line parallel to femoral condyles. Image entire knee. Patella Med Fem Condyle Lat Fem Condyle
68 Knee-Sagittal Imaging Plane Relevant Anatomy Sagittal Imaging Plane *Prescribe plane perpendicular to coronal plane ( ). Scan from the medial to the lateral femoral condyle. Patella Med Fem Condyle Lat Fem Condyle * *
69 Lower Extremity/Shin Indication: Shin Splints IMPORTANT: Acquire coronal and axial (STIR) sequences covering both shins, but sagittal and axial (t only of side in question Place a marker on pain / tenderness
70 Lower Extremity/Shin Area Seq. FOV Matrix/ Slice TR TE TI Flip ETL BW Nex Coronal T1 SE Non x minimal Coronal STIR x 19 > STIR x 19 > T FSE (through marker region) x 56 > Sag T FSE 56 x 56 >
71 Ankle Indications Routine Routine Ankle Ligament Sprain/Tendon pathology/tarsal Tunnel/Sinus Tarsi/Occult fracture, PTT, Plantar fasciitis Ankle Ankle Arthrogram Indications: Intra-articular articular Body Post Post Gadolinium Ankle
72 Ankle-Routine Seq. FOV Matrix/ Slice TR TE TI Flip ETL BW Nex Sag T1 SE Non x / Minimal Sag STIR x /1 > PD FSE Non x T FSE x 56 > Coronal T FSE x /1 >
73 MR Arthrogram Ankle (dir or ind) Seq. FOV Matrix/ Slice TR TE TI Flip ETL BW Nex Sag T1 SE 56 x minimal Sag STIR 1 56 x 19 > T1 SE x min PD FSE Non x Coronal T1 SE x minimal Coronal T FSE x 56 >
74 Ankle-Post Contrast Seq. FOV Matrix/ Slice TR TE TI Flip ETL BW Nex FMPSPGR Pre/Post x XX 00? 4? Sag T1 SE Non 56 x minimal T1 SE 1 56 x 56?00 Minimal PD FSE x 56 > Cor T1 SE x minimal
75 Ankle- Imaging Plane Relevant Anatomy Imaging Plane Prescribe plane parallel to axis of calcaneus. Scan ankle from distal tibia through subcutaneous soft tissues (include plantar fascia). Tibia Talus Calcaneus Black band is plantar fascia
76 Ankle-Coronal Imaging Plane Relevant Anatomy Coronal Imaging Plane Prescribe plane perpendicular to axial imaging plane. Scan ankle from calcaneus through metatarsal bases. Talus M E T A T A R Cuboid Calcaneus S A L S
77 Ankle-Sagittal Imaging Plane Relevant Anatomy Sagittal Imaging Plane Prescribe plane with line parallel to talus. Cover ankle from medial through lateral malleolus. Talus Med Mal Lat Mal Ach
78 Midfoot
79 Forefoot
80 Foot-Indications Routine Foot Indications Plantar Plate Injury, R/O fracture, Lisfranc injury, tarsal/metatarsal fracture Post Gadolinium Foot Indications: Morton s Neuroma Osteomyelitis IMPORTANT: Perform routine foot plus coronal FMPSPGR fat saturated pre and post gad images and axial POST gad FMPSPGR fat saturated images.
81 Foot-Routine Seq. FOV Matrix/ Slice TR TE TI Flip ETL BW Nex Coronal (short axis) T1 Non Coronal (short axis) T FSE Sag STIR x x x /0.5 3/0.5 3/ >000 >1500 minimal Sag T1 Non x / minimal (long axis) PD FSE Non x 56 3/0.5 > (long axis) T FSE x 56 3/0.5 >000 90
82 Foot-Mass/Osteomyelitis Seq. FOV Matrix/ Slice TR TE TI Flip ETL BW Nex Coronal T1 SE Non Coronal T FSE Sag STIR x x x 19 3/0.5 3/0.5 3/ >000 >1500 minimal Sag T1 Non x / minimal Coronal FMPSPGR Pre/Post x 19 3/ FMPSPGR Post x 19 3/
83 Foot- Imaging Plane Relevant Anatomy Imaging Plane Prescribe plane parallel to rd or 3rd metatarsal. Scan foot from navicular through phalanges. Phalanges nd metatarsal C U N N A V
84 Foot-Coronal Imaging Plane Relevant Anatomy Coronal Plane *Prescribe plane parallel to 1 st and 5th metatarsal Shafts. Scan through entire foot. Metatarsals 1 3 * 4 5
85 Foot-Sagittal Imaging Plane Relevant Anatomy Sagittal Plane *Prescribe plane perpendicular to coronal Plane ( ). Scan through entire foot. Metatarsals * 1 3 * 4 5 *
86 Soft Tissue Mass Protocol General Recommendations Place Place Vitamin E capsule LIGHTLY on skin (do not depress skin with capsule) If post-operative: operative: place markers at each end of surgical scar FOV FOV determined by mass size / location Try to include adjacent joint for reference always; Sag or Cor depending on location of mass (speak with radiologist)
87 Soft Tissue Mass Seq. FOV Matrix/ Slice TR TE TI Flip ETL BW Nex T1 SE Non 56 x 19 5/ minimum T FSE 56 x 19 5/1 > Sag or Cor T1 SE Non 56 x 19 5/ minimum Sag or Cor STIR 56 x 19 5/1 > T1 GRE or SE Pre/Post Gd 56 x 19 5/ minimum Sag or Cor T1 GRE or SE Pre/Post Gd 56 x 19 5/ minimum
88 Metal Protocol general recommendations Assess Assess severity of artifact on scout discuss with MSK radiologist Maximize Maximize BW (bandwidth) Lower Lower TE (T and STIR) Remove Remove fat suppression (call MSK rad first) Avoid Avoid GRE Use Use STIR instead of Tw fat sat
89 MR Neurography Pelvis Seq. FOV Matrix/ Slice TR TE TI Flip ETL BW Nex Coronal (PELVIS) T1 SE Non x Minimum Coronal (PELVIS) FSE-STIR STIR x19 > T: T: 150 (PELVIS) T FSE 4 (hip to hip) 56 x /1 > > Coronal T vista (or equivalent) x345 1 / T1 3D FFE 4 76 x76 1 3/ M FFE 4 40x0 1 3/ Sagittal PD SPAIR 4- x 1 3.5/1 Max >
90 Marrow Survey
91 ER / Inpatient Protocols Hip / pelvis fracture Joint: Joint: survey exam Non-contrast R/O osteomyelitis Chest Chest wall / Abdominal wall Spine Spine survey
Upper Extremity Page Lower Extremity Special Cases
 MSK MRI PROTOCOLS Contents Upper Extremity Page Shoulder Elbow Wrist Finger Thumb Lower Extremity Hip Pelvis Thigh Knee Lower Extremity/Shin Ankle Foot Special Cases Soft Tissue Mass Metal Protocol MSK
MSK MRI PROTOCOLS Contents Upper Extremity Page Shoulder Elbow Wrist Finger Thumb Lower Extremity Hip Pelvis Thigh Knee Lower Extremity/Shin Ankle Foot Special Cases Soft Tissue Mass Metal Protocol MSK
Musculoskeletal MR Protocols
 Musculoskeletal MR Protocols Joint-based protocols MSK 1: Shoulder MRI MSK 1A: Shoulder MR arthrogram MSK 1AB: Shoulder MR arthrogram (instability protocol) MSK 2: Elbow MRI MSK 2A: Elbow MR arthrogram
Musculoskeletal MR Protocols Joint-based protocols MSK 1: Shoulder MRI MSK 1A: Shoulder MR arthrogram MSK 1AB: Shoulder MR arthrogram (instability protocol) MSK 2: Elbow MRI MSK 2A: Elbow MR arthrogram
Radiographic Positioning Summary (Basic Projections RAD 222)
 Lower Extremity Radiographic Positioning Summary (Basic Projections RAD 222) AP Pelvis AP Hip (Unilateral) (L or R) AP Femur Mid and distal AP Knee Lateral Knee Pt lies supine on table Align MSP to Center
Lower Extremity Radiographic Positioning Summary (Basic Projections RAD 222) AP Pelvis AP Hip (Unilateral) (L or R) AP Femur Mid and distal AP Knee Lateral Knee Pt lies supine on table Align MSP to Center
Pectoral (Shoulder) Girdle
 Chapter 8 Skeletal System: Appendicular Skeleton Pectoral girdle Pelvic girdle Upper limbs Lower limbs 8-1 Pectoral (Shoulder) Girdle Consists of scapula and clavicle Clavicle articulates with sternum
Chapter 8 Skeletal System: Appendicular Skeleton Pectoral girdle Pelvic girdle Upper limbs Lower limbs 8-1 Pectoral (Shoulder) Girdle Consists of scapula and clavicle Clavicle articulates with sternum
Chapter 8B. The Skeletal System: Appendicular Skeleton. The Appendicular Skeleton. Clavicle. Pectoral (Shoulder) Girdle
 The Appendicular Skeleton Chapter 8B The Skeletal System: Appendicular Skeleton 126 bones Pectoral (shoulder) girdle Pelvic (hip) girdle Upper limbs Lower limbs Functions primarily to facilitate movement
The Appendicular Skeleton Chapter 8B The Skeletal System: Appendicular Skeleton 126 bones Pectoral (shoulder) girdle Pelvic (hip) girdle Upper limbs Lower limbs Functions primarily to facilitate movement
10/12/2010. Upper Extremity. Pectoral (Shoulder) Girdle. Clavicle (collarbone) Skeletal System: Appendicular Skeleton
 Skeletal System: Appendicular Skeleton Pectoral girdle Pelvic girdle Upper limbs Lower limbs 8-1 Pectoral (Shoulder) Girdle Consists of scapula and clavicle Clavicle articulates with sternum (Sternoclavicular
Skeletal System: Appendicular Skeleton Pectoral girdle Pelvic girdle Upper limbs Lower limbs 8-1 Pectoral (Shoulder) Girdle Consists of scapula and clavicle Clavicle articulates with sternum (Sternoclavicular
Rad Tech 4643 MRI Torso and Extremities
 Rad Tech 4643 MRI Torso and Extremities Prostate Cancer Leiomyoma Retroverted Anteverted Ovarian Cyst Gone Wrong Fibroid (Leiomyoma) IUD Ovary Hysterectomy? What are we to see when imaging a female pelvis
Rad Tech 4643 MRI Torso and Extremities Prostate Cancer Leiomyoma Retroverted Anteverted Ovarian Cyst Gone Wrong Fibroid (Leiomyoma) IUD Ovary Hysterectomy? What are we to see when imaging a female pelvis
The Appendicular Skeleton
 8 The Appendicular Skeleton PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris 8-1 The Pectoral Girdle The Pectoral Girdle Also called shoulder girdle Connects the
8 The Appendicular Skeleton PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris 8-1 The Pectoral Girdle The Pectoral Girdle Also called shoulder girdle Connects the
Lab Activity 9. Appendicular Skeleton Martini Chapter 8. Portland Community College BI 231
 Lab Activity 9 Appendicular Skeleton Martini Chapter 8 Portland Community College BI 231 Appendicular Skeleton Upper & Lower extremities Shoulder Girdle Pelvic Girdle 2 Humerus 3 Humerus: Proximal End
Lab Activity 9 Appendicular Skeleton Martini Chapter 8 Portland Community College BI 231 Appendicular Skeleton Upper & Lower extremities Shoulder Girdle Pelvic Girdle 2 Humerus 3 Humerus: Proximal End
SKELETAL SYSTEM 206. AXIAL SKELETON 80 APPENDICULAR SKELETON 126 (see Figure 6.1) Clavicle. Clavicle. Pectoral girdles. Scapula. Scapula.
 SKELETAL SYSTEM 206 AXIAL SKELETON 80 APPENDICULAR SKELETON 126 (see Figure 6.1) Pectoral girdles 4 Clavicle Scapula 2 2 Clavicle Scapula Humerus 2 Humerus Upper limbs 60 Radius 2 Ulna Carpal bones Metacarpal
SKELETAL SYSTEM 206 AXIAL SKELETON 80 APPENDICULAR SKELETON 126 (see Figure 6.1) Pectoral girdles 4 Clavicle Scapula 2 2 Clavicle Scapula Humerus 2 Humerus Upper limbs 60 Radius 2 Ulna Carpal bones Metacarpal
UPPER EXTREMITY
 UPPER EXTREMITY 11-24-17 MSK TIPS: Ensure extremity of interest is as isocenter as possible SHIM all Fat sat scans!! Only use 4ch wrist if additional coverage needed If Contrast needed: Multihance.1mmol/kg
UPPER EXTREMITY 11-24-17 MSK TIPS: Ensure extremity of interest is as isocenter as possible SHIM all Fat sat scans!! Only use 4ch wrist if additional coverage needed If Contrast needed: Multihance.1mmol/kg
Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D. 1 SCCC BIO130 Lab 7 Appendicular Skeleton & Articulations
 The Skeletal System II: Appendicular Skeleton and Articulations Exercises 11, 13 (begins: page 145 in 9 th and 10 th editions) Exercises 10, 11 (begins: page 147 in 11 th edition, page 149 in 12 th edition)
The Skeletal System II: Appendicular Skeleton and Articulations Exercises 11, 13 (begins: page 145 in 9 th and 10 th editions) Exercises 10, 11 (begins: page 147 in 11 th edition, page 149 in 12 th edition)
Chapter 8. The Appendicular Skeleton. Lecture Presentation by Lee Ann Frederick University of Texas at Arlington Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 8 The Appendicular Skeleton Lecture Presentation by Lee Ann Frederick University of Texas at Arlington An Introduction to the Appendicular Skeleton The Appendicular Skeleton 126 bones Allows us
Chapter 8 The Appendicular Skeleton Lecture Presentation by Lee Ann Frederick University of Texas at Arlington An Introduction to the Appendicular Skeleton The Appendicular Skeleton 126 bones Allows us
Biology 152 Appendicular Skeleton Anatomy Objectives
 Biology 152 Appendicular Skeleton Anatomy Objectives We will learn proper bone names, left/right/medial, and the parts of bones in this exercise. Start by learning the names of the bones. As you gain comfort
Biology 152 Appendicular Skeleton Anatomy Objectives We will learn proper bone names, left/right/medial, and the parts of bones in this exercise. Start by learning the names of the bones. As you gain comfort
Biology 218 Human Anatomy. Adapted from Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 7 The Skeletal System Appendicular Division
 Adapted from Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 7 The Skeletal System Appendicular Division Introduction The appendicular skeleton includes: Pectoral girdle Shoulder bones Upper limbs Pelvic girdle
Adapted from Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 7 The Skeletal System Appendicular Division Introduction The appendicular skeleton includes: Pectoral girdle Shoulder bones Upper limbs Pelvic girdle
Biology 218 Human Anatomy
 Chapter 8 Adapted from Tortora 10 th ed. LECTURE OUTLINE A. Introduction (p. 203) 1. The appendicular skeleton contains 126 bones that form: i. two pectoral (shoulder) girdles two upper limbs i one pelvic
Chapter 8 Adapted from Tortora 10 th ed. LECTURE OUTLINE A. Introduction (p. 203) 1. The appendicular skeleton contains 126 bones that form: i. two pectoral (shoulder) girdles two upper limbs i one pelvic
A. Incorrect! The appendicular skeleton includes bones of the shoulder, arm, hand, pelvis, leg and foot.
 Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 08: The Skeletal System III No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following statements about the appendicular skeleton is correct? A. The appendicular skeleton includes bones
Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 08: The Skeletal System III No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following statements about the appendicular skeleton is correct? A. The appendicular skeleton includes bones
Chapter 8 The Skeletal System: The Appendicular Skeleton. Copyright 2009 John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
 Chapter 8 The Skeletal System: The Appendicular Skeleton Appendicular Skeleton It includes bones of the upper and lower limbs Girdles attach the limbs to the axial skeleton The pectoral girdle consists
Chapter 8 The Skeletal System: The Appendicular Skeleton Appendicular Skeleton It includes bones of the upper and lower limbs Girdles attach the limbs to the axial skeleton The pectoral girdle consists
PRE-LAB EXERCISES. Before we get started, look up the definitions of these common bone marking terms: Canal: Condyle: Facet: Fissure:
 1 PRE-LAB EXERCISES When studying the skeletal system, the bones are often sorted into two broad categories: the axial skeleton and the appendicular skeleton. This lab focuses on the appendicular skeleton,
1 PRE-LAB EXERCISES When studying the skeletal system, the bones are often sorted into two broad categories: the axial skeleton and the appendicular skeleton. This lab focuses on the appendicular skeleton,
Chapter 8 The Skeletal System: The Appendicular Skeleton. Copyright 2009 John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
 Chapter 8 The Skeletal System: The Appendicular Skeleton Appendicular Skeleton The primary function is movement It includes bones of the upper and lower limbs Girdles attach the limbs to the axial skeleton
Chapter 8 The Skeletal System: The Appendicular Skeleton Appendicular Skeleton The primary function is movement It includes bones of the upper and lower limbs Girdles attach the limbs to the axial skeleton
Exercise 11. The Appendicular Skeleton
 Exercise 11 The Appendicular Skeleton The Appendicular Skeleton The appendicular skeleton contains 126 bones. Consists of the upper and lower limbs, the pectoral girdles, and the pelvic girdles. The pectoral
Exercise 11 The Appendicular Skeleton The Appendicular Skeleton The appendicular skeleton contains 126 bones. Consists of the upper and lower limbs, the pectoral girdles, and the pelvic girdles. The pectoral
In-Depth Foundations: Anatomy Terms to Know
 Be familiar with / able to identify and define all the following parts. The Spine Cranium Vertebrae Cervical, Thoracic, Lumbar Sacrum Coccyx Bones of Upper Body Cranium Mastoid process; Occipital condyle,
Be familiar with / able to identify and define all the following parts. The Spine Cranium Vertebrae Cervical, Thoracic, Lumbar Sacrum Coccyx Bones of Upper Body Cranium Mastoid process; Occipital condyle,
Shoulder Position: Supine arm in the neutral position. Collateral arm above head Indication: fracture humerus, fracture scapula
 Shoulder Position: Supine arm in the neutral position. Collateral arm above head Indication: fracture humerus, fracture scapula No instrumentation With metal or cast KV/ Effective mas/rotation time 140/300/1.0
Shoulder Position: Supine arm in the neutral position. Collateral arm above head Indication: fracture humerus, fracture scapula No instrumentation With metal or cast KV/ Effective mas/rotation time 140/300/1.0
Exercise Science Section 2: The Skeletal System
 Exercise Science Section 2: The Skeletal System An Introduction to Health and Physical Education Ted Temertzoglou Paul Challen ISBN 1-55077-132-9 Role of the Skeleton Protection Framework Attachments for
Exercise Science Section 2: The Skeletal System An Introduction to Health and Physical Education Ted Temertzoglou Paul Challen ISBN 1-55077-132-9 Role of the Skeleton Protection Framework Attachments for
bio4165 lab quiz 1 Posterior View Anterior View Lateral View Anterior View bio fall.quarter lab.quiz.1...page.1 of 6
 B A Posterior View D C E Lateral View bio.4165...fall.quarter.2005...lab.quiz.1...page.1 of 6 F I G 35 Posterior View H bio.4165...fall.quarter.2005...lab.quiz.1...page.2 of 6 J Posterior View L K Inferior
B A Posterior View D C E Lateral View bio.4165...fall.quarter.2005...lab.quiz.1...page.1 of 6 F I G 35 Posterior View H bio.4165...fall.quarter.2005...lab.quiz.1...page.2 of 6 J Posterior View L K Inferior
Dr.Israa H. Mohsen. Lecture 5. The vertebral column
 Anatomy Lecture 5 Dr.Israa H. Mohsen The vertebral column The vertebral column a flexible structure consisting of 33 vertebrae holds the head and torso upright, serves as an attachment point for the legs,
Anatomy Lecture 5 Dr.Israa H. Mohsen The vertebral column The vertebral column a flexible structure consisting of 33 vertebrae holds the head and torso upright, serves as an attachment point for the legs,
Anatomy and Physiology 2016
 Anatomy and Physiology 2016 O = Temporal line I = coronoid process (Mandible) A = elevates mandible (chewing) O = galea aponeurotica (layer of dense fibrous tissue which covers the upper part of the cranium)
Anatomy and Physiology 2016 O = Temporal line I = coronoid process (Mandible) A = elevates mandible (chewing) O = galea aponeurotica (layer of dense fibrous tissue which covers the upper part of the cranium)
The Appendicular Skeleton
 8 The Appendicular Skeleton PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris An Introduction to the Appendicular Skeleton Learning Outcomes 8-1 Identify the bones
8 The Appendicular Skeleton PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris An Introduction to the Appendicular Skeleton Learning Outcomes 8-1 Identify the bones
Important Parts of Bones
 Important Parts of Bones For 2015 Know: Humerus (posterior) Clavical Femur (Anterior) Foot Hand Mandible Os Coxa Scapula Skull (Anterior, Inferior, Lateral) Sternum Humerus (posterior) A. olecranon fossa
Important Parts of Bones For 2015 Know: Humerus (posterior) Clavical Femur (Anterior) Foot Hand Mandible Os Coxa Scapula Skull (Anterior, Inferior, Lateral) Sternum Humerus (posterior) A. olecranon fossa
Bone Flashcards for 10a
 Bone Flashcards for 0a CLAVICLE (collar bone). Sternal extremity (end) flat end. Acromial extremity (end) rounded end. SCAPULA (shoulder blade). Right or left scapula?. Superior border (superior margin).
Bone Flashcards for 0a CLAVICLE (collar bone). Sternal extremity (end) flat end. Acromial extremity (end) rounded end. SCAPULA (shoulder blade). Right or left scapula?. Superior border (superior margin).
Appendicular Skeleton. Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi
 Appendicular Skeleton Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi a.alnuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk abdulameerh@yahoo.com Hi Prof, It is great to hear from you, I really enjoyed your teaching last year. You taught me the hardest
Appendicular Skeleton Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi a.alnuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk abdulameerh@yahoo.com Hi Prof, It is great to hear from you, I really enjoyed your teaching last year. You taught me the hardest
Basic Radiographic Principles Part II
 Basic Radiographic Principles Part II Kristopher Avant, D.O. October 19 th, 2016 I have no disclosures relevant to the material presented in this discussion. Good Stuff!!! 1 Really? Really! Musculoskeletal
Basic Radiographic Principles Part II Kristopher Avant, D.O. October 19 th, 2016 I have no disclosures relevant to the material presented in this discussion. Good Stuff!!! 1 Really? Really! Musculoskeletal
Bones of Lower Limb. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology
 Bones of Lower Limb Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Bones of the lower limb Hip Bone Made up of 3 bones: 1) Ilium (flat), superior in position 2) Ischium (L), postero-inferior
Bones of Lower Limb Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Bones of the lower limb Hip Bone Made up of 3 bones: 1) Ilium (flat), superior in position 2) Ischium (L), postero-inferior
Country Health SA Medical Imaging
 Country Health SA Medical Imaging REMOTE OPERATORS POSITIONING GUIDE Contents Image Evaluation Page 4 Positioning Guides Section 1 - THORAX 1.1 Chest Page 5 1.2 Bedside Chest Page 7 1.3 Ribs Page 8 Section
Country Health SA Medical Imaging REMOTE OPERATORS POSITIONING GUIDE Contents Image Evaluation Page 4 Positioning Guides Section 1 - THORAX 1.1 Chest Page 5 1.2 Bedside Chest Page 7 1.3 Ribs Page 8 Section
Practical 1 Worksheet
 Practical 1 Worksheet ANATOMICAL TERMS 1. Use the word bank to fill in the missing words. reference side stand body arms palms anatomical forward All anatomical terms have a(n) point which is called the
Practical 1 Worksheet ANATOMICAL TERMS 1. Use the word bank to fill in the missing words. reference side stand body arms palms anatomical forward All anatomical terms have a(n) point which is called the
11/25/2012. Chapter 7 Part 2: Bones! Skeletal Organization. The Skull. Skull Bones to Know Cranium
 Chapter 7 Part 2: Bones! 5) Distinguish between the axial and appendicular skeletons and name the major parts of each 6) Locate and identify the bones and the major features of the bones that compose the
Chapter 7 Part 2: Bones! 5) Distinguish between the axial and appendicular skeletons and name the major parts of each 6) Locate and identify the bones and the major features of the bones that compose the
Anatomy & Physiology Skeletal System Worksheet
 1. Name the five functions of the skeleton. c) d) e) Anatomy & Physiology Skeletal System Worksheet 2. The term for the shaft of a bone is:. 3. The bony struts found in spongy bone are called. 4. In ossification,
1. Name the five functions of the skeleton. c) d) e) Anatomy & Physiology Skeletal System Worksheet 2. The term for the shaft of a bone is:. 3. The bony struts found in spongy bone are called. 4. In ossification,
This presentation is the intellectual property of the author. Contact them for permission to reprint and/or distribute.
 MRI of the Knee Jennifer Swart, M.D. Musculoskeletal Radiology South Texas Radiology Group Outline Coils, Patient Positioning Acquisition Parameters, Planes and Pulse Sequences Knee Arthrography Normal
MRI of the Knee Jennifer Swart, M.D. Musculoskeletal Radiology South Texas Radiology Group Outline Coils, Patient Positioning Acquisition Parameters, Planes and Pulse Sequences Knee Arthrography Normal
Radiology Positioning Practical Test #2 Table (By Jung Park):
 Radiology Positioning Practical Test #2 Table (By Jung Park): (Lower Extremity): patient is fully gowned / no artifacts / properly shielded (exposure for femur and below : hold still, don t move ) (exposure
Radiology Positioning Practical Test #2 Table (By Jung Park): (Lower Extremity): patient is fully gowned / no artifacts / properly shielded (exposure for femur and below : hold still, don t move ) (exposure
This presentation is the intellectual property of the author. Contact them at for permission to reprint and/or distribute.
 MRI of the Knee Jennifer Swart, M.D. Musculoskeletal Radiology South Texas Radiology Group Financial Disclosure Dr. Jennifer Swart has no relevant financial relationships with commercial interests to disclose.
MRI of the Knee Jennifer Swart, M.D. Musculoskeletal Radiology South Texas Radiology Group Financial Disclosure Dr. Jennifer Swart has no relevant financial relationships with commercial interests to disclose.
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology
 Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14 th Edition CHAPTER 8 The Skeletal System: The Appendicular Skeleton The Appendicular Skeleton The 126 bones of the appendicular skeleton are primarily concerned
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14 th Edition CHAPTER 8 The Skeletal System: The Appendicular Skeleton The Appendicular Skeleton The 126 bones of the appendicular skeleton are primarily concerned
Perpendicular Plate Zygomatic Bone. Mental Foramen Mandible
 Glabella Frontal Middle Nasal Concha Nasal Lacrimal Perpendicular Plate Zygomatic Inferior Nasal Concha Maxilla Mental Mandible Skull (anterior view) Squamosal Suture Coronal Suture Frontal Parietal Nasal
Glabella Frontal Middle Nasal Concha Nasal Lacrimal Perpendicular Plate Zygomatic Inferior Nasal Concha Maxilla Mental Mandible Skull (anterior view) Squamosal Suture Coronal Suture Frontal Parietal Nasal
Bone List Anatomy
 1 Frontal Bone Skull 2 Parietal Bone Skull 3 Occipital Bone Skull 4 Temporal Bone Skull 5 Coronal Suture Skull 6 Sagittal Suture Skull 7 Squamous suture Skull 8 Lambdoid Suture Skull 9 Surpaorbital Ridge
1 Frontal Bone Skull 2 Parietal Bone Skull 3 Occipital Bone Skull 4 Temporal Bone Skull 5 Coronal Suture Skull 6 Sagittal Suture Skull 7 Squamous suture Skull 8 Lambdoid Suture Skull 9 Surpaorbital Ridge
Joints Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi
 Joints Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Function of Joints 1. Serve as functional junctions between bones. 2. Bind bones, strokes, and other related tissues together. 3. Allow bone growth to occur. 4. Permit certain
Joints Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Function of Joints 1. Serve as functional junctions between bones. 2. Bind bones, strokes, and other related tissues together. 3. Allow bone growth to occur. 4. Permit certain
A&P 1 Muscle In-Lab Guide
 A&P 1 Muscle In-Lab Guide This lab guide includes a table with all the muscles you need to ID, along with their origins, insertions and actions Dashed lines means ignore. If several actions are listed,
A&P 1 Muscle In-Lab Guide This lab guide includes a table with all the muscles you need to ID, along with their origins, insertions and actions Dashed lines means ignore. If several actions are listed,
MR Imaging in Athlete s Hip/Pelvis
 MR Imaging in Athlete s Hip/Pelvis Tara Lawrimore, MD FRCPC Department of Radiology Musculoskeletal Division Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School No disclosures MR and Hip Pain in the
MR Imaging in Athlete s Hip/Pelvis Tara Lawrimore, MD FRCPC Department of Radiology Musculoskeletal Division Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School No disclosures MR and Hip Pain in the
Chapter 8 Outline. Pectoral Girdle Upper Limb Pelvic Girdle Lower Limb Aging of the Appendicular Skeleton Development of the Appendicular Skeleton
 Chapter 8 Outline Pectoral Girdle Upper Limb Pelvic Girdle Lower Limb Aging of the Appendicular Skeleton Development of the Appendicular Skeleton Figure 8.1 Appendicular Skeleton Pectoral Girdle Clavicle
Chapter 8 Outline Pectoral Girdle Upper Limb Pelvic Girdle Lower Limb Aging of the Appendicular Skeleton Development of the Appendicular Skeleton Figure 8.1 Appendicular Skeleton Pectoral Girdle Clavicle
Lab Exercise #5 The Muscular System Student Performance Objectives
 Student Performance Objectives The material that you are required to learn in this exercise can be found in either the lecture text or the supplemental materials provided in lab. Prior to coming to class,
Student Performance Objectives The material that you are required to learn in this exercise can be found in either the lecture text or the supplemental materials provided in lab. Prior to coming to class,
Muscular Nomenclature and Kinesiology - One
 Chapter 16 Muscular Nomenclature and Kinesiology - One Lessons 1-3 (with lesson 4) 1 Introduction 122 major muscles covered in this chapter Chapter divided into nine lessons Kinesiology study of human
Chapter 16 Muscular Nomenclature and Kinesiology - One Lessons 1-3 (with lesson 4) 1 Introduction 122 major muscles covered in this chapter Chapter divided into nine lessons Kinesiology study of human
DART Diagnosis and Related Treatments
 DART Diagnosis and Related Treatments The DART Tool allows a user to obtain Treatment recommendations based on the disorder/condition. These recommendations are provided by ACOEM (American College of Occupational
DART Diagnosis and Related Treatments The DART Tool allows a user to obtain Treatment recommendations based on the disorder/condition. These recommendations are provided by ACOEM (American College of Occupational
Human Anatomy, First Edition McKinley & O'Loughlin
 Human Anatomy, First Edition McKinley & O'Loughlin Chapter 8 : Appendicular Skeleton 8-1 Appendicular Skeleton Includes the bones of the upper and lower limbs. The girdles of bones that attach the upper
Human Anatomy, First Edition McKinley & O'Loughlin Chapter 8 : Appendicular Skeleton 8-1 Appendicular Skeleton Includes the bones of the upper and lower limbs. The girdles of bones that attach the upper
MRI PEDIATRIC PROTOCOLS (Updated 6/19/2018)
 MRI PEDIATRIC PROTOCOLS (Updated 6/19/2018) *Please get or let us know where radiologist can review plain films. *For Texas Orthopedics and other Docs requesting only MSK section read for their pediatric
MRI PEDIATRIC PROTOCOLS (Updated 6/19/2018) *Please get or let us know where radiologist can review plain films. *For Texas Orthopedics and other Docs requesting only MSK section read for their pediatric
Balanced Body Movement Principles
 Balanced Body Movement Principles How the Body Works and How to Train it. Module 3: Lower Body Strength and Power Developing Strength, Endurance and Power The lower body is our primary source of strength,
Balanced Body Movement Principles How the Body Works and How to Train it. Module 3: Lower Body Strength and Power Developing Strength, Endurance and Power The lower body is our primary source of strength,
Lab 9: Learn origin and insertion for each of the listed muscles. For Exercise 15, do Activities 1-6 in 9 th edition, Activities 1-4 in 10 th edition
 The Muscular System Exercises 14, 15, and 16 (begins: page 187 in 9 th and 10 th editions) Exercises 12, 13, and 14 (begins: page 185 in 11 th edition, page 189 in 12 th edition) Lab 8 and 9 Objectives
The Muscular System Exercises 14, 15, and 16 (begins: page 187 in 9 th and 10 th editions) Exercises 12, 13, and 14 (begins: page 185 in 11 th edition, page 189 in 12 th edition) Lab 8 and 9 Objectives
ORTHOPAEDIC INJECTION AND ASPIRATION TECHNIQUES
 ORTHOPAEDIC INJECTION AND ASPIRATION TECHNIQUES OAAPN October 20, 2016 David H. Sohn, JD MD Chief, Shoulder and Sports Medicine University of Toledo Medical Center When to aspirate? To rule out infection
ORTHOPAEDIC INJECTION AND ASPIRATION TECHNIQUES OAAPN October 20, 2016 David H. Sohn, JD MD Chief, Shoulder and Sports Medicine University of Toledo Medical Center When to aspirate? To rule out infection
ARM Brachium Musculature
 ARM Brachium Musculature Coracobrachialis coracoid process of the scapula medial shaft of the humerus at about its middle 1. flexes the humerus 2. assists to adduct the humerus Blood: muscular branches
ARM Brachium Musculature Coracobrachialis coracoid process of the scapula medial shaft of the humerus at about its middle 1. flexes the humerus 2. assists to adduct the humerus Blood: muscular branches
Anatomage Table Instructors Guide- Lower Limb
 The Lower Limb Anatomage Table Instructors Guide- Lower Limb Table of Contents Lower Limb 1- The Skeletal System...3 1: Hip Bone...3 2: Hip Joint and Femur...4 3: Patella and Knee Joint...7 4: Tibia, Fibula,
The Lower Limb Anatomage Table Instructors Guide- Lower Limb Table of Contents Lower Limb 1- The Skeletal System...3 1: Hip Bone...3 2: Hip Joint and Femur...4 3: Patella and Knee Joint...7 4: Tibia, Fibula,
Hands PA; Obl. Lat.; Norgaard s Thumb AP; Lat. PA. PA; Lat.: Obls.; Elongated PA with ulnar deviation
 Projections Region Basic projections Additional / Modified projections Upper Limbs Hands PA; Obl. Lat.; Norgaard s Thumb ; Lat. PA Fingers PA; Lat. Wrist PA; Lat. Obls. Scaphoid Lunate Trapezium Triquetral
Projections Region Basic projections Additional / Modified projections Upper Limbs Hands PA; Obl. Lat.; Norgaard s Thumb ; Lat. PA Fingers PA; Lat. Wrist PA; Lat. Obls. Scaphoid Lunate Trapezium Triquetral
Chapter 8. The Pectoral Girdle & Upper Limb
 Chapter 8 The Pectoral Girdle & Upper Limb Pectoral Girdle pectoral girdle (shoulder girdle) supports the arm consists of two on each side of the body // clavicle (collarbone) and scapula (shoulder blade)
Chapter 8 The Pectoral Girdle & Upper Limb Pectoral Girdle pectoral girdle (shoulder girdle) supports the arm consists of two on each side of the body // clavicle (collarbone) and scapula (shoulder blade)
Chapter 7 Part C The Skeleton
 Chapter 7 Part C The Skeleton Part 2 The Appendicular Skeleton Consists of bones of the limbs and their girdles Pectoral girdle Attaches upper limbs to body trunk Pelvic girdle Attaches lower limbs to
Chapter 7 Part C The Skeleton Part 2 The Appendicular Skeleton Consists of bones of the limbs and their girdles Pectoral girdle Attaches upper limbs to body trunk Pelvic girdle Attaches lower limbs to
THE HIP. Cooler than cool, the pinnacle of what is "it". Beyond all trends and conventional coolness.
 THE HIP Cooler than cool, the pinnacle of what is "it". Beyond all trends and conventional coolness. Objectives Hip anatomy Causes of hip pain Hip exam Anatomy Bones Ilium Anterior Superior Iliac Spine
THE HIP Cooler than cool, the pinnacle of what is "it". Beyond all trends and conventional coolness. Objectives Hip anatomy Causes of hip pain Hip exam Anatomy Bones Ilium Anterior Superior Iliac Spine
MSK CT Extremities: Positioning and Reformations
 MSK CT Extremities: Positioning and Reformations Hand: Patient lying in prone position, with affected arm extended above head. Place body off centered in effort to set affected hand in isocenter. Hand
MSK CT Extremities: Positioning and Reformations Hand: Patient lying in prone position, with affected arm extended above head. Place body off centered in effort to set affected hand in isocenter. Hand
Take Pride in Performance
 2017 Take Pride in Performance Knee: Meniscal Tear FSE PD - Sagittal FSE PD - Coronal FSTIR - Coronal Knee: ACL Tibial Avulsion 3D SHARC ISO - Sagittal FSE PD - Sagittal FSTIR - Coronal Knee: Subchondral
2017 Take Pride in Performance Knee: Meniscal Tear FSE PD - Sagittal FSE PD - Coronal FSTIR - Coronal Knee: ACL Tibial Avulsion 3D SHARC ISO - Sagittal FSE PD - Sagittal FSTIR - Coronal Knee: Subchondral
Riverside Community College Anatomy & Physiology 2B SPRING 2012 EXAM #1-ABC (Nervous System)
 Riverside Community College Anatomy & Physiology 2B SPRING 2012 EXAM #1-ABC (Nervous System) Name: 1) This vertebra is an example of a(n). 1) A) thoracic B) axis C) atlas D) lumbar E) sacral 1 2) W hich
Riverside Community College Anatomy & Physiology 2B SPRING 2012 EXAM #1-ABC (Nervous System) Name: 1) This vertebra is an example of a(n). 1) A) thoracic B) axis C) atlas D) lumbar E) sacral 1 2) W hich
Muscles of Lesson Five. Muscular Nomenclature and Kinesiology - Two. Muscles of Lesson Five, cont. Chapter 16
 Chapter 16 Muscular Nomenclature and Kinesiology - Two Lessons 5-6 Muscles of Lesson Five Iliopsoas (psoas major, iliacus) Hip outward rotators (piriformis, gemellus superior, gemellus inferior, obturator
Chapter 16 Muscular Nomenclature and Kinesiology - Two Lessons 5-6 Muscles of Lesson Five Iliopsoas (psoas major, iliacus) Hip outward rotators (piriformis, gemellus superior, gemellus inferior, obturator
Anatomy. Anatomy deals with the structure of the human body, and includes a precise language on body positions and relationships between body parts.
 Anatomy deals with the structure of the human body, and includes a precise language on body positions and relationships between body parts. Proper instruction on safe and efficient exercise technique requires
Anatomy deals with the structure of the human body, and includes a precise language on body positions and relationships between body parts. Proper instruction on safe and efficient exercise technique requires
Why Talk About Technique? MRI of the Knee:
 Why Talk About Technique? MRI of the Knee: Part 1 - Imaging Techniques Mark Anderson, M.D. University of Virginia Health Sciences Center Charlottesville, Virginia Always had an interest teach our fellows
Why Talk About Technique? MRI of the Knee: Part 1 - Imaging Techniques Mark Anderson, M.D. University of Virginia Health Sciences Center Charlottesville, Virginia Always had an interest teach our fellows
Connects arm to thorax 3 joints. Glenohumeral joint Acromioclavicular joint Sternoclavicular joint
 Connects arm to thorax 3 joints Glenohumeral joint Acromioclavicular joint Sternoclavicular joint Scapula Elevation Depression Protraction (abduction) Retraction (adduction) Downward Rotation Upward Rotation
Connects arm to thorax 3 joints Glenohumeral joint Acromioclavicular joint Sternoclavicular joint Scapula Elevation Depression Protraction (abduction) Retraction (adduction) Downward Rotation Upward Rotation
YOGA ANATOMY. Part Three - Bones. Yoga Teacher Training Robin Bennett 200 RYT
 YOGA ANATOMY Yoga Teacher Training Part Three - Bones 2015 Robin Bennett 200 RYT THE HUMAN SKELETON BONE COMPOSITION A femur head with a cortex of compact bone and medulla of trabecular (spongy) bone OSTEOBLASTS
YOGA ANATOMY Yoga Teacher Training Part Three - Bones 2015 Robin Bennett 200 RYT THE HUMAN SKELETON BONE COMPOSITION A femur head with a cortex of compact bone and medulla of trabecular (spongy) bone OSTEOBLASTS
Copyright 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings. Dr. Nabil khouri
 Dr. Nabil khouri Appendicular Skeleton The appendicular skeleton is made up of the bones of the upper and lower limbs and their girdles Two girdles: Pectoral girdles attach the upper limbs to the body
Dr. Nabil khouri Appendicular Skeleton The appendicular skeleton is made up of the bones of the upper and lower limbs and their girdles Two girdles: Pectoral girdles attach the upper limbs to the body
ORTHOSCAN MOBILE DI POSITIONING GUIDE
 ORTHOSCAN MOBILE DI POSITIONING GUIDE Table of Contents SHOULDER A/P of Shoulder... 4 Tangential (Y-View) of Shoulder... 5 Lateral of Proximal Humerus... 6 ELBOW A/P of Elbow... 7 Extended Elbow... 8 Lateral
ORTHOSCAN MOBILE DI POSITIONING GUIDE Table of Contents SHOULDER A/P of Shoulder... 4 Tangential (Y-View) of Shoulder... 5 Lateral of Proximal Humerus... 6 ELBOW A/P of Elbow... 7 Extended Elbow... 8 Lateral
Lab 1: body, skeletal and axial systems
 Lab 1: body, skeletal and axial systems Types of tissue Epithelia tissue - Sheets of tissue covering other tissues or linin cavities - Protective tissue e.g. skin - Cell types: squamous, cuboid, columnar
Lab 1: body, skeletal and axial systems Types of tissue Epithelia tissue - Sheets of tissue covering other tissues or linin cavities - Protective tissue e.g. skin - Cell types: squamous, cuboid, columnar
8.2: Fibrous Joints. There are three (3) types of fibrous joints (synarthroses): Syndesmosis Suture Gomphosis. Interosseus membrane of leg.
 8.1: Introduction Are known as articulations Functional junctions between bones Bind parts of skeletal system together Make bone growth possible Permit parts of the skeleton to change shape during childbirth
8.1: Introduction Are known as articulations Functional junctions between bones Bind parts of skeletal system together Make bone growth possible Permit parts of the skeleton to change shape during childbirth
Table of Compensation for Injury 1/2015
 Table of Compensation for 1/2015 Valid from 01.04.2015 1. CRANIAL INJURIES 1.1 Cranial bone fractures: a) fracture of cranial dome 10 b) fracture of cranial base 15 c) fracture of cranial dome and base
Table of Compensation for 1/2015 Valid from 01.04.2015 1. CRANIAL INJURIES 1.1 Cranial bone fractures: a) fracture of cranial dome 10 b) fracture of cranial base 15 c) fracture of cranial dome and base
Bones of the Lower Limb Bone Structure Description Notes. border of the superior ramus. inferolaterally from the pubic symphysis
 Bones of the Lower Limb Bone Structure Description Notes pubis an angulated bone the forms the anterior part of the pelvis one of three bones that form the os coxae: ilium, ischium, pubis; its forms 1/5
Bones of the Lower Limb Bone Structure Description Notes pubis an angulated bone the forms the anterior part of the pelvis one of three bones that form the os coxae: ilium, ischium, pubis; its forms 1/5
It is formed by fusion of 3 bones: I. Ilium (superior bone). II. Pubis (antero-inferior bone). III. Ischium (postero-inferior bone).
 It is formed by fusion of 3 bones: I. Ilium (superior bone). II. Pubis (antero-inferior bone). III. Ischium (postero-inferior bone). Pubis Acetabulum Ana (242 ) The three constituent of bones of the hip
It is formed by fusion of 3 bones: I. Ilium (superior bone). II. Pubis (antero-inferior bone). III. Ischium (postero-inferior bone). Pubis Acetabulum Ana (242 ) The three constituent of bones of the hip
TABLES OF MUSCLE ACTIONS, INNERVATIONS, AND ATTACHMENTS
 TABLES OF MUSCLE ACTIONS, INNERVATIONS, AND ATTACHMENTS Table 1-1 ERECTOR SPINAE MUSCLES Intrinsic muscles producing extension and/or lateral of the spine Muscle Joint and Action Innervation Inferior Attachment
TABLES OF MUSCLE ACTIONS, INNERVATIONS, AND ATTACHMENTS Table 1-1 ERECTOR SPINAE MUSCLES Intrinsic muscles producing extension and/or lateral of the spine Muscle Joint and Action Innervation Inferior Attachment
RADIOGRAPHY OF THE WRIST
 RADIOGRAPHY OF THE WRIST Patient Position: WRIST PA Projection, elbow in same plane Part Position: Hand ; fingers centered to IR Central Ray: Structures Shown: NOTE: Optional AP projection best demonstrates
RADIOGRAPHY OF THE WRIST Patient Position: WRIST PA Projection, elbow in same plane Part Position: Hand ; fingers centered to IR Central Ray: Structures Shown: NOTE: Optional AP projection best demonstrates
Biology 2401 The Skeletal System
 Biology 2401 The Skeletal System Purpose: The lab will describe the microscopic and gross anatomy of bone, identify bones of the body, and identify important bone markings. I. Overview of the Skeleton
Biology 2401 The Skeletal System Purpose: The lab will describe the microscopic and gross anatomy of bone, identify bones of the body, and identify important bone markings. I. Overview of the Skeleton
Exercise 13. Articulations and Body Movements
 Exercise 13 Articulations and Body Movements Articulations Articulations, or joints, are points where a bone is connected to one or more other bones. Articulations hold the skeleton together. Articulations
Exercise 13 Articulations and Body Movements Articulations Articulations, or joints, are points where a bone is connected to one or more other bones. Articulations hold the skeleton together. Articulations
Chapter 7: Skeletal System: Gross Anatomy
 Chapter 7: Skeletal System: Gross Anatomy I. General Considerations A. How many bones in an average adult skeleton? B. Anatomic features of bones are based on II. Axial Skeleton A. Skull 1. Functionally
Chapter 7: Skeletal System: Gross Anatomy I. General Considerations A. How many bones in an average adult skeleton? B. Anatomic features of bones are based on II. Axial Skeleton A. Skull 1. Functionally
Bone Composition. Bone is very strong for its relatively light weight The major components of bone are:
 Human Bones Bone Composition Bone is very strong for its relatively light weight The major components of bone are: Calcium carbonate Calcium phosphate Collagen Water Cortical Bone Spongy Bone Medullary
Human Bones Bone Composition Bone is very strong for its relatively light weight The major components of bone are: Calcium carbonate Calcium phosphate Collagen Water Cortical Bone Spongy Bone Medullary
11/15/2018. Temporalis Elevates & retracts mandible. Masseter = Prime mover of jaw closure. Levator scapulae Supraspinatus Clavicle.
 Due in Lab 10 Lab 8 MUSCLES 2 weeks because of Thanksgiving Prelab #10 Both sides! Homework #8 Both sides! Refer to Muscles 22-23 Examples of Origin & Insertion Naming of muscles Origin Site of muscle
Due in Lab 10 Lab 8 MUSCLES 2 weeks because of Thanksgiving Prelab #10 Both sides! Homework #8 Both sides! Refer to Muscles 22-23 Examples of Origin & Insertion Naming of muscles Origin Site of muscle
The skeleton consists of: Bones: special connective tissue, hard. Cartilage: special connective tissue, less hard than bones. Joints: joint is the
 The skeleton consists of: Bones: special connective tissue, hard. Cartilage: special connective tissue, less hard than bones. Joints: joint is the location at witch two bones make contact, whereas ligaments
The skeleton consists of: Bones: special connective tissue, hard. Cartilage: special connective tissue, less hard than bones. Joints: joint is the location at witch two bones make contact, whereas ligaments
Anatomy & Physiology. Muscles of the Lower Limbs.
 Anatomy & Physiology Muscles of the Lower Limbs http://www.ishapeup.com/musclecharts.html Muscles of the Lower Limbs Among the strongest muscles in the body. Because pelvic girdle is composed of heavy,
Anatomy & Physiology Muscles of the Lower Limbs http://www.ishapeup.com/musclecharts.html Muscles of the Lower Limbs Among the strongest muscles in the body. Because pelvic girdle is composed of heavy,
Appendicular Skeleton. Dr. Carmen E. Rexach Anatomy 35 Mt. San Antonio College
 Appendicular Skeleton Dr. Carmen E. Rexach Anatomy 35 Mt. San Antonio College Pectoral girdle clavicle scapula Upper limb brachium antebrachium carpus manus Pelvic girdle oscoxae Lower limb femoral region
Appendicular Skeleton Dr. Carmen E. Rexach Anatomy 35 Mt. San Antonio College Pectoral girdle clavicle scapula Upper limb brachium antebrachium carpus manus Pelvic girdle oscoxae Lower limb femoral region
Healing Hands School of Holistic Health. Advanced Circulatory & Sports Massage Class Handouts
 Class Handouts 1 Posterior Trepidations Torso Rock Torso Rock half-step Torso Rock both sides Torso Rock down body Torso Side Stretch Erector Rock Spinal Rock Lumbo Rock Cha Cha Leg Clay Snake Flop Leg
Class Handouts 1 Posterior Trepidations Torso Rock Torso Rock half-step Torso Rock both sides Torso Rock down body Torso Side Stretch Erector Rock Spinal Rock Lumbo Rock Cha Cha Leg Clay Snake Flop Leg
BIO130 Lab Practice Exam 2 Questions
 BIO130 Lab Practice Exam 2 Questions 1. Refer to Figure 1 and answer the following: Name the covering labeled Name the tubular portion labeled Name the hollow part labeled Name the material labeled Name
BIO130 Lab Practice Exam 2 Questions 1. Refer to Figure 1 and answer the following: Name the covering labeled Name the tubular portion labeled Name the hollow part labeled Name the material labeled Name
Clarification of Terms
 Clarification of Terms The plantar aspect of the foot refers to the role or its bottom The dorsal aspect refers to the top or its superior portion The ankle and foot perform three main functions: 1. shock
Clarification of Terms The plantar aspect of the foot refers to the role or its bottom The dorsal aspect refers to the top or its superior portion The ankle and foot perform three main functions: 1. shock
BIOLOGY 113 LABORATORY Skeletal System
 BIOLOGY 113 LABORATORY Skeletal System Objectives Distinguish between the axial and appendicular skeleton. Distinguish between the cranium and facial skeleton. Locate and name the bones of the skull and
BIOLOGY 113 LABORATORY Skeletal System Objectives Distinguish between the axial and appendicular skeleton. Distinguish between the cranium and facial skeleton. Locate and name the bones of the skull and
Spring Written By: J. E. Sutton. Contents: I. Overview of the Skeleton: II. Appendicular Skeleton III. Axial Skeleton IV.
 Spring 2012 Written By: J. E. Sutton Contents: I. Overview of the Skeleton: II. Appendicular Skeleton III. Axial Skeleton IV. Articulations Overview of the Skeleton: I. Orientation to Human Skeleton: a.
Spring 2012 Written By: J. E. Sutton Contents: I. Overview of the Skeleton: II. Appendicular Skeleton III. Axial Skeleton IV. Articulations Overview of the Skeleton: I. Orientation to Human Skeleton: a.
Practical 2 Worksheet
 Practical 2 Worksheet Upper Extremity BONES 1. Which end of the clavicle is on the lateral side (acromial or sternal)? 2. Describe the difference in the appearance of the acromial and sternal ends of the
Practical 2 Worksheet Upper Extremity BONES 1. Which end of the clavicle is on the lateral side (acromial or sternal)? 2. Describe the difference in the appearance of the acromial and sternal ends of the
AP1 Lab 4 - Appendicular Skeleton
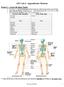 Project 1 Learn the Bone Names AP1 Lab 4 - Appendicular Skeleton Use Figure 7.1 and the hanging skeletons to learn the whole bones of the arms and legs. Don t learn the features of each bone yet just be
Project 1 Learn the Bone Names AP1 Lab 4 - Appendicular Skeleton Use Figure 7.1 and the hanging skeletons to learn the whole bones of the arms and legs. Don t learn the features of each bone yet just be
Bio 113 Anatomy and Physiology The Muscles. Muscles of the Head and Neck. Masseter. Orbicularis occuli. Orbicularis oris. Sternocleidomastoid
 Bio 113 Anatomy and Physiology The Muscles Muscles of the Head and Neck Masseter Orbicularis occuli Orbicularis oris Sternocleidomastoid Temporalis BIO 113 Fall 2011 Muscles Page 1 of 5 Muscles of the
Bio 113 Anatomy and Physiology The Muscles Muscles of the Head and Neck Masseter Orbicularis occuli Orbicularis oris Sternocleidomastoid Temporalis BIO 113 Fall 2011 Muscles Page 1 of 5 Muscles of the
Human Anatomy Biology 351
 Human Anatomy Biology 351 Lower Limb Please place your name on the back of the last page of this exam. You must answer all questions on this exam. Because statistics demonstrate that, on average, between
Human Anatomy Biology 351 Lower Limb Please place your name on the back of the last page of this exam. You must answer all questions on this exam. Because statistics demonstrate that, on average, between
Due in Lab weeks because of Thanksgiving Prelab #10. Homework #8. Both sides! Both sides!
 Lab 8 MUSCLES Due in Lab 10 2 weeks because of Thanksgiving Prelab #10 Both sides! Homework #8 Both sides! Refer to Muscles 22-23 Naming of muscles Origin Site of muscle attachment that doesn t move during
Lab 8 MUSCLES Due in Lab 10 2 weeks because of Thanksgiving Prelab #10 Both sides! Homework #8 Both sides! Refer to Muscles 22-23 Naming of muscles Origin Site of muscle attachment that doesn t move during
BONE CHALLENGE DANIL HAMMOUDI.MD
 BONE CHALLENGE DANIL HAMMOUDI.MD Bone Basic functions? A. support B. protection C. movement assistance in D. RBC formation-hemopoiesis E. mineral homeostasis +importance of calcium F. energy supply -yellow
BONE CHALLENGE DANIL HAMMOUDI.MD Bone Basic functions? A. support B. protection C. movement assistance in D. RBC formation-hemopoiesis E. mineral homeostasis +importance of calcium F. energy supply -yellow
Trauma & Orthopaedic Undergraduate Syllabus
 Trauma & Orthopaedic Undergraduate Syllabus Introduction The purpose of this document is to provide a recommended syllabus for medical students in Trauma & Orthopaedics (T&0). It should help students on
Trauma & Orthopaedic Undergraduate Syllabus Introduction The purpose of this document is to provide a recommended syllabus for medical students in Trauma & Orthopaedics (T&0). It should help students on
Index. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Acetabular fractures, 462 464 Achilles tendon rupture, 389 Acromioclavicular dislocations, 302 Acromion fractures, 301 Ankle, anatomy of, 376
Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Acetabular fractures, 462 464 Achilles tendon rupture, 389 Acromioclavicular dislocations, 302 Acromion fractures, 301 Ankle, anatomy of, 376
