De novo lipogenesis in human fat and liver is linked to ChREBP-b and metabolic health
|
|
|
- Marybeth Webster
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Received 2 Aug 2 Accepted 23 Jn 213 Pulished 26 Fe 213 DOI: 1.13/ncomms253 De novo lipogenesis in humn ft nd liver is linked to ChREBP- nd metolic helth Leh Eissing 1, *, Thoms Scherer 2, *,w, Klus Tödter 1, Uwe Knippschild 3, Jn Willem Greve 4, Wim A. Buurmn 5, Hns O. Pinnschmidt 6, Snder S. Rensen 5, Ann M. Wolf 3, Alexnder Brtelt 1, Joerg Heeren 1, Christoph Buettner 2 & Ludger Schej 1 Clinicl interest in de novo lipogenesis hs een sprked y recent studies in rodents demonstrting tht de novo lipogenesis specificlly in white dipose tissue produces the insulin-sensitizing ftty cid plmitolete. By contrst, heptic lipogenesis is thought to contriute to metolic disese. How de novo lipogenesis in white dipose tissue versus liver is ltered in humn oesity nd insulin resistnce is poorly understood. Here we show tht lipogenic enzymes nd the glucose trnsporter-4 re mrkedly decresed in white dipose tissue of insulin-resistnt oese individuls compred with non-oese controls. By contrst, lipogenic enzymes re sustntilly upregulted in the liver of oese sujects. Britric weight loss restored de novo lipogenesis nd glucose trnsporter-4 gene expression in white dipose tissue. Notly, lipogenic gene expression in oth white dipose tissue nd liver ws strongly linked to the expression of crohydrte-responsive element-inding protein- nd to metolic risk mrkers. Thus, de novo lipogenesis predicts metolic helth in humns in tissue-specific mnner nd is likely regulted y glucose-dependent crohydrte-responsive element-inding protein ctivtion. 1 Deprtment of Biochemistry nd Moleculr Cell Biology, University Medicl Center Hmurg-Eppendorf, D-2246 Hmurg, Germny. 2 Deprtment of Medicine, Mount Sini School of Medicine, New York, New York, USA. 3 Deprtment of Generl-, nd Viscerl Surgery, University of Ulm, D-1 Ulm, Germny. 4 Deprtment of Generl Surgery, Atrium Medicl Centre Prkstd, 641CX Heerlen, The Netherlnds. 5 Deprtment of Generl Surgery, NUTRIM School for Nutrition, Toxicology nd Metolism Reserch Mstricht, Mstricht University Medicl Centre, 622ER Mstricht, The Netherlnds. 6 Deprtment of Medicl Biometry nd Epidemiology, University Medicl Center Hmurg-Eppendorf, D-2246 Hmurg, Germny. * These uthors contriuted eqully to this work. w Present ddress: Division of Endocrinology nd Metolism, Deprtment of Internl Medicine III, Medicl University of Vienn, Wehringer Guertel 1-2, 1 Vienn, Austri. Correspondence nd requests for mterils should e ddressed to L.S. (emil: l.schej@uke.de). NATURE COMMUNICATIONS 4:152 DOI: 1.13/ncomms & 213 Mcmilln Pulishers Limited. All rights reserved.
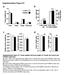
2 NATURE COMMUNICATIONS DOI: 1.13/ncomms253 Lipid metolism in white dipose tissue (WAT) nd the liver contriute to whole-ody metolic homoeostsis 1 3. Recent rodent studies demonstrted tht de novo lipogenesis (DNL), the synthesis of ftty cids from non-lipid precursors, in WAT is downregulted in oesity nd tht restoring DNL selectively in WAT reverts oesity-dependent insulin resistnce 4,5, suggesting tht reduction in DNL or ltertions in the relevnt products such s monounsturted ftty cids is n importnt contriutor to systemic insulin resistnce nd metolic disese. Plmitolete (C16:1n), DNL-derived ftty cid, ppers to medite the insulin-sensitizing effects of DNL in murine WAT 4,6,. In contrst to WAT, DNL in the liver hs een found to e upregulted in rodent nd humn oesity, where it is elieved to promote lipotoxicity, insulin resistnce, non-lcoholic ftty liver disese (NAFLD) nd therogenic dyslipidemi. Proposed moleculr mechnisms of DNL-induced lipotoxicity re, for exmple, exggerted synthesis of insulin resistnce-inducing cermides from plmitte (C16:) (ref. ) nd ctivtion of the innte immune system y sturted ftty cids 1. Bsed on this ssocition etween heptic DNL nd the metolic syndrome, it is elieved tht inhiition of DNL my e vile pproch to treting oesity-relted disorders such s type 2 dietes (T2D) (ref. ). However, ssuming tht DNL in humn WAT is ssocited with metolic helth, this my not e promising pproch when used systemiclly. Britric surgery hs ecome n importnt therpeutic option for the tretment of severe oesity-ssocited insulin resistnce nd T2D. Weight loss fter ritric surgery increses insulin sensitivity in liver, muscle nd ft. Furthermore, it improves metolic inflmmtion 13, therogenic dyslipidemi 14 s well s NAFLD (ref. 15). With regrd to WAT function, ritric surgery ws reported to normlize lipolysis nd plsm levels of dipokines 16. Thus, it is well recognized tht ritric surgery cn improve overll metolic helth, ut it remins uncler how it improves insulin sensitivity 1, nd whether DNL in WAT chnges fter ritric surgery-induced weight loss. To explore the effect of oesity on WAT nd liver DNL nd the potentil reversiility of oesity-induced DNL chnges fter ritric weight loss, we nlysed the expression of key DNL enzymes nd regultors in viscerl nd sucutneous WAT (SAT) s well s liver smples collected in two cohorts of metoliclly well-chrcterized humn sujects. Furthermore, we determined the ftty cid composition of WAT to study the potentil impct of DNL-derived ftty cids on metolic helth. Finlly, the reltion of ltered DNL in WAT nd liver, respectively, to metolic risk ws investigted y determining the correltions of DNL proteins nd ftty cids with mesures of insulin resistnce nd NAFLD. Results Oesity is ssocited with reduced DNL in viscerl WAT. We ssessed the effects of oesity on WAT DNL y mrna expression nlyses in viscerl WAT (VAT) specimens of ll 165 study sujects, focusing on four key enzymes: cetyl-coa croxylse (ACC) nd ftty cid synthse (FASN), the enzymes converting cetyl-coa to plmitte (C16:) (ref. 1), steroyl-coa desturse (SCD) tht crries out D-desturtion of sturted ftty cids such s the C16: conversion to C16:1n (ref. 1) nd ftty cid elongse 6 (ELOVL6), which elongtes C16 to C1 ftty cids 2. FASN nd ELOVL6 mrna were downregulted in VAT of oese sujects, wheres SCD ws incresed, s demonstrted y sttisticl model (nlysis of covrince, ANCOVA) ddressing the ssocition of ody mss index (BMI) with DNL gene expression nd its reltionship with ge nd gender (Fig. 1 c). Within the model, the expression of FASN nd SCD ws independent of gender, wheres ELOVL6 expression ws somewht lower, nd less dependent on BMI, in femles (Supplementry Tle S1). Furthermore, the negtive ssocitions of BMI with FASN nd ELOVL6 mrna were exggerted with higher ge, s reveled y significnt interction terms: BMI ge in the ANCOVA model (Supplementry Tle S1). To ccount for the possiility tht these pprent ge effects were cused y n ge is inherent to the cohort, with oese sujects eing on verge much younger thn non-oese, further detiled nlyses were performed with three prtilly ge-mtched nd fully gendermtched sugroups of the study popultion (n ¼ 2; see Tle 1 for nthropometric nd clinicl prmeters). The control group consists of non-oese ptients undergoing lower intestine surgery. The oese groups include oese ritric surgery ptients either without or with T2D, herefter referred to s oese nd oese-dietic. In keeping with our findings in the totl cohort, VAT mrna expression levels of FASN nd ELOVL6 (Fig. 1d,e) were lower in oth oese nd oese-dietic individuls compred to non-oese controls, wheres SCD mrna showed trend for higher expression in oese sujects (Fig. 1f). No significnt ssocitions with gender or ge were oserved. The insulin-sensitive glucose trnsporter GLUT4 is protein of prticulr interest for DNL, ecuse it is rte-limiting for shuttling the DNL sustrte glucose into dipocytes. Previously, GLUT4 ws shown to e downregulted in SAT of oese or dietic sujects 21. Consistent with these results, we oserved tht VAT GLUT4 mrna ws mrkedly downregulted in oth oese groups (Fig. 1g). Importntly, these findings were confirmed t the protein level. The expression of GLUT4, FASN nd ACC ws sustntilly decresed in oese nd oese-dietic individuls, s ssessed y western lot nlysis in the exct sme cohort (Fig. 1h k). VAT DNL is linked to ChREBP- nd metolic risk fctors. The oserved strong regultion of VAT DNL proteins prompted us to study known trnscriptionl regultors of DNL nd to check whether they were downregulted themselves. Gene expression of the lipogenic trnscription fctor sterol response element-inding protein-1 (SREBP1) ws unltered in VAT of oese compred with non-oese sujects (Fig. 2). Another importnt lipogenic trnscription fctor is crohydrte-responsive element-inding protein (ChREBP), which is ctivted y incresed glucose flux 22 nd, therefore, is intimtely linked to GLUT4 function in dipocytes. Interestingly, the expression of ChREBP-, recently discovered short isoform correlting strongly with ChREBP ctivity 23, ut not tht of the conventionl full length isoform, now termed ChREBP-, ws mrkedly reduced in oese nd oese-dietic compred to non-oese controls (Fig. 2,c). Overll, ChREBP- expression levels were, however, much lower thn those of ChREBP-. It ws previously demonstrted tht reduced cpcity for DNL in WAT is linked to insulin resistnce in mice 4,23. Furthermore, there is evidence tht WAT DNL suppresses liver DNL nd, consequently, reduces liver stetosis 4. Therefore, we next sked whether the DNL-relted molecules showing the strongest oesity-dependent regultion in VAT, nmely ChREBP-, FASN nd GLUT4, were ssocited with insulin resistnce nd liver stetosis. Indeed, VAT GLUT4 protein, FASN protein nd ChREBP- mrna correlted inversely with homeostsis model ssessment of insulin resistnce (HOMA-IR) (Fig. 2d f) nd the degree of liver stetosis (Fig. 2g i). HOMA-IR nd liver stetosis were, however, not independently ssocited with the DNL prmeters, proly ecuse they strongly correlte with ech other (R ¼.6, P ¼ 1.4 1, Person correltion, two-tiled t-test). When oth prmeters were comined in n ANCOVA, 2 NATURE COMMUNICATIONS 4:152 DOI: 1.13/ncomms253 & 213 Mcmilln Pulishers Limited. All rights reserved.
3 NATURE COMMUNICATIONS DOI: 1.13/ncomms253 ARTICLE ln FASN mrna 1 η 2 =. P=.1* n =164 n = BMI ln ELOVL6 mrna η 2 =.213 P= * BMI ln SCD mrna (cpoy no.) η 2 =.151 P=3. 1 * 1 n = BMI FASN mrna 45, 4, 35, 3, 25, 2, 15, 1, 5, P=.2* +T2D ELOVL6 mrna 2,5 2, 1,5 1, 5 P=.13 +T2D SCD mrna 1,,, 6, 4, 2, +T2D GLUT4 mrna 25, 2, 15, 1, 5, P=. 1 6 * +T2D FASN ACC GLUT4 HSP β-actin s -dietic 265 kd 2 kd 45 kd kd 42 kd FASN/β-ctin (fold) P =.1* 2. P=1.4 1 * P=4. 1 * 1. +T2D ACC/β-ctin (fold).5. +T2D GLUT4/β-ctin (fold) T2D Figure 1 Expression of metolic nd lipogenic genes in VAT of oese sujects. Log-trnsformed copy numers of FASN (), ELOVL6 () nd SCD (c) mrna in VAT plotted ginst BMI (logrithmic scle, non-logrithmic numers), nd group nlysis compring FASN (d), ELOVL6 (e), SCD (f) nd GLUT4 (g) mrna (n ¼ 1 21), s well s FASN (i), ACC (j) nd GLUT4 (k) protein (n ¼ 14 1) in VAT of non-oese, oese nd oese-dietic (oese þ T2D) sujects. c, open nd closed circles re femles nd mles, respectively. Trend lines s determined y ANCOVA including BMI s independent vrile nd gender s confounder re depicted s roken nd solid lines for femles nd mles, respectively. Effect size for BMI is descried y prtil et-squred vlues (Z2), descriing the proportion of totl vrition ttriutle to BMI 6. ANCOVA including ge nd interction terms, see Supplementry Tle S1. (h) Representtive VAT western lot. d g nd i k, estimted mrginl mens with 5% confidence intervls s determined y ANCOVA. GLUT4 protein nd mrna levels were significntly higher in femles compred with mles (Supplementry Fig. S4). Groups identified y the sme superscript letters (,) re not significntly different from ech other (PZ.5). *Significnt fter djustment for multiple testing. only one of them showed significnt ssocition, respectively, nmely VAT ChREBP- mrna with liver stetosis, nd VAT FASN nd GLUT4 protein expression with HOMA-IR (Supplementry Tle S2). Regultion of DNL my differ etween WAT depots nd, lthough excessive SAT is elieved to e less hrmful thn excessive VAT 24, it is more undnt nd this my hve physiologicl implictions. Therefore, we determined SAT DNL gene expression in ll three experimentl groups. Similr to VAT, we found profound downregultion of FASN nd GLUT4, ut no significnt regultion of ELOVL6 or SCD mrna in SAT smples of oese nd oese-dietic sujects, wheres TNF mrna ws upregulted in oese-dietic sujects (Fig. 3 e). ChREBP- expression ws decresed in SAT of oese-dietic individuls (Fig. 3f), wheres ChREBP- mrna ws detectle y PCR ut expression ws too low for quntifiction y rel-time PCR (Supplementry Fig. S1). Oesity is ssocited with less C1: ut not C16:1n in VAT. DNL in mice is tightly linked to the synthesis nd undnce of C16:1n (ref. 4). In humns, C16:1n is elieved to reflect NATURE COMMUNICATIONS 4:152 DOI: 1.13/ncomms & 213 Mcmilln Pulishers Limited. All rights reserved.
4 NATURE COMMUNICATIONS DOI: 1.13/ncomms253 Tle 1 Anthropometric, demogrphic nd clinicl prmeters of the experimentl sugroups. -dietic P-vlue n (femle/mle) (/1) (/1) (1/) Age (yer) 5. ( ) 45. ( ) 4. ( ), * BMI (kg m 2 ) 25. ( ) 51.4 ( ) 54. (5.3 5.) * CRP (mg l 1 ) 2. (1.4 3.).4 (5..).4 (.2 15.) * Liver stetosis (%) 2.6 (1.2 4.) 1. (.3 3) 34. ( ) * HA1c (%) 5.1 (4. 5.5) 5. ( ).3 (6..) * HOMA-IR 1.1 (. 1.6) 4.6 (3.1 6.).6 (6..4) * TG (mg dl 1 ) ( ) 13 (5 165) 14 (5 14). HDL-C (mg dl 1 ) 46 (41 51),w 42 (3 46),w 41 (3 45),w.41 LDL-C (mg dl 1 ) 14 ( 3) ( 13) (6 4).236 SBP (mm Hg) (3 5) 136 ( 142) 136 (13 142) DBP (mm Hg) 6 (1 2) 6 ( 3) 4 ( ). Arevitions: CRP, C-rective protein; DBP, distolic lood pressure; HDL-C, plsm high-density lipoprotein cholesterol, LDL-C, plsm low-density lipoprotein cholesterol; SBP, systolic lood pressure; TG, totl plsm triglycerides. Estimted mens (5% confidence intervls) nd P-vlue for effect of group s determined y ANCOVA. Groups identified y the sme superscript letter (,) re not significntly different from ech other (PZ.5). whdl-c ws higher in femles compred with mles (P ¼.4). *Significnt fter djustment for multiple testing. SREBP1 mrna 14,, 1,, 6, 4, 2, + T2D ChREBP-α mrna 5, 4, 3, 2, 1, + T2D ChREBP-β mrna P= * + T2D R=.32 P=.1 2. R=.63 P= * 2. R=.61 P= 1 5 * ln ChREBP-β mrna GLUT4/β-ctin (fold) n=52 n=43 n= ln HOMA-IR ln HOMA-IR ln HOMA-IR FASN/β-ctin (fold) R=.56 P= * 2. R=.4 P=.1 2. R =.41 P =. ln ChREBP-β mrna GLUT4/β-ctin (fold) 1..5 n=5 n=41 n= Percentge Percentge Percentge stetotic heptocytes (ln(%+1)) stetotic heptocytes (ln(%+1)) stetotic heptocytes (ln(%+1)) FASN/β-ctin (fold) 1. Figure 2 VAT ChREBP-, FASN nd GLUT4 re inversely linked to HOMA-IR nd liver stetosis. Group nlysis (n ¼ 1 21) compring mrna copy numers of SREBP1 (), ChREBP- () nd ChREBP- (c) in VAT of non-oese, oese nd oese-dietic sujects. Person correltion nlysis of VAT ChREBP- mrna (d,g), GLUT4 protein (e,h) nd FASN protein (f,i) with HOMA-IR (d f) nd liver stetosis (g i). c, estimted mrginl mens with 5% confidence intervls s determined y ANCOVA. Groups identified y the sme letters (,) re not significntly different from ech other (PZ.5). SREBP1 nd ChREBP- mrna were significntly higher in femles compred with mles (Supplementry Fig. S4). *Significnt fter djustment for multiple testing. D-desturse ctivity, tht is, endogenous metolism rther thn diet 25. To investigte whether decresed C16:1n could ccount for the insulin resistnce in humn oesity s descried for mice 4,6,, we compred C16:1n concentrtions in VAT of non-oese with those in oese nd oese-dietic sujects. VAT content of C16:1n ws not diminished in oese sujects nd 4 NATURE COMMUNICATIONS 4:152 DOI: 1.13/ncomms253 & 213 Mcmilln Pulishers Limited. All rights reserved.
5 NATURE COMMUNICATIONS DOI: 1.13/ncomms253 ARTICLE FASN mrna 5, 4, 3, 2, 1, P= * + T2D ELOVL6 mrna 3, 2,5 2, 1,5 1, 5 + T2D SCD mrna, 6, 4, 2, + T2D GLUT4 mrna 3, 25, 2, 15, 1, 5, P =.3* + T2D TNFα mrna 1,4 1,2 1, P =.1 + T2D ChREBPα mrna 2, 16,,, 4, P =.5 + T2D Figure 3 SAT lipogenic gene expression in oese compred with non-oese sujects. Expression of FASN (), ELOVL6 (), SCD (c), GLUT4 (d), tumour necrosis fctor- (e) nd ChREBP- (f) mrna in SAT. The sujects re suset of the experimentl groups descried in Tle 1. Numers (femle/mle): controls (6/6), oese (/1), oese-dietic (2/5). Estimted mrginl mens with 5% confidence intervls, s determined y ANCOVA. Groups identified y the sme letters (,) re not significntly different from ech other (PZ.5). FASN, SCD nd GLUT4 expressions were higher in femles compred with mles (Supplementry Fig. S4). *Significnt fter djustment for multiple testing. only moderte trend for decrese ws oserved in oesedietic compred with oese (Fig. 4 d). C16:1n concentrtion correlted positively with expression of oth FASN nd SCD in VAT (Fig. 4e,f). The fct tht FASN nd SCD re inversely ltered in the oese stte (Fig. 1,c) my explin why C16:1n is not lower in humn oesity. In contrst to C16:1n, we detected strong decrese in oese nd oese-dietic sujects for sterte (C1:) (Fig. 4 c) nd very long chin-ftty cids derived from C1: (C2:, C22:, C24:, C24:1, Supplementry Fig. S2). C16: ws unchnged etween groups (Fig. 4 c). C1: trended to correlte positively with FASN (R ¼.21, P ¼.13) nd ELOVL6 expression (R ¼.2, P ¼.4), ut negtively with SCD (R ¼.3, P ¼.4) in VAT (Person correltions, two-tiled t-test). Thus, the decrese of FASN nd ELOVL6 comined with the increse of SCD in VAT of oese ptients might explin the reduction of VAT C1: in oesity. Next, we sked whether DNL-derived ftty cid species in VAT re linked to insulin resistnce. C16:1n did not significntly correlte with HOMA-IR (R ¼.14, P ¼.33). By contrst, C1: demonstrted strong, negtive correltion comprle to those of the DNL proteins with HOMA-IR (R ¼.5, P ¼.16), while olete (C1:1n) exhiited positive ut weker correltion (R ¼.2, P ¼.46; Person correltions, two-tiled t-test). SAT DNL gene expression is restored fter ritric surgery. Britric surgery is clinicl intervention tht often leds to mrked weight loss nd n improvement of metolic helth with the potentil to cure T2D. The mechnisms mediting the slutry effects of ritric surgery re not fully understood. To ddress the question whether incresed WAT DNL my e one of them, we determined the expression of DNL genes in SAT otined from oese ptients efore nd fter ritric weight loss. As expected, ritric surgery resulted in significntly reduced ody weight nd overll improvement of their metolic stte (Tle 2). Expression of FASN, ELOVL6 nd GLUT4, ut not SCD, in SAT incresed fter weight loss (Fig. 5 d). Expression of ChREBP- ws modertely incresed fter weight loss (Fig. 5e), wheres ChREBP- expression ws elow the level of detection. In contrst to upregultion of DNL, expression of TNF ws reduced fter weight loss (Fig. 5f), which is consistent with recent report 26. Oesity is ssocited with incresed liver ChREBP- nd DNL. Elevted liver DNL in oesity cn contriute to the development of insulin resistnce. The role of liver DNL in metolic disese in humns nd especilly its reltionship to WAT DNL is, however, not well understood. Therefore we nlysed DNL expression in liver iopsies of the exct sme individuls hving een used for nlyses of VAT DNL. In contrst to VAT (Fig. 1 f), we found tht the mrnas of FASN nd ELOVL6 were significntly upregulted in livers of oese sujects (Fig. 6,; Supplementry Fig. S3,). Liver SCD mrna exhiited higher vriility nd less pronounced increse in oese sujects (Fig. 6c; Supplementry Fig. S3c). Liver FASN mrna correlted inversely with VAT FASN protein (Fig. 6g), indicting potentil mechnistic link etween VAT nd liver FASN regultion in oesity. Regultion of DNL in liver ws further studied y western lot nlysis. Owing to smple limittions we were only le to nlyse smll set of liver tissue specimens, different from the sugroups descried in Tle 1 (see Supplementry Tle S3). FASN protein expression in oese sujects tended to e incresed, lthough this nlysis ws underpowered, nd we therefore filed to rech sttisticl significnce in the ANCOVA (Supplementry Fig. S3d). FASN protein levels were, however, higher when oth NATURE COMMUNICATIONS 4:152 DOI: 1.13/ncomms & 213 Mcmilln Pulishers Limited. All rights reserved.
6 NATURE COMMUNICATIONS DOI: 1.13/ncomms253 vs controls + T2D vs controls c + T2D vs oese C1:1n P =.1 C1:1n P = * P =5.6 1 * C1: P =. P =. C16:1n C16: C14:1 C14: Femle Mle P = Chnge (mg%) Chnge (mg%) Chnge (mg%) d C16:1n (mg%) T2D e ln FASN mrna 1 R =.2 P =.2 n=5 1 n= Logit C16:1n (mg%) f ln SCD mrna R =.26 P =.4 Logit C16:1n (mg%) Figure 4 VAT ftty cid concentrtions re chnged in oesity. Men chnge (5% confidence intervl) reltive to totl VAT ftty cids in oese versus controls (), oese-dietic versus controls (), oese-dietic versus oese (c). Estimted mens nd 5% confidence intervls of C16:1n (d) in controls, oese, oese-dietic (n ¼ 15 21). Correltion of VAT C16:1n with mrna expression of FASN (e) nd SCD (f). Open rs nd symols re femles; R, Person correltion coefficient. *Significnt fter djustment for multiple testing. Tle 2 Anthropometric nd clinicl dt of ptients (n ¼ 2) efore nd fter ritric intervention. Before After P-vlue BMI (kg m 2 ) 46.2 ( ) 36.5 ( ) * HOMA-IR 5. (3.6 6.) 1.4 (1. 1.).4 1 * Glucose (mmol l 1 ) 5. ( ) 5. ( ) * Insulin (muml 1 ) 1.1 ( ) 6.4 (4..4) * HA1c (%) 6.3 (5. 6.) 5.6 (5.2 6.). HDL-C (mg dl 1 ) 34 (2 4) 3 (32 4).13 LDL-C (mg dl 1 ) 131 (1 154) 5 ( 5).2* TG (mg dl 1 ) 153 (1 214) 15 (4 131).1 CRP (mgml 1 ). (4.3.5) 3.6 (1..1).13 Arevitions: CRP, C-rective protein; DBP, distolic lood pressure; HDL-C, plsm highdensity lipoprotein cholesterol, LDL-C, plsm low-density lipoprotein cholesterol; TG, totl plsm triglycerides. Mens (5% confidence intervls) nd P-vlues (pired t-test of log-trnsformed vlues). *Significnt fter djustment for multiple testing oese groups were comined nd compred with the non-oese sujects (Fig. 6h) nd they correlted with FASN mrna quntified in the sme liver specimens (Supplementry Fig. S3f), indicting tht FASN mrna levels reflect FASN protein levels in humn livers. Next, we sked whether the expression of lipogenic trnscription fctors ws ltered in livers of oese sujects in fshion similr to their puttive trget genes. Liver mrna levels of SREBP1 (Fig. 6d) were not incresed in oesity. However, the expression of ChREBP- ws sustntilly elevted, wheres ChREBP- ws slightly decresed in livers of oese individuls (Fig. 6e,f), suggesting n importnt role for ChREBP- in regulting liver DNL. In line with liver ChREBP- nd its trget genes hving role in stetosis nd potentilly lso with insulin resistnce, we oserved positive correltion of ChREBP- nd FASN mrna with HOMA-IR nd the degree of liver stetosis (Fig. 6i l). The ssocition with liver stetosis ws, however, weker nd not independent of tht with HOMA- IR (Supplementry Tle S2). Discussion In the present study we demonstrte tht WAT DNL is suppressed in humn oesity nd T2D y showing tht the expression of the key DNL enzymes ACC nd FASN is mrkedly decresed in VAT of oese sujects. These findings re in line with previous pulictions reporting downregultion of lipogenic mrnas in WAT of oese humns 2 2 nd rodents 3,31. In ddition to the suppression of DNL enzymes, we oserved profound downregultion of GLUT4 in VAT of oese sujects (Fig. 1), complementing previous studies tht were limited to humn SAT 21,32. Moreover, we re the first to demonstrte coordinted upregultion of WAT DNL genes nd GLUT4 fter ritric weight loss (Fig. 5). In light of trnsgenic mouse studies demonstrting tht dipose tissue GLUT4 is n importnt regultor of whole-ody insulin sensitivity 33, the oesitydependent GLUT4 decrese nd the mrked inverse correltion of GLUT4 protein with HOMA-IR oserved in this study (Fig. 2) strongly support the notion tht GLUT4 promotes insulin sensitivity lso in humns, possily s pcemker of dipocyte DNL. GLUT4 does not only provide sustrte for DNL, it is lso 6 NATURE COMMUNICATIONS 4:152 DOI: 1.13/ncomms253 & 213 Mcmilln Pulishers Limited. All rights reserved.
7 NATURE COMMUNICATIONS DOI: 1.13/ncomms253 ARTICLE FASN mrna 4, 3, 2, 1, P =.63 ELOVL6 mrna 16,,, 4, P =.45 SCD mrna 1,6, 1,2,, 4, Before After Before After Before After GLUT4 mrna 6, 5, 4, 3, 2, 1, P =.* ChREBPα mrna 3, P =.24 25, 2, 15, 1, 5, 1,4 1,2 1, P =.* Before After Before After Before After TNFα mrna Figure 5 Britric intervention increses expression of DNL-relted genes nd decreses tumour necrosis fctor- (TNF-) expression in SAT. FASN (), ELOVL6 (), SCD (c), GLUT4 (d), ChREBP- (e) nd TNF- (f) mrna in SAT smples of ritric surgery ptients (n ¼ 16 2) efore nd fter weight loss. Mens nd 5% confidence intervls, pired t-test of log-trnsformed vlues. *Significnt fter djustment for multiple testing. criticl for the lipogenic trnscription fctor ChREBP, which is ctivted on incresed glucose flux 22. Diminished ChREBP ctivtion due to defective GLUT4 expression, nd presumly GLUT4 trnsloction, my thus e responsile for the reduced DNL gene expression in oesity. While this mnuscript ws under preprtion, novel ChREBP isoform (ChREBP-), derived from n lterntive promoter, ws descried 23. ChREBP is shorter thn the conventionl isoform (ChREBP-) nd hs higher ctivity due to constitutive nucler locliztion. We found cler coregultion of ChREBP- ut not ChREBP- with DNL genes in VAT (Fig. 2). Our dt, thus, complement the finding y Hermn et l. 23, which demonstrted link of humn SAT ChREBP- to insulin sensitivity nd GLUT4 expression. We did not oserve downregultion of the quntittively dominnt isoform ChREBP- in VAT of oese sujects, s reported recently 34, nd only moderte one in SAT (Fig. 3). The discrepncy my e due to the younger ge nd the lener phenotype of the non-oese controls in tht study compred with ours. In ddition to WAT, we show here for the first time tht ChREBP- is coregulted with DNL enzymes in liver (Fig. 6). Given tht the well-studied isoform ChREBP- is regulted mostly t the posttrnsltionl level, previous studies using gene expression redout could not relily ssess ChREBP ctivity. ChREBP- mrna levels etter reflect ctivity ecuse the ChREBP- promoter is utoctivted y ChREBP 23. Tken together, our dt indicte tht ChREBP regultes DNL in humn liver, supporting the view tht ChREBP, ctivted through elevted heptic hexose flux, for exmple, y fructose-rich nutrition 35 or SREBP1-dependent induction of glucokinse 36,is mjor mechnism y which DNL is induced in livers of oese nd insulin-resistnt humns. Activity of DNL enzymes influences tissue ftty cid profiles 4,3. We found tht, in contrst to FASN, SCD ws modertely upregulted in VAT of oese individuls (Fig. 1). This suggests incresed SCD ctivity in dipose tissue of oese individuls nd cn explin the most prominent ftty cid chnges we oserved in oese sujects, nmely decrese in C1: nd n increse in C1:1n (Fig. 4). Similrly, it my explin nother importnt oservtion in our study, the lck of sustntil oesity-dependent chnges in VAT C16:1n concentrtion (Fig. 4), which is consistent with recent humn study reporting positive correltion of WAT C16:1n with BMI 3. In oese mice, the murine SCD homologue SCD1 ws found to e downregulted in WAT 4, explining the decrese of C16:1n, ut not C1: in ll mjor lipid clsses of WAT in these mice 4. Thus, regultion of dipose tissue SCD seems to differ etween humns nd mice. Our dt indicte higher cpcity of oese humns versus mice to dpt to n unhelthy excess of C1: nd other sturted ftty cids through D-desturtion. Although not studied in detil so fr, there is some experimentl evidence indicting tht C1: in diet or s free ftty cid (FFA) induces insulin resistnce Accordingly, the negtive correltion of C1: with BMI nd HOMA-IR tht we nd others 3 oserved my rther reflect protective conversion of the unhelthy ftty cid C1: thn (hypotheticl) insulinsensitizing effect of C1:. On the other hnd, SCD1 nd C1:1n were recently demonstrted to medite oesity-induced inflmmtion nd insulin resistnce in WAT 42. Thus, the oserved induction of SCD in VAT of oese sujects cn lso e interpreted s mldptive stte nd it remins difficult to estimte the net effect on metolic helth. To wht extent C16:1n is n insulin-sensitizing fctor in humns, s it is in mice 4,6,, is mtter of ongoing dete nd cnnot e directly inferred from our dt. The current model ssigns the insulin-sensitizing role to C16:1n within FFA, the mjor lipid clss relesed from WAT 4. For technicl resons, we did not mesure ftty cids in the FFA frction of VAT ut determined totl VAT ftty cid profiles. The ltter closely correspond to serum FFA profiles in humns, t lest with regrd to C16:1n nd other DNL-derived ftty cids 44,46. In ny event, the preserved concentrtion of C16:1n in VAT of oese sujects (Fig. 4) my explin why C16:1n does not significntly correlte with HOMA-IR, in strk contrst to FASN nd GLUT4 protein levels (Fig. 2). It is conceivle tht DNL-linked molecules other thn FFA, which we my hve missed in the totl tissue ftty cid nlysis, re relesed from dipose tissue nd counterct insulin resistnce. Clerly, more work is needed to unrvel potentil mechnisms connecting dipose DNL to systemic insulin sensitivity in humns, which my led to the identifiction of NATURE COMMUNICATIONS 4:152 DOI: 1.13/ncomms253 & 213 Mcmilln Pulishers Limited. All rights reserved.
8 NATURE COMMUNICATIONS DOI: 1.13/ncomms253 FASN mrna 3, 25, 2, 15, 1, 5, P=.1* P = * 3, 25, + T2D ELOVL6 mrna 2, 15, 1, 5, + T2D SCD mrna 25, 2, 15, 1, 5, P =.24 + T2D SREBP1 mrna, 1,, 6, 4, 2, + T2D ChREBPα mrna 4, 35, 3, 25, 2, 15, 1, 5, P =.2* 25, P =6.6 1 * 2, 15, + T2D ChREBP-β mrna 1, 5, + T2D ln FASN mrna R=.3 P =. 1 n = VAT FASN/β-ctin (fold) FASN/β-ctin (fold) P =. Comined oese ln FASN mrna 1 R=.6 P = * n= ln HOMA-IR ln FASN mrna R=.4 13 R=.6 13 R =.54 P =.2* P = * P = * n=55 n=55 n= Percentge ln HOMA-IR Percentge stetotic heptocytes (ln(%+1)) stetotic heptocytes (ln(%+1)) ln ChREBP-β mrna Figure 6 Heptic DNL is linked to higher BMI, HOMA-IR nd liver stetosis. Group nlysis (n ¼ 1 21) compring liver mrna expression of FASN (), ELOVL6 (), SCD (c), SREBP1 (d), ChREBP- (e) nd ChREBP- (f) of non-oese, oese nd oese-dietic sujects. ( f) Estimted mrginl mens with 5% confidence intervls s determined y ANCOVA. FASN mrna is significntly higher in femles compred with mles (Supplementry Fig. S4). Groups identified y the sme letters (,) re not significntly different from ech other (PZ.5). Correltion of liver FASN mrna with VAT FASN protein (g). FASN protein expression in non-oese sujects (n ¼ 13) compred with comined oese nd oese-dietic (n ¼ 15) (h), mens±s.e.m., two-tiled t-test. Person correltion nlysis of liver FASN mrna (i,j) nd liver ChREBP- mrna (k,l) with HOMA-IR (i,k) nd liver stetosis (j,l). *Significnt fter djustment for multiple testing. ln ChREBP-β mrna lterntive lipid species or non-lipid molecules with similr iologicl functions s C16:1n in rodents. In contrst to the downregultion of DNL in WAT we oserved profound induction of FASN, ELOVL6 nd SCD in livers of oese sujects (Fig. 6). This oservtion is very importnt s (i) it complements previous humn studies tht could ssess heptic DNL only indirectly through trcer incorportion into VLDL ftty cids 4,4 nd (ii) it shows for the first time tht there is n inverse correltion etween liver nd WAT FASN expression (Fig. 6). The correltion of liver FASN expression with HOMA-IR nd the degree of liver stetosis (Fig. 6) supports the concept tht heptic lipogenic induction cn promote the development of NAFLD nd insulin resistnce. However, elevted liver DNL does not led to insulin resistnce in every cse, s elegntly demonstrted in recent study using denovirl heptic overexpression of ChREBP- in mice. Despite mssive liver triglyceride ccumultion, these mice were not insulin resistnt, nd on high-ft diet even more insulin sensitive thn controls 4. Contrsting with these results, denovirl ChREBP- knockdown improved insulin resistnce in leptin-deficient oese mice 5. Furthermore, inducing DNL in liver through trnsgenic overexpression of SREBP1 induced insulin resistnce in mice on norml diet 51. Thus, excessive heptic DNL does not invrily cuse insulin resistnce. Clerly, more reserch is needed to understnd how distured liver lipid metolism nd ptterns re linked to liver metolic dysfunction 3 nd whether DNL-linked stetosis in oese humns is cuse or consequence of metolic disese. At lest, severl rodent studies demonstrte tht reducing NATURE COMMUNICATIONS 4:152 DOI: 1.13/ncomms253 & 213 Mcmilln Pulishers Limited. All rights reserved.
9 NATURE COMMUNICATIONS DOI: 1.13/ncomms253 ARTICLE the ctivity of DNL enzymes cn e used to tret metolic disorders. For exmple, it ws reported tht inhiiting liver FASN or ELOVL6 (ref. 52) improved insulin resistnce nd therosclerosis in mice. In light of these therpeutic proof-ofconcept studies indicting eneficil effects on insulin resistnce nd therosclerosis, our liver dt provide importnt trget vlidtion for phrmcologicl DNL inhiitors. However, one needs to tke into ccount tht inhiition of these enzymes in WAT my promote systemic insulin resistnce, s discussed ove, nd DNL inhiition with concomitntly reduced monounsturted ftty cids my lso hve dverse effects in other cell types, especilly in mcrophges 53 nd pncretic -cells Selective inhiition using molecules preferentilly tken up y liver such s the FASN inhiitor pltensimycin could e wy to prevent unwnted consequences of DNL suppression in extr-heptic tissues. As n dditionl mesure, nutritionl C16:1n supplementtion could e used to mitigte negtive effects of DNL inhiition. Given the strong effects of C16:1n on cultured mcrophges nd -cells 53 55, nd positive results in mouse studies 6,, this is promising pproch tht does, however, require in vivo vlidtion studies in humns. In summry, our study demonstrtes tht DNL enzymes re mrkedly suppressed in WAT of oese sujects, s is GLUT4. This suppression is closely linked to impired metolic control nd cn e reversed y weight loss through ritric intervention. Furthermore, we show tht in oesity, liver DNL is profoundly upregulted, nd is closely linked to insulin resistnce s well s liver stetosis. Thus, DNL inversely correltes etween WAT nd liver nd is closely linked with mrkers of metolic helth. The novel ChREBP isoform ChREBP- is tightly ssocited with DNL gene expression in oth VAT nd liver, indicting key role of glucose metolism in the regultion of lipogenesis. Methods Study sujects. Ptients undergoing ritric surgery (n ¼ 61), dominl surgery for erly colorectl cncer (n ¼ 4), pncretic cncer (n ¼ 22), other cncers of the gstrointestinl trct or enign diseses such s sigm-diverticulosis t the Deprtment of Generl nd Viscerl Surgery, University of Ulm, Germny, from were included in the study. Exclusion criteri were type 1 dietes nd cute inflmmtory disese. None of the cncer ptients exhiited signs of metstses or reported excessive, unintended recent weight loss. Unlike in other ritric centres, ritric ptients were not sujected to weight loss regimen efore surgery, ut were commended to dhere to regulr mel pttern nd tke multi-vitmin nd minerl supplement 4 weeks efore ritric intervention, minimizing confounding effects of negtive weight lnce. Anthropometric nd clinicl dt descriing the study cohort re listed in Supplementry Tle S4. Surgicl resection specimens, VAT, dominl SAT, liver iopsies nd lood were immeditely plced on ice nd susequently snp-frozen in liquid nitrogen nd stored in liquid nitrogen or t C. For detiled nlyses, gender-mtched sugroups including non-oese nondietic sujects (controls), oese non-dietic sujects (oese) nd oese sujects with T2D (oese-dietic) were selected from the totl cohort. To reduce the ge gp etween oese sujects (mostly moridly oese, ritric ptients) nd nonoese sujects (mostly cncer ptients) the youngest oese ptients (ge o33 yers) nd the oldest non-oese ptients (ge 4 yers) were excluded from the sugroups. Eventully, colorectl cncer (n ¼ 15) nd sigm-diverticulosis (n ¼ 4) ptients were selected s the control group. Most control sujects hd no signs of overt inflmmtion, with only three individuls exhiiting elevted C-rective protein (Z5 mgml 1, rnge mgml 1 ). See Tle 1 for nthropometric nd clinicl dt chrcterizing the sugroups. A seprte popultion ws used to investigte chnges fter ritric surgery. Adominl SAT resection specimens were otined from 2 ptients (15 femles, 5 mles) during ritric surgery performed t Mstricht University Hospitl, The Netherlnds, from Procedures were gstric ypss (n ¼ ), gstric nding (n ¼ 4), gstric sleeve (n ¼ 3), iliopncretic diversion (n ¼ 3) nd Scopinro (n ¼ 1). Post-weight loss of dominl SAT smples were tken from the sme ptients y excision 6 months (n ¼ ), months (n ¼ 1) or 24 months (n ¼ 3) fter ritric surgery. All smples were tken in the fsted stte nd frozen immeditely in liquid nitrogen efore storge t C. Ptients with type 1 dietes, inflmmtory diseses, nd ptients using nti-inflmmtory drugs nd/or reported lcohol consumption (more thn 1 g per dy) were excluded from the study. All lood smples were tken in fsted stte efore surgery nd prmeters were mesured y routine methods in the clinicl chemistry lortories of Ulm nd Mstricht University Hospitls. Liver stetosis (% of heptocytes with visile lipid droplets) ws estimted y the nlysis of hemtoxylin eosin-stined liver specimens. In ech cse, permission ws given from the locl ethics committees in Mstricht, The Netherlnds, nd Ulm, Germny, nd informed consent in writing ws otined from ech suject. Gene expression nlysis. Totl RNA ws isolted nd purified from tissue specimens using NucleoSpin RNA II kit (Mcherey& Ngel). cdna ws synthesized using SuperScript III Reverse Trnscriptse (Invitrogen). Quntittive reltime PCRs for indicted genes were performed on HT sequence detection system (Applied Biosystems) using TqMn Assy-on-Demnd primer-proe sets supplied y Applied Biosystems nd selected to recognize ll RefSeq sequences nd mximum of GenBnk ESTs (Supplementry Tle S5). The ChREBP- TqMn ssy (Hs2632_m1) recognizes intron 1. ChREBP- expression ws determined y SYBR green-sed quntittive rel-time PCR using n Mx3P system (Strtgene) nd primers s pulished 23 (forwrd: 5 -AGCGGATTCCAGGTGAG G-3, reverse: 5 -TTGTTCAGGCGGATCTTGTC-3 ). Gene expression ws clculted s copy numer per 1 4 copies of the housekeeper gene TATA inding protein-ssocited fctor 1 (revited s copy no.). Western lot nlysis. Protein extrction nd western lot nlysis were performed s descried 5. Briefly, frozen VAT (5 1 mg) or liver (3 5 mg) iopsies were homogenized in 2 mm MOPS, 2 mm EGTA, 5 mm EDTA, 3 mm sodium fluoride, 4 mm -glycerophosphte, 1 mm sodium pyrophosphte, 2 mm sodium orthovndte,.5% NP-4 nd complete protese inhiitor cocktil (Roche) nd centrifuged t 13, g for 2 min t either 3 C (VAT) or þ 4 C (liver). The superntnt ws then collected while crefully voiding the lipid lyer on top nd protein concentrtion ws mesured with BCA protein quntifiction kit (Thermo Scientific). Protein extrcts were seprted on 4 % NuPAGE gels (Invitrogen) nd lotted onto Immoilon FL PVDF (Millipore) memrnes. Memrnes were locked t room temperture for 1 h in Odyssey LI-COR Blocking Buffer (LI-COR) 1:2 diluted in TBS nd incuted in primry ntiodies in Blocking Buffer diluted 1:2 in TBS-T (.1%) overnight t 4 C. Primry ntiodies ginst ACC (Cell Signling Technology, dilution 1:1,), FASN (BD Bioscience, 1:1,), Hsp (BD Bioscience, 1:1,), -ctin (Acm, 1:1,), GLUT4 (Acm, 1:2,) nd Hsc (Snt Cruz Biotechnology, 1:1,) were used. After three consecutive 5 min wshes in TBS-T (.1%), lots were incuted with Dylight 6-conjugted got nti-rit IgG nd Dylight -conjugted got nti-mouse IgG (oth Thermo Scientific) for 1 h t room temperture in locking uffer contining.1% TBS-T nd.1% SDS. After three wshes in TBS-T nd finl wsh in TBS, the lots were scnned with the LI-COR Odyssey (LI-COR) nd quntified with Odyssey 3. softwre sed on direct fluorescence mesurement. For quntifiction, proteins were normlized to -ctin. Ftty cid profiling. Ftty cid composition in totl lipid extrcts of VAT ws determined y gs chromtogrphy, s descried previously 5. Briefly, 25 ml of utylhydroxytoluene (.1 mol l 1 in methnol) nd 6 ml of chloroform/methnol (2/1, v/v) were dded to B1 mg of tissue. After homogeniztion using n Ultrturrx homogenizer, the smples were heted to 5 C for 3 min nd centrifuged (1, g, 5 min). Ftty cid methyl esters were prepred y heting 1 ml of tissue extrct, 2 ml methnol/toluene (4/1, v/v), 5 ml heptdecnoic cid (2 mgml 1 in methnol/toluene, 4/1) nd 2 ml cetylchloride in cpped tue for 1 h t 1 C. After cooling to room temperture, 5 ml of 6% sodium cronte nd 1.6 ml of toluene were dded. The mixture ws centrifuged (1, g, 5 min) nd 15 2 ml of the upper lyer ws trnsferred to uto smpler vils. Gs chromtogrphy nlyses were performed using n HP 5 gs chromtogrph (Hewlett Pckrd) equipped with flme ioniztion detectors (Sttionry phse: DB m.25 mm i.d., film thickness.25 mm; Agilent). Pek identifiction nd quntifiction ws performed y compring retention times nd pek res, respectively, to stndrd chromtogrms. All clcultions re sed on ftty cid methyl ester vlues. Concentrtion of ftty cid species ws clculted s mg% (mg ftty cid species/1 mg totl ftty cids). Sttisticl methods. Assocition of FASN gene expression with BMI in the whole cohort nd pprent group effects were exmined y ANCOVA, including gender nd ge s well s two-wy interction terms of independent vriles in the initil models. Nonsignificnt terms were hierrchiclly-ckwrd eliminted s suggested y Kleinum nd Klein 5. Significnt effects of ge nd gender re denoted in the results section when present. Bonferroni djustment ws pplied in multiple group comprisons. To ccount for multiple testing, the threshold for sttisticl significnce ws set t P ¼.5 divided y the numer of sttisticl tests pplied (n ¼ 1, Po.5, min cohort; n ¼ 15, Po.33, ritric intervention cohort). Pired t-tests were conducted to compre prmeters efore nd fter ritric surgery. Dt were trnsformed to nturl logrithm when necessry to chieve norml distriution nd/or homoscedsticity. Ftty cid concentrtions were logit-trnsformed (ln[x/(1 x)]). IBM SPSS Sttistics version 1 ws used for ll sttisticl nlyses. NATURE COMMUNICATIONS 4:152 DOI: 1.13/ncomms253 & 213 Mcmilln Pulishers Limited. All rights reserved.
10 NATURE COMMUNICATIONS DOI: 1.13/ncomms253 References 1. Rosen, E. D. & Spiegelmn, B. Adipocytes s regultors of energy lnce nd glucose homeostsis. Nture 444, 4 53 (26). 2. Virtue, S. & Vidl-Puig, A. Adipose tissue expndility, lipotoxicity nd the metolic syndrome n llosttic perspective. Biochim. Biophys. Act. 11, (21). 3. Frese, Jr R. V., Zechne,r, R., Newgrd, C. B. & Wlther, T. C. The prolem of estlishing reltionships etween heptic stetosis nd heptic insulin resistnce. Cell Met. 15, 5 53 (2). 4. Co, H. et l. Identifiction of lipokine, lipid hormone linking dipose tissue to systemic metolism. Cell 134, (2). 5. Huo, Y. et l. Trgeted overexpression of inducile 6-phosphofructo-2-kinse in dipose tissue increses ft deposition ut protects ginst diet-induced insulin resistnce nd inflmmtory responses. J. Biol. Chem. 2, (2). 6. Yng, Z. H., Miyhr, H. & Htnk, A. Chronic dministrtion of plmitoleic cid reduces insulin resistnce nd heptic lipid ccumultion in KK-Ay Mice with genetic type 2 dietes. Lipids Helth Dis. 1, (2).. Guo, X. et l. Plmitolete induces heptic stetosis ut suppresses liver inflmmtory response in mice. PLoS One, e326 (2).. Postic, C. & Girrd, J. Contriution of de novo ftty cid synthesis to heptic stetosis nd insulin resistnce: lessons from geneticlly engineered mice. J. Clin. Invest., 2 3 (2).. Chvez, J. A. & Summers, S. A. A cermide-centric view of insulin resistnce. Cell Met. 15, (2). 1. Fessler, M. B., Rudel, L. L. & Brown, J. M. Toll-like receptor signling links dietry ftty cids to the metolic syndrome. Curr. Opin. Lipidol. 2, 3 35 (2).. Wu, M. et l. Antidietic nd ntistetotic effects of the selective ftty cid synthse (FAS) inhiitor pltensimycin in mouse models of dietes. Proc. Ntl Acd. Sci. USA 1, (2).. Cmstr, S. et l. Erly nd longer term effects of gstric ypss surgery on tissue-specific insulin sensitivity nd et cell function in moridly oese ptients with nd without type 2 dietes. Dietologi 54, 23 2 (2). 13. vn Dielen, F. M., Buurmn, W. A., Hdfoune, M., Nijhuis, J. & Greve, J. W. Mcrophge inhiitory fctor, plsminogen ctivtor inhiitor-1, other cute phse proteins, nd inflmmtory meditors normlize s result of weight loss in moridly oese sujects treted with gstric restrictive surgery. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Met., (24). 14. Dixon, J. B. & O Brien, P. E. Lipid profile in the severely oese, chnges with weight loss fter lp-nd surgery. Oes. Res. 1, 3 1 (22). 15. Dixon, J. B., Bhthl, P. S., Hughes, N. R. & O Brien, P. E. Nonlcoholic ftty liver disese, Improvement in liver histologicl nlysis with weight loss. Heptology 3, (24). 16. Frj, M. et l. Plsm cyltion-stimulting protein, diponectin, leptin, nd ghrelin efore nd fter weight loss induced y gstric ypss surgery in moridly oese sujects. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Met., (23). 1. Srruf, D. A., Bonner-Weir, S. & Schwrtz, M. W. New clues to ritric surgery s enefits. Nt. Med. 1, 6 61 (2). 1. Hellerstein, M. K., Schwrz, J. M. & Neese, R. A. Regultion of heptic de novo lipogenesis in humns. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 16, (16). 1. Enoch, H. G., Ctl, A. & Strittmtter, P. Mechnism of rt liver microsoml steryl-coa desturse. Studies of the sustrte specificity, enzyme-sustrte interctions, nd the function of lipid. J. Biol. Chem. 251, (16). 2. Moon, Y. A., Shh, N. A., Mohptr, S., Wrrington, J. A. & Horton, J. D. Identifiction of mmmlin long chin ftty cyl elongse regulted y sterol regultory element inding proteins. J. Biol. Chem. 26, (21). 21. Grvey, W. T. et l. Pretrnsltionl suppression of glucose trnsporter protein cuses insulin resistnce in dipocytes from ptients with non-insulindependent dietes mellitus nd oesity. J. Clin. Invest., (). 22. Ymshit, H. et l. A glucose-responsive trnscription fctor tht regultes crohydrte metolism in the liver. Proc. Ntl Acd. Sci. USA, 6 1 (21). 23. Hermn, M. A. et l. A novel ChREBP isoform in dipose tissue regultes systemic glucose metolism. Nture 44, (2). 24. Després, J. P. & Lemieux, I. Adominl oesity nd metolic syndrome. Nture 444, 1 (26). 25. Vessy, B. Dietry ft, ftty cid composition in plsm nd the metolic syndrome. Curr. Opin. Lipidol. 14, 15 1 (23). 26. Prdin, E. et l. Only C-rective protein, ut not TNF- or IL6, reflects the improvement in inflmmtion fter ritric surgery. Oes. Surg. 22, (2). 2. Orteg, F. J. et l. The gene expression of the min lipogenic enzymes is downregulted in viscerl dipose tissue of oese sujects. Oesity 1, 13 2 (21). 2. Dirison, F., Dusserre, E., Vidl, H., Sothier, M. & Beylot, M. Incresed heptic lipogenesis ut decresed expression of lipogenic gene in dipose tissue in humn oesity. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Met. 22, E46 E51 (22). 2. Hudgins, L. C. et l. The effect of dietry crohydrte on genes for ftty cid synthse nd inflmmtory cytokines in dipose tissues from len nd oese sujects. J. Nutr. Biochem. 1, (2). 3. Richrdson, D. K. & Czech, M. P. Diminished ctivities of ftty cid synthesis enzymes in insulin-resistnt dipocytes from spontneously oese rts. Horm. Met. Res., (1). 31. Ndler, S. T. et l. The expression of dipogenic genes is decresed in oesity nd dietes mellitus. Proc. Ntl Acd. Sci. USA, (2). 32. Kouidhi, S. et l. Humn sucutneous dipose tissue Glut 4 mrna expression in oesity nd type 2 dietes. Act. Dietol. (e-pu hed of print 22 My 2). 33. Ael, E. D. et l. Adipose-selective trgeting of the GLUT4 gene impirs insulin ction in muscle nd liver. Nture 4, 2 33 (21). 34. Hurtdo del Pozo, C. et l. ChREBP expression in the liver, dipose tissue nd differentited predipocytes in humn oesity. Biochim. Biophys. Act. 1, 4 (2). 35. Stnhope, K. L. et l. Consuming fructose-sweetened, not glucose-sweetened, everges increses viscerl diposity nd lipids nd decreses insulin sensitivity in overweight/oese humns. J. Clin. Invest., (2). 36. Peter, A. et l. Heptic glucokinse expression is ssocited with lipogenesis nd ftty liver in humns. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Met. 6, E26 E3 (2). 3. Roerts, R. et l. Mrkers of de novo lipogenesis in dipose tissue: ssocitions with smll dipocytes nd insulin sensitivity in humns. Dietologi 52, 2 (2). 3. Gong, J. et l. Adipose tissue plmitoleic cid nd oesity in humns: does it ehve s lipokine? Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 3, 16 (2). 3. Chvez, J. A. & Summers, S. A. Chrcterizing the effects of sturted ftty cids on insulin signling nd cermide nd dicylglycerol ccumultion in 3T3-L1 dipocytes nd C2C myotues. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 41, 1 (23). 4. Hommelerg, P. P., Plt, J., Lngen, R. C., Schols, A. M. & Mensink, R. P. Ftty cid-induced NF-kppB ctivtion nd insulin resistnce in skeletl muscle re chin length dependent. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Met. 26, E4 E (2). 41. vn den Berg, S. A. et l. High levels of dietry sterte promote diposity nd deteriorte heptic insulin sensitivity. Nutr. Met., 24 (21). 42. Liu, X. et l. Loss of steroyl-coa desturse-1 ttenutes dipocyte inflmmtion: effects of dipocyte-derived olete. Arterioscler. Throm. Vsc. Biol. 3, 31 3 (21). 43. Stefn, N. et l. Circulting plmitolete strongly nd independently predicts insulin sensitivity in humns. Dietes Cre 33, 45 4 (21). 44. Frini, E. et l. Insulin sensitivity is not ssocited with plmitolete vilility in oese humns. J. Lipid Res. 52, (2). 45. Pinnick, K. E. et l. Gluteofemorl dipose tissue plys mjor role in production of the lipokine plmitolete in humns. Dietes 61, (2). 46. Yli-Jm, P. et l. Selective moilistion of ftty cids from humn dipose tissue. Eur. J. Intern. Med., 1 5 (21). 4. Fix, D. et l. Quntifiction of menstrul nd diurnl periodicities in rtes of cholesterol nd ft synthesis in humns. J. Lipid Res. 34, (13). 4. Donnelly, K. L., Smith, C. I., Schwrzenerg, S. J., Jessurun, J., Boldt, M. D. & Prks, E. J. Sources of ftty cids stored in liver nd secreted vi lipoproteins in ptients with nonlcoholic ftty liver disese. J. Clin. Invest. 5, (25). 4. Benhmed, F. et l. The lipogenic trnscription fctor ChREBP dissocites heptic stetosis from insulin resistnce in mice nd humns. J. Clin. Invest. 2, (2). 5. Dentin, R. et l. Liver-specific inhiition of ChREBP improves heptic stetosis nd insulin resistnce in o/o mice. Dietes 55, (26). 51. Kneel, B. et l. Liver-specific expression of trnscriptionlly ctive SREBP-1c is ssocited with ftty liver nd incresed viscerl ft mss. PLoS One, e31 (2). 52. Mtsuzk, T. et l. Crucil role of long-chin ftty cid elongse, Elovl6, in oesity-induced insulin resistnce. Nt. Med. 13, 3 2 (2). 53. Ery, E. et l. Reducing endoplsmic reticulum stress through mcrophge lipid chperone llevites therosclerosis. Nt. Med. 15, (2). 54. Medler, K. et l. Monounsturted ftty cids prevent the deleterious effects of plmitte nd high glucose on humn pncretic et-cell turnover nd function. Dietes 52, (23). 55. Green, C. D. & Olson, L. K. Modultion of plmitte-induced endoplsmic reticulum stress nd poptosis in pncretic -cells y steroyl-coa desturse nd Elovl6. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Met. 3, E64 E64 (2). 56. Flowers, J. B. et l. Loss of steroyl-coa desturse-1 improves insulin sensitivity in len mice ut worsens dietes in leptin-deficient oese mice. Dietes 56, 2 3 (2). 5. Scherer, T. et l. Brin insulin controls dipose tissue lipolysis nd lipogenesis. Cell Met. 13, (2). 5. Schej, L. et l. Liver TAG trnsiently decreses while PL n-3 nd n-6 ftty cids re persistently elevted in insulin resistnt mice. Lipids 43, (2). 1 NATURE COMMUNICATIONS 4:152 DOI: 1.13/ncomms253 & 213 Mcmilln Pulishers Limited. All rights reserved.
EFFECTS OF AN ACUTE ENTERIC DISEASE CHALLENGE ON IGF-1 AND IGFBP-3 GENE EXPRESSION IN PORCINE SKELETAL MUSCLE
 Swine Dy 22 Contents EFFECTS OF AN ACUTE ENTERIC DISEASE CHALLENGE ON IGF-1 AND IGFBP-3 GENE EXPRESSION IN PORCINE SKELETAL MUSCLE B. J. Johnson, J. P. Kyser, J. D. Dunn, A. T. Wyln, S. S. Dritz 1, J.
Swine Dy 22 Contents EFFECTS OF AN ACUTE ENTERIC DISEASE CHALLENGE ON IGF-1 AND IGFBP-3 GENE EXPRESSION IN PORCINE SKELETAL MUSCLE B. J. Johnson, J. P. Kyser, J. D. Dunn, A. T. Wyln, S. S. Dritz 1, J.
Supplementary figure 1
 Supplementry figure 1 Dy 8 post LCMV infection Vsculr Assoc. Prenchym Dy 3 post LCMV infection 1 5 6.7.29 1 4 1 3 1 2 88.9 4.16 1 2 1 3 1 4 1 5 1 5 1.59 5.97 1 4 1 3 1 2 21.4 71 1 2 1 3 1 4 1 5 1 5.59.22
Supplementry figure 1 Dy 8 post LCMV infection Vsculr Assoc. Prenchym Dy 3 post LCMV infection 1 5 6.7.29 1 4 1 3 1 2 88.9 4.16 1 2 1 3 1 4 1 5 1 5 1.59 5.97 1 4 1 3 1 2 21.4 71 1 2 1 3 1 4 1 5 1 5.59.22
The effect of dietary α-linolenic acid levels on regulation of omega-3 lipid synthesis in rat
 The effect of dietry α-linolenic cid levels on regultion of omeg-3 lipid synthesis in rt Wei-Chun Tu School of Agriculture Food nd Wine The University of Adelide Conversion of PUFA to LCPUFA PUFA LCPUFA
The effect of dietry α-linolenic cid levels on regultion of omeg-3 lipid synthesis in rt Wei-Chun Tu School of Agriculture Food nd Wine The University of Adelide Conversion of PUFA to LCPUFA PUFA LCPUFA
2018 American Diabetes Association. Published online at
 Supplementry Figure S1. Ft-1 mice exhibit reduced diposity when fed n HFHS diet. WT nd ft-1 mice were fed either control or n HFHS diet for 18 weeks. A: Representtive photogrphs for side-by-side comprison
Supplementry Figure S1. Ft-1 mice exhibit reduced diposity when fed n HFHS diet. WT nd ft-1 mice were fed either control or n HFHS diet for 18 weeks. A: Representtive photogrphs for side-by-side comprison
Feeding state and age dependent changes in melaninconcentrating hormone expression in the hypothalamus of broiler chickens
 Supplementry Mterils Epub: No 2017_23 Vol. 65, 2018 https://doi.org/10.183/bp.2017_23 Regulr pper Feeding stte nd ge dependent chnges in melninconcentrting hormone expression in the hypothlmus of broiler
Supplementry Mterils Epub: No 2017_23 Vol. 65, 2018 https://doi.org/10.183/bp.2017_23 Regulr pper Feeding stte nd ge dependent chnges in melninconcentrting hormone expression in the hypothlmus of broiler
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementry Figure 1 c d Wistr SHR Wistr AF-353 SHR AF-353 n = 6 n = 6 n = 28 n = 3 n = 12 n = 12 Supplementry Figure 1 Neurophysiologicl properties of petrosl chemoreceptive neurones in Wistr nd SH rts.
Supplementry Figure 1 c d Wistr SHR Wistr AF-353 SHR AF-353 n = 6 n = 6 n = 28 n = 3 n = 12 n = 12 Supplementry Figure 1 Neurophysiologicl properties of petrosl chemoreceptive neurones in Wistr nd SH rts.
Clinical Study Report Synopsis Drug Substance Naloxegol Study Code D3820C00018 Edition Number 1 Date 01 February 2013 EudraCT Number
 EudrCT Number 2012-001531-31 A Phse I, Rndomised, Open-lbel, 3-wy Cross-over Study in Helthy Volunteers to Demonstrte the Bioequivlence of the Nloxegol 25 mg Commercil nd Phse III Formultions nd to Assess
EudrCT Number 2012-001531-31 A Phse I, Rndomised, Open-lbel, 3-wy Cross-over Study in Helthy Volunteers to Demonstrte the Bioequivlence of the Nloxegol 25 mg Commercil nd Phse III Formultions nd to Assess
* * * * * liver kidney ileum. Supplementary Fig.S1
 Supplementry Fig.S1 liver kidney ileum Fig.S1. Orlly delivered Fexrmine is intestinlly-restricted Mice received vehicle or Fexrmine (100mg/kg) vi per os (PO) or intrperitonel (IP) injection for 5 dys (n=3/group).
Supplementry Fig.S1 liver kidney ileum Fig.S1. Orlly delivered Fexrmine is intestinlly-restricted Mice received vehicle or Fexrmine (100mg/kg) vi per os (PO) or intrperitonel (IP) injection for 5 dys (n=3/group).
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 X p -lu c ct ivi ty doi:.8/nture8 S CsA - THA + DAPI Merge FSK THA TUN Supplementry Figure : A. Ad-Xp luc ctivity in primry heptocytes exposed to FSK, THA, or TUN s indicted. Luciferse ctivity normlized
X p -lu c ct ivi ty doi:.8/nture8 S CsA - THA + DAPI Merge FSK THA TUN Supplementry Figure : A. Ad-Xp luc ctivity in primry heptocytes exposed to FSK, THA, or TUN s indicted. Luciferse ctivity normlized
Supplementary Figure S1
 Supplementry Figure S Tissue weights (g).... Liver Hert Brin Pncres Len mss (g) 8 6 -% +% 8 6 Len mss Len mss (g) (% ody weight) Len mss (% ody weight) c Tiilis nterior weight (g).6...... Qudriceps weight
Supplementry Figure S Tissue weights (g).... Liver Hert Brin Pncres Len mss (g) 8 6 -% +% 8 6 Len mss Len mss (g) (% ody weight) Len mss (% ody weight) c Tiilis nterior weight (g).6...... Qudriceps weight
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 1.138/nc286 Figure S1 e f Medium DMSO AktVIII PP242 Rp S6K1-I Gr1 + + + + + + Strvtion + + + + + IB: Akt-pT38 IB: Akt K-pT389 K IB: Rptor Gr1 shs6k1-a shs6k1-b shs6k1-c shrictor shrptor Gr1 c IB:
DOI: 1.138/nc286 Figure S1 e f Medium DMSO AktVIII PP242 Rp S6K1-I Gr1 + + + + + + Strvtion + + + + + IB: Akt-pT38 IB: Akt K-pT389 K IB: Rptor Gr1 shs6k1-a shs6k1-b shs6k1-c shrictor shrptor Gr1 c IB:
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Prentl doi:.8/nture57 Figure S HPMECs LM Cells Cell lines VEGF (ng/ml) Prentl 7. +/-. LM 7. +/-.99 LM 7. +/-.99 Fold COX induction 5 VEGF: - + + + Bevcizum: - - 5 (µg/ml) Reltive MMP LM mock COX MMP LM+
Prentl doi:.8/nture57 Figure S HPMECs LM Cells Cell lines VEGF (ng/ml) Prentl 7. +/-. LM 7. +/-.99 LM 7. +/-.99 Fold COX induction 5 VEGF: - + + + Bevcizum: - - 5 (µg/ml) Reltive MMP LM mock COX MMP LM+
The Journal of Physiology
 J Physiol 595.13 (2017) pp 4379 4398 4379 Impct of perintl exposure to sucrose or high fructose corn syrup (HFCS-55) on diposity nd heptic lipid composition in rt offspring Crl R. Toop 1, Beverly S. Muhlhusler
J Physiol 595.13 (2017) pp 4379 4398 4379 Impct of perintl exposure to sucrose or high fructose corn syrup (HFCS-55) on diposity nd heptic lipid composition in rt offspring Crl R. Toop 1, Beverly S. Muhlhusler
THE EVALUATION OF DEHULLED CANOLA MEAL IN THE DIETS OF GROWING AND FINISHING PIGS
 THE EVALUATION OF DEHULLED CANOLA MEAL IN THE DIETS OF GROWING AND FINISHING PIGS THE EVALUATION OF DEHULLED CANOLA MEAL IN THE DIETS OF GROWING AND FINISHING PIGS John F. Ptience nd Doug Gillis SUMMARY
THE EVALUATION OF DEHULLED CANOLA MEAL IN THE DIETS OF GROWING AND FINISHING PIGS THE EVALUATION OF DEHULLED CANOLA MEAL IN THE DIETS OF GROWING AND FINISHING PIGS John F. Ptience nd Doug Gillis SUMMARY
Copy Number ID2 MYCN ID2 MYCN. Copy Number MYCN DDX1 ID2 KIDINS220 MBOAT2 ID2
 Copy Numer Copy Numer Copy Numer Copy Numer DIPG38 DIPG49 ID2 MYCN ID2 MYCN c DIPG01 d DIPG29 ID2 MYCN ID2 MYCN e STNG2 f MYCN DIPG01 Chr. 2 DIPG29 Chr. 1 MYCN DDX1 Chr. 2 ID2 KIDINS220 MBOAT2 ID2 Supplementry
Copy Numer Copy Numer Copy Numer Copy Numer DIPG38 DIPG49 ID2 MYCN ID2 MYCN c DIPG01 d DIPG29 ID2 MYCN ID2 MYCN e STNG2 f MYCN DIPG01 Chr. 2 DIPG29 Chr. 1 MYCN DDX1 Chr. 2 ID2 KIDINS220 MBOAT2 ID2 Supplementry
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nture11225 Numer of OTUs sed on 3% distnce Numer of 16s rrna-sed V2-V4 tg sequences LF MF PUFA Supplementry Figure 1. High-ft diets decrese the richness nd diversity
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nture11225 Numer of OTUs sed on 3% distnce Numer of 16s rrna-sed V2-V4 tg sequences LF MF PUFA Supplementry Figure 1. High-ft diets decrese the richness nd diversity
Effects of physical exercise on working memory and prefrontal cortex function in post-stroke patients
 Effects of physicl exercise on working memory nd prefrontl cortex function in post-stroke ptients M Moriy, C Aoki, K Sktni Grdute School of Helth Sciences Reserch, Mjor of Physicl Therpy, TeikyoHeisei
Effects of physicl exercise on working memory nd prefrontl cortex function in post-stroke ptients M Moriy, C Aoki, K Sktni Grdute School of Helth Sciences Reserch, Mjor of Physicl Therpy, TeikyoHeisei
Acute and gradual increases in BDNF concentration elicit distinct signaling and functions in neurons
 nd grdul increses in BDNF concentrtion elicit distinct signling nd functions in neurons Yunyun Ji,, Yun Lu, Feng Yng, Wnhu Shen, Tin Tze-Tsng Tng,, Linyin Feng, Shumin Dun, nd Bi Lu,.. - Grdul (normlized
nd grdul increses in BDNF concentrtion elicit distinct signling nd functions in neurons Yunyun Ji,, Yun Lu, Feng Yng, Wnhu Shen, Tin Tze-Tsng Tng,, Linyin Feng, Shumin Dun, nd Bi Lu,.. - Grdul (normlized
SYNOPSIS Final Abbreviated Clinical Study Report for Study CA ABBREVIATED REPORT
 Finl Arevited Clinicl Study Report Nme of Sponsor/Compny: Bristol-Myers Squi Ipilimum Individul Study Tle Referring to the Dossier (For Ntionl Authority Use Only) Nme of Finished Product: Yervoy Nme of
Finl Arevited Clinicl Study Report Nme of Sponsor/Compny: Bristol-Myers Squi Ipilimum Individul Study Tle Referring to the Dossier (For Ntionl Authority Use Only) Nme of Finished Product: Yervoy Nme of
Adipocyte in vascular wall can induce the rupture of abdominal aortic aneurysm
 Adipocyte in vsculr wll cn induce the rupture of dominl ortic neurysm Hiron Kugo 1 *, Nouhiro Zim 1 *, Hiroki Tnk 2 *, Youhei Mouri 1, Kenichi Yngimoto 3, Kohsuke Hymizu 3,4, Keisuke Hshimoto 1, Tkeshi
Adipocyte in vsculr wll cn induce the rupture of dominl ortic neurysm Hiron Kugo 1 *, Nouhiro Zim 1 *, Hiroki Tnk 2 *, Youhei Mouri 1, Kenichi Yngimoto 3, Kohsuke Hymizu 3,4, Keisuke Hshimoto 1, Tkeshi
TNF-α (pg/ml) IL-6 (ng/ml)
 Xio, et l., Supplementry Figure 1 IL-6 (ng/ml) TNF-α (pg/ml) 16 12 8 4 1,4 1,2 1, 8 6 4 2 med Cl / Pm3CSK4 zymosn curdln Poly (I:C) LPS flgelin MALP-2 imiquimod R848 CpG TNF-α (pg/ml) IL-6 (ng/ml) 2 1.6
Xio, et l., Supplementry Figure 1 IL-6 (ng/ml) TNF-α (pg/ml) 16 12 8 4 1,4 1,2 1, 8 6 4 2 med Cl / Pm3CSK4 zymosn curdln Poly (I:C) LPS flgelin MALP-2 imiquimod R848 CpG TNF-α (pg/ml) IL-6 (ng/ml) 2 1.6
Using Paclobutrazol to Suppress Inflorescence Height of Potted Phalaenopsis Orchids
 Using Pcloutrzol to Suppress Inflorescence Height of Potted Phlenopsis Orchids A REPORT SUBMITTED TO FINE AMERICAS Linsey Newton nd Erik Runkle Deprtment of Horticulture Spring 28 Using Pcloutrzol to Suppress
Using Pcloutrzol to Suppress Inflorescence Height of Potted Phlenopsis Orchids A REPORT SUBMITTED TO FINE AMERICAS Linsey Newton nd Erik Runkle Deprtment of Horticulture Spring 28 Using Pcloutrzol to Suppress
PNEUMOVAX 23 is recommended by the CDC for all your appropriate adult patients at increased risk for pneumococcal disease 1,2 :
 PNEUMOVAX 23 is recommended y the CDC for ll your pproprite dult ptients t incresed risk for pneumococcl disese 1,2 : Adults ged
PNEUMOVAX 23 is recommended y the CDC for ll your pproprite dult ptients t incresed risk for pneumococcl disese 1,2 : Adults ged
Effect of supplemental fat from dried distillers grains with solubles or corn oil on cow performance, IGF-1, GH, and NEFA concentrations 1
 Effect of supplementl ft from dried distillers grins with solules or corn oil on cow performnce, IGF-1, GH, nd NEFA concentrtions 1 Aigil Brtosh 2, Cody Wright 3, Aimee Wertz-Lutz 4, nd George Perry 5
Effect of supplementl ft from dried distillers grins with solules or corn oil on cow performnce, IGF-1, GH, nd NEFA concentrtions 1 Aigil Brtosh 2, Cody Wright 3, Aimee Wertz-Lutz 4, nd George Perry 5
ESM Table 1. Characterisation of the human non-diabetic cohort used for MRIbased assessment of pancreatic fat and insulin secretion via OGTT.
 ESM Tle 1. Chrcteristion of the humn non-dietic cohort used for MRIsed ssessment of pncretic ft nd insulin secretion vi OGTT. Trit sex Medin (IQR) 86 femles, 5 mles ge (yers) 4.4 (.5-5.57) BMI (kg/m²).62
ESM Tle 1. Chrcteristion of the humn non-dietic cohort used for MRIsed ssessment of pncretic ft nd insulin secretion vi OGTT. Trit sex Medin (IQR) 86 femles, 5 mles ge (yers) 4.4 (.5-5.57) BMI (kg/m²).62
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 . Norml Physiologicl Conditions. SIRT1 Loss-of-Function S1. Model for the role of SIRT1 in the regultion of memory nd plsticity. () Our findings suggest tht SIRT1 normlly functions in coopertion with YY1,
. Norml Physiologicl Conditions. SIRT1 Loss-of-Function S1. Model for the role of SIRT1 in the regultion of memory nd plsticity. () Our findings suggest tht SIRT1 normlly functions in coopertion with YY1,
The Effect of Substituting Sugar with Artificial. Sweeteners on the Texture and Palatability of Pancakes
 The Effect of Sustituting Sugr with Artificil NUTR 453 Sweeteners on the Texture nd Pltility of Pnckes Jmie Wldron, Rquel Reyes, nd Reecc Legi 1 I. Astrct The effects of replcing sugr with Stevi nd Splend
The Effect of Sustituting Sugr with Artificil NUTR 453 Sweeteners on the Texture nd Pltility of Pnckes Jmie Wldron, Rquel Reyes, nd Reecc Legi 1 I. Astrct The effects of replcing sugr with Stevi nd Splend
Supplementary Figure 1
 doi: 1.138/nture6188 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementry Figure 1 c CFU-F colonies per 1 5 stroml cells 14 12 1 8 6 4 2 Mtrigel plug Neg. MCF7/Rs MDA-MB-231 * * MCF7/Rs-Lung MDA-MB-231-Lung MCF7/Rs-Kidney
doi: 1.138/nture6188 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementry Figure 1 c CFU-F colonies per 1 5 stroml cells 14 12 1 8 6 4 2 Mtrigel plug Neg. MCF7/Rs MDA-MB-231 * * MCF7/Rs-Lung MDA-MB-231-Lung MCF7/Rs-Kidney
Expression of Three Cell Cycle Inhibitors during Development of Adipose Tissue
 Expression of Three Cell Cycle Inhiitors during Development of Adipose Tissue Jiin Zhng Deprtment of Animl Sciences Advisor: Michel E. Dvis Co-dvisor: Kichoon Lee Development of niml dipose tissue Hypertrophy
Expression of Three Cell Cycle Inhiitors during Development of Adipose Tissue Jiin Zhng Deprtment of Animl Sciences Advisor: Michel E. Dvis Co-dvisor: Kichoon Lee Development of niml dipose tissue Hypertrophy
How adaptations of substrate utilization regulate body composition
 (27) 1 6 & 27 Nture Pulishing Group All rights reserved 37-565/7 $3. www.nture.com/ijo ORIGINAL ARTICLE How dpttions of sustrte utiliztion regulte ody composition KD Hll, HL Bin nd CC Chow Lortory of Biologicl
(27) 1 6 & 27 Nture Pulishing Group All rights reserved 37-565/7 $3. www.nture.com/ijo ORIGINAL ARTICLE How dpttions of sustrte utiliztion regulte ody composition KD Hll, HL Bin nd CC Chow Lortory of Biologicl
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:1.138/nture1794 BR EPFs BRI1? ERECTA TMM BSKs YDA PP2A BSU1 BIN2 pbzr1/2 BZR1/2 MKK4/5/7/9 MPK3/6 SPCH Cell growth Stomtl production Supplementry Figure 1. The model of BR nd stomtl signling pthwys.
doi:1.138/nture1794 BR EPFs BRI1? ERECTA TMM BSKs YDA PP2A BSU1 BIN2 pbzr1/2 BZR1/2 MKK4/5/7/9 MPK3/6 SPCH Cell growth Stomtl production Supplementry Figure 1. The model of BR nd stomtl signling pthwys.
Effect of kazunoko lipid on the concentrations of plasma glucose and lipids and liver lipids in mice
 Effect of kzunoko lipid on the concentrtions of plsm glucose nd lipids nd liver lipids in mice Ntionl Food Reserch Institute Tomoyuki Higuchi, Nouy Shiri nd Hirmitsu Suzuki INTRODUCTION Kzunoko, which
Effect of kzunoko lipid on the concentrtions of plsm glucose nd lipids nd liver lipids in mice Ntionl Food Reserch Institute Tomoyuki Higuchi, Nouy Shiri nd Hirmitsu Suzuki INTRODUCTION Kzunoko, which
British Journal of Nutrition
 (11), 16, 1449 1456 q The Authors 11 doi:1.117/s71145111917 Fish oil comined with SCFA synergisticlly prevent tissue ccumultion of NEFA during weight loss in oese mice Miken H. Pedersen 1,, Lotte Luritzen
(11), 16, 1449 1456 q The Authors 11 doi:1.117/s71145111917 Fish oil comined with SCFA synergisticlly prevent tissue ccumultion of NEFA during weight loss in oese mice Miken H. Pedersen 1,, Lotte Luritzen
Supplementary Figure 1
 Roles of endoplsmic reticulum stress-medited poptosis in -polrized mcrophges during mycocteril infections Supplementry informtion Yun-Ji Lim, Min-Hee Yi, Ji-Ae Choi, Jung-hwn Lee, Ji-Ye Hn, Sung-Hee Jo,
Roles of endoplsmic reticulum stress-medited poptosis in -polrized mcrophges during mycocteril infections Supplementry informtion Yun-Ji Lim, Min-Hee Yi, Ji-Ae Choi, Jung-hwn Lee, Ji-Ye Hn, Sung-Hee Jo,
Health-Related Quality of Life and Symptoms of Depression in Extremely Obese Persons Seeking Bariatric Surgery
 Oesity Surgery, 15, 3-39 Helth-Relted Qulity of Life nd Symptoms of Depression in Extremely Oese Persons Seeking Britric Surgery Anthony N. Frictore, PhD; Thoms A. Wdden, PhD; Dvid B. Srwer, PhD; Myles
Oesity Surgery, 15, 3-39 Helth-Relted Qulity of Life nd Symptoms of Depression in Extremely Oese Persons Seeking Britric Surgery Anthony N. Frictore, PhD; Thoms A. Wdden, PhD; Dvid B. Srwer, PhD; Myles
SESSIONE I: RELATORI. Ghrelin: from oroxigenic signal to metabolic master regulator?
 SESSIONE I: RELATORI Ghrelin: from oroxigenic signl to metbolic mster regultor? Prof. Rocco Brzzoni Professore ssocito di Medicin Intern Università degli Studi di Trieste Ghrelin: d segnle oressizznte
SESSIONE I: RELATORI Ghrelin: from oroxigenic signl to metbolic mster regultor? Prof. Rocco Brzzoni Professore ssocito di Medicin Intern Università degli Studi di Trieste Ghrelin: d segnle oressizznte
Optimisation of diets for Atlantic cod (Gadus morhua) broodstock: effect of arachidonic acid on egg & larval quality
 Optimistion of diets for Atlntic cod (Gdus morhu) roodstock: effect of rchidonic cid on egg & lrvl qulity Dr Gordon Bell, Ms. An Blnco, Dr Bill Roy, Dr Derek Roertson, Dr Jim Henderson nd Mr Richrd Prickett,
Optimistion of diets for Atlntic cod (Gdus morhu) roodstock: effect of rchidonic cid on egg & lrvl qulity Dr Gordon Bell, Ms. An Blnco, Dr Bill Roy, Dr Derek Roertson, Dr Jim Henderson nd Mr Richrd Prickett,
*** *** *** *** T-cells T-ALL. T-cells T-ALL. T-cells T-ALL. T-cells T-ALL. T-cells T-ALL. Relative ATP content. Relative ATP content RLU RLU
 RLU Events 1 1 1 Luciferin (μm) T-cells T-ALL 1 1 Time (min) T-cells T-ALL 1 1 1 1 DCF-DA Reltive ATP content....1.1.. T-cells T-ALL RLU 1 1 T-cells T-ALL Luciferin (μm) 1 1 Time (min) c d Control e DCFH-DA
RLU Events 1 1 1 Luciferin (μm) T-cells T-ALL 1 1 Time (min) T-cells T-ALL 1 1 1 1 DCF-DA Reltive ATP content....1.1.. T-cells T-ALL RLU 1 1 T-cells T-ALL Luciferin (μm) 1 1 Time (min) c d Control e DCFH-DA
British Journal of Nutrition
 British Journl of Nutrition (215), 113, 1862 1875 q The Authors 215 doi:1.117/s7114515121x Anormlities in myo-inositol metolism ssocited with type 2 dietes in mice fed high-ft diet: enefits of dietry myo-inositol
British Journl of Nutrition (215), 113, 1862 1875 q The Authors 215 doi:1.117/s7114515121x Anormlities in myo-inositol metolism ssocited with type 2 dietes in mice fed high-ft diet: enefits of dietry myo-inositol
PROVEN ANTICOCCIDIAL IN NEW FORMULATION
 PROVEN ANTICOCCIDIAL IN NEW FORMULATION Coxidin 100 microgrnulte A coccidiosttic dditive for roilers, chickens rered for lying nd turkeys Contins 100 g of monensin sodium per kg Aville s homogenous grnules
PROVEN ANTICOCCIDIAL IN NEW FORMULATION Coxidin 100 microgrnulte A coccidiosttic dditive for roilers, chickens rered for lying nd turkeys Contins 100 g of monensin sodium per kg Aville s homogenous grnules
Combined deletion of SCD1 from adipose tissue and liver does not protect
 Comined deletion of SCD1 from dipose tissue nd liver does not protect mice from oesity Mtthew T. Flowers 1, Lcmouh de 1, Mggie S. Strle 2 nd Jmes M. Ntmi 1,2,* Deprtments of 1 Biochemistry nd 2 Nutritionl
Comined deletion of SCD1 from dipose tissue nd liver does not protect mice from oesity Mtthew T. Flowers 1, Lcmouh de 1, Mggie S. Strle 2 nd Jmes M. Ntmi 1,2,* Deprtments of 1 Biochemistry nd 2 Nutritionl
Input from external experts and manufacturer on the 2 nd draft project plan Stool DNA testing for early detection of colorectal cancer
 Input externl experts nd mnufcturer on the 2 nd drft project pln Stool DNA testing for erly detection of colorectl cncer (Project ID:OTJA10) All s nd uthor s replies on the 2nd drft project pln Stool DNA
Input externl experts nd mnufcturer on the 2 nd drft project pln Stool DNA testing for erly detection of colorectl cncer (Project ID:OTJA10) All s nd uthor s replies on the 2nd drft project pln Stool DNA
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi: 10.1038/nture07679 Emryonic Stem (ES) cell Hemngiolst Flk1 + Blst Colony 3 to 3.5 Dys 3-4 Dys ES differentition Sort of Flk1 + cells Supplementry Figure 1. Chrcteristion of lst colony development.
doi: 10.1038/nture07679 Emryonic Stem (ES) cell Hemngiolst Flk1 + Blst Colony 3 to 3.5 Dys 3-4 Dys ES differentition Sort of Flk1 + cells Supplementry Figure 1. Chrcteristion of lst colony development.
Invasive Pneumococcal Disease Quarterly Report. July September 2017
 Invsive Pneumococcl Disese Qurterly Report July September 2017 Prepred s prt of Ministry of Helth contrct for scientific services by Rebekh Roos Helen Heffernn October 2017 Acknowledgements This report
Invsive Pneumococcl Disese Qurterly Report July September 2017 Prepred s prt of Ministry of Helth contrct for scientific services by Rebekh Roos Helen Heffernn October 2017 Acknowledgements This report
NappHS. rrna. transcript abundance. NappHS relative con W+W 0.8. nicotine [µg mg -1 FM]
![NappHS. rrna. transcript abundance. NappHS relative con W+W 0.8. nicotine [µg mg -1 FM] NappHS. rrna. transcript abundance. NappHS relative con W+W 0.8. nicotine [µg mg -1 FM]](/thumbs/92/110177253.jpg) (A) W+OS 3 min 6 min con L S L S RNA loding control NppHS rrna (B) (C) 8 1 k NppHS reltive trnscript undnce 6 4.5 *** *** *** *** 3 k. + + + line 1 line (D) nicotine [µg mg -1 FM] 1..8.4. con W+W Supplementl
(A) W+OS 3 min 6 min con L S L S RNA loding control NppHS rrna (B) (C) 8 1 k NppHS reltive trnscript undnce 6 4.5 *** *** *** *** 3 k. + + + line 1 line (D) nicotine [µg mg -1 FM] 1..8.4. con W+W Supplementl
Debra A. Ignaut, R.N., B.S., C.D.E., and Haoda Fu, Ph.D.
 Journl of Dietes Science nd Technology Volume 6, Issue 2, Mrch 2012 Dietes Technology Society TECHNOLOGY REPORT Comprison of Insulin Diluent Lekge Postinjection Using Two Different Needle Lengths nd Injection
Journl of Dietes Science nd Technology Volume 6, Issue 2, Mrch 2012 Dietes Technology Society TECHNOLOGY REPORT Comprison of Insulin Diluent Lekge Postinjection Using Two Different Needle Lengths nd Injection
Gene expression phenotypic models that predict the activity of oncogenic pathways
 3 Nture Pulishing Group http://www.nture.com/nturegenetics Gene expression phenotypic models tht predict the ctivity of oncogenic pthwys Erich Hung,, Seiichi Ishid,7, Jennifer Pittmn,3, Holly Dressmn,,4,
3 Nture Pulishing Group http://www.nture.com/nturegenetics Gene expression phenotypic models tht predict the ctivity of oncogenic pthwys Erich Hung,, Seiichi Ishid,7, Jennifer Pittmn,3, Holly Dressmn,,4,
% Inhibition of MERS pseudovirus infection. 0 h 0.5 h 1 h 2 h 4 h 6 h Time after virus addition
 % Inhiition of MERS pseudovirus infection 1 8 h.5 h 1 h 2 h 4 h 6 h Time fter virus ddition Supplementry Figure S1. Inhiition of on MERS pseudovirus infection t the different intervls postinfection. A
% Inhiition of MERS pseudovirus infection 1 8 h.5 h 1 h 2 h 4 h 6 h Time fter virus ddition Supplementry Figure S1. Inhiition of on MERS pseudovirus infection t the different intervls postinfection. A
Hypoxia-induced inflammatory cytokine secretion in human adipose tissue stromovascular cells
 Dietologi (211) 54:148 149 DOI 1.17/s125-11-213-y ARTICLE Hypoxi-induced inflmmtory cytokine secretion in humn dipose tissue stromovsculr cells R. W. O Rourke & A. E. White & M. D. Metclf & A. S. Olivs
Dietologi (211) 54:148 149 DOI 1.17/s125-11-213-y ARTICLE Hypoxi-induced inflmmtory cytokine secretion in humn dipose tissue stromovsculr cells R. W. O Rourke & A. E. White & M. D. Metclf & A. S. Olivs
A rt i c l e s. a Events (% of max)
 Continuous requirement for the TCR in regultory T cell function Andrew G Levine 1,, Aron Arvey 1,,4, Wei Jin 1,,4 & Alexnder Y Rudensky 1 3 14 Nture Americ, Inc. All rights reserved. Foxp3 + regultory
Continuous requirement for the TCR in regultory T cell function Andrew G Levine 1,, Aron Arvey 1,,4, Wei Jin 1,,4 & Alexnder Y Rudensky 1 3 14 Nture Americ, Inc. All rights reserved. Foxp3 + regultory
Inheritance of cholesterol metabolism of probands with high or low cholesterol absorption
 Inheritnce of cholesterol metolism of pronds with high or low cholesterol sorption Helen Gylling* nd Ttu A. Miettinen 1, Deprtment of Clinicl Nutrition,* University of Kuopio, nd Kuopio University Hospitl,
Inheritnce of cholesterol metolism of pronds with high or low cholesterol sorption Helen Gylling* nd Ttu A. Miettinen 1, Deprtment of Clinicl Nutrition,* University of Kuopio, nd Kuopio University Hospitl,
Curcumin attenuates Nrf2 signaling defect, oxidative stress in muscle and glucose intolerance in high fat diet-fed mice
 Online Sumissions: http://www.wjgnet.com/1948-938of fice wjd@wjgnet.com doi:239/wjd.v3.i.94 World J Dietes 212 My 1; 3(): 94-14 ISSN 1948-938 (online) 212 Bishideng. All rights reserved. ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Online Sumissions: http://www.wjgnet.com/1948-938of fice wjd@wjgnet.com doi:239/wjd.v3.i.94 World J Dietes 212 My 1; 3(): 94-14 ISSN 1948-938 (online) 212 Bishideng. All rights reserved. ORIGINAL ARTICLE
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:0.08/nture0987 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE Structure of rbbit Xist gene. Exons re shown in boxes with romn numbers, introns in thin lines. Arrows indicte the locliztion of primers used for mplifiction. WWW.NATURE.COM/NATURE
doi:0.08/nture0987 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE Structure of rbbit Xist gene. Exons re shown in boxes with romn numbers, introns in thin lines. Arrows indicte the locliztion of primers used for mplifiction. WWW.NATURE.COM/NATURE
Check your understanding 3
 1 Wht is the difference etween pssive trnsport nd ctive trnsport? Pssive trnsport is the movement of prticles not requiring energy. Movement of prticles in ctive trnsport uses energy. 2 A gs tp in the
1 Wht is the difference etween pssive trnsport nd ctive trnsport? Pssive trnsport is the movement of prticles not requiring energy. Movement of prticles in ctive trnsport uses energy. 2 A gs tp in the
Hormonal networks involved in phosphate deficiencyinduced cluster root formation of Lupinus albus L.
 Institute of Crop Science (34h) Hormonl networks involved in phosphte deficiencyinduced cluster root formtion of Lupinus lus L. For PSP5 in Montpellier, 214 Zhengrui Wng, A.B.M. Moshiur Rhmn, Guoying Wng,
Institute of Crop Science (34h) Hormonl networks involved in phosphte deficiencyinduced cluster root formtion of Lupinus lus L. For PSP5 in Montpellier, 214 Zhengrui Wng, A.B.M. Moshiur Rhmn, Guoying Wng,
TLR7 induces anergy in human CD4 + T cells
 TLR7 induces nergy in humn CD T cells Mrgrit Dominguez-Villr 1, Anne-Sophie Gutron 1, Mrine de Mrcken 1, Mrl J Keller & Dvid A Hfler 1 The recognition of microil ptterns y Toll-like receptors (TLRs) is
TLR7 induces nergy in humn CD T cells Mrgrit Dominguez-Villr 1, Anne-Sophie Gutron 1, Mrine de Mrcken 1, Mrl J Keller & Dvid A Hfler 1 The recognition of microil ptterns y Toll-like receptors (TLRs) is
Heparanase promotes tumor infiltration and antitumor activity of CAR-redirected T- lymphocytes
 Supporting Online Mteril for Heprnse promotes tumor infiltrtion nd ntitumor ctivity of -redirected T- lymphocytes IgnzioCrun, Brr Svoldo, VlentinHoyos, Gerrit Weer, Ho Liu, Eugene S. Kim, Michel M. Ittmnn,
Supporting Online Mteril for Heprnse promotes tumor infiltrtion nd ntitumor ctivity of -redirected T- lymphocytes IgnzioCrun, Brr Svoldo, VlentinHoyos, Gerrit Weer, Ho Liu, Eugene S. Kim, Michel M. Ittmnn,
Invasive Pneumococcal Disease Quarterly Report July September 2018
 Invsive Pneumococcl Disese Qurterly Report July Septemer Introduction Since 17 Octoer 2008, invsive pneumococcl disese (IPD) hs een notifile to the locl Medicl Officer of Helth under the Helth Act 1956.
Invsive Pneumococcl Disese Qurterly Report July Septemer Introduction Since 17 Octoer 2008, invsive pneumococcl disese (IPD) hs een notifile to the locl Medicl Officer of Helth under the Helth Act 1956.
Abstract ABSTRACT #69. Abstract. Introduction & Methods. Methods & Results. Results. Results & Conclusions
 Effects of dietry β-glucn on Growth Performnce, Dirrhe, nd Gut Permeility of Wening Pigs Experimentlly Infected with Pthogenic E. coli Kwngwook Kim, Amy Ehrlich, Vivin Perng, Jennifer Chse, Helen Ryould,
Effects of dietry β-glucn on Growth Performnce, Dirrhe, nd Gut Permeility of Wening Pigs Experimentlly Infected with Pthogenic E. coli Kwngwook Kim, Amy Ehrlich, Vivin Perng, Jennifer Chse, Helen Ryould,
Interleukin-4 Restores Insulin Sensitivity in Lipid-Induced Insulin-Resistant Adipocytes
 ISSN 6-2979, Biochemistry (Moscow), 21, Vol. 3, No. 5, pp. 49-56. Pleides Pulishing, Ltd., 21. Originl Russin Text I. S. Stfeev, S. S. Michurin,3, N. V. Podkuychenko, A. V. Vorotnikov, M. Yu. Menshikov,
ISSN 6-2979, Biochemistry (Moscow), 21, Vol. 3, No. 5, pp. 49-56. Pleides Pulishing, Ltd., 21. Originl Russin Text I. S. Stfeev, S. S. Michurin,3, N. V. Podkuychenko, A. V. Vorotnikov, M. Yu. Menshikov,
USE OF SORGHUM-BASED DISTILLERS GRAINS IN DIETS FOR NURSERY AND FINISHING PIGS
 Swine Dy 1996 USE OF SORGHUM-BASED DISTILLERS GRAINS IN DIETS FOR NURSERY AND FINISHING PIGS B. W. Senne, J. D. Hncock, I. Mvromichlis, S. L. Johnston, P. S. Sorrell, I. H. Kim, nd R. H. Hines Summry Two
Swine Dy 1996 USE OF SORGHUM-BASED DISTILLERS GRAINS IN DIETS FOR NURSERY AND FINISHING PIGS B. W. Senne, J. D. Hncock, I. Mvromichlis, S. L. Johnston, P. S. Sorrell, I. H. Kim, nd R. H. Hines Summry Two
Effect of fungicide timing and wheat varietal resistance on Mycosphaerella graminicola and its sterol 14 α-demethylation-inhibitorresistant
 Effect of fungicide timing nd whet vrietl resistnce on Mycospherell grminicol nd its sterol 14 α-demethyltion-inhiitorresistnt genotypes Didierlurent L., Roisin-Fichter C., Snssené J., Selim S. Pltform
Effect of fungicide timing nd whet vrietl resistnce on Mycospherell grminicol nd its sterol 14 α-demethyltion-inhiitorresistnt genotypes Didierlurent L., Roisin-Fichter C., Snssené J., Selim S. Pltform
Meat and Food Safety. B.A. Crow, M.E. Dikeman, L.C. Hollis, R.A. Phebus, A.N. Ray, T.A. Houser, and J.P. Grobbel
 Met nd Food Sfety Needle-Free Injection Enhncement of Beef Strip Loins with Phosphte nd Slt Hs Potentil to Improve Yield, Tenderness, nd Juiciness ut Hrm Texture nd Flvor B.A. Crow, M.E. Dikemn, L.C. Hollis,
Met nd Food Sfety Needle-Free Injection Enhncement of Beef Strip Loins with Phosphte nd Slt Hs Potentil to Improve Yield, Tenderness, nd Juiciness ut Hrm Texture nd Flvor B.A. Crow, M.E. Dikemn, L.C. Hollis,
Introduction. Lance Baumgard. Introduction con t. Research Emphasis at AZ. Teaching and Advising. Research Emphasis at ISU 4/29/2010
 Introduction Lnce Bumgrd Associte Professor Ntive of southwest Minnesot BS: U of Minnesot MS: U of Minnesot Advisor: Brin Crooker Thesis: Effects of genetic selection for milk yield on somtotropin prmeters
Introduction Lnce Bumgrd Associte Professor Ntive of southwest Minnesot BS: U of Minnesot MS: U of Minnesot Advisor: Brin Crooker Thesis: Effects of genetic selection for milk yield on somtotropin prmeters
The role of insulin and glucose in goose primary hepatocyte triglyceride accumulation
 1553 The Journl of Experimentl Biology 212, 1553-1558 Pulished y The Compny of Biologists 2009 doi:10.1242/je.022210 The role of insulin nd glucose in goose primry heptocyte triglyceride ccumultion Chunchun
1553 The Journl of Experimentl Biology 212, 1553-1558 Pulished y The Compny of Biologists 2009 doi:10.1242/je.022210 The role of insulin nd glucose in goose primry heptocyte triglyceride ccumultion Chunchun
The effect of encapsulated butyric acid and zinc on performance, gut integrity and meat quality in male broiler chickens 1
 The effect of encpsulted utyric cid nd zinc on performnce, gut integrity nd met qulity in mle roiler chickens 1 Astrct This study evluted the impct of encpsulted utyric cid nd zinc (ButiPEARL Z) on performnce
The effect of encpsulted utyric cid nd zinc on performnce, gut integrity nd met qulity in mle roiler chickens 1 Astrct This study evluted the impct of encpsulted utyric cid nd zinc (ButiPEARL Z) on performnce
EFFECTS OF INGREDIENT AND WHOLE DIET IRRADIATION ON NURSERY PIG PERFORMANCE
 Swine Dy 21 EFFECTS OF INGREDIENT AND WHOLE DIET IRRADIATION ON NURSERY PIG PERFORMANCE J. M. DeRouchey, M. D. Tokch, J. L. Nelssen, R. D. Goodbnd, S. S. Dritz 1, J. C. Woodworth, M. J. Webster, B. W.
Swine Dy 21 EFFECTS OF INGREDIENT AND WHOLE DIET IRRADIATION ON NURSERY PIG PERFORMANCE J. M. DeRouchey, M. D. Tokch, J. L. Nelssen, R. D. Goodbnd, S. S. Dritz 1, J. C. Woodworth, M. J. Webster, B. W.
Brown adipose tissue activity controls triglyceride clearance
 Supplementry informtion Brown dipose tissue ctivity s triglyceride clernce Alexnder Brtelt 1, Oliver T. Bruns 2, Rudolph Reimer 2, Heinz Hohenerg 2, Hrld Ittrich 3, Kersten Peldschus 3, Michel G. Kul 3,
Supplementry informtion Brown dipose tissue ctivity s triglyceride clernce Alexnder Brtelt 1, Oliver T. Bruns 2, Rudolph Reimer 2, Heinz Hohenerg 2, Hrld Ittrich 3, Kersten Peldschus 3, Michel G. Kul 3,
supplementary information
 DOI: 10.1038/nc2089 H3K4me1 H3K4me1 H3K4me1 H3K4me1 H3K4me1 H3K4me1 5 PN N1-2 PN H3K4me1 H3K4me1 H3K4me1 2-cell stge 2-c st cell ge Figure S1 Pttern of loclistion of H3K4me1 () nd () during zygotic development
DOI: 10.1038/nc2089 H3K4me1 H3K4me1 H3K4me1 H3K4me1 H3K4me1 H3K4me1 5 PN N1-2 PN H3K4me1 H3K4me1 H3K4me1 2-cell stge 2-c st cell ge Figure S1 Pttern of loclistion of H3K4me1 () nd () during zygotic development
Supplementary Figure S1
 Supplementry Figure S Connexin4 TroponinI Merge Plsm memrne Met Intrcellulr Met Supplementry Figure S H9c rt crdiomyolsts cell line. () Immunofluorescence of crdic mrkers: Connexin4 (green) nd TroponinI
Supplementry Figure S Connexin4 TroponinI Merge Plsm memrne Met Intrcellulr Met Supplementry Figure S H9c rt crdiomyolsts cell line. () Immunofluorescence of crdic mrkers: Connexin4 (green) nd TroponinI
Consumer perceptions of meat quality and shelf-life in commercially raised broilers compared to organic free range broilers
 Consumer perceptions of met qulity nd shelf-life in commercilly rised roilers compred to orgnic free rnge roilers C.Z. ALVARADO 1 *, E. WENGER 2 nd S. F. O KEEFE 3 1 Texs Tech University, Box 42141 Luock,
Consumer perceptions of met qulity nd shelf-life in commercilly rised roilers compred to orgnic free rnge roilers C.Z. ALVARADO 1 *, E. WENGER 2 nd S. F. O KEEFE 3 1 Texs Tech University, Box 42141 Luock,
Chapter 5: The peripheral nervous system Learning activity suggested answers
 Chpter 5: The peripherl nervous system Lerning ctivity suggested nswers Lerning Activity 5.1 (p. 222) 1 Briefly descrie the two min functions of the somtic nervous system. Description should refer to:
Chpter 5: The peripherl nervous system Lerning ctivity suggested nswers Lerning Activity 5.1 (p. 222) 1 Briefly descrie the two min functions of the somtic nervous system. Description should refer to:
Comparison of three simple methods for the
 J. clin. Pth. (1967), 2, 5 Comprison of three simple methods for the ssessment of 'free' thyroid hormone T. M. D. GIMLETTE1 From the Rdio-Isotope Lbortory, St. Thoms's Hospitl, London SYNOPSIS A dilysis
J. clin. Pth. (1967), 2, 5 Comprison of three simple methods for the ssessment of 'free' thyroid hormone T. M. D. GIMLETTE1 From the Rdio-Isotope Lbortory, St. Thoms's Hospitl, London SYNOPSIS A dilysis
A FACTORIAL STUDY ON THE EFFECTS OF β CYCLODEXTRIN AND POLOXAMER 407 ON THE SOLUBILITY AND DISSOLUTION RATE OF PIROXICAM
 IJRPC 20, (3) Chowdry et l. ISSN: 223 278 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF RESEARCH IN PHARMACY AND CHEMISTRY Aville online t www.ijrpc.com Reserch Article A FACTORIAL STUDY ON THE EFFECTS OF β CYCLODEXTRIN AND
IJRPC 20, (3) Chowdry et l. ISSN: 223 278 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF RESEARCH IN PHARMACY AND CHEMISTRY Aville online t www.ijrpc.com Reserch Article A FACTORIAL STUDY ON THE EFFECTS OF β CYCLODEXTRIN AND
Supplementary information for: Low bone mass and changes in the osteocyte network in mice lacking autophagy in the osteoblast lineage
 Supplementry informtion for: Low one mss nd chnges in the osteocyte network in mice lcking utophgy in the osteolst linege Mrilin Piemontese, Meld Onl, Jinhu Xiong, Li Hn, Jeff D. Thostenson, Mri Almeid,
Supplementry informtion for: Low one mss nd chnges in the osteocyte network in mice lcking utophgy in the osteolst linege Mrilin Piemontese, Meld Onl, Jinhu Xiong, Li Hn, Jeff D. Thostenson, Mri Almeid,
Excessive fructose intake causes 1,25-(OH) 2 D 3 -dependent inhibition of intestinal and renal calcium transport in growing rats
 Am J Physiol Endocrinol Met 3: E33 E33, 3. First pulished April 9, 3; doi:.5/jpendo.58.. Excessive fructose intke cuses,5-(oh) D 3 -dependent inhiition of intestinl nd renl clcium trnsport in growing rts
Am J Physiol Endocrinol Met 3: E33 E33, 3. First pulished April 9, 3; doi:.5/jpendo.58.. Excessive fructose intke cuses,5-(oh) D 3 -dependent inhiition of intestinl nd renl clcium trnsport in growing rts
Effect of Aqueous Extract of Carica papaya Dry Root Powder on Lactation of Albino Rats
 Effect of Aqueous Extrct of Cric ppy Dry Root Powder on Lcttion of Alino Rts G. Tosswnchuntr nd S. Aritjt Deprtment of Biology Fculty of Science Ching Mi University Ching Mi 50200 Thilnd Keywords: mmmry
Effect of Aqueous Extrct of Cric ppy Dry Root Powder on Lcttion of Alino Rts G. Tosswnchuntr nd S. Aritjt Deprtment of Biology Fculty of Science Ching Mi University Ching Mi 50200 Thilnd Keywords: mmmry
DOI /mnfr
 3 Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 15, 59, 3 35 DOI 1.1/mnfr.1399 RESEARCH ARTICLE Ursolic cid improves lipid nd glucose metolism in high-ft-fed C57BL/6J mice y ctivting peroxisome prolifertor-ctivted receptor lph
3 Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 15, 59, 3 35 DOI 1.1/mnfr.1399 RESEARCH ARTICLE Ursolic cid improves lipid nd glucose metolism in high-ft-fed C57BL/6J mice y ctivting peroxisome prolifertor-ctivted receptor lph
Ndfip-mediated degradation of Jak1 tunes cytokine signalling to limit expansion of CD4 þ effector T cells
 Received 4 Jul 15 Accepted 9 Fe 16 Pulished 18 Apr 16 DOI: 1.138/ncomms116 OPEN Ndfip-medited degrdtion of Jk1 tunes cytokine signlling to limit expnsion of CD4 þ effector T cells Clire E. O Lery 1, Christopher
Received 4 Jul 15 Accepted 9 Fe 16 Pulished 18 Apr 16 DOI: 1.138/ncomms116 OPEN Ndfip-medited degrdtion of Jk1 tunes cytokine signlling to limit expnsion of CD4 þ effector T cells Clire E. O Lery 1, Christopher
Anti-Obesity Potential of Gallic Acid from Labisia pumila, through Augmentation of Adipokines in High Fat Diet Induced Obesity in C57BL/6 Mice
 Advnces in Reserch 2(10): 556-570, 2014, Article no. AIR.2014.10.004 SCIENCEDOMAIN interntionl www.sciencedomin.org Anti-Oesity Potentil of Gllic Acid from Lisi pumil, through Augmenttion of Adipokines
Advnces in Reserch 2(10): 556-570, 2014, Article no. AIR.2014.10.004 SCIENCEDOMAIN interntionl www.sciencedomin.org Anti-Oesity Potentil of Gllic Acid from Lisi pumil, through Augmenttion of Adipokines
CheckMate 153: Randomized Results of Continuous vs 1-Year Fixed-Duration Nivolumab in Patients With Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
 CheckMte 53: Rndomized Results of Continuous vs -Yer Fixed-Durtion Nivolumb in Ptients With Advnced Non-Smll Cell Lung Cncer Abstrct 297O Spigel DR, McCleod M, Hussein MA, Wterhouse DM, Einhorn L, Horn
CheckMte 53: Rndomized Results of Continuous vs -Yer Fixed-Durtion Nivolumb in Ptients With Advnced Non-Smll Cell Lung Cncer Abstrct 297O Spigel DR, McCleod M, Hussein MA, Wterhouse DM, Einhorn L, Horn
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:1.138/nture1188 1mM CCl 2 (min) 3 4 6 CCl 2 (mm) for 4min.1. 1 (mm) Pro- d WT GdCl 3 R-68 -/- P2x7r -/- -/- Csp1 -/- WT -/- P2x7r -/- -/- Csp1 -/- Csp1 (p2) (p17) Pro-Csp1
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:1.138/nture1188 1mM CCl 2 (min) 3 4 6 CCl 2 (mm) for 4min.1. 1 (mm) Pro- d WT GdCl 3 R-68 -/- P2x7r -/- -/- Csp1 -/- WT -/- P2x7r -/- -/- Csp1 -/- Csp1 (p2) (p17) Pro-Csp1
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Supplementry Figure 1. Genertion of N- nd C-tgged cyclin D1 knock-in mice., N-tgged cyclin D1 gene trgeting construct, cyclin D1 genomic locus, cyclin D1 locus following homologous recomintion (trgeted
Supplementry Figure 1. Genertion of N- nd C-tgged cyclin D1 knock-in mice., N-tgged cyclin D1 gene trgeting construct, cyclin D1 genomic locus, cyclin D1 locus following homologous recomintion (trgeted
British Journal of Nutrition
 British Journl of Nutrition (2012), 108, 2166 2175 q The Authors 2012 doi:10.1017/s0007114512000347 Differentil effects of low-dose resvertrol on diposity nd heptic stetosis in diet-induced oese mice Su-Jung
British Journl of Nutrition (2012), 108, 2166 2175 q The Authors 2012 doi:10.1017/s0007114512000347 Differentil effects of low-dose resvertrol on diposity nd heptic stetosis in diet-induced oese mice Su-Jung
IGF-1 vs insulin: Respective roles in modulating sodium transport via the PI-3 kinase/sgk1 pathway in a cortical collecting duct cell line
 originl rticle http://www.kidney-interntionl.org & 27 Interntionl Society of Nephrology IGF-1 vs insulin: Respective roles in modulting sodium trnsport vi the PI-3 kinse/sgk1 pthwy in corticl collecting
originl rticle http://www.kidney-interntionl.org & 27 Interntionl Society of Nephrology IGF-1 vs insulin: Respective roles in modulting sodium trnsport vi the PI-3 kinse/sgk1 pthwy in corticl collecting
Naringenin prevents cholesterol-induced systemic inflammation, metabolic dysregulation and atherosclerosis in Ldlr -/- mice.
 Nringenin prevents cholesterol-induced systemic inflmmtion, metolic dysregultion nd therosclerosis in Ldlr -/- mice. Juli M. Assini 1,2, Erin E. Mulvihill 1,2, Brin G. Sutherlnd 1, Dwn E. Telford 1,3,
Nringenin prevents cholesterol-induced systemic inflmmtion, metolic dysregultion nd therosclerosis in Ldlr -/- mice. Juli M. Assini 1,2, Erin E. Mulvihill 1,2, Brin G. Sutherlnd 1, Dwn E. Telford 1,3,
INFLUENCE OF DIFFERENT STRAINS AND WAYS OF INOCULATION ON THE RABBIT S RESPONSE TO EXPERIMENTAL INFECTION WITH PASTEURELLA MULTOCIDA
 Pthology nd Hygiene INFLUENCE OF DIFFERENT STRAINS AND WAYS OF INOCULATION ON THE RABBIT S RESPONSE TO EXPERIMENTAL INFECTION WITH PASTEURELLA MULTOCIDA Kulcsár G. 1, Fáián K. 1 *, Brn T. 1, Virág Gy.
Pthology nd Hygiene INFLUENCE OF DIFFERENT STRAINS AND WAYS OF INOCULATION ON THE RABBIT S RESPONSE TO EXPERIMENTAL INFECTION WITH PASTEURELLA MULTOCIDA Kulcsár G. 1, Fáián K. 1 *, Brn T. 1, Virág Gy.
Comparison of pro- and anti-inflammatory responses in paired human primary airway epithelial cells and alveolar macrophages
 Murk et l. Respirtory Reserch (2018) 19:126 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12931-018-0825-9 RESEARCH Comprison of pro- nd nti-inflmmtory responses in pired humn primry irwy epithelil cells nd lveolr mcrophges
Murk et l. Respirtory Reserch (2018) 19:126 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12931-018-0825-9 RESEARCH Comprison of pro- nd nti-inflmmtory responses in pired humn primry irwy epithelil cells nd lveolr mcrophges
Microtubule-driven spatial arrangement of mitochondria promotes activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome
 Supplementry Informtion Microtuule-driven sptil rrngement of mitochondri promotes ctivtion of the NLRP3 inflmmsome Tkum Misw 1,2, Michihiro Tkhm 1,2, Ttsuy Kozki 1,2, Hnn Lee 1,2, Jin Zou 1,2, Ttsuy Sitoh
Supplementry Informtion Microtuule-driven sptil rrngement of mitochondri promotes ctivtion of the NLRP3 inflmmsome Tkum Misw 1,2, Michihiro Tkhm 1,2, Ttsuy Kozki 1,2, Hnn Lee 1,2, Jin Zou 1,2, Ttsuy Sitoh
Systemic Anti-TNFa Treatment Restores Diabetes-Impaired Skin Repair in ob/ob Mice by Inactivation of Macrophages
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Systemic Anti-TNF Tretment Restores Dietes-Impired Skin Repir in o/o Mice y Inctivtion of Mcrophges Itmr Goren 1, Elke Müller 1, Dn Schiefelein 1, Urs Christen 1, Josef Pfeilschifter 1,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Systemic Anti-TNF Tretment Restores Dietes-Impired Skin Repir in o/o Mice y Inctivtion of Mcrophges Itmr Goren 1, Elke Müller 1, Dn Schiefelein 1, Urs Christen 1, Josef Pfeilschifter 1,
Supplementary Online Content
 Supplementry Online Content Zulmn DM, Pl Chee C, Ezeji-Okoye SC, et l. Effect of n intensive outptient progrm to ugment primry cre for high-need Veterns Affirs ptients: rndomized clinicl tril. JAMA Intern
Supplementry Online Content Zulmn DM, Pl Chee C, Ezeji-Okoye SC, et l. Effect of n intensive outptient progrm to ugment primry cre for high-need Veterns Affirs ptients: rndomized clinicl tril. JAMA Intern
XII. HIV/AIDS. Knowledge about HIV Transmission and Misconceptions about HIV
 XII. HIV/AIDS Knowledge bout HIV Trnsmission nd Misconceptions bout HIV One of the most importnt prerequisites for reducing the rte of HIV infection is ccurte knowledge of how HIV is trnsmitted nd strtegies
XII. HIV/AIDS Knowledge bout HIV Trnsmission nd Misconceptions bout HIV One of the most importnt prerequisites for reducing the rte of HIV infection is ccurte knowledge of how HIV is trnsmitted nd strtegies
Supplementary Information. SAMHD1 Restricts HIV-1 Infection in Resting CD4 + T Cells
 Supplementry Informtion SAMHD Restricts HIV- Infection in Resting CD T Cells Hnn-Mri Blduf,2,, Xioyu Pn,, Elin Erikson,2, Srh Schmidt, Wqo Dddch 3, Mnj Burggrf, Kristin Schenkov, In Amiel,2, Guido Wnitz
Supplementry Informtion SAMHD Restricts HIV- Infection in Resting CD T Cells Hnn-Mri Blduf,2,, Xioyu Pn,, Elin Erikson,2, Srh Schmidt, Wqo Dddch 3, Mnj Burggrf, Kristin Schenkov, In Amiel,2, Guido Wnitz
The Journal of Physiology
 J Physiol 596.4 (218) pp 623 645 623 Restortion of metolic helth y decresed consumption of rnched-chin mino cids Nicole E. Cummings 1,2,3, Elizeth M. Willims 1,2,IldikoKsz 4, Elizeth N. Konon 1,2, Michel
J Physiol 596.4 (218) pp 623 645 623 Restortion of metolic helth y decresed consumption of rnched-chin mino cids Nicole E. Cummings 1,2,3, Elizeth M. Willims 1,2,IldikoKsz 4, Elizeth N. Konon 1,2, Michel
Synergistic effects of metformin, resveratrol, and hydroxymethylbutyrate on insulin sensitivity
 Dietes, Metolic Syndrome nd Oesity: Trgets nd Therpy Open Access Full Text Article open ccess to scientific nd medicl reserch Originl Reserch Synergistic effects of metformin, resvertrol, nd hydroxymethylutyrte
Dietes, Metolic Syndrome nd Oesity: Trgets nd Therpy Open Access Full Text Article open ccess to scientific nd medicl reserch Originl Reserch Synergistic effects of metformin, resvertrol, nd hydroxymethylutyrte
The Impact of CDH13 Polymorphism and Statin Administration on TG/HDL Ratio in Cardiovascular Patients
 Originl Article Yonsei Med J 2015 Nov;56(6):1604-1612 pissn: 0513-5796 eissn: 1976-2437 The Impct of CDH13 Polymorphism nd Sttin Administrtion on TG/HDL Rtio in Crdiovsculr Ptients Jung Rn Choi 1, Yngsoo
Originl Article Yonsei Med J 2015 Nov;56(6):1604-1612 pissn: 0513-5796 eissn: 1976-2437 The Impct of CDH13 Polymorphism nd Sttin Administrtion on TG/HDL Rtio in Crdiovsculr Ptients Jung Rn Choi 1, Yngsoo
EFFECT OF DIETARY ENZYME ON PERFORMANCE OF WEANLING PIGS
 EFFECT OF DIETARY ENZYME ON PERFORMANCE OF WEANLING PIGS Finl report sumitted to Dniso Animl Nutrition E. vn Heugten nd B. Frederik North Crolin Stte University, Deprtment of Animl Siene Summry The urrent
EFFECT OF DIETARY ENZYME ON PERFORMANCE OF WEANLING PIGS Finl report sumitted to Dniso Animl Nutrition E. vn Heugten nd B. Frederik North Crolin Stte University, Deprtment of Animl Siene Summry The urrent
Dr. Javier Polo Vice President Research & Development
 Efecto de l suplementción con concentrdo de inmunoglobulins prtir del suero bovino en l Microbiot y su contribución l slud intestinl y l sistem nervioso centrl Dr. Jvier Polo Vice President Reserch & Development
Efecto de l suplementción con concentrdo de inmunoglobulins prtir del suero bovino en l Microbiot y su contribución l slud intestinl y l sistem nervioso centrl Dr. Jvier Polo Vice President Reserch & Development
Supplemental Materials
 Supplementl Mterils Cellulose deficiency of shv3svl1 is enhnced y hyper ccumultion of exogenous sucrose vi the plsm memrne sucrose/h symporter SUC1 Trevor H. Yets, Hgit Sorek, Dvid E. Wemmer, Chris R.
Supplementl Mterils Cellulose deficiency of shv3svl1 is enhnced y hyper ccumultion of exogenous sucrose vi the plsm memrne sucrose/h symporter SUC1 Trevor H. Yets, Hgit Sorek, Dvid E. Wemmer, Chris R.
 DOI: 10.1038/nc2331 PCre;Ros26R 12 h induction 48 h induction Vegfr3 i EC c d ib4 24 h induction VEGFR3 e Fold chnge 1.0 0.5 P < 0.05 Vegfr3 i EC Vegfr3 Figure S1 Cre ctivtion leds to genetic deletion
DOI: 10.1038/nc2331 PCre;Ros26R 12 h induction 48 h induction Vegfr3 i EC c d ib4 24 h induction VEGFR3 e Fold chnge 1.0 0.5 P < 0.05 Vegfr3 i EC Vegfr3 Figure S1 Cre ctivtion leds to genetic deletion
