OCT4 Expression Enhances Features of Cancer Stem Cells in a Mouse Model of Breast Cancer
|
|
|
- Dale Tyler
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Lab Anim Res 2011: 27(2), DOI: /lar OCT4 Expression Enhances Features of Cancer Stem Cells in a Mouse Model of Breast Cancer Ran-Ju Kim and Jeong-Seok Nam* Laboratory of Tumor Suppressor, Lee Gil Ya Cancer and Diabetes Institute, Gachon University of Medicine and Science, Incheon, Republic of Korea The cancer stem cell (CSC) hypothesis proposes that CSCs are responsible for metastasis and disease recurrence. Therefore, targeting CSCs has the potential to significantly improve outcomes for cancer patients. The OCT4 transcription factor gene is a master gene that plays a key role in the self-renewal and pluripotency of stem cells. In this study, we introduced an OCT4 reporting vector into 4T1 mouse breast cancer cells and sorted OCT4 high and OCT4 low cell populations. We then determined whether OCT4 expression is associated with maintenance and expansion of CSCs. We found that OCT4 high 4T1 cells have an increased ability to form tumorsphere and a high expression of stem cell markers such as Sca-1, CD133, CD34, and ALDH1, when compared with OCT4 low 4T1 cells. In addition, OCT4 high 4T1 cells have greater tumorigenic potential in vivo. These findings suggest that OCT4 expression may be a useful target for stem cell-specific cancer therapy. Key words: Cancer stem cell, OCT4, breast cancer Received 6 May 2011; Revised version received 6 June 2011; Accepted 7 June 2011 The cancer stem cell (CSC) hypothesis proposes that CSCs, which constitute a small population of cells within a tumor, are able to self-renew and to give rise to diverse cellular progeny. Indeed, CSCs may be responsible for the escape of tumors from conventional therapies, resulting in residual CSCs that can lead to disease recurrence and metastasis [1-3]. Therefore, CSC-specific therapies might prevent cancer relapse and completely destroy cancer at its root. The OCT4 (also known as POU5F1) transcription factor gene is known as a master pluripotency gene [4,5]. Kim and colleagues showed that OCT4 alone is sufficient to directly reprogram adult mouse neural stem cells to pluripotent stem (ips) cells [6]. Clinical studies have shown that tumors with intense expression of the OCT4 stem cell marker are associated with further disease progression, greater metastasis, and shorter cancer-related survival compared with tumors with moderate and low OCT4 expression [7]. Furthermore, OCT4 is reported to be a core regulator of stem cell selfrenewal and differentiation, and was recently validated as a CSC target [8]. Based on these findings, our study attempts to identify the CSC population characterized by the OCT4 phenotype among 4T1 mouse breast cancer cells. To this end, we stably infected 4T1 cells with a retroviral particle which contains the mouse OCT4 promoter and drives expression of red fluorescent protein (RFP). The goal was to determine whether targeting of OCT4 expression is a feasible strategy for stem specific cancer therapy in a rigorously defined mouse 4T1 breast tumor model. Materials and Methods Cell culture Mouse breast cancer cell lines (67NR and 4T1) and human breast cancer cell lines (MCF-7, T-47D, MDA-MB-231, and Hs578T) were cultured in DMEM (Invitrogen, Grand Island, NY, USA) containing 10% FBS and 1% penicillin /streptomycin *Corresponding author: Jeong-Seok Nam, Lee Gil Ya Cancer and Diabetes Institute, Gachon University of Medicine and Science, 7-45 Songdo-dong, Yeonsu-ku, Incheon , Korea Tel/Fax: / ; namjs@gachon.ac.kr This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License ( by-nc/3.0) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. 147
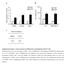
2 148 Ran-Ju Kim and Jeong-Seok Nam (Invitrogen), as previously described [9-11]. The 4T1-Luc- OCT4 cell line was established by infection of 4T1-Luc cells (Caliper Life Sciences, Hopkinton, MA, USA) with a mouse OCT4-pRFPZeo packaged virus particle (System Biosciences, Mountain View, CA, USA) according to the manufacturer s protocol. Stable transfectants were selected by incubation with zeocin (300 mg/ml, Invitrogen), and OCT4 expression was determined using a fluorescent microscope (Carl Zeiss, Thornwood, NY, USA). Flow cytometry FACS analysis and sorting were performed using a FACS Calibur and FACSAria (Becton Dickinson, Franklin Lakes, NJ, USA), respectively. FACS data were analyzed using Flowjo software (Tree Star, Ashland, OR, USA). The Aldefluor kit (Stem Cell Technologies, Vancouver, Canada) was used to isolate a population with high aldehyde dehydrogenase (ALDH) enzymatic activity, according to the manufacturer s instructions. The following antibody was used: OCT4 (Abcam, Cambridge, MA, USA). An APC-conjugated rabbit IgG antibody (Molecular Probes, Eugene, OR, USA) was used for visualization. Tumorsphere culture Tumor sphere culturing was performed as previously described [12,13]. After 7 to 10 days of culturing, wells were examined under an inverted microscope at x50 magnification, and the number and diameter of spheres was determined for independent fields per well using the Image-Pro Plus program (Media Cybernetics, Bethesda, MD, USA). In vivo limiting dilution assay All animals were maintained according to IACUC approved protocols of the Lee Gil Ya Cancer and Diabetes Institute, Korea. For titration experiments, the left and right thoracic (#2) mammary fat pads (m.f.p.) of anesthetized 7-week-old female Balb/c mice (Orient Charles River Technology, Seoul, Korea) were surgically exposed and sorted 4T1 cells were inoculated into m.f.p. in a 50 ml volume (n=3/group). Tumor incidence was assessed via in vivo bioluminescence measurement using an IVIS Imaging System (Caliper Life Sciences). For luciferase detection, 150 mg/ml D-luciferin (Caliper Life Sciences) in PBS was injected intraperitoneally before imaging. Photometric measurement of tumors was done by Living Image software (V , Caliper Life Sciences). SYBR green PCR master mix (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA, USA) and the ABI 7300 real-time PCR system according to the manufacturer s instructions. The quantitative RT-PCR was done in triplicate. Mouse mrna levels were normalized with mouse hypoxanthine-guanine phosphoribosyltransferase (HPRT). The primer sets used in this study were as follows: OCT4: 5'-GCATTCAAACTGAGGCACCA-3' (forward) and 5'- AGCTTCTTTCCCCATCCCA-3' (reverse); Sca-1: 5'-TCA GTC CTC CTG CAG ACC TT-3' (forward), 5'-ACTCCCACCTTGGA GCTTCT-3' (reverse); ALDH1: 5'-GCTAGCTACAATGGAGG CACTCA-3' (forward), 5'-GCA GCCTCCTAAATCCGACA-3' (reverse); CD133: 5'-CACTTGATGCCACTGCCAAA-3' (forward), 5'-TGACACTGAACGTAATGCCCAT (reverse); CD34: 5'- AAAGGCCAATGTGACCCGA-3' (forward), 5'-TGCCACTTTC CTGCATACCAC-3' (reverse); CD90: 5'-TCCAAGCCCTGGAC TTCA TTT C-3' (forward), 5 -CCGTTT CTCCCCATGTTCT GAG-3' (reverse); HPRT: 5'-GCCTAAGATGAGCGCAA GTTG- 3' (forward), 5'-TACTAGGCAGATGGCCACAGG-3' (reverse). Statistical analysis All experiments were done 3 or more times, and the results are expressed as mean±sd. Statistical analyses of these data were done using an unpaired Student s t-test for parametric analysis or the Mann-Whitney U test for nonparametric analysis. Results The ALDH pos CSC population has a high OCT4 expression The expression of ALDH as assessed by the Aldefluor assay has been recognized as a marker for malignant stem cells in breast cancers [14]. To evaluate OCT4 expression in the CSC population characterized by high ALDH activity, we compared the expression of OCT4 in ALDH neg and ALDH pos cell population sorted from 4T1 cells. RTQ-PCR analysis showed a significant increase (~3.3-fold) of OCT4 mrna expression in ALDH pos 4T1 cells (Figure 1A). To confirm the correlation between ALDH activity and OCT4 expression, we examined OCT4 expression in ALDH neg and ALDH pos cell population from various mouse and human breast cancer cell lines. FACS analysis showed that expression of OCT4 significantly increased (3.3- to 9.5-fold) in ALDH pos cell population compared with ALDH neg cell population of breast cancer cell lines (Figure 1B). Quantitative reverse-transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RTQ-PCR) RTQ-PCR for quantification of cdna was performed using OCT4 high 4T1 cell population has high tumorsphere forming ability It has been reported that cancer stem-cell like cells can
3 The role of OCT4 expression in 4T1 breast cancer model 149 Figure 1. ALDH pos 4T1 cells show a large increase in OCT4 expression in breast cancer cells. (A) RTQ-PCR analysis of OCT4 in ALDH neg and ALDH pos 4T1 cells. Left panel, the contour plot shows the percentage of ALDH activity in 4T1 cells. (B) Flow cytometry profiles of OCT4 expression on ALDH neg or ALDH pos cell population derived from breast cancer cell lines (67NR, 4T1, MCF-7, T- 47D, MDA-MB-231, and Hs578T). Values are mean±sd. *P<0.05 is a statistically significant difference. be cultured in vitro to test stem cell properties such as selfrenewal in serum-free medium with bfgf and EGF [12]. To determine whether 4T1 cells showing OCT4 high have high sphere-forming ability, we introduced an OCT4-RFP vector into 4T1-Luc cells (Figure 1A), sorted 4T1-Luc cells into OCT4 low and OCT4 high cell population, and plated the freshly isolated cell populations under tumorsphere forming culture conditions (Figure 2A). Only the OCT4 high cell population grew into typical spheres and they showed much larger and greater numbers of spheres than did the OCT4 low cell population (Figure 2B). OCT4 high 4T1 cell population has more tumorigenic potential in vivo in immune-competent mice To investigate the in vivo tumorigenic ability of OCT4 high cell population, we injected sorted cells into the mammary glands of mice. As shown in Table 1, OCT4 high 4T1-Luc cells gave rise to tumors in five of six inoculations (83.3%) with as few as 100 cells. At the same injection dose (100 cells), OCT4 low 4T1-Luc cells gave rise to tumors in 16.6% of trials (one of six inoculations). The OCT4 high cell population showed ~5-fold enrichment compared with the OCT4 low cell population. At 100-cell inoculation, in vivo imaging showed
4 150 Ran-Ju Kim and Jeong-Seok Nam Figure 2. An OCT4 high cell population isolated from 4T1-Luc cells has a high efficiency of tumorsphere formation in vitro. (A) The level of red fluorescence was determined in moct4-rfp infected 4T1-Luc cells using a fluorescence microscope. (B) The ability of OCT4 low and OCT4 high 4T1-Luc cells cultured in low attachment dishes to form spheres was determined as described in Materials and Methods. Values are mean±sd. *P<0.05 is a statistically significant difference. Table 1. Tumor-initiating ability of the OCT4 high cell population in the 4T1 syngeneic mouse model Number of implanted cells Cell type a OCT4 low 3/6 2/6 1/6 OCT4 high 5/6 5/6 5/6 a These cells injected into mammary fat pad of Balb/c mice at varying initial cell counts. an increase (~2-fold) in bioluminescence in the primary tumor generated by OCT4 high 4T1-Luc cells, compared with OCT4 low 4T1-Luc cells (Figure 3). These results demonstrate that the OCT4 high cell population has more tumorigenic potential in vivo in an immune competent microenvironment. The OCT4 high 4T1 cell population has high expression of stem cell markers To further characterize the OCT4 high cell population, we compared expression profiles of stem cell marker genes [13-18] in OCT4 low and OCT4 high cell population sorted from 4T1-Luc cells. RTQ-PCR analysis showed significant increases (~2-fold to 3-fold) for Sca-1, CD133, CD34 and ALDH1 expression but no significant change in CD90 expression in the OCT4 high cell population over the OCT4 low cell population (Figure 4). Taken together, these results show that the expression of stem cell markers is highly increased in the OCT4 high cell population. Discussion The OCT4 gene, a member of the POU family of transcription factors, was shown to be expressed in stem cells [19,20]. In this study, we applied OCT4 positive cell analysis and sorting to cause enrichment in putative CSCs in the 4T1 mouse model. The 4T1 breast cancer model is widely considered to be one of the best syngeneic xenograft mouse
5 The role of OCT4 expression in 4T1 breast cancer model 151 Figure 3. OCT4 high 4T1-Luc cells have greater tumorigenic potential in vivo in immune-competent mice. Tumor growth was monitored and quantified by bioluminescence. Figure 4. OCT4 high 4T1 cells isolated from 4T1-Luc cells have high expression of stem cell markers. RTQ-PCR was performed using primers for stem cell markers. Values are mean±sd for 3 determinations. *P<0.05 is a statistically significant difference. models for the study of human cancer progression [21,22]. To our knowledge, this is the first report that OCT4 may be a good marker for CSC characterization in an immunecompetent syngeneic tumor microenvironment. This conclusion was supported by the following findings. First, the size of the OCT4 high cell population isolated from 4T1 cells was positively correlated with tumorigenicity in immunecompetent mice compared with the OCT4 low cell population. Second, CSCs expressing OCT4 displayed high tumorsphere forming ability in vitro. Third, the OCT4 high cell population had high expression of stem cell markers compared with the OCT4 low cell population. Self-renewal and pluripotency are central features in the definition of stem cell populations, and OCT4 is a key regulator in these processes [19, 23]. Further, the expression of OCT4 has been shown in human breast cancer stem-like cells, implicating its involvement in self-renewal and tumorigenesis [24]. Recently, Hu and colleagues suggested that a reduction in OCT4 expression in lung CSCs induces apoptosis and the inhibition of tumor growth partly through the OCT4/Tcl1/ Akt1 pathway [8]. In addition, OCT4 was recently reported to play a critical role in survival/apoptosis of embryonic stem cells via stat3/survivin [25]. However, the detailed molecular roles of OCT4 in cancer stemness have not yet been fully elucidated. Therefore, additional studies are necessary to look into downstream molecular mechanisms by which OCT4 regulates the maintenance and expansion of CSCs. In summary, the present work suggests that high expression of OCT4 enhances stem cell properties in a mouse model of breast cancer. Thus, OCT4 may represent a target molecule for the treatment of advanced cancer. Acknowledgment This work was supported by the Korea Research Foundation Grant funded by the Korean Government (MOEHRD, Basic Research Promotion Fund) (KRF E00259). References 1. Dean M, Fojo T, Bates S. Tumour stem cells and drug resistance. Nat Rev Cancer 2005; 5(4): Charafe-Jauffret E, Monville F, Ginestier C, Dontu G, Birnbaum D, Wicha MS. Cancer Stem Cells in Breast: Current Opinion and Future Challenges. Pathobiology 2008; 75(2): Gangemi R, Paleari L, Orengo AM, Cesario A, Chessa L, Ferrini S, et al. Cancer stem cells: a new paradigm for understanding tumor growth and progression and drug resistance. Curr Med Chem 2009; 16(14): Hansis C, Grifo JA, Krey LC. Oct-4 expression in inner cell mass and trophectoderm of human blastocysts. Mol Hum Reprod 2000; 6(11): Burdon T, Smith A, Savatier P. Signalling, cell cycle and pluripotency in embryonic stem cells. Trends Cell Biol 2002; 12(9): Kim JB, Greber B, Arauzo-Bravo MJ, Meyer J, Park KI, Zaehres H, et al. Direct reprogramming of human neural stem cells by OCT4. Nature 2009; 461(7264):
6 152 Ran-Ju Kim and Jeong-Seok Nam 7. Chang CC, Shieh GS, Wu P, Lin CC, Shiau AL, Wu CL. Oct- 3/4 expression reflects tumor progression and regulates motility of bladder cancer cells. Cancer Res 2008; 68 (15): Hu T, Liu S, Breiter DR, Wang F, Tang Y, Sun S. Octamer 4 small interfering RNA results in cancer stem cell-like cell apoptosis. Cancer Res 2008; 68(16): Nam JS, Kang MJ, Suchar AM, Shimamura T, Kohn EA, Michalowska AM, et al. Chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 2 mediates the prometastatic effect of dysadherin in human breast cancer cells. Cancer Res 2006; 66(14): Nam JS, Suchar AM, Kang MJ, Stuelten CH, Tang B, Michalowska AM, et al. Bone sialoprotein mediates the tumor cell-targeted prometastatic activity of transforming growth factor beta in a mouse model of breast cancer. Cancer Res 2006; 66(12): Choi ES, Cho SD, Jeon JG, Cho NP. The Apoptotic Effect of the Hexane Extract of Rheum undulatum L. in Oral Cancer Cells through the Down-regulation of Specificity Protein 1 and Survivin. Lab Anim Res 2011; 27(1): Dontu G, Abdallah WM, Foley JM, Jackson KW, Clarke MF, Kawamura MJ, et al. In vitro propagation and transcriptional profiling of human mammary stem/progenitor cells. Genes Dev 2003; 17(10): Kim RJ, Kim SR, Roh KJ, Park SB, Park JR, Kang KS, et al. Ras activation contributes to the maintenance and expansion of Sca-1pos cells in a mouse model of breast cancer. Cancer Lett 2010; 287(2): Ginestier C, Hur MH, Charafe-Jauffret E, Monville F, Dutcher J, Brown M, et al. ALDH1 Is a Marker of Normal and Malignant Human Mammary Stem Cells and a Predictor of Poor Clinical Outcome. Cell Stem Cell 2007; 1(5): Bao S, Wu Q, McLendon RE, Hao Y, Shi Q, Hjelmeland AB, et al. Glioma stem cells promote radioresistance by preferential activation of the DNA damage response. Nature 2006; 444(7120): Bonnet D, Dick JE. Human acute myeloid leukemia is organized as a hierarchy that originates from a primitive hematopoietic cell. Nat Med 1997; 3(7): Welm BE, Tepera SB, Venezia T, Graubert TA, Rosen JM, Goodell MA. Sca-1(pos) cells in the mouse mammary gland represent an enriched progenitor cell population. Dev Biol 2002; 245(1): Yang ZF, Ho DW, Ng MN, Lau CK, Yu WC, Ngai P, et al. Significance of CD90+ cancer stem cells in human liver cancer. Cancer Cell 2008; 13(2): Nichols J, Zevnik B, Anastassiadis K, Niwa H, Klewe- Nebenius D, Chambers I, et al. Formation of pluripotent stem cells in the mammalian embryo depends on the POU transcription factor Oct4. Cell 1998; 95(3): Babaie Y, Herwig R, Greber B, Brink TC, Wruck W, Groth D, et al. Analysis of Oct4-dependent transcriptional networks regulating self-renewal and pluripotency in human embryonic stem cells. Stem Cells 2007; 25(2): Kuperwasser C, Chavarria T, Wu M, Magrane G, Gray JW, Carey L, et al. Reconstruction of functionally normal and malignant human breast tissues in mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2004; 101(14): Lelekakis M, Moseley JM, Martin TJ, Hards D, Williams E, Ho P, et al. A novel orthotopic model of breast cancer metastasis to bone. Clin Exp Metastasis 1999; 17(2): Boiani M, Scholer HR. Regulatory networks in embryoderived pluripotent stem cells. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2005; 6(11): Ponti D, Costa A, Zaffaroni N, Pratesi G, Petrangolini G, Coradini D, et al. Isolation and in vitro propagation of tumorigenic breast cancer cells with stem/progenitor cell properties. Cancer Res 2005; 65(13): Guo Y, Mantel C, Hromas RA, Broxmeyer HE. Oct-4 is critical for survival/antiapoptosis of murine embryonic stem cells subjected to stress: effects associated with Stat3/survivin. Stem Cells 2008; 26(1):
Inhibitor of DNA-binding 4 contributes to the maintenance and expansion of cancer stem cells in 4T1 mouse mammary cancer cell line
 Lab Anim Res 2011: 27(4), 333-338 http://dx.doi.org/10.5625/lar.2011.27.4.333 Inhibitor of DNA-binding 4 contributes to the maintenance and expansion of cancer stem cells in 4T1 mouse mammary cancer cell
Lab Anim Res 2011: 27(4), 333-338 http://dx.doi.org/10.5625/lar.2011.27.4.333 Inhibitor of DNA-binding 4 contributes to the maintenance and expansion of cancer stem cells in 4T1 mouse mammary cancer cell
Material and Methods. Flow Cytometry Analyses:
 Material and Methods Flow Cytometry Analyses: Immunostaining of breast cancer cells for HER2 was performed by incubating cells with anti- HER2/neu APC (Biosciences, Cat# 340554), anti-her2/neu PE (Biosciences,
Material and Methods Flow Cytometry Analyses: Immunostaining of breast cancer cells for HER2 was performed by incubating cells with anti- HER2/neu APC (Biosciences, Cat# 340554), anti-her2/neu PE (Biosciences,
TUMOR INITIATING CELLS: THE STEM CELL THEORY OF CANCER
 Pr John DE VOS Département d Ingénierie Cellulaire et Tissulaire INSERM 1183 - IRMB Hôpital St Eloi - CHU de Montpellier john.devos@inserm.fr @_jdevos_ TUMOR INITIATING CELLS: THE STEM CELL THEORY OF CANCER
Pr John DE VOS Département d Ingénierie Cellulaire et Tissulaire INSERM 1183 - IRMB Hôpital St Eloi - CHU de Montpellier john.devos@inserm.fr @_jdevos_ TUMOR INITIATING CELLS: THE STEM CELL THEORY OF CANCER
5K ALDEFLUOR-positive/ CXCR1-negative. 5K ALDEFLUOR-positive/ CXCR1-positive BAAA BAAA CXCR1-APC BAAA BAAA CXCR1-APC
 A +DEAB -DEAB K ALDEFLUOR-positive/ CXCR-negative BAAA BAAA CXCR-APC B +DEAB -DEAB K ALDEFLUOR-positive/ CXCR-positive BAAA BAAA CXCR-APC C Supplemental Figure. Tumorigenicity of the ALDEFLUOR-positive/CXCR-positive
A +DEAB -DEAB K ALDEFLUOR-positive/ CXCR-negative BAAA BAAA CXCR-APC B +DEAB -DEAB K ALDEFLUOR-positive/ CXCR-positive BAAA BAAA CXCR-APC C Supplemental Figure. Tumorigenicity of the ALDEFLUOR-positive/CXCR-positive
Supplementary Materials and Methods
 DD2 suppresses tumorigenicity of ovarian cancer cells by limiting cancer stem cell population Chunhua Han et al. Supplementary Materials and Methods Analysis of publicly available datasets: To analyze
DD2 suppresses tumorigenicity of ovarian cancer cells by limiting cancer stem cell population Chunhua Han et al. Supplementary Materials and Methods Analysis of publicly available datasets: To analyze
Effective activity of cytokine-induced killer cells against autologous metastatic melanoma including cells with stemness features
 Effective activity of cytokine-induced killer cells against autologous metastatic melanoma including cells with stemness features Loretta Gammaitoni, Lidia Giraudo, Valeria Leuci, et al. Clin Cancer Res
Effective activity of cytokine-induced killer cells against autologous metastatic melanoma including cells with stemness features Loretta Gammaitoni, Lidia Giraudo, Valeria Leuci, et al. Clin Cancer Res
Supplementary Figures
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Confirmation of Dnmt1 conditional knockout out mice. a, Representative images of sorted stem (Lin - CD49f high CD24 + ), luminal (Lin - CD49f low CD24 + )
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Confirmation of Dnmt1 conditional knockout out mice. a, Representative images of sorted stem (Lin - CD49f high CD24 + ), luminal (Lin - CD49f low CD24 + )
PRODUCTS FOR CANCER RESEARCH
 PRODUCTS FOR CANCER RESEARCH TABLE OF CONTENTS 3 4 6 10 11 12 Introduction ALDEFLUOR A Powerful Tool to Study Cancer Stem Cells Culture Media for Cancer Research Culture Media Products for Breast Cancer
PRODUCTS FOR CANCER RESEARCH TABLE OF CONTENTS 3 4 6 10 11 12 Introduction ALDEFLUOR A Powerful Tool to Study Cancer Stem Cells Culture Media for Cancer Research Culture Media Products for Breast Cancer
Differential Connexin Function Enhances Self-Renewal in Glioblastoma
 CSU ID: 2558414 Name: Sonal Patel Differential Connexin Function Enhances Self-Renewal in Glioblastoma Cancer is one of the most common disease in the US with more than a million people affected every
CSU ID: 2558414 Name: Sonal Patel Differential Connexin Function Enhances Self-Renewal in Glioblastoma Cancer is one of the most common disease in the US with more than a million people affected every
MATERIALS AND METHODS. Neutralizing antibodies specific to mouse Dll1, Dll4, J1 and J2 were prepared as described. 1,2 All
 MATERIALS AND METHODS Antibodies (Abs), flow cytometry analysis and cell lines Neutralizing antibodies specific to mouse Dll1, Dll4, J1 and J2 were prepared as described. 1,2 All other antibodies used
MATERIALS AND METHODS Antibodies (Abs), flow cytometry analysis and cell lines Neutralizing antibodies specific to mouse Dll1, Dll4, J1 and J2 were prepared as described. 1,2 All other antibodies used
HEK293FT cells were transiently transfected with reporters, N3-ICD construct and
 Supplementary Information Luciferase reporter assay HEK293FT cells were transiently transfected with reporters, N3-ICD construct and increased amounts of wild type or kinase inactive EGFR. Transfections
Supplementary Information Luciferase reporter assay HEK293FT cells were transiently transfected with reporters, N3-ICD construct and increased amounts of wild type or kinase inactive EGFR. Transfections
Extended Mammosphere Culture of Human Breast Cancer Cells
 Extended Mammosphere Culture of Human Breast Cancer Cells Application Note The PromoCell 3D Tumorsphere Medium XF The PromoCell 3D Tumorsphere Medium XF has been designed to meet your requirements for
Extended Mammosphere Culture of Human Breast Cancer Cells Application Note The PromoCell 3D Tumorsphere Medium XF The PromoCell 3D Tumorsphere Medium XF has been designed to meet your requirements for
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 3 3 3 1 1 Bregma -1.6mm 3 : Bregma Ref) Http://www.mbl.org/atlas165/atlas165_start.html Bregma -.18mm Supplementary Figure 1 Schematic representation of the utilized brain slice
Supplementary Figure 1 3 3 3 1 1 Bregma -1.6mm 3 : Bregma Ref) Http://www.mbl.org/atlas165/atlas165_start.html Bregma -.18mm Supplementary Figure 1 Schematic representation of the utilized brain slice
Roles of microrna-mediated Drug Resistance in Tumor Stem Cells of Small Cell Lung Carcinoma
 AD Award Number: W81XWH-12-1-0479 TITLE: Roles of microrna-mediated Drug Resistance in Tumor Stem Cells of Small Cell Lung Carcinoma PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Kounosuke Watabe, Ph.D. CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION:
AD Award Number: W81XWH-12-1-0479 TITLE: Roles of microrna-mediated Drug Resistance in Tumor Stem Cells of Small Cell Lung Carcinoma PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Kounosuke Watabe, Ph.D. CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION:
Supplementary Table; Supplementary Figures and legends S1-S21; Supplementary Materials and Methods
 Silva et al. PTEN posttranslational inactivation and hyperactivation of the PI3K/Akt pathway sustain primary T cell leukemia viability Supplementary Table; Supplementary Figures and legends S1-S21; Supplementary
Silva et al. PTEN posttranslational inactivation and hyperactivation of the PI3K/Akt pathway sustain primary T cell leukemia viability Supplementary Table; Supplementary Figures and legends S1-S21; Supplementary
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES AND TABLE
 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES AND TABLE Supplementary Figure S1: Characterization of IRE1α mutants. A. U87-LUC cells were transduced with the lentiviral vector containing the GFP sequence (U87-LUC Tet-ON GFP).
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES AND TABLE Supplementary Figure S1: Characterization of IRE1α mutants. A. U87-LUC cells were transduced with the lentiviral vector containing the GFP sequence (U87-LUC Tet-ON GFP).
CXCR1 blockade selectively targets human breast cancer stem cells in vitro and in xenografts
 Research article CXCR1 blockade selectively targets human breast cancer stem cells in vitro and in xenografts Christophe Ginestier, 1,2 Suling Liu, 1 Mark E. Diebel, 1 Hasan Korkaya, 1 Ming Luo, 3 Marty
Research article CXCR1 blockade selectively targets human breast cancer stem cells in vitro and in xenografts Christophe Ginestier, 1,2 Suling Liu, 1 Mark E. Diebel, 1 Hasan Korkaya, 1 Ming Luo, 3 Marty
Bmi-1 regulates stem cell-like properties of gastric cancer cells via modulating mirnas
 Wang et al. Journal of Hematology & Oncology (2016) 9:90 DOI 10.1186/s13045-016-0323-9 RESEARCH Bmi-1 regulates stem cell-like properties of gastric cancer cells via modulating mirnas Open Access Xiaofeng
Wang et al. Journal of Hematology & Oncology (2016) 9:90 DOI 10.1186/s13045-016-0323-9 RESEARCH Bmi-1 regulates stem cell-like properties of gastric cancer cells via modulating mirnas Open Access Xiaofeng
Supplementary Figure 1. Characterization of ALDH-positive cell population in MCF-7 cells. (a) Expression level of stem cell markers in MCF-7 cells or
 Supplementary Figure 1. Characterization of ALDH-positive cell population in MCF-7 cells. (a) Expression level of stem cell markers in MCF-7 cells or ALDH-positive cell population by qpcr. Data represent
Supplementary Figure 1. Characterization of ALDH-positive cell population in MCF-7 cells. (a) Expression level of stem cell markers in MCF-7 cells or ALDH-positive cell population by qpcr. Data represent
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature12215 Supplementary Figure 1. The effects of full and dissociated GR agonists in supporting BFU-E self-renewal divisions. BFU-Es were cultured in self-renewal medium with indicated GR
doi:10.1038/nature12215 Supplementary Figure 1. The effects of full and dissociated GR agonists in supporting BFU-E self-renewal divisions. BFU-Es were cultured in self-renewal medium with indicated GR
Type of file: PDF Size of file: 0 KB Title of file for HTML: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures
 Type of file: PDF Size of file: 0 KB Title of file for HTML: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1 mir-128-3p is highly expressed in chemoresistant, metastatic
Type of file: PDF Size of file: 0 KB Title of file for HTML: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1 mir-128-3p is highly expressed in chemoresistant, metastatic
Head and neck cancer is a common malignancy
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE SINGLE-MARKER IDENTIFICATION OF HEAD AND NECK SQUAMOUS CELL CARCINOMA CANCER STEM CELLS WITH ALDEHYDE DEHYDROGENASE Matthew R. Clay, BSc, 1 Mark Tabor, MD, 2 John Henry Owen, BSc, 3 Thomas
ORIGINAL ARTICLE SINGLE-MARKER IDENTIFICATION OF HEAD AND NECK SQUAMOUS CELL CARCINOMA CANCER STEM CELLS WITH ALDEHYDE DEHYDROGENASE Matthew R. Clay, BSc, 1 Mark Tabor, MD, 2 John Henry Owen, BSc, 3 Thomas
RNA extraction, RT-PCR and real-time PCR. Total RNA were extracted using
 Supplementary Information Materials and Methods RNA extraction, RT-PCR and real-time PCR. Total RNA were extracted using Trizol reagent (Invitrogen,Carlsbad, CA) according to the manufacturer's instructions.
Supplementary Information Materials and Methods RNA extraction, RT-PCR and real-time PCR. Total RNA were extracted using Trizol reagent (Invitrogen,Carlsbad, CA) according to the manufacturer's instructions.
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Sasportas et al. 10.1073/pnas.0806647106 SI Methods Lentiviral Transduction. MSC and glioma cells were transduced with LVs at varying multiplicity of infection (moi) by incubating
Supporting Information Sasportas et al. 10.1073/pnas.0806647106 SI Methods Lentiviral Transduction. MSC and glioma cells were transduced with LVs at varying multiplicity of infection (moi) by incubating
PREPARED FOR: U.S. Army Medical Research and Materiel Command Fort Detrick, Maryland
 AD Award Number: W81XWH-12-1-0337 TITLE: Molecular Innovations Toward Theranostics of Aggressive Prostate Cancer PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Hsieh, Jer-Tsong CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: University of Texas Southwestern
AD Award Number: W81XWH-12-1-0337 TITLE: Molecular Innovations Toward Theranostics of Aggressive Prostate Cancer PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Hsieh, Jer-Tsong CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: University of Texas Southwestern
Supplemental figure 1. PDGFRα is expressed dominantly by stromal cells surrounding mammary ducts and alveoli. A) IHC staining of PDGFRα in
 Supplemental figure 1. PDGFRα is expressed dominantly by stromal cells surrounding mammary ducts and alveoli. A) IHC staining of PDGFRα in nulliparous (left panel) and InvD6 mouse mammary glands (right
Supplemental figure 1. PDGFRα is expressed dominantly by stromal cells surrounding mammary ducts and alveoli. A) IHC staining of PDGFRα in nulliparous (left panel) and InvD6 mouse mammary glands (right
let-7 Regulates Self Renewal and Tumorigenicity of Breast Cancer Cells
 let-7 Regulates Self Renewal and Tumorigenicity of Breast Cancer Cells Fengyan Yu, 1,2 Herui Yao, 1 Pengcheng Zhu, 2 Xiaoqin Zhang, 1 Qiuhui Pan, 1 Chang Gong, 1 Yijun Huang, 3 Xiaoqu Hu, 1 Fengxi Su,
let-7 Regulates Self Renewal and Tumorigenicity of Breast Cancer Cells Fengyan Yu, 1,2 Herui Yao, 1 Pengcheng Zhu, 2 Xiaoqin Zhang, 1 Qiuhui Pan, 1 Chang Gong, 1 Yijun Huang, 3 Xiaoqu Hu, 1 Fengxi Su,
Supplemental Data. TGF-β-mediated mir-181a expression promotes breast cancer metastasis by targeting Bim.
 Supplemental Data TGF-β-mediated mir-181a expression promotes breast cancer metastasis by targeting Bim. Molly A. Taylor 1, Khalid Sossey-Alaoui 2, Cheryl L. Thompson 3, David Danielpour 4, and William
Supplemental Data TGF-β-mediated mir-181a expression promotes breast cancer metastasis by targeting Bim. Molly A. Taylor 1, Khalid Sossey-Alaoui 2, Cheryl L. Thompson 3, David Danielpour 4, and William
Pre-made Reporter Lentivirus for JAK-STAT Signaling Pathway
 Pre-made Reporter for JAK-STAT Signaling Pathway Cat# Product Name Amounts LVP937-P or: LVP937-P-PBS ISRE-GFP (Puro) LVP938-P or: LVP938-P-PBS ISRE-RFP (Puro) LVP939-P or: LVP939-P-PBS ISRE-Luc (Puro)
Pre-made Reporter for JAK-STAT Signaling Pathway Cat# Product Name Amounts LVP937-P or: LVP937-P-PBS ISRE-GFP (Puro) LVP938-P or: LVP938-P-PBS ISRE-RFP (Puro) LVP939-P or: LVP939-P-PBS ISRE-Luc (Puro)
Combined Rho-kinase inhibition and immunogenic cell death triggers and propagates immunity against cancer
 Supplementary Information Combined Rho-kinase inhibition and immunogenic cell death triggers and propagates immunity against cancer Gi-Hoon Nam, Eun-Jung Lee, Yoon Kyoung Kim, Yeonsun Hong, Yoonjeong Choi,
Supplementary Information Combined Rho-kinase inhibition and immunogenic cell death triggers and propagates immunity against cancer Gi-Hoon Nam, Eun-Jung Lee, Yoon Kyoung Kim, Yeonsun Hong, Yoonjeong Choi,
(A) PCR primers (arrows) designed to distinguish wild type (P1+P2), targeted (P1+P2) and excised (P1+P3)14-
 1 Supplemental Figure Legends Figure S1. Mammary tumors of ErbB2 KI mice with 14-3-3σ ablation have elevated ErbB2 transcript levels and cell proliferation (A) PCR primers (arrows) designed to distinguish
1 Supplemental Figure Legends Figure S1. Mammary tumors of ErbB2 KI mice with 14-3-3σ ablation have elevated ErbB2 transcript levels and cell proliferation (A) PCR primers (arrows) designed to distinguish
Supplementary Fig. 1: ATM is phosphorylated in HER2 breast cancer cell lines. (A) ATM is phosphorylated in SKBR3 cells depending on ATM and HER2
 Supplementary Fig. 1: ATM is phosphorylated in HER2 breast cancer cell lines. (A) ATM is phosphorylated in SKBR3 cells depending on ATM and HER2 activity. Upper panel: Representative histograms for FACS
Supplementary Fig. 1: ATM is phosphorylated in HER2 breast cancer cell lines. (A) ATM is phosphorylated in SKBR3 cells depending on ATM and HER2 activity. Upper panel: Representative histograms for FACS
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 1: Cryopreservation alters CD62L expression by CD4 T cells. Freshly isolated (left) or cryopreserved PBMCs (right) were stained with the mix of antibodies described
Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 1: Cryopreservation alters CD62L expression by CD4 T cells. Freshly isolated (left) or cryopreserved PBMCs (right) were stained with the mix of antibodies described
Supplemental Figure 1 ELISA scheme to measure plasma total, mature and furin-cleaved
 1 Supplemental Figure Legends Supplemental Figure 1 ELISA scheme to measure plasma total, mature and furin-cleaved PCSK9 concentrations. 4 Plasma mature and furin-cleaved PCSK9s were measured by a sandwich
1 Supplemental Figure Legends Supplemental Figure 1 ELISA scheme to measure plasma total, mature and furin-cleaved PCSK9 concentrations. 4 Plasma mature and furin-cleaved PCSK9s were measured by a sandwich
Supplemental Table 1. Primer sequences for transcript analysis
 Supplemental Table 1. Primer sequences for transcript analysis Primer Sequence (5 3 ) Primer Sequence (5 3 ) Mmp2 Forward CCCGTGTGGCCCTC Mmp15 Forward CGGGGCTGGCT Reverse GCTCTCCCGGTTTC Reverse CCTGGTGTGCCTGCTC
Supplemental Table 1. Primer sequences for transcript analysis Primer Sequence (5 3 ) Primer Sequence (5 3 ) Mmp2 Forward CCCGTGTGGCCCTC Mmp15 Forward CGGGGCTGGCT Reverse GCTCTCCCGGTTTC Reverse CCTGGTGTGCCTGCTC
Low levels of serum mir-99a is a predictor of poor prognosis in breast cancer
 Low levels of serum mir-99a is a predictor of poor prognosis in breast cancer J. Li 1, Z.J. Song 2, Y.Y. Wang 1, Y. Yin 1, Y. Liu 1 and X. Nan 1 1 Tumor Research Department, Shaanxi Provincial Tumor Hospital,
Low levels of serum mir-99a is a predictor of poor prognosis in breast cancer J. Li 1, Z.J. Song 2, Y.Y. Wang 1, Y. Yin 1, Y. Liu 1 and X. Nan 1 1 Tumor Research Department, Shaanxi Provincial Tumor Hospital,
Pre-made Reporter Lentivirus for MAPK/ERK Signal Pathway
 Pre-made Reporter for MAPK/ERK Signal Pathway Cat# Product Name Amounts LVP957-P or: LVP957-P-PBS SRE-GFP (Puro) LVP958-P or: LVP958-P-PBS SRE-RFP (Puro) LVP959-P or: LVP959-P-PBS SRE-Luc (Puro) LVP960-P
Pre-made Reporter for MAPK/ERK Signal Pathway Cat# Product Name Amounts LVP957-P or: LVP957-P-PBS SRE-GFP (Puro) LVP958-P or: LVP958-P-PBS SRE-RFP (Puro) LVP959-P or: LVP959-P-PBS SRE-Luc (Puro) LVP960-P
sequences of a styx mutant reveals a T to A transversion in the donor splice site of intron 5
 sfigure 1 Styx mutant mice recapitulate the phenotype of SHIP -/- mice. (A) Analysis of the genomic sequences of a styx mutant reveals a T to A transversion in the donor splice site of intron 5 (GTAAC
sfigure 1 Styx mutant mice recapitulate the phenotype of SHIP -/- mice. (A) Analysis of the genomic sequences of a styx mutant reveals a T to A transversion in the donor splice site of intron 5 (GTAAC
Supplementary figure 1. Systemic delivery of anti-cd47 antibody controls tumor growth in
 T u m o r v o lu m e (m m 3 ) P e rc e n t s u rv iv a l P e rc e n t s u rv iv a l Supplementary data a 1 8 6 4 2 5 1 1 5 2 2 5 3 3 5 4 T im e a fte r tu m o r in o c u la tio n (d ) b c 1 5 1 1 5 * *
T u m o r v o lu m e (m m 3 ) P e rc e n t s u rv iv a l P e rc e n t s u rv iv a l Supplementary data a 1 8 6 4 2 5 1 1 5 2 2 5 3 3 5 4 T im e a fte r tu m o r in o c u la tio n (d ) b c 1 5 1 1 5 * *
Supplemental information
 Carcinoemryonic antigen-related cell adhesion molecule 6 (CEACAM6) promotes EGF receptor signaling of oral squamous cell carcinoma metastasis via the complex N-glycosylation y Chiang et al. Supplemental
Carcinoemryonic antigen-related cell adhesion molecule 6 (CEACAM6) promotes EGF receptor signaling of oral squamous cell carcinoma metastasis via the complex N-glycosylation y Chiang et al. Supplemental
Supplementary Information and Figure legends
 Supplementary Information and Figure legends Table S1. Primers for quantitative RT-PCR Target Sequence (5 -> 3 ) Target Sequence (5 -> 3 ) DAB2IP F:TGGACGATGTGCTCTATGCC R:GGATGGTGATGGTTTGGTAG Snail F:CCTCCCTGTCAGATGAGGAC
Supplementary Information and Figure legends Table S1. Primers for quantitative RT-PCR Target Sequence (5 -> 3 ) Target Sequence (5 -> 3 ) DAB2IP F:TGGACGATGTGCTCTATGCC R:GGATGGTGATGGTTTGGTAG Snail F:CCTCCCTGTCAGATGAGGAC
Chapter 3. Use of Stem Cell Markers in Dissociated Mammary Populations
 Chapter 3 Use of Stem Cell Markers in Dissociated Mammary Populations Dawne N. Shelton, Rodrigo Fernandez-Gonzalez, Irineu Illa-Bochaca, Carlos Ortiz-de-Solorzano, Mary Helen Barcellos-Hoff, and Bryan
Chapter 3 Use of Stem Cell Markers in Dissociated Mammary Populations Dawne N. Shelton, Rodrigo Fernandez-Gonzalez, Irineu Illa-Bochaca, Carlos Ortiz-de-Solorzano, Mary Helen Barcellos-Hoff, and Bryan
Soft Agar Assay. For each cell pool, 100,000 cells were resuspended in 0.35% (w/v)
 SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL AND METHODS Soft Agar Assay. For each cell pool, 100,000 cells were resuspended in 0.35% (w/v) top agar (LONZA, SeaKem LE Agarose cat.5004) and plated onto 0.5% (w/v) basal agar.
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL AND METHODS Soft Agar Assay. For each cell pool, 100,000 cells were resuspended in 0.35% (w/v) top agar (LONZA, SeaKem LE Agarose cat.5004) and plated onto 0.5% (w/v) basal agar.
well for 2 h at rt. Each dot represents an individual mouse and bar is the mean ±
 Supplementary data: Control DC Blimp-1 ko DC 8 6 4 2-2 IL-1β p=.5 medium 8 6 4 2 IL-2 Medium p=.16 8 6 4 2 IL-6 medium p=.3 5 4 3 2 1-1 medium IL-1 n.s. 25 2 15 1 5 IL-12(p7) p=.15 5 IFNγ p=.65 4 3 2 1
Supplementary data: Control DC Blimp-1 ko DC 8 6 4 2-2 IL-1β p=.5 medium 8 6 4 2 IL-2 Medium p=.16 8 6 4 2 IL-6 medium p=.3 5 4 3 2 1-1 medium IL-1 n.s. 25 2 15 1 5 IL-12(p7) p=.15 5 IFNγ p=.65 4 3 2 1
Stem cells and Cancer. John Glod. December 2, 2009
 Stem cells and Cancer John Glod Lehigh University Lehigh University December 2, 2009 The Tumor Microenvironment Littlepage et al Cancer Cell 2005 Cancer Stem Cells A small group of cells within the larger
Stem cells and Cancer John Glod Lehigh University Lehigh University December 2, 2009 The Tumor Microenvironment Littlepage et al Cancer Cell 2005 Cancer Stem Cells A small group of cells within the larger
Supplementary Figure (OH) 22 nanoparticles did not affect cell viability and apoposis. MDA-MB-231, MCF-7, MCF-10A and BT549 cells were
 Supplementary Figure 1. Gd@C 82 (OH) 22 nanoparticles did not affect cell viability and apoposis. MDA-MB-231, MCF-7, MCF-10A and BT549 cells were treated with PBS, Gd@C 82 (OH) 22, C 60 (OH) 22 or GdCl
Supplementary Figure 1. Gd@C 82 (OH) 22 nanoparticles did not affect cell viability and apoposis. MDA-MB-231, MCF-7, MCF-10A and BT549 cells were treated with PBS, Gd@C 82 (OH) 22, C 60 (OH) 22 or GdCl
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb2607 Figure S1 Elf5 loss promotes EMT in mammary epithelium while Elf5 overexpression inhibits TGFβ induced EMT. (a, c) Different confocal slices through the Z stack image. (b, d) 3D rendering
DOI: 10.1038/ncb2607 Figure S1 Elf5 loss promotes EMT in mammary epithelium while Elf5 overexpression inhibits TGFβ induced EMT. (a, c) Different confocal slices through the Z stack image. (b, d) 3D rendering
Cell isolation. Spleen and lymph nodes (axillary, inguinal) were removed from mice
 Supplementary Methods: Cell isolation. Spleen and lymph nodes (axillary, inguinal) were removed from mice and gently meshed in DMEM containing 10% FBS to prepare for single cell suspensions. CD4 + CD25
Supplementary Methods: Cell isolation. Spleen and lymph nodes (axillary, inguinal) were removed from mice and gently meshed in DMEM containing 10% FBS to prepare for single cell suspensions. CD4 + CD25
Oncolytic Adenovirus Complexes Coated with Lipids and Calcium Phosphate for Cancer Gene Therapy
 Oncolytic Adenovirus Complexes Coated with Lipids and Calcium Phosphate for Cancer Gene Therapy Jianhua Chen, Pei Gao, Sujing Yuan, Rongxin Li, Aimin Ni, Liang Chu, Li Ding, Ying Sun, Xin-Yuan Liu, Yourong
Oncolytic Adenovirus Complexes Coated with Lipids and Calcium Phosphate for Cancer Gene Therapy Jianhua Chen, Pei Gao, Sujing Yuan, Rongxin Li, Aimin Ni, Liang Chu, Li Ding, Ying Sun, Xin-Yuan Liu, Yourong
CD34+ Cells: A Comparison of Stem and Progenitor Cells in Cord Blood, Peripheral Blood, and the Bone Marrow
 White Paper September 2016 CD34+ Cells: A Comparison of Stem and Progenitor Cells in Cord Blood, Peripheral Blood, and the Bone Marrow Lily C. Trajman, PhD Introduction: Hematopoietic Stem Cells (HSCs)
White Paper September 2016 CD34+ Cells: A Comparison of Stem and Progenitor Cells in Cord Blood, Peripheral Blood, and the Bone Marrow Lily C. Trajman, PhD Introduction: Hematopoietic Stem Cells (HSCs)
Pair-fed % inkt cells 0.5. EtOH 0.0
 MATERIALS AND METHODS Histopathological analysis Liver tissue was collected 9 h post-gavage, and the tissue samples were fixed in 1% formalin and paraffin-embedded following a standard procedure. The embedded
MATERIALS AND METHODS Histopathological analysis Liver tissue was collected 9 h post-gavage, and the tissue samples were fixed in 1% formalin and paraffin-embedded following a standard procedure. The embedded
Supplementary Figure 1 Role of Raf-1 in TLR2-Dectin-1-mediated cytokine expression
 Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 1 Role of Raf-1 in TLR2-Dectin-1-mediated cytokine expression. Quantitative real-time PCR of indicated mrnas in DCs stimulated with TLR2-Dectin-1 agonist zymosan
Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 1 Role of Raf-1 in TLR2-Dectin-1-mediated cytokine expression. Quantitative real-time PCR of indicated mrnas in DCs stimulated with TLR2-Dectin-1 agonist zymosan
Heterogeneity of functional properties of clone 66 murine breast cancer cells expressing various stem cell phenotypes
 University of Nebraska Medical Center DigitalCommons@UNMC Journal Articles: Genetics, Cell Biology & Anatomy Genetics, Cell Biology & Anatomy 11-2013 Heterogeneity of functional properties of clone 66
University of Nebraska Medical Center DigitalCommons@UNMC Journal Articles: Genetics, Cell Biology & Anatomy Genetics, Cell Biology & Anatomy 11-2013 Heterogeneity of functional properties of clone 66
Supplementary Fig. 1. Delivery of mirnas via Red Fluorescent Protein.
 prfp-vector RFP Exon1 Intron RFP Exon2 prfp-mir-124 mir-93/124 RFP Exon1 Intron RFP Exon2 Untransfected prfp-vector prfp-mir-93 prfp-mir-124 Supplementary Fig. 1. Delivery of mirnas via Red Fluorescent
prfp-vector RFP Exon1 Intron RFP Exon2 prfp-mir-124 mir-93/124 RFP Exon1 Intron RFP Exon2 Untransfected prfp-vector prfp-mir-93 prfp-mir-124 Supplementary Fig. 1. Delivery of mirnas via Red Fluorescent
Nature Immunology: doi: /ni Supplementary Figure 1. Huwe1 has high expression in HSCs and is necessary for quiescence.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Huwe1 has high expression in HSCs and is necessary for quiescence. (a) Heat map visualizing expression of genes with a known function in ubiquitin-mediated proteolysis (KEGG: Ubiquitin
Supplementary Figure 1 Huwe1 has high expression in HSCs and is necessary for quiescence. (a) Heat map visualizing expression of genes with a known function in ubiquitin-mediated proteolysis (KEGG: Ubiquitin
Original Article TNF-α induced epithelial mesenchymal transition increases stemness properties in renal cell carcinoma cells
 Int J Clin Exp Med 2014;7(12):4951-4958 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0002516 Original Article TNF-α induced epithelial mesenchymal transition increases stemness properties in renal cell carcinoma
Int J Clin Exp Med 2014;7(12):4951-4958 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0002516 Original Article TNF-α induced epithelial mesenchymal transition increases stemness properties in renal cell carcinoma
SHREE ET AL, SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIALS. (A) Workflow for tumor cell line derivation and orthotopic implantation.
 SHREE ET AL, SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIALS SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE AND TABLE LEGENDS Supplemental Figure 1. Derivation and characterization of TS1-TGL and TS2-TGL PyMT cell lines and development of an orthotopic
SHREE ET AL, SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIALS SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE AND TABLE LEGENDS Supplemental Figure 1. Derivation and characterization of TS1-TGL and TS2-TGL PyMT cell lines and development of an orthotopic
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Bertolini et al. 10.1073/pnas.0905653106 SI Text Lung Tissue Disaggregation. Solid tissues were finely minced by razorblade, washed in DMEM/F12 (Lonza), and then incubated with Accumax
Supporting Information Bertolini et al. 10.1073/pnas.0905653106 SI Text Lung Tissue Disaggregation. Solid tissues were finely minced by razorblade, washed in DMEM/F12 (Lonza), and then incubated with Accumax
hexahistidine tagged GRP78 devoid of the KDEL motif (GRP78-His) on SDS-PAGE. This
 SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE LEGEND Fig. S1. Generation and characterization of. (A) Coomassie staining of soluble hexahistidine tagged GRP78 devoid of the KDEL motif (GRP78-His) on SDS-PAGE. This protein was expressed
SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE LEGEND Fig. S1. Generation and characterization of. (A) Coomassie staining of soluble hexahistidine tagged GRP78 devoid of the KDEL motif (GRP78-His) on SDS-PAGE. This protein was expressed
MicroRNA sponges: competitive inhibitors of small RNAs in mammalian cells
 MicroRNA sponges: competitive inhibitors of small RNAs in mammalian cells Margaret S Ebert, Joel R Neilson & Phillip A Sharp Supplementary figures and text: Supplementary Figure 1. Effect of sponges on
MicroRNA sponges: competitive inhibitors of small RNAs in mammalian cells Margaret S Ebert, Joel R Neilson & Phillip A Sharp Supplementary figures and text: Supplementary Figure 1. Effect of sponges on
Correlations of ALDH1 expression with molecular subtypes and ABCG2 in breast cancer
 Original Article Correlations of ALDH1 expression with molecular subtypes and ABCG2 in breast cancer Xiaokai Bi, Chengyi Wu, Mingli Han, Jianying Cai Department of Endocrine and Breast Surgery, the First
Original Article Correlations of ALDH1 expression with molecular subtypes and ABCG2 in breast cancer Xiaokai Bi, Chengyi Wu, Mingli Han, Jianying Cai Department of Endocrine and Breast Surgery, the First
CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: University of Michigan Ann Arbor, MI
 AD Award Number: W81XWH-04-1-0471 TITLE: Chemo Resistance of Breast Cancer Stem Cells PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Max S. Wicha, M.D. CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: University of Michigan Ann Arbor, MI 48109-1274
AD Award Number: W81XWH-04-1-0471 TITLE: Chemo Resistance of Breast Cancer Stem Cells PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Max S. Wicha, M.D. CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: University of Michigan Ann Arbor, MI 48109-1274
Profiles of gene expression & diagnosis/prognosis of cancer. MCs in Advanced Genetics Ainoa Planas Riverola
 Profiles of gene expression & diagnosis/prognosis of cancer MCs in Advanced Genetics Ainoa Planas Riverola Gene expression profiles Gene expression profiling Used in molecular biology, it measures the
Profiles of gene expression & diagnosis/prognosis of cancer MCs in Advanced Genetics Ainoa Planas Riverola Gene expression profiles Gene expression profiling Used in molecular biology, it measures the
B6.SJL (Ly5.2) mice were obtained from Taconic Farms. Rag1-deficient mice were
 Supplementary Methods Mice. B6.SJL (Ly5.2) mice were obtained from Taconic Farms. Rag1-deficient mice were purchased from The Jackson Laboratory. Real-time PCR Total cellular RNA was extracted from the
Supplementary Methods Mice. B6.SJL (Ly5.2) mice were obtained from Taconic Farms. Rag1-deficient mice were purchased from The Jackson Laboratory. Real-time PCR Total cellular RNA was extracted from the
A549 and A549-fLuc cells were maintained in high glucose Dulbecco modified
 Cell culture and animal model A549 and A549-fLuc cells were maintained in high glucose Dulbecco modified Eagle medium supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum at 37 C in humidified atmosphere containing
Cell culture and animal model A549 and A549-fLuc cells were maintained in high glucose Dulbecco modified Eagle medium supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum at 37 C in humidified atmosphere containing
Markers of Tumor-Initiating Cells Predict Chemoresistance in Breast Cancer
 Markers of Tumor-Initiating Cells Predict Chemoresistance in Breast Cancer Chang Gong 1., Herui Yao 1., Qiang Liu 1,2, Jingqi Chen 1, Junwei Shi 1, Fengxi Su 1, Erwei Song 1,3 * 1 Breast Tumor Center,
Markers of Tumor-Initiating Cells Predict Chemoresistance in Breast Cancer Chang Gong 1., Herui Yao 1., Qiang Liu 1,2, Jingqi Chen 1, Junwei Shi 1, Fengxi Su 1, Erwei Song 1,3 * 1 Breast Tumor Center,
Acidic extracellular ph of tumors induces octamerbinding transcription factor 4 expression in murine fibroblasts in vitro and in vivo
 Washington University School of Medicine Digital Commons@Becker Open Access Publications 2016 Acidic extracellular ph of tumors induces octamerbinding transcription factor 4 expression in murine fibroblasts
Washington University School of Medicine Digital Commons@Becker Open Access Publications 2016 Acidic extracellular ph of tumors induces octamerbinding transcription factor 4 expression in murine fibroblasts
Supplemental Information. Tissue Myeloid Progenitors Differentiate. into Pericytes through TGF-b Signaling. in Developing Skin Vasculature
 Cell Reports, Volume 18 Supplemental Information Tissue Myeloid Progenitors Differentiate into Pericytes through TGF-b Signaling in Developing Skin Vasculature Tomoko Yamazaki, Ani Nalbandian, Yutaka Uchida,
Cell Reports, Volume 18 Supplemental Information Tissue Myeloid Progenitors Differentiate into Pericytes through TGF-b Signaling in Developing Skin Vasculature Tomoko Yamazaki, Ani Nalbandian, Yutaka Uchida,
The toll-like receptor 4 ligands Mrp8 and Mrp14 play a critical role in the development of autoreactive CD8 + T cells
 1 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION The toll-like receptor 4 ligands Mrp8 and Mrp14 play a critical role in the development of autoreactive CD8 + T cells Karin Loser 1,2,6, Thomas Vogl 2,3, Maik Voskort 1, Aloys
1 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION The toll-like receptor 4 ligands Mrp8 and Mrp14 play a critical role in the development of autoreactive CD8 + T cells Karin Loser 1,2,6, Thomas Vogl 2,3, Maik Voskort 1, Aloys
Erzsebet Kokovay, Susan Goderie, Yue Wang, Steve Lotz, Gang Lin, Yu Sun, Badrinath Roysam, Qin Shen,
 Cell Stem Cell, Volume 7 Supplemental Information Adult SVZ Lineage Cells Home to and Leave the Vascular Niche via Differential Responses to SDF1/CXCR4 Signaling Erzsebet Kokovay, Susan Goderie, Yue Wang,
Cell Stem Cell, Volume 7 Supplemental Information Adult SVZ Lineage Cells Home to and Leave the Vascular Niche via Differential Responses to SDF1/CXCR4 Signaling Erzsebet Kokovay, Susan Goderie, Yue Wang,
CRIPTO-1 A POSSIBLE NEW BIOMARKER IN GLIOBLASTOMA MULTIFORME PIA OLESEN, MD, PHD STUDENT
 CRIPTO-1 A POSSIBLE NEW BIOMARKER IN GLIOBLASTOMA MULTIFORME PIA OLESEN, MD, PHD STUDENT Glioblastoma WHO Grade IV Glioma Heterogenic Undiffenrentiated phenotype 50% of all Gliomas Around 600 patients
CRIPTO-1 A POSSIBLE NEW BIOMARKER IN GLIOBLASTOMA MULTIFORME PIA OLESEN, MD, PHD STUDENT Glioblastoma WHO Grade IV Glioma Heterogenic Undiffenrentiated phenotype 50% of all Gliomas Around 600 patients
Tumorsphere Culture of Cancer Stem Cells (CSC) with the Cancer Stem Cell Medium, Application Note
 Tumorsphere Culture of Cancer Stem Cells (CSC) with the Cancer Stem Cell Medium, Application Note Interest in any of the products, request or order them at Bio-Connect. Bio-Connect B.V. T NL +31 (0)26
Tumorsphere Culture of Cancer Stem Cells (CSC) with the Cancer Stem Cell Medium, Application Note Interest in any of the products, request or order them at Bio-Connect. Bio-Connect B.V. T NL +31 (0)26
Supplementary Figure 1. Identification of tumorous sphere-forming CSCs and CAF feeder cells. The LEAP (Laser-Enabled Analysis and Processing)
 Supplementary Figure 1. Identification of tumorous sphere-forming CSCs and CAF feeder cells. The LEAP (Laser-Enabled Analysis and Processing) platform with laser manipulation to efficiently purify lung
Supplementary Figure 1. Identification of tumorous sphere-forming CSCs and CAF feeder cells. The LEAP (Laser-Enabled Analysis and Processing) platform with laser manipulation to efficiently purify lung
CD14 + S100A9 + Monocytic Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells and Their Clinical Relevance in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
 CD14 + S1A9 + Monocytic Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells and Their Clinical Relevance in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Po-Hao, Feng M.D., Kang-Yun, Lee, M.D. Ph.D., Ya-Ling Chang, Yao-Fei Chan, Lu- Wei, Kuo,Ting-Yu
CD14 + S1A9 + Monocytic Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells and Their Clinical Relevance in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Po-Hao, Feng M.D., Kang-Yun, Lee, M.D. Ph.D., Ya-Ling Chang, Yao-Fei Chan, Lu- Wei, Kuo,Ting-Yu
Toluidin-Staining of mast cells Ear tissue was fixed with Carnoy (60% ethanol, 30% chloroform, 10% acetic acid) overnight at 4 C, afterwards
 Toluidin-Staining of mast cells Ear tissue was fixed with Carnoy (60% ethanol, 30% chloroform, 10% acetic acid) overnight at 4 C, afterwards incubated in 100 % ethanol overnight at 4 C and embedded in
Toluidin-Staining of mast cells Ear tissue was fixed with Carnoy (60% ethanol, 30% chloroform, 10% acetic acid) overnight at 4 C, afterwards incubated in 100 % ethanol overnight at 4 C and embedded in
Evaluation of STAT3 Signaling in Macrophages Using a Lentiviral Reporter System
 Evaluation of STAT3 Signaling in Macrophages Using a Lentiviral Reporter System Schwertfeger Laboratory Emily Hartsough Breast Cancer Prevalence Adapted from Siegel et. al Cancer Statistics. 2016 Tumor
Evaluation of STAT3 Signaling in Macrophages Using a Lentiviral Reporter System Schwertfeger Laboratory Emily Hartsough Breast Cancer Prevalence Adapted from Siegel et. al Cancer Statistics. 2016 Tumor
TMA-VARESE COHORT-1 TMA-BERN COHORT-2
 Supplementary Figure 1 TMA-VARESE COHORT-1 TOTAL SAMPLES #5 GLEASON SCORE Number Percentage 6 16 32% = 7 17 34% >7 17 34% TUMOR STAGE T2C 28 56% T3A- 21 42% T3C-T4 1 2% NODE STATUS N 42 84% N1 8 16% PSA
Supplementary Figure 1 TMA-VARESE COHORT-1 TOTAL SAMPLES #5 GLEASON SCORE Number Percentage 6 16 32% = 7 17 34% >7 17 34% TUMOR STAGE T2C 28 56% T3A- 21 42% T3C-T4 1 2% NODE STATUS N 42 84% N1 8 16% PSA
Abbreviations: P- paraffin-embedded section; C, cryosection; Bio-SA, biotin-streptavidin-conjugated fluorescein amplification.
 Supplementary Table 1. Sequence of primers for real time PCR. Gene Forward primer Reverse primer S25 5 -GTG GTC CAC ACT ACT CTC TGA GTT TC-3 5 - GAC TTT CCG GCA TCC TTC TTC-3 Mafa cds 5 -CTT CAG CAA GGA
Supplementary Table 1. Sequence of primers for real time PCR. Gene Forward primer Reverse primer S25 5 -GTG GTC CAC ACT ACT CTC TGA GTT TC-3 5 - GAC TTT CCG GCA TCC TTC TTC-3 Mafa cds 5 -CTT CAG CAA GGA
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION. Involvement of IL-21 in the epidermal hyperplasia of psoriasis
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Involvement of IL-21 in the epidermal hyperplasia of psoriasis Roberta Caruso 1, Elisabetta Botti 2, Massimiliano Sarra 1, Maria Esposito 2, Carmine Stolfi 1, Laura Diluvio 2,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Involvement of IL-21 in the epidermal hyperplasia of psoriasis Roberta Caruso 1, Elisabetta Botti 2, Massimiliano Sarra 1, Maria Esposito 2, Carmine Stolfi 1, Laura Diluvio 2,
TITLE: Increase in Breast Cancer Stem Cells in Response to Prostaglandin E2. CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: University of Michigan Ann Arbor, MI
 AD Award Number: W81XWH-9-1-683 TITLE: Increase in Breast Cancer Stem Cells in Response to Prostaglandin E2 PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Monica Liebert, Ph.D. CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: University of Michigan
AD Award Number: W81XWH-9-1-683 TITLE: Increase in Breast Cancer Stem Cells in Response to Prostaglandin E2 PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Monica Liebert, Ph.D. CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: University of Michigan
ice-cold 70% ethanol with gentle vortexing, incubated at -20 C for 4 hours, and washed with PBS.
 Cell cycle analysis For cell cycle analysis, single cell suspensions of E12.5 fetal liver cells were suspended in 4 ml ice-cold 7% ethanol with gentle vortexing, incubated at -2 C for 4 hours, and washed
Cell cycle analysis For cell cycle analysis, single cell suspensions of E12.5 fetal liver cells were suspended in 4 ml ice-cold 7% ethanol with gentle vortexing, incubated at -2 C for 4 hours, and washed
Supplementary data Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 2
 Supplementary data Supplementary Figure 1 SPHK1 sirna increases RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis in RAW264.7 cell culture. (A) RAW264.7 cells were transfected with oligocassettes containing SPHK1 sirna
Supplementary data Supplementary Figure 1 SPHK1 sirna increases RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis in RAW264.7 cell culture. (A) RAW264.7 cells were transfected with oligocassettes containing SPHK1 sirna
Supplementary Materials for
 immunology.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/2/16/eaan6049/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Enzymatic synthesis of core 2 O-glycans governs the tissue-trafficking potential of memory CD8 + T cells Jossef
immunology.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/2/16/eaan6049/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Enzymatic synthesis of core 2 O-glycans governs the tissue-trafficking potential of memory CD8 + T cells Jossef
Supplementary Figure 1 IL-27 IL
 Tim-3 Supplementary Figure 1 Tc0 49.5 0.6 Tc1 63.5 0.84 Un 49.8 0.16 35.5 0.16 10 4 61.2 5.53 10 3 64.5 5.66 10 2 10 1 10 0 31 2.22 10 0 10 1 10 2 10 3 10 4 IL-10 28.2 1.69 IL-27 Supplementary Figure 1.
Tim-3 Supplementary Figure 1 Tc0 49.5 0.6 Tc1 63.5 0.84 Un 49.8 0.16 35.5 0.16 10 4 61.2 5.53 10 3 64.5 5.66 10 2 10 1 10 0 31 2.22 10 0 10 1 10 2 10 3 10 4 IL-10 28.2 1.69 IL-27 Supplementary Figure 1.
Department of Pharmaceutical Sciences, School of Pharmacy, Northeastern University, Boston, MA 02115, USA 2
 Pancreatic Cancer Cell Exosome-Mediated Macrophage Reprogramming and the Role of MicroRNAs 155 and 125b2 Transfection using Nanoparticle Delivery Systems Mei-Ju Su 1, Hibah Aldawsari 2, and Mansoor Amiji
Pancreatic Cancer Cell Exosome-Mediated Macrophage Reprogramming and the Role of MicroRNAs 155 and 125b2 Transfection using Nanoparticle Delivery Systems Mei-Ju Su 1, Hibah Aldawsari 2, and Mansoor Amiji
Jung Sun Lee 1, Woo Gyeong Kim 2. Introduction
 Case Report Page 1 of 5 Cutaneous metastases of breast cancer during adjuvant chemotherapy correlates with increasing CD44 + /CD24 and ALDH-1 expression: a case report and literature review Jung Sun Lee
Case Report Page 1 of 5 Cutaneous metastases of breast cancer during adjuvant chemotherapy correlates with increasing CD44 + /CD24 and ALDH-1 expression: a case report and literature review Jung Sun Lee
Ets-1 identifying polynucleotide sequence for targeted delivery of anti-cancer drugs
 Ets-1 identifying polynucleotide sequence for targeted delivery of anti-cancer drugs Indian Patent Application No. 1623/DEL/2014 Inventors: Prof. Kulbhushan Tikoo and Jasmine Kaur Department of Pharmacology
Ets-1 identifying polynucleotide sequence for targeted delivery of anti-cancer drugs Indian Patent Application No. 1623/DEL/2014 Inventors: Prof. Kulbhushan Tikoo and Jasmine Kaur Department of Pharmacology
Metastatic breast cancer stem cells
 Metastatic breast cancer stem cells Christophe GINESTIER, PhD Centre de Recherche en Cancérologie de Marseille Laboratoire d Oncologie Moléculaire Breast Stem Cell Group U168/Inserm/Institut Paoli-Calmettes
Metastatic breast cancer stem cells Christophe GINESTIER, PhD Centre de Recherche en Cancérologie de Marseille Laboratoire d Oncologie Moléculaire Breast Stem Cell Group U168/Inserm/Institut Paoli-Calmettes
CD34 + VEGFR-3 + progenitor cells have a potential to differentiate towards lymphatic endothelial cells
 CD34 + VEGFR-3 + progenitor cells have a potential to differentiate towards lymphatic endothelial cells Tan YZ et al. J Cell Mol Med. (2014 Mar;18(3):422-33) Denise Traxler-Weidenauer April 2014 Introduction
CD34 + VEGFR-3 + progenitor cells have a potential to differentiate towards lymphatic endothelial cells Tan YZ et al. J Cell Mol Med. (2014 Mar;18(3):422-33) Denise Traxler-Weidenauer April 2014 Introduction
Supplemental Table S1
 Supplemental Table S. Tumorigenicity and metastatic potential of 44SQ cell subpopulations a Tumorigenicity b Average tumor volume (mm ) c Lung metastasis d CD high /4 8. 8/ CD low /4 6./ a Mice were injected
Supplemental Table S. Tumorigenicity and metastatic potential of 44SQ cell subpopulations a Tumorigenicity b Average tumor volume (mm ) c Lung metastasis d CD high /4 8. 8/ CD low /4 6./ a Mice were injected
(a) Significant biological processes (upper panel) and disease biomarkers (lower panel)
 Supplementary Figure 1. Functional enrichment analyses of secretomic proteins. (a) Significant biological processes (upper panel) and disease biomarkers (lower panel) 2 involved by hrab37-mediated secretory
Supplementary Figure 1. Functional enrichment analyses of secretomic proteins. (a) Significant biological processes (upper panel) and disease biomarkers (lower panel) 2 involved by hrab37-mediated secretory
Pre-made Reporter Lentivirus for NF-κB Signal Pathway
 Pre-made Reporter for NF-κB Signal Pathway Cat# Product Name Amounts LVP965-P or: LVP965-P-PBS NFKB-GFP (Puro) LVP966-P or: LVP966-P-PBS NFKB-RFP (Puro) LVP967-P or: LVP967-P-PBS NFKB-Luc (Puro) LVP968-P
Pre-made Reporter for NF-κB Signal Pathway Cat# Product Name Amounts LVP965-P or: LVP965-P-PBS NFKB-GFP (Puro) LVP966-P or: LVP966-P-PBS NFKB-RFP (Puro) LVP967-P or: LVP967-P-PBS NFKB-Luc (Puro) LVP968-P
Research Article Retinal Targets ALDH Positive Cancer Stem Cell and Alters the Phenotype of Highly Metastatic Osteosarcoma Cells
 Sarcoma Volume 215, Article ID 784954, 8 pages http://dx.doi.org/1.1155/215/784954 Research Article Retinal Targets ALDH Positive Cancer Stem Cell and Alters the Phenotype of Highly Metastatic Osteosarcoma
Sarcoma Volume 215, Article ID 784954, 8 pages http://dx.doi.org/1.1155/215/784954 Research Article Retinal Targets ALDH Positive Cancer Stem Cell and Alters the Phenotype of Highly Metastatic Osteosarcoma
IL-13 Augments Compressive Stress-induced Tissue Factor Expression in Human Airway Epithelial Cells
 IL-13 Augments Compressive Stress-induced Tissue Factor Expression in Human Airway Epithelial Cells Jennifer A. Mitchel, Silvio Antoniak, Joo-Hyeon Lee, Sae-Hoon Kim, Maureen McGill, David I. Kasahara,
IL-13 Augments Compressive Stress-induced Tissue Factor Expression in Human Airway Epithelial Cells Jennifer A. Mitchel, Silvio Antoniak, Joo-Hyeon Lee, Sae-Hoon Kim, Maureen McGill, David I. Kasahara,
were isolated from the freshly drawn blood of healthy donors and ACS patients using the
 Supplemental Figure 1. Quality control of CD4 + T-cell purification. CD4 + T cells were isolated from the freshly drawn blood of healthy donors and ACS patients using the RosetteSep CD4 + T Cell Enrichment
Supplemental Figure 1. Quality control of CD4 + T-cell purification. CD4 + T cells were isolated from the freshly drawn blood of healthy donors and ACS patients using the RosetteSep CD4 + T Cell Enrichment
BIOLUMINESCENT ANIMAL MODELS OF HUMAN BREAST CANCER
 BIOLUMINESCENT ANIMAL MODELS OF HUMAN BREAST CANCER FOR TUMOR BIOMASS EVALUATION AND METASTASIS DETECTION Introduction: Convenient animal models are needed to study the progression and treatment of human
BIOLUMINESCENT ANIMAL MODELS OF HUMAN BREAST CANCER FOR TUMOR BIOMASS EVALUATION AND METASTASIS DETECTION Introduction: Convenient animal models are needed to study the progression and treatment of human
Downregulation of serum mir-17 and mir-106b levels in gastric cancer and benign gastric diseases
 Brief Communication Downregulation of serum mir-17 and mir-106b levels in gastric cancer and benign gastric diseases Qinghai Zeng 1 *, Cuihong Jin 2 *, Wenhang Chen 2, Fang Xia 3, Qi Wang 3, Fan Fan 4,
Brief Communication Downregulation of serum mir-17 and mir-106b levels in gastric cancer and benign gastric diseases Qinghai Zeng 1 *, Cuihong Jin 2 *, Wenhang Chen 2, Fang Xia 3, Qi Wang 3, Fan Fan 4,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION FOR Liver X Receptor α mediates hepatic triglyceride accumulation through upregulation of G0/G1 Switch Gene 2 (G0S2) expression I: SUPPLEMENTARY METHODS II: SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION FOR Liver X Receptor α mediates hepatic triglyceride accumulation through upregulation of G0/G1 Switch Gene 2 (G0S2) expression I: SUPPLEMENTARY METHODS II: SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES
University of North Carolina Chapel Hill, NC Approved for Public Release; Distribution Unlimited
 oa AD Award Number: DAMD17-03-1-0401 TITLE: Non-Classical NF-kappaB Forms and Bcl-3 in Breast Cancer Development and Resistance to Cancer Therapy PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Albert S. Baldwin, Ph.D. CONTRACTING
oa AD Award Number: DAMD17-03-1-0401 TITLE: Non-Classical NF-kappaB Forms and Bcl-3 in Breast Cancer Development and Resistance to Cancer Therapy PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Albert S. Baldwin, Ph.D. CONTRACTING
Selec%ve killing of cancer cells by a small molecule targe%ng the stress response to ROS
 Selec%ve killing of cancer cells by a small molecule targe%ng the stress response to RS L Raj et al. Nature 475, 231-234 (2011) doi:10.1038/nature10167 Current literature Presented by Zhuzhu WANG 9/3/11
Selec%ve killing of cancer cells by a small molecule targe%ng the stress response to RS L Raj et al. Nature 475, 231-234 (2011) doi:10.1038/nature10167 Current literature Presented by Zhuzhu WANG 9/3/11
