18/01/2015. Review Session 4. Concept 1: Fluids. Def: Anything that can flow and take shape of container. Two types: Compressible and Incompressible
|
|
|
- Julie Cameron
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Review Session 4 PRESSURE, ORGANIZATION IN THE HUMAN BODY, MUSCU LOSK E LETAL SYSTEM Concept 1: Fluids Def: Anything that can flow and take shape of container Two types: Compressible and Incompressible 1
2 Compressible Fluid Pushing against piston of syringe will compress the fluid and volume decreases Incompressible Fluid Pushing against piston of syringe will not compress the fluid, and volume stays the same 2
3 Concept 2: Pressure Def: Force applied perpendicular to the surface in question Two factors affect pressure, force and surface area Force, Pressure Surface area, Pressure **No pressure calculations, however, need to determine which scenario has higher or lower pressure, and explain why** Concept 2: Pressure Factors affecting pressure in a incompressible fluid Mass of fluid above object; mass, pressure Density of fluid; density, pressure 3
4 Concept 2: Pressure Factors affecting pressure in a compressible fluid Number of particle collisions; #particles, #collisions, pressure Volume of container; volume, empty space, #collisions, pressure Temperature of particles; temperature, speed of particle movement, #collisions, pressure temperature, speed of particle movement, #collisions, pressure State in which scenario the pressure is greater and why 100 ml of water (D=1.0 g/ml) 100 ml of mud (D=1.73 g/ml) 4
5 State in which scenario the pressure is greater and why 100 ml of water (D=1.0 g/ml) 150 ml of water (D=1.0 g/ml) State in which scenario the pressure is greater and why Gas particles with high temperature Gas particles with low temperature 5
6 Concept 3: Organization in the Human Body- Levels of Hierarchy Level 7: Organism Level 6: Systems Level 5: Organs Level 4: Tissue Level 3: Cells Level 2: Molecules Level 1: Atoms Concept 3: Organization in the Human Body- Levels of Hierarchy Level 1: Atom Level 2: Molecule Fundamental unit of matter Proton Electron Neutron Two or more atoms which are chemically bounded 6
7 Level 3: Cells Need to know what an animal cell looks like Require organelles to know (function and location) Nucleus Cytoplasm Cellular Membrane Concept 3: Organization in the Human Body- Levels of Hierarchy Level 4: Tissue Level 5: Organ A group of similar cells that have a common structure and function Four types Epithelial Connective Muscle Nerve Structure composed of two or more different tissue types that perform one or more specific functions Need to know specific examples 7
8 Concept 3: Organization in the Human Body- Levels of Hierarchy Level 6: Organ System Level 7: Organism A group of organs and tissues working together to do a common function Need to know organs in common organ systems Need to know basic function of organ system Living entity produced as a result of multiple different organ systems working together The heart and the aorta are part of what organ system: a) Cardiovascular b) Digestive c) Respiratory d) Reproductive 8
9 The trachea and the lungs are part of what organ system: a) Cardiovascular b) Digestive c) Respiratory d) Reproductive The esophagus and the stomach are part of what organ system: a) Cardiovascular b) Digestive c) Respiratory d) Reproductive 9
10 The function of the respiratory system is to a) Allow for sexual reproduction b) Break down food into simple nutrients c) Transport blood and nutrients around the body d) Exchange oxygen and carbon dioxide The function of the reproduction system is to a) Allow for sexual reproduction b) Break down food into simple nutrients c) Transport blood and nutrients around the body d) Exchange oxygen and carbon dioxide 10
11 The function of the cardiovascular system is to a) Allow for sexual reproduction b) Break down food into simple nutrients c) Transport blood and nutrients around the body d) Exchange oxygen and carbon dioxide The function of the musculoskeletal system is to a) Allow for organs to move internally and externally b) Break down food into simple nutrients c) Maintain body posture d) Both b and d 11
12 Concept 4: Musculoskeletal System Composed of Bones Joints Muscles Bones: need to know Type of bone (compact and spongy) Categories of bone (long, short, flat, irregular) Main bones in body (see skeleton) Anatomy of long bone Concept 4: Musculoskeletal System Joints: need to know Main categories of joints (fixed, semi-movable, freely-movable) Hinge : move along one axis, elbow/knee Pivot: move along mult. Axis in circle; neck Ball and socket: move along mult. axis; shoulder, hip Types of movement Extension: angle Flexion: angle Abduction: away from midline Adduction: towards midline Rotation 12
13 Concept 4: Musculoskeletal System Muscle: need to know Key function; move, posture, joint stabilization Types: skeletal, smooth, cardiac **(details and i.d. sketch) Main muscles in body Antagonist Muscles Two pairs of muscles for voluntary movement One muscle contracts in pair, the other muscle relaxes, allowing for bone to move Bicep and Triceps Quadriceps and Hamstring 13
REVISION BOOKLET. The Body Systems
 REVISION BOOKLET The Body Systems GCSE PE 2016 Skeletal System Functions of the skeleton Joints for movement Muscle attachment Protection of vital organs Red and white blood cell production platelets Storage
REVISION BOOKLET The Body Systems GCSE PE 2016 Skeletal System Functions of the skeleton Joints for movement Muscle attachment Protection of vital organs Red and white blood cell production platelets Storage
Comparing Bones, Joints, and Muscles
 Chapter 36 Skeletal, Muscular, and Integumentary Systems Comparing Bones, Joints, and Muscles You may want to refer students to Chapter 36 in the textbook for a general discussion of skeletal and muscular
Chapter 36 Skeletal, Muscular, and Integumentary Systems Comparing Bones, Joints, and Muscles You may want to refer students to Chapter 36 in the textbook for a general discussion of skeletal and muscular
THe Skeletal System 1
 THe Skeletal System 1 What the Skeletal System DOes! Skeleton: works as the framework of your body and is made up of all of the bones in your body The number of bones in your skeleton depends on your age.
THe Skeletal System 1 What the Skeletal System DOes! Skeleton: works as the framework of your body and is made up of all of the bones in your body The number of bones in your skeleton depends on your age.
2º ESO - PE Workbook - IES Joan Miró Physical Education Department THE MUSCULAR SYSTEM
 THE MUSCULAR SYSTEM The muscular system is one of 10 organ systems in the human body. The human body has more than 650 muscles, which make up half of a person's body weight. Without muscles, we would not
THE MUSCULAR SYSTEM The muscular system is one of 10 organ systems in the human body. The human body has more than 650 muscles, which make up half of a person's body weight. Without muscles, we would not
Anatomy and Physiology for Exercise Level 2
 Anatomy and Physiology for Exercise Level 2 H/600/9013 Mock Paper There are 30 questions within this paper To achieve a pass you will need to score 21 out of 30 marks All questions are multiple choice
Anatomy and Physiology for Exercise Level 2 H/600/9013 Mock Paper There are 30 questions within this paper To achieve a pass you will need to score 21 out of 30 marks All questions are multiple choice
The Skeletal System. Chapter 8
 The Skeletal System Chapter 8 1 Introduction Movement is essential for animals. This is done by moving muscles with the skeleton. 2 Functions of the skeleton 1. Gives shape and support to the body. The
The Skeletal System Chapter 8 1 Introduction Movement is essential for animals. This is done by moving muscles with the skeleton. 2 Functions of the skeleton 1. Gives shape and support to the body. The
The Skeletal System. Functions of the Skeletal System
 Skeletal System The Skeletal System Functions of the Skeletal System Provide support Protect internal organs Allows your body to move Stores and produced materials that your body needs You have 206 bones
Skeletal System The Skeletal System Functions of the Skeletal System Provide support Protect internal organs Allows your body to move Stores and produced materials that your body needs You have 206 bones
Applied anatomy and physiology: definitions of key terms
 Applied anatomy and physiology: definitions of key terms See pages 5 46 These are the key terms from Chapter 1. Try cutting them out and then matching the key terms with their definitions, or asking friends
Applied anatomy and physiology: definitions of key terms See pages 5 46 These are the key terms from Chapter 1. Try cutting them out and then matching the key terms with their definitions, or asking friends
Anatomy and physiology for sport
 Anatomy and physiology for sport UV21527 D/502/5474 Learner name: VRQ Learner number: VTCT is the specialist awarding body for the Hairdressing, Beauty Therapy, Complementary Therapy, Hospitality and Catering
Anatomy and physiology for sport UV21527 D/502/5474 Learner name: VRQ Learner number: VTCT is the specialist awarding body for the Hairdressing, Beauty Therapy, Complementary Therapy, Hospitality and Catering
Challenge Question: Prediction: (Wait for directions) Evidence: (Draw, color and label how your Clay model looked when it was complete)
 Activity #12 What s happening inside? Challenge Question: Prediction: (Wait for directions) Evidence: (Draw, color and label how your Clay model looked when it was complete) Act #12 pg 1 of 3 Analysis
Activity #12 What s happening inside? Challenge Question: Prediction: (Wait for directions) Evidence: (Draw, color and label how your Clay model looked when it was complete) Act #12 pg 1 of 3 Analysis
BODY SYSTEMS UNIT ANCHOR CHARTS:
 BODY SYSTEMS UNIT ANCHOR CHARTS: LEVELS OF ORGANIZATION smallest unit Cells Tissues Organs Organ Systems largest unit Body TISSUES IN THE HUMAN BODY Tissue Function Example Muscle makes parts of the body
BODY SYSTEMS UNIT ANCHOR CHARTS: LEVELS OF ORGANIZATION smallest unit Cells Tissues Organs Organ Systems largest unit Body TISSUES IN THE HUMAN BODY Tissue Function Example Muscle makes parts of the body
SKELETAL AND MUSCULAR SYSTEMS WHAT MOVES YOU!
 SKELETAL AND MUSCULAR SYSTEMS WHAT MOVES YOU! WHAT ARE THE MAIN FUNCTIONS OF THE SKELETAL SYSTEM? THE SKELETAL SYSTEM The skeletal system is the organ system that supports and protects the body and allows
SKELETAL AND MUSCULAR SYSTEMS WHAT MOVES YOU! WHAT ARE THE MAIN FUNCTIONS OF THE SKELETAL SYSTEM? THE SKELETAL SYSTEM The skeletal system is the organ system that supports and protects the body and allows
THE MUSCULAR SYSTEM FUNCTION OF MUSCLES
 FUNCTION OF MUSCLES THE MUSCULAR SYSTEM The 600 muscles in your body that function to move the skeleton are called skeletal muscles. The skeletal muscles make up the voluntary muscle system. They are called
FUNCTION OF MUSCLES THE MUSCULAR SYSTEM The 600 muscles in your body that function to move the skeleton are called skeletal muscles. The skeletal muscles make up the voluntary muscle system. They are called
Yoga Anatomy & Physiology
 Yoga Anatomy & Physiology Anatomy & Physiology Anatomy- One of the basic essential sciences of medicine that studies the structure of an organism. Physiology- The biological study of the functions of living
Yoga Anatomy & Physiology Anatomy & Physiology Anatomy- One of the basic essential sciences of medicine that studies the structure of an organism. Physiology- The biological study of the functions of living
Unsaved Test, Version: 1 1
 Name: Choose the letter of the best answer. 1. Functions of the skeletal system include A. forcing blood to circulate through the body B. sending electrical signals to the brain C. providing support and
Name: Choose the letter of the best answer. 1. Functions of the skeletal system include A. forcing blood to circulate through the body B. sending electrical signals to the brain C. providing support and
PiXL Independence: PE Answer Booklet KS4. Applied Anatomy and Physiology. Contents: Answers
 PiXL Independence: PE Answer Booklet KS4 Applied Anatomy and Physiology Contents: Answers 1 I. Quizzes Multiple Choice Quiz 1. Which one of the following statements is false? a. The scapula, cranium and
PiXL Independence: PE Answer Booklet KS4 Applied Anatomy and Physiology Contents: Answers 1 I. Quizzes Multiple Choice Quiz 1. Which one of the following statements is false? a. The scapula, cranium and
How can sportspeople train the body systems to ensure there are long term benefits? Excercise Physiology. Chapter 2. GCSE Physical Education
 How can sportspeople train the body systems to ensure there are long term benefits? Excercise Physiology GCSE Physical Education To answer the big question you will need to be able to complete the following
How can sportspeople train the body systems to ensure there are long term benefits? Excercise Physiology GCSE Physical Education To answer the big question you will need to be able to complete the following
36.3 The Integumentary System The Skin. KEY CONCEPT The integumentary system has many tissues that protect the body.
 36.3 The Integumentary System The Skin KEY CONCEPT The integumentary system has many tissues that protect the body. 36.3 The Integumentary System The Skin The integument is the body system that surrounds
36.3 The Integumentary System The Skin KEY CONCEPT The integumentary system has many tissues that protect the body. 36.3 The Integumentary System The Skin The integument is the body system that surrounds
In Activity 12, What s Happening Inside? you learned about the functions
 16 Support System: Bones, Joints and Muscles l a b o r at o ry In Activity 12, What s Happening Inside? you learned about the functions of the skeletal and muscular systems in supporting and moving your
16 Support System: Bones, Joints and Muscles l a b o r at o ry In Activity 12, What s Happening Inside? you learned about the functions of the skeletal and muscular systems in supporting and moving your
CHAPTER 3 What Is Anatomy?
 CHAPTER 3 What Is Anatomy? Kinesiology Books Publisher 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS The Language of Anatomy Anatomical Position Directional Terms Body Planes Movements Musculoskeletal System Human Skeleton Types
CHAPTER 3 What Is Anatomy? Kinesiology Books Publisher 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS The Language of Anatomy Anatomical Position Directional Terms Body Planes Movements Musculoskeletal System Human Skeleton Types
Equipment on table: Pen, ruler, pencil and planner.
 Question 1 Name two flat bones and, using a sporting action of your choice, suggest how these bones provide protection during performance. Question 2 Describe 4 ranges of movement. Question 3 Question
Question 1 Name two flat bones and, using a sporting action of your choice, suggest how these bones provide protection during performance. Question 2 Describe 4 ranges of movement. Question 3 Question
Nervous System. Skeletal System. Muscular System. Reproductive System. Circulatory System. Endocrine System. Respiratory System. Integumentary System
 The Human Body Skeletal System Muscular System Circulatory System Respiratory System Digestive System Nervous System Reproductive System Endocrine System Integumentary System Excretory System Lymphatic/Immune
The Human Body Skeletal System Muscular System Circulatory System Respiratory System Digestive System Nervous System Reproductive System Endocrine System Integumentary System Excretory System Lymphatic/Immune
1.1 The structure and functions of the musculo-skeletal system Learning objectives
 1.1 The structure and functions of the musculo-skeletal system Learning objectives To be able to describe the functions of the skeleton. To understand different bone classifications and functioning. To
1.1 The structure and functions of the musculo-skeletal system Learning objectives To be able to describe the functions of the skeleton. To understand different bone classifications and functioning. To
Level 2 Anatomy and Physiology for Exercise and Fitness Instructors (K/616/7823) - Sample Assessment Student: XXXXXX Sample 4
 MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION PAPER Paper number: SAMPLE 4 Please ensure that this paper number is referenced on your candidate answer sheet Title: Student: XXXXXX Sample 4 Special Instructions: Level 2 Anatomy
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION PAPER Paper number: SAMPLE 4 Please ensure that this paper number is referenced on your candidate answer sheet Title: Student: XXXXXX Sample 4 Special Instructions: Level 2 Anatomy
The Human Body: An Orientation
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Human Body: An Orientation 1 PART A The Human Body An Orientation Anatomy Study of the structure
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Human Body: An Orientation 1 PART A The Human Body An Orientation Anatomy Study of the structure
Regulation and Homeostasis in the Human Body: Quick view
 Human Body Systems Regulation and Homeostasis in the Human Body: Quick view Eleven Body Systems work together to maintain homeostasis. 1. Nervous System 2. Endocrine System 3. Lymphatic System 4. Circulatory
Human Body Systems Regulation and Homeostasis in the Human Body: Quick view Eleven Body Systems work together to maintain homeostasis. 1. Nervous System 2. Endocrine System 3. Lymphatic System 4. Circulatory
Regulation and Homeostasis in the Human Body: Quick view
 Human Body Systems Regulation and Homeostasis in the Human Body: Quick view Eleven Body Systems work together to maintain homeostasis. 1. Nervous System 2. Endocrine System 3. Lymphatic System 4. Circulatory
Human Body Systems Regulation and Homeostasis in the Human Body: Quick view Eleven Body Systems work together to maintain homeostasis. 1. Nervous System 2. Endocrine System 3. Lymphatic System 4. Circulatory
Topic Guide 1: Applied Anatomy and Physiology. GCSE (9-1) Physical Education
 Topic Guide 1: Applied Anatomy and Physiology GCSE (9-1) Physical Education Pearson Edexcel Level 1/Level 2 GCSE (9-1) in Physical Education (1PE0) Pearson Edexcel Level 1/Level 2 GCSE (9-1) in Physical
Topic Guide 1: Applied Anatomy and Physiology GCSE (9-1) Physical Education Pearson Edexcel Level 1/Level 2 GCSE (9-1) in Physical Education (1PE0) Pearson Edexcel Level 1/Level 2 GCSE (9-1) in Physical
Grade 10 Intro to Resistance Training
 Grade 10 Intro to Resistance Training Benefits to Training with Weights Hypertrophy - Increase in existing muscle fibers Strengthening of tendons and ligament tissues Improve posture Decrease the size
Grade 10 Intro to Resistance Training Benefits to Training with Weights Hypertrophy - Increase in existing muscle fibers Strengthening of tendons and ligament tissues Improve posture Decrease the size
YEAR 9 GCSE PE Learning Programme
 YEAR 9 GCSE PE Learning Programme Half Term/Term Learning objective Learning activity Differentiation and extension Bones. Knowledge of the bones at the following locations: head/neck cranium, vertebrae
YEAR 9 GCSE PE Learning Programme Half Term/Term Learning objective Learning activity Differentiation and extension Bones. Knowledge of the bones at the following locations: head/neck cranium, vertebrae
Secondary 3 Final Exam Review
 Topics to know: Secondary 3 Final Exam Review - Technological/Material World o Mechanical functions (guiding, linking, sealing, lubricating) o Forces - Matter o Be able to identify chemical and physical
Topics to know: Secondary 3 Final Exam Review - Technological/Material World o Mechanical functions (guiding, linking, sealing, lubricating) o Forces - Matter o Be able to identify chemical and physical
Year 10 GCSE Revision - Physical Education Paper 1 Fitness and Body Systems Topic Areas for Revision Key questions
 Year 10 GCSE Revision - Physical Education Paper 1 Fitness and Body Systems Topic Areas for Revision Key questions 1.1 The structure and functions of the musculoskeletal s Functions of the Skeleton for
Year 10 GCSE Revision - Physical Education Paper 1 Fitness and Body Systems Topic Areas for Revision Key questions 1.1 The structure and functions of the musculoskeletal s Functions of the Skeleton for
Skeletal System Joints, Relationship with other systems
 Skeletal System Joints, Relationship with other systems Review the Types of Bones Articulations Classification of Joints (Articulations) Joint Where two bones interact Three functional classes of joint
Skeletal System Joints, Relationship with other systems Review the Types of Bones Articulations Classification of Joints (Articulations) Joint Where two bones interact Three functional classes of joint
OBJECTIVES. Unit 7:5 PROPERTIES OR CHARACTERISTICS OF MUSCLES. Introduction. 3 Kinds of Muscles. 3 Kinds of Muscles 4/17/2018 MUSCULAR SYSTEM
 OBJECTIVES Unit 7:5 MUSCULAR SYSTEM Compare the three main kinds of muscles by describing the action of each Differentiate between voluntary and involuntary muscles List at least three functions of muscles
OBJECTIVES Unit 7:5 MUSCULAR SYSTEM Compare the three main kinds of muscles by describing the action of each Differentiate between voluntary and involuntary muscles List at least three functions of muscles
Name: BLK. Anatomy Test.. Good Luck :)
 Name: BLK Anatomy Test.. Good Luck :) 1) A boy jumps into a cold swimming pool and his body temperature goes down. His muscles, blood vessels, and nervous system work together to restore his body temperature.which
Name: BLK Anatomy Test.. Good Luck :) 1) A boy jumps into a cold swimming pool and his body temperature goes down. His muscles, blood vessels, and nervous system work together to restore his body temperature.which
Level 2 Mock Paper Anatomy and Physiology For Exercise. Unit Accreditation Number H/600/9013
 MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION PAPER Paper number MPAPEH Please insert this reference number in the appropriate boxes on your candidate answer sheet Title Time allocation 60 minutes Level 2 Mock Paper Anatomy
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION PAPER Paper number MPAPEH Please insert this reference number in the appropriate boxes on your candidate answer sheet Title Time allocation 60 minutes Level 2 Mock Paper Anatomy
SUMMER WORK MRS KANSARA
 Name: A LEVEL PE Anatomy and Physiology SUMMER WORK MRS KANSARA Complete the following activities throughout the summer It is important that you understand and remember all the information included in
Name: A LEVEL PE Anatomy and Physiology SUMMER WORK MRS KANSARA Complete the following activities throughout the summer It is important that you understand and remember all the information included in
Major Functions of the Skeletal System
 Skeletal System Major Functions of the Skeletal System 1. Provide shape and support. 2. Enables you to move 3. Protects your organs 4. Produces blood cells 5. stores minerals and other materials until
Skeletal System Major Functions of the Skeletal System 1. Provide shape and support. 2. Enables you to move 3. Protects your organs 4. Produces blood cells 5. stores minerals and other materials until
THE MUSCULOSKELETAL SYSTEM Thompson Educational Publishing, Inc. 1
 THE MUSCULOSKELETAL SYSTEM 2015 Thompson Educational Publishing, Inc. 1 The Musculoskeletal System The musculoskeletal system consists of bones, joints, and muscles that provide support, and stability
THE MUSCULOSKELETAL SYSTEM 2015 Thompson Educational Publishing, Inc. 1 The Musculoskeletal System The musculoskeletal system consists of bones, joints, and muscles that provide support, and stability
Chapter 16. Human Anatomy
 Chapter 16 Human Anatomy Each System we will examine: Structures types Problems or health concerns How to care for that system Skeletal System Made up of bones, joints, connective tissue Is the frame for
Chapter 16 Human Anatomy Each System we will examine: Structures types Problems or health concerns How to care for that system Skeletal System Made up of bones, joints, connective tissue Is the frame for
Level 2 Anatomy and Physiology for Exercise and Fitness Instructors (K/616/7823) - Sample Assessment Student: XXXXXX Sample 3
 MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION PAPER Paper number: SAMPLE 3 Please ensure that this paper number is referenced on your candidate answer sheet Title: Student: XXXXXX Sample 3 Special Instructions: Level 2 Anatomy
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION PAPER Paper number: SAMPLE 3 Please ensure that this paper number is referenced on your candidate answer sheet Title: Student: XXXXXX Sample 3 Special Instructions: Level 2 Anatomy
The muscles in the body each fall into one of three groups:
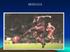 MUSCLES The muscles in the body each fall into one of three groups: 1. VOLUNTARY or SKELETAL MUSCLESthese muscles are under the control of our will. All these muscles are attached to the skeleton. These
MUSCLES The muscles in the body each fall into one of three groups: 1. VOLUNTARY or SKELETAL MUSCLESthese muscles are under the control of our will. All these muscles are attached to the skeleton. These
A Healthy, Active. Lifestyle and Your. Muscular System
 A Healthy, Active Lifestyle and Your Muscular System 1. Muscular System 2. Types of Muscle muscle - Smooth Muscle that works without consciousness. a. Arteries - The walls of the arteries contract and
A Healthy, Active Lifestyle and Your Muscular System 1. Muscular System 2. Types of Muscle muscle - Smooth Muscle that works without consciousness. a. Arteries - The walls of the arteries contract and
Unit 7: Skeletal and muscular systems
 Unit 7: Skeletal and muscular systems 1. The locomotor system 2. The skeletal system 2.1. The human skeleton 2.2. Bones 2.3. Joints 2.4. Tendons and ligaments 3. The muscular system 3.1. Muscles of the
Unit 7: Skeletal and muscular systems 1. The locomotor system 2. The skeletal system 2.1. The human skeleton 2.2. Bones 2.3. Joints 2.4. Tendons and ligaments 3. The muscular system 3.1. Muscles of the
SUPPORT, MOVEMENT AND LOCOMOTION
 SUPPORT, MOVEMENT AND LOCOMOTION Overview Bones Joints Antagonistic Muscles Forelimbs Bones Functions of the skeleton Locomotion The ability to move from place to place Support Holds the body off the ground
SUPPORT, MOVEMENT AND LOCOMOTION Overview Bones Joints Antagonistic Muscles Forelimbs Bones Functions of the skeleton Locomotion The ability to move from place to place Support Holds the body off the ground
Muscular System. IB Sports, exercise and health science 1.2
 Muscular System IB Sports, exercise and health science 1.2 Characteristics Common to Contractility-ability to shorten the muscles length Extensibility-ability to lengthen the muscles length Elasticity-muscle
Muscular System IB Sports, exercise and health science 1.2 Characteristics Common to Contractility-ability to shorten the muscles length Extensibility-ability to lengthen the muscles length Elasticity-muscle
Bodies and Systems. What is your body made of?
 What is your body made of? You might say that you are made of organs like skin and a heart. You might say that you are made of tissue, cells, or even atoms. All these answers are correct. Multicellular
What is your body made of? You might say that you are made of organs like skin and a heart. You might say that you are made of tissue, cells, or even atoms. All these answers are correct. Multicellular
The Human Body. Mrs. Green
 The Human Body Mrs. Green Bell Work Which of the following helps the body to cool down? a) Shivering b) Sweating c) Running a fever d) Taking a deep breath Which of the following is a function of the digestive
The Human Body Mrs. Green Bell Work Which of the following helps the body to cool down? a) Shivering b) Sweating c) Running a fever d) Taking a deep breath Which of the following is a function of the digestive
Level 2 Anatomy and Physiology for Exercise Assessment Workbook
 Fitness Instructor Level 2 Anatomy and Physiology for Exercise Assessment Workbook IMPORTANT: YOU MUST COMPLETE THE FOLLOWING DETAILS BEFORE RETURNING THIS WORKBOOK TO LIFETIME Name of learner: Email address:
Fitness Instructor Level 2 Anatomy and Physiology for Exercise Assessment Workbook IMPORTANT: YOU MUST COMPLETE THE FOLLOWING DETAILS BEFORE RETURNING THIS WORKBOOK TO LIFETIME Name of learner: Email address:
Revision Booklet Paper 1
 OCR GCSE Physical Education Paper 1 Revision Booklet Revision Booklet Paper 1 Name.. Tutor. Teacher.. 1 OCR GCSE Physical Education Paper 1 Revision Booklet Paper 1 Anatomy & Physiology About the Paper:
OCR GCSE Physical Education Paper 1 Revision Booklet Revision Booklet Paper 1 Name.. Tutor. Teacher.. 1 OCR GCSE Physical Education Paper 1 Revision Booklet Paper 1 Anatomy & Physiology About the Paper:
What type of tissue is this
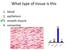 What type of tissue is this 1. blood 2. epithelium 3. smooth muscle 4. connective 83% 1 7% blood epithelium smooth muscle connective What type of tissue is this 1. connective 2. nervous 3. smooth muscle
What type of tissue is this 1. blood 2. epithelium 3. smooth muscle 4. connective 83% 1 7% blood epithelium smooth muscle connective What type of tissue is this 1. connective 2. nervous 3. smooth muscle
Table of Contents. Introduction to the Teacher...1. Body Organization...2 Cells, tissues, organs, and systems
 Table of Contents Table of Contents Introduction to the Teacher...1 Body Organization...2 Cells, tissues, organs, and systems...3 Purpose and parts of the skeletal system, bones, joints, cartilage, etc....8
Table of Contents Table of Contents Introduction to the Teacher...1 Body Organization...2 Cells, tissues, organs, and systems...3 Purpose and parts of the skeletal system, bones, joints, cartilage, etc....8
Chapter 19 Musculoskeletal
 Musculoskeletal System Chapter 19 Musculoskeletal System 1 Consists of Bones and Muscles Along with associated connective tissues Tendons, ligaments, cartilage Skeleton provides support to body and protection
Musculoskeletal System Chapter 19 Musculoskeletal System 1 Consists of Bones and Muscles Along with associated connective tissues Tendons, ligaments, cartilage Skeleton provides support to body and protection
Skeletal Considerations for Movement. Kinesiology RHS 341 Lecture 2 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa
 Skeletal Considerations for Movement Kinesiology RHS 341 Lecture 2 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa The Skeletal System Bones, cartilage, ligaments, & joints Consists of approximately 20% of total body weight Bone constitutes
Skeletal Considerations for Movement Kinesiology RHS 341 Lecture 2 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa The Skeletal System Bones, cartilage, ligaments, & joints Consists of approximately 20% of total body weight Bone constitutes
Muscular System. Jannet Musleh Zahra Omairat Namera Khan Aala Omer
 Muscular System Jannet Musleh Zahra Omairat Namera Khan Aala Omer I can: Learn about the Muscular system. Do now: What comes to mind when you hear Muscular system? Major Functions of the Muscular system.
Muscular System Jannet Musleh Zahra Omairat Namera Khan Aala Omer I can: Learn about the Muscular system. Do now: What comes to mind when you hear Muscular system? Major Functions of the Muscular system.
Mock Paper Level 2 Anatomy and Physiology for Exercise. Unit Reference Number H/600/9013
 MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION PAPER Paper number MPAPEH2.01 Please insert this reference number in the appropriate boxes on your candidate answer sheet Title Time allocation 60 minutes Mock Paper Level 2 Anatomy
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION PAPER Paper number MPAPEH2.01 Please insert this reference number in the appropriate boxes on your candidate answer sheet Title Time allocation 60 minutes Mock Paper Level 2 Anatomy
Heal a th t y h y B o B dy d Systems
 Chapter 16 Healthy Body Systems The Cell The smallest unit of structure in a living organism Robert Hooke Identified & coined the term Cell when he saw cork under the microscope He used a compound microscope
Chapter 16 Healthy Body Systems The Cell The smallest unit of structure in a living organism Robert Hooke Identified & coined the term Cell when he saw cork under the microscope He used a compound microscope
CHAPTER 4: The musculo-skeletal system. Practice questions - text book pages QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS. Answers
 CHAPTER 4: The musculo-skeletal system Practice questions - text book pages 64-66 1) A prime mover of hip flexion is the: a. rectus femoris. b. Iliopsoas. c. vastus muscles. d. gluteus maximus. b. Key
CHAPTER 4: The musculo-skeletal system Practice questions - text book pages 64-66 1) A prime mover of hip flexion is the: a. rectus femoris. b. Iliopsoas. c. vastus muscles. d. gluteus maximus. b. Key
The Musculoskeletal system
 Level 3 BTEC Applied Science Summer Homework The Musculoskeletal system Student name:.. Tutor name: 1 Student Instructions This workbook incorporates elements of Unit 8 Learning Aim A: Understand the impact
Level 3 BTEC Applied Science Summer Homework The Musculoskeletal system Student name:.. Tutor name: 1 Student Instructions This workbook incorporates elements of Unit 8 Learning Aim A: Understand the impact
Anatomy. Anatomy deals with the structure of the human body, and includes a precise language on body positions and relationships between body parts.
 Anatomy deals with the structure of the human body, and includes a precise language on body positions and relationships between body parts. Proper instruction on safe and efficient exercise technique requires
Anatomy deals with the structure of the human body, and includes a precise language on body positions and relationships between body parts. Proper instruction on safe and efficient exercise technique requires
Anatomy & Physiology. An Introduction
 Anatomy & Physiology An Introduction An Overview of Anatomy Anatomy - The study of the structure of the human body Physiology - The study of body function Branches of Anatomy Surface anatomy Gross anatomy
Anatomy & Physiology An Introduction An Overview of Anatomy Anatomy - The study of the structure of the human body Physiology - The study of body function Branches of Anatomy Surface anatomy Gross anatomy
LEVEL 3 DIPLOMA IN AROMATHERAPY MODULE 10 KNOWLEDGE OF ANATOMY, PHYSIOLOGY & PATHOLOGY FOR COMPLEMENTARY THERAPIES THE ARTICULAR SYSTEM COURSE MANUAL
 LEVEL 3 DIPLOMA IN AROMATHERAPY MODULE 10 KNOWLEDGE OF ANATOMY, PHYSIOLOGY & PATHOLOGY FOR COMPLEMENTARY THERAPIES THE ARTICULAR SYSTEM COURSE MANUAL CHRISTINA LYNE christina@aromalyne.com 1 THE ARTICULAR
LEVEL 3 DIPLOMA IN AROMATHERAPY MODULE 10 KNOWLEDGE OF ANATOMY, PHYSIOLOGY & PATHOLOGY FOR COMPLEMENTARY THERAPIES THE ARTICULAR SYSTEM COURSE MANUAL CHRISTINA LYNE christina@aromalyne.com 1 THE ARTICULAR
The Human Body. Lesson Goal. Lesson Objectives 9/10/2012. Provide a brief overview of body systems, anatomy, physiology, and topographic anatomy
 The Human Body Lesson Goal Provide a brief overview of body systems, anatomy, physiology, and topographic anatomy Medial Lateral Proximal Distal Superior Inferior Anterior Lesson Objectives Explain the
The Human Body Lesson Goal Provide a brief overview of body systems, anatomy, physiology, and topographic anatomy Medial Lateral Proximal Distal Superior Inferior Anterior Lesson Objectives Explain the
Boardworks Ltd Types of Synovial Joint
 1 of 37 Types of Synovial Joint Definition: 2 of 37 3 of 37 3. Freely movable or synovial joints 90% of the joints in the body are synovial joints. They are freely movable. Synovial joints contain synovial
1 of 37 Types of Synovial Joint Definition: 2 of 37 3 of 37 3. Freely movable or synovial joints 90% of the joints in the body are synovial joints. They are freely movable. Synovial joints contain synovial
Human Anatomy & Physiology
 Human Anatomy & Physiology Hey I thought those were the same thing! Nope they ain t Anatomy-Where everything is and to what it is connected. Physiology-How all that stuff works to keep you alive! Morphology-How
Human Anatomy & Physiology Hey I thought those were the same thing! Nope they ain t Anatomy-Where everything is and to what it is connected. Physiology-How all that stuff works to keep you alive! Morphology-How
What is homeostasis? How is the human body organized? What are the 11 different human organ systems?
 CHAPTER 22 1 Body Organization SECTION Body Organization and Structure BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is homeostasis? How is the human body
CHAPTER 22 1 Body Organization SECTION Body Organization and Structure BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is homeostasis? How is the human body
Edexcel GCSE Physical Education Revision and Examination Tips
 Edexcel GCSE Physical Education Revision and Examination Tips Benefits of a Healthy, Active lifestyle Unit 1 (Full and Short Course) Healthy Active Lifestyle = complete state of mental, physical and social
Edexcel GCSE Physical Education Revision and Examination Tips Benefits of a Healthy, Active lifestyle Unit 1 (Full and Short Course) Healthy Active Lifestyle = complete state of mental, physical and social
Locomotion: The act or power of moving from place to place
 Locomotion Locomotion: The act or power of moving from place to place Vocabulary 1. Motile = The ability to move from place to place 2. Sessile = 3. Muscle contraction = 4. Exoskeleton = 5. Endoskeleton
Locomotion Locomotion: The act or power of moving from place to place Vocabulary 1. Motile = The ability to move from place to place 2. Sessile = 3. Muscle contraction = 4. Exoskeleton = 5. Endoskeleton
1. Use the following words to complete the text below. Terms may be used more than once.
 THE NERVOUS AND MUSCULOSKELETAL SYSTEMS Nervous system, neuron, nerve impulse, peripheral nervous system, nerves STUDENT BOOK Ch. 7, pp. 202 206 1. Use the following words to complete the text below. Terms
THE NERVOUS AND MUSCULOSKELETAL SYSTEMS Nervous system, neuron, nerve impulse, peripheral nervous system, nerves STUDENT BOOK Ch. 7, pp. 202 206 1. Use the following words to complete the text below. Terms
Assignment 2: Human Anatomy
 Assignment 2: Human Anatomy Chapter 2 Quiz: How Much Do You Know About Anatomy? 1. Which of the following is not a feature of the anatomical position: A) The body stands erect. B) The body is facing forward.
Assignment 2: Human Anatomy Chapter 2 Quiz: How Much Do You Know About Anatomy? 1. Which of the following is not a feature of the anatomical position: A) The body stands erect. B) The body is facing forward.
Lecture 5. Skeletal and Muscular Systems. Skeletal and Muscular Systems. 1. Skeletal System Bones Cartilage Ligaments & Tendons Joints 2.
 Lecture 5 Skeletal and Muscular Systems 1 Skeletal and Muscular Systems 1. Skeletal System Bones Cartilage Ligaments & Tendons Joints 2. Muscles 2 1 Skeletal System 3 Functions of Skeleton Support of the
Lecture 5 Skeletal and Muscular Systems 1 Skeletal and Muscular Systems 1. Skeletal System Bones Cartilage Ligaments & Tendons Joints 2. Muscles 2 1 Skeletal System 3 Functions of Skeleton Support of the
Cells Tissues Organs Organ Systems Organism. A collection of the same type of cells working together to perform a function.
 Name the 5 Basic Levels of Organization in Living Things Cells Tissues Organs Organ Systems Organism What is HOMEOSTASIS? The process by which your body maintains a stable internal environment. What is
Name the 5 Basic Levels of Organization in Living Things Cells Tissues Organs Organ Systems Organism What is HOMEOSTASIS? The process by which your body maintains a stable internal environment. What is
Y12 Transition Pack Sports Leadership
 Y12 Transition Pack Sports Leadership Name: Base School: Section 1: The Muscular System Read through the following information on the Muscular System Cardiac muscle is unique to the heart. It never tires.
Y12 Transition Pack Sports Leadership Name: Base School: Section 1: The Muscular System Read through the following information on the Muscular System Cardiac muscle is unique to the heart. It never tires.
VCE PHYSICAL EDUCATION WORKBOOK UNIT 1 BODIES IN MOTION NAME:
 VCE PHYSICAL EDUCATION WORKBOOK UNIT 1 BODIES IN MOTION NAME: SKELETAL SYSTEM List the 5 functions of the skeletal system and complete the following table. FUNCTION DESCRIPTION Label the following features
VCE PHYSICAL EDUCATION WORKBOOK UNIT 1 BODIES IN MOTION NAME: SKELETAL SYSTEM List the 5 functions of the skeletal system and complete the following table. FUNCTION DESCRIPTION Label the following features
CHAPTER 1: 1.1 Muscular skeletal system. Question - text book page 16. Question - text book page 20 QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS. Answers
 QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS CHAPTER 1: 1.1 Muscular skeletal system Question - text book page 16 Using the information on pages 12 to 14 above, complete the table below. joint joint type articulating bones associated
QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS CHAPTER 1: 1.1 Muscular skeletal system Question - text book page 16 Using the information on pages 12 to 14 above, complete the table below. joint joint type articulating bones associated
WTC II Term 3 Notes & Assessments
 Term 3 Notes & Assessments Planes of Motion/Axes The body moves in a number of various ways and directions. In the past you have learned about the terminology for movements at specific joints, for example,
Term 3 Notes & Assessments Planes of Motion/Axes The body moves in a number of various ways and directions. In the past you have learned about the terminology for movements at specific joints, for example,
PE Improvement Targets
 PE Improvement Targets VCERT - Year 10 11 6. Ensure key words and terminology is used Try to use a variety sports related vocabulary in your answers. Below are vocabulary lists and brief teaching points
PE Improvement Targets VCERT - Year 10 11 6. Ensure key words and terminology is used Try to use a variety sports related vocabulary in your answers. Below are vocabulary lists and brief teaching points
1. Describe the main functions of the skeletal system that keep the body healthy and active. [4]
![1. Describe the main functions of the skeletal system that keep the body healthy and active. [4] 1. Describe the main functions of the skeletal system that keep the body healthy and active. [4]](/thumbs/79/80173575.jpg) GCSE PE Structured questions 1a Applied anatomy and physiology Understand the structure and functions of the skeleton 1. Describe the main functions of the skeletal system that keep the body healthy and
GCSE PE Structured questions 1a Applied anatomy and physiology Understand the structure and functions of the skeleton 1. Describe the main functions of the skeletal system that keep the body healthy and
Microanatomy, Physiology of Bone & Joints
 Microanatomy, Physiology of Bone & Joints The Skeleton There are 206 bones in the human body. The bones that are required in this syllabus are the cranium, mandible, clavicle, sternum, scapula, ribs, humerous,
Microanatomy, Physiology of Bone & Joints The Skeleton There are 206 bones in the human body. The bones that are required in this syllabus are the cranium, mandible, clavicle, sternum, scapula, ribs, humerous,
Chapter 22. Body Organization & Structure
 Chapter 22 Body Organization & Structure Start-Up Activity Too Cold for Comfort Hold a few pieces of ice in one hand. Hold the ice until the cold is uncomfortable. Then release the ice into the dish. Compare
Chapter 22 Body Organization & Structure Start-Up Activity Too Cold for Comfort Hold a few pieces of ice in one hand. Hold the ice until the cold is uncomfortable. Then release the ice into the dish. Compare
VCE PHYSICAL EDUCATION WORKBOOK UNIT 1 BODIES IN MOTION NAME:
 VCE PHYSICAL EDUCATION WORKBOOK UNIT 1 BODIES IN MOTION NAME: SKELETAL SYSTEM List the 5 functions of the skeletal system and complete the following table. FUNCTION DESCRIPTION Label the following features
VCE PHYSICAL EDUCATION WORKBOOK UNIT 1 BODIES IN MOTION NAME: SKELETAL SYSTEM List the 5 functions of the skeletal system and complete the following table. FUNCTION DESCRIPTION Label the following features
CHAPTER 14 Bones, Muscles, Skin
 CHAPTER 14 Bones, Muscles, Skin SECTION 1 Body Organization and Homeostasis Levels of Organization Basic to Complex Cells Tissues Organs Organ Systems CELLS Basic unit in living thing Main Parts: Cell
CHAPTER 14 Bones, Muscles, Skin SECTION 1 Body Organization and Homeostasis Levels of Organization Basic to Complex Cells Tissues Organs Organ Systems CELLS Basic unit in living thing Main Parts: Cell
Department of Science Second Term: Revision Worksheet - 1 L-1.6, 1.7 & 1.8 Muscles and bones
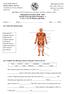 Department of Science 2018-2019 Second Term: Revision Worksheet - 1 L-1.6, 1.7 & 1.8 Muscles and bones Grade 4... Name:... Date:.../.../2019 Q.1 Label each muscle group. neck muscles shoulder muscles thigh
Department of Science 2018-2019 Second Term: Revision Worksheet - 1 L-1.6, 1.7 & 1.8 Muscles and bones Grade 4... Name:... Date:.../.../2019 Q.1 Label each muscle group. neck muscles shoulder muscles thigh
Lab Report Sheet. Title: Hypothesis (What I Think Will Happen) Materials (What We Used) Procedure (What We Did)
 Appendix 107 108 Lab Report Sheet Title: Hypothesis (What I Think Will Happen) Materials (What We Used) Procedure (What We Did) Observations and Results (What I Saw and Measured) Worksheet prepared by
Appendix 107 108 Lab Report Sheet Title: Hypothesis (What I Think Will Happen) Materials (What We Used) Procedure (What We Did) Observations and Results (What I Saw and Measured) Worksheet prepared by
GCSE PERSONAL LEARNING CHECKLIST PHYSICAL EDUCATION
 GCSE PERSONAL LEARNING CHECKLIST PHYSICAL EDUCATION PLC KEY: COMPONENT 1: FITNESS AND BODY SYSTEMS 1.1-4.1 You have covered the concept in lesson by the teacher. You have extended the concept in your file
GCSE PERSONAL LEARNING CHECKLIST PHYSICAL EDUCATION PLC KEY: COMPONENT 1: FITNESS AND BODY SYSTEMS 1.1-4.1 You have covered the concept in lesson by the teacher. You have extended the concept in your file
Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology. The Muscular System
 Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology The Muscular System The Muscular System Muscles are responsible for all types of body movement they contract or shorten and are the machine of the body Three basic
Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology The Muscular System The Muscular System Muscles are responsible for all types of body movement they contract or shorten and are the machine of the body Three basic
Nervous System. Functions Controls all body s functions Senses and recognizes information from inside and outside of the body
 Human Body Systems Nervous System Functions Controls all body s functions Senses and recognizes information from inside and outside of the body Nervous System Main Parts Brain Nerves Spinal cord What it
Human Body Systems Nervous System Functions Controls all body s functions Senses and recognizes information from inside and outside of the body Nervous System Main Parts Brain Nerves Spinal cord What it
Anatomy Review-INTRODUCTION. The study of the function of the body parts is called. Examples include:
 Anatomy Review-INTRODUCTION The study of the organs and parts of the body is called Examples include: The study of the function of the body parts is called. Examples include: Use the numbers from the diagram
Anatomy Review-INTRODUCTION The study of the organs and parts of the body is called Examples include: The study of the function of the body parts is called. Examples include: Use the numbers from the diagram
Muscular Strength and Endurance:
 PE 1- Assignment #5 6 1 Name: Per: Date: Teacher: STRESS BREAK Participating in physical activities that improve your self-esteem is a great way to deal with stress. The better you feel about yourself,
PE 1- Assignment #5 6 1 Name: Per: Date: Teacher: STRESS BREAK Participating in physical activities that improve your self-esteem is a great way to deal with stress. The better you feel about yourself,
Bodies and Systems. What is your body made of?
 What is your body made of? You might say that you are made of organs like skin and a heart. You might say that you are made of tissue, cells, or even atoms. All these answers are correct. Multicellular
What is your body made of? You might say that you are made of organs like skin and a heart. You might say that you are made of tissue, cells, or even atoms. All these answers are correct. Multicellular
Learning Objectives (1&2)
 Learning Objectives (1&2) By the end of the session, students should be able to: 1) Identify anatomical position seated, standing, prone, supine. 2) Pronounce, define and be able to use directional and
Learning Objectives (1&2) By the end of the session, students should be able to: 1) Identify anatomical position seated, standing, prone, supine. 2) Pronounce, define and be able to use directional and
S7L Which part of the body receives messages transmitted by nerve cells located throughout the body?
 S7L2-3 1. Which of the following is the heart's function? A. pumping blood B. breaking down food C. removing wastes from the blood D. taking in oxygen and releasing carbon dioxide 2. The body takes in
S7L2-3 1. Which of the following is the heart's function? A. pumping blood B. breaking down food C. removing wastes from the blood D. taking in oxygen and releasing carbon dioxide 2. The body takes in
Please do the following
 Please do the following 1. Read the Learners must know section (see below) 2. Watch the GCSE POD video 3. Attempt Exam Questions 4. Mark your answers 5. Reflect and repeat until you are successful and
Please do the following 1. Read the Learners must know section (see below) 2. Watch the GCSE POD video 3. Attempt Exam Questions 4. Mark your answers 5. Reflect and repeat until you are successful and
amygdala (ah MIG da la) a region of the brain involved in emotional memory, such as fear (SRB)
 FOSS Human Systems Interactions, Next Generation Edition Glossary abnormal different from what is usual (SRB) aerobic cellular respiration the process by which a cell releases energy using chemical reactions
FOSS Human Systems Interactions, Next Generation Edition Glossary abnormal different from what is usual (SRB) aerobic cellular respiration the process by which a cell releases energy using chemical reactions
1.1 The Structure and Functions of the Musculo- Skeletal System Teacher Answer Booklet
 GCSE EDEXCEL 1.1 1.1 The Structure and Functions of the Musculo- Skeletal System Teacher Answer Booklet GCSE EDEXCEL 1.1 WWW.THEPECLASSROOM.COM Topic Description from Specification Pupil comments How confident
GCSE EDEXCEL 1.1 1.1 The Structure and Functions of the Musculo- Skeletal System Teacher Answer Booklet GCSE EDEXCEL 1.1 WWW.THEPECLASSROOM.COM Topic Description from Specification Pupil comments How confident
Lifting your toes up towards your tibia would be an example of what movement around the ankle joint?
 NAME: TEST 1 ANATOMY IN SPORT SCIENCE: SEMESTER 1, 2017 TOTAL MARKS = 58 Total: / 58 marks Percentage: Grade: TERMINOLOGY: The structures that connect bone to bone are called: The ankle joint is to the
NAME: TEST 1 ANATOMY IN SPORT SCIENCE: SEMESTER 1, 2017 TOTAL MARKS = 58 Total: / 58 marks Percentage: Grade: TERMINOLOGY: The structures that connect bone to bone are called: The ankle joint is to the
REVIEW: Section 1: Human Organization and the chemistry of life A) Chemistry of life I. Elements II. Atoms III. Matter Matter
 REVIEW: Section 1: Human Organization and the chemistry of life A) Chemistry of life I. Elements Cannot be broken down by chemical means and still retain the same chemical and physical characteristics
REVIEW: Section 1: Human Organization and the chemistry of life A) Chemistry of life I. Elements Cannot be broken down by chemical means and still retain the same chemical and physical characteristics
Function of the skeleton
 Function of the skeleton Yr9 Biology Revision The skeleton has four main functions: to support the body to protect some of the vital organs of the body to help the body move to make blood cells Label the
Function of the skeleton Yr9 Biology Revision The skeleton has four main functions: to support the body to protect some of the vital organs of the body to help the body move to make blood cells Label the
Chapter 9 The body and its movement
 Chapter 9 The body and its movement 1) All living things are made up of cells. 2) Cells make up tissues, tissues make up organs, organs make up organ system and organ systems make up the human body. 3)
Chapter 9 The body and its movement 1) All living things are made up of cells. 2) Cells make up tissues, tissues make up organs, organs make up organ system and organ systems make up the human body. 3)
