Nervous Systems. 26 April 2017
|
|
|
- Aubrie Bryan
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Nervous Systems 26 April 2017
2 Nervous systems consist of circuits of neurons and supporting cells Each single-celled organism can respond to stimuli in its environment Animals are multicellular and most groups respond to stimuli using systems of neurons
3 Simple Nervous Systems The simplest animals with nervous systems, the cnidarians, have neurons arranged in nerve nets A nerve net is a series of interconnected nerve cells More complex animals have nerves Nerves are bundles that consist of the axons of multiple nerve cells Sea stars have a nerve net in each arm connected by radial nerves to a central nerve ring
4 Figure 49.2a Radial nerve Nerve net Nerve ring (a) Hydra (cnidarian) (b) Sea star (echinoderm)
5 Evolu7on of Nervous Systems Bilaterally symmetrical animals exhibit cephalization, the clustering of sensory organs at the front end of the body Relatively simple cephalized animals, such as flatworms, have a central nervous system (CNS) The CNS consists of a brain and longitudinal nerve cords Annelids and arthropods have segmentally arranged clusters of neurons called ganglia
6 Figure 49.2b Eyespot Brain Nerve cords Transverse nerve Brain Ventral nerve cord Segmental ganglia (c) Planarian (flatworm) (d) Leech (annelid)
7 Nervous system organization usually correlates with lifestyle Sessile molluscs (for example, clams and chitons) have simple systems, whereas more complex molluscs (for example, octopuses and squids) have more sophisticated systems Anterior nerve ring Ganglia Brain Longitudinal nerve cords Ganglia (f) Chiton (mollusc) (g) Squid (mollusc)
8 Figure 48.2 Ganglia Nerves with giant axons Brain Arm Nerve Eye Mantle
9 Organization of the Vertebrate Nervous System In vertebrates The CNS is composed of the brain and spinal cord The peripheral nervous system (PNS) is composed of nerves and ganglia Brain Spinal cord (dorsal nerve cord) Sensory ganglia (h) Salamander (vertebrate)
10 Organization of the Vertebrate Nervous System The spinal cord conveys information from and to the brain The spinal cord also produces reflexes independently of the brain A reflex is the body s automatic response to a stimulus For example, a doctor uses a mallet to trigger a knee-jerk reflex
11 Figure 49.3 Quadriceps muscle Cell body of sensory neuron in dorsal root ganglion Gray matter White matter Hamstring muscle Spinal cord (cross section) Sensory neuron Motor neuron Interneuron
12 Figure 49.4 Central nervous system (CNS) Brain Spinal cord Peripheral nervous system (PNS) Cranial nerves Ganglia outside CNS Spinal nerves
13 Composi7on of the CNS The brain and spinal cord contain Gray matter, which consists of neuron cell bodies, dendrites, and unmyelinated axons White matter, which consists of bundles of myelinated axons The central canal of the spinal cord and the ventricles of the brain are hollow and filled with cerebrospinal fluid The cerebrospinal fluid is filtered from blood and functions to cushion the brain and spinal cord as well as to provide nutrients and remove wastes
14 Figure 49.5 Gray matter White matter Ventricles
15 Glia Glia have numerous functions to nourish, support, and regulate neurons Embryonic radial glia form tracks along which newly formed neurons migrate Astrocytes induce cells lining capillaries in the CNS to form tight junctions, resulting in a blood-brain barrier and restricting the entry of most substances into the brain
16 Figure 49.6 VENTRICLE Cilia CNS Neuron Astrocyte PNS Oligodendrocyte Schwann cell Microglial cell Capillary Ependymal cell 50 µm LM
17 The Peripheral Nervous System The PNS transmits information to and from the CNS and regulates movement and the internal environment The PNS has two efferent components: the motor system and the autonomic nervous system The motor system carries signals to skeletal muscles and is voluntary The autonomic nervous system regulates smooth and cardiac muscles and is generally involuntary
18 Figure 49.7 Central Nervous System (information processing) Peripheral Nervous System Afferent neurons Efferent neurons Sensory receptors Autonomic nervous system Motor system Control of skeletal muscle Internal and external stimuli Sympathetic division Parasympathetic division Control of smooth muscles, cardiac muscles, glands Enteric division
19 Autonomic Nervous System Three divisions sympathetic, parasympathetic, and enteric The sympathetic division regulates arousal and energy generation ( fight-or-flight response) The parasympathetic division has antagonistic effects on target organs and promotes calming and a return to rest and digest functions The enteric division controls activity of the digestive tract, pancreas, and gallbladder
20 Figure 49.8 Parasympathetic division Sympathetic division Action on target organs: Action on target organs: Constricts pupil of eye Dilates pupil of eye Stimulates salivary gland secretion Inhibits salivary gland secretion Constricts bronchi in lungs Cervical Sympathetic ganglia Relaxes bronchi in lungs Slows heart Accelerates heart Stimulates activity of stomach and intestines Stimulates activity of pancreas Thoracic Inhibits activity of stomach and intestines Inhibits activity of pancreas Stimulates gallbladder Lumbar Stimulates glucose release from liver; inhibits gallbladder Stimulates adrenal medulla Promotes emptying of bladder Inhibits emptying of bladder Promotes erection of genitalia Synapse Sacral Promotes ejaculation and vaginal contractions
21 The vertebrate brain is regionally specialized Specific brain structures are particularly specialized for diverse functions These structures arise during embryonic development
22 Figure 49.9ba Midbrain Hindbrain Mesencephalon Metencephalon Diencephalon Myelencephalon Forebrain Telencephalon Spinal cord Embryo at 1 month Embryo at 5 weeks
23 Figure 49.9bb Cerebrum Diencephalon Midbrain Pons Medulla oblongata Cerebellum Spinal cord Child
24 Figure 49.9d Diencephalon Thalamus Pineal gland Hypothalamus Pituitary gland Brainstem Midbrain Pons Medulla oblongata Spinal cord
25 Arousal and Sleep The brainstem controls arousal and sleep The core of the brainstem has a diffuse network of neurons called the reticular formation This regulates the amount and type of information that reaches the cerebral cortex and affects alertness The hormone melatonin is released by the pineal gland and plays a role in bird and mammal sleep cycles
26 Figure Eye Reticular formation Input from nerves of ears Input from touch, pain, and temperature receptors
27 Biological Clock Regulation Cycles of sleep and wakefulness are examples of circadian rhythms, daily cycles of biological activity Mammalian circadian rhythms rely on a biological clock, molecular mechanism that directs periodic gene expression Biological clocks are typically synchronized to light and dark cycles
28 Sleep is essential and may play a role in the consolidation of learning and memory Dolphins sleep with one brain hemisphere at a time and are therefore able to swim while asleep
29 Figure RESULTS Wild-type hamster Wild-type hamster with SCN from τ hamster τ hamster τ hamster with SCN from wild-type hamster Circadian cycle period (hours) Before procedures After surgery and transplant
30 Emotions Generation and experience of emotions involve many brain structures including the amygdala, hippocampus, and parts of the thalamus These structures are grouped as the limbic system The limbic system also functions in motivation, olfaction, behavior, and memory
31 Figure Hypothalamus Thalamus Olfactory bulb Amygdala Hippocampus
32 Generation and experience of emotion also require interaction between the limbic system and sensory areas of the cerebrum The structure most important to the storage of emotion in the memory is the amygdala, a mass of nuclei near the base of the cerebrum
33 Func7onal MRI Nucleus accumbens Amygdala Happy music Sad music Figure 49.14
34 Optogene7cs
35 The cerebral cortex controls voluntary movement and cogni7ve func7ons Frontal lobe Prefrontal cortex (decision making, planning) Broca s area (forming speech) Motor cortex (control of skeletal muscles) Somatosensory cortex (sense of touch) Parietal lobe Sensory association cortex (integration of sensory information) Visual association cortex (combining images and object recognition) Temporal lobe Auditory cortex (hearing) Wernicke s area (comprehending language) Cerebellum Occipital lobe Visual cortex (processing visual stimuli and pattern recognition)
36 Language and Speech Studies of brain activity have mapped areas responsible for language and speech Broca s area in the frontal lobe is active when speech is generated Wernicke s area in the temporal lobe is active when speech is heard These areas belong to a larger network of regions involved in language
37 Figure Max Hearing words Seeing words Min Speaking words Generating words
38 Information Processing The cerebral cortex receives input from sensory organs and somatosensory receptors Somatosensory receptors provide information about touch, pain, pressure, temperature, and the position of muscles and limbs Adjacent areas process features in the sensory input and integrate information from different sensory areas Integrated sensory information passes to the prefrontal cortex, which helps plan actions and movements In the somatosensory cortex and motor cortex, neurons are arranged according to the part of the body that generates input or receives commands
39 Figure Frontal lobe Parietal lobe Trunk Shoulder Knee Hip Upper arm Leg Hip Trunk Neck Head Brow Eye Face Toes Genitalia Lips Jaw Tongue Primary motor cortex Teeth Gums Jaw Tongue Pharynx Abdominal organs Primary somatosensory cortex
40 Frontal Lobe Function Frontal lobe damage may impair decision making and emotional responses but leave intellect and memory intact The frontal lobes have a substantial effect on executive functions
41 Changes in synaptic connections underlie memory and learning Two processes dominate embryonic development of the nervous system Neurons compete for growth-supporting factors in order to survive Only half the synapses that form during embryo development survive into adulthood Neural plasticity describes the ability of the nervous system to be modified after birth Changes can strengthen or weaken signaling at a synapse
42 Figure N 1 N 1 N 2 N 2 (a) Synapses are strengthened or weakened in response to activity. (b) If two synapses are often active at the same time, the strength of the postsynaptic response may increase at both synapses.
43 Memory and Learning The formation of memories is an example of neural plasticity Short-term memory is accessed via the hippocampus The hippocampus also plays a role in forming long-term memory, which is stored in the cerebral cortex Some consolidation of memory is thought to occur during sleep
44 Long-Term Potentiation In the vertebrate brain, a form of learning called long-term potentiation (LTP) involves an increase in the strength of synaptic transmission LTP involves glutamate receptors If the presynaptic and postsynaptic neurons are stimulated at the same time, the set of receptors present on the postsynaptic membranes changes
45 Figure PRESYNAPTIC NEURON Ca 2+ Na + Glutamate Mg 2+ NMDA receptor (open) POSTSYNAPTIC NEURON Stored AMPA receptor NMDA receptor (closed) (a) Synapse prior to long-term potentiation (LTP) (b) Establishing LTP 1 3 (c) Synapse exhibiting LTP 2 Depolarization 4 Action potential
46 Nervous system disorders can be explained in molecular terms Disorders of the nervous system include schizophrenia, depression, drug addiction, Alzheimer s disease, and Parkinson s disease Genetic and environmental factors contribute to diseases of the nervous system
47 Drug Addiction and the Brain s Reward System The brain s reward system rewards motivation with pleasure Some drugs are addictive because they increase activity of the dopamine pathway, the brain s reward system These drugs include cocaine, amphetamine, heroin, alcohol, and tobacco Drug addiction is characterized by compulsive consumption and an inability to control intake Drug addiction leads to long-lasting changes in the reward circuitry that cause craving for the drug
48 Figure Nicotine stimulates dopaminereleasing VTA neuron. Inhibitory neuron Dopaminereleasing VTA neuron Opium and heroin decrease activity of inhibitory neuron. Cocaine and amphetamines block removal of dopamine from synaptic cleft. Cerebral neuron of reward pathway Reward system response
49 Alzheimer s Disease Alzheimer s disease is a mental deterioration characterized by confusion and memory loss Alzheimer s disease is caused by the formation of neurofibrillary tangles and amyloid plaques in the brain There is no cure for this disease though some drugs are effective at relieving symptoms
50 Figure Amyloid plaque Neurofibrillary tangle 20 µm
51 Parkinson s Disease Parkinson s disease is a motor disorder caused by death of dopamine-secreting neurons in the midbrain It is characterized by muscle tremors, flexed posture, and a shuffling gait There is no cure, although drugs and various other approaches are used to manage symptoms
Big Ideas. (e.g. puberty, immune function (autoimmune disorders)) 2011 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Nervous Systems Big Ideas 2.E.1: Timing and coordination of specific events are necessary for the normal development of an organism, and these events are regulated by a variety of mechanisms. (e.g. puberty,
Nervous Systems Big Ideas 2.E.1: Timing and coordination of specific events are necessary for the normal development of an organism, and these events are regulated by a variety of mechanisms. (e.g. puberty,
Chapter 49 Nervous Systems
 Chapter 49 Nervous Systems Concept 49.1 Nervous systems consist of circuits of neurons and supporting cells Nervous System Organization The simplest animals with nervous systems, the cnidarians, have neurons
Chapter 49 Nervous Systems Concept 49.1 Nervous systems consist of circuits of neurons and supporting cells Nervous System Organization The simplest animals with nervous systems, the cnidarians, have neurons
Cell body of sensory neuron in dorsal root ganglion. Hamstring. muscle
 The nervous system In vertebrates The CNS (central nervous system) is composed of the brain and spinal cord The PNS (peripheral nervous system is composed of nerves and ganglia The spinal cord conveys
The nervous system In vertebrates The CNS (central nervous system) is composed of the brain and spinal cord The PNS (peripheral nervous system is composed of nerves and ganglia The spinal cord conveys
Nervous Systems. Chapter 49. Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece. PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for
 Chapter 49 Nervous Systems PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from Joan Sharp Concept
Chapter 49 Nervous Systems PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from Joan Sharp Concept
Nervous System: Part IV The Central Nervous System The Brain
 Nervous System: Part IV The Central Nervous System The Brain Can you survive when part of your brain is destroyed? 2 Essential Knowledge 3.D.2 2. Cells communicate with each other through direct contact
Nervous System: Part IV The Central Nervous System The Brain Can you survive when part of your brain is destroyed? 2 Essential Knowledge 3.D.2 2. Cells communicate with each other through direct contact
Nervous Systems. Nerves are bundles that consist of the axons of multiple nerve cells
 Chapter 49 Fig. 49-1 Nervous Systems PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from Joan
Chapter 49 Fig. 49-1 Nervous Systems PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from Joan
Nervous Systems. Chapter 49. Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece. PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for
 Chapter 49 Nervous Systems PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from Joan Sharp Key
Chapter 49 Nervous Systems PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from Joan Sharp Key
Cephalization. Nervous Systems Chapter 49 11/10/2013. Nervous systems consist of circuits of neurons and supporting cells
 Nervous Systems Chapter 49 Cephalization Nervous systems consist of circuits of neurons and supporting cells Nervous system organization usually correlates with lifestyle Organization of the vertebrate
Nervous Systems Chapter 49 Cephalization Nervous systems consist of circuits of neurons and supporting cells Nervous system organization usually correlates with lifestyle Organization of the vertebrate
Nervous Systems. Chapter 49. PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece
 Chapter 49 Nervous Systems PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from Joan Sharp Overview:
Chapter 49 Nervous Systems PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from Joan Sharp Overview:
Overview: Command and Control Center. The circuits in the brain are more complex than the most powerful computers
 Overview: Command and Control Center Chapter 49 Fig. 49-1 The circuits in the brain are more complex than the most powerful computers Nervous Systems Functional magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) can be
Overview: Command and Control Center Chapter 49 Fig. 49-1 The circuits in the brain are more complex than the most powerful computers Nervous Systems Functional magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) can be
Nervous System. Oct 15 10:00 AM
 Nervous System Oct 15 10:00 AM 1 Nerve net = series of interconnected nerve cells Nerve = axons of many nerve cells Oct 15 10:10 AM 2 bilateral organisms exhibit cephalization (evolutionary trend towards
Nervous System Oct 15 10:00 AM 1 Nerve net = series of interconnected nerve cells Nerve = axons of many nerve cells Oct 15 10:10 AM 2 bilateral organisms exhibit cephalization (evolutionary trend towards
CHAPTER 48: NERVOUS SYSTEMS
 CHAPTER 48: NERVOUS SYSTEMS Name I. AN OVERVIEW OF NERVOUS SYSTEMS A. Nervous systems perform the three overlapping functions of sensory input, integration, and motor output B. Networks of neurons with
CHAPTER 48: NERVOUS SYSTEMS Name I. AN OVERVIEW OF NERVOUS SYSTEMS A. Nervous systems perform the three overlapping functions of sensory input, integration, and motor output B. Networks of neurons with
Chapter 17. Nervous System Nervous systems receive sensory input, interpret it, and send out appropriate commands. !
 Chapter 17 Sensory receptor Sensory input Integration Nervous System Motor output Brain and spinal cord Effector cells Peripheral nervous system (PNS) Central nervous system (CNS) 28.1 Nervous systems
Chapter 17 Sensory receptor Sensory input Integration Nervous System Motor output Brain and spinal cord Effector cells Peripheral nervous system (PNS) Central nervous system (CNS) 28.1 Nervous systems
CHAPTER 48. Nervous System
 CHAPTER 48 Nervous System Nervous System Function: coordinates and controls bodily functions with nerves and electrical impulses The human brain Contains an estimated 100 billion nerve cells, or neurons
CHAPTER 48 Nervous System Nervous System Function: coordinates and controls bodily functions with nerves and electrical impulses The human brain Contains an estimated 100 billion nerve cells, or neurons
E) A, B, and C Answer: D Topic: Concept 49.1 Skill: Knowledge/Comprehension
 Chapter 49 Nervous Systems Multiple-Choice Questions 1) Which of the following is (are) characteristic of a simple nervous system? A) a nerve net such as is found in cnidarians B) nerve cell ganglia C)
Chapter 49 Nervous Systems Multiple-Choice Questions 1) Which of the following is (are) characteristic of a simple nervous system? A) a nerve net such as is found in cnidarians B) nerve cell ganglia C)
Chapter 28 Nervous Systems
 Chapter 28 Nervous Systems PowerPoint Lectures for Biology: Concepts & Connections, Sixth Edition Campbell, Reece, Taylor, Simon, and Dickey Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Lecture by Edward J.
Chapter 28 Nervous Systems PowerPoint Lectures for Biology: Concepts & Connections, Sixth Edition Campbell, Reece, Taylor, Simon, and Dickey Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Lecture by Edward J.
Nervous Systems. Brain Development
 Nervous Systems Brain Development 2007-2008 Nervous system Central nervous system Peripheral nervous system Brain Spinal cord Sensory pathways Motor pathways Sympathetic arousal & energy production fight
Nervous Systems Brain Development 2007-2008 Nervous system Central nervous system Peripheral nervous system Brain Spinal cord Sensory pathways Motor pathways Sympathetic arousal & energy production fight
NERVOUS SYSTEM. Chapter 48-49
 NERVOUS SYSTEM Chapter 48-49 Nervous System Function: coordinates and controls bodily functions with nerves and electrical impulses The system is composed of different types of nerve cells called neurons
NERVOUS SYSTEM Chapter 48-49 Nervous System Function: coordinates and controls bodily functions with nerves and electrical impulses The system is composed of different types of nerve cells called neurons
Lesson 14. The Nervous System. Introduction to Life Processes - SCI 102 1
 Lesson 14 The Nervous System Introduction to Life Processes - SCI 102 1 Structures and Functions of Nerve Cells The nervous system has two principal cell types: Neurons (nerve cells) Glia The functions
Lesson 14 The Nervous System Introduction to Life Processes - SCI 102 1 Structures and Functions of Nerve Cells The nervous system has two principal cell types: Neurons (nerve cells) Glia The functions
Nervous System - PNS and CNS. Bio 105
 Nervous System - PNS and CNS Bio 105 Outline I. Central Nervous System vs Peripheral Nervous System II. Peripheral Nervous System A. Autonomic Nervous Systems B. Somatic Nervous Systems III. Autonomic
Nervous System - PNS and CNS Bio 105 Outline I. Central Nervous System vs Peripheral Nervous System II. Peripheral Nervous System A. Autonomic Nervous Systems B. Somatic Nervous Systems III. Autonomic
3/15/17. Outline. Nervous System - PNS and CNS. Two Parts of the Nervous System
 Nervous System - PNS and CNS Bio 105 Outline I. Central Nervous System vs Peripheral Nervous System II. Peripheral Nervous System A. Autonomic Nervous Systems B. Somatic Nervous Systems III. Autonomic
Nervous System - PNS and CNS Bio 105 Outline I. Central Nervous System vs Peripheral Nervous System II. Peripheral Nervous System A. Autonomic Nervous Systems B. Somatic Nervous Systems III. Autonomic
Big Questions. 1. How do nervous systems help animals coordinate and control their physiology? 2. Why are nervous systems an animals only phenomenon?
 Nervous Systems Big Questions 1. How do nervous systems help animals coordinate and control their physiology? 2. Why are nervous systems an animals only phenomenon? Why do animals need a nervous system?
Nervous Systems Big Questions 1. How do nervous systems help animals coordinate and control their physiology? 2. Why are nervous systems an animals only phenomenon? Why do animals need a nervous system?
Nervous Systems: Part IV The organiza8on and func8on of major parts of the nervous system.
 Nervous Systems: Part IV The organiza8on and func8on of major parts of the nervous system. KP1: The Peripheral Nervous System handles inputs/outputs while the Central Nervous System makes decisions/processes
Nervous Systems: Part IV The organiza8on and func8on of major parts of the nervous system. KP1: The Peripheral Nervous System handles inputs/outputs while the Central Nervous System makes decisions/processes
Somatic Nervous Systems. III. Autonomic Nervous System. Parasympathetic Nervous System. Sympathetic Nervous Systems
 7/21/2014 Outline Nervous System - PNS and CNS I. II. Two Parts of the Nervous System Central Nervous System vs Peripheral Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System A. B. Brain and Spinal Cord III. Autonomic
7/21/2014 Outline Nervous System - PNS and CNS I. II. Two Parts of the Nervous System Central Nervous System vs Peripheral Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System A. B. Brain and Spinal Cord III. Autonomic
14 - Central Nervous System. The Brain Taft College Human Physiology
 14 - Central Nervous System The Brain Taft College Human Physiology Development of the Brain The brain begins as a simple tube, a neural tube. The tube or chamber (ventricle) is filled with cerebrospinal
14 - Central Nervous System The Brain Taft College Human Physiology Development of the Brain The brain begins as a simple tube, a neural tube. The tube or chamber (ventricle) is filled with cerebrospinal
biological psychology, p. 40 The study of the nervous system, especially the brain. neuroscience, p. 40
 biological psychology, p. 40 The specialized branch of psychology that studies the relationship between behavior and bodily processes and system; also called biopsychology or psychobiology. neuroscience,
biological psychology, p. 40 The specialized branch of psychology that studies the relationship between behavior and bodily processes and system; also called biopsychology or psychobiology. neuroscience,
Primary Functions. Monitor changes. Integrate input. Initiate a response. External / internal. Process, interpret, make decisions, store information
 NERVOUS SYSTEM Monitor changes External / internal Integrate input Primary Functions Process, interpret, make decisions, store information Initiate a response E.g., movement, hormone release, stimulate/inhibit
NERVOUS SYSTEM Monitor changes External / internal Integrate input Primary Functions Process, interpret, make decisions, store information Initiate a response E.g., movement, hormone release, stimulate/inhibit
1. NERVOUS SYSTEM FUNCTIONS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM. FUNCTION The major function of the nervous system can be summarized as follows (Figure 1-1).
 1. NERVOUS SYSTEM FUNCTION The major function of the nervous system can be summarized as follows (Figure 1-1). Sensory input. Multiple signals from both, internal and external environment are detected
1. NERVOUS SYSTEM FUNCTION The major function of the nervous system can be summarized as follows (Figure 1-1). Sensory input. Multiple signals from both, internal and external environment are detected
NEURONS ARE ORGANIZED INTO NERVOUS SYSTEMS 34.5
 NEURONS ARE ORGANIZED INTO NERVOUS SYSTEMS 34.5 INTRODUCTION The cnidarians have nerve nets, the most simple type of nervous system. The sea anemone has a nerve net that serves simple behaviours such as
NEURONS ARE ORGANIZED INTO NERVOUS SYSTEMS 34.5 INTRODUCTION The cnidarians have nerve nets, the most simple type of nervous system. The sea anemone has a nerve net that serves simple behaviours such as
Chapter 9. Nervous System
 Chapter 9 Nervous System Central Nervous System (CNS) vs. Peripheral Nervous System(PNS) CNS Brain Spinal cord PNS Peripheral nerves connecting CNS to the body Cranial nerves Spinal nerves Neurons transmit
Chapter 9 Nervous System Central Nervous System (CNS) vs. Peripheral Nervous System(PNS) CNS Brain Spinal cord PNS Peripheral nerves connecting CNS to the body Cranial nerves Spinal nerves Neurons transmit
Page 1. Neurons Transmit Signal via Action Potentials: neuron At rest, neurons maintain an electrical difference across
 Chapter 33: The Nervous System and the Senses Neurons: Specialized excitable cells that allow for communication throughout the body via electrical impulses Neuron Anatomy / Function: 1) Dendrites: Receive
Chapter 33: The Nervous System and the Senses Neurons: Specialized excitable cells that allow for communication throughout the body via electrical impulses Neuron Anatomy / Function: 1) Dendrites: Receive
Parts of the Brain. Hindbrain. Controls autonomic functions Breathing, Heartbeat, Blood pressure, Swallowing, Vomiting, etc. Upper part of hindbrain
 Parts of the Brain The human brain is made up of three main parts: 1) Hindbrain (or brainstem) Which is made up of: Myelencephalon Metencephalon 2) Midbrain Which is made up of: Mesencephalon 3) Forebrain
Parts of the Brain The human brain is made up of three main parts: 1) Hindbrain (or brainstem) Which is made up of: Myelencephalon Metencephalon 2) Midbrain Which is made up of: Mesencephalon 3) Forebrain
The neurvous system senses, interprets, and responds to changes in the environment. Two types of cells makes this possible:
 NERVOUS SYSTEM The neurvous system senses, interprets, and responds to changes in the environment. Two types of cells makes this possible: the neuron and the supporting cells ("glial cells"). Neuron Neurons
NERVOUS SYSTEM The neurvous system senses, interprets, and responds to changes in the environment. Two types of cells makes this possible: the neuron and the supporting cells ("glial cells"). Neuron Neurons
Nervous System and Brain Review. Bio 3201
 Nervous System and Brain Review Bio 3201 Dont worry about: glial cells Oligodendrocytes Satelite cells etc Nervous System - Vital to maintaining homeostasis in organisms - Comprised of : brain, spinal
Nervous System and Brain Review Bio 3201 Dont worry about: glial cells Oligodendrocytes Satelite cells etc Nervous System - Vital to maintaining homeostasis in organisms - Comprised of : brain, spinal
Neural Control. Chapter 33 Part 2
 Neural Control Chapter 33 Part 2 33.6 A Smorgasbord of Signals Different types of neurons release different neurotransmitters; Parkinson s disease involves dopamine-secreting neurons and motor control
Neural Control Chapter 33 Part 2 33.6 A Smorgasbord of Signals Different types of neurons release different neurotransmitters; Parkinson s disease involves dopamine-secreting neurons and motor control
Nervous Systems: Diversity & Functional Organization
 Nervous Systems: Diversity & Functional Organization Diversity of Neural Signaling The diversity of neuron structure and function allows neurons to play many roles. 3 basic function of all neurons: Receive
Nervous Systems: Diversity & Functional Organization Diversity of Neural Signaling The diversity of neuron structure and function allows neurons to play many roles. 3 basic function of all neurons: Receive
Nervous Systems. What happens in your brain when you solve a math problem or listen to. Command and Control Center KEY CONC EPTS
 49 Nervous Systems KEY CONC EPTS 49.1 Nervous systems consist of circuits of neurons and supporting cells 49.2 The vertebrate brain is regionally specialized 49.3 The cerebral cortex controls voluntary
49 Nervous Systems KEY CONC EPTS 49.1 Nervous systems consist of circuits of neurons and supporting cells 49.2 The vertebrate brain is regionally specialized 49.3 The cerebral cortex controls voluntary
Human Nervous System. The nervous system has three functions
 Chapter 37 Human Nervous System The nervous system has three functions 1) Receive sensory input from both external and internal stimuli 2) Perform integration. (Coordinating all of the various inputs of
Chapter 37 Human Nervous System The nervous system has three functions 1) Receive sensory input from both external and internal stimuli 2) Perform integration. (Coordinating all of the various inputs of
Nervous system. Made up of. Peripheral nervous system. Central nervous system. The central nervous system The peripheral nervous system.
 Made up of The central nervous system The peripheral nervous system Nervous system Central nervous system Peripheral nervous system Brain Spinal Cord Cranial nerve Spinal nerve branch from the brain connect
Made up of The central nervous system The peripheral nervous system Nervous system Central nervous system Peripheral nervous system Brain Spinal Cord Cranial nerve Spinal nerve branch from the brain connect
Nervous System. 1. What N.S. division controls skeletal muscles? 3. What kind of neuroglia myelinates axons in the PNS?
 . What N.S. division controls skeletal muscles? Nervous System SRS Review %. Central nervous system %. Peripheral nervous system %. Afferent division %. Somatic division %. Autonomic division %. Sympathetic
. What N.S. division controls skeletal muscles? Nervous System SRS Review %. Central nervous system %. Peripheral nervous system %. Afferent division %. Somatic division %. Autonomic division %. Sympathetic
Chapter 49. Nervous Systems
 Chapter 49 Nervous Systems Lecture Outline Overview: Command and Control System The human brain contains an estimated 10 11 (100 billion) neurons. o Enormously complex circuits interconnect these brain
Chapter 49 Nervous Systems Lecture Outline Overview: Command and Control System The human brain contains an estimated 10 11 (100 billion) neurons. o Enormously complex circuits interconnect these brain
Chapter 49. Nervous Systems
 Chapter 49 Nervous Systems Lecture Outline Overview: Command and Control System The human brain contains an estimated 10 11 (100 billion) neurons. o Enormously complex circuits interconnect these brain
Chapter 49 Nervous Systems Lecture Outline Overview: Command and Control System The human brain contains an estimated 10 11 (100 billion) neurons. o Enormously complex circuits interconnect these brain
Biological Bases of Behavior. 3: Structure of the Nervous System
 Biological Bases of Behavior 3: Structure of the Nervous System Neuroanatomy Terms The neuraxis is an imaginary line drawn through the spinal cord up to the front of the brain Anatomical directions are
Biological Bases of Behavior 3: Structure of the Nervous System Neuroanatomy Terms The neuraxis is an imaginary line drawn through the spinal cord up to the front of the brain Anatomical directions are
The Nervous System. Divisions of the Nervous System. Branches of the Autonomic Nervous System. Central versus Peripheral
 The Nervous System Divisions of the Nervous System Central versus Peripheral Central Brain and spinal cord Peripheral Everything else Somatic versus Autonomic Somatic Nerves serving conscious sensations
The Nervous System Divisions of the Nervous System Central versus Peripheral Central Brain and spinal cord Peripheral Everything else Somatic versus Autonomic Somatic Nerves serving conscious sensations
Unit 3: The Biological Bases of Behaviour
 Unit 3: The Biological Bases of Behaviour Section 1: Communication in the Nervous System Section 2: Organization in the Nervous System Section 3: Researching the Brain Section 4: The Brain Section 5: Cerebral
Unit 3: The Biological Bases of Behaviour Section 1: Communication in the Nervous System Section 2: Organization in the Nervous System Section 3: Researching the Brain Section 4: The Brain Section 5: Cerebral
ACTIVITY2.15 Text:Campbell,v.8,chapter48 DATE HOUR NERVOUS SYSTEMS NEURON
 AP BIOLOGY ACTIVITY2.15 Text:Campbell,v.8,chapter48 NAME DATE HOUR NERVOUS SYSTEMS NEURON SIMPLE REFLEX RESTING POTENTIAL ACTION POTENTIAL ACTION POTENTIAL GRAPH TRANSMISSION ACROSS A SYNAPSE QUESTIONS:
AP BIOLOGY ACTIVITY2.15 Text:Campbell,v.8,chapter48 NAME DATE HOUR NERVOUS SYSTEMS NEURON SIMPLE REFLEX RESTING POTENTIAL ACTION POTENTIAL ACTION POTENTIAL GRAPH TRANSMISSION ACROSS A SYNAPSE QUESTIONS:
The Nervous System. Biological School. Neuroanatomy. How does a Neuron fire? Acetylcholine (ACH) TYPES OF NEUROTRANSMITTERS
 Biological School The Nervous System It is all about the body!!!! It starts with an individual nerve cell called a NEURON. Synapse Neuroanatomy Neurotransmitters (chemicals held in terminal buttons that
Biological School The Nervous System It is all about the body!!!! It starts with an individual nerve cell called a NEURON. Synapse Neuroanatomy Neurotransmitters (chemicals held in terminal buttons that
CNS composed of: Grey matter Unmyelinated axons Dendrites and cell bodies White matter Myelinated axon tracts
 CNS composed of: Grey matter Unmyelinated axons Dendrites and cell bodies White matter Myelinated axon tracts The Brain: A Quick Tour Frontal Lobe Control of skeletal muscles Personality Concentration
CNS composed of: Grey matter Unmyelinated axons Dendrites and cell bodies White matter Myelinated axon tracts The Brain: A Quick Tour Frontal Lobe Control of skeletal muscles Personality Concentration
THE NERVOUS SYSTEM CONCEPT 2: THE VERTEBRATE BRAIN IS REGIONALLY SPECIALIZED
 THE NERVOUS SYSTEM CONCEPT 2: THE VERTEBRATE BRAIN IS REGIONALLY SPECIALIZED Images of the human brain in popular culture almost always focus on the cerebrum, the part of the brain whose surface lies just
THE NERVOUS SYSTEM CONCEPT 2: THE VERTEBRATE BRAIN IS REGIONALLY SPECIALIZED Images of the human brain in popular culture almost always focus on the cerebrum, the part of the brain whose surface lies just
CHAPTER 13&14: The Central Nervous System. Anatomy of the CNS
 CHAPTER 13&14: The Central Nervous System Anatomy of the CNS in human consists of brain and spinal cord as stated earlier neurons have little support from their extracellular matrix and depend on glial
CHAPTER 13&14: The Central Nervous System Anatomy of the CNS in human consists of brain and spinal cord as stated earlier neurons have little support from their extracellular matrix and depend on glial
CHAPTER 13 NERVOUS SYSTEM
 CHAPTER 13 NERVOUS SYSTEM LEARNING OUTCOMES 13.1 Overview of the Nervous System 1. Distinguish between the central nervous system and peripheral nervous system with regard to location and function. 2.
CHAPTER 13 NERVOUS SYSTEM LEARNING OUTCOMES 13.1 Overview of the Nervous System 1. Distinguish between the central nervous system and peripheral nervous system with regard to location and function. 2.
Chapter 3. Structure and Function of the Nervous System. Copyright (c) Allyn and Bacon 2004
 Chapter 3 Structure and Function of the Nervous System 1 Basic Features of the Nervous System Neuraxis: An imaginary line drawn through the center of the length of the central nervous system, from the
Chapter 3 Structure and Function of the Nervous System 1 Basic Features of the Nervous System Neuraxis: An imaginary line drawn through the center of the length of the central nervous system, from the
action potential afferent neuron Weblike; specifically, the weblike middle layer of the three meninges. arachnoid astrocytes autonomic nervous system
 action potential A large transient depolarization event, including polarity reversal, that is conducted along the membrane of a muscle cell or a nerve fiber. afferent neuron Nerve cell that carries impulses
action potential A large transient depolarization event, including polarity reversal, that is conducted along the membrane of a muscle cell or a nerve fiber. afferent neuron Nerve cell that carries impulses
The Human Brain. I Think Therefore I am
 The Human Brain I Think Therefore I am The Beginning The simplest creatures have very simple nervous systems made up of nothing but a bunch of nerve cells They have neural nets, individual neurons linked
The Human Brain I Think Therefore I am The Beginning The simplest creatures have very simple nervous systems made up of nothing but a bunch of nerve cells They have neural nets, individual neurons linked
Good Morning! Take out your notes and vocab 1-10! Copyright 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
 Good Morning! Take out your notes and vocab 1-10! Functions of the Nervous System 1. Sensory input gathering information To monitor changes occurring inside and outside the body (changes = stimuli) 2.
Good Morning! Take out your notes and vocab 1-10! Functions of the Nervous System 1. Sensory input gathering information To monitor changes occurring inside and outside the body (changes = stimuli) 2.
UNIT 5 REVIEW GUIDE - NERVOUS SYSTEM 1) State the 3 functions of the nervous system. 1) 2) 3)
 UNIT 5 REVIEW GUIDE - NERVOUS SYSTEM State the 3 functions of the nervous system. Briefly describe the general function(s) of each of the following neuron types: a) SENSORY NEURONS: b) INTERNEURONS: c)
UNIT 5 REVIEW GUIDE - NERVOUS SYSTEM State the 3 functions of the nervous system. Briefly describe the general function(s) of each of the following neuron types: a) SENSORY NEURONS: b) INTERNEURONS: c)
The CNS and PNS: How is our Nervous System Organized?
 Honors Biology Guided Notes Chapter 28 Nervous System Name 28.10 28.19 The CNS and PNS: How is our Nervous System Organized? ANIMAL NERVOUS SYSTEMS Define Cephalization and Centralization. What type of
Honors Biology Guided Notes Chapter 28 Nervous System Name 28.10 28.19 The CNS and PNS: How is our Nervous System Organized? ANIMAL NERVOUS SYSTEMS Define Cephalization and Centralization. What type of
1. NERVOUS SYSTEM FUNCTIONS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM FUNCTION STRUCTURE AND DIVISIONS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM
 1. NERVOUS SYSTEM FUNCTION The major functions of the nervous system can be summarized as follows (Figure 1-1). FUNCTIONS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM a memory (the smell of a meal), or it could be discarded
1. NERVOUS SYSTEM FUNCTION The major functions of the nervous system can be summarized as follows (Figure 1-1). FUNCTIONS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM a memory (the smell of a meal), or it could be discarded
1. Processes nutrients and provides energy for the neuron to function; contains the cell's nucleus; also called the soma.
 1. Base of brainstem; controls heartbeat and breathing 2. tissue destruction; a brain lesion is a naturally or experimentally caused destruction of brain tissue 3. A thick band of axons that connects the
1. Base of brainstem; controls heartbeat and breathing 2. tissue destruction; a brain lesion is a naturally or experimentally caused destruction of brain tissue 3. A thick band of axons that connects the
The nervous system regulates most body systems using direct connections called nerves. It enables you to sense and respond to stimuli
 The nervous system regulates most body systems using direct connections called nerves. It enables you to sense and respond to stimuli The basic function of nervous system are: Receive sensory input internal
The nervous system regulates most body systems using direct connections called nerves. It enables you to sense and respond to stimuli The basic function of nervous system are: Receive sensory input internal
Nervous and Endocrine System Exam Review
 Directions: Read each question and complete the statement using the multiple choice responses I. Nervous System 1. The interpretation of olfactory receptor information would fall under which general function
Directions: Read each question and complete the statement using the multiple choice responses I. Nervous System 1. The interpretation of olfactory receptor information would fall under which general function
Functional Organization of the Central Nervous System
 Functional Organization of the Central Nervous System Hierarchical orgnization CNS consists of the brain and the spinal cord The brain analyzes and interprets the information Response messages are
Functional Organization of the Central Nervous System Hierarchical orgnization CNS consists of the brain and the spinal cord The brain analyzes and interprets the information Response messages are
Biology. A Guide to the Natural World. Chapter 27 Lecture Outline Communication and Control 1: The Nervous System. Fifth Edition.
 Biology A Guide to the Natural World Chapter 27 Lecture Outline Communication and Control 1: The Nervous System Fifth Edition David Krogh The Nervous System Nervous tissue is composed of two kinds of cells:
Biology A Guide to the Natural World Chapter 27 Lecture Outline Communication and Control 1: The Nervous System Fifth Edition David Krogh The Nervous System Nervous tissue is composed of two kinds of cells:
Chapter 8. The Nervous System
 Chapter 8 The Nervous System The Nervous System Consists of the Central and Peripheral Nervous Systems Principle Parts of Nervous System Central Nervous System (CNS) Components: brain and spinal cord
Chapter 8 The Nervous System The Nervous System Consists of the Central and Peripheral Nervous Systems Principle Parts of Nervous System Central Nervous System (CNS) Components: brain and spinal cord
Okami Study Guide: Chapter 2 1
 Okami Study Guide: Chapter 2 1 Chapter in Review 1. The human nervous system is a complex biological system designed for nearly instantaneous communication among billions of neurons throughout the body.
Okami Study Guide: Chapter 2 1 Chapter in Review 1. The human nervous system is a complex biological system designed for nearly instantaneous communication among billions of neurons throughout the body.
Neural Basis of Motor Control
 Neural Basis of Motor Control Central Nervous System Skeletal muscles are controlled by the CNS which consists of the brain and spinal cord. Determines which muscles will contract When How fast To what
Neural Basis of Motor Control Central Nervous System Skeletal muscles are controlled by the CNS which consists of the brain and spinal cord. Determines which muscles will contract When How fast To what
Nervous System C H A P T E R 2
 Nervous System C H A P T E R 2 Input Output Neuron 3 Nerve cell Allows information to travel throughout the body to various destinations Receptive Segment Cell Body Dendrites: receive message Myelin sheath
Nervous System C H A P T E R 2 Input Output Neuron 3 Nerve cell Allows information to travel throughout the body to various destinations Receptive Segment Cell Body Dendrites: receive message Myelin sheath
II. Nervous System (NS) Organization: can be organized by location/ structure or by function A. Structural Organization 1. Central N.S.
 Nervous System I. Nervous system Functions A. Detect Changes in the environment (stimuli) B. Interpret/evaluate those stimuli C. Initiate responses (trigger muscle contractions or glandular response) II.
Nervous System I. Nervous system Functions A. Detect Changes in the environment (stimuli) B. Interpret/evaluate those stimuli C. Initiate responses (trigger muscle contractions or glandular response) II.
Chapter 18: The Brain & Cranial Nerves. Origin of the Brain
 Chapter 18: The Brain & Cranial Nerves BIO 218 Fall 2015 Origin of the Brain The brain originates from a structure called the neural tube, which arises during a developmental stage called neurulation.
Chapter 18: The Brain & Cranial Nerves BIO 218 Fall 2015 Origin of the Brain The brain originates from a structure called the neural tube, which arises during a developmental stage called neurulation.
Human Anatomy. Autonomic Nervous System
 Human Anatomy Autonomic Nervous System 1 Autonomic Nervous System ANS complex system of nerves controls involuntary actions. Works with the somatic nervous system (SNS) regulates body organs maintains
Human Anatomy Autonomic Nervous System 1 Autonomic Nervous System ANS complex system of nerves controls involuntary actions. Works with the somatic nervous system (SNS) regulates body organs maintains
Neurology study of the nervous system. nervous & endocrine systems work together to maintain homeostasis
 Nervous System Neurology study of the nervous system nervous & endocrine systems work together to maintain homeostasis Nervous System works very fast Uses electrical signals called nerve impulses Short-lived
Nervous System Neurology study of the nervous system nervous & endocrine systems work together to maintain homeostasis Nervous System works very fast Uses electrical signals called nerve impulses Short-lived
THE CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM. The Brain & Spinal Cord
 THE CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM The Brain & Spinal Cord Review: Nervous System Parallel Distributed Processing Composition of the CNS Nuclei: Clusters of neurons in the CNS ( neighborhoods ) Fiber Tracts/Pathways:
THE CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM The Brain & Spinal Cord Review: Nervous System Parallel Distributed Processing Composition of the CNS Nuclei: Clusters of neurons in the CNS ( neighborhoods ) Fiber Tracts/Pathways:
Central Nervous System (CNS) -> brain and spinal cord. Major Divisions of the nervous system:
 Central Nervous System (CNS) -> brain and spinal cord Major Divisions of the nervous system: Afferent (sensory input) -> cell bodies outside of the central nervous system (CNS), carry info into the CNS
Central Nervous System (CNS) -> brain and spinal cord Major Divisions of the nervous system: Afferent (sensory input) -> cell bodies outside of the central nervous system (CNS), carry info into the CNS
Neural Communication. Central Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System. Communication in the Nervous System. 4 Common Components of a Neuron
 Neural Communication Overview of CNS / PNS Electrical Signaling Chemical Signaling Central Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System Somatic = sensory & motor Autonomic = arousal state Parasympathetic =
Neural Communication Overview of CNS / PNS Electrical Signaling Chemical Signaling Central Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System Somatic = sensory & motor Autonomic = arousal state Parasympathetic =
Support, Movement, Senses The Brain
 Support, Movement, Senses The Brain References- chapters 48, 49 Nervous systems consist of circuits of neurons and supporting cells By the Cambrian explosion, specialized systems of neurons enabled animals
Support, Movement, Senses The Brain References- chapters 48, 49 Nervous systems consist of circuits of neurons and supporting cells By the Cambrian explosion, specialized systems of neurons enabled animals
Fig Copyright 2002 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings
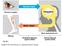 Fig. 48.1 Fig. 48.2 Axon endings are called synaptic terminals. They contain neurotransmitters which conduct a signal across a synapse. A synapse is the junction between a presynaptic and postsynaptic
Fig. 48.1 Fig. 48.2 Axon endings are called synaptic terminals. They contain neurotransmitters which conduct a signal across a synapse. A synapse is the junction between a presynaptic and postsynaptic
Bell Work. Materials Needed: writing utensil and A&P book. Quietly pick up a Lesson 6.5 worksheet from the back table and work on it independently.
 Bell Work Materials Needed: writing utensil and A&P book Quietly pick up a Lesson 6.5 worksheet from the back table and work on it independently. The Nervous System ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY Overview Controls
Bell Work Materials Needed: writing utensil and A&P book Quietly pick up a Lesson 6.5 worksheet from the back table and work on it independently. The Nervous System ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY Overview Controls
NERVOUS SYSTEM C H A P T E R 2 8
 NERVOUS SYSTEM C H A P T E R 2 8 CAN AN INJURED SPINAL CORD BE FIXED? Injuries to the spinal cord disrupt communication between the central nervous system (brain and spinal cord) and the rest of the body
NERVOUS SYSTEM C H A P T E R 2 8 CAN AN INJURED SPINAL CORD BE FIXED? Injuries to the spinal cord disrupt communication between the central nervous system (brain and spinal cord) and the rest of the body
All questions below pertain to mandatory material: all slides, and mandatory homework (if any).
 ECOL 182 Spring 2008 Dr. Ferriere s lectures Lecture 6: Nervous system and brain Quiz Book reference: LIFE-The Science of Biology, 8 th Edition. http://bcs.whfreeman.com/thelifewire8e/ All questions below
ECOL 182 Spring 2008 Dr. Ferriere s lectures Lecture 6: Nervous system and brain Quiz Book reference: LIFE-The Science of Biology, 8 th Edition. http://bcs.whfreeman.com/thelifewire8e/ All questions below
Campbell's Biology: Concepts and Connections, 7e (Reece et al.) Chapter 28 Nervous Systems Multiple-Choice Questions
 Campbell's Biology: Concepts and Connections, 7e (Reece et al.) Chapter 28 Nervous Systems 28.1 Multiple-Choice Questions 1) The central communication conduit between the brain and the rest of the body
Campbell's Biology: Concepts and Connections, 7e (Reece et al.) Chapter 28 Nervous Systems 28.1 Multiple-Choice Questions 1) The central communication conduit between the brain and the rest of the body
The Nervous System An overview
 Nervous System The Nervous System An overview Includes Nerve tissue Sense organs Functions to Sense environment Process information it receives Respond to information 1 Copyright 2009 Pearson Education,
Nervous System The Nervous System An overview Includes Nerve tissue Sense organs Functions to Sense environment Process information it receives Respond to information 1 Copyright 2009 Pearson Education,
Chapter 7 Nervous System
 Chapter 7 Nervous System Two message centers: Functions of these systems: 1. * 2. * Overview of the Nervous System Parts: General Functions: Functions Sensory input: Sensation via nerves Integration: interpretation
Chapter 7 Nervous System Two message centers: Functions of these systems: 1. * 2. * Overview of the Nervous System Parts: General Functions: Functions Sensory input: Sensation via nerves Integration: interpretation
The Nervous System and the Endocrine System
 The Nervous System and the Endocrine System Neurons: The Building Blocks of the Nervous System Nervous System The electrochemical communication system of the body Sends messages from the brain to the
The Nervous System and the Endocrine System Neurons: The Building Blocks of the Nervous System Nervous System The electrochemical communication system of the body Sends messages from the brain to the
Name: Period: Test Review: Chapter 2
 Name: Period: Test Review: Chapter 2 1. The function of dendrites is to A) receive incoming signals from other neurons. B) release neurotransmitters into the spatial junctions between neurons. C) coordinate
Name: Period: Test Review: Chapter 2 1. The function of dendrites is to A) receive incoming signals from other neurons. B) release neurotransmitters into the spatial junctions between neurons. C) coordinate
Laboratory Manual for Comparative Anatomy and Physiology Figure 15.1 Transparency Master 114
 Neuron Capillary Astrocyte Microglial cell Neuron Fluid-filled cavity Process of oligodendrocyte Ependymal cells Brain or spinal cord tissue Myelin sheath Nerve fibers Figure 15.1 Transparency Master 114
Neuron Capillary Astrocyte Microglial cell Neuron Fluid-filled cavity Process of oligodendrocyte Ependymal cells Brain or spinal cord tissue Myelin sheath Nerve fibers Figure 15.1 Transparency Master 114
Overview of Brain Structures
 First Overview of Brain Structures Psychology 470 Introduction to Chemical Additions Steven E. Meier, Ph.D. All parts are interrelated. You need all parts to function normally. Neurons = Nerve cells Listen
First Overview of Brain Structures Psychology 470 Introduction to Chemical Additions Steven E. Meier, Ph.D. All parts are interrelated. You need all parts to function normally. Neurons = Nerve cells Listen
Chapter 9 Nervous System
 Chapter 9 Nervous System Introduction: A. The nervous system is composed of neurons and neuroglia. 1. Neurons transmit nerve impulses to other neurons. 2. Nerves are made up of bundles of nerve fibers
Chapter 9 Nervous System Introduction: A. The nervous system is composed of neurons and neuroglia. 1. Neurons transmit nerve impulses to other neurons. 2. Nerves are made up of bundles of nerve fibers
Body control systems. Nervous system. Organization of Nervous Systems. The Nervous System. Two types of cells. Organization of Nervous System
 Body control systems Nervous system Nervous system Quick Sends message directly to target organ Endocrine system Sends a hormone as a messenger to the target organ Slower acting Longer lasting response
Body control systems Nervous system Nervous system Quick Sends message directly to target organ Endocrine system Sends a hormone as a messenger to the target organ Slower acting Longer lasting response
Biology 218 Human Anatomy
 Chapter 17 Adapted form Tortora 10 th ed. LECTURE OUTLINE A. Overview of the Nervous System (p. 537) 1. The nervous system and the endocrine system are the body s major control and integrating centers.
Chapter 17 Adapted form Tortora 10 th ed. LECTURE OUTLINE A. Overview of the Nervous System (p. 537) 1. The nervous system and the endocrine system are the body s major control and integrating centers.
The Nervous System 7PART B. PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Nervous System 7PART B What is a reflex? What is a reflex? What is meant by the statement that
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Nervous System 7PART B What is a reflex? What is a reflex? What is meant by the statement that
Composed by Natalia Leonidovna Svintsitskaya, Associate professor of the Chair of Human Anatomy, Candidate of Medicine
 Theoretical background to the study of the autonomic nervous system. Sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions of the autonomic nervous system. Features of the structure, function Composed by Natalia Leonidovna
Theoretical background to the study of the autonomic nervous system. Sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions of the autonomic nervous system. Features of the structure, function Composed by Natalia Leonidovna
The Nervous System. B. The Components: 1) Nerve Cells Neurons are the cells of the body and are specialized to carry messages through an process.
 The Nervous System A. The Divisions: 1) The Central Nervous System includes the and. The brain contains billions of nerve cells called, and trillions of support cells called. 2) The Peripheral Nervous
The Nervous System A. The Divisions: 1) The Central Nervous System includes the and. The brain contains billions of nerve cells called, and trillions of support cells called. 2) The Peripheral Nervous
Basic Brain Structure
 The Human Brain Basic Brain Structure Composed of 100 billion cells Makes up 2% of bodies weight Contains 15% of bodies blood supply Uses 20% of bodies oxygen and glucose Brain Protection Surrounded by
The Human Brain Basic Brain Structure Composed of 100 billion cells Makes up 2% of bodies weight Contains 15% of bodies blood supply Uses 20% of bodies oxygen and glucose Brain Protection Surrounded by
Organization and Overview of the Central Nervous System CNS 424. By Prof. Hisham Al-Matubsi
 Organization and Overview of the Central Nervous System CNS 424 By Prof. Hisham Al-Matubsi Components Brain, spinal cord, nerves, sensory receptors Responsible for Sensory perceptions, mental activities,
Organization and Overview of the Central Nervous System CNS 424 By Prof. Hisham Al-Matubsi Components Brain, spinal cord, nerves, sensory receptors Responsible for Sensory perceptions, mental activities,
8.3 The Central Nervous System. SBI4U Ms. Ho-Lau
 8.3 The Central Nervous System SBI4U Ms. Ho-Lau The Central Nervous System the structural and functional centre for the entire nervous system the site of neural integration and processing The Central
8.3 The Central Nervous System SBI4U Ms. Ho-Lau The Central Nervous System the structural and functional centre for the entire nervous system the site of neural integration and processing The Central
Brain-Behavior Network. Central Nervous System. Cerebral Cortex Gyrus and Sulcus. Nervous System
 Brain-Behavior Network Nervous System Sensory information comes into and decisions come out of the central nervous system (CNS) Central Nervous System The nerves outside the CNS are called the peripheral
Brain-Behavior Network Nervous System Sensory information comes into and decisions come out of the central nervous system (CNS) Central Nervous System The nerves outside the CNS are called the peripheral
Okami Study Guide: Chapter 2 1
 Okami Study Guide: Chapter 2 1 Chapter Test 1. A cell that receives information and transmits it to other cells via an electrochemical process is called a(n) a. neuron b. hormone c. glia d. endorphin Answer:
Okami Study Guide: Chapter 2 1 Chapter Test 1. A cell that receives information and transmits it to other cells via an electrochemical process is called a(n) a. neuron b. hormone c. glia d. endorphin Answer:
Warm-Up. Label the parts of the neuron below.
 Warm-Up Label the parts of the neuron below. A B C D E F G Warm-Up 1. One neuron transmits a nerve impulse at 40 m/s. Another conducts at the rate of 1 m/s. Which neuron has a myelinated axon? 2. List
Warm-Up Label the parts of the neuron below. A B C D E F G Warm-Up 1. One neuron transmits a nerve impulse at 40 m/s. Another conducts at the rate of 1 m/s. Which neuron has a myelinated axon? 2. List
Nervous System Worksheet
 Nervous System Worksheet Name Section A: Intro to Nervous System The Nervous System regulates and coordinates activities within the body. It detects, interprets and responds to changes that occur internally
Nervous System Worksheet Name Section A: Intro to Nervous System The Nervous System regulates and coordinates activities within the body. It detects, interprets and responds to changes that occur internally
NOTES CHAPTER 9 (Brief) The Nervous System LECTURE NOTES
 NOTES CHAPTER 9 (Brief) The Nervous System LECTURE NOTES I. Divisions of the Nervous System two major divisions A. Central Nervous System (CNS) 1. brain 2. spinal cord B. Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
NOTES CHAPTER 9 (Brief) The Nervous System LECTURE NOTES I. Divisions of the Nervous System two major divisions A. Central Nervous System (CNS) 1. brain 2. spinal cord B. Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
