Metabolism dysregulation induces a specific lipid signature of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis in patients
|
|
|
- Spencer Lamb
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Metaolism dysregulation induces a specific lipid signature of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis in patients Franck Chiappini, Audrey Coilly, Hanane Kadar, Philippe Gual, Alert Tran, Christophe Desterke, Didier Samuel, Jean-Charles Duclos-Vallée, David Tououl, Justine Bertrand- Michel Alain Brunelle, Catherine Guettier François Le Naour Supplementary information (Online) Supplemental Figure S Supplemental Figure S Supplemental Figure S3 Supplemental Figure S4 Supplemental Figure S Supplemental Figure S6 Supplemental Tale S
2 Total TG< 46. Total TG Total TG< NAFL3 ///8 of protein Total TG< 4.7 NAFL /// Control 7/// NAFL /9// Control NAFL NAFL NAFL3 Supplemental Figure S. Total hepatic triglycerides clustered the four groups of patients with different grades of NAFL ased on cluster analysis regression tree (CART). (a) Data are represented as a regression tree where each node of the tree corresponds to the total triglycerides (TG): Ranges of Total TG liver content determine the four groups of patients. () Total TG content from human liver iopsies in clustered patients ased on the CART analysis from (A). Data are represented as oxplot. p<., y unpaired t-test compared to each other groups after ANOVA analysis. Control n=7; NAFL n=9; NAFL n=; NAFL3 n=8. NAFL: nonalcoholic fatty liver.
3 OOB Error.3.3. Confusion matrix No. of variales tried at each split: 9 Control NAFL NAFL NAFL3 NASH class error Control 7. NAFL 8. NAFL.6 NAFL NASH_Lds 3.3 OOB estimate of error rate:4.7%. c TG(6/6/8) TG(6/8/8) TG(6/6/6) TG(8/8/8) C8:n-9 C6:n-7 Cer(d8:/6:) PS(6:/6:) Cer(d8:/4:) PE(6:/6:) PI(8:/8:) PC(8:/:4) C6: PC(8:/8:) CE(C6) TG(4/6/6) PI(8:/:3) PC(8:/:3) SM(8:/6:) PC(6:/8:) PC(6:/8:) PI(8:/:4) PS(6:/8:) PS(8:/8:) PC(8:/8:) C4: PS(8:/:4) C8:n-6 DG(6/6) DG(6:8) m try Mean Decrease Accuracy d TG(6/6/8) TG(6/8/8) TG(6/6/6) TG(8/8/8) C8:n-9 C6:n-7 Cer(d8:/6:) Cer(d8:/4:) PS(6:/6:) PE(6:/6:) PI(8:/8:) C6: PC(8:/:4) PC(8:/8:) TG(4/6/6) CE(C6) PI(8:/:3) PC(8:/:3) PC(6:/8:) C8:n-6 SM(8:/6:) PS(6:/8:) PI(8:/:4) PS(8:/8:) C8: C8:n-7 PC(6:/8:) DG(6/6) DG(8/8) PS(8:/:4) 3 4 Mean Decrease Gini Supplemental Figure S. Some of lipids selected after random forests analysis clustered NASH patients compared to other groups of patients with different grades of liver steatosis. (a) Determination of the est m try (i.e. the est numer of randomly preselected splitting variales) associated to the minimum out-of-ag (OOB) estimate of error rate. () associated to the confusion matrix The 3 first lipids sorted y random forests analysis and classified ased on their (c) mean decrease accuracy and (d) mean decrease Gini indexes to discriminate NASH patients versus the 4 other groups. Control n=7; NAFL n=9; NAFL n=; NAFL3 n=8; NASH_Lds n=. NAFL: nonalcoholic fatty liver disease; NASH_Lds: nonalcoholic steatohepatitis learning dataset.
4 ELOVL C:n-6/C:n-3 Control NAFL NAFL NAFL3 NASH_Lds NASH_Vds f ELOVL FADS C:4n-6/C8:3n-6 Control NAFL NAFL NAFL3 NASH_Lds NASH_Vds FADS C8:3n-6/C8:n-6 g ELOVL FADS FADS.7 C:4n-6/C8:n Control NAFL NAFL NAFL3 NASH_Lds NASH_Vds Control NAFL NAFL NAFL3 NASH_Lds NASH_Vds c h SCD ELOVL FADS 4 C8:n-9/C8: C:n-3/C8:3n Control NAFL NAFL NAFL3 NASH_Lds NASH_Vds Control NAFL NAFL NAFL3 NASH_Lds NASH_Vds d i ELOVL ELOVL6 n-6/n-3 C8:n-7/C6:n Control NAFL NAFL NAFL3 NASH_Lds NASH_Vds Control NAFL NAFL NAFL3 NASH_Lds NASH_Vds e ELOVL ELOVL6 SCD n-3 index C8:n-7/C6: Control NAFL NAFL NAFL3 NASH_Lds NASH_Vds Control NAFL NAFL NAFL3 NASH_Lds NASH_Vds Supplemental Figure S3. Decrease in FADS and ELVOL6 index activities in NASH patients. (a) Evaluation of ELOVL activity using c:n-6 to c:n-3; () evaluation of FADS activity using c8:3n-6 to c8:n-6 ratio. (c) evaluation of SCD using c8:n-9 to c8: ratio (d) oth ELOVL and ELOVL6 activities using c8:n-7 to c6:n-7; (e) gloal ELOVL. ELOVL6 and SCD activities using c8:n-7 to c6: ratio; (f) oth ELOVL and FADS activities using c:4n-6 to c8:3n-6 ratio. (g) Gloal ELOVL. FADS and FADS activities using :4n-6 to c8:n-6 ratio towards the n-6 pathway, and (h) gloal ELOVL and FADS activities using :n-3 to c8:3n-3 ratio towards the n-3 pathway. (i) Hepatic n-6 to n-3 ratio and n-3 index of the different study groups. in order to evaluate enzyme activities. a ratio etween product-to-precursor of each reaction has een used as descried efore. Data are shown as means ± SEM. p<. and p<. y unpaired t-test compared to each other groups <. y unpaired t-test compared to Control. NAFL and NAFL. <. y unpaired t-test compared to Control and NAFL. <. y unpaired t-test compared to Control. NAFL and NAFL3 after ANOVA analysis. Control n= 7; NAFL n=9; NAFL n=; NAFL3 n=8; NASH_Lds n=, NASH_Vds n= 7. ELOVL: elongase of very long chain fatty acid; FADS: fatty acid desaturase; NAFL: nonalcoholic fatty liver; NASH: nonalcoholic steatohepatitis; NASH_Lds: learning dataset; NASH_Vds: validation dataset; SCD: stearoyl-coa desaturase.
5 C4: 7 C6: 4 3 C6:n C8:n-7 C8:n C8:n-6 CE(C6) 6 4 CE(C8) DG(6/6) TG(4/6/6) TG(6/6/6) TG(6/6/8) TG(6/8/8) 6 4 TG(8/8/8) to total Cer Cer(d8:/6:) to total Cer.4.3 Cer(d8:/4:)...7. PC(6:/8:)...7. PC(8:/8:) PC(8:/:3) PC(6:/8:)..7.. PC(8:/:4)... PC(8:/8:) to total PE.... PE(6:/6:) to total PI PI(8:/:4) to total PI.... PI(8:/8:) to total PI PI(8:/:3) to total PS... PS(8/:3) to total PS.... PS(6:/6:) to total PS PS(6:/8:) to total PS PS(8:/8:) to total SM SM(8:/4:) to total SM SM(8:/6:) Control n=6; NAFL/3 n=6; NASH n=8 Supplemental Figure S4. Hepatic levels of the 3 lipids discriminating NASH group ased on random forests analysis from liver iopsies used to look at metaolic gene expression levels involved in de novo lipid synthesis. (A) 4 fatty acids including free fatty acids, cholesteryl ester (CE), diglycerides (DG) and triglycerides (TG) up-regulated in NASH group. Relative aundance of phospholipids up-regulated (n=9) or down-regulated (n=9) in NASH group. Data are represented as oxplot. p<., y unpaired t-test compared to Control and NAFL/3 groups. p<. y unpaired t-test compared NAFL/3 group. p<. y unpaired t-test compared to Control group. Unpaired t-test was done after ANOVA test. Control n=6; NAFL/3 n=6; NASH n=8. NAFL/3 group matched age, sex, grade od steatosis to NASH composed y patients from Paul Brousse and Nice hospitals. Cer: Ceramides; NAFL: nonalcoholic fatty liver; NASH: nonalcoholic steatohepatitis; PC: Phosphatidylcholines; PE: Phosphatidylethanolamines; PI: Phosphatidylinositols; PS: Phosphatidylserines; SM: Sphingomyelins
6 ... ELOVL mrna d SCD mrna g FASN mrna ELOVL6 mrna e FADS mrna h ACC mrna c FADS mrna f SREBPc mrna Supplemental Figure S. Elongases and desaturases involved in LCPUFA synthesis are partially regulated at a transcriptional level. (a) ELOVL. () ELOVL6. (c) FADS. (d) SCD. (e) FADS. (f) SREBPc. (g) FASN and (h) ACC genes expression from human liver iopsies analyzed y RT-Q-PCR. Data are mean ± SEM. Control patients (n=6). NAFL patients (n=6) were matched to NASH patients (n=8). ). NASH are matched to NAFL regarding to the total lipid content and no difference in age. gender and BMI etween the two groups. p. compared to Control. p. compared to NAFL y unpaired t-test. ACC: Acetyl-CoA Caroxylase; ELOVL: elongase of very long-chain; FADS: fatty acid desaturase; FASN: fatty acid synthase; NAFL: nonalcoholic fatty liver; NASH: nonalcoholic steatohepatitis; SCD: stearoyl-coa desaturase. p=
7 HepG Human primary hepatocytes Percentage (%) of toxicity Compared to control Myristic acid Palmitic acid Palmitoleic acid Vaccenic acid Oleic acid Myristic acid Palmitic acid Palmitoleic acid Vaccenic acid Oleic acid µm lipids Percentage (%) of toxicity Compared to control µm lipids SupplementalFigure S6. Hepatic cells exhiit high toxicity after treatment with lipids from the NASH signature. Percentage of toxicity over control cells (non-treated) assessed y total ATP content into HepG human hepatoma cell line (left panel) and human primary hepatocytes (right panel). (a) HepG cell and () human primary hepatocytes treated with individual lipids at different concentrations. Two independent experiments were done. Data are mean ± SEM. p<. y unpaired t-test compared to Control Mix and NAFL Mix at the same concentration, after ANOVA analysis. NAFL: nonalcoholic fatty liver; NASH: nonalcoholic steatohepatitis.
8 Supplemental Tale S: List of primers used for Q-RT-PCR and implicated in hepatic human lipogenesis Genes Accession numer NCB Primer Forward '-3' Primer Reverse '-3' TM ELOVL6_human AK73 NM_49 GCAAACACAAAACCCAAGGC TGGCTTGCTTTTGTTCTCCC 8,99 ELOVL_human AF398 NM_84 GGACTCACACTGCTGTCTCT GTTGTTCTTGCGCAGGATGA 9, ELOVL3_human BC34344 NM_3 AACCTCATTCCCCATAGCCC AGCACACGGTTTGCTTTAGG 9, SCD (delta(9)-desaturase)_human AF974 NM_63 TGAAAGCCAACAACTCTGCC GCTGGACACTGAGCAAAGAC 9 FADS (delta(6)-desaturase)_human AF6799 NM_46 TTCCAAGGAGCAGAGAGGTG CCCTATGAACCCCAAGAGCA 9 FADS (delta()-desaturase)_human AF9996 NM_34 TGCAATGTCCACAAGTCTGC AGCTGCCCTGACTCCTTTAG 9 SREBPc_human AB37399 NM_476 ACACAGCAACCAGAAACTCAAG AGTGTGTCCTCCACCTCAGTCT 9 FASN_human BC634 NM_44 CCCTCATCTCCCCACTCATC CAGCGTCTTCCACACTATGC 9 ACC_human AY367 NM_98834 TTGACTCCTCCATCAACCCC AATTCCTCCCGCTCCTTCAA 9 Actin Beta_human X3 NM_ CATCCGCAAAGACCTGTACG CCTGCTTGCTGATCCACATC 9 Primers were design ased on the mrna sequence found in Uniprot dataase and using Primer3 software and BLASTed (Basic Local Alignment Search Tool) on genomes ACC: acetyl CoA caroxylase; ELOVL: elongase of very long chain fatty aid; FADS: fatty acid desaturase; FASN: fatty acid synthesis; SCD: stearoyl CoA desaturase; SREBP; sterol-regulated transcription factors.
Hmgcoar AGCTTGCCCGAATTGTATGTG TCTGTTGTAACCATGTGACTTC. Cyp7α GGGATTGCTGTGGTAGTGAGC GGTATGGAATCAACCCGTTGTC
 Supplement Table I: primers for Real Time RT-PCR Gene Foward Reverse Hmgcoar AGCTTGCCCGAATTGTATGTG TCTGTTGTAACCATGTGACTTC Cyp7α GGGATTGCTGTGGTAGTGAGC GGTATGGAATCAACCCGTTGTC Cyp27a1 GTGGTCTTATTGGGTACTTGC
Supplement Table I: primers for Real Time RT-PCR Gene Foward Reverse Hmgcoar AGCTTGCCCGAATTGTATGTG TCTGTTGTAACCATGTGACTTC Cyp7α GGGATTGCTGTGGTAGTGAGC GGTATGGAATCAACCCGTTGTC Cyp27a1 GTGGTCTTATTGGGTACTTGC
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 A B mir-141, human cell lines mir-2c, human cell lines mir-141, hepatocytes mir-2c, hepatocytes Relative RNA.1.8.6.4.2 Relative RNA.3.2.1 Relative RNA 1.5 1..5 Relative RNA 2. 1.5
Supplementary Figure 1 A B mir-141, human cell lines mir-2c, human cell lines mir-141, hepatocytes mir-2c, hepatocytes Relative RNA.1.8.6.4.2 Relative RNA.3.2.1 Relative RNA 1.5 1..5 Relative RNA 2. 1.5
ANSC/NUTR 618 LIPIDS & LIPID METABOLISM. Fatty Acid Elongation and Desaturation
 ANSC/NUTR 618 LIPIDS & LIPID METABOLISM I. Fatty acid elongation A. General 1. At least 60% of fatty acids in triacylglycerols are C18. 2. Free palmitic acid (16:0) synthesized in cytoplasm is elongated
ANSC/NUTR 618 LIPIDS & LIPID METABOLISM I. Fatty acid elongation A. General 1. At least 60% of fatty acids in triacylglycerols are C18. 2. Free palmitic acid (16:0) synthesized in cytoplasm is elongated
Lipid and Bile Acids as NAFLD- Related Biomarkers
 Lipid and Bile Acids as NAFLD- Related Biomarkers Puneet Puri, MBBS, MD Division of Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition Virginia Commonwealth University, Richmond, VA 1st International Workshop
Lipid and Bile Acids as NAFLD- Related Biomarkers Puneet Puri, MBBS, MD Division of Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition Virginia Commonwealth University, Richmond, VA 1st International Workshop
Gene Polymorphisms and Carbohydrate Diets. James M. Ntambi Ph.D
 Gene Polymorphisms and Carbohydrate Diets James M. Ntambi Ph.D Fatty Acids that Flux into Tissue Lipids are from Dietary Sources or are Made De novo from Glucose or Fructose Glucose Fructose Acetyl-CoA
Gene Polymorphisms and Carbohydrate Diets James M. Ntambi Ph.D Fatty Acids that Flux into Tissue Lipids are from Dietary Sources or are Made De novo from Glucose or Fructose Glucose Fructose Acetyl-CoA
Supplemental Table 1 Primer sequences (mouse) used for real-time qrt-pcr studies
 Supplemental Table 1 Primer sequences (mouse) used for real-time qrt-pcr studies Gene symbol Forward primer Reverse primer ACC1 5'-TGAGGAGGACCGCATTTATC 5'-GCATGGAATGGCAGTAAGGT ACLY 5'-GACACCATCTGTGATCTTG
Supplemental Table 1 Primer sequences (mouse) used for real-time qrt-pcr studies Gene symbol Forward primer Reverse primer ACC1 5'-TGAGGAGGACCGCATTTATC 5'-GCATGGAATGGCAGTAAGGT ACLY 5'-GACACCATCTGTGATCTTG
18s AAACGGCTACCACATCCAAG CCTCCAATGGATCCTCGTTA. 36b4 GTTCTTGCCCATCAGCACC AGATGCAGCAGATCCGCAT. Acc1 AGCAGATCCGCAGCTTG ACCTCTGCTCGCTGAGTGC
 Supplementary Table 1. Quantitative PCR primer sequences Gene symbol Sequences (5 to 3 ) Forward Reverse 18s AAACGGCTACCACATCCAAG CCTCCAATGGATCCTCGTTA 36b4 GTTCTTGCCCATCAGCACC AGATGCAGCAGATCCGCAT Acc1
Supplementary Table 1. Quantitative PCR primer sequences Gene symbol Sequences (5 to 3 ) Forward Reverse 18s AAACGGCTACCACATCCAAG CCTCCAATGGATCCTCGTTA 36b4 GTTCTTGCCCATCAGCACC AGATGCAGCAGATCCGCAT Acc1
ANSC/NUTR 601 GENERAL ANIMAL NUTRITION Stearoyl-CoA desaturase, VLDL metabolism, and obesity
 ANSC/NUTR 601 GENERAL ANIMAL NUTRITION Stearoyl-CoA desaturase, VLDL metabolism, and obesity I. Stearoyl coenzyme A desaturase and obesity in rodents A. Stearoyl coenzyme A desaturase (SCD) is the 9 desaturase.
ANSC/NUTR 601 GENERAL ANIMAL NUTRITION Stearoyl-CoA desaturase, VLDL metabolism, and obesity I. Stearoyl coenzyme A desaturase and obesity in rodents A. Stearoyl coenzyme A desaturase (SCD) is the 9 desaturase.
Poly-unsaturated phospholipids WE (FA18:1) A B C D OAHFA 18:1/24:0 OAHFA 18:1/30:2 PS 38:4 C18:1C23:0 OAHFA 18:1/25:0 OAHFA 18:1/30:1
 Figure S1, related to Figure 1. Correlation scatter plots illustrating individual lipid species from various classes that exhibited statistically significant correlations to age. (A-B) Various species
Figure S1, related to Figure 1. Correlation scatter plots illustrating individual lipid species from various classes that exhibited statistically significant correlations to age. (A-B) Various species
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb3461 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. Supplementary Figure 1 (associated to Figure 1). Cpeb4 gene-targeted mice develop liver steatosis. a, Immunoblot displaying CPEB4
DOI: 10.1038/ncb3461 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. Supplementary Figure 1 (associated to Figure 1). Cpeb4 gene-targeted mice develop liver steatosis. a, Immunoblot displaying CPEB4
PROMINENT ROLE OF LIVER IN ELEVATED PLASMA PALMITOLEATE LEVELS IN RESPONSE TO ROSIGLITAZONE IN MICE FED HIGH-FAT DIET
 JOURNAL OF PHYSIOLOGY AND PHARMACOLOGY 2009, 60, 4, 135-140 www.jpp.krakow.pl O. KUDA 1, B. STANKOVA 2, E. TVRZICKA 2, M. HENSLER 1, T. JELENIK 1, M. ROSSMEISL 1, P. FLACHS 1, J. KOPECKY 1 PROMINENT ROLE
JOURNAL OF PHYSIOLOGY AND PHARMACOLOGY 2009, 60, 4, 135-140 www.jpp.krakow.pl O. KUDA 1, B. STANKOVA 2, E. TVRZICKA 2, M. HENSLER 1, T. JELENIK 1, M. ROSSMEISL 1, P. FLACHS 1, J. KOPECKY 1 PROMINENT ROLE
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION FOR Liver X Receptor α mediates hepatic triglyceride accumulation through upregulation of G0/G1 Switch Gene 2 (G0S2) expression I: SUPPLEMENTARY METHODS II: SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION FOR Liver X Receptor α mediates hepatic triglyceride accumulation through upregulation of G0/G1 Switch Gene 2 (G0S2) expression I: SUPPLEMENTARY METHODS II: SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES
Large-scale plasma lipidomic profiling identifies lipids that predict cardiovascular events in secondary prevention
 Large-scale plasma lipidomic profiling identifies lipids that predict cardiovascular events in secondary prevention Piyushkumar A. Mundra,, Peter J. Meikle, LIPID Study Investigators JCI Insight. 2018;3(17):e121326..
Large-scale plasma lipidomic profiling identifies lipids that predict cardiovascular events in secondary prevention Piyushkumar A. Mundra,, Peter J. Meikle, LIPID Study Investigators JCI Insight. 2018;3(17):e121326..
ANSC/NUTR 618 Lipids & Lipid Metabolism
 I. Overall concepts A. Definitions ANC/NUTR 618 Lipids & Lipid Metabolism 1. De novo synthesis = synthesis from non-fatty acid precursors a. Carbohydrate precursors (glucose, lactate, and pyruvate) b.
I. Overall concepts A. Definitions ANC/NUTR 618 Lipids & Lipid Metabolism 1. De novo synthesis = synthesis from non-fatty acid precursors a. Carbohydrate precursors (glucose, lactate, and pyruvate) b.
Overview on the identification of different classes of. lipids by HPTLC (High Performance Thin Layer. Chromatography) and ITLC (Immuno Thin Layer
 Overview on the identification of different classes of lipids by HPTLC (High Performance Thin Layer Chromatography) and ITLC (Immuno Thin Layer Chromatography) Iuliana Popa 1, Marie-Jeanne David 2, Daniel
Overview on the identification of different classes of lipids by HPTLC (High Performance Thin Layer Chromatography) and ITLC (Immuno Thin Layer Chromatography) Iuliana Popa 1, Marie-Jeanne David 2, Daniel
Genetic Analysis of Fatty Acid Composition of Milk: Basis for Improvement of the Healthfulness of the U.S. Milk Supply
 Animal Industry Report AS 654 ASL R2299 2008 Genetic Analysis of Fatty Acid Composition of Milk: Basis for Improvement of the Healthfulness of the U.S. Milk Supply Jon P. Schoonmaker Rafael A. Nafikov
Animal Industry Report AS 654 ASL R2299 2008 Genetic Analysis of Fatty Acid Composition of Milk: Basis for Improvement of the Healthfulness of the U.S. Milk Supply Jon P. Schoonmaker Rafael A. Nafikov
The art of tracing dietary fat in humans. Leanne Hodson
 The art of tracing dietary fat in humans Leanne Hodson Dietary fat Other lipoproteins: IDL, LDL, HDL Hodson and Fielding linical Lipidology (2010) Relationship between blood & dietary fatty acids Typically:
The art of tracing dietary fat in humans Leanne Hodson Dietary fat Other lipoproteins: IDL, LDL, HDL Hodson and Fielding linical Lipidology (2010) Relationship between blood & dietary fatty acids Typically:
Supplementary Table 2. Plasma lipid profiles in wild type and mutant female mice submitted to a HFD for 12 weeks wt ERα -/- AF-1 0 AF-2 0
 Supplementary Table 1. List of specific primers used for gene expression analysis. Genes Primer forward Primer reverse Hprt GCAGTACAGCCCCAAAATGG AACAAAGTCTGGCCTGTATCCA Srebp-1c GGAAGCTGTCGGGGTAGCGTC CATGTCTTCAAATGTGCAATCCAT
Supplementary Table 1. List of specific primers used for gene expression analysis. Genes Primer forward Primer reverse Hprt GCAGTACAGCCCCAAAATGG AACAAAGTCTGGCCTGTATCCA Srebp-1c GGAAGCTGTCGGGGTAGCGTC CATGTCTTCAAATGTGCAATCCAT
Supplemental Information. Genetic Regulation of Plasma Lipid Species. and Their Association with Metabolic Phenotypes
 Cell Systems, Volume 6 Supplemental Information Genetic Regulation of Plasma Lipid Species and Their Association with Metabolic Phenotypes Pooja Jha, Molly T. McDevitt, Emina Halilbasic, Evan G. Williams,
Cell Systems, Volume 6 Supplemental Information Genetic Regulation of Plasma Lipid Species and Their Association with Metabolic Phenotypes Pooja Jha, Molly T. McDevitt, Emina Halilbasic, Evan G. Williams,
ALT (U/L) (Relative expression) HDL (mm) (Relative expression) ALT (U/L) (Relative expression)
 a DMT mrna () 8 6 r =.96 P =. DMT mrna () 8 6 r =. P =.6 DMT mrna () 8 6 r =.99 P =.6 DMT mrna () 8 6 r =. P =.9 DMT mrna () BMI (kg/m ) 8 6 r =.7 P =.966 DMT mrna () 8 ALT (U/L) 8 6 r = -.66 P =.76 DMT
a DMT mrna () 8 6 r =.96 P =. DMT mrna () 8 6 r =. P =.6 DMT mrna () 8 6 r =.99 P =.6 DMT mrna () 8 6 r =. P =.9 DMT mrna () BMI (kg/m ) 8 6 r =.7 P =.966 DMT mrna () 8 ALT (U/L) 8 6 r = -.66 P =.76 DMT
AAV-TBGp-Cre treatment resulted in hepatocyte-specific GH receptor gene recombination
 AAV-TBGp-Cre treatment resulted in hepatocyte-specific GH receptor gene recombination Supplementary Figure 1. Generation of the adult-onset, liver-specific GH receptor knock-down (alivghrkd, Kd) mouse
AAV-TBGp-Cre treatment resulted in hepatocyte-specific GH receptor gene recombination Supplementary Figure 1. Generation of the adult-onset, liver-specific GH receptor knock-down (alivghrkd, Kd) mouse
Supplementary Figure S1
 Lipidomic-based investigation into the regulatory effect of Schisandrin B on palmitic acid level in non-alcoholic steatotic livers Hiu Yee Kwan 1,2, Xuyan Niu 3, Wenlin Dai 4, Tiejun Tong 4, Xiaojuan Chao
Lipidomic-based investigation into the regulatory effect of Schisandrin B on palmitic acid level in non-alcoholic steatotic livers Hiu Yee Kwan 1,2, Xuyan Niu 3, Wenlin Dai 4, Tiejun Tong 4, Xiaojuan Chao
AN ABSTRACT OF THE DISSERTATION OF. Sasmita Tripathy for the Doctor of Philosophy in Nutrition presented on July 11, 2012.
 AN ABSTRACT OF THE DISSERTATION OF Sasmita Tripathy for the Doctor of Philosophy in Nutrition presented on July 11, 2012. Title: Polyunsaturated Fatty Acid Synthesis and Type 2 Diabetes Complications Abstract
AN ABSTRACT OF THE DISSERTATION OF Sasmita Tripathy for the Doctor of Philosophy in Nutrition presented on July 11, 2012. Title: Polyunsaturated Fatty Acid Synthesis and Type 2 Diabetes Complications Abstract
Phospholipids Metabolism
 Chapter VI: Phospholipids Metabolism Dr. Sameh Sarray Hlaoui Phospholipids Features: Amphipatic: - Hydrophobic head: fatty acids - Hydropholic head: P group+ alcohol Composed of alcohol attached by a phosphodiester
Chapter VI: Phospholipids Metabolism Dr. Sameh Sarray Hlaoui Phospholipids Features: Amphipatic: - Hydrophobic head: fatty acids - Hydropholic head: P group+ alcohol Composed of alcohol attached by a phosphodiester
number Done by Corrected by Doctor Faisal Al-Khatibe
 number 24 Done by Mohammed tarabieh Corrected by Doctor Faisal Al-Khatibe 1 P a g e *Please look over the previous sheet about fatty acid synthesis **Oxidation(degradation) of fatty acids, occurs in the
number 24 Done by Mohammed tarabieh Corrected by Doctor Faisal Al-Khatibe 1 P a g e *Please look over the previous sheet about fatty acid synthesis **Oxidation(degradation) of fatty acids, occurs in the
Supplementary Figure 1. PAQR3 knockdown inhibits SREBP-2 processing in CHO-7 cells CHO-7 cells were transfected with control sirna or a sirna
 Supplementary Figure 1. PAQR3 knockdown inhibits SREBP-2 processing in CHO-7 cells CHO-7 cells were transfected with control sirna or a sirna targeted for hamster PAQR3. At 24 h after the transfection,
Supplementary Figure 1. PAQR3 knockdown inhibits SREBP-2 processing in CHO-7 cells CHO-7 cells were transfected with control sirna or a sirna targeted for hamster PAQR3. At 24 h after the transfection,
The use of mass spectrometry in lipidomics. Outlines
 The use of mass spectrometry in lipidomics Jeevan Prasain jprasain@uab.edu 6-2612 utlines Brief introduction to lipidomics Analytical methodology: MS/MS structure elucidation of phospholipids Phospholipid
The use of mass spectrometry in lipidomics Jeevan Prasain jprasain@uab.edu 6-2612 utlines Brief introduction to lipidomics Analytical methodology: MS/MS structure elucidation of phospholipids Phospholipid
Biomarkers of NAFLD progression an omics approach to an epidemic
 Biomarkers of NAFLD progression an omics approach to an epidemic D. Lee Gorden 1,2, David S. Myers 3, Pavlina T. Ivanova 3, Eoin Fahy 4, Mano R. Maurya 4, Shakti Gupta 4, Jun Min 4, Nathanael J. Spann
Biomarkers of NAFLD progression an omics approach to an epidemic D. Lee Gorden 1,2, David S. Myers 3, Pavlina T. Ivanova 3, Eoin Fahy 4, Mano R. Maurya 4, Shakti Gupta 4, Jun Min 4, Nathanael J. Spann
Synthesis and elongation of fatty acids
 Synthesis and elongation of fatty acids A molecular caliper mechanism for determining very long-chain fatty acid length Vladimir Denic and Jonathan S. Weissman (2007) Cell 130, 663-677 February 28, 2008
Synthesis and elongation of fatty acids A molecular caliper mechanism for determining very long-chain fatty acid length Vladimir Denic and Jonathan S. Weissman (2007) Cell 130, 663-677 February 28, 2008
The lipogenic transcription factor ChREBP dissociates hepatic steatosis from insulin resistance in mice and humans
 Research article The lipogenic transcription factor ChREBP dissociates hepatic steatosis from insulin resistance in mice and humans Fadila Benhamed, 1,2,3 Pierre-Damien Denechaud, 1,2,3 Maud Lemoine, 4,5,6
Research article The lipogenic transcription factor ChREBP dissociates hepatic steatosis from insulin resistance in mice and humans Fadila Benhamed, 1,2,3 Pierre-Damien Denechaud, 1,2,3 Maud Lemoine, 4,5,6
LC/MS Method for Comprehensive Analysis of Plasma Lipids
 Application Note omics LC/MS Method for Comprehensive Analysis of Plasma s Authors Tomas Cajka and Oliver Fiehn West Coast Metabolomics Center, University of California Davis, 451 Health Sciences Drive,
Application Note omics LC/MS Method for Comprehensive Analysis of Plasma s Authors Tomas Cajka and Oliver Fiehn West Coast Metabolomics Center, University of California Davis, 451 Health Sciences Drive,
Chem 431A-L24-F 07 admin: Last time: We finished Chapt 7, started Chapt 10 FA s and TG s FA=fatty acid, TG=triglycerides or triacylglycerols
 Chem 431A-L24-F'07 page 1 of 5 Chem 431A-L24-F 07 admin: Last time: We finished Chapt 7, started Chapt 10 FA s and TG s FA=fatty acid, TG=triglycerides or triacylglycerols (0) REVIEW: FA s are very reduced
Chem 431A-L24-F'07 page 1 of 5 Chem 431A-L24-F 07 admin: Last time: We finished Chapt 7, started Chapt 10 FA s and TG s FA=fatty acid, TG=triglycerides or triacylglycerols (0) REVIEW: FA s are very reduced
Supplementary Table 1. Metabolic parameters in GFP and OGT-treated mice
 Supplementary Table 1. Metabolic parameters in GFP and OGT-treated mice Fasted Refed GFP OGT GFP OGT Liver G6P (mmol/g) 0.03±0.01 0.04±0.02 0.60±0.04 0.42±0.10 A TGs (mg/g of liver) 20.08±5.17 16.29±0.8
Supplementary Table 1. Metabolic parameters in GFP and OGT-treated mice Fasted Refed GFP OGT GFP OGT Liver G6P (mmol/g) 0.03±0.01 0.04±0.02 0.60±0.04 0.42±0.10 A TGs (mg/g of liver) 20.08±5.17 16.29±0.8
Control 7 d cold 7 d CL
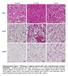 Control 7 d cold 7 d ibat iwat gwat Supplementary Figure 1. Histology of adipose tissues after cold or 3-adrenergic receptor stimulation. C57BL/6J wild-type mice were housed at 4 C or injected daily with
Control 7 d cold 7 d ibat iwat gwat Supplementary Figure 1. Histology of adipose tissues after cold or 3-adrenergic receptor stimulation. C57BL/6J wild-type mice were housed at 4 C or injected daily with
Supporting Information. Supporting Tables. S-Table 1 Primer pairs for RT-PCR. Product size. Gene Primer pairs
 Supporting Information Supporting Tables S-Table 1 Primer pairs for RT-PCR. Gene Primer pairs Product size (bp) FAS F: 5 TCTTGGAAGCGATGGGTA 3 429 R: 5 GGGATGTATCATTCTTGGAC 3 SREBP-1c F: 5 CGCTACCGTTCCTCTATCA
Supporting Information Supporting Tables S-Table 1 Primer pairs for RT-PCR. Gene Primer pairs Product size (bp) FAS F: 5 TCTTGGAAGCGATGGGTA 3 429 R: 5 GGGATGTATCATTCTTGGAC 3 SREBP-1c F: 5 CGCTACCGTTCCTCTATCA
Sphingolipid de novo synthesis: its relevance to metabolic diseases and cell polarity
 Sphingolipid de novo synthesis: its relevance to metabolic diseases and cell polarity Xian-Cheng Jiang (shian-chen chiang) SUNY Downstate Medical Center Cell plasma membrane Lipid rafts Sphingolipid =
Sphingolipid de novo synthesis: its relevance to metabolic diseases and cell polarity Xian-Cheng Jiang (shian-chen chiang) SUNY Downstate Medical Center Cell plasma membrane Lipid rafts Sphingolipid =
ALTERATIONS IN NEURAL FATTY ACID METABOLISM CAUSED BY VITAMIN E DEFICIENCY
 ALTERATIONS IN NEURAL FATTY ACID METABOLISM CAUSED BY VITAMIN E DEFICIENCY Bonnie Buckingham Faculty Mentor: Dr. Maret Traber Linus Pauling Institute HHMI Summer 2011 Outline Significance Background Hypothesis
ALTERATIONS IN NEURAL FATTY ACID METABOLISM CAUSED BY VITAMIN E DEFICIENCY Bonnie Buckingham Faculty Mentor: Dr. Maret Traber Linus Pauling Institute HHMI Summer 2011 Outline Significance Background Hypothesis
Fats and Lipids (Ans570)
 Fats and Lipids (Ans570) Outlines Fats and Lipids Structure, nomenclature Phospholipids, Sterols, and Lipid Derivatives Lipid Oxidation Roles of fat in food processing and dietary fat Lipid and fat analysis:
Fats and Lipids (Ans570) Outlines Fats and Lipids Structure, nomenclature Phospholipids, Sterols, and Lipid Derivatives Lipid Oxidation Roles of fat in food processing and dietary fat Lipid and fat analysis:
Roles of Lipids. principal form of stored energy major constituents of cell membranes vitamins messengers intra and extracellular
 Roles of Lipids principal form of stored energy major constituents of cell membranes vitamins messengers intra and extracellular = Oxidation of fatty acids Central energy-yielding pathway in animals. O
Roles of Lipids principal form of stored energy major constituents of cell membranes vitamins messengers intra and extracellular = Oxidation of fatty acids Central energy-yielding pathway in animals. O
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Serum and synovial fluid lipidomic profiles predict obesity-associated osteoarthritis, synovitis, and wound repair Chia-Lung Wu 1,2, Kelly A. Kimmerling 1,2, Dianne Little 3,
Supplementary Information Serum and synovial fluid lipidomic profiles predict obesity-associated osteoarthritis, synovitis, and wound repair Chia-Lung Wu 1,2, Kelly A. Kimmerling 1,2, Dianne Little 3,
Organochloride pesticides impaired mitochondrial function in hepatocytes and. aggravated disorders of fatty acids metabolism
 Supplementary Materials Organochloride pesticides impaired mitochondrial function in hepatocytes and aggravated disorders of fatty acids metabolism Qian Liu 1,2,3*, Qihan Wang 4*, Cheng Xu 2,3, Wentao
Supplementary Materials Organochloride pesticides impaired mitochondrial function in hepatocytes and aggravated disorders of fatty acids metabolism Qian Liu 1,2,3*, Qihan Wang 4*, Cheng Xu 2,3, Wentao
Fatty Acids, lipolysis and goat flavour (1) Specificities of lipid metabolim in goats :
 Specificities of lipid metabolim in goats : Yves Chilliard INRA Clermont-Ferrand / Theix France - milk FA profile (high C8 & C1, and B-CFA) - lipolytic system (LPL regulations; flavour) (e.g. Chilliard
Specificities of lipid metabolim in goats : Yves Chilliard INRA Clermont-Ferrand / Theix France - milk FA profile (high C8 & C1, and B-CFA) - lipolytic system (LPL regulations; flavour) (e.g. Chilliard
Fig. S1. Dose-response effects of acute administration of the β3 adrenoceptor agonists CL316243, BRL37344, ICI215,001, ZD7114, ZD2079 and CGP12177 at
 Fig. S1. Dose-response effects of acute administration of the β3 adrenoceptor agonists CL316243, BRL37344, ICI215,001, ZD7114, ZD2079 and CGP12177 at doses of 0.1, 0.5 and 1 mg/kg on cumulative food intake
Fig. S1. Dose-response effects of acute administration of the β3 adrenoceptor agonists CL316243, BRL37344, ICI215,001, ZD7114, ZD2079 and CGP12177 at doses of 0.1, 0.5 and 1 mg/kg on cumulative food intake
Diagnostic des maladies du foie par spectroscopie et imagerie multimodale
 Diagnostic des maladies du foie par spectroscopie et imagerie multimodale François Le Naour Inserm U1193, Centre HépatoBiliaire, Villejuif Médecine moléculaire et modèles animaux: pathologie hépatique
Diagnostic des maladies du foie par spectroscopie et imagerie multimodale François Le Naour Inserm U1193, Centre HépatoBiliaire, Villejuif Médecine moléculaire et modèles animaux: pathologie hépatique
Mass-Spectrometric Analysis of Lipids (Lipidomics)
 Mass-Spectrometric Analysis of Lipids (Lipidomics) 1. Identification 2. Quantification 3. Metabolism Why to do lipidomics? Biology: Functions of different lipids? Medicine: Diagnostics and Therapy Industry:
Mass-Spectrometric Analysis of Lipids (Lipidomics) 1. Identification 2. Quantification 3. Metabolism Why to do lipidomics? Biology: Functions of different lipids? Medicine: Diagnostics and Therapy Industry:
Quantitative Real-Time PCR was performed as same as Materials and Methods.
 Supplemental Material Quantitative Real-Time PCR Quantitative Real-Time PCR was performed as same as Materials and Methods. Expression levels in the aorta were normalized to peptidylprolyl isomerase B
Supplemental Material Quantitative Real-Time PCR Quantitative Real-Time PCR was performed as same as Materials and Methods. Expression levels in the aorta were normalized to peptidylprolyl isomerase B
The role of apolipoprotein D in lipid metabolism and metabolic syndrome
 UQÀM: Department of Biological Sciences The role of apolipoprotein D in lipid metabolism and metabolic syndrome Catherine Mounier PhD Apolipoprotein D Apolipoprotéine D (apod) Secreted protein Associated
UQÀM: Department of Biological Sciences The role of apolipoprotein D in lipid metabolism and metabolic syndrome Catherine Mounier PhD Apolipoprotein D Apolipoprotéine D (apod) Secreted protein Associated
Supplementary Figure 1. AdipoR1 silencing and overexpression controls. (a) Representative blots (upper and lower panels) showing the AdipoR1 protein
 Supplementary Figure 1. AdipoR1 silencing and overexpression controls. (a) Representative blots (upper and lower panels) showing the AdipoR1 protein content relative to GAPDH in two independent experiments.
Supplementary Figure 1. AdipoR1 silencing and overexpression controls. (a) Representative blots (upper and lower panels) showing the AdipoR1 protein content relative to GAPDH in two independent experiments.
Suppl. Table 1: CV of pooled lipoprotein fractions analysed by ESI-MS/MS
 Supplement VLDL LDL HDL PC 3.3 1.77 1.3 LPC 4.82 2.5.35 SM 3.1 4.6 1.92 CER 2.17 6.3 4.15 PE 3.18 1.93 2.79 PE-pl 13.18 1.9 2.32 CE 2.9.65.4 FC.36 3.5 2.54 Suppl. Table 1: CV of pooled lipoprotein fractions
Supplement VLDL LDL HDL PC 3.3 1.77 1.3 LPC 4.82 2.5.35 SM 3.1 4.6 1.92 CER 2.17 6.3 4.15 PE 3.18 1.93 2.79 PE-pl 13.18 1.9 2.32 CE 2.9.65.4 FC.36 3.5 2.54 Suppl. Table 1: CV of pooled lipoprotein fractions
Fatty acids and phospholipids
 PYS 4xx Intro 2 1 PYS 4xx Intro 2 - Molecular building blocks We now describe in more detail the nomenclature and composition of several classes of compounds of relevance to the cell, including: membrane
PYS 4xx Intro 2 1 PYS 4xx Intro 2 - Molecular building blocks We now describe in more detail the nomenclature and composition of several classes of compounds of relevance to the cell, including: membrane
Supplementary Fig. 1 eif6 +/- mice show a reduction in white adipose tissue, blood lipids and normal glycogen synthesis. The cohort of the original
 Supplementary Fig. 1 eif6 +/- mice show a reduction in white adipose tissue, blood lipids and normal glycogen synthesis. The cohort of the original phenotypic screening was n=40. For specific tests, the
Supplementary Fig. 1 eif6 +/- mice show a reduction in white adipose tissue, blood lipids and normal glycogen synthesis. The cohort of the original phenotypic screening was n=40. For specific tests, the
Supplementary Figure S I: Effects of D4F on body weight and serum lipids in apoe -/- mice.
 Supplementary Figures: Supplementary Figure S I: Effects of D4F on body weight and serum lipids in apoe -/- mice. Male apoe -/- mice were fed a high-fat diet for 8 weeks, and given PBS (model group) or
Supplementary Figures: Supplementary Figure S I: Effects of D4F on body weight and serum lipids in apoe -/- mice. Male apoe -/- mice were fed a high-fat diet for 8 weeks, and given PBS (model group) or
Physical effects underlying the transition from primitive to modern cell membranes
 Physical effects underlying the transition from primitive to modern cell membranes Itay Budin and Jack W. Szostak* *To whom correspondence should be addressed. Email: szostak@molbio.mgh.harvard.edu This
Physical effects underlying the transition from primitive to modern cell membranes Itay Budin and Jack W. Szostak* *To whom correspondence should be addressed. Email: szostak@molbio.mgh.harvard.edu This
The SCAP/SREBP Pathway: A Mediator of Hepatic Steatosis
 Review Article Endocrinol Metab 2017;32:6-10 https://doi.org/10.3803/enm.2017.32.1.6 pissn 2093-596X eissn 2093-5978 The SCAP/SREBP Pathway: A Mediator of Hepatic Steatosis Young-Ah Moon Department of
Review Article Endocrinol Metab 2017;32:6-10 https://doi.org/10.3803/enm.2017.32.1.6 pissn 2093-596X eissn 2093-5978 The SCAP/SREBP Pathway: A Mediator of Hepatic Steatosis Young-Ah Moon Department of
Sex-specific lipid molecular signatures in obesity-associated metabolic dysfunctions revealed by lipidomic characterization in ob/ob mouse
 González-Granillo et al. Biology of Sex Differences (2019) 10:11 https://doi.org/10.1186/s13293-019-0225-y RESEARCH Sex-specific lipid molecular signatures in obesity-associated metabolic dysfunctions
González-Granillo et al. Biology of Sex Differences (2019) 10:11 https://doi.org/10.1186/s13293-019-0225-y RESEARCH Sex-specific lipid molecular signatures in obesity-associated metabolic dysfunctions
By: Dr Hadi Mozafari 1
 Biological lipids are a chemically diverse group of compounds, the common and defining feature of which is their insolubility in water. By: Dr Hadi Mozafari 1 Fats and oils are the principal stored forms
Biological lipids are a chemically diverse group of compounds, the common and defining feature of which is their insolubility in water. By: Dr Hadi Mozafari 1 Fats and oils are the principal stored forms
Dietary α-linolenic acid-rich flaxseed oil prevents against alcoholic hepatic steatosis
 Dietary α-linolenic acid-rich flaxseed oil prevents against alcoholic hepatic steatosis via ameliorating lipid homeostasis at adipose tissue-liver axis in mice Meng Wang a, Xiao-Jing Zhang a, Kun Feng
Dietary α-linolenic acid-rich flaxseed oil prevents against alcoholic hepatic steatosis via ameliorating lipid homeostasis at adipose tissue-liver axis in mice Meng Wang a, Xiao-Jing Zhang a, Kun Feng
MEMBRANE LIPIDS I and II: GLYCEROPHOSPHOLIPIDS AND SPHINGOLIPIDS
 December 6, 2011 Lecturer: Eileen M. Lafer MEMBRANE LIPIDS I and II: GLYCEROPHOSPHOLIPIDS AND SPHINGOLIPIDS Reading: Stryer Edition 6: Chapter 26 Images: All images in these notes were taken from Lehninger,
December 6, 2011 Lecturer: Eileen M. Lafer MEMBRANE LIPIDS I and II: GLYCEROPHOSPHOLIPIDS AND SPHINGOLIPIDS Reading: Stryer Edition 6: Chapter 26 Images: All images in these notes were taken from Lehninger,
An allostatic control of membrane lipid composition by SREBP1
 FEBS Letters 584 (2010) 2689 2698 journal homepage: www.febsletters.org Review An allostatic control of membrane lipid composition by SREBP1 Rachel M. Hagen *, Sergio Rodriguez-Cuenca, Antonio Vidal-Puig
FEBS Letters 584 (2010) 2689 2698 journal homepage: www.febsletters.org Review An allostatic control of membrane lipid composition by SREBP1 Rachel M. Hagen *, Sergio Rodriguez-Cuenca, Antonio Vidal-Puig
Table S1. Quantitative RT-PCR primers
 Table S1. Quantitative RT-PCR primers Gene Forward Primer Reverse Primer Human ApoB gcaagcagaagccagaagta ccatttggagaagcagtttgg Human ApoA1 gaaagctgcggtgctgac agtggccaggtccttcact Human MTP acggccattcccattgtg
Table S1. Quantitative RT-PCR primers Gene Forward Primer Reverse Primer Human ApoB gcaagcagaagccagaagta ccatttggagaagcagtttgg Human ApoA1 gaaagctgcggtgctgac agtggccaggtccttcact Human MTP acggccattcccattgtg
Synthesis of Fatty Acids and Triacylglycerol
 Fatty Acid Synthesis Synthesis of Fatty Acids and Triacylglycerol Requires Carbon Source: Reducing Power: NADPH Energy Input: ATP Why Energy? Why Energy? Fatty Acid Fatty Acid + n(atp) ΔG o : -ve Fatty
Fatty Acid Synthesis Synthesis of Fatty Acids and Triacylglycerol Requires Carbon Source: Reducing Power: NADPH Energy Input: ATP Why Energy? Why Energy? Fatty Acid Fatty Acid + n(atp) ΔG o : -ve Fatty
Supplemental Table 1. List of primers used for real time PCR.
 Supplemental Table 1. List of primers used for real time PCR. Primer Sequence Primer Sequence Mouse Pcsk9-F TTGCAGCAGCTGGGAACTT Mouse Scd1-F CATCATTCTCATGGTCCTGCT Mouse Pcsk9-R CCGACTGTGATGACCTCTGGA Mouse
Supplemental Table 1. List of primers used for real time PCR. Primer Sequence Primer Sequence Mouse Pcsk9-F TTGCAGCAGCTGGGAACTT Mouse Scd1-F CATCATTCTCATGGTCCTGCT Mouse Pcsk9-R CCGACTGTGATGACCTCTGGA Mouse
Increasing Marbling Gene Expression in Beef Cattle with Dietary Lipids
 Increasing Marbling Gene Expression in Beef Cattle with Dietary Lipids Stephen B. Smith and Seong Ho Choi Texas A&M University Bradley J. Johnson Texas Tech University, Lubbock RMC 2012 June 18, 2012 Researchers
Increasing Marbling Gene Expression in Beef Cattle with Dietary Lipids Stephen B. Smith and Seong Ho Choi Texas A&M University Bradley J. Johnson Texas Tech University, Lubbock RMC 2012 June 18, 2012 Researchers
Synthesis of Fatty Acids and Triacylglycerol
 Synthesis of Fatty Acids and Triacylglycerol Lippincott s Chapter 16 Fatty Acid Synthesis Mainly in the Liver Requires Carbon Source: Acetyl CoA Reducing Power: NADPH 8 CH 3 COO C 15 H 33 COO Energy Input:
Synthesis of Fatty Acids and Triacylglycerol Lippincott s Chapter 16 Fatty Acid Synthesis Mainly in the Liver Requires Carbon Source: Acetyl CoA Reducing Power: NADPH 8 CH 3 COO C 15 H 33 COO Energy Input:
MCQS ON LIPIDS. Dr. RUCHIKA YADU
 MCQS ON LIPIDS Dr. RUCHIKA YADU Q1. THE FATS AND OILS ARE RESPECTIVELY RICH IN a) Unsaturated fatty acids b) Saturated fatty acids c) Saturated and unsaturated fatty acids d) None of these Q2. ESSENTIAL
MCQS ON LIPIDS Dr. RUCHIKA YADU Q1. THE FATS AND OILS ARE RESPECTIVELY RICH IN a) Unsaturated fatty acids b) Saturated fatty acids c) Saturated and unsaturated fatty acids d) None of these Q2. ESSENTIAL
Hepatic oleate regulates adipose tissue lipogenesis and fatty acid oxidation
 Hepatic oleate regulates adipose tissue lipogenesis and fatty acid oxidation Maggie S. Burhans 1, Matthew T. Flowers 2, Kristin R. Harrington 2, Laura M. Bond 2, Chang-An Guo 2, Rozalyn M. Anderson 3,4,
Hepatic oleate regulates adipose tissue lipogenesis and fatty acid oxidation Maggie S. Burhans 1, Matthew T. Flowers 2, Kristin R. Harrington 2, Laura M. Bond 2, Chang-An Guo 2, Rozalyn M. Anderson 3,4,
Dengue Virus Infection Perturbs Lipid Homeostasis in Infected Mosquito Cells
 University of Nebraska - Lincoln DigitalCommons@University of Nebraska - Lincoln Biochemistry -- Faculty Publications Biochemistry, Department of 2012 Dengue Virus Infection Perturbs Lipid Homeostasis
University of Nebraska - Lincoln DigitalCommons@University of Nebraska - Lincoln Biochemistry -- Faculty Publications Biochemistry, Department of 2012 Dengue Virus Infection Perturbs Lipid Homeostasis
Kaurenoic acid, a Diterpene Derived from Aralia continentalis, Alleviates Lipogenesis in HepG2 Cells.
 J Korean Med. 2015;36(4):74-79 pissn 1010-0695 eissn 2288-3339 Original Article Kaurenoic acid, a Diterpene Derived from Aralia continentalis, Alleviates Lipogenesis in HepG2 Cells. Yu Gon Kim 1*, Jae
J Korean Med. 2015;36(4):74-79 pissn 1010-0695 eissn 2288-3339 Original Article Kaurenoic acid, a Diterpene Derived from Aralia continentalis, Alleviates Lipogenesis in HepG2 Cells. Yu Gon Kim 1*, Jae
HIV VPR alters fat metabolism. Dorothy E Lewis PhD/Ashok Balasubramanyam MD
 HIV VPR alters fat metabolism Dorothy E Lewis PhD/Ashok Balasubramanyam MD Old Dogma for HIV associated lipodystrophy Differentiation Block (PI) Lipoatrophy Apoptosis (NRTI) Stem cell Preadipocyte Adipocyte
HIV VPR alters fat metabolism Dorothy E Lewis PhD/Ashok Balasubramanyam MD Old Dogma for HIV associated lipodystrophy Differentiation Block (PI) Lipoatrophy Apoptosis (NRTI) Stem cell Preadipocyte Adipocyte
LIPID METABOLISM
 LIPID METABOLISM LIPOGENESIS LIPOGENESIS LIPOGENESIS FATTY ACID SYNTHESIS DE NOVO FFA in the blood come from :- (a) Dietary fat (b) Dietary carbohydrate/protein in excess of need FA TAG Site of synthesis:-
LIPID METABOLISM LIPOGENESIS LIPOGENESIS LIPOGENESIS FATTY ACID SYNTHESIS DE NOVO FFA in the blood come from :- (a) Dietary fat (b) Dietary carbohydrate/protein in excess of need FA TAG Site of synthesis:-
Fat Metabolism, Insulin and MTHFR
 Fat Metabolism, Insulin and MTHFR BCAA, SAMe and ACAT Carolyn Ledowsky Overview of This Presentation 1. Fat Metabolism and MTHFR 2. SAMe and Fat Metabolism 3. Acetyl Co A and Fat Metabolism 4. How to Maintain
Fat Metabolism, Insulin and MTHFR BCAA, SAMe and ACAT Carolyn Ledowsky Overview of This Presentation 1. Fat Metabolism and MTHFR 2. SAMe and Fat Metabolism 3. Acetyl Co A and Fat Metabolism 4. How to Maintain
Supporting information
 Supporting information A novel lipidomics workflow for improved human plasma identification and quantification using RPLC-MSn methods and isotope dilution strategies Evelyn Rampler 1,2,3, Angela Criscuolo
Supporting information A novel lipidomics workflow for improved human plasma identification and quantification using RPLC-MSn methods and isotope dilution strategies Evelyn Rampler 1,2,3, Angela Criscuolo
Nafith Abu Tarboush DDS, MSc, PhD
 Nafith Abu Tarboush DDS, MSc, PhD natarboush@ju.edu.jo www.facebook.com/natarboush Lipids (cholesterol, cholesterol esters, phospholipids & triacylglycerols) combined with proteins (apolipoprotein) in
Nafith Abu Tarboush DDS, MSc, PhD natarboush@ju.edu.jo www.facebook.com/natarboush Lipids (cholesterol, cholesterol esters, phospholipids & triacylglycerols) combined with proteins (apolipoprotein) in
Unit IV Problem 3 Biochemistry: Cholesterol Metabolism and Lipoproteins
 Unit IV Problem 3 Biochemistry: Cholesterol Metabolism and Lipoproteins - Cholesterol: It is a sterol which is found in all eukaryotic cells and contains an oxygen (as a hydroxyl group OH) on Carbon number
Unit IV Problem 3 Biochemistry: Cholesterol Metabolism and Lipoproteins - Cholesterol: It is a sterol which is found in all eukaryotic cells and contains an oxygen (as a hydroxyl group OH) on Carbon number
Suppl. Figure 1. T 3 induces autophagic flux in hepatic cells. (A) RFP-GFP-LC3 transfected HepG2/TRα cells were visualized and cells were quantified
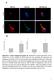 Suppl. Figure 1. T 3 induces autophagic flux in hepatic cells. (A) RFP-GFP-LC3 transfected HepG2/TRα cells were visualized and cells were quantified for RFP-LC3 puncta (red dots) representing both autolysosomes
Suppl. Figure 1. T 3 induces autophagic flux in hepatic cells. (A) RFP-GFP-LC3 transfected HepG2/TRα cells were visualized and cells were quantified for RFP-LC3 puncta (red dots) representing both autolysosomes
COR 011 Lecture 9: ell membrane structure ept 19, 2005
 COR 011 Lecture 9: ell membrane structure ept 19, 2005 Cell membranes 1. What are the functions of cell membranes? 2. What is the current model of membrane structure? 3. Evidence supporting the fluid mosaic
COR 011 Lecture 9: ell membrane structure ept 19, 2005 Cell membranes 1. What are the functions of cell membranes? 2. What is the current model of membrane structure? 3. Evidence supporting the fluid mosaic
Mass Spectrometry based metabolomics
 Mass Spectrometry based metabolomics Metabolomics- A realm of small molecules (
Mass Spectrometry based metabolomics Metabolomics- A realm of small molecules (
DECLARATION OF CONFLICT OF INTEREST. None
 DECLARATION OF CONFLICT OF INTEREST None Plasma Lipidomic Analysis of Stable and Unstable Coronary Artery Disease Peter J Meikle 1, Gerard Wong 1, Despina Tsorotes 1, Christopher K Barlow 1, Jacquelyn
DECLARATION OF CONFLICT OF INTEREST None Plasma Lipidomic Analysis of Stable and Unstable Coronary Artery Disease Peter J Meikle 1, Gerard Wong 1, Despina Tsorotes 1, Christopher K Barlow 1, Jacquelyn
Reduced dietary levels of EPA and DHA have a major impact on the composition of
 Supplementary materials Reduced dietary levels of EA and DHA have a major impact on the composition of skin membrane lipids in Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.) Ken Cheng *,, Marta Bou, Bente Ruyter, Jana
Supplementary materials Reduced dietary levels of EA and DHA have a major impact on the composition of skin membrane lipids in Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.) Ken Cheng *,, Marta Bou, Bente Ruyter, Jana
Requires Signaling though Akt2 Independent of the. Transcription Factors FoxA2, FoxO1, and SREBP1c
 Cell Metabolism, Volume 14 Supplemental Information Postprandial Hepatic Lipid Metabolism Requires Signaling though Akt2 Independent of the Transcription Factors FoxA2, FoxO1, and SREBP1c Min Wan, Karla
Cell Metabolism, Volume 14 Supplemental Information Postprandial Hepatic Lipid Metabolism Requires Signaling though Akt2 Independent of the Transcription Factors FoxA2, FoxO1, and SREBP1c Min Wan, Karla
HCBP6 upregulates human SREBP1c expression by binding to C/EBPβ-binding site in the SREBP1c promoter
 BMB Reports BMB Rep. 2018; 51(1): 33-38 www.bmbreports.org HCBP6 upregulates human SREBP1c expression by binding to C/EBPβ-binding site in the SREBP1c promoter Xueliang Yang 1,#, Ming Han 2,3,#, Shunai
BMB Reports BMB Rep. 2018; 51(1): 33-38 www.bmbreports.org HCBP6 upregulates human SREBP1c expression by binding to C/EBPβ-binding site in the SREBP1c promoter Xueliang Yang 1,#, Ming Han 2,3,#, Shunai
EXPRESSION OF FATTY ACID OXIDATION-RELATED GENES IN Acsl4 L -/- PRIMARY HEPATOCYTES. Dennis Lin
 EXPRESSION OF FATTY ACID OXIDATION-RELATED GENES IN Acsl4 L -/- PRIMARY HEPATOCYTES Dennis Lin Senior Honors Thesis Department of Nutrition University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill April 2018 Approved
EXPRESSION OF FATTY ACID OXIDATION-RELATED GENES IN Acsl4 L -/- PRIMARY HEPATOCYTES Dennis Lin Senior Honors Thesis Department of Nutrition University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill April 2018 Approved
UNIVERSITY OF CALGARY. Fatty acid synthesis in colorectal cancer: characterization of lipid metabolism in serum, tumour, and normal host tissues
 UNIVERSITY OF CALGARY Fatty acid synthesis in colorectal cancer: characterization of lipid metabolism in serum, tumour, and normal host tissues by Emily Megan Mackay A THESIS SUBMITTED TO THE FACULTY OF
UNIVERSITY OF CALGARY Fatty acid synthesis in colorectal cancer: characterization of lipid metabolism in serum, tumour, and normal host tissues by Emily Megan Mackay A THESIS SUBMITTED TO THE FACULTY OF
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES
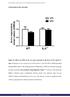 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES Figure S1. Effect of a HFD on the Acox gene expression in the livers of WT and IL-6 -/- mice. Expression of Acox in the livers of WT and IL-6 -/- mice fed STD or HFD determined through
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES Figure S1. Effect of a HFD on the Acox gene expression in the livers of WT and IL-6 -/- mice. Expression of Acox in the livers of WT and IL-6 -/- mice fed STD or HFD determined through
Nature Genetics: doi: /ng.3561
 Supplementary Figure 1 Pedigrees of families with APOB p.gln725* mutation and APOB p.gly1829glufs8 mutation (a,b) Pedigrees of families with APOB p.gln725* mutation. (c) Pedigree of family with APOB p.gly1829glufs8
Supplementary Figure 1 Pedigrees of families with APOB p.gln725* mutation and APOB p.gly1829glufs8 mutation (a,b) Pedigrees of families with APOB p.gln725* mutation. (c) Pedigree of family with APOB p.gly1829glufs8
Supplementary Information. MicroRNA-33b knock-in mice for an intron of sterol regulatory
 Supplementary Information MicroRNA-33b knock-in mice for an intron of sterol regulatory element-binding factor 1 (Srebf1) exhibit reduced HDL-C in vivo Takahiro Horie, Tomohiro Nishino, Osamu Baba, Yasuhide
Supplementary Information MicroRNA-33b knock-in mice for an intron of sterol regulatory element-binding factor 1 (Srebf1) exhibit reduced HDL-C in vivo Takahiro Horie, Tomohiro Nishino, Osamu Baba, Yasuhide
Leen Alsahele. Razan Al-zoubi ... Faisal
 25 Leen Alsahele Razan Al-zoubi... Faisal last time we started talking about regulation of fatty acid synthesis and degradation *regulation of fatty acid synthesis by: 1- regulation of acetyl CoA carboxylase
25 Leen Alsahele Razan Al-zoubi... Faisal last time we started talking about regulation of fatty acid synthesis and degradation *regulation of fatty acid synthesis by: 1- regulation of acetyl CoA carboxylase
Blood fatty acids understanding the relevance of different tissue fractions and interpreting circulating concentrations.
 Blood fatty acids understanding the relevance of different tissue fractions and interpreting circulating concentrations Leanne Hodson Fatty acid composition as a biomarker of intake Complements dietary
Blood fatty acids understanding the relevance of different tissue fractions and interpreting circulating concentrations Leanne Hodson Fatty acid composition as a biomarker of intake Complements dietary
The liver plays a key role in controlling lipid
 STEATOHEPATITIS/METABOLIC LIVER DISEASE Endoplasmic Reticulum-Tethered Transcription Factor camp Responsive Element-Binding Protein, Hepatocyte Specific, Regulates Hepatic Lipogenesis, Fatty Acid Oxidation,
STEATOHEPATITIS/METABOLIC LIVER DISEASE Endoplasmic Reticulum-Tethered Transcription Factor camp Responsive Element-Binding Protein, Hepatocyte Specific, Regulates Hepatic Lipogenesis, Fatty Acid Oxidation,
Octopus (Enterocopus dofleini) Liver Extract Displays Triglyceride-Lowering Effect in HepG2 Cells
 Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries 2017; 6(6): 214-218 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/aff doi: 10.11648/j.aff.20170606.15 ISSN:2328-563X (Print); ISSN:2328-5648 (Online) Octopus (Enterocopus
Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries 2017; 6(6): 214-218 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/aff doi: 10.11648/j.aff.20170606.15 ISSN:2328-563X (Print); ISSN:2328-5648 (Online) Octopus (Enterocopus
Supplemental Information. Human Carboxylesterase 2 Reverses. Obesity-Induced Diacylglycerol Accumulation. and Glucose Intolerance
 Cell Reports, Volume 18 Supplemental Information Human Carboxylesterase 2 Reverses Obesity-Induced Diacylglycerol Accumulation and Glucose Intolerance Maxwell A. Ruby, Julie Massart, Devon M. Hunerdosse,
Cell Reports, Volume 18 Supplemental Information Human Carboxylesterase 2 Reverses Obesity-Induced Diacylglycerol Accumulation and Glucose Intolerance Maxwell A. Ruby, Julie Massart, Devon M. Hunerdosse,
ACC ELOVL MCAD. CPT1α 1.5 *** 0.5. Reverbα *** *** 0.5. Fasted. Refed
 Supplementary Figure A 8 SREBPc 6 5 FASN ELOVL6.5.5.5 ACC.5.5 CLOCK.5.5 CRY.5.5 PPARα.5.5 ACSL CPTα.5.5.5.5 MCAD.5.5 PEPCK.5.5 G6Pase 5.5.5.5 BMAL.5.5 Reverbα.5.5 Reverbβ.5.5 PER.5.5 PER B Fasted Refed
Supplementary Figure A 8 SREBPc 6 5 FASN ELOVL6.5.5.5 ACC.5.5 CLOCK.5.5 CRY.5.5 PPARα.5.5 ACSL CPTα.5.5.5.5 MCAD.5.5 PEPCK.5.5 G6Pase 5.5.5.5 BMAL.5.5 Reverbα.5.5 Reverbβ.5.5 PER.5.5 PER B Fasted Refed
BCM 221 LECTURES OJEMEKELE O.
 BCM 221 LECTURES BY OJEMEKELE O. OUTLINE INTRODUCTION TO LIPID CHEMISTRY STORAGE OF ENERGY IN ADIPOCYTES MOBILIZATION OF ENERGY STORES IN ADIPOCYTES KETONE BODIES AND KETOSIS PYRUVATE DEHYDROGENASE COMPLEX
BCM 221 LECTURES BY OJEMEKELE O. OUTLINE INTRODUCTION TO LIPID CHEMISTRY STORAGE OF ENERGY IN ADIPOCYTES MOBILIZATION OF ENERGY STORES IN ADIPOCYTES KETONE BODIES AND KETOSIS PYRUVATE DEHYDROGENASE COMPLEX
Dietary supplementation in treating non-alcoholic fatty liver disease Dr. Ahmad Saedi Associate Professor School of Nutritional Sciences and
 Dietary supplementation in treating non-alcoholic fatty liver disease Dr. Ahmad Saedi Associate Professor School of Nutritional Sciences and Dietetics Tehran University of Medical Sciences Honorary Academic
Dietary supplementation in treating non-alcoholic fatty liver disease Dr. Ahmad Saedi Associate Professor School of Nutritional Sciences and Dietetics Tehran University of Medical Sciences Honorary Academic
Heterogeneity of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Genetic and Nutritional Modulation of Hepatic Lipid Metabolism
 dissertationes scholae doctoralis ad sanitatem investigandam universitatis helsinkiensis 46/2018 PANU LUUKKONEN Heterogeneity of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Genetic and Nutritional Modulation of
dissertationes scholae doctoralis ad sanitatem investigandam universitatis helsinkiensis 46/2018 PANU LUUKKONEN Heterogeneity of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Genetic and Nutritional Modulation of
Biosynthesis of Triacylglycerides (TG) in liver. Mobilization of stored fat and oxidation of fatty acids
 Biosynthesis of Triacylglycerides (TG) in liver Mobilization of stored fat and oxidation of fatty acids Activation of hormone sensitive lipase This enzyme is activated when phosphorylated (3,5 cyclic AMPdependent
Biosynthesis of Triacylglycerides (TG) in liver Mobilization of stored fat and oxidation of fatty acids Activation of hormone sensitive lipase This enzyme is activated when phosphorylated (3,5 cyclic AMPdependent
Plasma long-chain free fatty acids predict mammalian longevity
 Plasma long-chain free fatty acids predict mammalian longevity Mariona Jové 1, Alba Naudí 1, Juan Carlos Aledo, Rosanna Cabré 1, Victoria Ayala 1, Manuel Portero-Otin 1, Gustavo Barja & Reinald Pamplona
Plasma long-chain free fatty acids predict mammalian longevity Mariona Jové 1, Alba Naudí 1, Juan Carlos Aledo, Rosanna Cabré 1, Victoria Ayala 1, Manuel Portero-Otin 1, Gustavo Barja & Reinald Pamplona
Metformin attenuates triglyceride accumulation in HepG2 cells through decreasing stearyl-coenzyme A desaturase 1 expression
 Zhu et al. Lipids in Health and Disease (2018) 17:114 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12944-018-0762-0 RESEARCH Metformin attenuates triglyceride accumulation in HepG2 cells through decreasing stearyl-coenzyme
Zhu et al. Lipids in Health and Disease (2018) 17:114 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12944-018-0762-0 RESEARCH Metformin attenuates triglyceride accumulation in HepG2 cells through decreasing stearyl-coenzyme
Metabolic defects underlying dyslipidemia in abdominal obesity
 Metabolic defects underlying dyslipidemia in abdominal obesity Professor Marja-Riitta Taskinen Department of Medicine, Division of Cardiology Helsinki University Hospital, Finland Disclosures: Honorariums/
Metabolic defects underlying dyslipidemia in abdominal obesity Professor Marja-Riitta Taskinen Department of Medicine, Division of Cardiology Helsinki University Hospital, Finland Disclosures: Honorariums/

 Supplementary Figure 1 a OD c. 1. 1... Time [min] 1 p
Supplementary Figure 1 a OD c. 1. 1... Time [min] 1 p