Comparing Bones, Joints, and Muscles
|
|
|
- Lillian Black
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Chapter 36 Skeletal, Muscular, and Integumentary Systems Comparing Bones, Joints, and Muscles You may want to refer students to Chapter 36 in the textbook for a general discussion of skeletal and muscular systems. Time required: 40 minutes Introduction Bones contain both living and nonliving materials. The living part of bone tissue consists of bone cells surrounded by hard, nonliving materials such as the minerals calcium and phosphorus. Canals in the bone tissue contain blood vessels and nerves. Together with the muscular system, bones make movement possible. The bones are connected at junctions called joints. The human body has three types of muscle tissue. Skeletal muscle, or striated muscle, is used to move such body parts as the arms and legs. The second type of muscle, smooth muscle, is found in the walls of the digestive tract and of some blood vessels. The third type of muscle tissue, cardiac muscle, is found only in the heart. In this investigation you will study bone tissue, compare the movements of various joints, and compare the three types of muscle tissue. Problem What is the internal structure of bone? How do various joints move? What are the similarities and differences among the three types of muscle tissue? Pre-Lab Discussion Read the entire investigation. Then, work with a partner to answer the following questions. 1. a. What makes up the living tissue of bone? Bone cells. b.what makes up the nonliving part? Nonliving materials, such as the minerals calcium and phosphorous. 2. How does movement occur in the body? Muscle tissues are attached to bones. The muscle tissue contracts and moves the bones. 3. What types of joint movements are shown in Figure 2? Flexion, extension, abduction, adduction, rotation. 4. What would you expect the striations in skeletal and cardiac muscles to look like under a microscope? The striations will look like bands or stripes. Biology Laboratory Manual B/Chapter
2 5. In what part of the body can each of the three types of muscle tissue be found? Skeletal muscle tissue Smooth muscle tissue Cardiac muscle tissue Materials Any part of the body that requires voluntary movement. The digestive tract and walls of some blood muscles. The heart. compound light microscope prepared slide of human compact bone with Haversian system prepared slides of human skeletal, smooth, and cardiac muscle Safety Always handle the microscope with extreme care. You are responsible for its proper care and use. Use caution when handling microscope slides, as they can break easily and cut you. Be careful not to force any joint to move in a direction that is uncomfortable. Note all safety alert symbols and review the meaning of each symbol by referring to Safety Symbols on page 8. Procedure Part A. Bone Tissue 1. Observe a prepared slide of a compact bone section under the low-power objective lens of the microscope. CAUTION: Microscope slides break easily. 2. Switch to the high-power objective lens. CAUTION: When turning to the high-power objective lens, you should always look at the objective from the side of your microscope so that the objective lens does not hit or damage the slide. Locate the Haversian canals. Locate the osteocytes (bone cells) within the spaces between the layers of bone. Use Figure 1 as your guide. Draw and label what you see in the circle labeled Compact Bone. Record the magnification you use. Figure 1 Osteocyte Blood vessel Haversian canal Compact Bone 234 Biology Laboratory Manual B/Chapter 36
3 Part B. Joints and Movements 1. Study Figure 2, which shows the various movements that joints permit. 2. Have your partner try to move each of the joints listed in the Data Table on p For each joint, place a plus sign ( ) in the appropriate box to indicate that a type of movement is possible. Use a minus sign ( ) to indicate that a movement is not possible. CAUTION: Be careful not to force any movements. A Flexion Flexion the angle between the two bones decreases Extension the angle between the two bones increases Extension Abduction B Abduction a bone is moved away from the midline of the body Adduction a bone is moved toward the midline of the body Adduction Rotation a body part partially revolves on its axis Figure 2 C Rotation Biology Laboratory Manual B/Chapter
4 Data Table Joint Flexion Extension Adduction Abduction Rotation Neck Shoulder Elbow Wrist Finger Hip Knee Ankle Part C. Muscle Tissue 1. Obtain prepared slides of skeletal, smooth, and cardiac muscle. Observe each slide under the low-power objective lens of the microscope. 2. Switch to the high-power objective lens. CAUTION: When turning to the high-power objective lens, you should always look at the objective from the side of your microscope so that the objective lens does not hit or damage the slide. Make a sketch of each muscle type in the appropriate space. Skeletal Muscle Smooth Muscle Cardiac Muscle Analysis and Conclusions 1. Observing Where are the blood vessels found in bone tissue? They are found in the Haversian canals. 2. Inferring Why are the Haversian canals in bone tissue important to the living cells? The Haversian canals provide a way for the blood vessels to carry oxygen and nutrients to the living cells. 236 Biology Laboratory Manual B/Chapter 36
5 3. Observing Which joint(s) permit the most possible movement? Neck, shoulder, and hip. 4. Analyzing Data Which of the various movements do all of the joints in the Data Table permit? Flexion and extension. 5. Inferring Many athletes injure their knee joints. Suggest a reason for the fact that knee injuries are quite common. Knee joints move forward and backward in one plane. In many sports, knees may be twisted in other directions and thus injured. 6. Comparing and Contrasting How are skeletal muscle tissue and cardiac muscle tissue similar? How are they different? Both tissues have striations. Skeletal muscle tissue consists of long fibers that contain many nuclei. Cardiac muscle tissue has many branched cells. 7. Comparing and Contrasting How is smooth muscle tissue different from the other two types of muscle tissue? Smooth muscle tissue consists of small, spindle-shaped cells, each containing a nucleus. There are no striations in smooth muscle tissue. 8. Predicting What would you expect to happen to the striated bands in a skeletal muscle cell when the muscle contracts? The bands get closer together. Going Further Using reference materials, find out the different types of joints and where they are found in the body. Indicate the type of joint in the hip, knee, wrist, ankle, shoulder, elbow, and neck. Record this information in a data table. Biology Laboratory Manual B/Chapter
THe Skeletal System 1
 THe Skeletal System 1 What the Skeletal System DOes! Skeleton: works as the framework of your body and is made up of all of the bones in your body The number of bones in your skeleton depends on your age.
THe Skeletal System 1 What the Skeletal System DOes! Skeleton: works as the framework of your body and is made up of all of the bones in your body The number of bones in your skeleton depends on your age.
36.3 The Integumentary System The Skin. KEY CONCEPT The integumentary system has many tissues that protect the body.
 36.3 The Integumentary System The Skin KEY CONCEPT The integumentary system has many tissues that protect the body. 36.3 The Integumentary System The Skin The integument is the body system that surrounds
36.3 The Integumentary System The Skin KEY CONCEPT The integumentary system has many tissues that protect the body. 36.3 The Integumentary System The Skin The integument is the body system that surrounds
Major Functions of the Skeletal System
 Skeletal System Major Functions of the Skeletal System 1. Provide shape and support. 2. Enables you to move 3. Protects your organs 4. Produces blood cells 5. stores minerals and other materials until
Skeletal System Major Functions of the Skeletal System 1. Provide shape and support. 2. Enables you to move 3. Protects your organs 4. Produces blood cells 5. stores minerals and other materials until
What type of tissue is this
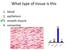 What type of tissue is this 1. blood 2. epithelium 3. smooth muscle 4. connective 83% 1 7% blood epithelium smooth muscle connective What type of tissue is this 1. connective 2. nervous 3. smooth muscle
What type of tissue is this 1. blood 2. epithelium 3. smooth muscle 4. connective 83% 1 7% blood epithelium smooth muscle connective What type of tissue is this 1. connective 2. nervous 3. smooth muscle
04/10/2013. Pick up a Human Body Book and PUT YOUR NAME ON IT!
 04/10/2013 Pick up a Human Body Book and PUT YOUR NAME ON IT! Did you know?? 1. The adult body is made up of: 100 trillion cells, 206 bones, 600 muscles, and 22 internal organs. 2. Every square inch of
04/10/2013 Pick up a Human Body Book and PUT YOUR NAME ON IT! Did you know?? 1. The adult body is made up of: 100 trillion cells, 206 bones, 600 muscles, and 22 internal organs. 2. Every square inch of
BODY SYSTEMS UNIT ANCHOR CHARTS:
 BODY SYSTEMS UNIT ANCHOR CHARTS: LEVELS OF ORGANIZATION smallest unit Cells Tissues Organs Organ Systems largest unit Body TISSUES IN THE HUMAN BODY Tissue Function Example Muscle makes parts of the body
BODY SYSTEMS UNIT ANCHOR CHARTS: LEVELS OF ORGANIZATION smallest unit Cells Tissues Organs Organ Systems largest unit Body TISSUES IN THE HUMAN BODY Tissue Function Example Muscle makes parts of the body
SKELETAL AND MUSCULAR SYSTEMS WHAT MOVES YOU!
 SKELETAL AND MUSCULAR SYSTEMS WHAT MOVES YOU! WHAT ARE THE MAIN FUNCTIONS OF THE SKELETAL SYSTEM? THE SKELETAL SYSTEM The skeletal system is the organ system that supports and protects the body and allows
SKELETAL AND MUSCULAR SYSTEMS WHAT MOVES YOU! WHAT ARE THE MAIN FUNCTIONS OF THE SKELETAL SYSTEM? THE SKELETAL SYSTEM The skeletal system is the organ system that supports and protects the body and allows
The Musculoskeletal System
 The Musculoskeletal System Introduction The skeletal system and muscular system are often considered together because they are close in terms of structure and function. The two systems are referred to
The Musculoskeletal System Introduction The skeletal system and muscular system are often considered together because they are close in terms of structure and function. The two systems are referred to
18/01/2015. Review Session 4. Concept 1: Fluids. Def: Anything that can flow and take shape of container. Two types: Compressible and Incompressible
 Review Session 4 PRESSURE, ORGANIZATION IN THE HUMAN BODY, MUSCU LOSK E LETAL SYSTEM Concept 1: Fluids Def: Anything that can flow and take shape of container Two types: Compressible and Incompressible
Review Session 4 PRESSURE, ORGANIZATION IN THE HUMAN BODY, MUSCU LOSK E LETAL SYSTEM Concept 1: Fluids Def: Anything that can flow and take shape of container Two types: Compressible and Incompressible
2º ESO - PE Workbook - IES Joan Miró Physical Education Department THE MUSCULAR SYSTEM
 THE MUSCULAR SYSTEM The muscular system is one of 10 organ systems in the human body. The human body has more than 650 muscles, which make up half of a person's body weight. Without muscles, we would not
THE MUSCULAR SYSTEM The muscular system is one of 10 organ systems in the human body. The human body has more than 650 muscles, which make up half of a person's body weight. Without muscles, we would not
THE SKELETAL, MUSCULAR AND INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEMS. Chapter 22 Sections
 THE SKELETAL, MUSCULAR AND INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEMS Chapter 22 Sections THE MUSCULAR SYSTEM Ch. 22 Section 3 (588-591) Muscles of the Body WHAT ARE THE THREE TYPES OF MUSCLES? 1.Skeletal muscle - move us
THE SKELETAL, MUSCULAR AND INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEMS Chapter 22 Sections THE MUSCULAR SYSTEM Ch. 22 Section 3 (588-591) Muscles of the Body WHAT ARE THE THREE TYPES OF MUSCLES? 1.Skeletal muscle - move us
Unit 7: Skeletal and muscular systems
 Unit 7: Skeletal and muscular systems 1. The locomotor system 2. The skeletal system 2.1. The human skeleton 2.2. Bones 2.3. Joints 2.4. Tendons and ligaments 3. The muscular system 3.1. Muscles of the
Unit 7: Skeletal and muscular systems 1. The locomotor system 2. The skeletal system 2.1. The human skeleton 2.2. Bones 2.3. Joints 2.4. Tendons and ligaments 3. The muscular system 3.1. Muscles of the
33.2. Muscular System. Humans have three types of muscle.
 33.2 Muscular System VOCABULARY muscular system muscle fiber skeletal muscle tendon smooth muscle cardiac muscle myofibril sarcomere 10A, 10C, 11A Key Concept Muscles are tissues that can contract, enabling
33.2 Muscular System VOCABULARY muscular system muscle fiber skeletal muscle tendon smooth muscle cardiac muscle myofibril sarcomere 10A, 10C, 11A Key Concept Muscles are tissues that can contract, enabling
December 3, Name five bones in your body. Are bones living or dead? Explain. What is the function of bone marrow?
 December 3, 2013 Name five bones in your body. Are bones living or dead? Explain. What is the function of bone marrow? Skeletal, Muscular, and Integumentary Systems Chapter 36: Biology II The Skeleton
December 3, 2013 Name five bones in your body. Are bones living or dead? Explain. What is the function of bone marrow? Skeletal, Muscular, and Integumentary Systems Chapter 36: Biology II The Skeleton
Anatomy. Anatomy deals with the structure of the human body, and includes a precise language on body positions and relationships between body parts.
 Anatomy deals with the structure of the human body, and includes a precise language on body positions and relationships between body parts. Proper instruction on safe and efficient exercise technique requires
Anatomy deals with the structure of the human body, and includes a precise language on body positions and relationships between body parts. Proper instruction on safe and efficient exercise technique requires
Experiment Note the locations of the epidermis, dermis, dermal papillae, and the sweat glands. Note that fat cells that comprise the
 Experiment 1 Examining Skin, Bones and Muscle Histology Experiment Inventory Skin Digital Slide Images Cortical (Compact) Bone Digital Slide Image Trabecular (Spongy) Bone Digital Slide Image Cardiac Muscle
Experiment 1 Examining Skin, Bones and Muscle Histology Experiment Inventory Skin Digital Slide Images Cortical (Compact) Bone Digital Slide Image Trabecular (Spongy) Bone Digital Slide Image Cardiac Muscle
LECTURE TOPIC ASSIGNMENTS
 BASICS LECTURE TOPIC ASSIGNMENTS LECTURE TOPIC: ANATOMICAL TERMINOLOGY Read the textbook: Ch. 1: The Human Body: An Orientation Go To: Web Site > Folder: AnatTerm > A25terms09.pdf. Download the file &
BASICS LECTURE TOPIC ASSIGNMENTS LECTURE TOPIC: ANATOMICAL TERMINOLOGY Read the textbook: Ch. 1: The Human Body: An Orientation Go To: Web Site > Folder: AnatTerm > A25terms09.pdf. Download the file &
Outline. Bio 105: Tissues Laboratory. Organization of the Human Body. Tissue - Epithelium. Tissues 3/2/ Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc
 Outline Bio 105: Tissues Laboratory Laboratory 5 Reading: Chapter 4 I. Cell to cell contact II. Body Cavities III. Membranes IV. Homeostasis V. Integumentary System I. Includes skin, hair and nails 1 2
Outline Bio 105: Tissues Laboratory Laboratory 5 Reading: Chapter 4 I. Cell to cell contact II. Body Cavities III. Membranes IV. Homeostasis V. Integumentary System I. Includes skin, hair and nails 1 2
OBJECTIVES. Unit 7:5 PROPERTIES OR CHARACTERISTICS OF MUSCLES. Introduction. 3 Kinds of Muscles. 3 Kinds of Muscles 4/17/2018 MUSCULAR SYSTEM
 OBJECTIVES Unit 7:5 MUSCULAR SYSTEM Compare the three main kinds of muscles by describing the action of each Differentiate between voluntary and involuntary muscles List at least three functions of muscles
OBJECTIVES Unit 7:5 MUSCULAR SYSTEM Compare the three main kinds of muscles by describing the action of each Differentiate between voluntary and involuntary muscles List at least three functions of muscles
A&P 1 Muscle Lab #1 - Muscle Tissue, Muscle Types, and Movement Terms Pre-lab Exercises
 1 A&P 1 Muscle Lab #1 - Muscle Tissue, Muscle Types, and Movement Terms Pre-lab Exercises Have someone in your group read the following out loud, while the others read along: In this "Lab Exercise Guide",
1 A&P 1 Muscle Lab #1 - Muscle Tissue, Muscle Types, and Movement Terms Pre-lab Exercises Have someone in your group read the following out loud, while the others read along: In this "Lab Exercise Guide",
Lab Exercise 8. BIOPAC Exercise. Muscle Tissue. Muscles. What you need to be able to do on the exam after completing this lab exercise:
 Lab Exercise 8 BIOPAC Exercise Muscle Tissue Muscles Textbook Reference: See Chapters 9 & 10 What you need to be able to do on the exam after completing this lab exercise: Be able to answer questions covering
Lab Exercise 8 BIOPAC Exercise Muscle Tissue Muscles Textbook Reference: See Chapters 9 & 10 What you need to be able to do on the exam after completing this lab exercise: Be able to answer questions covering
Why are cells shaped the way they are?
 Why are cells shaped the way they are? # 1 Cheek Cells These cells were gently scraped from the inner surface of a person s cheek, and placed on a microscope slide. The cheek lining cells are thin and
Why are cells shaped the way they are? # 1 Cheek Cells These cells were gently scraped from the inner surface of a person s cheek, and placed on a microscope slide. The cheek lining cells are thin and
High School Biology - Problem Drill 20: Skeletal, Muscular, and Integumentary Systems
 High School Biology - Problem Drill 20: Skeletal, Muscular, and Integumentary Systems Question No. 1 of 10 Which of the following about the skeletal system is true? Question #01 A. There are two types
High School Biology - Problem Drill 20: Skeletal, Muscular, and Integumentary Systems Question No. 1 of 10 Which of the following about the skeletal system is true? Question #01 A. There are two types
CHAPTER 14. Bones Muscles Skin
 CHAPTER 14 Bones Muscles Skin Chapter 14 Objectives Section 1 Body Organization and Homeostasis 1. Define homeostasis and a give a specific example. 2. Explain why energy is important to the human body.
CHAPTER 14 Bones Muscles Skin Chapter 14 Objectives Section 1 Body Organization and Homeostasis 1. Define homeostasis and a give a specific example. 2. Explain why energy is important to the human body.
Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology. The Muscular System
 Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology The Muscular System The Muscular System Muscles are responsible for all types of body movement they contract or shorten and are the machine of the body Three basic
Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology The Muscular System The Muscular System Muscles are responsible for all types of body movement they contract or shorten and are the machine of the body Three basic
Muscular system MOVE ME!
 Muscular system MOVE ME! MUSCLES Day 1 Nov 13 and 16 TYPES OF MUSCLES, STRUCTURE AND FUNCTIONS. FUNCTIONS of MUSCLE Movement Maintains posture Stabilize joints Generates heat Byproduct of muscular contraction
Muscular system MOVE ME! MUSCLES Day 1 Nov 13 and 16 TYPES OF MUSCLES, STRUCTURE AND FUNCTIONS. FUNCTIONS of MUSCLE Movement Maintains posture Stabilize joints Generates heat Byproduct of muscular contraction
Chapter 7 The Muscular System. Mosby items and derived items 2012 by Mosby, Inc., an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. 1
 Chapter 7 The Muscular System Mosby items and derived items 2012 by Mosby, Inc., an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. 1 INTRODUCTION A. Muscular tissue enables the body and its parts to move 1. Three types of
Chapter 7 The Muscular System Mosby items and derived items 2012 by Mosby, Inc., an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. 1 INTRODUCTION A. Muscular tissue enables the body and its parts to move 1. Three types of
Lab Animal Tissue. LEARNING OBJECTIVES: To understand the relationship between the structure and function of different animal tissues
 Name: Bio A.P. PURPOSE: HYPOTHESIS: NONE Lab Animal Tissue BACKGROUND: In animals, groups of closely related cells specialized to perform the same function are called tissues. There are four general classes
Name: Bio A.P. PURPOSE: HYPOTHESIS: NONE Lab Animal Tissue BACKGROUND: In animals, groups of closely related cells specialized to perform the same function are called tissues. There are four general classes
or Everything you ever wanted to know about Muscles, but were afraid to ask!!!
 The Muscular System or Everything you ever wanted to know about Muscles, but were afraid to ask!!! Did you know that? - more than 50% of body weight is muscle! - And muscle is made up of proteins and water
The Muscular System or Everything you ever wanted to know about Muscles, but were afraid to ask!!! Did you know that? - more than 50% of body weight is muscle! - And muscle is made up of proteins and water
Yoga Anatomy & Physiology
 Yoga Anatomy & Physiology Anatomy & Physiology Anatomy- One of the basic essential sciences of medicine that studies the structure of an organism. Physiology- The biological study of the functions of living
Yoga Anatomy & Physiology Anatomy & Physiology Anatomy- One of the basic essential sciences of medicine that studies the structure of an organism. Physiology- The biological study of the functions of living
The Muscular System. Muscles are. There are more than 600 muscles in the Human Body!!! Needed for all types of movement. Needed to pump blood
 The Muscular System There are more than 600 muscles in the Human Body!!! Muscles are Needed for all types of movement. Needed to pump blood Needed to breathe (diaphragm muscle). Needed to produce body
The Muscular System There are more than 600 muscles in the Human Body!!! Muscles are Needed for all types of movement. Needed to pump blood Needed to breathe (diaphragm muscle). Needed to produce body
Skeletal, Muscular, and Integumentary Systems 929
 The Muscular System Key Questions What are the principal types of muscle tissue? How do muscles contract? How do muscle contractions produce movement? Vocabulary muscle fiber myofibril myosin actin sarcomere
The Muscular System Key Questions What are the principal types of muscle tissue? How do muscles contract? How do muscle contractions produce movement? Vocabulary muscle fiber myofibril myosin actin sarcomere
Chp. 6: Bones and Skeletal Tissue Student Worksheet. 1. The skeletal system is composed of bones,,, and.
 Chp. 6: Bones and Skeletal Tissue Student Worksheet 1. The skeletal system is composed of bones,,, and. 2. What are 5 functions of the skeletal system? 3. Besides osseous tissue (connective tissue with
Chp. 6: Bones and Skeletal Tissue Student Worksheet 1. The skeletal system is composed of bones,,, and. 2. What are 5 functions of the skeletal system? 3. Besides osseous tissue (connective tissue with
LAB: The Skeletal System System
 WLHS/A&P/Oppelt Name LAB: The Skeletal System System Background: The skeletal system is primarily responsible for supporting the body and protecting vital organs. We are bone with more than 270 bones that
WLHS/A&P/Oppelt Name LAB: The Skeletal System System Background: The skeletal system is primarily responsible for supporting the body and protecting vital organs. We are bone with more than 270 bones that
PHYSICAL EDUCATION. 4º E.S.O. 2nd TERM. The skeletal and muscular systems.
 PHYSICAL EDUCATION 4º E.S.O. 2nd TERM. The skeletal and muscular systems. PARTS OF THE BODY Head Torso / Trunk Dorsal: Back Ventral: Thorax y Abdomen Extremities Superior: Arm Forearm Hand Joint: Shoulder
PHYSICAL EDUCATION 4º E.S.O. 2nd TERM. The skeletal and muscular systems. PARTS OF THE BODY Head Torso / Trunk Dorsal: Back Ventral: Thorax y Abdomen Extremities Superior: Arm Forearm Hand Joint: Shoulder
Human Anatomy and Physiology I Laboratory
 Human Anatomy and Physiology I Laboratory Microscopic Anatomy and Organization of Skeletal Muscle This lab involves study of the laboratory exercise Microscopic Anatomy and Organization of Skeletal Muscle,
Human Anatomy and Physiology I Laboratory Microscopic Anatomy and Organization of Skeletal Muscle This lab involves study of the laboratory exercise Microscopic Anatomy and Organization of Skeletal Muscle,
Muscular System. IB Sports, exercise and health science 1.2
 Muscular System IB Sports, exercise and health science 1.2 Characteristics Common to Contractility-ability to shorten the muscles length Extensibility-ability to lengthen the muscles length Elasticity-muscle
Muscular System IB Sports, exercise and health science 1.2 Characteristics Common to Contractility-ability to shorten the muscles length Extensibility-ability to lengthen the muscles length Elasticity-muscle
Lab Exercise 6a-2. Classification of connective tissues. Connective Tissue. Connective tissues. Areolar. Areolar tissue
 Classification of connective tissues Lab Exercise 6a-2 Connective Tissue Nervous Muscle Connective Tissue Connective tissues Connective tissue proper Fluid connective tissue Supportive connecting tissue
Classification of connective tissues Lab Exercise 6a-2 Connective Tissue Nervous Muscle Connective Tissue Connective tissues Connective tissue proper Fluid connective tissue Supportive connecting tissue
33.1. Skeletal System. Your skeletal system is made up of the appendicular and axial skeletons.
 33.1 Skeletal System VOCABULARY skeletal system appendicular skeleton axial skeleton vertebrae cartilage joint ligament calcification Key Concept The skeletal system includes bones and tissues that are
33.1 Skeletal System VOCABULARY skeletal system appendicular skeleton axial skeleton vertebrae cartilage joint ligament calcification Key Concept The skeletal system includes bones and tissues that are
In Activity 12, What s Happening Inside? you learned about the functions
 16 Support System: Bones, Joints and Muscles l a b o r at o ry In Activity 12, What s Happening Inside? you learned about the functions of the skeletal and muscular systems in supporting and moving your
16 Support System: Bones, Joints and Muscles l a b o r at o ry In Activity 12, What s Happening Inside? you learned about the functions of the skeletal and muscular systems in supporting and moving your
Anatomy & Physiology B. Chapter 6: Muscles
 Anatomy & Physiology B Chapter 6: Muscles Warm-up What are the three types of muscle tissue? Where are each located? Which are voluntary and which are involuntary? Which are striated which are unstriated?
Anatomy & Physiology B Chapter 6: Muscles Warm-up What are the three types of muscle tissue? Where are each located? Which are voluntary and which are involuntary? Which are striated which are unstriated?
STUDY GUIDE a comprehensive review of the:
 STUDY GUIDE a comprehensive review of the: NFPT PERSONAL FITNESS TRAINERMANUAL Study & Reference: The Fundamentals for the CERTIFIED PERSONAL TRAINERR (CPT) Third Edition 2015 All Rights Reserved National
STUDY GUIDE a comprehensive review of the: NFPT PERSONAL FITNESS TRAINERMANUAL Study & Reference: The Fundamentals for the CERTIFIED PERSONAL TRAINERR (CPT) Third Edition 2015 All Rights Reserved National
Skeletal Muscle. Move your bones. Voluntary ( ) Over. Long. Cardiac Muscle. The muscle of the heart. Involuntary ( ) Works. Strongest. Only.
 Muscular System Tour Name Hour Skeletal Muscle Move your bones. Muscular System There are more than muscles in the Human Body!!! Muscles are: Voluntary ( ) Over Needed for Needed for Needed for Needed
Muscular System Tour Name Hour Skeletal Muscle Move your bones. Muscular System There are more than muscles in the Human Body!!! Muscles are: Voluntary ( ) Over Needed for Needed for Needed for Needed
The Muscular System. Myology the study of muscles
 The Muscular System Myology the study of muscles Functions of muscles: 1. Movement 2. Stability /support posture 3. Heat production 85% of our body heat 4. Communication 5. Constriction of organs and vessels
The Muscular System Myology the study of muscles Functions of muscles: 1. Movement 2. Stability /support posture 3. Heat production 85% of our body heat 4. Communication 5. Constriction of organs and vessels
Copyright Glencoe/McGraw-Hill, a division of the McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Name Date Class Structure and Movement 33 Chapter 17 Structure and
 Copyright Glencoe/McGraw-Hill, a division of the McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Name Date Class Structure and Movement 33 Chapter 17 Structure and Movement Section 1 The Skeletal System A. All the in your
Copyright Glencoe/McGraw-Hill, a division of the McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Name Date Class Structure and Movement 33 Chapter 17 Structure and Movement Section 1 The Skeletal System A. All the in your
Connective Tissue Nervous Muscle. Classification of connective tissues
 Connective Tissue Nervous Muscle Lab Exercise 6a-2 Classification of connective tissues 1 Connective Tissue Connective tissue proper Fluid connective tissue Supportive connecting tissue Connective tissues
Connective Tissue Nervous Muscle Lab Exercise 6a-2 Classification of connective tissues 1 Connective Tissue Connective tissue proper Fluid connective tissue Supportive connecting tissue Connective tissues
THE MUSCULAR SYSTEM FUNCTION OF MUSCLES
 FUNCTION OF MUSCLES THE MUSCULAR SYSTEM The 600 muscles in your body that function to move the skeleton are called skeletal muscles. The skeletal muscles make up the voluntary muscle system. They are called
FUNCTION OF MUSCLES THE MUSCULAR SYSTEM The 600 muscles in your body that function to move the skeleton are called skeletal muscles. The skeletal muscles make up the voluntary muscle system. They are called
The Skeletal System (Lexile 930L)
 7.12: Systems of the Human ody The Skeletal System (Lexile 930L) 1 id you know that babies are born with a total of 350 bones, compared to an adult with about 206 of them? The infant bones fuse as the
7.12: Systems of the Human ody The Skeletal System (Lexile 930L) 1 id you know that babies are born with a total of 350 bones, compared to an adult with about 206 of them? The infant bones fuse as the
Skin. the largest organ of the body 1 mm to 2 mm thick almost 2 square meters 6% of a person s body weight
 Skin the largest organ of the body 1 mm to 2 mm thick almost 2 square meters 6% of a person s body weight Functions of the Skin protection disease-causing organisms dangerous chemicals blood loss fluid
Skin the largest organ of the body 1 mm to 2 mm thick almost 2 square meters 6% of a person s body weight Functions of the Skin protection disease-causing organisms dangerous chemicals blood loss fluid
Shoulder Rehab Program
 Range of Stage A Motion 1 External rotation Lying on your back, with elbows bent at right angles and held in against your body. Hold a stick with both hands and using your unaffected side push your other
Range of Stage A Motion 1 External rotation Lying on your back, with elbows bent at right angles and held in against your body. Hold a stick with both hands and using your unaffected side push your other
Muscular System. I. Introduction. A. Over 600 muscles make up muscular system. B. 45% of total body weight of an adult. C.
 I. Introduction A. Over 600 muscles make up muscular system B. 45% of total body weight of an adult C. Properties 1. Excitability: ability to receive and respond to a stimulus a. Skeletal muscle responds
I. Introduction A. Over 600 muscles make up muscular system B. 45% of total body weight of an adult C. Properties 1. Excitability: ability to receive and respond to a stimulus a. Skeletal muscle responds
HOLE S ANATOMY CHAPTER 5, PART II Lecture notes
 HOLE S ANATOMY CHAPTER 5, PART II Lecture notes I. Connective Tissue A. Structure 1. have few cells that are spaced apart and can divide; two categories: a. fixed cells cells that are present in tissue
HOLE S ANATOMY CHAPTER 5, PART II Lecture notes I. Connective Tissue A. Structure 1. have few cells that are spaced apart and can divide; two categories: a. fixed cells cells that are present in tissue
BIOLOGY - CLUTCH CH.49 - MUSCLE SYSTEMS.
 !! www.clutchprep.com BIOLOGY - CLUTCH Muscle system organ system that includes skeletal, cardiac, and smooth muscle Muscle tissue capable of contracting through the interaction of actin and myosin proteins
!! www.clutchprep.com BIOLOGY - CLUTCH Muscle system organ system that includes skeletal, cardiac, and smooth muscle Muscle tissue capable of contracting through the interaction of actin and myosin proteins
On The Road. Training Manual
 On The Road Training Manual ST - 1 Standing External Rotation Strength Training Injury prevention Strengthening the rotator cuff Attach the tubing to a secure location like a fence or the net post. Start
On The Road Training Manual ST - 1 Standing External Rotation Strength Training Injury prevention Strengthening the rotator cuff Attach the tubing to a secure location like a fence or the net post. Start
HASPI Medical Anatomy & Physiology 08a Lab Activity
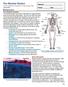 HASPI Medical Anatomy & Physiology 08a Lab Activity Name(s): Period: Date: The Skeletal System The skeletal system is primarily responsible for supporting the body and protecting vital organs. We are born
HASPI Medical Anatomy & Physiology 08a Lab Activity Name(s): Period: Date: The Skeletal System The skeletal system is primarily responsible for supporting the body and protecting vital organs. We are born
REVISION BOOKLET. The Body Systems
 REVISION BOOKLET The Body Systems GCSE PE 2016 Skeletal System Functions of the skeleton Joints for movement Muscle attachment Protection of vital organs Red and white blood cell production platelets Storage
REVISION BOOKLET The Body Systems GCSE PE 2016 Skeletal System Functions of the skeleton Joints for movement Muscle attachment Protection of vital organs Red and white blood cell production platelets Storage
Certified Personal Trainer Re-Certification Manual
 Certified Personal Trainer Re-Certification Manual Section II 1 Anatomy & Physiology Terms Anatomy and physiology are closely related fields of study: anatomy is the study of form, and physiology is the
Certified Personal Trainer Re-Certification Manual Section II 1 Anatomy & Physiology Terms Anatomy and physiology are closely related fields of study: anatomy is the study of form, and physiology is the
HASPI Medical Anatomy & Physiology 09a Lab Activity
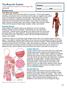 HASPI Medical Anatomy & Physiology 09a Lab Activity Name(s): Period: Date: http://www.fallingpixel.com/products/33817/mains/0000-malemuscular_1.jpg The Muscular System The main function of the muscular
HASPI Medical Anatomy & Physiology 09a Lab Activity Name(s): Period: Date: http://www.fallingpixel.com/products/33817/mains/0000-malemuscular_1.jpg The Muscular System The main function of the muscular
Table of Contents. Introduction to the Teacher...1. Body Organization...2 Cells, tissues, organs, and systems
 Table of Contents Table of Contents Introduction to the Teacher...1 Body Organization...2 Cells, tissues, organs, and systems...3 Purpose and parts of the skeletal system, bones, joints, cartilage, etc....8
Table of Contents Table of Contents Introduction to the Teacher...1 Body Organization...2 Cells, tissues, organs, and systems...3 Purpose and parts of the skeletal system, bones, joints, cartilage, etc....8
Microanatomy, Physiology of Bone & Joints
 Microanatomy, Physiology of Bone & Joints The Skeleton There are 206 bones in the human body. The bones that are required in this syllabus are the cranium, mandible, clavicle, sternum, scapula, ribs, humerous,
Microanatomy, Physiology of Bone & Joints The Skeleton There are 206 bones in the human body. The bones that are required in this syllabus are the cranium, mandible, clavicle, sternum, scapula, ribs, humerous,
Muscular System. Human A & P
 Muscular System Human A & P There are 3 types of muscle tissue: A. Skeletal B. Smooth C. Cardiac The essential function of a muscle is contraction, or shortening, and are responsible for essentially all
Muscular System Human A & P There are 3 types of muscle tissue: A. Skeletal B. Smooth C. Cardiac The essential function of a muscle is contraction, or shortening, and are responsible for essentially all
Muscle Tissue. Isometric Contraction. Isotonic Contractions 11/22/2016. Muscles. Anatomy Two Joints And Movements
 Muscles Anatomy Two Joints And Movements Structure of a Muscle Organ Copyright 2008 by Saunders Muscle Tissue Highly elastic and vascularized, produces movement through elongation and contraction Types
Muscles Anatomy Two Joints And Movements Structure of a Muscle Organ Copyright 2008 by Saunders Muscle Tissue Highly elastic and vascularized, produces movement through elongation and contraction Types
Chapter 9 The body and its movement
 Chapter 9 The body and its movement 1) All living things are made up of cells. 2) Cells make up tissues, tissues make up organs, organs make up organ system and organ systems make up the human body. 3)
Chapter 9 The body and its movement 1) All living things are made up of cells. 2) Cells make up tissues, tissues make up organs, organs make up organ system and organ systems make up the human body. 3)
Unit I Problem 5 Anatomy: Types of Movements and Joints
 Unit I Problem 5 Anatomy: Types of Movements and Joints - Anatomical position: The person is standing erect, with the upper limbs by the sides and the face and palms of the hands directed forward. - Imaginary
Unit I Problem 5 Anatomy: Types of Movements and Joints - Anatomical position: The person is standing erect, with the upper limbs by the sides and the face and palms of the hands directed forward. - Imaginary
Muscular System- Part 1. Unit 5 Miss Wheeler
 Muscular System- Part 1 Unit 5 Miss Wheeler Fun Facts! The tongue is the strongest muscle in your body The smallest muscles in the body are in the middle ear The largest muscle in the body is the gluteus
Muscular System- Part 1 Unit 5 Miss Wheeler Fun Facts! The tongue is the strongest muscle in your body The smallest muscles in the body are in the middle ear The largest muscle in the body is the gluteus
A Single Neuron from the Brain
 Nervous Tissue A Single Neuron from the Brain Dendrites Cell Body Axon Nerve cells, called neurons, transmit signals throughout our bodies. These signals tell our bodies what to do. Dendrites transmit
Nervous Tissue A Single Neuron from the Brain Dendrites Cell Body Axon Nerve cells, called neurons, transmit signals throughout our bodies. These signals tell our bodies what to do. Dendrites transmit
K cgs^rt??*?s?^ss?y?^5^'^isi5^^s. CXCB0033Q5»B,0'f?'r'''?'-i".l".lt''17Sro3R3: i^ti<i^<^"l'ixl>i, 'l:l"l333ssa;i
 ^yi^ ^ K M@»jmf What is the muscular system? teiteftrtttkssossi g'^sfissffi^^&^^s^s^sss^^s^^^^s^s'iwi'?'1!^"! ScoSS tisf8^ff^i^^^^^^^^5:t^wf7 r^^si^^ffr WW^W^^ ^^ cgs^rt??*?s?^ss?y?^5^'^isi5^^s row;i3wul)a3toi6ifi!3w?i
^yi^ ^ K M@»jmf What is the muscular system? teiteftrtttkssossi g'^sfissffi^^&^^s^s^sss^^s^^^^s^s'iwi'?'1!^"! ScoSS tisf8^ff^i^^^^^^^^5:t^wf7 r^^si^^ffr WW^W^^ ^^ cgs^rt??*?s?^ss?y?^5^'^isi5^^s row;i3wul)a3toi6ifi!3w?i
The Muscular System. Specialized tissue that enable the body and its parts to move.
 The Muscular System Specialized tissue that enable the body and its parts to move. Anterior View Posterior View TRIVIA! How many muscles are there in the human body? Answer: 640 Muscles The muscles make
The Muscular System Specialized tissue that enable the body and its parts to move. Anterior View Posterior View TRIVIA! How many muscles are there in the human body? Answer: 640 Muscles The muscles make
For more information, and to purchase the complete book on Warrior Fitness, please see
 Hello, Warrior! Here is your free sample chapter on Joint Mobility from Warrior Fitness. Work these exercises on a daily basis as a morning wake up, or use them as a warm-up for a more strenuous workout.
Hello, Warrior! Here is your free sample chapter on Joint Mobility from Warrior Fitness. Work these exercises on a daily basis as a morning wake up, or use them as a warm-up for a more strenuous workout.
Maximal isokinetic and isometric muscle strength of major muscle groups related to age, body weight, height, and sex in 178 healthy subjects
 Maximal isokinetic and isometric muscle strength of major muscle groups related to age, body weight, height, and sex in 178 healthy subjects Test protocol Muscle test procedures. Prior to each test participants
Maximal isokinetic and isometric muscle strength of major muscle groups related to age, body weight, height, and sex in 178 healthy subjects Test protocol Muscle test procedures. Prior to each test participants
Phase II Health Sciences as Applied to Coaching.
 Phase II Health Sciences as Applied to Coaching www.topform.us Overview What is going to be covered today is.. Skeletal System Muscular System Most common injuries to know about in your sport Part One:
Phase II Health Sciences as Applied to Coaching www.topform.us Overview What is going to be covered today is.. Skeletal System Muscular System Most common injuries to know about in your sport Part One:
36 1 The Skeletal System Slide 1 of 40
 1 of 40 The Skeleton All organisms need structural support. Unicellular organisms have a cytoskeleton. Multicellular animals have either an exoskeleton (arthropods) or an endoskeleton (vertebrates). 2
1 of 40 The Skeleton All organisms need structural support. Unicellular organisms have a cytoskeleton. Multicellular animals have either an exoskeleton (arthropods) or an endoskeleton (vertebrates). 2
Introduction to The Human Body
 1 Introduction to The Human Body FOCUS: The human organism is often examined at seven structural levels: chemical, organelle, cell, tissue, organ, organ system, and the organism. Anatomy examines the structure
1 Introduction to The Human Body FOCUS: The human organism is often examined at seven structural levels: chemical, organelle, cell, tissue, organ, organ system, and the organism. Anatomy examines the structure
X-Plain Muscles Reference Summary
 X-Plain Reference Summary Introduction are very important elements of the human body. They account for about half of a person s weight. Understanding how muscles work and how they can be injured is necessary
X-Plain Reference Summary Introduction are very important elements of the human body. They account for about half of a person s weight. Understanding how muscles work and how they can be injured is necessary
Terms of Movements by Prof. Dr. Muhammad Imran Qureshi
 Terms of Movements by Prof. Dr. Muhammad Imran Qureshi Three systems of the body work in coordination to perform various movements of the body. These are: A System of Bones (Osteology), A System of Muscles
Terms of Movements by Prof. Dr. Muhammad Imran Qureshi Three systems of the body work in coordination to perform various movements of the body. These are: A System of Bones (Osteology), A System of Muscles
Lesson 9A Tissues in Animals
 Lesson 9A Tissues in Animals Levels of Organization in the Human Body Similar types of cells Different types of tissues Different organs Many organ systems cell tissue organ organ system organism Levels
Lesson 9A Tissues in Animals Levels of Organization in the Human Body Similar types of cells Different types of tissues Different organs Many organ systems cell tissue organ organ system organism Levels
Copyright 2004 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. 2. Bone Structure. Copyright 2004 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins
 Chapter 7 The Skeleton: Bones and Joints The Skeleton Skeletal system is made up of bones and joints and supporting connective tissue. 1. Bone Functions 1. To store calcium salts 2. To protect delicate
Chapter 7 The Skeleton: Bones and Joints The Skeleton Skeletal system is made up of bones and joints and supporting connective tissue. 1. Bone Functions 1. To store calcium salts 2. To protect delicate
A Healthy, Active. Lifestyle and Your. Muscular System
 A Healthy, Active Lifestyle and Your Muscular System 1. Muscular System 2. Types of Muscle muscle - Smooth Muscle that works without consciousness. a. Arteries - The walls of the arteries contract and
A Healthy, Active Lifestyle and Your Muscular System 1. Muscular System 2. Types of Muscle muscle - Smooth Muscle that works without consciousness. a. Arteries - The walls of the arteries contract and
Chapter 6 part 2. Skeletal Muscles of the Body
 Chapter 6 part 2 Skeletal Muscles of the Body Basic Principles 600 + muscles in the human body (you are required to learn 45, lucky kids)! Skeletal Muscles pull on bones Origin of a muscle = point of attachment
Chapter 6 part 2 Skeletal Muscles of the Body Basic Principles 600 + muscles in the human body (you are required to learn 45, lucky kids)! Skeletal Muscles pull on bones Origin of a muscle = point of attachment
Since we ll be studying muscular and nervous tissue extensively later on in the year, this is just a brief overview of these two tissue types.
 1 Since we ll be studying muscular and nervous tissue extensively later on in the year, this is just a brief overview of these two tissue types. Muscular tissue is unique because it is the only tissue
1 Since we ll be studying muscular and nervous tissue extensively later on in the year, this is just a brief overview of these two tissue types. Muscular tissue is unique because it is the only tissue
Learning Objectives (1&2)
 Learning Objectives (1&2) By the end of the session, students should be able to: 1) Identify anatomical position seated, standing, prone, supine. 2) Pronounce, define and be able to use directional and
Learning Objectives (1&2) By the end of the session, students should be able to: 1) Identify anatomical position seated, standing, prone, supine. 2) Pronounce, define and be able to use directional and
BIOL 2457 CHAPTER 4 Part 2 SI All connective tissues arise from, an embryonic tissue.
 BIOL 2457 CHAPTER 4 Part 2 SI 1 1. All connective tissues arise from, an embryonic tissue. 2. Describe the vascularity of connective tissues, which are very diverse. 3. Describe the innervation of connective
BIOL 2457 CHAPTER 4 Part 2 SI 1 1. All connective tissues arise from, an embryonic tissue. 2. Describe the vascularity of connective tissues, which are very diverse. 3. Describe the innervation of connective
1.1 The structure and functions of the musculo-skeletal system Learning objectives
 1.1 The structure and functions of the musculo-skeletal system Learning objectives To be able to describe the functions of the skeleton. To understand different bone classifications and functioning. To
1.1 The structure and functions of the musculo-skeletal system Learning objectives To be able to describe the functions of the skeleton. To understand different bone classifications and functioning. To
How many skeletal muscles are present in our body? Muscles are excitable & contractile, extensible and elastic to some extent.
 Muscles How many skeletal muscles are present in our body? -646 muscles The functions of the muscles are: Movement Maintenance of posture Generation of heat Stabilization of joints : amount of muscle surrounding
Muscles How many skeletal muscles are present in our body? -646 muscles The functions of the muscles are: Movement Maintenance of posture Generation of heat Stabilization of joints : amount of muscle surrounding
1. Use the following words to complete the text below. Terms may be used more than once.
 THE NERVOUS AND MUSCULOSKELETAL SYSTEMS Nervous system, neuron, nerve impulse, peripheral nervous system, nerves STUDENT BOOK Ch. 7, pp. 202 206 1. Use the following words to complete the text below. Terms
THE NERVOUS AND MUSCULOSKELETAL SYSTEMS Nervous system, neuron, nerve impulse, peripheral nervous system, nerves STUDENT BOOK Ch. 7, pp. 202 206 1. Use the following words to complete the text below. Terms
Chapter 7 The Muscular System - Part 2. Mosby items and derived items 2012 by Mosby, Inc., an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. 1
 Chapter 7 The Muscular System - Part 2 Mosby items and derived items 2012 by Mosby, Inc., an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. 1 FUNCTIONS OF SKELETAL MUSCLE A. Functions 1. Movement 2. Posture or muscle tone
Chapter 7 The Muscular System - Part 2 Mosby items and derived items 2012 by Mosby, Inc., an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. 1 FUNCTIONS OF SKELETAL MUSCLE A. Functions 1. Movement 2. Posture or muscle tone
The Muscular System. Muscle tissue is one of the 4 tissue types in vertebrates Muscle
 The Muscular System The Muscular System Muscle tissue is one of the 4 tissue types in vertebrates Muscle The Muscular System Muscle tissue is one of the 4 tissue types in vertebrates Muscle Nervous The
The Muscular System The Muscular System Muscle tissue is one of the 4 tissue types in vertebrates Muscle The Muscular System Muscle tissue is one of the 4 tissue types in vertebrates Muscle Nervous The
Anatomy & Physiology. An Introduction
 Anatomy & Physiology An Introduction An Overview of Anatomy Anatomy - The study of the structure of the human body Physiology - The study of body function Branches of Anatomy Surface anatomy Gross anatomy
Anatomy & Physiology An Introduction An Overview of Anatomy Anatomy - The study of the structure of the human body Physiology - The study of body function Branches of Anatomy Surface anatomy Gross anatomy
Muscles Unit TEST and Final Exam Study Guide May 2017
 Muscles Unit TEST and Final Exam Study Guide May 2017 Part 1 of final exam is pictures, see bottom of the study guide Part 2 of the final exam is only going to cover muscles unit. If you do this study
Muscles Unit TEST and Final Exam Study Guide May 2017 Part 1 of final exam is pictures, see bottom of the study guide Part 2 of the final exam is only going to cover muscles unit. If you do this study
Muscle Tissue. Bio211 Laboratory 3. Tissues. Tissues Muscle, Nerve, Integument. Three types of muscle tissue. Skeletal (slide #21) Cardiac (slide #24)
 Bio211 Laboratory 3 Tissues Muscle, Nerve, Integument 1 Tissues Tissues to be examined under the microscope Muscle/Nervous Tissues (p. 109/117 Lab Manual) [TODAY] Skin (Integument) (p. 123 Lab Manual)
Bio211 Laboratory 3 Tissues Muscle, Nerve, Integument 1 Tissues Tissues to be examined under the microscope Muscle/Nervous Tissues (p. 109/117 Lab Manual) [TODAY] Skin (Integument) (p. 123 Lab Manual)
WTC II Term 3 Notes & Assessments
 Term 3 Notes & Assessments Planes of Motion/Axes The body moves in a number of various ways and directions. In the past you have learned about the terminology for movements at specific joints, for example,
Term 3 Notes & Assessments Planes of Motion/Axes The body moves in a number of various ways and directions. In the past you have learned about the terminology for movements at specific joints, for example,
Body Organizations Flashcards
 1. What are the two main regions of the body? 2. What three structures are in the Axial Region? 1. Axial Region (Goes down midline of the body) 2. Appendicular Region (limbs) 3. Axial Region (Goes down
1. What are the two main regions of the body? 2. What three structures are in the Axial Region? 1. Axial Region (Goes down midline of the body) 2. Appendicular Region (limbs) 3. Axial Region (Goes down
The Ergonomic Alternative
 The Economics Of Ergonomics What Is Ergonomics? Ergonomics is the field of study concerned with finding ways to keep people safe, comfortable, and productive while they perform tasks at work. We Refer
The Economics Of Ergonomics What Is Ergonomics? Ergonomics is the field of study concerned with finding ways to keep people safe, comfortable, and productive while they perform tasks at work. We Refer
SHHS Gen Bio Muscular System Lab
 SHHS Gen Bio Muscular System Lab Background: Skeletal muscle is the most abundant tissue in the body of healthy adults, comprising anywhere from about 30 to 50% of total body mass. The amount of muscle
SHHS Gen Bio Muscular System Lab Background: Skeletal muscle is the most abundant tissue in the body of healthy adults, comprising anywhere from about 30 to 50% of total body mass. The amount of muscle
Introduction to the Human Body
 Introduction to the Human Body Chapter Test A Multiple Choice Write the letter of the correct answer on the line at the left. 1. Your brain is a structure composed of different kinds of tissue. What is
Introduction to the Human Body Chapter Test A Multiple Choice Write the letter of the correct answer on the line at the left. 1. Your brain is a structure composed of different kinds of tissue. What is
CHAPTER 3 What Is Anatomy?
 CHAPTER 3 What Is Anatomy? Kinesiology Books Publisher 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS The Language of Anatomy Anatomical Position Directional Terms Body Planes Movements Musculoskeletal System Human Skeleton Types
CHAPTER 3 What Is Anatomy? Kinesiology Books Publisher 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS The Language of Anatomy Anatomical Position Directional Terms Body Planes Movements Musculoskeletal System Human Skeleton Types
9/6/2012. Less risk of injury Fewer back & posture problems Function more efficiently
 Unit 4 Ability to use your joints fully through a wide range of motion Having long muscles that allow your joints to be free enough to allow adequate movement. People who are flexible are often involved
Unit 4 Ability to use your joints fully through a wide range of motion Having long muscles that allow your joints to be free enough to allow adequate movement. People who are flexible are often involved
Types of Muscle: Skeletal- muscle involved in movement of the skeleton. Striated, has alternating bands of light and dark due to overlapping
 Types of Muscle: Skeletal- muscle involved in movement of the skeleton. Striated, has alternating bands of light and dark due to overlapping filaments within the muscle cell. Skeletal muscle can be consciously
Types of Muscle: Skeletal- muscle involved in movement of the skeleton. Striated, has alternating bands of light and dark due to overlapping filaments within the muscle cell. Skeletal muscle can be consciously
SKELETAL MUSCLE CHARACTERISTICS
 THE MUSCULAR SYSTEM SKELETAL MUSCLE CHARACTERISTICS Most are attached by tendons to bones Cells are multinucleate Striated have visible banding Voluntary subject to conscious control Cells are surrounded
THE MUSCULAR SYSTEM SKELETAL MUSCLE CHARACTERISTICS Most are attached by tendons to bones Cells are multinucleate Striated have visible banding Voluntary subject to conscious control Cells are surrounded
GLOSSARY. Active assisted movement: movement where the actions are assisted by an outside force.
 GLOSSARY The technical words used in this guide are listed here in alphabetic order. The first time one of these words is used in the guide, it is written in italics. Sometimes there is reference to a
GLOSSARY The technical words used in this guide are listed here in alphabetic order. The first time one of these words is used in the guide, it is written in italics. Sometimes there is reference to a
