Regulation of neuronal morphology and function by the tumor suppressors Tsc1 and Tsc2
|
|
|
- Roger Wood
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Regultion of neuronl morphology nd funtion y the tumor suppressors Ts nd Ts Sohil F Tvzoie,3,4, Veroni A Alvrez,4, Dennis A Ridenour, Dvid J Kwitkowski & Bernrdo L Stini Muttions in the TSC or TSC tumor suppressor genes led to tuerous slerosis omplex (TSC), dominnt hmrtomtous disorder tht often presents with mentl retrdtion, epilepsy nd utism. The etiology of these neurologil symptoms is unler nd the funtion of the TSC pthwy in neurons is unknown. We found tht in post-mitoti, hippompl pyrmidl neurons of mie nd rts, loss of Ts or Ts triggered enlrgement of soms nd dendriti spines nd ltered the properties of glutmtergi synpses. Furthermore, loss of single opy of the Ts gene ws suffiient to pertur dendriti spine struture. Morphologil hnges required regultion of the tin-depolymeriztion ftor ofilin t onserved LIM-kinse phosphoryltion site, the phosphoryltion of whih ws inresed y loss of Ts. Thus, the TSC pthwy regultes growth nd synpse funtion in neurons, nd perturtions of neuronl struture nd funtion re likely to ontriute to the pthogenesis of the neurologil symptoms of TSC. TSC nd TSC re tumor suppressor genes whose protein produts, hmrtin (TSC) nd tuerin (TSC), negtively regulte ell growth in vriety of systems. In humns, heterozygous muttions in either TSC or TSC led to TSC, n utosoml-dominnt hmrtomtous disorder hrterized y enign tumors in multiple orgns inluding the rin, kidneys, hert nd eyes. TSC lso typilly presents with onstelltion of neurologil defiits tht inlude epilepsy, mentl retrdtion nd utism. Biohemil nd geneti nlyses in mmmlin systems nd Drosophil melnogster hve reveled tht TSC nd TSC prtiipte in onserved growth-regulting pthwy involving the mmmlin trget of rpmyin (mtor) 5. In rief, the tivtion of growthpromoting reeptor tyrosine kinses, suh s the insulin reeptor, stimultes phosphoinositide 3-kinse (PI3K) nd the serine/threonine kinse Akt. In vitro, Akt phosphoryltes TSC t onserved onsensus phosphoryltion sequenes nd downregultes its GTPse-tivting protein (GAP) tivity 6 8. Redued GAP tivity llows the uildup of GTP-ound Rhe 9, nd upregultes mtor, whih, through multiple tions, enhnes protein trnsltion nd ell growth.thus,giventhe loss of heterozygosity of TSC or TSC found in hmrtoms of TSC ptients, the growth of these enign tumors is thought to result from the inresed mtor tivity nd unontrolled ell growth tht ompnies interruption of the TSC pthwy. The pthogenesis of the neurologil symptoms of TSC is unler, nd loss of heterozygosity is not seen within the rins of TSC ptients 3. The funtion of TSC nd TSC in mmmlin neurons nd the defets tht rise from hemizygosity of TSC or TSC re unknown. Mny prllels exist, however, etween the TSC pthwy nd those tht link extrellulr stimuli to synpti refinement in neurons. For exmple, tivtion of the TrkB reeptor tyrosine kinse y rinderived neurotrophi ftor (BDNF) stimultes PI3K nd Akt to promote dendriti growth 4. BDNF lso triggers long-term potentition of synpti strength in n mtor-dependent mnner 5. Similrly, strong tivtion of metotropi glutmte reeptors depresses synpti trnsmission through PI3K- nd mtor-dependent pthwy 6,7. Here we exmine the role of the TSC pthwy in regulting the growth of post-mitoti, differentited neurons. We show tht the TSC pthwy regultes som size, the density nd size of dendriti spines, nd the properties of exittory synpses in hippompl pyrmidl neurons. These morphologil effets re independent of regultion of Ts y Akt t onserved phosphoryltion sites ut do require regultion of ofilin t onserved LIM-kinse (LIMK) phosphoryltion site. Furthermore, the TSC pthwy is sensitive to gene-dosge effets, suh tht loss of single opy of Ts, s is present in ll neurons of TSC ptients, is suffiient to pertur dendriti spine struture. Our results indite tht the TSC pthwy regultes neuronl struture nd funtion nd suggest tht the neurologil symptoms of TSC re, t lest in prt, due to ell-utonomous perturtions of synpse funtion. RESULTS To unover defets in neuronl struture nd funtion used y perturtion of the TSC pthwy, we used trnsgeni mie rrying onditionl Ts llele (Ts C ) in whih exons 7 nd 8 re flnked y loxp sequenes 8. Loss of Ts protein in neurons following trnsfetion with plsmid enoding reominse nuler loliztion sequene fusion protein () ws onfirmed in dissoited hippompl Deprtment of Neuroiology, Hrvrd Medil Shool, Longwood Avenue, Boston, Msshusetts 5, USA. Deprtment of Mediine, Brighm nd Women s Hospitl, Hrvrd Medil Shool, Longwood Avenue, Boston, Msshusetts 5, USA. 3 Present ddress: Deprtment of Medil Onology/Hemtology, Memoril Slon-Kettering Cner Center, 75 York Avenue, New York, New York, USA. 4 These uthors ontriuted eqully to this work. Correspondene should e ddressed to B.L.S. (stini@hms.hrvrd.edu). Reeived 8 June; epted 5 Septemer; pulished online 6 Novemer 5; doi:.38/nn566 NATURE NEUROSCIENCE VOLUME 8 [ NUMBER [ DECEMBER 5 77
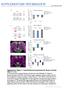
2 Ts C/C ; Ts C/C e MAP/ Ts Ts C/C ;..5. Ts C/C Ts C/C ; Ts immunostining (u) Ts C/C ; ; MAP/ ultures prepred from mie homozygous for the onditionl llele (Ts C/C ). Beuse trnsfetion effiieny of neurons is low, we monitored Ts levels y fluoresene immunohistohemistry (fihc) (Fig.,). In neurons expressing, ytoplsmi Ts levels were signifintly redued t 6 dys post-trnsfetion (6 DPT) ompred to untrnsfeted neighoring neurons (P o.5, n ¼ 6 67) (Fig. ). In severl ell types, downregultion of TSC/TSC upregultes mtor tivity nd inreses phosphoryltion of the riosoml protein S6 3,5,8. Immunostining ginst phosphorylted S6 (ps6) reveled perinuler ytoplsmi signl in neurons (Fig. ) tht ws olished y pplition of rpmyin, seletive phrmologil inhiitor of mtor (dt not shown). PS6 levels were sustntilly higher in -trnsfeted Ts C/C neurons thn in neighoring ontrol neurons (P o.5, n ¼ 68) (Fig.,d). Thus, trnsfetion in post-mitoti, differentited Ts C/C neurons indues reomintion of the Ts C llele, loss of Ts protein nd upregultion of mtor. Ts/ regulte ell growth in differentited neurons Widespred loss of Ts in the mouse rin, even when limited to stroytes, leds to pronouned seizures 8, whih my trigger hnges in gene expression nd synpti trnsmission. To identify Ts C/C Ts C/C ; g Phospho-S6 d..5 Ts C/C Ts C/C ;. 5 ps6 immunostining (u) f Ts C/C ; Ts C/C ; ; Som re (µm ) 6 4 Ts C/C 5 µm d d + Ts Ros C/C shts shts + htsc Figure expression in hippompl neurons of Ts C/C mie leds to loss of Ts protein, inresed phosphoryltion of S6 nd inresed som size. () Untrnsfeted (top) nd -trnsfeted (ottom) neurons in dissoited hippompl ulture from Ts C/C mie with immunoretivity to MAP nd (red) nd to Ts (green). Arrow highlights red nuleus inditive of expression of the -NLS fusion protein. () Cumultive distriution of Ts immunostining in -trnsfeted nd untrnsfeted neurons t 6 DPT. () Untrnsfeted (top) nd -trnsfeted (ottom) neurons with immunoretivity to MAP nd (red) nd to ps6 (green). Arrow highlights red nuleus inditive of expression of the -NLS fusion protein. (d) Cumultive distriution of ps6 immunostining in -trnsfeted nd untrnsfeted neurons t 6 DPT. (e) Imges of -trnsfeted (left) nd / otrnsfeted (right) pyrmidl neurons in orgnotypi hippompl slie from Ts C/C mie. Sle r, 5 mm. (f) Enlrged views of the soms from neurons shown in e. (g) Summry of effets of loss of Ts or Ts on ross-setionl re of soms of hippompl pyrmidl neurons. Expression of Ts or humn TSC suppressed the effets of Ts loss t DPT nd Ts knokdown t DPT, respetively. Expression of in neurons from ontrol ROSA6 lous (Ros C/C ) mie hd no ffet on som size. P o.5 ompred to ontrol, nd P o.5 for resue experiments ompred to pertured phenotype (- or shts-expressing ells, s pproprite). ell-utonomous neuronl defets used diretly y loss of Ts, we generted genetilly mosi rin tissue in whih smll numer of neurons lking Ts were loted in otherwise norml rin tissue. This ws omplished y sprse trnsfetion of pyrmidl neurons with nd green fluoresent protein () in orgnotypi hippompl slies prepred from Ts C/C mie. -trnsfeted pyrmidl hippompl neurons were identified y their hrteristi morphology (Fig. e) nd lotion in elldense nd. Soms of -trnsfeted Ts C/C pyrmidl neurons were lrger thn those of -trnsfeted neurons, rehing roughly twofold enlrgement t DPT (n ¼ 3, P o.5) (Fig. e g). Chnges in som size were prevented y otrnsfetion with plsmid enoding Ts (n ¼ 8). To ontrol for nonspeifi effets of -medited DNA reomintion, similr mesurements were mde in tissue prepred from B6;9-Gt(RO- SA)6Sor tmsho /J mie tht rry floxed trnsriptionl stop upstrem of the E oding sequene in the Ros6 lous (Ros C/C ). expression in Ros C/C neurons hd no effet on som size (n ¼ 7 8) (Fig. g), onfirming tht the inresed som size in Ts C/C neurons trnsfeted with ws due to loss of Ts. Som size ws lso mesured in rt neurons in whih loss of Ts ws indued y RNA interferene (RNAi; see Methods nd Fig. g). Trnsfetion of dissoited rt hippompl pyrmidl neurons with dul-promoter plsmid enoding ytomeglovirus (CMV) promoter-driven nd U6-driven short-hirpin RNA trgeting Ts (shts) redued Ts nd inresed ps6 (Supplementry Fig. online). In orgnotypi hippompl slie ultures, soms of pyrmidl neurons trnsfeted with shts were enlrged reltive to ontrol neurons t DPT (n ¼ 7 3, P o.5) (Fig. g). This effet ws oluded y otrnsfetion with humn TSC, whih ontins nine se pir hnges within the region trgeted y shts (n ¼ 9) (Fig. g). Thus, som size of post-mitoti, hippompl pyrmidl neurons is ontrolled y the TSC pthwy. Somti enlrgement ourred with shorter lteny fter shts trnsfetion thn fter trnsfetion of Ts C/C neurons, likely refleting the rpid degrdtion of mrna triggered y RNAi. Ts/ regulte density nd size of dendriti spines In pyrmidl neurons, the vst mjority of exittory synpses re mde onto the heds of dendriti spines, nd the morphology nd density of dendriti spines reflet the properties nd numer of synpses. At DPT, dendriti spines of Ts C/C neurons expressing lone displyed roughly spheril spine heds seprted from the dendrite y thin neks (Fig. ). In ontrst, dendrites of Ts C/C neurons oexpressing nd possessed elongted spines with gretly enlrged, ulous heds. Quntifition of these hnges showed tht Ts loss inresed spine length nd hed width nd deresed the density of dendriti spines (n ¼ 9 6 ells nd 78 VOLUME 8 [ NUMBER [ DECEMBER 5 NATURE NEUROSCIENCE
3 Ts C/C ; ; Ts C/C ; Apil Bsl..5. Density (µm ) Length Hed width ,,, Ts Spine length d d Ts C/C d d + Ts Spine hed width d shts d shts + htsc d d shts d Figure Loss of Ts leds to inresed size ut deresed density of dendriti spines. () Imges of pil (left) nd sl (right) dendrites from Ts C/C pyrmidl neurons in hippompl orgnotypi slie ulture. Neurons were trnsfeted with lone (top) or nd (ottom). Sle r, mm. () Cumultive distriution of spine length nd hed width from Ts C/C neurons trnsfeted with lone; nd ; or, nd Ts t DPT. () Summry of effets of Ts or Ts loss on dendriti spine density, length nd hed width. P o.5 ompred to ontrol neurons. P o.5 for resue experiments ompred to pertured phenotype (- or shts-expressing ells s pproprite).,44 4,344 spines, P o.5; Fig.,). Similr effets on spine size nd morphology were seen t DPT (n ¼ 7 8 ells nd,577 3,338 spines, P o.5; Fig. ), time point t whih loss of Ts hs no effet on som size (Fig. g). Chnges in spine morphology nd density were prevented y expression of Ts (n ¼ 8 ells nd,96 spines; Fig.,) nd no hnges in spine density or morphology were seen with expression in Ros C/C neurons (Supplementry Tle online), onfirming tht the morphologil hnges seen with expression in Ts C/C neurons were due to loss of Ts protein. The perturtions of spine morphology triggered y loss of Ts were phenoopied y RNAi-medited knok-down of Ts in rt hippompl neurons (Fig. ). Thus, t oth DPT (n ¼ 7 3 ells nd,75 5,3 spines) nd DPT (5 3 ells nd 993 4,6 spines), dendriti spines of shts-expressing neurons were elongted with enlrged spine heds (P o.5). These effets were resued y expression of htsc (n ¼ 9 ells nd,68 spines; Fig. ). Summries of morphologil prmeters nd numers of ells nd spines nlyzed for eh experimentl ondition re given in Supplementry Tle. Funtionl defets ssoited with loss of Ts Do the enlrged spine heds seen fter loss of Ts ontin funtionlly pertured synpses? To ddress this question, we otined whole-ell voltge-lmp reordings from Ts C/C pyrmidl neurons trnsfeted with nd from untrnsfeted neighoring neurons. Spontneous miniture exittory postsynpti urrents (mepscs) were reorded (Fig. 3). A red fluorophore ws inluded in the reording pipette solution in order to fill the neuron nd onfirm its identity. At DPT, mepsc mplitude ws roughly % higher in -expressing neurons Figure 3 Loss of Ts inreses AMPAR-medited synpti urrents. () Left, lser-snning DIC imge of the pyrmidl ell lyer of n orgnotypi slie ulture from Ts C/C mouse with superimposed green fluoresene from -expressing neuron. Note gold prtile (rrow) in the nuleus of the trnsfeted neuron. Imge of /-trnsfeted pyrmidl neuron efore (middle) nd fter (right) filling with red fluorophore through the whole-ell reording eletrode. Sle rs, 5 mm. () Representtive tres of mepscs reorded from ontrol nd trnsfeted Ts C/C neurons. Sle rs: pa, ms. () Cumultive distriutions showing inresed mepsc mplitudes in -trnsfeted (lk tre) Ts C/C neurons ompred to ontrol neurons (gry tre) reorded t DPT (left). Frequeny of mepscs in untrnsfeted nd trnsfeted Ts C/C pyrmidl neurons t DPT (right). (d) Wide-field imge of hippompl orgnotypi slie ulture from Ts C/C mouse showing sprse trnsfetion of neurons in the pyrmidl ell lyer (pl) nd shemti of reltive positions of the reording eletrode (re) nd stimulting eletrode (stim) within the slie. Sle r, mm. (e) Evoked EPSCs reorded t..5. Amplitude (pa) 6mV (negtive urrent) nd +4mV (positive urrent) with rrowheds showing the times t whih AMPAR (negtive) nd NMDAR (positive) medited urrents were mesured (left). Men AMPAR/NMDAR urrent rtios for ontrol (gry r) nd -trnsfeted (lk r) Ts C/C neurons t DPT (right). (f) Pired-pulse filittion mesured t 5 ms interpulse intervl in -trnsfeted Ts C/C neuron t DPT nd summry dt for ontrol nd trnsfeted neurons. P o.5. 4 mepsc freq (Hz)... A d e f re A PPF = A/A pa ms pa 5 ms AMPA/NMDA rtio PPF 4 stim pl NATURE NEUROSCIENCE VOLUME 8 [ NUMBER [ DECEMBER 5 79
4 Perentge of ontrol 5 5 Ts C/+ ; Ts C/+ ; Ts C/C ; Som re Spine density Spine length Spine hed width ompred to neighoring ontrol neurons (n ¼ ells nd events, P o.5; Fig. 3,), inditing n enhned sensitivity to relesed neurotrnsmitter. No hnges in mepsc frequeny (Fig. 3) or in resting memrne resistne (R in ) nd ell pitne (C m ) were seen (ontrols: R in ¼ 97 ± 43 MO, C m ¼ 56 ± 6 pf; -expressing neurons: R in ¼ ± 63 MO, C m ¼ 8 ± 34 pf). In ontrst, t DPT, ells lking Ts hd gretly redued R in (7 ± 5 MO vs. 85 ± MO in ontrol neurons, P o.5) nd inresed C m (34 ± 4 pf vs. 7 ± 7 pf in ontrol neurons) (n ¼ 3 in eh ondition), mking the omprison of mepscs etween Ts-lking neurons nd ontrol neurons diffiult. At DPT, EPSCs evoked y stimultion of Shffer ollterls (Fig. 3d) were monitored in CA pyrmidl neurons t holding potentil of 6 mv, t whih AMPARs re tivted, nd t +4 mv, t whih the lok of NMDA-type glutmte reeptors (NMDARs) y Mg + is relieved nd the long-lived NMDAR urrent is reveled (Fig. 3e). The rtio of evoked AMPAR- to NMDAR-medited urrents normlly inreses during development s well s fter indution of long-term potentition. In -trnsfeted neurons, the AMPAR/ NMDAR urrent rtio ws signifintly inresed reltive to tht in ontrols (3.7 ±.7 vs.. ±.35 in ontrols, n ¼ 3 in eh ondition, P o.5), inditing n errnt reltive enhnement of synpti AMPARs. To exmine possile hnges in presynpti funtion indued retrogrdely y postsynpti loss of Ts, we reorded responses to pir of stimuli nd mesured the pired-pulse filittion (PPF). PPF ws similr in untrnsfeted nd -trnsfeted neurons (.73 ±. nd.75 ±.5, respetively, n ¼ 3; Fig. 3f), suggesting tht relese proility is not ffeted y postsynpti loss of TSC. Ts C/+ ; Figure 4 Neuronl morphology is sensitive to hemizygosity of Ts. () Dendrites of / (left) nd (right) trnsfeted pyrmidl neurons in hippompl orgnotypi slie ultures prepred from Ts C/+ mie t DPT. Sle r, 5 mm. () Reltive som ross-setionl re, spine density, length nd hed width for -trnsfeted Ts C/+ nd Ts C/C neurons ompred to -trnsfeted neurons of eh genotype. P o.5. Figure 5 mtor-dependent regultion of neuronl morphology. (,) Lowpower imges of the whole ell (left) nd enlrged views of spiny dendrites (right) of () - nd() shtsc-trnsfeted pyrmidl neurons in ontrol medi t DPT (top) or for 4 d in ontrol medi followed y 6 d in nm rpmyin (ottom). Sle rs, 3 mm (left) nd 5 mm (right). () Summry of mesured spine density, length, hed size nd som re following pplition of rpmyin. Shded res indite the men ± s.e.m. of eh prmeter for ontrol (drk gry) nd shts (light gry) neurons determined in Figures nd. P o.5 ompred to ells in ontrol medi. Morphologil effets of hploinsuffiieny of Ts Individuls fflited with TSC rry heterozygous muttions in either the TSC or TSC genes nd loss of heterozygosity, lthough present in hmrtoms, is not seen within the rin. Therefore we tested whether loss of single opy of Ts is suffiient to trigger hnges in neuronl morphology (Fig. 4). In tissue prepred from Ts C/+ mie, expressing neurons hd inresed som size, deresed spine density, inresed spine length nd inresed spine hed width reltive to expressing neurons (n ¼ ells nd,996 spines, P o.5). The morphologil hnges were less pronouned fter loss of single opy thn fter loss of oth opies of Ts (Fig. 4), suggesting tht the TSC pthwy is sensitive to gene dosge. Regultion of neuronl morphology y mtor Rpmyin is potent nd speifi inhiitor of mtor, nd is predited to t downstrem of TSC nd TSC. To determine whether the effets of loss of Ts or Ts on neuronl morphology re medited y inresed tivity of mtor, we exmined the ility of rpmyin to reverse defets in neuronl morphology (Fig. 5). Neurons in hippompl orgnotypi slies were trnsfeted nd mintined in ulture for 4 d, time point t whih the effets of -medited loss of Ts nd RNAi-medited loss of Ts were pprent. Rpmyin ( nm) ws then dded to the ulture medi, nd the ultures were mintined for six more dys efore morphologil nlysis (totl of DPT). Applition of rpmyin to ontrol -expressing rt neurons hd no effet on som size ut indued the growth of long, thin spines (n ¼ 6 ells nd,7 spines; Fig. 5,). Surprisingly, the men length of dendriti spines on ontrol ells in the presene of rpmyin ws similr to tht of Ts knokdown ells (Fig. 5,). Unlike the phenotype resulting from loss of Ts, however, the rpmyin-indued spine phenotype did not show enlrged spine heds. Applition of rpmyin to shts-expressing ells reversed the enlrgement of the som nd spine heds ut further inresed spine length (n ¼ 8 ells nd,63 spines, P o.5; Fig. 5,). In these ells, it ws diffiult to distinguish long filopodi nd spines from nsent dendriti rnhes, rtiftully lowering the mesured spine density. Similr effets were seen in -expressing Ts C/C ells, suh tht pplition of rpmyin Rpmyin Rpmyin shts Hed width Spine length Spine density (µm ) Som re (µm ).5. shts rp /6d shts + rp /6d 73 VOLUME 8 [ NUMBER [ DECEMBER 5 NATURE NEUROSCIENCE
5 Akt CA Akt CA + htsc AA shts + htsc AA Spine density (µm ) Spine length Hed width Som re (µm ) prevented the inrese in som nd spine hed sizes ut further inresed spine length (Supplementry Tle ). Thus, rpmyinsensitive mtor tivity is epistti to Ts with respet to the regultion of som nd spine hed sizes. Epistti nlysis of Ts nd Akt It hs een proposed tht Akt inhiits TSC y phosphoryltion t two sites (S939 nd T46, numered y the humn sequene) tht re onserved in D. melnogster nd mmmls 7. We investigted whether Akt regultes neuronl morphology nd, if so, whether it ours through phosphoryltion of sites S939 nd T46 of Ts (Fig. 6). Expression in rt hippompl pyrmidl neurons of onstitutively tive Akt (Akt CA ), onsisting of myristoylted Akt lking its plekstrin homology domin (myraktd4-9) 9, phenoopied loss of Ts/Ts, resulting in lrge soms, long spines nd inresed spine hed size (n ¼ 5 ells nd,5 spines, P o.5; Fig. 6,). Three experiments were performed to determine if these effets re medited y downregultion of Ts y Akt through phosphoryltion of S939 nd T46 (Fig. 6 nd Supplementry Tle ). First, htsc AA ws expressed lone nd found to hve no effet on spine or somti morphology (n ¼ 5 ells nd,4 spines). Seond, expression of htsc AA did not olude the hnges triggered y overexpression of Akt CA (n ¼ 5 ells nd,49 spines). Third, htsc AA expression in Ts knokdown ells resued spine nd som morphology with n effiieny equl to tht of wild-type htsc (n ¼ 5 ells nd,84 spines). Thus, phosphoryltion of S939 nd T46 is not neessry for regultion of neuronl som nd spine size y Ts, nd htsc AA is unle to t s dominnt negtive with respet to the neuronl enlrgement triggered y upregultion of Akt shts Akt CA htsc AA Akt CA + htsc AA shts + htsc AA Figure 6 Akt upregultion phenoopies Ts/Ts loss ut does not require phosphoryltion of Ts t onserved Akt phosphoryltion sites. () Imges of pyrmidl neurons (ottom) in orgnotypi slie ultures of rt hippompus nd enlrged views of spiny dendrites (top). Neurons were trnsfeted with n Akt CA (left); Akt CA nd htsc AA (middle); or shts nd htsc AA (right) nd imged t DPT. Sle rs, 5 mm (top) nd 3 mm (ottom). () Summry of effets on spine density, length nd hed width. Shded res represent men ± s.e.m. of eh prmeter for ontrol (drk gry) nd shts (light gry) neurons determined in Figures nd. P o.5 ompred to ontrol neurons. P o.5 for htsc AA resue experiments ompred to shts or Akt CA expressing neurons, s pproprite. Morphologil hnges require signling through ofilin The mehnism y whih the TSC pthwy regultes neuronl morphology is unknown. Cofilin, protein tht depolymerizes nd severs tin filments nd is widely expressed in the mmmlin rin, hs reently een shown to regulte spine size,. Cofilin is negtively regulted y LIMK through phosphoryltion t onserved site (serine 3). We exmined whether phosphoryltion t this site is regulted y the TSC pthwy using fihc to monitor levels of Ser3-phosphorylted ofilin (p-ofilin) in ultures of dissoited hippompl neurons (Fig. 7,). At DPT, shts-trnsfeted ells hd higher p-ofilin levels thn ontrol neurons (Fig. 7; n ¼ 34 4 ells), wheres totl ofilin levels were unhnged (n ¼ 6 3 ells). In ddition, p-ofilin, ut not totl ofilin, ws inresed in Ts / mouse emryoni firolsts (MEFs) ompred to Ts +/+ MEFs (n ¼ 3 5, P o.5; Fig. 7,d). Similr results were otined with seond ommeril p-ofilin-speifi ntiody (see Methods, dt not shown). Furthermore, the intensity of the B9 kd nd reognized y the p-ofilin ntiody on western lots refleted levels of phosphorylted ofilin s its intensity ws redued in HEK93T ells trnsfeted with the ofilin Ser3 phosphtse slingshot-l 3. No hnges in intensity were noted following LIMK trnsfetion, possily refleting dditionl regultion of the kinse tivity independently of its expression level. To determine whether inresed ofilin phosphoryltion is neessry for the spine enlrgement desried ove, we expressed wild-type ofilin or ofilin with the LIMK phosphoryltion site mutted to lnine (ofilin S3A) in shts-trnsfeted neurons in rt orgnotypi slie ultures (Fig. 7e). At DPT, neurons expressing ofilin nd shts hd slightly redued spine length ompred to those expressing shts lone (n ¼ 9 ells nd,336 spines, P o.5) ut similr som size, spine hed width nd spine density. In ontrst, expression of ofilin S3A in shts-trnsfeted neurons restored som size, spine hed width nd spine density to ontrol levels nd deresed spine length to levels slightly elow those of ontrol neurons (n ¼ 6 ells nd 3, spines, P o.5 ompred to shts neurons; Fig. 7e). Cofilin S3A expression in ontrol neurons hd no effet on som size, spine hed width nd spine density, ut it did redue spine length (n ¼ 6 ells nd 4,43 spines, P o.5; Fig. 7f). The morphology of ofilin S3A/ shts-expressing ells ws identil to tht of ofilin S3A/expressing neurons (Fig. 7g), inditing tht ofilin lies downstrem of Ts nd tht phosphoryltion t Ser3 is neessry for the morphologil hnges indued y loss of Ts. DISCUSSION We hve shown tht the TSC pthwy regultes the morphology nd funtion of post-mitoti, hippompl pyrmidl neurons. Loss of Ts/Ts triggered multiple hnges in neuronl morphology, inluding inresed som nd dendriti spine size s well s deresed dendriti spine density. These effets required oth rpmyin-sensitive mtor tivity nd regultion of ofilin t onserved LIMK phosphoryltion site. Furthermore, phosphoryltion of ofilin, n tindepolymeriztion ftor not previously linked to the TSC pthwy, ws inresed following loss of Ts. Synpti strength nd pssive memrne properties were lso ltered in neurons lking Ts, suggest tht primry defets in neuronl funtion ontriute to the neurologil symptoms of TSC. Reltionship of Ts nd Akt We found tht expression of onstitutively tive Akt phenoopies the morphologil defets seen with loss of Ts or Ts. Inresed Akt tivity leds to enlrged neuronl size, in greement with studies using overexpression of Akt or downregultion of PTEN, the lipid NATURE NEUROSCIENCE VOLUME 8 [ NUMBER [ DECEMBER 5 73
6 phosphtse tht ntgonizes PI3K 6,4 7. However, we found tht the somti nd dendriti spine enlrgement indued y inresed Akt tivity is independent of phosphoryltion of TSC t S939 nd T46, the onsensus sites onserved ross D. melnogster, rts, mie nd humns. This is in ontrst to findings in D. melnogster in whih expression of dts S94A/T58A suppresses the enlrgement of ommtidi triggered y overexpression of Akt 6. Furthermore, we found tht expression of htsc AA does not pertur spine or som size nd tht it reverses the effets of loss of endogenous Ts. Agin, these results re in ontrst with the mrked redution in ommtidi size following dts S94A/T58A expression 6 ut in greement with reent findings tht dts S94A/T58A is le to resue the dts-null phenotype in D. melnogster development 8. Lstly, our results re onsistent with reent findings tht indite tht Akt is regulted y mtor 9 nd thus lies downstrem of Ts/Ts. In summry, our dt indite tht, lthough upregultion of Akt nd downregultion of Ts/Ts result in similr phenotypes, phosphoryltion of Ts t S939 nd T46 is not neessry for the norml ontrol of neuronl size or for the neuronl enlrgement indued y upregultion of Akt. MAP- p-ofilin e shts g p-of α-tu d..5. Intensity (% ontrol) p-ofilin (u) Ts +/+ Ts /..5. HEK HEK + LIMK HEK + SSH p-ofilin Cofilin Tuulin shts Cof Cofilin (u) α-tu LIMK SSH Ts +/+ Ts / f shts + of shts + ofs3a + ofs3a Spine density (µm ) Spine length Hed width Som re (µm ). shts + of shts + ofs3a shts + ofs3a Figure 7 Phosphoryltion of ofilin is regulted y Ts nd is neessry for inresed ell growth. () Cultured hippompl neurons trnsfeted with shts showing fluoresene (green, left), immunostining for MAP (lue, left) nd immunostining for phosphorylted ofilin (p-ofilin) (red, right). Arrows nd sterisks highlight shts-trnsfeted neurons nd nontrnsfeted neighors, respetively. Sle r, mm. () Cumultive distriution of p-ofilin (left) nd totl ofilin (right) immunostining in shts-trnsfeted nd -trnsfeted neurons t DPT. () Left, western lots of p-ofilin (left) from Ts +/+ MEFs, Ts / MEFs, ontrol HEK93T ells nd HEK93T ells trnsfeted with LIMK or slingshot-l. Right, western lot of totl ofilin in Ts +/+ nd Ts / MEFs. (d) Summry of nd intensities for p-ofilin, ofilin nd tuulin in Ts / MEFs reltive to Ts +/+ MEFs (left), nd the intensities of p-ofilin nds in HEK ells trnsfeted with LIMK or slingshot-l reltive to untrnsfeted ells (right). P o.5. (e) Dendrites of pyrmidl neurons in orgnotypi hippompl slies trnsfeted with shts (top), shts+ofilin (middle) or shts+ofilins3a (ottom). Sle r, 5 mm. (f) Dendrites of pyrmidl neurons trnsfeted with (top) or + ofilin S3A (ottom) imged t DPT. (g) Summry of the effets of the mnipultions shown in e nd f on spine density, length, hed width nd som re. Shded res represent the men ±s.e.m. of eh prmeter for ontrol (drk gry) nd shts (light gry) neurons. P o.5 ompred to neurons trnsfeted with or shts lone, s pproprite. Moleulr mehnisms of morphologil perturtions In ddition to regulting mtor tivity, TSC nd TSC re reported to prtiipte in mtor-independent signling sdes tht my regulte ell morphology. TSC interts with nd regultes the ytoskeleton vi C- terminl domin tht inds ezrin-rdixin-moesin (ERM) fmily proteins nd n N-terminl domin tht is ple of tivting Rho GTPse in humn endothelil ells 3. TSC hs een shown to tivte Rho (in MDCK nd ELT3 ells) 3, nd inresed Rho tivity dereses spine length in hippompl pyrmidl neurons 3. Furthermore, Rho GDP/GTP exhnge ftors (Rho-GEFs) regulte dendriti spine morphology nd density 3,33. TSC lso interts with proteins 34,35, whose mny ellulr funtions inlude trffiking of ion hnnels from the endoplsmi retiulum 36 nd regultion of the tin ytoskeleton 37. Importntly, TSC nd TSC proteins stilize eh other 38, nd thus redued expression of either protein my indue ommon set of morphologil perturtions medited through disruption of these mtor-independent signling sdes. Whih of these pthwys is responsile for the hnges in neuronl morphology oserved here? Applition of rpmyin to neurons with redued Ts or Ts levels restores neuronl som nd dendriti spine hed sizes to ontrol levels, onsistent with mtor eing downstrem of Ts/Ts. In ontrst, in the presene of rpmyin, spine morphology is lerly different in ontrol neurons thn in neurons with redued Ts/Ts, rguing ginst stritly epistti reltionship. Thus, Ts/Ts my regulte som nd spine size vi rpmyinsensitive mtor-dependent pthwy nd spine length vi rpmyininsensitive pthwy. However, two vets must e onsidered. First, long-term pplition of rpmyin my indiretly inhiit rpmyininsensitive mtor tivity y sequestering mtor nd preventing formtion of ritor-mtor omplexes 9,39. Seond, rpmyin my hve mtor-independent effets through the sequestrtion of FK56- inding proteins. The entrl role of tin dynmis in determining spine struture strongly suggests tht pertured regultion of the tin ytoskeleton underlies the morphologil hnges desried ove. Indeed, we find link etween the TSC pthwy nd regultion of the ytoskeleton through ofilin. Cofilin is n tin depolymeriztion ftor whose tivity is downregulted following phosphoryltion y LIM kinse t Ser3 (S3) 4. Hploinsuffiieny of LIMK, downstrem effetor of the Rho fmily of GTPses, results in the ognitive disorder Willims syndrome 4. Both ofilin nd LIMK, s well s upstrem regultors of the pthwy suh s PAK nd Rho, hve een shown to regulte dendriti spine morphology,4 45. We found tht phosphoryltion of ofilin t S3 is neessry for the morphologil hnges triggered y loss of Ts, s they re oluded y expression of ofilin with this site eliminted (S3A). Our results lso demonstrte tht the lne of tive nd intive ofilin is regulted y the TSC pthwy in oth neurons nd MEFs, suh tht loss of Ts leds to inresed VOLUME 8 [ NUMBER [ DECEMBER 5 NATURE NEUROSCIENCE
7 S3-phosphorylted ofilin without hnges in totl ofilin. Possile mehnisms for this effet inlude mtor-dependent trnsltionl ontrol of key regultory protein s well s diret regultion of the enzymti tivity of PAK, LIMK, or slingshot y mtor or downstrem kinse suh s Akt 9. Alterntively, regultion of Rho through Ts-dependent protein-protein intertions 3 might medite downstrem regultion of ofilin. Implition for tuerous slerosis omplex Individuls with TSC show perturtions of ortil rhiteture inluding tuers, whih re disorgnized regions of the rin with distured lmintion ontining inresed numers of stroytes nd sprse neurons. The orreltion etween the numer of ortil tuers nd the severity of seizure symptoms hs led to the ide tht the neurologil defiits in TSC ould rise from disruptions of ortil rhiteture 46. Here we show tht loss of single opy of Ts results in defets in neuronl morphology, inluding inresed som size, deresed spine density nd inresed spine size. Therefore we propose tht ell-utonomous neuronl defets due to hploinsuffiieny of TSC or TSC, in ddition to the perturtions of rin rhiteture used y ortil tuers, suependyml nodules nd gint ell stroytoms, ontriute to the pthogenesis of the neurologil symptoms of TSC. METHODS Animls. We used mie rrying onditionl Ts llele 8 (Ts C ) onsisting of loxp elements upstrem of exon 7 nd downstrem of exon 8, s well s Sprgue-Dwley rts (Chrles River Lortory). Ts C/+ mie were generted y rossing Ts C/C mie with C57Bl6 mie (Chrles River Lortories). Ros C/C mie (Jkson Lortories) ontin the E oding sequene with n upstrem loxp-flnked stop in the Gt(ROSA)6Sor lous. All niml proedures were onduted following Hrvrd Medil Shool guidelines. Ts C genotyping ws performed using til genomi DNA nd primers F4536 (5 -ACGAGGCCTCTTCTGCTACC-3 ) nd R483 (5 -CAGCTCCGACCAT GAAGT-3 ), yielding 95-p nd 48-p produts from wild-type nd onditionl lleles, respetively. Plsmids. All enzymes were otined from New Englnd Biols. The following plsmids were gifts: pbs::-tin-nls-re (S. Dymeki, Hrvrd Medil Shool); htsc nd htsc AA (E. Henske, Fox Chse Cner Center, Phildelphi, Pennsylvni); pbs/u6 (Y. Shi, Hrvrd Medil Shool); ofilin nd ofilins3a (A. Minden, Columi University); SlingshotL nd LIM-kinse (K. Mizuno, Tohoku University, Jpn). pe-n (Invitrogen) ws used s ontrol. For onstrution of the dul promoter CMV-E/U6-shRNA vetor, pe-n ws digested with BmHI nd BglII to remove the multiple loning site (MCS) nd designted s pe-n::dmcs. The U6 promoter nd its downstrem MCS from pbs/u6 were inserted into pe-n::dmcs t filled-in AflII site downstrem of the SV4 polydenyltion sequene in the forwrd (pguf) or reverse (pgur) orienttion reltive to E. Four sets of shrnas direted ginst Ts were designed from 9 p oding sequenes onserved in mie nd rts with roughly 5% gunosines nd ytidines rtio. Oligonuleotides ontining the trget sequene, restrition site, the reverse omplement of the trget sequene, five threonine residues for U6 polymerse termintion nd n EoRI site were synthesized (Integrted DNA Tehnologies). The shts lone used in this study ws onstruted from the following oligonuleotides: GGTGAAGAGAGCCGTATCACAAAGCTTTGTGATACGGC TCTCTTCACCCTTTTTG nd AATTCAAAAAGGGTGAAGAGAGCCGTATC ACAAAGCTTTGTGATACGGCTCTCTTCACC. For prodution of shts, pguf ws digested with ApI, klenowed, digested with EoRI nd treted with lf intestinl lkline phosphtse. Oligonuleotides were nneled, phosphorylted with T4 polynuleotide kinse nd ligted into the digested pguf to yield shts. Cultures nd trnsfetion. Dissoited hippompl ultures were prepred from P3 rts nd mie 47 nd plted t 8 4 ells/well on glil monolyers on -mm glss overslips. Cultures were trnsfeted with Lipofetmine (Invitrogen) fter 3 5 dys in vitro (d.i.v.) in neuronl NEU medi lking iotin. Orgnotypi slie ultures were prepred from P5 P7 mie nd rts 48 nd iolistilly trnsfeted with Helios Gene Gun (Biord) fter d.i.v.. Bullets were prepred using.5 mg of.6 mm gold prtiles nd 4 8 mg of plsmid DNA. Immunofluoresene. Dissoited hippompl neurons were fixed in 3.7% prformldehyde/4% surose for 5 min t 4 C, permeilized with.% Triton X-/PBS (Sigm) for min, loked with % got serum/pbs (Jkson ImmunoLs) nd inuted with the following primry ntiodies: nti-phospho-s6 riosoml protein (:, Ser35/36; Cell Signling), nti- MAP- (mouse, :5, Sigm), nti-map- (rit, :5, Chemion), nti- reominse (mouse, :,, Chemion), nti- reominse (rit, :,, Novgen), nti-p-ofilin (Ser3) (:, Snt Cruz) nd nti-ofilin (:, Cell Signlling). Antiodies speifi to tuerin nd hmrtin (BA8 nd HF6, respetively) were kindly provided y V. Rmesh (Msshusetts Generl Hospitl). The following seondry ntiodies from Jkson Immunoreserh were used t dilution of :5: Cy3-onjugted got nti-rit, Cy3-onjugted got nti-mouse, Cy5-onjugted got nti-rit nd Cy5- onjugted got nti-mouse. Seondry ntiody fluoresene ws mesured in trnsfeted nd untrnsfeted neurons using n LSM5 onfol (Zeiss). Western lotting. Lystes of Ts / nd Ts +/+ MEFs, nd HEK93T ells (ontrol or 4 h fter trnsfetion with LIMK or SSHL), were seprted y SDS-PAGE using 8 6% Tris-HCl gels (BioRd). Proteins were trnsferred onto polyvinylidene difluoride memrne (PVDF, BioRd) overnight t 4 C. Memrnes were inuted in loking solution (5% BSA,.% Tween in Tris-uffered sline) for h t 4 C, inuted overnight t 4 C with primry ntiodies (rit nti-p-ofilin S3 (:, Snt Cruz), rit nti-pofilin S3 (:,, Cell Signlling), rit nti-ofilin (:,, Cell Signlling) or rit nti--tuulin ( mg/ml, ACAM), wshed nd inuted for h t 4 C with horserdish peroxidse (HRP)-onjugted got nti-rit (:,, BioRd). Memrnes were wshed nd inuted for 5 min with hemiluminesent sustrte (Piere) efore exposure to film. Bnd densitometry ws performed using Quntity One 4.5. softwre (BioRd). Two-photon lser snning mirosopy nd imge nlysis. Neurons were imged with ustom-uilt two-photon lser snning mirosopes 49 with n exittion wvelength of 9 nm. Imges of trnsfeted pyrmidl neurons were quired t.8 zoom (imge field, 3 7 mm), wheres spiny regions of sl nd pil dendrites were imged t 5 mgnifition (imge field, 4 4 mm). Optil setions were tken t.-mm sping. Spine density, length nd width, s well s som size, were mesured mnully using ustom softwre 5 y oservers who were lind to genotype. Spine lengths were mesured from the juntion with the dendriti shft to the tip. To determine hed width nd primry dendrite thikness, the fluoresene ws mesured in line ross eh struture nd the width of the distriution where fluoresent intensity fell to 3% of mximum ws lulted. Mesurements performed on -nm dimeter yellow-green fluoresent mirospheres (FluorSpheres, Moleulr Proes) indited tht the point-spred funtion pled lower limit on mesurle widths of 55 nm. The pprent width is the onvolution of the true fluoresene distriution nd point-spred funtion of the mirosope nd hs lower limit of B55 nm. Therefore, the summries of spine hed widths re plotted from this lower ound. Som ross-setionl re ws mesured in the mximum intensity projetion of low-power imge stk y ounting the numer of pixels within n outline drwn round the som. Proximl dendrites of Ts C/C ontrol nd -expressing neurons were of similr thikness (ontrol,.6 ±. mm;,.49 ±. mm; n ¼ 9 3 ells). Eletrophysiology. Hippompl slie ultures from Ts C/C mie were pled in reording hmer perfused with rtifiil ererospinl fluid (ACSF) ontining 7 mm NCl, 5 mm NHCO 3,.5mMN HPO 4,.5mMKCl, mmccl, mm MgCl, 5 mm gluose nd sturted with 95% O,5% CO t 4 C. Whole-ell voltge-lmp reordings were otined using n Axopth B mplifier (Axon Instruments) from -trnsfeted pyrmidl neurons (green fluoresene nd visile gold prtile in som) nd NATURE NEUROSCIENCE VOLUME 8 [ NUMBER [ DECEMBER 5 733
8 untrnsfeted neighors t DPT nd 8 DPT. Trnsfetion with lone hd no effet on memrne properties (dt not shown). Borosilite glss pipettes (3 5 MO tip resistne; Wrner Instruments In.) were filled with mm esium methne-sulfonte, mm HEPES, mm EGTA, 4 mm MgCl,.4 mm NGTP, 4 mm MgATP, mm phosphoretine nd. mm Alex Fluor-594 (Moleulr Proes) t ph of 7.3 (9 mosm). Biuulline ( mm, Toris) ws dded to the th to lok GABA A reeptors in ll experiments nd tetrodotoxin ( mm, Sigm) ws inluded to lok sodium hnnels for mepsc reordings. Series resistne (8 9 MO, o MO for inlusion in dt set), input resistne nd memrne pitne were monitored online. mepsc frequeny nd mplitude were nlyzed in Igor Pro (Wvemetris) using ustom softwre. EPSCs were evoked t.5 Hz with ipolr eletrode pled in the strtum rditum 5 35 mm from the som. The AMPAR/NMDAR urrent rtio ws lulted from the rtio of the EPSC pek mplitude t 6 mv to the urrent t +4 mv ms fter the pek. To mesure PPF, pired stimuli t n interpulse intervl of 5 ms were delivered nd the rtio of pek mplitudes of the EPSCs ws lulted. Sttistis. Sttistil signifine ws tested y nlysis of vrine (ANOVA) with, when pproprite, Tukey-Krmer orretion for multiple pirwise omprisons in Mtl (Mthworks) or Mirosoft Exel. Distriutions of mepsc mplitudes nd immunostining intensities were ompred using Kolmogorov- Smirnov tests. Bnd intensities of western lots were ompred with pired t- tests. Summry dt is presented s men ± stndrd error of the men (s.e.m.). Note: Supplementry informtion is ville on the Nture Neurosiene wesite. ACKNOWLEDGMENTS We thnk memers of the Stini l, D. Shmuker nd D. Stini for omments on the mnusript; E. Hong, A. Crter nd R. Witt for tehnil ssistne nd dvie; nd K. Mizuno, A. Minden, S. Dymeki, E. Henske, V. Rmesh, L. Cntley nd Y. Shi for the gift of regents. This work ws supported y the US Ntionl Institutes of Helth (5T3 NS7484) (to V.A.A.), Burroughs Wellome Fund er Awrd, the Serle Sholrs Fund, the Giovnni Armenise Foundtion, the Smith Fmily Foundtion nd the US Deprtment of Defense (TS34). COMPETING INTERESTS STATEMENT The uthors delre tht they hve no ompeting finnil interests. Pulished online t Reprints nd permissions informtion is ville online t reprintsndpermissions/. Gomez, M.R., Smpson, J.R. & Whittemore, V.H. (eds.) Tuerous Slerosis Complex (Oxford Univ. Press, New York, 999).. Ito, N. & Ruin, G.M. Gigs, Drosophil homolog of tuerous slerosis gene produt-, regultes the ell yle. Cell 96, (999). 3. Potter, C.J., Hung, H. & Xu, T. Drosophil Ts funtions with Ts to ntgonize insulin signling in regulting ell growth, ell prolifertion, nd orgn size. Cell 5, (). 4. Tpon, N., Ito, N., Dikson, B.J., Treismn, J.E. & Hrihrn, I.K. The Drosophil tuerous slerosis omplex gene homologs restrit ell growth nd ell prolifertion. Cell 5, (). 5. Go, X. & Pn, D. TSC nd TSC tumor suppressors ntgonize insulin signling in ell growth. Genes Dev. 5, (). 6. Potter, C.J., Pedrz, L.G. & Xu, T. Akt regultes growth y diretly phosphorylting Ts. Nt. Cell Biol. 4, (). 7. Mnning, B.D., Tee, A.R., Logsdon, M.N., Blenis, J. & Cntley, L.C. Identifition of the tuerous slerosis omplex- tumor suppressor gene produt tuerin s trget of the phosphoinositide 3-kinse/kt pthwy. Mol. Cell, 5 6 (). 8. Inoki, K., Li, Y., Zhu, T., Wu, J. & Gun, K.L. TSC is phosphorylted nd inhiited y Akt nd suppresses mtor signlling. Nt. Cell Biol. 4, (). 9. Stoker, H. et l. Rhe is n essentil regultor of S6K in ontrolling ell growth in Drosophil. Nt. Cell Biol. 5, (3).. Grmi, A. et l. Insulin tivtion of Rhe, meditor of mtor/s6k/4e-bp signling, is inhiited y TSC nd. Mol. Cell, (3).. Hy, N. & Sonenerg, N. Upstrem nd downstrem of mtor. Genes Dev. 8, (4).. Sepp, T., Ytes, J.R. & Green, A.J. Loss of heterozygosity in tuerous slerosis hmrtoms. J. Med. Genet. 33, (996). 3. Rmesh, V. Aspets of tuerous slerosis omplex (TSC) protein funtion in the rin. Biohem. So. Trns. 3, (3). 4. Dijkhuizen, P.A. & Ghosh, A. BDNF regultes primry dendrite formtion in ortil neurons vi the PI3-kinse nd MAP kinse signling pthwys. J. Neuroiol. 6, (5). 5. Tng, S.J. et l. A rpmyin-sensitive signling pthwy ontriutes to long-term synpti plstiity in the hippompus. Pro. Ntl. Ad. Si. USA 99, (). 6. Hou, L. & Klnn, E. Ativtion of the phosphoinositide 3-kinse-Akt-mmmlin trget of rpmyin signling pthwy is required for metotropi glutmte reeptordependent long-term depression. J. Neurosi. 4, (4). 7. Huer, K.M., Kyser, M.S. & Ber, M.F. Role for rpid dendriti protein synthesis in hippompl mglur-dependent long-term depression. Siene 88, (). 8. Uhlmnn, E.J. et l. Astroyte-speifi TSC onditionl knokout mie exhiit norml neuronl orgniztion nd seizures. Ann. Neurol. 5, (). 9. Kohn, A.D. et l. Constrution nd hrteriztion of onditionlly tive version of the serine/threonine kinse Akt. J. Biol. Chem. 73, (998).. Meng, Y., Zhng, Y., Tregouov, V., Flls, D.L. & Ji, Z. Regultion of spine morphology nd synpti funtion y LIMK nd the tin ytoskeleton. Rev. Neurosi. 4, 33 4 (3).. Zhou, Q., Homm, K.J. & Poo, M.M. Shrinkge of dendriti spines ssoited with longterm depression of hippompl synpses. Neuron 44, (4).. Zhng, H. et l. Loss of Ts/Ts tivtes mtor nd disrupts PI3K-Akt signling through downregultion of PDGFR. J. Clin. Invest., 3 33 (3). 3. Mshimo, J., Mniw, R., Sugino, H. & Nose, K. Derese in the expression of novel TGF et-induile nd rs-reision gene, TSC-36, in humn ner ells. Cner Lett. 3, 3 9 (997). 4. Tuttle, R.L. et l. Regultion of pnreti et-ell growth nd survivl y the serine/ threonine protein kinse Akt/PKBlph. Nt. Med. 7, (). 5. Verdu, J., Burtovih, M.A., Wilder, E.L. & Birnum, M.J. Cell-utonomous regultion of ell nd orgn growth in Drosophil y Akt/PKB. Nt. Cell Biol., 5 56 (999). 6. Kwon, C.H. et l. Pten regultes neuronl som size: mouse model of Lhermitte-Dulos disese. Nt. Genet. 9, 44 4 (). 7. Bkmn, S.A. et l. Deletion of Pten in mouse rin uses seizures, txi nd defets in som size resemling Lhermitte-Dulos disese. Nt. Genet. 9, (). 8. Dong, J. & Pn, D. Ts is not ritil trget of Akt during norml Drosophil development. Genes Dev. 8, (4). 9. Srssov, D.D., Guertin, D.A., Ali, S.M. & Stini, D.M. Phosphoryltion nd regultion of Akt/PKB y the ritor-mtor omplex. Siene 37, 98 (5). 3. Lm, R.F. et l. The TSC tumour suppressor hmrtin regultes ell dhesion through ERM proteins nd the GTPse Rho. Nt. Cell Biol., 8 87 (). 3. Govek, E.E. et l. The X-linked mentl retrdtion protein oligophrenin- is required for dendriti spine morphogenesis. Nt. Neurosi. 7, (4). 3. Penzes, P. et l. The neuronl Rho-GEF Klirin-7 interts with PDZ domin-ontining proteins nd regultes dendriti morphogenesis. Neuron 9, 9 4 (). 33. Penzes, P. et l. Rpid indution of dendriti spine morphogenesis y trns-synpti ephrinb-ephbreeptor tivtionofthe Rho-GEF klirin.neuron 37, (3). 34. Li, Y., Inoki, K., Yeung, R. & Gun, K.L. Regultion of TSC y inding. J. Biol. Chem. 77, (). 35. Hengstshlger, M., Rosner, M., Fountoulkis, M. & Lue, G. Tuerous slerosis genes regulte ellulr protein levels. Biohem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 3, (3). 36. Nufer, O. & Huri, H.P. ER export: ll Curr. Biol. 3, R39 R393 (3). 37. Gohl, A. & Bokoh, G.M regultes tin dynmis y stilizing phosphorylted ofilin. Curr. Biol., 74 7 (). 38. Benvenuto, G. et l. The tuerous slerosis- (TSC) gene produt hmrtin suppresses ell growth nd ugments the expression of the TSC produt tuerin y inhiiting its uiquitintion. Onogene 9, (). 39. Srssov, D.D. et l. Ritor, novel inding prtner of mtor, defines rpmyininsensitive nd rptor-independent pthwy tht regultes the ytoskeleton. Curr. Biol. 4, 96 3 (4). 4. Arer, S. et l. Regultion of tin dynmis through phosphoryltion of ofilin y LIMkinse. Nture 393, (998). 4. Tssehji, M. et l. LIM-kinse deleted in Willims syndrome. Nt. Genet. 3, 7 73 (996). 4. Hyshi, M.L. et l. Altered ortil synpti morphology nd impired memory onsolidtion in forerin-speifi dominnt-negtive PAK trnsgeni mie. Neuron 4, (4). 43. Bryn, B. et l. GEFT, Rho fmily gunine nuleotide exhnge ftor, regultes neurite outgrowth nd dendriti spine formtion. J. Biol. Chem. 79, (4). 44. Meng, Y. et l. Anorml spine morphology nd enhned LTP in LIMK- knokout mie. Neuron 35, 33 (). 45. Chng, H. et l. Identifition of DNA enoding thizide-sensitive sodium-hloride otrnsporter from the humn nd its mrna expression in vrious tissues. Biohem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 3, (996). 46. Shepherd, C.W., Houser, O.W. & Gomez, M.R. MR findings in tuerous slerosis omplex nd orreltion with seizure development nd mentl impirment. AJNR Am. J. Neurordiol. 6, (995). 47. Boyer, C., Shikorski, T. & Stevens, C.F. Comprison of hippompl dendriti spines in ulture nd in rin. J. Neurosi. 8, (998). 48. Stoppini, L., Buhs, P.A. & Muller, D.A. A simple method for orgnotypi ultures of nervous tissue. J. Neurosi. Methods 37, 73 8 (99). 49. Crter, A.G. & Stini, B.L. Stte dependent lium signling in dendriti spines of stritl medium spiny neurons. Neuron (4). 5. Trhtenerg, J.T. et l. Long-term in vivo imging of experiene-dependent synpti plstiity in dult ortex. Nture 4, (). 734 VOLUME 8 [ NUMBER [ DECEMBER 5 NATURE NEUROSCIENCE
LHb VTA. VTA-projecting RMTg-projecting overlay. Supplemental Figure 2. Retrograde labeling of LHb neurons. a. VTA-projecting LHb
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementl Figure 1 doi:10.1038/nture09742 Lterl 1.0 mm from midline mpfc BNST mpfc BNST Lterl 2.1 mm from midline LHA LHA Lterl 2.7 mm from midline SUPPLEMENTAL INFORMATION
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementl Figure 1 doi:10.1038/nture09742 Lterl 1.0 mm from midline mpfc BNST mpfc BNST Lterl 2.1 mm from midline LHA LHA Lterl 2.7 mm from midline SUPPLEMENTAL INFORMATION
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi: 1.138/nture862 humn hr. 21q MRPL39 murine Chr.16 Mrpl39 Dyrk1A Runx1 murine Chr. 17 ZNF295 Ets2 Znf295 murine Chr. 1 COL18A1 -/- lot: nti-dscr1 IgG hevy hin DSCR1 DSCR1 expression reltive to hevy
doi: 1.138/nture862 humn hr. 21q MRPL39 murine Chr.16 Mrpl39 Dyrk1A Runx1 murine Chr. 17 ZNF295 Ets2 Znf295 murine Chr. 1 COL18A1 -/- lot: nti-dscr1 IgG hevy hin DSCR1 DSCR1 expression reltive to hevy
Alimonti_Supplementary Figure 1. Pten +/- Pten + Pten. Pten hy. β-actin. Pten - wt hy/+ +/- wt hy/+ +/- Pten. Pten. Relative Protein level (% )
 Alimonti_Supplementry Figure 1 hy 3 4 5 3 Neo 4 5 5 Proe 5 Proe hy/ hy/ /- - 3 6 Neo β-tin d Reltive Protein level (% ) 15 1 5 hy/ /- Reltive Gene Expr. (% ) 15 1 5 hy/ /- Supplementry Figure 1 Chrteriztion
Alimonti_Supplementry Figure 1 hy 3 4 5 3 Neo 4 5 5 Proe 5 Proe hy/ hy/ /- - 3 6 Neo β-tin d Reltive Protein level (% ) 15 1 5 hy/ /- Reltive Gene Expr. (% ) 15 1 5 hy/ /- Supplementry Figure 1 Chrteriztion
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 1.138/n358 TLR2 nd MyD88 expression in murine mmmry epithelil supopultions. CD24 min plus MRU Myo-epithelil Luminl progenitor (CD61 pos ) Mture luminl (CD61 neg ) CD49f CD61 Reltive expression Krt5
DOI: 1.138/n358 TLR2 nd MyD88 expression in murine mmmry epithelil supopultions. CD24 min plus MRU Myo-epithelil Luminl progenitor (CD61 pos ) Mture luminl (CD61 neg ) CD49f CD61 Reltive expression Krt5
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 1.13/n7 Reltive Pprg mrna 3 1 1 Time (weeks) Interspulr Inguinl Epididyml Reltive undne..1.5. - 5 5-51 51-1 1-7 7 - - 1 1-1 Lipid droplet size ( m ) 1-3 3 - - - 1 1-1 1-1 1-175 175-3 3-31 31-5 >5
DOI: 1.13/n7 Reltive Pprg mrna 3 1 1 Time (weeks) Interspulr Inguinl Epididyml Reltive undne..1.5. - 5 5-51 51-1 1-7 7 - - 1 1-1 Lipid droplet size ( m ) 1-3 3 - - - 1 1-1 1-1 1-175 175-3 3-31 31-5 >5
Cos7 (3TP) (K): TGFβ1(h): (K)
 IP#2: IP#1: Totl Lystes luiferse tivity (K): 6-4 - (K): luiferse tivity luiferse tivity (K): 2 1 RL-: - + + + + + Sm4-3F: + - + + + + MYC-Sm3: - - - - + + TβRI-HA(T204D): - - - + - + α-ha Luiferse Ativity
IP#2: IP#1: Totl Lystes luiferse tivity (K): 6-4 - (K): luiferse tivity luiferse tivity (K): 2 1 RL-: - + + + + + Sm4-3F: + - + + + + MYC-Sm3: - - - - + + TβRI-HA(T204D): - - - + - + α-ha Luiferse Ativity
SK channels and NMDA receptors form aca 2+ -mediated feedback loop in dendritic spines
 25 Nture Pulishing Group http://www.nture.om/ntureneurosiene SK hnnels nd NMDA reeptors form C 2+ -medited feedk loop in dendriti spines Thu Jennifer Ngo-Anh 1,4, Brend L Bloodgood 2,4, Mihel Lin 1, Bernrdo
25 Nture Pulishing Group http://www.nture.om/ntureneurosiene SK hnnels nd NMDA reeptors form C 2+ -medited feedk loop in dendriti spines Thu Jennifer Ngo-Anh 1,4, Brend L Bloodgood 2,4, Mihel Lin 1, Bernrdo
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 % ells with ili (mrke y A-Tu) Reltive Luiferse % ells with ili (mrke y Arl13) % ells with ili DOI: 1.138/n2259 A-Tuulin Hoehst % Cilite Non-ilite -Serum 9% 8% 7% 1 6% % 4% +Serum 1 3% 2% 1% % Serum: -
% ells with ili (mrke y A-Tu) Reltive Luiferse % ells with ili (mrke y Arl13) % ells with ili DOI: 1.138/n2259 A-Tuulin Hoehst % Cilite Non-ilite -Serum 9% 8% 7% 1 6% % 4% +Serum 1 3% 2% 1% % Serum: -
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 { OI: 1.138/n31 Srifie n nlyze APs on week 1 s of iet 1 4 6 High-ft iet BrU High-ft iet BrU 4 High-ft iet BrU 6 High-ft iet BrU Lin - Lin - : C34 + : C9 + 1 1 3 1 4 1 5 C45 1 C34 1 1 1 1 3 1 4 1 5 S-1
{ OI: 1.138/n31 Srifie n nlyze APs on week 1 s of iet 1 4 6 High-ft iet BrU High-ft iet BrU 4 High-ft iet BrU 6 High-ft iet BrU Lin - Lin - : C34 + : C9 + 1 1 3 1 4 1 5 C45 1 C34 1 1 1 1 3 1 4 1 5 S-1
Supplementary Figure 1. Scheme of unilateral pyramidotomy used for detecting compensatory sprouting of intact CST axons.
 () BDA 2 weeks fter Py () AAVs Cre or GFP t P1 BDA 2 weeks fter Py CSMN CST () Py t P7 or 2 months () Py t 2 months Supplementry Figure 1. Sheme of unilterl pyrmidotomy used for deteting ompenstory sprouting
() BDA 2 weeks fter Py () AAVs Cre or GFP t P1 BDA 2 weeks fter Py CSMN CST () Py t P7 or 2 months () Py t 2 months Supplementry Figure 1. Sheme of unilterl pyrmidotomy used for deteting ompenstory sprouting
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:.8/nture98 : hr NEMO :5 hr IKK IKK NF-κB p65 p5 p65/-rel NF-κB p65 p5 p65/-rel Cytoplsm Cytoplsm p65/p5 Nuleus Nuleus NEMO IKK IKK d : hr > : hr p65/-rel NF- p65 p5 Cytoplsm Cytoplsm p65/p5 p65/-rel
doi:.8/nture98 : hr NEMO :5 hr IKK IKK NF-κB p65 p5 p65/-rel NF-κB p65 p5 p65/-rel Cytoplsm Cytoplsm p65/p5 Nuleus Nuleus NEMO IKK IKK d : hr > : hr p65/-rel NF- p65 p5 Cytoplsm Cytoplsm p65/p5 p65/-rel
Supplementary Figure S1
 Supplementry Figure S1 - UTR m - 3HA - 2-1 hgh - 1 Uiquitin *! *! lk distl promoter m K3R/ K121R-3HA UTR hgh founder lines - HA - - founder lines TG- E1 L A2 B1 F9 G6 H4 H6 B C D2 G1 H3 J2 L - 7 IP: lk
Supplementry Figure S1 - UTR m - 3HA - 2-1 hgh - 1 Uiquitin *! *! lk distl promoter m K3R/ K121R-3HA UTR hgh founder lines - HA - - founder lines TG- E1 L A2 B1 F9 G6 H4 H6 B C D2 G1 H3 J2 L - 7 IP: lk
Lesions of prefrontal cortex reduce attentional modulation of neuronal responses. and synchrony in V4
 Lesions of prefrontl ortex reue ttentionl moultion of neuronl responses n synhrony in V4 Georgi G. Gregoriou,, Anrew F. Rossi, 3 Leslie G Ungerleier, 4 Roert Desimone 5 Deprtment of Bsi Sienes, Fulty of
Lesions of prefrontl ortex reue ttentionl moultion of neuronl responses n synhrony in V4 Georgi G. Gregoriou,, Anrew F. Rossi, 3 Leslie G Ungerleier, 4 Roert Desimone 5 Deprtment of Bsi Sienes, Fulty of
Letter. Autocrine BDNF TrkB signalling within a single dendritic spine
 Letter doi:1.138/nture19766 Autorine BDNF TrkB signlling within single dendriti spine Stephen C. Hrwrd 1, Nthn G. Hedrik 1, Chrles E. Hll 1, Pul Prr-Bueno 2, Teres A. Milner 3,4, Enhui Pn 1, Tl Lviv 2,
Letter doi:1.138/nture19766 Autorine BDNF TrkB signlling within single dendriti spine Stephen C. Hrwrd 1, Nthn G. Hedrik 1, Chrles E. Hll 1, Pul Prr-Bueno 2, Teres A. Milner 3,4, Enhui Pn 1, Tl Lviv 2,
EFFECT OF DIETARY ENZYME ON PERFORMANCE OF WEANLING PIGS
 EFFECT OF DIETARY ENZYME ON PERFORMANCE OF WEANLING PIGS Finl report sumitted to Dniso Animl Nutrition E. vn Heugten nd B. Frederik North Crolin Stte University, Deprtment of Animl Siene Summry The urrent
EFFECT OF DIETARY ENZYME ON PERFORMANCE OF WEANLING PIGS Finl report sumitted to Dniso Animl Nutrition E. vn Heugten nd B. Frederik North Crolin Stte University, Deprtment of Animl Siene Summry The urrent
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 . Norml Physiologicl Conditions. SIRT1 Loss-of-Function S1. Model for the role of SIRT1 in the regultion of memory nd plsticity. () Our findings suggest tht SIRT1 normlly functions in coopertion with YY1,
. Norml Physiologicl Conditions. SIRT1 Loss-of-Function S1. Model for the role of SIRT1 in the regultion of memory nd plsticity. () Our findings suggest tht SIRT1 normlly functions in coopertion with YY1,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:.8/nture89 4 4 Ilr -/- Ilr -/- Ilr -/- Cspse- -/- As -/- Nlrp -/- Il8 -/- Ilr -/- Supplementl figure. Inresed severity of NASH in inflmmsome-defiient mie, ut not in Ilr-defiient
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:.8/nture89 4 4 Ilr -/- Ilr -/- Ilr -/- Cspse- -/- As -/- Nlrp -/- Il8 -/- Ilr -/- Supplementl figure. Inresed severity of NASH in inflmmsome-defiient mie, ut not in Ilr-defiient
TNF-a Downregulates Filaggrin and Loricrin through c-jun N-terminal Kinase: Role for TNF-a Antagonists to Improve Skin Barrier
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE TNF- Downregultes Filggrin nd Loririn through -Jun N-terminl Kinse: Role for TNF- Antgonists to Improve Skin Brrier Byung Eui Kim, Mihel D. Howell,, Emm Guttmn,, Ptrii M. Gilleudeu, Irm
ORIGINAL ARTICLE TNF- Downregultes Filggrin nd Loririn through -Jun N-terminl Kinse: Role for TNF- Antgonists to Improve Skin Brrier Byung Eui Kim, Mihel D. Howell,, Emm Guttmn,, Ptrii M. Gilleudeu, Irm
The Hippo/YAP pathway interacts with EGFR signaling and HPV oncoproteins to regulate cervical cancer progression
 Reserh Artile The Hippo/ pthwy interts with EGFR signling nd HPV onoproteins to regulte ervil ner progression Chuno He 1,, Dgn Mo 1,3, Guohu Hu 1,, Xingmin Lv 1, Xingheng Chen, Peter C Angeletti 5, Jixin
Reserh Artile The Hippo/ pthwy interts with EGFR signling nd HPV onoproteins to regulte ervil ner progression Chuno He 1,, Dgn Mo 1,3, Guohu Hu 1,, Xingmin Lv 1, Xingheng Chen, Peter C Angeletti 5, Jixin
Enrichment induces structural changes and recovery from nonspatial memory deficits in CA1 NMDAR1-knockout mice
 rtiles Enrihment indues struturl hnges nd reovery from nonsptil memory defiits in CA1 NMDAR1-knokout mie Clire Rmpon, Y-Ping Tng, Joe Goodhouse, Eiji Shimizu, Mureen Kyin nd Joe Z. Tsien Deprtment of Moleulr
rtiles Enrihment indues struturl hnges nd reovery from nonsptil memory defiits in CA1 NMDAR1-knokout mie Clire Rmpon, Y-Ping Tng, Joe Goodhouse, Eiji Shimizu, Mureen Kyin nd Joe Z. Tsien Deprtment of Moleulr
GSK-3 is a master regulator of neural progenitor homeostasis
 GSK-3 is mster regultor of neurl progenitor homeostsis Woo-Yng Kim 1, Xinshuo Wng 1, Yohong Wu 1, Brdley W Dole 2, Stish Ptel 3, Jmes R Woodgett 3 & Willim D Snider 1 The development of the rin requires
GSK-3 is mster regultor of neurl progenitor homeostsis Woo-Yng Kim 1, Xinshuo Wng 1, Yohong Wu 1, Brdley W Dole 2, Stish Ptel 3, Jmes R Woodgett 3 & Willim D Snider 1 The development of the rin requires
Input normalization by global feedforward inhibition expands cortical dynamic range
 Input normliztion y glol feedforwrd inhiition expnds ortil dynmi rnge Frédéri Pouille 1,2, Antoni Mrin-Burgin 1,2, Hillel Adesnik 1, Bssm V Atllh 1 & Mssimo Snzini 1 29 Nture Ameri, In. All rights reserved.
Input normliztion y glol feedforwrd inhiition expnds ortil dynmi rnge Frédéri Pouille 1,2, Antoni Mrin-Burgin 1,2, Hillel Adesnik 1, Bssm V Atllh 1 & Mssimo Snzini 1 29 Nture Ameri, In. All rights reserved.
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Prentl doi:.8/nture57 Figure S HPMECs LM Cells Cell lines VEGF (ng/ml) Prentl 7. +/-. LM 7. +/-.99 LM 7. +/-.99 Fold COX induction 5 VEGF: - + + + Bevcizum: - - 5 (µg/ml) Reltive MMP LM mock COX MMP LM+
Prentl doi:.8/nture57 Figure S HPMECs LM Cells Cell lines VEGF (ng/ml) Prentl 7. +/-. LM 7. +/-.99 LM 7. +/-.99 Fold COX induction 5 VEGF: - + + + Bevcizum: - - 5 (µg/ml) Reltive MMP LM mock COX MMP LM+
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 2 weeks high holesterol diet 2 weeks high holesterol diet 2 weeks high holesterol diet 2 μm Mrophges Crystls Hoehst μm Mrophges Crystls Hoehst Hoehst Crystls Mrophges 2 μm 2 μm Supplementry Fig. 1: Erly
2 weeks high holesterol diet 2 weeks high holesterol diet 2 weeks high holesterol diet 2 μm Mrophges Crystls Hoehst μm Mrophges Crystls Hoehst Hoehst Crystls Mrophges 2 μm 2 μm Supplementry Fig. 1: Erly
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 1.138/n2977 Numer of ells per field 6 4 2 P =.1 Orthotopi eum Normlized ventrl photon flux 1E7 1E6 1E5 1E4 1E3 1E2 n=8 n=9 1 2 3 4 5 6 Dys Dy54 1.5E5 2.4E7 d Mie with lymph node metstsis (%) 1 8 6
DOI: 1.138/n2977 Numer of ells per field 6 4 2 P =.1 Orthotopi eum Normlized ventrl photon flux 1E7 1E6 1E5 1E4 1E3 1E2 n=8 n=9 1 2 3 4 5 6 Dys Dy54 1.5E5 2.4E7 d Mie with lymph node metstsis (%) 1 8 6
The GCN5-CITED2-PKA signalling module controls hepatic glucose metabolism through a camp-induced substrate switch
 Reeived 6 Apr 216 Aepted 8 Sep 216 Pulished 22 Nov 216 DOI: 1.138/nomms13147 OPEN The GCN5-CITED2-PKA signlling module ontrols hepti gluose metolism through AMP-indued sustrte swith Mshito Ski 1, Tomoko
Reeived 6 Apr 216 Aepted 8 Sep 216 Pulished 22 Nov 216 DOI: 1.138/nomms13147 OPEN The GCN5-CITED2-PKA signlling module ontrols hepti gluose metolism through AMP-indued sustrte swith Mshito Ski 1, Tomoko
YAP transcriptionally regulates COX-2 expression and GCCSysm-4 (G-4), a dual YAP/COX-2 inhibitor, overcomes drug resistance in colorectal cancer
 Li et l. Journl of Experimentl & Clinil Cner Reserh (7) 36:44 DOI.86/s346-7-6-3 RESEARCH Open Aess trnsriptionlly regultes expression nd GCCSysm-4 (G-4), dul / inhiitor, overomes drug resistne in oloretl
Li et l. Journl of Experimentl & Clinil Cner Reserh (7) 36:44 DOI.86/s346-7-6-3 RESEARCH Open Aess trnsriptionlly regultes expression nd GCCSysm-4 (G-4), dul / inhiitor, overomes drug resistne in oloretl
I h -mediated depolarization enhances the temporal precision of neuronal integration
 Reeived 5 Apr 2 Aepted 9 Jn 2 Pulished 5 Fe 2DOI:.38/nomms22 I h -medited depolriztion enhnes the temporl preision of neuronl integrtion Ivn Pvlov, Annlis Simemi,, Leonid Svthenko, Dimitri M. Kullmnn &
Reeived 5 Apr 2 Aepted 9 Jn 2 Pulished 5 Fe 2DOI:.38/nomms22 I h -medited depolriztion enhnes the temporl preision of neuronl integrtion Ivn Pvlov, Annlis Simemi,, Leonid Svthenko, Dimitri M. Kullmnn &
Laminar sources of synaptic input to cortical inhibitory interneurons and pyramidal neurons
 rtiles Lminr soures of synpti input to ortil inhiitory interneurons nd pyrmidl neurons J. L. Dntzker nd E. M. Cllwy Systems Neuroiology Lortories, The Slk Institute for Biologil Studies, N. Torrey Pines
rtiles Lminr soures of synpti input to ortil inhiitory interneurons nd pyrmidl neurons J. L. Dntzker nd E. M. Cllwy Systems Neuroiology Lortories, The Slk Institute for Biologil Studies, N. Torrey Pines
Selective reconfiguration of layer 4 visual cortical circuitry by visual deprivation
 Seletive reonfigurtion of lyer 4 visul ortil iruitry y visul deprivtion Arinn Mffei, Sh B Nelson & Gin G Turrigino Visul deprivtion during developmentl sensitive period mrkedly lters visul ortil response
Seletive reonfigurtion of lyer 4 visul ortil iruitry y visul deprivtion Arinn Mffei, Sh B Nelson & Gin G Turrigino Visul deprivtion during developmentl sensitive period mrkedly lters visul ortil response
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nture10754 Supplementry note 1 To ompre our dt with previous studies, we mesured the width of spikes from identified dopminergi neurons nd unidentified neurons from DATCre mie. Previous studies
doi:10.1038/nture10754 Supplementry note 1 To ompre our dt with previous studies, we mesured the width of spikes from identified dopminergi neurons nd unidentified neurons from DATCre mie. Previous studies
The microrna mir-31 inhibits CD8 + T cell function in chronic viral infection
 A rt i l e s The mirorna mir-3 inhiits CD8 + T ell funtion in hroni virl infetion Howell F Moffett, Adm N R Crtwright, Hye-Jung Kim, Jernej Gode, Json Pyrdol, Trmo Äijö 3, Gustvo J Mrtinez,6, Anjn Ro,
A rt i l e s The mirorna mir-3 inhiits CD8 + T ell funtion in hroni virl infetion Howell F Moffett, Adm N R Crtwright, Hye-Jung Kim, Jernej Gode, Json Pyrdol, Trmo Äijö 3, Gustvo J Mrtinez,6, Anjn Ro,
AUTHOR COPY ONLY. Glycogen synthase kinase 3b mediates high glucose-induced ubiquitination and proteasome degradation of insulin receptor substrate 1
 Glyogen synthse kinse 3 medites high gluose-indued uiquitintion nd protesome degrdtion of insulin reeptor sustrte 1 171 Snhu Leng, Wenshuo Zhng, Ynin Zheng, Ziv Liermn 1, Christopher J Rhodes, Hgit Eldr-Finkelmn
Glyogen synthse kinse 3 medites high gluose-indued uiquitintion nd protesome degrdtion of insulin reeptor sustrte 1 171 Snhu Leng, Wenshuo Zhng, Ynin Zheng, Ziv Liermn 1, Christopher J Rhodes, Hgit Eldr-Finkelmn
FAK integrates growth-factor and integrin signals to promote cell migration
 integrtes growth-ftor nd integrin signls to promote ell migrtion rtiles Dvid J. Sieg*, Christof R. Huk*, Dusko Ili, Cndie K. Klingeil*, Erik Shefer, Croline H. Dmsky nd Dvid D. Shlepfer* *Deprtment of
integrtes growth-ftor nd integrin signls to promote ell migrtion rtiles Dvid J. Sieg*, Christof R. Huk*, Dusko Ili, Cndie K. Klingeil*, Erik Shefer, Croline H. Dmsky nd Dvid D. Shlepfer* *Deprtment of
ARTICLE. I. Chopra & H. F. Li & H. Wang & K. A. Webster
 Dietologi (212) 55:783 794 DOI 1.17/s125-11-247-y ARTICLE Phosphoryltion of the insulin reeptor y AMP-tivted protein kinse (AMPK) promotes lignd-independent tivtion of the insulin signlling pthwy in rodent
Dietologi (212) 55:783 794 DOI 1.17/s125-11-247-y ARTICLE Phosphoryltion of the insulin reeptor y AMP-tivted protein kinse (AMPK) promotes lignd-independent tivtion of the insulin signlling pthwy in rodent
LETTERS. Chfr is required for tumor suppression and Aurora A regulation
 25 Nture Pulishing Group http://www.nture.om/nturegenetis Chfr is required for tumor suppression nd Auror A regultion Xiohun Yu 1, Ktherine Minter-Dykhouse 1, Liviu Mlurenu 2, Wei-Meng Zho 3, Dongwei Zhng
25 Nture Pulishing Group http://www.nture.om/nturegenetis Chfr is required for tumor suppression nd Auror A regultion Xiohun Yu 1, Ktherine Minter-Dykhouse 1, Liviu Mlurenu 2, Wei-Meng Zho 3, Dongwei Zhng
Title of Experiment: Author, Institute and address:
 Title of Experiment: Trsfetion of murine mrophge RAW264.7 ells with METAFECTENE PRO. Author, Institute n ress: Ptrizi Pellegtti n Frneso Di Virgilio. Deprtment of Experimentl n Dignosti Meiine, Setion
Title of Experiment: Trsfetion of murine mrophge RAW264.7 ells with METAFECTENE PRO. Author, Institute n ress: Ptrizi Pellegtti n Frneso Di Virgilio. Deprtment of Experimentl n Dignosti Meiine, Setion
Interplay of LRRK2 with chaperone-mediated autophagy
 Interply of with hperone-medited utophgy Smnth J Orenstein,, Sheng-Hn Kuo,, Inmuld Tsset,,, Espernz Aris,, Hiroshi Kog,, Irene Fernndez-Crs, Etty Cortes,5, Lwrene S Honig,5, Willim Duer 6, Antonell Consiglio,7,
Interply of with hperone-medited utophgy Smnth J Orenstein,, Sheng-Hn Kuo,, Inmuld Tsset,,, Espernz Aris,, Hiroshi Kog,, Irene Fernndez-Crs, Etty Cortes,5, Lwrene S Honig,5, Willim Duer 6, Antonell Consiglio,7,
Acute and gradual increases in BDNF concentration elicit distinct signaling and functions in neurons
 nd grdul increses in BDNF concentrtion elicit distinct signling nd functions in neurons Yunyun Ji,, Yun Lu, Feng Yng, Wnhu Shen, Tin Tze-Tsng Tng,, Linyin Feng, Shumin Dun, nd Bi Lu,.. - Grdul (normlized
nd grdul increses in BDNF concentrtion elicit distinct signling nd functions in neurons Yunyun Ji,, Yun Lu, Feng Yng, Wnhu Shen, Tin Tze-Tsng Tng,, Linyin Feng, Shumin Dun, nd Bi Lu,.. - Grdul (normlized
Roles of the PI-3K and MEK pathways in Ras-mediated chemoresistance in breast cancer cells
 ritish Journl of Cner (23) 89, 18 191 & 23 Cner Reserh UK All rights reserved 7 92/3 $2. www.jner.om Roles of the PI-3K nd MEK pthwys in Rs-medited hemoresistne in rest ner ells W Jin 1,LWu 1, K Ling 1,
ritish Journl of Cner (23) 89, 18 191 & 23 Cner Reserh UK All rights reserved 7 92/3 $2. www.jner.om Roles of the PI-3K nd MEK pthwys in Rs-medited hemoresistne in rest ner ells W Jin 1,LWu 1, K Ling 1,
Inhibition of mtor induces autophagy and reduces toxicity of polyglutamine expansions in fly and mouse models of Huntington disease
 Inhiition of mtor indues utophgy nd redues toxiity of polyglutmine expnsions in fly nd mouse models of Huntington disese Brind Rvikumr 1,6, Corlie Vher 1,6, Zdenek Berger 1,2, Jnet E Dvies 1, Shouqing
Inhiition of mtor indues utophgy nd redues toxiity of polyglutmine expnsions in fly nd mouse models of Huntington disese Brind Rvikumr 1,6, Corlie Vher 1,6, Zdenek Berger 1,2, Jnet E Dvies 1, Shouqing
Mechanisms underlying cross-orientation suppression in cat visual cortex
 Mehnisms underlying ross-orienttion suppression in t visul ortex 6 Nture Pulishing Group http://www.nture.om/ntureneurosiene Nihols J Priee & Dvid Ferster In simple ells of the t primry visul ortex, null-oriented
Mehnisms underlying ross-orienttion suppression in t visul ortex 6 Nture Pulishing Group http://www.nture.om/ntureneurosiene Nihols J Priee & Dvid Ferster In simple ells of the t primry visul ortex, null-oriented
Methylphenidate facilitates learning-induced amygdala plasticity
 Methylphenidte filittes lerning-indued mygdl plstiity Ky M Tye 1,2, Lynne D Tye 1,3, Jkson J Cone 1, Evelien F Hekkelmn 1, Ptrii H Jnk 1,2,, & Antonello Boni 1,2,, 21 Nture Ameri, In. All rights reserved.
Methylphenidte filittes lerning-indued mygdl plstiity Ky M Tye 1,2, Lynne D Tye 1,3, Jkson J Cone 1, Evelien F Hekkelmn 1, Ptrii H Jnk 1,2,, & Antonello Boni 1,2,, 21 Nture Ameri, In. All rights reserved.
(% of adherent cells) *** PBL firm adhesion. Frequency (% ) 4 1 L 2 CXCR3 DP-2
 Chemotxis (% of dded ells) PBL totl dhesion (N ells/mm 2 /1.1 6 PBL) Frequeny (% ) PBL firm dhesion Supplementry Figure 1 4 4 3 3 2 2 1.1-4 1-3 1.1.2. 1 1 8 6 4 2 Adiponetin ( g/ml) - + Adiponetin ( g/ml)
Chemotxis (% of dded ells) PBL totl dhesion (N ells/mm 2 /1.1 6 PBL) Frequeny (% ) PBL firm dhesion Supplementry Figure 1 4 4 3 3 2 2 1.1-4 1-3 1.1.2. 1 1 8 6 4 2 Adiponetin ( g/ml) - + Adiponetin ( g/ml)
A p75 NTR and Nogo receptor complex mediates repulsive signaling by myelin-associated glycoprotein
 A p75 NTR nd Nogo reeptor omplex medites repulsive signling y myelin-ssoited glyoprotein Sott T. Wong 1, John R. Henley 1, Kevin C. Knning 2, Kuo-hu Hung 1, Mrk Bothwell 2 nd Mu-ming Poo 1 1 Division of
A p75 NTR nd Nogo reeptor omplex medites repulsive signling y myelin-ssoited glyoprotein Sott T. Wong 1, John R. Henley 1, Kevin C. Knning 2, Kuo-hu Hung 1, Mrk Bothwell 2 nd Mu-ming Poo 1 1 Division of
BTLA is a lymphocyte inhibitory receptor with similarities to CTLA-4 and PD-1
 BTLA is lymphoyte inhiitory reeptor with similrities to CTLA-4 nd PD-1 Norihiko Wtne 1,5, My Gvrieli 1, John R Sedy 1, Jinfei Yng 1,5, Frnes Fllrino 2, Susn K Loftin 1, Mihelle A Hurhl 1, Ntlie Zimmermn
BTLA is lymphoyte inhiitory reeptor with similrities to CTLA-4 nd PD-1 Norihiko Wtne 1,5, My Gvrieli 1, John R Sedy 1, Jinfei Yng 1,5, Frnes Fllrino 2, Susn K Loftin 1, Mihelle A Hurhl 1, Ntlie Zimmermn
Long-term modification of cortical synapses improves sensory perception
 Long-term modifition of ortil synpses improves sensory pereption Roert C Froemke 1 4,8, Ion Cre 1 3,8, Alison J Brker 4, Kexin Yun 4, Bryn A Seyold 4, An Rquel O Mrtins 1 3,5, Ntly Zik 1,2, Hnnh Bernstein
Long-term modifition of ortil synpses improves sensory pereption Roert C Froemke 1 4,8, Ion Cre 1 3,8, Alison J Brker 4, Kexin Yun 4, Bryn A Seyold 4, An Rquel O Mrtins 1 3,5, Ntly Zik 1,2, Hnnh Bernstein
Protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B deficiency or inhibition delays ErbB2-induced mammary tumorigenesis and protects from lung metastasis
 Protein tyrosine phosphtse 1B defiieny or inhiition delys ErB2-indued mmmry tumorigenesis nd protets from lung metstsis Sofi G Julien 1,5, Ndi Dué 1,6, Mihelle Red 1, Jnie Penney 1, Mrilene Pquet 2, Yongxin
Protein tyrosine phosphtse 1B defiieny or inhiition delys ErB2-indued mmmry tumorigenesis nd protets from lung metstsis Sofi G Julien 1,5, Ndi Dué 1,6, Mihelle Red 1, Jnie Penney 1, Mrilene Pquet 2, Yongxin
P AND K IN POTATOES. Donald A Horneck Oregon State University Extension Service
 P AND K IN POTATOES Donld A Hornek Oregon Stte University Extension Servie INTRODUCTION Phosphorous nd potssium re importnt to grow high yielding nd qulity pottoes. Muh of the northwest hs hd trditionlly
P AND K IN POTATOES Donld A Hornek Oregon Stte University Extension Servie INTRODUCTION Phosphorous nd potssium re importnt to grow high yielding nd qulity pottoes. Muh of the northwest hs hd trditionlly
Neuronal circuitry mechanism regulating adult quiescent neural stem-cell fate decision NO pa. 10 s ETMD
 doi:1.138/nture1136 Neuronl iruitry mehnism regulting dult quiesent neurl stem-ell fte deision Jun Song 1,2, Chun Zhong 1,2, Mihel A. Bonguidi 1,2, Gerld J. Sun 1,3, Derek Hsu 1, Yn Gu 4, Konstntinos Meletis
doi:1.138/nture1136 Neuronl iruitry mehnism regulting dult quiesent neurl stem-ell fte deision Jun Song 1,2, Chun Zhong 1,2, Mihel A. Bonguidi 1,2, Gerld J. Sun 1,3, Derek Hsu 1, Yn Gu 4, Konstntinos Meletis
Tbp. Per Relative mrna levels Circadian Time. Liver weight/ body weight (%) n.s. Pernull
 Liver weight/ ody weight (%) Dy Body weight (g) Reltive mrna levels Reltive mrna levels Reltive mrna levels Reltive mrna levels Dy Per1 Per2 Per3 Tp 8 2 8 2. 6 2 8 12162 Cirdin Time 3 2 1 2 1 1 8 12162
Liver weight/ ody weight (%) Dy Body weight (g) Reltive mrna levels Reltive mrna levels Reltive mrna levels Reltive mrna levels Dy Per1 Per2 Per3 Tp 8 2 8 2. 6 2 8 12162 Cirdin Time 3 2 1 2 1 1 8 12162
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:.38/nture277 d 25 25 2 Time from sound onset (ms) 25 25 2 Time from sound onset (ms) Firing rte (spikes/s) Firing rte (spikes/s).8.6..2 e f g h.8.6..2 Frtion of neurons Frtion of neurons N = 53 2 2
doi:.38/nture277 d 25 25 2 Time from sound onset (ms) 25 25 2 Time from sound onset (ms) Firing rte (spikes/s) Firing rte (spikes/s).8.6..2 e f g h.8.6..2 Frtion of neurons Frtion of neurons N = 53 2 2
Neuroligin-1 dependent competition regulates cortical synaptogenesis and synapse number
 Neuroligin- epenent ompetition regultes ortil synptogenesis n synpse numer Hyung-Be Kwon,3, Yevgeni Kozorovitskiy, Won-Jong Oh 2, Rui T Peixoto, Nzi Akhtr, Jessi L Sulnier, Chenghu Gu 2 & Bernro L Stini
Neuroligin- epenent ompetition regultes ortil synptogenesis n synpse numer Hyung-Be Kwon,3, Yevgeni Kozorovitskiy, Won-Jong Oh 2, Rui T Peixoto, Nzi Akhtr, Jessi L Sulnier, Chenghu Gu 2 & Bernro L Stini
LKB1 and AMPK regulate synaptic remodeling in old age
 LKB1 nd AMPK regulte synpti remodeling in old ge Melnie A Smuel 1,8, P Emnuel Voinesu 1,8, Brendn N Lilley 1, Rf de Co 2, Mr Foretz 3 5, Benoit Viollet 3 5, Bsil Pwlyk, Mihel A Snderg, Demetrios G Vvvs
LKB1 nd AMPK regulte synpti remodeling in old ge Melnie A Smuel 1,8, P Emnuel Voinesu 1,8, Brendn N Lilley 1, Rf de Co 2, Mr Foretz 3 5, Benoit Viollet 3 5, Bsil Pwlyk, Mihel A Snderg, Demetrios G Vvvs
A thalamic input to the nucleus accumbens mediates opiate dependence
 doi:1.138/nture16954 A thlmi input to the nuleus umens medites opite dependene Yingjie Zhu1, Crl F. R. Wieneke1, Gregory Nhtr1 & Xioke Chen1 1 feed-forwrd inhiition in lol NA iruit. Consistent with this
doi:1.138/nture16954 A thlmi input to the nuleus umens medites opite dependene Yingjie Zhu1, Crl F. R. Wieneke1, Gregory Nhtr1 & Xioke Chen1 1 feed-forwrd inhiition in lol NA iruit. Consistent with this
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementry Figure 1 c d Wistr SHR Wistr AF-353 SHR AF-353 n = 6 n = 6 n = 28 n = 3 n = 12 n = 12 Supplementry Figure 1 Neurophysiologicl properties of petrosl chemoreceptive neurones in Wistr nd SH rts.
Supplementry Figure 1 c d Wistr SHR Wistr AF-353 SHR AF-353 n = 6 n = 6 n = 28 n = 3 n = 12 n = 12 Supplementry Figure 1 Neurophysiologicl properties of petrosl chemoreceptive neurones in Wistr nd SH rts.
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 oi:1.138/nture1134 CS+ CS- MCH 3 OCT OCT 3 MCH CS- CS+ OCT MCH 3 MCH OCT 3 OCT vs MCH OCT vs MCH ppetitive memory (PI) A 1-1 Unpire onitioning DDC-GAL4/UAS-Trp UAS-Trp/+ -2 MCH OCT OCT MCH sugr OCT MCH
oi:1.138/nture1134 CS+ CS- MCH 3 OCT OCT 3 MCH CS- CS+ OCT MCH 3 MCH OCT 3 OCT vs MCH OCT vs MCH ppetitive memory (PI) A 1-1 Unpire onitioning DDC-GAL4/UAS-Trp UAS-Trp/+ -2 MCH OCT OCT MCH sugr OCT MCH
In vivo intracellular recording and perturbation of persistent activity in a neural integrator
 rtiles 21 Nture Pulishing Group http://neurosi.nture.om 21 Nture Pulishing Group http://neurosi.nture.om In vivo intrellulr reording nd perturtion of persistent tivity in neurl integrtor E. Aksy 1,2, G.
rtiles 21 Nture Pulishing Group http://neurosi.nture.om 21 Nture Pulishing Group http://neurosi.nture.om In vivo intrellulr reording nd perturtion of persistent tivity in neurl integrtor E. Aksy 1,2, G.
Osteoblasts secrete Cxcl9 to regulate angiogenesis in bone
 Reeived 2 De 215 Aepted 9 Nov 216 Pulished 14 De 216 DOI: 1.138/nomms13885 OPEN Osteolsts serete to regulte ngiogenesis in one Bin Hung 1,, Wenho Wng 1,, Qinghu Li 1,, Zhenyu Wng 1,BoYn 1, Zhongmin Zhng
Reeived 2 De 215 Aepted 9 Nov 216 Pulished 14 De 216 DOI: 1.138/nomms13885 OPEN Osteolsts serete to regulte ngiogenesis in one Bin Hung 1,, Wenho Wng 1,, Qinghu Li 1,, Zhenyu Wng 1,BoYn 1, Zhongmin Zhng
Fates-shifted is an F box protein that targets Bicoid for degradation and regulates developmental fate determination in Drosophila embryos
 ARTICLES Ftes-shifted is n F ox protein tht trgets Bioid for degrdtion nd regultes developmentl fte determintion in Drosophil emryos Juno Liu 1 nd Jun M 1,2,3 Bioid (Bd) is morphogeneti protein tht instruts
ARTICLES Ftes-shifted is n F ox protein tht trgets Bioid for degrdtion nd regultes developmentl fte determintion in Drosophil emryos Juno Liu 1 nd Jun M 1,2,3 Bioid (Bd) is morphogeneti protein tht instruts
Rapamycin toxicity in MIN6 cells and rat and human islets is mediated by the inhibition of mtor complex 2 (mtorc2)
 Dietologi (212) 55:1355 1365 DOI 1.17/s125-12-2475-7 ARTICLE myin toxiity in MIN6 ells nd rt nd humn islets is medited y the inhiition of mtor omplex 2 (mtorc2) A. D. Brlow & J. Xie & C. E. Moore & S.
Dietologi (212) 55:1355 1365 DOI 1.17/s125-12-2475-7 ARTICLE myin toxiity in MIN6 ells nd rt nd humn islets is medited y the inhiition of mtor omplex 2 (mtorc2) A. D. Brlow & J. Xie & C. E. Moore & S.
BDNF release from single cells elicits local dendritic growth in nearby neurons
 BDNF relese from single ells eliits lol enriti growth in nery neurons Hley Wilson Horh 1,2 n Lwrene C. Ktz 1 1 Howr Hughes Meil Institute, Deprtment of Neuroiology, Duke University Meil Center, Box 3209,
BDNF relese from single ells eliits lol enriti growth in nery neurons Hley Wilson Horh 1,2 n Lwrene C. Ktz 1 1 Howr Hughes Meil Institute, Deprtment of Neuroiology, Duke University Meil Center, Box 3209,
The Journal of Physiology
 J Physiol 595.23 (217) pp 7185 722 7185 Heteromeri α/β glyine reeptors regulte exitility in prvlumin-expressing dorsl horn neurons through phsi nd toni glyinergi inhiition M. A. Grdwell 1,2,K.A.Boyle 3,R.J.llister
J Physiol 595.23 (217) pp 7185 722 7185 Heteromeri α/β glyine reeptors regulte exitility in prvlumin-expressing dorsl horn neurons through phsi nd toni glyinergi inhiition M. A. Grdwell 1,2,K.A.Boyle 3,R.J.llister
Chow KD CR HFD. Fed Fast Refed
 Supplementry Figure 1 Control d/d Chow KD CR Fed Fst Refed Supplementry Figure 1: Liver expression in diet nd disese models. () expression in the livers of ontrol nd d/d mie. () expression in the livers
Supplementry Figure 1 Control d/d Chow KD CR Fed Fst Refed Supplementry Figure 1: Liver expression in diet nd disese models. () expression in the livers of ontrol nd d/d mie. () expression in the livers
Poultry No The replacement value of betaine for DL-methionine and Choline in broiler diets
 Poultry No. 1573 The replement vlue of etine for DL-methionine nd Choline in roiler diets Key Informtion In roiler diets defiient in sulfur mino ids ut dequtely supplemented with methyl groups vi dded
Poultry No. 1573 The replement vlue of etine for DL-methionine nd Choline in roiler diets Key Informtion In roiler diets defiient in sulfur mino ids ut dequtely supplemented with methyl groups vi dded
Inhibitory effect of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase inhibitors on cytokine release from human macrophages
 British Journl of Phrmology (26) 149, 393 44 & 26 Nture Pulishing Group All rights reserved 7 1188/6 $3. www.rjphrmol.org RESEARCH PAPER Inhiitory effet of p38 mitogen-tivted protein kinse inhiitors on
British Journl of Phrmology (26) 149, 393 44 & 26 Nture Pulishing Group All rights reserved 7 1188/6 $3. www.rjphrmol.org RESEARCH PAPER Inhiitory effet of p38 mitogen-tivted protein kinse inhiitors on
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:1.138/nture1794 BR EPFs BRI1? ERECTA TMM BSKs YDA PP2A BSU1 BIN2 pbzr1/2 BZR1/2 MKK4/5/7/9 MPK3/6 SPCH Cell growth Stomtl production Supplementry Figure 1. The model of BR nd stomtl signling pthwys.
doi:1.138/nture1794 BR EPFs BRI1? ERECTA TMM BSKs YDA PP2A BSU1 BIN2 pbzr1/2 BZR1/2 MKK4/5/7/9 MPK3/6 SPCH Cell growth Stomtl production Supplementry Figure 1. The model of BR nd stomtl signling pthwys.
RESEARCH ARTICLE. Supplemental Figure 5
 11.5 2 2 11. RESEARCH ARTICLE RBC ( 1 12 /L) 1.5 1. 9.5 PLT ( 1 9 /L) 1 16 14 HGB (g/l) 19 1 17 16 9. 12 4 4 46 Cellulr & Moleulr Immunology dvne online pulition, PCV (%) 44 MCV (fl) 46 44 ; doi:1.13/mi.214.16
11.5 2 2 11. RESEARCH ARTICLE RBC ( 1 12 /L) 1.5 1. 9.5 PLT ( 1 9 /L) 1 16 14 HGB (g/l) 19 1 17 16 9. 12 4 4 46 Cellulr & Moleulr Immunology dvne online pulition, PCV (%) 44 MCV (fl) 46 44 ; doi:1.13/mi.214.16
Stable reprogrammed heterokaryons form spontaneously in Purkinje neurons after bone marrow transplant
 Stle reprogrmmed heterokryons form spontneously in Purkinje neurons fter one mrrow trnsplnt Jmes M. Weimnn 1,2,Cls B. Johnsson 1,Angeli Trejo 1 nd Helen M. Blu 1,2 Heterokryons re the produt of ell fusion
Stle reprogrmmed heterokryons form spontneously in Purkinje neurons fter one mrrow trnsplnt Jmes M. Weimnn 1,2,Cls B. Johnsson 1,Angeli Trejo 1 nd Helen M. Blu 1,2 Heterokryons re the produt of ell fusion
Imaging analysis of clock neurons reveals light buffers the wake-promoting effect of dopamine
 Imging nlysis of lok neurons revels light uffers the wke-promoting effet of dopmine Yuhu Shng 1,2, Pul Hynes 2, Niolás Pírez 2, Kyle I Hrrington 3, Fng Guo 1,2, Jordn Pollk 3, Pengyu Hong 3, Leslie C Griffith
Imging nlysis of lok neurons revels light uffers the wke-promoting effet of dopmine Yuhu Shng 1,2, Pul Hynes 2, Niolás Pírez 2, Kyle I Hrrington 3, Fng Guo 1,2, Jordn Pollk 3, Pengyu Hong 3, Leslie C Griffith
Whangarei District Council Class 4 Gambling Venue Policy
 Whngrei Distrit Counil Clss 4 Gmling Venue Poliy April 2013 Whngrei Distrit Counil Clss 4 Gmling Venue Poliy Tle of ontents Introdution... 3 1 Ojetives of the poliy in so fr s promoted y the Gmling At
Whngrei Distrit Counil Clss 4 Gmling Venue Poliy April 2013 Whngrei Distrit Counil Clss 4 Gmling Venue Poliy Tle of ontents Introdution... 3 1 Ojetives of the poliy in so fr s promoted y the Gmling At
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 oi:1.138/nture1138 Supplementl Figure 1 Inflmmtory Monoytes Host ells CCR2 CCL2 Disseminting Tumor Cells Metstsis Assoite Mrophges VEGF Extrvstion & Metstti Seeing Supplementl Figure 1 The t from this
oi:1.138/nture1138 Supplementl Figure 1 Inflmmtory Monoytes Host ells CCR2 CCL2 Disseminting Tumor Cells Metstsis Assoite Mrophges VEGF Extrvstion & Metstti Seeing Supplementl Figure 1 The t from this
Activation of Akt as a Mechanism for Tumor Immune Evasion
 The Amerin Soiety of Gene Therpy originl rtile Ativtion of Akt s Mehnism for Tumor Immune Evsion Kyung Hee Noh 1, Te Heung Kng 1, Jin Hee Kim 1, Sr I Pi 2, Ken Y Lin 3, Chien-Fu Hung 4, T-C Wu 4 7 nd Te
The Amerin Soiety of Gene Therpy originl rtile Ativtion of Akt s Mehnism for Tumor Immune Evsion Kyung Hee Noh 1, Te Heung Kng 1, Jin Hee Kim 1, Sr I Pi 2, Ken Y Lin 3, Chien-Fu Hung 4, T-C Wu 4 7 nd Te
Supplementary Figure S1
 Supplementry Figure S Connexin4 TroponinI Merge Plsm memrne Met Intrcellulr Met Supplementry Figure S H9c rt crdiomyolsts cell line. () Immunofluorescence of crdic mrkers: Connexin4 (green) nd TroponinI
Supplementry Figure S Connexin4 TroponinI Merge Plsm memrne Met Intrcellulr Met Supplementry Figure S H9c rt crdiomyolsts cell line. () Immunofluorescence of crdic mrkers: Connexin4 (green) nd TroponinI
RNAi Targeting CXCR4 Inhibits Tumor Growth Through Inducing Cell Cycle Arrest and Apoptosis
 originl rtile RNAi Trgeting CXCR4 Inhiits Tumor Growth Through Induing Cell Cyle Arrest nd Apoptosis To Yu 1,2, Yingying Wu 2, Yi Hung 1,2, Chorn Yn 1, Ying Liu 1, Zongsheng Wng 3, Xioyi Wng 1, Yuming
originl rtile RNAi Trgeting CXCR4 Inhiits Tumor Growth Through Induing Cell Cyle Arrest nd Apoptosis To Yu 1,2, Yingying Wu 2, Yi Hung 1,2, Chorn Yn 1, Ying Liu 1, Zongsheng Wng 3, Xioyi Wng 1, Yuming
Change detection by thalamic reticular neurons
 Chnge detetion y thlmi retiulr neurons Xiong-Jie Yu 1,2, Xin-Xiu Xu 1, Shigng He 1 & Jufng He 1,2 The thlmi retiulr nuleus (TRN) is thought to funtion in the ttentionl serhlight. We nlyzed the detetion
Chnge detetion y thlmi retiulr neurons Xiong-Jie Yu 1,2, Xin-Xiu Xu 1, Shigng He 1 & Jufng He 1,2 The thlmi retiulr nuleus (TRN) is thought to funtion in the ttentionl serhlight. We nlyzed the detetion
Role of HCP5-miR-139-RUNX1 Feedback Loop in Regulating Malignant Behavior of Glioma Cells
 originl rtile The Amerin Soiety of Gene & Cell Therpy Role of HCP-miR-19-RUNX1 Feedk Loop in Regulting Mlignnt Behvior of Gliom Cells Ho Teng 1,2, Ping Wng, Yixue Xue, Xioi Liu 1,2, Jun M, Heng Ci 1,2,
originl rtile The Amerin Soiety of Gene & Cell Therpy Role of HCP-miR-19-RUNX1 Feedk Loop in Regulting Mlignnt Behvior of Gliom Cells Ho Teng 1,2, Ping Wng, Yixue Xue, Xioi Liu 1,2, Jun M, Heng Ci 1,2,
regulates stem cells through Wnt/β-catenin signalling
 LETTERS O regultes stem ells through Wnt/β-tenin signlling Jolly Mzumdr,,7, W. Timothy O Brien, Rndll S. Johnson, Joseph C. LMnn, Jun C. Chvez 5, Peter S. Klein nd M. Celeste Simon,, Stem ells reside in
LETTERS O regultes stem ells through Wnt/β-tenin signlling Jolly Mzumdr,,7, W. Timothy O Brien, Rndll S. Johnson, Joseph C. LMnn, Jun C. Chvez 5, Peter S. Klein nd M. Celeste Simon,, Stem ells reside in
Olfactory behavior and physiology are disrupted in prion protein knockout mice
 Olftory ehvior nd physiology re disrupted in prion protein knokout mie Clire E Le Pihon 1, Mtthew T Vlley 1, Mgdlini Polymenidou 2,3, Alexnder T Chesler 1, Botir T Sgdullev 1,3, Adrino Aguzzi 2 & Sturt
Olftory ehvior nd physiology re disrupted in prion protein knokout mie Clire E Le Pihon 1, Mtthew T Vlley 1, Mgdlini Polymenidou 2,3, Alexnder T Chesler 1, Botir T Sgdullev 1,3, Adrino Aguzzi 2 & Sturt
Thioredoxin-interacting protein links oxidative stress to inflammasome activation
 A rt i l e s Thioredoxin-interting protein links oxidtive stress to inflmmsome tivtion Rongin Zhou 1, Aury Trdivel 1, Bernrd Thorens 2, Inpyo Choi 3 & Jürg Tshopp 1 29 Nture Ameri, In. All rights reserved.
A rt i l e s Thioredoxin-interting protein links oxidtive stress to inflmmsome tivtion Rongin Zhou 1, Aury Trdivel 1, Bernrd Thorens 2, Inpyo Choi 3 & Jürg Tshopp 1 29 Nture Ameri, In. All rights reserved.
Ulk λ PPase. 32 P-Ulk1 32 P-GST-TSC2. Ulk1 GST (TSC2) : Ha-Ulk1 : AMPK. WB: Ha (Ulk1) : Glu. h CON - Glu - A.A WB: LC3 AMPK-WT AMPK-DKO
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb2152 C.C + - + - : Glu b Ulk1 - - + λ PPse c AMPK + - + + : ATP P-GST-TSC2 WB: Flg (Ulk1) WB Ulk1 WB: H (Ulk1) GST (TSC2) C.C d e WT K46R - + - + : H-Ulk1 : AMPK - + - + + + AMPK H-Ulk1
DOI: 10.1038/ncb2152 C.C + - + - : Glu b Ulk1 - - + λ PPse c AMPK + - + + : ATP P-GST-TSC2 WB: Flg (Ulk1) WB Ulk1 WB: H (Ulk1) GST (TSC2) C.C d e WT K46R - + - + : H-Ulk1 : AMPK - + - + + + AMPK H-Ulk1
ARTICLES. Lateral presynaptic inhibition mediates gain control in an olfactory circuit. Shawn R. Olsen 1 & Rachel I. Wilson 1
 doi:1.138/nture6864 ARTICLES Lterl presynpti inhiition medites gin ontrol in n olftory iruit Shwn R. Olsen 1 & Rhel I. Wilson 1 Olftory signls re trnsdued y lrge fmily of odornt reeptor proteins, eh of
doi:1.138/nture6864 ARTICLES Lterl presynpti inhiition medites gin ontrol in n olftory iruit Shwn R. Olsen 1 & Rhel I. Wilson 1 Olftory signls re trnsdued y lrge fmily of odornt reeptor proteins, eh of
N6-methyladenosine (m6a) is the most prevalent messenger
 https://oi.org/8/s556-8-7- m 6 A mrna methyltion regultes tivity to promote the prolifertion n tumorigeniity of enometril ner Jun Liu,,, Mrk A. Ekert,, Bryn T. Hr,,, Song-Mei Liu,, Zhike Lu,, Kngkng Yu,,5,
https://oi.org/8/s556-8-7- m 6 A mrna methyltion regultes tivity to promote the prolifertion n tumorigeniity of enometril ner Jun Liu,,, Mrk A. Ekert,, Bryn T. Hr,,, Song-Mei Liu,, Zhike Lu,, Kngkng Yu,,5,
WNK1 kinase balances T cell adhesion versus migration in vivo
 WNK1 kinse lnes T ell dhesion versus migrtion in vivo Roert Köhl 1, Flvin Thelen, Lesley Vnes 1, Tigo F Brzão 1, Kthryn Fountin 1, Jin Xie 3, Chou-Long Hung 3, Ruth Lyk, Jens V Stein & Vitor L J Tyulewiz
WNK1 kinse lnes T ell dhesion versus migrtion in vivo Roert Köhl 1, Flvin Thelen, Lesley Vnes 1, Tigo F Brzão 1, Kthryn Fountin 1, Jin Xie 3, Chou-Long Hung 3, Ruth Lyk, Jens V Stein & Vitor L J Tyulewiz
ANGPTL binding ANGPTL binding ANGPTL4 GST ANGPTL5 ANGPTL6 ANGPTL7. A5+LILRB2 Fc. A5+Tie-2 Fc 10,000 7,500. Tie-2 Fc LILRB2 Fc. 5,000 K d = 5.
 doi:1.138/nture1195 ; Inhiitory reeptors ind ANGPTLs nd support < lood stem ells nd leukemi development Junke Zheng 1,2, Msto Umikw 1,3, Chngho Cui 1, Jiyun Li 1, Xioli Chen 1, Chozheng Zhng 1, HongDinh
doi:1.138/nture1195 ; Inhiitory reeptors ind ANGPTLs nd support < lood stem ells nd leukemi development Junke Zheng 1,2, Msto Umikw 1,3, Chngho Cui 1, Jiyun Li 1, Xioli Chen 1, Chozheng Zhng 1, HongDinh
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION CD169 + MACROPHAGES PRESENT LIPID ANTIGENS TO MEDIATE EARLY ACTIVATION OF INVARIANT NKT CELLS IN LYMPH NODES Ptrii Brrl, Polo Polzell, Andres Brukuer, Nio vn Rooijen, Gurdyl S.
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION CD169 + MACROPHAGES PRESENT LIPID ANTIGENS TO MEDIATE EARLY ACTIVATION OF INVARIANT NKT CELLS IN LYMPH NODES Ptrii Brrl, Polo Polzell, Andres Brukuer, Nio vn Rooijen, Gurdyl S.
The Ia-2β intronic mirna, mir-153, is a negative regulator of insulin and dopamine secretion through its effect on the Cacna1c gene in mice
 Dietologi (5) 58:98 36 DOI.7/s5536838 ARTICLE The I introni mirna, mir53, is negtive regultor of insulin nd dopmine seretion through its effet on the Cn gene in mie Hunyu Xu & Liron Auhtzir & Gilerto N.
Dietologi (5) 58:98 36 DOI.7/s5536838 ARTICLE The I introni mirna, mir53, is negtive regultor of insulin nd dopmine seretion through its effet on the Cn gene in mie Hunyu Xu & Liron Auhtzir & Gilerto N.
AMP-activated protein kinase regulates glucagon secretion from mouse pancreatic alpha cells
 Dietologi (2) 54:25 34 DOI.7/s25--929-z ARTICLE AMP-tivted protein kinse regultes glugon seretion from mouse pnreti lph ells I. Leler & G. Sun & C. Morris & E. Fernndez-Milln & M. Nyirend & G. A. Rutter
Dietologi (2) 54:25 34 DOI.7/s25--929-z ARTICLE AMP-tivted protein kinse regultes glugon seretion from mouse pnreti lph ells I. Leler & G. Sun & C. Morris & E. Fernndez-Milln & M. Nyirend & G. A. Rutter
Hydrogen sulfide-induced inhibition of L-type Ca 2+ channels and insulin secretion in mouse pancreatic beta cells
 Dietologi (213) 56:533 541 DOI 1.17/s125-12-286-8 ARTICLE Hydrogen sulfide-indued inhiition of L-type C 2 hnnels nd insulin seretion in mouse pnreti et ells G. Tng & L. Zhng & G. Yng & L. Wu & R. Wng Reeived:
Dietologi (213) 56:533 541 DOI 1.17/s125-12-286-8 ARTICLE Hydrogen sulfide-indued inhiition of L-type C 2 hnnels nd insulin seretion in mouse pnreti et ells G. Tng & L. Zhng & G. Yng & L. Wu & R. Wng Reeived:
 DOI: 10.1038/nc2331 PCre;Ros26R 12 h induction 48 h induction Vegfr3 i EC c d ib4 24 h induction VEGFR3 e Fold chnge 1.0 0.5 P < 0.05 Vegfr3 i EC Vegfr3 Figure S1 Cre ctivtion leds to genetic deletion
DOI: 10.1038/nc2331 PCre;Ros26R 12 h induction 48 h induction Vegfr3 i EC c d ib4 24 h induction VEGFR3 e Fold chnge 1.0 0.5 P < 0.05 Vegfr3 i EC Vegfr3 Figure S1 Cre ctivtion leds to genetic deletion
Supplementary figure 1
 Supplementry figure 1 Dy 8 post LCMV infection Vsculr Assoc. Prenchym Dy 3 post LCMV infection 1 5 6.7.29 1 4 1 3 1 2 88.9 4.16 1 2 1 3 1 4 1 5 1 5 1.59 5.97 1 4 1 3 1 2 21.4 71 1 2 1 3 1 4 1 5 1 5.59.22
Supplementry figure 1 Dy 8 post LCMV infection Vsculr Assoc. Prenchym Dy 3 post LCMV infection 1 5 6.7.29 1 4 1 3 1 2 88.9 4.16 1 2 1 3 1 4 1 5 1 5 1.59 5.97 1 4 1 3 1 2 21.4 71 1 2 1 3 1 4 1 5 1 5.59.22
Involvement of thioredoxin-interacting protein (TXNIP) in glucocorticoid-mediated beta cell death
 Dietologi (12) 55:148 157 DOI 1.7/s125-11-2422-z ARTICLE Involvement of thioredoxin-interting protein (TXNIP) in gluoortioid-medited et ell deth E. Reih & A. Tmry & R. Vogt Sionov & D. Melloul Reeived:
Dietologi (12) 55:148 157 DOI 1.7/s125-11-2422-z ARTICLE Involvement of thioredoxin-interting protein (TXNIP) in gluoortioid-medited et ell deth E. Reih & A. Tmry & R. Vogt Sionov & D. Melloul Reeived:
a3 Chains of type V collagen regulate breast tumour growth via glypican-1
 Reeive 5 Aug 16 Aepte De 16 Pulishe 19 Jn 17 3 Chins of type V ollgen regulte rest tumour growth vi glypin-1 Guorui Hung 1, Goxing Ge 1,w, Vlerio Izzi & Dniel S. Greenspn 1 DOI: 1.138/nomms1351 OPEN Periellulr
Reeive 5 Aug 16 Aepte De 16 Pulishe 19 Jn 17 3 Chins of type V ollgen regulte rest tumour growth vi glypin-1 Guorui Hung 1, Goxing Ge 1,w, Vlerio Izzi & Dniel S. Greenspn 1 DOI: 1.138/nomms1351 OPEN Periellulr
Control of timing, rate and bursts of hippocampal place cells by dendritic and somatic inhibition
 Control of timing, rte nd ursts of hippompl ple ells y dendriti nd somti inhiition Séstien Royer,2, Boris V Zemelmn,5, Attil Losonzy,3, Jinhyun Kim,2, Frnes Chne, Jeffrey C Mgee & György Buzsáki,4 22 Nture
Control of timing, rte nd ursts of hippompl ple ells y dendriti nd somti inhiition Séstien Royer,2, Boris V Zemelmn,5, Attil Losonzy,3, Jinhyun Kim,2, Frnes Chne, Jeffrey C Mgee & György Buzsáki,4 22 Nture
Hippocampal CA1 pyramidal cells form functionally distinct sublayers
 r t i l e s Hippompl CA pyrmidl ells form funtionlly distint sulyers Kenji Mizuseki, Kmrn Di,2, Ev Pstlkov,2 & György Buzsáki 2 Nture Ameri, In. All rights reserved. Hippompl CA pyrmidl neurons hve frequently
r t i l e s Hippompl CA pyrmidl ells form funtionlly distint sulyers Kenji Mizuseki, Kmrn Di,2, Ev Pstlkov,2 & György Buzsáki 2 Nture Ameri, In. All rights reserved. Hippompl CA pyrmidl neurons hve frequently
Introduction to Study Designs II
 Introdution to Study Designs II Commonly used study designs in publi helth & epidemiologi reserh Benjmin Rihrd H. Muthmbi, DrPH, MPH Stte HIV Epidemiologist HIV Epidemiology Investigtion Setion PA Deprtment
Introdution to Study Designs II Commonly used study designs in publi helth & epidemiologi reserh Benjmin Rihrd H. Muthmbi, DrPH, MPH Stte HIV Epidemiologist HIV Epidemiology Investigtion Setion PA Deprtment
Sonic Hedgehog promotes proliferation of Notch-dependent monociliated choroid plexus tumour cells
 Soni Hedgehog promotes prolifertion of Noth-dependent monoilited horoid plexus tumour ells Li Li, Ktie B. Grusm,2, Jun Wng 3, Melody P. Lun 4,5, Jsmin Ohli 6, Hrt G. W. Lidov 4, Moni L. Clihio 4, Erling
Soni Hedgehog promotes prolifertion of Noth-dependent monoilited horoid plexus tumour ells Li Li, Ktie B. Grusm,2, Jun Wng 3, Melody P. Lun 4,5, Jsmin Ohli 6, Hrt G. W. Lidov 4, Moni L. Clihio 4, Erling
The nucleotide exchange factor SIL1 is required for glucose-stimulated insulin secretion from mouse pancreatic beta cells in vivo
 Dietologi (1) 7:11 119 DOI 1.17/s1-1-33-z ARTICLE The nuleotide exhnge ftor SIL1 is required for gluose-stimulted insulin seretion from mouse pnreti et ells in vivo Arne A. Ittner & Josefine Bertz & Tse
Dietologi (1) 7:11 119 DOI 1.17/s1-1-33-z ARTICLE The nuleotide exhnge ftor SIL1 is required for gluose-stimulted insulin seretion from mouse pnreti et ells in vivo Arne A. Ittner & Josefine Bertz & Tse
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
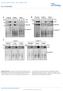 DOI:.3/n95 Thymus Kiney (kd) TA T7 T TA T7 T Hert TA T7 T: +Dox Cylin B (kd) Thymus Kiney Hert TA T5 T TA T5 T TA T5 T: +Dox Cylin B Poneu S Poneu S CnB T7 CnB T Thymus (kd) + Liver Colon + + (kd) Thymus
DOI:.3/n95 Thymus Kiney (kd) TA T7 T TA T7 T Hert TA T7 T: +Dox Cylin B (kd) Thymus Kiney Hert TA T5 T TA T5 T TA T5 T: +Dox Cylin B Poneu S Poneu S CnB T7 CnB T Thymus (kd) + Liver Colon + + (kd) Thymus
ARTICLES. Dendritic organization of sensory input to cortical neurons in vivo
 Vol 6 9 April 00 doi:0.08/nture0897 ARTICLES Dendriti orgniztion of sensory input to ortil neurons in vivo Hongbo Ji *, Nthlie L. Rohefort *, Xiowei Chen & Arthur Konnerth In sensory ortex regions, neurons
Vol 6 9 April 00 doi:0.08/nture0897 ARTICLES Dendriti orgniztion of sensory input to ortil neurons in vivo Hongbo Ji *, Nthlie L. Rohefort *, Xiowei Chen & Arthur Konnerth In sensory ortex regions, neurons
