P eriodontal diseases are mainly chronic infectious diseases result from response to a complex dental plaque
|
|
|
- Melina Norman
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 OPEN SUBJECT AREAS: PERIODONTITIS METABOLIC DISORDERS Received 15 Jnury 214 Accepted 9 April 214 Pulished 6 My 214 Correspondence nd requests for mterils should e ddressed to K.Y. (kz@dent. niigt-u.c.jp) Orl pthoiont induces systemic inflmmtion nd metolic chnges ssocited with ltertion of gut microiot Kei Arimtsu 1,2, Hitomi Ymd 1,2, Hrun Miyzw 1,2, Tkyoshi Mingw 1,2, Myuk Nkjim 1,2, Mrk I. Ryder 3, Kzuyoshi Gotoh 4, Disuke Motook 4, Shot Nkmur 4, Tetsuy Iid 4 & Kzuhis Ymzki 1 1 Lortory of Periodontology nd Immunology, Division of Orl Science for Helth Promotion, Niigt University Grdute School of Medicl nd Dentl Sciences, Niigt, Jpn, 2 Division of Periodontology, Deprtment of Orl Biologicl Science, Niigt University Grdute School of Medicl nd Dentl Sciences, Niigt, Jpn, 3 Division of Periodontology, Deprtment of Orofcil Sciences, School of Dentistry, University of Cliforni, Sn Frncisco, USA, 4 Deprtment of Infection Metgenomics, Reserch Institute for Microil Diseses, Osk University, Osk, Jpn. Periodontitis hs een implicted s risk fctor for metolic disorders such s type 2 dietes, therosclerotic vsculr diseses, nd non-lcoholic ftty liver disese. Although cteremis from dentl plque nd/or elevted circulting inflmmtory cytokines emnting from the inflmed gingiv re suspected mechnisms linking periodontitis nd these diseses, direct evidence is lcking. We hypothesize tht disturnces of the gut microiot y swllowed cteri induce metolic endotoxemi leding metolic disorders. To investigte this hypothesis, chnges in the gut microiot, insulin nd glucose intolernce, nd levels of tissue inflmmtion were nlysed in mice fter orl dministrtion of Porphyromons gingivlis, representtive periodontopthogens. Pyrosequencing reveled tht the popultion elonging to Bcteroidles ws significntly elevted in -dministered mice which coincided with increses in insulin resistnce nd systemic inflmmtion. In -dministered mice lood endotoxin levels tended to e higher, wheres gene expression of tight junction proteins in the ileum ws significntly decresed. These results provide new prdigm for the interreltionship etween periodontitis nd systemic diseses. P eriodontl diseses re minly chronic infectious diseses result from response to complex dentl plque microiome contining vrious periodontopthic cteri species. Periodontl diseses destroys the toothsupporting tissues nd leds to tooth loss if not dequtely treted. Advnced form of the diseses ffects,1% to 15% of dults worldwide 1. Epidemiologicl evidence suggests tht periodontl infection is ssocited with n incresed risk of vriety of diseses such s therosclerotic vsculr diseses 2,3, type 2 dietes 4,5, nd non-lcoholic ftty liver disese 6. Among the vrious periodontopthic cteri, considerle reserch hs focused on the role of Porphyromons gingivlis in possile mechnisms linking periodontl diseses nd other humn diseses, due to its unique pthogenicity 7 nd its ssocition with these vrious diseses. Once n inflmmtory lesion in the periodontium is estlished, cteri from the dentl plque cn invde into the gingivl tissue through the ulcerted sulculr epithelil lining of periodontl pockets nd then disseminte into the systemic circultion 8. In ddition, vrious proinflmmtory cytokines re produced in the inflmed periodontl tissue 9 which cn lso enter the systemic circultion. Although the precise mechnisms hve not een clrified, the resulting cteremi nd increse in circulting inflmmtory meditors my potentite n inflmmtory rection in other tissues or orgns. In fct, numer of studies hve demonstrted elevted levels of serum hs-crp 1 nd IL-6 11,12 in periodontitis ptients when compred with periodontlly helthy sujects. By contrst, there is little evidence for n incresed detection nd/or numers of orl cteri in the lood of periodontitis ptients when compred with periodontlly helthy sujects 13. In ddition, we hve shown tht repeted orl inocultion of induced elevtion of serum inflmmtory mrkers (serum myloid A nd IL-6) in SCIENTIFIC REPORTS 4 : 4828 DOI: 1.138/srep4828 1
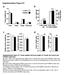
2 mice. However, no ws detected in the lood t ny time point of these experiments 14. Moreover, in this mouse model, limited inflmmtory cell infiltrte ws seen in the gingivl tissue. It is well-known tht oesity, chronic disese chrcterized y n excessive growth of dipose tissue, increses the risk of insulin resistnce, dietes, therosclerosis, hypertension, chronic kidney disese, nd crdiovsculr moridity nd mortlity Interestingly, mny of these diseses re lso ssocited with inflmmtory periodontl diseses. Insulin resistnce, key feture of oesity, is stte in which the sensitivity of trget cells to respond to ordinry levels of insulin is reduced. This insulin sensitivity is modulted in prt y dipokines. In oesity, dipokine production is either up-regulted or down-regulted. Specificlly, insulin resistnce-ssocited dipokines re usully up-regulted wheres insulin-sensitivity-ssocited dipokines re down-regulted 18. Oesity is reported to e ssocited with periodontl diseses. Sito et l. first reported tht oese Jpnese sujects were more likely to hve periodontl disese thn thin sujects 19. Although lter studies supported the positive ssocition etween oesity nd periodontitis 2 22, there re lso studies showing no ssocition etween these two conditions 23. While there re severl epidemiologicl studies demonstrting this ssocition, there re few reports on the mechnism linking oesity nd periodontl diseses. One proposed mechnism involves the dipocyte hypertrophy found in oesity. This dipocyte hypertrophy leds to infiltrtion of mcrophges nd other inflmmtory cells. This phenomenon results in low-grde chronic inflmmtion nd enhnced proinflmmtory cytokine production 24,25. Among the mny dipokines, TNF- is considered key plyer in inflmmtory cell ctivtion nd recruitment 26.TNF- produced y the dipocytes together with TNF- produced in the periodontl tissue my induce further periodontl tissue destruction. However, severl reports hve shown tht serum TNF- levels of periodontitis ptients re either not elevted or lower in periodontitis ptients compred with non-periodontitis sujects 27. Thus, the pthogenic mechnisms for the effects of periodontl disese ffecting systemic disese nd the specific effects of the infection with periodontopthic cteri on the pthology of vrious tissues remin to e elucidted. In this study, we propose tht endotoxemi is responsile for inflmmtion of vrious orgns nd tissues in this mouse model through orl dministrtion. However, this endotoxemi my not e induced directly y cteri from the orl cvity, ut rther through chnges in gut microiot induced y inocultion of cteri from the orl cvity into the gut through swllowing. Susequent ctivtion of proinflmmtory genes within lood vessels, dipose tissue nd liver could increse the risk of therosclerosis, insulin resistnce nd non-lcoholic ftty liver disese (NAFLD), respectively. Results Locl nd systemic inflmmtion in -dministered mice. Our previous study nd others demonstrted tht repeted orl gvge dministrtion of induced lveolr one resorption. However, whether this could e due to locl inflmmtion of gingivl tissue is still unresolved. Although serum IL-6 levels significntly incresed in -dministered mice compred with shm-dministered mice, no difference of gingivl inflmmtion, which ws miniml, etween -dministered nd shmdministered mice ws oserved (Fig. 1). dministrtion induces insulin resistnce, liver stetosis, nd mcrophge infiltrtion in dipose tissue. To explore the effects of orl gvge dministrtion of on insulin resistnce, we performed glucose nd insulin tolernce tests. As shown in Fig. 2, oth glucose tolernce nd insulin sensitivity ws diminished in P. gingivlis-dministered mice compred with shm-dministered mice, despite similr ody weight chnges during the experimentl period (Supplementry Fig. S1). Although the effect of dministrtion ws reltively wek, significnt difference ws oserved t 15 min for the insulin tolernce test, nd n overll effect ws evident s shown in Figs. 2 nd 2d. However, there were no differences in lood insulin levels etween -dministered mice nd shm-dministered mice (Supplementry Fig. S2). Orl gvge dministrtion of promoted mcrophge infiltrtion into the dipose tissue nd typicl crown-like structure ws oserved histologiclly (Fig. 3). Histologicl nlysis showed tht dministered mice hd ccumulted much higher mounts of heptic ft (Fig. 3) nd triglyceride (Fig. 3c), s compred to the shmdministered mice. dministrtion induces n inflmmtory response in dipose tissue. Next we compred gene expression profiles of epididyml dipose tissue etween -dministered nd shm-dministered mice (Fig. 4). In -dministered mice, expression of proinflmmtory genes Tnf, Ccl2, Il6, nd Il1 were significntly upregulted, wheres the genes tht improve insulin sensitivity Pprc, Ppr, C1qtnf9, Irs1, Sirt1, nd Slc24 were downregulted. In ddition to proinflmmtory genes, expression of Angptl4 which is involved in insulin resistnce ws lso upregulted. These results suggest tht orl gvge dministrtion of induces n inflmmtory response nd insulin resistnce in dipose tissue. There ws no difference in the expression of three regultors of insulin signlling, Grn, Retn, nd Lep, etween P. gingivlis-dministered mice nd shm-dministered mice. dministrtion induces n inflmmtory response in the liver nd n inflmmtion-relted gene response. Orl dministrtion of led to incresed mrna expression of the proinflmmtory cytokines TNF- nd IL-6, s well s of Fitm2 nd Plin2, oth of which re strongly ssocited with lipid droplet formtion in the liver. Furthermore, Acc nd G6pc, which positively regulte ftty cid synthesis nd gluconeogenesis respectively, were lso upregulted. On the other hnd, mrna expression of the molecules hving potentilly nti-inflmmtory properties Pprc nd Sirt1, were downregulted. In ddition, expression of the insulin signlling gene Irs1 ws lso decresed compred with shm-dministered mice. We oserved tht not only gene expression (Fig. 5) ut lso protein levels of TNF- were incresed in the liver of -dministered mice (Fig. 5). Orl dministrtion of lters the gut microil ecology. After 1 cycles of orl dministrtion of live W83, the contents of the distl 3cm of the smll intestine (ileum) were recovered immeditely fter euthniztion y mnul extrusion. We defined the extent to which orl dministrtion of ltered the composition of the microiot y pyrosequencing the 16S riosoml RNA genes in the ileum contents. In totl, 41,557 (men 6,926 reds/smple) nd 32,18 (men 5,351 reds/smple) sequencing reds for the -dministered smples nd the shmdministered smples, respectively, were otined y two sequencing runs. The mjority of ligned reds were determined to e from the phyl Firmicutes nd Bcteroidetes, representing 55.4% nd 38.7% of the flor respectively in -dministered mice, nd 72.8% nd 17.%, respectively in shm-dministered mice. The difference of the proportion of Bcteroidetes nd Firmicutes etween -dministered mice nd shm-dministered mice ws sttisticlly significnt (Fig. 6). Notly, opertionl txonomy unit (OTU)-sed cteril diversity nlysis reveled tht the popultion elonging to Bcteroidles ws significntly elevted in -dministered mice compred with shm-dministered mice (Fig. 6 nd 6c). Becuse elongs to the order Bcteroidles, incresed proportions of the order Bcteroidles could e due to the dministered. To clrify this possile mechnism, DNA smples SCIENTIFIC REPORTS 4 : 4828 DOI: 1.138/srep4828 2
3 2 *** IL-6 (pg/ml) Figure 1 Systemic nd locl inflmmtion in -dministered nd shm-dministered mice (N 5 8 in ech group). () Serum level of IL-6. All dt re mens 6 SD. Significnt differences were oserved etween the -dministered groups nd the shm-dministered group (***p,.1, Mnn-Whitney U-test). () Histologicl findings of gingivl tissues of -dministered nd shm-dministered mice. Sections of the periodontium round the disto-uccl root of the first molr were H-E stined. Right pnels re mgnified views of the oxed res. No difference of gingivl inflmmtion ws oserved etween -dministered nd shm-dministered mice. of the ileum contents were mplified using -specific primers. However, no -specific DNA ws detected (Supplementry Fig. S3). dministrtion increses serum endotoxin level. As it hs een reported tht chnges in the gut microiot influence metolic endotoxemi, we compred the serum endotoxin levels etween -dministered mice nd shm-dministered mice. As shown in Fig. 7, endotoxin levels were very low fter overnight fsting, with no difference etween -dministered mice nd shm-dministered mice. However, the endotoxin levels drmticlly incresed if the mice were fed d liitum irrespective of dministrtion. The endotoxin level tended to e higher in -dministered mice compred to shm-dministered mice. However, this difference ws not sttisticlly significnt (Fig. 7). In order to further exmine the effect of orl dministrtion of on endotoxemi, the serum endotoxin levels were monitored t 1, 3, 12 hrs. fter single dministrtion of P. Blood glucose (mg/dl) c Blood glucose (%) Time (min) ** -1, 6 9 Time(min) d AUC (min mg/dl) Inverse AUC of ITT (min %) 4, 3, 2, 1, -2, -3, -4, -5, * ** Figure 2 induced insulin resistnce. () Intrperitonel glucose tolernce test. Blood glucose levels were determined t the indicted times fter intrperitonel lod of glucose (1 g/kg). () Are under lood concentrtion curve (AUC) of the Fig. 2. (c) Intrperitonel insulin tolernce test (ITT). Blood glucose levels were determined t the indicted times fter intrperitonel lod of insulin (.5 unit/kg). (N 5 6 in ech group). (d) Insulin sensitivity ws ssessed y inverse AUC of ITT. All dt re mens 6 SD. (*p,.5; **p,.1, Mnn-Whitney U-test). SCIENTIFIC REPORTS 4 : 4828 DOI: 1.138/srep4828 3
4 c Triglyceride (nmol/μg) ** Figure 3 Reltionship etween dministrtion nd inflmmtory chnges of epididyml dipose tissue nd liver. () Epididyml dipose tissues were fixed 1% formlin, sectioned, nd stined with rt nti-mouse F4/8 primry ntiody (Ad Serotec). Arrow heds indicte F4/8 positive mcrophges. () Oil red O stining of the liver tissue re shown. Incresed numer of lipid contining heptocytes (rrow heds) re seen in -dministered mice. (c) dministrtion incresed heptic triglyceride content. (N 5 8 in ech group). All dt re mens 6 SD. (**p,.1, Mnn-Whitney U-test). gingivlis. Serum endotoxin levels incresed s erly s 1 hr. fter dministrtion, peked t 3 hrs., nd mintined these higher levels until 12 hrs. (Fig. 7). One hour fter orl dministrtion, ws detected in the jejunum nd ileum, nd its proportion in the microil flor decresed t 3 hrs. Although DNA ws detected in the colon t 16 hrs, the proportion of DNA ws extremely low ecuse of fr lrger quntities of other cteri in the colon (Supplementry Fig. S4). At these time points, no ws detected in the lood smples of -dminstered mice wheres other cteril DNA ws detected (Supplementry Fig. S5). Chnges in gene expression profiles in the intestine y orl dministrtion of. Next we exmined the effect of P. gingivlis dministrtion on the expression of genes tht ply importnt role for prevention of metolic syndrome nd metolic endotoxemi in the smll intestine (Fig. 8) nd inflmmtory responses in the lrge intestine (Fig. 8). The expression of genes tht code intestinl lkline phosphtse (Akp3) nd tight junction protein (Tjp1) in the smll intestine were oth downregulted in P. gingivlis-dministered mice compred to shm-dministered mice. In the smples of lrge intestine, mrna expression of the proinflmmtory cytokines IL-6, IL-12, IFN-c nd IL-17c were significntly upregulted in -dministered mice compred to shm-dministered mice. However, there ws no difference in expression of IL-1 nd TNF-. Discussion Periodontl disese is chronic inflmmtory disese where groups of periodontopthic cteri such s plys mjor role in Reltive gene expression CTRP9 (ng/mg) 1,5 1, 5 **. Figure 4 Effect of orl dministrtion of on the gene nd protein expressions in epididyml dipose tissue. () Comprison of reltive gene expression levels in the dipose tissue etween the -dministered nd the shm-dministered mice (N 5 8 in ech group). The reltive quntity of experimentl mrna ws normlized to the reltive quntity of glycerldehyde-3-phosphte dehydrogense (GAPDH) mrna. () CTRP9 contents in the epididyml dipose tissue were determined y ELISA of tissue lystes. All dt re mens 6 SD. (*p,.5; **p,.1; ***p,.1, Mnn-Whitney U-test). SCIENTIFIC REPORTS 4 : 4828 DOI: 1.138/srep4828 4
5 Reltive gene expression TNF-α (pg/mg) 5 *** Figure 5 Effect of orl dministrtion of on the gene nd protein expressions in liver. () Comprison of reltive gene expression levels in the liver tissue etween the -dministered nd the shm-dministered mice (N 5 8 in ech group). The reltive quntity of experimentl mrna ws normlized to the reltive quntity of glycerldehyde-3-phosphte dehydrogense (GAPDH) mrna. () TNF- levels in the liver tissue were determined y ELISA of tissue lystes. All dt re mens 6 SD. (*p,.5; **p,.1; ***p,.1, Mnn-Whitney U-test). its initition nd progression. A numer of epidemiologicl studies hve suggested tht periodontl disese is risk fctor for vrious systemic diseses nd conditions, including crdiovsculr disese, type 2 dietes, NAFLD, nd rheumtoid rthritis 28. Interestingly, oesity increses the risk of these diseses In ddition, oesity is lso ssocited with n incresed risk of periodontl disese. Therefore, it is possile tht periodontl disese nd oesity hve similr effects on these systemic conditions. The common systemic effect of oesity nd periodontl disese is considered to e low-grde inflmmtion 13. It is well-known tht diet-induced oesity is implicted in systemic low grde inflmmtion. Nutritionl ftty cids ctivte Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) signlling in dipocytes nd mcrophges. In ddition, the cpcity of ftty cids to induce inflmmtory signlling in dipocytes or mcrophges is lunted in the sence of TLR4 32,33. Furthermore, dipose tissue lipolysis from hypertrophied dipocytes, could serve s nturlly occurring lignd for TLR4 to induce inflmmtion. It is pprent tht gut microil ecology could e n importnt fctor in the development of oesity y ffecting energy homeostsis. For exmple, Cni et l. elegntly demonstrted tht the composition of the gut microiot is influenced y high-ft diet- nd geneticlly oese o/o-induced metolic endotoxemi 34. Components originting from the gut microiot, such s lipopolyscchride, lipoteichoic cid, peptidoglycn, flgellin, nd cteril DNA cn cuse immune system ctivtion nd susequent inflmmtion. Proposed mechnisms for periodontl diseses inducing systemic inflmmtion hve included: (i) the direct effect of infectious gents or their products, nd (ii) incresed expression of cytokines, chemokines, nd cell dhesion molecules produced in periodontitis lesions 35. Additionl mechnisms my include, (iii) trnsloction of swllowed from the gut to the circultiong system, nd (iv) ltertion of gut microil composition-induced increses in gut epithelil permeility y swllowed. The first hypothesis is sed on the lesion size of periodontl disese (periodontitis). It is reported tht the men dentogingivl epithelil surfce re of periodontitis ptients where sugingivl iofilm is contcting thinning nd/or ulcerted gingivl sulculr epithelium is pproximtely 2 cm This re is considered to ct s n entrnce of periodontopthic cteri into the systemic circultion. This mechnism is supported y numer of studies tht hve demonstrted n ssocition etween periodontl disese nd endotoxemi. However, periodontl tretment-induced endotoxemi is detectle s erly s 5 min fter instrumenttion nd disppers t 3 min 37,38. In our study, increses in the serum endotoxin level ws oserved 1 hr fter single dministrtion of nd peked t 3 hrs. For the second hypothesis, there is no direct evidence tht incresed inflmmtory mrkers in periodontitis ptients re in fct derived from inflmed periodontl tissues. For the third possiility, lthough ws detected in the jejunl nd ilel contents, nd colonic contents up to 3 hrs nd 16 hrs fter single dministrtion, respectively, it ws not detected in the lood of P. ginigivlis-dministered mice wheres other cteril DNA ws detected in the lood. Therefore, it is highly likely tht detected endotoxins re not derived from. Given tht recent findings hve implicted n ltered gut microiot s contriutor of not only metolic diseses such s therosclerosis 39,4, type 2 dietes 41, nd NAFLD 42 ut lso immune diseses such s rheumtoid rthritis 43 tht re lso ssocited with periodontitis, it is resonle to ssume tht the systemic inflmmtory chnges seen in -dministered mice could e ttriutle to this ltered gut microiot. Furthermore, periodontl diseses themselves could e modulted y ltertion of gut microiot-induced systemic inflmmtion. In support of this hypothesis, it hs een reported tht high-ft diet-induced oesity incresed lveolr one resorption, chrcteristic feture of periodontitis 44,45. The swllowed sliv of periodontitis ptients is reported to contin up to 1 9 cteri/ml, in L/dy 46 48, mking totl of greter thn 1 12 cteri/dy. Since the cteril flor of the orl cvity is distinct from tht of the gut 49, it is possile tht swllowed cteri could ffect the composition of the gut microflor. In fct, it hs een reported tht orl proiotic intervention lters gut cteril composition 5. Thus, it is unlikely tht orl cteri lone could e custive gents of endotoxemi in periodontitis ptients. In the present study, orl dministrtion of induced chnge of cteril composition in the ilel microflor. Although severl studies hve shown the eneficil effect of Bcteroidetes phylum on the gut 51,52, we oserved n incresed proportion of the order Bcteroidles elonging Bcteroidetes phylum, ccompnied y insulin resistnce nd the ltertion of gene expression in dipose tissue nd liver. The expression of severl proinflmmtory genes nd nti-inflmmtory or insulin sensitivity-improving genes were upregulted or downregulted, respectively, in the dipose tissue nd the liver of -dministered mice. In ddition, expression of Sirt1 which is reported to induce n increse in glucose uptke nd insulin signlling ws lso downregulted. It hs lso een reported tht SIRT1 expression is inversely relted to inflmmtory gene expression, prticulrly TNF-. These chnges in proinflmmtory nd nti-inflmmtory gene expression my contriute to increses in serum glucose levels nd in insulin intolernce. Although the effect of is not roust, continuous deteriortion of glucose metolism could hve significnt effect. SCIENTIFIC REPORTS 4 : 4828 DOI: 1.138/srep4828 5
6 c (/) Figure 6 Comprison of the gut microiot etween -dministerd nd shm-dministered mice y 16S rrna sequencing nlysis. Reltive undnces of ech cteril group in Phylum () nd OTU () level re indicted y oxplot. Ech defined OTU otined from 16S rrna deep sequencing ws compred to the genome dtse (GenomeDB) from NCBI using lstin (c). Close reltive species nd percent similrities re shown. Fold increses indicte the men rtio of reltive undnce of the OTU in the gut microiot from the -dministered group to shmdministered group. (*p,.5, **p,.1, Mnn-Whitney U-test). One of the possile resons for the discrepncy of inflmmtionssocited chnge of microiot etween previous studies nd our study could e the difference of the site from where the smples were otined. Previous studies nlyzed fecl or cecl smples, wheres we nlysed ilel contents. The ileum is considered to e n importnt orgn ecuse chylomicron is formed into smll vesicles in the epithelil cells of the ileum, nd lipid is minly sored from the ileum. In ddition, Peyer s Ptches re locted in the ilel wll. Therefore, s previously demonstrted with cecl cteril 53, the cteril composition in the ileum my hve significnt impct on systemic inflmmtion. It is lso noteworthy tht in humns, Bcteroidetes my promote type 2 dietes through n endotoxininduced inflmmtory response 54. Heno-Meji et l., demonstrted tht significnt expnsion of Porphyrmondcee ws found following HFD or with methioninecholine-deficient diet dministrtion in the fecl microiot in the inflmmsome-deficient setting nd ws ssocited with progression of NAFLD nd oesity 55. We propose tht dministered is not directly responsile for the increse of the fmily Porphyromondcee in the gut, s we did not detect in the gut y using specific primers. However, cteri elonging to this fmily of cteri my ply role in the induction of endotoxemi nd susequent inflmmtory responses. Alterntively, my suppress inflmmsome ctivtion y other cteri. For exmple, it hs een reported tht suppresses inflmmsome ctivity through inhiition of endocytosis 56. Another interesting finding from this study ws tht mrna expression of lkline phosphtse ws downregulted in the ileum of -dministered mice. Klnnen et l. previously demonstrted tht defect in intestinl lkline phosphtse (IAP), ws ssocited with high-ft diet-induced metolic syndrome, nd endogenous nd orlly supplemented IAP inhiited endotoxin sorption, s well s reversed metolic syndrome in mice 57. Therefore, IAP is considered to ply n importnt role in the SCIENTIFIC REPORTS 4 : 4828 DOI: 1.138/srep4828 6
7 Serum endotoxin (EU/ml) Serum endotoxin (EU/ml) * * Overnight fsting Non-fsting Figure 7 Effect of orl dministrtion of on the serum endotoxin levels. () Serum endotoxin (LPS) concentrtion (EU/ml) were determined fter 1 cycles of dministrtion or shm dministrtion (N 5 8 in ech group). All dt re mens 6 SD. () Serum endotoxin (LPS) concentrtion (EU/ml) were determined t the indicted times fter single dministrtion of (N 5 6 in ech group). All dt re mens 6 SD. (*p,.5, one-wy ANOVA). suppression of endotoxemi. Although the underlying mechnisms y which orl dministrtion of nd/or ltertion of gut microiot downregulte the mrna of lkline phosphtse hs not een clrified, downregultion of the Akp3 gene my e fctor for elevted systemic inflmmtion. Moreover, gene expression nlysis of the smll intestine demonstrted downregulted mrna expression of the tight junction protein ZO-1 in -dministered mice. In previous studies on mouse models, the endotoxemi following high-ft diet dministrtion ws ssocited with reduced expression of genes encoding for ZO-1 nd occludin 34. These results suggest tht dministered lters the gut microiot, nd lters the gut epithelil cell rrier function, resulting in incresed gut permeility. However, the mechnism for how this chnge in the gut microiot impirs gut rrier function hs not een elucidted. P. gingivlis dministrtion-induced ltertions of the gut microiot lso induced upregulted mrna expression of vrious proinflmmtory cytokines. It is not known whether these inflmmtory chnges of the lrge intestine ffect systemic inflmmtory responses. In conclusion, in the present study, we demonstrted tht orl dministrtion of induced ltertion of gut microiot s well s inflmmtory chnges in vrious tissues nd orgns. These chnges re considered to e ttriutle to increses in levels of endotoxin in the lood. However, s with previous oservtions on the influence of high-ft diet-induced metolic endotoxemi induced chnges of the gut microiot, it remins to e elucidted whether cuse-nd-effect reltionship exists etween orl dministrtion of -induced systemic inflmmtion nd chnges in the gut microiot. Also, further investigtions re needed to exmine whether other orl cteri hve similr effects on the systemic metolism. Becuse the composition of the orl microflor nd gut microflor re quite distinct, the considerle flow of lrge quntities of orl cteri into gut during the frequent ct of swllowing could distur the lnce of the gut microflor. Furthermore, cteril components responsile for the ltertion of gut cteril composition hve lso not een elucidted. Therefore, further studies re needed to clrify the exct mechnisms of how induces shifts in the gut microiot towrds the production of metolic products nd shifts in the composition of cteril species responsile for the induction of metolic syndrome. Methods Mice. All experiments were performed in ccordnce with the Regultions nd Guidelines on Scientific nd Ethicl Cre nd Use of Lortory Animls of the Science Council of Jpn, enforced on June 1, 26, nd pproved y the Institutionl Reltive gene expression ** Akp3 * Tjp1 Reltive gene expression Figure 8 Comprison of reltive gene expression levels in the smll intestine () nd colon tissue () etween the shm-dministered group nd the P. gingivlis-dministered group (N 5 8 in ech group). The reltive quntity of experimentl mrna ws normlized to the reltive quntity of glycerldehyde-3-phosphte dehydrogense (GAPDH) mrna. All dt re mens 6 SD. (*p,.5; **p,.1, ***p,.1, Mnn-Whitney U-test). SCIENTIFIC REPORTS 4 : 4828 DOI: 1.138/srep4828 7
8 Animl Cre nd Use Committee t Niigt University (permit numer 39). Sixweek-old mle C57BL/6N mice were otined from Jpn SLC, Inc. (Shizuok, Jpn). The mice were cclimtized under specific pthogen-free conditions nd fed regulr chow nd sterile wter until the commencement of infection t 8 weeks of ge. Bcteril cultures. strin W83 ws cultured in modified Gifu neroic medium (GAM) roth (Nissui, Tokyo, Jpn) in n neroic jr (Becton Dickinson Microiology System, Cockeysville, MD) in the presence of n AneroPckTM (Mitsuishi Gs Chemicl Co. Inc., Tokyo, Jpn) for 48 hours t 37uC. Bcteril suspensions were prepred in phosphte-uffered sline (PBS) without Mg 21 /C 21 using estlished growth curves nd spectrophotometric nlysis. The numer of CFUs ws stndrdized y mesuring opticl density (6 nm). Orl dministrtion. The murine experimentl periodontitis model ws developed ccording to Bker et l. 58 with slight modifictions. A totl of 1 9 CFU s of live P. gingivlis suspended in 1 ml of PBS with 2% croxymethyl cellulose (Sigm- Aldrich, St. Louis, MO) ws given to ech mouse vi feeding needle. This suspension ws given 2 times week for 5 weeks. The control group ws shm-dministered without the. During the experimentl period, ll mice were llowed to et nd drink d liitum. One dy fter the finl tretment, orl sws were otined nd tested for the presence of s previously descried 59. Mice were then euthnized with CO 2, nd their tissues were removed. Detection of in lood nd intestinl contents. Whole lood ws tken t t 15 min, 3, 12, nd 24 hrs fter single dministrtion of. Intestinl contents were otined t 1, 3, nd 16 hrs fter dministrtion of.dna ws extrcted from whole lood nd intestinl contents using QIAmpDNA Blood Mini Kit (Qigen, Hilden, Germny) nd QIAmp DNA Stool Mini Kit (Qigen), respectively. Quntittive rel-time PCR ws performed on LightCyclerH 96 System (Roche) using Fst Strt Essentil DNA Green Mster (Roche). Universl 16S rrna ws mplified using forwrd primer 59-ACTCCTACGGGAGGCAGCAGT-39 nd reverse primer 59-ATTACCGCGGCTGCTGGC S rrna ws mplified using forwrd primer 59- AGGCAGCTTGCCATACTGCG-39nd reverse primer 59- ACTGTTAGCAACTACCGATGT-39. Gut microiot nlysis y pyrosequencing. The ileum ws removed nd the ilel contents were collected using sterile wter (Bio-Rd Lortories, Hercules, CA). The otined ilel contents were homogenised nd DNA ws extrcted using PowerSoilH DNA isoltion kit (MO BIO, Crlsd, CA). PCR ws performed using primer set (784F:59-AGGATTAGATACCCTGGTA-39 nd 161R: 59- CRRCACGAGCTGACGAC-39) trgeting the V5-V6 region of the 16S rrna genes 6. To mplify the trgeted region, 1 ml of extrcted DNA served s the templte in 5-ml rections using KAPA HiFi HS Redy Mix (KAPA Biosystems, Wourn, MA). The PCR protocols were 95uC for 3 min, 25 cycles of 98uC for 2 s, 6uC for 15 s, nd 72uC for 15 s nd 72uC for 1 min. Two 1 ml of 3-cycle reconditioning PCR rections were performed per smple to eliminte heteroduplexes, with 1-ml liquots of the initil PCR product mixture s the templte nd other PCR conditions unchnged. Products of the two reconditioning PCR rections per smple were comined nd purified using DNA clen nd Concentrtor-5 (ZYMO RESEARCH, Irvine, CA). Pyrosequencing of the 16S rrna mplicons ws crried out on the 454 GS Junior pltform (Roche, Bsel, Switzerlnd). Denoising, txonomic ssignments, nd estimting reltive undnce of sequencing dt were performed y the nlysis pipeline of the QIIME softwre pckge 61. An opertionl txonomic unit (OTU) ws defined t 97% similrity. OTU indicting reltive undnce of under.1% ws filtered to remove noise. Glucose nd insulin tolernce tests. GTTs were performed in mice orlly dministered nd shm-dministered mice. Mice were injected i.p. with single dose of 1 g of glucose per kg of ody weight. For the insulin tolernce test, insulin (.5 unit/kg) ws dministered y n i.p. injection. Blood smples were collected through the til vein efore glucose or insulin injection nd t 15, 3, 6, 9, nd 12 min. Blood glucose concentrtions were immeditely determined y the Glucose Pilot ssy (Aventir Biotech, LLC CA). The serum insulin concentrtion ws determined for y ELISA (Moring, Tokyo, Jpn). Periodontl tissue, liver nd dipose tissue histology. The fixed mndiles were dissected, declcified, emedded, nd sectioned s descried previously 62. Seril sections 5 mm thick were otined in the sgittl direction long the long xis of the teeth nd stined with hemtoxylin nd eosin. Mouse livers were emedded in Tissue- Tek OCT (Finetechnicl Skur, Tokyo, Jpn) nd frozen in liquid nitrogen. Frozen 7 mm sections were otined in cryostt (LEICA, Wetzlr, Germny), dried t room temperture for 6 min, fixed in 1% formldehyde for 1 min, stined with oil red O for 2 min, nd counter-stined with hemtoxylin. Adipose tissue smples from shm-dministered nd -dministered mice were fixed in 1% formlin for immunohistochemistry. Briefly, smples were emedded in prffin, sectioned, nd stined with rt nti-mouse F4/8 ntiody (ABd Serotec, Rleigh, NC; 155 dilution). Cytokine ssy. Proteins were extrcted using T-PER Mmmlin Protein Extrction Regent (Pierce Biotechnology, Rockford, IL). C1q/TNF-relted protein 9 (CTRP9) nd TNF- were mesured using the Mouse CTRP9 ELISA kit (Aviscer Bioscience, Snt Clr, CA) nd the Mouse TNF ELISA kit (Thermo Scientific, Settle, WA), respectively. The totl protein concentrtions were mesured y the Pierce BCA Protein Assy kit (Thermo Scientific). Individul protein concentrtions were clculted s the undnce of specific protein constituents divided y the totl protein concentrtions. Serum IL-6 level ws determined y using commercil ELISA kit (Thermo Scientific). Endotoxin ssy. Endotoxin levels were determined in ser collected t 16 hrs fter finl dministrtion of from the til veins of mice using limulus moeocyte lyste test (QCL-1TM, BioWhittker, Wlkersville, MD) ccording to the mnufcturer s instruction. Serum smples were diluted t 1 to 4 for the ssy. Opticl densities were mesured using n ELISA plte reder (Model 68, Bio-Rd Lortories) t 45 nm. Liver triglyceride content. Liver triglycerides were determined with Triglyceride Quntifiction Colorimetric kit (Bio Vision, Milpits, CA). Triglyceride vlues were expressed s the concentrtion of triglycerides divided y the totl protein concentrtion. The totl protein concentrtions were mesured y the Pierce BCA Protein Assy kit (Thermo Scientific). Anlysis of gene expression in dipose tissue, liver, nd intestine. Totl RNA from dipose tissue, liver, smll intestine nd lrge intestine smples ws extrcted using n RNesy Mini kit nd treted with DNse I (Qigen, Germntown, MD) ccording to the mnufcturer s instructions. Aliquots of RNA were then reverse-trnscried to cdna using rndom primers (Tkr Bio Inc., Shig, Jpn) nd M-MLV reverse trnscriptse (Life Technologies Corportion, Crlsd, CA). Primers nd proes specific for rel-time PCR were purchsed from Life Technologies Corportion. Rections were crried out in 25-ml mixture in LightCyclerH 96 System(Roche) using TqMn Gene Expression Assys (Life Technologies Corportion) contining 9 nm primer nd 25 nm proe. The rections consisted of 1-minute incution t 95uC, followed y 4 cycles of two-step mplifiction procedure consisting of nneling/extension t 6uC for 1 minute nd denturtion for 15 seconds t 95uC. LightCyclerH 96 softwre (Roche) ws used to nlyze the stndrds nd crry out the quntifictions. The reltive quntity of ech mrna ws normlized to the reltive quntity of glycerldehyde-3-phosphte dehydrogense (GAPDH) mrna. Sttisticl nlysis. Nonprmetric dt were evluted using the Mnn-Whitney U- test for two-group comprisons, wheres comprisons of three or more groups were nlysed y one-wy ANOVA with d hoc Bonferroni post tests using Grphpd PrismH (GrphPd Softwre, Inc., L Joll, CA). A proility vlue of p,.5 ws considered sttisticlly significnt. For ssessing significnt differences etween the P. gingivlis-dministered nd shm-dministered smples, we used the Mnn Whitney U-test from the R pckge ( 1. Petersen, P. E. & Ogw, H. Strengthening the prevention of periodontl disese: the WHO pproch. J Periodontol. 76, (25). 2. Bhekr, A. A., Singh, S., Sh, S., Molnr, J. & Aror, R. The prevlence nd incidence of coronry hert disese is significntly incresed in periodontitis: met-nlysis. Am Hert J. 154, (27). 3. Humphrey, L. L., Fu, R., Buckley, D. I., Freemn, M. & Helfnd, M. Periodontl disese nd coronry hert disese incidence: systemtic review nd metnlysis. J Gen Intern Med. 23, (28). 4. Chávrry, N. G., Vettore, M. V., Snsone, C. & Sheihm, A. The reltionship etween dietes mellitus nd destructive periodontl disese: met-nlysis. Orl Helth Prev Dent. 7, (29). 5. Slvi, G. E., Crollo-Bittel, B. & Lng, N. P. Effects of dietes mellitus on periodontl nd peri-implnt conditions: updte on ssocitions nd risks. J Clin Periodontol. 35, (28). 6. Yoned, M. et l. Involvement of periodontl pthogen, Porphyromons gingivlis on the pthogenesis of non-lcoholic ftty liver disese. BMC Gstroenterol. 12, 16 (212). 7. Bostnci, N. & Beliskis, G. N. Porphyromons gingivlis: n invsive nd evsive opportunistic orl pthogen. FEMS Microiol Lett. 333, 1 9 (212). 8. Tomás, I., Diz, P., Toís, A., Scully, C. & Donos, N. Periodontl helth sttus nd cteremi from dily orl ctivities: systemtic review/met-nlysis. J Clin Periodontol. 39, (212). 9. Preshw, P. M. & Tylor, J. J. How hs reserch into cytokine interctions nd their role in driving immune responses impcted our understnding of periodontitis? J Clin Periodontol. 38 Suppl 11, 6 84 (211). 1. Prskevs, S., Huizing, J. D. & Loos, B. G. A systemtic review nd metnlyses on C-rective protein in reltion to periodontitis. J Clin Periodontol. 35, (28). 11. Ide, M. et l. Effect of tretment of chronic periodontitis on levels of serum mrkers of cute-phse inflmmtory nd vsculr responses. J Clin Periodontol. 3, (23). 12. Loos, B. G., Crndijk, J., Hoek, F. J., Wertheim-vn Dillen, P. M. & vn der Velden, U. Elevtion of systemic mrkers relted to crdiovsculr diseses in the peripherl lood of periodontitis ptients. J Periodontol. 71, (2). SCIENTIFIC REPORTS 4 : 4828 DOI: 1.138/srep4828 8
9 13. Schenkein, H. A. & Loos, B. G. Inflmmtory mechnisms linking periodontl diseses to crdiovsculr diseses. J Clin Periodontol. 4 Suppl 14, S51 69 (213). 14. Mekw, T. et l. Chronic orl infection with Porphyromons gingivlis ccelertes therom formtion y shifting the lipid profile. PLoS One 6, e224 (211). 15. Greenerg, A. S. & Oin, M. S. Oesity nd the role of dipose tissue in inflmmtion nd metolism. Am J Clin Nutr. 83, 461S 465S (26). 16. Lee, D. E., Kehlenrink, S., Lee, H., Hwkins, M. & Yudkin, J. S. Getting the messge cross: mechnisms of physiologicl cross tlk y dipose tissue. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Met. 296, E (29). 17. Tryhurn, P., Bing, C. & Wood, I. S. Adipose tissue nd dipokines--energy regultion from the humn perspective. J Nutr. 136, 1935S 1939S (26). 18. Ouchi, N., Prker, J. L., Lugus, J. J. & Wlsh, K. Adipokines in inflmmtion nd metolic disese. Nt Rev Immunol. 11, (211). 19. Sito, T., Shimzki, Y. & Skmoto, M. Oesity nd periodontitis. N Engl J Med. 339, (1998). 2. Aldulkrim, M., Bissd, N., Al-Zhrni, M., Ficr, A. & Siegel, B. Alveolr one loss in oese sujects. J Int Acd Periodontol. 7, (25). 21. Al-Zhrni, M. S., Bissd, N. F. & Borwski, E. A. Oesity nd periodontl disese in young, middle-ged, nd older dults. J Periodontol. 74, (23). 22. Buhlin, K., Gustfsson, A., Pockley, A. G., Frostegård, J. & Klinge, B. Risk fctors for crdiovsculr disese in ptients with periodontitis. Eur Hert J. 24, (23). 23. Torrungrung, K. et l. Risk indictors of periodontl disese in older Thi dults. J Periodontol. 76, (25). 24. Weiserg, S. P. et l. Oesity is ssocited with mcrophge ccumultion in dipose tissue. J Clin Invest. 112, (23). 25. Xu, H. et l. Chronic inflmmtion in ft plys crucil role in the development of oesity-relted insulin resistnce. J Clin Invest. 112, (23). 26. Hotmisligil, G. S., Shrgill, N. S. & Spiegelmn, B. M. Adipose expression of tumor necrosis fctor-: direct role in oesity-linked insulin resistnce. Science 259, (1993). 27. Ymzki, K. et l. Effect of periodontl tretment on the C-rective protein nd proinflmmtory cytokine levels in Jpnese periodontitis ptients. J Periodontl Res. 4, (25). 28. Pischon, N. et l. Assocition mong rheumtoid rthritis, orl hygiene, nd periodontitis. J Periodontol. 79, (28). 29. Bys, H. E. Adiposopthy is sick ft crdiovsculr disese? J Am Coll Crdiol. 57, (211). 3. Mensh, G. A. et l. Oesity, metolic syndrome, nd type 2 dietes: emerging epidemics nd their crdiovsculr implictions. Crdiol Clin. 22, (24). 31. Conde, J. et l. Adipokines: novel plyers in rheumtic diseses. Discov Med. 15, (213). 32. Shi, H. et l. TLR4 links innte immunity nd ftty cid-induced insulin resistnce. J Clin Invest. 116, (26). 33. Sugnmi, T. et l. Role of the Toll-like receptor 4/NF-kB pthwy in sturted ftty cid-induced inflmmtory chnges in the interction etween dipocytes nd mcrophges. Arterioscler Throm Vsc Biol. 27, (27). 34. Cni, P. D. et l. Chnges in gut microiot control metolic endotoxemiinduced inflmmtion in high-ft diet-induced oesity nd dietes in mice. Dietes 57, (28). 35. Epstein, S. E., Zhou, Y. F. & Zhu, J. Infection nd therosclerosis: emerging mechnistic prdigms. Circultion 1, e2 28 (1999). 36. Hujoel, P. P., White, B. A., Grcí, R. I. & Listgrten, M. A. The dentogingivl epithelil surfce re revisited. J Periodontl Res. 36, (21). 37. Lee, M. K., Ide, M., Cowrd, P. Y. & Wilson, R. F. Effect of ultrsonic deridement using chlorhexidine irrignt on circulting levels of lipopolyscchrides nd interleukin-6. J Clin Periodontol. 35, (28). 38. Lucrtorto, F. M., Frnker, C. K. & Mz, J. Postscling cteremi in HIVssocited gingivitis nd periodontitis. Orl Surg Orl Med Orl Pthol. 73, (1992). 39. Krlsson, F. H. et l. Symptomtic therosclerosis is ssocited with n ltered gut metgenome. Nt Commun. 3, 1245 (212). 4. Koeth, R. A. et l. Intestinl microiot metolism of L-crnitine, nutrient in red met, promotes therosclerosis. Nt Med. 19, (213). 41. Qin, J. et l. A metgenome-wide ssocition study of gut microiot in type 2 dietes. Nture 49, 55 6 (212). 42. Moschen, A. R., Kser, S. & Tilg, H. Non-lcoholic stetoheptitis: microiotdriven disese. Trends Endocrinol Met. 24, (213). 43. Scher, J. U. & Armson, S. B. The microiome nd rheumtoid rthritis. Nt Rev Rheumtol. 7, (211). 44. Blsco-Bque, V. et l. High-ft diet induces periodontitis in mice through lipopolyscchrides (LPS) receptor signling: protective ction of estrogens. PLoS One 7, e4822 (212). 45. Cvgni, J. et l. Oesity my increse the occurrence of spontneous periodontl disese in Wistr rts. Arch Orl Biol. 58, (213). 46. Boutg, K., Svelkoul, P. H., Winkel, E. G. & vn Winkelhoff, A. J. Comprison of sugingivl cteril smpling with orl lvge for detection nd quntifiction of periodontl pthogens y rel-time polymerse chin rection. J Periodontol. 78, (27). 47. Sygun, I. et l. Slivry infectious gents nd periodontl disese sttus. J Periodontl Res. 46, (211). 48. von Troil-Lindén, B., Torkko, H., Alluusu, S., Jousimies-Somer, H. & Asikinen, S. Slivry levels of suspected periodontl pthogens in reltion to periodontl sttus nd tretment. J Dent Res. 74, (1995). 49. Koren, O. et l. Humn orl, gut, nd plque microiot in ptients with therosclerosis. Proc Ntl Acd Sci U S A. 18 Suppl 1, (211). 5. O Toole, P. W. & Cooney, J. C. Proiotic cteri influence the composition nd function of the intestinl microiot. Interdiscip Perspect Infect Dis. 28, (28). 51. Ley, R. E. et l. Oesity lters gut microil ecology. Proc Ntl Acd Sci U S A. 12, (25). 52. Turnugh, P. J., Bäckhed, F., Fulton, L. & Gordon, J. I. Diet-induced oesity is linked to mrked ut reversile ltertions in the mouse distl gut microiome. Cell Host Microe. 3, (28). 53. Hotmisligil, G. S. & Ery, E. Nutrient sensing nd inflmmtion in metolic diseses. Nt Rev Immunol. 8, (28). 54. Lrsen, N. et l. Gut microiot in humn dults with type 2 dietes differs from non-dietic dults. PLoS One 5, e985 (21). 55. Heno-Meji, J. et l. Inflmmsome-medited dysiosis regultes progression of NAFLD nd oesity. Nture 482, (212). 56. Txmn, D. J. et l. Porphyromons gingivlis medites inflmmsome repression in polymicroil cultures through novel mechnism involving reduced endocytosis. J Biol Chem. 287, (212). 57. Klinnn, K. et l. Intestinl lkline phosphtse prevents metolic syndrome in mice. Proc Ntl Acd Sci U S A. 11, (213). 58. Bker, P. J., Evns, R. T. & Roopenin, D. C. Orl infection with Porphyromons gingivlis nd induced lveolr one loss in immunocompetent nd severe comined immunodeficient mice. Arch Orl Biol. 39, (1994). 59. Ashimoto, A., Chen, C., Bkker, I. & Slots, J. Polymerse chin rection detection of 8 puttive periodontl pthogens in sugingivl plque of gingivitis nd dvnced periodontitis lesions. Orl Microiol Immunol. 11, (1996). 6. Andersson, A. F. et l. Comprtive nlysis of humn gut microiot y rcoded pyrosequencing. PLoS One 3, e2836 (28). 61. Cporso, J. G. et l. QIIME llows nlysis of high-throughput community sequencing dt. Nt Methods 7, (21). 62. Sulniute, R., Lindh, T., Wilczynsk, M., Li, J. & Ny, T. Plsmin is essentil in preventing periodontitis in mice. Am J Pthol. 179, (211). Acknowledgments This work ws supported y JSPS KAKENHI Grnt Numers nd , nd Sunstr Inc. (Osk, Jpn). The uthors thnk Dr. Bruce Beutler (Center for Genetics of Host Defense, University of Texs Southwestern Medicl Center, Dlls, TX) nd Dr. Tomoyuki Hond (Division of Periodontology, Deprtment of Orl Biologicl Science, Niigt University Grdute School of Medicl nd Dentl Sciences, Niigt, Jpn) for the criticl reding nd preprtion of the mnuscript, respectively. Author contriutions K.A. reserched dt nd wrote the mnuscript. H.Y., H.M., T.M., M.N., K.G. nd D.M. reserched dt. S.N. reserched dt nd contriuted to discussion. M.R. nd T.I. contriuted to discussion nd reviewed/edited mnuscript. K.Y. wrote the mnuscript. All uthors reviewed the mnuscript. Additionl informtion Supplementry informtion ccompnies this pper t scientificreports Competing finncil interests: The uthors declre no competing finncil interests. How to cite this rticle: Arimtsu, K. et l. Orl pthoiont induces systemic inflmmtion nd metolic chnges ssocited with ltertion of gut microiot. Sci. Rep. 4, 4828; DOI:1.138/srep4828 (214). This work is licensed under Cretive Commons Attriution 3. Unported License. Theimgesinthisrticlereincludedintherticle scretivecommonslicense, unless indicted otherwise in the imge credit; if the imge is not included under the Cretive Commons license, users will need to otin permissionfrom the license holder in order to reproduce the imge. To view copy of this license, visit SCIENTIFIC REPORTS 4 : 4828 DOI: 1.138/srep4828 9
10 1 Supplementry informtion Orl pthoiont induces systemic inflmmtion nd metolic chnges ssocited with ltertion of gut microiot Kei Arimtsu 1,2, Hitomi Ymd 1,2, Hrun Miyzw 1,2, Tkyoshi Mingw 1,2, Myuk Nkjim 1,2, Mrk I. Ryder 3, Kzuyoshi Gotoh 4, Disuke Motook 4, Shot Nkmur 4, Tetsuy Iid 4 nd Kzuhis Ymzki 1* 1 Lortory of Periodontology nd Immunology, Division of Orl Science for Helth Promotion, Niigt University Grdute School of Medicl nd Dentl Sciences, Niigt, Jpn 2 Division of Periodontology, Deprtment of Orl Biologicl Science, Niigt University Grdute School of Medicl nd Dentl Sciences, Niigt, Jpn 3 Division of Periodontology, Deprtment of Orofcil Sciences, School of Dentistry, University of Cliforni, Sn Frncisco, USA 4 Deprtment of Infection Metgenomics, Reserch Institute for Microil Diseses, Osk University, Osk, Jpn * Correspondence: Prof. Kzuhis Ymzki, Lortory of Periodontology nd Immunology, Division of Orl Science for Helth Promotion, Niigt University Grdute School of Medicl nd Dentl Sciences, 5274 Gkkocho 2-n-cho, Chuo-ku, Niigt , Jpn Tel: , Fx: , E-mil: kz@dent.niigt-u.c.jp
11 Body weight (g) Supplementry Figure S Dy Dy24 Dy39 Chnges in ody weight during experimentl period (N = 8 in ech group).
12 Serum insulin (ng/ml) Supplementry Figure S Insulin levels of -dministered nd shm-dministered mice. Fsting serum insulin level were determined y ELISA (N = 1 in ech group).
13 Supplementry Figure S3 Detection of in the ilel smples of -dministered nd shmdministered mice. Representtive 1.2% grose gels showing the results of PCR mplifiction of DNA extrcted from ilel smples for detection of 16S rrna.
14 16S rrna / Universl 16S rrna Supplementry Figure S Jejunum Ileum Colon Trnsloction of dministered in the intestinl trct. After single dministrtion of, intestinl contents were recovered from the jejunum, ileum, nd colon t 1, 3, nd 16 hrs. Reltive undnce of -specific 16S rrna gene to universl 16S rrna genes re shown.
15 Supplementry Figure S Detection of -specific 16S rrna gene () or universl 16S rrna genes () in the lood smples of -dministered nd shm-dministered mice. After single dministrtion of orlly or intrvenously (infroritl vein), lood drws were tken from left ventricle of the hert t, 3, 12, nd 24 hrs or 15 min, respectively. Representtive results of one of the three independent experiments re shown. The numer of PCR cycles is shown ove lnes.
EFFECTS OF AN ACUTE ENTERIC DISEASE CHALLENGE ON IGF-1 AND IGFBP-3 GENE EXPRESSION IN PORCINE SKELETAL MUSCLE
 Swine Dy 22 Contents EFFECTS OF AN ACUTE ENTERIC DISEASE CHALLENGE ON IGF-1 AND IGFBP-3 GENE EXPRESSION IN PORCINE SKELETAL MUSCLE B. J. Johnson, J. P. Kyser, J. D. Dunn, A. T. Wyln, S. S. Dritz 1, J.
Swine Dy 22 Contents EFFECTS OF AN ACUTE ENTERIC DISEASE CHALLENGE ON IGF-1 AND IGFBP-3 GENE EXPRESSION IN PORCINE SKELETAL MUSCLE B. J. Johnson, J. P. Kyser, J. D. Dunn, A. T. Wyln, S. S. Dritz 1, J.
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nture11225 Numer of OTUs sed on 3% distnce Numer of 16s rrna-sed V2-V4 tg sequences LF MF PUFA Supplementry Figure 1. High-ft diets decrese the richness nd diversity
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nture11225 Numer of OTUs sed on 3% distnce Numer of 16s rrna-sed V2-V4 tg sequences LF MF PUFA Supplementry Figure 1. High-ft diets decrese the richness nd diversity
* * * * * liver kidney ileum. Supplementary Fig.S1
 Supplementry Fig.S1 liver kidney ileum Fig.S1. Orlly delivered Fexrmine is intestinlly-restricted Mice received vehicle or Fexrmine (100mg/kg) vi per os (PO) or intrperitonel (IP) injection for 5 dys (n=3/group).
Supplementry Fig.S1 liver kidney ileum Fig.S1. Orlly delivered Fexrmine is intestinlly-restricted Mice received vehicle or Fexrmine (100mg/kg) vi per os (PO) or intrperitonel (IP) injection for 5 dys (n=3/group).
PNEUMOVAX 23 is recommended by the CDC for all your appropriate adult patients at increased risk for pneumococcal disease 1,2 :
 PNEUMOVAX 23 is recommended y the CDC for ll your pproprite dult ptients t incresed risk for pneumococcl disese 1,2 : Adults ged
PNEUMOVAX 23 is recommended y the CDC for ll your pproprite dult ptients t incresed risk for pneumococcl disese 1,2 : Adults ged
TNF-α (pg/ml) IL-6 (ng/ml)
 Xio, et l., Supplementry Figure 1 IL-6 (ng/ml) TNF-α (pg/ml) 16 12 8 4 1,4 1,2 1, 8 6 4 2 med Cl / Pm3CSK4 zymosn curdln Poly (I:C) LPS flgelin MALP-2 imiquimod R848 CpG TNF-α (pg/ml) IL-6 (ng/ml) 2 1.6
Xio, et l., Supplementry Figure 1 IL-6 (ng/ml) TNF-α (pg/ml) 16 12 8 4 1,4 1,2 1, 8 6 4 2 med Cl / Pm3CSK4 zymosn curdln Poly (I:C) LPS flgelin MALP-2 imiquimod R848 CpG TNF-α (pg/ml) IL-6 (ng/ml) 2 1.6
Effects of physical exercise on working memory and prefrontal cortex function in post-stroke patients
 Effects of physicl exercise on working memory nd prefrontl cortex function in post-stroke ptients M Moriy, C Aoki, K Sktni Grdute School of Helth Sciences Reserch, Mjor of Physicl Therpy, TeikyoHeisei
Effects of physicl exercise on working memory nd prefrontl cortex function in post-stroke ptients M Moriy, C Aoki, K Sktni Grdute School of Helth Sciences Reserch, Mjor of Physicl Therpy, TeikyoHeisei
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Prentl doi:.8/nture57 Figure S HPMECs LM Cells Cell lines VEGF (ng/ml) Prentl 7. +/-. LM 7. +/-.99 LM 7. +/-.99 Fold COX induction 5 VEGF: - + + + Bevcizum: - - 5 (µg/ml) Reltive MMP LM mock COX MMP LM+
Prentl doi:.8/nture57 Figure S HPMECs LM Cells Cell lines VEGF (ng/ml) Prentl 7. +/-. LM 7. +/-.99 LM 7. +/-.99 Fold COX induction 5 VEGF: - + + + Bevcizum: - - 5 (µg/ml) Reltive MMP LM mock COX MMP LM+
Abstract ABSTRACT #69. Abstract. Introduction & Methods. Methods & Results. Results. Results & Conclusions
 Effects of dietry β-glucn on Growth Performnce, Dirrhe, nd Gut Permeility of Wening Pigs Experimentlly Infected with Pthogenic E. coli Kwngwook Kim, Amy Ehrlich, Vivin Perng, Jennifer Chse, Helen Ryould,
Effects of dietry β-glucn on Growth Performnce, Dirrhe, nd Gut Permeility of Wening Pigs Experimentlly Infected with Pthogenic E. coli Kwngwook Kim, Amy Ehrlich, Vivin Perng, Jennifer Chse, Helen Ryould,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 X p -lu c ct ivi ty doi:.8/nture8 S CsA - THA + DAPI Merge FSK THA TUN Supplementry Figure : A. Ad-Xp luc ctivity in primry heptocytes exposed to FSK, THA, or TUN s indicted. Luciferse ctivity normlized
X p -lu c ct ivi ty doi:.8/nture8 S CsA - THA + DAPI Merge FSK THA TUN Supplementry Figure : A. Ad-Xp luc ctivity in primry heptocytes exposed to FSK, THA, or TUN s indicted. Luciferse ctivity normlized
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementry Figure 1 c d Wistr SHR Wistr AF-353 SHR AF-353 n = 6 n = 6 n = 28 n = 3 n = 12 n = 12 Supplementry Figure 1 Neurophysiologicl properties of petrosl chemoreceptive neurones in Wistr nd SH rts.
Supplementry Figure 1 c d Wistr SHR Wistr AF-353 SHR AF-353 n = 6 n = 6 n = 28 n = 3 n = 12 n = 12 Supplementry Figure 1 Neurophysiologicl properties of petrosl chemoreceptive neurones in Wistr nd SH rts.
Supplementary figure 1
 Supplementry figure 1 Dy 8 post LCMV infection Vsculr Assoc. Prenchym Dy 3 post LCMV infection 1 5 6.7.29 1 4 1 3 1 2 88.9 4.16 1 2 1 3 1 4 1 5 1 5 1.59 5.97 1 4 1 3 1 2 21.4 71 1 2 1 3 1 4 1 5 1 5.59.22
Supplementry figure 1 Dy 8 post LCMV infection Vsculr Assoc. Prenchym Dy 3 post LCMV infection 1 5 6.7.29 1 4 1 3 1 2 88.9 4.16 1 2 1 3 1 4 1 5 1 5 1.59 5.97 1 4 1 3 1 2 21.4 71 1 2 1 3 1 4 1 5 1 5.59.22
Feeding state and age dependent changes in melaninconcentrating hormone expression in the hypothalamus of broiler chickens
 Supplementry Mterils Epub: No 2017_23 Vol. 65, 2018 https://doi.org/10.183/bp.2017_23 Regulr pper Feeding stte nd ge dependent chnges in melninconcentrting hormone expression in the hypothlmus of broiler
Supplementry Mterils Epub: No 2017_23 Vol. 65, 2018 https://doi.org/10.183/bp.2017_23 Regulr pper Feeding stte nd ge dependent chnges in melninconcentrting hormone expression in the hypothlmus of broiler
2018 American Diabetes Association. Published online at
 Supplementry Figure S1. Ft-1 mice exhibit reduced diposity when fed n HFHS diet. WT nd ft-1 mice were fed either control or n HFHS diet for 18 weeks. A: Representtive photogrphs for side-by-side comprison
Supplementry Figure S1. Ft-1 mice exhibit reduced diposity when fed n HFHS diet. WT nd ft-1 mice were fed either control or n HFHS diet for 18 weeks. A: Representtive photogrphs for side-by-side comprison
The effect of encapsulated butyric acid and zinc on performance, gut integrity and meat quality in male broiler chickens 1
 The effect of encpsulted utyric cid nd zinc on performnce, gut integrity nd met qulity in mle roiler chickens 1 Astrct This study evluted the impct of encpsulted utyric cid nd zinc (ButiPEARL Z) on performnce
The effect of encpsulted utyric cid nd zinc on performnce, gut integrity nd met qulity in mle roiler chickens 1 Astrct This study evluted the impct of encpsulted utyric cid nd zinc (ButiPEARL Z) on performnce
Effect of supplemental fat from dried distillers grains with solubles or corn oil on cow performance, IGF-1, GH, and NEFA concentrations 1
 Effect of supplementl ft from dried distillers grins with solules or corn oil on cow performnce, IGF-1, GH, nd NEFA concentrtions 1 Aigil Brtosh 2, Cody Wright 3, Aimee Wertz-Lutz 4, nd George Perry 5
Effect of supplementl ft from dried distillers grins with solules or corn oil on cow performnce, IGF-1, GH, nd NEFA concentrtions 1 Aigil Brtosh 2, Cody Wright 3, Aimee Wertz-Lutz 4, nd George Perry 5
Supplementary Figure 1
 Roles of endoplsmic reticulum stress-medited poptosis in -polrized mcrophges during mycocteril infections Supplementry informtion Yun-Ji Lim, Min-Hee Yi, Ji-Ae Choi, Jung-hwn Lee, Ji-Ye Hn, Sung-Hee Jo,
Roles of endoplsmic reticulum stress-medited poptosis in -polrized mcrophges during mycocteril infections Supplementry informtion Yun-Ji Lim, Min-Hee Yi, Ji-Ae Choi, Jung-hwn Lee, Ji-Ye Hn, Sung-Hee Jo,
Adipocyte in vascular wall can induce the rupture of abdominal aortic aneurysm
 Adipocyte in vsculr wll cn induce the rupture of dominl ortic neurysm Hiron Kugo 1 *, Nouhiro Zim 1 *, Hiroki Tnk 2 *, Youhei Mouri 1, Kenichi Yngimoto 3, Kohsuke Hymizu 3,4, Keisuke Hshimoto 1, Tkeshi
Adipocyte in vsculr wll cn induce the rupture of dominl ortic neurysm Hiron Kugo 1 *, Nouhiro Zim 1 *, Hiroki Tnk 2 *, Youhei Mouri 1, Kenichi Yngimoto 3, Kohsuke Hymizu 3,4, Keisuke Hshimoto 1, Tkeshi
Meat and Food Safety. B.A. Crow, M.E. Dikeman, L.C. Hollis, R.A. Phebus, A.N. Ray, T.A. Houser, and J.P. Grobbel
 Met nd Food Sfety Needle-Free Injection Enhncement of Beef Strip Loins with Phosphte nd Slt Hs Potentil to Improve Yield, Tenderness, nd Juiciness ut Hrm Texture nd Flvor B.A. Crow, M.E. Dikemn, L.C. Hollis,
Met nd Food Sfety Needle-Free Injection Enhncement of Beef Strip Loins with Phosphte nd Slt Hs Potentil to Improve Yield, Tenderness, nd Juiciness ut Hrm Texture nd Flvor B.A. Crow, M.E. Dikemn, L.C. Hollis,
Bioactive milk components to secure growth and gut development in preterm pigs ESTER ARÉVALO SUREDA PIGUTNET FA1401 STSM
 Bioctive milk components to secure growth nd gut development in preterm pigs ESTER ARÉVALO SUREDA PIGUTNET FA1401 STSM STSM Pigutnet FA1401 STSM 03/Septemer 30/Novemer/2017 (3 months) Host: Home: Thoms
Bioctive milk components to secure growth nd gut development in preterm pigs ESTER ARÉVALO SUREDA PIGUTNET FA1401 STSM STSM Pigutnet FA1401 STSM 03/Septemer 30/Novemer/2017 (3 months) Host: Home: Thoms
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 1 SUPPLEMENARY INFORMAION 13 supplementry figures, 2 supplementry tles, nd supplementry note he leukocyte integrin ntgonist Del-1 inhiits IL-17 medited inflmmtory one loss Mehmet A. Eskn 1,2, Rvi Jotwni
1 SUPPLEMENARY INFORMAION 13 supplementry figures, 2 supplementry tles, nd supplementry note he leukocyte integrin ntgonist Del-1 inhiits IL-17 medited inflmmtory one loss Mehmet A. Eskn 1,2, Rvi Jotwni
Effect of Aqueous Extract of Carica papaya Dry Root Powder on Lactation of Albino Rats
 Effect of Aqueous Extrct of Cric ppy Dry Root Powder on Lcttion of Alino Rts G. Tosswnchuntr nd S. Aritjt Deprtment of Biology Fculty of Science Ching Mi University Ching Mi 50200 Thilnd Keywords: mmmry
Effect of Aqueous Extrct of Cric ppy Dry Root Powder on Lcttion of Alino Rts G. Tosswnchuntr nd S. Aritjt Deprtment of Biology Fculty of Science Ching Mi University Ching Mi 50200 Thilnd Keywords: mmmry
Supplementary Figure 1
 doi: 1.138/nture6188 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementry Figure 1 c CFU-F colonies per 1 5 stroml cells 14 12 1 8 6 4 2 Mtrigel plug Neg. MCF7/Rs MDA-MB-231 * * MCF7/Rs-Lung MDA-MB-231-Lung MCF7/Rs-Kidney
doi: 1.138/nture6188 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementry Figure 1 c CFU-F colonies per 1 5 stroml cells 14 12 1 8 6 4 2 Mtrigel plug Neg. MCF7/Rs MDA-MB-231 * * MCF7/Rs-Lung MDA-MB-231-Lung MCF7/Rs-Kidney
The Journal of Physiology
 J Physiol 595.13 (2017) pp 4379 4398 4379 Impct of perintl exposure to sucrose or high fructose corn syrup (HFCS-55) on diposity nd heptic lipid composition in rt offspring Crl R. Toop 1, Beverly S. Muhlhusler
J Physiol 595.13 (2017) pp 4379 4398 4379 Impct of perintl exposure to sucrose or high fructose corn syrup (HFCS-55) on diposity nd heptic lipid composition in rt offspring Crl R. Toop 1, Beverly S. Muhlhusler
TLR7 induces anergy in human CD4 + T cells
 TLR7 induces nergy in humn CD T cells Mrgrit Dominguez-Villr 1, Anne-Sophie Gutron 1, Mrine de Mrcken 1, Mrl J Keller & Dvid A Hfler 1 The recognition of microil ptterns y Toll-like receptors (TLRs) is
TLR7 induces nergy in humn CD T cells Mrgrit Dominguez-Villr 1, Anne-Sophie Gutron 1, Mrine de Mrcken 1, Mrl J Keller & Dvid A Hfler 1 The recognition of microil ptterns y Toll-like receptors (TLRs) is
Intestinal microbiota and energy balance pro s and con s
 Technicl University of Munich Nutrition nd Immunology Intestinl microiot nd energy lnce pro s nd con s Prof. Dr. Dirk Hller Chir of Nutrition nd Immunology School of Life Sciences Weihenstephn (WZW) Reserch
Technicl University of Munich Nutrition nd Immunology Intestinl microiot nd energy lnce pro s nd con s Prof. Dr. Dirk Hller Chir of Nutrition nd Immunology School of Life Sciences Weihenstephn (WZW) Reserch
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 1.138/nc286 Figure S1 e f Medium DMSO AktVIII PP242 Rp S6K1-I Gr1 + + + + + + Strvtion + + + + + IB: Akt-pT38 IB: Akt K-pT389 K IB: Rptor Gr1 shs6k1-a shs6k1-b shs6k1-c shrictor shrptor Gr1 c IB:
DOI: 1.138/nc286 Figure S1 e f Medium DMSO AktVIII PP242 Rp S6K1-I Gr1 + + + + + + Strvtion + + + + + IB: Akt-pT38 IB: Akt K-pT389 K IB: Rptor Gr1 shs6k1-a shs6k1-b shs6k1-c shrictor shrptor Gr1 c IB:
Supplementary information for: Low bone mass and changes in the osteocyte network in mice lacking autophagy in the osteoblast lineage
 Supplementry informtion for: Low one mss nd chnges in the osteocyte network in mice lcking utophgy in the osteolst linege Mrilin Piemontese, Meld Onl, Jinhu Xiong, Li Hn, Jeff D. Thostenson, Mri Almeid,
Supplementry informtion for: Low one mss nd chnges in the osteocyte network in mice lcking utophgy in the osteolst linege Mrilin Piemontese, Meld Onl, Jinhu Xiong, Li Hn, Jeff D. Thostenson, Mri Almeid,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:.8/nture89 4 4 Ilr -/- Ilr -/- Ilr -/- Cspse- -/- As -/- Nlrp -/- Il8 -/- Ilr -/- Supplementl figure. Inresed severity of NASH in inflmmsome-defiient mie, ut not in Ilr-defiient
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:.8/nture89 4 4 Ilr -/- Ilr -/- Ilr -/- Cspse- -/- As -/- Nlrp -/- Il8 -/- Ilr -/- Supplementl figure. Inresed severity of NASH in inflmmsome-defiient mie, ut not in Ilr-defiient
EFFECTS OF INGREDIENT AND WHOLE DIET IRRADIATION ON NURSERY PIG PERFORMANCE
 Swine Dy 21 EFFECTS OF INGREDIENT AND WHOLE DIET IRRADIATION ON NURSERY PIG PERFORMANCE J. M. DeRouchey, M. D. Tokch, J. L. Nelssen, R. D. Goodbnd, S. S. Dritz 1, J. C. Woodworth, M. J. Webster, B. W.
Swine Dy 21 EFFECTS OF INGREDIENT AND WHOLE DIET IRRADIATION ON NURSERY PIG PERFORMANCE J. M. DeRouchey, M. D. Tokch, J. L. Nelssen, R. D. Goodbnd, S. S. Dritz 1, J. C. Woodworth, M. J. Webster, B. W.
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 . Norml Physiologicl Conditions. SIRT1 Loss-of-Function S1. Model for the role of SIRT1 in the regultion of memory nd plsticity. () Our findings suggest tht SIRT1 normlly functions in coopertion with YY1,
. Norml Physiologicl Conditions. SIRT1 Loss-of-Function S1. Model for the role of SIRT1 in the regultion of memory nd plsticity. () Our findings suggest tht SIRT1 normlly functions in coopertion with YY1,
Supplementary Figure S1
 Supplementry Figure S Tissue weights (g).... Liver Hert Brin Pncres Len mss (g) 8 6 -% +% 8 6 Len mss Len mss (g) (% ody weight) Len mss (% ody weight) c Tiilis nterior weight (g).6...... Qudriceps weight
Supplementry Figure S Tissue weights (g).... Liver Hert Brin Pncres Len mss (g) 8 6 -% +% 8 6 Len mss Len mss (g) (% ody weight) Len mss (% ody weight) c Tiilis nterior weight (g).6...... Qudriceps weight
Expression of Three Cell Cycle Inhibitors during Development of Adipose Tissue
 Expression of Three Cell Cycle Inhiitors during Development of Adipose Tissue Jiin Zhng Deprtment of Animl Sciences Advisor: Michel E. Dvis Co-dvisor: Kichoon Lee Development of niml dipose tissue Hypertrophy
Expression of Three Cell Cycle Inhiitors during Development of Adipose Tissue Jiin Zhng Deprtment of Animl Sciences Advisor: Michel E. Dvis Co-dvisor: Kichoon Lee Development of niml dipose tissue Hypertrophy
Maternal omega-3 fatty acids regulate offspring obesity through persistent modulation of gut microbiota
 Roertson et l. Microiome (218) 6:95 https://doi.org/1.1186/s4168-18-476-6 RESEARCH Open Access Mternl omeg-3 ftty cids regulte offspring oesity through persistent modultion of gut microiot Ruiri C. Roertson
Roertson et l. Microiome (218) 6:95 https://doi.org/1.1186/s4168-18-476-6 RESEARCH Open Access Mternl omeg-3 ftty cids regulte offspring oesity through persistent modultion of gut microiot Ruiri C. Roertson
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:1.138/nture1794 BR EPFs BRI1? ERECTA TMM BSKs YDA PP2A BSU1 BIN2 pbzr1/2 BZR1/2 MKK4/5/7/9 MPK3/6 SPCH Cell growth Stomtl production Supplementry Figure 1. The model of BR nd stomtl signling pthwys.
doi:1.138/nture1794 BR EPFs BRI1? ERECTA TMM BSKs YDA PP2A BSU1 BIN2 pbzr1/2 BZR1/2 MKK4/5/7/9 MPK3/6 SPCH Cell growth Stomtl production Supplementry Figure 1. The model of BR nd stomtl signling pthwys.
11/7/2011. Disclosures. Psoriatic Arthritis (PsA) DC-STAMP I II III IV. None
 unstimulte stimulte 11/7/11 Ientifiction of Unique Suset + (Denritic Cell-Specific Trnsmemrne Protein) T cells with Th17 Signture in Psoritic rthritis () Ptients Disclosures None Y.H. Chiu, E.M. Schwrz,
unstimulte stimulte 11/7/11 Ientifiction of Unique Suset + (Denritic Cell-Specific Trnsmemrne Protein) T cells with Th17 Signture in Psoritic rthritis () Ptients Disclosures None Y.H. Chiu, E.M. Schwrz,
Not for Citation or Publication Without Consent of the Author
 Not for Cittion or Puliction Without Consent of the Author AN AUTOMATED SEX PHEROMONE TRAP FOR MONITORING ADULT CM AND OFM AND THE INFLUENCE OF TRAP COLOR ON MOTH AND NON-TARGET CAPTURES Brin L. Lehmn
Not for Cittion or Puliction Without Consent of the Author AN AUTOMATED SEX PHEROMONE TRAP FOR MONITORING ADULT CM AND OFM AND THE INFLUENCE OF TRAP COLOR ON MOTH AND NON-TARGET CAPTURES Brin L. Lehmn
Chronic high-sodium diet intake after weaning lead to neurogenic hypertension in adult Wistar rats
 Chronic high-sodium diet intke fter wening led to neurogenic hypertension in dult Wistr rts 1 Pul Mglhães Gomes; 2 Rento Willin Mrtins Sá; 1 Giovn Lopes Aguir; 1 Milede Hnner Sriv Pes; 1 Andréi Crvlho
Chronic high-sodium diet intke fter wening led to neurogenic hypertension in dult Wistr rts 1 Pul Mglhães Gomes; 2 Rento Willin Mrtins Sá; 1 Giovn Lopes Aguir; 1 Milede Hnner Sriv Pes; 1 Andréi Crvlho
DR. MARC PAGÈS Project Manager R&D Biologicals - Coccidia Projects, HIPRA
 DR. MARC PAGÈS Project Mnger R&D Biologicls - Coccidi Projects, HIPRA Dr. Mrc Pgès Bosch otined Microiology nd Genetics degree t the University of Brcelon in 1998. He otined his PhD working on the synptoneml
DR. MARC PAGÈS Project Mnger R&D Biologicls - Coccidi Projects, HIPRA Dr. Mrc Pgès Bosch otined Microiology nd Genetics degree t the University of Brcelon in 1998. He otined his PhD working on the synptoneml
SESSIONE I: RELATORI. Ghrelin: from oroxigenic signal to metabolic master regulator?
 SESSIONE I: RELATORI Ghrelin: from oroxigenic signl to metbolic mster regultor? Prof. Rocco Brzzoni Professore ssocito di Medicin Intern Università degli Studi di Trieste Ghrelin: d segnle oressizznte
SESSIONE I: RELATORI Ghrelin: from oroxigenic signl to metbolic mster regultor? Prof. Rocco Brzzoni Professore ssocito di Medicin Intern Università degli Studi di Trieste Ghrelin: d segnle oressizznte
Enhanced Chemopreventive Effect by Combining Quercetin and Green tea in Prostate Cancer
 Enhnced Chemopreventive Effect y Comining Quercetin nd Green te in Prostte Cncer Piwen Wng, MD, PhD Assistnt Professor, Division of Cncer Reserch nd Trining Chrles R. Drew University of Medicine nd Science
Enhnced Chemopreventive Effect y Comining Quercetin nd Green te in Prostte Cncer Piwen Wng, MD, PhD Assistnt Professor, Division of Cncer Reserch nd Trining Chrles R. Drew University of Medicine nd Science
The Ever Changing World of Feed Additives in The Poultry Industry
 The Ever Chnging World of Feed Additives in The Poultry Industry B. S. Lumpkins nd G.F. Mthis Southern Poultry Reserch Inc. Athens, GA, USA Outline Southern Poultry Reserch Impct of ethnol production of
The Ever Chnging World of Feed Additives in The Poultry Industry B. S. Lumpkins nd G.F. Mthis Southern Poultry Reserch Inc. Athens, GA, USA Outline Southern Poultry Reserch Impct of ethnol production of
Signaling by IL-6 promotes alternative activation of macrophages to limit endotoxemia and obesity-associated resistance to insulin
 Signling y promotes lterntive ctivtion of mcrophges to limit endotoxemi nd oesity-ssocited resistnce to insulin Nture Americ, Inc. All rights reserved. Jn Muer,9, Bhgirth Chursi,9, Juli Goldu, Merly C
Signling y promotes lterntive ctivtion of mcrophges to limit endotoxemi nd oesity-ssocited resistnce to insulin Nture Americ, Inc. All rights reserved. Jn Muer,9, Bhgirth Chursi,9, Juli Goldu, Merly C
Clinical Study Report Synopsis Drug Substance Naloxegol Study Code D3820C00018 Edition Number 1 Date 01 February 2013 EudraCT Number
 EudrCT Number 2012-001531-31 A Phse I, Rndomised, Open-lbel, 3-wy Cross-over Study in Helthy Volunteers to Demonstrte the Bioequivlence of the Nloxegol 25 mg Commercil nd Phse III Formultions nd to Assess
EudrCT Number 2012-001531-31 A Phse I, Rndomised, Open-lbel, 3-wy Cross-over Study in Helthy Volunteers to Demonstrte the Bioequivlence of the Nloxegol 25 mg Commercil nd Phse III Formultions nd to Assess
THE EVALUATION OF DEHULLED CANOLA MEAL IN THE DIETS OF GROWING AND FINISHING PIGS
 THE EVALUATION OF DEHULLED CANOLA MEAL IN THE DIETS OF GROWING AND FINISHING PIGS THE EVALUATION OF DEHULLED CANOLA MEAL IN THE DIETS OF GROWING AND FINISHING PIGS John F. Ptience nd Doug Gillis SUMMARY
THE EVALUATION OF DEHULLED CANOLA MEAL IN THE DIETS OF GROWING AND FINISHING PIGS THE EVALUATION OF DEHULLED CANOLA MEAL IN THE DIETS OF GROWING AND FINISHING PIGS John F. Ptience nd Doug Gillis SUMMARY
Optimisation of diets for Atlantic cod (Gadus morhua) broodstock: effect of arachidonic acid on egg & larval quality
 Optimistion of diets for Atlntic cod (Gdus morhu) roodstock: effect of rchidonic cid on egg & lrvl qulity Dr Gordon Bell, Ms. An Blnco, Dr Bill Roy, Dr Derek Roertson, Dr Jim Henderson nd Mr Richrd Prickett,
Optimistion of diets for Atlntic cod (Gdus morhu) roodstock: effect of rchidonic cid on egg & lrvl qulity Dr Gordon Bell, Ms. An Blnco, Dr Bill Roy, Dr Derek Roertson, Dr Jim Henderson nd Mr Richrd Prickett,
Effect of kazunoko lipid on the concentrations of plasma glucose and lipids and liver lipids in mice
 Effect of kzunoko lipid on the concentrtions of plsm glucose nd lipids nd liver lipids in mice Ntionl Food Reserch Institute Tomoyuki Higuchi, Nouy Shiri nd Hirmitsu Suzuki INTRODUCTION Kzunoko, which
Effect of kzunoko lipid on the concentrtions of plsm glucose nd lipids nd liver lipids in mice Ntionl Food Reserch Institute Tomoyuki Higuchi, Nouy Shiri nd Hirmitsu Suzuki INTRODUCTION Kzunoko, which
Effects of Sini San used alone and in combination with fluoxetine on central and peripheral 5-HT levels in a rat model of depression
 Online Sumissions:http://www.journltcm.com J Trdit Chin Med 2013 Octoer 15; 33(5): 674-681 info@journltcm.com ISSN 0255-2922 2013 JTCM. All rights reserved. EXPERIMENTAL STUDY TOPIC Effects of Sini Sn
Online Sumissions:http://www.journltcm.com J Trdit Chin Med 2013 Octoer 15; 33(5): 674-681 info@journltcm.com ISSN 0255-2922 2013 JTCM. All rights reserved. EXPERIMENTAL STUDY TOPIC Effects of Sini Sn
Heparanase promotes tumor infiltration and antitumor activity of CAR-redirected T- lymphocytes
 Supporting Online Mteril for Heprnse promotes tumor infiltrtion nd ntitumor ctivity of -redirected T- lymphocytes IgnzioCrun, Brr Svoldo, VlentinHoyos, Gerrit Weer, Ho Liu, Eugene S. Kim, Michel M. Ittmnn,
Supporting Online Mteril for Heprnse promotes tumor infiltrtion nd ntitumor ctivity of -redirected T- lymphocytes IgnzioCrun, Brr Svoldo, VlentinHoyos, Gerrit Weer, Ho Liu, Eugene S. Kim, Michel M. Ittmnn,
British Journal of Nutrition
 (11), 16, 1449 1456 q The Authors 11 doi:1.117/s71145111917 Fish oil comined with SCFA synergisticlly prevent tissue ccumultion of NEFA during weight loss in oese mice Miken H. Pedersen 1,, Lotte Luritzen
(11), 16, 1449 1456 q The Authors 11 doi:1.117/s71145111917 Fish oil comined with SCFA synergisticlly prevent tissue ccumultion of NEFA during weight loss in oese mice Miken H. Pedersen 1,, Lotte Luritzen
Supplementary Online Content
 Supplementry Online Content Zulmn DM, Pl Chee C, Ezeji-Okoye SC, et l. Effect of n intensive outptient progrm to ugment primry cre for high-need Veterns Affirs ptients: rndomized clinicl tril. JAMA Intern
Supplementry Online Content Zulmn DM, Pl Chee C, Ezeji-Okoye SC, et l. Effect of n intensive outptient progrm to ugment primry cre for high-need Veterns Affirs ptients: rndomized clinicl tril. JAMA Intern
PROVEN ANTICOCCIDIAL IN NEW FORMULATION
 PROVEN ANTICOCCIDIAL IN NEW FORMULATION Coxidin 100 microgrnulte A coccidiosttic dditive for roilers, chickens rered for lying nd turkeys Contins 100 g of monensin sodium per kg Aville s homogenous grnules
PROVEN ANTICOCCIDIAL IN NEW FORMULATION Coxidin 100 microgrnulte A coccidiosttic dditive for roilers, chickens rered for lying nd turkeys Contins 100 g of monensin sodium per kg Aville s homogenous grnules
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION. Cytochrome P450-2E1 promotes fast food-mediated hepatic fibrosis
 SUPPLEMENTARY INRMATION Cytochrome P-E1 promotes fst food-medited heptic fibrosis Mohmed A. Abdelmegeed, Youngshim Choi, Grzegorz Godlewski b, Seung-Kwon H, Atryee Bnerjee, Sehwn Jng, nd Byoung-Joon Song
SUPPLEMENTARY INRMATION Cytochrome P-E1 promotes fst food-medited heptic fibrosis Mohmed A. Abdelmegeed, Youngshim Choi, Grzegorz Godlewski b, Seung-Kwon H, Atryee Bnerjee, Sehwn Jng, nd Byoung-Joon Song
A Specific Gut Microbiota Dysbiosis of Type 2 Diabetic Mice Induces GLP-1 Resistance through an Enteric NO-Dependent and Gut-Brain Axis Mechanism
 Article A Specific Gut Microiot Dysiosis of Type 2 Dietic Mice Induces GLP-1 Resistnce through n Enteric NO-Dependent nd Gut-Brin Axis Mechnism Grphicl Astrct Authors Estelle Grsset, Anthony Puel, Julie
Article A Specific Gut Microiot Dysiosis of Type 2 Dietic Mice Induces GLP-1 Resistnce through n Enteric NO-Dependent nd Gut-Brin Axis Mechnism Grphicl Astrct Authors Estelle Grsset, Anthony Puel, Julie
Anti-Obesity Potential of Gallic Acid from Labisia pumila, through Augmentation of Adipokines in High Fat Diet Induced Obesity in C57BL/6 Mice
 Advnces in Reserch 2(10): 556-570, 2014, Article no. AIR.2014.10.004 SCIENCEDOMAIN interntionl www.sciencedomin.org Anti-Oesity Potentil of Gllic Acid from Lisi pumil, through Augmenttion of Adipokines
Advnces in Reserch 2(10): 556-570, 2014, Article no. AIR.2014.10.004 SCIENCEDOMAIN interntionl www.sciencedomin.org Anti-Oesity Potentil of Gllic Acid from Lisi pumil, through Augmenttion of Adipokines
CheckMate 153: Randomized Results of Continuous vs 1-Year Fixed-Duration Nivolumab in Patients With Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
 CheckMte 53: Rndomized Results of Continuous vs -Yer Fixed-Durtion Nivolumb in Ptients With Advnced Non-Smll Cell Lung Cncer Abstrct 297O Spigel DR, McCleod M, Hussein MA, Wterhouse DM, Einhorn L, Horn
CheckMte 53: Rndomized Results of Continuous vs -Yer Fixed-Durtion Nivolumb in Ptients With Advnced Non-Smll Cell Lung Cncer Abstrct 297O Spigel DR, McCleod M, Hussein MA, Wterhouse DM, Einhorn L, Horn
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:.3/nture93 d 5 Rttlesnke DRG (reds) Rttlesnke TG (reds) c 3 TRPV1 other TRPs 1 1 3 Non-pit snke TG (reds) SFig. 1 5 5 3 other TRPs TRPV1 1 1 3 Non-pit snke DRG (reds) 5 Antomy of the pit orgn nd comprison
doi:.3/nture93 d 5 Rttlesnke DRG (reds) Rttlesnke TG (reds) c 3 TRPV1 other TRPs 1 1 3 Non-pit snke TG (reds) SFig. 1 5 5 3 other TRPs TRPV1 1 1 3 Non-pit snke DRG (reds) 5 Antomy of the pit orgn nd comprison
DOI /mnfr
 3 Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 15, 59, 3 35 DOI 1.1/mnfr.1399 RESEARCH ARTICLE Ursolic cid improves lipid nd glucose metolism in high-ft-fed C57BL/6J mice y ctivting peroxisome prolifertor-ctivted receptor lph
3 Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 15, 59, 3 35 DOI 1.1/mnfr.1399 RESEARCH ARTICLE Ursolic cid improves lipid nd glucose metolism in high-ft-fed C57BL/6J mice y ctivting peroxisome prolifertor-ctivted receptor lph
Effect of Oral Administration of Propylene Glycol on Serum Glucose Concentrations in Periparturient Dairy Cows
 Ksetsrt J. (Nt. Sci.) 37 : 145-149 (2003) Effect of Orl Administrtion of Propylene Glycol on Serum Glucose Concentrtions in Periprturient Diry Cows Theer Rukkwmsuk, Nrongpol Petploi, Ing-orn Preechnvinit,
Ksetsrt J. (Nt. Sci.) 37 : 145-149 (2003) Effect of Orl Administrtion of Propylene Glycol on Serum Glucose Concentrtions in Periprturient Diry Cows Theer Rukkwmsuk, Nrongpol Petploi, Ing-orn Preechnvinit,
Effect of fungicide timing and wheat varietal resistance on Mycosphaerella graminicola and its sterol 14 α-demethylation-inhibitorresistant
 Effect of fungicide timing nd whet vrietl resistnce on Mycospherell grminicol nd its sterol 14 α-demethyltion-inhiitorresistnt genotypes Didierlurent L., Roisin-Fichter C., Snssené J., Selim S. Pltform
Effect of fungicide timing nd whet vrietl resistnce on Mycospherell grminicol nd its sterol 14 α-demethyltion-inhiitorresistnt genotypes Didierlurent L., Roisin-Fichter C., Snssené J., Selim S. Pltform
Comparison of pro- and anti-inflammatory responses in paired human primary airway epithelial cells and alveolar macrophages
 Murk et l. Respirtory Reserch (2018) 19:126 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12931-018-0825-9 RESEARCH Comprison of pro- nd nti-inflmmtory responses in pired humn primry irwy epithelil cells nd lveolr mcrophges
Murk et l. Respirtory Reserch (2018) 19:126 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12931-018-0825-9 RESEARCH Comprison of pro- nd nti-inflmmtory responses in pired humn primry irwy epithelil cells nd lveolr mcrophges
Extraction and Some Functional Properties of Protein Extract from Rice Bran
 Ksetsrt J. (Nt. Sci.) 40 : 209-214 (2006) Extrction nd Some Functionl Properties of Protein Extrct from Rice Brn Chockchi Theerkulkit*, Siree Chiseri nd Siriwt Mongkolknchnsiri ABSTRACT Rice brn protein
Ksetsrt J. (Nt. Sci.) 40 : 209-214 (2006) Extrction nd Some Functionl Properties of Protein Extrct from Rice Brn Chockchi Theerkulkit*, Siree Chiseri nd Siriwt Mongkolknchnsiri ABSTRACT Rice brn protein
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMEARY IFORMAIO doi:./nture correction to Supplementry Informtion Adenom-linked rrier defects nd microil products drive IL-/IL-7-medited tumour growth Sergei I. Grivennikov, Kepeng Wng, Dniel Mucid,
SUPPLEMEARY IFORMAIO doi:./nture correction to Supplementry Informtion Adenom-linked rrier defects nd microil products drive IL-/IL-7-medited tumour growth Sergei I. Grivennikov, Kepeng Wng, Dniel Mucid,
Check your understanding 3
 1 Wht is the difference etween pssive trnsport nd ctive trnsport? Pssive trnsport is the movement of prticles not requiring energy. Movement of prticles in ctive trnsport uses energy. 2 A gs tp in the
1 Wht is the difference etween pssive trnsport nd ctive trnsport? Pssive trnsport is the movement of prticles not requiring energy. Movement of prticles in ctive trnsport uses energy. 2 A gs tp in the
Significance of Expression of TGF- in Pulmonary Metastasis in Non-small Cell Lung Cancer Tissues
 Originl Article Significnce of Expression of in Pulmonry Metstsis in Non-smll Cell Lung Cncer Tissues Hisshi Sji, Hruhiko Nkmur, Idiris Awut, Norihito Kwski, Msru Hgiwr, Akihiko Ogt, Mkoto Hosk, Tkmoto
Originl Article Significnce of Expression of in Pulmonry Metstsis in Non-smll Cell Lung Cncer Tissues Hisshi Sji, Hruhiko Nkmur, Idiris Awut, Norihito Kwski, Msru Hgiwr, Akihiko Ogt, Mkoto Hosk, Tkmoto
ABSTRACT. Marek s disease virus (MDV) infection causes atherosclerosis, and prior
 ABSTRACT Title of Document: Directed By: COMPARATIVE STUDY OF LIPOPROTEIN METABOLISM IN MAREK S DISEASE SUSCEPTIBLE AND RESISTANT LINES Ping Yun, Mster of Science, 2010 Assistnt professor Dr. Jiuzhou Song,
ABSTRACT Title of Document: Directed By: COMPARATIVE STUDY OF LIPOPROTEIN METABOLISM IN MAREK S DISEASE SUSCEPTIBLE AND RESISTANT LINES Ping Yun, Mster of Science, 2010 Assistnt professor Dr. Jiuzhou Song,
mir-155 is dispensable in monosodium urate-induced gouty inflammation in mice
 Yng et l. Arthritis Reserch & Therpy (2018) 20:144 https://doi.org/10.1186/s13075-018-1550-y RESEARCH ARTICLE mir-155 is dispensle in monosodium urte-induced gouty inflmmtion in mice Qiin Yng 1,3,4, Quno
Yng et l. Arthritis Reserch & Therpy (2018) 20:144 https://doi.org/10.1186/s13075-018-1550-y RESEARCH ARTICLE mir-155 is dispensle in monosodium urte-induced gouty inflmmtion in mice Qiin Yng 1,3,4, Quno
INFLUENCE OF DIFFERENT STRAINS AND WAYS OF INOCULATION ON THE RABBIT S RESPONSE TO EXPERIMENTAL INFECTION WITH PASTEURELLA MULTOCIDA
 Pthology nd Hygiene INFLUENCE OF DIFFERENT STRAINS AND WAYS OF INOCULATION ON THE RABBIT S RESPONSE TO EXPERIMENTAL INFECTION WITH PASTEURELLA MULTOCIDA Kulcsár G. 1, Fáián K. 1 *, Brn T. 1, Virág Gy.
Pthology nd Hygiene INFLUENCE OF DIFFERENT STRAINS AND WAYS OF INOCULATION ON THE RABBIT S RESPONSE TO EXPERIMENTAL INFECTION WITH PASTEURELLA MULTOCIDA Kulcsár G. 1, Fáián K. 1 *, Brn T. 1, Virág Gy.
Brown adipose tissue activity controls triglyceride clearance
 Supplementry informtion Brown dipose tissue ctivity s triglyceride clernce Alexnder Brtelt 1, Oliver T. Bruns 2, Rudolph Reimer 2, Heinz Hohenerg 2, Hrld Ittrich 3, Kersten Peldschus 3, Michel G. Kul 3,
Supplementry informtion Brown dipose tissue ctivity s triglyceride clernce Alexnder Brtelt 1, Oliver T. Bruns 2, Rudolph Reimer 2, Heinz Hohenerg 2, Hrld Ittrich 3, Kersten Peldschus 3, Michel G. Kul 3,
Dr. Javier Polo Vice President Research & Development
 Efecto de l suplementción con concentrdo de inmunoglobulins prtir del suero bovino en l Microbiot y su contribución l slud intestinl y l sistem nervioso centrl Dr. Jvier Polo Vice President Reserch & Development
Efecto de l suplementción con concentrdo de inmunoglobulins prtir del suero bovino en l Microbiot y su contribución l slud intestinl y l sistem nervioso centrl Dr. Jvier Polo Vice President Reserch & Development
Systemic Anti-TNFa Treatment Restores Diabetes-Impaired Skin Repair in ob/ob Mice by Inactivation of Macrophages
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Systemic Anti-TNF Tretment Restores Dietes-Impired Skin Repir in o/o Mice y Inctivtion of Mcrophges Itmr Goren 1, Elke Müller 1, Dn Schiefelein 1, Urs Christen 1, Josef Pfeilschifter 1,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Systemic Anti-TNF Tretment Restores Dietes-Impired Skin Repir in o/o Mice y Inctivtion of Mcrophges Itmr Goren 1, Elke Müller 1, Dn Schiefelein 1, Urs Christen 1, Josef Pfeilschifter 1,
Inflammation & Cell Signaling 2014; 1: e117. doi: /ics.117; 2014 by Nirmal Verma, et al.
 Inflmmtion & Cell Signling 14; 1: e117. doi: 1.148/ics.117; 14 y Nirml Verm, et l. http://www.smrtscitech.com/index.php/ics RESEARCH HIGHLIGHT Siliinin meliortes Dextrn Sodium Slt induced colitis in mice
Inflmmtion & Cell Signling 14; 1: e117. doi: 1.148/ics.117; 14 y Nirml Verm, et l. http://www.smrtscitech.com/index.php/ics RESEARCH HIGHLIGHT Siliinin meliortes Dextrn Sodium Slt induced colitis in mice
Associations of Psoriatic Arthritis and Cardiovascular Conditions in a Large Population
 ville online: www.kp.org/permnentejournl Originl rticle Associtions of Psoritic Arthritis nd Crdiovsculr Conditions in Lrge Popultion Svetln Kondrtiouk, DO Ntli Udltsov, PhD Arthur L Kltsky, MD Astrct
ville online: www.kp.org/permnentejournl Originl rticle Associtions of Psoritic Arthritis nd Crdiovsculr Conditions in Lrge Popultion Svetln Kondrtiouk, DO Ntli Udltsov, PhD Arthur L Kltsky, MD Astrct
Curcumin attenuates Nrf2 signaling defect, oxidative stress in muscle and glucose intolerance in high fat diet-fed mice
 Online Sumissions: http://www.wjgnet.com/1948-938of fice wjd@wjgnet.com doi:239/wjd.v3.i.94 World J Dietes 212 My 1; 3(): 94-14 ISSN 1948-938 (online) 212 Bishideng. All rights reserved. ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Online Sumissions: http://www.wjgnet.com/1948-938of fice wjd@wjgnet.com doi:239/wjd.v3.i.94 World J Dietes 212 My 1; 3(): 94-14 ISSN 1948-938 (online) 212 Bishideng. All rights reserved. ORIGINAL ARTICLE
A rt i c l e s. a Events (% of max)
 Continuous requirement for the TCR in regultory T cell function Andrew G Levine 1,, Aron Arvey 1,,4, Wei Jin 1,,4 & Alexnder Y Rudensky 1 3 14 Nture Americ, Inc. All rights reserved. Foxp3 + regultory
Continuous requirement for the TCR in regultory T cell function Andrew G Levine 1,, Aron Arvey 1,,4, Wei Jin 1,,4 & Alexnder Y Rudensky 1 3 14 Nture Americ, Inc. All rights reserved. Foxp3 + regultory
Development of a Diagnostic Test for Anaerobic Periodontal Infections Based on Plaque Hydrolysis of Benzoyl-
 JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, July 1990, p. 1551-1559 0095-1137/90/071551-09$02.00/0 Copyright 1990, Americn Society for Microiology Vol. 28, No. 7 Development of Dignostic Test for Aneroic Periodontl
JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, July 1990, p. 1551-1559 0095-1137/90/071551-09$02.00/0 Copyright 1990, Americn Society for Microiology Vol. 28, No. 7 Development of Dignostic Test for Aneroic Periodontl
Supplementary Online Content
 Supplementry Online Content Rieckmnn N, Kronish IM, Shpiro PA, Whng W, Dvidson KW. Serotonin reuptke inhibitor use, depression, nd long-term outcomes fter n cute coronry : prospective cohort study. JAMA
Supplementry Online Content Rieckmnn N, Kronish IM, Shpiro PA, Whng W, Dvidson KW. Serotonin reuptke inhibitor use, depression, nd long-term outcomes fter n cute coronry : prospective cohort study. JAMA
ENERGY CONTENT OF BARLEY
 ENERGY CONTENT OF BARLEY VARIATION IN THE DIETARY ENERGY CONTENT OF BARLEY Shwn Firbirn, John Ptience, Hnk Clssen nd Ruurd Zijlstr SUMMARY Formultion of commercil pig diets requires n incresing degree
ENERGY CONTENT OF BARLEY VARIATION IN THE DIETARY ENERGY CONTENT OF BARLEY Shwn Firbirn, John Ptience, Hnk Clssen nd Ruurd Zijlstr SUMMARY Formultion of commercil pig diets requires n incresing degree
Invasive Pneumococcal Disease Quarterly Report. July September 2017
 Invsive Pneumococcl Disese Qurterly Report July September 2017 Prepred s prt of Ministry of Helth contrct for scientific services by Rebekh Roos Helen Heffernn October 2017 Acknowledgements This report
Invsive Pneumococcl Disese Qurterly Report July September 2017 Prepred s prt of Ministry of Helth contrct for scientific services by Rebekh Roos Helen Heffernn October 2017 Acknowledgements This report
THE EFFECT OF FASTING ON ANTI-INFLAMMATORY MEDIATORS, IL-1RA AND IL-1R2, AND THEIR ROLE IN RESISTANCE TO SICKNESS BEHAVIORS IN MICE
 THE EFFECT OF FASTING ON ANTI-INFLAMMATORY MEDIATORS, IL-1RA AND IL-1R2, AND THEIR ROLE IN RESISTANCE TO SICKNESS BEHAVIORS IN MICE BY JENNIFER J. JOESTING THESIS Sumitted in prtil fulfillment of the requirements
THE EFFECT OF FASTING ON ANTI-INFLAMMATORY MEDIATORS, IL-1RA AND IL-1R2, AND THEIR ROLE IN RESISTANCE TO SICKNESS BEHAVIORS IN MICE BY JENNIFER J. JOESTING THESIS Sumitted in prtil fulfillment of the requirements
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi: 10.1038/nture07679 Emryonic Stem (ES) cell Hemngiolst Flk1 + Blst Colony 3 to 3.5 Dys 3-4 Dys ES differentition Sort of Flk1 + cells Supplementry Figure 1. Chrcteristion of lst colony development.
doi: 10.1038/nture07679 Emryonic Stem (ES) cell Hemngiolst Flk1 + Blst Colony 3 to 3.5 Dys 3-4 Dys ES differentition Sort of Flk1 + cells Supplementry Figure 1. Chrcteristion of lst colony development.
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:1.138/nture1188 1mM CCl 2 (min) 3 4 6 CCl 2 (mm) for 4min.1. 1 (mm) Pro- d WT GdCl 3 R-68 -/- P2x7r -/- -/- Csp1 -/- WT -/- P2x7r -/- -/- Csp1 -/- Csp1 (p2) (p17) Pro-Csp1
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:1.138/nture1188 1mM CCl 2 (min) 3 4 6 CCl 2 (mm) for 4min.1. 1 (mm) Pro- d WT GdCl 3 R-68 -/- P2x7r -/- -/- Csp1 -/- WT -/- P2x7r -/- -/- Csp1 -/- Csp1 (p2) (p17) Pro-Csp1
The intrinsic prostaglandin E 2 EP 4 system of the renal tubular epithelium limits the development of tubulointerstitial fibrosis in mice
 originl rticle http://www.kidney-interntionl.org & 1 Interntionl Society of Nephrology see commentry on pge 13 The intrinsic prostglndin E EP system of the renl tuulr epithelium limits the development
originl rticle http://www.kidney-interntionl.org & 1 Interntionl Society of Nephrology see commentry on pge 13 The intrinsic prostglndin E EP system of the renl tuulr epithelium limits the development
Input from external experts and manufacturer on the 2 nd draft project plan Stool DNA testing for early detection of colorectal cancer
 Input externl experts nd mnufcturer on the 2 nd drft project pln Stool DNA testing for erly detection of colorectl cncer (Project ID:OTJA10) All s nd uthor s replies on the 2nd drft project pln Stool DNA
Input externl experts nd mnufcturer on the 2 nd drft project pln Stool DNA testing for erly detection of colorectl cncer (Project ID:OTJA10) All s nd uthor s replies on the 2nd drft project pln Stool DNA
De novo lipogenesis in human fat and liver is linked to ChREBP-b and metabolic health
 Received 2 Aug 2 Accepted 23 Jn 213 Pulished 26 Fe 213 DOI: 1.13/ncomms253 De novo lipogenesis in humn ft nd liver is linked to ChREBP- nd metolic helth Leh Eissing 1, *, Thoms Scherer 2, *,w, Klus Tödter
Received 2 Aug 2 Accepted 23 Jn 213 Pulished 26 Fe 213 DOI: 1.13/ncomms253 De novo lipogenesis in humn ft nd liver is linked to ChREBP- nd metolic helth Leh Eissing 1, *, Thoms Scherer 2, *,w, Klus Tödter
ARTICLE. E. Pavlova 1, N. Atanassova 1, C. McKinnell 2, R.M. Sharpe 2 1 Institute of Experimental Morphology, Pathology and Anthropology with Museum,
 DOI:.554/5YRTIMB..3 OPPOSITE MODELS OF EXPRESSION OF ANDROGEN RECEPTOR (AR) AND RETINOIC ACID RECEPTOR-α (RAR-α) IN THE ONSET OF MALE GERM CELL DEVELOPMENT IN HORMONALLY MANIPULATED RATS E. Pvlov, N. Atnssov,
DOI:.554/5YRTIMB..3 OPPOSITE MODELS OF EXPRESSION OF ANDROGEN RECEPTOR (AR) AND RETINOIC ACID RECEPTOR-α (RAR-α) IN THE ONSET OF MALE GERM CELL DEVELOPMENT IN HORMONALLY MANIPULATED RATS E. Pvlov, N. Atnssov,
I n the immune response against viruses like influenza, NK cells play an important role1. NK cells express both
 OPEN SUBJECT AREAS: INFECTION MUCOSAL IMMUNOLOGY NK CELLS INFLUENZA VIRUS Differentil lung NK cell responses in vin influenz virus infected chickens correlte with pthogenicity Christine A. Jnsen 1, Eveline
OPEN SUBJECT AREAS: INFECTION MUCOSAL IMMUNOLOGY NK CELLS INFLUENZA VIRUS Differentil lung NK cell responses in vin influenz virus infected chickens correlte with pthogenicity Christine A. Jnsen 1, Eveline
Effects of Cinnamomum zeylanicum (Ceylon cinnamon) on blood glucose and lipids in a diabetic and healthy rat model
 PHCOG RES. ORIGINAL ARTICLE Effects of Cinnmomum zeylnicum (Ceylon cinnmon) on lood glucose nd lipids in dietic nd helthy rt model Priyng Rnsinghe, Snj Perer, Mngl Guntilke 1, Erng Aeywrdene, Nuwn Gunpl,
PHCOG RES. ORIGINAL ARTICLE Effects of Cinnmomum zeylnicum (Ceylon cinnmon) on lood glucose nd lipids in dietic nd helthy rt model Priyng Rnsinghe, Snj Perer, Mngl Guntilke 1, Erng Aeywrdene, Nuwn Gunpl,
Study of Stress Distribution in the Tibia During Stance Phase Running Using the Finite Element Method
 Ksetsrt J. (Nt. Sci.) 48 : 729-739 (2014) Study of Stress Distriution in the Tii During Stnce Phse Running Using the Finite Element Method Thepwchr Ruchirh 1, Tumrong Puttpitukporn 1, * nd Siriporn Ssimontonkul
Ksetsrt J. (Nt. Sci.) 48 : 729-739 (2014) Study of Stress Distriution in the Tii During Stnce Phse Running Using the Finite Element Method Thepwchr Ruchirh 1, Tumrong Puttpitukporn 1, * nd Siriporn Ssimontonkul
Severe Gummy Smile with Class II Malocclusion Treated with LeFort I Osteotomy Combined with Horseshoe Osteotomy and Intraoral Vertical Ramus
 2013 67 1 5560 Severe Gummy Smile with Clss II Mlocclusion Treted with LeFort I Osteotomy Comined with Horseshoe Osteotomy nd Introrl Verticl Rmus Osteotomy * 56 Shimo et l. Act Med. Okym Vol. 67, No.
2013 67 1 5560 Severe Gummy Smile with Clss II Mlocclusion Treted with LeFort I Osteotomy Comined with Horseshoe Osteotomy nd Introrl Verticl Rmus Osteotomy * 56 Shimo et l. Act Med. Okym Vol. 67, No.
Consumer perceptions of meat quality and shelf-life in commercially raised broilers compared to organic free range broilers
 Consumer perceptions of met qulity nd shelf-life in commercilly rised roilers compred to orgnic free rnge roilers C.Z. ALVARADO 1 *, E. WENGER 2 nd S. F. O KEEFE 3 1 Texs Tech University, Box 42141 Luock,
Consumer perceptions of met qulity nd shelf-life in commercilly rised roilers compred to orgnic free rnge roilers C.Z. ALVARADO 1 *, E. WENGER 2 nd S. F. O KEEFE 3 1 Texs Tech University, Box 42141 Luock,
Using Paclobutrazol to Suppress Inflorescence Height of Potted Phalaenopsis Orchids
 Using Pcloutrzol to Suppress Inflorescence Height of Potted Phlenopsis Orchids A REPORT SUBMITTED TO FINE AMERICAS Linsey Newton nd Erik Runkle Deprtment of Horticulture Spring 28 Using Pcloutrzol to Suppress
Using Pcloutrzol to Suppress Inflorescence Height of Potted Phlenopsis Orchids A REPORT SUBMITTED TO FINE AMERICAS Linsey Newton nd Erik Runkle Deprtment of Horticulture Spring 28 Using Pcloutrzol to Suppress
PDGF-BB secreted by preosteoclasts induces angiogenesis during coupling with osteogenesis
 Supplementry Informtion PDGF-BB secreted y preosteoclsts induces ngiogenesis during coupling with osteogenesis Hui Xie, Zhung Cui, Long Wng, Zhuying Xi, Yin Hu, Lingling Xin, Chngjun Li, Ling Xie, Jnet
Supplementry Informtion PDGF-BB secreted y preosteoclsts induces ngiogenesis during coupling with osteogenesis Hui Xie, Zhung Cui, Long Wng, Zhuying Xi, Yin Hu, Lingling Xin, Chngjun Li, Ling Xie, Jnet
EVALUATION OF DIFFERENT COPPER SOURCES AS A GROWTH PROMOTER IN SWINE FINISHING DIETS 1
 Swine Dy 2001 Contents EVALUATION OF DIFFERENT COPPER SOURCES AS A GROWTH PROMOTER IN SWINE FINISHING DIETS 1 C. W. Hstd, S. S. Dritz 2, J. L. Nelssen, M. D. Tokch, nd R. D. Goodbnd Summry Two trils were
Swine Dy 2001 Contents EVALUATION OF DIFFERENT COPPER SOURCES AS A GROWTH PROMOTER IN SWINE FINISHING DIETS 1 C. W. Hstd, S. S. Dritz 2, J. L. Nelssen, M. D. Tokch, nd R. D. Goodbnd Summry Two trils were
Relationship between serum irisin, glycemic indices, and renal function in type 2 diabetic patients
 J Renl Inj Prev. 2017; 6(2): 88-92. http://journlrip.com Journl of Renl Injury Prevention DOI: 10.15171/jrip.2017.17 Reltionship between serum irisin, glycemic indices, nd renl function in type 2 dibetic
J Renl Inj Prev. 2017; 6(2): 88-92. http://journlrip.com Journl of Renl Injury Prevention DOI: 10.15171/jrip.2017.17 Reltionship between serum irisin, glycemic indices, nd renl function in type 2 dibetic
 DOI: 10.1038/nc2331 PCre;Ros26R 12 h induction 48 h induction Vegfr3 i EC c d ib4 24 h induction VEGFR3 e Fold chnge 1.0 0.5 P < 0.05 Vegfr3 i EC Vegfr3 Figure S1 Cre ctivtion leds to genetic deletion
DOI: 10.1038/nc2331 PCre;Ros26R 12 h induction 48 h induction Vegfr3 i EC c d ib4 24 h induction VEGFR3 e Fold chnge 1.0 0.5 P < 0.05 Vegfr3 i EC Vegfr3 Figure S1 Cre ctivtion leds to genetic deletion
RSV-specific airway resident memory CD8 þ T cells and differential disease severity after experimental human infection
 Received Oct 15 Accepted 1 Nov 15 Pulished 1 Dec 15 DOI: 1.138/ncomms1 OPEN RSV-specific irwy resident memory CD8 þ T cells nd differentil disese severity fter experimentl humn infection Agnieszk Jozwik
Received Oct 15 Accepted 1 Nov 15 Pulished 1 Dec 15 DOI: 1.138/ncomms1 OPEN RSV-specific irwy resident memory CD8 þ T cells nd differentil disese severity fter experimentl humn infection Agnieszk Jozwik
Dietary oil composition differentially modulates intestinal endotoxin transport and postprandial endotoxemia
 Mni et l. Nutrition & Metolism 2013, 10:6 http://www.nutritionndmetolism.com/content/10/1/6 RESEARCH Open Access Dietry oil composition differentilly modultes intestinl endotoxin trnsport nd postprndil
Mni et l. Nutrition & Metolism 2013, 10:6 http://www.nutritionndmetolism.com/content/10/1/6 RESEARCH Open Access Dietry oil composition differentilly modultes intestinl endotoxin trnsport nd postprndil
Agilent G6825AA MassHunter Pathways to PCDL Software Quick Start Guide
 Agilent G6825AA MssHunter Pthwys to PCDL Softwre Quick Strt Guide Wht is Agilent Pthwys to PCDL? Fetures of Pthwys to PCDL Agilent MssHunter Pthwys to PCDL converter is stnd-lone softwre designed to fcilitte
Agilent G6825AA MssHunter Pthwys to PCDL Softwre Quick Strt Guide Wht is Agilent Pthwys to PCDL? Fetures of Pthwys to PCDL Agilent MssHunter Pthwys to PCDL converter is stnd-lone softwre designed to fcilitte
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 TM TM tip link horizontl top connectors 1 leucine-rich (21 %) otoncorin-like 1809 ntigenic peptides B D signl peptide hydrophoic segment proline/threonine-rich (79 %) Supplementry Figure 1. () The outer
TM TM tip link horizontl top connectors 1 leucine-rich (21 %) otoncorin-like 1809 ntigenic peptides B D signl peptide hydrophoic segment proline/threonine-rich (79 %) Supplementry Figure 1. () The outer
IL-18 induction of IgE: dependence on CD4 + T cells, IL-4 and STAT6
 ARTICLES IL-18 induction of IgE: dependence on CD4 + T cells, IL-4 nd STAT6 Tomohiro Yoshimoto 1,2,7, Hitoshi Mizutni 3, Hiroko Tsutsui 1, Nncy Noen-Truth 6, Kei-ichi Ymnk 3, Minoru Tnk 4, Shinzo Izumi
ARTICLES IL-18 induction of IgE: dependence on CD4 + T cells, IL-4 nd STAT6 Tomohiro Yoshimoto 1,2,7, Hitoshi Mizutni 3, Hiroko Tsutsui 1, Nncy Noen-Truth 6, Kei-ichi Ymnk 3, Minoru Tnk 4, Shinzo Izumi
