MicroRNA-146a Ameliorates Inflammation via TRAF6/NF-kB Pathway in Intervertebral Disc Cells
|
|
|
- Richard Rich
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 e-issn DOI: /MSM Received: Accepted: Published: MicroRNA-146a Ameliorates Inflammation via TRAF6/NF-kB Pathway in Intervertebral Disc Cells Authors Contribution: Study Design A Data Collection B Statistical Analysis C Data Interpretation D Manuscript Preparation E Literature Search F Funds Collection G A 1,2 Feng Lv BE 3 Yingzi Huang C 4 Wentao Lv C 2 Longbiao Yang F 3 Feng Li B 5 Jingli Fan A 1 Jianmin Sun 1 Department of Spine Surgery, Shandong Provincial Hospital Affiliated to Shandong University, Jinan, Shandong, P.R. China 2 Department of Orthopedics, Shandong Energy Zibo Mining Group Co. Ltd. Central Hospital, Zibo, Shandong, P.R China 3 Special Inspection Section, The Fifth People s Hospital of Zibo City, Zibo, Shandong, P.R. China 4 Department of Orthopedics, The Sixth People s Hospital of Zibo City, Zibo, Shandong, P.R. China 5 Thyroid Disease Prevention and Control Center, Endemic Disease Control and Prevention Institute of Shandong Province, Jinan, Shandong, P.R. China Corresponding Author: Source of support: Jianmin Sun, sunjianmin222@163.com Departmental sources Background: Material/Methods: Results: Conclusions: MeSH Keywords: Full-text PDF: Intervertebral disc degeneration (IDD) has been widely recognized as a major contributor to low back pain. Accumulating evidence suggests that IDD is linked to various pro-inflammatory cytokines and metabolites. Recently, numerous studies have demonstrated that micrornas (mirnas) play a pivotal role in the development of most disorders, including degenerative disc diseases. Previous reports have revealed that mirna-146a (mir-146a) could attenuate neuropathic pain in the spinal cord. The aim of this study was to investigate the role of mir-146a in the inflammatory response of IDD. Quantitative real-time (RT)-PCR was performed to investigate the levels of mir-146a in the PBMCs (peripheral blood mononuclear cells) of patients with IDD. Human nucleus pulposus (NP) cells were transiently transfected with mir-146a mimic; control NP cell transfections lacked mir-146a. Then all NP cells were treated with LPS (1 μm) to induce inflammation. The mrna levels of mir-146a in NP cells were determined by RT-PCR. In addition, the mrna and protein expression levels of tumor necrosis factor (TNF), receptor-associated factor 6 (TRAF6), and nuclear factor (NF)-kB in NP cells were evaluated by quantitative RT-PCR and Western blot analysis, respectively. We found that mir-146a was significantly downregulated in the PBMCs of patients. Moreover, overexpression of mir-146a significantly decreased the levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines in LPS-stimulated NP cells. The mrna and protein levels of TRAF6 and NF-kB were downregulated by mir-146a overexpression. These results suggest that overexpression of mir-146a could promote IDD through the TRAF/NF-kB pathway. Our findings also highlight mir-146a as a novel possible therapeutic target for IDD. Inflammation Intervertebral Disc Degeneration MicroRNAs NF-kappa B TNF Receptor-Associated Factor
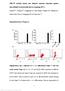
2 Lv F. et al.: Background Low back pain (LBP) is the sixth leading cause of disability worldwide and one of the most costly musculoskeletal pain syndromes of modern society [1]; 84% of all people suffer from LBP at some time in their life [2]. The absolute number of people with low back pain is likely to increase substantially over the coming decades as the population ages [3]. Intervertebral disc degeneration (IDD) plays a central role in the pathogenesis of discogenic pain, disc herniation, and spinal instability and stenosis, and is widely recognized as a contributor to low back pain [4,5]. Numerous investigations have proven that IDD is linked to various pro-inflammatory cytokines and metabolites, including interleukin (IL)-1b, IL-6, and tumor necrosis factor-a (TNF-a). MicroRNAs (mirnas) are a type of small non-coding RNA molecule of 2-22 nucleotides in length [6]. Increasing evidence suggests these newly defined gene regulators, mirnas, play a pivotal role in the development of most disorders [7,8], including degenerative disc diseases [9]. MicroRNA-146a (mir- 146a), one of the earliest mirnas identified in cartilage, has been implicated in some degenerative diseases, including osteoarthritis [1,11]. Moreover, it has been suggested that mir- 146a functions as a negative feedback regulator of inflammation response by targeting TRAF6 [12], a member of the tumor necrosis factor (TNF) receptor-associated factors (TRAFs) family [13]. TRAF6 participates in signal transduction of both the TNF receptor (TNFR) and interleukin (IL)-1 receptor/toll-like receptor (IL-1R/TLR) superfamily [14]; it triggers the IkB kinase, and in turn, the downstream nuclear factor (NF)-kB transcription factors, and results in overexpression of pro-inflammatory cytokine secretion. Recently, mir-146a was demonstrated to attenuate neuropathic pain in the spinal cord partially through the suppression of inflammation [15], which suggests a potential role for mir-146a in inhibiting inflammation in IDD. Thus, the aim of the present study was to investigate the expression and role of mir-146a in IDD and explore the pathological links between mir-146a, IDD, and inflammatory pathways associated with IDD. In this study, we found mir-146a expression was significantly downregulated in patients with IDD versus healthy controls. Subsequently, we investigated the role of mir-146a in a series of experiments performed in LPS-stimulated human nucleus pulposus (NP) cells using mir- 146a mimics. Material and Methods Materials and reagents Lipopolysaccharides (LPS) were purchased from Sigma (St. Louis, MO, USA). ELISA kits for TNF-a, IL-1b, and IL-6 were obtained from Dakewe Biotech Co., Ltd. (Shenzhen, P. R. China). Antibodies against TRAF6, NF-kB, and b-actin and horseradish peroxidase (HRP)-linked anti-rabbit IgG antibody were obtained from Cell Signaling Technology (Danvers, MA, USA). All of the other chemicals and reagents were of analytical grade and purchased from Sinopharm Chemical Reagent (Shanghai, P. R. China). Patients and control participants Between May 213 and March 214, a total of 21 patients with degenerative disc disease (IDD) and 21 healthy human volunteers were enrolled in the study. Routine MRI scans of the lumbar spine were taken of these patients, the degree of disc degeneration was graded from T2-weighted images using a modified Pfirrmann classification [16]. According to the modified classification system of the International Society for the Study of the Lumbar Spine [17], 12 samples were protrusions, five were sequestration, and four were subligamentous extrusion. PBMCs (peripheral blood mononuclear cells) were isolated from the peripheral blood of IDD patients and from healthy human volunteers as described previously and collected in heparinized tubes. Separation of human PBMCs was performed using density centrifugation with Lymphoprep (Fresenius Kabi Norge AS, Oslo, Norway). The study protocol were approved by the Ethics Committee of Shandong Provincial Hospital Affiliated to Shandong University, and informed written consents were obtained from all participants. Culture of human NP cells Human NP cells were purchased from ScienCell Research Laboratories (Carlsbad, CA, USA) and cultured in NP cell medium containing 1% fetal bovine serum (FBS) (GIBCO, NY, USA), 1 mg/ml streptomycin, 1 U/mL penicillin, and 1% NP cell growth supplement, and then incubated at 37 C in a humidified atmosphere with 95% (v/v) air and 5% (v/v) CO 2. The medium was changed every two days. Treatment of human NP cells Human NP cells were transiently transfected with mir-146a mimic (pre-microrna mimics, Applied Biosystems) using Lipofectamine plus (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA, USA), with control transfections lacking mir-146a. After 24 hours, cells were stimulated with LPS (1 ng/ml) in serum-free medium for 24 hours at 37 C under 5% CO 2. Supernatants were collected 24 hours after the initiation of each treatment and prepared for either cell lysates or total RNA extraction followed by qrt-pcr analyses. mir-146a quantitative RT-PCR Total RNA was isolated from human PBMCs and human NP cells using the total RNA isolation system according to 66
3 Lv F. et al.: LAB/IN VITRO RESEARCH Table 1. Sequences of primers. Gene name Forward primer Reverse primer mirna-146a 5 -GGGTGAGAACTGAATTCCA-3 5 -CAGTGCGTGTCGTGGAGT-3 TRAF6 5 -GAGTTTGACCCACCTCTGGA-3 5 -TTTCATTGTCAACTGGGCACT-3 NF-kB 5 -GAGGTGTATTTCACGGGACC-3 5 -GAAGTCCATGTCCGCAATGG-3 GAPDH 5 -GCACCGTCAAGGCTGAGAAC-3 5 -TGGTGAAGACGCCAGTGGA-3 manufacturer recommendations. RT reactions were performed using the TaqMan microrna Reverse Transcription Kit (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA, USA) according to the manufacturer s instructions. All mirna quantification data were normalized to 5S rrna expression and mrna quantification data were normalized to glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH). Relative amounts of transcript were calculated using the comparative Ct method. ELISA kits Relative mirna expression (fold) mir-146a Cellular supernatant IL-1b, IL-6, and TNF-a levels were determined by ELISA kits following the manufacturer s instructions.. None-IDD IDD Real-time PCR RT-PCR was performed using standard procedures with the QuantiTect SYBR Green PCR kit (Qiagen) in ABI PRISM 79HT detection systems (Applied Biosystems). Sequences of primers used for qpcr are presented in Table 1. Expression levels of each gene were normalized to GAPDH and expressed as a fold of control. Western blot analysis Western bolt analysis was performed as previously described [18]. In general, the cell lysates were centrifuged at 12, rpm for 15 minutes at 4 C, and the supernatants were collected to obtain the total proteins. A BCA protein assay kit (Pierce Biotechnology, Inc., Rockford, IL, USA) was used to determine the protein concentration. Then, the proteins were resolved by 1% SDS-PAGE (1% (v/v) gel and transferred to PVDF membrane (Millipore, Billerica, MA, USA). The membrane was incubated with primary antibodies against TRAF6 (1:1,), NF-kB (1:1,), and b-actin (1:1,) overnight at 4 C, and Western blot bands were visualized using Super Signal West Pico Chemiluminescent Substrate (Thermo Scientific, Rockford, IL, USA). Statistical analysis The data were expressed as the means ±SEM. The number of independent experiments was represented by n. Multiple comparisons were performed using one-way ANOVA followed Figure 1. Quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction analysis of expression of mir-146a in PBMCs separated from patients with IDD and control participants. Values are the mean ±SD, n=21 for each group. * p<.5, patients with IDD compared to control participants (non-idd). by Tukey s multiple-comparison test, where p<.5 was considered significant. Results Downregulation of mir-146a in the PBMCs To investigate the potential role of mirna-146 in IDD, we first measured the relative mrna expression of mir-146a in PBMCs separated from IDD patients and control participants. As shown in Figure 1, obviously decreased mrna levels of mir- 146a were observed in PBMCs of patients with IDD in comparison to those in control participants. Overexpression of mir-146a decreased pro-inflammatory cytokine levels in LPS-stimulated NP cells In order to evaluate the effects of mir-146a in IDD, we induced mir-146a expression using mir-146a mimic, while NC oligonucleotides were used as the control. NP cells were transfected with mir-146a mimic and NC oligonucleotides. Then mir-146a 661
4 Lv F. et al.: A C Relative mir-146a mrna expression Cellular supernantant IL-6 levels (pg/ml) mir-146a IL-6 B D Cellular supernantant IL-1β levels (pg/ml) Cellular supernantant TNF-α levels (pg/ml) IL-1β ** TNF-α Figure 2. Effects of mir-146a on pro-inflammatory cytokine levels in NP cells. (A) mir-146a mrna expression was increased after mimic treatment. (B, C) Overexpression of mir-146a decreased IL-1b, IL-6, and TNF-a in LPS-stimulated NP cells. Values are the mean ±SD, n=4 for each group. * p<.5, compared to LPS treated group. expression was analyzed using RT-PCR. As shown in Figure 2A, mir-146a expression was upregulated efficiently. Compared with the LPS group, the overexpression of mir-146a significantly decreased the levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines, including IL-1b, TNF-a, and IL-6 (Figure 2B 2D). Overexpression of mir-146a suppressed the activation of TRAF6/NF-kB in LPS-stimulated NP cells We next investigated whether mir-146a could regulate inflammation via the TRAF6/NF-kB pathway. As shown in Figure 3, overexpression of mir-146a significantly reduced the mrna levels of TRAF6 and its downstream effector, NF-kB in LPSstimulated NP cells, while NC oligonucleotides showed no significant effect on the expression of TRAF6/NF-kB in LPSstimulated NP cells. Discussion Increasing evidence shows that mirnas play an important role in many normal physiological processes and in the development of most diseases. In the present study, we found that mir-146a was significantly downregulated in PBMCs separated from patients and control subjects. Furthermore, overexpression of mir-146a greatly increased the levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines, including IL-1b, TNF-a and IL-6, in LPS-stimulated NP cells. In addition, mir-146a could regulate LPS-induced inflammation via the TRAF6/NF-kB pathway in NP cells. MiR-146a has been reported to be implicated in multiple diseases, including age-related macular degeneration [19], sepsis [2], atherosclerosis [21], Alzheimer s disease [22], and osteoarthritis [1]. However, expression of mir-146a and its role in IDD are still not clear. In this study, mir-146a levels were significantly decreased in PBMCs in patients with IDD. Decreased levels of mir-146a may be associated with the inflammation in intervertebral discs. Previous studies have shown that inflammatory processes exacerbated by cytokines TNF-a, IL-1b, and IL-6 are believed to be key mediators of disc degeneration and low back pain [23 25]. In the present study, we found that the overexpression of mir-146a markedly decreased pro-inflammatory cytokines levels in NP cells. These data suggest that increased pro-inflammatory cytokines levels induced by downregulation of mir-146a might participate in the development of IDD. TRAF6, an essential factor that mediates receptor signaling in response to ligands of the TNFa superfamily, has been identified 662
5 Lv F. et al.: LAB/IN VITRO RESEARCH A Relative TRAF6 mrna expression (fold) TRAF6 B 3 Relative NF-κB mrna expression (fold) 2 1 NF-κB C TRAF6 NF-κB β-actin Figure 3. Effects of mir-146a on mrna (A, B) and protein (C) expression of TRAF6 and NF-kB in NP cells. Values are the mean ±SD, n=4 for each group. * p<.5, compared to LPS treated group. as the target of mir-146a. In the present study, overexpression of mir-146a led to the decrease of TRAF6 and its downstream NF-kB expression both in mrna and in protein levels. It has been demonstrated that overexpression of mir-146 controls cytokine signaling through a negative feedback regulation loop by inhibiting TRAF6 expression and impairing NF-kB activity [12,26]. These findings are in agreement with previous work that showed that mir-146a negatively regulates TRAF6 activity and the inflammatory pathway in the spinal cord [15]. Therefore, these data indicate that overexpression of mir-146a might play an important role in IDD development, in part by suppressing TRAF6/NF-kB expression. Conclusions The results in the present study showed that mir-146a was decreased in the PBMCs of IDD patients compared to healthy controls. Moreover, overexpression of mir-146a significantly decreased the levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines by targeting the TARF6/NF-kB pathway, indicating a role for mir-146a in IDD. Furthermore, our findings suggest that overexpression of mir-146a might potentially be a therapeutic target in IDD. Conflicts of Interest The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest. References: 1. Morlion B: Chronic low back pain: pharmacological, interventional and surgical strategies. Nat Rev Neurol, 213; 9: Walker BF: The prevalence of low back pain: A systematic review of the literature from 1966 to J Spinal Disord Tech, 2; 13: Hoy D, Bain C, Williams G et al: A systematic review of the global prevalence of low back pain. Arthritis Rheum, 212; 64: Colombier P, Clouet J, Hamel O et al: The lumbar intervertebral disc: From embryonic development to degeneration. Joint Bone Spine, 214; 81: Ren S, Liu Y, Ma J et al: Treatment of rabbit intervertebral disc degeneration with co-transfection by adeno-associated virus-mediated SOX9 and osteogenic protein-1 double genes in vivo. Int J Mol Med, 213; 32: Van Wynsberghe PM, Chan SP, Slack FJ, Pasquinelli AE: Analysis of micror- NA expression and function. Methods Cell Biol, 211; 16:
6 Lv F. et al.: 7. Min W, Wang B, Li J et al: The expression and significance of five types of mirnas in breast cancer. Med Sci Monit Basic Res, 214; 2: Lu M, Zhang Q, Deng M et al: An analysis of human microrna and disease associations. PloS One, 28; 3: e Wang C, Wang W-J, Yan Y-G et al: MicroRNAs: New players in intervertebral disc degeneration. Clin Chim Acta, 215; 45: Li X, Gibson G, Kim J-S et al: MicroRNA-146a is linked to pain-related pathophysiology of osteoarthritis. Gene, 211; 48: Li X, Kroin JS, Kc R et al: Altered apinal microrna-146a and the micror- NA-183 cluster contribute to osteoarthritic pain in knee joints. J Bone Miner Res, 213; 28: Taganov KD, Boldin MP, Chang K-J, Baltimore D: NF-kB-dependent induction of microrna mir-146, an inhibitor targeted to signaling proteins of innate immune responses. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 26; 13: Cao Z, Xiong J, Takeuchi M et al: TRAF6 is a signal transducer for interleukin-1. Nature, 1996; 383: Ye H, Arron JR, Lamothe B et al: Distinct molecular mechanism for initiating TRAF6 signalling. Nature, 22; 418: Lu Y, Cao D-L, Jiang B-C et al: MicroRNA-146a-5p attenuates neuropathic pain via suppressing TRAF6 signaling in the spinal cord. Brain Behav Immun, 215; 49: Pfirrmann CW, Metzdorf A, Zanetti M et al: Magnetic resonance classification of lumbar intervertebral disc degeneration. Spine, 21; 26: Williams AL, Haughton VM, Meyer GA, Ho KC: Computed tomographic appearance of the bulging annulus. Radiology, 1982; 142: Wang X-H, Hong X, Zhu L et al: Tumor necrosis factor alpha promotes the proliferation of human nucleus pulposus cells via nuclear factor-kb, c-jun N-terminal kinase, and p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase. Exp Biol Med, 215; 24: Szemraj M, Bielecka-Kowalska A, Oszajca K et al: Serum micrornas as potential biomarkers of AMD. Med Sci Monit, 215; 21: Cheng HS, Sivachandran N, Lau A et al: MicroRNA-146 represses endothelial activation by inhibiting pro-inflammatory pathways. Embo Mol Med, 213; 5: Guo M, Mao X, Ji Q et al: mir-146a in PBMCs modulates Th1 function in patients with acute coronary syndrome. Immunol Cell Biol, 21; 88: Wang L-L, Huang Y, Wang G, Chen S-D: The potential role of microrna-146 in Alzheimer s disease: Biomarker or therapeutic target? Med Hypotheses, 212; 78: Johnson Z, Schoepflin Z, Choi H et al: Disc in flames: Roles of TNF-a and IL- 1b in intervertebral disc degeneration. Eur Cell Mater, 215; 3: Yang W, Yu X-H, Wang C et al: Interleukin-1b in intervertebral disk degeneration. Clin Chim Acta, 215; 45: Risbud MV, Shapiro IM: Role of cytokines in intervertebral disc degeneration: Pain and disc content. Nat Rev Rheumatol, 214; 1: Bhaumik D, Scott G, Schokrpur S et al: Expression of microrna-146 suppresses NF-kB activity with reduction of metastatic potential in breast cancer cells. Oncogene, 28; 27:
Supplementary data Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 2
 Supplementary data Supplementary Figure 1 SPHK1 sirna increases RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis in RAW264.7 cell culture. (A) RAW264.7 cells were transfected with oligocassettes containing SPHK1 sirna
Supplementary data Supplementary Figure 1 SPHK1 sirna increases RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis in RAW264.7 cell culture. (A) RAW264.7 cells were transfected with oligocassettes containing SPHK1 sirna
Mechanism of mirna-21-5p on apoptosis of IL-1β- induced rat. synovial cells
 Mechanism of mirna-21-5p on apoptosis of IL-1β- induced rat synovial cells Zhen Li 1,2,3,4, Xiaofu Li 4, Yi Wang 4, Qingjun Wei 1,2,3,* 1 Orthopaedic Department, the First Affiliated Hospital of Guangxi
Mechanism of mirna-21-5p on apoptosis of IL-1β- induced rat synovial cells Zhen Li 1,2,3,4, Xiaofu Li 4, Yi Wang 4, Qingjun Wei 1,2,3,* 1 Orthopaedic Department, the First Affiliated Hospital of Guangxi
MicroRNAs Modulate the Noncanonical NF- B Pathway by Regulating IKK Expression During Macrophage Differentiation
 MicroRNAs Modulate the Noncanonical NF- B Pathway by Regulating IKK Expression During Macrophage Differentiation Tao Li 1 *, Michael J. Morgan 1 *, Swati Choksi 1, Yan Zhang 1, You-Sun Kim 2#, Zheng-gang
MicroRNAs Modulate the Noncanonical NF- B Pathway by Regulating IKK Expression During Macrophage Differentiation Tao Li 1 *, Michael J. Morgan 1 *, Swati Choksi 1, Yan Zhang 1, You-Sun Kim 2#, Zheng-gang
MTC-TT and TPC-1 cell lines were cultured in RPMI medium (Gibco, Breda, The Netherlands)
 Supplemental data Materials and Methods Cell culture MTC-TT and TPC-1 cell lines were cultured in RPMI medium (Gibco, Breda, The Netherlands) supplemented with 15% or 10% (for TPC-1) fetal bovine serum
Supplemental data Materials and Methods Cell culture MTC-TT and TPC-1 cell lines were cultured in RPMI medium (Gibco, Breda, The Netherlands) supplemented with 15% or 10% (for TPC-1) fetal bovine serum
RNA-Seq profiling of circular RNAs in human colorectal Cancer liver metastasis and the potential biomarkers
 Xu et al. Molecular Cancer (2019) 18:8 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-018-0932-8 LETTER TO THE EDITOR RNA-Seq profiling of circular RNAs in human colorectal Cancer liver metastasis and the potential biomarkers
Xu et al. Molecular Cancer (2019) 18:8 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-018-0932-8 LETTER TO THE EDITOR RNA-Seq profiling of circular RNAs in human colorectal Cancer liver metastasis and the potential biomarkers
Intracellular MHC class II molecules promote TLR-triggered innate. immune responses by maintaining Btk activation
 Intracellular MHC class II molecules promote TLR-triggered innate immune responses by maintaining Btk activation Xingguang Liu, Zhenzhen Zhan, Dong Li, Li Xu, Feng Ma, Peng Zhang, Hangping Yao and Xuetao
Intracellular MHC class II molecules promote TLR-triggered innate immune responses by maintaining Btk activation Xingguang Liu, Zhenzhen Zhan, Dong Li, Li Xu, Feng Ma, Peng Zhang, Hangping Yao and Xuetao
The lncrna MIR4435-2HG is upregulated in hepatocellular carcinoma and promotes cancer cell proliferation by upregulating mirna-487a
 Kong et al. Cellular & Molecular Biology Letters (2019) 24:26 https://doi.org/10.1186/s11658-019-0148-y Cellular & Molecular Biology Letters RESEARCH LETTER Open Access The lncrna MIR4435-2HG is upregulated
Kong et al. Cellular & Molecular Biology Letters (2019) 24:26 https://doi.org/10.1186/s11658-019-0148-y Cellular & Molecular Biology Letters RESEARCH LETTER Open Access The lncrna MIR4435-2HG is upregulated
HEK293FT cells were transiently transfected with reporters, N3-ICD construct and
 Supplementary Information Luciferase reporter assay HEK293FT cells were transiently transfected with reporters, N3-ICD construct and increased amounts of wild type or kinase inactive EGFR. Transfections
Supplementary Information Luciferase reporter assay HEK293FT cells were transiently transfected with reporters, N3-ICD construct and increased amounts of wild type or kinase inactive EGFR. Transfections
Mir-595 is a significant indicator of poor patient prognosis in epithelial ovarian cancer
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 21: 4278-4282 Mir-595 is a significant indicator of poor patient prognosis in epithelial ovarian cancer Q.-H. ZHOU 1, Y.-M. ZHAO 2, L.-L.
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 21: 4278-4282 Mir-595 is a significant indicator of poor patient prognosis in epithelial ovarian cancer Q.-H. ZHOU 1, Y.-M. ZHAO 2, L.-L.
Anti-inflammatory properties of SM04690, a small molecule inhibitor of the Wnt pathway as a potential treatment for knee osteoarthritis
 Anti-inflammatory properties of SM04690, a small molecule inhibitor of the Wnt pathway as a potential treatment for knee osteoarthritis V. Deshmukh 1, T. Seo 1, C. Swearingen 1, Y. Yazici 1 1 Samumed,
Anti-inflammatory properties of SM04690, a small molecule inhibitor of the Wnt pathway as a potential treatment for knee osteoarthritis V. Deshmukh 1, T. Seo 1, C. Swearingen 1, Y. Yazici 1 1 Samumed,
Islet viability assay and Glucose Stimulated Insulin Secretion assay RT-PCR and Western Blot
 Islet viability assay and Glucose Stimulated Insulin Secretion assay Islet cell viability was determined by colorimetric (3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5- diphenyltetrazolium bromide assay using CellTiter
Islet viability assay and Glucose Stimulated Insulin Secretion assay Islet cell viability was determined by colorimetric (3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5- diphenyltetrazolium bromide assay using CellTiter
Cellular Physiology and Biochemistry
 Original Paper 2015 The Author(s). 2015 Published The Author(s) by S. Karger AG, Basel Published online: November 27, 2015 www.karger.com/cpb Published by S. Karger AG, Basel 2194 1421-9778/15/0376-2194$39.50/0
Original Paper 2015 The Author(s). 2015 Published The Author(s) by S. Karger AG, Basel Published online: November 27, 2015 www.karger.com/cpb Published by S. Karger AG, Basel 2194 1421-9778/15/0376-2194$39.50/0
Downregulation of serum mir-17 and mir-106b levels in gastric cancer and benign gastric diseases
 Brief Communication Downregulation of serum mir-17 and mir-106b levels in gastric cancer and benign gastric diseases Qinghai Zeng 1 *, Cuihong Jin 2 *, Wenhang Chen 2, Fang Xia 3, Qi Wang 3, Fan Fan 4,
Brief Communication Downregulation of serum mir-17 and mir-106b levels in gastric cancer and benign gastric diseases Qinghai Zeng 1 *, Cuihong Jin 2 *, Wenhang Chen 2, Fang Xia 3, Qi Wang 3, Fan Fan 4,
Electronic Supplementary Information. Direct chemiluminescence detection of circulating. micrornas in serum samples using a single-strand specific
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Chemical Communications. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Electronic Supplementary Information Direct chemiluminescence detection of circulating
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Chemical Communications. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Electronic Supplementary Information Direct chemiluminescence detection of circulating
SUPPORTING MATREALS. Methods and Materials
 SUPPORTING MATREALS Methods and Materials Cell Culture MC3T3-E1 (subclone 4) cells were maintained in -MEM with 10% FBS, 1% Pen/Strep at 37ºC in a humidified incubator with 5% CO2. MC3T3 cell differentiation
SUPPORTING MATREALS Methods and Materials Cell Culture MC3T3-E1 (subclone 4) cells were maintained in -MEM with 10% FBS, 1% Pen/Strep at 37ºC in a humidified incubator with 5% CO2. MC3T3 cell differentiation
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/7/310/ra11/dc1 Supplementary Materials for STAT3 Induction of mir-146b Forms a Feedback Loop to Inhibit the NF-κB to IL-6 Signaling Axis and STAT3-Driven Cancer
www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/7/310/ra11/dc1 Supplementary Materials for STAT3 Induction of mir-146b Forms a Feedback Loop to Inhibit the NF-κB to IL-6 Signaling Axis and STAT3-Driven Cancer
Original Article Suppression of mir-301a alleviates LPS-induced inflammatory injury in ATDC5 chondrogenic cells by targeting Sirt1
 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2017;10(8):8991-9000 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0057081 Original Article Suppression of mir-301a alleviates LPS-induced inflammatory injury in ATDC5 chondrogenic cells by
Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2017;10(8):8991-9000 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0057081 Original Article Suppression of mir-301a alleviates LPS-induced inflammatory injury in ATDC5 chondrogenic cells by
Original Article Regulation of diabetes-induced inflammation in macrophages by microrna-26a-5p
 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2016;9(10):10074-10079 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0034290 Original Article Regulation of diabetes-induced inflammation in macrophages by microrna-26a-5p Xin-Ge Yue, Su-Jun
Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2016;9(10):10074-10079 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0034290 Original Article Regulation of diabetes-induced inflammation in macrophages by microrna-26a-5p Xin-Ge Yue, Su-Jun
Protection against doxorubicin-induced myocardial dysfunction in mice by cardiac-specific expression of carboxyl terminus of hsp70-interacting protein
 Protection against doxorubicin-induced myocardial dysfunction in mice by cardiac-specific expression of carboxyl terminus of hsp70-interacting protein Lei Wang 1, Tian-Peng Zhang 1, Yuan Zhang 2, Hai-Lian
Protection against doxorubicin-induced myocardial dysfunction in mice by cardiac-specific expression of carboxyl terminus of hsp70-interacting protein Lei Wang 1, Tian-Peng Zhang 1, Yuan Zhang 2, Hai-Lian
CircHIPK3 is upregulated and predicts a poor prognosis in epithelial ovarian cancer
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2018; 22: 3713-3718 CircHIPK3 is upregulated and predicts a poor prognosis in epithelial ovarian cancer N. LIU 1, J. ZHANG 1, L.-Y. ZHANG 1, L.
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2018; 22: 3713-3718 CircHIPK3 is upregulated and predicts a poor prognosis in epithelial ovarian cancer N. LIU 1, J. ZHANG 1, L.-Y. ZHANG 1, L.
Ephrin receptor A2 is an epithelial cell receptor for Epstein Barr virus entry
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Letters https://doi.org/10.1038/s41564-017-0080-8 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. Ephrin receptor A2 is an epithelial cell receptor for Epstein Barr virus
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Letters https://doi.org/10.1038/s41564-017-0080-8 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. Ephrin receptor A2 is an epithelial cell receptor for Epstein Barr virus
Annals of Oncology Advance Access published January 10, 2005
 Annals of Oncology Advance Access published January 10, 2005 Original article Annals of Oncology doi:10.1093/annonc/mdi077 Expression of survivin and bax/bcl-2 in peroxisome proliferator activated receptor-g
Annals of Oncology Advance Access published January 10, 2005 Original article Annals of Oncology doi:10.1093/annonc/mdi077 Expression of survivin and bax/bcl-2 in peroxisome proliferator activated receptor-g
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/4/199/ra75/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Signaling by the Matrix Proteoglycan Decorin Controls Inflammation and Cancer Through PDCD4 and MicroRNA-21 Rosetta
www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/4/199/ra75/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Signaling by the Matrix Proteoglycan Decorin Controls Inflammation and Cancer Through PDCD4 and MicroRNA-21 Rosetta
Inhibition of Autophagy by MiR-30A Induced by Mycobacteria tuberculosis as a Possible Mechanism of Immune Escape in Human Macrophages
 Jpn. J. Infect. Dis., 68, 420 424, 2015 Short Communication Inhibition of Autophagy by MiR-30A Induced by Mycobacteria tuberculosis as a Possible Mechanism of Immune Escape in Human Macrophages Zhi Chen
Jpn. J. Infect. Dis., 68, 420 424, 2015 Short Communication Inhibition of Autophagy by MiR-30A Induced by Mycobacteria tuberculosis as a Possible Mechanism of Immune Escape in Human Macrophages Zhi Chen
Department of Pharmaceutical Sciences, School of Pharmacy, Northeastern University, Boston, MA 02115, USA 2
 Pancreatic Cancer Cell Exosome-Mediated Macrophage Reprogramming and the Role of MicroRNAs 155 and 125b2 Transfection using Nanoparticle Delivery Systems Mei-Ju Su 1, Hibah Aldawsari 2, and Mansoor Amiji
Pancreatic Cancer Cell Exosome-Mediated Macrophage Reprogramming and the Role of MicroRNAs 155 and 125b2 Transfection using Nanoparticle Delivery Systems Mei-Ju Su 1, Hibah Aldawsari 2, and Mansoor Amiji
Long noncoding RNA CASC2 inhibits metastasis and epithelial to mesenchymal transition of lung adenocarcinoma via suppressing SOX4
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 21: 4584-4590 Long noncoding RNA CASC2 inhibits metastasis and epithelial to mesenchymal transition of lung adenocarcinoma via suppressing
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 21: 4584-4590 Long noncoding RNA CASC2 inhibits metastasis and epithelial to mesenchymal transition of lung adenocarcinoma via suppressing
INTRODUCTION. Induction of Monocyte Chemoattractant Protein-1 (MCP-1) Expression by Angiotensin II (AngII) in the Pancreatic Islets and Beta Cells
 Induction of Monocyte Chemoattractant Protein-1 (MCP-1) Expression by Angiotensin II (AngII) in the Pancreatic Islets and Beta Cells Galina Chipitsyna, Qiaoke Gong, Chance F. Gray et al. Endocrinology,
Induction of Monocyte Chemoattractant Protein-1 (MCP-1) Expression by Angiotensin II (AngII) in the Pancreatic Islets and Beta Cells Galina Chipitsyna, Qiaoke Gong, Chance F. Gray et al. Endocrinology,
Original Article Differential expression profile analysis of mirnas with HER-2 overexpression and intervention in breast cancer cells
 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2017;10(5):5039-5062 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0052419 Original Article Differential expression profile analysis of mirnas with HER-2 overexpression and intervention in breast
Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2017;10(5):5039-5062 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0052419 Original Article Differential expression profile analysis of mirnas with HER-2 overexpression and intervention in breast
Supplementary Figures
 MiR-29 controls innate and adaptive immune responses against intracellular bacterial infection by targeting IFN-γ Feng Ma 1,2,5, Sheng Xu 1,5, Xingguang Liu 1, Qian Zhang 1, Xiongfei Xu 1, Mofang Liu 3,
MiR-29 controls innate and adaptive immune responses against intracellular bacterial infection by targeting IFN-γ Feng Ma 1,2,5, Sheng Xu 1,5, Xingguang Liu 1, Qian Zhang 1, Xiongfei Xu 1, Mofang Liu 3,
Research progress on the use of estrogen receptor agonist for treatment of spinal cord injury
 Research progress on the use of estrogen receptor agonist for treatment of spinal cord injury Swapan K. Ray, PhD Professor, Department of Pathology, Microbiology, and Immunology USC School of Medicine,
Research progress on the use of estrogen receptor agonist for treatment of spinal cord injury Swapan K. Ray, PhD Professor, Department of Pathology, Microbiology, and Immunology USC School of Medicine,
Low levels of serum mir-99a is a predictor of poor prognosis in breast cancer
 Low levels of serum mir-99a is a predictor of poor prognosis in breast cancer J. Li 1, Z.J. Song 2, Y.Y. Wang 1, Y. Yin 1, Y. Liu 1 and X. Nan 1 1 Tumor Research Department, Shaanxi Provincial Tumor Hospital,
Low levels of serum mir-99a is a predictor of poor prognosis in breast cancer J. Li 1, Z.J. Song 2, Y.Y. Wang 1, Y. Yin 1, Y. Liu 1 and X. Nan 1 1 Tumor Research Department, Shaanxi Provincial Tumor Hospital,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION FOR Liver X Receptor α mediates hepatic triglyceride accumulation through upregulation of G0/G1 Switch Gene 2 (G0S2) expression I: SUPPLEMENTARY METHODS II: SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION FOR Liver X Receptor α mediates hepatic triglyceride accumulation through upregulation of G0/G1 Switch Gene 2 (G0S2) expression I: SUPPLEMENTARY METHODS II: SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES
Expression of mir-146a-5p in patients with intracranial aneurysms and its association with prognosis
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2018; 22: 726-730 Expression of mir-146a-5p in patients with intracranial aneurysms and its association with prognosis H.-L. ZHANG 1, L. LI 2, C.-J.
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2018; 22: 726-730 Expression of mir-146a-5p in patients with intracranial aneurysms and its association with prognosis H.-L. ZHANG 1, L. LI 2, C.-J.
Upregulation of mir-107 expression following hyperbaric oxygen treatment suppresses HMGB1/RAGE signaling in degenerated human nucleus pulposus cells
 Niu et al. Arthritis Research & Therapy (2019) 21:42 https://doi.org/10.1186/s13075-019-1830-1 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Upregulation of mir-107 expression following hyperbaric oxygen treatment suppresses
Niu et al. Arthritis Research & Therapy (2019) 21:42 https://doi.org/10.1186/s13075-019-1830-1 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Upregulation of mir-107 expression following hyperbaric oxygen treatment suppresses
Index. Index 439. Aequorin, 84, 94 Affinity precipitation, 372, AP-1, 100 Asthma, 170, 305
 Index 439 Index A Aequorin, 84, 94 Affinity precipitation, 372, 376 381 AP-1, 100 Asthma, 170, 305 B Bioassay, 185, comparison with ELISA, 318 GM-CSF bioassay, 351 IL-2 bioassay, 185 192, 300 IL-3 IL-6
Index 439 Index A Aequorin, 84, 94 Affinity precipitation, 372, 376 381 AP-1, 100 Asthma, 170, 305 B Bioassay, 185, comparison with ELISA, 318 GM-CSF bioassay, 351 IL-2 bioassay, 185 192, 300 IL-3 IL-6
Is Discography or Discoblock Safe for Human Intervertebral Disc cells?
 Is Discography or Discoblock Safe for Human Intervertebral Disc cells? KOJI IWASAKI 1, Hideki Sudo 2, Katsuhisa Yamada 1, Norimasa Iwasaki 1. 1 Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Hokkaido University Graduate
Is Discography or Discoblock Safe for Human Intervertebral Disc cells? KOJI IWASAKI 1, Hideki Sudo 2, Katsuhisa Yamada 1, Norimasa Iwasaki 1. 1 Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Hokkaido University Graduate
Expression of mir-1294 is downregulated and predicts a poor prognosis in gastric cancer
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2018; 22: 5525-5530 Expression of mir-1294 is downregulated and predicts a poor prognosis in gastric cancer Y.-X. SHI, B.-L. YE, B.-R. HU, X.-J.
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2018; 22: 5525-5530 Expression of mir-1294 is downregulated and predicts a poor prognosis in gastric cancer Y.-X. SHI, B.-L. YE, B.-R. HU, X.-J.
Supplementary Figure 1. Normal T lymphocyte populations in Dapk -/- mice. (a) Normal thymic development in Dapk -/- mice. Thymocytes from WT and Dapk
 Supplementary Figure 1. Normal T lymphocyte populations in Dapk -/- mice. (a) Normal thymic development in Dapk -/- mice. Thymocytes from WT and Dapk -/- mice were stained for expression of CD4 and CD8.
Supplementary Figure 1. Normal T lymphocyte populations in Dapk -/- mice. (a) Normal thymic development in Dapk -/- mice. Thymocytes from WT and Dapk -/- mice were stained for expression of CD4 and CD8.
LncRNA AWPPH promotes the growth of triple-negative breast cancer by. up-regulating frizzled homolog 7 (FZD7)
 Bioscience Reports: this is an Accepted Manuscript, not the final Version of Record. You are encouraged to use the Version of Record that, when published, will replace this version. The most up-to-date
Bioscience Reports: this is an Accepted Manuscript, not the final Version of Record. You are encouraged to use the Version of Record that, when published, will replace this version. The most up-to-date
alveolar macrophages (AMs) after 24 hours of in vitro culture in complete medium
 Online Supplement for: NF-κB ACTIVATION IN ALVEOLAR MACROPHAGES REQUIRES IκB KINASE-β, BUT NOT NF-κB INDUCING KINASE Supershift and Competition Assays for NF-κB Competition and supershift assays were performed
Online Supplement for: NF-κB ACTIVATION IN ALVEOLAR MACROPHAGES REQUIRES IκB KINASE-β, BUT NOT NF-κB INDUCING KINASE Supershift and Competition Assays for NF-κB Competition and supershift assays were performed
Ling Xu, Wei-Qi Dai, Xuan-Fu Xu, Fan Wang, Lei He, Chuan-Yong Guo*
 DOI:http://dx.doi.org/10.7314/APJCP.2012.13.7.3203 RESEARCH ARTICLE Effects of Multiple-target Anti-microRNA Antisense Oligodeoxyribonucleotides on Proliferation and Migration of Gastric Cancer Cells Ling
DOI:http://dx.doi.org/10.7314/APJCP.2012.13.7.3203 RESEARCH ARTICLE Effects of Multiple-target Anti-microRNA Antisense Oligodeoxyribonucleotides on Proliferation and Migration of Gastric Cancer Cells Ling
Profiles of gene expression & diagnosis/prognosis of cancer. MCs in Advanced Genetics Ainoa Planas Riverola
 Profiles of gene expression & diagnosis/prognosis of cancer MCs in Advanced Genetics Ainoa Planas Riverola Gene expression profiles Gene expression profiling Used in molecular biology, it measures the
Profiles of gene expression & diagnosis/prognosis of cancer MCs in Advanced Genetics Ainoa Planas Riverola Gene expression profiles Gene expression profiling Used in molecular biology, it measures the
MicroRNA-338-3p inhibits glucocorticoidinduced osteoclast formation through RANKL targeting
 MicroRNA-338-3p inhibits glucocorticoidinduced osteoclast formation through RANKL targeting X.H. Zhang 1 *, G.L. Geng 2 *, B. Su 1, C.P. Liang 1, F. Wang 1 and J.C. Bao 3 1 Department of Physical Therapy,
MicroRNA-338-3p inhibits glucocorticoidinduced osteoclast formation through RANKL targeting X.H. Zhang 1 *, G.L. Geng 2 *, B. Su 1, C.P. Liang 1, F. Wang 1 and J.C. Bao 3 1 Department of Physical Therapy,
95% CI: , P=0.037).
 Biomedical Research 2017; 28 (21): 9248-9252 Reduced expression level of mir-205 predicts poor prognosis in Qiang Yang 1*#, Peng Sun 2#, Haotian Feng 1, Xin Li 1, Jianmin Li 1 1 Department of Orthopedics,
Biomedical Research 2017; 28 (21): 9248-9252 Reduced expression level of mir-205 predicts poor prognosis in Qiang Yang 1*#, Peng Sun 2#, Haotian Feng 1, Xin Li 1, Jianmin Li 1 1 Department of Orthopedics,
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information M1 macrophage-derived nanovesicles potentiate the anticancer efficacy of immune checkpoint inhibitors Yeon Woong Choo, 1, Mikyung Kang, 2, Han Young Kim, 1 Jin Han, 1 Seokyung Kang,
Supporting Information M1 macrophage-derived nanovesicles potentiate the anticancer efficacy of immune checkpoint inhibitors Yeon Woong Choo, 1, Mikyung Kang, 2, Han Young Kim, 1 Jin Han, 1 Seokyung Kang,
Supporting Information Table of content
 Supporting Information Table of content Supporting Information Fig. S1 Supporting Information Fig. S2 Supporting Information Fig. S3 Supporting Information Fig. S4 Supporting Information Fig. S5 Supporting
Supporting Information Table of content Supporting Information Fig. S1 Supporting Information Fig. S2 Supporting Information Fig. S3 Supporting Information Fig. S4 Supporting Information Fig. S5 Supporting
Identification of a Novel Common Genetic Risk Factor for Lumbar Disk Disease Original Contribution JAMA, Vol. 285 No. 14: , April 11, 2001
 1 Identification of a Novel Common Genetic Risk Factor for Lumbar Disk Disease Original Contribution JAMA, Vol. 285 No. 14:1843-1849, April 11, 2001 Petteri Paassilta; Jaana Lohiniva; Harald H. H. Göring;
1 Identification of a Novel Common Genetic Risk Factor for Lumbar Disk Disease Original Contribution JAMA, Vol. 285 No. 14:1843-1849, April 11, 2001 Petteri Paassilta; Jaana Lohiniva; Harald H. H. Göring;
Advances in Computer Science Research, volume 59 7th International Conference on Education, Management, Computer and Medicine (EMCM 2016)
 7th International Conference on Education, Management, Computer and Medicine (EMCM 2016) Expression of Beta-Adrenergic Receptor in Glioma LN229 Cells and Its Effect on Cell Proliferation Ping Wang1, Qingluan
7th International Conference on Education, Management, Computer and Medicine (EMCM 2016) Expression of Beta-Adrenergic Receptor in Glioma LN229 Cells and Its Effect on Cell Proliferation Ping Wang1, Qingluan
McAb and rhil-2 activated bone marrow on the killing and purging of leukemia cells
 Effects of McAb and rhil-2 activated bone marrow on the killing and purging of leukemia cells X.C. Wei, D.D. Yang, X.R. Han, Y.A. Zhao, Y.C. Li, L.J. Zhang and J.J. Wang Institute of hematological research,
Effects of McAb and rhil-2 activated bone marrow on the killing and purging of leukemia cells X.C. Wei, D.D. Yang, X.R. Han, Y.A. Zhao, Y.C. Li, L.J. Zhang and J.J. Wang Institute of hematological research,
Research Communication
 IUBMB Life, 64(7): 628 635, July 2012 Research Communication MicroRNA-181b Targets camp Responsive Element Binding Protein 1 in Gastric Adenocarcinomas Lin Chen*, Qian Yang*, Wei-Qing Kong*, Tao Liu, Min
IUBMB Life, 64(7): 628 635, July 2012 Research Communication MicroRNA-181b Targets camp Responsive Element Binding Protein 1 in Gastric Adenocarcinomas Lin Chen*, Qian Yang*, Wei-Qing Kong*, Tao Liu, Min
Original Article Up-regulation of mir-10a and down-regulation of mir-148b serve as potential prognostic biomarkers for osteosarcoma
 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2016;9(1):186-190 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0018032 Original Article Up-regulation of mir-10a and down-regulation of mir-148b serve as potential prognostic biomarkers for
Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2016;9(1):186-190 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0018032 Original Article Up-regulation of mir-10a and down-regulation of mir-148b serve as potential prognostic biomarkers for
Original Article Regulation of macrophage cholesterol efflux and liver X receptor α activation by nicotine
 Int J Clin Exp Med 2015;8(9):16374-16378 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0010359 Original Article Regulation of macrophage cholesterol efflux and liver X receptor α activation by nicotine Hongming Zhang
Int J Clin Exp Med 2015;8(9):16374-16378 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0010359 Original Article Regulation of macrophage cholesterol efflux and liver X receptor α activation by nicotine Hongming Zhang
Effects of AFP gene silencing on Survivin mrna expression inhibition in HepG2 cells
 mrna expression inhibition in HepG2 cells Z.L. Fang 1, N. Fang 2, X.N. Han 3, G. Huang 2, X.J. Fu 2, G.S. Xie 2, N.R. Wang 2 and J.P. Xiong 1 1 Department of Medical Oncology, The First Affiliated Hospital
mrna expression inhibition in HepG2 cells Z.L. Fang 1, N. Fang 2, X.N. Han 3, G. Huang 2, X.J. Fu 2, G.S. Xie 2, N.R. Wang 2 and J.P. Xiong 1 1 Department of Medical Oncology, The First Affiliated Hospital
Astragaloside IV ameliorates 2,4,6-trinitrobenzene sulfonic acid (TNBS)-induced
 Astragaloside IV ameliorates 2,4,6-trinitrobenzene sulfonic acid (TNBS)-induced colitis implicating regulation of energy metabolism Xu-Guang Jiang 1,2,, Kai Sun 1,3,4,5,, Yu-Ying Liu 1,4,5, Li Yan 1,4,5,
Astragaloside IV ameliorates 2,4,6-trinitrobenzene sulfonic acid (TNBS)-induced colitis implicating regulation of energy metabolism Xu-Guang Jiang 1,2,, Kai Sun 1,3,4,5,, Yu-Ying Liu 1,4,5, Li Yan 1,4,5,
Doctoral Degree Program in Marine Biotechnology, College of Marine Sciences, Doctoral Degree Program in Marine Biotechnology, Academia Sinica, Taipei,
 Cyclooxygenase 2 facilitates dengue virus replication and serves as a potential target for developing antiviral agents Chun-Kuang Lin 1,2, Chin-Kai Tseng 3,4, Yu-Hsuan Wu 3,4, Chih-Chuang Liaw 1,5, Chun-
Cyclooxygenase 2 facilitates dengue virus replication and serves as a potential target for developing antiviral agents Chun-Kuang Lin 1,2, Chin-Kai Tseng 3,4, Yu-Hsuan Wu 3,4, Chih-Chuang Liaw 1,5, Chun-
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL. Supplementary Methods
 SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL Supplementary Methods Culture of cardiomyocytes, fibroblasts and cardiac microvascular endothelial cells The isolation and culturing of neonatal rat ventricular cardiomyocytes was
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL Supplementary Methods Culture of cardiomyocytes, fibroblasts and cardiac microvascular endothelial cells The isolation and culturing of neonatal rat ventricular cardiomyocytes was
Integrin CD11b negatively regulates TLR-triggered inflammatory responses by. activating Syk and promoting MyD88 and TRIF degradation via cbl-b
 Integrin CD11b negatively regulates TLR-triggered inflammatory responses by activating Syk and promoting MyD88 and TRIF degradation via cbl-b Chaofeng Han, Jing Jin, Sheng Xu, Haibo Liu, Nan Li, and Xuetao
Integrin CD11b negatively regulates TLR-triggered inflammatory responses by activating Syk and promoting MyD88 and TRIF degradation via cbl-b Chaofeng Han, Jing Jin, Sheng Xu, Haibo Liu, Nan Li, and Xuetao
Mir-138-5p acts as a tumor suppressor by targeting pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase 1 in human retinoblastoma
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 21: 5624-5629 Mir-138-5p acts as a tumor suppressor by targeting pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase 1 in human retinoblastoma Z. WANG 1, Y.-J.
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 21: 5624-5629 Mir-138-5p acts as a tumor suppressor by targeting pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase 1 in human retinoblastoma Z. WANG 1, Y.-J.
Berberine Sensitizes Human Ovarian Cancer Cells to Cisplatin Through mir-93/ PTEN/Akt Signaling Pathway
 Chen Accepted: et al.: February Berberine 24, Sensitizes 2015 Ovarian Cancer Cells to Cisplatin www.karger.com/cpb 956 1421-9778/15/0363-0956$39.50/0 Original Paper This is an Open Access article licensed
Chen Accepted: et al.: February Berberine 24, Sensitizes 2015 Ovarian Cancer Cells to Cisplatin www.karger.com/cpb 956 1421-9778/15/0363-0956$39.50/0 Original Paper This is an Open Access article licensed
Original Article Reduced expression of mir-506 in glioma is associated with advanced tumor progression and unfavorable prognosis
 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2016;9(1):181-185 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0017823 Original Article Reduced expression of mir-506 in glioma is associated with advanced tumor progression and unfavorable
Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2016;9(1):181-185 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0017823 Original Article Reduced expression of mir-506 in glioma is associated with advanced tumor progression and unfavorable
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/9/439/ra78/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Small heterodimer partner mediates liver X receptor (LXR) dependent suppression of inflammatory signaling by promoting
www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/9/439/ra78/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Small heterodimer partner mediates liver X receptor (LXR) dependent suppression of inflammatory signaling by promoting
Li et al. Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research (2018) 37:108
 Li et al. Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research (2018) 37:108 https://doi.org/10.1186/s13046-018-0774-7 CORRECTION Correction to: Novel smac mimetic APG- 1387 elicits ovarian cancer cell killing
Li et al. Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research (2018) 37:108 https://doi.org/10.1186/s13046-018-0774-7 CORRECTION Correction to: Novel smac mimetic APG- 1387 elicits ovarian cancer cell killing
Study on the clinical value of mirna98b as a potential biomarker for osteoarthritis.
 Biomedical Research 2018; 29 (3): 549-553 ISSN 0970-938X www.biomedres.info Study on the clinical value of mirna98b as a potential biomarker for osteoarthritis. Qian Wang 1, Xiaoqing Ma 2, Zhongyang Xu
Biomedical Research 2018; 29 (3): 549-553 ISSN 0970-938X www.biomedres.info Study on the clinical value of mirna98b as a potential biomarker for osteoarthritis. Qian Wang 1, Xiaoqing Ma 2, Zhongyang Xu
Original Article High serum mir-203 predicts the poor prognosis in patients with pancreatic cancer
 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2017;10(4):4688-4693 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0047128 Original Article High serum mir-203 predicts the poor prognosis in patients with pancreatic cancer Jun Ma, Xiaokun
Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2017;10(4):4688-4693 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0047128 Original Article High serum mir-203 predicts the poor prognosis in patients with pancreatic cancer Jun Ma, Xiaokun
A novel bfgf antagonist peptide inhibits breast cancer cell growth
 210 A novel bfgf antagonist peptide inhibits breast cancer cell growth QUCHOU LI 1, SUSU GAO 1, YONGLIN YU 1, WENHUI WANG 1, XILEI CHEN 1, RUIXUE WANG 1, TAO LI 1, CONG WANG 1, XIAOKUN LI 1,2 and XIAOPING
210 A novel bfgf antagonist peptide inhibits breast cancer cell growth QUCHOU LI 1, SUSU GAO 1, YONGLIN YU 1, WENHUI WANG 1, XILEI CHEN 1, RUIXUE WANG 1, TAO LI 1, CONG WANG 1, XIAOKUN LI 1,2 and XIAOPING
GFP/Iba1/GFAP. Brain. Liver. Kidney. Lung. Hoechst/Iba1/TLR9!
 Supplementary information a +KA Relative expression d! Tlr9 5!! 5! NSC Neuron Astrocyte Microglia! 5! Tlr7!!!! NSC Neuron Astrocyte! GFP/Sβ/! Iba/Hoechst Microglia e Hoechst/Iba/TLR9! GFP/Iba/GFAP f Brain
Supplementary information a +KA Relative expression d! Tlr9 5!! 5! NSC Neuron Astrocyte Microglia! 5! Tlr7!!!! NSC Neuron Astrocyte! GFP/Sβ/! Iba/Hoechst Microglia e Hoechst/Iba/TLR9! GFP/Iba/GFAP f Brain
DNA context and promoter activity affect gene expression in lentiviral vectors
 ACTA BIOMED 2008; 79: 192-196 Mattioli 1885 O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E DNA context and promoter activity affect gene expression in lentiviral vectors Gensheng Mao 1, Francesco Marotta 2, Jia Yu 3, Liang
ACTA BIOMED 2008; 79: 192-196 Mattioli 1885 O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E DNA context and promoter activity affect gene expression in lentiviral vectors Gensheng Mao 1, Francesco Marotta 2, Jia Yu 3, Liang
Original Article Reduced serum mir-138 is associated with poor prognosis of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma
 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2017;10(10):10276-10281 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0059849 Original Article Reduced serum mir-138 is associated with poor prognosis of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma
Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2017;10(10):10276-10281 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0059849 Original Article Reduced serum mir-138 is associated with poor prognosis of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma
Bin Liu, Lei Yang, Binfang Huang, Mei Cheng, Hui Wang, Yinyan Li, Dongsheng Huang, Jian Zheng,
 The American Journal of Human Genetics, Volume 91 Supplemental Data A Functional Copy-Number Variation in MAPKAPK2 Predicts Risk and Survival of Lung Cancer Bin Liu, Lei Yang, Binfang Huang, Mei Cheng,
The American Journal of Human Genetics, Volume 91 Supplemental Data A Functional Copy-Number Variation in MAPKAPK2 Predicts Risk and Survival of Lung Cancer Bin Liu, Lei Yang, Binfang Huang, Mei Cheng,
Cells and reagents. Synaptopodin knockdown (1) and dynamin knockdown (2)
 Supplemental Methods Cells and reagents. Synaptopodin knockdown (1) and dynamin knockdown (2) podocytes were cultured as described previously. Staurosporine, angiotensin II and actinomycin D were all obtained
Supplemental Methods Cells and reagents. Synaptopodin knockdown (1) and dynamin knockdown (2) podocytes were cultured as described previously. Staurosporine, angiotensin II and actinomycin D were all obtained
Online Data Supplement. Anti-aging Gene Klotho Enhances Glucose-induced Insulin Secretion by Upregulating Plasma Membrane Retention of TRPV2
 Online Data Supplement Anti-aging Gene Klotho Enhances Glucose-induced Insulin Secretion by Upregulating Plasma Membrane Retention of TRPV2 Yi Lin and Zhongjie Sun Department of physiology, college of
Online Data Supplement Anti-aging Gene Klotho Enhances Glucose-induced Insulin Secretion by Upregulating Plasma Membrane Retention of TRPV2 Yi Lin and Zhongjie Sun Department of physiology, college of
microrna 181 promotes prostate cancer cell proliferation by regulating DAX 1 expression
 1296 microrna 181 promotes prostate cancer cell proliferation by regulating DAX 1 expression SHI JUN TONG *, JUN LIU *, XIANG WANG and LIAN XI QU Department of Urologic Surgery, Huashan Hospital Affiliated
1296 microrna 181 promotes prostate cancer cell proliferation by regulating DAX 1 expression SHI JUN TONG *, JUN LIU *, XIANG WANG and LIAN XI QU Department of Urologic Surgery, Huashan Hospital Affiliated
UCA1 impacts progress of rheumatoid arthritis by inducing the apoptosis of fibroblast-like synoviocyte
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2018; 22: 914-920 UCA1 impacts progress of rheumatoid arthritis by inducing the apoptosis of fibroblast-like synoviocyte Z.-F. YAN 1, X.-Y. ZHAO
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2018; 22: 914-920 UCA1 impacts progress of rheumatoid arthritis by inducing the apoptosis of fibroblast-like synoviocyte Z.-F. YAN 1, X.-Y. ZHAO
Inhibition of andrographolide in RAW murine macrophage osteoclastogenesis by downregulating the nuclear factor-kappab signaling pathway
 Inhibition of andrographolide in RAW 264.7 murine macrophage osteoclastogenesis by downregulating the nuclear factor-kappab signaling pathway Y.Q. Ren 1 and Y.B. Zhou 2 1 Department of Orthopedics 1, Yuyao
Inhibition of andrographolide in RAW 264.7 murine macrophage osteoclastogenesis by downregulating the nuclear factor-kappab signaling pathway Y.Q. Ren 1 and Y.B. Zhou 2 1 Department of Orthopedics 1, Yuyao
RAW264.7 cells stably expressing control shrna (Con) or GSK3b-specific shrna (sh-
 1 a b Supplementary Figure 1. Effects of GSK3b knockdown on poly I:C-induced cytokine production. RAW264.7 cells stably expressing control shrna (Con) or GSK3b-specific shrna (sh- GSK3b) were stimulated
1 a b Supplementary Figure 1. Effects of GSK3b knockdown on poly I:C-induced cytokine production. RAW264.7 cells stably expressing control shrna (Con) or GSK3b-specific shrna (sh- GSK3b) were stimulated
mir-542-3p targets sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor 1 and regulates cell proliferation and invasion of breast cancer cells
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 21: 108-114 mir-542-3p targets sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor 1 and regulates cell proliferation and invasion of breast cancer cells H.-X.
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 21: 108-114 mir-542-3p targets sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor 1 and regulates cell proliferation and invasion of breast cancer cells H.-X.
Effect of Bifidobacterium on the mrna expression levels of TRAF6, GSK-3β, and microrna-146a in LPS-stimulated rat intestinal epithelial cells
 Effect of Bifidobacterium on the mrna expression levels of TRAF6, GSK-3β, and microrna-146a in LPS-stimulated rat intestinal epithelial cells W. Zhou, Y. Yuan, J. Li, W.M. Yuan, L.G. Huang and S.W. Zheng
Effect of Bifidobacterium on the mrna expression levels of TRAF6, GSK-3β, and microrna-146a in LPS-stimulated rat intestinal epithelial cells W. Zhou, Y. Yuan, J. Li, W.M. Yuan, L.G. Huang and S.W. Zheng
DYNAMICS IN EXPRESSION OF THE IL-12 RELATED CYTOKINE TRANSCRIPTS OF IL-12A, IL-12B AND IL-23 AFTER STIMULATION OF HUMAN PBMC
 Trakia Journal of Sciences, Vol. 6, No. 1, pp 7-11, 2008 Copyright 2008 Trakia University Available online at: http://www.uni-sz.bg ISSN 1312-1723 (print) ISSN 1313-3551 (online) Original Contribution
Trakia Journal of Sciences, Vol. 6, No. 1, pp 7-11, 2008 Copyright 2008 Trakia University Available online at: http://www.uni-sz.bg ISSN 1312-1723 (print) ISSN 1313-3551 (online) Original Contribution
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI:.38/ncb3399 a b c d FSP DAPI 5mm mm 5mm 5mm e Correspond to melanoma in-situ Figure a DCT FSP- f MITF mm mm MlanaA melanoma in-situ DCT 5mm FSP- mm mm mm mm mm g melanoma in-situ MITF MlanaA mm mm
DOI:.38/ncb3399 a b c d FSP DAPI 5mm mm 5mm 5mm e Correspond to melanoma in-situ Figure a DCT FSP- f MITF mm mm MlanaA melanoma in-situ DCT 5mm FSP- mm mm mm mm mm g melanoma in-situ MITF MlanaA mm mm
MiR-181a promotes epithelial to mesenchymal transition of prostate cancer cells by targeting TGIF2
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 21: 4835-4843 MiR-181a promotes epithelial to mesenchymal transition of prostate cancer cells by targeting TGIF2 C. ZHIPING 1,2, T. SHIJUN
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 21: 4835-4843 MiR-181a promotes epithelial to mesenchymal transition of prostate cancer cells by targeting TGIF2 C. ZHIPING 1,2, T. SHIJUN
Blocking the expression of the hepatitis B virus S gene in hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines with an anti-gene locked nucleic acid in vitro
 Blocking the expression of the hepatitis B virus S gene in hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines with an anti-gene locked nucleic acid in vitro Y.-B. Deng, H.-J. Qin, Y.-H. Luo, Z.-R. Liang and J.-J. Zou
Blocking the expression of the hepatitis B virus S gene in hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines with an anti-gene locked nucleic acid in vitro Y.-B. Deng, H.-J. Qin, Y.-H. Luo, Z.-R. Liang and J.-J. Zou
General Laboratory methods Plasma analysis: Gene Expression Analysis: Immunoblot analysis: Immunohistochemistry:
 General Laboratory methods Plasma analysis: Plasma insulin (Mercodia, Sweden), leptin (duoset, R&D Systems Europe, Abingdon, United Kingdom), IL-6, TNFα and adiponectin levels (Quantikine kits, R&D Systems
General Laboratory methods Plasma analysis: Plasma insulin (Mercodia, Sweden), leptin (duoset, R&D Systems Europe, Abingdon, United Kingdom), IL-6, TNFα and adiponectin levels (Quantikine kits, R&D Systems
IMMP8-1. Different Mechanisms of Androg and IPAD on Apoptosis Induction in Cervical Cancer Cells
 IMMP8-1 Different Mechanisms of Androg and IPAD on Apoptosis Induction in Cervical Cancer Cells Assanan Dokmaikaew* Tipaya Ekalaksananan** Dr.Chamsai Pientong** ABSTRACT Androg and IPAD are recently known
IMMP8-1 Different Mechanisms of Androg and IPAD on Apoptosis Induction in Cervical Cancer Cells Assanan Dokmaikaew* Tipaya Ekalaksananan** Dr.Chamsai Pientong** ABSTRACT Androg and IPAD are recently known
Analysis of regulatory T cell subsets in the peripheral blood of immunoglobulin A nephropathy (IgAN) patients
 Analysis of regulatory T cell subsets in the peripheral blood of immunoglobulin A nephropathy (IgAN) patients S. Yang, B. Chen, J. Shi, F. Chen, J. Zhang and Z. Sun Department of Nephrology, Huaihe Hospital
Analysis of regulatory T cell subsets in the peripheral blood of immunoglobulin A nephropathy (IgAN) patients S. Yang, B. Chen, J. Shi, F. Chen, J. Zhang and Z. Sun Department of Nephrology, Huaihe Hospital
Effect of High-fat or High-glucose Diet on Obesity and Visceral Adipose Tissue in Mice
 ACTA ACADEMIAE MEDICINAE SINICAE 410011 0731-85295846 lixia2014@vip. 163. com 4 C57BL /6 20-1 mrna 20 P < 0. 05 O 20 P > 0. 05 M2 P < 0. 05-1 mrna P < 0. 05 P > 0. 05 R589. 2 DOI 10. 3881 /j. issn. 1000-503X.
ACTA ACADEMIAE MEDICINAE SINICAE 410011 0731-85295846 lixia2014@vip. 163. com 4 C57BL /6 20-1 mrna 20 P < 0. 05 O 20 P > 0. 05 M2 P < 0. 05-1 mrna P < 0. 05 P > 0. 05 R589. 2 DOI 10. 3881 /j. issn. 1000-503X.
Epithelial interleukin-25 is a key mediator in Th2-high, corticosteroid-responsive
 Online Data Supplement: Epithelial interleukin-25 is a key mediator in Th2-high, corticosteroid-responsive asthma Dan Cheng, Zheng Xue, Lingling Yi, Huimin Shi, Kan Zhang, Xiaorong Huo, Luke R. Bonser,
Online Data Supplement: Epithelial interleukin-25 is a key mediator in Th2-high, corticosteroid-responsive asthma Dan Cheng, Zheng Xue, Lingling Yi, Huimin Shi, Kan Zhang, Xiaorong Huo, Luke R. Bonser,
Research Article mir-155 Promotes ox-ldl-induced Autophagy in Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells
 Hindawi Mediators of Inflammation Volume 2017, Article ID 9174801, 7 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/9174801 Research Article mir-155 Promotes -Induced Autophagy in Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial
Hindawi Mediators of Inflammation Volume 2017, Article ID 9174801, 7 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/9174801 Research Article mir-155 Promotes -Induced Autophagy in Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial
Expression and clinical significance of ADAM17 protein in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
 Expression and clinical significance of ADAM17 protein in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma H.B. Liu, Y. Zhu, Q.C. Yang, Y. Shen, X.J. Zhang and H. Chen Department of Pathology First People s Hospital
Expression and clinical significance of ADAM17 protein in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma H.B. Liu, Y. Zhu, Q.C. Yang, Y. Shen, X.J. Zhang and H. Chen Department of Pathology First People s Hospital
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure 1. CD4 + T cell activation and lack of apoptosis after crosslinking with anti-cd3 + anti-cd28 + anti-cd160. (a) Flow cytometry of anti-cd160 (5D.10A11) binding
Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure 1. CD4 + T cell activation and lack of apoptosis after crosslinking with anti-cd3 + anti-cd28 + anti-cd160. (a) Flow cytometry of anti-cd160 (5D.10A11) binding
Effects of metallothionein-3 and metallothionein-1e gene transfection on proliferation, cell cycle, and apoptosis of esophageal cancer cells
 Effects of metallothionein-3 and metallothionein-1e gene transfection on proliferation, cell cycle, and apoptosis of esophageal cancer cells Z.Q. Tian 1, Y.Z. Xu 1, Y.F. Zhang 1, G.F. Ma 1, M. He 1 and
Effects of metallothionein-3 and metallothionein-1e gene transfection on proliferation, cell cycle, and apoptosis of esophageal cancer cells Z.Q. Tian 1, Y.Z. Xu 1, Y.F. Zhang 1, G.F. Ma 1, M. He 1 and
The levels of mrna expression in the mouse brain were measured at 52 dpi after the brains were divided into five regions: cortex, hippocampus,
 Supplemental material Supplemental method RNA extraction, reverse transcription, and real-time PCR The levels of mrna expression in the mouse brain were measured at 52 dpi after the brains were divided
Supplemental material Supplemental method RNA extraction, reverse transcription, and real-time PCR The levels of mrna expression in the mouse brain were measured at 52 dpi after the brains were divided
Transduction of lentivirus to human primary CD4+ T cells
 Transduction of lentivirus to human primary CD4 + T cells Human primary CD4 T cells were stimulated with anti-cd3/cd28 antibodies (10 µl/2 5 10^6 cells of Dynabeads CD3/CD28 T cell expander, Invitrogen)
Transduction of lentivirus to human primary CD4 + T cells Human primary CD4 T cells were stimulated with anti-cd3/cd28 antibodies (10 µl/2 5 10^6 cells of Dynabeads CD3/CD28 T cell expander, Invitrogen)
Effect of NF-kB signaling pathway on the expression of MIF, TNF-α, IL-6 in the regulation of intervertebral disc degeneration
 J Musculoskelet Neuronal Interact 2018; 18(4):551-556 Journal of Musculoskeletal and Neuronal Interactions Original Article Effect of NF-kB signaling pathway on the expression of MIF, TNF-α, IL-6 in the
J Musculoskelet Neuronal Interact 2018; 18(4):551-556 Journal of Musculoskeletal and Neuronal Interactions Original Article Effect of NF-kB signaling pathway on the expression of MIF, TNF-α, IL-6 in the
Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2015;8(11): /ISSN: /IJCEP
 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2015;8(11):14562-14567 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0010516 Original Article MiR-451 inhibits synovial fibroblasts proliferation and inflammatory cytokines secretion in rheumatoid
Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2015;8(11):14562-14567 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0010516 Original Article MiR-451 inhibits synovial fibroblasts proliferation and inflammatory cytokines secretion in rheumatoid
p47 negatively regulates IKK activation by inducing the lysosomal degradation of polyubiquitinated NEMO
 Supplementary Information p47 negatively regulates IKK activation by inducing the lysosomal degradation of polyubiquitinated NEMO Yuri Shibata, Masaaki Oyama, Hiroko Kozuka-Hata, Xiao Han, Yuetsu Tanaka,
Supplementary Information p47 negatively regulates IKK activation by inducing the lysosomal degradation of polyubiquitinated NEMO Yuri Shibata, Masaaki Oyama, Hiroko Kozuka-Hata, Xiao Han, Yuetsu Tanaka,
Extracellular Vesicle RNA isolation Kits
 Extracellular Vesicle RNA isolation Kits Summary Section 4 Introduction 42 Exo-TotalRNA and TumorExo-TotalRNA isolation kits 43 Extracellular Vesicle RNA extraction kits Ordering information Products can
Extracellular Vesicle RNA isolation Kits Summary Section 4 Introduction 42 Exo-TotalRNA and TumorExo-TotalRNA isolation kits 43 Extracellular Vesicle RNA extraction kits Ordering information Products can
Serum mirna expression profile as a prognostic biomarker of stage II/III
 Serum mirna expression profile as a prognostic biomarker of stage II/III colorectal adenocarcinoma Jialu Li a,b,, Yang Liu c,, Cheng Wang d,, Ting Deng a,, Hongwei Liang b, Yifei Wang e, Dingzhi Huang
Serum mirna expression profile as a prognostic biomarker of stage II/III colorectal adenocarcinoma Jialu Li a,b,, Yang Liu c,, Cheng Wang d,, Ting Deng a,, Hongwei Liang b, Yifei Wang e, Dingzhi Huang
Molecular mechanisms involved in HIV-1 Tat-mediated induction of IL-6 and IL-8 in astrocytes
 Nookala and Kumar Journal of Neuroinflammation (2014) 11:214 DOI 10.1186/s12974-014-0214-3 JOURNAL OF NEUROINFLAMMATION RESEARCH Open Access Molecular mechanisms involved in HIV-1 Tat-mediated induction
Nookala and Kumar Journal of Neuroinflammation (2014) 11:214 DOI 10.1186/s12974-014-0214-3 JOURNAL OF NEUROINFLAMMATION RESEARCH Open Access Molecular mechanisms involved in HIV-1 Tat-mediated induction
The study of phospholipids in single cells using an integrated microfluidic device
 Supporting Information: The study of phospholipids in single cells using an integrated microfluidic device combined with matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry Weiyi Xie,, Dan Gao,
Supporting Information: The study of phospholipids in single cells using an integrated microfluidic device combined with matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry Weiyi Xie,, Dan Gao,
MicroRNA sponges: competitive inhibitors of small RNAs in mammalian cells
 MicroRNA sponges: competitive inhibitors of small RNAs in mammalian cells Margaret S Ebert, Joel R Neilson & Phillip A Sharp Supplementary figures and text: Supplementary Figure 1. Effect of sponges on
MicroRNA sponges: competitive inhibitors of small RNAs in mammalian cells Margaret S Ebert, Joel R Neilson & Phillip A Sharp Supplementary figures and text: Supplementary Figure 1. Effect of sponges on
