Last part: PuBng it all together
|
|
|
- Henry Robinson
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Last part: PuBng it all together Define project Define ques)on: Find genes that do XYZ Define biological model system Define assays to read out phenotypes of interest Primary screen feasibility and execu9on Op)mize model system, assay(s); posi)ve and nega)ve controls Select gene set to interrogate Execute pilot and primary screen select hits What happens to the cells? Need: Follow up on interes9ng genes/pathways Reagents to perturb every gene Good 9ssue culture model Good readouts of cell state Confirm assay result Confirm target gene specificity mul)ple RNAi reagents, target KD Elaborate the biological effects, e.g. mechanism generality/context, biomedical sig?
2 Focus on follow- up Figures 3-7 Project )melines Paths to valida)on what does valida)on mean? More detailed follow- up studies
3 Timelines: be realis)c!! A typical project lasts months - the screen itself taking up a small percentage of the )me. Most )me- consuming part of a screening project, by far, is valida)on and follow up aeer the screen. Assay Development Screen Valida)on Follow up 2-4 months months 2 6 months months
4 Screen chroma)n regulators in 2 cell lines Real examples Assay Dev DND41 and DND41R Screen DND41 Screen DND41R Paper in submission 3 mo. 22 mo. ORF genome- wide screen in 1 cell line 4 drugs Assay Dev A375 previously op)mized ORF genome- wide screen Paper submiked 2 mo. 18 mo.
5 Screen valida9on
6 Paths to valida9on what does valida9on mean?.two kinds of things to validate: The phenotype Repeat original assay In different orthogonal assay(s) for phenotype In different cell model systems VALIDATION The gene(s) Is phenotype due to expected effect of the shrna or ORF? e.g. discount off- target effects, non- specific effects Mechanism, flesh- out process, Relate to disease, etc. FOLLOW- UP Gene dose v. phenotype, Enzyma)c ac)vity, structural feature? Isoforms, protein modifica)ons
7 On- Target confirma1on for RNAi hits - > How to confirm that phenotype is due to target gene knockdown? Mul9ple effec9ve shrna sequences! Control Gene #1 Gene #2 Gene #3 Complex phenotype characteriza1on - High- content (Image- based) - FACS Moffat et. al. Cell GE- HTS
8 On- Target confirma1on for RNAi hits - > How to confirm that phenotype is due to target gene knockdown? KD vs. phenotype correla9on Phenotype Top hit TOP2A Perfect Perfect Not perfect BUT THIS KD v. PT RELATIONSHIP DOESN T ALWAYS HOLD
9 On- Target confirma1on for RNAi hits - > How to confirm that phenotype is due to target gene knockdown? Perturb gene in more than one way RNAi v. Overexpression DLG5 knockdown increases cell migra)on. à DLG5 overexpression decreases cell migra)on KD RNAi v. Targeted small molecule shrsk1 blocks shdlg5- induced cell migra)on RSK inhibitor (BI- D1870) also blocks shdlg5- induced cell migra)on OE
10 On- Target confirma1on for RNAi hits - > How to confirm that phenotype is due to target gene knockdown? 1. Require mul)ple shrnas for same gene to induce same phenotype. Obtain more shrnas, sirnas if needed. 2. Expand phenotypic characteriza)on to show detailed agreement among hairpins targe)ng same hit gene (see example) 3. Determine if knockdown of target gene correlates with phenotype across the mul)ple hairpins helpful when true, but not always true. 4. Perturb gene in other ways (small molecule, overexpression, genome engineering). 5. Perturb known rela)ves of the hit gene if known (e.g. genes in same pathway). 6. cdna rescue
11 Paths to follow up : What does it mean to learn a gene s func9on? What does it mean to define the genes invovled in a process The phenotype Repeat original assay Different orthogonal assay(s) for phenotype Different cell model systems VALIDATION The gene(s) Is phenotype due to expected effect of the shrna or ORF? e.g. discount off- target effects, non- specific effects Detailed nature of the process Context? Tissue types, in vivo What defines/governs process? - more players, further assays Mechanism biochemistry Rela)onship to disease, etc. Cross to other data sets FOLLOW- UP Detailed nature of the protein(s) and the proximal effects: Gene dose v. phenotype, Enzyma)c ac)vity, structural feature? Isoforms, protein modifica)ons Immediate substrates, binding partners The LONGEST part of a screening project!
12 Pubng it all together: Project Examples Emphasis on what s in Figures 3-7
13 A pooled screen for cell migration Gromek Smolen, Daniel Haber Smolen et. al., Genes & Dev. 2010
14 Endogenous nega+ve regulators of cell migra+on a pooled screen approach Gromek Smolen! Daniel Haber Lab Breast Cancer: MCF10A cells Non-migratory cells CELL MIGRATION Roles in normal development: pakerning during gastrula)on neural crest migra)on heart valve forma)on Roles in disease: congenital birth defects cancer metastasis Determinants of cell migra9on : morphology ECM architecture cytoskeleton gene regulatory network
15 Regulators of Cell Migration Pooled Screen: Hit Gene Confirmation! 163 shrnas 63 shrnas 169 shrnas 31 hit genes
16 Representative migration phenotypes! Diverse gene annotations, Test one at a time: strong hits! Gromek Smolen! Daniel Haber Lab
17 EMT marker analysis! Several hits increase fibronectin but produce inconsistent reduction of epithelial markers Gromek Smolen! Daniel Haber Lab
18 DLG5 knockdown increases cell migration! DLG: novel migration gene, downregulated upon YAP-induced migration Gromek Smolen! Daniel Haber Lab
19 DLG5 overexpression decreases cell migration! Use MDA-MB-231 Migratory breast cancer line Gromek Smolen! Daniel Haber Lab
20 DLG5 expression in breast tumors! Compare to orthogonal data Gromek Smolen! Daniel Haber Lab
21 More mechanism?? Knockdown of DLG5 à Use phospho- Ab array to monitor signaling pathways Prominent increases in phosphoryla)on of ERK1 and ERK2, a downstream kinase, RSK1, and AKT1 3 were observed Ac)va)on of ERK1/2 caused migra)on. Ac)vated AKT1 3 did not. ERK/RSK inhibitors blocked shdlg5- induced migra)on shrsk1 blocked shdlg5- induced migra)on
22 Mechanis9c convergence of 31 migra9on hit genes à All increase phospho- ERK1/2 RSK inhibitor (BI- D1870) blocks migra)on induced by all 31 gene knockdowns phospho- ERK1/2 up RSK inhibitor suppresses Migra)on by all hit shrnas
23 Integrated func+onal genomic approach to cancer: Oncogene discovery in colon cancer WNT signaling ac)va)on in nearly all colon cancer 1. APC loss (85% of colon cancers) 2. GOF muta)ons in β- catenin (5-10% ) Ron Firestein, Bill Hahn Nature Sept. 2008
24 B- catenin assay and cell viability assay Two phenotypes 1000 genes 5,000 shrnas - 95% of all human kinases cell viability assay B- catenin transcrip9on ac9va9on assay So Young Kim Ian Dunn Essen9al genes Prolifera9on screen β- catenin dependent cells (HCT116) Proliferation Screen" 9 Ron Firestein B-catenin screen β- catenin dependent cells (DLD-1) Firestein, Hahn
25 Compare to 3 rd dataset very different type RNAi: β- catenin ac)vity 34 genes 9 genes CDK8 166 genes? RNAi: prolifera)on/viability Amplified in colon tumors
26 CDK8 is amplified in colon cancers MAP3K14 ZAK PLK4 CSNK1G3 TAOK1 CSNK1E CDK8 SNP ARRAY (GISTIC) q-value HEAT MAP AT 13q q12.11 CDK8 123 Colon Cancer Samples q13.3 Adam Bass, Matthew Meyerson
27 Iden9fica9on of Minimal Region of Copy Gain at 13q Inferrred CN ATP8A2 TMEM46 RNF6 CDK8 (25.7) WASF3 GPR2 USP12 RPL21 RASL11A MTIF3 POLRID LNX2 IPF1 GSH1 CDX2 FLT3 Copy number! 22 Chromosome 13 Position (Mb) 30 Proliferation/RNAi!
28 Novel oncogene CDK8 SNP analysis of amplified genes in colon cancer shrna interference screen of cell viability CDK8 shrna interference screen of β- catenin ac9vity
29 CDK8 overexpression drives transformation NIH3T3 cells CDK8 amplification promotes tumorgenicity via the pathway of β-catenin transcription activation Firestein, Hahn
30 Drug resistance in BRAF- mutant melanoma Cory Johannessen, Levi Garraway
31 Resistance genes via ORF based rescue screens Cellular phenotype (drug sensitivity) Ectopic expression of human genes Phenotype rescue (resistance) Resistance to Rescue Screen: PLX4720 Sensi)ve Cell Line A375:B- RAF V600E Annotated Kinases (788) CCSB/Broad Ins+tute Kinase ORF Collec+on (597) Phenotypic Rescue of 1 µm PLX4720 (rela)ve cell number)
32 A screen for kinases that bypass B-RAF inhibition >2 st.dev. from average Average (all ORFs)
33 COT and C-RAF: candidate resistance kinases Priori)za)on Screen (2 cell lines, 8- point GI 50 ) Rank Gene 1 COT 2 C-RAF 3 CRKL 4 FGR 5 PRKCE 6 PRKCH 7 ERBB2 8 AXL 9 PAK3 C- RAF/RAF1 Heterodimerizes with BRAF to ac)vate the canonical MAPK signaling casseke Has been suggested to mediate resistance to RAF inhibi)on. COT/TPL2/MAP3K8 Like B- & C- RAF, COT is a MAP3K Has been shown to directly phosphorylate MEK1, ac)va)ng ERK Not linked to melanoma
34 COT and C- RAF re- ac9vate the MAPK pathway COT GFP MEK1 DD COT C-RAF COT CRAF BRAF +P PLX (µm): perk pmek CRAF BRAF +P MEK V5-C-RAF MEK V5-COT ERK V5-GFP ERK ERK MEK VINC
35 Identification of model systems to interrogate COT-mediated resistance Candidate kinases Broad-Novartis Cancer Cell Line Encyclopedia Expression profiling Drug Sensi9vity Muta9on analysis Copy number analysis >1000 cancer cell lines Model Cell Systems +B-RAF V600E +/-COT amplification
36 Iden9fy COT- amplified BRAFV600E mutant cell lines Cancer cell lines: 752 SNP/Oncomap: 534 B-RAF V600E Cancer Cell Lines COT Non-amplified AMP COT B-RAF V600E : 38 B-RAF V600E + COT copy no. gains: 2 VINC A375 SKMEL28 SKMEL5 COLO-679 MALME 3M OUMS-23 RPMI-7951
37 COT amplifica9on predicts resistance in BRAFV600E cancer cell lines B-RAF V600E Cancer Cell Lines
38 A mouse in vivo screen Rich Possemato, David Sabatini
39 Effects of oncogene activation on all metabolism is poorly understo Which metabolic genes and pathways are required for cancer cell proliferation and survival?
40 Cells in a tumor exist in a poorly understood environment 2000 mg/l Glucose 300 mg/l Glutamine 30 mg/l Serine 10 mg/l Glycine 1 mg/l Folate 1 mg/l Glutathione 20 mg/l Glutamate 15 mg/l Histidine???? mg/l Glucose??? mg/l Glutamine?? mg/l Serine?? mg/l Glycine? mg/l Folate? mg/l Glutathione?? mg/l Glutamate?? mg/l Histidine O. Brawley
41 Outline of in vivo pooled screening strategy iden)fying PHGDH as essen)al for tumorigenesis. For five hit genes (PHGDH, GMPS, SLC16A3, PYCR1 and VDAC1), two scoring shrnas were tested for their effects on tumour forma)on. Each of these shrnas suppressed expression of their targets in MCF10DCIS.com cells and reduced tumour- forming capacity. (Fig. 1e and Supplementary Fig. 2c). For reasons discussed later, PHGDH was of par)cular interest. R Possemato et al. Nature 000, 1-5 (2011) doi: /nature10350
42 In Vivo Screened Samples In Vitro Screened Samples Pearson Coefficient
43 Genomic amplifica)ons of PHGDH in cancer and associa)on of PHGDH expression with aggressive breast cancer markers. To priori)ze genes for follow- up studies we consulted a recently available analysis of copy number altera)ons across cancer genomes. Indeed, PHGDH exists in a region of chromosome 1p commonly amplified in breast cancer and melanoma R Possemato et al. Nature 000, 1-5 (2011) doi: /nature10350
44 Cell lines with elevated PHGDH expression have increased serine biosynthe)c pathway ac)vity and are sensi)ve to PHGDH suppression. To inves)gate whether PHGDH suppression can affect the growth of established tumours, we generated an inducible shrna that, upon doxycycline treatment, reduced PHGDH protein levels in MDA- MB- 468 cells. (different cells) R Possemato et al. Nature 000, 1-5 (2011) doi: /nature10350
45 Suppression of PHGDH results in a deficiency in anaplerosis of glutamine to akg. However, PHGDH suppression inhibited prolifera)on even in cells growing in media containing normal levels of extracellular serine, and supplementa)on with addi)onal serine or a cell- permeable methyl- serine- ester did not blunt the effects of the PHGDH suppression Uh- oh In fact, of the major metabolites measured, akg was the one with the most significant and largest change Ah, maybe ok upon PHGDH suppression, whereas Knock down PSAT1 serine levels were not significantly changed R Possemato et al. Nature 000, 1-5 (2011) doi: /nature10350
46 Paths to follow up : What does it mean to learn a gene s func9on? What does it mean to define the genes invovled in a process The phenotype Repeat original assay Different orthogonal assay(s) for phenotype Different cell model systems VALIDATION The gene(s) Is phenotype due to expected effect of the shrna or ORF? e.g. discount off- target effects, non- specific effects Detailed nature of the process Context? Tissue types, in vivo What defines/governs process? - more players, further assays Mechanism biochemistry Rela)onship to disease, etc. Cross to other data FOLLOW- UP Detailed nature of the protein(s) and the proximal effects: Gene dose v. phenotype, Enzyma)c ac)vity, structural feature? Isoforms, protein modifica)ons Immediate substrates, binding partners The LONGEST part of a screening project!
47 Some interes)ng quotes.. QUESTIONING VALIDITY OF MODEL AND/OR READOUT "In this highly ar)ficial model, the authors iden)fy poten)al enhancers and inhibitors of the loss of ASSAY staining when cells overexpressing GENE are.treated WITH X. To my knowledge no one has shown that this phenomenon actually occurs in vivo with endogenous VERSION OF TREATMENT... "The authors have mainly used indirect measures for PHENOTYPE. All these phenotypes could have alterna)ve explana)ons. Could the authors perform a TYPEOFASSAY assay to directly measure PHENOTYPE in CELL TYPE lines...?" Since they use a model of GENEX overexpression for their screen it is difficult to know whether this modifier (HIT GENE) regulates endogenous GENEX. Moreover the CELLS PLUS TREATMENT model system u)lized probably has likle relevance to DISEASE pathogenesis. "The study of more specific markers of PHENOTYPE that are exquisitely more sensi)ve to PERTURBATION may be informa)ve." NOT ENOUGH FOLLOW- UP "... the mechanis)c part of this study (biochemical and gene)c follow up) is not sufficient to unequivocally support the presented hypothesis". "The molecular mechanisms of ac)on of these genes in PHENOTYPE are tested only very superficially and not in sufficient depth for a journal like JOURNAL. A strong focus on PHENOTYPE and no ASSOCIATED PHENOTYPE data obtained by quan)ta)ve techniques (such as ASSAYS) leaves the reader surprised and unsa)sfied. "...they chose to pursue just one hit, GENE, in much detail. They have now provided conclusive evidence of GENE's func)onal involvement in selec)ve autophagy, but they have not yet understood its mechanis)c role. In this light, the present contribu)on of this work is to generate a poten)ally valuable but largely unproven resource of selec)ve PHENOTYPE genes, and to validate conclusively that ONE GENE is involved in PHENOTYPE while leaving its mechanis)c role in this process unresolved." NOT ENOUGH VALIDATION "... the authors should dissipate any poten)al concern on off target effects by performing a phenotype rescue experiment with RNAi- resistant versions of the inac)vated genes. "The bioinforma)cs analysis is interes)ng, but specula)ve." "...the authors select one of the genes, GENE, for in- depth analysis.... it is difficult to draw any conclusions about the involvement of the other (HIT) genes in PHENOTYPE based on this single example."
48 Define project Screen projects Define ques)on: Find genes that do XYZ Define biological model system Define assays to read out phenotypes of interest Primary screen feasibility and execu9on Op)mize model system, assay(s); posi)ve and nega)ve controls Select gene set to interrogate Execute pilot and primary screen select hits What happens to the cells? Need: Follow up on interes9ng genes/pathways Reagents to perturb every gene Good 9ssue culture model Good readouts of cell state Confirm assay result Confirm target gene specificity mul)ple RNAi reagents, target KD Elaborate the biological effects, e.g. mechanism generality/context, biomedical sig? Good luck! Come with ques+ons.
Understanding Signaling Pathways by Modifying Sensitivity to PLX4720 in B-RAF V600E Melanoma
 Understanding Signaling Pathways by Modifying Sensitivity to PLX4720 in B-RAF V600E Melanoma Muska Hassan NCI-ICBP Summer Fellow Broad Institute of MIT and Harvard: Cancer Program Mentor: Cory Johannessen,
Understanding Signaling Pathways by Modifying Sensitivity to PLX4720 in B-RAF V600E Melanoma Muska Hassan NCI-ICBP Summer Fellow Broad Institute of MIT and Harvard: Cancer Program Mentor: Cory Johannessen,
Functional genomics reveal that the serine synthesis pathway is essential in breast cancer
 Functional genomics reveal that the serine synthesis pathway is essential in breast cancer Results Presented by Stacey Lin Lloyd Lab http://www.amsbio.com/expression-ready-lentiviral-particles.aspx Overview
Functional genomics reveal that the serine synthesis pathway is essential in breast cancer Results Presented by Stacey Lin Lloyd Lab http://www.amsbio.com/expression-ready-lentiviral-particles.aspx Overview
Func%onal Genomic Screens in the RNAi Pla7orm
 Func%onal Genomic Screens in the RNAi Pla7orm Broad Ins*tute of MIT and Harvard Broad RNAi Platform Func%onal Genomic Screens in the RNAi Pla7orm Func*onal genomics à Gene func*on in context. in cells
Func%onal Genomic Screens in the RNAi Pla7orm Broad Ins*tute of MIT and Harvard Broad RNAi Platform Func%onal Genomic Screens in the RNAi Pla7orm Func*onal genomics à Gene func*on in context. in cells
Leucine Deprivation Reveals a Targetable Liability
 Cancer Cell, 19 Supplemental Information Defective Regulation of Autophagy upon Leucine Deprivation Reveals a Targetable Liability of Human Melanoma Cells In Vitro and In Vivo Joon-Ho Sheen, Roberto Zoncu,
Cancer Cell, 19 Supplemental Information Defective Regulation of Autophagy upon Leucine Deprivation Reveals a Targetable Liability of Human Melanoma Cells In Vitro and In Vivo Joon-Ho Sheen, Roberto Zoncu,
Novel treatments for SCC Andrés Felipe Cardona, MD MS PhD.
 Novel treatments for SCC Andrés Felipe Cardona, MD MS PhD. Clinical and Transla,onal Oncology Group Ins,tute of Oncology, Fundación Santa fe de Bogotá Clinical Epidemiology Cochrane Colombian Branch /
Novel treatments for SCC Andrés Felipe Cardona, MD MS PhD. Clinical and Transla,onal Oncology Group Ins,tute of Oncology, Fundación Santa fe de Bogotá Clinical Epidemiology Cochrane Colombian Branch /
BRAF: dal melanoma alla HCL
 ISTITUTO NAZIONALE PER LO STUDIO E LA CURA DEI TUMORI FONDAZIONE G. Pascale NAPOLI SC Biologia Cellulare e Bioterapie CENTRO RICERCHE ONCOLOGICHE MERCOGLIANO (AV) Laboratorio di Farmacogenomica BRAF: dal
ISTITUTO NAZIONALE PER LO STUDIO E LA CURA DEI TUMORI FONDAZIONE G. Pascale NAPOLI SC Biologia Cellulare e Bioterapie CENTRO RICERCHE ONCOLOGICHE MERCOGLIANO (AV) Laboratorio di Farmacogenomica BRAF: dal
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:.38/nature83 Supplementary figure An Overview of Experimental Flow Hypothesis: The tumor microenvironment has a significant impact on cancer cell chemoresistance. Screen Coculture
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:.38/nature83 Supplementary figure An Overview of Experimental Flow Hypothesis: The tumor microenvironment has a significant impact on cancer cell chemoresistance. Screen Coculture
Supplementary Figure 1. Basal level EGFR across a panel of ESCC lines. Immunoblots demonstrate the expression of phosphorylated and total EGFR as
 Supplementary Figure 1. Basal level EGFR across a panel of ESCC lines. Immunoblots demonstrate the expression of phosphorylated and total EGFR as well as their downstream effectors across a panel of ESCC
Supplementary Figure 1. Basal level EGFR across a panel of ESCC lines. Immunoblots demonstrate the expression of phosphorylated and total EGFR as well as their downstream effectors across a panel of ESCC
w ª wy xvwz A ª vw xvw P ª w} xvw w Æ w Æ V w,x Æ w Æ w Æ y,z Æ { Æ y,z, w w w~ w wy}æ zy Æ wyw{ xæ wz w xywæ xx Æ wv Æ } w x w x w Æ w Æ wy} zy Æ wz
 w ª wy xvwz A ª vw xvw P ª w} xvw w Æ w Æ V w,x Æ w Æ w Æ y,z Æ { Æ y,z, w w w~ w wy}æ zy Æ wyw{ xæ wz w xywæ xx Æ wv Æ } w x w x w Æ w Æ wy} zy Æ wz {w Æ Æ wyw{ x w Germ-line mutations in BRCA1 are associated
w ª wy xvwz A ª vw xvw P ª w} xvw w Æ w Æ V w,x Æ w Æ w Æ y,z Æ { Æ y,z, w w w~ w wy}æ zy Æ wyw{ xæ wz w xywæ xx Æ wv Æ } w x w x w Æ w Æ wy} zy Æ wz {w Æ Æ wyw{ x w Germ-line mutations in BRCA1 are associated
Cancer. The fundamental defect is. unregulated cell division. Properties of Cancerous Cells. Causes of Cancer. Altered growth and proliferation
 Cancer The fundamental defect is unregulated cell division. Properties of Cancerous Cells Altered growth and proliferation Loss of growth factor dependence Loss of contact inhibition Immortalization Alterated
Cancer The fundamental defect is unregulated cell division. Properties of Cancerous Cells Altered growth and proliferation Loss of growth factor dependence Loss of contact inhibition Immortalization Alterated
Negative Regulation of c-myc Oncogenic Activity Through the Tumor Suppressor PP2A-B56α
 Negative Regulation of c-myc Oncogenic Activity Through the Tumor Suppressor PP2A-B56α Mahnaz Janghorban, PhD Dr. Rosalie Sears lab 2/8/2015 Zanjan University Content 1. Background (keywords: c-myc, PP2A,
Negative Regulation of c-myc Oncogenic Activity Through the Tumor Suppressor PP2A-B56α Mahnaz Janghorban, PhD Dr. Rosalie Sears lab 2/8/2015 Zanjan University Content 1. Background (keywords: c-myc, PP2A,
Normal Skin. Tissue Samples and Melanoma Cell Lines. BRAF Mut. RAS Mut RAS WT /BRAF WT
 Supplemental Figure 1. MERTK gene expression in melanoma cell line panel from Cancer Cell Line Encyclopedia. A. Microarray analysis of melanoma cell lines from UNC collection grouped by oncogenic mutation.
Supplemental Figure 1. MERTK gene expression in melanoma cell line panel from Cancer Cell Line Encyclopedia. A. Microarray analysis of melanoma cell lines from UNC collection grouped by oncogenic mutation.
GENETIC ANALYSIS OF RAS SIGNALING PATHWAYS IN CELL PROLIFERATION, MIGRATION AND SURVIVAL
 Manuscript EMBO-2009-72496 GENETIC ANALYSIS OF RAS SIGNALING PATHWAYS IN CELL PROLIFERATION, MIGRATION AND SURVIVAL Matthias Drosten, Alma Dhawahir, Eleanor Sum, Jelena Urosevic, Carmen Lechuga, Luis Esteban,
Manuscript EMBO-2009-72496 GENETIC ANALYSIS OF RAS SIGNALING PATHWAYS IN CELL PROLIFERATION, MIGRATION AND SURVIVAL Matthias Drosten, Alma Dhawahir, Eleanor Sum, Jelena Urosevic, Carmen Lechuga, Luis Esteban,
Selec%ve killing of cancer cells by a small molecule targe%ng the stress response to ROS
 Selec%ve killing of cancer cells by a small molecule targe%ng the stress response to RS L Raj et al. Nature 475, 231-234 (2011) doi:10.1038/nature10167 Current literature Presented by Zhuzhu WANG 9/3/11
Selec%ve killing of cancer cells by a small molecule targe%ng the stress response to RS L Raj et al. Nature 475, 231-234 (2011) doi:10.1038/nature10167 Current literature Presented by Zhuzhu WANG 9/3/11
Cancer Genomics (Current technologies & clinical implication)
 Cancer Genomics (Current technologies & clinical implication) Jeonghee Cho, Ph.D. Samsung Medical Center Samsung Cancer Research Institute Robert Weinberg (M.I.T) Douglas Hanahan (ISREC) The Hallmarks
Cancer Genomics (Current technologies & clinical implication) Jeonghee Cho, Ph.D. Samsung Medical Center Samsung Cancer Research Institute Robert Weinberg (M.I.T) Douglas Hanahan (ISREC) The Hallmarks
Cancer. The fundamental defect is. unregulated cell division. Properties of Cancerous Cells. Causes of Cancer. Altered growth and proliferation
 Cancer The fundamental defect is unregulated cell division. Properties of Cancerous Cells Altered growth and proliferation Loss of growth factor dependence Loss of contact inhibition Immortalization Alterated
Cancer The fundamental defect is unregulated cell division. Properties of Cancerous Cells Altered growth and proliferation Loss of growth factor dependence Loss of contact inhibition Immortalization Alterated
Classifica4on. CSCI1950 Z Computa4onal Methods for Biology Lecture 18. Ben Raphael April 8, hip://cs.brown.edu/courses/csci1950 z/
 CSCI1950 Z Computa4onal Methods for Biology Lecture 18 Ben Raphael April 8, 2009 hip://cs.brown.edu/courses/csci1950 z/ Binary classifica,on Given a set of examples (x i, y i ), where y i = + 1, from unknown
CSCI1950 Z Computa4onal Methods for Biology Lecture 18 Ben Raphael April 8, 2009 hip://cs.brown.edu/courses/csci1950 z/ Binary classifica,on Given a set of examples (x i, y i ), where y i = + 1, from unknown
supplementary information
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb1875 Figure S1 (a) The 79 surgical specimens from NSCLC patients were analysed by immunohistochemistry with an anti-p53 antibody and control serum (data not shown). The normal bronchi served
DOI: 10.1038/ncb1875 Figure S1 (a) The 79 surgical specimens from NSCLC patients were analysed by immunohistochemistry with an anti-p53 antibody and control serum (data not shown). The normal bronchi served
Award Number: W81XWH TITLE: Characterizing an EMT Signature in Breast Cancer. PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Melanie C.
 AD Award Number: W81XWH-08-1-0306 TITLE: Characterizing an EMT Signature in Breast Cancer PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Melanie C. Bocanegra CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: Leland Stanford Junior University Stanford,
AD Award Number: W81XWH-08-1-0306 TITLE: Characterizing an EMT Signature in Breast Cancer PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Melanie C. Bocanegra CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: Leland Stanford Junior University Stanford,
Supplementary Figure 1. a. b. Relative cell viability. Nature Genetics: doi: /ng SCR shyap1-1 shyap
 Supplementary Figure 1. a. b. p-value for depletion in vehicle (DMSO) 1e-05 1e-03 1e-01 1 0 1000 2000 3000 4000 5000 Genes log2 normalized shrna counts in T0 0 2 4 6 8 sh1 shluc 0 2 4 6 8 log2 normalized
Supplementary Figure 1. a. b. p-value for depletion in vehicle (DMSO) 1e-05 1e-03 1e-01 1 0 1000 2000 3000 4000 5000 Genes log2 normalized shrna counts in T0 0 2 4 6 8 sh1 shluc 0 2 4 6 8 log2 normalized
Introduc)on to Immunology. T Cell Development
 Introduc)on to Immunology T Cell Development Adolfo Ferrando af2196@columbia.edu Thymic stroma cells provide the microenvironment for T cell development. T cells develop from progenitors that are derived
Introduc)on to Immunology T Cell Development Adolfo Ferrando af2196@columbia.edu Thymic stroma cells provide the microenvironment for T cell development. T cells develop from progenitors that are derived
AWARD NUMBER: W81XWH TITLE: An in Vivo shrna-drug Screen to Identify Novel Targeted Therapy Combinations for KRAS Mutant Cancers
 AWARD NUMBER: W81XWH-12-1-0420 TITLE: An in Vivo shrna-drug Screen to Identify Novel Targeted Therapy Combinations for KRAS Mutant Cancers PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Ryan B. Corcoran, M.D., Ph.D. CONTRACTING
AWARD NUMBER: W81XWH-12-1-0420 TITLE: An in Vivo shrna-drug Screen to Identify Novel Targeted Therapy Combinations for KRAS Mutant Cancers PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Ryan B. Corcoran, M.D., Ph.D. CONTRACTING
Development of Carcinoma Pathways
 The Construction of Genetic Pathway to Colorectal Cancer Moriah Wright, MD Clinical Fellow in Colorectal Surgery Creighton University School of Medicine Management of Colon and Diseases February 23, 2019
The Construction of Genetic Pathway to Colorectal Cancer Moriah Wright, MD Clinical Fellow in Colorectal Surgery Creighton University School of Medicine Management of Colon and Diseases February 23, 2019
Emerging gene)cs in schizophrenia: Real challenges for crea)ng animal models
 Emerging gene)cs in schizophrenia: Real challenges for crea)ng animal models Steven A McCarroll, PhD Stanley Center for Psychiatric Research, Broad Ins7tute Department of Gene7cs, Harvard Medical School
Emerging gene)cs in schizophrenia: Real challenges for crea)ng animal models Steven A McCarroll, PhD Stanley Center for Psychiatric Research, Broad Ins7tute Department of Gene7cs, Harvard Medical School
Combined γ- Tocotrienol and Met Inhibitor Treatment Suppresses Mammary Cancer Cell Prolifera;on, Epithelial- to- Mesenchymal Transi;on, and Migra;on
 Combined γ Tocotrienol and Met Inhibitor Treatment Suppresses Mammary Cancer Cell Prolifera;on, Epithelial to Mesenchymal Transi;on, and Migra;on Paul W. Sylvester, Ph.D. Pfizer Endowed Professor of Pharmacy
Combined γ Tocotrienol and Met Inhibitor Treatment Suppresses Mammary Cancer Cell Prolifera;on, Epithelial to Mesenchymal Transi;on, and Migra;on Paul W. Sylvester, Ph.D. Pfizer Endowed Professor of Pharmacy
Karyotype analysis reveals transloction of chromosome 22 to 9 in CML chronic myelogenous leukemia has fusion protein Bcr-Abl
 Chapt. 18 Cancer Molecular Biology of Cancer Student Learning Outcomes: Describe cancer diseases in which cells no longer respond Describe how cancers come from genomic mutations (inherited or somatic)
Chapt. 18 Cancer Molecular Biology of Cancer Student Learning Outcomes: Describe cancer diseases in which cells no longer respond Describe how cancers come from genomic mutations (inherited or somatic)
Complexity of intra- and inter-pathway loops in colon cancer and melanoma: implications for targeted therapies
 Complexity of intra- and inter-pathway loops in colon cancer and melanoma: implications for targeted therapies René Bernards The Netherlands Cancer Institute Amsterdam The Netherlands Molecular versus
Complexity of intra- and inter-pathway loops in colon cancer and melanoma: implications for targeted therapies René Bernards The Netherlands Cancer Institute Amsterdam The Netherlands Molecular versus
The mutations that drive cancer. Paul Edwards. Department of Pathology and Cancer Research UK Cambridge Institute, University of Cambridge
 The mutations that drive cancer Paul Edwards Department of Pathology and Cancer Research UK Cambridge Institute, University of Cambridge Previously on Cancer... hereditary predisposition Normal Cell Slightly
The mutations that drive cancer Paul Edwards Department of Pathology and Cancer Research UK Cambridge Institute, University of Cambridge Previously on Cancer... hereditary predisposition Normal Cell Slightly
Hunk is required for HER2/neu-induced mammary tumorigenesis
 Research article Hunk is required for HER2/neu-induced mammary tumorigenesis Elizabeth S. Yeh, 1 Thomas W. Yang, 1 Jason J. Jung, 1 Heather P. Gardner, 1 Robert D. Cardiff, 2 and Lewis A. Chodosh 1 1 Department
Research article Hunk is required for HER2/neu-induced mammary tumorigenesis Elizabeth S. Yeh, 1 Thomas W. Yang, 1 Jason J. Jung, 1 Heather P. Gardner, 1 Robert D. Cardiff, 2 and Lewis A. Chodosh 1 1 Department
Carcinoma mammario triple nega0ve Nuove acquisizioni biologiche. Giuseppe Curigliano MD PhD UNIMI & IEO
 Carcinoma mammario triple nega0ve Nuove acquisizioni biologiche Giuseppe Curigliano MD PhD UNIMI & IEO Outline San Antonio Breast Cancer Symposium, December 5-9, 2017 The year of DNA Repair targe?ng Olaparib
Carcinoma mammario triple nega0ve Nuove acquisizioni biologiche Giuseppe Curigliano MD PhD UNIMI & IEO Outline San Antonio Breast Cancer Symposium, December 5-9, 2017 The year of DNA Repair targe?ng Olaparib
Opposing activities of the Ras and Hippo pathways converge on regulation of YAP protein turnover
 The EMBO Journal Peer Review Process File - EMBO-2014-89385 Manuscript EMBO-2014-89385 Opposing activities of the Ras and Hippo pathways converge on regulation of YAP protein turnover Xin Hong, Hung Thanh
The EMBO Journal Peer Review Process File - EMBO-2014-89385 Manuscript EMBO-2014-89385 Opposing activities of the Ras and Hippo pathways converge on regulation of YAP protein turnover Xin Hong, Hung Thanh
Epstein-Barr virus driven promoter hypermethylated genes in gastric cancer
 RESEARCH FUND FOR THE CONTROL OF INFECTIOUS DISEASES Epstein-Barr virus driven promoter hypermethylated genes in gastric cancer J Yu *, KF To, QY Liang K e y M e s s a g e s 1. Somatostatin receptor 1
RESEARCH FUND FOR THE CONTROL OF INFECTIOUS DISEASES Epstein-Barr virus driven promoter hypermethylated genes in gastric cancer J Yu *, KF To, QY Liang K e y M e s s a g e s 1. Somatostatin receptor 1
Understanding PI3K/mTOR/MEK signalling in breast cancer. Euphemia Leung Auckland Cancer Society Research Centre University of Auckland
 Understanding PI3K/mTOR/MEK signalling in breast cancer Euphemia Leung Auckland Cancer Society Research Centre University of Auckland Receptor status of human breast cancer On a popula>on basis ER+/PR+
Understanding PI3K/mTOR/MEK signalling in breast cancer Euphemia Leung Auckland Cancer Society Research Centre University of Auckland Receptor status of human breast cancer On a popula>on basis ER+/PR+
Genetic Tests and Genetic Counseling How to Analyze Your Own Genome
 Genetic Tests and Genetic Counseling 02-223 How to Analyze Your Own Genome Genetic Tests for Huntington Disease Hun7ngton Disease Incurable brain disorder that runs in families Movement, cogni7ve, and
Genetic Tests and Genetic Counseling 02-223 How to Analyze Your Own Genome Genetic Tests for Huntington Disease Hun7ngton Disease Incurable brain disorder that runs in families Movement, cogni7ve, and
Biosta's'cs Board Review. Parul Chaudhri, DO Family Medicine Faculty Development Fellow, UPMC St Margaret March 5, 2016
 Biosta's'cs Board Review Parul Chaudhri, DO Family Medicine Faculty Development Fellow, UPMC St Margaret March 5, 2016 Review key biosta's'cs concepts Understand 2 X 2 tables Objec'ves By the end of this
Biosta's'cs Board Review Parul Chaudhri, DO Family Medicine Faculty Development Fellow, UPMC St Margaret March 5, 2016 Review key biosta's'cs concepts Understand 2 X 2 tables Objec'ves By the end of this
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature23291 Supplementary discussion part 1 Our model suggests that, in tumours that express Class 3 BRAF mutants and activated RAS, both BRAF MUT /RAF WT heterodimers and WT RAF dimers are
doi:10.1038/nature23291 Supplementary discussion part 1 Our model suggests that, in tumours that express Class 3 BRAF mutants and activated RAS, both BRAF MUT /RAF WT heterodimers and WT RAF dimers are
Does EMT Contribute to Radiation Resistance in Human Breast Cancer?
 AD Award Number: W81XWH-10-1-0592 TITLE: Does EMT Contribute to Radiation Resistance in Human Breast Cancer? PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Anupama Munshi, Ph.D CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: University of Oklahoma
AD Award Number: W81XWH-10-1-0592 TITLE: Does EMT Contribute to Radiation Resistance in Human Breast Cancer? PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Anupama Munshi, Ph.D CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: University of Oklahoma
MolEcular Taxonomy of BReast cancer International Consortium (METABRIC)
 PERSPECTIVE 1 LARGE SCALE DATASET EXAMPLES MolEcular Taxonomy of BReast cancer International Consortium (METABRIC) BC Cancer Agency, Vancouver Samuel Aparicio, PhD FRCPath Nan and Lorraine Robertson Chair
PERSPECTIVE 1 LARGE SCALE DATASET EXAMPLES MolEcular Taxonomy of BReast cancer International Consortium (METABRIC) BC Cancer Agency, Vancouver Samuel Aparicio, PhD FRCPath Nan and Lorraine Robertson Chair
Paget s Disease of Bone
 Paget s Disease of Bone Copyright Copyright 2019 American 2019 American Associa7on Associa7on of Clinical of Clinical Endocrinologists Endocrinologists 1 A Common Bone Disorder Paget s disease of bone
Paget s Disease of Bone Copyright Copyright 2019 American 2019 American Associa7on Associa7on of Clinical of Clinical Endocrinologists Endocrinologists 1 A Common Bone Disorder Paget s disease of bone
effects on organ development. a-f, Eye and wing discs with clones of ε j2b10 show no
 Supplementary Figure 1. Loss of function clones of 14-3-3 or 14-3-3 show no significant effects on organ development. a-f, Eye and wing discs with clones of 14-3-3ε j2b10 show no obvious defects in Elav
Supplementary Figure 1. Loss of function clones of 14-3-3 or 14-3-3 show no significant effects on organ development. a-f, Eye and wing discs with clones of 14-3-3ε j2b10 show no obvious defects in Elav
Failure to properly synthesize glycoproteins and other glycosylated molecules results in human disease
 Failure to properly synthesize glycoproteins and other glycosylated molecules results in human disease - muta6ons in genes encoding enzymes involved in glycoprotein biosynthesis: congenital disorders of
Failure to properly synthesize glycoproteins and other glycosylated molecules results in human disease - muta6ons in genes encoding enzymes involved in glycoprotein biosynthesis: congenital disorders of
Normal RAS-RAF (MAPK) pathway signaling
 BRAF-Mutations in Melanomas L. Mazzucchelli Istituto Cantonale di Patologia, Locarno 77. Annual Meeting Swiss Society of Pathology, Lucerne 2011 Sponsored by Roche Pharma Switzerland Melanoma has increased
BRAF-Mutations in Melanomas L. Mazzucchelli Istituto Cantonale di Patologia, Locarno 77. Annual Meeting Swiss Society of Pathology, Lucerne 2011 Sponsored by Roche Pharma Switzerland Melanoma has increased
Supplementary Figure 1. HOPX is hypermethylated in NPC. (a) Methylation levels of HOPX in Normal (n = 24) and NPC (n = 24) tissues from the
 Supplementary Figure 1. HOPX is hypermethylated in NPC. (a) Methylation levels of HOPX in Normal (n = 24) and NPC (n = 24) tissues from the genome-wide methylation microarray data. Mean ± s.d.; Student
Supplementary Figure 1. HOPX is hypermethylated in NPC. (a) Methylation levels of HOPX in Normal (n = 24) and NPC (n = 24) tissues from the genome-wide methylation microarray data. Mean ± s.d.; Student
Response and resistance to BRAF inhibitors in melanoma
 Response and resistance to BRAF inhibitors in melanoma Keith T. Flaherty, M.D. Massachusetts General Hospital Cancer Center Disclosures Roche/Genentech: consultant GlaxoSmithKline: consultant BRAF mutations
Response and resistance to BRAF inhibitors in melanoma Keith T. Flaherty, M.D. Massachusetts General Hospital Cancer Center Disclosures Roche/Genentech: consultant GlaxoSmithKline: consultant BRAF mutations
Introduction: 年 Fas signal-mediated apoptosis. PI3K/Akt
 Fas-ligand (CD95-L; Fas-L) Fas (CD95) Fas (apoptosis) 年 了 不 度 Fas Fas-L 力 不 Fas/Fas-L T IL-10Fas/Fas-L 不 年 Fas signal-mediated apoptosis 度降 不 不 力 U-118, HeLa, A549, Huh-7 MCF-7, HepG2. PI3K/Akt FasPI3K/Akt
Fas-ligand (CD95-L; Fas-L) Fas (CD95) Fas (apoptosis) 年 了 不 度 Fas Fas-L 力 不 Fas/Fas-L T IL-10Fas/Fas-L 不 年 Fas signal-mediated apoptosis 度降 不 不 力 U-118, HeLa, A549, Huh-7 MCF-7, HepG2. PI3K/Akt FasPI3K/Akt
RAS Genes. The ras superfamily of genes encodes small GTP binding proteins that are responsible for the regulation of many cellular processes.
 ۱ RAS Genes The ras superfamily of genes encodes small GTP binding proteins that are responsible for the regulation of many cellular processes. Oncogenic ras genes in human cells include H ras, N ras,
۱ RAS Genes The ras superfamily of genes encodes small GTP binding proteins that are responsible for the regulation of many cellular processes. Oncogenic ras genes in human cells include H ras, N ras,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb2607 Figure S1 Elf5 loss promotes EMT in mammary epithelium while Elf5 overexpression inhibits TGFβ induced EMT. (a, c) Different confocal slices through the Z stack image. (b, d) 3D rendering
DOI: 10.1038/ncb2607 Figure S1 Elf5 loss promotes EMT in mammary epithelium while Elf5 overexpression inhibits TGFβ induced EMT. (a, c) Different confocal slices through the Z stack image. (b, d) 3D rendering
Part-4. Cell cycle regulatory protein 5 (Cdk5) A novel target of ERK in Carb induced cell death
 Part-4 Cell cycle regulatory protein 5 (Cdk5) A novel target of ERK in Carb induced cell death 95 1. Introduction The process of replicating DNA and dividing cells can be described as a series of coordinated
Part-4 Cell cycle regulatory protein 5 (Cdk5) A novel target of ERK in Carb induced cell death 95 1. Introduction The process of replicating DNA and dividing cells can be described as a series of coordinated
Supplementary Figure 1: Digitoxin induces apoptosis in primary human melanoma cells but not in normal melanocytes, which express lower levels of the
 Supplementary Figure 1: Digitoxin induces apoptosis in primary human melanoma cells but not in normal melanocytes, which express lower levels of the cardiac glycoside target, ATP1A1. (a) The percentage
Supplementary Figure 1: Digitoxin induces apoptosis in primary human melanoma cells but not in normal melanocytes, which express lower levels of the cardiac glycoside target, ATP1A1. (a) The percentage
WNT5A enhances resistance of melanoma cells to targeted BRAF inhibitors
 Research article WNT5A enhances resistance of melanoma cells to targeted BRAF inhibitors Jamie N. Anastas, 1,2 Rima M. Kulikauskas, 3 Tigist Tamir, 4 Helen Rizos, 5 Georgina V. Long, 5 Erika M. von Euw,
Research article WNT5A enhances resistance of melanoma cells to targeted BRAF inhibitors Jamie N. Anastas, 1,2 Rima M. Kulikauskas, 3 Tigist Tamir, 4 Helen Rizos, 5 Georgina V. Long, 5 Erika M. von Euw,
Mul$ Voxel Pa,ern Analysis (fmri) Mul$ Variate Pa,ern Analysis (more generally) Magic Voxel Pa,ern Analysis (probably not!)
 Mul$ Voxel Pa,ern Analysis (fmri) Mul$ Variate Pa,ern Analysis (more generally) Magic Voxel Pa,ern Analysis (probably not!) all MVPA really shows is that there are places where, in most people s brain,
Mul$ Voxel Pa,ern Analysis (fmri) Mul$ Variate Pa,ern Analysis (more generally) Magic Voxel Pa,ern Analysis (probably not!) all MVPA really shows is that there are places where, in most people s brain,
New Fron)ers in Therapies for Autoimmunity
 New Fron)ers in Therapies for Autoimmunity Preview Discuss spectrum of autoimmune research at MUSC Iden)fy some of the key inves)gators in basic and clinical research at MUSC Discuss specific areas of
New Fron)ers in Therapies for Autoimmunity Preview Discuss spectrum of autoimmune research at MUSC Iden)fy some of the key inves)gators in basic and clinical research at MUSC Discuss specific areas of
Supplementary Figure 1. Characterization of NMuMG-ErbB2 and NIC breast cancer cells expressing shrnas targeting LPP. NMuMG-ErbB2 cells (a) and NIC
 Supplementary Figure 1. Characterization of NMuMG-ErbB2 and NIC breast cancer cells expressing shrnas targeting LPP. NMuMG-ErbB2 cells (a) and NIC cells (b) were engineered to stably express either a LucA-shRNA
Supplementary Figure 1. Characterization of NMuMG-ErbB2 and NIC breast cancer cells expressing shrnas targeting LPP. NMuMG-ErbB2 cells (a) and NIC cells (b) were engineered to stably express either a LucA-shRNA
Considera*ons when undergoing personal genotyping
 Considera*ons when undergoing personal genotyping Kelly Ormond, MS, CGC Louanne Hudgins, MD, FACMG January 19, 2011 GENE 210 Disclosures and introduc*ons Professor Ormond provided paid consulta*on for
Considera*ons when undergoing personal genotyping Kelly Ormond, MS, CGC Louanne Hudgins, MD, FACMG January 19, 2011 GENE 210 Disclosures and introduc*ons Professor Ormond provided paid consulta*on for
Supplementary Information Titles Journal: Nature Medicine
 Supplementary Information Titles Journal: Nature Medicine Article Title: Corresponding Author: Supplementary Item & Number Supplementary Fig.1 Fig.2 Fig.3 Fig.4 Fig.5 Fig.6 Fig.7 Fig.8 Fig.9 Fig. Fig.11
Supplementary Information Titles Journal: Nature Medicine Article Title: Corresponding Author: Supplementary Item & Number Supplementary Fig.1 Fig.2 Fig.3 Fig.4 Fig.5 Fig.6 Fig.7 Fig.8 Fig.9 Fig. Fig.11
Supplementary Information Supplementary Fig. 1. Elevated Usp9x in melanoma and NRAS mutant melanoma cells are dependent on NRAS for 3D growth.
 Supplementary Information Supplementary Fig. 1. Elevated Usp9x in melanoma and NRAS mutant melanoma cells are dependent on NRAS for 3D growth. a. Immunoblot for Usp9x protein in NRAS mutant melanoma cells
Supplementary Information Supplementary Fig. 1. Elevated Usp9x in melanoma and NRAS mutant melanoma cells are dependent on NRAS for 3D growth. a. Immunoblot for Usp9x protein in NRAS mutant melanoma cells
Supplementary Figure 1. BMS enhances human T cell activation in vitro in a
 Supplementary Figure 1. BMS98662 enhances human T cell activation in vitro in a concentration-dependent manner. Jurkat T cells were activated with anti-cd3 and anti-cd28 antibody in the presence of titrated
Supplementary Figure 1. BMS98662 enhances human T cell activation in vitro in a concentration-dependent manner. Jurkat T cells were activated with anti-cd3 and anti-cd28 antibody in the presence of titrated
Supplementary Figures
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1 DOT1L regulates the expression of epithelial and mesenchymal markers. (a) The expression levels and cellular localizations of EMT markers were confirmed by
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1 DOT1L regulates the expression of epithelial and mesenchymal markers. (a) The expression levels and cellular localizations of EMT markers were confirmed by
Epigene.cs: What is it and how it effects our health? Overview. Dr. Bill Stanford, PhD OFawa Hospital Research Ins.tute University of OFawa
 Epigene.cs: What is it and how it effects our health? Dr. Bill Stanford, PhD OFawa Hospital Research Ins.tute University of OFawa Overview Basic Background Epigene.cs in general Epigene.cs in cancer Epigene.cs
Epigene.cs: What is it and how it effects our health? Dr. Bill Stanford, PhD OFawa Hospital Research Ins.tute University of OFawa Overview Basic Background Epigene.cs in general Epigene.cs in cancer Epigene.cs
Small RNAs and how to analyze them using sequencing
 Small RNAs and how to analyze them using sequencing Jakub Orzechowski Westholm (1) Long- term bioinforma=cs support, Science For Life Laboratory Stockholm (2) Department of Biophysics and Biochemistry,
Small RNAs and how to analyze them using sequencing Jakub Orzechowski Westholm (1) Long- term bioinforma=cs support, Science For Life Laboratory Stockholm (2) Department of Biophysics and Biochemistry,
RNA- seq Introduc1on. Promises and pi7alls
 RNA- seq Introduc1on Promises and pi7alls DNA is the same in all cells but which RNAs that is present is different in all cells There is a wide variety of different func1onal RNAs Which RNAs (and some1mes
RNA- seq Introduc1on Promises and pi7alls DNA is the same in all cells but which RNAs that is present is different in all cells There is a wide variety of different func1onal RNAs Which RNAs (and some1mes
A View to the Future: The Development of Targeted Therapy for Melanoma. Michael Davies, M.D., Ph.D.
 A View to the Future: Science to Survivorship Symposium September 26, 2009 The Development of Targeted Therapy for Melanoma Michael Davies, M.D., Ph.D. Assistant Professor, Melanoma Medical Oncology How
A View to the Future: Science to Survivorship Symposium September 26, 2009 The Development of Targeted Therapy for Melanoma Michael Davies, M.D., Ph.D. Assistant Professor, Melanoma Medical Oncology How
Reviewers' comments: Reviewer #1 (Remarks to the Author):
 Reviewers' comments: Reviewer #1 (Remarks to the Author): The authors have presented data demonstrating activation of AKT as a common resistance mechanism in EGFR mutation positive, EGFR TKI resistant
Reviewers' comments: Reviewer #1 (Remarks to the Author): The authors have presented data demonstrating activation of AKT as a common resistance mechanism in EGFR mutation positive, EGFR TKI resistant
Type of file: PDF Size of file: 0 KB Title of file for HTML: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures
 Type of file: PDF Size of file: 0 KB Title of file for HTML: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1 mir-128-3p is highly expressed in chemoresistant, metastatic
Type of file: PDF Size of file: 0 KB Title of file for HTML: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1 mir-128-3p is highly expressed in chemoresistant, metastatic
SALL1 functions as a tumor suppressor in breast cancer by regulating cancer cell senescence and metastasis through the NuRD complex
 Ma et al. Molecular Cancer (2018) 17:78 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-018-0824-y RESEARCH SALL1 functions as a tumor suppressor in breast cancer by regulating cancer cell senescence and metastasis through
Ma et al. Molecular Cancer (2018) 17:78 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-018-0824-y RESEARCH SALL1 functions as a tumor suppressor in breast cancer by regulating cancer cell senescence and metastasis through
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/8/364/ra18/dc1 Supplementary Materials for The tyrosine phosphatase (Pez) inhibits metastasis by altering protein trafficking Leila Belle, Naveid Ali, Ana Lonic,
www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/8/364/ra18/dc1 Supplementary Materials for The tyrosine phosphatase (Pez) inhibits metastasis by altering protein trafficking Leila Belle, Naveid Ali, Ana Lonic,
Genetic Alteration Panels
 TM Genetic Alteration Panels GENETIC ALTERATION PANELS Table of Contents AKT Genetic Alteration Panel (ATCC No. TCP-1029 )...1 BRAF Genetic Alteration Panel (ATCC No. TCP-1032 )...5 EGFR Genetic Alteration
TM Genetic Alteration Panels GENETIC ALTERATION PANELS Table of Contents AKT Genetic Alteration Panel (ATCC No. TCP-1029 )...1 BRAF Genetic Alteration Panel (ATCC No. TCP-1032 )...5 EGFR Genetic Alteration
Characteriza*on of Soma*c Muta*ons in Cancer Genomes
 Characteriza*on of Soma*c Muta*ons in Cancer Genomes Ben Raphael Department of Computer Science Center for Computa*onal Molecular Biology Soma*c Muta*ons and Cancer Clonal Theory (Nowell 1976) Passenger
Characteriza*on of Soma*c Muta*ons in Cancer Genomes Ben Raphael Department of Computer Science Center for Computa*onal Molecular Biology Soma*c Muta*ons and Cancer Clonal Theory (Nowell 1976) Passenger
Tissue Factor/PAR2 signaling enhances the malignancy and radiation resistance of lung cancer brain metastases
 Tissue Factor/PAR2 signaling enhances the malignancy and radiation resistance of lung cancer brain metastases Dusten Unruh, PhD 8 th Annual Brain Metastases Research and Emerging Therapy Conference Tissue
Tissue Factor/PAR2 signaling enhances the malignancy and radiation resistance of lung cancer brain metastases Dusten Unruh, PhD 8 th Annual Brain Metastases Research and Emerging Therapy Conference Tissue
Systematic approaches to. overcoming limitations of MAPK pathway inhibition in melanoma.
 Systematic approaches to overcoming limitations of MAPK pathway inhibition in melanoma The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story
Systematic approaches to overcoming limitations of MAPK pathway inhibition in melanoma The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story
What is the Warburg Effect
 What is the Warburg Effect Roles nutrients play in the biochemistry of a cell Thus, proliferating cells must acquire more nutrients, convert them into biosynthetic building blocks, and coordinate the reactions
What is the Warburg Effect Roles nutrients play in the biochemistry of a cell Thus, proliferating cells must acquire more nutrients, convert them into biosynthetic building blocks, and coordinate the reactions
Relative Rates. SUM159 CB- 839-Resistant *** n.s Intracellular % Labeled by U- 13 C-Asn 0.
 A Relative Growth Rates 1.2 1.8.6.4.2 B Relative Rates 1.6 1.4 1.2 1.8.6.4.2 LPS2 Parental LPS2 Q-Independent SUM159 Parental SUM159 CB-839-Resistant LPS2 Parental LPS2 Q- Independent SUM159 Parental SUM159
A Relative Growth Rates 1.2 1.8.6.4.2 B Relative Rates 1.6 1.4 1.2 1.8.6.4.2 LPS2 Parental LPS2 Q-Independent SUM159 Parental SUM159 CB-839-Resistant LPS2 Parental LPS2 Q- Independent SUM159 Parental SUM159
mirna Dr. S Hosseini-Asl
 mirna Dr. S Hosseini-Asl 1 2 MicroRNAs (mirnas) are small noncoding RNAs which enhance the cleavage or translational repression of specific mrna with recognition site(s) in the 3 - untranslated region
mirna Dr. S Hosseini-Asl 1 2 MicroRNAs (mirnas) are small noncoding RNAs which enhance the cleavage or translational repression of specific mrna with recognition site(s) in the 3 - untranslated region
Gene+c fate mapping. x loxp. Foxp3 3 UTR ROSA26 RFP IRES GFP CRE. STOP loxp. Stable Foxp3 expression. Foxp3 expression in new Treg.
 1 Introduc+on (CD4 + CD25 + Foxp3 + )are indispensable for immune homeostasis. Muta+ons in Foxp3 gene leads to fatal autoimmune disorder. Condi+onal dele+on of Foxp3 reprograms cells into pathogenic Th
1 Introduc+on (CD4 + CD25 + Foxp3 + )are indispensable for immune homeostasis. Muta+ons in Foxp3 gene leads to fatal autoimmune disorder. Condi+onal dele+on of Foxp3 reprograms cells into pathogenic Th
Supplementary Figure 1: Comparison of acgh-based and expression-based CNA analysis of tumors from breast cancer GEMMs.
 Supplementary Figure 1: Comparison of acgh-based and expression-based CNA analysis of tumors from breast cancer GEMMs. (a) CNA analysis of expression microarray data obtained from 15 tumors in the SV40Tag
Supplementary Figure 1: Comparison of acgh-based and expression-based CNA analysis of tumors from breast cancer GEMMs. (a) CNA analysis of expression microarray data obtained from 15 tumors in the SV40Tag
m 6 A mrna methylation regulates AKT activity to promote the proliferation and tumorigenicity of endometrial cancer
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Articles https://doi.org/10.1038/s41556-018-0174-4 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. m 6 A mrna methylation regulates AKT activity to promote the proliferation
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Articles https://doi.org/10.1038/s41556-018-0174-4 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. m 6 A mrna methylation regulates AKT activity to promote the proliferation
Supplementary Information and Figure legends
 Supplementary Information and Figure legends Table S1. Primers for quantitative RT-PCR Target Sequence (5 -> 3 ) Target Sequence (5 -> 3 ) DAB2IP F:TGGACGATGTGCTCTATGCC R:GGATGGTGATGGTTTGGTAG Snail F:CCTCCCTGTCAGATGAGGAC
Supplementary Information and Figure legends Table S1. Primers for quantitative RT-PCR Target Sequence (5 -> 3 ) Target Sequence (5 -> 3 ) DAB2IP F:TGGACGATGTGCTCTATGCC R:GGATGGTGATGGTTTGGTAG Snail F:CCTCCCTGTCAGATGAGGAC
Supplementary Figure 1. Spatial distribution of LRP5 and β-catenin in intact cardiomyocytes. (a) and (b) Immunofluorescence staining of endogenous
 Supplementary Figure 1. Spatial distribution of LRP5 and β-catenin in intact cardiomyocytes. (a) and (b) Immunofluorescence staining of endogenous LRP5 in intact adult mouse ventricular myocytes (AMVMs)
Supplementary Figure 1. Spatial distribution of LRP5 and β-catenin in intact cardiomyocytes. (a) and (b) Immunofluorescence staining of endogenous LRP5 in intact adult mouse ventricular myocytes (AMVMs)
The Neurobiology of Au0sm. Computa0onal Psychiatry Seminar HS 14 Isabel Berwian
 The Neurobiology of Au0sm Computa0onal Psychiatry Seminar HS 14 Isabel Berwian 07.11.2014 Content NeurotransmiFer (Lam et al., 2006) Gene0cs (Klei et al., 2012) Animal models (Schneider, 2010) Why study
The Neurobiology of Au0sm Computa0onal Psychiatry Seminar HS 14 Isabel Berwian 07.11.2014 Content NeurotransmiFer (Lam et al., 2006) Gene0cs (Klei et al., 2012) Animal models (Schneider, 2010) Why study
Supplemental Data. TGF-β-mediated mir-181a expression promotes breast cancer metastasis by targeting Bim.
 Supplemental Data TGF-β-mediated mir-181a expression promotes breast cancer metastasis by targeting Bim. Molly A. Taylor 1, Khalid Sossey-Alaoui 2, Cheryl L. Thompson 3, David Danielpour 4, and William
Supplemental Data TGF-β-mediated mir-181a expression promotes breast cancer metastasis by targeting Bim. Molly A. Taylor 1, Khalid Sossey-Alaoui 2, Cheryl L. Thompson 3, David Danielpour 4, and William
Reviewers' comments: Reviewer #1 (Remarks to the Author):
 Reviewers' comments: Reviewer #1 (Remarks to the Author): In this study the authors analysed 18 deep penetrating nevi for oncogenic genomic changes (single nucleotide variations, insertions/deletions,
Reviewers' comments: Reviewer #1 (Remarks to the Author): In this study the authors analysed 18 deep penetrating nevi for oncogenic genomic changes (single nucleotide variations, insertions/deletions,
Enzyme-coupled Receptors. Cell-surface receptors 1. Ion-channel-coupled receptors 2. G-protein-coupled receptors 3. Enzyme-coupled receptors
 Enzyme-coupled Receptors Cell-surface receptors 1. Ion-channel-coupled receptors 2. G-protein-coupled receptors 3. Enzyme-coupled receptors Cell-surface receptors allow a flow of ions across the plasma
Enzyme-coupled Receptors Cell-surface receptors 1. Ion-channel-coupled receptors 2. G-protein-coupled receptors 3. Enzyme-coupled receptors Cell-surface receptors allow a flow of ions across the plasma
Translational Bioinformatics: Connecting Genes with Drugs
 Translational Bioinformatics: Connecting Genes with Drugs Aik Choon Tan, Ph.D. Associate Professor of Bioinformatics Division of Medical Oncology Department of Medicine aikchoon.tan@ucdenver.edu 11/14/2017
Translational Bioinformatics: Connecting Genes with Drugs Aik Choon Tan, Ph.D. Associate Professor of Bioinformatics Division of Medical Oncology Department of Medicine aikchoon.tan@ucdenver.edu 11/14/2017
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/7/322/ra38/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Dynamic Reprogramming of Signaling Upon Met Inhibition Reveals a Mechanism of Drug Resistance in Gastric Cancer Andrea
www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/7/322/ra38/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Dynamic Reprogramming of Signaling Upon Met Inhibition Reveals a Mechanism of Drug Resistance in Gastric Cancer Andrea
SOS1 and Ras regulate epithelial tight junction formation in the human airway through EMP1
 Manuscript EMBOR-2014-39218 SOS1 and Ras regulate epithelial tight junction formation in the human airway through EMP1 Joanne Durgan, Guangbo Tao, Matthew S. Walters, Oliver Florey, Anja Schmidt, Vanessa
Manuscript EMBOR-2014-39218 SOS1 and Ras regulate epithelial tight junction formation in the human airway through EMP1 Joanne Durgan, Guangbo Tao, Matthew S. Walters, Oliver Florey, Anja Schmidt, Vanessa
Differential effects of oncogenic K-Ras and N-Ras on proliferation, differentiation, and tumor progression in the colon
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Differential effects of oncogenic K-Ras and N-Ras on proliferation, differentiation, and tumor progression in the colon Kevin M. Haigis, Krystle Kendall, Yufang Wang, Ann Cheung,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Differential effects of oncogenic K-Ras and N-Ras on proliferation, differentiation, and tumor progression in the colon Kevin M. Haigis, Krystle Kendall, Yufang Wang, Ann Cheung,
Src-INACTIVE / Src-INACTIVE
 Biology 169 -- Exam 1 February 2003 Answer each question, noting carefully the instructions for each. Repeat- Read the instructions for each question before answering!!! Be as specific as possible in each
Biology 169 -- Exam 1 February 2003 Answer each question, noting carefully the instructions for each. Repeat- Read the instructions for each question before answering!!! Be as specific as possible in each
Supplementary Figure 1: Tissue of Origin analysis on 152 cell lines. (a) Heatmap representation of the 30 Tissue scores for the 152 cell lines.
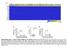 Supplementary Figure 1: Tissue of Origin analysis on 152 cell lines. (a) Heatmap representation of the 30 Tissue scores for the 152 cell lines. The scores summarize the global expression of the tissue
Supplementary Figure 1: Tissue of Origin analysis on 152 cell lines. (a) Heatmap representation of the 30 Tissue scores for the 152 cell lines. The scores summarize the global expression of the tissue
p53 and Apoptosis: Master Guardian and Executioner Part 2
 p53 and Apoptosis: Master Guardian and Executioner Part 2 p14arf in human cells is a antagonist of Mdm2. The expression of ARF causes a rapid increase in p53 levels, so what would you suggest?.. The enemy
p53 and Apoptosis: Master Guardian and Executioner Part 2 p14arf in human cells is a antagonist of Mdm2. The expression of ARF causes a rapid increase in p53 levels, so what would you suggest?.. The enemy
CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: Massachusetts General Hospital Boston, MA
 AD Award Number: W81XWH-12-1-0420 TITLE: An in vivo shrna-drug screen to identify novel targeted therapy combinations for KRAS mutant cancers PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Ryan B. Corcoran, MD PhD CONTRACTING
AD Award Number: W81XWH-12-1-0420 TITLE: An in vivo shrna-drug screen to identify novel targeted therapy combinations for KRAS mutant cancers PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Ryan B. Corcoran, MD PhD CONTRACTING
Tips for genome-wide shrna pooled screen
 Tips for genome-wide shrna pooled screen 鄭金松 1 Approaches to large-scale RNAi screen/selection (I) Arrayed RNAi screen To address the hits by arrayed information (a) sirna / plasmid shrna (b) Arrayed viral
Tips for genome-wide shrna pooled screen 鄭金松 1 Approaches to large-scale RNAi screen/selection (I) Arrayed RNAi screen To address the hits by arrayed information (a) sirna / plasmid shrna (b) Arrayed viral
Protein kinases are enzymes that add a phosphate group to proteins according to the. ATP + protein OH > Protein OPO 3 + ADP
 Protein kinase Protein kinases are enzymes that add a phosphate group to proteins according to the following equation: 2 ATP + protein OH > Protein OPO 3 + ADP ATP represents adenosine trisphosphate, ADP
Protein kinase Protein kinases are enzymes that add a phosphate group to proteins according to the following equation: 2 ATP + protein OH > Protein OPO 3 + ADP ATP represents adenosine trisphosphate, ADP
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Fig. S1. Overexpression of Rpr causes progenitor cell death. (A) TUNEL assay of control intestines. No progenitor cell death could be observed, except that some ECs are undergoing
Supporting Information Fig. S1. Overexpression of Rpr causes progenitor cell death. (A) TUNEL assay of control intestines. No progenitor cell death could be observed, except that some ECs are undergoing
Validation & Assay Performance Summary
 Validation & Assay Performance Summary CellSensor DBE-bla MDA-MB-468 Cell Line Cat. no. K1814 Pathway Description The phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase (PI3K) signaling cascade is essential for cell growth
Validation & Assay Performance Summary CellSensor DBE-bla MDA-MB-468 Cell Line Cat. no. K1814 Pathway Description The phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase (PI3K) signaling cascade is essential for cell growth
Cellecta Overview. Started Operations in 2007 Headquarters: Mountain View, CA
 Cellecta Overview Started Operations in 2007 Headquarters: Mountain View, CA Focus: Development of flexible, scalable, and broadly parallel genetic screening assays to expedite the discovery and characterization
Cellecta Overview Started Operations in 2007 Headquarters: Mountain View, CA Focus: Development of flexible, scalable, and broadly parallel genetic screening assays to expedite the discovery and characterization
An epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition-inducing potential of. granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor in colon. cancer
 An epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition-inducing potential of granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor in colon cancer Yaqiong Chen, Zhi Zhao, Yu Chen, Zhonglin Lv, Xin Ding, Renxi Wang, He Xiao,
An epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition-inducing potential of granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor in colon cancer Yaqiong Chen, Zhi Zhao, Yu Chen, Zhonglin Lv, Xin Ding, Renxi Wang, He Xiao,
Sta$s$cs, the Law, and the Future of Personalized Medicine. (What happened over spring break)
 Sta$s$cs, the Law, and the Future of Personalized Medicine (What happened over spring break) Mayo v. Prometheus Prometheus Laboratories, Inc. developed a diagnos$c test for direc$ng treatment of immune-
Sta$s$cs, the Law, and the Future of Personalized Medicine (What happened over spring break) Mayo v. Prometheus Prometheus Laboratories, Inc. developed a diagnos$c test for direc$ng treatment of immune-
Inhibition of DDR1-BCR signaling by nilotinib as a new therapeutic strategy for metastatic colorectal cancer
 Inhibition of DDR1-BCR signaling by nilotinib as a new therapeutic strategy for metastatic colorectal cancer Maya Jeitany, Cedric Leroy, Priscillia Tosti, Marie Lafitte, Jordy Le Guet, Valérie Simon, Debora
Inhibition of DDR1-BCR signaling by nilotinib as a new therapeutic strategy for metastatic colorectal cancer Maya Jeitany, Cedric Leroy, Priscillia Tosti, Marie Lafitte, Jordy Le Guet, Valérie Simon, Debora
Regarding techniques of proteomics, there is:
 Molecular الحلقة biology 14 واألخيرة To put you back in the context; the discussion was about Trancriptomics (the study of transcription). The following topic will be PROTEOMICS, which is the study of
Molecular الحلقة biology 14 واألخيرة To put you back in the context; the discussion was about Trancriptomics (the study of transcription). The following topic will be PROTEOMICS, which is the study of
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Nature. Author manuscript; available in PMC 2011 September 22.
 NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Nature. 2010 March 18; 464(7287): 427 430. doi:10.1038/nature08902. RAF inhibitors transactivate RAF dimers and ERK signaling in cells
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Nature. 2010 March 18; 464(7287): 427 430. doi:10.1038/nature08902. RAF inhibitors transactivate RAF dimers and ERK signaling in cells
