Stevens - Johnson syndrome (SJS) and Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis (TEN) In Sarawak: A Four Years Review
|
|
|
- Evelyn Atkinson
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Stevens - Johnson syndrome (SJS) and Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis (TEN) In Sarawak: A Four Years Review Yap FBB, MRCP; Wahiduzzaman M, MBBS; Pubalan M, MRCP. Egyptian Dermatology Online Journal 4 (1): 1, June Department of Dermatology, Sarawak General Hospital, Jalan Hospital, Kuching, Sarawak Mail to: woodzlamp@yahoo.com Submitted for Publication: May 10th, 2008 Accepted for publication: May 28th, 2008 Abstract: Background and Objectives: A retrospective review of cases admitted to Sarawak General Hospital with Stevens-Johnson syndrome (SJS), toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN) and SJS-TEN Overlap from January 2004 to December 2007 was undertaken aiming to determine the causes and management outcome. 1
2 Methods and Results: Twenty four cases were admitted with 54.2% having SJS, 25% having SJS-TEN Overlap and 20.8% having TEN. Seventy nine percent were drugs induced. Anticonvulsants were the main culprit followed by Allopurinol. A 12.5% mortality rate was recorded. All cases given intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG) survived. Conclusion: It was concluded that SJS, SJS-TEN Overlap and TEN were mainly drug- induced and have high mortality. IVIG treatment seems promising. Judicious use of medications is needed. Early recognition is essential. Optimal care in institution with dermatology service is preferable. Introduction Stevens-Johnson syndrome (SJS) and Toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN) are rare bullous muco-cutaneous disease. Although rare with an incidence of 0.05 to 2 persons per 1 million populations per year, it has significant impact on the public health in view of its high morbidity and mortality [1, 2] [3, 4,. Majority of cases were drug- induced 5]. They are also grossly under reported worldwide. Few studies on SJS and TEN are available in Malaysia due to its rarity [4]. There are no reported studies from East Malaysia. Hence, our study aim to determine the causes and management outcome of cases with SJS, SJS-TEN Overlap and TEN admitted to Sarawak General Hospital for a 4 years period from January 2004 to December
3 Materials and Methods A retrospective review of cases admitted to the Sarawak General Hospital with SJS, SJS-TEN Overlap and TEN was done for a period of 4 years from January 2004 to December Data were retrieved from clinical notes in the Medical Records Department. A clinical diagnosis of SJS, SJS-TEN and TEN was done based on the clinical features of the cases. No skin biopsy was performed. They were classified as SJS, SJS-TEN Overlap and TEN based on Bastuji- Garin et al [6]. SJS is characterized by widespread small blisters and skin detachment levels of less than 10% of the body surface area, SJS-TEN Overlap by skin detachment levels of 10% to 29% of the body surface area, and TEN by skin detachment levels of more than 30% of the body surface area. Clinical notes were studied in detail regarding the demographics, causative drugs implicated, clinical course and management outcome. Data collected were compiled on a Microsoft excel sheet and subjected to descriptive statistical analysis. Results Table I shows the demographics of patients admitted to Sarawak General Hospital from January 2004 to December A total of 24 cases were admitted with 54.2% having SJS, 25% having SJS-TEN Overlap and 20.8% having TEN. There was a male preponderance of 3
4 58%. The mean age for cases with TEN was 23.3, SJS-TEN Overlap 44.5 and SJS 40.3 years. They range from 8 to 73 years. Table I: Demographic data of Patients SJS SJS-TEN Overlap TEN Cases Sex Male Female Age Mean Age (Years) Range Age (Years) Race Chinese Malay Iban Bidayuh Seventy nine percent of the cases were due to drugs. Anticonvulsants and Allopurinol were the major culprits, contributing to 7 and 5 cases respectively. Traditional medications were implicated in 2 cases. Other drugs included antibiotics, non steroidal antiinflammatory drugs, sulpha drugs and anti- helminthes (Table II). 4
5 Table II: Drugs Implicated SJS (n=11) SJS-TEN Overlap (n=5) TEN (n=3) Anticonvulsant Carbamazepine Phenytoin Non Steroidal Anti Inflammatory Drugs Ibuprofen Mefenemic Acid Traditional Medications Asam Urat Chinese Herbs Anti Gout Allopurinol Others Sulfasalazine Amoxycillin Albendazole Four cases were given anticonvulsants for pain disorders while 2 were given for seizure prophylaxis for intracranial haemorrhage. Only one case was on anticonvulsants for epilepsy. All the cases on Allopurinol were given for asymptomatic hyperuricemia. Table III depicts that the mean incubation time i.e. time from drug initiation to onset of disease ranging from 4.7 days in TEN to 21.6 days in SJS. The hospital stay in cases with TEN were also longer with a mean of 12.4 days compared to only 8.9 days in cases with SJS (Table IV). 5
6 Table III: Incubation Period of Drugs SJS SJS-TEN Overlap TEN Mean (Days) Range (Days) a T Table IV: Duration of Hospital Stay SJS SJS-TEN Overlap TEN Mean (Days) Range (Days) ble V represents the treatment administered. All the patients with SJS and two third of cases with SJS-TEN Overlap were given corticosteroids. Eighty percent of cases with TEN were given intravenous Immuno-globulins. Table V: Treatment Outcome SJS SJS-TEN Overlap TEN (n=13) (n=6) (n=5) Treatment Corticosteroids IVIG Cyclosporine Nursing Care only Outcome Survive Succumb There were only 3 deaths noted with a mortality rate of 12.5%. They succumbed to acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) and sepsis. The culprit drug was Jamu Asam Urat containing phenylbutazone (a type of non steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs) in one case whereas no drug was implicated in the other two. They were 6
7 given corticosteroids and cyclosporine on admission. All the cases with TEN who were given IVIG survived. Morbidities seen include skin dyspigmentation (52%), nail dystrophies (10%) and ophthalmic complications (10%). Two patients had visual impairment as a result of severe keratitis. Discussion The spectrum of disease from SJS to TEN is mainly druginduced. We have found that almost 4 out of 5 cases admitted to our centre were drug- induced. Regional and international studies quoted a rate of 50% to 90% of cases [3, 4, 5, 7]. Anticonvulsants are one of the commonest culprit agents implicated [4, 8]. The estimated incidence per 10,000 new users is 1 to 10 depending on the agent used [9]. The drug reactions are more commonly seen in slow drug metabolizer due of genetic polymorphism. In carbamazepine hypersensitivity, the polymorphism is in position 308 and 328 of the promoter region of TNF-α gene [10]. SJS and TEN are considered T cell mediated disorders in which activation of CD8 T lymphocytes lead to destruction and apoptosis of keratinocytes [11]. Drugs can activate T cells by acting as a hapten, as a prohapten or by direct pharmacologic interaction among the drug, Major Histocompatibility Complex (MHC) molecule and a T cell receptor. It is postulated that carbamazepine in its chemically inert form can bind with the MHC and T cell receptor causing activation of T cells contributing to SJS and TEN [12]. 7
8 We found that 36% of our cases were due to anticonvulsants. Among the anticonvulsant, the majority of cases (71%) were due to carbamazepine. This trend was also seen in India, Taiwan, Singapore and northeastern Malaysia [4, 8, 13]. The increasing utilization of anticonvulsants in pain management and in prophylaxis in neurosurgical patients might explain this. The benefit of prophylactic anticonvulsants in neurologic critical care is controversial and is often not evidence based [14]. Carbamazepine induced SJS and TEN was also found to be more common in Han Chinese with HLA-B1502 phenotype in Taiwan [15]. This might explain the trend in Singapore and some of our cases although no phenotyping was done. Cases developing adverse drug reactions to carbamazepine should not be given other aromatic anticonvulsants namely phenytoin and phenobarbitone because of the cross reaction among the drugs. Mockenhaupt et al., found that SJS and TEN occurred in 1 to 10 per 1000 new users of aromatic anti-convulsants and 2.5 per 1000 new users of Lamotrigine, a newer class of anticonvulsants [9]. Sodium valproate and other newer anticonvulsants rarely cause adverse cutaneous drug reactions. Therefore, we would suggest that aromatic anticonvulsants be used cautiously. Safer alternatives for pain management should be used. They should also be used with care in those with Han Chinese lineage. Allopurinol contributed to 26% our cases. Halevy et al., found that in Europe and Israel, Allopurinol is the most common cause of SJS and TEN. They found an increased risk with dosage 200 mg per day or more [16]. All our cases had taken 300mg per day as it is the only form available in Malaysia. Halevy et al. also did not find an 8
9 increased risk of Allopurinol induced SJS and TEN with comedications with diuretics, aminopenicillins, angiotensin converting enzymes inhibitors (ACEI), non steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and aspirin [16]. In Han Chinese, HLA-B5801 allele was strongly associated with severe cutaneous adverse reactions to Allopurinol [17]. Allopurinol was administered in all our cases for asymptomatic hyperuricemia. Other published studies also revealed inappropriate indications for Allopurinol in up to 86% of patients [18, 19]. So, we recommend judicious prescription of Allopurinol. A proper guideline on prescription of Allopurinol should be established in Malaysia to prevent such inappropriate usage. This will hopefully reduce the Allopurinol related life threatening adverse drug reactions. The highest risk for development of SJS and TEN with drug use occurs within 2 months of initiation [9, 16]. We also noted a similar trend with longest incubation period of only 40 days. Interestingly, we also observed that the shorter mean incubation period was associated with more severe clinical presentation. This observation need to be further clarified by future studies as it has prognostic significance. Our overall mortality was 12.5% with mortality for SJS-TEN Overlap of 33.3% and TEN of 20%. The reported mortality rate ranges from 5% to 40% [4, 5, 7, 8, 20]. Two of our 3 deaths were children with no apparent drug- related cause. We postulate that they had very severe viral infection and probably had secondary bacterial sepsis. Their immunity was further depressed by the administration of corticosteroids and cyclosporine leading to their death. Hence, immunosuppressive drugs should be used cautiously especially in those with suspected underlying infection. Systemic corticosteroids 9
10 has unproven benefit in early cases of SJS and TEN and deleterious in the advanced forms [19, 20]. We noted a 100% survival of the TEN cases that were given IVIG. IVIG is derived from plasma pool of several thousand donors and consists mainly of IgG. It interferes with Fas- Fas Ligand interactions by blocking the Fas binding to its ligand thereby blocking the apoptosis of the keratinocytes [21]. Stella et al., in Turin noted a reduction in mortality from 75% to 26% with the use of IVIG [22]. In a review of 8 studies on the use of IVIG in SJS and TEN, French et al., found that 6 studies points towards a benefit of IVIG on mortality associated with TEN [23]. Thus, the use of IVIG in TEN is very promising. Prospective studies should be done in Malaysia to determine the efficacy of IVIG as a first line treatment in TEN. Conclusion We would like to conclude that drugs especially anticonvulsants and Allopurinol were the major causes of SJS and TEN. Thus, a registry for antiepileptic and Allopurinol will help determine the national incidence of SJS and TEN on these medications. This will further enhance our knowledge of these reactions. The mortality rate of SJS and TEN remained high despite major advances in the medical field. IVIG usage in TEN is very promising. A prospective study on the use of IVIG in SJS and TEN will help to determine its benefit in our population. It will also help in establishing a guideline for IVIG use. Finally, we would recommend judicious use of medications to prevent iatrogenic drug eruption with high morbidity and mortality. 10
11 References 1. Rzany B, Mockenhunpt M, Baur S et al., Epidemiology of erythema exsudativum multiforme majus, Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis in Germany ( ): Structure and results of a population-based registry, J Clin Epidemiol. 49(7): , Li LF, MaC, Epidemiological study of severe cutaneous adverse drug reactions in a city district in China, Clin Exp Dermatol. 31(5): 642-7, Schopf E, Stuhmer A, Rzany B, Victor N, Zentgraf R, Kapp JF, Toxic epidermal necrolysis and Stevens-Johnson syndrome: An epidemiologic study from West Germany, Arch Dermatol. 127: , Kamaliah MD, Zainal D, Mokhtar N, Nazmi N, Erythema multiforme, Stevens Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis in north eastern Malaysia, Int J Dermatol. 37: 520-3, Yamane Y, Aihara M, Ikezawa Z, Analysis of Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis in Japan from , Allergol Int. 56(4): , Bastuji-Garin S, Rzany B, Stern RS, A clinical classification of cases of toxic epidermal necrolysis, Stevens-Johnson syndrome and erythema multiforme, Arch Dermatol. 129: 92-6, Auquier-Dunant A, Mockenhaupt M, Naldi L, Correia O, Schroder W, Correlations between clinical patterns and causes of erythema multiforme majus, Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis, Arch Dermatol. 138: , Devi K, Sandhya G, Criton S, Suja V, Sridevi PK, Carbamazepine The commonest cause of toxic epidermal necrolysis and Stevens-Johnson syndrome: A study of 7 years, Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 71: ,
12 9. Mockenhaupt M, Messenhaimer J, Tennis P, Schlingmann J, Risk of Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis in new users of anticonvulsants, Neurology. 64: , Pirmohamed M, Lin K, Chadwick D, Park BK, TNF-alpha promoter region gene polymorphism in carbamazepinehypersensitive patients, Neurology. 56: 890-6, Kehren J, Desvignes C, Krasteva M et al., Cytotoxicity is mandatory for CD8 (+) T cell-mediated contact hypersensitivity, J Exp Med. 189: , Pichler WJ, Delayed drug hypersensitivity reactions, Ann Intern Med. 139: , Khoo AKM, Foo CL, Toxic epidermal necrolysis in a burns centre: a 6 year review, Burns. 22: 275-8, Liu KC, Bhardwaj A, Use of prophylactic anticonvulsants in neurologic critical care: A critical appraisal, Neurocrit Care. 7(2): , Chung WH, Hung SI, Hong HS et al., Medical genetics: a marker for Stevens-Johnson syndrome, Nature. 428: 486, Halevy S, Ghislain PD, Mockenhaupt M et al., Allopurinol is the most common cause of Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis in Europe and Isreal, J Am Acad Dermatol doi: /j.jaad Published online October 3, Hung SI, Chung WH, Liou LB et al., HLA-B5801 allele as a genetic marker for severe cutaneous adverse reactions caused by Allopurinol, Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 102: , Bellamy N, Brooks PM, Emmerson BT, Gilbert JR, Campbell J, McCredie M, A survey of current prescribing practices of antiinflammatory and urate lowering drugs in gouty arthritis in New South Wales and Queensland, Med J Aust. 151: 531-7, Stuart RA, Gow PJ, Bellamy N, Campbell J, Grigor R, A survey of current prescribing practices of anti-inflammatory and uratelowering drugs in gouty arthritis, NZ Med J. 104: 115-7,
13 20. Ghislain PD, Roujeau JC, Treatment of severe drug reactions: Stevens- Johnson syndrome, toxic epidermal necrolysis and hypersensitivity syndrome, Dermatol Online J. 8(1): 5, Pereira FA, Mudgil AV, Rosmarin DM, Toxic epidermal necrolysis, J Am Acad Dermatol. 56: , Stella M, Clemete A, Bollero D, Risso D, Dalmasso P, Toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN) and Stevens-Johnson syndrome (SJS): Experience with high dose intravenous immuno-globulins and topical conservative approach- A retrospective review, Burns. 33: 452-9, French LE, Trent JT, Kerdel FA, Use of intravenous immunoglobulin in toxic epidermal necrolysis and Stevens-Johnson syndrome: Our current understanding, International Immunopharmacology. 6: 543-9,
OXCARBAZEPINE-INDUCED STEVENS-JOHNSON SYNDROME: A CASE REPORT
 OXCARBAZEPINE-INDUCED STEVENS-JOHNSON SYNDROME: A CASE REPORT Lung-Chang Lin, 1,2 Ping-Chin Lai, 3 Sheau-Fang Yang, 4 and Rei-Cheng Yang 1,5 Departments of 1 Pediatrics and 4 Pathology, Kaohsiung Medical
OXCARBAZEPINE-INDUCED STEVENS-JOHNSON SYNDROME: A CASE REPORT Lung-Chang Lin, 1,2 Ping-Chin Lai, 3 Sheau-Fang Yang, 4 and Rei-Cheng Yang 1,5 Departments of 1 Pediatrics and 4 Pathology, Kaohsiung Medical
allergy Asia Pacific Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis in Dr. Hasan Sadikin General Hospital Bandung, Indonesia from
 pissn -876 eissn -868 Original Article Asia Pac Allergy 6;6:-7 Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis in Dr. Hasan Sadikin General Hospital Bandung, Indonesia from 9 Oki Suwarsa *, Wulan
pissn -876 eissn -868 Original Article Asia Pac Allergy 6;6:-7 Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis in Dr. Hasan Sadikin General Hospital Bandung, Indonesia from 9 Oki Suwarsa *, Wulan
Correspondence should be addressed to Wanjarus Roongpisuthipong; rr
 Dermatology Research and Practice, Article ID 237821, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/237821 Research Article Retrospective Analysis of Corticosteroid Treatment in Stevens-Johnson Syndrome and/or
Dermatology Research and Practice, Article ID 237821, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/237821 Research Article Retrospective Analysis of Corticosteroid Treatment in Stevens-Johnson Syndrome and/or
Dilantin (phenytoin) ROBERT A. SCHWARTZ
 Dilantin (phenytoin) ROBERT A. SCHWARTZ Bailey & Galyen Attorney in Charge, Mass Tort Litigation Managing Attorney, Houston 18333 Egret Bay Blvd., Suite 120 Houston, Texas 77058 Toll Free: (866) 715-1529
Dilantin (phenytoin) ROBERT A. SCHWARTZ Bailey & Galyen Attorney in Charge, Mass Tort Litigation Managing Attorney, Houston 18333 Egret Bay Blvd., Suite 120 Houston, Texas 77058 Toll Free: (866) 715-1529
Prevention of severe cutaneous adverse drug reactions: the emerging value of pharmacogenetic screening
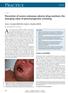 CMAJ Cases Prevention of severe cutaneous adverse drug reactions: the emerging value of pharmacogenetic screening Suran L. Fernando MB BS PhD, Andrew J. Broadfoot MB BS Previously published at www.cmaj.ca
CMAJ Cases Prevention of severe cutaneous adverse drug reactions: the emerging value of pharmacogenetic screening Suran L. Fernando MB BS PhD, Andrew J. Broadfoot MB BS Previously published at www.cmaj.ca
Stevens Johnson Syndrome: How Diagnosis Impacts Disease Course
 Southern Adventist Univeristy KnowledgeExchange@Southern Graduate Research Projects Nursing 12-4-2015 Stevens Johnson Syndrome: How Diagnosis Impacts Disease Course Sharon K. Hart Southern Adventist University,
Southern Adventist Univeristy KnowledgeExchange@Southern Graduate Research Projects Nursing 12-4-2015 Stevens Johnson Syndrome: How Diagnosis Impacts Disease Course Sharon K. Hart Southern Adventist University,
Department of Pharmacology & NIPER-Guwahati, Gauhati Medical College & Hospital, Guwahati , Assam, INDIA. 3
 J Young Pharm, 2016; 8(2): 149-153 A multifaceted peer reviewed journal in the field of Pharmacy www.jyoungpharm.org www.phcog.net Short Communication A study on drug induced Stevens-Johnson Syndrome (SJS),
J Young Pharm, 2016; 8(2): 149-153 A multifaceted peer reviewed journal in the field of Pharmacy www.jyoungpharm.org www.phcog.net Short Communication A study on drug induced Stevens-Johnson Syndrome (SJS),
CARBAMAZEPINE INDUCED STEVENS JOHNSON SYNDROME- A CASE STUDY
 WORLD JOURNAL OF PHARMACY AND PHARMACEUTICAL SCIENCES Ragesh SJIF Impact Factor 2.786 Volume 3, Issue 6, 1599-1604. Case Study ISSN 2278 4357 CARBAMAZEPINE INDUCED STEVENS JOHNSON SYNDROME- A CASE STUDY
WORLD JOURNAL OF PHARMACY AND PHARMACEUTICAL SCIENCES Ragesh SJIF Impact Factor 2.786 Volume 3, Issue 6, 1599-1604. Case Study ISSN 2278 4357 CARBAMAZEPINE INDUCED STEVENS JOHNSON SYNDROME- A CASE STUDY
Original Article. Barvaliya M, Sanmukhani J, Patel T, Paliwal N, Shah H 1, Tripathi C
 Original Article Drug-induced Stevens-Johnson syndrome (SJS), toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN), and SJS-TEN overlap: A multicentric retrospective study Barvaliya M, Sanmukhani J, Patel T, Paliwal N, Shah
Original Article Drug-induced Stevens-Johnson syndrome (SJS), toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN), and SJS-TEN overlap: A multicentric retrospective study Barvaliya M, Sanmukhani J, Patel T, Paliwal N, Shah
Risk of Stevens Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis in new users of antiepileptics
 Risk of Stevens Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis in new users of antiepileptics Maja Mockenhaupt, MD; John Messenheimer, MD; Pat Tennis, PhD; and Juergen Schlingmann Abstract Background:
Risk of Stevens Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis in new users of antiepileptics Maja Mockenhaupt, MD; John Messenheimer, MD; Pat Tennis, PhD; and Juergen Schlingmann Abstract Background:
Profile and Pattern of Stevens-Johnson Syndrome and Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis in a General Hospital in Singapore: Treatment Outcomes
 Acta Derm Venereol 2012; 92: 62 66 CLINICAL REPORT Profile and Pattern of Stevens-Johnson Syndrome and Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis in a General Hospital in Singapore: Treatment Outcomes Siew-Kiang Tan and
Acta Derm Venereol 2012; 92: 62 66 CLINICAL REPORT Profile and Pattern of Stevens-Johnson Syndrome and Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis in a General Hospital in Singapore: Treatment Outcomes Siew-Kiang Tan and
1 Introduction. Kenneth Irungu 1 David Nyamu
 Drugs - Real World Outcomes (2017) 4:79 85 DOI 10.1007/s40801-017-0105-x ORIGINAL RESEARCH ARTICLE Characterization of Stevens Johnson Syndrome and Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis Among Patients Admitted to
Drugs - Real World Outcomes (2017) 4:79 85 DOI 10.1007/s40801-017-0105-x ORIGINAL RESEARCH ARTICLE Characterization of Stevens Johnson Syndrome and Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis Among Patients Admitted to
PHENYTION, CARBAMAZEPINE, SODIUM VALPROATE AND LAMOTRIGINE INDUCED CUTANEOUS REACTIONS
 PHENYTION, CARBAMAZEPINE, SODIUM VALPROATE AND LAMOTRIGINE INDUCED CUTANEOUS REACTIONS M. Ghaffarpour *, S. S. Hejazie, M. H. Harirchian and H. Pourmahmoodian Department of Neurology, Imam Khomeini Hospital,
PHENYTION, CARBAMAZEPINE, SODIUM VALPROATE AND LAMOTRIGINE INDUCED CUTANEOUS REACTIONS M. Ghaffarpour *, S. S. Hejazie, M. H. Harirchian and H. Pourmahmoodian Department of Neurology, Imam Khomeini Hospital,
Analysis of Stevens-Johnson Syndrome and Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis in Japan from 2000 to 2006 Yumiko Yamane 1, Michiko Aihara 1 and Zenro Ikezawa 1
 Allergology International. 7;:9- DOI:. allergolint.o-7- ORIGINAL ARTICLE Analysis of Stevens-Johnson Syndrome and Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis in Japan from to Yumiko Yamane, Michiko Aihara and Zenro Ikezawa
Allergology International. 7;:9- DOI:. allergolint.o-7- ORIGINAL ARTICLE Analysis of Stevens-Johnson Syndrome and Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis in Japan from to Yumiko Yamane, Michiko Aihara and Zenro Ikezawa
Risk Factors and Management of Mood Stabilizer-associated Stevens-Johnson Syndrome/Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis: A Mini-review
 140 Taiwanese Journal of Psychiatry (Taipei) Vol. 25 No. 3 2011 Overview Risk Factors and Management of Mood Stabilizer-associated Stevens-Johnson Syndrome/Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis: A Mini-review Gen-Tang
140 Taiwanese Journal of Psychiatry (Taipei) Vol. 25 No. 3 2011 Overview Risk Factors and Management of Mood Stabilizer-associated Stevens-Johnson Syndrome/Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis: A Mini-review Gen-Tang
A Case Report on Amoxicillin Induced Stevens- Johnson Syndrome
 Open Journal of Clinical & Medical Case Reports Volume 2 (2016) Issue 11 A Case Report on Amoxicillin Induced Stevens- Johnson Syndrome Rajendra Singh Airee*; Aastha Rawal; Binu Mathew; H. Doddayya Abstract
Open Journal of Clinical & Medical Case Reports Volume 2 (2016) Issue 11 A Case Report on Amoxicillin Induced Stevens- Johnson Syndrome Rajendra Singh Airee*; Aastha Rawal; Binu Mathew; H. Doddayya Abstract
SEVERE CUTANEOUS ADVERSE DRUG REACTIONS: STEVENS-JOHNSON SYNDROME AND TOXIC EPIDERMAL NECROLYSISA, A REPORT OF 4 CASES SEEN AT UMMC
 SEVERE CUTANEOUS ADVERSE DRUG REACTIONS: STEVENS-JOHNSON SYNDROME AND TOXIC EPIDERMAL NECROLYSISA, A REPORT OF 4 CASES SEEN AT UMMC Shasha Khairullah, Rokiah Che Ismail Department of Medicine, Faculty
SEVERE CUTANEOUS ADVERSE DRUG REACTIONS: STEVENS-JOHNSON SYNDROME AND TOXIC EPIDERMAL NECROLYSISA, A REPORT OF 4 CASES SEEN AT UMMC Shasha Khairullah, Rokiah Che Ismail Department of Medicine, Faculty
A 10-years retrospective study on Severe Cutaneous Adverse Reactions (SCARs) in a tertiary hospital in Penang, Malaysia
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE A 10-years retrospective study on Severe Cutaneous Adverse Reactions (SCARs) in a tertiary hospital in Penang, Malaysia Chai Har Loo, MRCP, Wooi Chiang Tan, AdvMDerm, Yek Huan Khor, AdvMDerm,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE A 10-years retrospective study on Severe Cutaneous Adverse Reactions (SCARs) in a tertiary hospital in Penang, Malaysia Chai Har Loo, MRCP, Wooi Chiang Tan, AdvMDerm, Yek Huan Khor, AdvMDerm,
Causes and Treatment Outcomes of Stevens-Johnson Syndrome and Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis in 82 Adult Patients
 original article korean j intern med 2012;27:203-210 pissn 1226-3303 eissn 2005-6648 Causes and Treatment Outcomes of Stevens-Johnson Syndrome and Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis in 82 Adult Patients Hye-In
original article korean j intern med 2012;27:203-210 pissn 1226-3303 eissn 2005-6648 Causes and Treatment Outcomes of Stevens-Johnson Syndrome and Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis in 82 Adult Patients Hye-In
STEVENS-JOHNSON SYNDROME: A CASE REPORT
 STEVENS-JOHNSON SYNDROME: A CASE REPORT Castana O., Rempelos G., Anagiotos G., Apostolopoulou C., Dimitrouli A., Alexakis D. Department of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, Evangelismos General Hospital,
STEVENS-JOHNSON SYNDROME: A CASE REPORT Castana O., Rempelos G., Anagiotos G., Apostolopoulou C., Dimitrouli A., Alexakis D. Department of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, Evangelismos General Hospital,
HIV-Associated Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis at San Francisco General Hospital: A 13-Year Retrospective Review
 HIV Clinical Management HIV-Associated Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis at San Francisco General Hospital: A 13-Year Retrospective Review Journal of the International Association of Providers of AIDS Care 2017,
HIV Clinical Management HIV-Associated Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis at San Francisco General Hospital: A 13-Year Retrospective Review Journal of the International Association of Providers of AIDS Care 2017,
Address for correspondence: Dr. Patel Raksha M. R-3, Doctor s Quarters, Jail Road, Vadodara- 01, Gujarat, India.
 Clinical study of cutaneous drug eruptions in 200 patients Raksha M. Patel, Y. S. Marfatia Department of Skin and V.D, Medical College, Vadodara, Gujarat, India Address for correspondence: Dr. Patel Raksha
Clinical study of cutaneous drug eruptions in 200 patients Raksha M. Patel, Y. S. Marfatia Department of Skin and V.D, Medical College, Vadodara, Gujarat, India Address for correspondence: Dr. Patel Raksha
Department of Ophthalmology, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea 2
 pissn: 1011-8942 eissn: 2092-9382 Korean J Ophthalmol 2013;27(5):331-340 http://dx.doi.org/10.3341/kjo.2013.27.5.331 Original Article Effect of Age and Early Intervention with a Systemic Steroid, Intravenous
pissn: 1011-8942 eissn: 2092-9382 Korean J Ophthalmol 2013;27(5):331-340 http://dx.doi.org/10.3341/kjo.2013.27.5.331 Original Article Effect of Age and Early Intervention with a Systemic Steroid, Intravenous
Stevens-Johnson s Syndrome / Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis: An update
 Stevens-Johnson s Syndrome / Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis: An update Robert G. Micheletti, MD Assistant Professor of Dermatology and Medicine Director, Cutaneous Vasculitis Clinic, Penn Vasculitis Center
Stevens-Johnson s Syndrome / Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis: An update Robert G. Micheletti, MD Assistant Professor of Dermatology and Medicine Director, Cutaneous Vasculitis Clinic, Penn Vasculitis Center
HLA-A*24:02 as a common risk factor for antiepileptic drug induced cutaneous adverse reactions
 Published Ahead of Print on May 5, 2017 as 10.1212/WNL.0000000000004008 HLA-A*24:02 as a common risk factor for antiepileptic drug induced cutaneous adverse reactions Yi-Wu Shi, PhD* Fu-Li Min, MD* Dong
Published Ahead of Print on May 5, 2017 as 10.1212/WNL.0000000000004008 HLA-A*24:02 as a common risk factor for antiepileptic drug induced cutaneous adverse reactions Yi-Wu Shi, PhD* Fu-Li Min, MD* Dong
SKIN REACTIONS WITH PSYCHOTROPICS: A SYSTEMATIC REVIEW
 SKIN REACTIONS WITH PSYCHOTROPICS: A SYSTEMATIC REVIEW *Anderson Isaac, PharmD Candidate, 2019 Pooja Patel, PharmD Candidate, 2019 Katelyn Thomasson, PharmD Candidate, 2019 Erika Tillery, PharmD, BCPP,
SKIN REACTIONS WITH PSYCHOTROPICS: A SYSTEMATIC REVIEW *Anderson Isaac, PharmD Candidate, 2019 Pooja Patel, PharmD Candidate, 2019 Katelyn Thomasson, PharmD Candidate, 2019 Erika Tillery, PharmD, BCPP,
Prevalence and pattern of adverse cutaneous drug reactions presenting to a tertiary care hospital
 International Journal of Research in Dermatology Janardhan B et al. Int J Res Dermatol. 2017 Mar;3(1):74-78 http://www.ijord.com Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/issn.2455-4529.intjresdermatol20164248
International Journal of Research in Dermatology Janardhan B et al. Int J Res Dermatol. 2017 Mar;3(1):74-78 http://www.ijord.com Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/issn.2455-4529.intjresdermatol20164248
Case Report Cephazolin-Induced Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis Treated with Intravenous Immunoglobulin and N-Acetylcysteine
 Case Reports in Immunology Volume 2012, Article ID 931528, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2012/931528 Case Report Cephazolin-Induced Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis Treated with Intravenous Immunoglobulin and N-Acetylcysteine
Case Reports in Immunology Volume 2012, Article ID 931528, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2012/931528 Case Report Cephazolin-Induced Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis Treated with Intravenous Immunoglobulin and N-Acetylcysteine
Cutaneous Conditions Associated with Systemic Disease
 Cutaneous Conditions Associated with Systemic Disease Johnnie M Woodson, M.D., F.A.A.D. Assistant Professor of Dermatology University of Nevada School of Medicine Director of J. Woodson Dermatology & Associates,
Cutaneous Conditions Associated with Systemic Disease Johnnie M Woodson, M.D., F.A.A.D. Assistant Professor of Dermatology University of Nevada School of Medicine Director of J. Woodson Dermatology & Associates,
Stevens-Johnson syndrome (SJS) and toxic epidermal. necrolysis in Asian children
 Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis in Asian children Mark Jean-Aan Koh, MD, and Yong-Kwang Tay, MD Singapore Background: Stevens-Johnson syndrome (SJS) and toxic epidermal necrolysis
Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis in Asian children Mark Jean-Aan Koh, MD, and Yong-Kwang Tay, MD Singapore Background: Stevens-Johnson syndrome (SJS) and toxic epidermal necrolysis
Warfarin-induced toxic epidermal necrolysis in combination therapy of Henoch- Schönlein purpura nephritis: a case report
 Kasahara et al. BMC Nephrology (2017) 18:237 DOI 10.1186/s12882-017-0648-9 CASE REPORT Open Access Warfarin-induced toxic epidermal necrolysis in combination therapy of Henoch- Schönlein purpura nephritis:
Kasahara et al. BMC Nephrology (2017) 18:237 DOI 10.1186/s12882-017-0648-9 CASE REPORT Open Access Warfarin-induced toxic epidermal necrolysis in combination therapy of Henoch- Schönlein purpura nephritis:
Carbamazepine-Induced Incomplete Stevens-Johnson Syndrome: Report of a Case in Children without Mycoplasma pneumoniae Infection
 Case Report Carbamazepine-Induced Incomplete Stevens-Johnson Syndrome: Report of a Case in Children without Mycoplasma pneumoniae Infection J Med Assoc Thai 2015; 98 (Suppl. 7): S243-S247 Full text. e-journal:
Case Report Carbamazepine-Induced Incomplete Stevens-Johnson Syndrome: Report of a Case in Children without Mycoplasma pneumoniae Infection J Med Assoc Thai 2015; 98 (Suppl. 7): S243-S247 Full text. e-journal:
Stevens Johnson Syndrome and Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis Associated with Acetaminophen Use during Viral Infections
 BRIEF COMMUNICATION http://dx.doi.org/10.4110/in.2016.16.4.256 pissn 1598-2629 eissn 2092-6685 Stevens Johnson Syndrome and Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis Associated with Acetaminophen Use during Viral Infections
BRIEF COMMUNICATION http://dx.doi.org/10.4110/in.2016.16.4.256 pissn 1598-2629 eissn 2092-6685 Stevens Johnson Syndrome and Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis Associated with Acetaminophen Use during Viral Infections
Mechanisms of Drug Hypersensitivity Reactions
 18/5/213 Mechanisms of Drug Hypersensitivity Reactions Munir Pirmohamed NHS Chair of Pharmacogenetics Department of Molecular and Clinical Pharmacology Institute of Translational Medicine University of
18/5/213 Mechanisms of Drug Hypersensitivity Reactions Munir Pirmohamed NHS Chair of Pharmacogenetics Department of Molecular and Clinical Pharmacology Institute of Translational Medicine University of
A Clinical Study of Stevens-Johnson Syndrome and Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis: Efficacy of Treatment in Burn Intensive Care Unit
 J Korean Surg Soc 0;:133-139 DOI:.414/jkss.0..3.133 원 저 A Clinical Study of Stevens-Johnson Syndrome and Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis: Efficacy of Treatment in Burn Intensive Care Unit Departments of Surgery
J Korean Surg Soc 0;:133-139 DOI:.414/jkss.0..3.133 원 저 A Clinical Study of Stevens-Johnson Syndrome and Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis: Efficacy of Treatment in Burn Intensive Care Unit Departments of Surgery
A Retrospective Study of Spectrum of Nevirapine Induced Cutaneous Drug Reactions in HIV Positive Patients
 Journal of US-China Medical Science 12 (2015) 85-89 doi: 10.17265/1548-6648/2015.02.008 D DAVID PUBLISHING A Retrospective Study of Spectrum of Nevirapine Induced Cutaneous Drug Reactions in HIV Positive
Journal of US-China Medical Science 12 (2015) 85-89 doi: 10.17265/1548-6648/2015.02.008 D DAVID PUBLISHING A Retrospective Study of Spectrum of Nevirapine Induced Cutaneous Drug Reactions in HIV Positive
PEER REVIEW HISTORY ARTICLE DETAILS VERSION 1 - REVIEW
 PEER REVIEW HISTORY BMJ Paediatrics Open publishes all reviews undertaken for accepted manuscripts. Reviewers are asked to complete a checklist review form and are provided with free text boxes to elaborate
PEER REVIEW HISTORY BMJ Paediatrics Open publishes all reviews undertaken for accepted manuscripts. Reviewers are asked to complete a checklist review form and are provided with free text boxes to elaborate
REGISTRY OF SEVERE CUTANEOUS ADVERSE REACTIONS TO DRUGS AND COLLECTION OF BIOLOGICAL SAMPLES. R e g i S C A R PATIENT'S DATA. Age country of birth
 REGISTRY OF SEVERE CUTANEOUS ADVERSE REACTIONS TO DRUGS AND COLLECTION OF BIOLOGICAL SAMPLES R e g i S C A R PATIENT'S DATA Initials of the patient date of birth Age country of birth Gender male female
REGISTRY OF SEVERE CUTANEOUS ADVERSE REACTIONS TO DRUGS AND COLLECTION OF BIOLOGICAL SAMPLES R e g i S C A R PATIENT'S DATA Initials of the patient date of birth Age country of birth Gender male female
Stevens-Johnson Syndrome : A Case Report
 https://doi.org/10.5933/jkapd.2017.44.4.455 J Korean Acad Pediatr Dent 44(4) 2017 ISSN (print) 1226-8496 ISSN (online) 2288-3819 Stevens-Johnson Syndrome : A Case Report Yongho Song, Nanyoung Lee, Sangho
https://doi.org/10.5933/jkapd.2017.44.4.455 J Korean Acad Pediatr Dent 44(4) 2017 ISSN (print) 1226-8496 ISSN (online) 2288-3819 Stevens-Johnson Syndrome : A Case Report Yongho Song, Nanyoung Lee, Sangho
Emergency Dermatology Dr Melissa Barkham
 Emergency Dermatology Dr Melissa Barkham Spotlight Seminar 30 th September 2010 Why is this important? Urgent recognition and treatment of dermatologic emergencies can be life saving and prevent long term
Emergency Dermatology Dr Melissa Barkham Spotlight Seminar 30 th September 2010 Why is this important? Urgent recognition and treatment of dermatologic emergencies can be life saving and prevent long term
Clinical profile of skin diseases in accident and emergency department attenders
 Hong Kong J. Dermatol. Venereol. (2007) 15, 4-9 Original Article Clinical profile of skin diseases in accident and emergency department attenders CY Chan, KL Kam, CA Graham, TH Rainer, NM Luk Skin problems
Hong Kong J. Dermatol. Venereol. (2007) 15, 4-9 Original Article Clinical profile of skin diseases in accident and emergency department attenders CY Chan, KL Kam, CA Graham, TH Rainer, NM Luk Skin problems
STEVENS-JOHNSON SYNDROME AND TOXIC EPIDERMAL NECROLYSIS IN CHILDREN: A LITERATURE REVIEW OF CURRENT TREATMENTS
 STEVENS-JOHNSON SYNDROME AND TOXIC EPIDERMAL NECROLYSIS IN CHILDREN: A LITERATURE REVIEW OF CURRENT TREATMENTS *Blanca R. Del Pozzo-Magaña, 1 Alejandro Lazo-Langner 2,3 1. Department of Pediatrics, University
STEVENS-JOHNSON SYNDROME AND TOXIC EPIDERMAL NECROLYSIS IN CHILDREN: A LITERATURE REVIEW OF CURRENT TREATMENTS *Blanca R. Del Pozzo-Magaña, 1 Alejandro Lazo-Langner 2,3 1. Department of Pediatrics, University
Health economics and drug safety
 Health economics and drug safety Professor Dyfrig Hughes FFRPS FBPhS FLSW Centre for Health Economics & Medicines Evaluation Bangor University, Wales @HughesDyfrig ADEs that are not reactions to a medicine
Health economics and drug safety Professor Dyfrig Hughes FFRPS FBPhS FLSW Centre for Health Economics & Medicines Evaluation Bangor University, Wales @HughesDyfrig ADEs that are not reactions to a medicine
A Middle-Aged Man with Newly Diagnosed HIV Infection and Rash
 CLINICAL CASE OF THE MONTH A Middle-Aged Man with Newly Diagnosed HIV Infection and Rash Patrick Njoku, MD; Temeka Tate, MD; Sousan Zadeh, MD; Erin Hauck, MD; Anila Chaudhry, MD; Betty Lo-Blais, MD; Lee
CLINICAL CASE OF THE MONTH A Middle-Aged Man with Newly Diagnosed HIV Infection and Rash Patrick Njoku, MD; Temeka Tate, MD; Sousan Zadeh, MD; Erin Hauck, MD; Anila Chaudhry, MD; Betty Lo-Blais, MD; Lee
Acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis: A histologic study of forty-five cases
 Original Article Acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis: A histologic study of forty-five cases Mai P Hoang MD, Meera Mahalingam, MD FRC Path, Jag Bhawan MD, Payal Kapur,3 MD and Whitney A High 4 MD
Original Article Acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis: A histologic study of forty-five cases Mai P Hoang MD, Meera Mahalingam, MD FRC Path, Jag Bhawan MD, Payal Kapur,3 MD and Whitney A High 4 MD
An unpredictable, dose-independent adverse drug reaction which is immunologically or IgEmediated.
 R H E U M A T I S M D I S O R D E R S A N D A L L E R G I E S APPROACH TO DRUG ALLERGY Dr Bernard Thong DEFINITION OF DRUG ALLERGY An unpredictable, dose-independent adverse drug reaction which is immunologically
R H E U M A T I S M D I S O R D E R S A N D A L L E R G I E S APPROACH TO DRUG ALLERGY Dr Bernard Thong DEFINITION OF DRUG ALLERGY An unpredictable, dose-independent adverse drug reaction which is immunologically
Dexamethasone Pulse Therapy for Stevens-Johnson Syndrome/ Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis
 Acta Derm Venereol 2007; 87: 144 148 CLINICAL REPORT Dexamethasone Pulse Therapy for Stevens-Johnson Syndrome/ Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis Sylvia H. Kardaun and Marcel F. Jonkman Center for Blistering Diseases,
Acta Derm Venereol 2007; 87: 144 148 CLINICAL REPORT Dexamethasone Pulse Therapy for Stevens-Johnson Syndrome/ Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis Sylvia H. Kardaun and Marcel F. Jonkman Center for Blistering Diseases,
Carbamazepine Hypersensitivity: Progress Toward Predicting the Unpredictable
 Carbamazepine Hypersensitivity: Progress Toward Predicting the Unpredictable Current Literature In Clinical Science HLA-A*3101 and Carbamazepine-Induced Hypersensitivity Reactions in Europeans. McCormack
Carbamazepine Hypersensitivity: Progress Toward Predicting the Unpredictable Current Literature In Clinical Science HLA-A*3101 and Carbamazepine-Induced Hypersensitivity Reactions in Europeans. McCormack
Drug Allergy A Guide to Diagnosis and Management
 Drug Allergy A Guide to Diagnosis and Management (Version 1 April 2015 updated April 2018) Author: Jed Hewitt Chief Pharmacist, Governance & Professional Practice Date of Preparation: April 2015 Updated:
Drug Allergy A Guide to Diagnosis and Management (Version 1 April 2015 updated April 2018) Author: Jed Hewitt Chief Pharmacist, Governance & Professional Practice Date of Preparation: April 2015 Updated:
PedsCases Podcast Scripts
 PedsCases Podcast Scripts This is a text version of a podcast from Pedscases.com on Drug Allergy. These podcasts are designed to give medical students an overview of key topics in pediatrics. The audio
PedsCases Podcast Scripts This is a text version of a podcast from Pedscases.com on Drug Allergy. These podcasts are designed to give medical students an overview of key topics in pediatrics. The audio
Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis and SJS : Case Reports & Brief Review
 Case Report Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis and SJS : Case Reports & Brief Review Deepali P. Mohite*, Satyajitraje Tekade*, Amol Gadbail*, M. S. Chaudhary** Abstract : Toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN) and Stevens
Case Report Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis and SJS : Case Reports & Brief Review Deepali P. Mohite*, Satyajitraje Tekade*, Amol Gadbail*, M. S. Chaudhary** Abstract : Toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN) and Stevens
Severe cutaneous adverse reactions (SCAR) are life-threatening
 Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis: clinical patterns, diagnostic considerations, etiology, and therapeutic management Maja Mockenhaupt, MD, PhD n Abstract Severe cutaneous adverse
Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis: clinical patterns, diagnostic considerations, etiology, and therapeutic management Maja Mockenhaupt, MD, PhD n Abstract Severe cutaneous adverse
Analysis of Individual Case Safety Reports of Severe Cutaneous Adverse Reactions in Korea
 Original Article Yonsei Med J 2019 Feb;60(2):208-215 pissn: 0513-5796 eissn: 1976-2437 Analysis of Individual Case Safety Reports of Severe Cutaneous Adverse Reactions in Korea Min-Gyu Kang 1,2,3, Kyung-Hee
Original Article Yonsei Med J 2019 Feb;60(2):208-215 pissn: 0513-5796 eissn: 1976-2437 Analysis of Individual Case Safety Reports of Severe Cutaneous Adverse Reactions in Korea Min-Gyu Kang 1,2,3, Kyung-Hee
Drug-induced stevens-johnson syndrome : Experience from a tertiary care hospital
 Original article: Drug-induced stevens-johnson syndrome : Experience from a tertiary care hospital *Arjun R 1,Mahalingeshwara Bhat K P 2, Sara C 1 1 PG student in General Medicine, KS Hegde Medical Acadamy,
Original article: Drug-induced stevens-johnson syndrome : Experience from a tertiary care hospital *Arjun R 1,Mahalingeshwara Bhat K P 2, Sara C 1 1 PG student in General Medicine, KS Hegde Medical Acadamy,
Adverse Drug Reactions (ADRs) Outline
 Adverse Drug Reactions (ADRs) Outline 1. What are Adverse Drug Reactions (ADRs)? WHAT WHY HOW 2. How important are ADRs and are they preventable? 3. What are the classifications and mechanisms of ADRs?
Adverse Drug Reactions (ADRs) Outline 1. What are Adverse Drug Reactions (ADRs)? WHAT WHY HOW 2. How important are ADRs and are they preventable? 3. What are the classifications and mechanisms of ADRs?
Toxic epidermal necrolysis and Stevens Johnson syndrome in South Africa: a 3-year prospective study
 Q J Med 2012; 105:839 846 doi:10.1093/qjmed/hcs078 Advance Access Publication 28 April 2012 Toxic epidermal necrolysis and Stevens Johnson syndrome in South Africa: a 3-year prospective study S.M.H. KANNENBERG
Q J Med 2012; 105:839 846 doi:10.1093/qjmed/hcs078 Advance Access Publication 28 April 2012 Toxic epidermal necrolysis and Stevens Johnson syndrome in South Africa: a 3-year prospective study S.M.H. KANNENBERG
Cutaneous drug eruptions are seen commonly
 REVIEW ARTICLE Cutaneous drug reactions in children Sandipan Dhar, Raghubir Banerjee, Rajib Malakar Department of Pediatric Dermatology, Institute of Child Health, Kolkata, West Bengal, India ABSTRACT
REVIEW ARTICLE Cutaneous drug reactions in children Sandipan Dhar, Raghubir Banerjee, Rajib Malakar Department of Pediatric Dermatology, Institute of Child Health, Kolkata, West Bengal, India ABSTRACT
2/28/2010. Pharmacogenomics and the Asian Population. Limited efficacy/response to drugs already on the market
 Pharmacogenomics and the Asian Population Majority are medication related Alan H.B. Wu, Ph.D. Professor, Laboratory Medicine, UCSF Section Chief, Clinical Chemistry, February 27, 20 Limited efficacy/response
Pharmacogenomics and the Asian Population Majority are medication related Alan H.B. Wu, Ph.D. Professor, Laboratory Medicine, UCSF Section Chief, Clinical Chemistry, February 27, 20 Limited efficacy/response
Bugs and Drugs: What s New in Hypersensitivity Reactions?
 Bugs and Drugs: What s New in Hypersensitivity Reactions? Erin Mathes, MD Associate Professor of Dermatology and Pediatrics University of California, San Francisco DISCLOSURE OF RELATIONSHIPS WITH INDUSTRY
Bugs and Drugs: What s New in Hypersensitivity Reactions? Erin Mathes, MD Associate Professor of Dermatology and Pediatrics University of California, San Francisco DISCLOSURE OF RELATIONSHIPS WITH INDUSTRY
International Journal of Basic & Clinical Pharmacology. Profile of cutaneous adverse drug reactions of carbamazepine
 Print ISSN: 2319-2003 Online ISSN: 2279-0780 IJBCP International Journal of Basic & Clinical Pharmacology DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2319-2003.ijbcp20175211 Original Research Article Profile of cutaneous
Print ISSN: 2319-2003 Online ISSN: 2279-0780 IJBCP International Journal of Basic & Clinical Pharmacology DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2319-2003.ijbcp20175211 Original Research Article Profile of cutaneous
Research. Original Investigation
 Research Original Investigation Relationship Between the HLA-B*1502 Allele and Carbamazepine-Induced Stevens-Johnson Syndrome and Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis Wimonchat
Research Original Investigation Relationship Between the HLA-B*1502 Allele and Carbamazepine-Induced Stevens-Johnson Syndrome and Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis Wimonchat
Severe Cutaneous Adverse Reactions Related to Systemic Antibiotics
 MAJOR ARTICLE Severe Cutaneous Adverse Reactions Related to Systemic Antibiotics Ying-Fang Lin, 1 Chih-Hsun Yang, 2,3 Hu Sindy, 1,3 Jing-Yi Lin, 2,3 Chung-Yee Rosaline Hui, 2,3 Yun-Chen Tsai, 2 Ting-Shu
MAJOR ARTICLE Severe Cutaneous Adverse Reactions Related to Systemic Antibiotics Ying-Fang Lin, 1 Chih-Hsun Yang, 2,3 Hu Sindy, 1,3 Jing-Yi Lin, 2,3 Chung-Yee Rosaline Hui, 2,3 Yun-Chen Tsai, 2 Ting-Shu
Title: Cutaneous Adverse Drug Reactions in Indian population: A systematic review
 Title: Cutaneous Adverse Drug Reactions in Indian population: A systematic review Review question(s) To carry out a systematic review of the published evidence of the cutaneous adverse drug reactions in
Title: Cutaneous Adverse Drug Reactions in Indian population: A systematic review Review question(s) To carry out a systematic review of the published evidence of the cutaneous adverse drug reactions in
The liver and skin are two of the commonest
 AMERICAN ASSOCIATION FOR THE STUDY OFLIVERD I S E ASES HEPATOLOGY, VOL. 63, NO. 3, 2016 LIVER INJURY/REGENERATION Drug-Induced Liver Injury Associated With Stevens-Johnson Syndrome/Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis:
AMERICAN ASSOCIATION FOR THE STUDY OFLIVERD I S E ASES HEPATOLOGY, VOL. 63, NO. 3, 2016 LIVER INJURY/REGENERATION Drug-Induced Liver Injury Associated With Stevens-Johnson Syndrome/Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis:
Successful re-introduction of lamotrigine after initial rash
 Seizure 2000; 9: 282 286 doi: 10.1053/seiz.2000.0394, available online at http://www.idealibrary.com on Successful re-introduction of lamotrigine after initial rash F. M. C. BESAG, G. Y. T. NG & F. POOL
Seizure 2000; 9: 282 286 doi: 10.1053/seiz.2000.0394, available online at http://www.idealibrary.com on Successful re-introduction of lamotrigine after initial rash F. M. C. BESAG, G. Y. T. NG & F. POOL
Stevens-Johnson Syndrome in patients receiving cranial irradiation and concomitant diphenylhydantoin
 Turkish Journal of Cancer Vol. 32/ No. 4/2002 Stevens-Johnson Syndrome in patients receiving cranial irradiation and concomitant diphenylhydantoin ERKAN TOPKAN, FARUK ZORLU, MURAT GÜRKAYNAK Hacettepe University
Turkish Journal of Cancer Vol. 32/ No. 4/2002 Stevens-Johnson Syndrome in patients receiving cranial irradiation and concomitant diphenylhydantoin ERKAN TOPKAN, FARUK ZORLU, MURAT GÜRKAYNAK Hacettepe University
Skin Manifestations of Drug Reactions
 Skin Manifestations of Drug Reactions Dr Carol Hlela, Division of Dermatology Department of Medicine, University of Cape Town and Red Cross Children s Hospital What are the Skin Manifestations of Drug
Skin Manifestations of Drug Reactions Dr Carol Hlela, Division of Dermatology Department of Medicine, University of Cape Town and Red Cross Children s Hospital What are the Skin Manifestations of Drug
Scratching the Surface: A Review of SJS/TEN
 Scratching the Surface: A Review of SJS/TEN Sarah Smith, PharmD Pharmacy Grand Rounds 2018 November 27, 2018 2018 MFMER slide 1 Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis Cutaneous Anthrax Stevens Johnson Syndrome Necrotizing
Scratching the Surface: A Review of SJS/TEN Sarah Smith, PharmD Pharmacy Grand Rounds 2018 November 27, 2018 2018 MFMER slide 1 Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis Cutaneous Anthrax Stevens Johnson Syndrome Necrotizing
Future of Pediatrics: Blisters, Hives and Other Tales from the Emergency Room June 14 th, 2016
 A. Yasmine Kirkorian MD Assistant Professor of Dermatology & Pediatrics Children s National Health System George Washington University School of Medicine & Health Sciences Future of Pediatrics: Blisters,
A. Yasmine Kirkorian MD Assistant Professor of Dermatology & Pediatrics Children s National Health System George Washington University School of Medicine & Health Sciences Future of Pediatrics: Blisters,
Pediatric Dermatology
 Pediatric Dermatology --------- Emergencies & Urgencies Nicholas V. Nguyen, M.D. Director, Pediatric Dermatology Disclosures In the past 12 months, I have had the following financial relationships with
Pediatric Dermatology --------- Emergencies & Urgencies Nicholas V. Nguyen, M.D. Director, Pediatric Dermatology Disclosures In the past 12 months, I have had the following financial relationships with
The Burden of Heart Failure in the Asia Pacific. Eugenio B. Reyes, M.D. Associate Professor, University of the Philippines, College of Medicine
 The Burden of Heart Failure in the Asia Pacific Eugenio B. Reyes, M.D. Associate Professor, University of the Philippines, College of Medicine Q1. The most prevalent risk factor for heart failure in the
The Burden of Heart Failure in the Asia Pacific Eugenio B. Reyes, M.D. Associate Professor, University of the Philippines, College of Medicine Q1. The most prevalent risk factor for heart failure in the
Dr. Venkateswari. R. Dr. Janani Sankar s unit Kanchi Kamakoti CHILDS Trust Hospital
 Dr. Venkateswari. R. Dr. Janani Sankar s unit Kanchi Kamakoti CHILDS Trust Hospital Acknowledgements: KKCTH Dr. Ramkumar Consultant Dermatologist Dr. Ramprakash Consultant Ophthalmologist Dr. Prasad Manne
Dr. Venkateswari. R. Dr. Janani Sankar s unit Kanchi Kamakoti CHILDS Trust Hospital Acknowledgements: KKCTH Dr. Ramkumar Consultant Dermatologist Dr. Ramprakash Consultant Ophthalmologist Dr. Prasad Manne
Implementing AHRQ Effective Health Care Reviews Helping Clinicians Make Better Treatment Choices
 Implementing AHRQ Effective Health Care Reviews Helping Clinicians Make Better Treatment Choices Gout: Diagnosis and Management Practice Pointers by MATTHEW R. NOSS, DO, MSEd, U.S. Army Health Clinic,
Implementing AHRQ Effective Health Care Reviews Helping Clinicians Make Better Treatment Choices Gout: Diagnosis and Management Practice Pointers by MATTHEW R. NOSS, DO, MSEd, U.S. Army Health Clinic,
EFAVIRENZ ASSOCIATED STEVENS-JOHNSON SYNDROME
 EFAVIRENZ ASSOCIATED STEVENS-JOHNSON SYNDROME To the Editor: Persons with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection are highly susceptible to adverse dermatological reactions to specific medications
EFAVIRENZ ASSOCIATED STEVENS-JOHNSON SYNDROME To the Editor: Persons with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection are highly susceptible to adverse dermatological reactions to specific medications
Accepted Manuscript. Wound Management Strategies in Stevens-Johnson syndrome/toxic Epidermal Necrolysis: An unmet need
 Accepted Manuscript Wound Management Strategies in Stevens-Johnson syndrome/toxic Epidermal Necrolysis: An unmet need Lee Haur Yueh, MBBS, MRCP, MMed, FAMS PII: S0190-9622(18)32138-8 DOI: 10.1016/j.jaad.2018.05.1258
Accepted Manuscript Wound Management Strategies in Stevens-Johnson syndrome/toxic Epidermal Necrolysis: An unmet need Lee Haur Yueh, MBBS, MRCP, MMed, FAMS PII: S0190-9622(18)32138-8 DOI: 10.1016/j.jaad.2018.05.1258
Severe cutaneous adverse reactions: an evidence based approach
 Original Article 21 Severe cutaneous adverse reactions: an evidence based approach D.P. Shrestha, D. Gurung, A. Kumar Department of Dermatology and Venereology, Maharagunj Campus, Institute of Medicine,
Original Article 21 Severe cutaneous adverse reactions: an evidence based approach D.P. Shrestha, D. Gurung, A. Kumar Department of Dermatology and Venereology, Maharagunj Campus, Institute of Medicine,
Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis - A Case Report
 The Journal of Critical Care Medicine 2017;3(1):29-33 CASE REPORT Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis - A Case Report Laura Stătescu¹, Magda Constantin², Horia Silviu Morariu³ *, Laura Gheucă Solovăstru¹ ¹ Dermatology
The Journal of Critical Care Medicine 2017;3(1):29-33 CASE REPORT Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis - A Case Report Laura Stătescu¹, Magda Constantin², Horia Silviu Morariu³ *, Laura Gheucă Solovăstru¹ ¹ Dermatology
Genetic Screening for ADR
 Genetic Screening for ADR Mahidol University Faculty of Medicine Siriraj Hospital Manop Pithukpakorn, MD Division of Medical Genetics Department of Medicine concentration Drug level over time toxic optimum
Genetic Screening for ADR Mahidol University Faculty of Medicine Siriraj Hospital Manop Pithukpakorn, MD Division of Medical Genetics Department of Medicine concentration Drug level over time toxic optimum
Cutaneous Drug Reactions
 Cutaneous Drug Reactions Andrei Metelitsa, MD, FRCPC, FAAD Co-Director, Institute for Skin Advancement Clinical Associate Professor, Dermatology University of Calgary, Canada Copyright 2017 by Sea Courses
Cutaneous Drug Reactions Andrei Metelitsa, MD, FRCPC, FAAD Co-Director, Institute for Skin Advancement Clinical Associate Professor, Dermatology University of Calgary, Canada Copyright 2017 by Sea Courses
They are updated regularly as new NICE guidance is published. To view the latest version of this NICE Pathway see:
 bring together everything NICE says on a topic in an interactive flowchart. are interactive and designed to be used online. They are updated regularly as new NICE guidance is published. To view the latest
bring together everything NICE says on a topic in an interactive flowchart. are interactive and designed to be used online. They are updated regularly as new NICE guidance is published. To view the latest
Cutaneous drug reactions to antiepileptic drugs and relation with HLA alleles in the Turkish population
 O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E Eur Ann Allergy Clin Immunol Vol 50, N 1, 36-41, 2018 S. Büyüköztürk 1, Ç. Kekik 2, A.Z. Gökyiğit 3, F.İ. Tezer Filik 4i, G. Karakaya 4, S. Saygı 4i, A.B. Dursun 5, S. Kirbaş
O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E Eur Ann Allergy Clin Immunol Vol 50, N 1, 36-41, 2018 S. Büyüköztürk 1, Ç. Kekik 2, A.Z. Gökyiğit 3, F.İ. Tezer Filik 4i, G. Karakaya 4, S. Saygı 4i, A.B. Dursun 5, S. Kirbaş
Carbamazepine-Induced Toxic Effects and HLA-B*1502 Screening in Taiwan
 T h e n e w e ngl a nd j o u r na l o f m e dic i n e original article Carbamazepine-Induced Toxic Effects and HLA-B*1502 Screening in Taiwan Pei Chen, Ph.D., Juei-Jueng Lin, M.D., Chin-Song Lu, M.D.,
T h e n e w e ngl a nd j o u r na l o f m e dic i n e original article Carbamazepine-Induced Toxic Effects and HLA-B*1502 Screening in Taiwan Pei Chen, Ph.D., Juei-Jueng Lin, M.D., Chin-Song Lu, M.D.,
Severe Desquamating Disorder After Liver Transplant: Toxic Epidermal Necrolyis or Graft Versus Host Disease?
 Severe Desquamating Disorder After Liver Transplant: Toxic Epidermal Necrolyis or Graft Versus Host Disease? John T. Schulz III, MD, PhD, FACS, and Robert L. Sheridan, MD, FACS Bridgeport Hospital, Bridgeport,
Severe Desquamating Disorder After Liver Transplant: Toxic Epidermal Necrolyis or Graft Versus Host Disease? John T. Schulz III, MD, PhD, FACS, and Robert L. Sheridan, MD, FACS Bridgeport Hospital, Bridgeport,
Toxic epidermal necrolysis
 REVIEW Anaesthesiology Intensive Therapy 2015, vol. 47, no 3, 257 262 ISSN 0209 1712 10.5603/AIT.2015.0037 www.ait.viamedica.pl Toxic epidermal necrolysis Joanna Hinc-Kasprzyk, Agnieszka Polak-Krzemińska,
REVIEW Anaesthesiology Intensive Therapy 2015, vol. 47, no 3, 257 262 ISSN 0209 1712 10.5603/AIT.2015.0037 www.ait.viamedica.pl Toxic epidermal necrolysis Joanna Hinc-Kasprzyk, Agnieszka Polak-Krzemińska,
Oral Acetazolamide after Boston Keratoprosthesis in Stevens Johnson Syndrome
 Oral Acetazolamide after Boston Keratoprosthesis in Stevens Johnson Syndrome The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters
Oral Acetazolamide after Boston Keratoprosthesis in Stevens Johnson Syndrome The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters
Spontaneous reporting of Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis associated with antiepileptic drugs
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences Spontaneous reporting of Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis associated with antiepileptic drugs L. ORDOÑEZ, E. SALGUEIRO, F.J.
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences Spontaneous reporting of Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis associated with antiepileptic drugs L. ORDOÑEZ, E. SALGUEIRO, F.J.
α chain β chain C N C N β 2 α 1 β 1 α 2
 a α chain c β chain C N C N β 2 m α chain b d N C N C β 1 α 2 Supplemental Figure 1 Major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class I and class II structures. (a, b)representation of the structure of the
a α chain c β chain C N C N β 2 m α chain b d N C N C β 1 α 2 Supplemental Figure 1 Major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class I and class II structures. (a, b)representation of the structure of the
Lam0 trig he-induced Severe Cutaneous Adverse Reactions
 Epilepsia, 39(Suppl. 7):S22-S26, 1998 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Philadelphia 0 International League Against Epilepsy Lam0 trig he-induced Severe Cutaneous Adverse Reactions *Raymond G. Schlienger,
Epilepsia, 39(Suppl. 7):S22-S26, 1998 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Philadelphia 0 International League Against Epilepsy Lam0 trig he-induced Severe Cutaneous Adverse Reactions *Raymond G. Schlienger,
Agenda* The 9th International Congress on Cutaneous Adverse Drug Reactions (iscar 2015)
 1 of 5 Agenda* The 9th International Congress on Cutaneous Adverse Drug Reactions (iscar 2015) Co-chairs: Dr. Neil H. Shear at the 23rd World Congress of Dermatology in Vancouver, Canada. Division of Dermatology,
1 of 5 Agenda* The 9th International Congress on Cutaneous Adverse Drug Reactions (iscar 2015) Co-chairs: Dr. Neil H. Shear at the 23rd World Congress of Dermatology in Vancouver, Canada. Division of Dermatology,
In the past few years, beta-lactam-resistant gram-positive
 Early Diagnosis Is Key in Vancomycin-Induced Linear IgA Bullous Dermatosis and Stevens-Johnson Syndrome Douglas H. Jones, MS Michael Todd, MD Timothy J. Craig, DO Background: With the emergence of highly
Early Diagnosis Is Key in Vancomycin-Induced Linear IgA Bullous Dermatosis and Stevens-Johnson Syndrome Douglas H. Jones, MS Michael Todd, MD Timothy J. Craig, DO Background: With the emergence of highly
Stevens Johnson Syndrome and Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis: Assessment of Medication Risks with Emphasis on Recently Marketed Drugs. The EuroSCAR-Study
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Stevens Johnson Syndrome and Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis: Assessment of Medication Risks with Emphasis on Recently Marketed Drugs. The EuroSCAR-Study Maja Mockenhaupt 1, Cecile Viboud 2,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Stevens Johnson Syndrome and Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis: Assessment of Medication Risks with Emphasis on Recently Marketed Drugs. The EuroSCAR-Study Maja Mockenhaupt 1, Cecile Viboud 2,
Cutaneous Adverse Drug Reactions in Domestic Animals. Katherine Doerr, DVM, Dip. ACVD. Veterinary Dermatology Center
 Cutaneous Adverse Drug Reactions in Domestic Animals Katherine Doerr, DVM, Dip. ACVD Veterinary Dermatology Center Maitland, Rockledge, Waterford Lakes, FL Not highly studied in veterinary medicine Unknown
Cutaneous Adverse Drug Reactions in Domestic Animals Katherine Doerr, DVM, Dip. ACVD Veterinary Dermatology Center Maitland, Rockledge, Waterford Lakes, FL Not highly studied in veterinary medicine Unknown
Adverse drug reactions
 Medications William Smith Adverse drug reactions Allergy? Side-effect? Intolerance? Background Adverse drug reactions (ADRs) vary from life-threatening anaphylaxis to minor common side-effects. Objective
Medications William Smith Adverse drug reactions Allergy? Side-effect? Intolerance? Background Adverse drug reactions (ADRs) vary from life-threatening anaphylaxis to minor common side-effects. Objective
STEVEN JOHNSON S SYNDROME: A BRIEF REVIEW
 STEVEN JOHNSON S SYNDROME: A BRIEF REVIEW G. Ramya sree*, Sreeram Vandavasi Guru 1, E. Sam Jeeva Kumar 2 * Pharm D, Intern, P. Rami Reddy Memorial College of Pharmacy, Kadapa. 1 Pharm-D Intern, P. Rami
STEVEN JOHNSON S SYNDROME: A BRIEF REVIEW G. Ramya sree*, Sreeram Vandavasi Guru 1, E. Sam Jeeva Kumar 2 * Pharm D, Intern, P. Rami Reddy Memorial College of Pharmacy, Kadapa. 1 Pharm-D Intern, P. Rami
Your letter Your reference The Hague, Subject Request for change in the product information following the PhVWP/CMDh decision
 Registratiehouder ( t.a.v. registratieafdeling) Your letter Your reference The Hague, -- --.. Case number Our reference../../ Case manager Telephone number Subject Request for change in the product information
Registratiehouder ( t.a.v. registratieafdeling) Your letter Your reference The Hague, -- --.. Case number Our reference../../ Case manager Telephone number Subject Request for change in the product information
cipro loxacin; stevens-johnson syndrome; urinary tract infection; adverse drug reaction
 Open Journal of Clinical & Medical Case Reports Volume 3 (2017) Issue 7 ISSN 2379-1039 Cipro loxacin induced Stevens Johnson syndrome: A case report on Dermatology department P Mohammed Sha i*; K Narotham
Open Journal of Clinical & Medical Case Reports Volume 3 (2017) Issue 7 ISSN 2379-1039 Cipro loxacin induced Stevens Johnson syndrome: A case report on Dermatology department P Mohammed Sha i*; K Narotham
FDA Approves Carnexiv (carbamazepine) injection as Intravenous Short-Term Replacement Therapy for Certain Seizure Types
 FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE FDA Approves Carnexiv (carbamazepine) injection as Intravenous Short-Term Replacement Therapy for Certain Seizure Types Carnexiv is the first FDA-approved intravenous carbamazepine
FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE FDA Approves Carnexiv (carbamazepine) injection as Intravenous Short-Term Replacement Therapy for Certain Seizure Types Carnexiv is the first FDA-approved intravenous carbamazepine
Spectrum of Cutaneous Adverse Reactions to Levetiracetam and Human Leukocyte Antigen Typing in North-Indian Patients
 Spectrum of Cutaneous Adverse Reactions to Levetiracetam and Human Leukocyte Antigen Typing in North-Indian Patients Original Article Journal of Epilepsy Research pissn 2233-6249 / eissn 2233-6257 Bhargavi
Spectrum of Cutaneous Adverse Reactions to Levetiracetam and Human Leukocyte Antigen Typing in North-Indian Patients Original Article Journal of Epilepsy Research pissn 2233-6249 / eissn 2233-6257 Bhargavi
Objectives Making CYP450, Drug Interactions, & Pharmacogenetics Easy
 Objectives Making, Drug Interactions, & Pharmacogenetics Easy Anthony J. Busti, MD, PharmD, FNLA, FAHA Describe the differences between phase I and phase II metabolic pathways. Identify the most common
Objectives Making, Drug Interactions, & Pharmacogenetics Easy Anthony J. Busti, MD, PharmD, FNLA, FAHA Describe the differences between phase I and phase II metabolic pathways. Identify the most common
The CARI Guidelines Caring for Australasians with Renal Impairment. Uric acid GUIDELINES. No recommendations possible based on Level I or II evidence.
 Date written: July 2004 Final submission: July 2004 Author: David Johnson Uric acid GUIDELINES No recommendations possible based on Level I or II evidence. SUGGESTIONS FOR CLINICAL CARE (Suggestions are
Date written: July 2004 Final submission: July 2004 Author: David Johnson Uric acid GUIDELINES No recommendations possible based on Level I or II evidence. SUGGESTIONS FOR CLINICAL CARE (Suggestions are
