Supplemental Information. Regulatory T Cells Exhibit Distinct. Features in Human Breast Cancer
|
|
|
- Moris Chandler
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Immunity, Volume 45 Supplemental Information Regulatory T Cells Exhibit Distinct Features in Human Breast Cancer George Plitas, Catherine Konopacki, Kenmin Wu, Paula D. Bos, Monica Morrow, Ekaterina V. Putintseva, Dmitriy M. Chudakov, and Alexander Y. Rudensky
2 Supplemental Figures A Tumor NBP PBMC B TNBC ER Max (%) Max (%) Comp-PE-A :: CCR8 Comp-PE-Cy7-A :: CCR4 CCR8 CCR4 CD Treg cell CD39 Tconv cell TIGIT ER PR CCR CCR5 CCR6 CCR7 Treg cells Tconv cell CD8 T cell Supplemental Figure 1, related to Figure 4. Tumor Treg specific genes identified by RNAseq are highly expressed by tumor Treg cells at the protein level. (A) Expression of several genes found to be differentially expressed in tumor Treg cells by RNAseq analysis was measured at the protein level by flow cytometry. MFI of genes gated on Treg cells (open histograms) and Tconv cells (shaded histograms) in breast tumor, NBP and peripheral blood. Plots represent data from individual specimens. (B) Expression of chemokine receptors found to be differentially expressed in tumor Treg or Tconv cells relative to peripheral blood T cells by RNA-seq analysis was measured at the protein level by flow cytometry. MFI of staining for indicated chemokine receptors gated on Treg cells (open histograms), Tconv cells (shaded histograms) and CD8 T cells (dashed histograms) in ER, PR and TNBC breast tumors.
3 Max (%) % 3% % Melanoma Non-small cell lung cancer Colon adenocarcinoma Treg cell Tconv cell Supplemental Figure, related to Figure 4. CD177 is highly expressed by a subset of tumor Treg cells in several types of cancer. Flow cytometric analysis of CD177 expression by intratumoral T cells. The data are shown as MFI of CD177 staining of single cell suspension dissociated gated on Treg cells (open histograms) and Tconv cells (shaded histograms) in colorectal adenocarcinoma, melanoma and non-small cell lung cancer. A -log (p Value) p<.1, log (FC)>1, 9 genes CDH5 CD4LG TCN1 NMB RBMS TCF7 CDCA7 CXCL13 CD177 5 Expression (log fold) CD177 - B Top 1 unique clones (fraction of all CDR3 sequencing reads) Oligoclonality of TCR beta repertoires CD177 Treg in tumor P=.33 - CD177 Treg in tumor vs CD177 tumor Treg cell Supplemental Figure 3. related to Figure 5. Analysis of gene expression and TCR oligoclonality of intratumoral CD177 and CD177 - Treg cells. (A) Volcano plot comparing the p-value versus fold-change for gene expression in patient matched CD177 versus CD177 - tumor resident Treg cells (n=5). Genes labeled in red are significantly differentially expressed (p<.1). (B) Frequency of the TCR beta CDR3 repertoire occupied by the 1 most abundant clones in CD177 and CD177 - intratumoral Treg cells. P-value was calculated using a paired two-tailed Student s t test.
4 1 Max (%) Tumor-involved axillary lymph node Breast adenocarcinoma Treg cell Tconv cell Supplemental Figure 4, related to Figure 6. CCR8 is expressed by a minor subset of Treg cells in axillary lymph nodes of stage III breast cancer patients. Representative flow cytometric analysis of CCR8 expression by Treg cells in an involved axillary lymph node from a breast cancer patient. MFI of CCR8 gated on Treg cells (open histograms) and Tconv cells (shaded histograms). The results represent one of three independent experiments (three patients total). A C B x 3 1 CCL4L CCL CCL5 CCL18 CCL CCL1 CCL8 CCL7 x Supplemental Figure 5, related to Figure 6. The CCR8 ligand CCL1 is expressed by CD11b CD14 myeloid cells in breast tumors. (A) Boxplots comparing CCL1 normalized mrna level in breast, colorectal and lung adenocarcinomas or melanomas versus adjacent normal tissues. (B) Volcano plot comparing the p-value versus fold-change for genes from intratumoral CD11b CD14 myeloid cells relative to CD11b CD14 myeloid cells isolated from peripheral blood of healthy donors (n=7, n=4, respectively). Genes labeled in red are significantly differentially expressed (p<.1). (C) CD11b CD14 myeloid cells, CD9 CD31 fibroblasts and CD31 endothelial cells were FACS purified from breast tumors and CCL1 and CCL18 mrna levels were quantified by qpcr with RP as a reference gene and calibrated to expression in peripheral blood T cells.
5 4 -CCL1 CCL1 (1 ng/ml) p<.1 [ 3 H] TdR (cpm) x : 1:1 Naive T cell/treg ratio Supplemental Figure 6, related to Figure 6. CCR8 signaling does not affect Treg cell suppressor function in vitro. Tumor resident CD4 CD5 hi Treg cells were FACS isolated and their capacity to suppress in vitro proliferation of naïve Tconv cells induced by plate-bound CD3 and CD8 antibodies in presence of recombinant CCL1 in vitro was assessed by 3 H-thymidine incorporation on day 4 (n=3, plot is representative of two independent experiments). A Overall Survival Disease-Free Survival Log (FOXP3 RSEM) r = Log (CCR RSEM) 1 5 P=n.s., n= P=n.s., n= High CCR/FOXP3 RSEM Low CCR/FOXP3 RSEM B C Log (FOXP3 RSEM) Log (FOXP3 RSEM) r = Log (CCR4 RSEM) r = Log (CCR5 RSEM) 1 5 P=.7, n= P=n.s., n= P=.4, n= Supplemental Figure 7, related to Figure 7. Ratio of chemokine receptor mrna to Foxp3 mrna does not correlate with survival outcome in the TCGA dataset. Analysis of breast cancer TCGA data for relative expression of indicated genes normalized against Foxp3 mrna expression. Spearman correlation (n=14), overall survival (n=14, Mantel-Cox test) and disease-free survival (n=93, Mantel-Cox test) of breast cancer patients in the TCGA dataset stratified by median tumor (A) CCR/FOXP3, (B) CCR4/FOXP3, (C) CCR5/FOXP3 normalized mrna ratios P=n.s., n= High CCR4/FOXP3 RSEM Low CCR4/FOXP3 RSEM High CCR5/FOXP3 RSEM Low CCR5/FOXP3 RSEM
6 Supplemental Tables Variable N=15 Age (median) 5 (4-88) Tumor Stage T1 T T3 5 (49.5%) 5 (47.6%) 3 (.9%) Nodal Stage Subtype N N1 N N3 Tumor Grade 1 3 ER Her TNBC 71 (67.6%) 8 (6.7%) (1.9%) 4 (3.8%) 78 (74.3%) 1 (9.5%) 19 (18.1%) 8 (7.6%) 38 (36.%) 59 (56.%) Supplemental Table 1, related to Figure 1. Clinical characteristics of the patients whose tumor specimens were used in this study. Description of patient age, tumor stage, nodal stage, cancer subtype and tumor grade for each patient. Supplemental Table, related to Figure 4. Differential gene expression analysis of T cells in breast tumor and peripheral blood. Differential gene expression tables comparing tumorassociated Treg cells, tumor-associated Tconv cells, activated Treg cells from PBMC and activated Tconv cells from PBMC. Supplemental Table 3, related to Figure 4. Differential gene expression analysis of T cells in breast tumor and normal breast parenchyma. Differential gene expression tables comparing tumor-associated Treg cells, tumor-associated Tconv cells, NBP-associated Treg cells and NBP-associated Tconv cells. Supplemental Table 4, related to Figure S3. Differential gene expression analysis of CD177 expressing Treg cells. Differential gene expression table comparing tumor-associated CD177 Treg cells to tumor-associated CD177 - Treg cells. Supplemental Table 5, related to Figure S5. Differential gene expression analysis of breast tumor-associated myeloid cells. Differential gene expression table comparing tumor-associated CD11b CD14 myeloid cells to cells to CD11b CD14 myeloid cells from PBMC. Supplemental Experimental Procedures In vitro assays For in vitro induction assays, CD4 CD5 hi Treg cells were isolated from PBMC and cultured in 4- well flat-bottom plates in presence of CD3 and CD8 antibody-coated beads at a 1:1 bead:cell ratio in RPMI164 supplemented as above. For induction of CCR8 by tumor and NBP slices,.4 µm Transwell inserts were placed in each well and thin tumor or NBP slices were laid onto the Transwell surface (Corning). After 1 hr, CCR8 expression was assessed by qpcr as described in Supplemental Experimental Procedures. For induction of CCR8 cells were cultured
7 in 96-well U bottom plates without or with 1U/mL recombinant human IFNα (R&D Systems) and CCR8 expression was assessed by flow cytometry. Quantitative RT-PCR RNA was isolated using the RNeasy Micro Kit (Qiagen) according to the manufacturer's instructions. The isolated RNA was used to synthesize cdna with the qscript cdna SuperMix (Quanta-bio). SYBR Green PCR Master Mix (Life Technologies) was used for quantitative RT- PCR. PCRs were performed in triplicate. The following primers were used: CCR8 forward, 5 - GGGCTTGAGAAGATATCAGGG-3 and reverse, 5 -TCCAGAACAAAGGCTGTCACT-3 ; CCL-1 forward, 5 -TTAAGCCCTCATTGGAGCAG-3 and reverse, 5 -AGATGTGGACAGCAAGAGCA-3 ; CCL-18 forward, 5 - GTGGAATCTGCCAGGAGGTA-3 and reverse, 5 - TCCTTGTCCTCGTCTGCAC-3 ; RP forward, 5 -CCCATTAAACTCCAAGGCAA-3 and reverse, 5 -AAGCTGAGGATGCTCAAAGG-3 ; ADAR forward, 5 -GGTGGCCTTTTGGAGTACG-3 and reverse, 5 -CCAACTTTTGCTTGGTAAACG-3. RNA Sequencing Total RNA was extracted and assessed for nucleic acid quantity and quality on the Agilent BioAnalyzer. For the first set of tumor Treg, Tconv and PBMC Treg and Tconv samples, after SMARTer amplification, total RNA was used for poly(a) selection and was used to create Ion Torrent compatible libraries using the Ion ChIP-Seq Kit starting with the end-repair process (Life Technologies), with 1 to 16 cycles of PCR. The resulting barcoded samples were loaded onto template-positive Ion PI Ion Sphere Particles (ISPs) using the Ion One Touch system II and Ion PI Template OT kit v Kit (Life Technologies). Enriched particles were sequenced on a Proton sequencing system using the bp version chemistry. On average of 7 to 8 million single-end reads were generated per sample. For the second set of tumor Treg, Tconv and PBMC Treg and Tconv samples, SMARTer amplification with 1-16 cycles of PCR was followed by Illumina TruSeq paired-end library preparation following manufacturer s protocols. Samples were sequenced on the Illumina HiSeq 5 to an average depth of million 5-bp read pairs per sample. Read alignment and processing followed the method described by Anders et al (Anders et al., 13). Briefly, raw reads were trimmed using Trimmomatic v.3 with standard settings to remove low-quality reads and adaptor contamination (Bolger et al., 14). The trimmed reads were then aligned to the human genome (Ensembl assembly GRCh38) using TopHat v..11 implementing Bowtie v.. with default settings (Kim et al., 13; Langmead and Salzberg,
8 1). Read alignments were sorted with SAMtools v.1.19 before being counted to genomic features using HTSeq v.6.1p1 (Anders et al., 13; Li et al., 9). Bioinformatic Analyses Differential gene expression was analyzed using DESeq in R version (Love et al., 14). Significantly up- and down-regulated genes in all comparisons were defined as expressed genes (threshold of 5 normalized reads) with FDR-adjusted p-value.1 and fold change of at least x. To determine transcriptional signatures, the GOrilla tool for discovery of enriched GO terms in ranked gene lists was used (Eden et al., 9). The target gene set was defined as significantly up-regulated expressed genes with FDR adjusted p-value.5 and was compared against a background set of genes defined as genes with average expression across all samples of at least normalized reads. TCR alpha and beta CDR3 repertoires were extracted from RNA-Seq data using MiXCR software (Bolotin et al. 15) in RNA-Seq mode. Comparative post-analysis of TCR repertoires was performed using VDJtools software (Shugay et al., 15). Supplemental References Anders, S., McCarthy, D.J., Chen, Y., Okoniewski, M., Smyth, G.K., Huber, W., and Robinson, M.D. (13). Count-based differential expression analysis of RNA sequencing data using R and Bioconductor. Nature protocols 8, Bolger, A.M., Lohse, M., and Usadel, B. (14). Trimmomatic: a flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data. Bioinformatics 3, Bolotin, D.A., Poslavsky, S., Mitrophanov, I., Shugay, M., Marnedov, I.Z., Putintzeva, E.V., Chudakov, D.M. (15). MiXCR: software for comprehensive adaptive immunity profiling. Mature Methods 1(5), Eden, E., Navon, R., Steinfeld, I., Lipson, D., and Yakhini, Z. (9). GOrilla: a tool for discovery and visualization of enriched GO terms in ranked gene lists. BMC bioinformatics 1, 48. Kim, D., Pertea, G., Trapnell, C., Pimentel, H., Kelley, R., and Salzberg, S.L. (13). TopHat: accurate alignment of transcriptomes in the presence of insertions, deletions and gene fusions. Genome biology 14, R36. Langmead, B., and Salzberg, S.L. (1). Fast gapped-read alignment with Bowtie. Nature methods 9, Li, H., Handsaker, B., Wysoker, A., Fennell, T., Ruan, J., Homer, N., Marth, G., Abecasis, G., Durbin, R., and Genome Project Data Processing, S. (9). The Sequence Alignment/Map format and SAMtools. Bioinformatics 5,
9 Love, M.I., Huber, W., and Anders, S. (14). Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq. Genome biology 15, 55. Shugay, M., Bagaev, D.V., Turchaninova, M.A., Bolotin, D.A., Britanova, O.V., Putintseva, E.V., Pogorelyy, M.V., Nazarov, V.I., Zvyagin, I.V., Kirgizova, V.I., Kirgizov, K.I., Skorobogatova, E.V., Chudakov, D.M. (15). VDJtools: Unifying Post-analysis of T Cell Receptor Repertoires. PLoS Comput Biol 11(11): e1453.
Regulatory T Cells Exhibit Distinct Features in Human Breast Cancer
 Resource Regulatory T Cells Exhibit Distinct Features in Human Breast Cancer Graphical Abstract Authors George Plitas, Catherine Konopacki, Kenmin Wu,..., Ekaterina V. Putintseva, Dmitriy M. Chudakov,
Resource Regulatory T Cells Exhibit Distinct Features in Human Breast Cancer Graphical Abstract Authors George Plitas, Catherine Konopacki, Kenmin Wu,..., Ekaterina V. Putintseva, Dmitriy M. Chudakov,
York criteria, 6 RA patients and 10 age- and gender-matched healthy controls (HCs).
 MATERIALS AND METHODS Study population Blood samples were obtained from 15 patients with AS fulfilling the modified New York criteria, 6 RA patients and 10 age- and gender-matched healthy controls (HCs).
MATERIALS AND METHODS Study population Blood samples were obtained from 15 patients with AS fulfilling the modified New York criteria, 6 RA patients and 10 age- and gender-matched healthy controls (HCs).
Supplemental Methods RNA sequencing experiment
 Supplemental Methods RNA sequencing experiment Mice were euthanized as described in the Methods and the right lung was removed, placed in a sterile eppendorf tube, and snap frozen in liquid nitrogen. RNA
Supplemental Methods RNA sequencing experiment Mice were euthanized as described in the Methods and the right lung was removed, placed in a sterile eppendorf tube, and snap frozen in liquid nitrogen. RNA
Human and mouse T cell regulation mediated by soluble CD52 interaction with Siglec-10. Esther Bandala-Sanchez, Yuxia Zhang, Simone Reinwald,
 Human and mouse T cell regulation mediated by soluble CD52 interaction with Siglec-1 Esther Bandala-Sanchez, Yuxia Zhang, Simone Reinwald, James A. Dromey, Bo Han Lee, Junyan Qian, Ralph M Böhmer and Leonard
Human and mouse T cell regulation mediated by soluble CD52 interaction with Siglec-1 Esther Bandala-Sanchez, Yuxia Zhang, Simone Reinwald, James A. Dromey, Bo Han Lee, Junyan Qian, Ralph M Böhmer and Leonard
fl/+ KRas;Atg5 fl/+ KRas;Atg5 fl/fl KRas;Atg5 fl/fl KRas;Atg5 Supplementary Figure 1. Gene set enrichment analyses. (a) (b)
 KRas;At KRas;At KRas;At KRas;At a b Supplementary Figure 1. Gene set enrichment analyses. (a) GO gene sets (MSigDB v3. c5) enriched in KRas;Atg5 fl/+ as compared to KRas;Atg5 fl/fl tumors using gene set
KRas;At KRas;At KRas;At KRas;At a b Supplementary Figure 1. Gene set enrichment analyses. (a) GO gene sets (MSigDB v3. c5) enriched in KRas;Atg5 fl/+ as compared to KRas;Atg5 fl/fl tumors using gene set
Supplementary Figure 1 IL-27 IL
 Tim-3 Supplementary Figure 1 Tc0 49.5 0.6 Tc1 63.5 0.84 Un 49.8 0.16 35.5 0.16 10 4 61.2 5.53 10 3 64.5 5.66 10 2 10 1 10 0 31 2.22 10 0 10 1 10 2 10 3 10 4 IL-10 28.2 1.69 IL-27 Supplementary Figure 1.
Tim-3 Supplementary Figure 1 Tc0 49.5 0.6 Tc1 63.5 0.84 Un 49.8 0.16 35.5 0.16 10 4 61.2 5.53 10 3 64.5 5.66 10 2 10 1 10 0 31 2.22 10 0 10 1 10 2 10 3 10 4 IL-10 28.2 1.69 IL-27 Supplementary Figure 1.
Supplemental Figure 1
 Supplemental Figure 1 1a 1c PD-1 MFI fold change 6 5 4 3 2 1 IL-1α IL-2 IL-4 IL-6 IL-1 IL-12 IL-13 IL-15 IL-17 IL-18 IL-21 IL-23 IFN-α Mut Human PD-1 promoter SBE-D 5 -GTCTG- -1.2kb SBE-P -CAGAC- -1.kb
Supplemental Figure 1 1a 1c PD-1 MFI fold change 6 5 4 3 2 1 IL-1α IL-2 IL-4 IL-6 IL-1 IL-12 IL-13 IL-15 IL-17 IL-18 IL-21 IL-23 IFN-α Mut Human PD-1 promoter SBE-D 5 -GTCTG- -1.2kb SBE-P -CAGAC- -1.kb
Supplementary Figure 1. Efficiency of Mll4 deletion and its effect on T cell populations in the periphery. Nature Immunology: doi: /ni.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Efficiency of Mll4 deletion and its effect on T cell populations in the periphery. Expression of Mll4 floxed alleles (16-19) in naive CD4 + T cells isolated from lymph nodes and
Supplementary Figure 1 Efficiency of Mll4 deletion and its effect on T cell populations in the periphery. Expression of Mll4 floxed alleles (16-19) in naive CD4 + T cells isolated from lymph nodes and
Cell isolation. Spleen and lymph nodes (axillary, inguinal) were removed from mice
 Supplementary Methods: Cell isolation. Spleen and lymph nodes (axillary, inguinal) were removed from mice and gently meshed in DMEM containing 10% FBS to prepare for single cell suspensions. CD4 + CD25
Supplementary Methods: Cell isolation. Spleen and lymph nodes (axillary, inguinal) were removed from mice and gently meshed in DMEM containing 10% FBS to prepare for single cell suspensions. CD4 + CD25
Characteristic repartition of monocyte subsets as a diagnostic signature of chronic myelomonocytic leukemia
 Characteristic repartition of monocyte subsets as a diagnostic signature of chronic myelomonocytic leukemia Dorothée Selimoglu-Buet, 1,2,3 Orianne Wagner-Ballon, 4,5 Véronique Saada, 2 Valérie Bardet,
Characteristic repartition of monocyte subsets as a diagnostic signature of chronic myelomonocytic leukemia Dorothée Selimoglu-Buet, 1,2,3 Orianne Wagner-Ballon, 4,5 Véronique Saada, 2 Valérie Bardet,
D CD8 T cell number (x10 6 )
 IFNγ Supplemental Figure 1. CD T cell number (x1 6 ) 18 15 1 9 6 3 CD CD T cells CD6L C CD5 CD T cells CD6L D CD8 T cell number (x1 6 ) 1 8 6 E CD CD8 T cells CD6L F Log(1)CFU/g Feces 1 8 6 p
IFNγ Supplemental Figure 1. CD T cell number (x1 6 ) 18 15 1 9 6 3 CD CD T cells CD6L C CD5 CD T cells CD6L D CD8 T cell number (x1 6 ) 1 8 6 E CD CD8 T cells CD6L F Log(1)CFU/g Feces 1 8 6 p
RNA-Seq Preparation Comparision Summary: Lexogen, Standard, NEB
 RNA-Seq Preparation Comparision Summary: Lexogen, Standard, NEB CSF-NGS January 22, 214 Contents 1 Introduction 1 2 Experimental Details 1 3 Results And Discussion 1 3.1 ERCC spike ins............................................
RNA-Seq Preparation Comparision Summary: Lexogen, Standard, NEB CSF-NGS January 22, 214 Contents 1 Introduction 1 2 Experimental Details 1 3 Results And Discussion 1 3.1 ERCC spike ins............................................
Supplementary Table 1 Clinicopathological characteristics of 35 patients with CRCs
 Supplementary Table Clinicopathological characteristics of 35 patients with CRCs Characteristics Type-A CRC Type-B CRC P value Sex Male / Female 9 / / 8.5 Age (years) Median (range) 6. (9 86) 6.5 (9 76).95
Supplementary Table Clinicopathological characteristics of 35 patients with CRCs Characteristics Type-A CRC Type-B CRC P value Sex Male / Female 9 / / 8.5 Age (years) Median (range) 6. (9 86) 6.5 (9 76).95
Simple, rapid, and reliable RNA sequencing
 Simple, rapid, and reliable RNA sequencing RNA sequencing applications RNA sequencing provides fundamental insights into how genomes are organized and regulated, giving us valuable information about the
Simple, rapid, and reliable RNA sequencing RNA sequencing applications RNA sequencing provides fundamental insights into how genomes are organized and regulated, giving us valuable information about the
MATERIALS AND METHODS. Neutralizing antibodies specific to mouse Dll1, Dll4, J1 and J2 were prepared as described. 1,2 All
 MATERIALS AND METHODS Antibodies (Abs), flow cytometry analysis and cell lines Neutralizing antibodies specific to mouse Dll1, Dll4, J1 and J2 were prepared as described. 1,2 All other antibodies used
MATERIALS AND METHODS Antibodies (Abs), flow cytometry analysis and cell lines Neutralizing antibodies specific to mouse Dll1, Dll4, J1 and J2 were prepared as described. 1,2 All other antibodies used
SUPPLEMENT Supplementary Figure 1: (A) (B)
 SUPPLEMENT Supplementary Figure 1: CD4 + naïve effector T cells (CD4 effector) were labeled with CFSE, stimulated with α-cd2/cd3/cd28 coated beads (at 2 beads/cell) and cultured alone or cocultured with
SUPPLEMENT Supplementary Figure 1: CD4 + naïve effector T cells (CD4 effector) were labeled with CFSE, stimulated with α-cd2/cd3/cd28 coated beads (at 2 beads/cell) and cultured alone or cocultured with
Nature Immunology: doi: /ni Supplementary Figure 1. Transcriptional program of the TE and MP CD8 + T cell subsets.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Transcriptional program of the TE and MP CD8 + T cell subsets. (a) Comparison of gene expression of TE and MP CD8 + T cell subsets by microarray. Genes that are 1.5-fold upregulated
Supplementary Figure 1 Transcriptional program of the TE and MP CD8 + T cell subsets. (a) Comparison of gene expression of TE and MP CD8 + T cell subsets by microarray. Genes that are 1.5-fold upregulated
Ambient temperature regulated flowering time
 Ambient temperature regulated flowering time Applications of RNAseq RNA- seq course: The power of RNA-seq June 7 th, 2013; Richard Immink Overview Introduction: Biological research question/hypothesis
Ambient temperature regulated flowering time Applications of RNAseq RNA- seq course: The power of RNA-seq June 7 th, 2013; Richard Immink Overview Introduction: Biological research question/hypothesis
AbSeq on the BD Rhapsody system: Exploration of single-cell gene regulation by simultaneous digital mrna and protein quantification
 BD AbSeq on the BD Rhapsody system: Exploration of single-cell gene regulation by simultaneous digital mrna and protein quantification Overview of BD AbSeq antibody-oligonucleotide conjugates. High-throughput
BD AbSeq on the BD Rhapsody system: Exploration of single-cell gene regulation by simultaneous digital mrna and protein quantification Overview of BD AbSeq antibody-oligonucleotide conjugates. High-throughput
Analysis of Massively Parallel Sequencing Data Application of Illumina Sequencing to the Genetics of Human Cancers
 Analysis of Massively Parallel Sequencing Data Application of Illumina Sequencing to the Genetics of Human Cancers Gordon Blackshields Senior Bioinformatician Source BioScience 1 To Cancer Genetics Studies
Analysis of Massively Parallel Sequencing Data Application of Illumina Sequencing to the Genetics of Human Cancers Gordon Blackshields Senior Bioinformatician Source BioScience 1 To Cancer Genetics Studies
Supplementary Figure 1. IL-12 serum levels and frequency of subsets in FL patients. (A) IL-12
 1 Supplementary Data Figure legends Supplementary Figure 1. IL-12 serum levels and frequency of subsets in FL patients. (A) IL-12 serum levels measured by multiplex ELISA (Luminex) in FL patients before
1 Supplementary Data Figure legends Supplementary Figure 1. IL-12 serum levels and frequency of subsets in FL patients. (A) IL-12 serum levels measured by multiplex ELISA (Luminex) in FL patients before
ESCs were lysed with Trizol reagent (Life technologies) and RNA was extracted according to
 Supplemental Methods RNA-seq ESCs were lysed with Trizol reagent (Life technologies) and RNA was extracted according to the manufacturer's instructions. RNAse free DNaseI (Sigma) was used to eliminate
Supplemental Methods RNA-seq ESCs were lysed with Trizol reagent (Life technologies) and RNA was extracted according to the manufacturer's instructions. RNAse free DNaseI (Sigma) was used to eliminate
Supplementary Material for IPred - Integrating Ab Initio and Evidence Based Gene Predictions to Improve Prediction Accuracy
 1 SYSTEM REQUIREMENTS 1 Supplementary Material for IPred - Integrating Ab Initio and Evidence Based Gene Predictions to Improve Prediction Accuracy Franziska Zickmann and Bernhard Y. Renard Research Group
1 SYSTEM REQUIREMENTS 1 Supplementary Material for IPred - Integrating Ab Initio and Evidence Based Gene Predictions to Improve Prediction Accuracy Franziska Zickmann and Bernhard Y. Renard Research Group
Transcript-indexed ATAC-seq for immune profiling
 Transcript-indexed ATAC-seq for immune profiling Technical Journal Club 22 nd of May 2018 Christina Müller Nature Methods, Vol.10 No.12, 2013 Nature Biotechnology, Vol.32 No.7, 2014 Nature Medicine, Vol.24,
Transcript-indexed ATAC-seq for immune profiling Technical Journal Club 22 nd of May 2018 Christina Müller Nature Methods, Vol.10 No.12, 2013 Nature Biotechnology, Vol.32 No.7, 2014 Nature Medicine, Vol.24,
Supplementary Online Content
 Supplementary Online Content Fumagalli D, Venet D, Ignatiadis M, et al. RNA Sequencing to predict response to neoadjuvant anti-her2 therapy: a secondary analysis of the NeoALTTO randomized clinical trial.
Supplementary Online Content Fumagalli D, Venet D, Ignatiadis M, et al. RNA Sequencing to predict response to neoadjuvant anti-her2 therapy: a secondary analysis of the NeoALTTO randomized clinical trial.
1,000 in silico simulated alpha, beta, gamma and delta TCR repertoires were created.
 938 939 940 941 942 Figure S1 Schematic of the in silico TCRminer and MiXCR validation. 1,000 in silico simulated alpha, beta, gamma and delta TCR repertoires were created. Then, 100,000 simulated 80 bp
938 939 940 941 942 Figure S1 Schematic of the in silico TCRminer and MiXCR validation. 1,000 in silico simulated alpha, beta, gamma and delta TCR repertoires were created. Then, 100,000 simulated 80 bp
Supplemental Information. T Cells Enhance Autoimmunity by Restraining Regulatory T Cell Responses via an Interleukin-23-Dependent Mechanism
 Immunity, Volume 33 Supplemental Information T Cells Enhance Autoimmunity by Restraining Regulatory T Cell Responses via an Interleukin-23-Dependent Mechanism Franziska Petermann, Veit Rothhammer, Malte
Immunity, Volume 33 Supplemental Information T Cells Enhance Autoimmunity by Restraining Regulatory T Cell Responses via an Interleukin-23-Dependent Mechanism Franziska Petermann, Veit Rothhammer, Malte
Supplementary Figure 1: High-throughput profiling of survival after exposure to - radiation. (a) Cells were plated in at least 7 wells in a 384-well
 Supplementary Figure 1: High-throughput profiling of survival after exposure to - radiation. (a) Cells were plated in at least 7 wells in a 384-well plate at cell densities ranging from 25-225 cells in
Supplementary Figure 1: High-throughput profiling of survival after exposure to - radiation. (a) Cells were plated in at least 7 wells in a 384-well plate at cell densities ranging from 25-225 cells in
Selective depletion of abundant RNAs to enable transcriptome analysis of lowinput and highly-degraded RNA from FFPE breast cancer samples
 DNA CLONING DNA AMPLIFICATION & PCR EPIGENETICS RNA ANALYSIS Selective depletion of abundant RNAs to enable transcriptome analysis of lowinput and highly-degraded RNA from FFPE breast cancer samples LIBRARY
DNA CLONING DNA AMPLIFICATION & PCR EPIGENETICS RNA ANALYSIS Selective depletion of abundant RNAs to enable transcriptome analysis of lowinput and highly-degraded RNA from FFPE breast cancer samples LIBRARY
Supplementary Figure 1. Characterization of basophils after reconstitution of SCID mice
 Supplementary figure legends Supplementary Figure 1. Characterization of after reconstitution of SCID mice with CD4 + CD62L + T cells. (A-C) SCID mice (n = 6 / group) were reconstituted with 2 x 1 6 CD4
Supplementary figure legends Supplementary Figure 1. Characterization of after reconstitution of SCID mice with CD4 + CD62L + T cells. (A-C) SCID mice (n = 6 / group) were reconstituted with 2 x 1 6 CD4
sequences of a styx mutant reveals a T to A transversion in the donor splice site of intron 5
 sfigure 1 Styx mutant mice recapitulate the phenotype of SHIP -/- mice. (A) Analysis of the genomic sequences of a styx mutant reveals a T to A transversion in the donor splice site of intron 5 (GTAAC
sfigure 1 Styx mutant mice recapitulate the phenotype of SHIP -/- mice. (A) Analysis of the genomic sequences of a styx mutant reveals a T to A transversion in the donor splice site of intron 5 (GTAAC
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 1.138/ncb3355 a S1A8 + cells/ total.1.8.6.4.2 b S1A8/?-Actin c % T-cell proliferation 3 25 2 15 1 5 T cells Supplementary Figure 1 Inter-tumoral heterogeneity of MDSC accumulation in mammary tumor
DOI: 1.138/ncb3355 a S1A8 + cells/ total.1.8.6.4.2 b S1A8/?-Actin c % T-cell proliferation 3 25 2 15 1 5 T cells Supplementary Figure 1 Inter-tumoral heterogeneity of MDSC accumulation in mammary tumor
Suppl Video: Tumor cells (green) and monocytes (white) are seeded on a confluent endothelial
 Supplementary Information Häuselmann et al. Monocyte induction of E-selectin-mediated endothelial activation releases VE-cadherin junctions to promote tumor cell extravasation in the metastasis cascade
Supplementary Information Häuselmann et al. Monocyte induction of E-selectin-mediated endothelial activation releases VE-cadherin junctions to promote tumor cell extravasation in the metastasis cascade
Cellecta Overview. Started Operations in 2007 Headquarters: Mountain View, CA
 Cellecta Overview Started Operations in 2007 Headquarters: Mountain View, CA Focus: Development of flexible, scalable, and broadly parallel genetic screening assays to expedite the discovery and characterization
Cellecta Overview Started Operations in 2007 Headquarters: Mountain View, CA Focus: Development of flexible, scalable, and broadly parallel genetic screening assays to expedite the discovery and characterization
Molecular Profiling of Tumor Microenvironment Alex Chenchik, Ph.D. Cellecta, Inc.
 Molecular Profiling of Tumor Microenvironment Alex Chenchik, Ph.D. Cellecta, Inc. Cellecta, Inc. Founded: April 2006 Headquarters: Mountain View, CA 12 SBIR Grants Custom Service Provider for Functional
Molecular Profiling of Tumor Microenvironment Alex Chenchik, Ph.D. Cellecta, Inc. Cellecta, Inc. Founded: April 2006 Headquarters: Mountain View, CA 12 SBIR Grants Custom Service Provider for Functional
Supplementary Data Table of Contents:
 Supplementary Data Table of Contents: - Supplementary Methods - Supplementary Figures S1(A-B) - Supplementary Figures S2 (A-B) - Supplementary Figures S3 - Supplementary Figures S4(A-B) - Supplementary
Supplementary Data Table of Contents: - Supplementary Methods - Supplementary Figures S1(A-B) - Supplementary Figures S2 (A-B) - Supplementary Figures S3 - Supplementary Figures S4(A-B) - Supplementary
Iso-Seq Method Updates and Target Enrichment Without Amplification for SMRT Sequencing
 Iso-Seq Method Updates and Target Enrichment Without Amplification for SMRT Sequencing PacBio Americas User Group Meeting Sample Prep Workshop June.27.2017 Tyson Clark, Ph.D. For Research Use Only. Not
Iso-Seq Method Updates and Target Enrichment Without Amplification for SMRT Sequencing PacBio Americas User Group Meeting Sample Prep Workshop June.27.2017 Tyson Clark, Ph.D. For Research Use Only. Not
Supplementary Figure S1: Alignment of CD28H. (a) Alignment of human CD28H with other known B7 receptors. (b) Alignment of CD28H orthologs.
 Supplementary Figure S1: Alignment of CD28H. (a) Alignment of human CD28H with other known B7 receptors. (b) Alignment of CD28H orthologs. Predicted CD28H protein sequences from human, chimpanzee (pan
Supplementary Figure S1: Alignment of CD28H. (a) Alignment of human CD28H with other known B7 receptors. (b) Alignment of CD28H orthologs. Predicted CD28H protein sequences from human, chimpanzee (pan
High Throughput TruSeq Stranded mrna Library Construction on the Biomek FX P
 High Throughput TruSeq Stranded mrna Library Construction on the Biomek FX P Zach Smith and Scott D. Michaels The Center for Genomics and Bioinformatics Indiana University Bloomington, IN USA Mary Blair
High Throughput TruSeq Stranded mrna Library Construction on the Biomek FX P Zach Smith and Scott D. Michaels The Center for Genomics and Bioinformatics Indiana University Bloomington, IN USA Mary Blair
Supplemental Information. Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor Controls. Monocyte Differentiation. into Dendritic Cells versus Macrophages
 Immunity, Volume 47 Supplemental Information Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor Controls Monocyte Differentiation into Dendritic Cells versus Macrophages Christel Goudot, Alice Coillard, Alexandra-Chloé Villani,
Immunity, Volume 47 Supplemental Information Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor Controls Monocyte Differentiation into Dendritic Cells versus Macrophages Christel Goudot, Alice Coillard, Alexandra-Chloé Villani,
m 6 A mrna methylation regulates AKT activity to promote the proliferation and tumorigenicity of endometrial cancer
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Articles https://doi.org/10.1038/s41556-018-0174-4 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. m 6 A mrna methylation regulates AKT activity to promote the proliferation
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Articles https://doi.org/10.1038/s41556-018-0174-4 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. m 6 A mrna methylation regulates AKT activity to promote the proliferation
ncounter Assay Automated Process Immobilize and align reporter for image collecting and barcode counting ncounter Prep Station
 ncounter Assay ncounter Prep Station Automated Process Hybridize Reporter to RNA Remove excess reporters Bind reporter to surface Immobilize and align reporter Image surface Count codes Immobilize and
ncounter Assay ncounter Prep Station Automated Process Hybridize Reporter to RNA Remove excess reporters Bind reporter to surface Immobilize and align reporter Image surface Count codes Immobilize and
Human Innate Lymphoid Cells: crosstalk with CD4 + regulatory T cells and role in Type 1 Diabetes
 Joint Lab Meeting 03/03/2015 Human Innate Lymphoid Cells: crosstalk with CD4 + regulatory T cells and role in Type 1 Diabetes Caroline Raffin Bluestone Lab ILCs: Definition - Common lymphoid progenitor
Joint Lab Meeting 03/03/2015 Human Innate Lymphoid Cells: crosstalk with CD4 + regulatory T cells and role in Type 1 Diabetes Caroline Raffin Bluestone Lab ILCs: Definition - Common lymphoid progenitor
Fluorochrome Panel 1 Panel 2 Panel 3 Panel 4 Panel 5 CTLA-4 CTLA-4 CD15 CD3 FITC. Bio) PD-1 (MIH4, BD) ICOS (C398.4A, Biolegend) PD-L1 (MIH1, BD)
 Additional file : Table S. Antibodies used for panel stain to identify peripheral immune cell subsets. Panel : PD- signaling; Panel : CD + T cells, CD + T cells, B cells; Panel : Tregs; Panel :, -T, cdc,
Additional file : Table S. Antibodies used for panel stain to identify peripheral immune cell subsets. Panel : PD- signaling; Panel : CD + T cells, CD + T cells, B cells; Panel : Tregs; Panel :, -T, cdc,
Supplementary Figure 1. Example of gating strategy
 Supplementary Figure 1. Example of gating strategy Legend Supplementary Figure 1: First, gating is performed to include only single cells (singlets) (A) and CD3+ cells (B). After gating on the lymphocyte
Supplementary Figure 1. Example of gating strategy Legend Supplementary Figure 1: First, gating is performed to include only single cells (singlets) (A) and CD3+ cells (B). After gating on the lymphocyte
Supplemental Materials for. Effects of sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor 1 phosphorylation in response to. FTY720 during neuroinflammation
 Supplemental Materials for Effects of sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor 1 phosphorylation in response to FTY7 during neuroinflammation This file includes: Supplemental Table 1. EAE clinical parameters of
Supplemental Materials for Effects of sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor 1 phosphorylation in response to FTY7 during neuroinflammation This file includes: Supplemental Table 1. EAE clinical parameters of
SUPPLEMENTARY APPENDIX
 SUPPLEMENTARY APPENDIX 1) Supplemental Figure 1. Histopathologic Characteristics of the Tumors in the Discovery Cohort 2) Supplemental Figure 2. Incorporation of Normal Epidermal Melanocytic Signature
SUPPLEMENTARY APPENDIX 1) Supplemental Figure 1. Histopathologic Characteristics of the Tumors in the Discovery Cohort 2) Supplemental Figure 2. Incorporation of Normal Epidermal Melanocytic Signature
Nature Immunology: doi: /ni Supplementary Figure 1. Huwe1 has high expression in HSCs and is necessary for quiescence.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Huwe1 has high expression in HSCs and is necessary for quiescence. (a) Heat map visualizing expression of genes with a known function in ubiquitin-mediated proteolysis (KEGG: Ubiquitin
Supplementary Figure 1 Huwe1 has high expression in HSCs and is necessary for quiescence. (a) Heat map visualizing expression of genes with a known function in ubiquitin-mediated proteolysis (KEGG: Ubiquitin
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Expression of apoptosis-related genes in tumor T reg cells. (a) Identification of FOXP3 T reg cells by FACS. CD45 + cells were gated as enriched lymphoid cell populations with low-granularity.
Supplementary Figure 1 Expression of apoptosis-related genes in tumor T reg cells. (a) Identification of FOXP3 T reg cells by FACS. CD45 + cells were gated as enriched lymphoid cell populations with low-granularity.
Supplementary Figure 1. SA-β-Gal positive senescent cells in various cancer tissues. Representative frozen sections of breast, thyroid, colon and
 Supplementary Figure 1. SA-β-Gal positive senescent cells in various cancer tissues. Representative frozen sections of breast, thyroid, colon and stomach cancer were stained with SA-β-Gal and nuclear fast
Supplementary Figure 1. SA-β-Gal positive senescent cells in various cancer tissues. Representative frozen sections of breast, thyroid, colon and stomach cancer were stained with SA-β-Gal and nuclear fast
Supplemental Figure 1. Signature gene expression in in vitro differentiated Th0, Th1, Th2, Th17 and Treg cells. (A) Naïve CD4 + T cells were cultured
 Supplemental Figure 1. Signature gene expression in in vitro differentiated Th0, Th1, Th2, Th17 and Treg cells. (A) Naïve CD4 + T cells were cultured under Th0, Th1, Th2, Th17, and Treg conditions. mrna
Supplemental Figure 1. Signature gene expression in in vitro differentiated Th0, Th1, Th2, Th17 and Treg cells. (A) Naïve CD4 + T cells were cultured under Th0, Th1, Th2, Th17, and Treg conditions. mrna
Transcriptome Analysis
 Transcriptome Analysis Data Preprocessing Sample Preparation Illumina Sequencing Demultiplexing Raw FastQ Reference Genome (fasta) Reference Annotation (GTF) Reference Genome Analysis Tophat Accepted hits
Transcriptome Analysis Data Preprocessing Sample Preparation Illumina Sequencing Demultiplexing Raw FastQ Reference Genome (fasta) Reference Annotation (GTF) Reference Genome Analysis Tophat Accepted hits
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure 1! a! b! Nfatc1!! Nfatc1"! P1! P2! pa1! pa2! ex1! ex2! exons 3-9! ex1! ex11!!" #" Nfatc1A!!" Nfatc1B! #"!" Nfatc1C! #" DN1! DN2! DN1!!A! #A!!B! #B!!C! #C!!A!
Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure 1! a! b! Nfatc1!! Nfatc1"! P1! P2! pa1! pa2! ex1! ex2! exons 3-9! ex1! ex11!!" #" Nfatc1A!!" Nfatc1B! #"!" Nfatc1C! #" DN1! DN2! DN1!!A! #A!!B! #B!!C! #C!!A!
The autoimmune disease-associated PTPN22 variant promotes calpain-mediated Lyp/Pep
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION The autoimmune disease-associated PTPN22 variant promotes calpain-mediated Lyp/Pep degradation associated with lymphocyte and dendritic cell hyperresponsiveness Jinyi Zhang, Naima
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION The autoimmune disease-associated PTPN22 variant promotes calpain-mediated Lyp/Pep degradation associated with lymphocyte and dendritic cell hyperresponsiveness Jinyi Zhang, Naima
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Identification of IFN-γ-producing CD8 + and CD4 + T cells with naive phenotype by alternative gating and sample-processing strategies. a. Contour 5% probability plots show definition
Supplementary Figure 1 Identification of IFN-γ-producing CD8 + and CD4 + T cells with naive phenotype by alternative gating and sample-processing strategies. a. Contour 5% probability plots show definition
Nature Immunology: doi: /ni Supplementary Figure 1. Cellularity of leukocytes and their progenitors in naive wild-type and Spp1 / mice.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Cellularity of leukocytes and their progenitors in naive wild-type and Spp1 / mice. (a, b) Gating strategies for differentiated cells including PMN (CD11b + Ly6G hi and CD11b + Ly6G
Supplementary Figure 1 Cellularity of leukocytes and their progenitors in naive wild-type and Spp1 / mice. (a, b) Gating strategies for differentiated cells including PMN (CD11b + Ly6G hi and CD11b + Ly6G
Supplementary Figure 1 a
 Supplementary Figure 1 a b d c Supplementary Figure 1. Poor sensitivity for mutation detection using established single-cell RNA-sequencing methods. (a) Representative bioanalyzer trace showing expected
Supplementary Figure 1 a b d c Supplementary Figure 1. Poor sensitivity for mutation detection using established single-cell RNA-sequencing methods. (a) Representative bioanalyzer trace showing expected
In vitro human regulatory T cell suppression assay
 Human CD4 + CD25 + regulatory T cell isolation, in vitro suppression assay and analysis In vitro human regulatory T cell suppression assay Introduction Regulatory T (Treg) cells are a subpopulation of
Human CD4 + CD25 + regulatory T cell isolation, in vitro suppression assay and analysis In vitro human regulatory T cell suppression assay Introduction Regulatory T (Treg) cells are a subpopulation of
Whole liver transcriptome analysis for the metabolic adaptation of dairy cows
 Whole liver transcriptome analysis for the metabolic adaptation of dairy cows Ngoc-Thuy Ha Animal Breeding and Genetics Group Department of Animal Sciences Georg-August-University Goettingen, Germany 1
Whole liver transcriptome analysis for the metabolic adaptation of dairy cows Ngoc-Thuy Ha Animal Breeding and Genetics Group Department of Animal Sciences Georg-August-University Goettingen, Germany 1
Supplemental Figures Supplemental Figure 1:
 Supplemental Figures Supplemental Figure 1: Representative FACS data showing Concurrent Brain cell type Acquisition using either Percoll PLUS (top row) or myelin removal beads (bottom two rows). Debris
Supplemental Figures Supplemental Figure 1: Representative FACS data showing Concurrent Brain cell type Acquisition using either Percoll PLUS (top row) or myelin removal beads (bottom two rows). Debris
Supplementary Figure S1. PTPN2 levels are not altered in proliferating CD8+ T cells. Lymph node (LN) CD8+ T cells from C57BL/6 mice were stained with
 Supplementary Figure S1. PTPN2 levels are not altered in proliferating CD8+ T cells. Lymph node (LN) CD8+ T cells from C57BL/6 mice were stained with CFSE and stimulated with plate-bound α-cd3ε (10µg/ml)
Supplementary Figure S1. PTPN2 levels are not altered in proliferating CD8+ T cells. Lymph node (LN) CD8+ T cells from C57BL/6 mice were stained with CFSE and stimulated with plate-bound α-cd3ε (10µg/ml)
Supplementary Figure 1. Using DNA barcode-labeled MHC multimers to generate TCR fingerprints
 Supplementary Figure 1 Using DNA barcode-labeled MHC multimers to generate TCR fingerprints (a) Schematic overview of the workflow behind a TCR fingerprint. Each peptide position of the original peptide
Supplementary Figure 1 Using DNA barcode-labeled MHC multimers to generate TCR fingerprints (a) Schematic overview of the workflow behind a TCR fingerprint. Each peptide position of the original peptide
Supplemental Figures: Supplemental Figure 1
 Supplemental Figures: Supplemental Figure 1 Suppl. Figure 1. BM-DC infection with H. pylori does not induce cytotoxicity and treatment of BM-DCs with H. pylori sonicate, but not heat-inactivated bacteria,
Supplemental Figures: Supplemental Figure 1 Suppl. Figure 1. BM-DC infection with H. pylori does not induce cytotoxicity and treatment of BM-DCs with H. pylori sonicate, but not heat-inactivated bacteria,
Eosinophils are required. for the maintenance of plasma cells in the bone marrow
 Eosinophils are required for the maintenance of plasma cells in the bone marrow Van Trung Chu, Anja Fröhlich, Gudrun Steinhauser, Tobias Scheel, Toralf Roch, Simon Fillatreau, James J. Lee, Max Löhning
Eosinophils are required for the maintenance of plasma cells in the bone marrow Van Trung Chu, Anja Fröhlich, Gudrun Steinhauser, Tobias Scheel, Toralf Roch, Simon Fillatreau, James J. Lee, Max Löhning
Supplemental Figure S1. RANK expression on human lung cancer cells.
 Supplemental Figure S1. RANK expression on human lung cancer cells. (A) Incidence and H-Scores of RANK expression determined from IHC in the indicated primary lung cancer subgroups. The overall expression
Supplemental Figure S1. RANK expression on human lung cancer cells. (A) Incidence and H-Scores of RANK expression determined from IHC in the indicated primary lung cancer subgroups. The overall expression
Obstacles and challenges in the analysis of microrna sequencing data
 Obstacles and challenges in the analysis of microrna sequencing data (mirna-seq) David Humphreys Genomics core Dr Victor Chang AC 1936-1991, Pioneering Cardiothoracic Surgeon and Humanitarian The ABCs
Obstacles and challenges in the analysis of microrna sequencing data (mirna-seq) David Humphreys Genomics core Dr Victor Chang AC 1936-1991, Pioneering Cardiothoracic Surgeon and Humanitarian The ABCs
HEK293FT cells were transiently transfected with reporters, N3-ICD construct and
 Supplementary Information Luciferase reporter assay HEK293FT cells were transiently transfected with reporters, N3-ICD construct and increased amounts of wild type or kinase inactive EGFR. Transfections
Supplementary Information Luciferase reporter assay HEK293FT cells were transiently transfected with reporters, N3-ICD construct and increased amounts of wild type or kinase inactive EGFR. Transfections
Lecture 8 Understanding Transcription RNA-seq analysis. Foundations of Computational Systems Biology David K. Gifford
 Lecture 8 Understanding Transcription RNA-seq analysis Foundations of Computational Systems Biology David K. Gifford 1 Lecture 8 RNA-seq Analysis RNA-seq principles How can we characterize mrna isoform
Lecture 8 Understanding Transcription RNA-seq analysis Foundations of Computational Systems Biology David K. Gifford 1 Lecture 8 RNA-seq Analysis RNA-seq principles How can we characterize mrna isoform
Nature Immunology: doi: /ni Supplementary Figure 1. Gene expression profile of CD4 + T cells and CTL responses in Bcl6-deficient mice.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Gene expression profile of CD4 + T cells and CTL responses in Bcl6-deficient mice. (a) Gene expression profile in the resting CD4 + T cells were analyzed by an Affymetrix microarray
Supplementary Figure 1 Gene expression profile of CD4 + T cells and CTL responses in Bcl6-deficient mice. (a) Gene expression profile in the resting CD4 + T cells were analyzed by an Affymetrix microarray
Nature Immunology: doi: /ni Supplementary Figure 1. Characteristics of SEs in T reg and T conv cells.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Characteristics of SEs in T reg and T conv cells. (a) Patterns of indicated transcription factor-binding at SEs and surrounding regions in T reg and T conv cells. Average normalized
Supplementary Figure 1 Characteristics of SEs in T reg and T conv cells. (a) Patterns of indicated transcription factor-binding at SEs and surrounding regions in T reg and T conv cells. Average normalized
Supplementary Appendix
 Supplementary Appendix This appendix has been provided by the authors to give readers additional information about their work. Supplement to: Choi YL, Soda M, Yamashita Y, et al. EML4-ALK mutations in
Supplementary Appendix This appendix has been provided by the authors to give readers additional information about their work. Supplement to: Choi YL, Soda M, Yamashita Y, et al. EML4-ALK mutations in
Emerging Tissue and Serum Markers
 Emerging Tissue and Serum Markers for Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors Kyong Hwa Park MD, PhD Medical Oncology Korea University College of Medicine Contents Immune checkpoint inhibitors in clinical practice
Emerging Tissue and Serum Markers for Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors Kyong Hwa Park MD, PhD Medical Oncology Korea University College of Medicine Contents Immune checkpoint inhibitors in clinical practice
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES
 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES Supplementary Figure 1: Chemokine receptor expression profiles of CCR6 + and CCR6 - CD4 + IL-17A +/ex and Treg cells. Quantitative PCR analysis of chemokine receptor transcript abundance
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES Supplementary Figure 1: Chemokine receptor expression profiles of CCR6 + and CCR6 - CD4 + IL-17A +/ex and Treg cells. Quantitative PCR analysis of chemokine receptor transcript abundance
Supplemental Table 1. Primer sequences for transcript analysis
 Supplemental Table 1. Primer sequences for transcript analysis Primer Sequence (5 3 ) Primer Sequence (5 3 ) Mmp2 Forward CCCGTGTGGCCCTC Mmp15 Forward CGGGGCTGGCT Reverse GCTCTCCCGGTTTC Reverse CCTGGTGTGCCTGCTC
Supplemental Table 1. Primer sequences for transcript analysis Primer Sequence (5 3 ) Primer Sequence (5 3 ) Mmp2 Forward CCCGTGTGGCCCTC Mmp15 Forward CGGGGCTGGCT Reverse GCTCTCCCGGTTTC Reverse CCTGGTGTGCCTGCTC
Arabidopsis thaliana small RNA Sequencing. Report
 Arabidopsis thaliana small RNA Sequencing Report September 2015 Project Information Client Name Client Company / Institution Macrogen Order Number Order ID Species Arabidopsis thaliana Reference UCSC hg19
Arabidopsis thaliana small RNA Sequencing Report September 2015 Project Information Client Name Client Company / Institution Macrogen Order Number Order ID Species Arabidopsis thaliana Reference UCSC hg19
Nature Medicine doi: /nm.3957
 Supplementary Fig. 1. p38 alternative activation, IL-21 expression, and T helper cell transcription factors in PDAC tissue. (a) Tissue microarrays of pancreatic tissue from 192 patients with pancreatic
Supplementary Fig. 1. p38 alternative activation, IL-21 expression, and T helper cell transcription factors in PDAC tissue. (a) Tissue microarrays of pancreatic tissue from 192 patients with pancreatic
Bayesian Inference for Single-cell ClUstering and ImpuTing (BISCUIT) Elham Azizi
 Bayesian Inference for Single-cell ClUstering and ImpuTing (BISCUIT) Elham Azizi BioC 2017: Where Software and Biology Connect Profiling Tumor-Immune Ecosystem in Breast Cancer Immunotherapy treatments
Bayesian Inference for Single-cell ClUstering and ImpuTing (BISCUIT) Elham Azizi BioC 2017: Where Software and Biology Connect Profiling Tumor-Immune Ecosystem in Breast Cancer Immunotherapy treatments
Supplementary Figure 1. Double-staining immunofluorescence analysis of invasive colon and breast cancers. Specimens from invasive ductal breast
 Supplementary Figure 1. Double-staining immunofluorescence analysis of invasive colon and breast cancers. Specimens from invasive ductal breast carcinoma (a) and colon adenocarcinoma (b) were staining
Supplementary Figure 1. Double-staining immunofluorescence analysis of invasive colon and breast cancers. Specimens from invasive ductal breast carcinoma (a) and colon adenocarcinoma (b) were staining
Single-strand DNA library preparation improves sequencing of formalin-fixed and paraffin-embedded (FFPE) cancer DNA
 www.impactjournals.com/oncotarget/ Oncotarget, Supplementary Materials 2016 Single-strand DNA library preparation improves sequencing of formalin-fixed and paraffin-embedded (FFPE) DNA Supplementary Materials
www.impactjournals.com/oncotarget/ Oncotarget, Supplementary Materials 2016 Single-strand DNA library preparation improves sequencing of formalin-fixed and paraffin-embedded (FFPE) DNA Supplementary Materials
Title: Human breast cancer associated fibroblasts exhibit subtype specific gene expression profiles
 Author's response to reviews Title: Human breast cancer associated fibroblasts exhibit subtype specific gene expression profiles Authors: Julia Tchou (julia.tchou@uphs.upenn.edu) Andrew V Kossenkov (akossenkov@wistar.org)
Author's response to reviews Title: Human breast cancer associated fibroblasts exhibit subtype specific gene expression profiles Authors: Julia Tchou (julia.tchou@uphs.upenn.edu) Andrew V Kossenkov (akossenkov@wistar.org)
Supplementary Figure 1. mrna expression of chitinase and chitinase-like protein in splenic immune cells. Each splenic immune cell population was
 Supplementary Figure 1. mrna expression of chitinase and chitinase-like protein in splenic immune cells. Each splenic immune cell population was sorted by FACS. Surface markers for sorting were CD11c +
Supplementary Figure 1. mrna expression of chitinase and chitinase-like protein in splenic immune cells. Each splenic immune cell population was sorted by FACS. Surface markers for sorting were CD11c +
Online Appendix Material and Methods: Pancreatic RNA isolation and quantitative real-time (q)rt-pcr. Mice were fasted overnight and killed 1 hour (h)
 Online Appendix Material and Methods: Pancreatic RNA isolation and quantitative real-time (q)rt-pcr. Mice were fasted overnight and killed 1 hour (h) after feeding. A small slice (~5-1 mm 3 ) was taken
Online Appendix Material and Methods: Pancreatic RNA isolation and quantitative real-time (q)rt-pcr. Mice were fasted overnight and killed 1 hour (h) after feeding. A small slice (~5-1 mm 3 ) was taken
Nature Medicine: doi: /nm.2109
 HIV 1 Infects Multipotent Progenitor Cells Causing Cell Death and Establishing Latent Cellular Reservoirs Christoph C. Carter, Adewunmi Onafuwa Nuga, Lucy A. M c Namara, James Riddell IV, Dale Bixby, Michael
HIV 1 Infects Multipotent Progenitor Cells Causing Cell Death and Establishing Latent Cellular Reservoirs Christoph C. Carter, Adewunmi Onafuwa Nuga, Lucy A. M c Namara, James Riddell IV, Dale Bixby, Michael
OncoPPi Portal A Cancer Protein Interaction Network to Inform Therapeutic Strategies
 OncoPPi Portal A Cancer Protein Interaction Network to Inform Therapeutic Strategies 2017 Contents Datasets... 2 Protein-protein interaction dataset... 2 Set of known PPIs... 3 Domain-domain interactions...
OncoPPi Portal A Cancer Protein Interaction Network to Inform Therapeutic Strategies 2017 Contents Datasets... 2 Protein-protein interaction dataset... 2 Set of known PPIs... 3 Domain-domain interactions...
Supplementary Figures. T Cell Factor-1 initiates T helper 2 fate by inducing GATA-3 and repressing Interferon-γ
 Supplementary Figures T Cell Factor-1 initiates T helper 2 fate by inducing GATA-3 and repressing Interferon-γ Qing Yu, Archna Sharma, Sun Young Oh, Hyung-Geun Moon, M. Zulfiquer Hossain, Theresa M. Salay,
Supplementary Figures T Cell Factor-1 initiates T helper 2 fate by inducing GATA-3 and repressing Interferon-γ Qing Yu, Archna Sharma, Sun Young Oh, Hyung-Geun Moon, M. Zulfiquer Hossain, Theresa M. Salay,
Supplement to SCnorm: robust normalization of single-cell RNA-seq data
 Supplement to SCnorm: robust normalization of single-cell RNA-seq data Supplementary Note 1: SCnorm does not require spike-ins, since we find that the performance of spike-ins in scrna-seq is often compromised,
Supplement to SCnorm: robust normalization of single-cell RNA-seq data Supplementary Note 1: SCnorm does not require spike-ins, since we find that the performance of spike-ins in scrna-seq is often compromised,
Phosphate buffered saline (PBS) for washing the cells TE buffer (nuclease-free) ph 7.5 for use with the PrimePCR Reverse Transcription Control Assay
 Catalog # Description 172-5080 SingleShot Cell Lysis Kit, 100 x 50 µl reactions 172-5081 SingleShot Cell Lysis Kit, 500 x 50 µl reactions For research purposes only. Introduction The SingleShot Cell Lysis
Catalog # Description 172-5080 SingleShot Cell Lysis Kit, 100 x 50 µl reactions 172-5081 SingleShot Cell Lysis Kit, 500 x 50 µl reactions For research purposes only. Introduction The SingleShot Cell Lysis
RNA preparation from extracted paraffin cores:
 Supplementary methods, Nielsen et al., A comparison of PAM50 intrinsic subtyping with immunohistochemistry and clinical prognostic factors in tamoxifen-treated estrogen receptor positive breast cancer.
Supplementary methods, Nielsen et al., A comparison of PAM50 intrinsic subtyping with immunohistochemistry and clinical prognostic factors in tamoxifen-treated estrogen receptor positive breast cancer.
ChIP-seq data analysis
 ChIP-seq data analysis Harri Lähdesmäki Department of Computer Science Aalto University November 24, 2017 Contents Background ChIP-seq protocol ChIP-seq data analysis Transcriptional regulation Transcriptional
ChIP-seq data analysis Harri Lähdesmäki Department of Computer Science Aalto University November 24, 2017 Contents Background ChIP-seq protocol ChIP-seq data analysis Transcriptional regulation Transcriptional
ChIP-seq hands-on. Iros Barozzi, Campus IFOM-IEO (Milan) Saverio Minucci, Gioacchino Natoli Labs
 ChIP-seq hands-on Iros Barozzi, Campus IFOM-IEO (Milan) Saverio Minucci, Gioacchino Natoli Labs Main goals Becoming familiar with essential tools and formats Visualizing and contextualizing raw data Understand
ChIP-seq hands-on Iros Barozzi, Campus IFOM-IEO (Milan) Saverio Minucci, Gioacchino Natoli Labs Main goals Becoming familiar with essential tools and formats Visualizing and contextualizing raw data Understand
ncounter Assay Automated Process Capture & Reporter Probes Bind reporter to surface Remove excess reporters Hybridize CodeSet to RNA
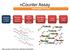 ncounter Assay Automated Process Hybridize CodeSet to RNA Remove excess reporters Bind reporter to surface Immobilize and align reporter Image surface Count codes mrna Capture & Reporter Probes slides
ncounter Assay Automated Process Hybridize CodeSet to RNA Remove excess reporters Bind reporter to surface Immobilize and align reporter Image surface Count codes mrna Capture & Reporter Probes slides
Peli1 negatively regulates T-cell activation and prevents autoimmunity
 Peli1 negatively regulates T-cell activation and prevents autoimmunity Mikyoung Chang 1,*, Wei Jin 1,5,*, Jae-Hoon Chang 1, Yi-chuan Xiao 1, George Brittain 1, Jiayi Yu 1, Xiaofei Zhou 1, Yi-Hong Wang
Peli1 negatively regulates T-cell activation and prevents autoimmunity Mikyoung Chang 1,*, Wei Jin 1,5,*, Jae-Hoon Chang 1, Yi-chuan Xiao 1, George Brittain 1, Jiayi Yu 1, Xiaofei Zhou 1, Yi-Hong Wang
Alessandra Franco, M.D., Ph.D. UCSD School of Medicine Department of Pediatrics Division of Allergy, Immunology and Rheumatology
 Natural regulatory T cells recognize the heavy constant region (Fc) of immunoglobulins: a novel mechanism for IVIG immunotherapy in Pediatric Immune-mediated diseases Alessandra Franco, M.D., Ph.D. UCSD
Natural regulatory T cells recognize the heavy constant region (Fc) of immunoglobulins: a novel mechanism for IVIG immunotherapy in Pediatric Immune-mediated diseases Alessandra Franco, M.D., Ph.D. UCSD
microrna PCR System (Exiqon), following the manufacturer s instructions. In brief, 10ng of
 SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIALS AND METHODS Quantitative RT-PCR Quantitative RT-PCR analysis was performed using the Universal mircury LNA TM microrna PCR System (Exiqon), following the manufacturer s instructions.
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIALS AND METHODS Quantitative RT-PCR Quantitative RT-PCR analysis was performed using the Universal mircury LNA TM microrna PCR System (Exiqon), following the manufacturer s instructions.
Supplemental Table I.
 Supplemental Table I Male / Mean ± SEM n Mean ± SEM n Body weight, g 29.2±0.4 17 29.7±0.5 17 Total cholesterol, mg/dl 534.0±30.8 17 561.6±26.1 17 HDL-cholesterol, mg/dl 9.6±0.8 17 10.1±0.7 17 Triglycerides,
Supplemental Table I Male / Mean ± SEM n Mean ± SEM n Body weight, g 29.2±0.4 17 29.7±0.5 17 Total cholesterol, mg/dl 534.0±30.8 17 561.6±26.1 17 HDL-cholesterol, mg/dl 9.6±0.8 17 10.1±0.7 17 Triglycerides,
Supplemental Table S1
 Supplemental Table S. Tumorigenicity and metastatic potential of 44SQ cell subpopulations a Tumorigenicity b Average tumor volume (mm ) c Lung metastasis d CD high /4 8. 8/ CD low /4 6./ a Mice were injected
Supplemental Table S. Tumorigenicity and metastatic potential of 44SQ cell subpopulations a Tumorigenicity b Average tumor volume (mm ) c Lung metastasis d CD high /4 8. 8/ CD low /4 6./ a Mice were injected
% of live splenocytes. STAT5 deletion. (open shapes) % ROSA + % floxed
 Supp. Figure 1. a 14 1 1 8 6 spleen cells (x1 6 ) 16 % of live splenocytes 5 4 3 1 % of live splenocytes 8 6 4 b 1 1 c % of CD11c + splenocytes (closed shapes) 8 6 4 8 6 4 % ROSA + (open shapes) % floxed
Supp. Figure 1. a 14 1 1 8 6 spleen cells (x1 6 ) 16 % of live splenocytes 5 4 3 1 % of live splenocytes 8 6 4 b 1 1 c % of CD11c + splenocytes (closed shapes) 8 6 4 8 6 4 % ROSA + (open shapes) % floxed
Cover Page. The handle holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation.
 Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/23854 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Marel, Sander van der Title: Gene and cell therapy based treatment strategies
Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/23854 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Marel, Sander van der Title: Gene and cell therapy based treatment strategies
Genetic alterations of histone lysine methyltransferases and their significance in breast cancer
 Genetic alterations of histone lysine methyltransferases and their significance in breast cancer Supplementary Materials and Methods Phylogenetic tree of the HMT superfamily The phylogeny outlined in the
Genetic alterations of histone lysine methyltransferases and their significance in breast cancer Supplementary Materials and Methods Phylogenetic tree of the HMT superfamily The phylogeny outlined in the
Supplementary Information and Figure legends
 Supplementary Information and Figure legends Table S1. Primers for quantitative RT-PCR Target Sequence (5 -> 3 ) Target Sequence (5 -> 3 ) DAB2IP F:TGGACGATGTGCTCTATGCC R:GGATGGTGATGGTTTGGTAG Snail F:CCTCCCTGTCAGATGAGGAC
Supplementary Information and Figure legends Table S1. Primers for quantitative RT-PCR Target Sequence (5 -> 3 ) Target Sequence (5 -> 3 ) DAB2IP F:TGGACGATGTGCTCTATGCC R:GGATGGTGATGGTTTGGTAG Snail F:CCTCCCTGTCAGATGAGGAC
