REPORT OF LABORATORY EXAMINATION
|
|
|
- Leslie York
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
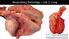
1 Director: Dr. Carole Bolin 4125 Beaumont Road Lansing, MI Phone: Fax: REPORT OF LABORATORY EXAMINATION Client: White Shepherd Genetics- (295483) Project - Attn: Judy Huston PO Box 404 Howell, MI Pine Lake Cedar Springs MI Rcvd Date: 5/18/ :01:00 PM Ordered By: N/A CR#: AP Breed: German Shepherd Age: 11 years Gender: Female Tag/Reg ID: Other ID: N e c r o p s y P r e l i m i n a r y R e p o r t NC /18/ :03:00 PM 5/19/ :53:14 PM Patterson, Jon S. History An 11-year-old, intact female white German shepherd was euthanized on 5/18/12. A brief history indicated that the dog became weak the night before. Abnormal laboratory findings on blood taken the day of euthanasia included elevated blood urea nitrogen (BUN), phosphorus, and total bilirubin concentrations; elevated alanine aminotransferase (ALT), alkaline phosphatase (ALP), gamma glutamyl transferase (GGT), amylase, and lipase activities; low sodium concentration; and severe panleukopenia (WBC=1,150/uL). Previous medical history indicated bouts of hematuria in 2008 and 2009 (treated with antibiotics), and mammary tumor removal in 2010 and Biopsy diagnosis of the tumor removed in 2011 was cystic papillary carcinoma of mammary gland origin (noninvasive, noninfiltrative). Gross Description A 36-kg dog in good nutritonal condition and good post mortem condition was presented dead for necropsy. The skin was shaved in a rectangular, 10x3-cm area on the dorsal aspect of the left antebrachium, and in a rectangular, 4x3-cm area on the dorsal aspect of the right antebrachium. The abdominal cavity contained approximately 800 ml of dark red, unclotted and clotted blood. The liver contained hundreds of spherical to irregularly shaped, 2 mm to 5 cm diameter, soft to firm, pink to dark red nodules, many of which caused elevation of the hepatic capsular surface. Nodules were present in all liver lobes, though over half were located in the cranial half of the liver, and more were present in the left lateral and medial lobes than in the right lobes. Overall, approximately 40% of the liver volume was consumed by neoplastic masses. Some nodules were dark gray red and friable to fluid in consistency, and 2 nodules with this consistency near the capsular surface had ragged surfaces, suggesting that these nodules had ruptured. Several of the lighter colored nodules on the capsular surface had umbilicated centers. The spleen had an irregular capsular surface because of the presence of numerous coalescing, irregularly shaped, raised, dark red purple areas involving approximately 25% of the parenchyma. These rather nodular areas were somewhat softer Print Date/Time: 5/29/2012 5:29 PM Page 1 of 5
2 N e c r o p s y P r e l i m i n a r y R e p o r t NC /18/ :03:00 PM 5/19/ :53:14 PM Patterson, Jon S. than the consistency of the rest of the spleen, which was lighter purple in color. The irregular nodules ranged in diameter from 6 mm to 3 cm. The capsular surfaces of the kidneys were somewhat mottled gray red and light brown, but the surfaces were smooth. The urinary bladder was contracted, with an external diameter of approximately 3.5 cm, and the wall was approximately 1.5 cm thick, firm, and tan. The bladder mucosa was grossly normal. The gastrointestinal tract, pancreas, adrenal glands, ovaries, and uterus were grossly normal. The mitral valve was mildly thickened and nodular, but the heart was otherwise normal. The lungs, thyroid gland, trachea, and esophagus were grossly normal. The brain was grossly normal. The entire spinal cord was removed, and was grossly normal. Intervertebral discs at T5-T6, T6-T7, T7-T8, T8-T9, and the lumbosacral junction (L7-S) showed evidence of degeneration. The discs at T5-T6, T6-T7, and T8-T9 were opaque white to tan white, and somewhat dry and flaky. Minimal disc material was present at T7-T8, and what was present was opaque white and flaky. The L7-S disc material was opaque white and fibrous, and there was slight (1 mm) protrusion of disc material into the vertebral canal at this site. Bridging spondylosis was mild (1-2 mm) at T5-T6, T6-T7, L5-L6, and L6-L7. Bridging was moderate (4 mm) at L7-S. Gross Diagnosis(es) liver: disseminated cancer, believed to be of hepatic origin abdomen: severe hemoabdomen vertebral column: multifocal intervertebral disc degeneration (T5-T6, T6-T7, T7-T8, T8-T9, L7-S); bridging spondylosis (T5-T6, T6-T7, L5-L6, L6-L7, L7-S) Comment: Rupture of one or more cancerous nodules in the liver probably led to hemoabdomen, and the dog probably became acutely weak because of blood loss. Histopathologic examination of all tissues, including complete assessment of spinal cord, is in progress. Jon S. Patterson, DVM, PhD, Dipl ACVP Anatomic Pathologist Jon S. Patterson, DVM, PhD, DACVP (Electronically signed by) JSP Verified: :53 JSP /JSP Print Date/Time: 5/29/2012 5:29 PM Page 2 of 5
3 History Gross Description Gross Diagnosis(es) Laboratory Findings NA Microscopic Description Sections of liver, spleen, heart, kidney, lung, adrenal gland, small intestine, pancreas, urinary bladder, uterus, and lymph node, 8 sections of brain, and 20 sections of spinal cord (from cervical through sacral segments, plus cauda equina) were examined. The liver contained numerous small to large, round to irregularly shaped nodules of neoplastic epithelial cells arranged in solid lobules or nests, cords, and subtle acinar or ductular structures. The neoplastic cells were markedly pleomorphic, but were generally cuboidal to polygonal, with large, round, hypochromatic to vesicular nuclei and a moderate to large quantity of pale eosinophilic to pale basophilic cytoplasm. Nuclei contained 1 to 3 prominent nucleoli, and there were 5-10 mitotic figures (including several atypical ones) per 10 HPF. Neoplastic nodules contained small to large areas of necrosis, and some contained small to large lakes of erythrocytes, with or without fibrin. Some nodules were completely necrotic and surrounded by a zone of degenerating neutrophils. Thin bands of fibrovascular tissue dissected through the larger neoplastic nodules, and some nodules were partially surrounded by a fibrous capsule. Many entrapped hepatocytes, or hepatocytes between neoplastic nodules contained yellow brown, fine granular, intracytoplasmic pigment (hemosiderin, bile pigments, or lipofuscin). Small numbers of remaining hepatocytes contained discrete, intracytoplasmic vacuoles. One section of lymph node was examined, and in it, the architecture was completely effaced because of infiltration by neoplastic cells similar to those described in the liver. The neoplastic cells were arranged primarily in solid sheets, but in some areas formed acini and cords as described above. In sections of brain, there was mild diffuse neuronal lipofuscinosis. Moderate numbers of neurons were surrounded by 2-3 glial cells (satellitosis). In the cerebrum, there was mild multifocal leptomeningeal fibrosis. There was mild multfocal lipofuscinosis in spinal motor neurons. The white matter of the spinal cord was essentially normal diffusely, except for minimal, isolated changes in a few sections. One ventral funiculus at the level of T3-T4 contained a swollen axon (spheroid) and one distended myelin sheath with an associated foamy macrophage. Single clusters of ellipsoids were present in the white matter of longitudinal sections of L1 and L2 segments. A longitudinal segment of one cauda equina nerve root was essentially devoid of myelinated axons, with replacement by proliferating Schwann cells, numerous foamy macrophages, macrophages with gray brown, granular pigment, and foci of cholesterol clefts. Similar changes were noted in portions of 3 other nerve roots, in cross sections. Print Date/Time: 5/29/2012 5:29 PM Page 3 of 5
4 The spleen was irregularly congested, with areas where erythrocytes obscured the architecture of both the red pulp and white pulp, and other areas where the parenchyma was devoid of erythrocytes, with increased density of fibromuscular trabeculae due to contraction. Aggregates of hemosiderin-laden macrophages were scattered throughout the spleen, especially near fibromuscular trabeculae. Renal corpuscles were slightly enlarged, as the glomerular tufts filled Bowman's spaces. The enlargement appeared to be due to increased mesangial matrix in the glomerulus. Occasional hypertrophic myocytes were present in the myocardium, and scattered myocytes contained noticeable lipofuscin pigment. In a section of lung, there was mild anthracosis. The zona reticularis of the adrenal cortex contained multiple small aggregates of large cells with pale eosinophilic, granular to finely vacuolated cytoplasm. In addition, a few irregular nodules of cortical cells were noted at the corticomedullary junction. The serosa of the urinary bladder was moderately thickened by dense granulation tissue, with foci of hemorrhage. In a few areas, lining mesothelial cells were hypertrophic and hyperplastic. The pancreas contained a nodule of hyperplastic acinar epithelium. Small to large numbers of myofibers within lumbar epaxial muscle bundles were smaller than normal, with hypereosinophilic sarcoplasm, suggesting atrophy. There also was multifocal replacement of myofibers with adipocytes. Morphologic Diagnosis(es) liver: hepatocellular carcinoma, with intrahepatic and regional lymph node metastases cauda equina: multifocal nerve fiber atrophy, loss, and Schwann cell proliferation brain, spinal cord: mild neuronal lipofuscinosis spleen: multifocal congestion and hemosiderosis kidneys: mild diffuse membranous glomerulopathy adrenal gland: multinodular adrenocortical hyperplasia lumbar epaxial muscles: multifocal myofiber atrophy and loss, with adipose replacement Final Diagnosis(es) liver: hepatocellular carcinoma, with focal or multifocal rupture of a neoplastic mass, leading to hemoabdomen Comment: As explained in the preliminary gross necropsy report, rupture of one or more of the cancerous nodules in the liver apparently led to blood loss into the abdomen and caused this dog to become acutely weak. Histopathology confirmed that the cancer was of liver (hepatocellular) origin. There was no histopathologic evidence of degenerative myelopathy. The major finding upon examination of nervous tissues was in the cauda equina--i.e., the nerve roots which extend past the end of the spinal cord. It is possible that the described changes resulted from nerve root compression near the lumbosacral junction. It is difficult to say with certainty, however, whether this dog had lumbosacral syndrome (lumbosacral stenosis) since accurate diagnosis of this condition requires high-quality radiographs ante mortem, or close inspection of the lumbosacral spine post mortem after all muscle tissue has been removed by means beyond simple dissection. I will say that in most cases of lumbosacral syndrome, there is severe bridging spondylosis at the L7-sacral joint, and bridging was not severe in this case. Essentially all of the other lesions described above were incidental (i.e., not clinically significant) and age-related. Print Date/Time: 5/29/2012 5:29 PM Page 4 of 5
5 Jon S. Patterson, DVM, PhD, Dipl ACVP Anatomic Pathologist Jon S. Patterson, DVM, PhD, DACVP (Electronically signed by) JSP Verified: :08 JSP /JSP S p e c i a l R e q u e s t s Collected Date/Time (If Provided) Procedure Notification * 05/18/ :11:00 "See Below" 5/18/ :11:00 PM Notification: This report informs you of laboratory results associated with an Anatomic Pathology case. Laboratory results should be interpreted in conjunction with pathologic findings. In some instances, laboratory results may be received prior to the pathology report. In all instances, a cumulative report will be issued. Print Date/Time: 5/29/2012 5:29 PM Page 5 of 5
REPORT OF LABORATORY EXAMINATION
 Director: Dr. Carole Bolin 4125 Beaumont Road Lansing, MI 48910-8104 Phone: 517-353-1683 Fax: 517-353-5096 www.animalhealth.msu.edu REPORT OF LABORATORY EXAMINATION Client: White Shepherd Genetics- (295483)
Director: Dr. Carole Bolin 4125 Beaumont Road Lansing, MI 48910-8104 Phone: 517-353-1683 Fax: 517-353-5096 www.animalhealth.msu.edu REPORT OF LABORATORY EXAMINATION Client: White Shepherd Genetics- (295483)
REPORT OF LABORATORY EXAMINATION. Owner:
 Phone: 517-353-1683 Fax: 517-353-5096 www.animalhealth.msu.edu REPORT OF LABORATORY EXAMINATION Client: Owner: White Shepherd Genetics Project (295483) Project PO Box 2068 Howell, MI 48844-2068 USA White
Phone: 517-353-1683 Fax: 517-353-5096 www.animalhealth.msu.edu REPORT OF LABORATORY EXAMINATION Client: Owner: White Shepherd Genetics Project (295483) Project PO Box 2068 Howell, MI 48844-2068 USA White
WSC , Conference 9, Case 1. Tissue from a nyala.
 WSC 2009-2010, Conference 9, Case 1. Tissue from a nyala. MICROSCOPIC DESCRIPTION: Heart, atrium (1 pt.): Approximately 40% of the atrial myocardium is replaced by areas of fibrous connective tissue (1
WSC 2009-2010, Conference 9, Case 1. Tissue from a nyala. MICROSCOPIC DESCRIPTION: Heart, atrium (1 pt.): Approximately 40% of the atrial myocardium is replaced by areas of fibrous connective tissue (1
HISTOPATHOLOGY. Shannon Martinson
 HISTOPATHOLOGY Shannon Martinson March 2013 Case #1 History: 8 year old beagle Neck pain for the past couple of weeks Paresis, followed by paralysis developed over the past few days Gross Description courtesy
HISTOPATHOLOGY Shannon Martinson March 2013 Case #1 History: 8 year old beagle Neck pain for the past couple of weeks Paresis, followed by paralysis developed over the past few days Gross Description courtesy
What s your diagnosis? Malori Marotz. Squirt, an 8month old mix breed puppy. History:
 What s your diagnosis? Malori Marotz Squirt, an 8month old mix breed puppy History: The owner obtained squirt at 12 weeks of age. The owner reported that Squirt was passing soft stools lately and he is
What s your diagnosis? Malori Marotz Squirt, an 8month old mix breed puppy History: The owner obtained squirt at 12 weeks of age. The owner reported that Squirt was passing soft stools lately and he is
2015 Descriptive Vet Path Course. Histo Exam #3 KEY
 2015 Descriptive Vet Path Course Histo Exam #3 KEY Test 3, Slide 1 Tissue from a guinea pig. MORPHOLOGIC DIAGNOSIS: Heart: Multifocally and randomly (1 pt), within the left and right ventricular myocardium
2015 Descriptive Vet Path Course Histo Exam #3 KEY Test 3, Slide 1 Tissue from a guinea pig. MORPHOLOGIC DIAGNOSIS: Heart: Multifocally and randomly (1 pt), within the left and right ventricular myocardium
MORPHOLOGIC DIAGNOSIS: Liver: Hepatitis, necrotizing, multifocal to coalescing, severe, with numerous trichomonads. (3 pt)
 Case 1. Tissue from a pelican. MICROSCOPIC DESCRIPTION: Liver: Approximately 80% (1 pt) of the liver is replaced by multifocal to coalescing areas of coagulative and lytic necrosis. Centrally, within these
Case 1. Tissue from a pelican. MICROSCOPIC DESCRIPTION: Liver: Approximately 80% (1 pt) of the liver is replaced by multifocal to coalescing areas of coagulative and lytic necrosis. Centrally, within these
Kidney Case 1 SURGICAL PATHOLOGY REPORT
 Kidney Case 1 Surgical Pathology Report February 9, 2007 Clinical History: This 45 year old woman was found to have a left renal mass. CT urography with reconstruction revealed a 2 cm medial mass which
Kidney Case 1 Surgical Pathology Report February 9, 2007 Clinical History: This 45 year old woman was found to have a left renal mass. CT urography with reconstruction revealed a 2 cm medial mass which
Avian Pathology. Bacterial diseases: histo slides. ECVP-ESVP Summer School 2012 Frédérique NGUYEN
 Avian Pathology Bacterial diseases: histo slides ECVP-ESVP Summer School 2012 Frédérique NGUYEN Bacterial diseases: histo slides B1. Turkey. Organs? Morphologic diagnosis? Special procedure? B2. Hen. Organ?
Avian Pathology Bacterial diseases: histo slides ECVP-ESVP Summer School 2012 Frédérique NGUYEN Bacterial diseases: histo slides B1. Turkey. Organs? Morphologic diagnosis? Special procedure? B2. Hen. Organ?
Describing and interpreting gross lesions. Prepared for VPM 4600, May 2018; Shannon Martinson
 Describing and interpreting gross lesions Prepared for VPM 4600, May 2018; Shannon Martinson How to Describe (and Interpret) Lesions Step 1 Step 2 Step 3 Step 4 Look at the specimen: Is it normal or abnormal
Describing and interpreting gross lesions Prepared for VPM 4600, May 2018; Shannon Martinson How to Describe (and Interpret) Lesions Step 1 Step 2 Step 3 Step 4 Look at the specimen: Is it normal or abnormal
Disorders of Cell Growth & Neoplasia. Histopathology Lab
 Disorders of Cell Growth & Neoplasia Histopathology Lab Paul Hanna April 2010 Case #84 Clinical History: 5 yr-old, West Highland White terrier. skin mass from axillary region. has been present for the
Disorders of Cell Growth & Neoplasia Histopathology Lab Paul Hanna April 2010 Case #84 Clinical History: 5 yr-old, West Highland White terrier. skin mass from axillary region. has been present for the
Inflammation Laboratory 3 Emphasis: Chronic inflammation and healing. Shannon Martinson: VPM 152: April 2013
 Inflammation Laboratory 3 Emphasis: Chronic inflammation and healing Shannon Martinson: http://people.upei.ca/smartinson VPM 152: April 2013 Example A Reproductive tract and colon/rectum from a sheep Previous
Inflammation Laboratory 3 Emphasis: Chronic inflammation and healing Shannon Martinson: http://people.upei.ca/smartinson VPM 152: April 2013 Example A Reproductive tract and colon/rectum from a sheep Previous
Case Scenario 1: Thyroid
 Case Scenario 1: Thyroid History and Physical Patient is an otherwise healthy 80 year old female with the complaint of a neck mass first noticed two weeks ago. The mass has increased in size and is palpable.
Case Scenario 1: Thyroid History and Physical Patient is an otherwise healthy 80 year old female with the complaint of a neck mass first noticed two weeks ago. The mass has increased in size and is palpable.
Cellular Pathology. Histopathology Lab #2 (web) Paul Hanna Jan 2018
 Cellular Pathology Histopathology Lab #2 (web) Paul Hanna Jan 2018 Slide #91 Clinical History: a necropsy was performed on an aged cat the gross pathological changes included: widespread subcutaneous edema
Cellular Pathology Histopathology Lab #2 (web) Paul Hanna Jan 2018 Slide #91 Clinical History: a necropsy was performed on an aged cat the gross pathological changes included: widespread subcutaneous edema
Bladder Case 1 SURGICAL PATHOLOGY REPORT. Procedure: Cystoscopy, transurethral resection of bladder tumor (TURBT)
 Bladder Case 1 February 17, 2007 Specimen (s) received: Bladder Tumor Pre-operative Diagnosis: Bladder Cancer Post operative Diagnosis: Bladder Cancer Procedure: Cystoscopy, transurethral resection of
Bladder Case 1 February 17, 2007 Specimen (s) received: Bladder Tumor Pre-operative Diagnosis: Bladder Cancer Post operative Diagnosis: Bladder Cancer Procedure: Cystoscopy, transurethral resection of
PROBABLE HODGKIN'S DISEASE IN A DOG: REPORT OF A CASE 1
 PROBABLE HODGKIN'S DISEASE IN A DOG: REPORT OF A CASE 1 LEONARD K. STALKER, M.D. Fellow in Surgery, The Mayo Foundation CARL F. SCHLOTTHAUER, D.V.M. AND WILLIAM H. FELDMAN, D.V.M., M.S. Division of Experimental
PROBABLE HODGKIN'S DISEASE IN A DOG: REPORT OF A CASE 1 LEONARD K. STALKER, M.D. Fellow in Surgery, The Mayo Foundation CARL F. SCHLOTTHAUER, D.V.M. AND WILLIAM H. FELDMAN, D.V.M., M.S. Division of Experimental
PATHOLOGY Intracellular Degeneration LAB 1
 PATHOLOGY Intracellular Degeneration LAB 1 Cellular swelling Liver Organ :- Liver Lesion :- 1. Narrowing of hepatic sinusoids due to the swelling of hepatocyte. 2. The cytoplasm of affected hepatocyte
PATHOLOGY Intracellular Degeneration LAB 1 Cellular swelling Liver Organ :- Liver Lesion :- 1. Narrowing of hepatic sinusoids due to the swelling of hepatocyte. 2. The cytoplasm of affected hepatocyte
Cell injury, adaptation and death. Unite one Second Lab.
 Cell injury, adaptation and death Unite one Second Lab. The two lung abscesses seen here are examples of liquefactive necrosis in which there is a liquid center in an area of tissue injury. One abscess
Cell injury, adaptation and death Unite one Second Lab. The two lung abscesses seen here are examples of liquefactive necrosis in which there is a liquid center in an area of tissue injury. One abscess
the urinary system pathology Dr. Fairoz A Eltorgman
 the urinary system pathology Dr. Fairoz A Eltorgman Tumors of the renal pelvis & kidney Benign tumors of the renal pelvis: Hemangioma Leiomyoma Malignant tumors: Transitional cell carcinoma Squamous cell
the urinary system pathology Dr. Fairoz A Eltorgman Tumors of the renal pelvis & kidney Benign tumors of the renal pelvis: Hemangioma Leiomyoma Malignant tumors: Transitional cell carcinoma Squamous cell
Inflammation Laboratory 1
 Inflammation Laboratory 1 Lab1 Emphasis: The exudates of acute inflammation Descriptions Morphologic Diagnoses Shannon Martinson: http://people.upei.ca/smartinson VPM 152: February 2012 Describing Lesions
Inflammation Laboratory 1 Lab1 Emphasis: The exudates of acute inflammation Descriptions Morphologic Diagnoses Shannon Martinson: http://people.upei.ca/smartinson VPM 152: February 2012 Describing Lesions
Disturbances of Circulation. Histopathology Lab #2 (Web)
 Disturbances of Circulation Histopathology Lab #2 (Web) Paul Hanna Winter 2015 Slide #96 History: pig was fine in the morning & found dead in the afternoon there was ~100 mls of clear fluid in the pericardial
Disturbances of Circulation Histopathology Lab #2 (Web) Paul Hanna Winter 2015 Slide #96 History: pig was fine in the morning & found dead in the afternoon there was ~100 mls of clear fluid in the pericardial
Inflammation Laboratory 2. Shannon Martinson: VPM 152: March 2012
 Inflammation Laboratory 2 Shannon Martinson: http://people.upei.ca/smartinson VPM 152: March 2012 Reminder - Creating a Morphologic Diagnosis for Inflammatory Lesions Organ and Process Exudate Distribution
Inflammation Laboratory 2 Shannon Martinson: http://people.upei.ca/smartinson VPM 152: March 2012 Reminder - Creating a Morphologic Diagnosis for Inflammatory Lesions Organ and Process Exudate Distribution
Pathology of the Hematopoietic System. Case studies
 Pathology of the Hematopoietic System Case studies Shannon Martinson, September 2015 Signalment: 9 yr-old MC cat Case Study 1 History: Cat had been anorexic and developed bleeding in the eyes Physical
Pathology of the Hematopoietic System Case studies Shannon Martinson, September 2015 Signalment: 9 yr-old MC cat Case Study 1 History: Cat had been anorexic and developed bleeding in the eyes Physical
Gross appearance of nodular hyperplasia in material obtained from suprapubic prostatectomy. Note the multinodular appearance and the admixture of
 Tiền liệt tuyến Tiền liệt tuyến Gross appearance of nodular hyperplasia in material obtained from suprapubic prostatectomy. Note the multinodular appearance and the admixture of solid and microcystic areas.
Tiền liệt tuyến Tiền liệt tuyến Gross appearance of nodular hyperplasia in material obtained from suprapubic prostatectomy. Note the multinodular appearance and the admixture of solid and microcystic areas.
Canine Liver Eneku Wilfred Bovine Pathology
 2012-1-3 Canine Liver Eneku Wilfred Bovine Pathology Contributor: New Mexico Department of Agriculture Veterinary Diagnostic Services Signalment: 5 month old male Weimaraner dog (Canis familiaris) History:
2012-1-3 Canine Liver Eneku Wilfred Bovine Pathology Contributor: New Mexico Department of Agriculture Veterinary Diagnostic Services Signalment: 5 month old male Weimaraner dog (Canis familiaris) History:
Normal thyroid tissue
 Thyroid Pathology Overview Normal thyroid tissue Normal thyroid tissue with follicles filled with colloid. Thyroid cells form follicles, spheres of epithelial cells (always single layered in health, usually
Thyroid Pathology Overview Normal thyroid tissue Normal thyroid tissue with follicles filled with colloid. Thyroid cells form follicles, spheres of epithelial cells (always single layered in health, usually
ataxia, head tremors and mild inappentence, was given palliative care
 2013-5-2 Cerebellum, Spleen-Raccoon Ahmed M. Abubakar BOVINE PATHOLOGY CONTRIBUTING INSTITUTION :College of Veterinary Medicine UC Davies Signalment: Wild-caught juvenile male raccoon, ( Procyon lotor)
2013-5-2 Cerebellum, Spleen-Raccoon Ahmed M. Abubakar BOVINE PATHOLOGY CONTRIBUTING INSTITUTION :College of Veterinary Medicine UC Davies Signalment: Wild-caught juvenile male raccoon, ( Procyon lotor)
Liver Lab #2. Bacterial Hepatitis
 Liver Lab #2 Bacterial Hepatitis Case: O12561-04. Adult ewe. Describe the lesion: Multifocal large nodules ranging in size from 1-3.5cm in greatest diameter are present within the liver and are filled
Liver Lab #2 Bacterial Hepatitis Case: O12561-04. Adult ewe. Describe the lesion: Multifocal large nodules ranging in size from 1-3.5cm in greatest diameter are present within the liver and are filled
Inflammation Laboratory 1
 Inflammation Laboratory 1 Lab1 Emphasis: The exudates of acute inflammation Descriptions Morphologic Diagnoses Shannon Martinson: http://people.upei.ca/smartinson VPM 152: March 2013 Describing Lesions
Inflammation Laboratory 1 Lab1 Emphasis: The exudates of acute inflammation Descriptions Morphologic Diagnoses Shannon Martinson: http://people.upei.ca/smartinson VPM 152: March 2013 Describing Lesions
Epithelia will be discussed according to the following scheme: Type Number of layers Shape Line drawing. Squamous Cuboidal Columnar
 Epithelia Epithelia will be discussed according to the following scheme: Type Number of layers Shape Line drawing Simple Squamous Cuboidal Columnar Covering and Lining epithelium Pseudostratified Stratified
Epithelia Epithelia will be discussed according to the following scheme: Type Number of layers Shape Line drawing Simple Squamous Cuboidal Columnar Covering and Lining epithelium Pseudostratified Stratified
XIII. Tumours of the liver and biliary system
 XIII. Tumours of the liver and biliary system V. PONOMARKOV 1 & L. J. MACKEY 2 In this histological classification of liver and gall bladder tumours the tumour types largely correspond to those found in
XIII. Tumours of the liver and biliary system V. PONOMARKOV 1 & L. J. MACKEY 2 In this histological classification of liver and gall bladder tumours the tumour types largely correspond to those found in
SESSION 1: GENERAL (BASIC) PATHOLOGY CONCEPTS Thursday, October 16, :30am - 11:30am FACULTY COPY
 SESSION 1: GENERAL (BASIC) PATHOLOGY CONCEPTS Thursday, October 16, 2008 9:30am - 11:30am FACULTY COPY GOAL: Describe the basic morphologic (structural) changes which occur in various pathologic conditions.
SESSION 1: GENERAL (BASIC) PATHOLOGY CONCEPTS Thursday, October 16, 2008 9:30am - 11:30am FACULTY COPY GOAL: Describe the basic morphologic (structural) changes which occur in various pathologic conditions.
Cellular Pathology Gross Pathology Laboratory 2 Cell Injury. VPM 152: General Pathology Instructor: Chelsea Martin Winter 2016
 Cellular Pathology Gross Pathology Laboratory 2 Cell Injury VPM 152: General Pathology Instructor: Chelsea Martin Winter 2016 Gross Specimens The following slides consist of images from the specimens presented
Cellular Pathology Gross Pathology Laboratory 2 Cell Injury VPM 152: General Pathology Instructor: Chelsea Martin Winter 2016 Gross Specimens The following slides consist of images from the specimens presented
The Endocrine System Pituitary
 The Endocrine System Pituitary Look at your slide of the human pituitary with your naked eye. You should see a cellular region and a more fibrous region. Then view each region with your microscope under
The Endocrine System Pituitary Look at your slide of the human pituitary with your naked eye. You should see a cellular region and a more fibrous region. Then view each region with your microscope under
Unit I Problem 9 Histology: Basic Tissues of The Body
 Unit I Problem 9 Histology: Basic Tissues of The Body - What is the difference between cytology and histology? Cytology: it is the study of the structure and functions of cells and their contents. Histology:
Unit I Problem 9 Histology: Basic Tissues of The Body - What is the difference between cytology and histology? Cytology: it is the study of the structure and functions of cells and their contents. Histology:
Sampled: 06/05/2017 Paramus, NJ Received: 06/13/2017 (201) Finalized: 07/27/2017. Anatomic Pathology
 Owner: 240 Farrier Road,, Ithaca, NY 14853 Ph: 607-253-3900 Fax: 607-253-3943 https://ahdc.vet.cornell.edu Page 1 of 7 Oradell Animal Hospital Inc - (3382) Dr John Lucy 580 Winters Ave Sampled: 06/05/2017
Owner: 240 Farrier Road,, Ithaca, NY 14853 Ph: 607-253-3900 Fax: 607-253-3943 https://ahdc.vet.cornell.edu Page 1 of 7 Oradell Animal Hospital Inc - (3382) Dr John Lucy 580 Winters Ave Sampled: 06/05/2017
2014 Descriptive Vet Path Course. Histo Exam #1 Key
 2014 Descriptive Vet Path Course Histo Exam #1 Key Test 1, Slide 1. Tissue from a dog. MICROSCOPIC DESCRIPTION: Prostate gland: Multifocally and extensively infiltrating the prostate gland (1 pt.), and
2014 Descriptive Vet Path Course Histo Exam #1 Key Test 1, Slide 1. Tissue from a dog. MICROSCOPIC DESCRIPTION: Prostate gland: Multifocally and extensively infiltrating the prostate gland (1 pt.), and
Pitfalls in thyroid tumor pathology. Prof.Valdi Pešutić-Pisac MD, PhD
 Pitfalls in thyroid tumor pathology Prof.Valdi Pešutić-Pisac MD, PhD Too many or... Tumour herniation through a torn capsule simulating capsular invasion fibrous capsule with a sharp discontinuity, suggestive
Pitfalls in thyroid tumor pathology Prof.Valdi Pešutić-Pisac MD, PhD Too many or... Tumour herniation through a torn capsule simulating capsular invasion fibrous capsule with a sharp discontinuity, suggestive
Neoplasia part I. Dr. Mohsen Dashti. Clinical Medicine & Pathology nd Lecture
 Neoplasia part I By Dr. Mohsen Dashti Clinical Medicine & Pathology 316 2 nd Lecture Lecture outline Review of structure & function. Basic definitions. Classification of neoplasms. Morphologic features.
Neoplasia part I By Dr. Mohsen Dashti Clinical Medicine & Pathology 316 2 nd Lecture Lecture outline Review of structure & function. Basic definitions. Classification of neoplasms. Morphologic features.
Pathological Classification of Hepatocellular Carcinoma
 3 rd APASL Single Topic Conference: HCC in 3D Pathological Classification of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Glenda Lyn Y. Pua, M.D. HCC Primary liver cancer is the 2 nd most common cancer in Asia HCC is the
3 rd APASL Single Topic Conference: HCC in 3D Pathological Classification of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Glenda Lyn Y. Pua, M.D. HCC Primary liver cancer is the 2 nd most common cancer in Asia HCC is the
What s Your Diagnosis? Signalment: Species: Canine Breed: Golden Retriever Sex: Female (spayed) Date of Birth: 04/01/99
 What s Your Diagnosis? Signalment: Species: Canine Breed: Golden Retriever Sex: Female (spayed) Date of Birth: 04/01/99 Presenting Complaint: Acute onset of lethargy Vomited twice (partially digested food)
What s Your Diagnosis? Signalment: Species: Canine Breed: Golden Retriever Sex: Female (spayed) Date of Birth: 04/01/99 Presenting Complaint: Acute onset of lethargy Vomited twice (partially digested food)
HISTOLOGY. Simple squamal lungs
 HISTOLOGY Lab Objectives: Students should be able to... 1. Visually identify each class of tissue and examples within each class 2. Indicate the location (in the human body and/or organ) and function of
HISTOLOGY Lab Objectives: Students should be able to... 1. Visually identify each class of tissue and examples within each class 2. Indicate the location (in the human body and/or organ) and function of
PLATES 24 TO 26. (Received for publication, December 4, 1935)
 Published Online: 1 March, 1936 Supp Info: http://doi.org/10.1084/jem.63.3.303 Downloaded from jem.rupress.org on January 19, 2019 THE VISCERAL LESIONS PRODUCED IN MICE BY THE SALIVARY GLAND VIRUS OF MICE*
Published Online: 1 March, 1936 Supp Info: http://doi.org/10.1084/jem.63.3.303 Downloaded from jem.rupress.org on January 19, 2019 THE VISCERAL LESIONS PRODUCED IN MICE BY THE SALIVARY GLAND VIRUS OF MICE*
What s Your Diagnosis?
 What s Your Diagnosis? Courtney S. Wait Signalment: 11 year old FS Labrador Retriever Presenting Complaint/History: The patient presented to the referring DVM for inappetance, vomiting, lethargy, and anorexia.
What s Your Diagnosis? Courtney S. Wait Signalment: 11 year old FS Labrador Retriever Presenting Complaint/History: The patient presented to the referring DVM for inappetance, vomiting, lethargy, and anorexia.
Endocrine Lab. Heather Fenton VPM 222 November
 Endocrine Lab Heather Fenton VPM 222 November 27 2012 Case 1: Nursery pig Case 1: Nursery pig Description: There are multifocal round (approximately 1cm diameter) firm lesions within the adrenal gland
Endocrine Lab Heather Fenton VPM 222 November 27 2012 Case 1: Nursery pig Case 1: Nursery pig Description: There are multifocal round (approximately 1cm diameter) firm lesions within the adrenal gland
Basic Histology. By Mrs. Bailey
 Basic Histology By Mrs. Bailey Primary Tissues 1. Epithelial Tissue 2. Connective Tissue 3. Muscle Tissue 4. Nervous Tissue Very cellular Supported by underlying connective tissue Epithelial & connective
Basic Histology By Mrs. Bailey Primary Tissues 1. Epithelial Tissue 2. Connective Tissue 3. Muscle Tissue 4. Nervous Tissue Very cellular Supported by underlying connective tissue Epithelial & connective
Evaluation of Breast Specimens Removed by Needle Localization Technique
 Evaluation of Breast Specimens Removed by Needle Localization Technique Specimen Handling: The breast specimen when received should be measured and grossly inspected for any orientation designated by the
Evaluation of Breast Specimens Removed by Needle Localization Technique Specimen Handling: The breast specimen when received should be measured and grossly inspected for any orientation designated by the
Neoplasms of the Canine, Feline and Lemur Liver:
 Neoplasms of the Canine, Feline and Lemur Liver: Classification and Prognosis Annual Seminar of the French Society of Veterinary Pathology John M. Cullen VMD PhD DACVP North Carolina State University Primary
Neoplasms of the Canine, Feline and Lemur Liver: Classification and Prognosis Annual Seminar of the French Society of Veterinary Pathology John M. Cullen VMD PhD DACVP North Carolina State University Primary
Pathology of the Hematopoietic System GROSS/HISTO LAB
 Pathology of the Hematopoietic System GROSS/HISTO LAB Paul Hanna (thanks to Dr s Aburto, Martinson & Fenton) Fall 2014 Slide 1 Spleen from a Beaver Give a morphologic diagnosis and possible etiology &
Pathology of the Hematopoietic System GROSS/HISTO LAB Paul Hanna (thanks to Dr s Aburto, Martinson & Fenton) Fall 2014 Slide 1 Spleen from a Beaver Give a morphologic diagnosis and possible etiology &
Basic Urinary Tract Anatomy and Histology
 Basic Urinary Tract Anatomy and Histology The two kidneys are located in the retroperitoneum on either side of the vertebral bladder and the contraction of the detrusor muscle. Any mechanical barrier,
Basic Urinary Tract Anatomy and Histology The two kidneys are located in the retroperitoneum on either side of the vertebral bladder and the contraction of the detrusor muscle. Any mechanical barrier,
Figure 2: Lymph node Cortical follicular (F) and paracortical (PC) atrophy, with narrowing of the cortex relative to the medulla (M).
 Figure 1: Lymph node Follicular hyperplasia, with expansion of the follicular germinal centres (F) by large blast cells. Paracortical hyperplasia, with expansion of the paracortex (PC) by small lymphocytes.
Figure 1: Lymph node Follicular hyperplasia, with expansion of the follicular germinal centres (F) by large blast cells. Paracortical hyperplasia, with expansion of the paracortex (PC) by small lymphocytes.
10/3/2012. Tissue: The Living Fabric: Part B. Extracellular matrix Ground substance Fibers Collagen fiber Elastic fiber Reticular fiber.
 PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Janice Meeking, Mount Royal College C H A P T E R 4 Tissue: The Living Fabric: Part B Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Janice Meeking, Mount Royal College C H A P T E R 4 Tissue: The Living Fabric: Part B Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
HOW TO DEAL WITH THOSE ABNORMAL LIVER ENZYMES David C. Twedt DVM, DACVIM Colorado State University Fort Collins, CO
 HOW TO DEAL WITH THOSE ABNORMAL LIVER ENZYMES David C. Twedt DVM, DACVIM Colorado State University Fort Collins, CO The identification of abnormal liver enzymes usually indicates liver damage but rarely
HOW TO DEAL WITH THOSE ABNORMAL LIVER ENZYMES David C. Twedt DVM, DACVIM Colorado State University Fort Collins, CO The identification of abnormal liver enzymes usually indicates liver damage but rarely
EMBRYONAL NEPHROMA IN THE CHICKEN: REPORT OF TWO CASES
 EMBRYONAL NEPHROMA IN THE CHICKEN: REPORT OF TWO CASES FRANK D. McKENNEY, V.M.D. (Di1!ision of Experimental Surgery and Pathology, The Mayo Foundation, Rochester, Minnesota) Few data have been collected
EMBRYONAL NEPHROMA IN THE CHICKEN: REPORT OF TWO CASES FRANK D. McKENNEY, V.M.D. (Di1!ision of Experimental Surgery and Pathology, The Mayo Foundation, Rochester, Minnesota) Few data have been collected
Slide 154: Pancreas, H&E
 Slide 154: Pancreas, H&E the pancreas, located adjacent to the duodenum, is a mixed exocrine and endocrine gland; it is usually readily identifiable by the presence of the interspersed endocrine pancreatic
Slide 154: Pancreas, H&E the pancreas, located adjacent to the duodenum, is a mixed exocrine and endocrine gland; it is usually readily identifiable by the presence of the interspersed endocrine pancreatic
Practical Histology. Lab 3: Connective tissue
 Practical Histology Lab 3: Connective tissue Connective tissues Connective tissue provides structural support for the body by binding cells and tissues together to form organs. It also provides metabolic
Practical Histology Lab 3: Connective tissue Connective tissues Connective tissue provides structural support for the body by binding cells and tissues together to form organs. It also provides metabolic
Body Tissues Pearson Education, Inc.
 Body Tissues Tissues Groups of cells with similar structure and function Four primary types: Epithelial tissue (epithelium).1 Connective tissue.2 Muscle tissue.3 Nervous tissue.4 Epithelial Tissues Locations:
Body Tissues Tissues Groups of cells with similar structure and function Four primary types: Epithelial tissue (epithelium).1 Connective tissue.2 Muscle tissue.3 Nervous tissue.4 Epithelial Tissues Locations:
WSC , Conference 9. Case 1. Tissue from a rhesus macaque.
 Case 1. Tissue from a rhesus macaque. MICROSCOPIC DESCRIPTION: Esophagus: There is multifocal loss of the mucosal lining (1 pt). In these areas, the denuded subepithelial fibrous connective tissue is infiltrated
Case 1. Tissue from a rhesus macaque. MICROSCOPIC DESCRIPTION: Esophagus: There is multifocal loss of the mucosal lining (1 pt). In these areas, the denuded subepithelial fibrous connective tissue is infiltrated
Cell and Tissue Types. Epithelial, Connective, Muscle, Nerve
 Cell and Tissue Types Epithelial, Connective, Muscle, Nerve Objectives Explain the major stages of the cell cycle and cellular division (mitosis). Describe specific events occurring in each of the phases
Cell and Tissue Types Epithelial, Connective, Muscle, Nerve Objectives Explain the major stages of the cell cycle and cellular division (mitosis). Describe specific events occurring in each of the phases
Epithelium. Four primary tissue types:
 Epithelium Four primary tissue types: Epithelial (covering) Connective (support) Nervous (control) Muscular (movement) Smooth muscle Cardiac muscle Skeletal muscle 1 Epithelial Tissue Features Epithelial
Epithelium Four primary tissue types: Epithelial (covering) Connective (support) Nervous (control) Muscular (movement) Smooth muscle Cardiac muscle Skeletal muscle 1 Epithelial Tissue Features Epithelial
Case Scenario 1. Discharge Summary
 Case Scenario 1 Discharge Summary A 69-year-old woman was on vacation and noted that she was becoming jaundiced. Two months prior to leaving on that trip, she had had a workup that included an abdominal
Case Scenario 1 Discharge Summary A 69-year-old woman was on vacation and noted that she was becoming jaundiced. Two months prior to leaving on that trip, she had had a workup that included an abdominal
Disclosures. Parathyroid Pathology. Objectives. The normal parathyroid 11/10/2012
 Disclosures Parathyroid Pathology I have nothing to disclose Annemieke van Zante MD/PhD Assistant Professor of Clinical Pathology Associate Chief of Cytopathology Objectives 1. Review the pathologic features
Disclosures Parathyroid Pathology I have nothing to disclose Annemieke van Zante MD/PhD Assistant Professor of Clinical Pathology Associate Chief of Cytopathology Objectives 1. Review the pathologic features
CYSTIC TUMORS OF THE KIDNEY JOHN N. EBLE, M.D. CYSTIC NEPHROMA
 Page 1 CYSTIC TUMORS OF THE KIDNEY JOHN N. EBLE, M.D. Department of Pathology & Laboratory Medicine Phone (317) 274-4806 Medical Science A-128 FAX: (317) 278-2018 635 Barnhill Drive jeble @iupui.edu Indianapolis,
Page 1 CYSTIC TUMORS OF THE KIDNEY JOHN N. EBLE, M.D. Department of Pathology & Laboratory Medicine Phone (317) 274-4806 Medical Science A-128 FAX: (317) 278-2018 635 Barnhill Drive jeble @iupui.edu Indianapolis,
Papillary Lesions of the breast
 Papillary Lesions of the breast Emad Rakha Professor of Breast Pathology The University of Nottingham Papillary lesions of the breast are a heterogeneous group of disease, which are characterised by neoplastic
Papillary Lesions of the breast Emad Rakha Professor of Breast Pathology The University of Nottingham Papillary lesions of the breast are a heterogeneous group of disease, which are characterised by neoplastic
PRACTICAL ROADMAP. GLANDS AFFECTING LIFESTYLE WJ van der Spuy & T Tshabalala
 PRACTICAL ROADMAP GLANDS AFFECTING LIFESTYLE WJ van der Spuy & T Tshabalala GLANDS AFFECTING LIFESTYLE Submandibular gland (salivary gland) Liver Pancreas Hypophysis (pituitary gland) Thyroid Suprarenal
PRACTICAL ROADMAP GLANDS AFFECTING LIFESTYLE WJ van der Spuy & T Tshabalala GLANDS AFFECTING LIFESTYLE Submandibular gland (salivary gland) Liver Pancreas Hypophysis (pituitary gland) Thyroid Suprarenal
Prelab #4 BLOOD; BONE MARROW; RESPIRATORY; INTEGUEMENT Page 1
 Prelab #4 BLOOD; BONE MARROW; RESPIRATORY; INTEGUEMENT Page 1 Blood Slide 101 This a classic slide of blood cells using a Wright stain. Inspect red blood cells and their appearance. Note the approximate
Prelab #4 BLOOD; BONE MARROW; RESPIRATORY; INTEGUEMENT Page 1 Blood Slide 101 This a classic slide of blood cells using a Wright stain. Inspect red blood cells and their appearance. Note the approximate
What s your diagnosis?
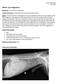 What s your diagnosis? Signalment: 9 year old MC 2.7 kg Papillion Presenting Complaint: Presented for work up of anorexia and vomiting History: He had presented to cardiology for work up of a grad IV/VI
What s your diagnosis? Signalment: 9 year old MC 2.7 kg Papillion Presenting Complaint: Presented for work up of anorexia and vomiting History: He had presented to cardiology for work up of a grad IV/VI
What s Your Diagnosis?
 What s Your Diagnosis? Signalment: 5 year old MC Belgian Malinois Presenting Complaint: Perineal hernia as well as not eating or defecating History: The patient presented to the KSU VHC on 7/28/2018 for
What s Your Diagnosis? Signalment: 5 year old MC Belgian Malinois Presenting Complaint: Perineal hernia as well as not eating or defecating History: The patient presented to the KSU VHC on 7/28/2018 for
BY: MURSHIDAH (D11A020) HERLINA (D11A010) HANIM (D11A033) TG. HAJAR (D11A036) WAN NUR SHAMIMI (D11 B046) NIK NUR AFINA BT NIK ALWI (D11A021)
 BY: MURSHIDAH (D11A020) HERLINA (D11A010) HANIM (D11A033) TG. HAJAR (D11A036) WAN NUR SHAMIMI (D11 B046) NIK NUR AFINA BT NIK ALWI (D11A021) The thymus is of a pinkish-gray colour, soft, and lobulated
BY: MURSHIDAH (D11A020) HERLINA (D11A010) HANIM (D11A033) TG. HAJAR (D11A036) WAN NUR SHAMIMI (D11 B046) NIK NUR AFINA BT NIK ALWI (D11A021) The thymus is of a pinkish-gray colour, soft, and lobulated
Tissue = groups of cells that are similar in structure and function
 Tissue = groups of cells that are similar in structure and function Types Epithelial - covering Connective - support Muscle - movement Nervous - control Membranes line body cavities and hold organs together
Tissue = groups of cells that are similar in structure and function Types Epithelial - covering Connective - support Muscle - movement Nervous - control Membranes line body cavities and hold organs together
Lymphoid Organs. Dr. Sami Zaqout. Dr. Sami Zaqout IUG Faculty of Medicine
 Lymphoid Organs Dr. Sami Zaqout Cells of the Immune System Lymphocytes Plasma cells Mast cells Neutrophils Eosinophils Cells of the mononuclear phagocyte system Distribution of cells of the immune system
Lymphoid Organs Dr. Sami Zaqout Cells of the Immune System Lymphocytes Plasma cells Mast cells Neutrophils Eosinophils Cells of the mononuclear phagocyte system Distribution of cells of the immune system
Non-Invasive Follicular Thyroid Neoplasm with Papillary-like Nuclei (NIFTP)
 Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma: Follicular Variant Encapsulated Type Replaced by: Non-Invasive Follicular Thyroid Neoplasm with Papillary-like Nuclei (NIFTP) Lester D. R. Thompson www.lester-thompson.com
Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma: Follicular Variant Encapsulated Type Replaced by: Non-Invasive Follicular Thyroid Neoplasm with Papillary-like Nuclei (NIFTP) Lester D. R. Thompson www.lester-thompson.com
CYTOLOGY OF THE LIVER
 CYTOLOGY OF THE LIVER Maxey L. Wellman, DVM, PhD, DACVP (Clinical Pathology) Professor, Department of Veterinary Biosciences, College of Veterinary Medicine, The Ohio State University, Columbus, OH, USA
CYTOLOGY OF THE LIVER Maxey L. Wellman, DVM, PhD, DACVP (Clinical Pathology) Professor, Department of Veterinary Biosciences, College of Veterinary Medicine, The Ohio State University, Columbus, OH, USA
Review of the AP Part II Practical Examination. Dr David Clift Co Chief Examiner
 Review of the AP Part II Practical Examination Dr David Clift Co Chief Examiner General Remarks The part II practical examination involved 15 cases which were presented with sufficient clinical data to
Review of the AP Part II Practical Examination Dr David Clift Co Chief Examiner General Remarks The part II practical examination involved 15 cases which were presented with sufficient clinical data to
Mammary Nodular Hyperplasia in Intact R hesus Monkeys
 Vet. Path. 10: 130-134 (1973) Mammary Nodular Hyperplasia in Intact R hesus Monkeys L. W NELSON and L. D. SHOTT Department of Pathology and Toxicology, Mead Johnson Research Center, Evansville, Ind., and
Vet. Path. 10: 130-134 (1973) Mammary Nodular Hyperplasia in Intact R hesus Monkeys L. W NELSON and L. D. SHOTT Department of Pathology and Toxicology, Mead Johnson Research Center, Evansville, Ind., and
VETERINARY HEMATOLOGY ATLAS OF COMMON DOMESTIC AND NON-DOMESTIC SPECIES COPYRIGHTED MATERIAL SECOND EDITION
 VETERINARY HEMATOLOGY ATLAS OF COMMON DOMESTIC AND NON-DOMESTIC SPECIES SECOND EDITION COPYRIGHTED MATERIAL CHAPTER ONE HEMATOPOIESIS GENERAL FEATURES All blood cells have a finite life span, but in normal
VETERINARY HEMATOLOGY ATLAS OF COMMON DOMESTIC AND NON-DOMESTIC SPECIES SECOND EDITION COPYRIGHTED MATERIAL CHAPTER ONE HEMATOPOIESIS GENERAL FEATURES All blood cells have a finite life span, but in normal
(Iteceived for publication December 3, 1915)
 TRANSPLANTABLE SARCOMATA OF THE RAT LIVER ARISING IN THE WALLS OF PARASITIC CYSTS G. L. ROHDENBURG, M.D., AND F. D. BULLOCK, M.D. From Colurnbia University, George Crocker Special Re-search Fund, F. C.
TRANSPLANTABLE SARCOMATA OF THE RAT LIVER ARISING IN THE WALLS OF PARASITIC CYSTS G. L. ROHDENBURG, M.D., AND F. D. BULLOCK, M.D. From Colurnbia University, George Crocker Special Re-search Fund, F. C.
2 to 3% of All New Visceral Cancers Peak Incidence is 6th Decade M:F = 2:1 Grossly is a Bright Yellow, Necrotic Mass with a Pseudocapsule
 GENITOURINARY PATHOLOGY Kathleen M. O Toole, M.D. Renal Cell Carcinoma 2 to 3% of All New Visceral Cancers Peak Incidence is 6th Decade M:F = 2:1 Grossly is a Bright Yellow Necrotic Mass Grossly is a Bright
GENITOURINARY PATHOLOGY Kathleen M. O Toole, M.D. Renal Cell Carcinoma 2 to 3% of All New Visceral Cancers Peak Incidence is 6th Decade M:F = 2:1 Grossly is a Bright Yellow Necrotic Mass Grossly is a Bright
Note: The cause of testicular neoplasms remains unknown
 - In the 15- to 34-year-old age group, they are the most common tumors of men. - Tumors of the testis are a heterogeneous group of neoplasms that include: I. Germ cell tumors : 95%; all are malignant.
- In the 15- to 34-year-old age group, they are the most common tumors of men. - Tumors of the testis are a heterogeneous group of neoplasms that include: I. Germ cell tumors : 95%; all are malignant.
Diseases of the breast (1 of 2)
 Diseases of the breast (1 of 2) Introduction A histology introduction Normal ducts and lobules of the breast are lined by two layers of cells a layer of luminal cells overlying a second layer of myoepithelial
Diseases of the breast (1 of 2) Introduction A histology introduction Normal ducts and lobules of the breast are lined by two layers of cells a layer of luminal cells overlying a second layer of myoepithelial
CELL AND TISSUE INJURY COURSE-II PATHOLOGY LABORATORY. PATHOLOGY of MASS LESIONS and TISSUE DEFECTS -MACROSCOPY Assoc. Professor Rengin Ahıskalı
 CELL AND TISSUE INJURY COURSE-II PATHOLOGY LABORATORY PATHOLOGY of MASS LESIONS and TISSUE DEFECTS -MACROSCOPY Assoc. Professor Rengin Ahıskalı M1 - RENAL TUBERCULOSIS cavitary areas caseous necrosis fibrous
CELL AND TISSUE INJURY COURSE-II PATHOLOGY LABORATORY PATHOLOGY of MASS LESIONS and TISSUE DEFECTS -MACROSCOPY Assoc. Professor Rengin Ahıskalı M1 - RENAL TUBERCULOSIS cavitary areas caseous necrosis fibrous
Gross appearance of peritoneal cysts. They have a thin, translucent wall and contain a clear fluid.
 Gross appearance of peritoneal cysts. They have a thin, translucent wall and contain a clear fluid. So-called multicystic benign mesothelioma. A, Gross appearance. So-called multicystic benign mesothelioma.
Gross appearance of peritoneal cysts. They have a thin, translucent wall and contain a clear fluid. So-called multicystic benign mesothelioma. A, Gross appearance. So-called multicystic benign mesothelioma.
Diagnostic Cytology of Cancer Cases
 Diagnostic Cytology of Cancer Cases Somporn Techangamsuwan Companion Animal Cancer Research Unit (CAC-RU) Department of Pathology, Faculty of Veterinary Science, Chulalongkorn University 1 Tumor or Non-tumor
Diagnostic Cytology of Cancer Cases Somporn Techangamsuwan Companion Animal Cancer Research Unit (CAC-RU) Department of Pathology, Faculty of Veterinary Science, Chulalongkorn University 1 Tumor or Non-tumor
G3.02 The malignant potential of the neoplasm should be recorded. CG3.02a
 G3.02 The malignant potential of the neoplasm should be recorded. CG3.02a Conventional adrenocortical neoplasm. Each of the below parameters is scored 0 when absent and 1 when present. 3 or more of these
G3.02 The malignant potential of the neoplasm should be recorded. CG3.02a Conventional adrenocortical neoplasm. Each of the below parameters is scored 0 when absent and 1 when present. 3 or more of these
This is the second learning component (Learning Component 2) in our first learning module (Learning Module 1). In this component we review a very
 This is the second learning component (Learning Component 2) in our first learning module (Learning Module 1). In this component we review a very basic response to injury inflammation. We ll look at examples
This is the second learning component (Learning Component 2) in our first learning module (Learning Module 1). In this component we review a very basic response to injury inflammation. We ll look at examples
PATHOLOGY OF LIVER TUMORS
 PATHOLOGY OF LIVER TUMORS Pathobasic, 31.05.2016 WHO Classification Approach to a Liver Mass Lesion in a patient with chronic liver disease? Lesion in a patient without chronic liver disease? Malignant
PATHOLOGY OF LIVER TUMORS Pathobasic, 31.05.2016 WHO Classification Approach to a Liver Mass Lesion in a patient with chronic liver disease? Lesion in a patient without chronic liver disease? Malignant
VPM Pigment and other tissue deposits. Shannon Martinson
 VPM 152 - Pigment and other tissue deposits Shannon Martinson http://people.upei.ca/smartinson/ Case 1 Signalment: 2 month old heifer beef calf Clinical History: Lateral recumbency for 4 days Tachycardia,
VPM 152 - Pigment and other tissue deposits Shannon Martinson http://people.upei.ca/smartinson/ Case 1 Signalment: 2 month old heifer beef calf Clinical History: Lateral recumbency for 4 days Tachycardia,
Fig. 59 Malignant phaeochromocytoma, hepatic metastasis.
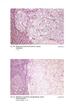 Fig. 59 Malignant phaeochromocytoma, hepatic metastasis. X 120 Hyperte nsion Fig. 60 Malignant sympathetic paraganglioma, lymph node metastasis Primary in bladder. x 1 20 Hypertension Fig. 61 Malignant
Fig. 59 Malignant phaeochromocytoma, hepatic metastasis. X 120 Hyperte nsion Fig. 60 Malignant sympathetic paraganglioma, lymph node metastasis Primary in bladder. x 1 20 Hypertension Fig. 61 Malignant
They cells can not function death.
 Jenna Hellack Jan 2001 Tissues What do you think happens when the cells use up their food and oxygen before there is time to replenish it? They cells can not function death. Blood Cell Cancer cell Plant
Jenna Hellack Jan 2001 Tissues What do you think happens when the cells use up their food and oxygen before there is time to replenish it? They cells can not function death. Blood Cell Cancer cell Plant
B. Classification of epithelium: by number of cell layers present and by shape of the superficial cell layers.
 I. Introduction - tissue: group of cells that are closely associated, similar in structure and function, and perform a common or related function. - four primary tissues: epithelial tissue, connective
I. Introduction - tissue: group of cells that are closely associated, similar in structure and function, and perform a common or related function. - four primary tissues: epithelial tissue, connective
Pathology Slides. [Pathology]
![Pathology Slides. [Pathology] Pathology Slides. [Pathology]](/thumbs/94/120604575.jpg) Pathology Slides MedicoNotes provides real laboratory pathological slides to aid you to differentiate between different pathological structures under microscope. www.mediconotes.com Histology slides example
Pathology Slides MedicoNotes provides real laboratory pathological slides to aid you to differentiate between different pathological structures under microscope. www.mediconotes.com Histology slides example
VPM Pigment and other tissue deposits. Shannon Martinson
 VPM 152 - Pigment and other tissue deposits Shannon Martinson http://people.upei.ca/smartinson/ Case 1: Signalment: 2 month old heifer beef calf Clinical History: Lateral recumbency for 4 days. Tachycardia,
VPM 152 - Pigment and other tissue deposits Shannon Martinson http://people.upei.ca/smartinson/ Case 1: Signalment: 2 month old heifer beef calf Clinical History: Lateral recumbency for 4 days. Tachycardia,
Major Structures of the Nervous System. Brain, cranial nerves, spinal cord, spinal nerves, ganglia, enteric plexuses and sensory receptors
 Major Structures of the Nervous System Brain, cranial nerves, spinal cord, spinal nerves, ganglia, enteric plexuses and sensory receptors Nervous System Divisions Central Nervous System (CNS) consists
Major Structures of the Nervous System Brain, cranial nerves, spinal cord, spinal nerves, ganglia, enteric plexuses and sensory receptors Nervous System Divisions Central Nervous System (CNS) consists
Lec. 11 & 12 Dr. Ali H. Murad Dental pulp 1- Coronal pulp
 Lec. 11 & 12 Dr. Ali H. Murad Dental pulp Is the soft connective tissue located in the central portion of each tooth. All pulps have similar morphologic characteristic, such as a soft, gelatinous consistency
Lec. 11 & 12 Dr. Ali H. Murad Dental pulp Is the soft connective tissue located in the central portion of each tooth. All pulps have similar morphologic characteristic, such as a soft, gelatinous consistency
Respiratory Pathology Lab 2: Lung. Shannon Martinson,
 Respiratory Pathology Lab 2: Lung Shannon Martinson, 2017 http://people.upei.ca/smartinson/ Case 1 Signalment: 9 month old DSH cat History: Poor doer with stunted growth One month of lethargy one day the
Respiratory Pathology Lab 2: Lung Shannon Martinson, 2017 http://people.upei.ca/smartinson/ Case 1 Signalment: 9 month old DSH cat History: Poor doer with stunted growth One month of lethargy one day the
Salivary Glands 3/7/2017
 Salivary Glands 3/7/2017 Goals and objectives Focus on the entities unique to H&N Common board type facts Information for your future practice Salivary Glands Salivary Glands Major gland. Paratid. Submandibular.
Salivary Glands 3/7/2017 Goals and objectives Focus on the entities unique to H&N Common board type facts Information for your future practice Salivary Glands Salivary Glands Major gland. Paratid. Submandibular.
RENAL CELL CARCINOMA 2 to 3% of All New Visceral Cancers Peak Incidence is 6th Decade M:F = 2:1 Grossly is a Bright Yellow, Necrotic Mass with a Pseud
 GENITOURINARY PATHOLOGY Kathleen M. O Toole Toole, M.D. RENAL CELL CARCINOMA 2 to 3% of All New Visceral Cancers Peak Incidence is 6th Decade M:F = 2:1 Grossly is a Bright Yellow, Necrotic Mass with a
GENITOURINARY PATHOLOGY Kathleen M. O Toole Toole, M.D. RENAL CELL CARCINOMA 2 to 3% of All New Visceral Cancers Peak Incidence is 6th Decade M:F = 2:1 Grossly is a Bright Yellow, Necrotic Mass with a
Objectives. Objectives 9/11/2012. Chapter 7 Body Systems. Define term connective tissue. Identify five body cavities
 Chapter 7 Body Systems Objectives Define term connective tissue Identify five body cavities Define terms joints, cartilage, ligaments, tendons Identify two major divisions of skeletal system and describe
Chapter 7 Body Systems Objectives Define term connective tissue Identify five body cavities Define terms joints, cartilage, ligaments, tendons Identify two major divisions of skeletal system and describe
Epithelial Tissue. Simple Cuboidal Function: secretion and absorption. Simple Squamous
 Epithelial Tissue General Functions: Lines and covers organs Absorbs / secretes substances Gas exchange Protection Special Characteristics: - have an apical surface on top - have a basement membrane below
Epithelial Tissue General Functions: Lines and covers organs Absorbs / secretes substances Gas exchange Protection Special Characteristics: - have an apical surface on top - have a basement membrane below
Presented by: Dr. Giuseppe Molinaro Dr. Davide De Biase
 Presented by: Dr. Giuseppe Molinaro Dr. Davide De Biase Dog Spayed Female LABRADOR RETRIEVER 3 Years old VACCINATIONS ANTIPARASITIC COMMERCIAL DIET VOMITING FOR A MONTH DULLNESS WEIGHT LOSS INAPPETANCE
Presented by: Dr. Giuseppe Molinaro Dr. Davide De Biase Dog Spayed Female LABRADOR RETRIEVER 3 Years old VACCINATIONS ANTIPARASITIC COMMERCIAL DIET VOMITING FOR A MONTH DULLNESS WEIGHT LOSS INAPPETANCE
