Supplemental Table S1: Inhibition of HDAC class I and class II family by CUDC-101 (IC50 in nm)
|
|
|
- Samuel Riley
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Supplemental Table S1: Inhibition of HDAC class I and class II family by CUDC-101 (IC50 in nm) Class I Class II HDAC1 HDAC2 HDAC3 HDAC8 HDAC4 HDAC5 HDAC6 HDAC7 HDAC9 HDAC For HDAC specificity assay, purified GST- (human HDAC1, 4, 5, 6, 7 and10) or His- (human HDAC 2, 3 and 9) tagged E. coli. expressed enzymes were used. For HDAC8, SIRT1, SIRT2 and SIRT3, full length purified E. coli. expressed enzymes were used. Substrate for HDAC8 is diacetylated peptide (Arg-His-Lys(Ac)- Lys(Ac)), which based on amino acid residues of p53 protein. For other HDAC enzymes, a single acetylated peptide (Arg-His-Lys- Lys(Ac)) was used.
2 Supplemental Figure S1: Inhibition of EGFR-T790M by CUDC-101 EGFR kinase activity was measured using the HTScan EGF receptor kinase assay kit (Cell Signaling Technology). Briefly, EGFR T790M mutant fusion protein was incubated with synthetic biotinylated peptide substrate and different concentrations of CUDC-101 and erlotinib, in the presence of 400uM ATP. Phosphorylated substrate was captured in strapavidin coated 96-well plates. Levels of phosphorylation were monitored using antiphospho-tyrosin and europium labeled secondary antibodies (DELFIA, Perkin Elmer) at a concentration of 1:1000 dilution. Enhancement solution was added at the end of the assay and enzyme activity measured in a Wallac Victor II 1420 microplate reader at 615nM.
3 Supplemental Figure S2: CUDC-101 increases acetylation of histones in cultured cancer cells A. H292 cells were treated with various concentrations of CUDC-101, vorinostat or DMSO as indicated for 24 hrs. Cells were fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde before immunocytochemistry analysis was performed. A Li-Cor Odyssey machine was used for detection of staining results. Results indicate that CUDC-101 increases the level of acetylated histone3 protein. B. MDA-MB-468 cells were treated with various concentrations of CUDC-101, vorinostat as indicated for 24 hrs. Cells were fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde before immunocytochemistry analysis was performed. A Li-Cor Odyssey machine was used for detection and quantification of staining results. Quantification of the results reveals the relative intensities of acetylated histone-4 and total tubulin protein increase in a dose-dependent-manner with the treatment of CUDC-101.
4 Supplemental Figure S3: CUDC-101 increases acetylation of p53 in cultured cancer cells A. H292 cells were treated with 1 μm of CUDC-101, vorinostat or DMSO (control) as indicated for 24 hrs before immunocytochemistry analyses were performed. Results indicate that CUDC-101 increases the level of acetylated p53 protein. B. H292, HCT-116 and SkBr-3 cells were treated with 1 μm of CUDC-101, vorinostat or DMSO as indicated for 24 hrs. Immunocytochemistry analysis was performed and a Li-Cor Odyssey machine was used for detection and quantification of staining results. Bar graph shows the relative intensities of acetylated p53 and total p53 protein levels.
5 Supplemental Figure S4: CUDC-101 inhibits EGFR auto-phosphorylation in cultured cancer cells A431 cell line Control CUDC-101 p-egfr EGFR EGF A431 cells were cultured and starved for 8 hours before treatment with DMSO (control) or 1 μm of CUDC-101 as indicated for 1 hour. EGF was added to culture medium for 5 minutes to stimulate the phosphorylation of EGFR as indicated (+). Results show that CUDC-101 inhibits EGFR phosphorylation.
6 Supplemental Table S2: CUDC-101 displays weak activities on other kinases Kinase % Inhibition of Control Kinase % Inhibition of Control Kinase % Inhibition of Control Abl 57 FGFR4 6 p38γ kinase 10 Akt1-2 FLT-3 85 PAK1 2 AMPKα 32 Fyn 1 PAK2 5 AurA 21 IGF1R 3 PDGFRβ 39 Etk -3 IKKα -3 PDK1 2 Brk 40 IRAK4 9 Pim1 32 CaMK2α 7 IRK -5 Pim2 2 CaMK4-5 JNK1 19 PKA 3 CDK1-5 JNK2 30 PKCα 0 CDK2-14 JNK3 12 PKCβ1-1 CDK5-4 KDR 64 PKCβ2-3 CHK1-1 Lck 56 PKCγ 0 CHK2 11 Lyn 95 PKG1β 7 CK2 17 MAPKAPK2 1 PKG2 11 c-met 24 MARK1 8 PYK2 8 CSK 15 MARK2 0 RAF-1 17 DAPK1 8 MARK4 8 RET 93 DAPK2 13 MEK1-3 ROCK2-3 EphB4 20 MKK6 8 RSK2 10 ERK1 1 NEK2-2 SGK1 6 ERK2 16 NEK4 15 Src 12 FGFR2 73 p38α kinase 9 Syk 1 FGFR3 15 p38δ kinase -4 TrkA 11 Kinase KDR Lyn Lck Abl-1 FGFR2 FLT3 RET IC50 (nm) In order to assess the selectivity of the EGFR and HER2 kinase activities, CUDC-101 was evaluated against a panel of 69 kinases. Standard kinase activity assays with appropriate reference compounds were used for each of the evaluated kinases. An initial assessment for inhibitory activity was made using single dose (5uM) of CUDC-101. An inhibition of greater than 50% of reference compound activity was considered to be a potentially significant effect and for those targets IC50s were measured. For the 69 enzyme kinases tested, 5 um of CUDC -101 inhibited Abl, FGFR2, Flt-3, KDR (VEGFR2), Lyn, Lck and Ret at a level of higher than 50% of reference compounds. Subsequently, the inhibition of KDR, Lyn, Lck, Abl-1, FGFR2, Flt-3 and Ret by CUDC-101 was determined with IC50 equal to 0.86uM, 0.84uM, 15.8uM, 2.89uM, 3.43uM, 1.5uM and 3.2uM, respectively. Additionally the IC50 of CUDC-101 against Src was determined to be 11 um. Overall, the results show that CUDC-101 potently inhibits EGFR and HER2 kinases (IC50s of 4 and 20 nm, respectively) at concentrations that are at least 40 fold lower than the other kinases evaluated in this
7 panel.
8 Supplemental Figure S5: CUDC-101 rapidly and durably inhibits Akt signaling BT-474 cells were cultured and treated with DMSO or 1 μm of CUDC-101 or vorinostat as indicated. Cell extracts were prepared after 0, 3, 8, 24 or 30 hours of treatment as indicated and Western analyses were performed. This time course studies were designed to monitor molecular events before massive protein degradation occurred due to apoptosis. CUDC- 101 showed a rapid and prolonged inhibition of Akt signaling in cultured cancer cells, with no subsequent reactivation during 30 hours of continuous exposure. Vorinostat also showed similar late-stage inhibition of Akt signaling, but the latter effect was observed only after 8 hours of treatment.
9 Supplemental Figure S6: CUDC-101 reduces estrogen receptor alpha protein levels BT-474 cells were treated with varying concentrations of CUDC-101, vorinostat, lapatinib or erlotinib as indicated for 0, 2, 7 or 24 hours before Western analyses were performed. Results show a significant reduction in estrogen receptor-α levels in CUDC-101 treated cells. Weaker effects are seen in vorinostat treated cells.
10 Supplemental Figure S7: CUDC-101 induces no significant change in body weight in treated animals A C % Body Weight Change E Body Weight Change (%) Vehicle CUDC-101 Vorinostat Erlotinib 25 mg/kg Days same experiment as Fig. 4A, HepG2 Cell Line Vehicle CUDC-101 Lapatinib Days same experiment as Fig. 4B, upper right, MDA-MB-468 cell line Body Weight Change (%) Vehicle CUDC-101 Paclitaxel C + P Days Same experiment as Fig. 4B, lower right panel, MDA-MB-468 cell line B Body Weight Change (%) Vehicle CUDC Days same experiment as Fig. 4B, upper left panel, A549 cell line D Body Weight Change (%) Vehicle CDUC Days Same experiment as Fig. 4B, lower left panel, Cal-27 cell line F
11 A-E. These results depict body weight results for the same experiment shown in Fig. 4. No significant weight loss was observed in tumor explanted animals treated with CUDC-101. Body weights were determined twice weekly for the duration of the study. F. Body weight results of the rat toxicity study. This was a 2-cycle study, with each cycle lasting 7 days and separated by a nondosing period of 7 days. CUDC-101 formulations were administered on study days 1 to 7 and 15 to 21 by intravenous infusion over a 30-minute period with different dose levels as indicated. Male and female animals were indicated as solid and dash lines respectively.
12 Supplemental Table S3: In vitro studies of CUDC-101 and its interactions with key receptors, channels and enzymes Summary of binding assays Protein % Inhibition of Control Protein % Inhibition of Control Protein % Inhibition of Control A1 34 AMPA 17 P2Y 12 A2A 55 Kainate 8 Rolipram 30 A3 78 NMDA 37 5-HT -3 α1 11 H1-1 σ 12 α2 11 H2 28 Glucocorticoid -20 β1 0 H3 7 Estrogen 1 β2 15 I1 0 Progesterone 3 AT1-3 I2 26 Androgen 0 AT2 3 LTB4 7 TRH1 3 BZD (central) 19 LTD4 6 V1a 8 B1 1 MC4-3 V2 2 B2-1 M 28 Ca 2+ channel (L, DHP) 17 CB1-1 NK1 93 Ca 2+ channel (L, diltiazem) 0 CB2-5 NK2 76 Ca 2+ channel (L, verapamil) 6 CCK1-3 NK3 38 K + ATP channel -4 CCK2 7 Y -15 K + V channel -3 CRF1-9 N 2 SK + ca Channel -1 D1 8 Opioid 65 Na + channel 12 D2S 5 ORL1 7 Cl - channel 13 D3-3 PPARγ 5 NE transporter 52 D4.4 2 PCP 21 DA transporter 47 ETA 10 EP4-3 GABA transporter 6 ETB 11 IP -3 Choline transporter 60 GABA 1 P2X 13 5-HT transporter 9 Summary of enzyme activity assays Enzyme % Inhibition of Control Enzyme % Inhibition of Control Enzyme % Inhibition of Control PDE1 53 COMT 15 Tyrosine hydroxylase 21 PDE2 75 ATPase 1 Acetylcholinesterase -20 PDE3 21 MAO-A -5 GABA Transaminase 5 PDE5 96 MAO-B 5 PNMT 4 % Stimulation of % Stimulation of Enzyme Enzyme Control Control Adenylyl cyclase 2 Guanylyl cyclase 5
13 We evaluated the potential interaction of CUDC-101 with major proteins, enzymes and channels known to be clinically relevant. Using standard binding competition or enzyme activity assays, the first screen was performed with a high concentration and single dose (10uM) of CUDC-101 against a panel of 86 targets. The percent inhibition by CUDC-101 relative to the specific binding of reference ligands to each target protein was obtained. Among the 86 proteins, enzymes and channels we studied, 10uM CUDC -101 inhibited the binding of labeled ligands to adenosine receptor A2A, A3, NK1, NK2, opioid receptor, NE transporter and choline transporter at a level of more than 50% of the control. The inhibition of NK1 receptor binding by CUDC-101 was shown to be greater than 90%. Subsequently, the binding affinity of CUDC-101 to NK1 was determined to have a ki of 2.3uM. CUDC-101, at 10uM, also inhibits PDE1 and PDE5 at a level of more than 50% of that of reference compound. These weak activities of CUDC-101 against other targets are predicted to be of minor concern for its future clinical development.
14 Supplemental Table S4: CUDC-101 displays a favorable safety profile in in vivo toxicity studies A 2-cycle 28-day dose toxicity study of CUDC-101 in Sprague-Dawley rats and Beagle dogs Maximum Tolerance Dose (MTD) Rats 75 mg/kg/day or 450 mg/m2/day Dogs 40 mg/kg/day or 800 mg/m2/day Exposure, AUC (um X h) 47.7 to 91.9 (male) 33.5 to 38.7 (male) 73.9 to (female) 44.2 to 61.1 (female) Mortality No death occurred No death occurred Food consumption and body weight Normal Normal Clinical Observation Normal Mild and transient emesis and soft feces Hematology Normal Non-adversely and transiently higher total white blood cells and neutrophil counts Serum Chemistry Histopathology Electrocardiographic Assessment Mild and reversible lower cholesterol and serum potassium s Normal Not available Normal Mild and reversible changes: 1. Interstitial inflammation in lung 2. Atrophy of Peyer s pathes in lymphoid tissues (female) No drug related effects were noted Summary of toxicity study results of CUDC-101 in Sprague-Dawley rats and Beagle dogs. Animals were administered by intravenous infusion with indicated dose of CUDC-101 for two seven day cycles (study days 1 to 7 and 15 to 21), in which both cycles were followed by a 7 day recovery. Clinical examinations were performed daily. Individual body weights were recorded at least twice weekly. Food consumption was recorded daily and weekly in dogs and rats respectively. Clinical hematology and serum chemistry analysis were performed prior to the initiation of dose administration, on the day following the last infusion for each dosing cycle (study days 8 and 22) and prior to the scheduled primary necropsy for histopathological analysis (day 29).
15 Supplemental Figure S8: CUDC-101 inhibits HIF1-α induction Control CUDC-101 vorinostat erlotinib HIF1-α Tubulin HCT-116 cells were cultured and treated with 1μM of CUDC-101, vorinostat or erlotinib as indicated in the presence of 100mM of CoCl2 to induce the expression of HIF-1α. CUDC- 101 effectively represses HIF-1α induction.
16 Supplemental Figure S9: CUDC-101 down-regulates EGFR protein in H1975 NSCLC cells Control CUDC-101 erlotinib μm EGFR Tubulin H1975 NSCLC cells were cultured and treated with 0.3 or 1 μm of CUDC-101 or erlotinib as indicated for 31 hours. CUDC-101 effectively represses EGFR expression.
Supplementary Material for Pacholec, M. et al. manuscript SRT1720, SRT2183, SRT1460, and
 Supplementary Material for Pacholec, M. et al. manuscript SRT1720, SRT2183, SRT1460, and resveratrol are not direct activators of SIRT1 Supplementary Figure Legends Figure S1. Determination of SIRT1 K
Supplementary Material for Pacholec, M. et al. manuscript SRT1720, SRT2183, SRT1460, and resveratrol are not direct activators of SIRT1 Supplementary Figure Legends Figure S1. Determination of SIRT1 K
Overcoming Resistance to HER2 Inhibitors Through State-Specific Kinase Binding
 Supplementary Information Overcoming Resistance to Inhibitors Through State-Specific Kinase Binding Chris J. Novotny 1, Sirkku Pollari 2, Jin H. Park 3, Mark A. Lemmon 3,4, Weijun Shen 2*, Kevan M. Shokat
Supplementary Information Overcoming Resistance to Inhibitors Through State-Specific Kinase Binding Chris J. Novotny 1, Sirkku Pollari 2, Jin H. Park 3, Mark A. Lemmon 3,4, Weijun Shen 2*, Kevan M. Shokat
Supplemental text file, including:
 Supplemental text file, including: Supplemental Table S1: Kinase profile for XL147 Supplemental Table S2: Effects of XL147 on PI3K Pathway Signaling in MCF7 and PC-3 Cells Supplemental Table S3: XL147
Supplemental text file, including: Supplemental Table S1: Kinase profile for XL147 Supplemental Table S2: Effects of XL147 on PI3K Pathway Signaling in MCF7 and PC-3 Cells Supplemental Table S3: XL147
Antitumor Activity of CUDC-305, a Novel Oral HSP90 Inhibitor, in Solid and Hematological Tumor Xenograft Models
 Antitumor Activity of CUDC-5, a Novel Oral HSP Inhibitor, in Solid and Hematological Tumor Xenograft Models Rudi Bao, MD/PhD April 1, 2 AACR 1th Annual Meeting 2 Experimental and Molecular Therapeutics
Antitumor Activity of CUDC-5, a Novel Oral HSP Inhibitor, in Solid and Hematological Tumor Xenograft Models Rudi Bao, MD/PhD April 1, 2 AACR 1th Annual Meeting 2 Experimental and Molecular Therapeutics
Staurosporine Tethered Peptide Ligands for camp-dependent Protein Kinase A (PKA): Optimization and Selectivity Profiling
 Staurosporine Tethered Peptide Ligands for camp-dependent Protein Kinase A (PKA): Optimization and Selectivity Profiling Carolyn D. Shomin, Scott C. Meyer and Indraneel Ghosh* Supplementary Information
Staurosporine Tethered Peptide Ligands for camp-dependent Protein Kinase A (PKA): Optimization and Selectivity Profiling Carolyn D. Shomin, Scott C. Meyer and Indraneel Ghosh* Supplementary Information
50 nmoles substrate. 8,000 Test Points based on 100 nm in reaction
 Product Insert IMAP Substrates About the IMAP Substrates To facilitate the customization of the IMAP assay to fit your specific needs, Molecular Devices offers a wide range of validated substrates and
Product Insert IMAP Substrates About the IMAP Substrates To facilitate the customization of the IMAP assay to fit your specific needs, Molecular Devices offers a wide range of validated substrates and
Supplemental Table 1. Biochemical and Cellular Potency and Selectivity of PF
 Supplemental Table 1. Biochemical and Cellular Potency and Selectivity of PF- 02341066 Assay IC 50 nm Selectivity Ratio d Biochemical Activity In Vitro c-met/hgfr enzyme (Ki, nm) a 4 NA Cellular Activity
Supplemental Table 1. Biochemical and Cellular Potency and Selectivity of PF- 02341066 Assay IC 50 nm Selectivity Ratio d Biochemical Activity In Vitro c-met/hgfr enzyme (Ki, nm) a 4 NA Cellular Activity
2. Appendix Tables legend General Legend applicable for Table S1 to S4 (Page 10)
 Appendix Data The hvps- signalling module counteracts inhibition of the PIK-Akt pathway to maintain mtorc activity and tumour growth Ruzica Bago, Eeva Sommer, Pau Castel, Claire Crafter, Fiona P. Bailey,
Appendix Data The hvps- signalling module counteracts inhibition of the PIK-Akt pathway to maintain mtorc activity and tumour growth Ruzica Bago, Eeva Sommer, Pau Castel, Claire Crafter, Fiona P. Bailey,
Supplementary information
 Supplementary information Pyk2 activates the NLRP3 inflammasome by directly phosphorylating ASC and contributes to inflammasome-dependent peritonitis I-Che Chung 1, Chun-Nan OuYang 1, Sheng-Ning Yuan 1,
Supplementary information Pyk2 activates the NLRP3 inflammasome by directly phosphorylating ASC and contributes to inflammasome-dependent peritonitis I-Che Chung 1, Chun-Nan OuYang 1, Sheng-Ning Yuan 1,
Mechanisms of resistance to JAK inhibitors. L. Knoops
 Mechanisms of resistance to JAK inhibitors L. Knoops 1 : Resistance to tyrosine kinase inhibition in cancer are related in sequence and structure. The main diagram illustrates the similarity between the
Mechanisms of resistance to JAK inhibitors L. Knoops 1 : Resistance to tyrosine kinase inhibition in cancer are related in sequence and structure. The main diagram illustrates the similarity between the
Yong Wu, Ph.D. Division of Cancer Research and Training (DCRT) Charles R. Drew University of Medicine & Science
 Yong Wu, Ph.D. Division of Cancer Research and Training (DCRT) Charles R. Drew University of Medicine & Science Jay Vadgama, Ph.D Chief, Division of Cancer Research and Training Background One in 8 women
Yong Wu, Ph.D. Division of Cancer Research and Training (DCRT) Charles R. Drew University of Medicine & Science Jay Vadgama, Ph.D Chief, Division of Cancer Research and Training Background One in 8 women
Supplementary Information. Targeting BRK-positive Breast Cancer with Small
 Supplementary Information Targeting BRK-positive Breast Cancer with Small Molecule Kinase Inhibitors Jie Jiang 1#, Fu Gui 1#, Zhixiang He 1#, Li Li 1, Yunzhan Li 1, Shunying Li 2, Xinrui Wu 1, Zhou Deng
Supplementary Information Targeting BRK-positive Breast Cancer with Small Molecule Kinase Inhibitors Jie Jiang 1#, Fu Gui 1#, Zhixiang He 1#, Li Li 1, Yunzhan Li 1, Shunying Li 2, Xinrui Wu 1, Zhou Deng
MAPK Pathway
 MAPK Pathway Mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPK) are proteins that are serine/ threonine specific kinases which are activated by a wide range of stimuli including proinflammatory cytokines, growth
MAPK Pathway Mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPK) are proteins that are serine/ threonine specific kinases which are activated by a wide range of stimuli including proinflammatory cytokines, growth
Improved Stability of the LANCE Ultra Signal in Kinase Assays
 Improved Stability of the LANCE Ultra Signal in Kinase Assays LANCE Ultra is a high throughput screening (HTS) technology platform optimized for homogeneous time-resolved fluorescence resonance energy
Improved Stability of the LANCE Ultra Signal in Kinase Assays LANCE Ultra is a high throughput screening (HTS) technology platform optimized for homogeneous time-resolved fluorescence resonance energy
Supplementary Figure 1. Basal level EGFR across a panel of ESCC lines. Immunoblots demonstrate the expression of phosphorylated and total EGFR as
 Supplementary Figure 1. Basal level EGFR across a panel of ESCC lines. Immunoblots demonstrate the expression of phosphorylated and total EGFR as well as their downstream effectors across a panel of ESCC
Supplementary Figure 1. Basal level EGFR across a panel of ESCC lines. Immunoblots demonstrate the expression of phosphorylated and total EGFR as well as their downstream effectors across a panel of ESCC
Optimization of a LanthaScreen Kinase assay for NTRK1 (TRKA)
 Optimization of a LanthaScreen Kinase assay for NTRK1 (TRKA) Overview This protocol describes how to develop a LanthaScreen kinase assay designed to detect and characterize kinase inhibitors. The development
Optimization of a LanthaScreen Kinase assay for NTRK1 (TRKA) Overview This protocol describes how to develop a LanthaScreen kinase assay designed to detect and characterize kinase inhibitors. The development
Receptor mediated Signal Transduction
 Receptor mediated Signal Transduction G-protein-linked receptors adenylyl cyclase camp PKA Organization of receptor protein-tyrosine kinases From G.M. Cooper, The Cell. A molecular approach, 2004, third
Receptor mediated Signal Transduction G-protein-linked receptors adenylyl cyclase camp PKA Organization of receptor protein-tyrosine kinases From G.M. Cooper, The Cell. A molecular approach, 2004, third
Content Prioritization And Content Entry and Quality Control Process
 Content Prioritization And Content Entry and Quality Control Process The process of data capture begins with the definition of the content module or sub-module to be built (see figure 1). Broadly we define
Content Prioritization And Content Entry and Quality Control Process The process of data capture begins with the definition of the content module or sub-module to be built (see figure 1). Broadly we define
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES
 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES Supplementary Figure S1: Fibroblast-induced elongation of cancer cells requires direct contact with living fibroblasts. A. Representative images of HT29-GFP cultured in the presence
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES Supplementary Figure S1: Fibroblast-induced elongation of cancer cells requires direct contact with living fibroblasts. A. Representative images of HT29-GFP cultured in the presence
ALM301: Allosteric Isoform selective Akt inhibitor
 ALM301: Allosteric Isoform selective Akt inhibitor Background Akt1/2 selective inhibitors ALM301 Back-up compounds Akt2 selective inhibitors Approaches to Akt Inhibition Both ATP competitive and allosteric
ALM301: Allosteric Isoform selective Akt inhibitor Background Akt1/2 selective inhibitors ALM301 Back-up compounds Akt2 selective inhibitors Approaches to Akt Inhibition Both ATP competitive and allosteric
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/7/322/ra38/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Dynamic Reprogramming of Signaling Upon Met Inhibition Reveals a Mechanism of Drug Resistance in Gastric Cancer Andrea
www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/7/322/ra38/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Dynamic Reprogramming of Signaling Upon Met Inhibition Reveals a Mechanism of Drug Resistance in Gastric Cancer Andrea
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:1.138/nature9814 a A SHARPIN FL B SHARPIN ΔNZF C SHARPIN T38L, F39V b His-SHARPIN FL -1xUb -2xUb -4xUb α-his c Linear 4xUb -SHARPIN FL -SHARPIN TF_LV -SHARPINΔNZF -SHARPIN
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:1.138/nature9814 a A SHARPIN FL B SHARPIN ΔNZF C SHARPIN T38L, F39V b His-SHARPIN FL -1xUb -2xUb -4xUb α-his c Linear 4xUb -SHARPIN FL -SHARPIN TF_LV -SHARPINΔNZF -SHARPIN
The Tissue Engineer s Toolkit
 The Tissue Engineer s Toolkit Stimuli Detection and Response Ken Webb, Ph. D. Assistant Professor Dept. of Bioengineering Clemson University Environmental Stimulus-Cellular Response Environmental Stimuli
The Tissue Engineer s Toolkit Stimuli Detection and Response Ken Webb, Ph. D. Assistant Professor Dept. of Bioengineering Clemson University Environmental Stimulus-Cellular Response Environmental Stimuli
ENMD-2076, an Oral Aurora A and Angiogenesis Kinase Inhibitor
 ENMD-2076, an Oral Aurora A and Angiogenesis Kinase Inhibitor Dr. Mark R. Bray VP Research, EntreMed, Inc. AACR Annual Meeting New Drugs on the Horizon 2 April 2008 1 Disclosure Information: AACR New Drugs
ENMD-2076, an Oral Aurora A and Angiogenesis Kinase Inhibitor Dr. Mark R. Bray VP Research, EntreMed, Inc. AACR Annual Meeting New Drugs on the Horizon 2 April 2008 1 Disclosure Information: AACR New Drugs
Supplementary Figure 1. MAT IIα is Acetylated at Lysine 81.
 IP: Flag a Mascot PTM Modified Mass Error Position Gene Names Score Score Sequence m/z [ppm] 81 MAT2A;AMS2;MATA2 35.6 137.28 _AAVDYQK(ac)VVR_ 595.83-2.28 b Pre-immu After-immu Flag- WT K81R WT K81R / Flag
IP: Flag a Mascot PTM Modified Mass Error Position Gene Names Score Score Sequence m/z [ppm] 81 MAT2A;AMS2;MATA2 35.6 137.28 _AAVDYQK(ac)VVR_ 595.83-2.28 b Pre-immu After-immu Flag- WT K81R WT K81R / Flag
Data Sheet. Fluorogenic HDAC 8 Assay Kit Catalog #: 50068
 Data Sheet Fluorogenic HDAC 8 Assay Kit Catalog #: 50068 DESCRIPTION: The Fluorogenic HDAC 8 Assay Kit is a complete assay system designed to measure histone deacetylase (HDAC) 8 activity for screening
Data Sheet Fluorogenic HDAC 8 Assay Kit Catalog #: 50068 DESCRIPTION: The Fluorogenic HDAC 8 Assay Kit is a complete assay system designed to measure histone deacetylase (HDAC) 8 activity for screening
blood mononuclear cells were stained with AAD, annexin, CD3, CD4, CD25, LAP and specific
 Supplementary figure legends Figure 1: Selective expression of regulatory markers on CD4 + LAP + T cells. Human peripheral blood mononuclear cells were stained with AAD, annexin, CD3, CD4, CD25, LAP and
Supplementary figure legends Figure 1: Selective expression of regulatory markers on CD4 + LAP + T cells. Human peripheral blood mononuclear cells were stained with AAD, annexin, CD3, CD4, CD25, LAP and
Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of Protein Kinase D Inhibitors
 Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of Protein Kinase D Inhibitors Celeste Alverez Topic Seminar October 26, 2013 Celeste Alverez @ Wipf Group 10/26/2013 1 Protein Kinase D (PKD) A novel family of serine/threonine
Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of Protein Kinase D Inhibitors Celeste Alverez Topic Seminar October 26, 2013 Celeste Alverez @ Wipf Group 10/26/2013 1 Protein Kinase D (PKD) A novel family of serine/threonine
Supplementary Figure 1.TRIM33 binds β-catenin in the nucleus. a & b, Co-IP of endogenous TRIM33 with β-catenin in HT-29 cells (a) and HEK 293T cells
 Supplementary Figure 1.TRIM33 binds β-catenin in the nucleus. a & b, Co-IP of endogenous TRIM33 with β-catenin in HT-29 cells (a) and HEK 293T cells (b). TRIM33 was immunoprecipitated, and the amount of
Supplementary Figure 1.TRIM33 binds β-catenin in the nucleus. a & b, Co-IP of endogenous TRIM33 with β-catenin in HT-29 cells (a) and HEK 293T cells (b). TRIM33 was immunoprecipitated, and the amount of
PI3K Background. The SignalRx R & D pipeline is shown below followed by a brief description of each program:
 PI3K Background The phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K) pathway is a key cell signaling node whose dysregulation commonly results in the transformation of normal cells into cancer cells. The role of PI3K
PI3K Background The phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K) pathway is a key cell signaling node whose dysregulation commonly results in the transformation of normal cells into cancer cells. The role of PI3K
11/8/16. Cell Signaling Mechanisms. Dr. Abercrombie 11/8/2016. Principal Parts of Neurons A Signal Processing Computer
 Cell Signaling Mechanisms Dr. Abercrombie 11/8/2016 Principal Parts of Neurons A Signal Processing Computer A Multitude of Synapses and Synaptic Actions Summation/Synaptic Integration 1 The Synapse Signal
Cell Signaling Mechanisms Dr. Abercrombie 11/8/2016 Principal Parts of Neurons A Signal Processing Computer A Multitude of Synapses and Synaptic Actions Summation/Synaptic Integration 1 The Synapse Signal
A Hepatocyte Growth Factor Receptor (Met) Insulin Receptor hybrid governs hepatic glucose metabolism SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES, LEGENDS AND METHODS
 A Hepatocyte Growth Factor Receptor (Met) Insulin Receptor hybrid governs hepatic glucose metabolism Arlee Fafalios, Jihong Ma, Xinping Tan, John Stoops, Jianhua Luo, Marie C. DeFrances and Reza Zarnegar
A Hepatocyte Growth Factor Receptor (Met) Insulin Receptor hybrid governs hepatic glucose metabolism Arlee Fafalios, Jihong Ma, Xinping Tan, John Stoops, Jianhua Luo, Marie C. DeFrances and Reza Zarnegar
The elements of G protein-coupled receptor systems
 The elements of G protein-coupled receptor systems Prostaglandines Sphingosine 1-phosphate a receptor that contains 7 membrane-spanning domains a coupled trimeric G protein which functions as a switch
The elements of G protein-coupled receptor systems Prostaglandines Sphingosine 1-phosphate a receptor that contains 7 membrane-spanning domains a coupled trimeric G protein which functions as a switch
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Supplementary Information S3 TAM- family small molecule kinase inhibitors in development Compound Indication(s) Target Profile Develop Primary Target MERTK TYRO3 Other targets ment Phase Refs Cabozantinib
Supplementary Information S3 TAM- family small molecule kinase inhibitors in development Compound Indication(s) Target Profile Develop Primary Target MERTK TYRO3 Other targets ment Phase Refs Cabozantinib
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 6 HE-50 HE-116 E-1 HE-108 Supplementary Figure 1. Targeted drug response curves of endometrial cancer cells. Endometrial cancer cell lines were incubated with serial dilutions of
Supplementary Figure 1 6 HE-50 HE-116 E-1 HE-108 Supplementary Figure 1. Targeted drug response curves of endometrial cancer cells. Endometrial cancer cell lines were incubated with serial dilutions of
Supplementary Material. Part I: Sample Information. Part II: Pathway Information
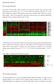 Supplementary Material Part I: Sample Information Three NPC cell lines, CNE1, CNE2, and HK1 were treated with CYC202. Gene expression of 380 selected genes were collected at 0, 2, 4, 6, 12 and 24 hours
Supplementary Material Part I: Sample Information Three NPC cell lines, CNE1, CNE2, and HK1 were treated with CYC202. Gene expression of 380 selected genes were collected at 0, 2, 4, 6, 12 and 24 hours
Part-4. Cell cycle regulatory protein 5 (Cdk5) A novel target of ERK in Carb induced cell death
 Part-4 Cell cycle regulatory protein 5 (Cdk5) A novel target of ERK in Carb induced cell death 95 1. Introduction The process of replicating DNA and dividing cells can be described as a series of coordinated
Part-4 Cell cycle regulatory protein 5 (Cdk5) A novel target of ERK in Carb induced cell death 95 1. Introduction The process of replicating DNA and dividing cells can be described as a series of coordinated
a b G75 G60 Sw-2 Sw-1 Supplementary Figure 1. Structure predictions by I-TASSER Server.
 a b G75 2 2 G60 Sw-2 Sw-1 Supplementary Figure 1. Structure predictions by I-TASSER Server. a. Overlay of top 10 models generated by I-TASSER illustrates the potential effect of 7 amino acid insertion
a b G75 2 2 G60 Sw-2 Sw-1 Supplementary Figure 1. Structure predictions by I-TASSER Server. a. Overlay of top 10 models generated by I-TASSER illustrates the potential effect of 7 amino acid insertion
hexahistidine tagged GRP78 devoid of the KDEL motif (GRP78-His) on SDS-PAGE. This
 SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE LEGEND Fig. S1. Generation and characterization of. (A) Coomassie staining of soluble hexahistidine tagged GRP78 devoid of the KDEL motif (GRP78-His) on SDS-PAGE. This protein was expressed
SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE LEGEND Fig. S1. Generation and characterization of. (A) Coomassie staining of soluble hexahistidine tagged GRP78 devoid of the KDEL motif (GRP78-His) on SDS-PAGE. This protein was expressed
Supplementary Figure 1. BMS enhances human T cell activation in vitro in a
 Supplementary Figure 1. BMS98662 enhances human T cell activation in vitro in a concentration-dependent manner. Jurkat T cells were activated with anti-cd3 and anti-cd28 antibody in the presence of titrated
Supplementary Figure 1. BMS98662 enhances human T cell activation in vitro in a concentration-dependent manner. Jurkat T cells were activated with anti-cd3 and anti-cd28 antibody in the presence of titrated
VEGFR. 1
 VEGFR VEGFRs (vascular endothelial growth factor receptors) are tyrosine kinase receptors responsible for binding with VEGF to initiate signal cascades that stimulate angiogenesis among other effects.
VEGFR VEGFRs (vascular endothelial growth factor receptors) are tyrosine kinase receptors responsible for binding with VEGF to initiate signal cascades that stimulate angiogenesis among other effects.
Supplementary Figure 1. Characterization of NMuMG-ErbB2 and NIC breast cancer cells expressing shrnas targeting LPP. NMuMG-ErbB2 cells (a) and NIC
 Supplementary Figure 1. Characterization of NMuMG-ErbB2 and NIC breast cancer cells expressing shrnas targeting LPP. NMuMG-ErbB2 cells (a) and NIC cells (b) were engineered to stably express either a LucA-shRNA
Supplementary Figure 1. Characterization of NMuMG-ErbB2 and NIC breast cancer cells expressing shrnas targeting LPP. NMuMG-ErbB2 cells (a) and NIC cells (b) were engineered to stably express either a LucA-shRNA
Cell Signaling part 2
 15 Cell Signaling part 2 Functions of Cell Surface Receptors Other cell surface receptors are directly linked to intracellular enzymes. The largest family of these is the receptor protein tyrosine kinases,
15 Cell Signaling part 2 Functions of Cell Surface Receptors Other cell surface receptors are directly linked to intracellular enzymes. The largest family of these is the receptor protein tyrosine kinases,
SelectScreen Biochemical Kinase Profiling Service
 Page 1 of 11 ASSAY THEORY 2 ADAPTA ASSAY CONDITIONS 3 ADAPTA ASSAY CONTROLS 4 ADAPTA DATA ANALYSIS 5 KINASE-SPECIFIC ASSAY CONDITIONS 6 CAMK1 (CaMK1) 6 CDK7/cyclin H/MNAT1 6 CDK9/cyclin T1 6 CHUK (IKK
Page 1 of 11 ASSAY THEORY 2 ADAPTA ASSAY CONDITIONS 3 ADAPTA ASSAY CONTROLS 4 ADAPTA DATA ANALYSIS 5 KINASE-SPECIFIC ASSAY CONDITIONS 6 CAMK1 (CaMK1) 6 CDK7/cyclin H/MNAT1 6 CDK9/cyclin T1 6 CHUK (IKK
p = formed with HCI-001 p = Relative # of blood vessels that formed with HCI-002 Control Bevacizumab + 17AAG Bevacizumab 17AAG
 A.. Relative # of ECs associated with HCI-001 1.4 1.2 1.0 0.8 0.6 0.4 0.2 0.0 ol b p < 0.001 Relative # of blood vessels that formed with HCI-001 1.4 1.2 1.0 0.8 0.6 0.4 0.2 0.0 l b p = 0.002 Control IHC:
A.. Relative # of ECs associated with HCI-001 1.4 1.2 1.0 0.8 0.6 0.4 0.2 0.0 ol b p < 0.001 Relative # of blood vessels that formed with HCI-001 1.4 1.2 1.0 0.8 0.6 0.4 0.2 0.0 l b p = 0.002 Control IHC:
HEK293FT cells were transiently transfected with reporters, N3-ICD construct and
 Supplementary Information Luciferase reporter assay HEK293FT cells were transiently transfected with reporters, N3-ICD construct and increased amounts of wild type or kinase inactive EGFR. Transfections
Supplementary Information Luciferase reporter assay HEK293FT cells were transiently transfected with reporters, N3-ICD construct and increased amounts of wild type or kinase inactive EGFR. Transfections
AlphaScreen : A Straightforward and Powerful Alternative to ELISA. Martina Bielefeld-Sévigny Ph.D., R&D Director
 AlphaScreen : A Straightforward and Powerful Alternative to ELISA Martina Bielefeld-Sévigny Ph.D., R&D Director Overview AlphaScreen - an alternative to ELISA Why an alternative to ELISA? Assay principle
AlphaScreen : A Straightforward and Powerful Alternative to ELISA Martina Bielefeld-Sévigny Ph.D., R&D Director Overview AlphaScreen - an alternative to ELISA Why an alternative to ELISA? Assay principle
AlphaScreen TNFα Binding Assay Kit: A Homogeneous, Sensitive and High-Throughput Assay for Screening TNFα Receptors
 AlphaScreen TNFα Binding Assay Kit: A Homogeneous, Sensitive and High-Throughput Assay for Screening TNFα Receptors Bouchard N., Legault M. and Wenham D. PerkinElmer BioSignal, 1744 William, suite 3, Montréal,
AlphaScreen TNFα Binding Assay Kit: A Homogeneous, Sensitive and High-Throughput Assay for Screening TNFα Receptors Bouchard N., Legault M. and Wenham D. PerkinElmer BioSignal, 1744 William, suite 3, Montréal,
Cellular Neurobiology / BIPN 140
 SECOND MIDTERM EXAMINATION Fall, 2015 GENERAL INSTRUCTIONS 1. Please write your name on ALL 6 pages. 2. Please answer each question IN THE SPACE ALLOTTED. 1) /10 pts 2) /10 pts 3) /15 pts 4) /15 pts 5)
SECOND MIDTERM EXAMINATION Fall, 2015 GENERAL INSTRUCTIONS 1. Please write your name on ALL 6 pages. 2. Please answer each question IN THE SPACE ALLOTTED. 1) /10 pts 2) /10 pts 3) /15 pts 4) /15 pts 5)
Human Obestatin ELISA
 K-ASSAY Human Obestatin ELISA For the quantitative determination of obestatin in human serum and plasma Cat. No. KT-495 For Research Use Only. 1 Rev. 081309 K-ASSAY PRODUCT INFORMATION Human Obestatin
K-ASSAY Human Obestatin ELISA For the quantitative determination of obestatin in human serum and plasma Cat. No. KT-495 For Research Use Only. 1 Rev. 081309 K-ASSAY PRODUCT INFORMATION Human Obestatin
Developing Best in Class BET Inhibitors for Oncology & AI: from Discovery to the Clinic. Kevin G. McLure, PhD EpiCongress July 2014
 Developing Best in Class BET Inhibitors for Oncology & AI: from Discovery to the Clinic Kevin G. McLure, PhD EpiCongress July 2014 Zenith Epigenetics Overview Formed from Resverlogix as an independent
Developing Best in Class BET Inhibitors for Oncology & AI: from Discovery to the Clinic Kevin G. McLure, PhD EpiCongress July 2014 Zenith Epigenetics Overview Formed from Resverlogix as an independent
SUPPLEMENTAL TABLES. Spectrum and Degree of CDK Drug Interactions Predicts Clinical Performance
 SUPPLEMENTAL TABLES Spectrum and Degree of CDK Drug Interactions Predicts Clinical Performance Ping Chen 1, Nathan V. Lee 2, Wenyue Hu 3, Meirong Xu 2, Rose Ann Ferre 1, Hieu Lam 2, Simon Bergqvist 2,
SUPPLEMENTAL TABLES Spectrum and Degree of CDK Drug Interactions Predicts Clinical Performance Ping Chen 1, Nathan V. Lee 2, Wenyue Hu 3, Meirong Xu 2, Rose Ann Ferre 1, Hieu Lam 2, Simon Bergqvist 2,
Phosphorylation Site Company Cat #
 Supplemental Table 1. Antibodies used for RPPA analysis. Label Protein Phosphorylation Site Company Cat # Used on MDA_CLSS Used on MDA_Pilot 4EBP1 4EBP1 Cell Signaling 9452 No 4EBP1.pS65 4EBP1 S65 Cell
Supplemental Table 1. Antibodies used for RPPA analysis. Label Protein Phosphorylation Site Company Cat # Used on MDA_CLSS Used on MDA_Pilot 4EBP1 4EBP1 Cell Signaling 9452 No 4EBP1.pS65 4EBP1 S65 Cell
Targeting the PI3K-Akt-mTOR pathway with GDC-0068, a novel selective ATP competitive Akt inhibitor
 Targeting the PI3K-Akt-mTOR pathway with GDC-0068, a novel selective ATP competitive Akt inhibitor Josep Tabernero, Andrés Cervantes, Cristina Saura, Desamparados Roda, Yibing Yan, Kui Lin, Sumati Murli,
Targeting the PI3K-Akt-mTOR pathway with GDC-0068, a novel selective ATP competitive Akt inhibitor Josep Tabernero, Andrés Cervantes, Cristina Saura, Desamparados Roda, Yibing Yan, Kui Lin, Sumati Murli,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:.38/nature83 Supplementary figure An Overview of Experimental Flow Hypothesis: The tumor microenvironment has a significant impact on cancer cell chemoresistance. Screen Coculture
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:.38/nature83 Supplementary figure An Overview of Experimental Flow Hypothesis: The tumor microenvironment has a significant impact on cancer cell chemoresistance. Screen Coculture
HDAC1 Inhibitor Screening Assay Kit
 HDAC1 Inhibitor Screening Assay Kit Item No. 10011564 www.caymanchem.com Customer Service 800.364.9897 Technical Support 888.526.5351 1180 E. Ellsworth Rd Ann Arbor, MI USA TABLE OF CONTENTS GENERAL INFORMATION
HDAC1 Inhibitor Screening Assay Kit Item No. 10011564 www.caymanchem.com Customer Service 800.364.9897 Technical Support 888.526.5351 1180 E. Ellsworth Rd Ann Arbor, MI USA TABLE OF CONTENTS GENERAL INFORMATION
AACR 101st Annual Meeting 2010, Washington D.C. Experimental and Molecular Therapeutics Section 29; Abstract #3855
 Investigation of the Growth Inhibitory Activity of the MEK Inhibitor ARRY-162 in Combination with Everolimus in a Variety of KRas and PI3K Pathway Mutant Cancers Brian Tunquist, Tyler Risom, Debbie Anderson,
Investigation of the Growth Inhibitory Activity of the MEK Inhibitor ARRY-162 in Combination with Everolimus in a Variety of KRas and PI3K Pathway Mutant Cancers Brian Tunquist, Tyler Risom, Debbie Anderson,
Supplemental Table I
 Supplemental Table I Cortex Hippocampus Age (weeks) Genotype STE 61 pste 61 STE 61 pste 61 8 100.0 ± 4.4 96.2 ± 6.0 99.8 ± 8.7 167.5 ± 7.8* 100.0 ± 7.0 90.5 ± 13.8 100.0 ± 12.8 260.4 ± 33.9** 12 100.0
Supplemental Table I Cortex Hippocampus Age (weeks) Genotype STE 61 pste 61 STE 61 pste 61 8 100.0 ± 4.4 96.2 ± 6.0 99.8 ± 8.7 167.5 ± 7.8* 100.0 ± 7.0 90.5 ± 13.8 100.0 ± 12.8 260.4 ± 33.9** 12 100.0
Supplementary material. Supplementary Figure legends
 Supplementary material Supplementary Figure legends Supplementary Figure 1: Senescence-associated proliferation stop in response to oncogenic N-RAS expression Proliferation of NHEM cells without (ctrl.)
Supplementary material Supplementary Figure legends Supplementary Figure 1: Senescence-associated proliferation stop in response to oncogenic N-RAS expression Proliferation of NHEM cells without (ctrl.)
Optimization of a LanthaScreen Kinase assay for ZAP70
 Optimization of a LanthaScreen Kinase assay for ZAP70 Overview This protocol describes how to develop a LanthaScreen kinase assay designed to detect and characterize kinase inhibitors. The development
Optimization of a LanthaScreen Kinase assay for ZAP70 Overview This protocol describes how to develop a LanthaScreen kinase assay designed to detect and characterize kinase inhibitors. The development
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure S1. Binding of full-length OGT and deletion mutants to PIP strips (Echelon Biosciences). Supplementary Figure S2. Binding of the OGT (919-1036) fragments with
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure S1. Binding of full-length OGT and deletion mutants to PIP strips (Echelon Biosciences). Supplementary Figure S2. Binding of the OGT (919-1036) fragments with
Supplementary Figures
 Supplementary Figures Figure S1. Validation of kinase regulators of ONC201 sensitivity. Validation and screen results for changes in cell viability associated with the combination of ONC201 treatment (1
Supplementary Figures Figure S1. Validation of kinase regulators of ONC201 sensitivity. Validation and screen results for changes in cell viability associated with the combination of ONC201 treatment (1
Executive Summary. Reproduction prohibited v
 Kinases are a large family of proteins that have now become firmly established as a major class of drug targets for the pharmaceutical industry. The sequencing of the Human Genome has led to the identification
Kinases are a large family of proteins that have now become firmly established as a major class of drug targets for the pharmaceutical industry. The sequencing of the Human Genome has led to the identification
Supplementary Figure 1 Role of Raf-1 in TLR2-Dectin-1-mediated cytokine expression
 Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 1 Role of Raf-1 in TLR2-Dectin-1-mediated cytokine expression. Quantitative real-time PCR of indicated mrnas in DCs stimulated with TLR2-Dectin-1 agonist zymosan
Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 1 Role of Raf-1 in TLR2-Dectin-1-mediated cytokine expression. Quantitative real-time PCR of indicated mrnas in DCs stimulated with TLR2-Dectin-1 agonist zymosan
Lecture #27 Lecturer A. N. Koval
 Lecture #27 Lecturer A. N. Koval Hormones Transduce Signals to Affect Homeostatic Mechanisms Koval A. (C), 2011 2 Lipophilic hormones Classifying hormones into hydrophilic and lipophilic molecules indicates
Lecture #27 Lecturer A. N. Koval Hormones Transduce Signals to Affect Homeostatic Mechanisms Koval A. (C), 2011 2 Lipophilic hormones Classifying hormones into hydrophilic and lipophilic molecules indicates
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Bommi-Reddy et al. 10.1073/pnas.0806574105 Fig. S1. Reintroducing wild-type pvhl in VHL / cells does not affect cell growth in vitro.(a) Immunoblot analysis of 786-O and RCC4 VHL
Supporting Information Bommi-Reddy et al. 10.1073/pnas.0806574105 Fig. S1. Reintroducing wild-type pvhl in VHL / cells does not affect cell growth in vitro.(a) Immunoblot analysis of 786-O and RCC4 VHL
Propagation of the Signal
 OpenStax-CNX module: m44452 1 Propagation of the Signal OpenStax College This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this section,
OpenStax-CNX module: m44452 1 Propagation of the Signal OpenStax College This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this section,
Regulation of cell function by intracellular signaling
 Regulation of cell function by intracellular signaling Objectives: Regulation principle Allosteric and covalent mechanisms, Popular second messengers, Protein kinases, Kinase cascade and interaction. regulation
Regulation of cell function by intracellular signaling Objectives: Regulation principle Allosteric and covalent mechanisms, Popular second messengers, Protein kinases, Kinase cascade and interaction. regulation
Response and resistance to BRAF inhibitors in melanoma
 Response and resistance to BRAF inhibitors in melanoma Keith T. Flaherty, M.D. Massachusetts General Hospital Cancer Center Disclosures Roche/Genentech: consultant GlaxoSmithKline: consultant BRAF mutations
Response and resistance to BRAF inhibitors in melanoma Keith T. Flaherty, M.D. Massachusetts General Hospital Cancer Center Disclosures Roche/Genentech: consultant GlaxoSmithKline: consultant BRAF mutations
Protein tyrosine kinase signaling
 rotein tyrosine kinase signaling Serge ROCHE CRBM CNRS/Montpellier University serge.roche@crbm.cnrs.fr rotein phosphorylation on Tyr A central mechanism to control cell communication in a multicellular
rotein tyrosine kinase signaling Serge ROCHE CRBM CNRS/Montpellier University serge.roche@crbm.cnrs.fr rotein phosphorylation on Tyr A central mechanism to control cell communication in a multicellular
Nature Immunology: doi: /ni Supplementary Figure 1. IC261 inhibits a virus-induced type I interferon response.
 Supplementary Figure 1 IC261 inhibits a virus-induced type I interferon response. (a) HEK293T cells were cultured in 384 wells and transiently transfected with 50 ng of the IFN-β promoter-luc construct
Supplementary Figure 1 IC261 inhibits a virus-induced type I interferon response. (a) HEK293T cells were cultured in 384 wells and transiently transfected with 50 ng of the IFN-β promoter-luc construct
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb3076 Supplementary Figure 1 btrcp targets Cep68 for degradation during mitosis. a) Cep68 immunofluorescence in interphase and metaphase. U-2OS cells were transfected with control sirna
DOI: 10.1038/ncb3076 Supplementary Figure 1 btrcp targets Cep68 for degradation during mitosis. a) Cep68 immunofluorescence in interphase and metaphase. U-2OS cells were transfected with control sirna
RayBio KinaseSTAR TM Akt Activity Assay Kit
 Activity Assay Kit User Manual Version 1.0 March 13, 2015 RayBio KinaseSTAR TM Akt Activity Kit Protocol (Cat#: 68AT-Akt-S40) RayBiotech, Inc. We Provide You With Excellent Support And Service Tel:(Toll
Activity Assay Kit User Manual Version 1.0 March 13, 2015 RayBio KinaseSTAR TM Akt Activity Kit Protocol (Cat#: 68AT-Akt-S40) RayBiotech, Inc. We Provide You With Excellent Support And Service Tel:(Toll
WHY TARGETTING SIGNALLING PATHWAYS?
 WHY TARGETTING SIGNALLING PATHWAYS? Cancer cells are particularly sensitive to stress therefore sensitive to inhibition of their hyper activated signaling proteins the re instatement of lost tumor suppressors.
WHY TARGETTING SIGNALLING PATHWAYS? Cancer cells are particularly sensitive to stress therefore sensitive to inhibition of their hyper activated signaling proteins the re instatement of lost tumor suppressors.
Supplementary Information. Induction of human pancreatic beta cell replication by inhibitors of dual specificity tyrosine regulated kinase
 Journal: Nature Medicine Supplementary Information Induction of human pancreatic beta cell replication by inhibitors of dual specificity tyrosine regulated kinase 1,2 Peng Wang PhD, 1,2 Juan-Carlos Alvarez-Perez
Journal: Nature Medicine Supplementary Information Induction of human pancreatic beta cell replication by inhibitors of dual specificity tyrosine regulated kinase 1,2 Peng Wang PhD, 1,2 Juan-Carlos Alvarez-Perez
ASSAY THEORY 2 ADAPTA ASSAY CONDITIONS 3 ADAPTA ASSAY CONTROLS 4 ADAPTA DATA ANALYSIS 5
 Page 1 of 11 ASSAY THEORY 2 ADAPTA ASSAY CONDITIONS 3 ADAPTA ASSAY CONTROLS 4 ADAPTA DATA ANALYSIS 5 KINASE-SPECIFIC ASSAY CONDITIONS 6 CAMK1 (CaMK1) 6 CDK4/cyclin D1 6 CDK4/cyclin D3 6 CDK6/cyclin D1
Page 1 of 11 ASSAY THEORY 2 ADAPTA ASSAY CONDITIONS 3 ADAPTA ASSAY CONTROLS 4 ADAPTA DATA ANALYSIS 5 KINASE-SPECIFIC ASSAY CONDITIONS 6 CAMK1 (CaMK1) 6 CDK4/cyclin D1 6 CDK4/cyclin D3 6 CDK6/cyclin D1
Oris Assays: An Innovative Platform for the Study of Cell Migration & Cell Invasion
 Bringing Science to the Surface Oris Assays: An Innovative Platform for the Study of Cell Migration & Cell Invasion AMS Biotechnology (Europe) - www.amsbio.com - info@amsbio.com UK +44 (0) 1235 828200
Bringing Science to the Surface Oris Assays: An Innovative Platform for the Study of Cell Migration & Cell Invasion AMS Biotechnology (Europe) - www.amsbio.com - info@amsbio.com UK +44 (0) 1235 828200
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Supplementary Table 1. Cell sphingolipids and S1P bound to endogenous TRAF2. Sphingolipid Cell pmol/mg TRAF2 immunoprecipitate pmol/mg Sphingomyelin 4200 ± 250 Not detected Monohexosylceramide 311 ± 18
Supplementary Table 1. Cell sphingolipids and S1P bound to endogenous TRAF2. Sphingolipid Cell pmol/mg TRAF2 immunoprecipitate pmol/mg Sphingomyelin 4200 ± 250 Not detected Monohexosylceramide 311 ± 18
Supplementary Figure 1. PD-L1 is glycosylated in cancer cells. (a) Western blot analysis of PD-L1 in breast cancer cells. (b) Western blot analysis
 Supplementary Figure 1. PD-L1 is glycosylated in cancer cells. (a) Western blot analysis of PD-L1 in breast cancer cells. (b) Western blot analysis of PD-L1 in ovarian cancer cells. (c) Western blot analysis
Supplementary Figure 1. PD-L1 is glycosylated in cancer cells. (a) Western blot analysis of PD-L1 in breast cancer cells. (b) Western blot analysis of PD-L1 in ovarian cancer cells. (c) Western blot analysis
Integrin CD11b negatively regulates TLR-triggered inflammatory responses by. activating Syk and promoting MyD88 and TRIF degradation via cbl-b
 Integrin CD11b negatively regulates TLR-triggered inflammatory responses by activating Syk and promoting MyD88 and TRIF degradation via cbl-b Chaofeng Han, Jing Jin, Sheng Xu, Haibo Liu, Nan Li, and Xuetao
Integrin CD11b negatively regulates TLR-triggered inflammatory responses by activating Syk and promoting MyD88 and TRIF degradation via cbl-b Chaofeng Han, Jing Jin, Sheng Xu, Haibo Liu, Nan Li, and Xuetao
QS S Assist KINASE_ADP-Glo TM Kit
 QS S Assist KINASE_ADP-Glo TM Kit Description KINASE ADP-Glo TM kit is designed for use in biochemical kinase assays based on a Luminescent ADP Detection Assay (ADP-Glo TM ). The kit includes human kinase,
QS S Assist KINASE_ADP-Glo TM Kit Description KINASE ADP-Glo TM kit is designed for use in biochemical kinase assays based on a Luminescent ADP Detection Assay (ADP-Glo TM ). The kit includes human kinase,
Supplementary Data Figure S1. A) PKI-587 suppression of p-akt in A498 and (+/- 10
 Supplementary Data Figure S1. A) PKI-587 suppression of p-akt in A498 and 786-0 (+/- 10 μm Verapamil), and B) PKI-587 suppression of p-akt in BT474, & U87MG. 3 1 0.3 0.1 0.03 0 [μm] A) 786-0 - + p-akt
Supplementary Data Figure S1. A) PKI-587 suppression of p-akt in A498 and 786-0 (+/- 10 μm Verapamil), and B) PKI-587 suppression of p-akt in BT474, & U87MG. 3 1 0.3 0.1 0.03 0 [μm] A) 786-0 - + p-akt
Chapter 9: Biochemical Mechanisms for Information Storage at the Cellular Level. From Mechanisms of Memory, second edition By J. David Sweatt, Ph.D.
 Chapter 9: Biochemical Mechanisms for Information Storage at the Cellular Level From Mechanisms of Memory, second edition By J. David Sweatt, Ph.D. Chapter 9: Dendritic Spine Figure 1 Summary: Three Primary
Chapter 9: Biochemical Mechanisms for Information Storage at the Cellular Level From Mechanisms of Memory, second edition By J. David Sweatt, Ph.D. Chapter 9: Dendritic Spine Figure 1 Summary: Three Primary
Supplementary Figure 1
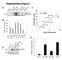 A B D Relative TAp73 mrna p73 Supplementary Figure 1 25 2 15 1 5 p63 _-tub. MDA-468 HCC1143 HCC38 SUM149 MDA-468 HCC1143 HCC38 SUM149 HCC-1937 MDA-MB-468 ΔNp63_ TAp73_ TAp73β E C Relative ΔNp63 mrna TAp73
A B D Relative TAp73 mrna p73 Supplementary Figure 1 25 2 15 1 5 p63 _-tub. MDA-468 HCC1143 HCC38 SUM149 MDA-468 HCC1143 HCC38 SUM149 HCC-1937 MDA-MB-468 ΔNp63_ TAp73_ TAp73β E C Relative ΔNp63 mrna TAp73
Figure S1. Effect of bafilomycin on EGF-induced Akt and Erk signaling. Effect of chloroquine on EGF-stimulated mtorc1, Akt and Erk
 EGF induced VATPase assembly and mtorc1 activation Supplemental Information Supplemental Figure Legends Figure S1. Effect of bafilomycin on EGFinduced Akt and Erk signaling. A. Hepatocytes were treated
EGF induced VATPase assembly and mtorc1 activation Supplemental Information Supplemental Figure Legends Figure S1. Effect of bafilomycin on EGFinduced Akt and Erk signaling. A. Hepatocytes were treated
Supplemental Figure 1. Western blot analysis indicated that MIF was detected in the fractions of
 Supplemental Figure Legends Supplemental Figure 1. Western blot analysis indicated that was detected in the fractions of plasma membrane and cytosol but not in nuclear fraction isolated from Pkd1 null
Supplemental Figure Legends Supplemental Figure 1. Western blot analysis indicated that was detected in the fractions of plasma membrane and cytosol but not in nuclear fraction isolated from Pkd1 null
Supplemental information
 Supplemental information PI(3)K p11δ controls the sucellular compartmentalization of TLR4 signaling and protects from endotoxic shock Ezra Aksoy, Salma Taoui, David Torres, Sandrine Delauve, Aderrahman
Supplemental information PI(3)K p11δ controls the sucellular compartmentalization of TLR4 signaling and protects from endotoxic shock Ezra Aksoy, Salma Taoui, David Torres, Sandrine Delauve, Aderrahman
Supplementary Materials for
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Integrative Biology. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 217 Supplementary Materials for Chemical genomic analysis of GPR35 signaling Heidi (Haibei)
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Integrative Biology. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 217 Supplementary Materials for Chemical genomic analysis of GPR35 signaling Heidi (Haibei)
Validation & Assay Performance Summary
 Validation & Assay Performance Summary CellSensor DBE-bla MDA-MB-468 Cell Line Cat. no. K1814 Pathway Description The phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase (PI3K) signaling cascade is essential for cell growth
Validation & Assay Performance Summary CellSensor DBE-bla MDA-MB-468 Cell Line Cat. no. K1814 Pathway Description The phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase (PI3K) signaling cascade is essential for cell growth
Neurotransmitters acting on G-protein coupled receptors
 Neurotransmitters acting on G-protein coupled receptors Part 1: Dopamine and Norepinephrine BIOGENIC AMINES Monoamines Diamine Overview of Neurotransmitters and Their Receptors Criteria for defining a
Neurotransmitters acting on G-protein coupled receptors Part 1: Dopamine and Norepinephrine BIOGENIC AMINES Monoamines Diamine Overview of Neurotransmitters and Their Receptors Criteria for defining a
2-D DIGE * 1,2. * src Src ras 2002 LC-MS/ MS. prefractionation. Proteome Letters
 Proteome Letters 2016 1 11-18 2015 2-D DIGE * 1,2 *E-mail: hattoris@pharm.kitasato-u.ac.jp 1 108-8639 4-6-1 2 108-8641 5-9-1 2016 4 22 2016 5 31 2016 6 1 two-dimensional fluorescence difference gel electrophoresis:
Proteome Letters 2016 1 11-18 2015 2-D DIGE * 1,2 *E-mail: hattoris@pharm.kitasato-u.ac.jp 1 108-8639 4-6-1 2 108-8641 5-9-1 2016 4 22 2016 5 31 2016 6 1 two-dimensional fluorescence difference gel electrophoresis:
RXDX-101 & RXDX-102. Justin Gainor, MD February 20 th, 2014
 RXDX-101 & RXDX-102 Justin Gainor, MD February 20 th, 2014 Background Chromosomal fusions are important oncogenic drivers in NSCLC - ALK Rearrangements (4-6%) - ROS1 Rearrangements (1-2%) - RET Rearrangements
RXDX-101 & RXDX-102 Justin Gainor, MD February 20 th, 2014 Background Chromosomal fusions are important oncogenic drivers in NSCLC - ALK Rearrangements (4-6%) - ROS1 Rearrangements (1-2%) - RET Rearrangements
Introduction. Figure 1 Experimental Strategy
 Beyond s: Interrogating the Purinome Tony A. Klink, Karen Kleman-Leyer, Matt Staeben, Robert G. Lowery BellBrook Labs, Madison, Wisconsin, USA 53711 Introduction The development of ATP-site ligands as
Beyond s: Interrogating the Purinome Tony A. Klink, Karen Kleman-Leyer, Matt Staeben, Robert G. Lowery BellBrook Labs, Madison, Wisconsin, USA 53711 Introduction The development of ATP-site ligands as
Degrading the Barriers to Drug Discovery in Ubiquitin E3 Ligase Pathways
 Degrading the Barriers to Drug Discovery in iquitin E3 Ligase Pathways Blaine N. Armbruster, PhD. Sr. Manager - Discovery & Development Solutions EMD Millipore 1 Oct, 2012 Outline Introduction ti to EMD
Degrading the Barriers to Drug Discovery in iquitin E3 Ligase Pathways Blaine N. Armbruster, PhD. Sr. Manager - Discovery & Development Solutions EMD Millipore 1 Oct, 2012 Outline Introduction ti to EMD
Alzheimer s disease (AD) is a neurodegenerative disease whose most common symptom is a progressive loss of cognitive functions and intellectual
 Maryam Farrokhnia 1 Alzheimer s disease (AD) is a neurodegenerative disease whose most common symptom is a progressive loss of cognitive functions and intellectual abilities, resulting in serious impairment
Maryam Farrokhnia 1 Alzheimer s disease (AD) is a neurodegenerative disease whose most common symptom is a progressive loss of cognitive functions and intellectual abilities, resulting in serious impairment
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Constitutive EGFR signaling does not activate canonical EGFR signals (a) U251EGFRInd cells with or without tetracycline exposure (24h, 1µg/ml) were treated with EGF for 15 minutes
Supplementary Figure 1 Constitutive EGFR signaling does not activate canonical EGFR signals (a) U251EGFRInd cells with or without tetracycline exposure (24h, 1µg/ml) were treated with EGF for 15 minutes
Signaling Through Immune System Receptors (Ch. 7)
 Signaling Through Immune System Receptors (Ch. 7) 1. General principles of signal transduction and propagation. 2. Antigen receptor signaling and lymphocyte activation. 3. Other receptors and signaling
Signaling Through Immune System Receptors (Ch. 7) 1. General principles of signal transduction and propagation. 2. Antigen receptor signaling and lymphocyte activation. 3. Other receptors and signaling
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature12652 Supplementary Figure 1. PRDM16 interacts with endogenous EHMT1 in brown adipocytes. Immunoprecipitation of PRDM16 complex by flag antibody (M2) followed by Western blot analysis
doi:10.1038/nature12652 Supplementary Figure 1. PRDM16 interacts with endogenous EHMT1 in brown adipocytes. Immunoprecipitation of PRDM16 complex by flag antibody (M2) followed by Western blot analysis
